Page 1

Switch-Pad™ SVR-1 Step Voltage Regulator
Instructions
Installation, Operation, and Maintenance
of SVR-1 Step Voltage Regulators
Howard Industries, Inc.
ISO-9001 Certied
Document No. 2.4.114
Revision: 03
Issued: March, 2012
Copyright © 2012 Howard Industries, Inc.
1
Page 2

Document 2.4.114SVR-1 Step Voltage Regulator
READ THIS IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
Read these instructions carefully and become familiar with the equipment before proceeding with
installation, operation, or maintenance activities. This equipment contains extremely hazardous
voltages. To prevent death, serious personal injury, or equipment damage, all information in these
instructions should be read and observed. Safe use of this equipment is dependent on proper
installation, operation, and maintenance procedures.
Certain information in this manual is marked with the words DANGER, WARNING, or CAUTION, which
indicate hazards.
DANGER indicates an imminently hazardous situation which, if not avoided, will result in death or
serious personal injury, and damage to the equipment.
WARNING indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, may result in death or
serious personal injury, and/or damage to the equipment.
CAUTION indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, may result in minor or
moderate personal injury, and/or damage to the equipment.
No one should attempt to service or perform maintenance activities on the equipment until it has
been effectively de-energized, and all high-voltage and low-voltage bushing terminals have been
properly grounded. Only qualied personnel should install, maintain, and operate this equipment.
Qualied personnel are those who are trained in the installation, maintenance, and operation
of high-voltage equipment, trained in the proper use of personal protective equipment (such as
rubber gloves, safety glasses, protective clothing, hard hats, etc.) and trained in appropriate rst aid
procedures.
The instructions contained herein are intended to be a general guide for the installation, operation
and maintenance of this equipment, when operated in “Usual Service Conditions” as dened in IEEE
Standard C57.15. Features presented herein may not be present in all equipment designs. Standard
and optional features are subject to change without notice.
Although efforts have been made to ensure accuracy and completeness, these instructions do
not address every conceivable application or circumstance that might be encountered. Howard
Industries makes no representation or warranty with respect to, and assumes no responsibility for
the completeness, accuracy, sufciency, or usefulness of, these instructions.
Questions regarding installation, operation, and maintenance of the equipment, particularly when
encountering unusual or special circumstances that may not be sufciently covered by these
instructions, should be directed to the Howard Industries Transformer Division.
These instructions do not cover operation or maintenance of the regulator control unit. Users should
refer to the control manual for information specic to the control unit.
2
Copyright © 2012 Howard Industries, Inc.
Document No. 2.4.114
Issued: March, 2012
Revision: 03
Page 3

Switch-Pad™ SVR-1 Step Voltage Regulator
TAblE OF CONTENTS
Receiving Inspection, Storage, and Handling .......................................................................................................................... 4
Receiving Inspection ............................................................................................................................................................ 4
Handling ................................................................................................................................................................................ 4
Storage .................................................................................................................................................................................. 4
Installation .................................................................................................................................................................................. 5
Introduction .......................................................................................................................................................................... 5
Pre-Installation Checklist ..................................................................................................................................................... 5
Installation Location ............................................................................................................................................................. 6
Mounting ............................................................................................................................................................................... 6
High-Voltage and Grounding Connections .......................................................................................................................... 6
Control Connections ............................................................................................................................................................. 7
Bypass Surge Arrester .......................................................................................................................................................... 7
Lightning Protection ............................................................................................................................................................. 7
Through Fault ........................................................................................................................................................................ 7
50 Hertz Operation .............................................................................................................................................................. 7
Placing a Regulator in Service ................................................................................................................................................. 10
Procedure ............................................................................................................................................................................ 10
Checking for Proper Operation .......................................................................................................................................... 11
Removing a Regulator from Service ...................................................................................................................................... 12
Procedure ........................................................................................................................................................................... 12
Returning a Regulator to Service .................................................................................................................................... 12
Maintenance ........................................................................................................................................................................... 13
General Instructions .......................................................................................................................................................... 13
Operational Checks ........................................................................................................................................................... 13
Insulation Fluid ................................................................................................................................................................... 14
Internal Inspection ............................................................................................................................................................. 14
Vacuum Oil Fill Process ........................................................................................................................................................15
Cooling Fans ....................................................................................................................................................................... 15
External Parts List ................................................................................................................................................................ 16-17
lIST OF FIGURES
Figure 1: Recommended method for lifting regulator ....................................................................................................... 4
Figure 2: Typical regulator nameplate ................................................................................................................................ 5
Figure 3: Cover-mounted terminal block ............................................................................................................................. 6
Figure 4: SVR-1 step voltage regulator .............................................................................................................................. 8
Figure 5: Connection diagram, one SVR-1 regulator in a single-phase system ............................................................... 9
Figure 6: Connection diagram, two SVR-1 regulators in an open delta three-phase system .......................................... 9
Figure 7: Connection diagram, three SVR-1 regulators wye connected in a three-phase four-wire system ................... 9
Figure 8: Connection diagram, three SVR-1 regulators delta connected in a three-phase three-wire system
Figure 9: HI-AMP™ switches .............................................................................................................................................. 10
Figure 10: Connector terminal strip (CTS) ........................................................................................................................ 14
Figure 11: Recommended lifting method for untanking regulator internal assembly .................................................. 15
Figure 12: External parts view ........................................................................................................................................... 16
Document No. 2.4.114
Revision: 03
Issued: March, 2012
Copyright © 2012 Howard Industries, Inc.
........................ 9
3
Page 4
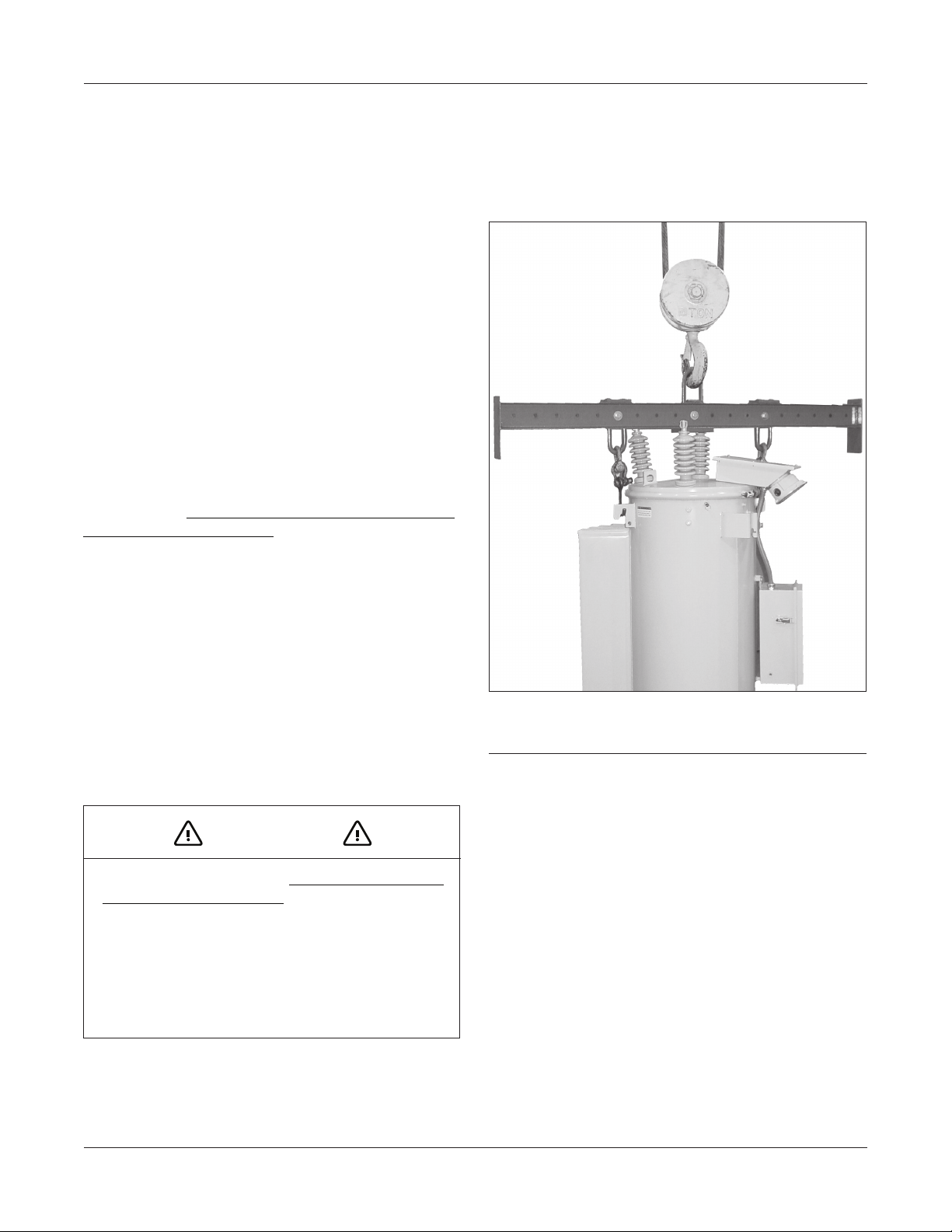
RECEIVING INSPECTION, STORAGE, AND HANDlING
RECEIVING INSPECTION
Immediately upon receipt the regulator should be
carefully inspected for evidence of shipping damage.
The shipping manifest should be checked to make sure
all listed materials have been received. Any damage or
material discrepancies should be noted on the shipping
manifest and a claim should be immediately led with the
freight carrier. Discrepancies should also be brought to
the attention of the Howard Industries Regulator Division.
HANDlING
The regulator can be moved using the lifting lugs on the
sides of the tank and a suitably rated lifting sling. Use of
a spreader bar is also recommended. Figure 1 illustrates
the recommended method for lifting the regulator using
a spreader bar. Do not use the cover-mounted ling eyes
for lifting the entire regulator. Cover-mounted lifting eyes
are to be used only for untanking the internal assembly.
A properly palletized regulator can also be lifted using a
forklift truck or pallet jack having the necessary weight
handling capacity. Refer to the regulator nameplate for
the unit’s weight to determine the suitability of a lifting
device.
Document 2.4.114SVR-1 Step Voltage Regulator
STORAGE
The regulator should be stored in a manner that will
prevent damage. The control cabinet door should be
closed and latched.
WARNING
Falling equipment can cause death, serious personal
injury, or property damage. When lifting the entire
regulator, the tank-mounted lifting lugs must be used.
Do not use the cover-mounted lifting eyes to lift the
entire regulator. Doing so may cause the cover to
fracture or separate completely from the regulator.
Cover-mounted lifting eyes should be used only for
untanking the internal assembly.
FIGURE 1: Recommended method for lifting regulator
using spreader bar
4
Copyright © 2012 Howard Industries, Inc.
Document No. 2.4.114
Revision: 03
Issued: March, 2012
Page 5
Switch-Pad™ SVR-1 Step Voltage Regulator
INSTAllATION
INTRODUCTION
An SVR-1 regulator can regulate the voltage on a singlephase circuit or one phase of a delta- or wye-connected
three-phase circuit as described below and as illustrated
in the connection diagrams on page 9.
One SVR-1 regulator in a single-phase application
Three SVR-1 regulators connected in a grounded wye
conguration on a four-wire three-phase system
Three SVR-1 regulators connected in a delta
conguration on an ungrounded three-wire threephase system
Two SVR-1 regulators connected in an open delta
conguration on an ungrounded three-phase system
WARNING
Due to the possibility of neutral shift, three SVR-1
regulators should not be connected together in an
ungrounded, wye-connected, three-wire, three-phase
system.
PRE-INSTAllATION CHECklIST
Before connecting the regulator, the following checks
should be made:
1. Check the oil level sight gauge for proper oil level (top
oil level visible in gauge). Add ASTM D-3487 Type 2
oil, if the level is found to be low. Check for visible
signs of oil leaks.
2. Measure the dielectric strength of the oil per ASTM
D-877. If found to be below 24 kV, the oil should be
ltered and retested (NOTE: This test is not necessary
if the regulator is being installed immediately after
receipt from the factory.)
3. Measure power factor from each bushing terminal
to tank ground. The reading should be less than 2.0
percent.
4. Inspect the porcelain bushings for damage or signs
of oil leaks. If it is suspected that moisture may have
entered the regulator, test the oil per ASTM D-3487
(Type 2). A positive indication for moisture will require
that the regulator be dried and the oil ltered before
placing into service.
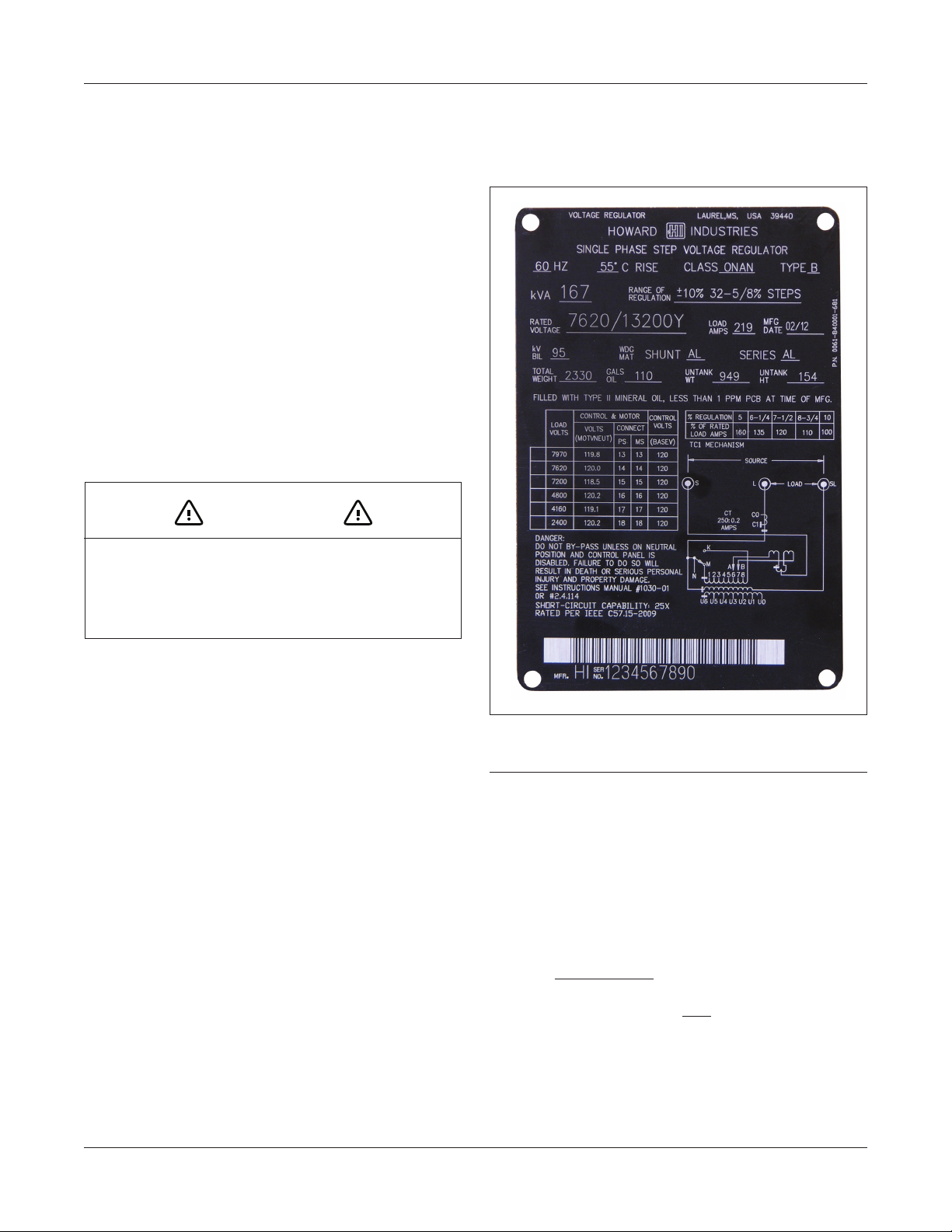
FIGURE 2: Typical regulator nameplate
5. Inspect the by-pass arrester (and shunt arresters, if
present) for damage. Damaged arresters should be
replaced with new arresters of the same voltage rating.
6. Refer to the nameplate (Figure 2) and conrm that
the regulator is connected for the proper output voltage, motor voltage, and control panel voltage. If not,
follow the procedure on pages 6 and 7 to make the
necessary connections.
7. Make absolutely sure that the regulator tap changer
is in the neutral tap position. This can be accomplished by observing that both of the following
conditions have been met: 1) The pointer on the tap
position indicator is pointing to “zero,” and 2) the
neutral indicator is continuously illuminated. (The
control panel can be powered from a 120 Volt external source.)
Document No. 2.4.114
Revision: 03
Issued: March, 2012
Copyright © 2012 Howard Industries, Inc.
5
Page 6

INSTAllATION (Continued)
INSTAllATION lOCATION
SVR-1 regulators are designed for outdoor applications.
Regulators with hanger brackets can be mounted on
utility poles of the proper weight-bearing class. Regulators
supplied with substation bases can be pedestal mounted.
In addition, any regulator can be platform mounted. For
pedestal-mounted substation applications, pedestal
height should be determined by the user to raise the
regulator’s cover-mounted high-voltage connections to a
safe elevation according to applicable codes and utility
installation practices.
DANGER
Document 2.4.114SVR-1 Step Voltage Regulator
When the regulator is energized, extremely dangerous
high voltage is present at the cover-mounted bushing
terminals and at the terminals of the lightning
arresters. Physical contact with or proximity to these
terminals without proper protection will cause death
or serious personal injury, and property damage.
The regulator should be de-energized and properly
grounded before servicing.
MOUNTING
SVR-1 regulators are suitable for mounting on a utility
pole, crossarm platform , or pedestal (optional accessory). Regulators are supplied with either pole-mounting
brackets or station platform base according to the regulator’s capacity rating. Refer to page 4 for handling instructions.
An optional pedestal can be supplied for substation
installations requiring a specic safe clearance below
live terminals. Pedestals are available from the factory in
4-inch height increments, with heights ranging from 21
inches to 49 inches. Regulators should be elevated to
provide adequate vertical clearance to live high-voltage
parts on the regulator cover.
FIGURE 3: Cover-mounted terminal block
1. Identify the “S”, “L”, and “SL” bushings by referring to
the designations embossed on the regulator cover.
The “SL” bushing should be the rst bushing connected. Then connect the “S” bushing to the source
and the “L” bushing to the load. Standard bushing
terminals for the SVR-1 are provided as indicated in
the following table and are suitable for connection
to copper or aluminum conductor. Clamp-type connectors are supplied for nameplate current ratings
through 668 Amps.
150 Amps & below: #8 to 4/0 clamp connector
151–300 Amps:
301–668 Amps:
669–1200 Amps:
1201–2000 Amps: 1-1/2—12 UNF-2A with 4-hole
2. Ground the regulator using the ground provisions
located at the base of the tank. Keep ground leads
as short and direct as possible.
#2 to 477 kCM clamp connector
#2 to 800 kCM clamp connector
1-1/8—12 UNF-2A with 4-hole
spade-9.5 mm (0.375 in) minimum
thickness
spade-12.7 mm (0.5 in) minimum
thickness
Regulator control units can be mounted on the regulator
tank or at a remote point, using an optional extendedlength control cable.
HIGH-VOlTAGE AND GROUND CONNECTIONS
Connect the regulator to the high-voltage system using
the following procedure. Refer to the appropriate connection diagram on page 9 (Figure 5, 6, 7 or 8).
6
Copyright © 2012 Howard Industries, Inc.
DANGER
It is unsafe to service ungrounded or improperly
grounded equipment. Contact or proximity to energized
equipment will cause death or severe personal injury,
and property damage.
Document No. 2.4.114
Revision: 03
Issued: March, 2012
Page 7

Switch-Pad™ SVR-1 Step Voltage Regulator
INSTAllATION (Continued)
CONTROl CONNECTIONS
SVR-1 regulators can be used on several different system
voltages. A cover-mounted terminal block (Figure 3) is
provided, so that control and fan leads (if present) can be
connected as necessary to accommodate the particular
system voltage to be regulated.
SVR-1 regulators may be operated at less than the rated
voltage as indicated on the nameplate. When operated at
less than rated voltage, regulator kVA is reduced, except
when operating a 7.62kV regulator at 7.2kV.
In order to properly connect the control leads, it is
necessary to refer to the control diagram found on the
nameplate (Figure 2). The control diagram will aid in the
identication of the appropriate terminal connections.
Follow the instructions listed below:
1. Referring to the regulator nameplate diagram,
connect the “PS” lead as indicated for the applicable
system voltage.
2. For some regulators the nameplate will indicate a
connection for the “MS” lead. Connect this lead as
indicated.
3. For regulators equipped with cooling fans,
connect fan leads as indicated.
THROUGH FAUlT
SVR-1 regulators are designed to withstand through-fault
currents of 25 times the nameplate rated ONAN current
as described in IEEE Standard C57.15-2009.
In order to limit through-fault current to acceptable levels
as described above, the user should consider the application of additional source impedance, bus sectionalizing,
or other methods.
50 HERTZ OPERATION
Regulators can be modied at factory for 50 Hertz
operation with appropriate derating of voltage. Contact
the Howard Industries Regulator Division for information
about regulators specically designed for 50 Hertz.
operation.
bY-PASS SURGE ARRESTER
Each SVR-1 regulator is equipped with an appropriately
sized by-pass surge arrester connected between the
“S” and “L” high-voltage bushing terminals. This by-pass
arrester (sometimes refered to as the “series arrester”)
is provided to protect the series winding of the regulator
from damage due to line surges. The by-pass arrester
does not provide complete lightning protection for the
regulator. Improved lightning protection can be provided
as described below. Refer to the connection diagrams on
page 9.
lIGHTNING PROTECTION
Lightning protection can be provided by adding appropriately sized surge arresters to the “S” and “L” bushing terminals. These arresters (called “shunt arresters”) should
be mounted on the regulator tank adjacent to both the
“S” and “L” bushings using the supplied mounting provisions. The top lead of each arrester should be connected
to the adjacent bushing terminal. Arrester grounding is
achieved through the arrester mounting brackets. Refer
to the connection diagrams on page 9.
Document No. 2.4.114
Revision: 03
Issued: March, 2012
Copyright © 2012 Howard Industries, Inc.
7
Page 8

By-pass arrester (MOV)
Document 2.4.114SVR-1 Step Voltage Regulator
High-voltage terminals (3)
High-voltage bushings (3)
Cover-mounted terminal
block enclosure
HI-AMP™ lower limit
switch (hidden)
Automatic pressure
relief device
Pole mount brackets (2)
Tap position indicator
Oil level sight gauge
Control cable
Control enclosure
Laser-engraved name-
plate
(mounted on
control enclosure)
Internal assembly lifting eyes (2)
HI-Amp™ upper limit
switch
Upper lter press and oil
ll connection
Shunt arrester mounting
provisions (3)
Regulator lifting lugs (2
or 4)
kVA label
Drain valve and oil
sampling device
8
FIGURE 4: SVR-1 step voltage regulator.
Copyright © 2012 Howard Industries, Inc.
Laser-engraved nameplate
(tank-mounted)
Tank grounding provisions (2)
Bolt-down provisions (4)
Document No. 2.4.114
Revision: 03
Issued: March, 2012
Page 9
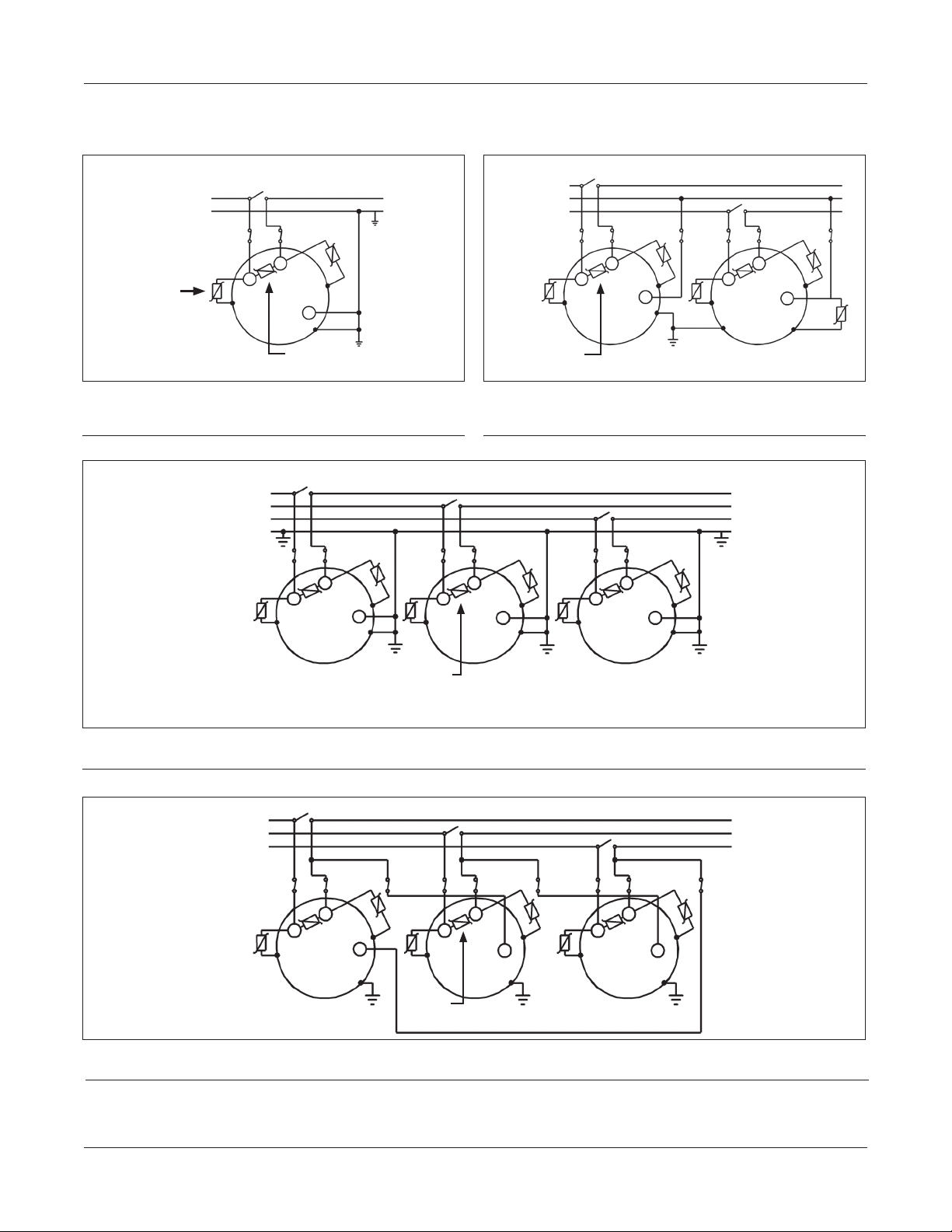
Switch-Pad™ SVR-1 Step Voltage Regulator
CONNECTION DIAGRAMS
FIGURE 5:
Neutral
Shunt
Arrester
Bypass Switch
Disconnects
Disconnects
Shunt
Arrester
SOURCE
S
A
B
C
N
SL
Series Arrester
Bypass Switch*
L
S
SL
LOAD
A
B
C
SOURCE
Disconnects
Series Arrester
Bypass Switch
Bypass Switch
S S
1 2
FIGURE 6: Two SVR-1 regulators in an open delta threephase system.
Bypass Switch*
L
S S
SL SL
Bypass Switch*
L
LOAD
LOAD
LL
SLSL
1 2
Series Arrester
3
FIGURE 7: Three SVR-1 regulators wye connected in a three-phase four-wire system.
Bypass Switch*
L
S
Bypass Switch*
L L
S S
SL SL
Series
Arrester
Bypass Switch*
SL
32
LOAD
Disconnects
Shunt
Arrester
SOURCE
A
B
C
FIGURE 8: Three SVR-1 regulators delta connected in a three-phase three-wire system.
*NOTE: Individual bypass and disconnect switches are shown in the diagrams above. Combination switches are available that perform disconnecting and bypass operations sequentially.
Document No. 2.4.114
Revision: 03
Issued: March, 2012
Copyright © 2012 Howard Industries, Inc.
9
Page 10

PlACING A REGUlATOR IN SERVICE
PROCEDURE FOR PlACING IN SERVICE
After completing the installation procedure outlined in the
previous section, the regulator can be placed into service
using the following procedure.
1. Set HI-AMP™ limits, if necessary, using the rotary
switches located on either side of the position
indicator (Figure 9). The HI-AMP™ feature allows the
SVR-1 regulator to be operated above rated load by
decreasing the range of operation in 1.25 percent
increments. Load current may be increased up to
160 percent of rated current (maximum of 668
Amps) when the regulator is operated at ± 5 percent
regulation. Percentages of current ratings for various
regulation ranges are as follows:
Document 2.4.114SVR-1 Step Voltage Regulator
Voltage Range (%)
±10
±8.75 110
±7.5 120
±6.25
±5 160
All that is necessary to adjust the range of regulation
anywhere from ±5 percent to ±10 percent is to
set the Hi-AMP™ switches to the desired range of
regulation is shown. The upper and lower limits
need not be the same. (Upper and lower limits of
operation can also be implemented with the digital
control unit.)
It is not necessary to remove the regulator from
service to make this adjustment; however, switches
should not be set while the motor is running.
2. Program the control unit as desired. Refer to the
manual supplied with the control unit.
3. Make absolutely certain that the regulator is in
neutral (0) position. Refer to both the position
indicator pointer and the neutral indicator on
the control panel. The position indicator must
point to “zero,” and the neutral indicator must be
continuously illuminated (The control panel can be
powered from a 120 Volt external source.)
4. Turn MAIN POWER and MOTOR CONTROL switches
to “OFF.”
5. Remove motor fuse.
Current Rating (%)
100
135
FIGURE 9: One of two HI-AMP™ switches located on each
side of control position indicator
6. Close the SL disconnect switch (Delta connections
only).
7. Sequentially close the source and then the load
disconnect switches.
8. Open the bypass switch.
9. Visually observe that bypass circuit is open.
10. Replace motor fuse.
11. Switch MAIN POWER switch to “INTERNAL.”
CAUTION
Operation of the regulator to extreme tap positions
can produce a line voltage that is above or below the
desired operating limit of the load.
10
Copyright © 2012 Howard Industries, Inc.
Document No. 2.4.114
Revision: 03
Issued: March, 2012
Page 11

Switch-Pad™ SVR-1 Step Voltage Regulator
PlACING A REGUlATOR IN SERVICE (Continued)
CHECkING FOR PROPER OPERATION
Refer to the control unit instruction manual and use
the following procedure to check for proper regulator
operation. (Switch designations referenced below are
applicable to the HI/ICMI control.)
1. Set the MOTOR CONTROL AUTO/MANUAL switch to
“MANUAL”.
2. Holding the the MOTOR CONTROL RAISE/LOWER
switch in the “LOWER” position, run the regulator in
the lower direction until the control panel LOW BAND
indicator illuminates.
3. Set the MOTOR CONTROL AUTO/MANUAL switch to
the “AUTO” position. After a time delay, the regulator
will automatically return to an IN-BAND condition. The
control panel IN-BAND indicator will illuminate.
4. Set the MOTOR CONTROL AUTO/MANUAL switch to
the “MANUAL” position.
5. Holding the MOTOR CONTROL RAISE/LOWER switch
in the “RAISE” position, run the regulator in the raise
direction until the control panel HIGH BAND indicator
illuminates.
6. Set the MOTOR CONTROL AUTO/MANUAL switch to
the “AUTO” position, After a time delay, the regulator
will automatically return to an IN-BAND condition. The
control panel IN-BAND indicator will illuminate.
Document No. 2.4.114
Revision: 03
Issued: March, 2012
Copyright © 2012 Howard Industries, Inc.
11
Page 12

REMOVING A REGUlATOR FROM SERVICE
The following procedure should be used to remove a
regulator from service. For additional information refer to
the manual supplied with the control unit (Switch desig-
nations referenced below are applicable to the HI/ICMI
control.).
1. Set MOTOR CONTROL AUTO/MANUAL switch to
MANUAL position.
2. Using the MOTOR CONTROL RAISE/LOWER switch,
run the regulator tap changer to the neutral position
as indicated by the tap position indicator dial.
3. Conrm that the regulator is in the neutral position.
The tap position indicator should point to “0”, and
the NEUTRAL LIGHT on the control panel should be
continuously illuminated. Do not proceed unless
both the tap position indicator dial and the NEUTRAL
LIGHT indicate that the regulator is in the neutral
position.
4. Place MOTOR CONTROL switch in the “OFF” position.
5. Remove the MOTOR fuse.
6. Place the MAIN POWER switch in the “OFF” position.
6. Close the bypass switch*.
7. Open the source “S” disconnect switch*.
8. Open the load “L” disconnect switch*.
Document 2.4.114SVR-1 Step Voltage Regulator
DANGER
A regulator must never be by-passed unless it has
rst been placed in the neutral position. By-passing
a regulator not in the neutral position will cause an
internal short circuit and will cause death or serious
personal injury, and property damage
9. Open the source/load “SL” disconnect switch (delta
connections only).
*Note: A combination by-pass/disconnect switch can be
used instead of separate switches to by-pass and disconnect in a sequential operation.
RETURNING A REGUlATOR TO SERVICE
After removing a regulator from service, it can be safely
returned to service according to the procedure discussed
on pages 10 and 11.
12
Copyright © 2012 Howard Industries, Inc.
Document No. 2.4.114
Revision: 03
Issued: March, 2012
Page 13
Switch-Pad™ SVR-1 Step Voltage Regulator
MAINTENANCE
GENERAl INSTRUCTIONS
SVR-1 step voltage regulators are designed for long
life and trouble-free operation. Periodic inspection and
maintenance will prolong life and minimize the likelihood
of service interruptions. Proper operation can be checked
without removing the regulator from service. Follow
the procedures in this section to perform in-service
inspection and maintenance.
The operational life of a regulator will depend somewhat
on the application and environment; hence, the
frequency and scope of maintenance should be tailored
to a regulators specic situation. Regulators subjected
to higher loads and/or more frequent tap changer
operations should be inspected more frequently than
regulators exposed to lighter duty.
In certain situations it might be advisable to periodically
remove a regulator from service for thorough testing and
internal inspection. In addition, anytime an operational
regulator is removed from service for any reason, the
opportunity should be used for testing and a thorough
inspection, following the procedure in the pre-installation
checklist (page 5) at a minimum.
The procedures outlined below are intended to verify
proper operation of the control unit, tap changer
mechanism, HI-AMP™ limiters, and cooling fans (if
present), and to check for tap changer contact wear and
the condition of the insulating uid. Other checks may be
advisable for certain regulators, particularly those serving
special applications or operating in severe environments.
The user should contact Howard Industries Regulator
Division for additional information.
WARNING
OPERATIONAl CHECkS
Periodic operational checks should be performed to verify
proper operation of the control unit, the tap changer
mechanism, and the HI-AMP™ limiters. These checks
can be made while the regulator is in service. Output
voltage should be monitored during the procedure using
a voltmeter connected to the control unit’s test terminals.
The control unit manual should be referenced for further
information.
The following procedure should be followed to check
operation of the control unit, the tap changer mechanism,
and the HI-AMP™ limiters.
1. Referring to control panel indicators, make sure
the regulator is “IN-BAND” and that line drop
compensation is set to zero (Return line drop
compensation to the proper setting after completing
the checklist.).
2. Verify that the voltmeter indicates a voltage within
one-half of the bandwidth tolerance.
3. Place the AUTO/MANUAL switch in the “MANUAL”
position.
4. Using the RAISE/LOWER switch run the tap changer
several steps in either direction, until control panel
indicates an out-of-band condition.
5. Return the AUTO/MANUAL switch to the “AUTO”
position. After a time delay, the control will
automatically return the regulator to an in-band
condition.
6. Repeat steps 3 through 5, but in the opposite
direction.
7. Check operation of the HI-AMP™ limit switches
(located on the either side control position indicator)
by attempting to run the regulator beyond the limits
set by the switches. The limit switches should stop
tap changer operation at the corresponding tap
position.
These maintenance instructions should be followed
to ensure proper and safe regulator operation.
Tampering or maintenance by unqualied personnel
can degrade operational performance and can cause
unsafe conditions that can cause death, serious
personal injury, or property damage.
Document No. 2.4.114
Revision: 03
Issued: March, 2012
Copyright © 2012 Howard Industries, Inc.
CAUTION
Operation of the regulator to extreme tap positions
can produce a line voltage that is above or below the
desired operating limit of the load, causing property
damage.
13
Page 14

MAINTENANCE (Continued)
Document 2.4.114SVR-1 Step Voltage Regulator
If the regulator is not operating properly, the rst step in
troubleshooting should be the replacement of the control
unit with one known to be in good operating condition.
WARNING
Dangerous voltage is present at the Connector
Terminal Strip and the motor capacitor terminals.
Contact with these voltages inside the control
enclosure can cause death or serious personal injury.
“C” – Current transformer positive (+)
“DHR” – Drag hand reset
“L” – Lower
“R” – Raise
“NS” – Neutral switch
“OC” – Operations counter
INSUlATING FlUID
Determine the condition of the insulating uid using the
following procedure:
1. Withdraw a sample of the insulating uid using the
sampling device located in the drain valve at the
bottom of the tank.
2. Measure the dielectric strength of the oil per
ASTM D-877. If found to be below 24 kV, the oil
should be ltered and retested. Other tests such as
“neutralization number,” “interfacial tension,” and
“power factor” are also useful and may be desired by
some users.
3. Add oxidation inhibitor (2,6-ditertiary-butylpara-cresol, DBPC) to the insulation uid at a
concentration of 0.2 to 0.3 percent, to replace
inhibitor that is naturally depleted over a period of a
few years.
FIGURE 10: Connector Terminal Strip (CTS) located in
control enclosure.
The control panel is hinged and may be removed
completely from the regulator control enclosure. It is
not necessary to bypass or de-energize the regulator to
remove the control panel. To remove the control panel,
remove the two wing nuts on the Connector Terminal Strip
(CTS) and disconnect the CTS (Figure 10). The springloaded shorting contacts in the CTS will automatically
maintain the necessary electrical connections to allow
removal and replacement of the control panel without
de-energizing it.
CTS terminal designations are as follows:
“PS” – Panel source
“MS” – Motor source
“G” – Ground
“CO” – Current transformer negative (–)
INTERNAl INSPECTION
Internal inspection, while not absolutely necessary, will
help identify problems that could cause future service
interruptions.
DANGER
Exercise extreme caution when moving the regulator.
Contact with energized overhead lines will cause death,
serious personal injury, and property damage.
1. Untank the regulator using the following procedure:
• Remove the regulator from service as described
on page 12.
• Move the regulator if necessary to provide
adequate working room and the necessary vertical
clearance to lift the internal assembly out of the
tank. Be careful to avoid overhead lines.
• Operate pressure relief valve to vent regulator
14
Copyright © 2012 Howard Industries, Inc.
Document No. 2.4.114
Revision: 03
Issued: March, 2012
Page 15

Switch-Pad™ SVR-1 Step Voltage Regulator
MAINTENANCE (Continued)
before beginning untanking procedures.
• Remove the control cable from the terminal block
enclosure and, if necessary, the control box from
the tank.
• Loosen the cover band and remove it from the
regulator.
• The regulator can now be removed from the main
tank using the cover lifting eyes (Figure 11).
2. Check to verify all hardware and connections are
tight.
3. Check the condition of wire insulation, looking for any
cracks or other deterioration.
4. Inspect the tap changer’s arcing contacts to verify
operational condition. Since numerous factors affect
a contact’s wear rate, no single criteria can be used
to predict a contact’s remaining life and the need to
replace it. Refer to “Maintenance Instructions, TC-1
and TC-2 Load Tap Changer” (Document 2.4.58) and
follow the recommended procedure for inspection
and maintenance of the load tap changer switch
mechanism.
5. Reinstall the regulator’s internal assembly using the
reverse procedure. After the inspection is completed,
the regulator can be safely returned to service
according to the procedure discussed on pages 10
and 11.
FIGURE 11:
VACUUM OIl FIll PROCESS
This procedure applies if the oil level in the regulator has
been lowered to a level that exposes part or all of the
coils to air or the internal assembly has been removed
from the tank.
1. Every container or tote of transformer oil used in
the lling process should be visually inspected and
tested for water or other possible contaminants
before proceeding with the lling process.
2. If the coils are out of oil for more than four hours,
the coils must be baked for at least 24 hours at a
temperature of 100°C (212°F) prior to re-tanking
the internal assembly. The tap changer must not be
exposed to a temperature above 110°C (230°F).
The unit should not be re-baked more than two
times.
3. Connect the vacuum pump suction line to the
pressure-vacuum tting near the top of the tank.
4. Connect the oil ll line to the tank at the bottom drain
valve connection.
5. Start the vacuum pump.
6. When the vacuum level inside the tank reaches 2000
microns (2 Torr) start timing. When this vacuum level
has been maintained for a minimum of 1 hour the oillling may be started.
7. Continue to ll the unit until the oil level lls the sight
glass (25°C oil level).
8. After the oil lling has been completed, continue to
hold the vacuum level for 1 additional hour.
9. If vacuum oil lling is not possible, the re-tanked
internal assembly should be allowed to soak in oil for
at least ve days before energizing.
COOlING FANS
Cooling fans (when present) have sealed bearings and do
not require maintenance.
Document No. 2.4.114
Revision: 03
Issued: March, 2012
Copyright © 2012 Howard Industries, Inc.
15
Page 16
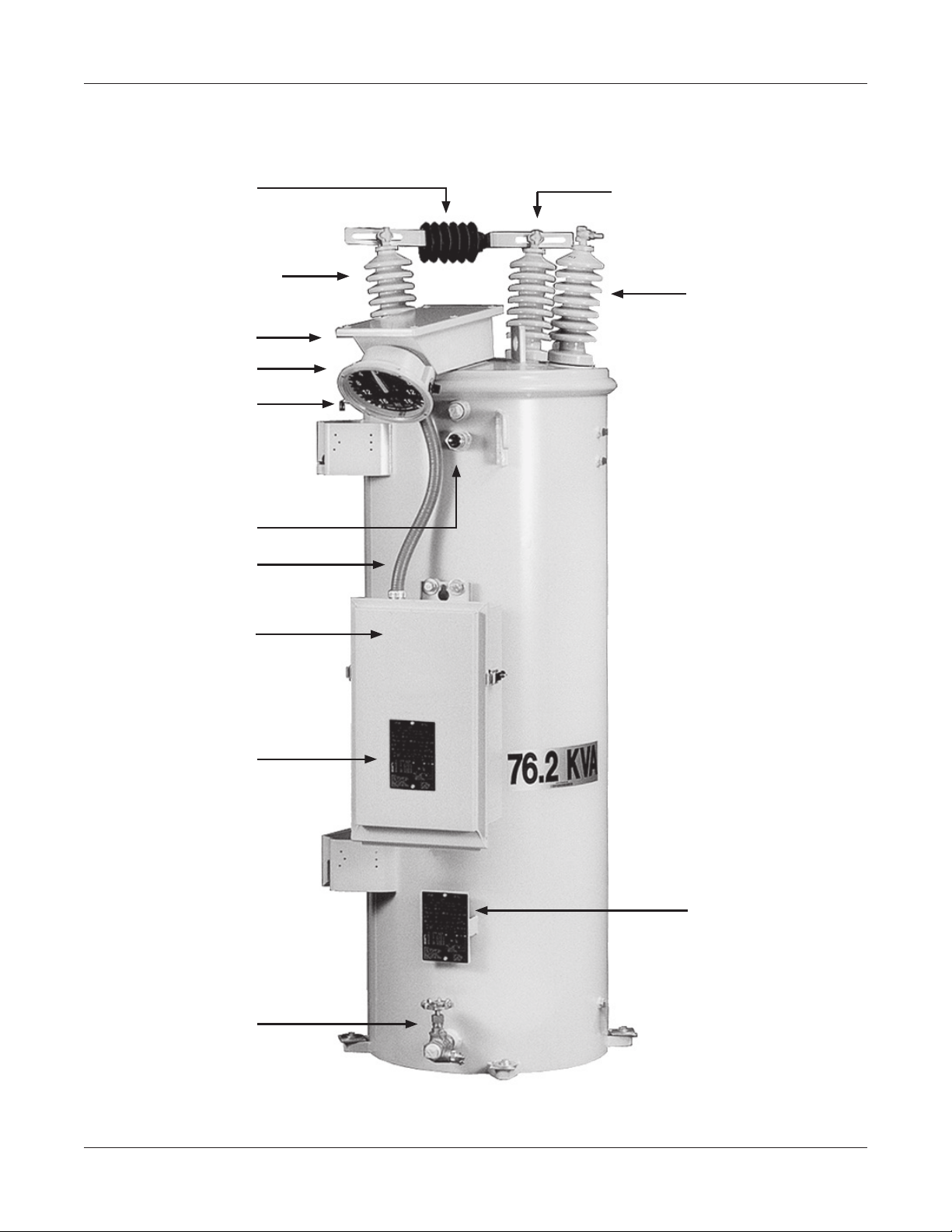
PARTS lIST
Document 2.4.114SVR-1 Step Voltage Regulator
151
163
158
004
057
160
161
020
015
015
16
003
003
060
FIGURE 12: External Parts View - refer to Table 1 on the following page for parts description.
Copyright © 2012 Howard Industries, Inc.
Document No. 2.4.114
Issued: March, 2012
Revision: 03
Page 17

Switch-Pad™ SVR-1 Step Voltage Regulator
PARTS lIST (CONTINUED)
TAblE 1: ExTERNAl PARTS - (Refer to Figure 1 on the previous page)
ITEM DESCRIPTION
REFERENCE
003 Nameplate
004 Pressure Relief Valve
015 Bushing Assembly (“S” or “SL” with standard mounting clamp)
020 Bushing Assembly (“L” with CT mounting clamp)
057 Oil Level Sight Gauge
060 Drain Valve with Sampling Device
151 By-Pass Arrester Assembly
158 Position Indicator
160 Flexible Conduit Assembly
161 Control Enclosure
163 Terminal Block Enclosure
162* Motor Capacitor (located inside control enclosure)
165* Control Panel (located inside control enclosure)
155* Cover Mounted Terminal Block (located inside terminal block)
156* Controller Terminal Strip (male connector, located inside control enclosure)
157* Controller Terminal Strip (female connector, located inside control enclosure)
*Not shown in reference Figure 12
Document No. 2.4.114
Revision: 03
Issued: March, 2012
Copyright © 2012 Howard Industries, Inc.
17
Page 18

Document 2.4.114SVR-1 Step Voltage Regulator
18
SVR-1 Step Voltage Regulator
Installation, Operation, and Maintenance Instructions
Document No. 2.4.114, Revision 3, March 2012
Copyright © 2012 Howard Industries, Inc.
Laurel, Mississippi
Telephone: 601-425-3151
Fax: 601-649-8090
Web howardtransformers.com
Copyright © 2012 Howard Industries, Inc.
Document No. 2.4.114
Revision: 03
Issued: March, 2012
 Loading...
Loading...