Page 1

HP 12500 Routing Switch Series
MPLS
Command Reference
Part number: 5998-3428
Software version: 12500-CMW710-R7128
Document version: 6W710-20121130
Page 2

Legal and notice information
© Copyright 2012 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
No part of this documentation may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means
without prior written consent of Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice.
HEWLETT-PACKARD COMPANY MAKES NO WARRANTY OF ANY KIND WITH REGARD TO THIS
MATERIAL, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY
AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. Hewlett-Packard shall not be liable for errors
contained herein or for incidental or consequential damages in connection with the furnishing,
performance, or use of this material.
The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth in the express warranty statements
accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an
additional warranty. HP shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained
herein.
Page 3

Contents
Basic MPLS commands ············································································································································································ 1
display mpls forwarding ilm ·························································································································································· 1
display mpls forwarding nhlfe ······················································································································································ 2
display mpls interface ······································································································································································· 4
display mpls label ··············································································································································································· 5
display mpls lsp ··················································································································································································· 6
display mpls lsp statistics ······························································································································································ 10
display mpls nid ················································································································································································ 11
display mpls summary ···································································································································································· 12
display mpls statistics ····································································································································································· 13
mpls enable ························································································································································································ 15
mpls label advertise ········································································································································································ 16
mpls lsr-id ···························································································································································································· 17
mpls mtu ······························································································································································································ 17
mpls ttl expiration enable ····························································································································································· 18
mpls ttl propagate ··········································································································································································· 19
Static LSP commands ············································································································································································· 21
display mpls static-lsp ···································································································································································· 21
static-lsp egress ················································································································································································ 21
static-lsp ingress ··············································································································································································· 22
static-lsp transit················································································································································································· 23
LDP commands ························································································································································································ 25
accept-label ························································································································································································ 25
advertise-label ··················································································································································································· 26
backoff ·································································································································································································· 27
display mpls ldp discovery ··························································································································································· 28
display mpls ldp fec········································································································································································· 30
display mpls ldp interface ····························································································································································· 33
display mpls ldp lsp ········································································································································································· 34
display mpls ldp parameter ························································································································································· 35
display mpls ldp peer ····································································································································································· 36
display mpls ldp summary ···························································································································································· 40
graceful-restart ·················································································································································································· 41
graceful-restart timer ······································································································································································ 42
label-distribution ·············································································································································································· 43
loop-detect ························································································································································································· 44
lsp-trigger ···························································································································································································· 45
lsr-id ······································································································································································································· 46
maxhops ······························································································································································································· 47
md5-authentication ········································································································································································ 48
mpls ldp ······························································································································································································· 49
mpls ldp enable ················································································································································································ 49
mpls ldp timer ··················································································································································································· 50
mpls ldp transport-address ·························································································································································· 52
pv-limit ································································································································································································· 53
reset mpls ldp ···················································································································································································· 54
session protection ············································································································································································ 55
i
Page 4

targeted-peer ····················································································································································································· 56
vpn-instance ······················································································································································································· 57
MPLS L3VPN commands ······································································································································································ 59
description (VPN instance view) ················································································································································· 59
display bgp group vpnv4 ······························································································································································ 59
display bgp peer vpnv4 ································································································································································· 61
display bgp routing-table ipv4 unicast inlabel ···················································································································· 64
display bgp routing-table ipv4 unicast outlabel ················································································································· 65
display bgp routing-table vpnv4 ··············································································································································· 66
display bgp routing-table vpnv4 advertise-info ·················································································································· 71
display bgp routing-table vpnv4 as-path-acl ······················································································································· 72
display bgp routing-table vpnv4 community-list ··············································································································· 73
display bgp routing-table vpnv4 inlabel ································································································································ 74
display bgp routing-table vpnv4 outlabel ····························································································································· 75
display bgp routing-table vpnv4 peer ····································································································································· 76
display bgp routing-table vpnv4 statistics ····························································································································· 78
display ip vpn-instance ·································································································································································· 79
domain-id ···························································································································································································· 80
export route-policy ·········································································································································································· 81
ext-community-type ······································································································································································· 82
import route-policy ········································································································································································· 83
ip binding vpn-instance ································································································································································· 84
ip vpn-instance (system view) ····················································································································································· 85
ipv4-family (VPN instance view) ················································································································································· 86
ipv4-family vpnv4 ············································································································································································· 86
nesting-vpn ························································································································································································· 87
peer next-hop-invariable ······························································································································································ 88
peer upe ······························································································································································································· 89
peer upe route-policy ····································································································································································· 89
policy vpn-target ·············································································································································································· 90
refresh bgp vpnv4 ············································································································································································ 91
reserve-vlan (VPN instance view)··············································································································································· 92
reset bgp vpnv4 ················································································································································································ 93
route-distinguisher (VPN instance view) ································································································································ 94
route-tag ······························································································································································································ 95
routing-table limit ············································································································································································ 96
rr-filter ··································································································································································································· 97
tnl-policy (VPN instance view/IPv4 VPN view/IPv6 VPN view) ······················································································ 98
vpn popgo ··························································································································································································· 99
vpn-instance-capability simple ················································································································································ 100
vpn-target (VPN instance view/IPv4 VPN view/IPv6 VPN view)················································································· 100
IPv6 MPLS L3VPN commands ························································································································································· 103
display bgp group vpnv6 ··························································································································································· 103
display bgp peer vpnv6 ······························································································································································ 104
display bgp routing-table vpnv6 ············································································································································ 108
display bgp routing-table vpnv6 advertise-info ··············································································································· 111
display bgp routing-table vpnv6 as-path-acl ···················································································································· 112
display bgp routing-table vpnv6 community-list ············································································································ 113
display bgp routing-table vpnv6 inlabel ····························································································································· 115
display bgp routing-table vpnv6 outlabel ·························································································································· 116
display bgp routing-table vpnv6 peer ·································································································································· 117
display bgp routing-table vpnv6 statistics ·························································································································· 118
ipv6-family (VPN instance view) ·············································································································································· 119
ii
Page 5

ipv6-family vpnv6 ·········································································································································································· 120
policy vpn-target ··········································································································································································· 120
refresh bgp vpnv6 ········································································································································································· 121
reset bgp vpnv6 ············································································································································································· 122
rr-filter ································································································································································································ 122
MPLS L2VPN commands ··································································································································································· 124
ac interface ······················································································································································································· 124
connection ······················································································································································································· 125
control-word enable ···································································································································································· 126
description ······················································································································································································· 127
display l2vpn ldp ··········································································································································································· 127
display l2vpn forwarding ···························································································································································· 129
display l2vpn interface ································································································································································ 132
display l2vpn pw ············································································································································································ 133
display l2vpn pw-class ································································································································································ 135
display l2vpn service-instance ················································································································································· 136
display l2vpn xconnect-group ················································································································································· 138
encapsulation ·················································································································································································· 139
l2vpn enable ···················································································································································································· 140
mtu ······································································································································································································ 141
peer ····································································································································································································· 142
pw-class ····························································································································································································· 143
pw-type ····························································································································································································· 144
service-instance ············································································································································································· 145
shutdown ·························································································································································································· 146
xconnect-group ············································································································································································· 146
MPLS OAM commands ······································································································································································ 148
ping mpls ipv4 ················································································································································································ 148
tracert mpls ipv4 ············································································································································································ 150
Index ·········································································································································································································· 152
iii
Page 6

Basic MPLS commands
The switch operates in IRF or standalone (the default) mode. For more information about IRF, see
IRF Configuration Guide.
display mpls forwarding ilm
Use display mpls forwarding ilm to display Incoming Label Map (ILM) entries.
Syntax
In standalone mode:
display mpls forwarding ilm [ label ] slot slot-number
In IRF mode:
display mpls forwarding ilm [ label ] chassis chassis-number slot slot-number
Views
Any view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
network-operator
mdc-admin
mdc-operator
Parameters
label: Displays the ILM entry with the specified incoming label. The value range for the incoming
label is 16 to 1000000. If you do not specify an incoming label, the command displays information
about all ILM entries on the specified card.
slot slot-number: Specifies a card by its slot number. (In standalone mode.)
chassis chassis-number slot slot-number: Specifies a card on an IRF member device. The
chassis-number argument specifies the ID of the IRF member device, and the slot-number argument
specifies the number of the slot that holds the card. (In IRF mode.)
Usage guidelines
An ILM entry records the label operation type, outgoing label, and other forwarding information.
After an LSR receives a labeled packet, it identifies the ILM entry that matches the top label of the
packet, performs the specified label operation, and forwards the packet.
Examples
# Display the ILM entry with incoming label 30.
<Sysname> display mpls forwarding ilm 30
Flags: T - Forwarded through a tunnel
N - Forwarded through the outgoing interface to the nexthop IP address
B - Backup forwarding information
A - Active forwarding information
1
Page 7
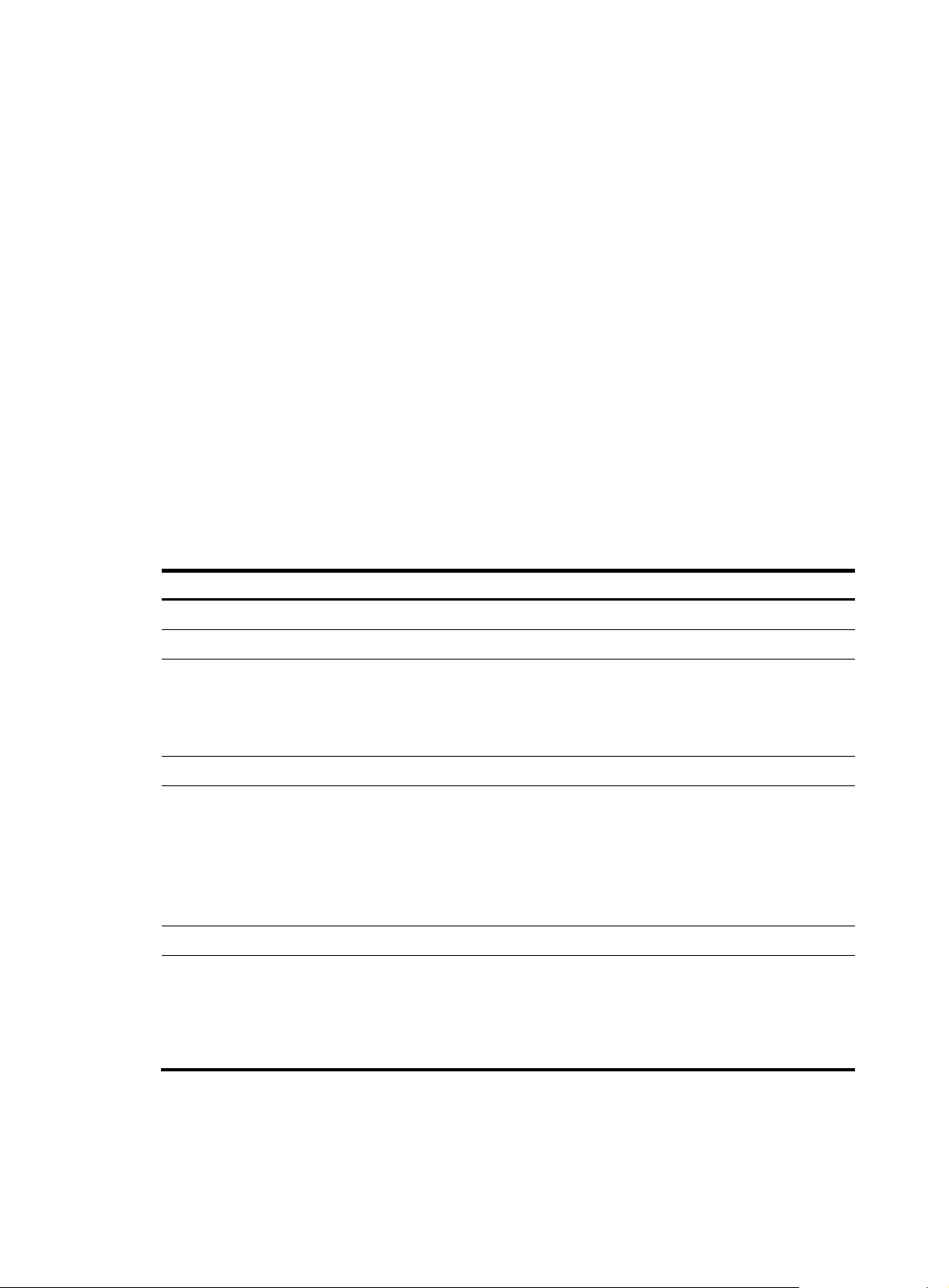
InLabel Oper VRF Flag SwapLabel Forwarding Info
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------30 SWAP 0 T 1300 1024
# Display all ILM entries.
<Sysname> display mpls forwarding ilm
Total ILM entries: 3
Flags: T - Forwarded through a tunnel
N - Forwarded through the outgoing interface to the nexthop IP address
B - Backup forwarding information
A - Active forwarding information
InLabel Oper VRF Flag SwapLabel Forwarding Info
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------30 SWAP 0 T 1300 1024
1279 POP 0 - - 1407 SWAP 0 NA 1271 GE3/0/3 50.2.0.2
NB 1270 Tun0 0.0.0.0
Table 1 Command output
Field Description
Total ILM entries Total number of ILM entries.
InLabel Incoming label.
Operation type:
Oper
• POP—Pops the label.
• POPGO—Pops the label and forwards the packet to another tunnel.
• SWAP—Swaps the label.
VRF Index of a VPN instance.
Forwarding flag:
• T—Forwarded through a tunnel.
Flag
• N—Forwarded through the outgoing interface to the nexthop IP
address.
• B—Backup forwarding information.
• A—Active forwarding information.
SwapLabel Outgoing label value.
Forwarding information:
• When the forwarding flag is N, the forwarding information records the
Forwarding Info
outgoing interface and the next hop.
• When the forwarding flag is T, the forwarding information records the
NID.
display mpls forwarding nhlfe
Use display mpls forwarding nhlfe to display Next Hop Label Forwarding Entry (NHLFE) entries.
2
Page 8

Syntax
In standalone mode:
display mpls forwarding nhlfe [ nid ] slot slot-number
In IRF mode:
display mpls forwarding nhlfe [ nid ] chassis chassis-number slot slot-number
Views
Any view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
network-operator
mdc-admin
mdc-operator
Parameters
nid: Displays the NHLFE entry with the specified NID. The value range for the NID is 0 to 1000000. If
you do not specify an NID, the command displays information about all NHLFE entries on the
specified card.
slot slot-number: Specifies a card by its slot number. (In standalone mode.)
chassis chassis-number slot slot-number: Specifies a card on an IRF member device. The
chassis-number argument specifies the ID of the IRF member device, and the slot-number argument
specifies the number of the slot that holds the card. (In IRF mode.)
Usage guidelines
An NHLFE entry records label forwarding information, such as the outgoing label and outgoing
interface. NHLFE entries are mainly used to add multiple labels to packets. To add multiple labels to
a packet, an LSR first obtains the bottom label and NID in the matching FIB or ILM entry, and then
obtains the outer label in the NHLFE entry identified by the NID.
Examples
# Display the NHLFE entry with NID 2048.
<Sysname> display mpls forwarding nhlfe 2048
Flags: T - Forwarded through a tunnel
N - Forwarded through the outgoing interface to the nexthop IP address
B - Backup forwarding information
A - Active forwarding information
NID Tnl-Type Flag OutLabel Forwarding Info
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------2048 LSP NA 2025 GE3/0/2 10.11.112.26
# Display all NHLFE entries.
<Sysname> display mpls forwarding nhlfe
Total NHLFE entries: 5
Flags: T - Forwarded through a tunnel
N - Forwarded through the outgoing interface to the nexthop IP address
3
Page 9
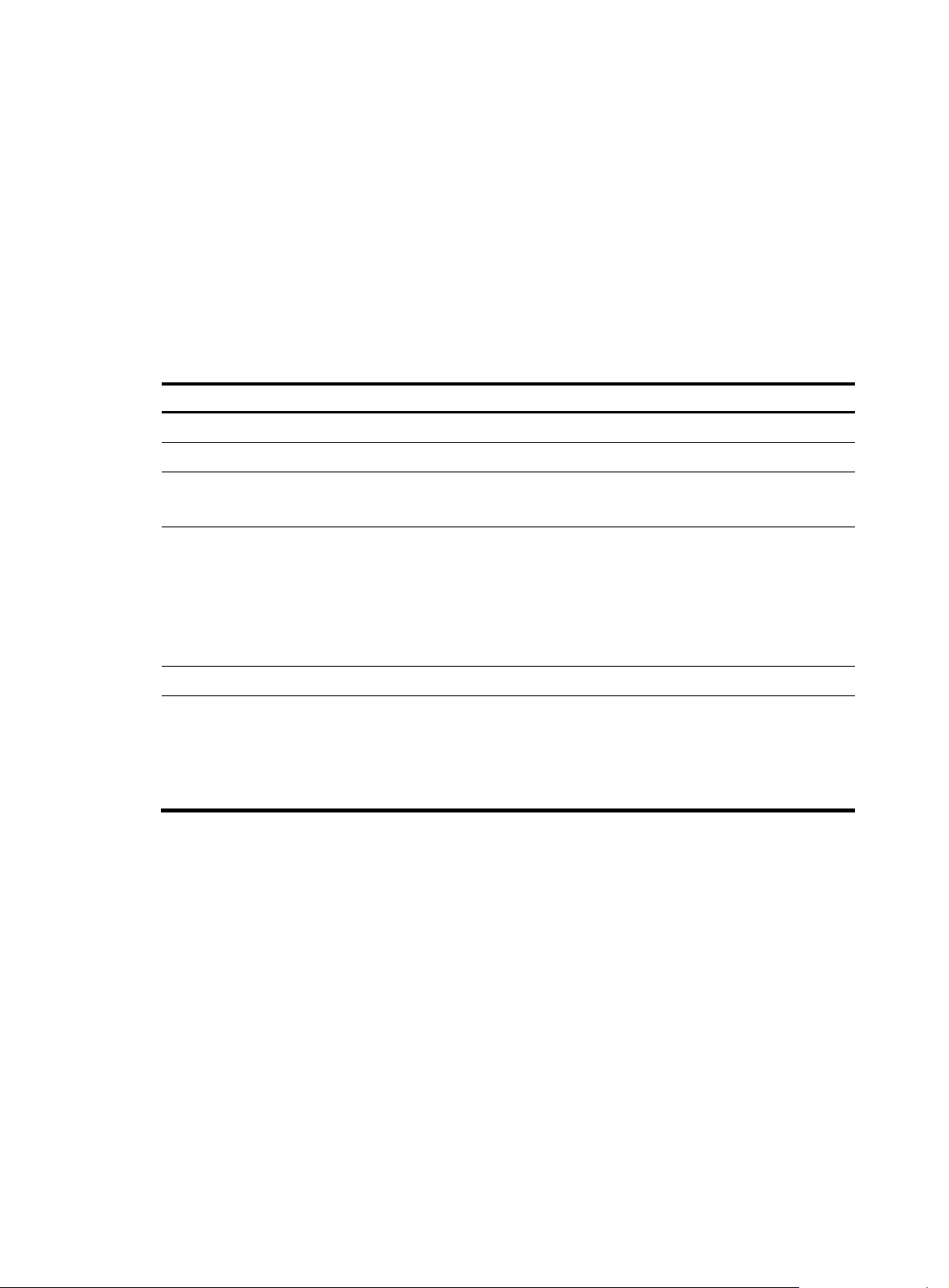
B - Backup forwarding information
A - Active forwarding information
NID Tnl-Type Flag OutLabel Forwarding Info
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------10 - TA - 2049
20 - TA - 2050
2048 LSP NA 2025 GE3/0/2 10.11.112.26
2049 LSP NA 3024 GE3/0/2 10.11.112.26
TB 3026 20
2050 LSP NA 3025 GE3/0/1 10.11.113.26
Table 2 Command output
Field Description
Total NHLFE entries Total number of NHLFE entries.
NID NHLFE entry index.
Tnl-Type
Flag
OutLabel Outgoing label.
Forwarding Info
display mpls interface
Use display mpls interface to display MPLS interface information, including the interface name,
interface status, and interface MPLS MTU.
Syntax
Tunnel type: LSP, GRE, or CRLSP.
If the tunnel type is an invalid value, this field displays a hyphen (-).
Forwarding flag:
• T—Forwarded through a tunnel.
• N—Forwarded through the outgoing interface to the nexthop IP
address.
• B—Backup forwarding information.
• A—Active forwarding information.
Forwarding information:
• When the forwarding flag is N, the forwarding information records the
outgoing interface and the next hop.
• When the forwarding flag is T, the forwarding information records the
NID.
display mpls interface [ interface-type interface-number ]
Views
Any view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
network-operator
mdc-admin
4
Page 10

mdc-operator
Parameters
interface-type interface-number: Specifies an interface by its type and number. If you do not specify
an interface, the command displays MPLS information for all MPLS-enabled interfaces.
Examples
# Displays all MPLS interfaces.
<Sysname> display mpls interface
Interface Status MPLS MTU
GE3/0/1 Up 1514
GE3/0/2 Up 1514
The MPLS MTU of an interface is in bytes.
Related commands
• mpls enable
• mpls mtu
display mpls label
Use display mpls label to display MPLS label usage information.
Syntax
display mpls label { label-value1 [ to label-value2 ] | all }
Views
Any view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
network-operator
mdc-admin
mdc-operator
Parameters
label-value1: Specifies a label in the range of 16 to 1000000. If used with the label-value2 argument,
the label-value1 argument represents the start label of a label range.
to label-value2: Specifies the end label in the range of 16 to 1000000. If you specify a label range
by using the label-value1 argument and the to label-value2 option, the command displays usage
information for the specified range of labels.
all: Specifies all labels.
Examples
# Display the usage information of labels 900 through 902.
<Sysname> display mpls label 900 to 902
Label Owner State
900 - Idle
901 - Idle
902 LDP Alloc
5
Page 11

Table 3 Command output
Field Description
Label Label value.
Owner
State
display mpls lsp
Use display mpls lsp to display LSP information.
Syntax
display mpls lsp [ egress | in-label label-value | ingress | outgoing-interface interface-type
interface-number | protocol { bgp | ldp | local | rsvp-te | static | static-cr } | transit ] [ vpn-instance
vpn-instance-name ] [ ipv4-dest mask-length | ipv6 [ ipv6-dest prefix-length ] ] [ verbose ]
Views
Any view
Predefined user roles
Protocol that is using the label. Possible values include LDP, BGP,
RSVP, and L2VPN.
Usage state of the label:
• Idle—The label is idle.
• Alloc—The label has been allocated.
• Pending—The label has been released but is still used by an
LSP entry.
• Inuse—The label has been allocated and used by an LSP entry.
network-admin
network-operator
mdc-admin
mdc-operator
Parameters
egress: Displays the LSPs taking the current LSR as the egress.
in-label label-value: Displays the LSPs using the specified label as the incoming label. The value
range for the label-value argument is 0 to 1000000.
ingress: Displays the LSPs taking the current LSR as the ingress.
outgoing-interface interface-type interface-number: Displays the LSPs using the specified interface
as the outgoing interface. The interface-type interface-number argument specifies an interface by
its type and number.
protocol: Displays the LSPs established by a specific protocol.
bgp: Displays BGP LSPs.
Ldp: Displays LDP LSPs.
local: Displays the direct LSP.
rsvp-te: Displays CR-LSPs established by RSVP-TE. The switch does not support this keyword.
6
Page 12

static: Displays static LSPs.
static-cr: Displays static CR-LSPs. The switch does not support this keyword.
transit: Displays the LSPs taking the current LSR as a transit LSR.
vpn-instance vpn-instance-name: Displays LSPs for the specified VPN. The vpn-instance-name is a
case-sensitive string of 1 to 31 characters. If you do not specify this option, the command displays
LSPs for the public network.
ipv4-dest mask-length: Displays the IPv4 LSP for a FEC specified by an IPv4 address and a mask
length. The value range for the mask length is 0 to 32.
ipv6: Displays IPv6 LSP information. If you do not specify this keyword, the command displays IPv4
LSP information.
ipv6-dest prefix-length: Displays the IPv6 LSP for a FEC specified by an IPv6 address and a prefix
length. The value range for the prefix length is 0 to 128.
verbose: Displays detailed LSP information. If you do not specify this keyword, the command
displays brief LSP information.
Usage guidelines
If no parameters are specified, the command displays brief information for all LSPs. If you specify
only the verbose keyword, the command displays detailed information for all LSPs.
Examples
# Display brief information for all IPv4 LSPs.
<Sysname> display mpls lsp
FEC Proto In/Out Label Interface/Out NHLFE
100.100.100.100/24 LDP -/1049 Vlan20
Backup -/1050 Vlan21
100.100.100.10/24 LDP -/1051 Vlan22
Backup -/1050 Vlan21
100.100.100.10/24 LDP -/1049 Vlan30
101.100.100.10/24 LDP 1026/1049 Vlan20
102.100.100.10/24 LDP 1027/- -
103.100.100.10/24 LDP 1028/1049 Tunnel10
110.100.100.20/24 BGP -/1049 Vlan20
111.100.100.10/24 BGP 2028/1049 Vlan20
112.100.100.10/24 BGP 2029/- Vlan20
113.100.100.10/24 BGP 2030/1049 NHLFE1500
114.100.100.10/24 BGP 2031/1050 Tunnel100
100.100.100.100 Local -/- Vlan20
101.101.101.101/32 Static -/100 Vlan20
- Static 100/200 Vlan20
- Static 101/- Vlan20
200.200.200.200/64000/64000 RSVP -/1030 Vlan10
201.200.200.200/64000/64000 RSVP 1024/1031 Vlan10
202.200.200.200/64000/64000 RSVP 1025/- -
150.140.150.100/64001/0 StaticCR -/1000 Vlan10
- StaticCR 50/1001 Vlan10
- StaticCR 51/- -
7
Page 13
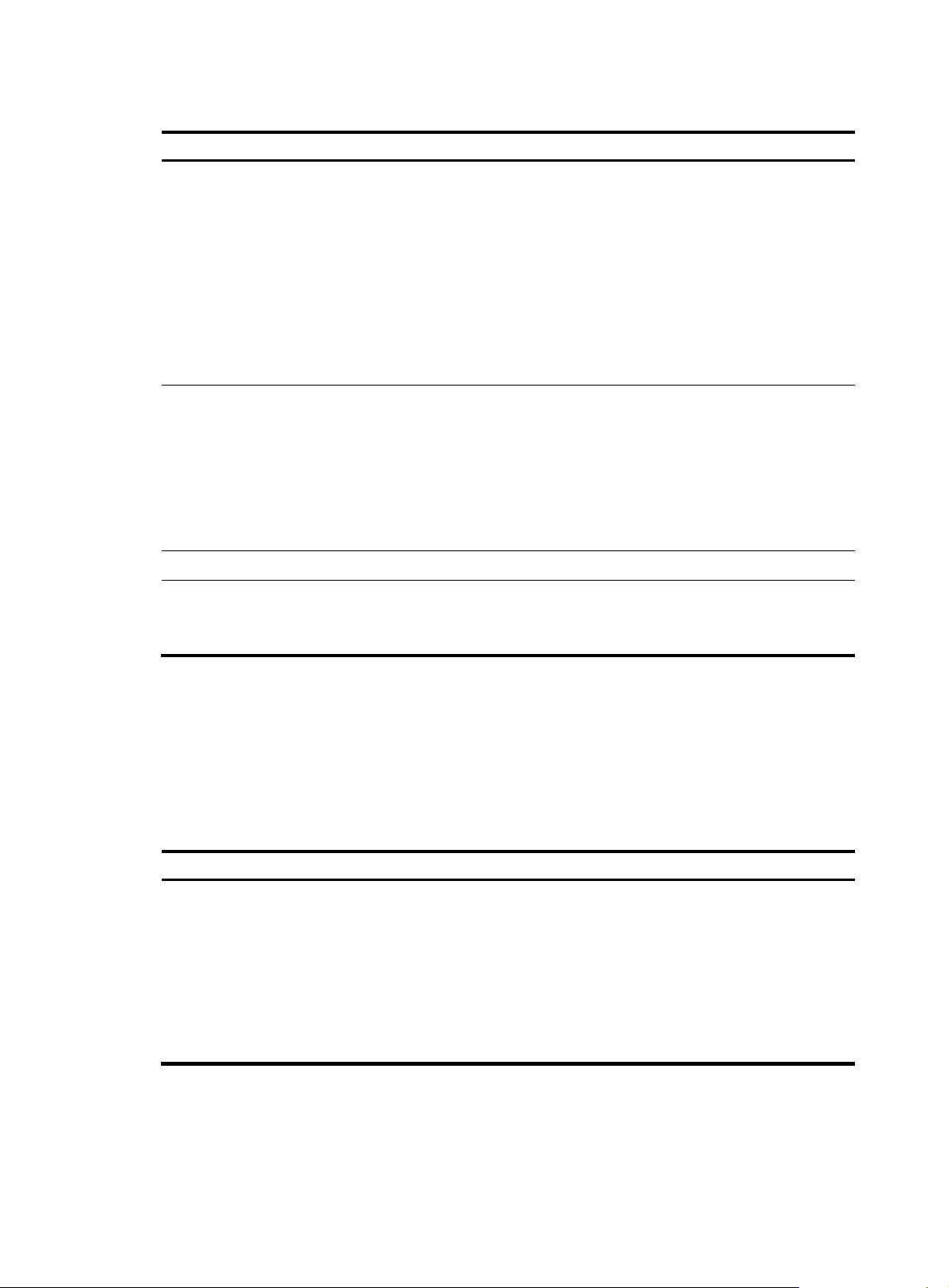
Table 4 Command output
Field Description
Forwarding equivalence class:
• IP address/mask—Classifies FECs by destination address.
• IP address—Classifies FECs by next hop.
• IP address/Out Label—Classifies FECs by next hop and outgoing
FEC
label.
• Ingress LSR ID/Tunnel ID/LSP ID—RSVP TE FEC.
• A hyphen (-)—The LSP is a static transit LSP, static egress LSP,
static transit CR-LSP, or static egress CR-LSP.
• Backup—If the LSP is a backup LSP of the previous LSP, this field
displays "Backup."
Label distribution protocol:
• LDP.
• BGP.
Proto
• RSVP.
• Static.
• StaticCR—Static CR-LSP.
• Local—The LSP is a direct LSP.
In/Out Label Incoming label/outgoing label.
Outgoing interface name or NHLFE entry index.
Interface/Out NHLFE
NHLFEnumber specifies the outer LSP that carries the current LSP. The
outer LSP is that matches the NHLFE entry with an NID of number.
# Display IPv6 LSP information.
<Sysname> display mpls lsp ipv6
FEC : 100:100:100:100:100:100:100:100/128
Protocol : BGP In-Label : 2050
Out-Label: 10003 Out-Interface: Vlan10
BkLabel : 10004 BkInterface : Vlan20
Table 5 Command output
Field Description
Forwarding equivalence class:
• IP address/mask—Classifies FECs by destination address.
• IP address—Classifies FECs by next hop.
FEC
• IP address/Out Label—Classifies FECs by next hop and outgoing
label.
• Ingress LSR ID/Tunnel ID/LSP ID—RSVP TE FEC.
• A hyphen (-)—The LSP is a static transit LSP, static egress LSP,
static transit CR-LSP, or static egress CR-LSP.
8
Page 14

Field Description
Label distribution protocol:
• LDP.
• BGP.
Protocol
• RSVP.
• Static.
• StaticCR—Static CR-LSP.
• Local—Direct LSP.
BkLabel Outgoing label of the backup LSP.
BkInterface Outgoing interface of the backup LSP.
# Display detailed information for all LSPs.
<Sysname> display mpls lsp verbose
Destination : 56.10.10.2
FEC : 56.10.10.2/32
Protocol : LDP
LSR Type : Egress
Service : -
In-Label : 1024
State : Active
Destination : 56.10.10.4
FEC : 56.10.10.2/32
Protocol : LDP
LSR Type : Transit
Service : -
In-Label : 1026
Path ID : 0x40000000.1
State : Active
Out-Label : 1800
Nexthop : 10.1.1.2
Out-Interface: Vlan10
BkLabel : 1900
BkNexthop : 20.1.1.2
BkInteface : Vlan20
Destination : 56.10.10.4
FEC : 56.10.10.2/32
Protocol : LDP
LSR Type : Ingress
Service : -
NHLFE ID : 2000
State : Active
Out-Label : 1800
Nexthop : 10.1.1.2
Out-Interface: Vlan10
9
Page 15

Table 6 Command output
Field Description
Destination LSP destination address.
Forwarding equivalence class:
• IP address/mask—Classifies FECs by destination address.
• IP address—Classifies FECs by next hop.
FEC
• IP address/Out Label—Classifies FECs by next hop and outgoing
label.
• Ingress LSR ID/Tunnel ID/LSP ID—RSVP TE FEC.
• A hyphen (-)—The LSP is a static transit LSP, s t a t ic e g r e s s L S P, s t at ic
transit CR-LSP, or static egress CR-LSP.
Label distribution protocol:
• LDP.
• BGP.
Proto
• RSVP.
• Static.
• StaticCR—Static CR-LSP.
• Local—Direct LSP.
LSR type:
LSR Type
• Ingress—The current LSR is the ingress node of the LSP.
• Transit—The current LSR is a transit node of the LSP.
• Egress—The current LSR is the egress node of the LSP.
Service Service deployed on the LSP.
Forwarding path. The value is in the format of 0xnn.m, where nn
Path ID
NHLFE ID NHLFE entry index.
Outgoing NID Index of the NHLFE entry for the outer tunnel.
State
represents the NHLFE group ID of the outer LSPs that carry the current
LSP, and m represents the sequence number of the equivalence path.
LSP state:
• Active—The LSP is in use.
• Inactive—The LSP is idle.
BkLabel Outgoing label of the backup LSP.
BkNexthop Next hop address of the backup LSP.
BkInterface Outgoing interface of the backup LSP.
Related commands
display mpls lsp statistics
display mpls lsp statistics
Use display mpls lsp statistics to display LSP statistics.
Syntax
display mpls lsp statistics
10
Page 16

Views
Any view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
network-operator
mdc-admin
mdc-operator
Examples
# Display LSP statistics.
<Sysname> display mpls lsp statistics
LSP Type Ingress/Transit/Egress Active
Static LSP 0/0/0 0/0/0
Static CRLSP 0/0/0 0/0/0
LDP LSP 2/2/1 2/2/1
RSVP CRLSP 0/0/0 0/0/0
BGP LSP 0/0/0 0/0/0
Local LSP 2/0/0 2/0/0
----------------------------------------------------Total 4/2/1 4/2/1
Table 7 Command output
Field Description
LSP Type
Total Total number of LSPs.
Ingress Number of LSPs that take the local device as the ingress node.
Transit Number of LSPs that take the local device as a transit node.
Egress Number of LSPs that take the local device as the egress node.
Active Number of active LSPs of a specific type.
display mpls nid
Use display mpls nid to display the NID usage information.
LSP types:
• Static LSP.
• Static CRLSP.
• LDP LSP.
• Local LSP (direct LSP).
• RSVP CRLSP.
• BGP LSP.
Syntax
display mpls nid [ nid-value1 [ to nid-value2 ] ]
11
Page 17

Views
Any view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
network-operator
mdc-admin
mdc-operator
Parameters
nid-value1: Specifies an NID in the range of 0 to 1000000. If used with the nid-value2 argument, the
nid-value1 argument represents the start NID of an NID range.
to nid-value2: Specifies the end NID in the range of 0 to 1000000. If you specify an NID range by
using the nid-value1 argument and the to nid-value2 option, the command displays the usage
information for the specified range of NIDs.
Usage guidelines
If you do not specify any parameter, the command displays the usage information of all NIDs.
Examples
# Display the usage information of NIDs 1028 through 1500.
<Sysname> display mpls nid 1028 to 1500
NID alloc state: '.' means not used, '$' means used
1028 :...$.... ........ ........ ........ ........ ........ ........ ........
1092 :........ ........ ........ ........ ........ ........ ........ ........
1156 :........ ........ ........ ........ ........ ........ ........ ........
1220 :........ ........ ........ ........ ........ ........ ........ ........
1284 :........ ........ ........ ........ ........ ........ ........ ........
1348 :........ ........ ........ ........ ........ ........ ........ ........
1412 :........ ........ ........ ........ ........ ........ ........ ........
1476 :........ ........ ........ .
display mpls summary
Use display mpls summary to display MPLS summary information.
Syntax
display mpls summary
Views
Any view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
network-operator
mdc-admin
mdc-operator
12
Page 18

Examples
# Display MPLS summary information.
<Sysname> display mpls summary
Memory State : Normal
MPLS LSR ID : 2.2.2.2
Egress Label Type: Implicit-null
Labels:
Range Idle
16-1023 1008
1024-13311 12288
65536-69631 4096
131072-139263 8192
Protocols:
Type State
BGP Normal
Static Normal
Table 8 Command output
Field Description
Memory state:
• Normal—The memory is normal.
Memory State
• Minor—The memory has a minor alarm.
• Severe—The memory has a severe alarm.
• Critical—The memory has a critical alarm.
Egress Label Type
Labels Label information.
Range Label range.
Idle Number of idle labels in the label range.
Protocols Running label distribution protocols and the related information.
Type Protocol type: LDP, BGP, RSVP, Static, Static CRLSP, or TE.
State
display mpls statistics
Use display mpls statistics to display MPLS forwarding statistics for each LSP, such as the number
of packets processed and dropped in the inbound and outbound directions.
Syntax
Label type that the egress assigns to the penultimate hop:
• Implicit-null.
• Explicit-null.
• Non-null.
Label distribution protocol running status:
• Normal.
• Recover—The protocol is in the GR process.
display mpls statistics { all | lsp-index index }
13
Page 19

Views
Any view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
network-operator
mdc-admin
mdc-operator
Parameters
all: Displays MPLS forwarding statistics for all LSPs.
lsp-index index: Displays MPLS forwarding statistics for the specified LSP. The index argument
represents the index of an LSP, in the range of 1 to 4294967295.
Usage guidelines
To use this command to view MPLS forwarding statistics for LSPs, you must first enable MPLS
forwarding statistics for LSPs by using the mpls statistics command. Otherwise, the statistics are all
0.
Examples
# Display MPLS forwarding statistics for all LSPs.
<Sysname> display mpls statistics all
Statistics for LSP (LSP index: 9218):
Inbound:
Octets : 0
Packets : 0
Errors : 0
Discards : 0
Start Time : 2006/05/20 15:52:30
End Time : 2006/05/20 15:52:30
Outbound:
Octets : 0
Packets : 0
Errors : 0
Discards : 0
Start Time : 0000/00/00 00:00:00
End Time : 0000/00/00 00:00:00
Statistics for LSP (LSP index: 9219):
Inbound:
Octets : 0
Packets : 0
Errors : 0
Discards : 0
Start Time : 0000/00/00 00:00:00
End Time : 0000/00/00 00:00:00
Outbound:
Octets : 0
Packets : 0
14
Page 20

Errors : 0
Discards : 0
Start Time : 2006/05/20 15:52:30
End Time : 2006/05/20 15:52:30
Table 9 Command output
Field Description
Statistics for LSP (LSP index: index) MPLS forwarding statistics for the LSP identified by the index.
Inbound Inbound direction.
Outbound Outbound direction.
Octets Bytes of packets processed.
Packets Number of packets processed.
Errors Number of errors.
Discards Number of packets discarded.
Start Time Start time of the statistics.
End Time End time of the statistics.
NOTE:
• On an ingress node, no statistics are collected in the inbound direction and the start
time and end time for inbound statistics are both 0.
• On an egress node, no statistics are collected in the outbound direction and the start
time and end time for outbound statistics are both 0.
Related commands
mpls statistics
mpls enable
Use mpls enable to enable MPLS on an interface.
Use undo mpls enable to disable MPLS on an interface.
Syntax
mpls enable
undo mpls enable
Default
MPLS is disabled on an interface.
Views
Interface view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
mdc-admin
15
Page 21

Usage guidelines
Execute this command on all interfaces that need to perform MPLS forwarding.
Examples
# Enable MPLS on VLAN-interface 2.
<Sysname> System-view
[Sysname] interface vlan-interface 2
[Sysname-Vlan-interface2] mpls enable
Related commands
display mpls interface
mpls label advertise
Use mpls label advertise to specify the type of label the egress will advertise to the penultimate
hop.
Use undo mpls label advertise to restore the default.
Syntax
mpls label advertise { explicit-null | implicit-null }
undo mpls label advertise
Default
As an egress, the device advertises an implicit null label to the penultimate hop.
Views
System view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
mdc-admin
Parameters
explicit-null: Specifies the egress to advertise an explicit null label of 0 to the penultimate hop.
implicit-null: Specifies the egress to advertise an implicit null label of 3 to the penultimate hop.
Usage guidelines
If the penultimate hop supports PHP, HP recommends that you configure the egress to advertise an
implicit null label to the penultimate hop. If you want to simplify packet forwarding on the egress
but keep labels in packets for the egress to determine QoS policies, you can configure the egress to
advertise an explicit null label to the penultimate hop.
As a penultimate hop, the device allows the egress to advertise to the penultimate hop an implicit
null label or an explicit null label.
The mpls label advertise command takes effect only for the LSPs established after the command is
executed. To apply the new setting to LSPs established before the command is executed, delete and
then re-establish those LSPs:
• To re-establish LDP LSPs, execute the reset mpls ldp command to reset the LDP session.
16
Page 22

• To re-establish BGP LSPs, delete the routes corresponding to the BGP LSPs, and then
redistribute the routes.
Examples
# Configure the egress device to advertise an explicit null label to the penultimate hop.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] mpls label advertise explicit-null
Related commands
reset mpls ldp
mpls lsr-id
Use mpls lsr-id to configure an LSR ID for the local LSR.
Use undo mpls lsr-id to delete the LSR ID of the local LSR.
Syntax
mpls lsr-id lsr-id
undo mpls lsr-id
Default
An LSR has no LSR ID.
Views
System view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
mdc-admin
Parameters
lsr-id: Specifies an ID for identifying the LSR, in dotted decimal notation.
Usage guidelines
HP recommends that you use the address of a loopback interface on the LSR as the LSR ID.
Examples
# Configure the LSR ID as 3.3.3.3 for the local node.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.3
Related commands
lsr-id
mpls mtu
Syntax
Use mpls mtu to configure the MPLS MTU for an interface.
Use undo mpls mtu to restore the default.
mpls mtu value
17
Page 23

undo mpls mtu
Default
The MPLS MTU of an interface is not configured. Fragmentation for MPLS packets is based on the
MTU of the interface, and the length of a fragment does not include that of the MPLS label. Thus,
after an MPLS label is inserted into a fragment, the length of the MPLS fragment may exceed the
interface MTU.
Views
Interface view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
mdc-admin
Parameters
value: Specifies the MPLS MTU of the interface, in the range of 46 to 65535 bytes.
Usage guidelines
This command is effective only when MPLS is enabled on the interface.
If the MPLS MTU is larger than the interface MTU, data forwarding may fail.
Examples
# Set the MPLS MTU of VLAN-interface 2 to 1000 bytes.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] interface vlan-interface 2
[Sysname-Vlan-interface2] mpls enable
[Sysname-Vlan-interface2] mpls mtu 1000
Related commands
display mpls interface
mpls ttl expiration enable
Use mpls ttl expiration enable to enable sending of MPLS TTL-expired messages.
Use undo mpls ttl expiration enable to disable the function.
Syntax
mpls ttl expiration enable
undo mpls ttl expiration enable
Default
The MPLS TTL-expired messages sending function is enabled.
Views
System view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
mdc-admin
18
Page 24

Usage guidelines
The mpls ttl expiration enable command enables an LSR to generate an ICMP TTL-expired
message upon receiving an MPLS packet with TTL being 1. If the MPLS packet has only one label,
the LSR sends the ICMP TTL-expired message back to the source through IP routing. If the MPLS
packet has multiple labels, the LSR forwards the ICMP TTL-expired message along the LSP of the
MPLS packet to the egress, which then sends the message back to the source.
Examples
# Disable the MPLS TTL-expired messages sending function.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] undo mpls ttl expiration enable
mpls ttl propagate
Use mpls ttl propagate to enable TTL propagation.
Use undo mpls ttl propagate to disable TTL propagation.
Syntax
mpls ttl propagate { public | vpn }
undo mpls ttl propagate { public | vpn }
Default
TTL propagation is enabled for public network packets and disabled for VPN packets.
Views
System view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
mdc-admin
Parameters
public: Specifies public network packets.
vpn: Specifies VPN packets.
Usage guidelines
When TTL propagation is enabled, MPLS copies the IP TTL to the label TTL for packets entering the
MPLS network, and copies the label TTL to the IP TTL for packets leaving the MPLS network. If you
enable TTL propagation on both the ingress and egress, the IP tracert facility can show the real path
in the MPLS network.
When TTL propagation is disabled, MPLS sets the label TTL to 255 for packets entering the MPLS
network, and pops the label for packets leaving the MPLS network, without copying the label TTL
value to the IP TTL. The IP tracert facility cannot show the real path in the MPLS network.
Within an MPLS network, TTL is always copied between the labels of an MPLS packet. The mpls ttl
propagate command affects only the propagation between IP TTL and label TTL.
HP recommends setting the same TTL processing mode on all LSRs of an LSP.
To enable TTL propagation for a VPN, you must enable it on all PE devices in the VPN, so that you
can get the same traceroute result (hop count) from those PEs.
19
Page 25

Examples
# Enable TTL propagation for VPN packets.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] mpls ttl propagate vpn
20
Page 26

Static LSP commands
display mpls static-lsp
Use display mpls static-lsp to display static LSP information.
Syntax
display mpls static-lsp [ lsp-name lsp-name ]
Views
Any view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
network-operator
mdc-admin
mdc-operator
Parameters
lsp-name lsp-name: Specifies a static LSP by its name, a case-sensitive string of 1 to 15 characters.
If you do not specify a static LSP, the command displays information about all static LSPs.
Examples
# Display information about all static LSPs.
<Sysname> display mpls static-lsp
Total: 4
Name FEC In/Out Label Nexthop/Out Interface State
egress123 -/- 16/NULL - Up
ingress123 202.118.224.132/32 NULL/1022 100.100.100.19 Down
transit123 -/- 32/1022 100.100.100.17 Down
transit124 -/- 34/1020 GE3/0/1 Down
Table 10 Command output
Field Description
Total Total number of static LSPs.
Name Name of the static LSP.
FEC Forwarding equivalence class—IP prefix and the prefix length.
In/Out Label Incoming label/outgoing label.
static-lsp egress
Use static-lsp egress to configure a static LSP on the egress node.
Use undo static-lsp egress to delete a static LSP on the egress node.
21
Page 27

Syntax
static-lsp egress lsp-name in-label in-label
undo static-lsp egress lsp-name
Default
No static LSP exists on the device.
Views
System view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
mdc-admin
Parameters
lsp-name: Specifies a name for the static LSP, a case-sensitive string of 1 to 15 characters.
in-label in-label: Specifies an incoming label, which can be 0, 3, or a value in the range of 16 to
1023.
Examples
# Configure a static LSP on the egress node: specify the LSP's name as bj-sh and incoming label as
233.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] static-lsp egress bj-sh in-label 233
Related commands
display mpls static-lsp
static-lsp ingress
Use static-lsp ingress to configure a static LSP on the ingress node.
Use undo static-lsp ingress to delete a static LSP on the ingress node.
Syntax
static-lsp ingress lsp-name destination dest-addr { mask | mask-length } { nexthop next-hop-addr |
outgoing-interface interface-type interface-number } out-label out-label
undo static-lsp ingress lsp-name
Default
No static LSP exists on the device.
Views
System view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
mdc-admin
Parameters
lsp-name: Specifies a name for the static LSP, a case-sensitive string of 1 to 15 characters.
22
Page 28

destination dest-addr: Specifies a destination IP address for the LSP.
mask: Specifies the mask of the destination IP address.
mask-length: Specifies the mask length of the destination address, in the range of 0 to 32.
nexthop next-hop-addr: Specifies a next hop address.
outgoing-interface interface-type interface-number: Specifies an outgoing interface by its type and
number. You can specify an outgoing interface only in a point-to-point network.
out-label out-label: Specifies an outgoing label, which can be 0, 3, or a value in the range of 16 to
1023.
Usage guidelines
The next hop or outgoing interface specified for the LSP must be consistent with the next hop or
outgoing interface of the optimal route destined for the specified address. If you configure a static
IP route for the LSP, be sure to specify the same next hop or outgoing interface for the static route
and the static LSP.
You must enable MPLS on the outgoing interface of the static LSP.
Examples
# Configure a static LSP on the ingress node: specify the LSP's name as bj-sh, destination address
as 202.25.38.1/24, next hop address as 202.55.25.33, and outgoing label as 237.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] static-lsp ingress bj-sh destination 202.25.38.1 24 nexthop 202.55.25.33
out-label 237
Related commands
display mpls static-lsp
static-lsp transit
Use static-lsp transit to configure a static LSP on a transit node.
Use undo static-lsp transit to delete a static LSP on a transit node.
Syntax
static-lsp transit lsp-name in-label in-label { nexthop next-hop-addr | outgoing-interface
interface-type interface-number } out-label out-label
undo static-lsp transit lsp-name
Default
No static LSP exists on the device.
Views
System view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
mdc-admin
Parameters
lsp-name: Specifies a name for the static LSP, a case-sensitive string of 1 to 15 characters.
23
Page 29

in-label in-label: Specifies an incoming label in the range of 16 to 1023.
nexthop next-hop-addr: Specifies a next hop address.
outgoing-interface interface-type interface-number: Specifies an outgoing interface by its type and
number. You can specify an outgoing interface only in a point-to-point network.
out-label out-label: Specifies an outgoing label, which can be 0, 3, or a value in the range of 16 to
1023.
Usage guidelines
You must enable MPLS on the outgoing interface of the static LSP.
Examples
# Configure a static LSP on the transit node: specify the LSP's name as bj-sh, incoming label as 123,
next hop address as 202.34.114.7, and outgoing label as 253.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] static-lsp transit bj-sh in-label 123 nexthop 202.34.114.7 out-label 253
Related commands
display mpls static-lsp
24
Page 30

LDP commands
accept-label
Use accept-label to configure a label acceptance policy.
Use undo accept-label to remove the label acceptance policy.
Syntax
accept-label peer peer-lsr-id prefix-list prefix-list-name
undo accept-label peer peer-lsr-id
Default
No label acceptance policy is configured. LDP accepts all label mappings from all peers.
Views
LDP view, LDP-VPN instance view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
mdc-admin
Parameters
peer peer-lsr-id: Specifies an LDP peer by its LSR ID.
prefix-list prefix-list-name: Specifies an IP prefix list by its name, a case-sensitive string of 1 to 63
characters.
Usage guidelines
Using the label acceptance policy, LDP accepts only the FEC-label mappings whose prefixes are
permitted by the specified IP prefix list from the specified peer.
This feature enables you to control the number of label mappings received from peers.
If you change the label acceptance policy to accept the previously denied label mappings from a
specific peer, for example, by using the undo accept-label command or by changing the IP prefix
list, you must execute the reset mpls ldp command to reset the LDP session with the specified peer
to apply the new policy.
Using a label advertisement policy on an LSR or using a label acceptance policy on its upstream LSR
can achieve the same purpose. HP recommends using the label advertisement policy to reduce
network load.
Examples
# Configure a label acceptance policy to accept only the FEC-label mappings containing prefixes
10.1.1.0/24 and 10.2.1.0/24 from the LDP peer 1.1.1.9.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] ip prefix-list prefix-from-RTA index 1 permit 10.1.1.0 24
[Sysname] ip prefix-list prefix-from-RTA index 2 permit 10.2.1.0 24
[Sysname] mpls ldp
25
Page 31

[Sysname-ldp] accept-label peer 1.1.1.9 prefix-list prefix-from-RTA
Related commands
• display mpls ldp peer verbose
• ip prefix-list (Layer 3—IP Routing Command Reference)
advertise-label
Use advertise-label to configure a label advertisement policy.
Use undo advertise-label to delete a label advertisement policy.
Syntax
advertise-label prefix-list prefix-list-name [ peer peer-prefix-list-name ]
undo advertise-label prefix-list prefix-list-name
Default
No label advertisement policy is configured. The device advertises label mappings permitted by the
LSP generation policy to all peers.
Views
LDP view, LDP-VPN instance view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
mdc-admin
Parameters
prefix-list prefix-list-name: Specifies an IP prefix list by its name, a case-sensitive string of 1 to 63
characters. This prefix list filters advertised label mappings.
peer peer-prefix-list-name: Specifies an IP prefix list by its name, a case-sensitive string of 1 to 63
characters. This prefix list filters LDP peers. If you do not specify this option, the device advertises
label mappings to all peers.
Usage guidelines
Use a label advertisement policy to filter label mappings advertised to peers.
You can configure multiple label advertisement policies by executing this command multiple times.
LDP follows these rules to control label advertisement:
• LDP advertises a label mapping to its peers only if the IP prefix in the mapping matches a
permit rule in any advertisement policy.
• If the IP prefix of a label mapping passes an advertisement policy that has no peer IP prefix list
(peer peer-prefix-list-name not specified), LDP advertises the label mapping to all peers.
• If the IP prefix of a label mapping passes an advertisement policy that has a peer IP prefix list,
LDP advertises the label mapping to the peers permitted by the peer IP prefix list.
• If the IP prefix of a label mapping passes multiple advertisement policies, LDP advertises the
label mapping according to the first configured policy.
Using a label advertisement policy on an LSR or using a label acceptance policy on its upstream LSR
can achieve the same purpose. HP recommends using the label advertisement policy to reduce
network load.
26
Page 32

Examples
# Configure two label advertisement policies. One policy advertises only the label mapping for
subnet 10.1.1.0/24 to the peer 3.3.3.9; the other policy advertises only the label mapping for subnet
10.2.1.0/24 to the peer 4.4.4.9.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] ip prefix-list prefix-to-C permit 10.1.1.0 24
[Sysname] ip prefix-list prefix-to-D permit 10.2.1.0 24
[Sysname] ip prefix-list peer-C permit 3.3.3.9 32
[Sysname] ip prefix-list peer-D permit 4.4.4.9 32
[Sysname] mpls ldp
[Sysname-ldp] advertise-label prefix-list prefix-to-C peer peer-C
[Sysname-ldp] advertise-label prefix-list prefix-to-D peer peer-D
Related commands
• display mpls ldp fec
• ip prefix-list (Layer 3—IP Routing Command Reference)
• lsp-trigger
backoff
Use backoff to configure the LDP backoff initial delay time and maximum delay time.
Use undo backoff to restore the default.
Syntax
backoff initial initial-time maximum maximum-time
undo backoff
Default
The LDP backoff initial delay time is 15 seconds and the maximum delay time is 120 seconds.
Views
LDP view, LDP-VPN instance view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
mdc-admin
Parameters
initial initial-time: Specifies the LDP backoff initial delay time in the range of 15 to 50331 seconds.
maximum maximum-time: Specifies the LDP backoff maximum delay time in the range of 120 to
50331 seconds.
Usage guidelines
LDP peers continually negotiate with each other until a session is set up. If LDP peers use
incompatible negotiation parameters (for example, different label advertisement modes), a large
amount of negotiation traffic will enter the network. To suppress LDP session negotiation traffic,
use this command to control the interval between negotiation attempts.
27
Page 33

After LDP fails to establish a session with a peer LSR for the first time, LDP does not start another
attempt until the initial delay timer expires. If the session setup fails again, LDP waits for two times
the initial delay before the next attempt. This process continues until the maximum delay time is
reached. After that, the maximum delay time always takes effect.
The maximum delay time must be larger than the initial delay time.
Examples
# Configure LDP backoff for the public network, and set the initial delay time to 100 seconds and
the maximum delay time to 300 seconds.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] mpls ldp
[Sysname-ldp] backoff initial 100 maximum 300
display mpls ldp discovery
Use display mpls ldp discovery to display the LDP discovery information.
Syntax
display mpls ldp discovery [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] [ interface interface-type
interface-number | peer peer-lsr-id | targeted-peer peer-lsr-id ] [ verbose ]
Views
Any view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
network-operator
mdc-admin
mdc-operator
Parameters
vpn-instance vpn-instance-name: Specifies an MPLS L3VPN instance by its name, a case-sensitive
string of 1 to 31 characters. The command displays LDP discovery information for the specified VPN.
If you do not specify a VPN instance, the command displays LDP discovery information for the
public network.
interface interface-type interface-number: Specifies an interface by its type and number. The
command displays information about basic discovery that uses the interface to send Link Hellos.
peer peer-lsr-id: Specifies an LDP peer by its LSR ID. The command displays information about both
basic discovery and extended discovery that have discovered the specified LDP peer.
targeted-peer peer-lsr-id: Specifies an LDP peer by its LSR ID. The command displays information
about extended discovery that has sent Targeted Hellos to the specified LDP peer.
verbose: Displays detailed LDP discovery information. If you do not specify this keyword, the
command displays brief LDP discovery information.
Usage guidelines
If you do not specify any parameters, the command displays all LDP basic and extended discovery
information.
28
Page 34

Examples
# Display brief LDP discovery information for the public network.
<Sysname> display mpls ldp discovery
Type: L - Link Hello, T - Targeted Hello
Discovery Source Peer LDP ID Hello Sent/Rcvd
(L) GigabitEthernet3/0/2 100.100.100.18:0 83/80
200.100.100.18:0 83/60
(T) 100.100.100.18 100.100.100.18:0 23/20
Table 11 Command output
Field Description
Type of LDP discovery:
Type
• L—Basic discovery, which sends Link Hellos to discover peers.
• T—Extended discovery, which sends Targeted Hellos to discover peers.
Discovery source.
Discovery Source
• If the LDP discovery type is L, this field displays the interface that
discovers the peer.
• If the LDP discovery type is T, this field displays the LSR ID of the peer.
Peer LDP ID LDP identifier of the LDP peer.
Hello Sent/Rcvd Number of hellos sent to the peer/number of hellos received from the peer.
# Display detailed LDP discovery information for the public network.
<Sysname> display mpls ldp discovery verbose
Link Hellos:
Interface GigabitEthernet3/0/2
Hello Interval : 5000 ms Hello Sent/Rcvd : 83/160
Transport Address: 100.100.100.17
Peer LDP ID : 100.100.100.18:0
Source Address : 202.118.224.18 Transport Address: 100.100.100.18
Hello Hold Time: 15 sec (Local: 15 sec, Peer: 15 sec)
Peer LDP ID : 100.100.100.20:0
Source Address : 202.118.224.20 Transport Address: 100.100.100.20
Hello Hold Time: 15 sec (Local: 15 sec, Peer: 15 sec)
Targeted Hellos:
100.100.100.17 -> 100.100.100.18 (Active, Passive)
Hello Interval : 15000 ms Hello Sent/Rcvd : 23/20
Transport Address: 100.100.100.17
Peer LDP ID : 100.100.100.18:0
Source Address : 100.100.100.18 Transport Address: 100.100.100.18
Hello Hold Time: 45 sec (Local: 45 sec, Peer: 45 sec)
100.100.100.17 -> 100.100.100.20 (Active, Passive)
Hello Interval : 15000 ms Hello Sent/Rcvd : 23/22
Transport Address: 100.100.100.17
Peer LDP ID : 100.100.100.20:0
Source Address : 100.100.100.20 Transport Address: 100.100.100.20
Hello Hold Time: 45 sec (Local: 45 sec, Peer: 45 sec)
29
Page 35

Table 12 Command output
Field Description
Information about basic discovery that sends Link Hellos on
Link Hellos
Interface Interface using basic discovery.
Hello Interval Hello interval in milliseconds.
Hello Sent/Rcvd Number of Hellos sent or received on the interface.
Transport Address Local transport address.
Peer LDP ID LDP identifier of the LDP peer.
Source Address Source IP address of received Hello messages.
interfaces.
In a non-point-to-point network, an interface may discover
multiple peers.
Transport Address
Hello Hold Time
Targeted Hellos
100.100.100.17 -> 100.100.100.18 (Active,
Passive)
Transport address in the received Hello messages—the
transport address of the LDP peer.
Hello hold time in seconds.
• Local—Local hello hold time.
• Peer—Peer hello hold time.
The negotiated hello hold time is the smaller one of the local
and peer hold time values.
Information about extended LDP discovery that sends
Targeted Hellos to peers.
• The address before -> (100.100.100.17 in this example) is
the local LSR ID.
• The address after -> (100.100.100.18 in this example) is
the LSR ID of the peer.
• (Active) indicates that the local LSR is the Targeted Hello
sender.
• (Passive) indicates that the local LSR is the Targeted Hello
receiver.
• (Active, Passive) indicates that the local LSR is both the
Targeted Hello sender and receiver.
display mpls ldp fec
Use display mpls ldp fec to display LDP FEC-label mappings.
Syntax
display mpls ldp fec [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] [ destination-address mask-length |
summary ]
Views
Any view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
30
Page 36

network-operator
mdc-admin
mdc-operator
Parameters
vpn-instance vpn-instance-name: Specifies an MPLS L3VPN instance by its name, a case-sensitive
string of 1 to 31 characters. The command displays FEC-label mappings for the specified VPN. If
you do not specify a VPN instance, the command displays FEC-label mappings for the public
network.
destination-address mask-length: Specifies an FEC by an IP address and a mask in the range of 0 to
32.
summary: Displays summary information about all FEC-label mappings learned by LDP.
Usage guidelines
If you do not specify the destination-address mask-length and summary parameters, the command
displays detailed information about all FEC-label mappings learned by LDP.
Examples
# Display detailed information about all FEC-label mappings learned by LDP for the public network.
<Sysname> display mpls ldp fec
FEC: 100.100.100.18/32
In Label: 1531
Upstream Info:
Peer: 100.100.100.18:0 State: Established (stale)
Downstream Info:
Peer: 100.100.100.18:0
Out Label: 3 State: Established (stale)
Next Hops: 202.118.224.18 GE3/0/2
100.19.100.18 XGE2/0/6
FEC: 200.100.100.18/32 (No route)
In Label: 1532
Upstream Info:
Peer: 200.200.200.28:0 State: Established
Downstream Info:
Peer: 120.100.100.18:0
Out Label: 3 State: Idle
Table 13 Command output
Field Description
FEC Forwarding equivalence class identified by an IP prefix.
In Label Incoming label assigned by the local LSR to the FEC.
Label Advertisement Policy Label advertisement policy.
FEC Prefix-list IP prefix list for filtering FEC prefixes.
Peer Prefix-list IP prefix list for filtering LDP peers.
31
Page 37

Field Description
Upstream Info
Peer LDP ID of an upstream peer.
Upstream peer to which the local LSR advertised the FEC-label mapping
and current state of the LSP.
Current state of the LSP established with the upstream peer:
• Established—Active state.
• Idle—Initial state.
State
• Release Awaited—Waiting for a Release message.
• Resource Awaited—Waiting for a label for the FEC.
If the state is marked as stale, the FEC-label mapping is under a GR
process.
Downstream Info
Peer LDP ID of a downstream peer.
Out Label Outgoing label assigned by the downstream LSR for the FEC.
Downstream peer from which the local LSR received the FEC-label
mapping, and current state of the LSP.
Current state of the LSP established with the downstream peer:
• Established—Active state.
State
• Idle—Inactive state.
If the state is marked as stale, the FEC-label mapping is under a GR
process.
Next Hops Next hops and outgoing interfaces.
# Display summary information about all FEC-label mappings learned by LDP for the public
network.
<Sysname> display mpls ldp fec summary
FECs : 3
Implicit Null: 1
Explicit Null: 0
Non-Null : 2
No Label : 0
No Route : 0
Sent : 3
Received : 3
Table 14 Command output
Field Description
FECs
Implicit Null Number of FECs that are bound to the implicit null label.
Explicit Null Number of FECs that are bound to the explicit null label.
Number of FECs that LDP has discovered from the routing
protocol or FEC-label mappings advertised by peers.
Non-Null Number of FECs that are bound to non-null labels.
No Label Number of FECs without a label.
No Route Number of FECs without matching routes.
32
Page 38

Field Description
Sent Number of label mappings sent and being sent.
Received Number of label mappings accepted.
display mpls ldp interface
Use display mpls ldp interface to display LDP interface information.
Syntax
display mpls ldp interface [ interface-type interface-number ]
Views
Any view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
network-operator
mdc-admin
mdc-operator
Parameters
interface-type interface-number: Specifies an interface by its type and number. If you do not specify
an interface, this command displays information about all LDP interfaces.
Examples
# Display information about all LDP interfaces.
<Sysname> display mpls ldp interface
Interface MPLS LDP Auto-config
GE3/0/2 Enabled Configured -
XGE2/0/6 Enabled Configured -
Table 15 Command output
Field Description
Interface Interface enabled with LDP.
MPLS Whether the interface is enabled with MPLS.
LDP Whether the interface is configured with the mpls ldp enable command.
Auto-config
Related commands
LDP automatic configuration information:
• If LDP autoconfiguration is enabled, this field displays IGP process
information, such as OSPF process ID and OSPF area ID.
• If LDP autoconfiguration is disabled, this field displays a hyphen (-).
• mpls ldp
• mpls ldp enable
33
Page 39

display mpls ldp lsp
Use display mpls ldp lsp to display information about LSPs generated by LDP.
Syntax
display mpls ldp lsp [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] [ destination-address mask-length ]
Views
Any view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
network-operator
mdc-admin
mdc-operator
Parameters
vpn-instance vpn-instance-name: Specifies an MPLS L3VPN instance by its name, a case-sensitive
string of 1 to 31 characters. The command displays LDP LSP information for the specified VPN. If
you do not specify a VPN instance, the command displays LDP LSP information for the public
network.
Examples
destination-address mask-length: Specifies an FEC by an IP address and a mask length in the range
of 0 to 32. If you do not specify a FEC, the command displays information about LDP LSPs for all
FECs.
# Display LDP LSP information for the public network.
<Sysname> display mpls ldp lsp
Status Flags: * - stale, L - liberal
Statistics:
FECs: 4 Ingress LSPs: 1 Transit LSPs: 1 Egress LSPs: 3
FEC In/Out Label Nexthop OutInterface
1.1.1.1/32 -/3 10.1.1.1 GE3/0/2
1151/3 10.1.1.1 GE3/0/2
2.2.2.2/32 3/-
-/1151(L)
10.1.1.0/24 1149/-
-/1149(L)
192.168.1.0/24 1150/-
-/1150(L)
Table 16 Command output
Field Description
LSP status:
Status Flags
• *—Stale, indicating the LSP is under a GR process.
• L—Liberal, indicating the LSP is not available.
34
Page 40

Field Description
Statistics
FEC Forwarding equivalence class identified by an IP prefix.
In/Out Label Incoming/outgoing label.
Nexthop Next hop address for the FEC.
OutInterface Outgoing interface for the FEC.
Related commands
display mpls lsp
LSP statistics:
• FECs—Total number of FECs.
• Ingress LSPs—Number of LSPs that take the local device as the
ingress node.
• Transit LSPs—Number of LSPs that take the local device as a
transit node.
• Egress LSPs—Number of LSPs that take the local device as the
egress node.
display mpls ldp parameter
Use display mpls ldp parameter to display LDP running parameters.
Syntax
display mpls ldp parameter [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ]
Views
Any view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
network-operator
mdc-admin
mdc-operator
Parameters
vpn-instance vpn-instance-name: Specifies an MPLS L3VPN instance by its name, a case-sensitive
string of 1 to 31 characters. The command displays the LDP running parameters for the specified
VPN. If you do not specify a VPN instance, the command displays the LDP running parameters for
the public network.
Examples
# Display LDP running parameters for the public network.
<Sysname> display mpls ldp parameter
Global Parameters:
Protocol Version : V1
Nonstop Routing : Off Graceful Restart : Off
Reconnect Time : 120 sec Forwarding State Hold Time: 360 sec
Instance Parameters:
35
Page 41

Instance ID : 0 Instance State : Active
LSR ID : 0.0.0.0
Loop Detection : Off
Hop Count Limit : 32 Path Vector Limit : 32
Label Retention Mode: Liberal Label Distribution Control Mode: Ordered
IGP Sync Delay : 0 sec IGP Sync Delay on Restart : -
Table 17 Command output
Field Description
Global Parameters Global parameters for all LDP-enabled networks.
Protocol Version LDP protocol version.
Whether the nonstop routing function is enabled.
Nonstop Routing
• On—Enabled.
• Off—Disabled.
Whether the GR function is enabled.
Graceful Restart
• On—Enabled.
• Off—Disabled.
Reconnect Time Value of the Reconnect timer, in seconds.
Forwarding State Hold Time Value of the MPLS Forwarding State Holding timer, in seconds.
Instance Parameters Running parameters for a specific VPN instance or public network.
Instance ID VPN instance ID. For the public network, this field displays 0.
Instance State LDP status in the VPN instance, Active or Inactive.
LSR ID LSR ID of the local device.
Loop Detection
Hop Count Limit Hop count limit specified for loop detection.
Path Vector Limit Path Vector length limit specified for loop detection.
Label Retention Mode The device supports only the Liberal mode.
IGP Sync Delay
IGP Sync Delay on Restart
display mpls ldp peer
Whether loop detection is enabled.
• On—Enabled.
• Off—Disabled.
Delay time (in seconds) that LDP must wait before it notifies IGP of
an LDP session-up event.
Delay time (in seconds) that LDP must wait before it notifies IGP of
an LDP session-up event in case of LDP restart.
Syntax
Views
Use display mpls ldp peer to display the LDP peer and session information.
display mpls ldp peer [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] [ peer-lsr-id ] [ verbose ]
Any view
36
Page 42

Predefined user roles
network-admin
network-operator
mdc-admin
mdc-operator
Parameters
vpn-instance vpn-instance-name: Specifies an MPLS L3VPN instance by its name, a case-sensitive
string of 1 to 31 characters. The command displays LDP peer and session information for the
specified VPN. If you do not specify a VPN instance, the command displays the LDP peer and
session information of the public network.
peer peer-lsr-id: Specifies an LDP peer by its LSR ID. If you do not specify this option, the command
displays all LDP peers and related session information.
verbose: Displays detailed LDP peer and session information. If you do not specify this keyword, the
command displays brief LDP peer and session information.
Examples
# Display brief information about all LDP peers and LDP sessions for the public network.
<Sysname> display mpls ldp peer
Total number of peers: 1
Peer LDP ID State LAM Role GR MD5 KA Sent/Rcvd
2.2.2.9:0 Operational DU Passive Off Off 39/39
Table 18 Command output
Field Description
Peer LDP ID LDP identifier of the peer.
State of the LDP session between the local LSR and the peer:
• Non Existent—No TCP connection is established.
State
• Initialized—A TCP connection has been established.
• OpenRecv—LDP has received an acceptable initialization message.
• OpenSent—LDP has sent an initialization message.
• Operational—An LDP session has been established.
LAM
Role
GR
Label advertisement mode. The device only supports the Downstream
Unsolicited (DU) mode.
Role of the local LSR in the session, Active or Passive.
In a session, the LSR with a higher IP address takes the Active role. The Active
LSR initiates a TCP connection to the passive LSR.
Whether GR is enabled on the peer.
• On—Enabled.
• Off—Disabled.
Whether MD5 authentication is enabled for the LDP session on the local device.
MD5
• On—Enabled.
• Off—Disabled.
KA Sent/Rcvd Number of Keepalive messages sent/received.
37
Page 43

# Display detailed information about all LDP peers and LDP sessions for the public network.
<Sysname> display mpls ldp peer verbose
Peer LDP ID : 100.100.100.20:0 Local LDP ID : 100.100.100.17:0
TCP Connection : 100.100.100.20:47515 -> 100.100.100.17:646
Session State : Operational Session Role : Passive
Session Up Time : 0000:00:03 (DD:HH:MM)
Max PDU Length : 4096 bytes (Local: 4096 bytes, Peer: 4096 bytes)
Keepalive Time : 45 sec (Local: 45 sec, Peer: 45 sec)
Keepalive Interval : 15 sec
Msgs Sent/Rcvd: 288/426 KA Sent/Rcvd : 13/13
Label Adv Mode : DU Graceful Restart : On
Reconnect Time : 120 sec Recovery Time : 360 sec
Loop Detection : On Path Vector Limit: 32
Discovery Sources:
Targeted Hello 100.100.100.17 -> 100.100.100.20 (Active, Passive)
Hello Hold Time: 45 sec Hello Interval : 15000 ms
GigabitEthernet3/0/2
Hello Hold Time: 15 sec Hello Interval : 5000 ms
Label Acceptance Policy : prefix-from-20
Session Protection : On
State : Ready Duration : 120 sec
Addresses received from peer:
202.118.224.20 100.100.100.20 11.22.33.44 1.2.3.10
1.2.3.4
Table 19 Command output
Field Description
Peer LDP ID LDP identifier of the peer.
Local LDP ID LDP identifier of the local LSR.
TCP connection information of the session, including the IP addresses
and port numbers used by both ends of the TCP connection, and
TCP connection
whether MD5 authentication is enabled for the TCP connection. If
MD5 authentication is enabled, MD5 On is displayed. If MD5 is not
enabled, this field is blank.
State of the LDP session:
• Non Existent—No TCP connection is established.
Session State
• Initialized—A TCP connection has been established.
• OpenRecv—LDP has received an acceptable initialization message.
• OpenSent—LDP has sent an initialization message.
• Operational—An LDP session has been established.
Session Role Role the local LSR in the session, Active or Passive.
Session Up time Duration of the session in Operational state.
Maximum PDU length negotiated, in bytes.
Max PDU Length
• Local—Maximum PDU length (in bytes) on the local LSR.
• Peer—Maximum PDU length (in bytes) on the peer.
38
Page 44

Field Description
Keepalive time negotiated, in seconds.
Keepalive Time
• Local—Locally configured Keepalive holding time, in seconds.
• Peer—Keepalive holding time (in seconds) configured on the peer.
Keepalive Interval Current Keepalive interval, in seconds.
Msgs Sent/Rcvd Total number of LDP messages sent and received.
KA Sent/Rcvd Total number of Keepalive messages sent and received.
Label Adv Mode
Graceful Restart
Label advertisement mode negotiated. The device only supports the
DU mode.
Whether GR is enabled on the peer.
• On—Enabled.
• Off—Disabled.
Reconnect Time Reconnect time negotiated, in seconds.
Recovery Time Recovery time (in seconds) carried in packets sent by the peer.
Whether loop detection is enabled on the peer.
Loop Detection
• On—Enabled.
• Off—Disabled.
Path Vector Limit Maximum Path Vector length configured on the peer.
Discovery Sources Discovery source of the LDP peer.
LDP peer discovered by the extended discovery mechanism.
• The address before -> (100.100.100.17 in this example) is the local
LSR ID.
• The address after -> (100.100.100.20 in this example) is the LSR ID
of the peer.
Targeted Hello
• (Active) indicates that the local LSR is the active end. It actively
sends Targeted Hellos to its peer.
• (Passive) indicates that the local LSR is the passive end. It passively
responds to the Targeted Hellos from its peer.
• (Active, Passive) indicates that the local LSR acts as both the active
end and the passive end.
GigabitEthernet3/0/2
Hello Hold Time Hello hold time negotiated, in seconds.
Hello Interval Current Hello interval, in milliseconds.
Label Acceptance Policy
Session Protection
Interface running LDP basic discovery. The device discovers the LDP
peer by sending Link Hellos out of the interface.
Label acceptance policy used to filter label mappings received from
the peer.
Whether session protection is enabled.
• On—Enabled.
• Off—Disabled.
Session protection state:
State
• Incomplete—Session protection is not ready.
• Ready—Session protection is ready.
• Protecting—The session is under protection.
39
Page 45

Field Description
Duration
Holdup time remaining
Addresses received from peer IP addresses received from the peer.
Local session protection duration, in seconds.
Infinite indicates that session protection takes effect permanently.
Remaining time of the session hold timer, in seconds.
This field is displayed only when the session protection state is
Protecting. A value of Infinite indicates that session protection takes
effect permanently.
display mpls ldp summary
Use display mpls ldp summary to display LDP summary information.
Syntax
display mpls ldp summary [ all | vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ]
Views
Any view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
network-operator
mdc-admin
mdc-operator
Parameters
all: Displays LDP summary information for the public network and all VPN instances.
vpn-instance vpn-instance-name: Displays LDP summary information for the specified VPN. The
vpn-instance-name is a case-sensitive string of 1 to 31 characters.
Usage guidelines
If you execute this command without any parameters, the command displays LDP summary
information for the public network.
Examples
# Display LDP summary information for the public network.
<Sysname> display mpls ldp summary
Global Information:
Memory State : Minor
Discarded Hellos: 60
VPN Instance Name : Public
Instance ID : 0
Instance State : Active
Interfaces : 1 (1 active)
Targeted Peers : 0
Adjacencies : 1
Peers : 1
40
Page 46

Operational : 1 (0 GR)
OpenSent : 0
OpenRecv : 0
Initialized : 0
Non-Existent: 0
Table 20 Command output
Field Description
Memory state:
• Normal—The memory is normal.
Memory State
• Minor—The memory has a minor alarm.
• Severe—The memory has a severe alarm.
• Critical—The memory has a critical alarm.
Discarded Hellos
Instance ID VPN instance identifier. A value of 0 represents the public network.
Instance State LDP status in the VPN instance, Active or Inactive.
Interfaces
Targeted Peers
Adjacencies Number of Hello adjacencies.
Peers Total number of peers.
Operational
OpenSent Number of peers in OpenSen state.
OpenRecv Number of peers in OpenRecv state.
Initialized Number of peers in Initialized state.
Non-Existent Number of peers in Non-Existent state.
Number of Hellos discarded when the memory is in an alarm state. If no
Hello is discarded, this filed is not displayed.
Number of interfaces enabled with LDP.
active: Number of interfaces running LDP.
Number of peers discovered by the LDP extended discovery mechanism,
including the manually specified peers and the automatically established
peers.
Number of peers in Operational state.
GR: Number of GR-capable peers.
graceful-restart
Use graceful-restart to enable Graceful Restart (GR) for LDP.
Use undo graceful-restart to disable LDP GR.
Syntax
graceful-restart
undo graceful-restart
Default
LDP GR is disabled.
41
Page 47

Views
LDP view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
mdc-admin
Usage guidelines
GR enables an LSR to retain MPLS forwarding entries during an LDP restart, ensuring continuous
MPLS forwarding.
The graceful-restart command does not take effect for LDP sessions established before the
command is executed. To apply the new setting, execute the reset mpls ldp command to
re-establish LDP sessions.
Examples
# Enable GR for LDP.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] mpls ldp
[Sysname-ldp] graceful-restart
Related commands
• display mpls ldp parameter
• reset mpls ldp
graceful-restart timer
Use graceful-restart timer to configure the MPLS Forwarding State Holding timer and the
Reconnect timer for GR.
Use undo graceful-restart timer to restore the default.
Syntax
graceful-restart timer { forwarding-hold hold-time | reconnect reconnect-time }
undo graceful-restart timer { forwarding-hold | reconnect }
Default
The MPLS Forwarding State Holding timer is 180 seconds and the Reconnect timer is 120 seconds.
Views
LDP view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
mdc-admin
Parameters
forwarding-hold hold-time: Specifies the MPLS Forwarding State Holding time in the range of 60 to
600 seconds. This time specifies how long the local LSR retains its MPLS forwarding entries after the
control plane of the local LSR restarts.
42
Page 48

reconnect timeout: Specifies the Reconnect time in the range of 60 to 300 seconds. This time
specifies the period the local LSR expects the peer to wait for LDP session re-establishment after
the peer detects an LDP session failure. The local LSR sends the Reconnect time to the peer.
Usage guidelines
The MPLS Forwarding State Holding time must be greater than the Reconnect time.
In a GR process, the timers work as follows:
1. When LDP restarts, the GR restarter starts the MPLS Forwarding State Holding timer, and
marks the MPLS forwarding entries as stale. When a GR helper detects that the LDP session
with the GR restarter is down, it marks the FEC-label mappings learned from the session as
stale and starts the Reconnect timer, the value of which is received from the GR restarter.
2. After the LDP restart, the GR restarter re-establishes an LDP session with the GR helper. If the
LDP session is not set up before the Reconnect timer expires, the GR helper deletes stale
FEC-label mappings and corresponding MPLS forwarding entries. If the LDP session is
successfully set up before the Reconnect timer expires, the GR restarter sends the remaining
time of the MPLS Forwarding State Holding timer as the LDP Recovery time to the GR helper.
3. After the LDP session is re-established, the GR helper starts the LDP Recovery timer.
4. The GR restarter and the GR helper exchange label mappings and update their MPLS
forwarding tables.
The GR restarter compares each received label mapping against stale MPLS forwarding entries.
If a match is found, the restarter deletes the stale mark for the matching entry. Otherwise, it
adds a new entry for the label mapping.
The GR helper compares each received label mapping against stale FEC-label mappings. If a
match is found, the helper deletes the stale mark for the matching mapping. Otherwise, it
adds the received FEC-label mapping and a new MPLS forwarding entry for the mapping.
5. When the MPLS Forwarding State Holding timer expires, the GR restarter deletes all stale
MPLS forwarding entries.
6. When the LDP Recovery timer expires, the GR helper deletes all stale FEC-label mappings.
Examples
# Set the MPLS Forwarding State Holding time to 200 seconds, and the Reconnect time to 100
seconds.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] mpls ldp
[Sysname-ldp] graceful-restart timer forwarding-hold 200
[Sysname-ldp] graceful-restart timer reconnect 100
Related commands
• display mpls ldp parameter
• graceful-restart
label-distribution
Use label-distribution to configure the label distribution control mode.
Use undo label-distribution to restore the default.
Syntax
label-distribution { independent | ordered }
43
Page 49

undo label-distribution
Default
The label distribution control mode is ordered.
Views
LDP view, LDP-VPN instance view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
mdc-admin
Parameters
independent: Specifies Independent label distribution mode. In this mode, an LSR can distribute
label mappings to the upstream LSR at any time.
ordered: Specifies Ordered label distribution mode. In this mode, an LSR distributes a label
mapping for a FEC to the upstream LSR only when the LSR receives a label mapping for that FEC
from the downstream LSR or the LSR is the egress node of that FEC.
Usage guidelines
In Ordered mode, an LSR can determine that the downstream LSR has established an LSP when the
LSR receives a FEC-label mapping from the downstream LSR.
The Independent mode enables faster LSP convergence because each LSR independently advertises
labels without waiting for labels from downstream LSRs.
Examples
# Set the Ordered LDP label distribution mode for the public network.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] mpls ldp
[Sysname-ldp] label-distribution independent
Related commands
display mpls ldp parameter
loop-detect
Use loop-detect to enable loop detection.
Use undo loop-detect to disable loop detection.
Syntax
loop-detect
undo loop-detect
Default
Views
Loop detection is disabled.
LDP view, LDP-VPN instance view
44
Page 50

Predefined user roles
network-admin
mdc-admin
Usage guidelines
This command enables LDP to detect and terminate LSP loops. LDP loop detection uses one of the
following methods:
• Hop count. For more information, see "maxhops."
• Path vector. For more information, see "pv-limit."
Use LDP loop
ATM switches. Do not use LDP loop detection on other networks because it only results in extra
LDP overhead.
Examples
# Enable LDP loop detection for the public network.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] mpls ldp
[Sysname-ldp] loop-detect
Related commands
• display mpls ldp parameter
• maxhops
• pv-limit
lsp-trigger
Use lsp-trigger to configure an LSP generation policy.
Use undo lsp-trigger to restore the default.
detection only in networks with devices that do not support TTL mechanism such as
Syntax
lsp-trigger { all | prefix-list prefix-list-name }
undo lsp-trigger
Default
LDP can only use host routes with a 32-bit mask to generate LSPs.
Views
LDP view, LDP-VPN instance view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
mdc-admin
Parameters
all: Enables LDP to use all routes to generate LSPs.
prefix-list prefix-name: Specifies an IP prefix list by its name, a case-sensitive string of 1 to 63
characters. LDP can only use the routes permitted by the IP prefix list to generate LSPs.
45
Page 51

Usage guidelines
The default LSP generation policy depends on the label distribution control mode.
• In Ordered mode, LDP can only use the Loopback interface address routes with a 32-bit mask
and the routes with a 32-bit mask that match the FECs of label mappings received from
downstream LSRs to generate LSPs.
• In Independent mode, LDP can use all routes with a 32-bit mask to generate LSPs.
After you configure an LSP generation policy, LDP uses all routes or the routes permitted by the IP
prefix list to generate LSPs, regardless of the label distribution control mode.
HP recommends using the default LSP generation policy.
Examples
# Configure an LSP generation policy to use only routes 10.10.1.0/24 and 10.20.1.0/24 to establish
LSPs for the public network.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] ip prefix-list egress-fec-list index 1 permit 10.10.1.0 24
[Sysname] ip prefix-list egress-fec-list index 2 permit 10.20.1.0 24
[Sysname] mpls ldp
[Sysname-ldp] lsp-trigger prefix-list egress-fec-list
Related commands
ip prefix-list (Layer 3—IP Services Command Reference)
lsr-id
Use lsr-id to configure an LDP LSR ID.
Use undo lsr-id to delete the configured LDP LSR ID.
Syntax
lsr-id lsr-id
undo lsr-id
Default
No LDP LSR ID is configured. LDP uses the MPLS LSR ID configured by the mpls lsr-id command for
both the public network and VPN instances.
Views
LDP view, LDP-VPN instance view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
mdc-admin
Parameters
lsr-id: Specifies an LDP LSR ID, in dotted decimal notation.
Usage guidelines
If you configure an LDP LSR ID by using the lsr-id command in LDP view or LDP-VPN instance view,
LDP uses the LDP LSR ID. Otherwise, LDP uses the LSR-ID configured by the mpls lsr-id command.
46
Page 52

LDP uses the same LSR ID for all sessions in the same VPN instance. After you configure a new LSR
ID for a VPN instance, LDP does not use the new LSR ID unless you use the reset mpls ldp
command to reestablish all LDP sessions in the VPN instance.
For the public network, HP recommends using the default LDP LSR ID configured by the mpls lsr-id
command. If you want to configure an LDP LSR ID for the public network by using the lsr-id
command, specify the IP address of a local Loopback interface as the LDP LSR ID for high reliability.
Examples
# Configure the LDP LSR ID as 2.2.2.2 for the public network.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] mpls ldp
[Sysname-ldp] lsr-id 2.2.2.2
Related commands
• display mpls ldp parameter
• mpls lsr-id
maxhops
Use maxhops to specify the maximum hop count for loop detection.
Use undo maxhops to restore the default.
Syntax
maxhops hop-number
undo maxhops
Default
The maximum hop count for loop detection is 32.
Views
LDP view, LDP-VPN instance view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
mdc-admin
Parameters
hop-number: Specifies the maximum hop count for loop detection, in the range of 1 to 32.
Usage guidelines
LDP adds a hop count in a label request or label mapping message. The hop count increments by 1
on each LSR. When the hop count reaches the maximum hop count configured by this command,
LDP considers that a loop occurs and terminates LSP establishment.
Examples
Set a proper maximum hop count according to the number of LSRs in your network. For example,
set a smaller maximum hop count in small networks to allow for fast loop detection; set a bigger
maximum hop count in large networks to make sure that LSPs can be successfully established.
# Set the maximum hop count to 25 for loop detection in the public network.
<Sysname> system-view
47
Page 53

[Sysname] mpls ldp
[Sysname-ldp] maxhops 25
Related commands
• display mpls ldp parameter
• loop-detect
• pv-limit
md5-authentication
Use md5-authentication to enable LDP MD5 authentication.
Use undo md5- authentication to restore the default.
Syntax
md5-authentication peer-lsr-id { cipher | plain } password
undo md5-authentication peer-lsr-id
Default
LDP MD5 authentication is disabled.
Views
LDP view, LDP-VPN instance view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
mdc-admin
Parameters
peer-lsr-id: Specifies the LSR ID of a peer.
cipher: Sets a ciphertext key.
plain: Sets a plaintext key.
password: Specifies a case-sensitive key string. If plain is specified, it must be a plaintext string of 1
to 16 characters. If cipher is specified, it must be a ciphertext string of 1 to 53 characters.
For secrecy, all keys, including keys configured in plain text, are saved in cipher text.
Usage guidelines
To improve security for LDP sessions, you can configure MD5 authentication for the underlying TCP
connections to check the integrity of LDP messages.
The local LSR and the peer LSR must have the same key. Otherwise, they cannot establish a TCP
connection.
Examples
After you change the MD5 authentication key, the local LSR uses the new key to re-establish an LDP
session with the specified peer.
# Enable LDP MD5 authentication for peer 3.3.3.3 in the public network, and set a plaintext key of
pass.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] mpls ldp
48
Page 54

[Sysname-ldp] md5-authentication 3.3.3.3 plain pass
Related commands
display mpls ldp peer
mpls ldp
Use mpls ldp to enable LDP globally and enter LDP view.
Use undo mpls ldp to disable LDP globally for an LSR and delete all LDP-VPN instances.
Syntax
mpls ldp
undo mpls ldp
Default
LDP is globally disabled.
Views
System view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
mdc-admin
Usage guidelines
You must enable LDP globally for an LSR to run LDP.
The GR commands, the session protection command, and the targeted-peer command are
available only in LDP view. All other commands available in LDP view are also available in LDP-VPN
instance view.
Commands executed in LDP view take effect only for the public network. Commands executed in
LDP-VPN instance view take effect only for the specified VPN instance. The GR commands are
global commands and take effect for all VPN instances and the public network.
Examples
# Enable LDP globally and enter LDP view.
<Sysname> System-view
[Sysname] mpls ldp
[Sysname-ldp]
Related commands
• mpls ldp enable
• vpn-instance
mpls ldp enable
Use mpls ldp enable to enable LDP for an interface.
Use undo mpls ldp enable to disable LDP for an interface.
49
Page 55

Syntax
mpls ldp enable
undo mpls ldp enable
Default
LDP is disabled on an interface.
Views
Interface view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
mdc-admin
Usage guidelines
Before you enable LDP for an interface, use the mpls ldp command in system view to enable LDP
globally.
Disabling LDP on an interface terminates all LDP sessions on the interface, and removes all LSPs
established through the sessions.
If the interface is bound with a VPN instance, you must also use the vpn-instance command to
enable LDP for the VPN instance.
An up interface enabled with LDP and MPLS sends Link Hellos for neighbor discovery.
LDP takes effect only on the VLAN interfaces, Layer 3 Ethernet interfaces/subinterfaces, and Layer 3
aggregate interfaces/subinterfaces.
Examples
# Enable LDP for VLAN-interface 2.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] mpls ldp
[Sysname-ldp] quit
[Sysname] interface vlan-interface 2
[Sysname-Vlan-interface2] mpls ldp enable
Related commands
• display mpls ldp interface
• mpls enable
• mpls ldp
mpls ldp timer
Syntax
Use mpls ldp timer to configure the Hello hold time, Hello interval, Keepalive hold time, and
Keepalive interval.
Use undo mpls ldp timer to restore the default.
mpls ldp timer { hello-hold timeout | hello-interval interval | keepalive-hold timeout |
keepalive-interval interval }
50
Page 56

undo mpls ldp timer { hello-hold | hello-interval | keepalive-hold | keepalive-interval }
Default
The Link Hello hold time is 15 seconds, the Link Hello interval is 5 seconds, the Targeted Hello hold
time is 45 seconds, the Targeted Hello interval is 15 seconds, the Keepalive hold time is 45 seconds,
and the Keepalive interval is 15 seconds.
Views
Interface view, LDP peer view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
mdc-admin
Parameters
hello-hold timeout: Specifies the Hello hold time in the range of 1 to 65535 seconds. LDP keeps the
hello adjacency during the Hello hold time. The negotiated Hello hold time takes the smaller value
of the local Hello hold time and the peer Hello hold time. If LDP receives no Hello message from
the peer before the Hello hold timer expires, LDP deletes the Hello adjacency with the peer. If you
set the Hello hold time to 65535, LDP permanently keeps the Hello adjacency.
hello-interval interval: Specifies the Hello interval in the range of 1 to 65535 seconds. LDP sends
Hello messages at this interval.
keepalive-hold timeout: Specifies the Keepalive hold time in the range of 15 to 65535 seconds. LDP
keeps the LDP session with the peer during the Keepalive hold time. The negotiated Keepalive hold
time takes the smaller value of the local Keepalive hold time and the peer Keepalive hold time. If
LDP receives no LDP message from the peer before the Keepalive hold timer expires, LDP deletes
the LDP session with the peer.
keepalive-interval interval: Specifies the Keepalive interval in the range of 1 to 65535 seconds. LDP
sends Keepalive messages to the peer at this interval.
Usage guidelines
Using this command in interface view, you set a Link Hello hold time and a Link Hello interval.
Using this command in LDP peer view, you set a Targeted Hello hold time and a Targeted Hello
interval.
If the Hello hold time and the Keepalive hold time values are too large, LDP cannot quickly detect
link failures. If the values are too small, LDP may mistakenly consider a normal link failed. HP
recommends using the default values.
If two LSRs have multiple LDP links in between, make sure that those links have the same Keepalive
hold time.
During LDP session negotiation, an LSR compares the local Hello hold time with the Hello hold time
of the peer LSR, and uses the smaller one as the negotiated Hello hold time. If the negotiated Hello
hold time is larger than three times the local Hello interval, the LSR sends Hello messages at the
local Hello interval. Otherwise, the LSR sends Hello messages at an interval 1/3 of the negotiated
Hello hold time.
During LDP session negotiation, an LSR compares the local Keepalive hold time with the Keepalive
hold time of the peer LSR, and uses the smaller one as the negotiated Keepalive hold time. If the
negotiated Keepalive hold time is larger than three times the local Keepalive interval, the LSR sends
51
Page 57

Examples
Keepalive messages at the local Keepalive interval. Otherwise, the LSR sends Keepalive messages at
an interval 1/3 of the negotiated Keepalive hold time.
# Set the Targeted Hello hold time to 1000 seconds, Targeted Hello interval to 50 seconds,
Keepalive hold time to 1000 seconds, and Keepalive interval to 50 seconds for peer 3.3.3.3.
<Sysname> System-view
[Sysname] mpls ldp
[Sysname-ldp] targeted-peer 3.3.3.3
[Sysname-ldp-peer-3.3.3.3] mpls ldp timer hello-hold 1000
[Sysname-ldp-peer-3.3.3.3] mpls ldp timer hello-interval 50
[Sysname-ldp-peer-3.3.3.3] mpls ldp timer keepalive-hold 1000
[Sysname-ldp-peer-3.3.3.3] mpls ldp timer keepalive-interval 50
# On VLAN-interface 2, set the Link Hello hold time to 100 seconds, Link Hello interval to 20
seconds, Keepalive hold time to 50 seconds, and Keepalive interval to 10 seconds.
<Sysname> System-view
[Sysname] interface vlan-interface 2
[Sysname-Vlan-interface2] mpls ldp timer hello-hold 100
[Sysname-Vlan-interface2] mpls ldp timer hello-interval 20
[Sysname-Vlan-interface2] mpls ldp timer keepalive-hold 50
[Sysname-Vlan-interface2] mpls ldp timer keepalive-interval 10
Related commands
• display mpls ldp discovery
• display mpls ldp peer
mpls ldp transport-address
Use mpls ldp transport-address to specify the LDP transport address.
Use undo mpls ldp transport-address to restore the default.
Syntax
In interface view:
mpls ldp transport-address { ip-address | interface }
undo mpls ldp transport-address
In LDP peer view:
mpls ldp transport-address ip-address
undo mpls ldp transport-address
Default
In interface view, if the interface belongs to the public network, the LDP transport address is the
local LSR ID. If the interface belongs to a VPN, the LDP transport address is the primary IP address
of the interface.
Views
In LDP peer view, the LDP transport address is the local LSR ID.
Interface view, LDP peer view
52
Page 58

Predefined user roles
network-admin
mdc-admin
Parameters
ip-address: Specifies the LDP transport address.
interface: Uses the IP address of the current interface as the LDP transport address.
Usage guidelines
Before two LSRs establish an LDP session, they must establish a TCP connection by using the LDP
transport address. LDP sends the local LDP transport address to the peer in Link Hello or Targeted
Hello messages.
Using mpls ldp transport-address in interface view, you specify the transport address carried in the
Link Hellos sent out of the interface.
Using mpls ldp transport-address in LDP peer view, you specify the transport address carried in the
Targeted Hellos sent to the LDP peer.
HP recommends using the default transport address.
If two LSRs have multiple links in between and you want to establish an LDP session on each link,
make sure that all the links use the same transport address.
Examples
# Specify the LDP transport address carried in Targeted Hellos sent to peer 3.3.3.3 as 2.2.2.2.
<Sysname> System-view
[Sysname] mpls ldp
[Sysname-ldp] targeted-peer 3.3.3.3
[Sysname-ldp-peer-3.3.3.3] mpls ldp transport-address 2.2.2.2
# On VLAN-interface 2, specify the transport address carried in Link Hellos as the IP address of the
interface.
<Sysname> System-view
[Sysname] interface vlan-interface 2
[Sysname-Vlan-interface2] mpls ldp transport-address interface
Related commands
display mpls ldp discovery
pv-limit
Use pv-limit to specify the path vector limit.
Use undo pv-limit to restore the default.
Syntax
Default
pv-limit pv-number
undo pv-limit
The path vector limit is 32.
53
Page 59

Views
LDP view, LDP-VPN instance view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
mdc-admin
Parameters
pv-number: Specifies the path vector limit in the range of 1 to 32.
Usage guidelines
LDP adds LSR ID information in a label request or label mapping message. Each LSR checks
whether its LSR ID is contained in the message. If not, the LSR adds its own LSR ID into the message.
If yes, the LSR considers that a loop occurs and terminates LSP establishment. In addition, when the
number of LSR IDs in the message reaches the path vector limit, LDP also considers that a loop
occurs and terminates LSP establishment.
Examples
# Set the path vector limit as 3 for LDP loop detection in the public network.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] mpls ldp
[Sysname-ldp] pv-limit 3
Related commands
• display mpls ldp parameter
• loop-detect
• maxhops
reset mpls ldp
Use reset mpls ldp to reset LDP sessions.
Syntax
reset mpls ldp [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] [ peer peer-id ]
Views
User view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
mdc-admin
Parameters
vpn-instance vpn-instance-name: Specifies an MPLS L3VPN instance by its name, a case-sensitive
string of 1 to 31 characters. The command resets the LDP sessions in the specified VPN. If you do
not specify a VPN instance, the command resets the LDP sessions in the public network.
peer peer-id: Specifies a peer by its LSR ID. If you do not specify a peer, the command resets all LDP
sessions in the specified VPN instance or the public network.
54
Page 60

Usage guidelines
Resetting an LDP session deletes and re-establishes the session and all LSPs based on the session.
To apply new parameters except the MD5 authentication key to an LDP session, you must use this
command to reset the LDP session.
Examples
# Reset all LDP sessions in the public network.
<Sysname> reset mpls ldp
# Reset all LDP sessions in the VPN instance vpn1.
<Sysname> reset mpls ldp vpn-instance vpn1
session protection
Use session protection to enable session protection.
Use undo session protection to disable session protection.
Syntax
session protection [ duration time ] [ peer peer-prefix-list-name ]
undo session protection
Default
Session protection is disabled.
Views
LDP view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
mdc-admin
Parameters
duration time: Specifies the session protection duration time in the range of 30 to 2147483 seconds.
If you do not specify the duration, session protection always takes effect.
peer peer-prefix-list-name: Specifies an IP prefix list by its name, a case-sensitive string of 1 to 63
characters. Sessions to the peers whose LSR IDs are permitted by the specified IP prefix list are
protected. If you do not specify this option, all sessions established by the Basic Discovery
mechanism are protected.
Usage guidelines
If two LDP peers have both a direct link and an indirect link in between, you can configure this
feature to protect their LDP session when the direct link fails.
LDP establishes both a Link Hello adjacency over the direct link and a Targeted Hello adjacency
over the indirect link with the peer. When the direct link fails, LDP deletes the Link Hello adjacency
but still maintains the Targeted Hello adjacency. In this way, the LDP session between the two peers
is kept available, and the FEC-label mappings based on this session are not deleted. When the
direct link recovers, the LDP peers do not need to re-establish the LDP session or re-learn the
FEC-label mappings.
55
Page 61

When you enable the session protection function, you can specify the session protection duration.
If the Link Hello adjacency does not recover within the duration, LDP deletes the Targeted Hello
adjacency and the LDP session. If you do not specify the session protection duration, the two peers
always maintain the LDP session over the Targeted Hello adjacency.
Examples
# Enable protection for the session to the peer 3.3.3.3, and set the session protection duration to
120 seconds.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] ip prefix-list protected-peer-list index 1 permit 3.3.3.3 32
[Sysname] mpls ldp
[Sysname-ldp] session protection duration 120 peer protected-peer-list
Related commands
display mpls ldp peer
targeted-peer
Use targeted-peer to allow sending Targeted Hellos to and receiving Targeted Hellos from the
specified peer, and to enter LDP peer view.
Use undo targeted-peer to cancel the configuration.
Syntax
targeted-peer peer-lsr-id
undo targeted-peer peer-lsr-id
Default
The device does not send Targeted Hellos to or receive Targeted Hellos from any peer.
Views
LDP view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
mdc-admin
Parameters
peer-lsr-id: Specifies the LSR ID of a peer.
Usage guidelines
This command is used in the LDP over MPLS TE network to establish a unidirectional MPLS TE
tunnel. You must configure the targeted-peer command on the egress node of the MPLS TE tunnel
and specify the peer-lsr-id as the LSR ID of the ingress node, so that the egress node can receive
Targeted Hellos from the ingress and sends Targeted Hellos to the ingress to establish an LDP
session over the MPLS TE tunnel.
Examples
The switch does not support MPLS TE tunnels.
# Configure the device to send Targeted Hellos to the peer 3.3.3.3, and enter LDP peer view.
<Sysname> system-view
56
Page 62

[Sysname] mpls ldp
[Sysname-ldp] targeted-peer 3.3.3.3
[Sysname-ldp-peer-3.3.3.3]
Related commands
• display mpls ldp discovery
• display mpls ldp peer
vpn-instance
Use vpn-instance to enable LDP for a VPN instance and enter LDP-VPN instance view.
Use undo vpn-instance to delete the LDP-VPN instance.
Syntax
vpn-instance vpn-instance-name
undo vpn-instance vpn-instance-name
Default
LDP is disabled for a VPN instance.
Views
LDP view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
mdc-admin
Parameters
vpn-instance-name: Specifies a VPN instance by its name, a case-sensitive string of 1 to 31
characters.
Usage guidelines
Enabling LDP for VPNs is used for the Carrier's Carrier network that uses LDP between the Level 1
carrier and Level 2 carrier PEs. In such a network, you must enable LDP for each VPN on each Level
1 carrier PE.
The VPN instance specified by this command must have been created by the ip vpn-instance
command in system view.
The GR commands, the session protection command, and the targeted-peer command are
available only in LDP view. All other commands available in LDP view are available in LDP-VPN
instance view.
Commands executed in LDP view take effect only for the public network. Commands executed in
LDP-VPN instance view take effect only for the specified VPN instance. The GR commands are
global commands and take effect for all VPN instances and the public network.
Examples
# Enable LDP for the VPN instance vpn1 and enter LDP-VPN instance view.
<Sysname> System-view
[Sysname] mpls ldp
[Sysname-ldp] vpn-instance vpn1
57
Page 63

[Sysname-ldp-vpn1]
Related commands
• ip vpn-instance
• mpls ldp
58
Page 64

MPLS L3VPN commands
description (VPN instance view)
Use description to configure a description for a VPN instance.
Use undo description to delete the description.
Syntax
description text
undo description
Default
No description is configured for a VPN instance.
Views
VPN instance view
Default command level
2: System level
Parameters
text: Description for the VPN instance, a case-sensitive string of 1 to 79 characters.
Examples
# Configure a description of "This is vpn1" for VPN instance vpn1.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[Sysname-vpn-instance-vpn1] description This is vpn1
display bgp group vpnv4
Use display bgp group vpnv4 to display information about a specific BGP VPNv4 peer group or all
BGP VPNv4 peer groups.
Syntax
display bgp group vpnv4 [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] [ group-name ]
Views
Any view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
network-operator
mdc-admin
mdc-operator
59
Page 65

Parameters
vpn-instance vpn-instance-name: Specifies a VPN instance by its name, a case-sensitive string of 1
to 31 characters. If no VPN instance is specified, this command displays BGP VPNv4 peer group
information for the public network.
group-name: Specifies a peer group by its name, a case-sensitive string of 1 to 47 characters. If no
peer group is specified, this command displays all peer groups.
Examples
# Display all BGP VPNv4 peer groups for the public network.
<Sysname> display bgp group vpnv4
BGP peer group: group1
Remote AS number: not specified
Type: external
Members:
10.1.1.1
# Display information about the BGP VPNv4 peer group named group1.
<Sysname> display bgp group vpnv4 group1
BGP peer group: group1
Remote AS: 600
Type: external
Maximum number of prefixes allowed: 4294967295
Threshold: 75%
Configured hold time: 180 seconds
Keepalive time: 60 seconds
Minimum time between advertisements: 30 seconds
Peer preferred value: 0
Routing policy configured:
No routing policy is configured
Members:
Peer AS MsgRcvd MsgSent OutQ PrefRcv Up/Down State
2.2.2.2 600 0 0 0 0 00:00:05 Idle
Table 21 Command output
Field Description
BGP peer-group Name of the BGP peer group.
Remote AS AS number of the peer group.
Type of the BGP peer group:
Type
• External—EBGP peer group
• Internal—IBGP peer group
Maximum number of prefixes allowed
60
Maximum number of routes that can be learned
from the peer group.
Page 66

Field Description
Warning threshold. When the percentage of
Threshold
Configured hold time Configured hold time, in seconds.
Keepalive time Keepalive interval, in seconds.
Minimum time between advertisements Minimum time between advertisements
Peer Preferred Value Preferred value for routes received from the peer.
Routing policy configured Routing policy configured for the peer group.
Members Peers in the peer group.
Peer IPv6 address of the peer.
AS AS number of the peer group.
MsgRcvd Number of messages received.
MsgSent Number of messages sent.
OutQ Number of messages waiting to be sent to the peer.
received route prefixes to the maximum number of
routes reaches this threshold, the device generates
a prompt.
PrefRcv Number of prefixes received.
Up/Down Duration of the BGP session in the current state.
State State of the peer.
display bgp peer vpnv4
Use display bgp peer vpnv4 to display information about BGP VPNv4 peers.
Syntax
display bgp peer vpnv4 [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] [ group-name log-info | ip-address
{ log-info | verbose } | verbose ]
Views
Any view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
network-operator
mdc-admin
mdc-operator
Parameters
vpn-instance vpn-instance-name: Specifies a VPN instance by its name, a case-sensitive string of 1
to 31 characters. If no VPN instance is specified, this command displays BGP VPNv4 peer
information for the public network.
group-name: Displays peers in the specified peer group. The group name is a case-sensitive string
of 1 to 47 characters.
61
Page 67

ip-address: Specifies a BGP VPNv4 peer.
log-info: Displays log information.
verbose: Displays detailed information.
Usage guidelines
With no parameters specified, this command displays brief information about all BGP VPNv4 peers.
Examples
# Display brief information about BGP VPNv4 peers for the public network.
<Sysname> display bgp peer vpnv4
BGP local router ID: 1.1.1.9
Local AS number: 100
Total number of peers: 2 Peers in established state: 1
Peer AS MsgRcvd MsgSent OutQ PrefRcv Up/Down State
3.3.3.9 100 50 51 0 2 00:37:19 Established
Table 22 Command output
Field Description
BGP Local router ID Router ID of the local BGP router.
Local AS number Local AS number
Total number of peers Total number of peers
Peers in established state Number of peers in the state of established.
Peer IP address of the peer.
AS AS number of the peer.
MsgRcvd Number of messages received.
MsgSent Number of messages sent.
OutQ Number of messages waiting to be sent to the peer.
PrefRcv Number of received prefixes.
Up/Down Duration of the BGP session in the current state.
State State of the peer.
# Display detailed information about BGP VPNv4 peer 10.1.1.1.
<Sysname> display bgp peer vpnv4 10.1.1.1 verbose
Peer: 10.1.1.1 Local: 192.168.1.136
Type: EBGP link
BGP version 4, remote router ID 192.168.1.135
BGP current state: Established, Up for 00h01m25s
BGP current event: KATimerExpired
BGP last state: OpenConfirm
Port: Local - 179 Remote - 1049
62
Page 68

Configured: Active Hold Time: 180 sec Keepalive Time: 60 sec
Received : Active Hold Time: 180 sec
Negotiated: Active Hold Time: 180 sec Keepalive Time: 60 sec
Peer optional capabilities:
Peer support BGP multi-protocol extended
Peer support BGP route refresh capability
Peer support BGP route AS4 capability
Address family IPv4 Unicast: received
Address family VPNv4: advertised and received
Received: Total 4 messages, Update messages 1
Sent: Total 17 messages, Update messages 1
Maximum allowed prefix number: 4294967295
Threshold: 75%
Minimum time between advertisements is 30 seconds
Optional capabilities:
Multi-protocol extended capability has been enabled
Route refresh capability has been enabled
Connect-interface has been configured
Peer Preferred Value: 0
BFD: Enabled
Routing policy configured:
No routing policy is configured
Table 23 Command output
Field Description
Peer IP address of the peer.
Local IP address of the local router.
Type BGP link type, IBGP link or EBGP link.
BGP version BGP version of the peer.
remote router ID Router ID of the peer.
BGP current state Current state of the BGP session.
Up for Duration since the peer is established.
BGP current event Current event of the BGP session.
BGP last state
Port Local and remote ports of the BGP session.
Configured
Received Received active hold interval.
Negotiated
State that the BGP session was in before
transitioning to the current state.
Settings of the local timers, including the active hold
interval and keepalive interval.
Negotiated active hold interval and keepalive
interval.
Peer optional capabilities Optional capabilities of the peer.
63
Page 69

Field Description
Peer support bgp multi-protocol extended The peer supports multiprotocol extension.
Peer support bgp route refresh capability The peer supports route refresh capability.
Peer support bgp route AS4 capability The peer supports 4-byte AS number capability.
Address family IPv4 Unicast IPv4 unicast family capability.
Received
Sent
Maximum allowed prefix number
Threshold
Optional capabilities Local optional capabilities.
Peer Preferred Value Preferred value for the routes from the peer.
BFD Indicates whether BFD is enabled for the peer.
Total number of received messages and the number
of received update messages.
Total number of sent messages and the number of
sent update messages.
Maximum number of routes that can be learned
from the peer.
Warning threshold. When the percentage of the
number of the received route prefixes to the
maximum number of routes supported reaches this
threshold, the device generates a prompt.
# Display log information for the BGP VPNv4 peer 10.1.1.1.
<Sysname> display bgp peer vpnv4 10.1.1.1 log-info
Peer: 10.1.1.1
Date Time State Notification
Error/SubError
21-Nov-2011 12:36:58 Up
21-Nov-2011 12:22:29 Down Send notification with error 6/6
Cease/Other Configuration Change
21-Nov-2011 12:07:09 Up
display bgp routing-table ipv4 unicast inlabel
Use display bgp routing-table ipv4 unicast inlabel to display incoming labels for BGP IPv4 unicast
routes.
Syntax
display bgp routing-table ipv4 [ unicast ] [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] inlabel
Views
Any view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
network-operator
64
Page 70

mdc-admin
mdc-operator
Parameters
vpn-instance vpn-instance-name: Specifies a VPN instance by its name, a case-sensitive string of 1
to 31 characters. If no VPN instance is specified, this command displays incoming labels for BGP
IPv4 unicast routes on the public network.
Usage guidelines
The unicast keyword does not affect the command output.
Examples
# Display incoming labels for all BGP IPv4 unicast routes on the public network.
<Sysname> display bgp routing-table ipv4 inlabel
Total number of routes: 1
BGP local router ID is 3.3.3.9
Status codes: * - valid, > - best, d - dampened, h - history,
s - suppressed, S - stale, i - internal, e - external
Origin: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network NextHop OutLabel InLabel
> 2.2.2.9/32 1.1.1.2 1151 1279
Table 24 Command output
Field Description
BGP Local router ID Router ID of the local BGP router.
Status Route status codes. See Table 26.
Origin Route origin codes. See Table 26.
In/Out Label Incoming/outgoing label.
display bgp routing-table ipv4 unicast outlabel
Use display bgp routing-table ipv4 unicast outlabel to display outgoing labels for BGP IPv4
unicast routes.
Syntax
display bgp routing-table ipv4 [ unicast ] [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] outlabel
Views
Any view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
network-operator
65
Page 71

mdc-admin
mdc-operator
Parameters
vpn-instance vpn-instance-name: Specifies a VPN instance by its name, a case-sensitive string of 1
to 31 characters. If no VPN instance is specified, this command displays outgoing labels for BGP
IPv4 unicast routes on the public network.
Usage guidelines
The unicast keyword does not affect the command output.
Examples
# Display outgoing labels for all BGP IPv4 unicast routes on the public network.
<Sysname> display bgp routing-table ipv4 outlabel
Total number of routes: 1
BGP local router ID is 3.3.3.9
Status codes: * - valid, > - best, d - dampened, h - history,
s - suppressed, S - stale, i - internal, e - external
Origin: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network NextHop OutLabel
> 2.2.2.9/32 1.1.1.2 1151
Table 25 Command output
Field Description
BGP Local router ID Router ID of the local BGP router.
Status Route status codes. See Table 26.
Origin Route origin codes. See Table 26.
OutLabel Outgoing label.
display bgp routing-table vpnv4
Use display bgp routing-table vpnv4 to display BGP VPNv4 routing information.
Syntax
display bgp routing-table vpnv4 [ route-distinguisher route-distinguisher ] [ network-address
[ { mask | mask-length } [ longest-match ] ] ]
Views
Any view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
network-operator
66
Page 72

mdc-admin
mdc-operator
Parameters
route-distinguisher route-distinguisher: Specifies an RD, a string of 3 to 21 characters in one of
these formats:
• 16-bit AS number:32-bit user-defined number. For example, 101:3.
• 32-bit IP address:16-bit user-defined number. For example, 192.168.122.15:1.
• 32-bit AS number:16-bit user-defined number, where the minimum value of the AS number is
65536. For example, 65536:1.
network-address: Destination network address.
mask: Network mask, in dotted decimal notation.
mask-length: Length of the network mask, in the range of 0 to 32.
longest-match: Displays the longest matching BGP VPNv4 route.
Usage guidelines
If none of network-address, mask, and mask-length are specified, the command displays brief
information about all BGP VPNv4 routes.
Examples
If network-address mask or network-address mask-length is specified, the command displays
detailed information about the BGP VPNv4 route that exactly matches the specified address and
mask.
If only network-address is specified, the command displays detailed information about the BGP
VPNv4 route that exactly matches the specified address and the natural mask.
# Display brief information about all BGP VPNv4 routes.
<Sysname> display bgp routing-table vpnv4
BGP local router ID is 1.1.1.9
Status codes: * - valid, > - best, d - dampened, h - history,
s - suppressed, S - stale, i - internal, e - external
Origin: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Total number of routes from all PEs: 2
Route distinguisher: 100:1(vpn1)
Total number of routes: 6
Network NextHop MED LocPrf PrefVal Path/Ogn
> 10.1.1.0/24 10.1.1.2 0 32768 ?
* e 10.1.1.1 0 0 65410?
> 10.1.1.2/32 127.0.0.1 0 32768 ?
>i 10.3.1.0/24 3.3.3.9 0 100 0 ?
>e 192.168.1.0 10.1.1.1 0 0 65410?
* i 3.3.3.9 0 100 0 65420?
67
Page 73

Route distinguisher: 200:1
Total number of routes: 2
Network NextHop MED LocPrf PrefVal Path/Ogn
>i 10.3.1.0/24 3.3.3.9 0 100 0 ?
>i 192.168.1.0 3.3.3.9 0 100 0 65420?
# Display brief information about BGP VPNv4 routes with RD 100:1..
<Sysname> display bgp routing-table vpnv4 route-distinguisher 100:1
BGP local router ID is 1.1.1.9
Status codes: * - valid, > - best, d - dampened, h - history,
s - suppressed, S - stale, i - internal, e - external
Origin: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Route distinguisher: 100:1(vpn1)
Total number of routes: 6
Network NextHop MED LocPrf PrefVal Path/Ogn
> 10.1.1.0/24 10.1.1.2 0 32768 ?
* e 10.1.1.1 0 0 65410?
> 10.1.1.2/32 127.0.0.1 0 32768 ?
>i 10.3.1.0/24 3.3.3.9 0 100 0 ?
>e 192.168.1.0 10.1.1.1 0 0 65410?
* i 3.3.3.9 0 100 0 65420?
Table 26 Command output
Field Description
BGP Local router ID Router ID of the local BGP router.
Route status codes:
• * - valid—Valid route.
• > - best—Common best route.
• d – damped—Route damped for route flap.
Status codes
• h - history—History route.
• i - internal—Internal route.
• e - external—External route.
• s - suppressed—Suppressed route.
• S - Stale—Stale route.
Route origin:
• i—IGP, originated in the AS. The origin of
summary routes and routes advertised by the
Origin
network command is IGP.
• e—EGP, learned through EGP.
• ?—Incomplete. The origin of routes
redistributed from IGP protocols is Incomplete.
68
Page 74

Field Description
Total number of routes from all PEs Total number of VPNv4 routes from all PEs.
Network Network address.
NextHop Address of the next hop.
MED MED value.
LocPrf Local preference value.
PrefVal Preferred value.
Path/Ogn AS_PATH and Origin attributes.
# Display detailed information about the BGP VPNv4 route destined for 10.3.1.0/24.
<Sysname> display bgp routing-table vpnv4 10.3.1.0 24
BGP local router ID: 1.1.1.9
Local AS number: 100
Route distinguisher: 100:1(vpn1)
Total number of routes: 1
Paths: 1 available, 1 best
BGP routing table information of 10.3.1.0/24:
From : 3.3.3.9 (3.3.3.9)
Relay nexthop : 172.1.1.2
Original nexthop: 3.3.3.9
OutLabel : 1279
Ext-Community : <RT: 111:1>
AS-path : (null)
Origin : incomplete
Attribute value : MED 0, localpref 100, pref-val 0
State : valid, internal, best,
Route distinguisher: 200:1
Total number of routes: 1
Paths: 1 available, 1 best
BGP routing table information of 10.3.1.0/24:
From : 3.3.3.9 (3.3.3.9)
Relay nexthop : 172.1.1.2
Original nexthop: 3.3.3.9
OutLabel : 1279
Ext-Community : <RT: 111:1>
AS-path : (null)
Origin : incomplete
Attribute value : MED 0, localpref 100, pref-val 0
State : valid, internal, best,
69
Page 75

# Display detailed information about the BGP VPNv4 route destined for 10.3.1.0/24 and with RD
100:1.
<Sysname> display bgp routing-table vpnv4 route-distinguisher 100:1 10.3.1.0 24
BGP local router ID: 1.1.1.9
Local AS number: 100
Route distinguisher: 100:1(vpn1)
Total number of routes: 1
Paths: 1 available, 1 best
BGP routing table information of 10.3.1.0/24:
From : 3.3.3.9 (3.3.3.9)
Relay nexthop : 172.1.1.2
Original nexthop: 3.3.3.9
OutLabel : 1279
Ext-Community : <RT: 111:1>
AS-path : (null)
Origin : incomplete
Attribute value : MED 0, localpref 100, pref-val 0
State : valid, internal, best,
Table 27 Command output
Field Description
Relay Nexthop
Original nexthop
Ext-Community Extended community attribute.
Recursive next hop. If no recursive next hop is
found, "not resolved" is displayed.
Original next hop. If the route is learned from a BGP
update, it is the next hop in the update message.
BGP route attribute information:
• MED—MED attribute.
Attribute value
• Localpref—Local preference.
• pref-val—Preferred value.
• pre—Protocol preference.
Route status:
• valid—Valid route.
• internal—Internal route.
State
• external—External route.
• local—Locally generated route.
• synchronize—Synchronized route.
• best—Best route.
70
Page 76

display bgp routing-table vpnv4 advertise-info
Use display bgp routing-table vpnv4 advertise-info to display advertisement information for BGP
VPNv4 routes.
Syntax
display bgp routing-table vpnv4 [ route-distinguisher route-distinguisher ] network-address [ mask
| mask-length ] advertise-info
Views
Any view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
network-operator
mdc-admin
mdc-operator
Parameters
route-distinguisher route-distinguisher: Specifies an RD, a string of 3 to 21 characters in one of
these formats:
• 16-bit AS number:32-bit user-defined number. For example, 101:3.
• 32-bit IP address:16-bit user-defined number. For example, 192.168.122.15:1.
• 32-bit AS number:16-bit user-defined number, where the minimum value of the AS number is
65536. For example, 65536:1.
network-address: Destination network address.
mask: Network mask, in dotted decimal notation.
mask-length: Length of the network mask, in the range of 0 to 32.
Usage guidelines
• If the mask and mask-length arguments are not specified, the system ANDs the specified
network address with the mask of each route. If the result matches the network address of the
route, the command displays advertisement information for the route.
• If the mask or mask-length argument is specified, the command displays advertisement
information for the BGP VPNv4 route that exactly matches the specified address and mask.
Examples
# Display advertisement information for the BGP VPNv4 route destined to network 10.2.1.0/24.
<Sysname> display bgp routing-table vpnv4 10.1.1.0 24 advertise-info
BGP local router ID: 1.1.1.9
Local AS number: 100
Route distinguisher: 100:1
Total number of routes: 1
Paths: 1 best
71
Page 77

BGP routing table information of 10.1.1.0/24:
Advertised to VPN peers (1 in total):
3.3.3.9
Inlabel : 1279
display bgp routing-table vpnv4 as-path-acl
Use display bgp routing-table vpnv4 as-path-acl to display BGP IPv4 unicast routes permitted by
an AS path ACL.
Syntax
display bgp routing-table vpnv4 [ route-distinguisher route-distinguisher ] as-path-acl
as-path-acl-number
Views
Any view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
network-operator
mdc-admin
mdc-operator
Parameters
route-distinguisher route-distinguisher: Specifies an RD, a string of 3 to 21 characters in one of
these formats:
• 16-bit AS number:32-bit user-defined number. For example, 101:3.
• 32-bit IP address:16-bit user-defined number. For example, 192.168.122.15:1.
• 32-bit AS number:16-bit user-defined number, where the minimum value of the AS number is
as-path-acl-number: Specifies an AS path ACL by its number in the range of 1 to 256.
Examples
# Display BGP VPNv4 routes permitted by AS path ACL 1.
<Sysname> display bgp routing-table vpnv4 as-path-acl 1
BGP local router ID is 1.1.1.9
Status codes: * - valid, > - best, d - dampened, h - history,
s - suppressed, S - stale, i - internal, e - external
Origin: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Total number of routes from all PEs: 2
Route distinguisher: 100:1(vpn1)
Total number of routes: 6
Network NextHop MED LocPrf PrefVal Path/Ogn
65536. For example, 65536:1.
72
Page 78

> 10.1.1.0/24 10.1.1.2 0 32768 ?
* e 10.1.1.1 0 0 65410?
> 10.1.1.2/32 127.0.0.1 0 32768 ?
>i 10.3.1.0/24 3.3.3.9 0 100 0 ?
>e 192.168.1.0 10.1.1.1 0 0 65410?
* i 3.3.3.9 0 100 0 65420?
Route distinguisher: 200:1
Total number of routes: 2
Network NextHop MED LocPrf PrefVal Path/Ogn
>i 10.3.1.0/24 3.3.3.9 0 100 0 ?
>i 192.168.1.0 3.3.3.9 0 100 0 65420?
For command output, see Tabl e 2 6.
Related commands
ip as-path (Layer 3—IP Routing Configuration Guide)
display bgp routing-table vpnv4 community-list
Use display bgp routing-table vpnv4 community-list to display BGP VPNv4 routing information
matching a specified BGP community list.
Syntax
display bgp routing-table vpnv4 [ route-distinguisher route-distinguisher ] community-list
{ { basic-community-list-number | comm-list-name } [ whole-match ] | adv-community-list-number }
Views
Any view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
network-operator
mdc-admin
mdc-operator
Parameters
route-distinguisher route-distinguisher: Specifies an RD, a string of 3 to 21 characters in one of
these formats:
• 16-bit AS number:32-bit user-defined number. For example, 101:3.
• 32-bit IP address:16-bit user-defined number. For example, 192.168.122.15:1.
• 32-bit AS number:16-bit user-defined number, where the minimum value of the AS number is
65536. For example, 65536:1.
basic-community-list-number: Specifies a basic community list by its number in the range of 1 to
99.
73
Page 79

Examples
comm-list-name: Specifies a community list by its name, a case-sensitive string of 1 to 63
characters.
whole-match: Displays routes exactly matching the specified community list. Without this keyword,
the command displays routes whose COMMUNITY attributes comprise the specified community
list.
adv-community-list-number: Specifies an advanced community list by its number in the range of
100 to 199.
# Display BGP VPNv4 routing information matching BGP community list 100.
<Sysname> display bgp routing-table vpnv4 community-list 100
BGP local router ID is 1.1.1.9
Status codes: * - valid, > - best, d - dampened, h - history,
s - suppressed, S - stale, i - internal, e - external
Origin: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Total number of routes from all PEs: 2
Route distinguisher: 100:1(vpn1)
Total number of routes: 6
Network NextHop MED LocPrf PrefVal Path/Ogn
> 10.1.1.0/24 10.1.1.2 0 32768 ?
* e 10.1.1.1 0 0 65410?
> 10.1.1.2/32 127.0.0.1 0 32768 ?
>i 10.3.1.0/24 3.3.3.9 0 100 0 ?
>e 192.168.1.0 10.1.1.1 0 0 65410?
* i 3.3.3.9 0 100 0 65420?
Route distinguisher: 200:1
Total number of routes: 2
Network NextHop MED LocPrf PrefVal Path/Ogn
>i 10.3.1.0/24 3.3.3.9 0 100 0 ?
>i 192.168.1.0 3.3.3.9 0 100 0 65420?
For command output, see Tabl e 2 6.
display bgp routing-table vpnv4 inlabel
Use display bgp routing-table vpnv4 inlabel to display incoming labels for BGP VPNv4 routes.
Syntax
display bgp routing-table vpnv4 inlabel
74
Page 80

Views
Any view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
network-operator
mdc-admin
mdc-operator
Examples
# Display incoming labels for all BGP VPNv4 routes.
<Sysname> display bgp routing-table vpnv4 inlabel
Total number of routes: 2
BGP local router ID is 1.1.1.9
Status codes: * - valid, > - best, d - dampened, h - history,
s - suppressed, S - stale, i - internal, e - external
Origin: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Route distinguisher: 100:1
Total number of routes: 2
Network NextHop OutLabel InLabel
> 10.1.1.0/24 10.1.1.2 NULL 1279
>e 192.168.1.0 10.1.1.1 NULL 1278
Table 28 Command output
Field Description
BGP Local router ID Router ID of the local BGP router.
Status codes Route status codes. See Table 26.
Origin Route origin. See Table 26.
display bgp routing-table vpnv4 outlabel
Use display bgp routing-table vpnv4 outlabel to display ougoing labels for BGP VPNv4 routes.
Syntax
display bgp routing-table vpnv4 outlabel
Views
Any view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
network-operator
75
Page 81

Examples
mdc-admin
mdc-operator
# Display outgoing labels for all BGP VPNv4 routes.
<Sysname> display bgp routing-table vpnv4 outlabel
BGP local router ID is 1.1.1.9
Status codes: * - valid, > - best, d - dampened, h - history,
s - suppressed, S - stale, i - internal, e - external
Origin: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Total number of routes from all PEs: 2
Route distinguisher: 100:1(vpn1)
Total number of routes: 2
Network NextHop OutLabel
>i 10.3.1.0/24 3.3.3.9 1279
* i 192.168.1.0 3.3.3.9 1278
Route distinguisher: 200:1
Total number of routes: 2
Network NextHop OutLabel
>i 10.3.1.0/24 3.3.3.9 1279
>i 192.168.1.0 3.3.3.9 1278
Table 29 Command output
Field Description
BGP Local router ID Router ID of the local BGP router.
Status Route status codes. See Table 26.
Origin Route origin codes. See Table 26.
OutLabel Outgoing label.
display bgp routing-table vpnv4 peer
Use display bgp routing-table vpnv4 peer to display BGP VPNv4 routing information advertised to
or received from a specified BGP peer.
Syntax
display bgp routing-table vpnv4 [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] peer ip-address
{ advertised-routes | received-routes } [ network-address [ mask | mask-length ] | statistics ]
76
Page 82

Views
Any view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
network-operator
mdc-admin
mdc-operator
Parameters
vpn-instance vpn-instance-name: Specifies an MPLS L3VPN instance by its name, a case-sensitive
string of 1 to 31 characters. If no VPN instance is specified, the command displays BGP VPNv4
routing information advertised to or received from the specified BGP peer on the public network.
ip-address: Specifies a peer by its IP address.
advertised-routes: Displays routing information advertised to the specified peer.
received-routes: Displays routing information received from the specified peer.
network-address: Specifies the IP address of the destination network.
mask: Specifies the mask of the destination network, in dotted decimal notation.
mask-length: Specifies a mask length in the range of 0 to 32.
statistics: Displays route statistics.
Usage guidelines
If none of network-address, mask, and mask-length are specified, the command displays all BGP
VPNv4 routing information advertised to or received from the specified BGP peer.
If the network-address argument is specified without mask or mask-length, the system ANDs the
network address with the mask of a route. If the result matches the network address of the route,
the command displays information about the route.
If network-address mask or network-address mask-length is specified, the command displays
information about the route that exactly matches the specified address and mask (or mask length).
Examples
# Display all BGP VPNv4 routing information advertised to BGP peer 3.3.3.9 on the public network.
<Sysname> display bgp routing-table vpnv4 peer 3.3.3.9 advertised-routes
Total number of routes: 2
BGP local router ID is 1.1.1.9
Status codes: * - valid, > - best, d - dampened, h - history,
s - suppressed, S - stale, i - internal, e - external
Origin: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Route distinguisher: 100:1
Total number of routes: 2
Network NextHop MED LocPrf Path/Ogn
77
Page 83

> 10.1.1.0/24 10.1.1.2 0 ?
>e 192.168.1.0 10.1.1.1 0 65410?
# Display all BGP VPNv4 routing information received from BGP peer 3.3.3.9 on the public network.
<Sysname> display bgp routing-table vpnv4 peer 3.3.3.9 received-routes
Total number of routes: 2
BGP local router ID is 1.1.1.9
Status codes: * - valid, > - best, d - dampened, h - history,
s - suppressed, S - stale, i - internal, e - external
Origin: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Route distinguisher: 200:1
Total number of routes: 2
Network NextHop MED LocPrf PrefVal Path/Ogn
>i 10.3.1.0/24 3.3.3.9 0 100 0 ?
>i 192.168.1.0 3.3.3.9 0 100 0 65420?
For command output, see Tabl e 2 6.
# Display statistics for BGP VPNv4 routes advertised to BGP peer 3.3.3.9 on the public network.
<Sysname> display bgp routing-table vpnv4 peer 3.3.3.9 advertised-routes statistics
Advertised routes total: 2
# Display statistics for BGP VPNv4 routes received from BGP peer 3.3.3.9 on the public network.
<Sysname> display bgp routing-table vpnv4 peer 3.3.3.9 received-routes statistic
Received routes total: 2
Table 30 Command output
Field Description
Advertised routes total Total number of routes advertised to the specified peer.
Received routes total Total number of routes received from the specified peer.
display bgp routing-table vpnv4 statistics
Use display bgp routing-table vpnv4 statistics to display BGP VPNv4 route statistics.
Syntax
Views
display bgp routing-table vpnv4 statistics
Any view
78
Page 84

Predefined user roles
network-admin
network-operator
mdc-admin
mdc-operator
Examples
# Display BGP VPNv4 route statistics for the public network.
<Sysname> display bgp routing-table vpnv4 statistics
Total number of routes from all PEs: 2
Route distinguisher: 100:1(vpn1)
Total number of routes: 6
Route distinguisher: 200:1
Total number of routes: 2
display ip vpn-instance
Use display ip vpn-instance to display information about VPN instances.
Syntax
display ip vpn-instance [ instance-name vpn-instance-name ]
Views
Any view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
network-operator
mdc-admin
mdc-operator
Parameters
instance-name vpn-instance-name: Displays information about the specified VPN instance. The
vpn-instance-name is a case-sensitive string of 1 to 31 characters. If no VPN instance is specified,
the command displays brief information about all VPN instances.
Examples
# Display brief information about all VPN instances.
<Sysname> display ip vpn-instance
Total VPN-Instances configured : 1
VPN-Instance Name RD Create time
abc 1:1 2011/05/18 10:48:17
79
Page 85

Table 31 Command output
Field Description
VPN-Instance Name Name of the VPN instance.
RD RD of the VPN instance.
Create Time Time when the VPN instance was created.
# Display detailed information about VPN instance vpn1.
<Sysname> display ip vpn-instance instance-name vpn1
VPN-Instance Name and ID : vpn1, 2
Route Distinguisher : 100:1
Description : vpn1
Interfaces : GigabitEthernet3/0/2
Ipv4-family:
Export VPN Targets :
2:2
Import VPN Targets :
3:3
Export Route Policy : outpolicy
Import Route Policy : inpolicy
Tunnel Policy : tunnel1
Maximum Routes Limit : 5000
Ipv6-family:
Export VPN Targets :
2:2
Import VPN Targets :
3:3
Export Route Policy : outpolicy
Import Route Policy : inpolicy
Tunnel Policy : tunnel1
Maximum Routes Limit : 5000
domain-id
Use domain-id to configure an OSPF domain ID.
Use undo domain-id to restore the default.
Syntax
domain-id domain-id [ secondary ]
undo domain-id [ domain-id ]
Default
The OSPF domain ID is 0.
Views
OSPF view
80
Page 86

Predefined user roles
network-admin
mdc-admin
Parameters
domain-id: OSPF domain ID, in one of these formats:
• Integer, in the range of 0 to 4294967295. For example, 1.
• Dotted decimal notation. For example, 0.0.0.1.
• Dotted decimal notation:16-bit user-defined number in the range of 0 to 65535. For example,
0.0.0.1:512.
secondary: Specifies a secondary domain ID. Without this keyword, the command specifies a
primary domain ID.
Usage guidelines
When you redistribute OSPF routes into BGP, BGP adds the configured OSPF domain ID to the
redistributed BGP VPN routes as a BGP extended community attribute and advertises the routes to
the BGP peer. When you redistribute the BGP VPN routes into OSPF on the BGP peer, OSPF uses the
domain ID to determine whether the routes belong to the same OSPF routing domain. If yes and
the routes are intra-area routes, OSPF advertises these routes in Summary LSAs (Type 3). If yes but
the routes are not intra-area routes, OSPF advertises these routes in AS External LSAs (Type 5) or
NSSA External LSAs (Type 7). If not, OSPF advertises these routes in Type 5 or Type 7 LSAs.
With no parameter specified, the undo domain-id command deletes all domain IDs.
Examples
# Configure an OSPF domain ID.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] ospf 100
[Sysname-ospf-100] domain-id 234
export route-policy
Use export route-policy to apply an export routing policy for a VPN instance.
Use undo export route-policy to remove the application.
Syntax
export route-policy route-policy
undo export route-policy
Default
No export routing policy is applied for a VPN instance.
Views
VPN instance view, IPv4 VPN view, IPv6 VPN view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
mdc-admin
81
Page 87

Parameters
route-policy: Specifies a routing policy by its name, a case-sensitive string of 1 to 63 characters.
Usage guidelines
You can specify an export routing policy to filter advertised routes or modify their route attributes
for the VPN instance.
An export routing policy specified in VPN instance view applies to both IPv4 VPN and IPv6 VPN.
An export routing policy specified in IPv4 VPN view or IPv6 VPN view applies to only IPv4 VPN or
IPv6 VPN.
IPv4/IPv6 VPN prefers the export routing policy specified in IPv4/IPv6 VPN view over the one
specified in VPN instance view.
Examples
# Apply export routing policy poly-1 for VPN instance vpn1.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[Sysname-vpn-instance-vpn1] export route-policy poly-1
# Apply export routing policy poly-2 for IPv4 VPN vpn2.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] ip vpn-instance vpn2
[Sysname-vpn-instance-vpn2] ipv4-family
[Sysname-vpn-ipv4-vpn2] export route-policy poly-2
# Apply export routing policy poly-3 for IPv6 VPN vpn3.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] ip vpn-instance vpn3
[Sysname-vpn-instance-vpn3] ipv6-family
[Sysname-vpn-ipv6-vpn3] export route-policy poly-3
Related commands
• import route-policy
• route-policy (Layer 3—IP Routing Configuration Guide)
ext-community-type
Use ext-community-type to configure the type code of an OSPF extended community attribute.
Use undo ext-community-type to restore the default.
Syntax
ext-community-type { domain-id type-code1 | router-id type-code2 | route-type type-code3 }
undo ext-community-type { domain-id | router-id | route-type }
Default
The type codes for domain ID, router ID, and route type are 0x0005, 0x0107, and 0x0306,
respectively.
Views
OSPF view
82
Page 88

Predefined user roles
network-admin
mdc-admin
Parameters
domain-id type-code1: Specifies the type code for domain ID. Valid values are 0x0005, 0x0105,
0x0205, and 0x8005.
router-id type-code2: Specifies the type code for router ID. Valid values are 0x0107 and 0x8001.
router-type type-code3: Specifies the type code for route type. Valid values are 0x0306 and 0x8000.
Examples
# Configure the type codes of domain ID, router ID, and route type as 0x8005, 0x8001, and 0x8000
for OSPF process 100.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] ospf 100
[Sysname-ospf-100] ext-community-type domain-id 8005
[Sysname-ospf-100] ext-community-type router-id 8001
[Sysname-ospf-100] ext-community-type route-type 8000
import route-policy
Use import route-policy to apply an import routing policy for a VPN instance.
Use undo import route-policy to remove the application.
Syntax
import route-policy route-policy
undo import route-policy
Default
All routes matching the import target attribute are accepted.
Views
VPN instance view, IPv4 VPN view, IPv6 VPN view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
mdc-admin
Parameters
route-policy: Specifies a routing policy by its name, a case-sensitive string of 1 to 63 characters.
Usage guidelines
You can specify an import routing policy to filter received routes or modify their route attributes for
the VPN instance.
An import routing policy specified in VPN instance view applies to both IPv4 VPN and IPv6 VPN.
An import routing policy specified in IPv4 VPN view or IPv6 VPN view applies to only the IPv4 VPN
or IPv6 VPN.
83
Page 89

IPv4/IPv6 VPN prefers the import routing policy specified in IPv4/IPv6 VPN view over the one
specified in VPN instance view.
Examples
# Apply import routing policy poly-1 for VPN instance vpn1.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[Sysname-vpn-instance-vpn1] import route-policy poly-1
# Apply import routing policy poly-2 for IPv4 VPN vpn2.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] ip vpn-instance vpn2
[Sysname-vpn-instance-vpn2] ipv4-family
[Sysname-vpn-ipv4-vpn2] import route-policy poly-2
# Apply import routing policy poly-3 for IPv6 VPN vpn3.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] ip vpn-instance vpn3
[Sysname-vpn-instance-vpn3] ipv6-family
[Sysname-vpn-ipv6-vpn3] import route-policy poly-3
Related commands
• export route-policy
• route-policy (Layer 3—IP Routing Configuration Guide)
ip binding vpn-instance
Use ip binding vpn-instance to associate an interface with a VPN instance.
Use undo ip binding vpn-instance to remove the association.
Syntax
ip binding vpn-instance vpn-instance-name
undo ip binding vpn-instance vpn-instance-name
Default
An interface is associated with no VPN instance and belongs to the public network.
Views
Interface view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
mdc-admin
Parameters
vpn-instance-name: Specifies a VPN instance by its name, a case-sensitive string of 1 to 31
characters.
Usage guidelines
Use the command to associate the VPN instance with the interface connected to the CE.
84
Page 90

This command or its undo form clears the IP address and routing protocol configuration on the
interface. After executing this command or its undo form, use the display this command to view
current configuration and re-configure the IP address and routing protocol on the interface.
The specified VPN instance must have been created by the ip vpn-instance command in system
view.
To associate a new VPN instance with an interface, you must remove the previous association with
the undo ip binding vpn-instance command and then use the ip binding vpn-instance command
to associate the new VPN instance with the interface.
If you configure an IPv6 address for an interface associated with a VPN instance, the number of
VPN instances that you can configure on the device decreases.
Examples
# Associate interface VLAN-interface 1 with VPN instance vpn1.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] interface vlan-interface 1
[Sysname-Vlan-interface1] ip binding vpn-instance vpn1
Related commands
ip vpn-instance (system view)
ip vpn-instance (system view)
Use ip vpn-instance to create a VPN instance and enter VPN instance view.
Use undo ip vpn-instance to delete a VPN instance.
Syntax
ip vpn-instance vpn-instance-name
undo ip vpn-instance vpn-instance-name
Default
No VPN instance is created.
Views
System view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
mdc-admin
Parameters
vpn-instance-name: Specifies the name of the VPN instance, a case-sensitive string of 1 to 31
characters.
Examples
# Create a VPN instance named vpn1.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[Sysname-vpn-instance-vpn1]
85
Page 91

Related commands
route-distinguisher
ipv4-family (VPN instance view)
Use ipv4-family in VPN instance view to enter IPv4 VPN view.
Use undo ipv4-family to remove all configurations from IPv4 VPN view.
Syntax
ipv4-family
undo ipv4-family
Views
VPN instance view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
mdc-admin
Usage guidelines
In IPv4 VPN view, you can configure IPv4 VPN parameters such as inbound and outbound routing
policies.
Examples
# Enter IPv4 VPN view.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[Sysname-vpn-instance-vpn1] ipv4-family
[Sysname-vpn-ipv4-vpn1]
Related commands
ipv6-family (VPN instance view)
ipv4-family vpnv4
Use ipv4-family vpnv4 to enter BGP VPNv4 address family view or BGP-VPN VPNv4 address family
view.
Use undo ipv4-family vpnv4 to remove all settings from BGP VPNv4 address family view or
BGP-VPN VPNv4 address family view.
Syntax
ipv4-family vpnv4
undo ipv4-family vpnv4
Views
BGP view, BGP-VPN view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
86
Page 92

mdc-admin
Usage guidelines
A VPNv4 address comprises an RD and an IPv4 prefix. VPNv4 routes comprise VPNv4 addresses.
For a PE to exchange BGP VPNv4 routes with a BGP peer, you must enable that peer by executing
the peer enable command in BGP VPNv4 address family view or BGP-VPN VPNv4 address family
view.
In BGP VPNv4 address family view, you can configure BGP VPNv4 route attributes, such as the
preferred value, and whether to allow the local AS number to appear in the AS_PATH attribute of
received route updates.
The settings in BGP VPNv4 address family view control VPNv4 route exchange between PEs.
The settings in BGP-VPN VPNv4 address family view control VPNv4 route exchange between
provide PE and provider CE in nested MPLS L3VPN.
Examples
# Enter BGP-VPNv4 address family view.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] bgp 100
[Sysname-bgp] ipv4-family vpnv4
[Sysname-bgp-vpnv4]
# Enter BGP-VPN VPNv4 address family view.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] bgp 100
[Sysname-bgp] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[Sysname-bgp-vpn1] ipv4-family vpnv4
[Sysname-bgp-vpnv4-vpn1]
nesting-vpn
Use nesting-vpn to enable the nested VPN function.
Use undo nesting-vpn to disable the nested VPN function.
Syntax
nesting-vpn
undo nesting-vpn
Default
The nested VPN function is disabled.
Views
BGP-VPNv4 address family view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
mdc-admin
87
Page 93

Usage guidelines
To exchange VPNv4 routes with a peer in nested VPN, you must enable nested VPN and then
execute the peer enable command to enable that peer in BGP VPNv4 view.
Examples
# Enable nested VPN.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] bgp 10
[Sysname-bgp] ipv4-family vpnv4
[Sysname-bgp-vpnv4] nesting-vpn
peer next-hop-invariable
Use peer next-hop-invariable to configure the device to not change the next hop of routes
advertised to an EBGP peer or peer group.
Use undo peer next-hop-invariable to restore the default.
Syntax
peer { group-name | ip-address } next-hop-invariable
undo peer { group-name | ip-address } next-hop-invariable
Default
The device uses its address as the next hop of routes advertised to an EBGP peer or peer group.
Views
BGP VPNv4 address family view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
mdc-admin
Parameters
group-name: Specifies a peer group by its name, a case-sensitive string of 1 to 47 characters.
ip-address: Specifies a peer by its IP address.
Usage guidelines
On an RR in an inter-AS option C scenario, you must configure next-hop-invariable to not change
the next hop of VPNv4 routes advertised to EBGP peers and RR clients.
This command is exclusive with the peer next-hop-local command.
Examples
# In BGP VPNv4 address family view, configure the device to not change the next hop of routes
advertised to EBGP peer 1.1.1.1.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] bgp 100
[Sysname-bgp] ipv4-family vpnv4
[Sysname-bgp-vpnv4] peer 1.1.1.1 next-hop-invariable
88
Page 94

Related commands
peer next-hop-local (Layer 3—IP Routing Command Reference)
peer upe
Use peer upe to configure a BGP peer or peer group as a HoVPN UPE in BGP VPNv4 address family
view.
Use undo peer upe to remove the configuration.
Syntax
peer { group-name | ip-address } upe
undo peer { group-name | ip-address } upe
Default
No BGP peer or peer group is configured as a UPE.
Views
BGP VPNv4 address family view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
mdc-admin
Parameters
group-name: Specifies a peer group by its name, a case-sensitive string of 1 to 47 characters. The
specified peer group must have been created.
ip-address: Specifies a peer by its IP address. The specified peer must have been created.
Usage guidelines
A UPE is a special VPNv4 peer. It can accept one default route for each related VPN instance and
routes permitted by the routing policy on the SPE. An SPE is a common VPN peer.
Examples
# Configure peer 1.1.1.1 as a UPE.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] bgp 100
[Sysname-bgp] ipv4-family vpnv4
[Sysname-bgp-vpnv4] peer 1.1.1.1 upe
peer upe route-policy
Use peer upe route-policy to advertise routes permitted by a routing policy to a UPE.
Syntax
Use undo peer upe route-policy to restore the default.
peer { group-name | ip-address } upe route-policy route-policy-name export
undo peer { group-name | ip-address } upe route-policy route-policy-name export
89
Page 95

Default
No routes are advertised to any peer.
Views
BGP VPNv4 address family view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
mdc-admin
Parameters
group-name: Specifies a peer group by its name, a case-sensitive string of 1 to 47 characters. The
specific peer group must have created.
ip-address: Specifies a peer by its IP address. The specific peer must have created.
route-policy-name: Specifies a routing policy by its name, a case-sensitive string of 1 to 63
characters.
export: Applies the filtering policy to routes to be advertised.
Usage guidelines
This command must be used together with the peer upe command
Examples
# In BGP VPNv4 address family view, configure peer 1.1.1.1 as a UPE and advertise routes permitted
by routing policy hope to peer 1.1.1.1.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] bgp 100
[Sysname-bgp] peer 1.1.1.1 as-number 200
[Sysname-bgp] ipv4-family vpnv4
[Sysname-bgp-vpnv4] peer 1.1.1.1 enable
[Sysname-bgp-vpnv4] peer 1.1.1.1 upe
[Sysname-bgp-vpnv4] peer 1.1.1.1 upe route-policy hope export
Related commands
• peer upe
• route-policy (Layer 3—IP Routing Configuration Guide)
policy vpn-target
Use policy vpn-target to enable route target filtering of received VPNv4 routes. Only VPNv4 routes
whose route target attribute matches local import route target attribute are added to the routing
table.
Syntax
Default
Use undo policy vpn-target to disable route target filtering, permitting all incoming VPNv4 routes.
policy vpn-target
undo policy vpn-target
The route target filtering function is enabled for received VPNv4 routes.
90
Page 96

Views
BGP VPNv4 address family view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
mdc-admin
Usage guidelines
In an inter-AS option B scenario, an ASBR-PE must save all incoming VPNv4 routes and advertises
those routes to the peer ASBR-PE. For this purpose, you must execute the undo policy vpn-target
command on the ASBR-PE to disable route target filtering.
Examples
# In BGP VPNv4 address family view, disable route target filtering of received VPNv4 routes.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] bgp 100
[Sysname-bgp] ipv4-family vpnv4
[Sysname-bgp-vpnv4] undo policy vpn-target
refresh bgp vpnv4
Use refresh bgp vpnv4 to soft reset BGP VPNv4 connections.
Syntax
refresh bgp { ip-address | all | external | group group-name | internal } { export | import } vpnv4
[ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ]
Views
User view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
mdc-admin
Parameters
ip-address: Soft resets the BGP VPNv4 connection with the BGP peer identified by this IP address.
all: Soft resets all BGP VPNv4 connections.
external: Soft resets EBGP VPNv4 connections.
group group-name: Soft resets BGP VPNv4 connections with the BGP peer group identified by this
name, a case-sensitive string of 1 to 47 characters.
internal: Soft resets IBGP VPNv4 connections.
export: Soft resets outbound EBGP VPNv4 connections.
import: Soft resets inbound EBGP VPNv6 connections.
vpn-instance vpn-instance-name: Soft resets BGP VPNv4 connections for the VPN instance
specified by its name, a case-sensitive string of 1 to 31 characters. If no VPN instance is specified,
this command soft resets BGP VPNv4 connections for the public network.
91
Page 97

Usage guidelines
Soft reset can update BGP VPNv4 routing information without breaking down BGP neighbor
relationships.
You can apply a new route selection policy by executing this command. If you execute this
command with the export keyword, BGP filters advertised routing information based on the new
policy and sends the matching routes to the BGP peer. If you execute this command with the
import keyword, BGP advertises a route-refresh message to the peer so the peer re-advertises its
routing information. After receiving the routing information from the peer, BGP filters the routing
information by using the new policy.
This command requires that both the local router and the peer support route refresh.
If the peer keep-all-routes command is configured, the refresh bgp vpnv4 import command does
not take effect.
Examples
# Soft reset all inbound BGP VPNv4 connections for the public network.
<Sysname> refresh bgp all import vpnv4
Related commands
• peer capability-advertise route-refresh (Layer 3—IP Routing Command Reference)
• peer keep-all-routes (Layer 3—IP Routing Command Reference)
reserve-vlan (VPN instance view)
Use reserve-vlan to specify a reserved VLAN for a VPN instance.
Use undo reserve-vlan to restore the default.
Syntax
reserve-vlan vlan-id
undo reserve-vlan
Default
No reserved VLAN is specified for a VPN instance.
Views
VPN instance view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
mdc-admin
Parameters
vlan-id: Specifies a reserved VLAN by its VLAN ID in the range of 1 to 4094.
Usage guidelines
The reserved VLAN of a VPN instance provides resources for the VPN instance to complete packet
forwarding.
92
Page 98

Examples
A common VLAN, including a default VLAN, a VLAN created by vlan, and a dynamically learned
VLAN, cannot be specified as a reserved VLAN. After you specify a VLAN as the reserved VLAN of a
VPN instance, the VLAN cannot be created by the vlan command, or dynamically learned.
Reserved VLANs specified for VPN instances must be different.
The reserved VLAN configuration takes effect only when the system is operating in standard mode.
For more information about system operating modes, see Fundamentals Configuration Guide.
When the system is operating in standard mode, you must configure a reserved VLAN for a created
VPN instance in the following cases:
• The VPN instance is connected to no CEs.
• There is no need to configure the multicast VPN function for the VPN instance.
• There is no need to bind the VPN instance to an IP tunnel.
When the system is operating in standard mode, if a VPN instance is not configured with a reserved
VLAN, you cannot configure URPF on the private network VLAN interface bound to the VPN
instance.
# Specify VLAN 100 as the reserved VLAN of VPN instance vpn1.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] ip vpn-instance vpn1
[Sysname-vpn-instance-vpn1] reserve-vlan 100
Related commands
vlan (Layer 2—LAN Switching Command Reference)
reset bgp vpnv4
Use reset bgp vpnv4 to reset BGP VPNv4 connections.
Syntax
reset bgp { as-number | ip-address | all | external | group group-name | internal } vpnv4
[ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ]
Views
User view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
mdc-admin
Parameters
as-number: Resets BGP VPNv4 connections in the AS specified by its number in the range of 1 to
4294967295.
ip-address: Resets the BGP VPNv4 connection with the BGP peer identified by this IP address.
all: Resets all BGP VPNv4 connections.
external: Resets EBGP VPNv4 connections.
group group-name: Resets BGP VPNv4 connections with the BGP peer group identified by this
name, a case-sensitive string of 1 to 47 characters.
93
Page 99

internal: Resets IBGP VPNv4 connections.
vpn-instance vpn-instance-name: Resets BGP VPNv4 connections for the VPN instance identified by
its name, a case-sensitive string of 1 to 31 characters. If no VPN instance is specified, the command
resets BGP VPNv4 connections for the public network.
Usage guidelines
This command tears down specified BGP neighbor relationships to update BGP VPNv4 routes with
the new policy.
Examples
# Reset all BGP VPNv4 connections for the public network.
<Sysname> reset bgp all vpnv4
route-distinguisher (VPN instance view)
Use route-distinguisher to configure an RD for a VPN instance.
Use undo route-distinguisher to remove the RD of a VPN instance.
Syntax
route-distinguisher route-distinguisher
undo route-distinguisher
Default
No RD is specified for a VPN instance.
Views
VPN instance view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
mdc-admin
Parameters
route-distinguisher: RD for the VPN instance, a string of 3 to 21 characters in one of these formats:
• 16-bit AS number:32-bit user-defined number. For example, 101:3.
• 32-bit IP address:16-bit user-defined number. For example, 192.168.122.15:1.
• 32-bit AS number:16-bit user-defined number, where the minimum value of the AS number is
65536. For example, 65536:1.
Usage guidelines
RDs enable VPNs to use the same address space. An RD and an IPv4 prefix comprise a unique VPN
IPv4 prefix.
Examples
To change the RD of a VPN instance, you must delete the RD with the undo route-distinguisher
command, and then use the route-distinguisher command to configure a new RD.
# Configure RD 22:1 for VPN instance vpn1.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] ip vpn-instance vpn1
94
Page 100

[Sysname-vpn-instance-vpn1] route-distinguisher 22:1
route-tag
Use route-tag to configure an external route tag for redistributed VPN routes.
Use undo route-tag to restore the default.
Syntax
route-tag tag-value
undo route-tag
Default
If the AS number is not greater than 65535, the first two octets of the default external route tag are
0xD000 and the last two octets is the local AS number. For example, if the local BGP AS number is
100, the default value of the external route tag is 3489661028. If the AS number is greater than
65535, the default external route tag is 0.
Views
OSPF view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
mdc-admin
Parameters
tag-value: External route tag for redistributed VPN routes, in the range of 0 to 4294967295.
Usage guidelines
If the PE-CE routing protocol is OSPF, the PE redistributes BGP VPNv4 routes received from the peer
PE into the OSPF routing table, and advertises these routes to the locally connected CE through
OSPF. If the routes are advertised to the CE in Type 5 or 7 LSAs, Type 5/7 LSAs must contain the
external route tag. An external route tag can be configured by different commands and has
different priorities. The following lists the commands used to configure the external route tag (in
the descending order of tag priority):
• import-route
• route-tag
• default tag
If the external route tag carried in a Type 5 or 7 LSA received by a PE is the same as the locally
configured external route tag, the PE ignores the LSA in route calculation to avoid routing loops.
HP recommends configuring the same external route tag for PEs in the same area.
An external route tag is not transferred in any BGP extended community attribute. It is only locally
significant and takes effect only on the PEs that receive BGP routes and generate OSPF Type 5 or 7
LSAs.
Examples
You can configure the same external route tag for different OSPF processes.
# In OSPF process 100, set the external route tag for redistributed VPN routes to 100.
<Sysname> system-view
95
 Loading...
Loading...