Page 1

HP 3PAR Recovery Manager 2.0 Software for Microsoft Hyper-V
User Guide
Abstract
This document provides information about using HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V for experienced Microsoft™
Windows™ System Administrators managing databases.
HP Part Number: QL226-97701
Published: February 2014
Page 2

© Copyright 2014 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
Confidential computer software. Valid license from HP required for possession, use or copying. Consistent with FAR 12.211 and 12.212, Commercial
Computer Software, Computer Software Documentation, and Technical Data for Commercial Items are licensed to the U.S. Government under
vendor's standard commercial license.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth in the express
warranty statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty. HP shall
not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
Acknowledgements
Intel®, Itanium®, Pentium®, Intel Inside®, and the Intel Inside logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries
in the United States and other countries.
Microsoft®, Windows®, Windows® XP, Windows NT®, and Hyper-V® are U.S. registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Adobe® and Acrobat® are trademarks of Adobe Systems Incorporated.
Java and Oracle are registered trademarks of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
UNIX® is a registered trademark of The Open Group.
Hyper-V is a trademark of Microsoft Corporation.
All other trademarks and registered trademarks are owned by their respective owners.
Documentation
For more information about this document, go to http://www.hp.com/go/3par/ and click Support for your product, and then click Manuals.
Page 3

Contents
Online Help for HP 3PAR Recovery Manager Software for Microsoft Hyper-V........6
1 Introducing HP 3PAR Recovery Manager Software for Microsoft Hyper-V............7
System Requirements.................................................................................................................7
Windows Server Requirements...............................................................................................7
Windows Server 2008.........................................................................................................7
Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2..........................7
About HP 3PAR Recovery Manager Software for Microsoft Hyper-V.................................................7
Features of HP Recovery Manager Software for Microsoft Hyper-V...................................................8
Types of User Interface..............................................................................................................9
Web Browser Graphical User Interface...................................................................................9
PowerShell Cmdlet Command Line Interface............................................................................9
About Virtual Copy Management.............................................................................................11
Virtual Copy Data Consistency............................................................................................11
Virtual Copy Policy.............................................................................................................11
Graphical User Interface Scheduling Tool..............................................................................12
2 Getting Started........................................................................................13
About Components of HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V......................................13
About Supported Operating Systems and Software Prerequisites...................................................14
Operating Systems.............................................................................................................14
Software Prerequisites.........................................................................................................15
About Supported System Configurations....................................................................................15
Hyper-V Virtual Machine Configuration.................................................................................15
Hyper-V Stand-Alone Host Configuration...............................................................................15
About Other Requirements.......................................................................................................16
Running Recovery Manager for Hyper-V on Japanese / Chinese OS.............................................16
About Supported Network Ports................................................................................................16
3 Installing HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V..........................17
Installing the Software.............................................................................................................17
Upgrading to Recovery Manager 2.0 for RMH...........................................................................20
Verifying the Upgrade.............................................................................................................21
Uninstalling the Software.........................................................................................................22
4 Using the Web Client Interface...................................................................24
Using Online Help..................................................................................................................24
Understanding the Web Client Interface....................................................................................24
Hyper-V Server View..........................................................................................................24
Virtual Machine View.........................................................................................................29
Accessing the Web Client........................................................................................................34
Connecting to Recovery Manager Server...................................................................................34
Setting Up the Recovery Manager Web Client............................................................................35
Connecting to Hyper-V Server..............................................................................................35
Installing Recovery Manager Agent......................................................................................35
Uninstalling Recovery Manager Agent..................................................................................36
Updating StoreServ Credentials...........................................................................................37
Adding HP 3PAR StoreServ System Credentials......................................................................37
Disconnecting Microsoft Hyper-V Servers...............................................................................37
Working with Virtual Copies....................................................................................................37
Creating Virtual Copies......................................................................................................38
Setting Policy to Virtual Copies............................................................................................39
Analyzing Virtual Copies....................................................................................................40
Contents 3
Page 4

Restoring Virtual Machines From Virtual Copies......................................................................40
Removing Virtual Copies.....................................................................................................41
Mounting Virtual Copies.....................................................................................................41
Unmounting Virtual Copies..................................................................................................43
Scheduling Virtual Copy Creation Tasks................................................................................44
Scheduling Virtual Copy Analysis Tasks................................................................................46
Last Run Output.............................................................................................................47
Working with Remote Copies...................................................................................................48
Creating Remote Virtual Copies...........................................................................................48
Repository Backup .................................................................................................................50
Saving a Repository ..........................................................................................................50
Scheduling Repository Backup.............................................................................................52
Importing Repository Backup...............................................................................................54
Logging Off From Session........................................................................................................54
5 Using PowerShell Snap-in Command Line Interface.......................................55
Connecting to RMH Server......................................................................................................55
Login-Rmh.........................................................................................................................55
Logout-Rmh.......................................................................................................................55
Configuring RMH Server..........................................................................................................56
Add-HyperV......................................................................................................................56
Add-StoreServ...................................................................................................................56
Set-RmhPolicy....................................................................................................................57
Get-ClusterNodeNames......................................................................................................58
Get-EncryptedLoginPassword...............................................................................................58
Get-RmhPolicy...................................................................................................................59
Get-VirtualMachine............................................................................................................59
Show-Connection...............................................................................................................60
Working with Virtual Copies....................................................................................................60
Create-vCopy....................................................................................................................60
Get-vCopy........................................................................................................................61
Mount-vCopy....................................................................................................................62
Restore-vCopyVm...............................................................................................................63
Analyze-vCopy..................................................................................................................64
Unmount-vCopy.................................................................................................................65
6 Support and Other Resources.....................................................................67
Contacting HP........................................................................................................................67
HP 3PAR documentation..........................................................................................................67
Typographic conventions.........................................................................................................70
HP 3PAR branding information.................................................................................................70
7 Documentation feedback...........................................................................71
A Enabling JavaScript on Web Client.............................................................72
B HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V Powershell Commands.......73
Add-HyperV...........................................................................................................................73
Add-RemoteStoreServ..............................................................................................................74
Add-StoreServ........................................................................................................................75
Analyze-vCopy.......................................................................................................................76
Create-vCopy.........................................................................................................................77
Get-ClusterNodeNames..........................................................................................................79
Get-EncryptedLoginPassword....................................................................................................80
Get-RmhPolicy........................................................................................................................80
Get-vCopy.............................................................................................................................81
Get-VirtualMachine.................................................................................................................82
4 Contents
Page 5

Import-Repository....................................................................................................................83
Login-Rmh..............................................................................................................................84
Logout-Rmh............................................................................................................................85
Mount-vCopy.........................................................................................................................86
Remove-HyperV......................................................................................................................88
Remove-RmhPolicy..................................................................................................................88
Remove-StoreServ...................................................................................................................89
Remove-vCopy.......................................................................................................................90
Remove-RemoteStoreServ.........................................................................................................91
Restore-vCopyVm....................................................................................................................92
Set-RmhPolicy.........................................................................................................................93
Show-Connection....................................................................................................................94
Unmount-vCopy......................................................................................................................95
Update-HyperV......................................................................................................................97
Update-StoreServ....................................................................................................................98
Update-RemoteStoreServ..........................................................................................................99
Save-Repository....................................................................................................................100
C Remote Copy for Recovery Manager for Hyper-V .......................................101
How Recovery Manager for Disaster Recovery Solution Works ..................................................101
Setting up Remote Copy........................................................................................................101
Synchronous Long Distance ...................................................................................................103
Support for Remote Copy modes and policies..........................................................................103
Support for Failover Cluster for Microsoft Windows...................................................................103
D Troubleshooting for HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V..........104
About installing McAfee Antivirus ..........................................................................................104
Port conflict on user site for port 5555.....................................................................................104
Remote Copy best practices...................................................................................................104
Index.......................................................................................................105
Contents 5
Page 6

Online Help for HP 3PAR Recovery Manager Software for Microsoft Hyper-V
Welcome to the online help for HP 3PAR Recovery Manager Software for Microsoft Hyper-V.
Searching the Online Help
To search the online help, click Search in the navigation pane on the left.
The Search feature supports:
• Case-insensitivity
If you search for host, the search displays topics containing host, Host, HOST, and so on.
• Exact matches and related variations only
If you search for host, the search displays topics containing host, hosts, hosting, and so on,
but does not include topics containing variants such as hostess or hostel.
• Phrase searches
You can search for host name and so on.
• Pasting search terms
You can paste in a search string copied from another source.
The Search does not support wildcards. If you search for host*, the search displays only topics
containing the term host*, not topics containing host, hosts, and so on.
Legal notice and copyright
6
Page 7

1 Introducing HP 3PAR Recovery Manager Software for
Microsoft Hyper-V
HP 3PAR Recovery Manger for Microsoft Hyper-V is the latest addition to HP 3PAR Solutions
portfolio and offers key management capabilities and facilitates the integration of HP 3PAR Virtual
Copy and Microsoft Hyper-V Virtual Machine environment.
System Requirements
Windows Server Requirements
Microsoft Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2012, or Windows
Server 2012 R2.
Windows Server 2008
x64-based computer:
• 1.4 GHz processor
• 2 GB or more RAM
• 40 GB hard disk space
Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2
• Either 1.4 GHz (x64) or 1.3GHz (Dual Core) processor
• 2+ GB RAM
• 32+ GB hard disk space
About HP 3PAR Recovery Manager Software for Microsoft Hyper-V
HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V is designed to work with Microsoft Hyper-V
servers and provides system administrators with important tools to manage and backup critical
Virtual Machines involving multiple virtualized machine environments. This application supplies
essential GUI and command line-based tools to create, manage, browse, and restore application
consistent HP 3PAR Virtual Copies of operating Hyper-V Virtual Machines to a point-in-time.
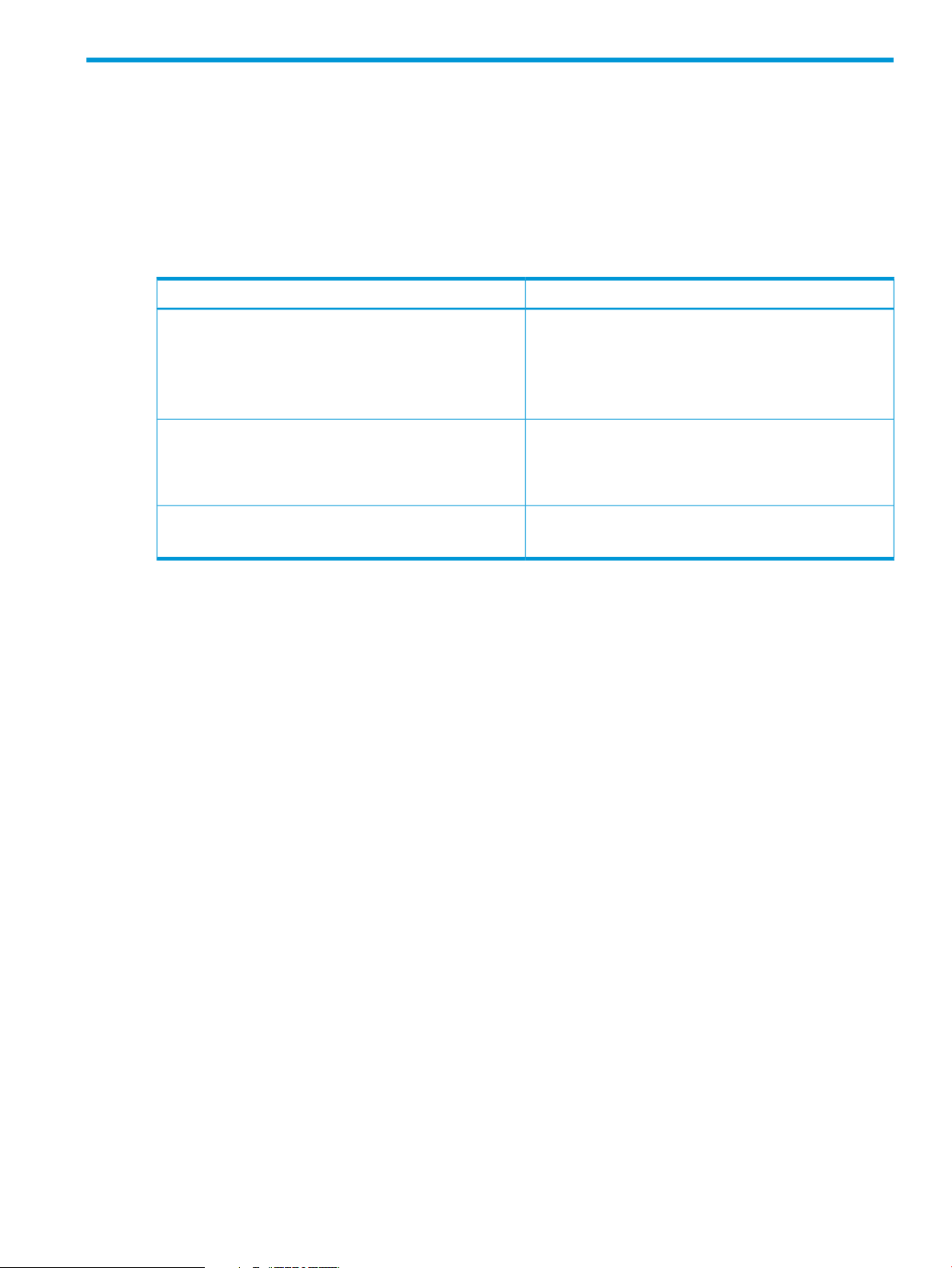
The following diagram displays a typical architecture and workflow involving HP 3PAR StoreServ
Storage System and Microsoft Hyper-V server.
System Requirements 7
Page 8

Figure 1 HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V Architecture
Features of HP Recovery Manager Software for Microsoft Hyper-V
HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V can be installed on any client and used for
automation. The software managing features include:
• Creating application consistent Virtual Copies of Microsoft Hyper-V environment
Access to PowerShell Commandlet (Cmdlet) and Web GUI◦
◦ Use of Hyper-V host as standalone host name or Hyper-V cluster name
◦ Set Virtual Copies with retention and expiry values at the time of creation
• Managing policy-base Virtual Copy lifecycle
• Accessing web graphical user interface (GUI)
Browse to get a list of Virtual Copies grouped by Virtual Machines and Hyper-V host◦
◦ Create new Virtual Copy of a Virtual Machine(s)
◦ Restore from a Virtual Copy; mount/unmount a Virtual Copy volume to any Hyper-V host
with installed agent.
◦ Administrative capabilities such as installing and monitoring RMH Agent
8 Introducing HP 3PAR Recovery Manager Software for Microsoft Hyper-V
Page 9

• Accessing Powershell Cmdlet-based RMH Command Line Interface (CLI)
◦ Virtual Copy commands include analyze, create, remove, mount, unmount, restore, and
show
• Policy commands include creation and show
• Connectivity commands include logging on and off of Hyper-V and multiple StoreServs and
showing current connections
Additional details of the new features for the software are included in the following table:
Table 1 Features Included in Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V
DescriptionFeature
Application Consistent Virtual Copy
Full VM Restore (VSS-Aware Restore)
RMH Browser Client
HP 3PAR StoreServ Credentials Management
Types of User Interface
Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V supports both GUI and command line application
interfaces to manage Virtual Machines and data.
Web Browser Graphical User Interface
The web client is accessible from any host and provides administrative tools to perform tasks such
as searching, viewing, managing, and scheduling tasks for Hyper-V servers, agents, Virtual
Machines, and HP 3PAR Virtual Volumes.
For more details about using the web client interface to perform administrative tasks, see “Using
the Web Client Interface” (page 24).
Creates VSS aware application consistent backup of Virtual
Machine (VM)
Supports VMs deployed on Cluster Shared VolumesHyper-V Clusters with Cluster Shared Volumes
Supports VMs deployed on standalone Hyper-V hostsHyper-V Standalone Hosts
Restores complete VM including its metadata and virtual
hard disks from a VSS aware backup
Provides browser based GUI to display and manage
mapping details of VCs, VMs, and VVs
Saves storage system (HP 3PAR StoreServ) credentials in
centralized database and streamlines usability
Offers tools to administrate RMH Server configurationAdministrative Tool CLI
Provides ability to install RMH agent from remote locationRemote Agent Installation
NOTE: You must have an HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V Software license
in order to use the Virtual Copy browser.
PowerShell Cmdlet Command Line Interface
HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for Hyper-V includes a customized PowerShell Snap-in as the default
client interface.
The default interface features command line interface (CLI) Cmdlets in RMH PowerShell Snap-in to
simplify complex managing tasks of Virtual Copies involving HP 3PAR Storage Systems and
Microsoft Hyper-V hosts:
Types of User Interface 9
Page 10

Table 2 RMH PowerShell Snap-in Cmdlets
DescriptionCommand
Adds Hyper-V credentials for usersAdd-HyperV
Adding an additional HP 3PAR StoreServ credentialAdd-StoreServ
Add-RemoteStoreServ
Get-vCopy
Get-VirtualMachine
Mount-vCopy
This is used to add each HP 3PAR StoreServ credentials
and is only required initially to set up the credentials.
Analyzes Virtual Copies for errorsAnalyze-vCopy
Creates Virtual Copy of a Virtual Machine (VM)Create-vCopy
Retrieves node names for the Hyper-V clusterGet-ClusterNodeNames
Retrieves a login password that may be using scriptingGet-EncryptedLoginPassword
Retrieves existing Virtual Copy details of a VM from an
RMH Repository
Retrieves current Virtual Machines available on an
active-session Hyper-V host/cluster
Initiates full restore of a VMRestore-vCopyVM
Mounts Virtual Copy volumes on to a Hyper-V host for
manual restoration of virtual hard disks.
Retrieves RMH policy of a VMGet-RmhPolicy
Modifies RMH policy of a VMSet-RmhPolicy
Cmdlet for user authenticationLogin-Rmh
Logs off user from RMH and terminates the sessionLogout-Rmh
Remove-HyperV
Remove-StoreServ
Show-Connection
Unmount-vCopy
Update-HyperV
Update-StoreServ
Removes Microsoft Hyper-V host/cluster credentials
associated with a RMH user
Removes RMH policy of a Virtual MachineRemove-RmhPolicy
Removes HP 3PAR StoreServ credentials associated with
a RMH user
Removes a Virtual CopyRemove-vCopy
This is used to delete the StorveServ credentials.Remove-RemoteStoreServ
Initiates a full restore or recovery of virtual machinesRestore-vCopyVm
Shows connection information for current login RMH user
name
Unmounts currently mounted Virtual Copy volume(s) for the
specified Virtual Copy and Virtual Machine name
Updates Microsoft Hyper-V credentials already present in
RMH database for user
Updates HP 3PAR StoreServ credentials already present
in RMH database for user
This is used to modify the StorveServ credentials.Update-RemoteStoreServ
For more information about using RMH PowerShell Cmdlets, see “Using PowerShell Snap-in
Command Line Interface” (page 55).
10 Introducing HP 3PAR Recovery Manager Software for Microsoft Hyper-V
Page 11

About Virtual Copy Management
HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V features an essential Virtual Copy management
tool with enhanced recovery commands that allow you to create and restore application consistent
Virtual Copies of running Hyper-V Virtual Machines (VMs). When creating a VM Virtual Copy,
Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V identifies all the underlying HP 3PAR volumes and creates
Virtual Copies simultaneously for all volumes to ensure consistency. Recovery Manager for Microsoft
Hyper-V manages the set of Virtual Copies as a single entity.
NOTE: HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V requires a license. In addition, specific
licenses are required for HP 3PAR Virtual Copy and HP 3PAR Virtual Lock when performing Virtual
Copy operations and setting volume retention policies.
Virtual Copy Data Consistency
Recovery Manager for Hyper-V creates application consistent Virtual copies of Hyper-V Virtual
Machines with Microsoft VSS technology and the HP 3PAR VSS Provider, using the Child VM
snapshot backup method.
For application consistent backups (Child VM Snapshot method) to be supported, the following
conditions must be met:
• All VM files must reside on HP 3PAR LUNs.
• Backup (volume snapshot) Integration Service is installed and running in the child VM. The
service name is Hyper-V Volume Shadow Copy Requestor.
• The child VM must be in the running state.
• The snapshot file location for the VM is set to be the same volume in the host operating system
as the VHD files for the VM.
• All volumes in the child VM are basic disks and there are no dynamic disks.
• All disks in the child VM must use a file system that supports snapshots. For example, NTFS.
If the preceding conditions are not met, then a saved state (crash consistent) backup is taken, where
the VM is put into saved state during the backup process, and then returned to its previous state
on completion.
Recovery Manager for Hyper-V saves the Virtual Copy details, along with the VSS backup document,
for browsing and restoring purposes.
Application consistency is provided for HP 3PAR snapshots of Virtual Machines for data compatibility
with supported applications through the VSS Child VM Snapshot method, and supports crash
consistent backups using the Saved state method.
Virtual Copy Policy
Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V provides the ability to create Virtual Copy policies for
VMs. Only a single policy is permitted for every Virtual Machine and the policies exist independently
of the virtual disks the VM is using.
In Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V, the Virtual Copy policy contains the following
attributes:
• Enable expirable Virtual Copies allows you to specify that created Virtual Copies are removed
according to a specified schedule and are not affected by the maximum count.
• Retain Virtual Copy Set supports the number of hours and days of a Virtual Copy set being
retained.
NOTE: The Retain Virtual Copy Set option requires a HP 3PAR Virtual Lock™ license. For
more information about obtaining a license for HP 3PAR Virtual Lock™, contact your local
service provider.
About Virtual Copy Management 11
Page 12

Graphical User Interface Scheduling Tool
You can automatically create Virtual Copies according to a specified schedule with RMH scheduling
tool and add policies to new Virtual Copies. For more information, see “Using the Web Client
Interface” (page 24).
12 Introducing HP 3PAR Recovery Manager Software for Microsoft Hyper-V
Page 13
2 Getting Started
The following sections provide information about HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V
components, types of supported platforms and environments, and installation requirements.
About Components of HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V
HP 3PAR Recovery Manager Software for Microsoft Hyper-V includes the following deployable
components:
DescriptionComponent
RMH Server
RMH Agent
RMH Client
• Installs on any operating Microsoft Windows server
• Access to a configuration database repository
• Repository management
• Serves as a web server for connecting clients
• Operates on every Hyper-V host
• Access to RMH VSS requestor and restore utilities
• Access to HP 3PAR VSS Provider
• Use of web browser and PowerShell Cmdlet to create
Virtual Copies
About Components of HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V 13
Page 14
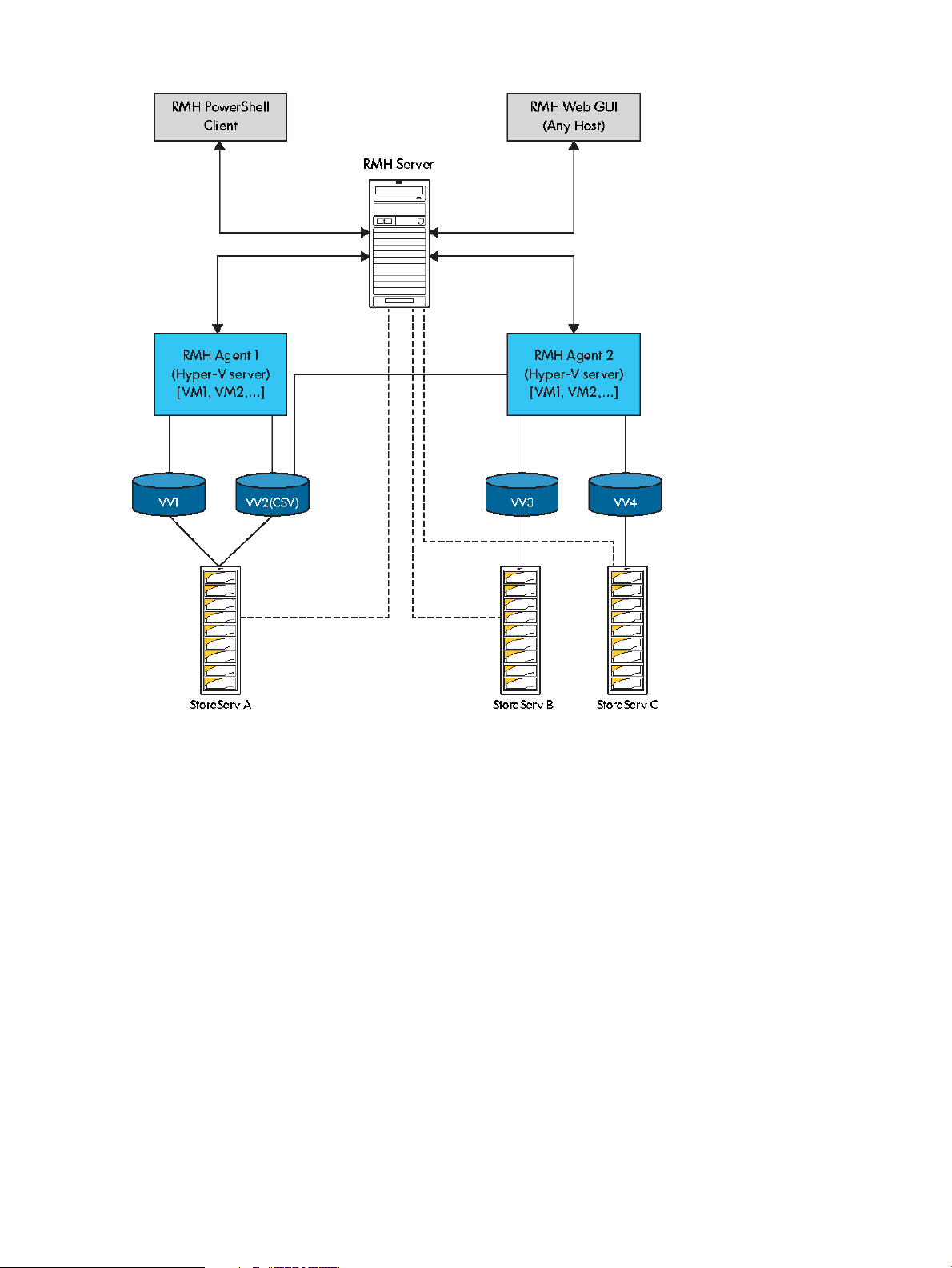
Figure 2 Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V Configuration
About Supported Operating Systems and Software Prerequisites
Before you begin installing HP 3PAR Recovery Manager Software for Microsoft Hyper-V, make
sure that you know the following requirements are satisfied:
Operating Systems
HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V Agent
• Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1 (x64) (Full and Core version)
• Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2 (x64) (Full and Core version)
HP 3PAR OS Software
• 3.1.1 MU1, MU2, MU3, P27
• 3.1.2, 3.1.2 MU1, MU2, MU3 P16
• 3.1.3
14 Getting Started
Page 15
Software Prerequisites
HP 3PAR OS Licenses
• HP 3PAR Virtual Copy
• HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V
• HP 3PAR Virtual Lock (Optional)
HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V Agent/Server/Client
• Microsoft .Net Framework 4.5 Full package
(Installer for Windows 2008 R2 SP1 Full and Core version are different.)
• Visual C++ Redistributable for Visual Studio 2012
HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V Agent
• MPIO
• Microsoft Hyper-V Server
• HP 3PAR VSS Provider (version 2.3.0 and above)
• HP 3PAR OS CLI (required by HP 3PAR VSS Provider)
HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V Client
• Microsoft Windows with Powershell 2.0
About Supported System Configurations
Hyper-V Virtual Machine Configuration
Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V supports the following configurations for Hyper-V Virtual
Machine and host:
• Single StoreServ per VM
• Multiple virtual hard disks per VM
• All VHDs from HP 3PAR VVs
• VM metadata on HP 3PAR volume
• Application consistent backups through child VM Snapshot method must use Microsoft Windows
OS with NTFS file system
Hyper-V Stand-Alone Host Configuration
• Windows 2008 R2 , 2012 and Hyper-V R2
• Full installation and Server core installation
• Standalone Hyper-V Host
• Hyper-V Clusters with Cluster Shared Volumes (CSV)
• All Hyper-V hosts/clusters under SCVMM management are individually supported
NOTE: An SCVMM configuration is not supported on a Hyper-V host.
For information about supported platforms, refer to the HP 3PAR OS Configuration Matrix. To
obtain a copy of this documentation, go to http://www.hp.com/go/3par/, navigate to your
product page, click Support for your product, and then click Manuals.
About Supported System Configurations 15
Page 16

About Other Requirements
Before you begin installing HP 3PAR Recovery Manager Software for Microsoft Hyper-V, make
sure that you know the following requirements are satisfied.
• HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V license, HP 3PAR Virtual Copy license for
Virtual Copy operation, and HP 3PAR Remote Copy license for Remote Copy operations.
• Virtual Machines must have Hyper-V integration services enabled in order to perform VC
operations with application consistency.
• HP 3PAR Recovery Manager Software for Microsoft Hyper-V currently only supports English
localization.
Running Recovery Manager for Hyper-V on Japanese / Chinese OS
The current release of Recovery Manager for Hyper-V is not localized, however it supports installation
on Windows server with English, Japanese and Chinese (Simplified) locale with object names
operations in English only.
The following prerequisites are required for Running Recovery Manager for Hyper-V on Japanese
/ Chinese OS.
CAUTION: For full compatibility with Recovery Manager for Hyper-V, you must use
English-language naming conventions in both Microsoft Hyper-V and Recovery Manager for Hyper-V
setup.
• Windows 2008 R2 SP1 Japanese / Chinese (Simplified) OS
• Windows 2012 / 2012 R2 Japanese / Chinese (Simplified) OS
• Set System locale to Japanese / Chinese (Simplified) and set the display language to Japanese
(Japan).
About Supported Network Ports
HP 3PAR Recovery Manager Software for Microsoft Hyper-V uses the following network ports:
• 5555 SSL for GUI and Powershell communications Client-to-Server and Server-to-Agent
• 5783 SSL port to HP 3PAR StoreServ
• Hyper-V Server HTTP port and Hyper-V Server HTTPS port for secure access (between the
Hyper-V Server, client, and HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V)
If firewalls settings are active, you must change the rules settings to allow traffic to these ports with
the outbound connections for HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V to work properly.
16 Getting Started
Page 17
3 Installing HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for Microsoft
Hyper-V
Before you begin using HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V (RMH), make sure that
your system hardware and software are both correctly set up.
Installing the Software
The software installation process includes three components: server, agent, and client. All three
components must be properly installed before using the software.
NOTE: RMH does not support Agent installation on Virtual Machines.
1. Insert the HP 3PAR Recovery Manager Software for Microsoft Hyper-V disc into your CD-ROM
drive.
2. Double-click the applicable installation package to launch the InstallShield wizard.
3. Click Next and follow the InstallShield Wizard instructions.
You can cancel at anytime during the installation. Click Cancel to end the installation process.
Figure 3 InstallShield Wizard dialog
4. Review the license agreement before accepting the terms and click Next.
Installing the Software 17
Page 18
Figure 4 License Agreement dialog
5. Enter the following information and click Next.
• User Name
• Organization
Figure 5 License Registration dialog
6. Do one of the following:
• Click Next to install this folder to the default location.
• Click Change to install to a different folder location.
18 Installing HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V
Page 19
Figure 6 Setting Destination Folder dialog
7. Choose a type of setup:
• Complete
• Custom
Select the feature to install: Agent, Client, or Server.
NOTE: You must select one or more feature to continue the installation process.
Click Next.
Figure 7 Installation Setup Type dialog
8. Review the feature installation settings and click Install to begin the installation.
Installing the Software 19
Page 20
Figure 8 Feature Installation Settings dialog
The process now initiates and provides status updates throughout the installation period.
9. Click Finish when the installation is complete. To review the Windows Installer log, check the
option box before clicking Finish.
Figure 9 Installation Complete dialog
Upgrading to Recovery Manager 2.0 for RMH
NOTE: RMH 2.0 does not support downgrade.
The following method helps you upgrade the Hyper-V and Backup servers.
1. Insert HP 3PAR Recovery Manager Software for Microsoft Hyper-V disc into your CD-ROM
drive.
2. Double-click the applicable installation package to launch the Install Shield wizard.
A pop-up message is displayed. Click Yes to continue.
3. File in Use wizard page displays all the Hyper-V applications that are currently in use,
with the option to close the application.
Select the appropriate option and click OK to continue.
20 Installing HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V
Page 21
Figure 10 File in Use
NOTE:
• Before upgrading make sure all Hyper-V GUI and PowerShell windows are closed and
there is no Hyper-V process running.
• Reboot is required, if the user selects Do not close application option.
4. Click Finish after the upgrade is complete. To review the Windows Installer log, select the
option before clicking Finish.
Figure 11 InstallShield Wizard Complete
NOTE: The upgrade steps for the Recovery Manager backup server also apply to the Remote
Copy backup server(s), if applicable to your setup.
Verifying the Upgrade
The following method helps you verify the upgrade.
1. Verify if Recovery Manager for Hyper-V service is currently running and user is able to launch
the web GUI.
2. Check if you can see the previously created virtual copies/schedules in the GUI.
Verifying the Upgrade 21
Page 22

3. Go to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\HP\RMHand check if CurrentVersion is
2.0.0 to verify the registry key.
Uninstalling the Software
You can use either the Microsoft Windows Control Panel or RMH InstallShield Wizard to uninstall
HP 3PAR Recovery Manager Software for Microsoft Hyper-V.
Using Microsoft Windows 2008 Control Panel
The following method completely removes all components of RMH.
1. Click Start→Control Panel→Programs→Programs and Features.
2. Select HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V from the list of programs.
3. Click Uninstall.
NOTE: If the secure network port is used, you need to unbind the port.
For installations on Windows 2008 R2, run netsh http show sslcert to view port
binding information.
Using Microsoft Windows 2012 and 2012 R2 Control Panel
The following method completely removes all components of RMH.
1. Click Start→Control Panel→Programs→Programs and Features.
2. Select HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V from the list of programs.
3. Click Uninstall.
NOTE: If the secure network port is used, you need to unbind the port.
For installations on Windows 2008 R2, run netsh http show sslcert to view port
binding information.
Using RMH InstallShield Wizard
When using the RMH InstallShield Wizard, you have the option to customize and remove specific
component features for RMH.
1. Launch the RMH InstallShield Wizard and click Next.
Figure 12 RMH InstallShield Wizard dialog
22 Installing HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V
Page 23
2. Choose Remove and click Next.
Figure 13 Program Maintenance Options
3. Review the message dialog. Click Remove.
Figure 14 Removing the Program dialog
Uninstalling the Software 23
Page 24

4 Using the Web Client Interface
HP 3PAR Recovery Manager Software for Microsoft Hyper-V provides GUI-based administrative
tools to monitor and manage the RMH server, RMH agents, and StoreServ. In addition, some of
the application configuration settings can be customized by the user.
HP 3PAR Recovery Manager supports the following web browsers:
Table 3 Supported Web Browsers
Using Online Help
For additional help and information about HP 3PAR Recovery Manager, locate the menu bar and
click Help.
Understanding the Web Client Interface
Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V provides a simplified web user interface with essential
tools to manage and perform specific operations relating to the maintenance of existing Virtual
Machines.
The following sections describe the views of default workspace for Hyper-V Server and Virtual
Machines.
VersionWeb Browser
22 or newerGoogle Chrome
8 or newerMicrosoft Internet Explorer
16 or newerMozilla Firefox
Hyper-V Server View
The default Hyper-V Server view displays:
• The Tree View pane lists all Hyper-V servers and associated Virtual Machines in the system.
• The Data View pane displays associated clusters and controller nodes details with specific
Hyper-V servers.
• The Task View pane provides status information about the status and results of user operations
such as creating a Virtual Copy.
24 Using the Web Client Interface
Page 25
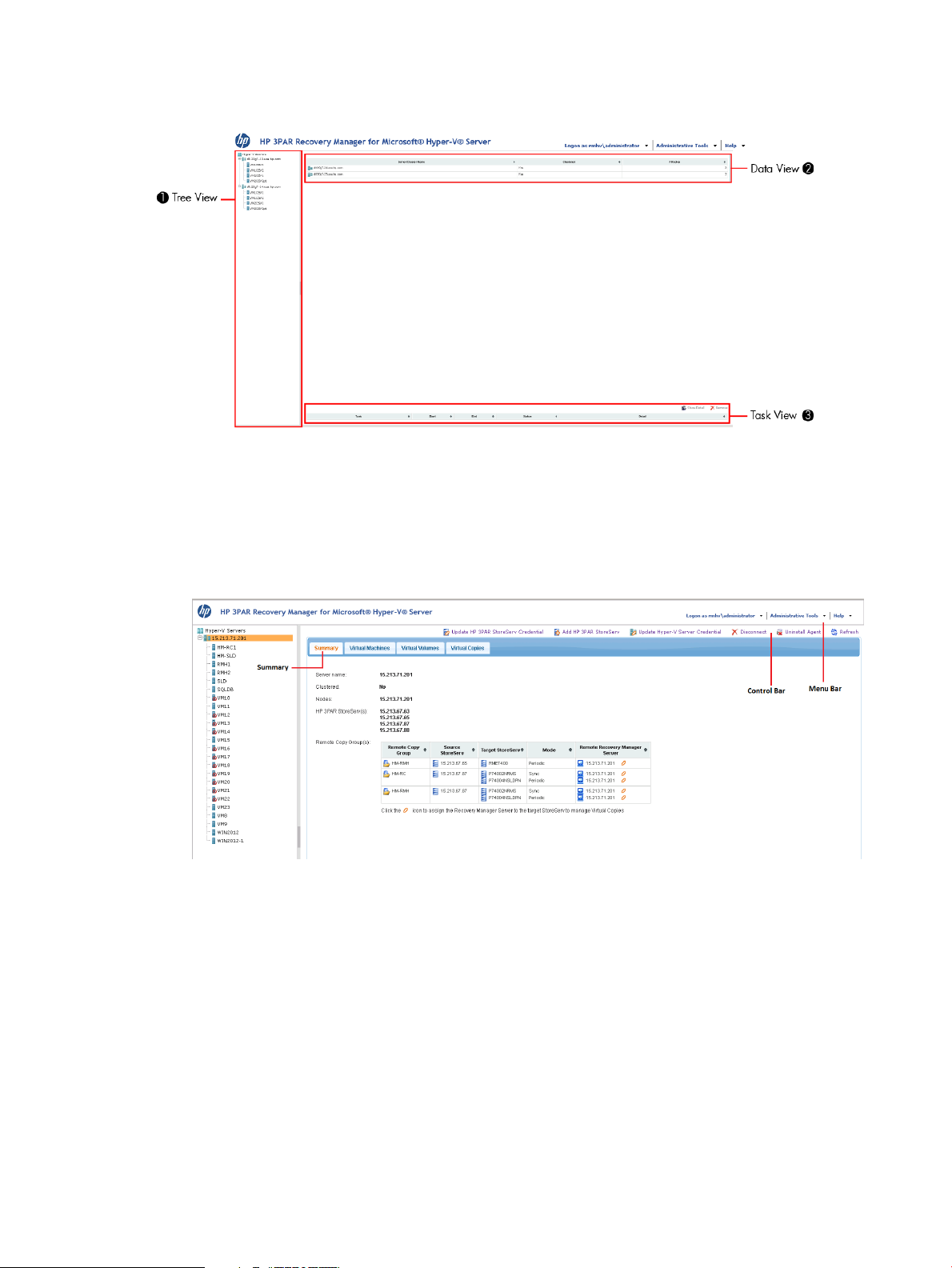
Figure 15 Recovery Manager Hyper-V Home Workspace View
When you select a specific server on the Tree View pane, the following tabs becomes available:
• The Summary tab provides a general system summary of a selected Hyper-V server.
Figure 16 Hyper-V Server Summary Tab
• The Virtual Machines tab lists all the Virtual Machines associated with a Hyper-V server. For
quick access, the tab provides Create Virtual Copy and Virtual Copy Policy tools to create
Virtual Copies and modify Virtual Copy policies of selected Virtual Machines.
For more information about working with a Virtual Copy, see “Creating Virtual Copies”
(page 38) and “Setting Policy to Virtual Copies” (page 39).
Understanding the Web Client Interface 25
Page 26
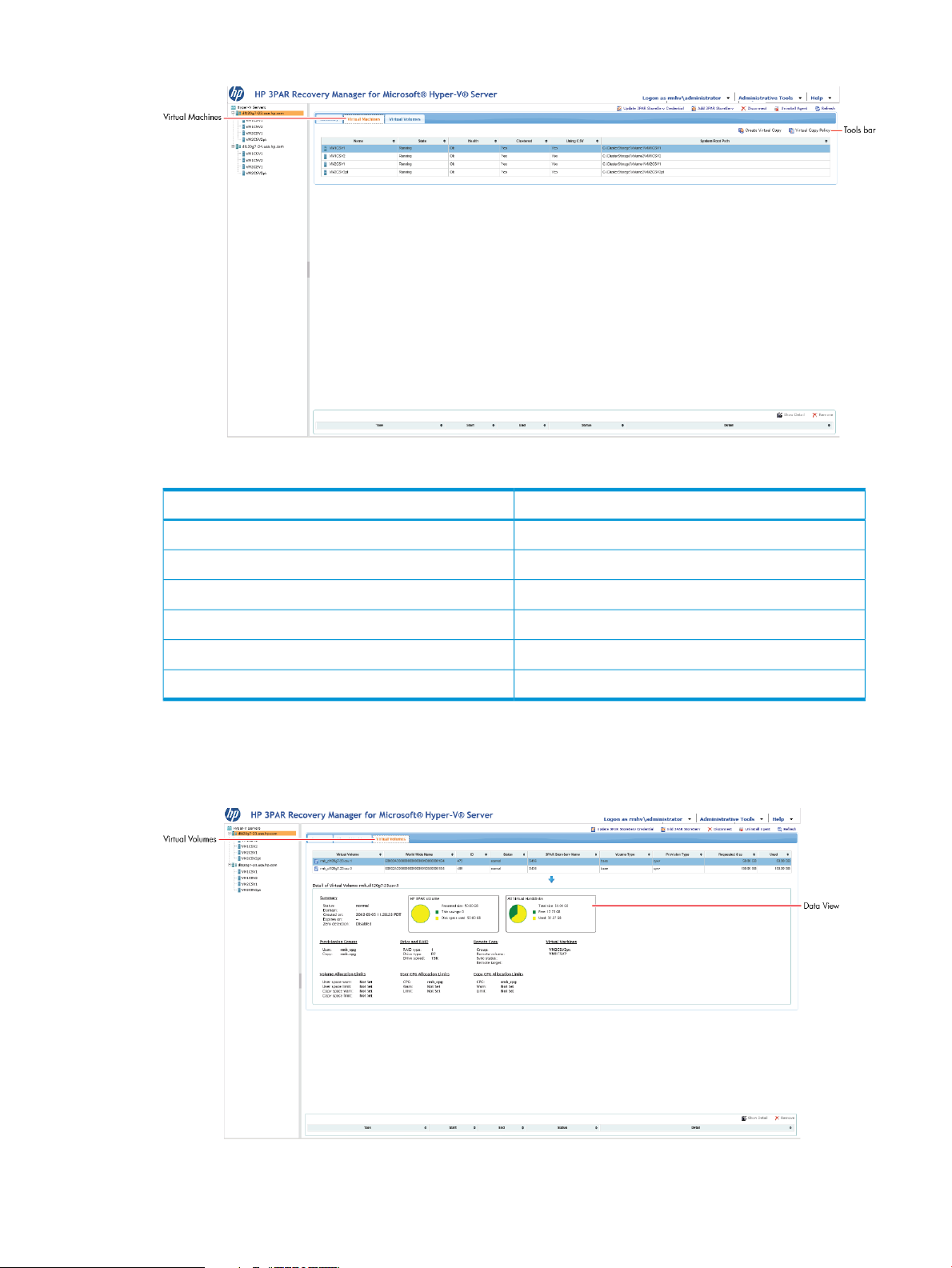
Figure 17 Hyper-V Server Virtual Machines Tab
Table 4 Hyper-V Server Virtual Machines Tab
DisplaysColumn
Name of Virtual MachineName
Activity status of the Virtual MachineState
Current system condition of the Virtual MachineHealth
Associated clusters belonging to the serverClustered
Current condition of CSVUsing CSV
Full path of the system root pathSystem Root Path
• The Virtual Volumes tab provides a comprehensive summary of all Virtual Volumes associated
with a Hyper-V server.
Figure 18 Hyper-V Server Virtual Volumes Tab
26 Using the Web Client Interface
Page 27

NOTE: Microsoft Internet Explorer version 8 will not display the pie charts. Use Microsoft
Internet Explorer version 9 or above for the best view results.
Table 5 Hyper-V Server Virtual Volumes Tab
DisplaysColumn
Description of virtual volumeVirtual Volume
Description of World Wide Name of virtual volumeWorld Wide Name
System IDID
Current status of virtual volumeStatus
Name of HP 3PAR StoreServ associated with virtual volumeHP 3PAR StoreServ Name
Description of volume typeVolume Type
Type of provisioningProvision Type
Size of storage spaceRequested Size
Current storage space usageUsed
Understanding the Web Client Interface 27
Page 28
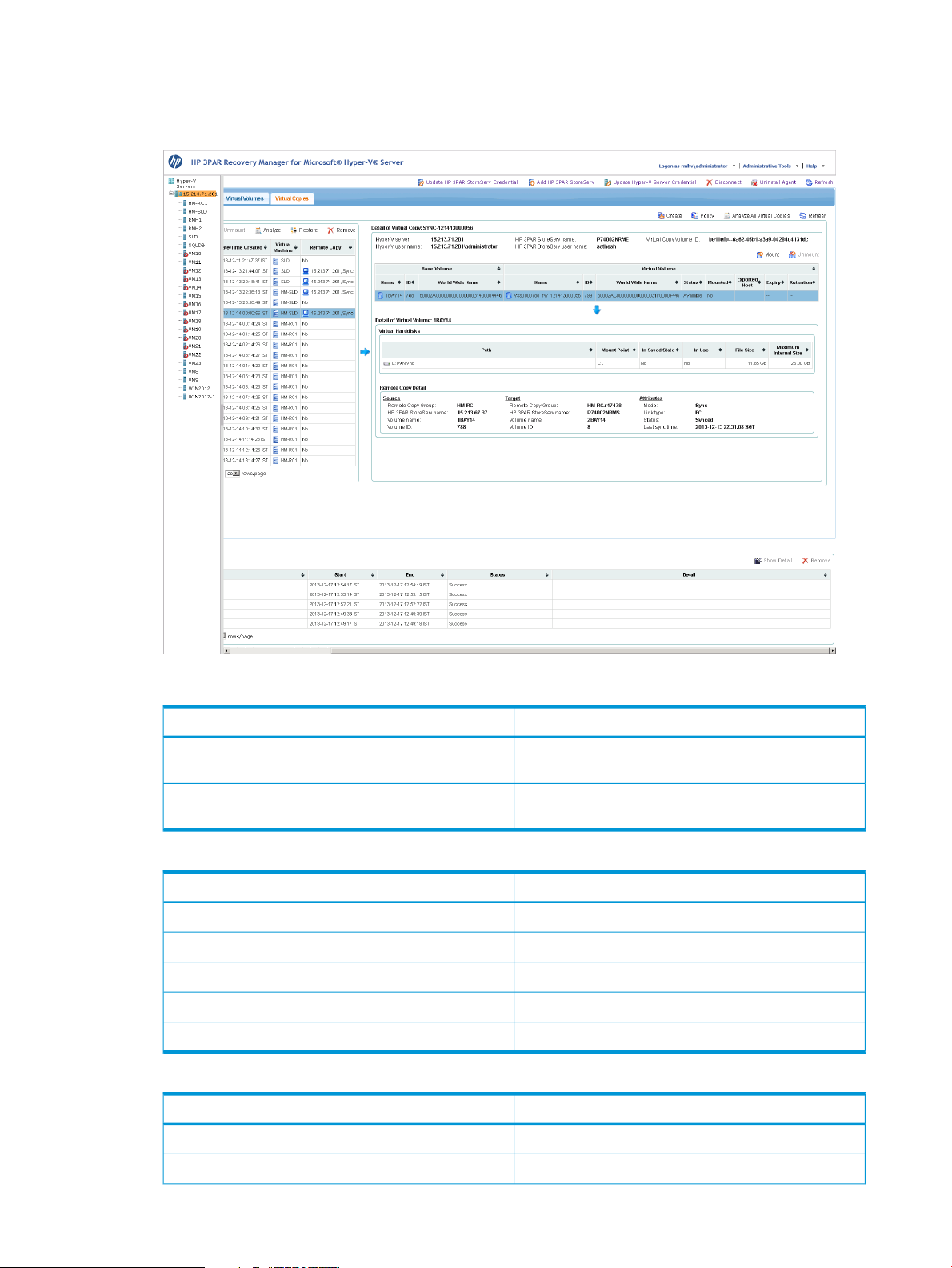
• The Virtual Copies tab provides a list of all Virtual Copies created from Virtual Machines on
the Hyper-V server.
Figure 19 Hyper-V Server Virtual Copies Tab
Table 6 Hyper-V Server Virtual Copy Control Bar
Create
Policy
Table 7 Hyper-V Server Virtual Copy Control Bar
Table 8 Hyper-V Server Virtual Copies Tab
ActionOption
Creates a Virtual Copy for all the Virtual Machines on
the Hyper-V Server
Sets the policy for all the Virtual Machines on the
Hyper-V Server
ActionOption
Mounts a virtual copy on the Virtual MachineMount
Unmounts a virtual copy from the Virtual MachineUnmount
Analyzes the selected virtual copy for its existenceAnalyze
Restores the selected virtual copyRestore
Removes the selected virtual copy from the listRemove
DisplaysColumn
Name of Virtual CopyName
28 Using the Web Client Interface
Date and time of Virtual Copy CreationCreated Date/Time
Page 29
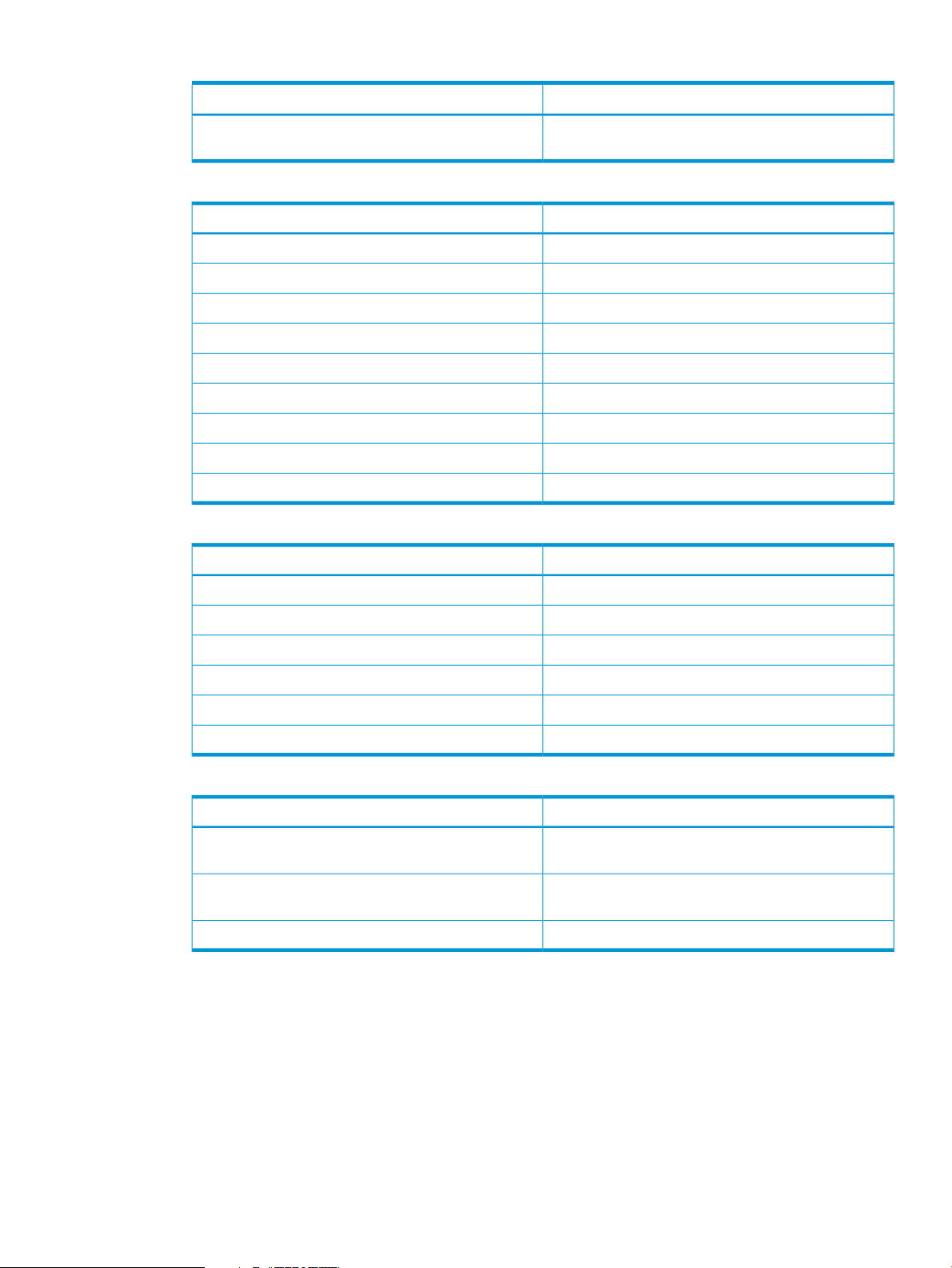
Table 8 Hyper-V Server Virtual Copies Tab (continued)
DisplaysColumn
Virtual Machine
Table 9 Details of Virtual Copy Pane
Table 10 Details of Virtual Volumes Pane
Name of the Virtual Machine the Virtual Copy was
created for
DisplaysColumn
Name of base volumeBase Volume
Base volume IDBase ID
Name of Virtual Copy volumeVirtual Copy Volume
Virtual Copy IDVirtual Copy ID
Status of the Virtual CopyStatus
Mounted or unmounted statusMounted
Name of the host receiving the exported Virtual CopyExported Host
Date of expirationExpiry
Date of retentionRetention
DisplaysColumn
Path of virtual volumePath
Table 11 Remote Copy Details
Source
Target
Virtual Machine View
Under the Tree View pane, a set of Virtual Machines are listed underneath a correlating Hyper-V
server.
The default Virtual Machine view displays:
Location to mount Virtual CopyMount Point
Status of virtual volumeIn Saved State
Activity of virtual volumeIn Use
Size of virtual volumeFile Size
Maximum size of hard diskMaximum Internal Size
DisplaysColumn
The source information of Remote Copy group, StoreServ
name, volume name, and volume ID
The target information of Remote Copy group, StoreServ
name, volume name, and volume ID
Details of RC link informationAttribute
• The Summary tab provides a general system summary of the Virtual Machine.
Understanding the Web Client Interface 29
Page 30
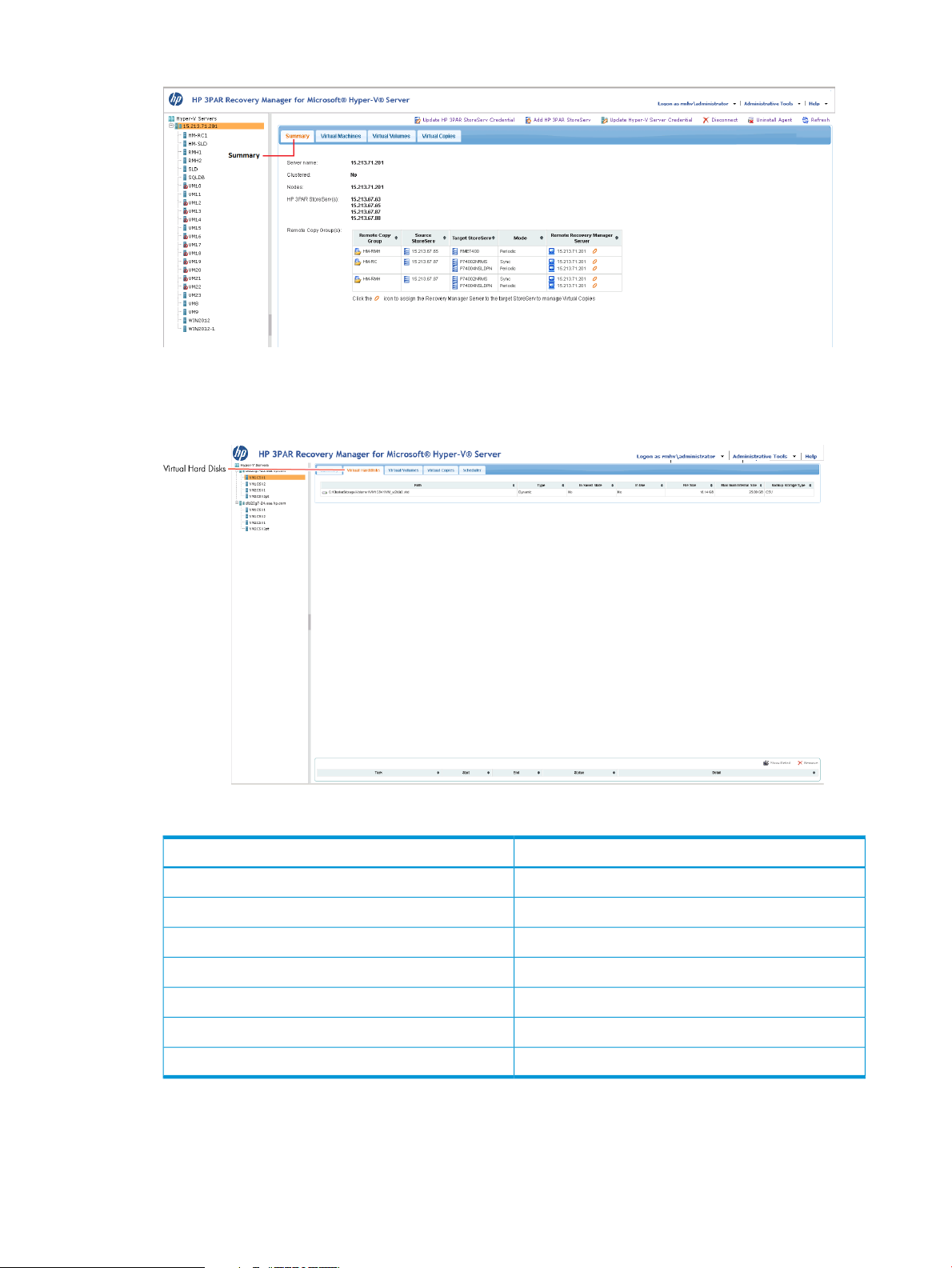
Figure 20 Virtual Machine Summary Tab
• The Virtual Hard Disks tab lists connecting hard disks associated with the Virtual Machine.
Figure 21 Virtual Hard Disks Tab
Table 12 Virtual Hard Disks Tab
• The Virtual Volumes tab displays a comprehensive summary of all Virtual Volumes associated
with the Virtual Machine.
30 Using the Web Client Interface
DisplaysColumn
Full address path of virtual hard disksPath
Type of hard disks: Dynamic or staticType
Yes or No valuesIn Saved State
Virtual HD in use or notIn Use
Size of file(s)File Size
Maximum storage capacityMaximum Internal Size
Type of backup storageBackup Storage Type
Page 31
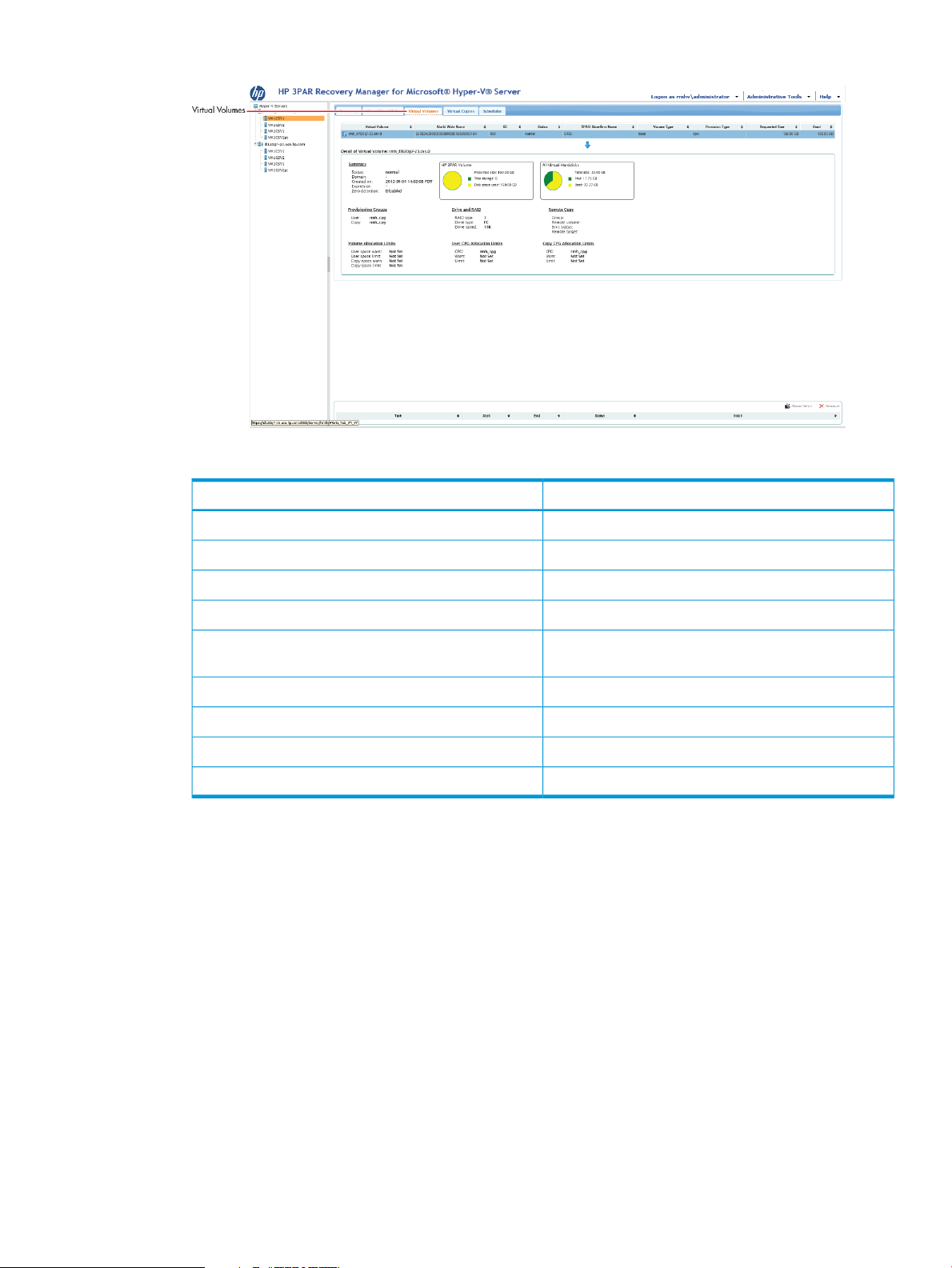
Figure 22 Virtual Volumes Tab
Table 13 Virtual Volumes Tab
DisplaysColumn
Description of virtual volumeVirtual Volume
Description of World Wide Name of virtual volumeWorld Wide Name
System IDID
Current status of virtual volumeStatus
HP 3PAR StoreServ Name
Name of HP 3PAR StoreServ associated with virtual
volume
Type of volumeVolume Type
Type of provisioningProvision Type
Size of storage spaceRequested Size
Current storage space usageUsed
• The Virtual Copies tab provides a list of all Virtual Copies created from a Virtual Machine.
Understanding the Web Client Interface 31
Page 32

Figure 23 Virtual Copies Tab
Table 14 Virtual Machine Control Bar
Table 15 Virtual Copy Pane
Table 16 Details of Virtual Copy Pane
ActionOption
Creates a Virtual Copy for the Virtual MachineCreate
Sets the policy for the Virtual MachinePolicy
DisplaysColumn
Name of Virtual CopyName
Date and time of Virtual Copy CreationCreated Date/Time
DisplaysColumn
Name of base volumeBase Volume
Base volume IDBase ID
Name of Virtual Copy volumeVirtual Copy Volume
Virtual Copy IDVirtual Copy ID
Status of the Virtual CopyStatus
32 Using the Web Client Interface
Mounted or unmounted statusMounted
Name of the host receiving the exported Virtual CopyExported Host
Date of expirationExpiry
Date of retentionRetention
Page 33

Table 17 Details of Virtual Volumes Pane
Table 18 Remote Copy Details
DisplaysColumn
Path of virtual volumePath
Location to mount Virtual CopyMount Point
Status of virtual volumeIn Saved State
Activity of virtual volumeIn Use
Size of virtual volumeFile Size
Maximum size of hard diskMaximum Internal Size
DisplaysColumn
Read and write of volumeSource
Read only volumeTarget
The type of mode:Attribute
◦ Sync
◦ Periodic
• The Scheduler tab enables you to create a schedule to create a Virtual Copy or analyze all
Virtual Copes.
Figure 24 Scheduler Tab
Table 19 Scheduler tab
DisplaysColumn
Name of policy taskTask Name
Scheduled policy time periodSchedule
Last scheduled policy run timeLast Run Time
Upcoming scheduled policy run timeNext Run Time
Understanding the Web Client Interface 33
Page 34

Table 19 Scheduler tab (continued)
Accessing the Web Client
1. Launch a preferred web browser.
2. Type https://<RmhServer>:5555/Server/Html5 in the address bar.
3. Read the security certificate message before you continue. Click Continue to this website (not
recommended).
Figure 25 Security Certificate of Website
DisplaysColumn
Expiration of scheduled policy run timeExpiry
Retention of policyRetention
Result status of last policy run timeLast Run Status
NOTE: The Web Client requires enabling JavaScript. If the page does not properly display
on your web browser, adjust the internet settings of the browser. For more information about
adjusting the internet settings, see “Enabling JavaScript on Web Client” (page 72).
Connecting to Recovery Manager Server
When you establish a connection, a logon dialog box appears.
1. Type your user name and password.
Figure 26 Connect to Recovery Manager Server Dialog Box
34 Using the Web Client Interface
Page 35

2. Click Connect.
Setting Up the Recovery Manager Web Client
Connecting to Hyper-V Server
If a Hyper-V server is not found in the repository, you can manually add a server.
1. Launch the Recovery Manager web client.
2. Type the required credentials:
• Hyper-V server hostname or IP address
• User name
• Password
Figure 27 Connect to Hyper-V Server Dialog Box
3. Click Connect.
Installing Recovery Manager Agent
To install HP 3PAR Recovery Manager agent on a Hyper-V server:
Setting Up the Recovery Manager Web Client 35
Page 36

1. From the menu bar, click Administrative Tools to open the drop-down menu.
Figure 28 Installing Recovery Manager Agent Dialog Box
2. Right-click context menu of the Hyper-V Servers tree node.
3. Continue to follow the prompts.
Uninstalling Recovery Manager Agent
To uninstall HP 3PAR Recovery Manager agent from a Hyper-V server:
1. From the menu bar, click Administrative Tools to open the drop-down menu.
2. Enter the user credentials as the following:
• Hyper-V server host name or IP address
• Domain or Hostname\User name
• Password
Figure 29 Uninstall Recovery Manager Agent Dialog Box
3. Right-click context menu of the Hyper-V Servers tree node.
4. Select the Hyper-V server in tree view pane.
5. Click the Uninstall Agent hyperlink.
36 Using the Web Client Interface
Page 37

Updating StoreServ Credentials
To update HP 3PAR StoreServ login credentials:
1. From the Tree view pane, select the Hyper-V server node.
2. Click the Update HP 3PAR StoreServ Credential hyperlink located on the control bar.
3. Enter the new user name and password.
4. Click Update.
Adding HP 3PAR StoreServ System Credentials
To add HP 3PAR StoreServ system credentials:
1. From the Tree view pane, select the Hyper-V server.
2. Click the Add HP 3PAR StoreServ Credential hyperlink located on the control bar.
3. Enter the credentials for the following:
• 3PAR StoreServ Name
• User name
• Password
Figure 30 Add 3PAR StoreServ Dialog Box
4. Click Add.
Disconnecting Microsoft Hyper-V Servers
To disconnect a Microsoft Hyper-V server:
1. From the Tree pane view, select the Hyper-V server.
2. Click Disconnect.
Figure 31 Disconnecting a Microsoft Hyper-V Server
Working with Virtual Copies
Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V provides essential tools to create, browse, and manage
VSS aware application consistent Virtual Copies of Microsoft Hyper-V and HP 3PAR StoreServ
system environments. The Virtual Copies are policy-based and its retention and expiration values
can be set at the time of creation.
Working with Virtual Copies 37
Page 38

The application also provides the capability to perform a full restoration of any Virtual Machines
to its original location from a point-in-time Virtual Copy or VSS aware Snapshot. Any existing
configuration files and virtual hard disks are overwritten.
Creating Virtual Copies
NOTE: There are three options to create a Virtual Copy:
• Select a Hyper-V Server from the tree and click the Virtual Machines tab then select one or
more Virtual Machines and click Create Virtual Copy.
• Select a Hyper-V Server from the tree and click the Virtual Copies tab then click Create.
• Select a Virtual Machine from the tree and click the Virtual Copies tab then click Create.
To create a Virtual Copy:
1. From the Tree view pane, select the Hyper-V server.
2. Click the Virtual Machines tab and select one or more Virtual Machines.
Figure 32 Virtual Machines Tab
3. Click Create Virtual Copy.
4. If applicable, set the values for the following options:
• Virtual Copy name prefix (optional) The name of the virtual copy and is optional.
• Set Virtual Copy expiration Virtual Copy will be removed by StoreServ system when it
expired.
• Set Virtual Copy retention Virtual Copy can not be removed until retention period end.
• Enable saved state backup If all conditions required for an application consistent backup
are not met, then Recovery Manager for Hyper-V can take a saved state (crash consistent)
backup for the VM, if this option is enabled. If the option has not been enabled and all
requirements for an application consistent backup are not met, then Recovery Manager
for Hyper-V will fail the backup request.
NOTE: By default, Recovery manager for Hyper-V will always attempt an application
consistent back up first, whether or not this option is enabled.
NOTE: Click the question mark for more details about the option.
38 Using the Web Client Interface
Page 39

Figure 33 Create Virtual Copy
5. Click Create.
NOTE: For more information about using the CLI feature to create a Virtual Copy, see HP 3PAR
Command Line Interface Reference
Setting Policy to Virtual Copies
You can set expiration and retention policies to any newly created Virtual Copies.
To set the Virtual Copy policy of one or more Virtual Machines:
1. From the Tree view pane, select the Hyper-V server.
2. Click the Virtual Machines tab and select one or more Virtual Machines.
Figure 34 Virtual Machines Tab
NOTE: When a single Virtual Machine is selected, RMH retrieves policy of the Virtual
Machine from the repository and displays the information. If multiple Virtual Machines are
selected, RMH only displays the default policy settings.
3. Click Virtual Copy Policy.
4. Set the values for the following options:
• Set Virtual Copy expiration
• Set Virtual Copy retention
• Enable saved state backup
NOTE: Click the question mark for more details about the option.
Working with Virtual Copies 39
Page 40

Figure 35 Virtual Copy Policy Dialog Box
5. Click Save.
Analyzing Virtual Copies
Analyze command displays inconsistencies in all virtual copy records by matching virtual copies
in the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage System against records in HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for
Hyper-V repository. Optionally, you can delete the virtual copies that are not found in HP 3PAR
StoreServ Storage System.
To analyze one or more Virtual Copies:
1. From the Tree view pane, select the Hyper-V server.
2. Click the Virtual Copies tab and select one or more Virtual Copies.
3. Click Analyze when a single Virtual Copy is selected or Analyze All Virtual Copies when
multiple Virtual Copies are selected.
The following output provides an analytical summary of all selected Virtual Copies.
Figure 36 Summary of Analyzed Virtual Copies
Restoring Virtual Machines From Virtual Copies
To restore a Virtual Machine from a Virtual Copy:
1. From the Tree view pane, select the Hyper-V server.
40 Using the Web Client Interface
Page 41

2. Click the Virtual Copies tab and select a Virtual Copy.
Figure 37 Restoring Virtual Machines from a Virtual Copy
3. Click Restore.
Removing Virtual Copies
To remove one or more Virtual Copies:
1. From the Tree view pane, select the Hyper-V server.
2. Click the Virtual Copies tab and select one or more Virtual Copies.
Figure 38 Removing Virtual Copies
3. Click Remove.
Mounting Virtual Copies
When a Virtual Copy is created, you can mount the Virtual Copy to a node cluster or Microsoft
Hyper-V server.
To mount a Virtual Copy to a node cluster or Microsoft Hyper-V server:
1. From the Tree view pane, select either a server or node cluster.
2. Click the Virtual Copies tab.
3. Select a Virtual Copy and then select one or more virtual volumes.
Working with Virtual Copies 41
Page 42

Figure 39 Selecting a Virtual Copy and Virtual Volume
4. Click Mount.
5. Set the values for the following options:
• Mount on cluster node
• Mount on another Hyper-V server
• Mount point prefix (optional)
NOTE: Click the question mark for more details about the option.
Figure 40 Mounting a Virtual Copy
6. Click Mount.
42 Using the Web Client Interface
Page 43

Unmounting Virtual Copies
When a Virtual Copy is under a Mounted state, use the following steps to unmount a Virtual Copy.
1. From the Tree view pane, select either a server or node cluster.
2. Click the Virtual Copy tab.
3. Select a Virtual Copy and then select one or more virtual volumes.
Figure 41 Selecting a Virtual Copy and Virtual Volume
4. Click Unmount.
5. Select the values for the following options:
• Unmount on cluster node
• Unmount on another Hyper-V server
NOTE: Click the question mark for more details about the option.
Figure 42 Unmounting a Virtual Copy
Working with Virtual Copies 43
Page 44

6. Click Unmount.
Scheduling Virtual Copy Creation Tasks
You can schedule Virtual Copy creation tasks according to a specified schedule.
To add a scheduled Virtual Copy creation task:
1. From the Tree view pane, select either a server or node cluster.
2. Click the Scheduler tab.
Figure 43 Scheduler Tab
3. Click the Create Virtual Copies tab.
4. Click Add.
5. Follow the wizard to complete the scheduling tasks and click Next.
Figure 44 Schedule Virtual Copy Task Wizard
6. Set the values for the following applicable options and click Next:
• Task name
• Create Virtual Copy
Virtual Copy name prefix (optional)
◦ Set Virtual Copy expiration
◦ Set Virtual Copy retention
◦ Enable saved state backup
44 Using the Web Client Interface
Page 45
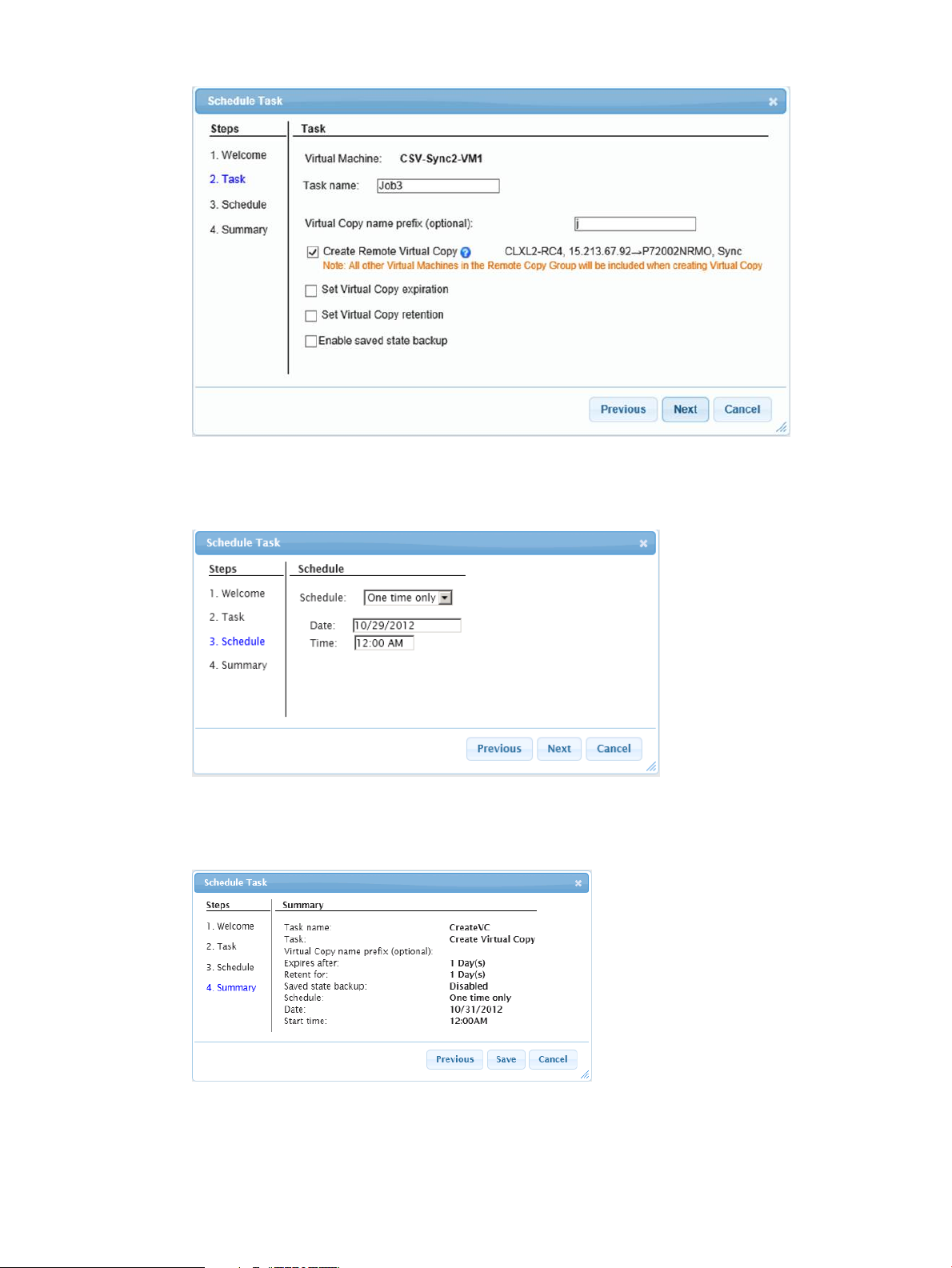
Figure 45 Schedule Virtual Copy Task Details
7. Set the values for the Schedule, Date, and Time and click Next.
Figure 46 Schedule Virtual Copy Task Date and Time
8. Review the summary of task and click Save.
Figure 47 Schedule Virtual Copy Creation Task Summary
9. If updating the schedule is necessary, select a schedule and click Update. Continue to follow
the wizard to update the scheduling tasks. When the update is complete, click Refresh to
update the data view of the selected tab.
Working with Virtual Copies 45
Page 46

Scheduling Virtual Copy Analysis Tasks
You can schedule Virtual Copy analysis tasks according to a specified schedule.
To add a scheduled Virtual Copy analysis task:
1. From the Tree view pane, select either a server or node cluster.
2. Click the Scheduler tab.
3. Click the Analyze All Virtual Copies tab.
4. Click Add.
5. Follow the wizard to complete the scheduling tasks and click Next.
Figure 48 Schedule Virtual Copy Analysis Task Wizard
6. Set the values for the following applicable options:
• Task name
• Analyze and clean up all Virtual Copies
Figure 49 Schedule Virtual Copy Analysis Task Details
7. Set the values for the Schedule, Date, and Time and click Next.
46 Using the Web Client Interface
Page 47

Figure 50 Schedule Virtual Copy Analysis Task Date and Time
8. Review the summary of task and click Save.
Figure 51 Schedule Virtual Copy Analysis Task Summary
9. If updating the schedule is necessary, select a schedule and click Update. Continue to follow
the wizard to update the scheduling tasks. When the update is complete, click Refresh to
update the data view of the selected tab.
Last Run Output
This function is optional when a scheduled task is run successfully from the windows scheduler but
may fail from the PowerShell. In this event you can click the Last Run Output button or right click
a Create Virtual Copy or Analyze All Virtual Copies schedule and the last run output will appear
with the status.
Figure 52 Last Run Output
Working with Virtual Copies 47
Page 48

Working with Remote Copies
HP 3PAR Remote Copy Software helps you to safeguard against disasters that can occur at one
location, by allowing you to keep copies of data on a separate server which can be placed at a
remote location. For example, if there were a fire or earthquake at one location, all of the data
stored there could be lost unless a backup copy can be recovered from a separate location not
affected by the disaster.
To maintain updated copies of data at a remote location, Remote Copy uses two HP 3PAR StoreServ
Storage Systems: a primary system (used for production) and a Remote Copy backup system, which
can be located anywhere. Therefore, when disaster strikes in one location, there is always a backup
of your data at the backup site.
For more information, see HP 3PAR Remote Copy Software User’s Guide.
Creating Remote Virtual Copies
To create a Remote Virtual Copy:
1. From the Tree view pane, select the Hyper-V server.
Figure 53 Hyper-V Server
2. Click Edit to assign the details of Remote Recovery Manager Server.
48 Using the Web Client Interface
Page 49

Figure 54 Remote Recovery Manager Server
3. Click the Virtual Machines tab and select one or more Virtual Machines.
4. Click Create Virtual Copy.
Working with Remote Copies 49
Page 50
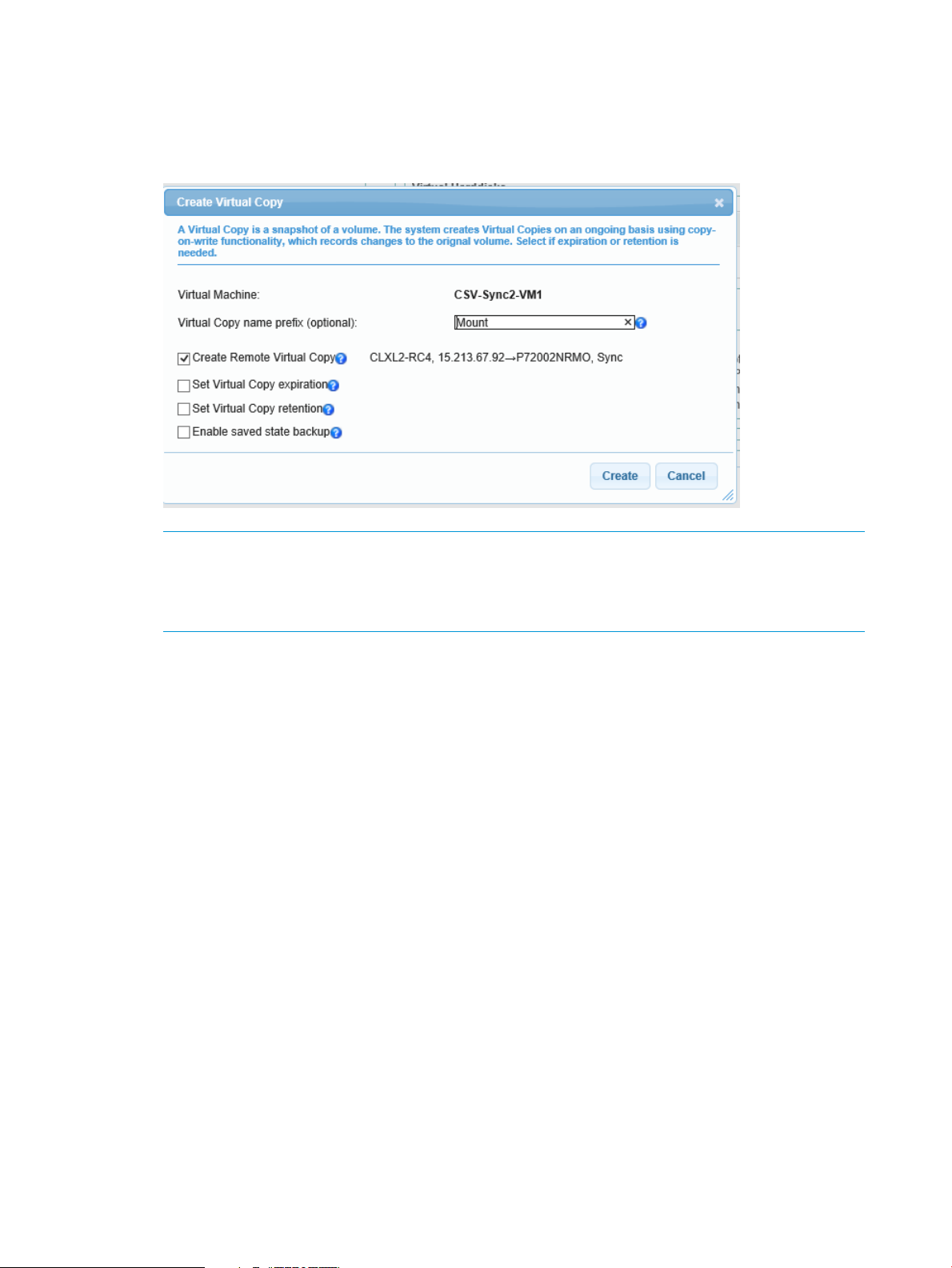
5. Enable the check box Create Remote Virtual Copy and from the list select:
• Sync
• Periodic
Figure 55 Create Remote Virtual Copy
NOTE: While it is not possible to send partial data within a Remote Copy group across data
sites. When there are multiple virtual machines configured to a same Remote Copy group
from StoreServ, virtual machines will be backed up, even if one of the Virtual Machine is
selected.
Repository Backup
Repository backup is vital for maintaining regular backups. If the RMH server fails, all the information
is no more accessible or lost forever. Moreover, if the RMH server (production server) fails, RMH
has to be reinstalled.
RMH server repository consists of two primary metadata files rmhv.db and settings.db. Both
these files are vital for repository backup as they have snapshot and credential information. Without
the rmhv.db file, RMH snapshot cannot be recovered and with no settings.db file, you have
to enter your RMH and HP 3PAR credential again.
Saving a Repository
To save a repository on a network path:
1. From the menu bar, click Administrative Tools to open the drop-down menu.
2. Select Save Repository.
50 Using the Web Client Interface
Page 51

Figure 56 Save Repository on Network Path
3. Select the option Save to a network path using the following credential. By default this option
is selected.
4. Enter the required credentials:
• Hyper-V server hostname or IP address
• User name
• Password
• Network path
5. Click Save to save the files on the network path.
NOTE: The repository backup takes only few seconds. Hence, it is recommended that you
avoid snapshot creation or mount/unmount operations while saving or importing repository.
To save a repository to a local path:
1. From the menu bar, click Administrative Tools to open the drop-down menu.
2. Select Save Repository.
Figure 57 Save Repository
3. Enter the location of the path and click Save to save on the local path.
Repository Backup 51
Page 52

Scheduling Repository Backup
To schedule a repository backup on a network path:
1. From the menu bar, click Administrative Tools to open the drop-down menu.
2. Select Schedule Save Repository and click Add.
Figure 58 Scheduling Repository Backup
3. Follow the wizard to complete the scheduling tasks and click Next.
Figure 59 Schedule Task
4. Set the values for the following applicable options and click Next:
• Task name
• Select the option Save to a network path using the following credential. By default this
option is selected.
• Hyper-V server hostname or IP address
• User name
• Password
• Network path
52 Using the Web Client Interface
Page 53

NOTE: The format of the location of the network path is: \\RemoteHost\<local
drive>\BackupRepository
Figure 60 Schedule Task
5. Set the values for the Schedule, Start time, Recur every , and click Next.
6. Review the summary of task and click Save.
Figure 61 Summary
7. If updating the schedule is necessary, select Save Repository and click Update. Continue to
follow the wizard to update the scheduling tasks.
When the update is complete, click Refresh to update the data view of the selected tab.
To schedule a repository backup to a local path:
1. From the menu bar, click Administrative Tools to open the drop-down menu.
2. Clear the option Save to a network path using the following credential
3. Set the values for the following applicable options and click Next:
• Task name
• Location of the path
NOTE: The format of the location of the network path is: c\BackupRepository.
Figure 62 Schedule Task
4. Set the values for the Task name, Path on and click Next.
5. Review the summary of task and click Save.
Repository Backup 53
Page 54

Importing Repository Backup
To import a repository from a Network path:
1. From the menu bar, click Administrative Tools to open the drop-down menu.
2. Click Import Repository.
Figure 63 Import Repository
3. Select the option Import from a network path using the following credential. By default this
option is selected.
4. Enter the required credentials:
• Windows hostname or IP address
• User name
• Password
• Network path
5. Select the option Refresh all servers after import is completed.
6. Click Import to import the files from the network path.
To import a repository from a local path:
1. From the menu bar, click Administrative Tools to open the drop-down menu.
2. Click Import Repository.
3. Clear the option Import from a network path using the following credential.
4. Enter the required credential:
• Path on
5. Click Import to import the files from the local path.
Logging Off From Session
To log off from the Recovery Manager Server:
1. From the menu bar, click Logon as <Administrator>.
2. Click Log off.
54 Using the Web Client Interface
Page 55

5 Using PowerShell Snap-in Command Line Interface
HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for Hyper-V includes custom Powershell snap-in as the default client
interface and provides essential command lines for administrative tasks.
NOTE: For the list of all command used in Recovery Manager for Hyper-V, see “HP 3PAR Recovery
Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V Powershell Commands” (page 73)
Connecting to RMH Server
Use the following command lines to establish a session with the Microsoft Hyper-V server.
Login-Rmh
Log on to RMH Server using Windows RMH account.
The optional login-Rmh enables the user to log on to Recovery Manager for Hyper-V. After a
successful login is established, the user is not required to enter additional credentials for subsequent
Cmdlets.
Syntax
Any optional parameters are enclosed in square brackets [ ] around them.
Login-Rmh-RmhServerName <-RmhServerName>-RmhUserName
<-RmhUserName>-RmhPassword <-RmhPassword>[-RmhEncrytedPassword]
Table 20 Login-Rmh parameters
-RmhEncrytedPassword
Logout-Rmh
The optional logout-Rmh Cmdlet logs off the user from the application.
Preconditions
The user must first login with Login-Rmh.
Syntax
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Required-RmhServerName
Required-RmhUserName
Required-RmhPassword
Host name of the RMH Server. This is
FQDN or IP address.
RMH user name. If not specified, a
dialog box will be presented to enter
credentials.
RMH user password. If not specified, a
dialog box will be presented to enter
credentials.
May be used instead of
-RmhPassword
Any optional parameters are enclosed in square brackets [ ] around them.
Logout-Rmh -RmhServerName <RmhServerName>
Table 21 Logout-Rmh parameters
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Required-RmhServerName
Host name of the RMH Server. This is
FQDN or IP address.
Connecting to RMH Server 55
Page 56

Configuring RMH Server
The section describes the command line usage and parameters for configuring Hyper-V servers.
Add-HyperV
Add-HyperV adds Hyper-V credentials for users. The command is used with each Microsoft
Hyper-V (cluster or standalone host) credentials and managed by the application.
Add-HyperV command completes when specifying <WORKGROUP or HOST NAME>\<USERNAME>
format as username.
Preconditions
• User must first log on with Login-Rmh
• Hyper-V name (or synonym) just not already exist
Syntax
Any optional parameters are enclosed in square brackets [ ] around them.
Add-HyperV -RmhServerName <RmhServerName> -HypervName <HypervName>
-HypervUsername <HypervUser> -HypervPassword <HypervPassword> [-Verbose]
Table 22 Add-HyperV parameters
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Add-StoreServ
Add-StoreServ is used for each HP 3PAR StoreServ credentials.
• HP 3PAR StoreServ credentials are associated to a specific Microsoft Hyper-V
Required-RmhServerName
Required-HypervName
Required-HypervUsername
Required-HypervPassword
Host name of the RMH Server. This is
FQDN or IP address.
Hyper-V host or cluster name. This is
FQDN or IP address. Synonyms are
checked. The localhost is not supported.
Hyper-V username. If cluster, ensure all
controller nodes in the cluster have the
same username. If not specified, a
dialog box will be presented to enter
credentials.
User name format: <WORKGROUP or
HOST NAME>\<USERNAME>.
Hyper-V password. If cluster, ensure all
controller nodes in the cluster have the
same password. If not specified, a
dialog box will be presented to enter
credentials.
Displays progress messages.Optional-Verbose
• This command is only required to initially set up credentials. The command is persisted by
RMH Server until the user removes it.
• The user can Add/Remove/Update HP 3PAR StoreServ credentials at any time during the
session
56 Using PowerShell Snap-in Command Line Interface
Page 57

Preconditions
• The user must first login with Login-Rmh.
• HP 3PAR StoreServ name must not already exist for specified Microsoft Hyper-V
Syntax
Any optional parameters are enclosed in square brackets [ ] around them.
Add-StoreServ -RmhServerName <RmhServerName> -HypervName <HypervName>
-StoreServName <StoreServName> -StoreServUsername <StoreServUsername>
-StoreServPassword <StoreServPassword> [-Verbose]
Table 23 Add-StoreServ parameters
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Set-RmhPolicy
The set-RmhPolicy Cmdlet provides the ability to edit the default RMH Policy settings of a Virtual
Machine.
Preconditions
The user must first login with Login-Rmh.
Required-RmhServerName
Required-HypervName
Required-StoreServName
Required-StoreServUsername
Required-StoreServPassword
Host name of the RMH Server. This is
FQDN or IP address.
This is FQDN or IP address. Synonyms
are supported. The localhost is not
supported.
This is FQDN or IP address, etc.
Synonyms for HP 3PAR StoreServ are
supported.
Note, if not provided, a dialog box will
pop up asking for credentials.
Note, if not provided, a dialog box will
pop up asking for credentials.
Displays progress messagesOptional-Verbose
Syntax
Any optional parameters are enclosed in square brackets [ ] around them.
Set-RmhPolicy -RmhServerName <RmhServerName> -HypervName <HypervName>
-VmNameUuid <VmNameUuid> [-Expiry] [-Retention] [-SavedStateBackups]
[-Verbose]
Table 24 Set-RmhPolicy parameters
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Required-RmhServerName
Required-HypervName
Required-VmNameUuid
Host name of the RMH Server. This is
FQDN or IP address.
Select Hyper-V host/cluster to use. This
is FQDN or IP address. Synonyms for
Hyper-V are supported. The
localhost is not supported.
Name/unique id of VM to set policy
for Virtual Machine.
Configuring RMH Server 57
Page 58

Table 24 Set-RmhPolicy parameters (continued)
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Get-ClusterNodeNames
The Get-ClusterNodeNames command retrieves cluster node names for the Hyper-V cluster.
Preconditions
The user must first login with Login-Rmh.
Syntax
Any optional parameters are enclosed in square brackets [ ] around them.
Get-ClusterNodeNames -RmhServerName <RmhServerName> -HypervName
<HypervName> [-Verbose]
Optional-Expiry
Optional-Retention
Optional-SavedStateBackups
Integer value followed by letter h or d
for Hours and Days respectively. Use 0
to reset.
Integer value followed by letter h or d
for Hours and Days respectively. Use 0
to reset
Disabled or enabled. Use reset to
reset.
Displays progress messagesOptional-Verbose
Table 25 Get-ClusterNodeNames parameters
Get-EncryptedLoginPassword
Get-EncryptedLoginPassword is used for scripting to return an encrypted password for the
currently logged-in RMH user.
Preconditions
The user must first login with Login-Rmh.
Syntax
Any optional parameters are enclosed in square brackets [ ] around them.
Get-EncryptedLoginPassword-RmhServerName <RmhServerName> [-Verbose]
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Required-RmhServerName
Required-HypervName
Host name of the RMH Server. This is
FQDN or IP address.
Select Hyper-V host/cluster to use. This
is FQDN or IP address. Synonyms for
Hyper-V are supported. The
localhost is not supported.
Displays progress messages.Optional-Verbose
58 Using PowerShell Snap-in Command Line Interface
Page 59

Table 26 Get-EncryptedLoginPassword parameters
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Get-RmhPolicy
The get-RmhPolicy retrieves the RMH policy settings of a Hyper-V Virtual Machine. An RMH
policy object retains the set default values for Virtual Copies. You can customize the attributes of
a Virtual Copy.
Preconditions
The user must first login with Login-Rmh.
Syntax
Any optional parameters are enclosed in square brackets [ ] around them.
Get-RmhPolicy -RmhServerName <RmhServerName> -HypervName <HypervName>
-VmNameUuid <VmNameUuid> [-Verbose]
Table 27 Get-RmhPolicy parameters
Required-RmhServerName
Required-RmhServerName
Host name of the RMH Server. This is
FQDN or IP address.
Displays progress messages.Optional-Verbose
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Host name of the RMH Server. This is
FQDN or IP address.
Get-VirtualMachine
Get-VirtualMachine retrieves current Virtual Machines available on an active-session Hyper-V
host/cluster.
Preconditions
The user must first login with Login-Rmh.
Syntax
Any optional parameters are enclosed in square brackets [ ] around them.
Get-VirtualMachine -RmhServerName <RmhServerName> -HypervName
<HypervName> [-Verbose]
Required-HypervName
Required-VmNameUuid
Select Hyper-V host/cluster to use. This
is FQDN or IP address. Synonyms for
Hyper-V are supported. The
localhost is not supported.
Name/unique id of VM to set policy
for Virtual Machine.
Displays progress messagesOptional-Verbose
Configuring RMH Server 59
Page 60

Table 28 Get-VirtualMachine parameters
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
The command returns multiple RMHirtualMachineInfo objects.
Show-Connection
Show-Connection displays connection information for current login RMH user name, all RMH
Hyper-V hosts/clusters, and all Hyper-V Storage Systems associated with the user. The actively
selected Hyper-V will also be shown.
Preconditions
The user must first login with Login-Rmh.
Syntax
Any optional parameters are enclosed in square brackets [ ] around them.
Show-Connection -RmhServerName <RmhServerName> [-HypervName]
[-ShowMissingStoreServs] [-Verbose]
Required-RmhServerName
Required-HypervName
Host name of the RMH Server. This is
FQDN or IP address.
Select Hyper-V host/cluster to use. This
is FQDN or IP address. Synonyms for
Hyper-V are supported. The
localhost is not supported.
Displays progress messages.Optional-Verbose
Table 29 Show-Connection parameters
Working with Virtual Copies
This section describes the command usage and parameters for working with Virtual Copies.
Create-vCopy
The create-vCopy Cmdlet creates a new Virtual Copy of a VM and includes the following
supported parameters.
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Required-RmhServerName
Optional-HypervName
Optional-ShowMissingStoreServs
Host name of the RMH Server. This is
FQDN or IP address.
Optionally select Hyper-V host/cluster
to use. This is FQDN or IP address.
Synonyms for Hyper-V are supported.
The localhost is not supported.
If specified, StoreServs used by
Hyper-V(s), but missing credentials, are
shown.
Displays progress messages.Optional-Verbose
Preconditions
The user must first login with Login-Rmh.
Syntax
Any optional parameters are enclosed in square brackets [ ] around them.
60 Using PowerShell Snap-in Command Line Interface
Page 61

Create-vCopy -RmhServerName <RmhServerName> -HypervName <HypervName>
-VmNamesUuids <VmNamesUuids> [-VcNamePrefix] [-Expiry] [-Retention]
[-SavedStateBackups] [-Verbose]
Table 30 Create-vCopy parameters
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Required-RmhServerName
Required-HypervName
Required-VmNamesUuids
Optional-VcNamePrefix
Optional-Expiry
Optional-Retention
Host name of the RMH Server. This is
FQDN or IP address.
Select Hyper-V host/cluster to use. This
is FQDN or IP address. Synonyms for
Hyper-V are supported. The
localhost is not supported.
Comma separated VM names (or
UUIDs) .
For best practice, if more than one VM
name specified, ensure all VMs use the
same Storage System volume.
The Virtual Copy name prefix. A unique
timestamp will be generated for this
new Virtual Copy and appended to this
prefix. If not specified, the VC name
will be vc-timestamp where
timestamp is generated for this new
Virtual Copy.
Integer value followed by letter h or d
for Hours and Days respectively Default:
use the RMH Policy.
Integer value followed by letter h or d
for Hours and Days respectively Default:
use the RMH Policy.
This Cmdlet returns a list of custom objects of type RmhCreateVirtualcopyResult, each for
every VM being used and includes following properties:
• VM Name or UUID
• Success/Failure status of the create-vCopy operation for the VM
• Detailed error message(s) when operation fails
• An instance of an object of type RMHirtualcopySet describing created Virtual Copy set.
Get-vCopy
Get-vCopy is used to retrieve existing Virtual Copies details of a Virtual Machine from the Recovery
Manager Hyper-V Repository of a specified Hyper-V server. This command has many filters to
reduce the number of Virtual Copies during retrieving process.
Preconditions
The user must first login with Login-Rmh.
Disabled or enabled.Optional-SavedStateBackups
Default: use the RMH policy.
Displays progress messagesOptional-Verbose
(See Get-vCopySet Cmdlet for details of this object)
Working with Virtual Copies 61
Page 62

Syntax
Any optional parameters are enclosed in square brackets [ ] around them.
Get-vCopy -RmhServerName <RmhServerName> -HypervName <HypervName>
[-VcNamesUuids] [-VmNamesUuids] [-Timestamp] [-Verbose]
Table 31 Get-vCopy parameters
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
The command returns multiple RMHirtualSet objects.
Mount-vCopy
Mount-vCopy exports and mounts specified Virtual Copy virtual volumes to a Hyper-V host for
manual restoration of virtual hard disks. This command can be repeated with unique mount point
prefixes if necessary.
Mount point is optional. Virtual volume(s) can be accessed using Volume GUID, if mount point
prefixes are not specified.
Required-RmhServerName
Required-HypervName
Optional-VcNamesUuids
Optional-VmNamesUuids
Optional-Timestamp
Host name of the RMH Server. This is
FQDN or IP address.
Select Hyper-V host/cluster to use. This
is FQDN or IP address. Synonyms for
Hyper-V are supported. The
localhost is not supported.
Select VCs by name/uuid using a
comma-separated list. If not specified,
VCs name/uuid is not used to filter
selection.
Select names/uuids to filter VC selection
by VM. If not specified, VM
names/uuids is not used to filter
selection.
Specify timestamp of VC to locate in
the format mmddyyhhmmss.
Displays progress messages.Optional-Verbose
Preconditions
The user must first login with Login-Rmh.
Syntax
Any optional parameters are enclosed in square brackets [ ] around them.
Mount-vCopy -RmhServerName <RmhServerName> -HypervName <HypervName>
-VcNameUuid <VcNameUuid> -VmNameUuid <VmNameUuid> [-Timestamp]
[-MountPointPrefix] [-Select] [-HypervHostName] [-Verbose]
Table 32 Mount-vCopy parameters
Required-RmhServerName
Required-HypervName
62 Using PowerShell Snap-in Command Line Interface
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Host name of the RMH Server. This is
FQDN or IP address.
Select Hyper-V host/cluster to use. This
is FQDN or IP address. Synonyms for
Hyper-V are supported. The
localhost is not supported.
Page 63

Table 32 Mount-vCopy parameters (continued)
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Select VC by name/uuid.Required-VcNameUuid
Required-VmNameUuid
Optional-Timestamp
Optional-MountPointPrefix
Optional-Select
Select name/uuid to filter VC selection
by Virtual Machine.
Specify timestamp of VC to locate in
the format mmddyyhhmmss.
Mount point prefix where RMH will
create a mount point for each Virtual
Volume mounted using an appended
mount point name in the format
RMHv.wwn.partition.guidtimestamp
where wwn is WWN of VV mounted,
partition is the partition number, and
timestamp is in format mmddyyhhmmss.
NOTE: If not specified, VVs will be
exported to host by Storage System, but
no mount points will be used. You will
need to access VVs using their volume
guid path (example:
\\?\Volume(wwn)\).
Specifies the virtual hard disk name,
virtual volume name, or virtual volume
WWN in a comma-separated list. For
virtual hard disk name, this is the full
filename with path, or just a partial
name. Wildcards are not allowed. By
default, RMH will mount all Virtual
Copy volumes in a VCS.
The command returns RmhMountVirtualCopySetResult objects and contains:
• RmhMountVirtualCopySet with current state updated
• Information on name, WWN, partition, volume guid path, and mount point of each Virtual
Volume mounted
Restore-vCopyVm
The restore-vCopyVm initiates a full restore or recovery of Virtual Machines.
Preconditions
The user must first login with Login-Rmh.
Syntax
Any optional parameters are enclosed in square brackets [ ] around them.
Restore-vCopyVm -RmhServerName <RmhServerName> [-HypervName] -VcNameUuid
<VcNameUuid> -VmNameUuid <VmNameUuid> [-Timestamp] [-Force] [-RestartVm]
[-Verbose]
Optional-HypervHostName
Hyper-V host name. Use this option to
specify host node in cluster. You may
also use this option in a non-cluster
environment. If not specified, host name
of the RMH Server is used from
Login-Rmh.
Displays progress messages.Optional-Verbose
Working with Virtual Copies 63
Page 64

Table 33 Restore-vCopyVm parameters
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
This command returns the location of restored Virtual Machine and host name.
Analyze-vCopy
The Analyze-vCopy analyzes Virtual Copies for errors. When any Virtual Copy records contain
a volume missing on storage system, the Virtual Copy with an error is flagged. The user can use
the option to analyze and repair inconsistent Virtual Copies.
Required-RmhServerName
Optional-HypervName
Required-VmNameUuid
Optional-Timestamp
Host name of the RMH Server. This is
FQDN or IP address.
Select Hyper-V host/cluster to use. This
is FQDN or IP address. Synonyms for
Hyper-V are supported. The
localhost is not supported.
Select VC by name/uuid.Required-VcNameUuid
Select name/uuid to filter VC selection
by VM.
Specify timestamp of VC to locate in
the format mmddyyhhmmss.
Bypass confirmation prompt.Optional-Force
If specified, VM will be restarted.Optional-RestartVm
Displays progress messages.Optional-Verbose
Preconditions
The user must first login with Login-Rmh.
Syntax
Any optional parameters are enclosed in square brackets [ ] around them.
Analyze-vCopy -RmhServerName <RmhServerName> -HypervName <HypervName>
[-VcNamesUuids] [-VmNamesUuids] [-Timestamp] [-Cleanup] [-Verbose]
Table 34 Analyze-vCopy parameters
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Required-RmhServerName
Required-HypervName
Optional-VcNamesUuids
Optional-VmNamesUuids
Host name of the RMH Server. This is
FQDN or IP address.
Select Hyper-V host/cluster to use. This
is FQDN or IP address. Synonyms for
Hyper-V are supported. The
localhost is not supported.
Select VCs by name/uuid using a
comma-separated list. If not specified,
VCs name/uuid is not used to filter
selection.
Select names/uuids to filter VC selection
by VM. If not specified, VM
names/uuids is not used to filter
selection.
Optional-Timestamp
64 Using PowerShell Snap-in Command Line Interface
Specify timestamp of VC to locate in
the format mmddyyhhmmss.
Page 65

Table 34 Analyze-vCopy parameters (continued)
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Unmount-vCopy
Unmount-vCopy unmounts currently mounted Virtual Copy volume(s) for the specified Virtual
Copy and Virtual Machine name.
Preconditions
The user must first login with Login-Rmh.
Syntax
Any optional parameters are enclosed in square brackets [ ] around them.
Unmount-vCopy -RmhServerName <RmhServerName> -HypervName <HypervName>
-VcNameUuid <VcNameUuid> -VmNameUuid <VmNameUuid> [-Timestamp] [-Select]
[-HypervHostName] [-Verbose]
Optional-Cleanup
If specified, Analyze-vCopy will
clean up the inconsistent VC by
removing it. Removing the inconsistent
VC will take the same action as the
Remove-vCopy command. If there are
no inconsistencies, the VC is not
removed. Without this option, the same
work is performed except no action is
taken to remove the VC. Instead, the
user will be given an error report.
Displays progress messages.Optional-Verbose
Table 35 Unmount-vCopy parameters
Required-RmhServerName
Required-HypervName
Required-VmNameUuid
Optional-Timestamp
Optional-Select
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Host name of the RMH Server. This is
FQDN or IP address.
Select Hyper-V host/cluster to use. This
is FQDN or IP address. Synonyms for
Hyper-V are supported. The
localhost is not supported.
Select VC by name/uuid.Required-VcNameUuid
Select name/uuid to filter VC selection
by Virtual Machine.
Specify timestamp of VC to locate in
the format mmddyyhhmmss.
Specifies the virtual hard disk name,
virtual volume name, or virtual volume
WWN in a comma-separated list. For
virtual hard disk name, this is the full
filename with path, or just a partial
name. Wildcards are not allowed. By
default, RMH will unmount all Virtual
Copy volumes in a VCS.
Optional-HypervHostName
Hyper-V host name. Use this option to
specify host node in cluster. You may
also use this option in a non-cluster
environment. If not specified, host name
Working with Virtual Copies 65
Page 66

Table 35 Unmount-vCopy parameters (continued)
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
of the RMH Server is used
fromLogin-Rmh.
Displays progress messages.Optional-Verbose
The command returns RmhMountVirtualCopySetResult objects and contains:
• RMHVirtualCopySet with current state updated
• Information on name, WWN, partition, volume guid path, and mount point of each Virtual
Volume mounted
66 Using PowerShell Snap-in Command Line Interface
Page 67

6 Support and Other Resources
Contacting HP
For worldwide technical support information, see the HP support website:
http://www.hp.com/support
Before contacting HP, collect the following information:
• Product model names and numbers
• Technical support registration number (if applicable)
• Product serial numbers
• Error messages
• Operating system type and revision level
• Detailed questions
Specify the type of support you are requesting:
systems
Support requestHP 3PAR storage system
StoreServ 7000 StorageHP 3PAR StoreServ 7200, 7400, and 7450 Storage
HP 3PAR T-Class storage systems
HP 3PAR F-Class storage systems
HP 3PAR documentation
Supported hardware and software platforms
and administer HP 3PAR storage systems
Using the HP 3PAR CLI to configure and administer storage
systems
3PAR or 3PAR StorageHP 3PAR StoreServ 10000 Storage systems
See:For information about:
The Single Point of Connectivity Knowledge for HP
Storage Products (SPOCK) website:
http://www.hp.com/storage/spock
The HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage site:Locating HP 3PAR documents
http://www.hp.com/go/3par
To access HP 3PAR documents, click the Support link for
your product.
HP 3PAR storage system software
HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage Concepts GuideStorage concepts and terminology
HP 3PAR Management Console User's GuideUsing the HP 3PAR Management Console (GUI) to configure
HP 3PAR Command Line Interface Administrator’s
Manual
to manage host configuration and connectivity information
Model (CIM) to manage HP 3PAR storage systems
HP 3PAR Command Line Interface ReferenceCLI commands
HP 3PAR System Reporter Software User's GuideAnalyzing system performance
HP 3PAR Host Explorer User’s GuideInstalling and maintaining the Host Explorer agent in order
HP 3PAR CIM API Programming ReferenceCreating applications compliant with the Common Information
Contacting HP 67
Page 68

See:For information about:
HP 3PAR-to-3PAR Storage Peer Motion GuideMigrating data from one HP 3PAR storage system to another
Configuring the Secure Service Custodian server in order to
monitor and control HP 3PAR storage systems
Copy
Identifying storage system components, troubleshooting
information, and detailed alert information
Server
HP 3PAR Secure Service Custodian Configuration Utility
Reference
HP 3PAR Remote Copy Software User’s GuideUsing the CLI to configure and manage HP 3PAR Remote
HP 3PAR Upgrade Pre-Planning GuideUpdating HP 3PAR operating systems
HP 3PAR F-Class, T-Class, and StoreServ 10000 Storage
Troubleshooting Guide
HP 3PAR Policy Server Installation and Setup GuideInstalling, configuring, and maintaining the HP 3PAR Policy
HP 3PAR Policy Server Administration Guide
68 Support and Other Resources
Page 69

See:For information about:
Planning for HP 3PAR storage system setup
Hardware specifications, installation considerations, power requirements, networking options, and cabling information
for HP 3PAR storage systems
HP 3PAR StoreServ 7000 Storage Site Planning ManualHP 3PAR 7200, 7400, and 7450 storage systems
HP 3PAR StoreServ 7450 Storage Site Planning Manual
HP 3PAR 10000 storage systems
Installing and maintaining HP 3PAR 7200, 7400, and 7450 storage systems
initializing the Service Processor
7450 storage systems
HP 3PAR host application solutions
Backing up Oracle databases and using backups for disaster
recovery
HP 3PAR StoreServ 10000 Storage Physical Planning
Manual
HP 3PAR StoreServ 10000 Storage Third-Party Rack
Physical Planning Manual
HP 3PAR StoreServ 7000 Storage Installation GuideInstalling 7200, 7400, and 7450 storage systems and
HP 3PAR StoreServ 7450 Storage Installation Guide
HP 3PAR StoreServ 7000 Storage SmartStart Software
User’s Guide
HP 3PAR StoreServ 7000 Storage Service GuideMaintaining, servicing, and upgrading 7200, 7400, and
HP 3PAR StoreServ 7450 Storage Service Guide
HP 3PAR StoreServ 7000 Storage Troubleshooting GuideTroubleshooting 7200, 7400, and 7450 storage systems
HP 3PAR StoreServ 7450 Storage Troubleshooting Guide
HP 3PAR Service Processor Software User GuideMaintaining the Service Processor
HP 3PAR Service Processor Onsite Customer Care
(SPOCC) User's Guide
HP 3PAR Recovery Manager Software for Oracle User's
Guide
Backing up Exchange databases and using backups for
disaster recovery
Backing up SQL databases and using backups for disaster
recovery
Backing up VMware databases and using backups for
disaster recovery
Installing and using the HP 3PAR VSS (Volume Shadow Copy
Service) Provider software for Microsoft Windows
Best practices for setting up the Storage Replication Adapter
for VMware vCenter
Troubleshooting the Storage Replication Adapter for VMware
vCenter Site Recovery Manager
Installing and using vSphere Storage APIs for Array
Integration (VAAI) plug-in software for VMware vSphere
HP 3PAR Recovery Manager Software for Microsoft
Exchange 2007 and 2010 User's Guide
HP 3PAR Recovery Manager Software for Microsoft SQL
Server User’s Guide
HP 3PAR Management Plug-in and Recovery Manager
Software for VMware vSphere User's Guide
HP 3PAR VSS Provider Software for Microsoft Windows
User's Guide
HP 3PAR Storage Replication Adapter for VMware
vCenter Site Recovery Manager Implementation Guide
HP 3PAR Storage Replication Adapter for VMware
vCenter Site Recovery Manager Troubleshooting Guide
HP 3PAR VAAI Plug-in Software for VMware vSphere
User's Guide
HP 3PAR documentation 69
Page 70

Typographic conventions
Table 36 Document conventions
ElementConvention
Bold text
Monospace text
<Monospace text in angle brackets>
Bold monospace text
• Keys that you press
• Text you typed into a GUI element, such as a text box
• GUI elements that you click or select, such as menu items, buttons,
and so on
• File and directory names
• System output
• Code
• Commands, their arguments, and argument values
• Code variables
• Command variables
• Commands you enter into a command line interface
• System output emphasized for scannability
WARNING! Indicates that failure to follow directions could result in bodily harm or death, or in
irreversible damage to data or to the operating system.
CAUTION: Indicates that failure to follow directions could result in damage to equipment or data.
NOTE: Provides additional information.
Required
Indicates that a procedure must be followed as directed in order to achieve a functional and
supported implementation based on testing at HP.
HP 3PAR branding information
• The server previously referred to as the "InServ" is now referred to as the "HP 3PAR StoreServ
Storage system."
• The operating system previously referred to as the "InForm OS" is now referred to as the "HP
3PAR OS."
• The user interface previously referred to as the "InForm Management Console (IMC)" is now
referred to as the "HP 3PAR Management Console."
• All products previously referred to as “3PAR” products are now referred to as "HP 3PAR"
products.
70 Support and Other Resources
Page 71

7 Documentation feedback
HP is committed to providing documentation that meets your needs. To help us improve the
documentation, send any errors, suggestions, or comments to Documentation Feedback
(docsfeedback@hp.com). Include the document title and part number, version number, or the URL
when submitting your feedback.
71
Page 72

A Enabling JavaScript on Web Client
The Web Client requires enabling JavaScript. If the page does not properly display, adjust the
browser settings for Internet Explorer:
1. Click Start→Control Panel→Network and Internet→Internet Options.
2. Click the Security tab, and click Custom Level.
Figure 64 Internet Options
3. Scroll to the Scripting section of the list. Select Prompt or Enable.
NOTE: When selecting the Prompt option in the security settings, the user may see a warning
message when launching the Web Client. Click Yes to continue.
4. Click Ok to confirm.
72 Enabling JavaScript on Web Client
Page 73

B HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V
Powershell Commands
This section provides additional information about custom Powershell Commandlets for users
performing administrative tasks.
Add-HyperV
Add-HyperV adds Hyper-V credentials for users. The command is used with each Microsoft
Hyper-V (cluster or standalone host) credentials and managed by the application.
Preconditions
• User must first log on with Login-Rmh.
• Hyper-V name (or synonym) does not already exist.
Syntax
Any optional parameters require square brackets [ ] around them.
Add-HyperV -RmhServerName <RmhServerName> -HypervName <HypervName>
-HypervUsername <HypervUser> -HypervPassword <HypervPassword> [-Verbose]
Table 37 Add-HyperV parameters
Required-RmhServerName
Required-HypervName
Required-HypervUsername
Required-HypervPassword
Success Paths
• Scenario 1: Add Hyper-V is successful.
Add Hyper-V successful for specified Hyper-V host.
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Host name of the RMH Server. This is
FQDN or IP address.
Hyper-V host or cluster name. This is
FQDN or IP address. Synonyms are
checked. The localhost is not supported.
Hyper-V username. If cluster, ensure all
controller nodes in the cluster have the
same username. If not specified, a
dialog box will be presented to enter
credentials.
Hyper-V password. If cluster, ensure all
controller nodes in the cluster have the
same password. If not specified, a
dialog box will be presented to enter
credentials.
Displays progress messages.Optional-Verbose
Failure Paths
• Scenario 1: Session owner is invalid.
Every session command received on RMH Server is validated to originate from the same IP
address that initiated the session. If IP does not match, the command fails.
• Scenario 2: Cannot communicate with host.
RMH Server cannot communicate with a specified Hyper-V host.
Add-HyperV 73
Page 74

• Scenario 3: Login failure on Hyper-V host.
RMH Server cannot authenticate with specified Hyper-V host.
• Scenario 4: Storage System session credentials are invalid.
Storage System session credentials provided are invalid.
• Scenario 5: Storage System credentials is already specified.
User is already logged in with specified Storage System.
• Scenario 6: Cannot start RMH session.
Failure occurred to start session. Reason displayed.
Add-RemoteStoreServ
Add-RemoteStoreServ is used for each HP 3PAR StoreServ credentials.
• HP 3PAR StoreServ credentials are associated to a specific Microsoft Hyper-V
• This command is only required to initially set up credentials. The command is persisted by
RMH Server until the user removes it.
• The user can Add/Remove/Update HP 3PAR StoreServ credentials at any time during the
session
• This will add StroveServ to Remote RMH Server.
Preconditions
• The user must first login with Login-Rmh.
• HP 3PAR StoreServ name must not already exist for specified Microsoft Hyper-V
Syntax
Any optional parameters require square brackets [ ] around them.
Add-RemoteStoreServ -RmhServerName <string> -RemoteStoreServName
<string> [-RemoteStoreServSerialNumber <string>]
[-RemoteStoreServUsername <string>] [-RemoteStoreServPassword <string>]
[-RemoteRmhServerName <string>] [-RemoteRmhServerUsername <string>]
[-RemoteRmhServerPassword <string>] [<CommonParameters>]
Table 38 Add-RemoteStoreServ parameters
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Required-RmhServerName
Required-RemoteStoreServName
Required-RemoteStoreServSerialNumber
Host name of the RMH Server. This is
FQDN or IP address.
This is FQDN or IP address. Synonyms
are supported. The localhost is not
supported.
This is FQDN or IP address, etc.
Synonyms for HP 3PAR StoreServ are
supported.
Required-RemoteStoreServUsername
Required-RemoteStoreServPassword
Optional-RemoteRmhServerName
74 HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V Powershell Commands
Note, if not provided, a dialog box will
pop up asking for credentials.
Note, if not provided, a dialog box will
pop up asking for credentials.
The Windows host name from which
the Remote Virtual copies of the target
array can be managed.
Page 75

Table 38 Add-RemoteStoreServ parameters (continued)
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Add-StoreServ
Add-StoreServ is used for each HP 3PAR StoreServ credentials.
• HP 3PAR StoreServ credentials are associated to a specific Microsoft Hyper-V
• This command is only required to initially set up credentials. The command is persisted by
RMH Server until the user removes it.
• The user can Add/Remove/Update HP 3PAR StoreServ credentials at any time during the
session
Preconditions
• The user must first login with Login-Rmh.
• HP 3PAR StoreServ name must not already exist for specified Microsoft Hyper-V
Syntax
Optional-RemoteRmhServerUsername
Optional-RemoteRmhServerPassword
OptionalCommonParameters
The user name of the Remote RMH
Server.
The password of the Remote RMH
Server.
All the common parameters across the
commands.
Any optional parameters require square brackets [ ] around them.
Add-StoreServ -RmhServerName <RmhServerName> -HypervName <HypervName>
-StoreServName <StoreServName> -StoreServUsername <StoreServUsername>
-StoreServPassword <StoreServPassword> [-Verbose]
Table 39 Add-StoreServ parameters
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Required-RmhServerName
Required-HypervName
Required-StoreServName
Required-StoreServUsername
Required-StoreServPassword
Host name of the RMH Server. This is
FQDN or IP address.
This is FQDN or IP address. Synonyms
are supported. The localhost is not
supported.
This is FQDN or IP address, etc.
Synonyms for HP 3PAR StoreServ are
supported.
Note, if not provided, a dialog box will
pop up asking for credentials.
Note, if not provided, a dialog box will
pop up asking for credentials.
Displays progress messagesOptional-Verbose
Add-StoreServ 75
Page 76

Success Paths
• Scenario 1: Add Storage System is successful.
Add Storage System is successful.
Failure Paths
• Scenario 1: Session owner is invalid.
Every session command received on RMH Server is validated to originate from the same IP
address that initiated the session. If IP does not match, the command fails.
• Scenario 2: Storage System session credentials are invalid.
Storage System session credentials provided are invalid.
• Scenario 3: Storage System credentials are already specified
User is already logged in with specified Storage System.
Analyze-vCopy
The Analyze-vCopy analyzes Virtual Copies for errors. When any Virtual Copy records contain
a volume missing on storage system, the Virtual Copy with an error is flagged. The user can use
the option to analyze and repair inconsistent Virtual Copies.
Preconditions
The user must first login with Login-Rmh.
Syntax
Any optional parameters require square brackets [ ] around them.
Analyze-vCopy -RmhServerName <RmhServerName> -HypervName <HypervName>
[-VcNamesUuids] [-VmNamesUuids] [-Timestamp] [-Cleanup] [-Verbose]
Table 40 Analyze-vCopy parameters
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Required-RmhServerName
Required-HypervName
Optional-VcNamesUuids
Optional-VmNamesUuids
Host name of the RMH Server. This is
FQDN or IP address.
Select Hyper-V host/cluster to use. This
is FQDN or IP address. Synonyms for
Hyper-V are supported. The
localhost is not supported.
Select VCs by name/uuid using a
comma-separated list. If not specified,
VCs name/uuid is not used to filter
selection.
Select names/uuids to filter VC selection
by VM. If not specified, VM
names/uuids is not used to filter
selection.
Optional-Timestamp
Optional-Cleanup
76 HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V Powershell Commands
Specify timestamp of VC to locate in
the format mmddyyhhmmss.
If specified, Analyze-vCopy will
clean up the inconsistent VC by
removing it. Removing the inconsistent
VC will take the same action as the
Remove-vCopy command. If there are
no inconsistencies, the VC is not
Page 77

Table 40 Analyze-vCopy parameters (continued)
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
removed. Without this option, the same
work is performed except no action is
taken to remove the VC. Instead, the
user will be given an error report.
Displays progress messages.Optional-Verbose
Success Paths
• Scenario 1: No errors are found in database.
The database repository is validated against Storage System and all Virtual Volumes are
available.
Failure Paths
• Scenario 1: Session owner is invalid.
Every session command received on RMH Server is validated to originate from the same IP
address that initiated the session. If IP does not match, this command fails.
• Scenario 2: Storage System session credentials are not provided.
Storage System session credentials are not provided for this command.
• Scenario 3: Database has missing Virtual Volumes.
The database repository is validated against Storage System and at least one Virtual Volume
is unavailable.
Create-vCopy
The create-vCopy Cmdlet creates a new Virtual Copy of a VM and includes the following
supported parameters.
Preconditions
The user must first login with Login-Rmh.
Syntax
Any optional parameters require square brackets [ ] around them.
Create-vCopy -RmhServerName <RmhServerName> -HypervName <HypervName>
-VmNamesUuids <VmNamesUuids> [-VcNamePrefix] [-Expiry] [-Retention]
[-SavedStateBackups] [-Verbose]
Table 41 Create-vCopy parameters
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Required-RmhServerName
Host name of the RMH Server. This is
FQDN or IP address.
Required-HypervName
Required-VmNamesUuids
Select Hyper-V host/cluster to use. This
is FQDN or IP address. Synonyms for
Hyper-V are supported. The
localhost is not supported.
Comma separated VM names (or
UUIDs) .
For best practice, if more than one VM
name specified, ensure all VMs use the
same Storage System volume.
Create-vCopy 77
Page 78

Table 41 Create-vCopy parameters (continued)
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Optional-VcNamePrefix
Optional-Expiry
Optional-Retention
Result with Description
• Multiple {RmhCreateVirtualcopyResult} objects.
◦ VM Name or UUID
The Virtual Copy name prefix. A unique
timestamp will be generated for this
new Virtual Copy and appended to this
prefix. If not specified, the VC name
will be vc-timestamp where
timestamp is generated for this new
Virtual Copy.
Integer value followed by letter h or d
for Hours and Days respectively Default:
use the RMH Policy.
Integer value followed by letter h or d
for Hours and Days respectively Default:
use the RMH Policy.
Disabled or enabled.Optional-SavedStateBackups
Default: use the RMH policy.
Displays progress messages.Optional-Verbose
◦ Success/Failure status of the create-vCopy operation for the VM
◦ Detailed error message(s) when operation fails
◦ An instance of an object of type RMHVirtualcopySet describing created Virtual Copy
set.
Success Paths
• Scenario 1: Virtual Copies are successfully created.
Virtual Copies on VM(s) specified are successfully created.
Failure Paths
• Scenario 1: Session owner is invalid.
Every session command received on RMH Server is validated to originate from the same IP
address that initiated the session. If IP does not match, the command fails.
• Scenario 2: Storage System session credentials are not provided.
Storage System session credentials are not provided for this command.
• Scenario 3: No VM is specified.
At least one VM must be specified for command.
• Scenario 4: Cannot communicate with the VMs.
VM is specified, but RMH Server cannot communicate with specified VMs.
• Scenario 5: Expiry is invalid.
Expiry specified is invalid. Valid: 1-43800h, 1-1825d.
• Scenario 6: Retention is invalid.
Retention specified is invalid. Valid: 1-336h, 1-14d.
78 HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V Powershell Commands
Page 79

• Scenario 7: VM(s) are not running.
VM(s) that are to be backed up must be running.
• Scenario 8: License is missing for RMH.
License is missing for RMH.
• Scenario 9: License is missing for Storage System Virtual Copy.
License is missing for Storage System Virtual Copy.
• Scenario 10: VHD(s) are not on NTFS volumes.
VHDs need to reside on NTFS volumes.
• Scenario 11: VSS is not operational.
VSS is not operational or not installed.
• Scenario 12: VSS requestor fails.
VSS requestor fails during backup. Reason is displayed.
• Scenario 13: Multiple Storage Systems is not supported.
RMH does not support multiple Storage Systems for VM.
Get-ClusterNodeNames
Get-ClusterNodeNames retrieves node names for the Hyper-V cluster.
Preconditions
The user must first login with Login-Rmh.
Syntax
Any optional parameters require square brackets [ ] around them.
Get-ClusterNodeNames -RmhServerName <RmhServerName> -HypervName
<HypervName> [-Verbose]
Table 42 Get-ClusterNodeNames parameters
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Required-RmhServerName
Required-HypervName
Host name of the RMH Server. This is
FQDN or IP address.
Select Hyper-V host/cluster to use. This
is FQDN or IP address. Synonyms for
Hyper-V are supported. The
localhost is not supported.
Displays progress messages.Optional-Verbose
Result with Description
• List of node names.
List of Hyper-V node names for cluster. Empty list if Hyper-V specified is not a cluster.
Success Paths
• Scenario 1: Hyper-V cluster node names are fetched.
At least one Hyper-V cluster node name is returned.
• Scenario 2: Hyper-V specified is not a cluster.
Successful without Hyper-V cluster node names returned.
Get-ClusterNodeNames 79
Page 80

Failure Paths
• Scenario 1: Session owner is invalid.
Every session command received on RMH Server is validated to originate from the same IP
address that initiated the session. If IP does not match, the command fails.
• Scenario 2: Unable to fetch Hyper-V.
A Hyper-V is required to fetch cluster node names.
Get-EncryptedLoginPassword
Get-EncryptedLoginPassword retrieves a login password that may be use scripting.
Preconditions
The user must first login with Login-Rmh.
Syntax
Any optional parameters require square brackets [ ] around them.
Get-EncryptedLoginPassword-RmhServerName <RmhServerName> [-Verbose]
Table 43 Get-EncryptedLoginPassword parameters
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Success Paths
• Scenario 1: Get is successful.
Get is successful.
Failure Paths
• Scenario 1: Session owner is invalid.
Every session command received on RMH Server is validated to originate from the same IP
address that initiated the session. If IP does not match, the command fails.
• Scenario 2: Failure to encrypt login password.
RMH Server cannot encrypt login password.
Get-RmhPolicy
The get-RmhPolicy retrieves the RMH policy settings of a Hyper-V Virtual Machine. An RMH
policy object retains the set default values for Virtual Copies. You can customize the attributes of
a Virtual Copy.
Required-RmhServerName
Host name of the RMH Server. This is
FQDN or IP address.
Displays progress messages.Optional-Verbose
Preconditions
The user must first login with Login-Rmh.
Syntax
Any optional parameters require square brackets [ ] around them.
Get-RmhPolicy -RmhServerName <RmhServerName> -HypervName <HypervName>
-VmNameUuid <VmNameUuid> [-Verbose]
80 HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V Powershell Commands
Page 81

Table 44 Get-RmhPolicy parameters
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Required-RmhServerName
Required-HypervName
Required-VmNameUuid
Host name of the RMH Server. This is
FQDN or IP address.
Select Hyper-V host/cluster to use. This
is FQDN or IP address. Synonyms for
Hyper-V are supported. The
localhost is not supported.
Name/unique id of VM to set policy
for Virtual Machine.
Displays progress messages.Optional-Verbose
Result with Description
• {RMHVirtualCopySet} has the following properties:
◦ IsVirtualCopyApplicationConsistent: if yes, an application consistent VC is
created.
◦ VirtualCopyExpirationTime: if non-zero, expiry values will be set in Storage System
for all VC volumes created.
◦ VirtualCopyRetentionTime: if non-zero, retention values will be set in Storage
System for all VC volumes created.
◦ SavedStateBackus: Enabled or Disabled.
Success Paths
• Scenario 1: RMH Policy is fetched.
Failure Paths
• Scenario 1: Session owner is invalid.
• Scenario 2: VM name/uuid is not specified.
• Scenario 3: VM name/uuid specified is invalid
• Scenario 4: RMH Policy does not exist.
Get-vCopy
Get-vCopy is used to retrieve existing Virtual Copies details of a Virtual Machine from the Recovery
Manager Hyper-V Repository of a specified Hyper-V server. This command has many filters to
reduce the number of Virtual Copies during retrieving process.
RMH Policy is fetched for specified VM.
Every session command received on RMH Server is validated to originate from the same IP
address that initiated the session. If IP does not match, the command fails.
VM name or uuid must be specified to fetch RMH Policy.
VM name or uuid must be valid to fetch RMH Policy.
RMH Policy does not exist for specified VM.
Preconditions
The user must first login with Login-Rmh.
Get-vCopy 81
Page 82

Syntax
Any optional parameters require square brackets [ ] around them.
Get-vCopy -RmhServerName <RmhServerName> -HypervName <HypervName>
[-VcNamesUuids] [-VmNamesUuids] [-Timestamp] [-Verbose]
Table 45 Get-vCopy parameters
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Required-RmhServerName
Required-HypervName
Optional-VcNamesUuids
Optional-VmNamesUuids
Optional-Timestamp
Result with Description
• Multiple {RMHVirtualCopySet} objects:
Multiple RMHVirtualCopySet objects (one per VM).
Host name of the RMH Server. This is
FQDN or IP address.
Select Hyper-V host/cluster to use. This
is FQDN or IP address. Synonyms for
Hyper-V are supported. The
localhost is not supported.
Select VCs by name/uuid using a
comma-separated list. If not specified,
VCs name/uuid is not used to filter
selection.
Select names/uuids to filter VC selection
by VM. If not specified, VM
names/uuids is not used to filter
selection.
Specify timestamp of VC to locate in
the format mmddyyhhmmss.
Displays progress messages.Optional-Verbose
Success Paths
• Scenario 1: Virtual Copy is fetched.
At least one Virtual Copy meeting the criteria is returned.
• Scenario 2: Virtual Copy is not fetched.
No Virtual Copies meeting the criteria are specified. Nothing is returned.
Failure Paths
• Scenario 1: Session owner is invalid.
Every session command received on RMH Server is validated to originate from the same IP
address that initiated the session. If IP does not match, the command fails.
• Scenario 2: Storage System session credentials are not provided.
Storage System session credentials are not provided for this command.
Get-VirtualMachine
Get-VirtualMachine retrieves current Virtual Machines available on an active-session Hyper-V
host/cluster.
Preconditions
The user must first login with Login-Rmh.
82 HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V Powershell Commands
Page 83

Syntax
Any optional parameters require square brackets [ ] around them.
Get-VirtualMachine -RmhServerName <RmhServerName> -HypervName
<HypervName> [-Verbose]
Table 46 Get-VirtualMachine parameters
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Required-RmhServerName
Required-HypervName
Result with Description
• Multiple {RMHirtualMachineInfo} objects:
Multiple RMHirtualMachineInfo objects (one per VM).
Success Paths
• Scenario 1: Virtual Machine(s) is fetched.
At least one Virtual Machine is returned.
• Scenario 2: Virtual Machine(s) is not fetched.
No Virtual Machines are available. Nothing is returned.
Failure Paths
Host name of the RMH Server. This is
FQDN or IP address.
Select Hyper-V host/cluster to use. This
is FQDN or IP address. Synonyms for
Hyper-V are supported. The
localhost is not supported.
Displays progress messages.Optional-Verbose
• Scenario 1: Session owner is invalid.
Every session command received on RMH Server is validated to originate from the same IP
address that initiated the session. If IP does not match, the command fails.
• Scenario 2: Unable to fetch Hyper-V.
A Hyper-V is required to fetch VMs.
Import-Repository
The following parameters explain how to import to a repository.
Preconditions
The user must first login with Login-Rmh.
Syntax
Any optional parameters require square brackets [ ] around them.
Import-Repository -RmhServerName <string> -FromPath <string>
[-FromMachine <string> [-MachineUsername <string>] [-MachinePassword
<string>] [-Force] [<Common Parameters>]
Import-Repository 83
Page 84

Table 47 Import-Repository parameters
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Login-Rmh
Log into RMH Server using Windows RMH account.
The optional login-Rmh enables the user to log on to Recovery Manager for Hyper-V. After a
successful login is established, the user is not required to enter additional credentials for subsequent
Cmdlets.
Required-RmhServerName
Required-FromPath
Optional-FromMachine
Optional-Force
OptionalCommonParameters
Host name of the RMH Server. This is
FQDN or IP address
The path of the destination computer
from where repository files need to be
copied.
The name of the destination computer
from where repository files need to be
copied.
The login user name of the computer.Optional-MachineUsername
The login password of the computer.Optional-MachinePassword
Use this option to skip the user prompt
before import repository.
All the common parameters across the
commands.
Preconditions
The user must first login with Login-Rmh.
Syntax
Any optional parameters require square brackets [ ] around them.
Login-Rmh-RmhServerName <-RmhServerName>-RmhUserName
<-RmhUserName>-RmhPassword <-RmhPassword>[-RmhEncrytedPassword]
Table 48 Login-Rmh parameters
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Required-RmhServerName
Required-RmhUserName
Required-RmhPassword
Optional-RmhEncrytedPassword
Host name of the RMH Server. This is
FQDN or IP address.
RMH user name. If not specified, a
dialog box will be presented to enter
credentials.
RMH user password. If not specified, a
dialog box will be presented to enter
credentials.
May be used instead of
-RmhPassword.
84 HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V Powershell Commands
Page 85

Success Paths
• Scenario 1: Login is successful.
Login to a specified Hyper-V host is successful.
Failure Paths
• Scenario 1: Session owner is invalid.
Every session command received on RMH Server is validated to originate from the same IP
address that initiated the session. If IP does not match, the command fails.
• Scenario 2: Cannot communicate with host.
RMH Server cannot communicate with a specified Hyper-V host.
• Scenario 3: Login failure on Hyper-V host.
RMH Server cannot authenticate with the specified Hyper-V host.
• Scenario 4: Storage System session credentials are invalid.
Storage System session credentials provided are invalid.
• Scenario 5: Storage System credentials are already specified.
User has already logged in with specified Storage System.
• Scenario 6: Cannot start RMH session.
A Hyper-V is required to fetch VMs.
• Scenario 7: Unable to fetch Hyper-V.
Failure occurred to start session. Reason displayed.
Logout-Rmh
The optional logout-Rmh Cmdlet logs off the user from the application.
Preconditions
The user must first login with Login-Rmh.
Syntax
Any optional parameters require square brackets [ ] around them.
Logout-Rmh -RmhServerName <RmhServerName> [-Remove]
Table 49 Logout-Rmh parameters
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Required-RmhServerName
Host name of the RMH Server. This is
FQDN or IP address.
Logout-Rmh 85
Page 86

Success Paths
• Scenario 1: Logout is successful.
Logout is successful.
Failure Paths
• Scenario 1: Session owner is invalid.
Every session command received on RMH Server is validated to originate from the same IP
address that initiated the session. If IP does not match, the command fails.
• Scenario 2: Session is unavailable.
Session specified is unavailable for logout. This means the session is previously closed by
logout or timeout from RMH Server.
Mount-vCopy
Mount-vCopy exports and mounts specified Virtual Copy virtual volumes to a Hyper-V host for
manual restoration of virtual hard disks. This command can be repeated with unique mount point
prefixes if necessary.
Mount point is not required. Volume Guid will only access virtual volume(s) if mount point prefixes
are not specified.
Preconditions
The user must first login with Login-Rmh.
Syntax
Any optional parameters require square brackets [ ] around them.
Mount-vCopy -RmhServerName <RmhServerName> -HypervName <HypervName>
-VcNameUuid <VcNameUuid> -VmNameUuid <VmNameUuid> [-Timestamp]
[-MountPointPrefix] [-Select] [-HypervHostName] [-Verbose]
Table 50 Mount-vCopy parameters
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Required-RmhServerName
Required-HypervName
Required-VmNameUuid
Optional-Timestamp
Host name of the RMH Server. This is
FQDN or IP address.
Select Hyper-V host/cluster to use. This
is FQDN or IP address. Synonyms for
Hyper-V are supported. The
localhost is not supported.
Select VC by name/uuid.Required-VcNameUuid
Select name/uuid to filter VC selection
by Virtual Machine.
Specify timestamp of VC to locate in
the format mmddyyhhmmss.
Optional-MountPointPrefix
86 HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V Powershell Commands
Mount point prefix where RMH will
create a mount point for each Virtual
Volume mounted using an appended
mount point name in the format
RMHv.wwn.partition.GUID.timestamp
where wwn is WWN of VV mounted,
partition is the partition number, and
timestamp is in format mmddyyhhmmss.
Page 87

Table 50 Mount-vCopy parameters (continued)
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
NOTE: If not specified, VVs will be
exported to host by Storage System, but
no mount points will be used. You will
need to access VVs using their volume
guid path (example:
\\?\Volume(wwn)\).
Optional-Select
Optional-HypervHostName
Specifies the virtual hard disk name,
virtual volume name, or virtual volume
WWN in a comma-separated list. For
virtual hard disk name, this is the full
filename with path, or just a partial
name. Wildcards are not allowed. By
default, RMH will mount all Virtual
Copy volumes in a VCS.
Hyper-V host name. Use this option to
specify host node in cluster. You may
also use this option in a non-cluster
environment. If not specified, host name
of the RMH Server is used
fromLogin-Rmh.
Displays progress messages.Optional-Verbose
Result with Description
• {RmhMountVirtualCopySetResult} has the following descriptions:
◦ RmhMountVirtualCopySet with current state updated.
◦ Information on name, WWN, partition, volume guid path, and mount point of each Virtual
Volume mounted.
Success Paths
• Scenario 1: Mount is successful.
Mount is successful.
Failure Paths
• Scenario 1: Session owner is invalid.
Every session command received on RMH Server is validated to originate from the same IP
address that initiated the session. If IP does not match, the command fails.
• Scenario 2: Storage System session credentials are not provided.
Storage System session credentials are not provided for this command.
• Scenario 3: License is missing for RMH.
License is missing for RMH.
• Scenario 4: Storage System host is not available to mount Virtual Volume(s).
A Storage System host must be available to mount Virtual Volume(s).
• Scenario 5: One or more Virtual Volumes mount points already exist.
Using specified mount point prefix and RMH format of RMH.vv-wwn, the mount point attempted
is already in use.
Mount-vCopy 87
Page 88

• Scenario 6: Storage System fails to export Virtual Volume.
Storage System fails to export Virtual Volume on requested host. Reason is displayed.
• Scenario 7: Assign mount points on Hyper-V host fails.
An attempt to assign mount points for Virtual Volumes fails on host.
• Scenario 8: Only one Virtual Copy may be mounted at a time
Filtering of Virtual Copies using –VcNameUuid/-VmNameUuid does not result in only one
Virtual Copy to mount.
Remove-HyperV
Remove-HyperV removes Microsoft Hyper-V host/cluster credentials associated with a RMH user.
Preconditions
The user must first login with Login-Rmh.
Syntax
Any optional parameters require square brackets [ ] around them.
Remove-HyperV -RmhServerName <RmhServerName> [-HypervName] [-Verbose]
Table 51 Remove-HyperV parameters
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Required-RmhServerName
Optional-HypervName
Host name of the RMH Server. This is
FQDN or IP address.
Optionally select Hyper-V host/cluster
to use. This is FQDN or IP address.
Synonyms for Hyper-V are supported.
The localhost is not supported.
Displays progress messages.Optional-Verbose
Success Paths
• Scenario 1: Remove is successful.
Remove is successful.
Failure Paths
• Scenario 1: Session owner is invalid.
Session command received on RMH Server is validated to originate from the same IP address
that initiated the session. If IP does not match, the command fails.
• Scenario 2: Session is not available.
Session specified is not available for logout. This means the session has been previously closed
by logout or timeout from RMH Server.
• Scenario 3: Not previously added.
Hyper-V is not previously added.
Remove-RmhPolicy
Remove-RmhPolicy removes RMH policy of a Virtual Machine.
88 HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V Powershell Commands
Page 89

Preconditions
The user must first login with Login-Rmh.
Syntax
Any optional parameters require square brackets [ ] around them.
Remove-RmhPolicy -RmhServerName <RmhServerName> [-HypervName] -VmNameUuid
<VmNameUuid> [-Verbose]
Table 52 Remove-RmhPolicy parameters
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Required-RmhServerName
Optional-HypervName
Required-VmNameUuid
Host name of the RMH Server. This is
FQDN or IP address.
Optionally select Hyper-V host/cluster
to use. This is FQDN or IP address.
Synonyms for Hyper-V are supported.
The localhost is not supported.
Select name/uuid to filter Virtual Copy
selection by Virtual Machine.
Displays progress messages.Optional-Verbose
Success Paths
• Scenario 1: RMH Policy is removed.
Specified RMH Policy is successfully removed.
Failure Paths
• Scenario 1: Session owner is invalid.
Every session command received on RMH Server is validated to originate from the same IP
address that initiated the session. If IP does not match, the command fails.
• Scenario 2: VM name/uuid is not specified.
VM name or uuid must be specified to fetch RMH Policy.
• Scenario 3: VM name/uuid specified is invalid.
VM name or uuid must be valid to fetch RMH Policy.
• Scenario 4: RMH Policy does not exist.
RMH Policy is not previously set for specified VM.
Remove-StoreServ
Remove-StoreServ removes HP 3PAR StoreServ credentials associated with a RMH user.
Preconditions
• The user must first login with Login-Rmh.
• HP 3PAR StoreServ credentials must already exist for specified Microsoft Hyper-V.
Syntax
Any optional parameters require square brackets [ ] around them.
Remove-StoreServ -RmhServerName <RmhServerName> -HypervName <HypervName>
-StoreServName <StoreServName> [-Verbose]
Remove-StoreServ 89
Page 90

Table 53 Remove-StoreServ parameters
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Required-RmhServerName
Required-HypervName
Required-StoreServName
Host name of the RMH Server. This is
FQDN or IP address.
This is FQDN or IP address. Synonyms
for Hyper-V are supported. The
localhost is not supported.
Synonyms for HP 3PAR StoreServ are
supported.
Displays progress messages.Optional-Verbose
Success Paths
• Scenario 1: Remove Storage System is successful.
Remove operation is successful.
Failure Paths
• Scenario 1: Session owner is invalid.
Every session command received on RMH Server is validated to originate from the same IP
address that initiated the session. If IP does not match, the command fails.
• Scenario 2: Not previously added.
Storage System specified is not previously added.
Remove-vCopy
Remove-vCopy removes a Virtual Copy.
Preconditions
The user must first login with Login-Rmh.
Post Conditions
• Virtual Copy removed and all available Virtual Volumes deleted, or
• Virtual Copy retained due to at least one Virtual Volume failing to delete with reason other
than not found on storage system.
Syntax
Any optional parameters require square brackets [ ] around them.
Remove-vCopy -RmhServerName <RmhServerName> [-HypervName] -VcNameUuid
<VcNameUuid> -VmNameUuid <VmNameUuid> [-Timestamp] [-Force] [-Verbose]
Table 54 Remove-vCopy parameters
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Required-RmhServerName
Host name of the RMH Server. This is
FQDN or IP address.
Optional-HypervName
90 HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V Powershell Commands
Optionally select Hyper-V host/cluster
to use. This is FQDN or IP address.
Synonyms for Hyper-V are supported.
The localhost is not supported.
Select VC by name/uuid.Required-VcNameUuid
Page 91

Table 54 Remove-vCopy parameters (continued)
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Required-VmNameUuid
Optional-Timestamp
Select name/uuid to filter VC selection
by VM.
Specify timestamp of VC to locate in
the format mmddyyhhmmss.
Bypass confirmation prompt.Optional-Force
Displays progress messages.Optional-Verbose
Success Paths
• Scenario 1: Specified Virtual Copy is removed.
Specified Virtual Copy is removed.
Failure Paths
• Scenario 1: Session owner is invalid.
Every session command received on RMH Server is validated to originate from the same IP
address that initiated the session. If IP does not match, the command fails.
• Scenario 2: Storage System session credentials are not provided.
Storage System session credentials are not provided for this command.
• Scenario 3: License is missing for RMH.
License is missing for RMH.
• Scenario 4: Virtual Volume(s) is mounted.
Virtual Copies cannot be removed while mounted.
• Scenario 5: RW Virtual Volume(s) is missing.
Message is displayed. Remove operation continues.
• Scenario 6: Virtual Volume(s) in use by other Virtual Copy records.
Unable to delete. In Use by other Virtual Copies. Remove operation continues and leaves
Virtual Volume alone.
• Scenario 7: Unable to delete RW Virtual Volume.
Unable to delete RW Virtual Volume. Remove operation continues.
• Scenario 8: License is missing for RMH.
Unable to delete RW Virtual Volume. Remove operation continues.
• Scenario 9: Only one Virtual Copy can be removed at a time.
Filtering of Virtual Copies using -VcNameUuid/-VmNameUuid does not result in only one
Virtual Copy to remove.
• Scenario 10: Virtual Copy is not removed.
If Storage System reports error other than virtual volume not found, the Virtual Copy is retained.
Remove-RemoteStoreServ
Remove-RemoteStoreServ removes HP 3PAR StoreServ credentials already present in RMH
database for user.
Remove-RemoteStoreServ 91
Page 92

Preconditions
• User must first login using Login-Rmh.
• Specified Microsoft Hyper-V credentials must already exist.
Post Conditions
HP 3PAR StoreServ credentials for this user are removed from the database.
Syntax
Any optional parameters require square brackets [ ] around them.
Remove-RemoteStoreServ -RmhServerName <string> -RemoteRmhServerName
<string> -RemoteStoreServName <string> [<CommonParameters>]
Table 55 Remove-RemoteStoreServ parameters
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Restore-vCopyVm
The restore-vCopyVm initiates a full restore or recovery of Virtual Machines.
Preconditions
The user must first login with Login-Rmh.
Syntax
Any optional parameters require square brackets [ ] around them.
Restore-vCopyVm -RmhServerName <RmhServerName> [-HypervName] -VcNameUuid
<VcNameUuid> -VmNameUuid <VmNameUuid> [-Timestamp] [-Force] [-RestartVm]
[-Verbose]
Required-RmhServerName
Required-RemoteRmhServerName
Required-RemoteStoreServName
OptionalCommonParameters
Host name of the RMH Server. This is
FQDN or IP address
The Windows host name from which
the Remote Virtual copies of the target
array can be managed.
The target array name for which Remote
Virtual copies need to be created.
All the common parameters across the
commands.
Table 56 Restore-vCopyVM parameters
Required-RmhServerName
Optional-HypervName
Required-VmNameUuid
Optional-Timestamp
92 HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V Powershell Commands
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Host name of the RMH Server. This is
FQDN or IP address.
Optionally select Hyper-V host/cluster
to use. This is FQDN or IP address.
Synonyms for Hyper-V are supported.
The localhost is not supported.
Select VC by name/uuid.Required-VcNameUuid
Select name/uuid to filter VC selection
by VM.
Specify timestamp of VC to locate in
the format mmddyyhhmmss.
Page 93

Table 56 Restore-vCopyVM parameters (continued)
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Bypass confirmation prompt.Optional-Force
If specified, VM will be restarted.Optional-RestartVm
Displays progress messages.Optional-Verbose
Result with Description
This command returns the location of restored Virtual Machine and host name.
Success Paths
• Scenario 1: VM(s) successfully restores.
Specified VM(s) are successfully restored.
Failure Paths
• Scenario 1: Session owner is invalid.
Every session command received on RMH Server is validated to originate from the same IP
address that initiated the session. If IP does not match, the command fails.
• Scenario 2: Storage System session credentials are not provided.
Storage System session credentials are not provided for this command.
• Scenario 3: License missing for RMH.
License is missing for RMH.
• Scenario 4: Original mount points do not exist.
The original mount points for VM system files and all VHDs must exist.
• Scenario 5: Fails to mount Virtual Volumes to Hyper-V host.
Unable to mount Virtual Volumes to Hyper-V host for restore.
• Scenario 6: Fails to unmount Virtual Volumes from Hyper-V host.
After restore is complete, unmount is unable to complete.
• Scenario 7: Only one Virtual Copy may be restored at a time.
Filtering of Virtual Copies using -VcNameUuid/-VmNameUuid does not result in only one
Virtual Copy to restore.
Set-RmhPolicy
Set-RmhPolicy modifies RMH policy of a VM.
Preconditions
User must first login using Login-Rmh.
Syntax
Any optional parameters require square brackets [ ] around them.
Set-RmhPolicy -RmhServerName <RmhServerName> -HypervName <HypervName>
-VmNameUuid <VmNameUuid> [-Expiry] [-Retention] [-SavedStateBackups]
[-Verbose]
Set-RmhPolicy 93
Page 94

Table 57 Set-RmhPolicy parameters
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Success Paths
• Scenario 1: RMH Policy is set.
RMH Policy successfully sets for VM.
Required-RmhServerName
Required-HypervName
Required-VmNameUuid
Optional-Expiry
Optional-Retention
Host name of the RMH Server. This is
FQDN or IP address
Select Hyper-V host/cluster to use. This
is FQDN or IP address. Synonyms for
Hyper-V are supported. The
localhost is not supported.
Name/unique id of VM used to set
policy.
Integer value followed by letter h or d
for Hours and Days respectively. Use 0
to reset.
Integer value followed by letter h or d
for Hours and Days respectively. Use 0
to reset
Disabled or enabled. Use reset to reset.Optional-SavedStateBackups
Display progress messages.Optional-Verbose
Failure Paths
• Scenario 1: Session owner is invalid.
Every session command received on RMH Server is validated to originate from the same IP
address that initiated the session. If IP does not match, the command fails.
• Scenario 2: VM name/uuid is not specified.
VM name or uuid must be specified to fetch RMH Policy.
• Scenario 3: Expiry is invalid.
Expiry specified is invalid. Valid: 1-43800 h, 1-1825 d, or 0 to reset.
• Scenario 4: Retention is invalid.
Retention specified is invalid. Valid: 1-336 h, 1-14 d, or 0 to reset.
• Scenario 5: Expiry/Retention settings conflict.
Expiry and retention settings conflict for valid cases on Storage System.
• Scenario 6: Cannot communicate with VM.
Cannot communicate with VM to validate VM.
Show-Connection
Show-Connection shows connection information for current login RMH user name, all RMH
Hyper-V hosts/clusters, and all Hyper-V Storage Systems associated with the RMH user. The actively
selected Hyper-V will also be shown.
Preconditions
User must first login using Login-Rmh.
94 HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V Powershell Commands
Page 95

Syntax
Any optional parameters require square brackets [ ] around them.
Show-Connection -RmhServerName <RmhServerName> [-HypervName]
[-ShowMissingStorageSystems] [-Verbose]
Table 58 Show-Connection parameters
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Required-RmhServerName
Optional-HypervName
Optional-ShowMissingStorageSystems
Host name of the RMH Server. This is
FQDN or IP address
If specified, the resulting connections
shown will be for this Hyper-V.
Synonyms for Hyper-V are supported.
The localhost is not supported.
If specified, Storage Systems used by
Hyper-V(s), but missing credentials, are
shown.
Display progress messages.Optional-Verbose
Success Paths
• Scenario 1: Connection information shown.
RMH Session and all Hyper-V/ Storage System connection information currently established
are shown.
Failure Paths
• Scenario 1: Session owner is invalid.
Every session command received on RMH Server is validated to originate from the same IP
address that initiated the session. If IP does not match, the command fails.
Unmount-vCopy
Unmount-vCopy unmounts currently mounted Virtual Copy volume(s) for the specified Virtual
Copy and Virtual Machine name.
Preconditions
The user must first login with Login-Rmh.
Syntax
Any optional parameters require square brackets [ ] around them.
Unmount-vCopy -RmhServerName <RmhServerName> [-HypervName] -VcNameUuid
<VcNameUuid> -VmNameUuid <VmNameUuid> [-Timestamp] [-Select]
[-HypervHostName] [-Verbose]
Table 59 Unmount-vCopy parameters
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Required-RmhServerName
Optional-HypervName
Host name of the RMH Server. This is
FQDN or IP address.
Optionally select Hyper-V host/cluster
to use. This is FQDN or IP address.
Synonyms for Hyper-V are supported.
the localhost is not supported.
Unmount-vCopy 95
Page 96

Table 59 Unmount-vCopy parameters (continued)
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Select VC by name/uuid.Required-VcNameUuid
Required-VmNameUuid
Optional-Timestamp
Optional-Select
Optional-HypervHostName
Select name/uuid to filter VC selection
by Virtual Machine.
Specify timestamp of VC to locate in
the format mmddyyhhmmss.
Specifies the virtual hard disk name,
virtual volume name, or virtual volume
WWN in a comma-separated list. For
virtual hard disk name, this is the full
filename with path, or just a partial
name. Wildcards are not allowed. By
default, RMH will unmount all Virtual
Copy volumes in a VCS.
Hyper-V host name. Use this option to
specify host node in cluster. You may
also use this option in a non-cluster
environment. If not specified, host name
of the RMH Server is used
fromLogin-Rmh.
Displays progress messages.Optional-Verbose
Result with Description
• RmhMountVirtualCopySetResult
The command returns RmhMountVirtualCopySetResult objects and contains:
◦ RMHVirtualCopySet with current state updated.
◦ Information on name, WWN, partition, volume guid path, and mount point of each Virtual
Volume mounted.
Success Paths
• Scenario 1: Unmount is unsuccessful.
Requested unmounts of Virtual Volume(s) is successful.
Failure Paths
• Scenario 1: Session owner is invalid.
Every session command received on RMH Server is validated to originate from the same IP
address that initiated the session. If IP does not match, the command fails.
• Scenario 2: Storage System session credentials are not provided.
Storage System session credentials are not provided for this command.
• Scenario 3: License missing for RMH.
License is missing for RMH.
• Scenario 4: One or more Virtual Volumes mount points do not exist.
Using a specified mount point prefix and RMH format of RMH.vv-wwn, the mount point
attempted is not available to unmount.
• Scenario 5: Storage System host is not available to unmount Virtual Volume(s).
A Storage System host must be available to unmount Virtual Volume(s).
96 HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V Powershell Commands
Page 97

• Scenario 6: Storage System fails to unexport Virtual Volume.
Storage System fails to unexport Virtual Volume on requested host. Reason is displayed.
• Scenario 7: Only one Virtual Copy can be unmounted at a time.
Filtering of Virtual Copies using –VcNameUuid/-VmNameUuid does not result in only one
Virtual Copy to be unmounted.
Update-HyperV
Update-HyperV updates Microsoft Hyper-V credentials already present in RMH database for
user.
Preconditions
• User must first login using Login-Rmh.
• Specified Microsoft Hyper-V credentials must already exist.
Syntax
Any optional parameters require square brackets [ ] around them.
Update-HyperV -RmhServerName <RmhServerName> -HypervName <HypervName>
-HypervUsername <HypervUsername> -HypervPassword <HypervPassword>
[-Verbose]
Table 60 Update-HyperV parameters
Required-RmhServerName
Required-HypervName
Required-HypervUsername
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Host name of the RMH Server. This is
FQDN or IP address
Microsoft Hyper-V host or cluster name.
This is FQDN or IP address. Synonyms
are supported. The localhost is not
supported.
Microsoft Hyper-V user name. If cluster,
ensure all controller nodes in the cluster
have the same username. Note: if not
provided, a dialog box will pop up
asking for credentials.
User name format: <WORKGROUP or
HOST NAME>\<USERNAME>.
Microsoft Hyper-V password.Required-HypervPassword
NOTE: If not provided, a dialog box
will pop up asking for credentials.
Display progress messages.Optional-Verbose
Update-HyperV 97
Page 98

Success Paths
• Scenario 1: Update Hyper-V is successful
Update Microsoft Hyper-V is successful.
Failure Paths
• Scenario 1: Session owner is invalid.
Every session command received on RMH Server is validated to originate from the same IP
address initiating the session. If IP does not match, the command fails.
• Scenario 2: Microsoft Hyper-V session credentials are invalid.
Microsoft Hyper-V session credentials provided are invalid.
• Scenario 3: Microsoft Hyper-V credentials are already specified.
User has already logged in with specified Microsoft Hyper-V.
Update-StoreServ
Update-StoreServ updates HP 3PAR StoreServ credentials already present in RMH database
for user.
Preconditions
• User must first login using Login-Rmh.
• Specified Microsoft Hyper-V credentials must already exist.
Post Conditions
HP 3PAR StoreServ credentials for this user are updated and persisted in database.
Syntax
Any optional parameters require square brackets [ ] around them.
Update-StoreServ -RmhServerName <RmhServerName> -HypervName <HypervName>
-StoreServName <StoreServName> -StoreServUsername <StoreServUsername>
-StoreServPassword <StoreServPassword> [-Verbose]
Table 61 Update-StoreServ parameters
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Required-RmhServerName
Required-HypervName
Required-StoreServName
Host name of the RMH Server. This is
FQDN or IP address
Microsoft Hyper-V host or cluster
name. This is FQDN or IP address.
Synonyms are supported. The localhost
is not supported.
This is FQDN or IP address, etc.
Synonyms for HP 3PAR StoreServ are
supported.
Required-StoreServUsername
Required-StoreServPassword
98 HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V Powershell Commands
NOTE: If not provided, a dialog box
will pop up asking for credentials.
NOTE: If not provided, a dialog box
will pop up asking for credentials.
Displays progress messages.Optional-Verbose
Page 99

Success Paths
• Scenario 1: Update HP 3PAR StoreServ is successful.
Update HP 3PAR StoreServ is successful.
Failure Paths
• Scenario 1: Session owner is invalid.
Every session command received on RMH Server is validated to originate from the same IP
address that initiated the session. If IP does not match, the command fails.
• Scenario 2: HP 3PAR StoreServ session credentials are invalid.
HP 3PAR StoreServ session credentials provided are invalid.
• Scenario 3: HP 3PAR StoreServ credentials are already specified.
User has already logged on with specified HP 3PAR StoreServ.
Update-RemoteStoreServ
Update-RemoteStoreServ remotely updates HP 3PAR StoreServ credentials already present
in RMH database for user. It also enables us to change the assigned Remote RMH server for the
Remote-Storeserv.
Preconditions
• User must first login using Login-Rmh.
• Specified Microsoft Hyper-V credentials must already exist.
Post Conditions
HP 3PAR StoreServ credentials for this user are updated and persisted in database.
Syntax
Any optional parameters require square brackets [ ] around them.
Update-RemoteStoreServ -RmhServerName <string> -RemoteStoreServName
<string> [-RemoteStoreServUsername <string>] [-RemoteStoreServPassword
<string>] [-RemoteRmhServerName <string>] [-RemoteRmhServerUsername
<string>] [-RemoteRmhServerPassword <string>][<CommonParameters>]
Table 62 Update-StoreServ parameters
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Required-RmhServerName
Required- RemoteStoreServName
Host name of the RMH Server. This is
FQDN or IP address
The target array name for which Remote
Virtual copies need to be created.
The user name of the target array.Optional- RemoteStoreServUsername
The password of the target array.Optional- RemoteStoreServPassword
Optional-RemoteRmhServerName
Optional-RemoteRmhServerUsername
The Windows host name from which
the Remote Virtual copies of the target
array can be managed.
The user name of the Remote RMH
Server.
Update-RemoteStoreServ 99
Page 100

Table 62 Update-StoreServ parameters (continued)
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Save-Repository
The following parameters explain how to save to a repository.
Preconditions
The user must first login with Login-Rmh.
Syntax
Any optional parameters require square brackets [ ] around them.
Save-Repository -RmhServerName <string> -ToPath <string> [-ToMachine
<string>] [-MachineUsername <string>] [-MachinePassword
<string>][-MachineEncryptedPassword <string>][-Force] [<Common
Parameters>]
Table 63 Save-Repository parameters
Optional-RemoteRmhServerPassword
OptionalCommonParameters
Required-RmhServerName
The password of the Remote RMH
Server.
All the common parameters across the
commands.
DescriptionOptional/RequiredParameter
Host name of the RMH Server. This is
FQDN or IP address
Required-ToPath
Optional-ToMachine
Optional-Force
OptionalCommonParameters
The path in the computer where it has
to be saved.
The name of the computer where it has
to be saved.
The destination machine user name.Optional-MachineUsername
The destination machine password.Optional-MachinePassword
Use this command to save the file
forcefully.
All the common parameters across the
commands.
NOTE: To save the repository to a local drive the command is Save-Repository
-RmhServerName <string> -ToPath <string>.
100 HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for Microsoft Hyper-V Powershell Commands
 Loading...
Loading...