Page 1

hp industry
november 2002
standard servers
technical
white paper
table of contents
Insight Manager 7 SNMP Extensions utility
abstract 2
take control of the management environment 2
management basics 2
information retrieved from MIBS 5
SNMP operations by agent 5
how can SNMP Extensions help? 6
SNMP Extensions features 7
setting up the environment 7
the set of installed MIBs 8
protecting source MIBs 8
managing MIBs from Insight Manager 7 8
registering a MIB 10
why registration fails 11
unregistering a MIB 12
uploading a MIB 12
editing registered MIB information 12
unregistering an installed MIB 14
unregistering a MIB from the MIB Registration page 14
deleting unregistered MIBS 14
using trap categories 15
using SNMP Explorer 16
managing MIBs from the batch command 19
command syntax conventions 19
the command syntax 19
command switches 20
running the mCompile command 21
a command line example 22
troubleshooting a failed registration 24
registration error messages 24
compiling a MIB with an Error: badmib.MIB 25
the referenced badmib.mib 25
for more information 34
1
Page 2

Insight Manager 7 SNMP Extensions utility
abstract
Insight Manager 7 is a systems management application that lets you monitor the status of a
device, its component objects, and their attributes. Insight Manager 7 reports on the device
status, creates event and trap reports on device conditions, and performs a specific set of actions
on managed devices.
Insight Manager 7 includes SNMP Extensions Toolkit, a group of components that allows you to
manipulate your management environment. You can use SNMP Extensions from the graphical
user interface of Insight Manager 7 or from the command line.
SNMP Extensions consists of the following components.
• SNMP MIB Registration
• SNMP MIB Upload
• MIB Check
• Trap Editor
• Trap Categories Editor
• Command Line Utility
take control of the management environment
management basics
Over time, the typical network changes in topology, function, and content. As an administrator,
you are challenged to manage devices that are not fully recognized by your management
application. How can you address the problem of classifying the devices? SNMP Extensions can
help you by providing ways to add input to your network management.
To use SNMP Extensions successfully, you should be familiar with the following terms and
concepts.
Management—Management is the process of acquiring information about devices on a network
or enterprise. Management if performed when an application, such as Insight Manager 7,
requests data or accepts traps (a type of message) from devices on a network. The management
application communicates the request and receives responses to the request using a protocol like
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) for communication.
SNMP—SNMP is the most commonly used protocol for exchanging management information
between devices. SNMP retrieves data from a target device. The data is accessed through an
SNMP agent, a program that interrogates the device and returns the response to the
management application. In order for the devices to be monitored (read) or controlled (written
to) by a management application, an agent must reside on the device or interact with the
device. The data about the device is found in a MIB (Management Information Base).
MIB—A MIB is a repository of information. A MIB describes manageable objects or devices. (An
SNMP manageable object and an Insight Manager 7 device are generally equivalent. Either
term refers to SNMP-manageable entities).
2
Page 3
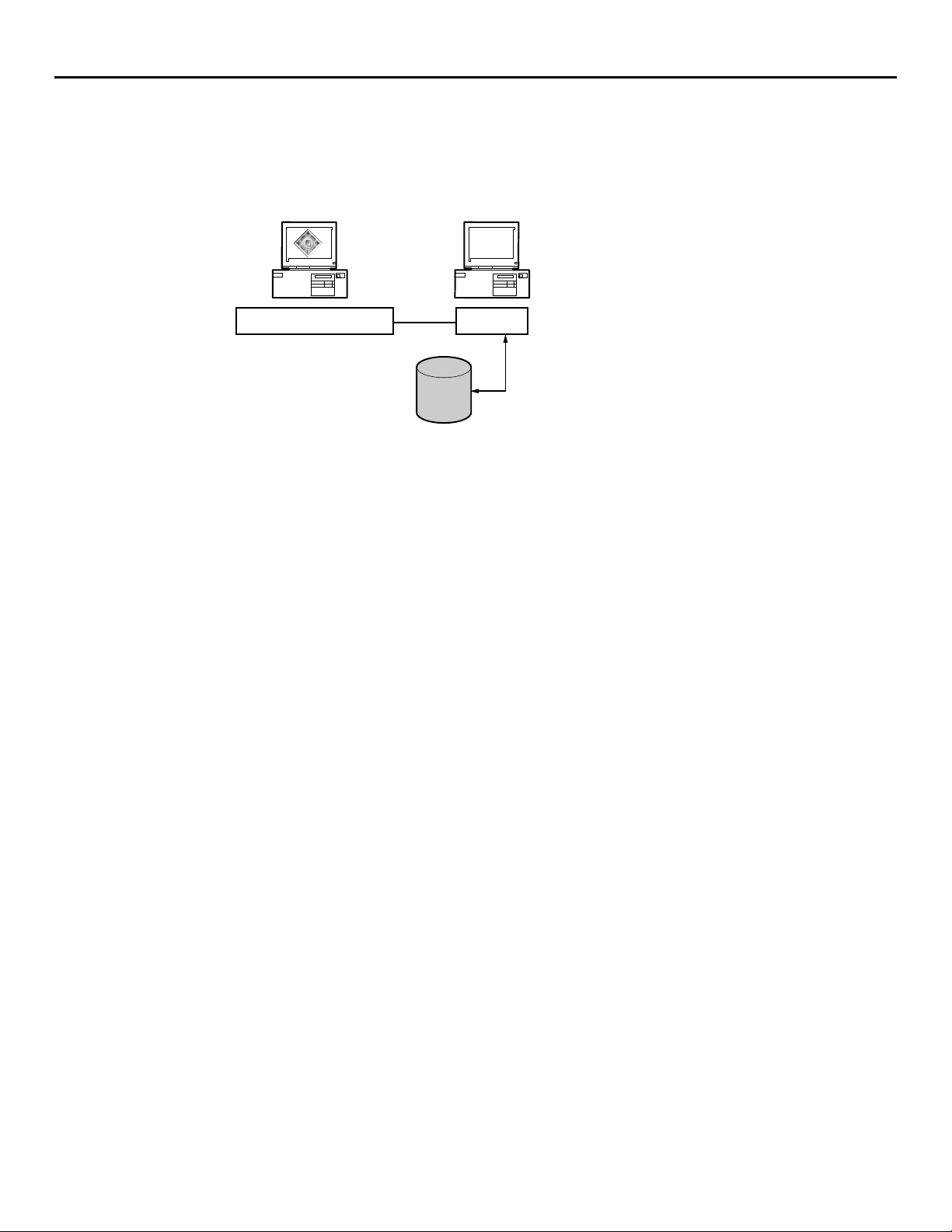
Insight Manager 7 SNMP Extensions utility
The MIB is a virtual mapping of variables to physical hardware and its related devices. SNMP
abstracts the control of the device through these variables. The below figure illustrates the
interaction of the management application, the agents on a device, and the MIB databases. The
configuration in this diagram shows two MIB databases. Multiple MIB databases within the
same configuration should have the same versions of a MIB. MIB databases must be
synchronized so interpretations of data are uniform.
Management Application Agents
MIBs
The MIB is analogous to a database schema because it represents data and data structures.
MIBs have been defined for TCP/IP routers and hosts, interface types, such as token ring and
FDDI, and devices, such as servers and bridges. HP has defined MIBs for all of its SNMPcapable devices. These MIBs are pre-compiled into the database and can be used by Insight
Manager 7.
Other third-party devices like routers and hubs exist on a network. Vendors of these network
devices also define MIBs. When the vendor MIB is registered into the database, you can use
Insight Manager 7 to monitor and control the devices.
The MIB structure is explained in the IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force) Standards RFC 1155.
Because the MIB structure resembles the directory and subdirectory file structure used for an
operating system, it is often referred to as a tree with a root.
MIB files often contain groups of variables that define the types of information that can be
retrieved from a device. MIB information and characteristics include an object identifier, or OID,
and a unique identifier that identifies the MIB and the variable. A variable can have one or
more values. The OID is in numeric dot format. The tree structure determines the unique name
and OID notation for each manageable entity.
MIB variables declare certain characteristics of the device, such as the operating system. HP
MIBs include information like version numbers and product names. For example, the following
table shows variables for an HP server running Windows NT 4.0. The values for the variables
include the product and other information derived from the MIB database.
3
Page 4
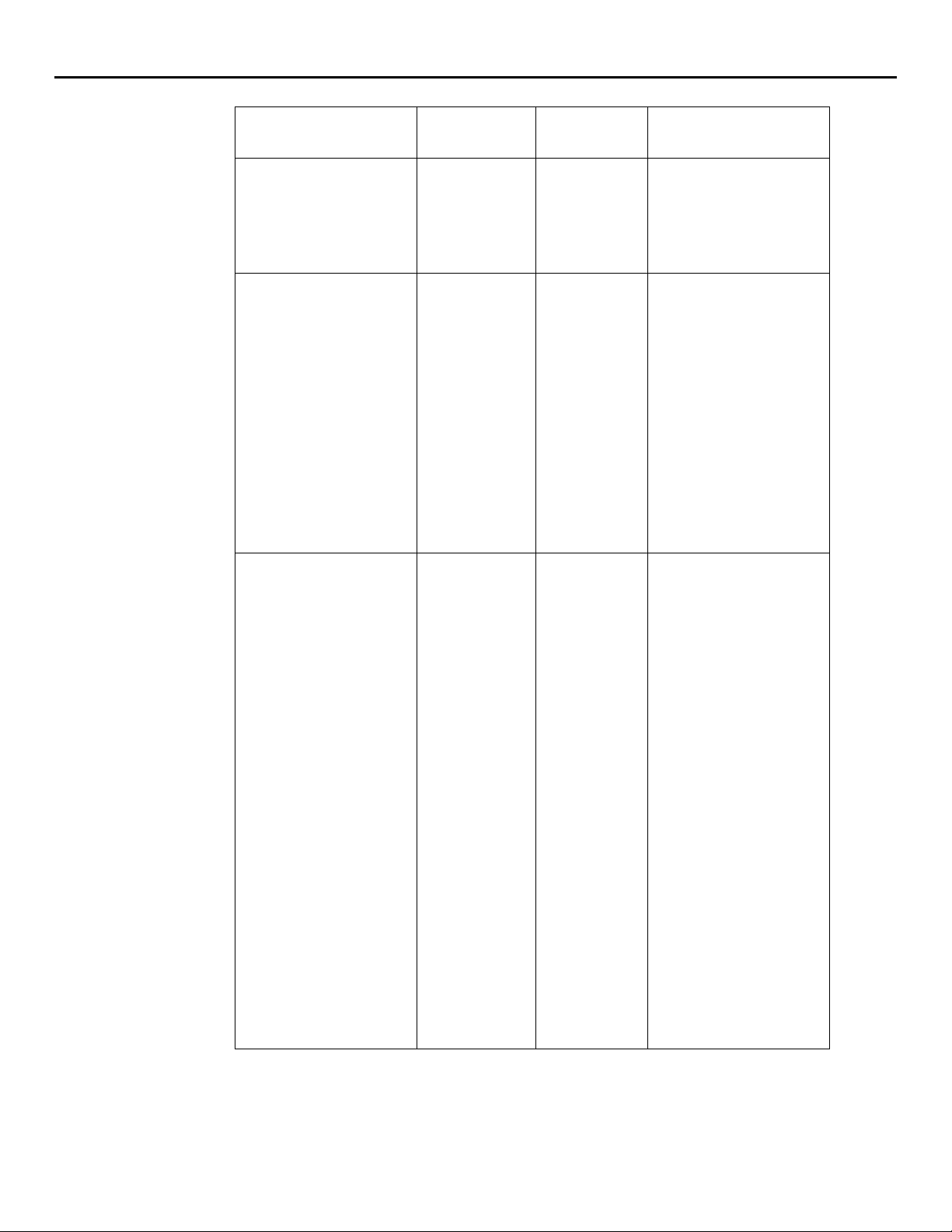
Insight Manager 7 SNMP Extensions utility
g
variable name and
description
Syslocation
The physical location of
this node. (For example,
the telephone closet, 3
floor).
SysDescr
A textual description of
the entity. This value
should include the full
name and version
identification of the
system’s hardware type,
software operating
system, and networking
software. It is mandatory
that this only contain
printable ASCII
characters.
SysObjectID
The vendor’s
authoritative
identification of the
network management
subsystem contained in
the entity.
OID data type value
1.3.6.1.2.1.1.6 ASCII String MRO1-2/KL24
rd
1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1 ASCII String Hardware: x86 Family 6
Model 3 Stepping 4
AT/AT COMPATIBLESoftware: Windows NT
Version 4.0 (Build
Number: 1381
Uniprocessor Free)
1.3.6.1.2.1.1.2 Object
Identifier
1.3.6.1.4.1.311.1.1.3.
1.1
This value is allocated
within the SMI enterprise
subtree (1.3.6.1.4.1)
and provides an easy
and unambi
uous means
for determining what
kind of box is being
managed.
For Example, if vendor
Flintstones, Inc. was
assigned the subtree
1.3.6.1.4.1.4242, it
could assign the
identifier
1.3.6.1.4.1.4242.1.1
to its Fred Router.
4
Page 5
Insight Manager 7 SNMP Extensions utility
information retrieved from MIBS
MIBs often organize their information by object groups that contain a related collection of
variables. MIB variables contain attributes that include:
• The data type
• A textual description
• The read or write access
• Whether the variable is mandatory or optional
MIBs contain the traps that the device can generate. Traps are messages the device sends when
specific conditions occur. Traps can include:
• The trap object identifier (trap OID)
• The agent IP address
A trap can be interpreted and formatted for display.
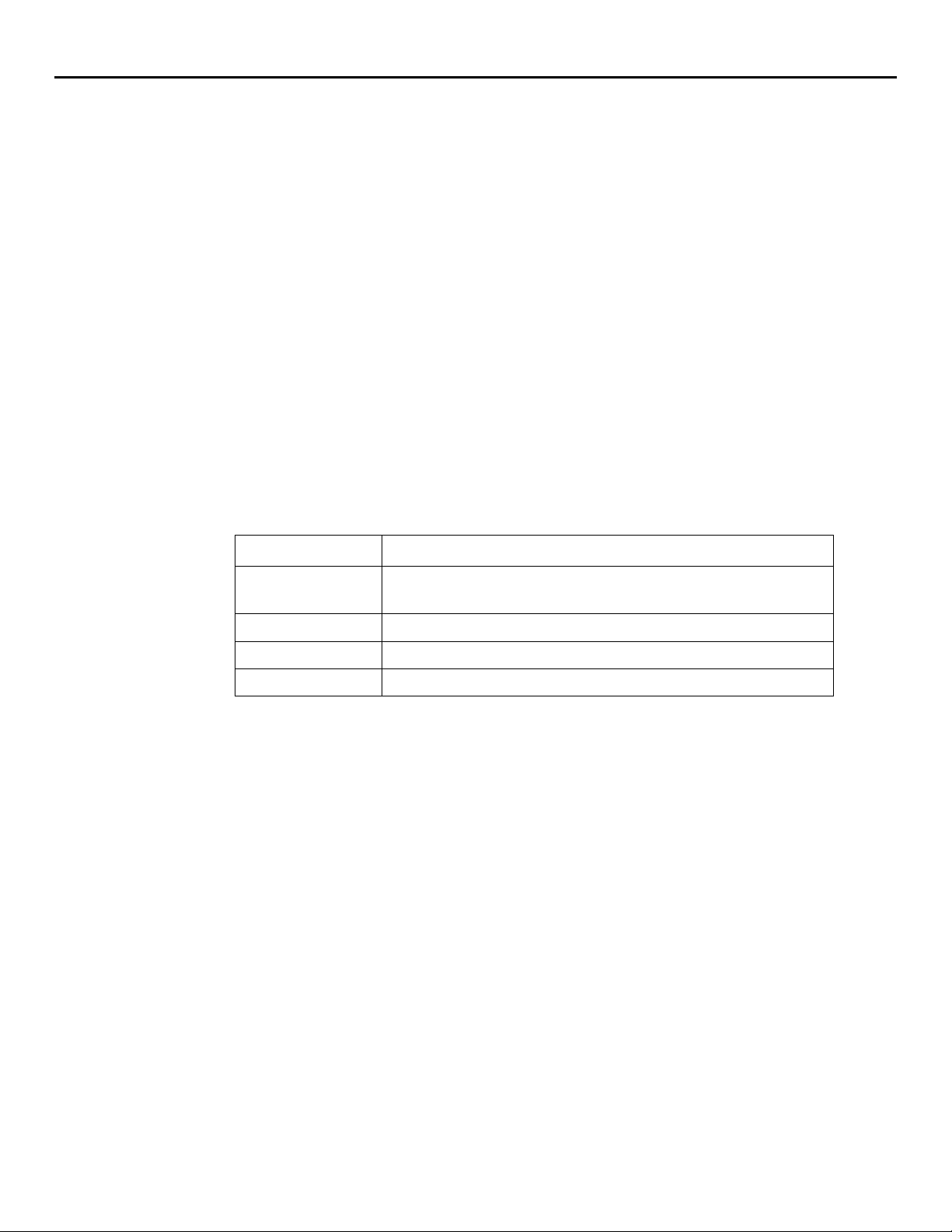
MIBs can contain one or more MIB variable bindings. Bindings convey useful information
associated with the condition that triggered the trap. Bindings include the Description, the Type,
the Category, and the Severity. For example, the trap cpqclusterFailed has the following
bindings:
SNMP operations by agent
binding content
Description This trap will be sent any time the condition of the cluster
becomes failed
Type Cluster Failed
Category Cluster
Severity Major
The agent performs the following SNMP operations:
GET and GET NEXT—Retrieve information about the managed device and return the information
to the management application. In Insight Manager 7, the terms Monitor and Read are
equivalent to a GET.
SET—Changes the value of a managed device variable in the MIB database. Only variables
whose device definitions have read and write access can be set. In Insight Manager 7, the terms
Control and Write are equivalent to a SET.
TRAP—Sends messages to the management application when a change or error occurs in a
managed object. The trap is the only operation initiated by the agent without a specific request
from the management program. The MIB defines the syntax of any trap messages initiated by
the agent. Systems must be configured to receive traps.
5
Page 6

Insight Manager 7 SNMP Extensions utility
In order to send and receive traps, the managed object and the management application must
be configured correctly:
• The managed object must have a trap destination to direct traps to the server running
the management application.
• The management server must be configured to receive the traps.
• The correct SNMP security needs to be established between the managed device and
the management server using SNMP community strings, a type of authentication. If the
community strings do not match, communication between the devices does not occur.
• The management application must understand the format of the trap.
how can SNMP Extensions help?
SNMP Extensions can help because it enables you to extend the SNMP V1.0 Management
Information Base (MIB) of Insight Manager 7. SNMP Extensions lets you fully explore most
devices on your network, broaden the scope of your network management, and prepare you to
manage the network of the future.
Exploring your network—You can achieve greater understanding of your network because you
can interrogate most MIB variables that have been incorporated into SNMP-compliant devices.
Better understanding of the variables makes it easier to create Insight Manager 7 tasks that are
based on SNMP events.
Broadening your management scope—Most likely, your network includes third-party devices.
Insight Manager 7 ships with a variety of third-party MIBs, not all Third-party MIBs are registered
by default. Using SNMP Extension, you can register the third-party MIBs.
Registration of third-party MIBs improves manageability in several ways:
• Registration enables the discovery process of third-party devices
• Registration adds event recognition
• Registration enhances event display
New versions of MIBs are available periodically. SNMP Extensions allows you to update your
MIB database to the latest MIB revisions so you can discover and identify new devices using the
latest information about the devices.
SNMP Extensions adds to event recognition by allowing you to optimize the event data to
individual network requirements. For Example, you can include references to maintenance
procedures. SNMP Extensions also permits you to construct your own interpretation of device
events through the use of Trap Categories. You can organize your device maintenance by
creating logical event categories. Then, exercise your judgment in assigning events to them.
Furthermore, you can use the event categories to query for events according to a category of
traps.
Preparing your network for the future—As time goes by, new network devices will be developed
that you wish to add to your network. You can add the new devices, discover, and identify them
if you have an associated MIB to register.
6
Page 7

Insight Manager 7 SNMP Extensions utility
In addition to external MIB sources for third-party devices, you can continue to register new
releases of HP MIBs that are distributed between releases of Insight Manager 7. New MIBs are
distributed periodically on Management CDs. For the latest versions of HP MIBs, visit the website
SNMP Extensions features
http://www.hp.com./
SNMP Extensions contains a graphical user interface to a MIB compiler that is a part of Insight
Manager 7. It also has a command line utility that you use from a DOS command box. The
command line utility performs a superset of the functions you can perform through the graphical
interface.
IMPORTANT: Simultaneous use of both tools can have adverse affects on SNMP Explorer,
Automatic Discovery, device identification, and event viewing.
SNMP Extensions contains the following functions:
MIB Registration—MIB Registration compiles new MIBs into the Insight Manager 7 database.
MIB Registration also includes the Unregister function. Unregister removes the information about
a registered MIB from the database. You might unregister a MIB before installing a new version
of the MIB or when the device associated with the MIB is removed from the network. You can
use MIB Register and MIB Unregister from either the Insight Manager 7 graphical user interface
or from the command utility.
MIB Trap Edit—Trap Edit lets you customize the MIB information by modifying the text that
describes traps. For example, replace cryptic default text with an easily understood message.
You might include instructions, such as Refer to our website http://… for faster
problem resolution. You can edit traps from either the Insight Manager 7 graphical user
interface or from the command utility.
setting up the environment
MIB Upload—Enables you to copy a MIB from your browser system to Insight Manager 7 server
and directory.
Trap Categories—Enables you to use default trap categories or create you own logical groups
for trap assignments. The same trap categories are available when you create a query. Using
your own category, you can monitor your choice of devices for specific traps. Trap Categories is
not a command line option
SNMP Explorer—Displays a selected, registered MIB and its variables on discovered devices.
Simply examining a MIB and its variables and descriptions enhances your understanding of the
MIB and how it works with the device. You might choose to modify the description or other
modifiable attributes of the variable. You can open SNMP Explorer from a Device Link from the
Device page of SNMP-compliant devices. SNMP Explorer is not a command line option.
The SNMP Extensions toolkit is intended for system administrators and network managers, who
are familiar with SNMP management, network fundamentals, and their operating system
environment. Refer to the specific documentation for your network and operating systems. SNMP
Extensions Toolkit requires the same hardware and software requirements of Insight Manager 7.
Consult the Insight Manager 7 Technical Reference Guide on the Management CD for details.
7
Page 8

Insight Manager 7 SNMP Extensions utility
The SNMP Extensions Toolkit is intended for administrators and network managers who also
have administrator privileges in Insight Manager 7. SNMP Extensions requires administrator
privileges because core server SNMP definitions of Insight Manager 7 might be modified.
the set of installed MIBs
Insight Manager 7 provides a set of MIBs that are already registered into the database. The
default location for registered and non-registered MIBs is the following directory unless you have
specified another at installation:
\Program Files\HP\ Insight Manager 7\compaq\protocol\snmp\Mibs
When you supplement the MIB set with new or revised MIBs, always copy them to this directory.
The MIB Upload feature always installs the MIBs into the correct location. The registered MIBs
and related files include:
• IETF Standard RFC 1213 Host Resources MIB and IETF Standard 1155 Structure of
Management Information
• A set of HP MIBs, which are identified by the prefix CPQ, such as CPQCLUS. MIB, the
HP cluster MIB or CPQIDE.MIB, the MIB for IDE drives.
• Third-party MIBs, such as the PATROL.MIB.
protecting source MIBs
managing MIBs from Insight Manager 7
An excellent practice in MIB management is to never modify the MIB. Therefore, SNMP
Extensions was designed to enable changes to trap declarations and other trap information
without modifying the source MIBs. SNMP Extensions creates an editable file called the editfile.
The editfile is a textual revision file identified by the file extension of REV. The editfile is applied
after the MIB is compiled
Because the changes are not made to the MIB, you can reinstall MIBs and replace the changes if
the database is corrupted or deleted. Therefore, keep backup copies of the REV editfiles. You
can find the REV files in the same directory as the set of installed MIBs.
\Program Files\HP\Insight Manager 7\compaq\protocol\snmp\Mibs
You can perform the most commonly used functions of SNMP from Insight Manager 7. These
include:
• Registration of new HP and third-party MIBs
• Modification of registered MIBs and related browsing of all MIB variables
• Deletion of obsolete or unused MIBs
• Uploading new MIBs to be registered
• Use of trap categories for organization and event queries
8
Page 9
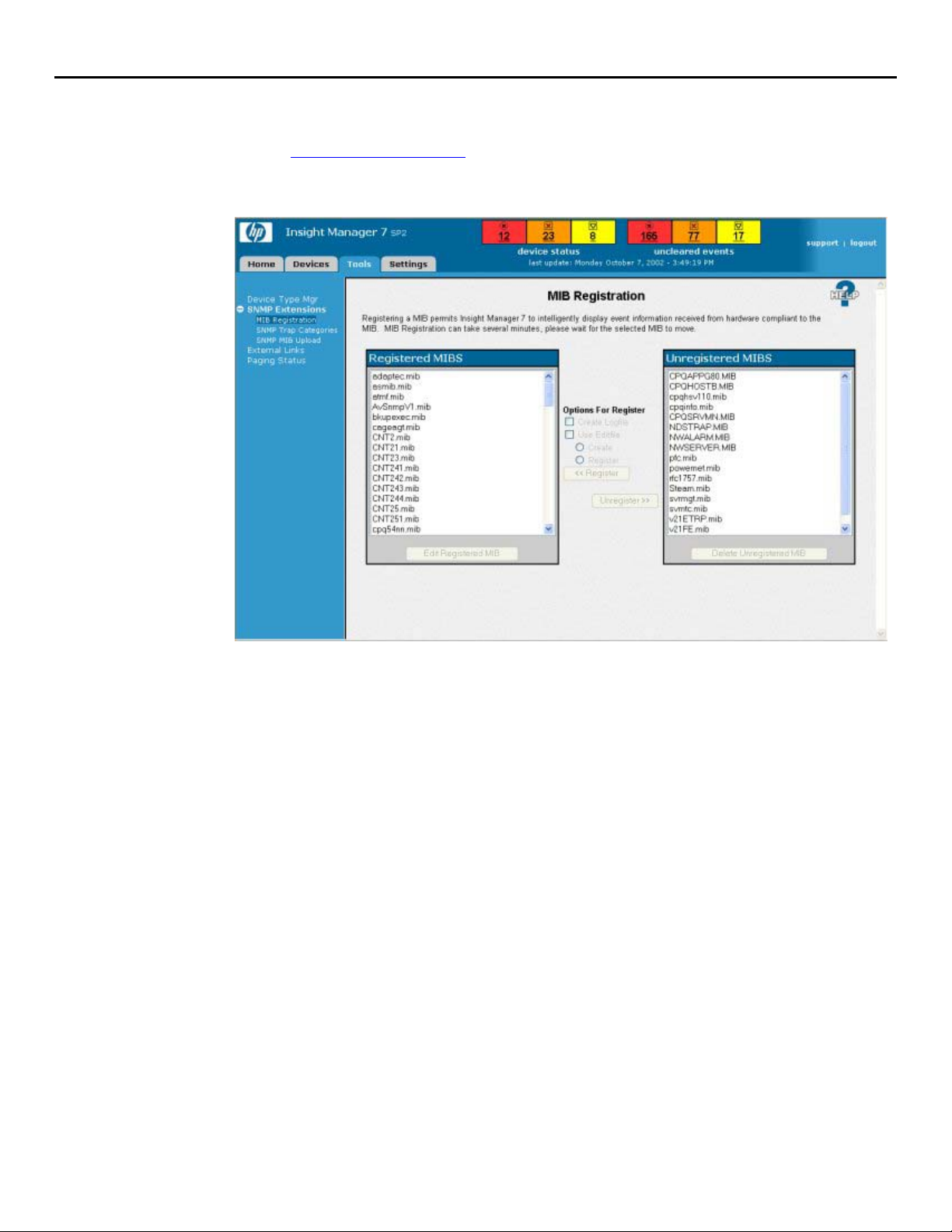
Insight Manager 7 SNMP Extensions utility
starting SNMP Extensions
1. Browse to Insight Manager 7 on the server system using the URL for the server. For
example:
http://server_name:280/
2. After the Device Overview page is displayed, click the Tools tab.
3. Select SNMP Extensions and click MIB Registration. The MIB Registration
page is displayed.
4. Examine the elements on the page. You will see the lists of registered and unregistered
MIBs and the options you have for working with them.
9
Page 10

Insight Manager 7 SNMP Extensions utility
registering a MIB
Registration of a MIB compiles the information into the Insight Manager 7 database. MIBs
require a short interval to become fully registered. The more information, such as the number of
traps, the longer the registration takes.
When you register, you can create a logfile and an editfile for a MIB.
Logfiles—A logfile is a record of the MIB registration. A logfile is created in the subdirectory
Program Files\HP\HP Insight Manager 7.07\log. It has the registered name of the MIB with the
suffix of TXT. For example, the CPQClus.MIB log file is CPQCLUS.TXT. You can find the logfiles
in the default directory:
\Program Files\HP\Insight Manager 7\log
Editfiles—An editfile, known as the REV file, is the mechanism that enables you to introduce
edited MIB information into the database without modifying the source MIB. The editfile has the
registered name of the MIB with the suffix REV. For example, the editfile for the CPQHLTH.MIB is
CPQHLTH.REV.
You can find the REV editfile in the same directory as the MIBs:
\Program Files\HP\Insight Manager 7\compaq\protocol\snmp\Mibs
The editfiles that are provided have the addition of modifiable fields called #TYPE, #SEVERITY,
and #CATEGORY. These fields have values for trap descriptions. When a MIB is registered
using the REV files, the additional information is placed into the database. Once a MIB is
registered, a REV file can be created from the database after the MIB is registered.
In the future, if you choose to register a MIB from its source file, the information that is contained
only in the REV file will no longer be in the database. In addition, the information would not be
in a REV file that was created from the database after the source MIB registration.
You should back up the REV file changes, so if the installed REV editfiles are lost or damaged,
you can reinstall them from from your back up copy.
You can use the REV editfile in any of the following ways:
• If an editfile exists, you can edit it and maintain more complete information in the
database. You can edit from the Insight Manager 7 or the command line.
• After you have registered a MIB, you can register the REV editfile.
• An accurate and recent MIB is your best source of device management information.
10
Page 11

Insight Manager 7 SNMP Extensions utility
registering a MIB
1. Click the Tools tab.
2. From the menu, select SNMP Extensions and click MIB Registration.
3. Select a MIB from the Unregistered MIBs column.
4. At Options for Register, select either or both file creation options:
Then choose one of the following options:
Create Logfile
Use Editfile.
• Create Editfile—Registers the selected MIB (using the source MIB file), and
creates a new REV file if one does not exist for the selected MIB.
• Replace Editfile—Registers the selected MIB (using the source MIB file) and
overwrites the existing REV file in the MIB folder.
• Register Editfile—Registers the selected MIB using the existing REV file
contents to populate the database MIB tables.
why registration fails
5. Click Register. When registration is complete, the MIB is removed from the
Unregistered MIBs column and is highlighted in the Registered MIBs column. If
you do not see the MIB immediately, scroll to find it.
MIB registration typically fails for the following reasons:
• The MIB contains a syntax error—Syntax errors affect the MIB compilation phase.
SNMP Extensions can resolve some syntax errors, but if the error cannot be
resolved, the registration fails. For example, if the MIB structure is invalid, the MIB
cannot be compiled.
• Elements in the MIB are not unique—MIB module names must be unique. If you try
to register a MIB with a module name that is already used by another registered
MIB, the compile will fail.
• The MIB has dependent MIBs that cannot be found—A new MIB will not have all
the components necessary to compile by itself. Most MIBs depend on other MIBs. If
a MIB imports variables from other MIBs, the importing MIB needs a copy of the
referenced MIBs to compile along with the specified new MIB. The importing MIB
will resolve the unknown references from dependent MIBs. If the referenced MIBs
are not in the correct directory, use the Upload feature and register them. Then
reregister the failed MIB.
Note: A registration may appear to fail if the browser times out before registration is complete.
However, the registration continues and will be successful as long as none of the failure
conditions exist. During a timeout, you will lose your connection. To resume working in Insight
Manager 7, log in again.
11
Page 12

Insight Manager 7 SNMP Extensions utility
unregistering a MIB
Unregistering removes the MIB information from the database along with the dependent MIBs
and removes any associated events, whether the information comes from the MIB or from its
REV editfile. Unless you remove the MIB from the \Mibs directory, it remains in the
Unregistered MIBs column.
1. Select the MIB from the Registered MIBs column.
2. Click Unregister. When the MIB is no longer registered, the MIB is highlighted in the
Unregistered MIBs column. You may need to scroll through the list to see the
highlighted MIB.
WARNING: Unregistering a root MIB, such as MIB-II (RFC1213.MIB), can cause all other MIBs
referenced by the root MIB to become unregistered.
uploading a MIB
MIB Upload browses for the source MIB files and copies them into the MIBs directory. Vendors
often provide MIBs through websites. If the MIB you need is on a website, on CD-ROM, or on a
diskette, you can upload it to the correct directory:
\Program Files\HP\Insight Manager 7\compaq\protocol\snmp\MIBs
If the MIB is already in the folder, uploading will fail with the status message MIB upload
failed: <mibname> already exists. When you rename the MIB, use only
alphanumeric characters.
editing registered MIB information
To upload a file, begin on the MIB Upload page.
1. Click the Tools tab.
2. From the menu, select SNMP Extensions and click SNMP MIB Upload.
3. On the MIB Upload page, click Browse to locate the file.
4. When you locate the MIB, select it and click Upload.
SNMP Extensions modify the database—not the MIB—with new information. HP does not
recommend opening the database tables or editing the source MIB. Instead, modify the MIB
information using the Edit Registered MIBs Trap Edit features. You can modify the information in
the following ways:
• Customize the trap description to include specific instructions, sources of information, or
company policy
• Change the trap type name
• Change the trap severity if vendor's default severity does not match conditions on your
network
• Specify whether traps are to be ignored. For example, disable informational traps or
repeat traps that are generated for non-critical situations. Enable trap handling if the
conditions change. Do this on a trap-by-trap basis.
• Change trap category assignment by moving the trap to a previously defined category
12
Page 13

Insight Manager 7 SNMP Extensions utility
editing a MIB
Begin on the SNMP Extensions MIB Registration page. Select a MIB from the
Registered MIBs column.
1. Click Edit Registered MIB. The SNMP Trap Edit page opens. On the edit page,
the traps associated with the selected MIB are displayed for editing.
2. Click the drop-down list to view the traps that are defined in the MIB. Select one. The
trap's corresponding information is displayed. Modify the MIB information in any of the
following ways. All are optional.
• Position the cursor in the Description field to modify the text.
• Position the cursor in the Type field and change how the trap is identified in the
Insight Manager 7 display.
• Position the cursor in the Severity field and enter your choice of Informational,
Minor, Major, or Critical.
• Select the Enable Trap Handling check-box to enable trap handling or deselect
it to disable trap handling.
• Reassign the trap category from the selection in the drop-down Category list.
3. Click Apply to save your changes or click Reset to restore the previous MIB
information.
13
Page 14

Insight Manager 7 SNMP Extensions utility
unregistering an installed MIB
When a device is removed from the network, you can remove the MIB that supports it. SNMP
Extensions Unregister function also removes all database references to the MIB and any
dependent MIBs. If you reinstall the device in the future, reregister the MIB into the database. If
you upgrade to a similar device from the same vendor, register the most current MIB that the
vendor supplies.
unregistering a MIB
1. Select a MIB from the Registered MIBs column.
from the MIB
Registration page
deleting unregistered
2. Click Unregister MIB. The MIB is removed from the database. It is also removed from
the Registered MIBs column and placed in the Unregistered MIBs column.
Deleting a MIB removes the MIB file from the Insight Manager 7 directory.
MIBS
Note: Do not delete an unregistered MIB unless you are certain it is unnecessary, obsolete, or
you plan to upload a new version. Because all references to the MIB are removed from the
database, you may see error messages regarding the deleted MIB if it is not replaced, but the
device it supports remains on the network.
Deleting an unregistered MIB
1. Select the MIB from the Unregistered MIBs column.
2. Click Delete Unregistered MIBs.
3. Click OK to confirm the deletion.
14
Page 15

Insight Manager 7 SNMP Extensions utility
using trap categories
Trap Categories are logical groupings of SNMP traps. Categories are used to sort the Event
by Type criteria list. SNMP Extensions lets you modify existing assignments by moving traps
between categories. SNMP Extensions also enables you to create new categories and move
traps from the default assignment to the new category.
Insight Manager 7 defines the following default categories:
• Generic—Traps from RFC standard MIBs and traps that are not associated with a
specific piece of software or a specific device. This category also includes some
generic traps from HP MIBs and Digital MIBs.
• System and Environmental—Temperature, CPU conditions, memory, chassis, and
other related traps generated from the server.
• Cluster—Cluster-generated traps, including fail-over, resource sharing, and the
physical components that comprise the cluster.
• NetWare—Traps specifically generated by a NetWare server. This category includes
traps generated by the NWALARM MIB.
• NDS—Traps generated by the NDSTRAP MIB.
• Remote Monitoring and Management—Traps generated from remote monitoring
and management processors, including the Remote Insight Board.
• Backup—Traps from software and hardware specifically assigned to a backup or
recovery task. Note that tape device-specific traps remain in the Storage category.
• Networking Devices—Traps from switches, routers, hubs, etc.
• NIC—Traps relating to network cards.
• UPS—Software and hardware for UPS use.
• Storage—Local and remote storage, RAID devices, tape, disk, controllers, SCSI, and
IDE devices.
15
Page 16

Insight Manager 7 SNMP Extensions utility
• Application—Traps generated by miscellaneous applications, such as the BMC Patrol
tools or Load Sharing Facility (LSF) V2.2 for UNIX systems. Note that this does not cover
the Novell specific traps. Due to the large volume of NetWare OS-specific traps, Novell
traps are categorized separately.
• Threshold—Traps generated when monitored variables that are not in a specific
category cross a defined threshold.
• Unknown—Traps not currently classified. This is the default for any traps not assigned
to a specific category.
changing trap category assignments
1. Click the Tools tab.
2. From the menu, select SNMP Extensions and click SNMP Trap Categories.
using SNMP Explorer
3. Click the drop-down list labeled Trap Category A to select the source category.
Individually select the traps you wish to move.
4. Click the drop-down list labeled Trap Category B to select the destination category.
5. Click Move>> to move the traps from category A to category B.
6. The display will be updated dynamically to show your action.
SNMP Explorer is a MIB Browser. It displays as a link for SNMP devices on the Device page.
The figure below illustrates the SNMP Explorer page that opens from a device link
16
Page 17

Insight Manager 7 SNMP Extensions utility
Note: To take full advantage of the SNMP Explorer, you should be familiar with MIB-II structure
and variables. You can examine MIB variables of any registered MIB in SNMP Explorer with
the exception of complex variables, which have OIDs with lists or tables or variable OIDs that
require you to specify a specific instance of the OID.
opening the SNMP Explorer:
1. Click the Devices tab.
2. From the menu, click Device Queries.
3. On the Device Queries page, select a device query for devices you know are using
SNMP.
4. On the query result list, click the device name link to open the Device page.
5. In the Device Links group, click the link to SNMP Explorer. The SNMP Explorer
page opens with the SNMP information for the target device as described
field purpose
Registered MIB Name of the MIB being explored. Click the arrow to
Variable from MIB Name of the variable. Click the arrow to view scalar
Variable Display Characteristics of the variable and a description of
view all MIBs registered in Insight Manager 7.
variables in this MIB. This field lists only variables for
the selected MIB and may not show all variables that
are declared with the MIB.
the variable. Attributes apply to the selected MIB
variable.
17
Page 18

Insight Manager 7 SNMP Extensions utility
field purpose
Type One of several types, including INTEGER, STRING,
Access One of several access types, including READ,
Status The status for the variable in this MIB, such as
Database Display Field Description of the variable and its purpose. Use this
SNMP Explorer Status Bar The result of the last operation on this variable.
Note: SNMP Explorer does not browse MIBs on target devices that are running only IPX.
You can view all kinds of variable information in a MIB. Viewing is equivalent to an SNMP get
operation. If you have the appropriate Administrator privileges, you can apply new values on
attributes with write access. Writing is equivalent to an SNMP set.
IP ADDRESS, COUNTER, TIMETICKS, and
GAUGE.
WRITE, or READ-WRITE.
MANDATORY, DEPRECATED, OPTIONAL, or
OBSOLETE.
field to review the meaning of a trap that includes this
variable, to read (GET) other agent information, and
to modify (SET) a new value when the variable has
READ-WRITE access.
viewing variable data
writing a new value to the variable
1. From the drop-down box of the Registered MIB field, select a MIB.
2. From the drop-down box of the Variable from MIB field, select a variable. The
variable information is displayed in the Database Display field.
3. Continue to select variables of MIBs. After each selection, click Read Device to
display the value of the variable as was read from the device. The OID, type, and the
value at the selected platform are displayed for each variable.
1. From the drop-down box of the Variable from MIB field, select a variable. The
variable information is displayed in the Database Display field.
2. Click Read Device to view the MIB variable on the target device.
3. Click Edit Device.
4. In the Database Display field, enter the MIB variable value you are adding at the
target device.
5. Click Write Value to Device.
18
Page 19

Insight Manager 7 SNMP Extensions utility
verifiying the SNMP settings
If you are an administrator, you can change the SNMP settings on the fly. This is useful if you
need to change the community string, timeouts, or retries.
1. Click Show Device Settings.
2. Change the settings as necessary on the SNMP Settings page.
3. Click Submit to change the settings or Reset to restore them.
4. Click Return to go back to the SNMP Explorer page.
managing MIBs
The alternative to using SNMP Extensions from Insight Manager 7 is to use the command line
program. The command line interface enables more complex operations, in addition to
from the batch
registering, modifying, and deleting, that you can perform from Insight Manager 7.
command
The commands are included in the program mCompile.bat. Use the command line interface
from a DOS command box. Although the purpose of the command line interface is not to
debug the MIBs, you can use the command line for this purpose.
command syntax conventions
The following table explains how to interpret the SNMP Extensions commands that are
described in the following section, “The Command Syntax.”
the command syntax
symbol or convention description
<parameter> Parameters enclosed in angle brackets indicate that
[optional parameters] Elements inside the braces are optional.
- (minus sign) followed by a switch The switch is optional, such as -D, -f.
| (vertical bar) between two elements The vertical bar represents a syntax that requires a
The command line program expects to find the MIBs in the following directory:
something must be added to complete the command,
such as a password or parameter. The elements
inside the brackets are meant to be placeholders that
are replaced with true values without the brackets.
For example, mCompile <mibfile.mib> becomes the
command line expression:
> mCompile foo.mib
choice of this OR that. For example,
>mCompile foo.mib | foo.rev
\program Files\HP\Insight Manager 7\Compaq\Protocol\snmp\Mibs
The command line batch file mCompile program has the following batch file procedures:
mCompile [-D][-L <logfile.txt>][-n "trapHandlerClass"]
<mibfile.mib>
The above command enables debug mode. The logfile name is the name of the MIB with the
extension .txt. The mibfile name is the name of the MIB with the .mib extension.
mCompile |-g] [-C] <mibfile.mib>
19
Page 20

Insight Manager 7 SNMP Extensions utility
The above command generates an editfile for corrections. The mibfile name is the name of the
MIB with the .mib extension added on.
mCompile [-c [-n "trapHandlerClass"] (-C <mibfile.mib> |
<mibfile.rev>)
The above command applies changes to the database that were made to the commented REV
file. The mibfile name is the name of the MIB with the .mib extension added on. The
corresponding REV file has the name of the MIB with the .rev extension.
mCompile -f <filelist.txt>
The above command registers multiple MIBs. For each MIB to be registered, create a text file to
be called by the program. In the file, name the import file that contains a list of MIBs, or list
each MIB to be registered on a separate line. The program reads the specified imports and MIB
file name and registers each in turn.
mCompile -d <mibfile.mib>
The above command deletes a registered MIB and any dependent MIBs from the database.
mCompile (-l|-t) [<mibfile.mib>]
command switches
The above command creates a list of all registered MIBs and the traps associated with them.
Commands, MIB names, and file names are case-insensitive. For example mcompile and
MCOMPILE execute the same operation. Switches are case-sensitive as described in the
following table.
The command line program uses the following switches:
switches purpose
-c Make database corrections (after a normal mib installation)
-C Compiles a MIB
-d Delete a MIB file (and all MIBs that import it)
-D Enable debug mode (to screen)
-f Specify a filename (with Full Path) containing a list of command lines
-g Generate an editfile for database corrections
-l List of mib files in database
-L Generate specified logfile to the \log directory
No switch Default is “compaq.protocol.snmp.trap.GenericTrapNoticeHandler”
-n Java ‘Notice' handler Default is:“compaq.protocol.snmp.trap.GenericTrapNoticeHandler
20
Page 21

Insight Manager 7 SNMP Extensions utility
running the
The command line program runs from an MS-DOS Prompt window. To open a DOS window:
mCompile command
1. From the desktop, click Start—>Run.
In the Open field, enter cmd.exe.
2. Click OK.
3. Change to the directory where Insight Manager 7 is installed. For example, the
command to change the default installation directory is:
CD C:\Program Files\HP\HP Insight Manager 7
4. On the command line, enter:
mcompile.bat
When you run the program, options and examples for writing the command are displayed.
Reference these when you enter the command.
21
Page 22

Insight Manager 7 SNMP Extensions utility
a command line example
The following shows the display of a mCompile command without parameters or switches. The
single command presents all mCompile options.
C:\Program Files\HP\Insight Manager 7>mcompile
C:\Program Files\HP\Insight Manager 7>runtime\bin\
jre -ms8m -mx750m -cp
lib\jgl3.1.0.jar;.;lib\swing.jar;lib\windows.jar;lib\msxml.jar;lib\
activation.jar;lib\mail.jar
compaq.protocol.snmp.MibMgr.MibCompiler.MibCompilerShell
Trying connection to database using property file:
\config\database.props
Database connection test successful for URL: jdbc:odbc:INSIGHT_DB_V2
User: sa pwd:
Database Machine:
SERVER1
Database Version:
Microsoft SQL Server 7.00 - 7.00.623 (Intel X86)
Nov 27 1998 22:20:07
Copyright (c) 1988-1998 Microsoft Corporation
Standard Edition on Windows NT 4.0 (Build 1381: Service
Pack 4)
Database Driver:
JDBC-ODBC Bridge (SQLSRV32.DLL) 1.1001 (03.70.0623)
Insight Manager 7 Command Line Compiler Usage:
Use one of the following forms:
------
(1) mCompile [-D][-L <logfile.txt>][-n "trapHandlerClass"]
<mibfile.mib>
(2) mCompile [-c [-n "trapHandlerClass"] (-C <mibfile.mib> |
<mibfile.rev>)
(3) mCompile |-g] [-C] <mibfile.mib>
(4) mCompile -f <filelist.txt>
(5) mCompile -d <mibfile.mib>
(6) mCompile -l[<mibfile.mib>
22
Page 23

Insight Manager 7 SNMP Extensions utility
where,
-c Make database corrections (after a normal mib
installation).
-C Compile MIB then perform editfile operation.
-d Delete a mib file (and all MIBs that import it).
-D Enable debug mode (to screen).
-f Specify a filename (with Full Path)containing a list of
mib files.
-g Generate an editfile for database corrections.
-l List of mib files in database.
-L Generate specified logfile.
-n Java 'Notice' handler.
Default is
'compaq.protocol.snmp.trap.GenericTrapNoticeHandler'
Examples:
mCompile cpqsvrmn.mib
mCompile -f list.txt
mCompile my.mib -n my.java.notice.handler
mCompile -g cpqsvrmn.mib
mCompile -c cpqsvrmn.rev
mCompile -d file1.mib
23
Page 24

Insight Manager 7 SNMP Extensions utility
troubleshooting a failed registration
The MIB may not register. If the MIB registration is unsuccessful, a message is displayed with a
possible explanation. Registration most often fails for the following circumstances:
• The program cannot import a dependency file. MIBs often refer to other MIBs, known
as dependents. Dependent MIBs must be in the same location as the MIB that names
them as dependents. Read the MIB you are registering to find the dependent MIBs.
• The import statement syntax is incorrect. Check the syntax of the import statement and
that the MIBs can be found as specified.
• The imported MIB contains invalid syntax or is not a valid MIB file. Some possibilities
are an invalid Definition within the MIB structure, duplicate module names, or incorrect
syntax for a variable entry.
Note: MIBs require varying amounts of time to compile. As long as none of the conditions exist
for failure, the MIB continues to compile. If the time required exceeds the browser timeout, you
will need to reconnect to Insight Manager 7. When the registration succeeds, the compiled MIB
is added to the list of registered MIBs.
registration error messages
The command mcompile generates progress messages during a compile and displays an error
if the registration is unsuccessful. Although, success or failure messages that are generated are
the same for both interfaces, you can view the progress in command line mode. The following
example shows the progress of the ntcmgt.mib.
>mcompile ntcmgt.mib
>runtime\bin\jre -ms8m -mx750m -cp
lib\jgl3.1.0.jar;.;lib\swing.jar;lib\windows.jar;lib\msxml.jar;lib\ac
tivation.jar;lib\mail.jar
compaq.protocol.snmp.MibMgr.MibCompiler.MibCompilerShell ntcmgt.mib
Trying connection to database using property file:
\config\database.props
Database connection test successful for URL: jdbc:odbc:INSIGHT_DB_V2
User: sa pwd:
Database Machine:
SERVER1
Database Version:
Microsoft SQL Server 7.00 - 7.00.623 (Intel X86)
Nov 27 1998 22:20:07
Copyright (c) 1988-1998 Microsoft Corporation
Standard Edition on Windows NT 4.0 (Build 1381: Service Pack 4)
Database Driver:
JDBC-ODBC Bridge (SQLSRV32.DLL) 1.1001 (03.70.0623)
++++ Processing file "ntcmgt.mib".
24
Page 25

Insight Manager 7 SNMP Extensions utility
MapleConnection: Real Close!! protocol.snmp.MibMgr.db.dbSql:173
freed: false
Compile Done
compiling a MIB with an Error: badmib.MIB
The following is an example of an invalid MIB. The nctmgt.mib was renamed to badmib.mib
and line 65 was commented out. The modification causes a compilation error.
>mcompile badmib.mib
>runtime\bin\jre -ms8m -mx750m -cp
lib\jgl3.1.0.jar;.;lib\swing.jar;lib\windows.jar;lib\msxml.jar;lib\ac
tivation.jar;lib\mail.jar
compaq.protocol.snmp.MibMgr.MibCompiler.MibCompilerShell badmib.mib
Trying connection to database using property file:
\config\database.props
Database connection test successful for URL: jdbc:odbc:INSIGHT_DB_V2
User: sa pwd:
Database Machine:
SERVER1
Database Version:
Microsoft SQL Server 7.00 - 7.00.623 (Intel X86)
the referenced badmib.mib
Nov 27 1998 22:20:07
Copyright (c) 1988-1998 Microsoft Corporation
Standard Edition on Windows NT 4.0 (Build 1381: Service
Pack 4)
Database Driver:
JDBC-ODBC Bridge (SQLSRV32.DLL) 1.1001 (03.70.0623)
++++ Processing file "badmib.mib".
Error: File'badmib.mib'.Error reading MIB: MIB node has no parent
File: C:\Program Files\HP\Insight Manager
7\compaq\protocol\snmp\mibs\badmib.mib Line: 65
Compile Done
Use the following code for badmib.mib as a reference. The code is a copy of the ntcmgt.mib
with line 65 commented out.
25
Page 26

Insight Manager 7 SNMP Extensions utility
-- ema OBJECT IDENTIFIER ::= { dec 2 }
-– BADMIB.mib
--
-- Description:
-- This BAD MIB
NTCMGT-MIB DEFINITIONS ::= BEGIN
IMPORTS
mgmt, enterprises, NetworkAddress, IpAddress, Counter, Gauge, TimeTicks
FROM RFC1155-SMI
OBJECT-TYPE
FROM RFC-1212
DisplayString
FROM RFC1213-MIB;
-- DEC-MIB { iso(1) org(3) dod(6) -nternet(1) private(4) enterprises(1) 36
}
dec OBJECT IDENTIFIER ::= { enterprises 36 }
-- ERROR LINE: the following line was commented out
-- ema OBJECT IDENTIFIER ::= { dec 2 }
-- textual conventions for types
ObjectType ::= INTEGER {
unknown(1) ,
other(2) ,
share(3) ,
disk(4) ,
application(5)
}
PolicyType ::= INTEGER {
unknown(1) ,
other(2) ,
inOrder(3) ,
random(4) ,
leastLoad(5) ,
roundRobin(6)
}
Boolean ::= INTEGER {
true(1) ,
false(2)
}
-- The DateAndTime size can be only 8 or 11 bytes long.
DateAndTime ::= DisplayString
FailoverReason ::= INTEGER {
unknown(1) ,
other(2) ,
reconfiguration(3) , -- transaction is a result of human
failure(4) , -- transaction is a result of hardware or
failback(5) -- transaction is a result of a failback
}
SoftwareStatus ::= INTEGER {
intervention
software failure
event
26
Page 27

Insight Manager 7 SNMP Extensions utility
unknown(1) ,
other(2) ,
notInstalled(3) ,
notRunning(4) ,
running(5) ,
runningFailed(6)
}
-- This MIB extension, private to Digital Equipment Corp., allows for
-- management of Digital NT clusters.
mib-extensions-1 OBJECT IDENTIFIER ::= { ema 18 }
svrSystem OBJECT IDENTIFIER ::= { mib-extensions-1 22
}
ntcMgt OBJECT IDENTIFIER ::= { svrSystem 3 }
-- groups in ntcmgt
ntcMgtMibInfo OBJECT IDENTIFIER ::= { ntcMgt 1 }
ntcMgtClusterInfo OBJECT IDENTIFIER ::= { ntcMgt 2 }
ntcLastTransition OBJECT IDENTIFIER ::= { ntcMgt 3 }
--
-- ntcMgtMibInfo
--
-- current state of this MIB.
ntcMgtMibMajorRev OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX INTEGER
ACCESS read-only
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
"Major revision of this MIB. Should equal 1."
::= { ntcMgtMibInfo 1 }
ntcMgtMibMinorRev OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX INTEGER
ACCESS read-only
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
"Minor Revision of the MIB. Should equal 0."
::= { ntcMgtMibInfo 2 }
--
-- ntcMgtClusterInfo
--
-- Lists and states of cluster members, groups and objects.
ntcSoftwareVendor OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX DisplayString
ACCESS read-only
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
"Cluster software vendor name."
::= { ntcMgtClusterInfo 1 }
ntcSoftwareVersion OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX DisplayString
ACCESS read-only
27
Page 28

Insight Manager 7 SNMP Extensions utility
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
"Cluster software version string."
::= { ntcMgtClusterInfo 2 }
ntcSoftwareStatus OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX SoftwareStatus
ACCESS read-only
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
"Status of the cluster software: installed, running, failed, etc."
::= { ntcMgtClusterInfo 3 }
ntcAlias OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX DisplayString
ACCESS read-only
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
"Cluster alias name."
::= { ntcMgtClusterInfo 4 }
ntcThisMember OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX INTEGER
ACCESS read-only
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
"Index into the member table of the member that corresponds to this
::= { ntcMgtClusterInfo 5 }
ntcMemberTable OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX SEQUENCE OF NtcMemberEntry
ACCESS not-accessible
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
"Table of ntcMemberEntry."
::= { ntcMgtClusterInfo 6 }
ntcMemberEntry OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX NtcMemberEntry
ACCESS not-accessible
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
"Lists all nodes that comprise this cluster."
INDEX {
ntcMemberIndex
}
::= { ntcMemberTable 1 }
NtcMemberEntry ::=
SEQUENCE {
ntcMemberIndex
INTEGER,
ntcMemberName
DisplayString,
ntcMemberComment
DisplayString
}
ntcMemberIndex OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX INTEGER
node."
28
Page 29

Insight Manager 7 SNMP Extensions utility
ACCESS read-only
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
"Unique index for each entry."
::= { ntcMemberEntry 1 }
ntcMemberName OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX DisplayString
ACCESS read-only
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
"Node name of this cluster member."
::= { ntcMemberEntry 2 }
ntcMemberComment OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX DisplayString
ACCESS read-only
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
"Description of the node."
::= { ntcMemberEntry 3 }
ntcGroupTable OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX SEQUENCE OF NtcGroupEntry
ACCESS not-accessible
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
"Table of ntcGroupEntry."
::= { ntcMgtClusterInfo 7 }
ntcGroupEntry OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX NtcGroupEntry
ACCESS not-accessible
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
"Lists all cluster groups for this cluster."
INDEX {
ntcGroupIndex
}
::= { ntcGroupTable 1 }
NtcGroupEntry ::=
SEQUENCE {
ntcGroupIndex
INTEGER,
ntcGroupName
DisplayString,
ntcGroupComment
DisplayString,
ntcGroupOnLine
INTEGER,
ntcGroupFailedOver
Boolean,
ntcGroupPolicy
PolicyType,
ntcGroupReevaluate
Boolean,
ntcGroupMembers
29
Page 30

Insight Manager 7 SNMP Extensions utility
ntcGroupObjects
DisplayString
}
ntcGroupIndex OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX INTEGER
ACCESS read-only
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
"Unique index for each entry."
::= { ntcGroupEntry 1 }
ntcGroupName OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX DisplayString
ACCESS read-only
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
"The group name."
::= { ntcGroupEntry 2 }
ntcGroupComment OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX DisplayString
ACCESS read-only
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
"Description of the group."
::= { ntcGroupEntry 3 }
ntcGroupOnLine OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX INTEGER
ACCESS read-only
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
"Index in the member table of the node that currently controls this
group."
::= { ntcGroupEntry 4 }
ntcGroupFailedOver OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX Boolean
ACCESS read-only
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
"True if this group is failed over from the primary Online server."
::= { ntcGroupEntry 5 }
ntcGroupPolicy OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX PolicyType
ACCESS read-only
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
"Reflects the policy of choosing the on-line node."
::= { ntcGroupEntry 6 }
DisplayString,
30
Page 31

Insight Manager 7 SNMP Extensions utility
ntcGroupReevaluate OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX Boolean
ACCESS read-only
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
“Indicates whether the object shall be reevaluated for
new server when nodes in the group go up or down.”
::= { ntcGroupEntry 7 }
ntcGroupMembers OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX DisplayString
ACCESS read-only
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
“This is a list of member names where each name is separated
space.”
::= { ntcGroupEntry 8 }
ntcGroupObjects OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX DisplayString
ACCESS read-only
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
“This is a list of object names – those that make up this
Each name is separated by a space.”
::= { ntcGroupEntry 9 }
ntcObjectTable OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX SEQUENCE OF NtcObjectEntry
ACCESS not-accessible
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
“Table of ntcObjectEntry.”
::= { ntcMgtClusterInfo 8 }
ntcObjectEntry OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX NtcObjectEntry
ACCESS not-accessible
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
“List of all cluster objects.”
INDEX {
ntcObjectIndex
}
::= { ntcObjectTable 1 }
NtcObjectEntry ::=
SEQUENCE {
ntcObjectIndex
INTEGER,
ntcObjectName
DisplayString,
movement to a
by a
group.
31
Page 32

Insight Manager 7 SNMP Extensions utility
ntcObjectComment
ntcObjectType
ObjectType,
ntcObjectDrives
DisplayString
}
ntcObjectIndex OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX INTEGER
ACCESS read-only
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
"Unique index for each entry."
::= { ntcObjectEntry 1 }
ntcObjectName OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX DisplayString
ACCESS read-only
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
"Name of the cluster object."
::= { ntcObjectEntry 2 }
ntcObjectComment OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX DisplayString
ACCESS read-only
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
"Description of the object."
::= { ntcObjectEntry 3 }
ntcObjectType OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX ObjectType
ACCESS read-only
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
"Type of cluster object - disk, share, app..."
::= { ntcObjectEntry 4 }
ntcObjectDrives OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX DisplayString
ACCESS read-only
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
"If instance is a disk, this object is a list of comma
letters (e.g. F:,G:)."
::= { ntcObjectEntry 5 }
--
-- ntcLastTransition
--
DisplayString,
separated drive
32
Page 33

Insight Manager 7 SNMP Extensions utility
-- Information that reflects the last significant event (failover,
failback,
-- etc)
-- Note - this is not a valid group but is a repository for those
variables
-- which need to be returned in a trap. Requesting a get or get-next
of any
-- variables in this group will result in a no such name error.
ntcLastTransMember OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX INTEGER
ACCESS read-only
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
"This is the index of the node in the ntcClusterMemberTable"
::= { ntcLastTransition 1 }
ntcLastTransGroup OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX INTEGER
ACCESS read-only
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
"This is the index of the group in the ntcClusterGroupTable"
::= { ntcLastTransition 2 }
ntcLastTransOnline OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX Boolean
ACCESS read-only
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
"true if this cluster member just gained control of this
group"
::= { ntcLastTransition 3 }
ntcLastTransTimestamp OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX DateAndTime
ACCESS read-only
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
"time of the last transition"
::= { ntcLastTransition 4 }
ntcLastTransSequence OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX INTEGER
ACCESS read-only
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
"This is a sequence number maintained by the agent"
::= { ntcLastTransition 5 }
ntcLastTransReason OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX FailoverReason
ACCESS read-only
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
"reason for the transition - hardware/software problem or
user
initiated"
::= { ntcLastTransition 6 }
33
Page 34

Insight Manager 7 SNMP Extensions utility
--
-- TRAP: ntcTransitionTrap
--
ntcTransitionTrap TRAP-TYPE
ENTERPRISE ntcMgt
VARIABLES {
ntcLastTransMember,
ntcLastTransGroup,
ntcLastTransOnline,
ntcLastTransTimestamp,
ntcLastTransSequence,
ntcLastTransReason }
DESCRIPTION
"Generated when a group transition occurs (failover or
failback)."
::= 100
END
for more
To learn more about Insight Manager 7, see the Insight Manager 7 Technical Reference Guide,
or visit our website at:
information
http://www.hp.com/servers/manage
under Management.
Microsoft and Windows are trademarks and/or registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Other product names mentioned herein may be trademarks and/or registered trademarks of their respective companies.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice.
© 2001, 2002 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
11/2002
5981-4760ENA1
34
 Loading...
Loading...