
HOTSPOT I 产品使用说明书
产品使用说明书
HOTSPOT I
第 1 页 / 共 18 页

HOTSPOT I 产品使用说明书
WAWRNING
Operator safety is of primary importance! The HOT SPOT
can generate potentially dangerous voltages, particularly if
the internal 80 V limiter fails. Care should be taken to avoid
coming into direct contact with the welder5 s electrodes.
This caution should be exercised for both AC and battery
powered operation. Those familiar with welding will not
have to be reminded of the danger from sparks and sprays of
molten metal. Avoid flammable clothing, inflammable or
explosive material in the area, and wear eye protection
devices. Use in a well ventilated location. Breathing of the
compounds generated by the high temperature welding arc
from the various components of the wire, insulation, and
base materials should be minimized. The internal sealed lead
acid battery may develop explosive hydrogen gas while
charging. This battery contains a corrosive sulfuric acid gel
and should be handled with caution.
警告
操作安全第一!Hotspot 可能产
生危险的电压,特别是内置 80
伏电压限制器失灵时。使用时应
该小心,身体防止与焊接机的电
极直接接触,在交流电源和电池
电源操作时都应该注意该警告。
焊接时注意熔融金属喷溅的火
花,易燃材料和易爆材料不要靠
近焊接区域。焊接时要佩戴护目
设备。在通风条件良好的环境下
使用,以减少操作人员对高温电
弧(来自金属丝、绝缘材料和基
材等成分产生的)产生的混合气
体的吸入。机壳内安装的铅酸电
池在充电时可能产生易爆炸的
氢气,并且该电池里面还含有腐
蚀性的硫酸液体,都应该小心处
理!
第 2 页 / 共 18 页
HOTSPOT I 产品使用说明书
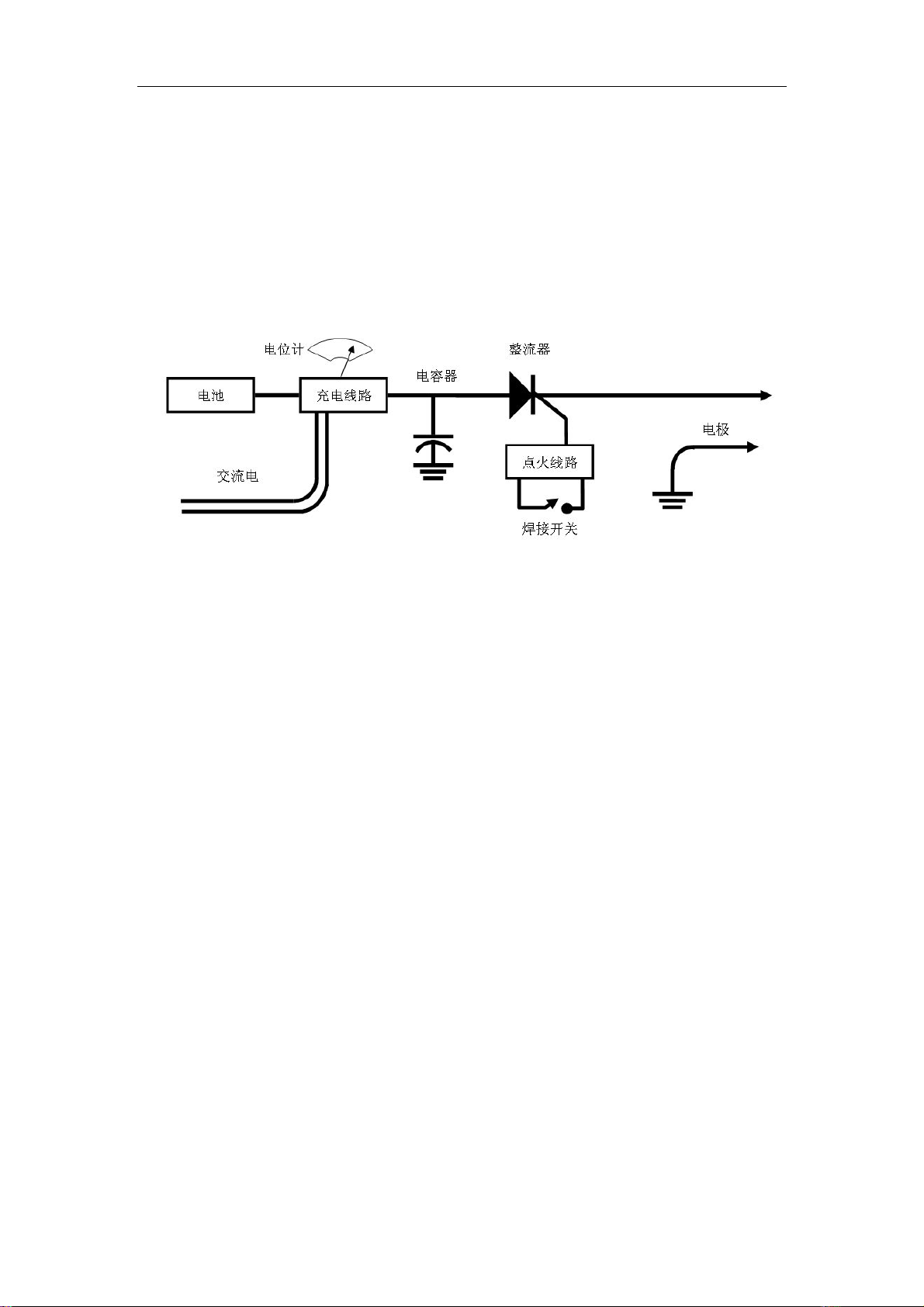
GENERAL DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
The Hot Spot Capacitive Discharge Welder is designed to help solve
your thermocouple fabrication and attachment problems. The welder
generates an electric arc for fusing standard couple elements and
welding them to any thickness base metal. This capability is handled
by the interaction of the various circuit functions shown in the block
diagram below.
The system is powered directly from the AC line through a step-down
transformer, or from a gel type storage battery. The storage battery is
automatically recharged whenever the unit is connected to AC power.
When the Hot Spot is turned on, the capacitor charging circuit charges
the large energy storage capacitor to the level set by the level control.
To perform a weld, the wire to be welded is held in the attachment
pliers, and the magnet electrode is connected to the base material.
With the wire pressed into contact with the base material the operator
depresses the firing switch. This triggers the SCR, discharging the
stored energy through the thermocouple wire and causing an arc
discharge at the contact point with the base material. This arc relea ses
a burst of heat to locally melt both the wire and base, producing a
fusion weld. More will be said about the steps to be taken to produce
good junctions in the other sections of this manual.
Using welded thermocouples solves the couple generation and
attachment problem in one operation. Merging these steps with the
HOT SPOT, generates obvious advantages in the areas of cost,
flexibility, accuracy, and the time required for installation.
第 3 页 / 共 18 页
概述与操作
Hotspot 电容放电焊接机是帮您解决
热电偶制造和焊接的设备。焊接机产生电
弧熔化标准热电偶元件并且把它焊接在
任何厚度的基体金属上。该性能是通过下
图显示的各种电路的相互作用来实现的。
该系统直接由降压变压器提供交流
电,或充电电池提供直流电。当该装置与
交流电源连接时就会自动充电。当打开焊
接机开关时,电容器充电电路会通过大容
量电容器的电位计达到被设定的级别。
为了执行焊接,被焊接的电线放在焊
接钳上,磁体电极和基体材料连在一起。
当电线被熔化与基体材料接触后,操作员
按下点火开关。该操作可以触发半导体整
流器,通过热电偶电线释放储存的能量并
在基体材料触点产生电弧。该电弧释放热
量来熔化导线和基体材料,从而产生熔化
焊接。在该手册的其它部分将会告诉你采
取何种步骤能产生好的接合。
只需一个操作,热电偶焊接就可以解
决热电偶结球和焊接问题。按照热电偶焊
接机操作手册规定的步骤操作,就会发现
它在成本、灵活性、精确性和效率上有明
显的优势。

WHA T YOU WANT , WHEN YOU WANT, WHERE YOU W ANT
您需要什么,什么时候需要,什么地方需要
Maybe you won't get all you want, but the Hot Spot is such a flexible
tool that you're going to find many new ways of making and
employing thermocouples. There's no lack of possible configurations
and attachment schemes. The photographs to the right show some
popular examples.
Many useful types can be formed Butt welds may be made using side
by side, end to end, and crossed or intersecting wires. Third party
junctions, employing another material in addition to the thermocouple
wires, can either incorporate the surface of the end item being sensed
or use a freestanding pad Such junctions will sense temperature at a
single point if a common weld spot is used or will sense an "average"
surface temperature if the welds of the two sensing wires are separated
by a length of intervening base material. However, situations should
generally be avoided where the separation spans material of
non-uniform temperature.
The Hot Spot can also perform simple fastening tasks using steel,
copper, stainless wire or thin plate. When using flat materials in place
of the normal wire, a corner or sharp edge of the flat strip should be
used as the weld point A spot welding mode is also possible. For this a
large round copper rod is held in the pliers’ jaws, and the material to be
welded pressed between the flat end of the rod and the base material.
Sufficient pressure is applied to eliminate arcing and so a "spot weld"
is produced when the circuit is fired. This approach is sometimes
used for attaching thermocouple wires of 30 gauge or finer to a flat
base. With non-standard materials and procedures, the results are
unpredictable and must be determined empirically.
HOTSPOT I 产品使用说明书
也许你不会得到所有你需要的,但是
Hotspot 是灵活的工具,你可以发现很多
新的制作热电偶和使用热电偶的方式。还
有很多可能的外形和配套方案。右边的图
解给你展示了一些通用的焊接例子。
很多型号的热电偶丝都可以通过并
排、首尾相连、交叉或相交来完成接焊接。
第三方接合,除了使用热电偶线外还需要
额外的材料,既可以与被测温部件尾部接
合,也可以使用垫圈连接。常见的结球会
感应到某个点上的温度,如果两根感应线
的焊接被一段距离的基体材料隔断时会
感应到“平均的”表面温度。
使用钢、铜和不锈钢线或薄板,
Hotspot 也能执行简单的固定操作。当用
扁平材料代替焊接线时,拐角或尖缘应作
为熔结点,同时进行点焊方式操作。对于
这个大圆形铜棒,焊接材料应压放在棒的
扁平面。操作时需要充分的压力来减少电
弧,通过线的燃烧来产生焊接点。该方法
有时用来把规格为#30(0.25mm)或更细
的热电偶线焊接在平面上。用非标的材料
和焊接程序,结果是难以预料的,应该根
据经验进行操作。
第 4 页 / 共 18 页

HOW TO
Variations in thermocouple and base materials, the site environment, as
well as the particular style employ ed by the operator, keep capacitive
discharge welding of thermocouple wire an art rather than a science.
The " flash" welding of thermocouples is a fusion or arc welding
process, where enough electrical energy is released at the weld site to
melt the materials being joined The numerous base and thermocouple
materials differ in compatibility with the process and with each other.
Where appearance and mechanical strength are important
considerations, more care will have to be taken in material selection
and operator training
The combination of operator ingenuity and Hot Spot flexibility allows
a wide variety of welded junctions to be produced. The photographs in
this manual illustrate some Hot Spot fabrication techniques and
results. They are provided as a suggestion of the range of possibilities
available to the TC fabricator. The thermocouple weld is produced by
fusing the wires in an arc generating electrical discharge formed
between the ends of the wire pair to be joined and a conductive base
material. Stripped wire pairs should be positioned in the plier electrode
so that each wire is contacted Asymmetrical contact can produce a
distorted bead. Other factors, including wire material, contribute to
bead distortions. If the first firing does not produce the expected result,
multiple discharges using the same junction may help in producing the
desired shape. The pliers holding electrode must grasp the
thermocouple wire firmly and near to the end which is to be welded
( 1/4" to 1/2"). Poor contact with the pliers will allow arcing at the
jaws, which will damage the pliers and the wire, and rob energy from
the intended weld.
HOTSPOT I 产品使用说明书
怎样操作
因热电偶基体材料、操作环境以及操
作员采用热电偶型号的不同,电容放电焊
接热电偶线,结果会有所不同。“闪光”
焊接热电偶是一个熔融或电弧焊接过程,
在焊接点会释放出足够的电能,从而熔化
需要焊接的材料。各种基材和热电偶的适
应各有不同,外形和机械强度是最重要
的,因此在基材选择和操作员培训上应该
特别注意。
操作人员的精明与 HotSpot 的灵活结
合使得多种焊接成为可能。操作手册上的
图解说明了一些 Hotspot 焊接机的制造技
术和效果。它们给热电偶焊接机的各种可
能操作提供了建议和指导。热电偶焊接机
是通过热电偶线末端和导电基体材料之
间产生的放电电弧来熔化热电偶线的。金
属丝热电偶线应该充分与电极接触而达
到完全焊接。非对称的接触会产生弯曲的
焊道。其他的因素,如导线材料也能引起
焊道变形。如果第一次焊接没有达到预期
的效果,那么在同一个接合处的多次放电
将有助于产生预期的形状。钳子的夹持端
必须紧紧夹住热电偶线并且靠近焊接末
端约 1/4 英寸~1/2 英寸(6.35mm~
12.7mm) 。与钳子接触不好会在钳子口
处产生电弧,这样会损坏钳子和热电偶
线,同时还会损耗焊接机的存储电能。
第 5 页 / 共 18 页

Free-standing junctions are produced by holding the paired wires in
the electrode pliers and touching them to the carbon block electrode,
while pushing the Hot Spot firing switch.
dial energy settings may be used as an initial guide for heat level.
However, they should be modified to suit the individual operator,
wire type, and desired result, #30 wire pairs, 20 Watt seconds; #26,
30 Watt seconds; #24,40 Watt seconds; and #20 wire pairs or.#16
single strands, full power. Wires may be welded by pressing the
firing button before or after the wire is in contact with the base.
Pre-firing allows somewhat larger wire to be welded, prepositioning
provides better placement precision. Pre-firing is also frequently
used when forming free-standing junctions with a carbon block (hold
in until contact is made).
The Hot Spot is very useful for welding thermocouples directly to
metal items which will be monitored or to brackets, nuts, bolts,
clamps, etc., which are assembled to such items. Best control and
attachment is obtained if free-standing junctions are first made, and
then "smacked" down to the metal surface (attached to the other
welder wire) while the firing button is depressed Where positioning
is critical, the junction can be held with light pressure (rather than
smacked) against the metal base, and then the firing button pushed
Neither approach is useful when the wires are finer than #26 or #28,
since they will not support the pressure needed to keep them in
contact with the base material during the welding period。
Release of the welding energy instantaneously raises the contact
point between the thermocouple wire and the base metal to the
melting temperature and a fusion weld is formed. Cutting the wires
evenly and to points helps to create the arc and to generate a more
symmetrical junction. A peak current of several thousand amperes
flows during the welding cycle. The circuit between the magnet and
pliers electrodes should be only a few inches in length and the
intervening materials a good conductor (under .01 ohm resistance) so
that excessive energy is not dissipated along this path.
The following calibrated
HOTSPOT I 产品使用说明书
通过把热电偶线夹在带电极的钳子上
并且使它们与碳块电极接触,与此同时按
下热电偶焊接机的点火开关就能产生自动
结球。能量调节旋钮刻度可作为焊接级别
的初始向导。尽管如此,操作员还应根据
电偶线类别、期望效果、焊接线需要的能
量(如#30(20w·s)、#26(30w·s)、#24(40
w·s)、#20 的热电偶线或.#16 的单根丝)
等进行适当的调节,从而便于操作。在热
电偶线与碳块接触之前或之后按点火按钮
就可以进行焊接热电偶线操作了。预焊接
是为了焊接某些大尺寸的电偶线,预先放
置或定位,产生更好的焊接角度。预焊接
也常用在通过碳块结热电偶球过程上(夹
住热电偶线直到球形成)。
Hot Spot 在把热电偶直接焊接到被监
控的金属部件或可以与这些金属部件组装
在一起的支架、螺母、螺钉、夹具上也是
很有用的。如果结球一开始就已经制成,
直接将其与金属表面(或与其他焊接线接
在一块的)碰触,按下点火按钮就可以产
生最好的监控装置。在那些关键的地方可
以使用钳子夹住接合处(而不是碰触)并
且紧靠金属基体, 然后按下点火按钮。当热
电偶线的尺寸比#26 ( 0.4mm )或
#28(0.315mm)还细时,以上的任何一种方法
都不可以使用,因为它们在焊接时没有支
持使它们与基体材料接触所需求的电压。
焊接能量的释放会把热电偶线和基部
材料的接触点的温度升高至熔化温度,然
后产生熔化焊接。把热电偶线对齐剪切好
有助于产生电弧和更对称的焊接。在焊接
周期会产生几千安培的峰值电流。钳子、
磁铁与机器的连接线必需是几英寸长,并
且传导材料的导电性必需很好(0.01 欧姆
以下的电阻),这样的话,额外的能量不会
在线路上被消耗。
第 6 页 / 共 18 页

HOTSPOT I 产品使用说明书
When attaching thermocouples to metal substrates there is no reason
to remove scale, dirt, plating, et cetera from the base metal surface.
Often, the first attempt to weld to a questionable surface will produce
a poorly attached result A second attempt to the same spot will
generally be satisfactory, the first "flash" serving as a surface
conditioner. In most instances on any surface, a second attempt at the
same site will produce a stronger attachment than a weld at a new
site.
The energy released at the weld point depends chiefly on the
resistance of the materials involved, the pressure and area at the
contact, and the stored energy available from the welder. When the
size and type of thermocouple wire or base material are changed,
even the experienced operator should expect some "relearning" to be
necessary. A relatively inexperienced operator should be able to
produce 3 out of 4 acceptable welds. Being a very simple welding
operation, poor welds can easily be corrected immediately.
热电偶附在金属表面上时,没有把金
属表面的氧化层、污垢、镀层和其它物质
清除掉就焊接的话,通常情况下,第一次
在不可靠的表面进行焊接操作会产生差的
焊接结果,但是第二次在同一地点上操作
会得到满意的结果,第一次焊接操作只是
作为金属表面的处理操作。大多数在表面
进行的操作实例说明,第二次在同一地点
进行焊接会产生比在新地点焊接更强的结
合。
在焊接点释放的能量主要由各种材料
的电阻、压强、触点的电弧和焊接机可用
储存的电能决定。当热电偶线或焊接材料
的尺寸和类型发生改变时,即使是有经验
的操作人员也需要进行一些必要的“再学
习”才能处理好该问题。一个相对来说经
验不是很丰富的操作人员在完成 3 到 4 个
焊接后,即可有能接受的焊接点出现。作
为非常简单的焊接操作,差的焊接点也可
以很容易并且快速地修正。
第 7 页 / 共 18 页

ADDITIONAL TECHNIQUES AND CONSIDERATIONS
Freestanding junctions of any fine gage wire, say #26 and above
are easily made. As heavier wires are joined, somewhat more care
must be taken to produce consistent results. Type J wire, probably
the best performer, can be pair-welded in wire sizes as heavy as #
18. Ty pe K can be pair-welded to #20 gage with little trouble and
type E performs similarly. Of the common thermocouple types, T
requires the most care because of the low melting temperature and
electrical resistance of its copper element
wire should be wrapped a turn or more around the constantan,
with the constantan exposed a sixteenth to eighth inch beyond the
copper "ring". One or more flashes will melt the constantan back
to form an "area" junction with the copper ring. This broad weld
will improve the strength of the constantan/ copper junction and
provide a large area pad for welding to third party base materials.
produce relatively flat junctions when welded Improvement in
junction strength and appearance can be obtained by flashing the
junction not only perpendicularly, but additionally at an angle to
either side. Multiple flashing using various angles between the
thermocouple wires and the carbon block is also helpful when
forming heavy wire junctions.
approach is to hold one wire in the jaws of a vice to which one
electrode wire is attached and the other thermocouple wire in the
pliers. The wires are pressed lightly together along the same axis,
and the welder discharged. If the initial weld is weak, break the
junction apart Then holding the jagged ends together, re-weld
them. With some materials, this process will have to be repeated
several times before a satisfactory butt weld is obtained. To reduce
the skill that must be developed to keep the wires coaxial and
touching while the welding arc is melting their contact point, a V
grooved ceramic block or perpendicular pair of rectangular blocks
can be fixtured to provide support.
HOTSPOT I 产品使用说明书
完成的。粗的线结球容易,细的线要小心点
焊接才能达到好的结果。J 型线,可能是最
好的焊接用线,# 18(1mm)粗的都没问题;
K 型线#20(0.8mm)能轻松完成;E 型也是
如此。在常见的热电偶线中,T 型线在操作
时应该小心点,因为它的熔点低,内部的铜
导线的电阻小。
To fabricate # 24 gauge or heavier type T junctions, the copper
型热电偶结,铜丝必需围绕康铜线(热电偶
线的另外一根丝)绕一圈或多圈,把康铜放
在一个距离铜环 16 到 18 英寸的地方。一次
或更多次的焊接将会熔化康铜,使它与铜环
形成一个“区域性”的接合。这种大面积的
焊接会增加康铜与铜接合的强度,从而提供
一个大范围的焊接点来与第三方基体材料
焊接。
High temperature thermocouple elements like platinum tend to
相对平的结点,垂直地碰触接合处,结点的
强度和外观便可以得到改善。碳块和热电偶
线不同角度的多次碰触,在制作粗的结点时
是有用的。
Large gage wires are most satisfactorily joined by butt welds. One
接合。用夹具夹住焊接线,用钳子夹住热电
偶线,然后把两根线头对头接触,之后按焊
接按钮。如果初始焊接不牢固,那么把接合
处折断,重新焊接,重复以上操作,直到获
得满意的对接焊点。为了减少焊接电弧熔化
结点而造成的对接难度,建议安装一个 V 形
陶瓷块或一对垂直的矩形块来协助焊接。
技术说明和注意事项
热电偶丝结球(#26 或更细),是很容易
为了制作#24(0.5mm)甚至更粗的 T
像铂这样的高温热电偶更趋向于制作
使用对接焊接时,粗线能产生很理想的
第 8 页 / 共 18 页

The Hot Spot Welder can be employed to connect wires which
may be difficult to bond by other means. Welds incorporating
nickel, nichrome, platinum, plated wires and solid/stranded
combinations are facilitated. While these can be butt welded with
some success, it is much easier to pair weld such combinations
and then spread the ends as needed.
Bonding thermocouples to ferrous materials presents few
problems. One should keep in mind the tremendous leverage
exerted on a thermocouple joint by bending a stiff wire welded
perpendicularly to a surface. Durability of the bond can be
improved by using smaller wire sizes which provide flexibility,
and filleting the joint with some stress relieving cement.
Bonding to aluminum, copper, titanium, zinc alloys and other
highly conductive low melting point materials is somewhat more
challenging. Surface bonds on aluminum produce a brittle junction
which is easily separated. Bonds to copper generally result in a
junction poorly attached to the bottom of a crater from which most
of the arc melted material has been expelled A successful
technique for bonding to such metals and alloys is to rap or smack
the thermocouple wires into the surface after the Hot Spot firing
button has been pressed (and held in). This produces some surface
penetration and tends to keep the molten material in the junction
area.The smacking technique can be employed with pre-formed
junctions or in some cases with equal or better success using very
sharply pointed paired wires. Additionally, a widely used approach
for welding wires to difficult base materials is to pass them
through a short stub tube of similar base metal and to weld the
assembly down with the above smacking action.
HOTSPOT I 产品使用说明书
Hotspot 焊接机可用来焊接比较难焊的
线,像镍基合金、铂、镀层的线会比较容易。
这些材料使用对接焊接会比较成功,很容易
成对的完成接合;如果需要的话还可以把末
端分开。
把热电偶丝焊接到含铁材料上也是没
有什么问题的。你应该记住,把丝末端弯曲
结球后,用钳子施加大的压力,然后进行焊
接。为了焊接的牢固,可使用一些尺寸小的
丝,或在接合处填充焊剂来改善其性能。
焊接铝、铜、钛、锌合金和其它的高导
电低熔点材料更富有挑战性。铝产品表面的
焊接容易断开。铜表面焊接一般会产生与基
材接合不牢的情况,大部分被焊接的材料会
脱落。成功焊接这种材料的方法就是在
Hotspot 焊接机点火按钮开启后,用热电偶
线轻击焊接表面,这样的话能使表面焊透并
且使熔融材料固定在焊接处。该轻击可使用
已经接好的球,或削尖的线。另外,使用上
述轻击操作,可把焊接线与各种基体材料焊
接,也可使焊接线穿过短小的管子(材质与
基体材料相同)后再焊接。
第 9 页 / 共 18 页

FLEXIBILITY
Most Hot Spot applications involve simple freestanding junctions or
straightforward grounded welds to ferrous bases. However, the
unique flexibility provided by the Hot Spot offers a number of
possibly useful alternatives. Sensors can be welded into small
diameter tubes to create needle probes. Sensors can be welded to
different fasteners to allow easy attachment and removal from test
specimens. Redundant sensors can be made up of multiple junctions
to hedge against open junction problems. Multiple lead wire
materials could be combined in the same junction to produce
E-J-K-T couples. Single wire junctions could be formed using a
constantan lead and the copper pipe being sensed (check the
calibration). A differential measurement could be obtained using two
constantan wires spaced on the copper pipe (ambient at the
measuring device would have to be subtracted). Heavy thermocouple
wires can be extended with lighter expendable or replaceable
sections. And other non-thermocouple material connections for RTD
leads, heating elements, etcetera, can be made. Think about it. You
may find something that saves time, improve s results, avoids delay s,
or offers a mode of operation previously not considered.
HOTSPOT I 产品使用说明书
灵活性
大多数 Hotspot使用在独立结球和直接
地与基座焊接。但是,Hotspot 焊接机特有
的独特灵活性提供了很多有用的备选方
案。传感元件(热电偶)能焊接到小直径
的管材上,从而形成针形探头。传感元件
也可以焊接到不同的紧固件上,而且可以
随便在测试样品上焊接和拆除。备用的传
感元件可以焊接成多重接合来避免焊接断
开的问题。各种线材能被焊接在同一个接
合处,产生 E-J-K-T 型热电偶。使用康铜导
线和铜管能形成单线结点(查看热电偶分
度表)。使用两根康铜导线与铜管隔开来获
得微差测量结点(周围没有测量装置干
扰)。粗的热电偶线能被拉伸成细的能使用
的或可更换的线。其它的非热电偶材料也
可以焊接电阻式温度检测器、加热元件和
其他配件。思考一下,你可能已经找到了
更节省时间、提高质量、防止延误或一种
原先没有考虑到的操作模式。
第 10 页 / 共 18 页

WARRANTY
DCC warrants to the original purchaser each HOT SPOT to
be free from defects in material and workmanship for the
period of one year from date of delivery. This warranty does
not include the internal storage battery or wear and tear due
to ordinary utilization of the unit. Neither does it cover
damage caused by misuse, negligence or improper supply
voltages. DCC will repair free of charge any units returned to
its factory and deemed by DCC to be defective under this
warranty. DCC shall not be liable for any special or
consequential damages caused directly or indirectly by the
use of the HOT SPOT or performance of this warranty.
SPECIFICATIONS
Size — 3V4" High, 6" Wide, 6W" Deep
Weight— 6% Pounds
Stored Weld Energy — 5 to 50 Watt seconds
Wire Ga uge —Welds wire pairs of #24 gauge or finer (#20
for J, K & E)
Cycle Time — Can perform 5 to 10 welds per minute,
depending on energy setting.
Controls — Provides energy adjustment control, and visual
and audio indication of weld charge cycle completioa
Power — From either 120 VAC 60 HZ lines or self-charging
internal battery. 220 VAC 50 HZ option.
HOTSPOT I 产品使用说明书
保证书
DCC 保证首次购买的 HOTSPOT 焊接机在发
货一年内,材料和生产工艺上没有任何缺陷。该
保证书承认内置充电电池在常规使用后的损耗,
并不保修因错误操作或非正常电源导致的损坏。
DCC 免费维修任何退回工厂的该担保书规定的被
DCC 公司确认为是产品缺陷的设备。DCC 公司不
会承担任何由 HOTSPOT 焊接机由引起的直接或
间接的损失,也不对该保证书的执行情况负责任。
参数
尺寸:高 3 1/4"(83mm),宽 6" (152mm),深 6
1/4"(159mm)
重量:6 1/4 磅(2.8kg)
存储焊接能量:5 ~50 w·s
可焊接线径:可焊接两根#24(Φ0.5mm)或更细的
金属丝,但#20(Φ0.813mm)的 J、K 、E 型热电偶
丝也可焊接。
周期:根据能量设定不同每分钟 5 到 10 个焊接点。
控制:提供能量调节控制旋钮、充电完成时的声
音警报和指示灯
电源:可在直流电或自动充电的蓄电池条件下操
作,充电池充满后能执行上百次焊接,有 120V
60HZ 和 220V 50HZ 两款电源配置可供选择。
第 11 页 / 共 18 页

HOTSPOT I 产品使用说明书
CONTROLS, INDICATORS AND OVERLOAD
PROTECTION
1、 The power control knob:The power level available for
welding is set by the position of the front control knob. This
control also functions as the on/off switch The knob is calibrated
in Watt seconds or Joules. The maximum available power is
approximately 50 Watt seconds. The control actually regulates the
voltage to which the energy storage capacitor is charged The
stored energy is proportional to the square of the voltage, and the
voltage can be varied between 15V and 80 V. Increasing the
setting of the control knob will cause the capacitor to be charged
to the higher level. However, decreasing the setting will not reduce
the value already stored, so a welding cycle will always release an
energy pulse equal to the highest setting since last recent
discharge.
2、Firing switch:When preparing to weld, press and ONLY press
this button to achieve the welding of thermocouple.
3、Incharge LED:When the internal circuitry has charged the
energy storage capacitor to the level set by the control knob, the
front panel LED and internal sounder are activated These inform
the operator that the unit is ready for another weld cycle. The
sounder also helps to conserve battery energy during portable
operation by reminding the operator that the welder had been left
on
4、Welding cable (with washer): Connects to carbon block or
magnetic iron. The cable Length: 1.5m, Diameter: 4mm (#6),
Voltage: 600V Temperature range: -50-105℃.
5、Welding cable (with plier sleeve ): Connects to carbon block
or magnetic iron. The cable Length: 1.5m, Diameter: 4mm (#6),
Voltage: 600V Temperature range: -50-105℃.
6、Double phase AC power cord:A solid state circuit breaker
opens the low voltage AC/DC supply if excessive current is being
drawn. A XA fuse mounted on the internal circuit board is in series
with the AC power cord.
第 12 页 / 共 18 页
控制、显示和超负荷保护
1、能量调节旋钮:此旋钮调节焊接能量,也作为
电源开关使用。这个控制旋钮是以瓦特秒或者是
焦耳来校准的。最大的输出能量大约是 50 瓦特秒。
控制旋钮可将电压值设置到能量电容器充电时的
所需电压。存储能量于电压的平方成正比。电压
值范围在 15 伏~80 伏之间。调整控制旋钮将能量
等级调高电容器的存储量随之变大。然而能量等
级调低后,电容器的存储量数值不会立刻减少,
因此每一个焊接周期继上一次能量释放后都要进
行再一次的释放,其释放能量等于最高存储能量。
2、焊接按钮:当焊接准备好时,点动且仅点动该
按钮实现热电偶的焊接。
3、充电指示灯(发光二极管):当内部线路已经
完成能量储存电容器按旋钮设定的等级完成充电
时,面板的发光二极管会变亮,警报器发出声音。
这些现象告知操作者设备已经准备好下一轮的循
环。警报器在移动操作中会提醒操作者焊接机处
于开启状态从而帮助节省电能。
4、焊接电缆(带连接圈):接碳块或磁铁,1.5 米长,
#6(4mm)粗,(600V,-50-105℃)。
5、焊 接 电 缆 (带钳子连接套筒):接钳子,1.5 米长,
#6(4mm)粗,(600V,-50-105℃)。
6、两相交流电源线:可接 120V 60HZ或 220V 50HZ
电源。线路发生超负荷(输出电流过多)的话,
线路断路器会将电压切到低电压交流或直流线
路。在内部线路板上安装的额定电流为 1/4 安培的
保险丝与交流电源线是串联在一起的,防止电流
过大引起的机器故障。

SYNOPSIS AND REVIEW
提要及回顾
HOTSPOT I 产品使用说明书
Cut the wire to be welded to a sharp
point. This is particularly important
with the heavier wire sizes. For parallel
or pair welding, trim so that both wires
can be in simultaneous contact with the
base metal at time of firing.
Heavy wires can be welded singly to
metal base parts. Lighter wires can be
welded in pairs. Using a carbon block
allows free-standing bead type
junctions to be formed Squeeze pliers
firmly。
Set the energy level control to the
desired value. LED and sonic
indicators will alert operators when
storage capacitor has charged to this
level. Remember, when decreasing
energy setting, that unit will retain last
maximum energy level since
discharge.
Maintain a respect for the high peak
power that can be released by this unit.
Do not operate it without eye
protection. Be sure that all users are
aware of its characteristics and have
been properly instructed. Careless
operation will provide poor results and
can be hazardous to the user.
把焊接线剪成尖锥形状,这
点对于粗丝特别重要。对于
平行焊接或对焊,需要对线
进行修整,这样两根线都可
以在点火后同时和基体金属
接触。
粗线能单独和金属基体部件
焊接在一块。细线能够成对
焊接。使用碳块可以结球焊
接,只需钳子用力挤压。
将能级设成期望值,发光二
极管和声音指示器将会在储
能电容器达到这个级别时提
醒操作人员可以焊接了。记
住,当能量设置降低时,放
电将会保持最后一次设置的
最大能级。
保持对设备释放峰值能量的
警惕。不要在没有防护眼罩
的情况下操作。确信所有的
使用者都明白设备的性能并
且进行了正确的操作指导后
操作。不小心的操作不仅会
产生不好的结果,而且还对
使用者有危险。
第 13 页 / 共 18 页

HOTSPOT I 产品使用说明书
Application Notes…
The combination of operator ingenuity and HotSpot flexibility allows a
wide variety of welded junctions to be produced. Illustrated here are
some HotSpot fabrication techniques and results. They provide a
suggestion of the range of possibilities and are not a definitive set of
weld examples.
●Free standing junctions are produced by holding the paired wires in the
electrode pliers and touching them to the carbon block electrode, after
the HotSpot firing switch has been pushed and continues to be held
in. The following energy settings may be used as an initial guide.
However, they should be modified to suit the individual operator, wire
type, and desired result. #30 wire pairs,20 Watt seconds; #26,30 Watt
seconds; #24,40 watt seconds; #20,50 Watt seconds; #16,100 Watt
seconds; and #14 pairs, 200 Watt seconds.
操作说明
操作人员的精明与热点焊接机的灵活的结合使
得多种焊接接合成为可能。这个操作手册上的图解说
明了一些热点焊接机的制造技术和效果。它们给各种
可能性焊接提供了建议或指导,但这并不是焊接方式
的最终模式。
●通过把热电偶线夹在带电极的钳子上并且使它们
与碳块电极接触,与此同时按一下 HotSpot 的点火开
关并且持续,就能产生结球。同时,已经有的能量设
置,可作为能量级别的参考。通过把热电偶线夹在带
电极的钳子上并且使它们与碳块电极接触,与此同时
按下热电偶焊接机的点火开关就能产生自动结球。能
量调节旋钮刻度可作为焊接级别的初始向导。尽管如
此,操作员还应根据热电偶线类别、期望效果、焊接
线需要的能量(如#30(20w·s)、#26(30w·s)、#24(40
w·s)、#20 的热电偶线或.#16 的单根丝)等进行适当
的调节,从而便于操作。
●Stripped wire pairs should be positioned in the plier electrode so that
each wire is contacted. Asymmetrical contact can produce a distorted
bead. Other factors, including wire material, contribute to bead
distortions. Multiple attempts with the same junction may help in
producing the desired shape.
第 14 页 / 共 18 页
●多根丝的热电偶线,应该保证所有的丝都和钳子接
触,达到充分的焊接。不对称的末端焊接,会使结球
不规则,材料的因素也会引起不规则。但在同一个接
合处的多次放电有助于产生预期的形状。

HOTSPOT I 产品使用说明书
●Junctions which have a quick response and easily attach to plane
surfaces can be made by flattening the bead, after it is formed. The
Function of the bead is to create an identical thermal and electrical
environment at the wire ends. The thermocouple output is not meant to
be produced by the bead, a unique alloy peculiar to that particular
junction, but by the temperature gradient along the wire themselves.
Therefore, the flattening should extend to the wires. For critical
applications, the resulting quick response couple should be compared
against an unmodified bead, since cold working during the'flattening may
effect the calibration. Unacceptable differences can be mitigated by
annealing or heat cycling.
●The HotSpot is very useful for welding thermocouples directly to
metal items which will be monitored or to brackets, nuts, bolts, clamps,
etc., which are assembled to such items. Best control and attachment is
obtained if free standing junctions are first made, and then touched down
to the metal surface (attached to the other welder wire) w hile the firing
button is depressed. Where positioning is critical, the junction can be
held with some slight pressure against the metal base, and then the firing
button pushed. Neither approach is useful when the wires are finer than
#26 or #28 since they will not support the pressure needed to keep them
in contact with the base material during the welding period.
●焊接点要迅速,并且给予压力,焊接点成扁平后,
就能焊接在表面上。热电偶结的功能是在焊接线末端
形成与基体同样的导热和导电环境,热电偶信号并不
是由结点产生的,结点仅仅是一个特殊的合金球,信
号是因为线的温度不同而产生的。因此,压扁的部分
应该与焊接线连接。对于特殊应用,快速形成的热电
偶应该和普通的
校对对比一下,
因为在压扁操作
过程中的冷处理
可能会影响校
准,通过退火或
热循环处理可以
减少差错的发生
●Hot Spot 在把热电偶直接焊接到被监控的金属部件
或可以与这些金属部件组装在一起的支架、螺母、螺
钉、夹具上也是很有用的。如果结球一开始就已经制
成,直接将其与金属表面(或与其他焊接线接在一块
的)碰触,按下点火按钮就可以产生最好的监控装置。
在那些关键的地方可以使用钳子夹住接合处(而不是
碰触)并且紧靠金属基体, 然后按下点火按钮。当热
电偶线的尺寸比#26(0.4mm)或#28(0.315mm)还细时,
以上的任何一种方法都不可以使用,因为它们在焊接
时没有支持使它们与基体材料接触所需求的电压
第 15 页 / 共 18 页

HOTSPOT I 产品使用说明书
●Welding to materials like aluminum, copper, white metal, and brass
that have low melting temperatures and are easily oxidized, can be
facilitated by flushing the welding spot with nitrogen, argon, helium,
carbon dioxide or some similar protective gas. Also, attachment is
improved if the wire is gently "smacked" into the surface after the firing
button is depressed.
●Different physical results will be obtained if the wires are twisted, or
one wrapped around the other. For "T" type junctions, the copper can be
given a turn around the constantan to keep it from melting back too
rapidly from the arc area. Start with the constantan extended beyond the
copper ring a short distance. For welding type "T" to a copper base, first
weld the constantan wire to the base. Then cut off the wire flush with the
surface, and weld a pre-formed junction over the resulting constantan
pad. Wires can be welded to difficult bases by first passing them through
a short stub tube of similar material, and the n welding the assembly to
the base.
●Fine wire thermocouples can be protected by first passing them
through a thin stainless tube and welding the end closed in a grounded
junction configuration. The HotSpot is capable of making needle probes,
using .60" or .90" O.D. tubes. Expectedly, larger tubes whose ends have
been swaged to a smaller diameter for a short distance can be similarly
closed. To protect a simple surface junction, the HotSpot Expansion Kit
includes a utility cement useful to temperatures exceeding 4000 F. This
provides stress protection and some thermal insulation at the
thermocouple attachment point. If unsuccessful in any operation, call
for help.
●焊接那些像铝、铜、白合金、黄铜这些熔点很低、
易于氧化的材料,使用氮气、氩气、氦气、二氧化碳
或一些类似的保护气体,吹洗焊接焊点。同样,如果
在按下点火按钮后,使用焊接线对焊接处表面进行轻
微的“敲击”的话,焊接效果会更好。
●如果焊接线弯曲了或一根线绕在另一根线上的话,
就会得到不同的物理性能。对于“T”型热电偶的结
球,铜能给康铜提供一个回转时间,防止它在电弧区
域快速熔化,只要让康铜线比铜线长出一小段即可。
对于在铜底座上焊接“T”型热电偶来说,先把康铜
线焊接到基体上,然后将焊接线烧红处切断留基体表
面,然后在这个康铜垫上焊
接一个热电偶结。或者,一
开始将焊接线穿过一个与基
体材料材质类似的短管,然
后把组件焊接到基体上,通
过这种方法可把任何的材料
焊接在基体上。
●一开始将细的热电偶线穿入一个细的不锈钢管并
且把结球与不锈钢管末端焊接,封住管,就可以对热
电偶线进行保护了。HotSpot 能制作针形探头,可用
外径为 0.6 英寸或 0.90 英寸的管子。同样,大的管子
在末端封口形成小的末端,也可以进行类似的封口操
作。为了保护简单的表面接合,HotSpot 扩充工具有
一种粘合剂,它在 4000 华氏度的高温环境下特别有
用,也能在热电偶附着点上提供压力保护和热绝缘。
如果在操作上不顺利的话,请打电话给我们,我们给
您提供帮助。
第 16 页 / 共 18 页

HOTSPOT I 产品使用说明书
CAUTION
注意事项
After each discharge, the HotSpot I automatically recharges.
An internal delay of a few seconds between the time the
discharge button is pushed and the start of the recharge cycle
allows the storage capacitors to discharge completely and the
output SCR switches to open (unlatch). A red LED indicator
comes on during the charging cycle.
Some welding conditions (like a dirty contract) extend the
discharge cycle. If the discharge interval is too long, the
charge/discharge cycle can overlap and the internal charging
circuitry may be damaged.
z THE RED CHARGING INDICATOR SHOULD
NEVER BE ON FOR MORE THAN 10 SECONDS
OR DAMAGE MAY RESULT.
z THE PLIERS CIRCUIT SHOULD BE OPENED
AFTER EACH DISCHARGE TO ASSURE THE
OUTPUT CIRCUIT IS OPEN.
z HIGH RESISTANCE DISCHARGE PATHS WHICH
EXTEND THE DISCHARGE INTERVAL SHOULD
BE AVOIDED.
每次放电后,HotSpot I 会自动充电。松开焊
接按钮后,再次充电前会有几秒的间歇,主要是
使储能电容器能彻底放电和断开(拔掉)SCR 输
出开关.。充结束后,一个红色 LED(发光二极
管)会亮起。
一些焊接条件(如:接触面不干净)会延长
放电周期。如果放电时间过长,充电或放电循环
可能重复,就会造成内部充电电路损坏。
z 红色充电指示灯熄灭不应超过 10 秒,否则
可能表明有故障。
z 每次放电后应断开钳子与碳块电极,以保
证输出电路打开,否则会烧毁电路元件。
z 应避免高电阻放电电路延长放电时间。
第 17 页 / 共 18 页

HOTSPOT I 产品使用说明书
Guarantee Clause
1 The length of warranty will last 1 year after the installation.
In the warranty period, when it is normally operated according to
the operational manual, attached note , in case of failure, our
company will be responsible for its maintenance or repair free of
charge.
2. Our company is not responsible for any direct or indirect damage
caused by the failure of our machine or using our machine.
3. The following repair cases will be charged in the warranty
period:
z Fault or damage caused by the improper operation, poor
repair or change.
z Repair and replacement for the wearing parts.
z Fault or damage caused by unintentional drop during the
transportation or movement.
z Fault or damage caused by the earthquake, fire, wind, flood,
thunder and other natural disasters; or caused by the
external factors such as abnormal voltage.
4. Repair cases beyond the length of warranty
If the machine can perform normally after the repair, we will
charge for the repair according to the user’s requirement.
5. After-sales service
Any repair requirement, components purchase and other unclear
points, please consult the suppliers. During the repair, please
inform the following information including name, model,
manufacture number, problem as well as the supplier’s name.
保修条款
1、保修期为收货验收合格之日起 1 年。保修期
内用户根据使用说明书、注意事项,正常使用
的情况下,万一发生故障时,本公司将免费负
责修理。
2、本公司不负责由于本装置的故障或者使用本
装置时所造成的直接或间接的损失。
3、保修期内以下的修理为有偿修理:
z 由于用户在操作上的错误以及不当的修
理或改造而造成的故障或者损坏。
z 易损件的修理和替换。
z 由于用户在运输、移动过程中跌落受冲击
等用户的使用不当而造成的故障或损坏。
z 由于地震、火灾、风水灾害、雷击以及其
它自然灾害,或者由于异常电压等外部因
素造成的故障或损害。
4、超过保修期的修理:修理后可维持本装置性
能的前提下,跟据用户的要求,进行有偿的修
理。
5、有关售后服务:如果有修理的要求、部件的
购买以及其它不清楚的地方,请向各供货商的
销售人员询问。另外,在商量修理时,请告知
购买机器的名称、型号、产品编号、状况以及
供货商名称等信息。
第 18 页 / 共 18 页
 Loading...
Loading...