Page 1

User Manual for
HE–RX371 / HERX371C101
MAN0924-01-EN
Page 2

Page 3

MAN0924-01-EN PREFACE
PREFACE
This manual explains how to use the RX-371 OCS Modules.
Copyright (C) 2009 Horner APG, LLC, 59 South State Avenue, Indianapolis, Indiana 46201. All rights
reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval
system, or translated into any language or computer language, in any form by any means, electronic,
mechanical, magnetic, optical, chemical, manual or otherwise, without the prior agreement and written
permission of Horner APG, Inc.
All software described in this document or media is also copyrighted material subject to the terms and
conditions of the Horner Software License Agreement.
Information in this document is subject to change without notice and does not represent a commitment on
the part of Horner APG.
Cscape, SmartStack, SmartStix and CsCAN are trademarks of Horner APG.
Ethernet is a trademark of Xerox Corporation.
Micro SD and CompactFlash are registered trademarks of Sandisk Corporation.
For user manual updates, contact Technical Support:
North America:
Tel: (+) (317) 916-4274
Fax: (+) (317) 639-4279
Web: www.heapg.com
Email:
techsppt@heapg.com
Europe:
Tel: (+) 353-21-4321-266
Fax: (+) 353-21-4321-826
Web: www.horner-apg.com
Email:
tech.support@hornerapg.com
February 8, 2010 Page 3 of 124 # 1018
Page 4

MAN0924-01-EN PREFACE
LIMITED WARRANTY AND LIMITATION OF LIABILITY
Horner APG, LLC, ("HE-APG") warrants to the original purchaser that the RX-371 OCS
HE-APG is free from defects in material and workmanship under normal use and service. The obligatio n of HE-APG
under this warranty shall be limited to the repair or exchange of a ny part or parts which may prove defective under
normal use and service within two (2) years from the date of manufacture or eighteen (18) months from the date of
installation by the original purchaser whichever occurs first, such defect to be disc losed t o the satisfaction of HE-APG
after examination by HE-APG of the allegedly defective part or parts. THIS WARRANTY IS EXPRESSLY IN LIEU OF
ALL OTHER WARRANTIES EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED INCLUDING THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILIT Y
AND FITNESS FOR USE AND OF ALL OTHER OBLIGATIONS OR LIABILITIES AND HE-APG NEITHER
ASSUMES, NOR AUTHORIZES ANY OTHER PERSON TO ASSUME FOR HE-APG, ANY OTHER LIABILITY IN
CONNECTION WITH THE SALE OF THIS RX-371 OCS
RX-371 OCS
ALTERATION, ABUSE, OR MISUSE. HE-APG MAKES NO WARRANTY WHATSOEVER IN RESPECT TO
ACCESSORIES OR PARTS NOT SUPPLIED BY HE-APG. THE TERM "ORIGINAL PURCHASER", AS USED IN
THIS WARRANTY, SHALL BE DEEMED TO MEAN THAT PERSON FOR WHOM THE RX-371 OCS
ORIGINALLY INSTALLED. THIS WARRANTY SHALL APPLY ONLY WITHIN THE BOUNDARIES OF THE
CONTINENTAL UNITED STATES.
In no event, whether as a result of breach of contract, warranty, tort (including negligence) or otherwise, shal l HEAPG or its suppliers be liable of any special, consequential, incidental or penal damages inclu ding, but not limited to,
loss of profit or revenues, loss of use of the products or any associated equipment, damage to associated equipm ent,
cost of capital, cost of substitute products, facilities, services or replacement power, down time costs, or claims of
original purchaser's customers for such damages.
To obtain warranty service, return the product to your distributor with a description of the problem, proof of
purchase, post paid, insured and in a suitable package.
module OR ANY PART THEREOF WHICH HAS BEEN SUBJECT TO ACCIDENT, NEGLIGENCE,
module. THIS WARRANTY SHALL NOT APPLY TO THIS
module manufactured by
MODULE IS
ABOUT PROGRAMMING EXAMPLES
Any example programs and program segments in t his manual or provided on accompanying diskettes are included
solely for illustrative purposes. Due to the many variables and requirements associated with any particular
installation, Horner APG cannot assume responsibility or liability for actual use based on the examples and diagr ams.
It is the sole responsibility of the system des igner utilizing the RX-37 1 OCS
system, to appropriately integrate the RX-371 OCS
is usual and customary in industrial applications as defined in any codes or standards which apply.
module and to make safety provisions for the end equipme nt as
module to appropriately design the end
Note: The programming examples shown in this manual are for illustrative
purpose only. Proper machine operation is the sole responsibility of the
system integrator.
February 8, 2010 Page 4 of 124 # 1018
Page 5

MAN0924-01-EN PREFACE
Table of Contents
PREFACE..................................................................................................................................................3
For user manual updates, contact Technical Support:..............................................................................3
LIMITED WARRANTY AND LIMITATION OF LIABILITY.........................................................................4
ABOUT PROGRAMMING EXAMPLES.....................................................................................................4
VISUAL MAP OF MAJOR TASKS AND THE KEY CHAPTERS TO ASSIST YOU...................................8
CHAPTER 1 : SAFETY / COMPLIANCE....................................................................................................9
1.1 Safety Warnings and Guidelines...................................................................................................9
1.2 Grounding....................................................................................................................................10
1.3 CE Compliance............................................................................................................................10
CHAPTER 2 : INTRODUCTION................................................................................................................11
2.1 Visual Overview...........................................................................................................................11
2.2 Connectivity to the RX-371..........................................................................................................13
2.3 Detailed Product Descriptions.....................................................................................................13
2.4 Product Specifications......................................................................................................... ........15
2.5 Required and Suggested Accessories........................................................................................15
2.6 Useful Documents and References.............................................................................................16
CHAPTER 3 : MECHANICAL INSTALLATION........................................................................................17
3.1 Overview......................................................................................................................................17
3.2 Mounting Requirements ..............................................................................................................17
3.3. Mounting Orientation...................................................................................................................18
3.4 Panel Cut-Out..............................................................................................................................19
3.5 RX-371 Dimensions.....................................................................................................................19
3.6 Factors Affecting Panel Layout Design and Clearances.............................................................20
3.7 Panel Layout Design and Clearance Checklist...........................................................................21
CHAPTER 4 : ELECTRICAL INSTALLATION.........................................................................................23
4.1 Initial Electrical Installation ..........................................................................................................23
4.2 Grounding Definition....................................................................................................................23
4.3 Ground Specifications .................................................................................................................23
4.4 How to Test for Good Ground .....................................................................................................23
4.5 RX-371 Primary Power Port........................................................................................................24
CHAPTER 5 : SERIAL COMMUNICATIONS ...........................................................................................25
5.1 Overview......................................................................................................................................25
5.2 Port Descriptions .........................................................................................................................25
5.3 Wiring...........................................................................................................................................25
5.4 RS-485 Termination ....................................................................................................................27
5.5 RS-485 Biasing............................................................................................................................27
5.6 Cscape Programming via Serial Port..........................................................................................27
5.7 Ladder-Controlled Serial Communication ...................................................................................27
5.8 Downloadable Serial Communication Protocols .........................................................................28
CHAPTER 6: CAN COMMUNICATIONS................................................................................................. 29
6.1 Overview......................................................................................................................................29
6.2 Port Description...........................................................................................................................29
6.3 CAN (NET1) Port Wiring..............................................................................................................29
6.4 Cscape Programming via CAN....................................................................................................30
6.5 Ladder-Controlled CAN Communication.....................................................................................30
6.6 Using CAN for I/O Expansion (Network I/O) ...............................................................................30
CHAPTER 7: ETHERNET COMMUNICATION.........................................................................................31
7.1 Ethernet Module Protocols and Features....................................................................................31
7.2 Ethernet System Requirements...................................................................................................31
7.3 Ethernet Module Specifications...................................................................................................31
February 8, 2010 Page 5 of 124 # 1018
Page 6

MAN0924-01-EN PREFACE
7.4 Ethernet Module Configuration....................................................................................................31
CHAPTER 8: REMOVABLE MEDIA.........................................................................................................37
8.1 Micro SD Overview......................................................................................................................37
8.1.1 Accessing Files with an RX-371 OCS................................................................................37
8.1.2 Accessing Files with a PC..................................................................................................37
8.2 Removable Media (RM) Function Blocks in Cscape...................................................................37
8.3 Configuring Removable Media Manager graphic object in Cscape............................................38
8.4 Filenames used with the Removable Media (RM) Function Blocks............................................38
8.5 System Registers used with RM..................................................................................................38
CHAPTER 9: SMARTSTACK I/O .............................................................................................................39
9.1 Configuration Procedures............................................................................................................39
CHAPTER 10: SYSTEM SETTINGS AND ADJUSTMENTS....................................................................45
10.1 System Menu - Overview ............................................................................................................45
10.2 System Menu – Navigation and Editing ......................................................................................46
10.3 System Menu – Details................................................................................................................46
10.4 Touch screen calibration .............................................................................................................58
CHAPTER 11: USER INTERFACE............................................................................................................61
11.1 Overview......................................................................................................................................61
11.2 Displaying and entering Data ......................................................................................................61
11.3 Alpha-numeric keypad.................................................................................................................62
11.4 Screen Navigation .......................................................................................................................64
11.5 Ladder Based Screen Navigation................................................................................................65
11.6 Beeper Acknowledgement...........................................................................................................65
11.7 Touch (Slip) Sensitivity................................................................................................................66
11.8 Alarms..........................................................................................................................................66
11.9 Removable Media........................................................................................................................67
11.10 OK and Run Status......................................................................................................................69
11.11 Screen Saver...............................................................................................................................70
11.12 Screen Brightness.......................................................................................................................70
CHAPTER 12: REGISTERS.......................................................................................................................71
12.1 RX-371 Resources......................................................................................................................71
12.1.1 Overview...............................................................................................................................71
12.1.2 Resource Limits ..................................................................................................................71
12.1.3 Resource Definitions ..........................................................................................................72
CHAPTER 13: CSCAPE CONFIGURATION............................................................................................77
13.1 Overview......................................................................................................................................77
13.2 Cscape Status Bar.......................................................................................................................77
13.3 Establishing Communications .....................................................................................................78
13.4 Models supported........................................................................................................................86
13.5 Configuration ...............................................................................................................................86
CHAPTER 14: FAIL–SAFE SYSTEM........................................................................................................ 89
14.1 Overview......................................................................................................................................89
14.2 Settings........................................................................................................................................89
14.3 Backup / Restore Data ................................................................................................................90
14.4 AutoLoad .....................................................................................................................................94
14.5 AutoRun.......................................................................................................................................96
CHAPTER 15: CLONE UNIT.....................................................................................................................97
15.1 Overview......................................................................................................................................97
15.2 Clone ...........................................................................................................................................97
15.3 Load Clone ..................................................................................................................................99
CHAPTER 16: SMTP (EMAIL) PROTOCOL ...........................................................................................101
16.1 Overview....................................................................................................................................101
16.2 Configuration .............................................................................................................................101
16.2.1 Email Configuration...................................................................................................................101
February 8, 2010 Page 6 of 124 # 1018
Page 7

MAN0924-01-EN PREFACE
16.2.2 Email Target Directory Settings.................................................................................................105
16.2.3 Outgoing Emails Settings (SEND): (Emails sent from the controller to Groups) ......................108
16.2.4 Email Status...............................................................................................................................111
CHAPTER 17: MAINTENANCE..............................................................................................................113
17.1 Firmware Updates.....................................................................................................................113
17.2 Backup Battery ..........................................................................................................................113
CHAPTER 18: TROUBLESHOOTING / TECHNICAL SUPPORT..........................................................117
18.1 Connecting to the RX-371.........................................................................................................117
18.1.1 Connecting Troubleshooting Checklist (Serial Port – MJ1/MJ2 Programming).........118
18.1.2 Connecting Troubleshooting Checklist (USB Port - Mini B Programming)................118
18.1.3 Connecting Troubleshooting Checklist (Ethernet port Progra mming).......................118
18.2 Local Controller and Local I/O...................................................................................................118
18.2.1 Local I/O Troubleshooting Checklist...............................................................................119
18.3 CsCAN Network ........................................................................................................................119
18.3.1 CsCAN Network Troubleshooting Checklist..................................................................119
18.4 Removable Media......................................................................................................................120
18.5 Technical Support Contacts ......................................................................................................120
INDEX .......................................................................................................................................................121
TABLE OF FIGURES...............................................................................................................................123
February 8, 2010 Page 7 of 124 # 1018
Page 8
MAN0924-01-EN PREFACE
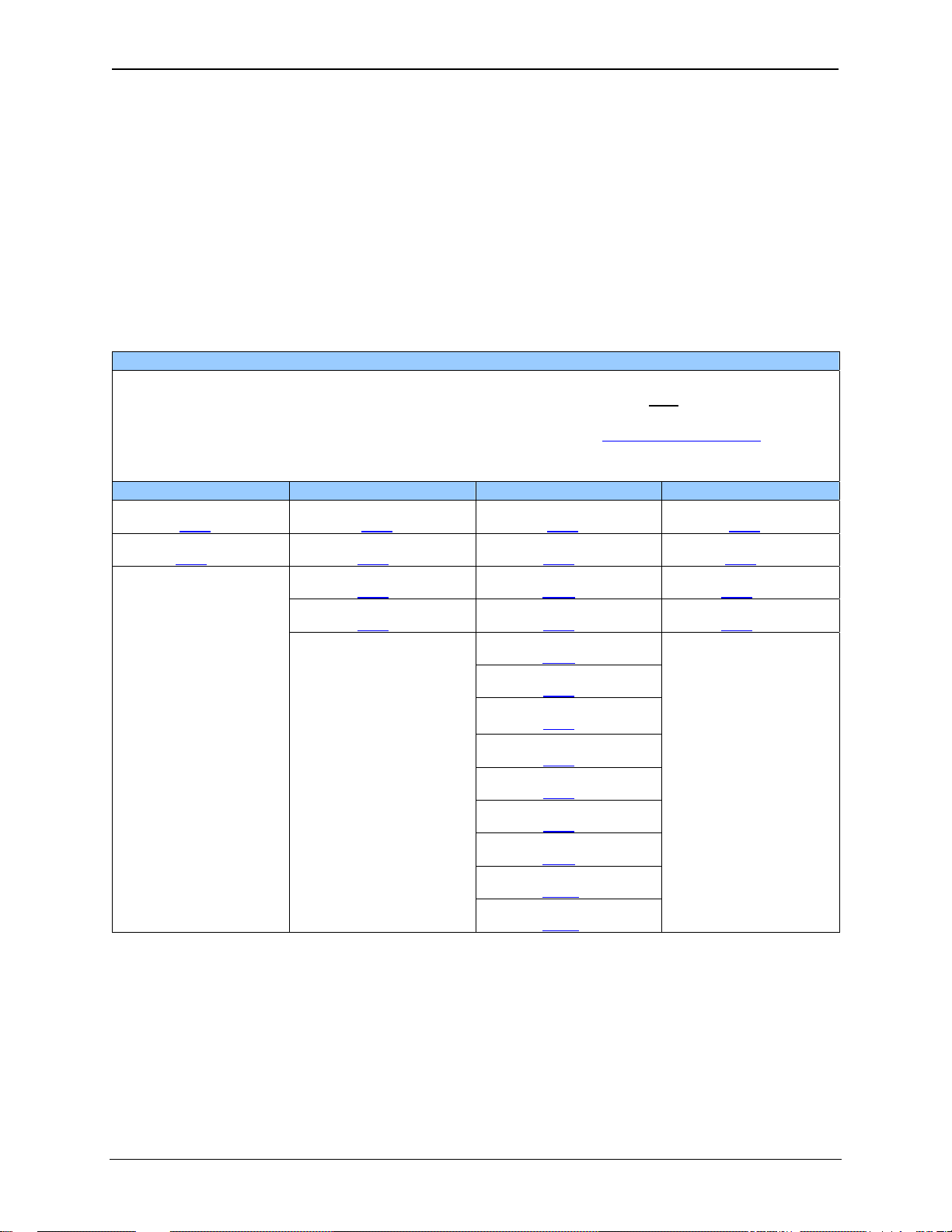
VISUAL MAP OF MAJOR TASKS AND THE KEY CHAPTERS TO ASSIST YOU
The following map is provided to show you the major types of tasks needed to be performed and the key
chapters in this manual you need to refer to for information and help.
Directions: Major tasks are listed at the top of the map with the key chapters listed beneath that you
need to consult in order to perform the tasks.
FIRST STEP of ANY TASK: DATASHEET
Each RX-371 unit is sent with a datasheet in the box. The datasheet is the first
to refer to for model-specific information related to RX-371 models such as pin-outs, jumper
settings, and other key installation information. Visit our website (
http://www.heapg.com/) to obtain
updates to datasheets, manuals and user documentation.
QUICK START INSTALLATION PROGRAMMING TROUBLESHOOTING
Safety / Compliance
page 9
Introduction
page 11
Safety / Compliance
page 9
Introduction
page 11
Mechanical Installation
page 17
Electrical Installation
page 23
Safety / Compliance
page 9
Introduction
page 11
Serial Communication
Page 25
CAN Communications
page 29
Ethernet Communication
Page 31
Removable Media
page 35
System Settings
page 43
User Interface
page 59
Registers
page 69
Cscape Configuration
page 75
Fail- Safe System
Page 87
Clone Unit
Page 95
Email
Page 99
document you need
Safety / Compliance
page 9
Introduction
page 11
Maintenance
page 111
Troubleshooting
page 113
February 8, 2010 Page 8 of 124 # 1018
Page 9
MAN0924-01-EN CH.1
CHAPTER 1: SAFETY / COMPLIANCE
1.1 Safety Warnings and Guidelines
When found on the product, the following symbols specify:
WARNING: EXPLOSION HAZARD: Do not disconnect equipmen t unless power has been sw itched off or
the area is known to be non-hazardous
WARNING: To avoid the risk of electric shock or burns, always connect the safety (or earth) ground
before making any other connections.
WARNING: To reduce the risk of fire, electrical shock, or physical injury it is strongly recommended to
fuse the voltage measurement inputs. Be sure to locate fuses as close to the source as possibl e.
WARNING: Replace fuse with the same type and rating to provide protection against risk of fire and
shock hazards.
WARNING: In the event of repeated failure, do not
defective condition that will not
WARNING: EXPLOSION HAZARD: Substitution of components may impair suitability for Class I, Division
2
WARNING: The USB parts are for operational maintenance only. Do not leave permanently connected
unless area is known to be non-hazardous
WARNING: EXPLOSION HAZARD: BATTERIES MUST ONLY BE CHANGED IN AN AREA KNOWN TO BE
NON-HAZARDOUS
WARNING: Battery May Explode If Mistreated. Do Not Recharge, Disassemble or Dispose Of In Fire
WARNING: Only qualified electrical personnel familiar with the construction and operation of this
equipment and the hazards involved should install, adjust, operate, or service this equipment. Read and
understand this manual and other applicable manuals in their entirety before proceeding. Failure to
observe this precaution could result in severe bodily injury or loss of life.
• All applicable codes and standards need to be followed in the installation of this product.
• For I/O wiring (discrete), use the following wire type or equivalent: Belden 9918, 18 AWG or
Adhere to the following safety precautions whenever any type of connection is made to the module.
• Connect the green safety (earth) ground first before making any other connections.
• When connecting to electric circuits or pulse-initiating equipment, open their related breakers. Do
• Make connections to the module first; then connect to the circuit to be monitored.
• Route power wires in a safe manner in accordance with good practice and local codes.
• Wear proper personal protective equipment including safety glasses and insulated gloves when
• Ensure hands, shoes, and floors are dry before making any connection to a power line.
Warning: Consult user documentation.
clear by replacing the fuse.
larger.
make connections to live power lines.
not
making connections to power circuits.
Warning: Electrical Shock Hazard.
replace the fuse again as a repeated failure indicates a
2/8/2010 Page 9 of 124 # 1018
Page 10
CH.1 MAN0924-01-EN
• Make sure the unit is turned OFF before making connection to terminals. Make sure all circuits
are de-energized before making connections.
• Before each use, inspect all cables for breaks or cracks in the insulation. Replace immediately if
defective.
1.2 Grounding
Grounding is covered in various chapters within this manual.
• For grounding specifications and testing for a good ground, refer to
• For Panel grounding, refer to
section 4.3
section 4.2
1.3 CE Compliance
To check for compliance and updates, visit our website at:
http://www.heapg.com/Pages/TechSupport/ProductCert.html
February 8, 2010 Page 10 of 124 # 1018
Page 11

MAN0924-01-EN CH.2
CHAPTER 2: INTRODUCTION
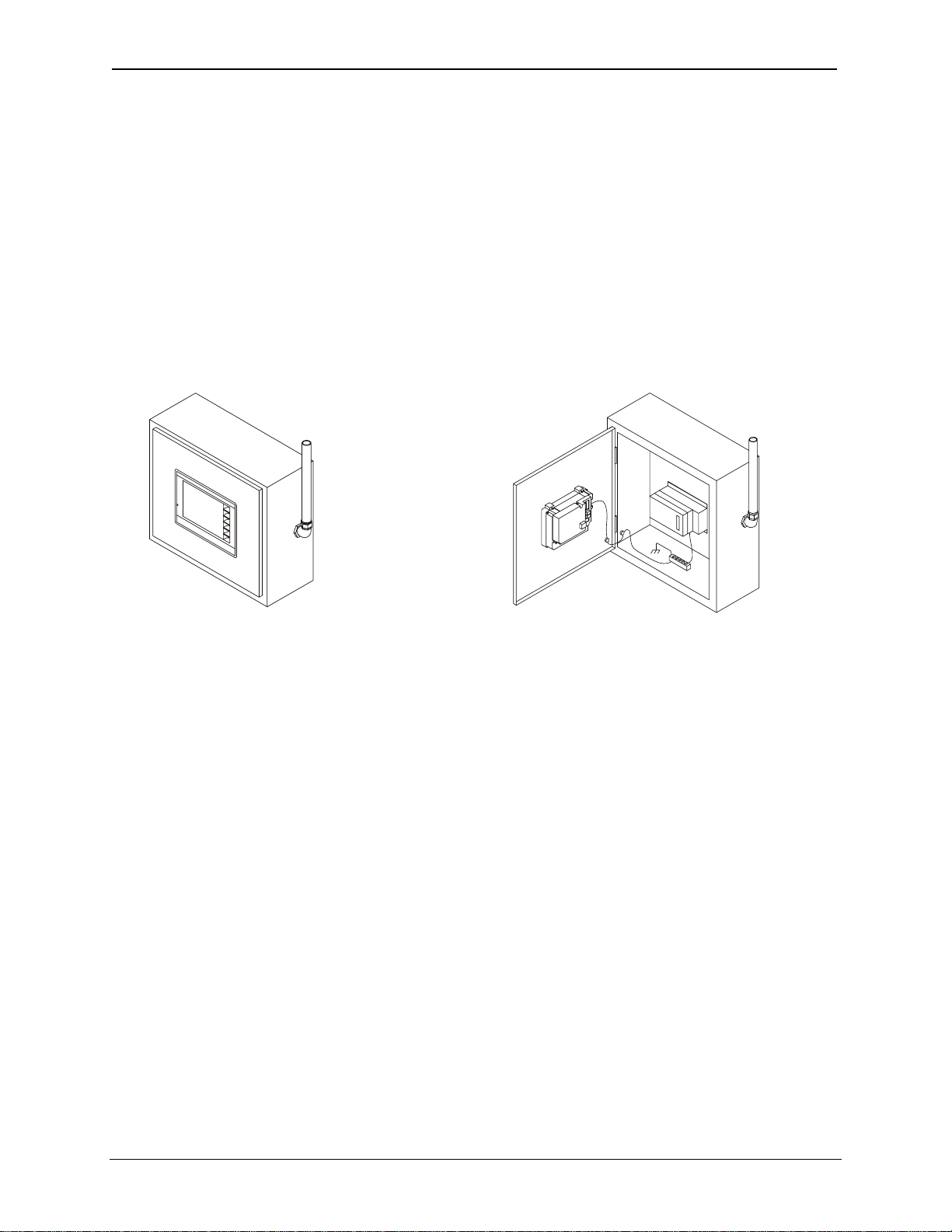
2.1 Visual Overview
The RX-371 OCS provides flexible options allowing you to choose the functionality you need.
User Interface
Front View
Smart Stack
Connector
Back View
February 8, 2010 Page 11 of 124 # 1018
Page 12
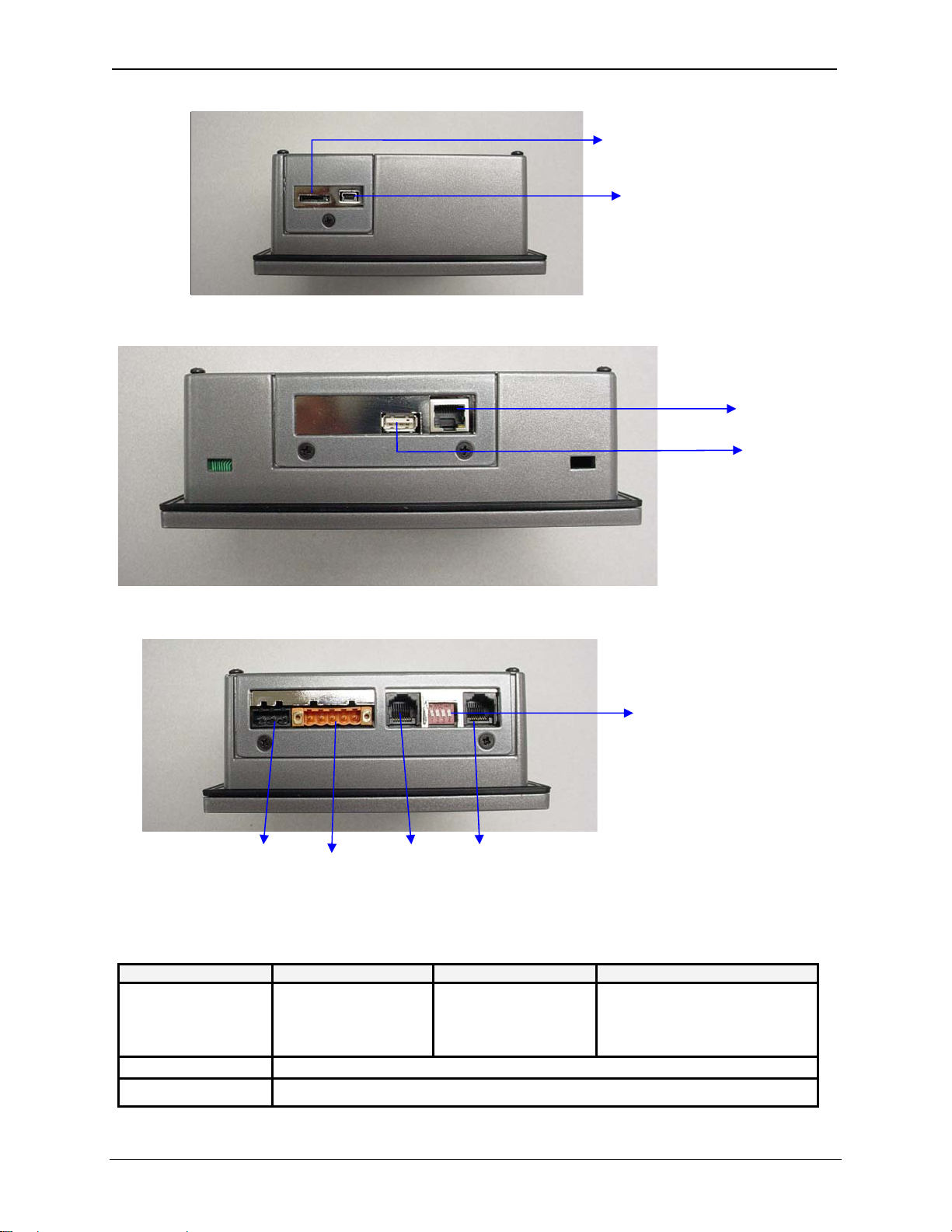
CH. 2 MAN0924-01-EN
Removable Media
USB B
Right Side
Ethernet
USB A
Bottom Side
DIP Switches
Power
CAN
MJ2
MJ1
Left Side
Figure 2.1: Visual Overview of RX-371
RX Model Network Screen Type Standard RX Features
RX-371 On-Board Ethernet
100BaseT
Metal SmartStack Provide a wide variety of I/O options. Requires little space and are easy to install.
SmartStix Modules It is a family of remote I/O products.
February 8, 2010 Page 12 of 124 # 1018
5.7"QVGA TFT
LCD with LED
backlight
Micro SD
2 Serial Ports
Ethernet
USB A & USB B
Page 13
MAN0924-01-EN CH.2
2.1.1 Where to Find Information about the RX-371
a. Datasheets - Refer datasheet for information related to specific model, RX371 is shipped
with MAN0925.
b. User Manual - This manual provides general information of RX-371 models. Visit our website
(
http://www.heapg.com/) to obtain user documentation and updates.
Four main types of information are covered in the manual.
Safety and Installation guidelines / instructions (Mechanical and Electrical)
Descriptions of features
Configuration and Use
Maintenance and Support
2.2 Connectivity to the RX-371
The RX-371 has tremendous capabilities for connecting to a variety of devices. The diagram below shows
some examples of devices that can be used with the RX-371
Other OCS Devices
Smart Stix I/O
OPC Server
Cscape
Sensors
Indicators
Alarms
Encoders
Pumps
Relays
Solenoids
CAN
Smart Stack
I/O
Serial
RX-371
Ethernet
USB
Cscape
Flash drive
Other OCS Devices
Drives
PLCs
Bar Code Readers
Printers
SCADA
OPC Servers
Serial I/O
OPC Server
Modbus TCP Devices
(CsCAN) Cscape.
Figure 2.2: Visual Overview of Types of Devices that can be connected to RX-371
2.3 Detailed Product Descriptions
a. Features
The RX-371 combines several desirable functions in one compact package. Each unit is a highly
integrated operator interface and controller with expandable I/O and networking capabilities have
standard features consisting of the following:
• Metal enclosure with aluminium front and steel back cover.
• Bright, 32000 Color graphical Touch sensing LCD display
• Domed keypad with magnetic contact.
• Plastic touch screen that is thicker and more damage resistant.
• Display of complex graphical objects including trends, gauges, meters and animations.
• CsCAN Networking port
February 8, 2010 Page 13 of 124 # 1018
Page 14
CH. 2 MAN0924-01-EN
• RS-232 / RS-485 Serial Ports
• Configurable serial protocols for communication to drives, PLC’s, or other serial peripherals.
• Advanced control capabilities including floating point, multiple auto tuning PID loops and string
handling capabilities.
• Removable Media for up to two gigabytes of storage of programs, data logging or screen captures.
• System Key and Configurable Function Keys
• USB networking port for communication with PC’s and programming of controller.
• USB supporting flash drive.
• Ethernet (10/100 Mbps)
• Smart Stack I/O Expansion and Smart Stix remote I/O.
• Cscape programming software allowing all aspects of RX-371 to be programmed and configured from
one integrated application.
b. CsCAN Network
The RX-371 has the CsCAN networking port for communication with remote I/O, other controllers or PC’s.
(CsCAN is pronounced “see-scan”). CAN-based network hardware is used in the controllers because of
CAN’s automatic error detection, ease of configuration, low-cost of design and implementation and ability
to operate in harsh environments. Networking abilities are built-in to the RX-371 and require no external
or additional modules.
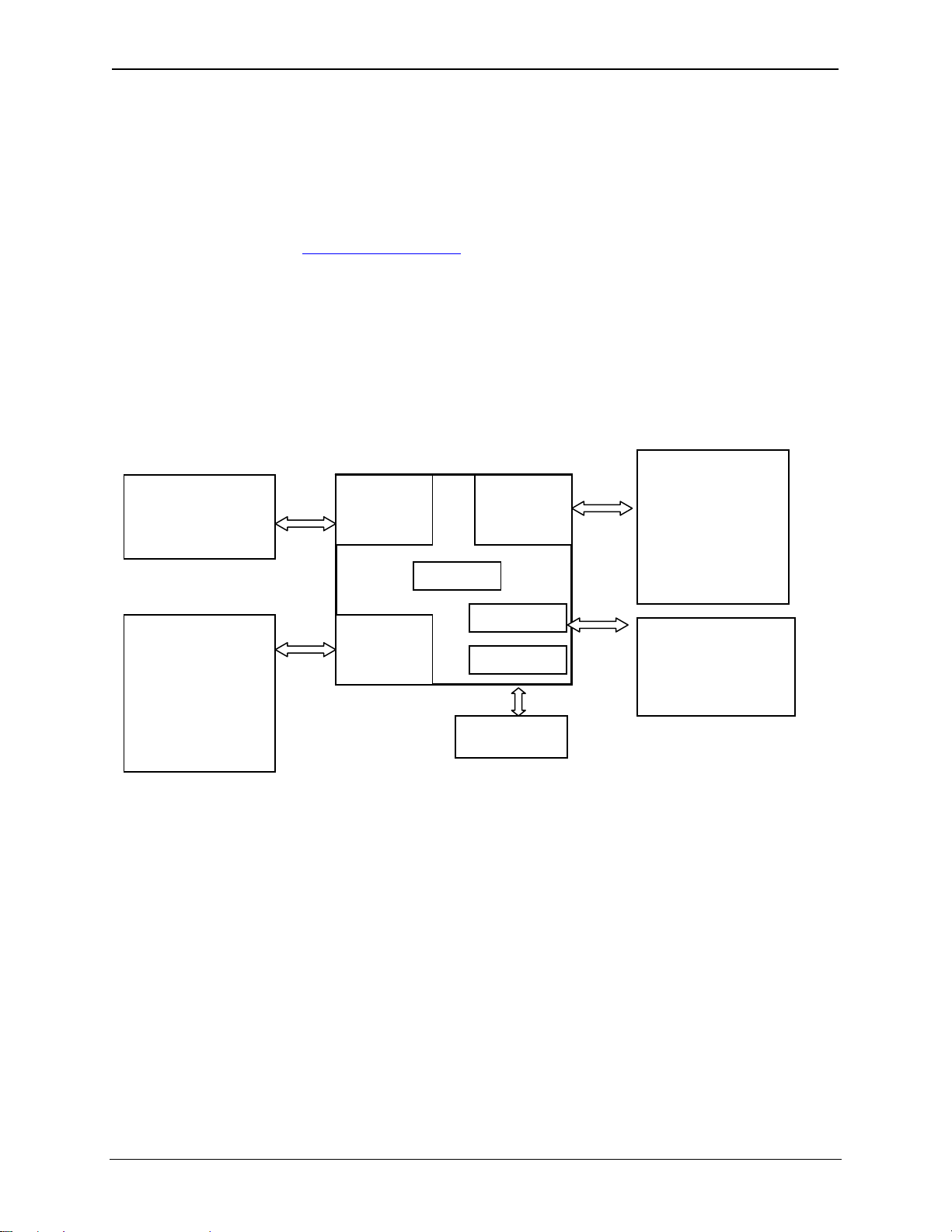
Figure 2.3: Pass through Function (Available in CsCAN Networks Only)
The RX-371 features the ability to pass through programming commands. When attached to a RX-371
serial port, a programming package (i.e., Cscape) can access other RX units or any other OCS unit
connected to a CsCAN network by passing the programming command through the serial port to the
network port. One Cscape package (connected to one RX unit) can program all RX or other OCS units on
the CsCAN network. When several RX models are networked together to achieve a specific purpose, the
system acts like a large parallel-processing controller.
c. Cscape Software
RX-371 hardware is programmed with a Windows-based PC application called Cscape (HE500OSW232).
Cscape (pronounced “see-scape”) stands for Control Station Central Application Programming
Environment. Provided there is one serial connection to one node on the network (i.e., CsCAN
Network), the operator has control over the entire system. The operator can upload, download, monitor
and debug to any node on the network.
This application can be used to program, configure, monitor and debug all aspects of the RX-371 unit. It
is used for programming RX-371 OCS ladder logic, programming user displays for the RX-371 OCS,
configuring the network for global digital and analog data, setting system-wide security and monitoring
controllers in the system.
February 8, 2010 Page 14 of 124 # 1018
Page 15
MAN0924-01-EN CH.2
2.4 Product Specifications
Table 1 - RX371 Specifications
Display Type (LCD with
Backlight)
Display Size 5.7”
Display Screen Dimensions 320 x 240
Display Memory 2.75MB
Display Life Minimum 40000 hours (50% brightness, 25 deg C)
User Keys 5 user-defined Function keys and a System key
Screens supported 1023
Colors 32768
Primary power 10 – 30 VDC
Steady state current 0.8A @ 24 VDC, 2 A @ 10 VDC
Inrush current
Height 5.964” (151.49mm)
Width 7.682” (195.12mm)
Depth 3.223” (81.86mm)
Serial Ports RS232 & RS485. Software Selectable
Terminal Type Screw Type, 5mm removable
Weight 54 oz (1.53kg)
Portable Memory Micro SD card slot
Temperature & Humidity
Clock Accuracy
Compliance USA:http://www.heapg.com/Pages/TechSupport/ProductCert.html
EUROPE:
http://www.horner-pg.com/en/support/certification.aspx
30 A for 1 ms @ 24 VDC – DC Switched
2.5 A for 4 ms @ 24 VDC - AC Switched
Product Descriptions
-30°C to +60°C & 5 to 95% Non-condensing
5.7” QVGA TFT
+/- 35 ppm maximum at 25° C
(+/- 1.53 Minutes per Month)
2.5 Required and Suggested Accessories
The following table contains a list of required and suggested RX-371 accessories. Visit our website
http://www.heapg.com/) to view updates on new products and accessories.
(
Note: The RX-371 is not
shipped with a programming cable in the box. To obtain a programming
cable, order HE500CBL300.
Table 2.1 – RX-371 Accessories
Part Number Description
HE500OSW232
HE500CBL300 OCS Programming Cable, 9-pin female (PC) to RJ-45 (OCS) - 6 feet.
HEUSB600
Part Number Description
HE-MC1 Removable Media card - compatible with RX-371.
HE-MR1
HE-X24-AS
HE-X24-AL
Cscape Software Package. Includes Cscape CD, 9-pin OCS Programming Cable, RJ-45
Programming Cable, Documentation
USB programming kit. Includes USB to RS-232 adapter, and 6-foot RS-232 cable with
D-sub connections. Requires HE500CBL300 to program the RX-371
Media Card Reader for HE-MC1. Portable device allows HE-MC1 to be plugged into the
USB port of personal computers as a portable hard drive
Power supply 100-240VAC or 140-340VDC Switching supply that outputs 1.5 A / 3 A
(HE-X24-AS/AL) at 24 VDC. Mounts on Standard DIN rail.
Power supply 100-240 VAC or 140-340 VDC Switching supply that o utputs 1.5 A / 3 A
(HE-X24-AS/AL) at 24VDC. Mounts on Standard DIN rail.
February 8, 2010 Page 15 of 124 # 1018
Page 16
CH. 2 MAN0924-01-EN
2.6 Useful Documents and References
The following information serves as a general listing of Horner controller products and other references of
interest with their corresponding manuals numbers. Visit our website (
http://www.heapg.com/) to obtain
user documentation and updates.
Table 2.2 – Additional References
Note: This list is not intended for users to determine which products are appropriate for their application;
controller products differ in the features that they support. If assistance is required, see the Technical
Support section in this document.
Controller Manual Number
XLE/t Series (e.g., HE-XExxx) MAN0878
QX Series 451/551/651 MAN0798
NX Series (e.g., HE-NXxxx) MAN0781
QX351 manual MAN0892
QX751 manual MAN0890
LX Series (e.g., LX-xxx; also covers RCS116) MAN0755
XL6/XL6e manual MAN0883
Color Touch OCS (e.g., OCSxxx) MAN0465
RX371 datasheet MAN0925
OCS (Operator Control Station) (e.g., OCS1xx / 2xx; Graphic OCS250)
Remote Control Station (e.g., RCS2x0)
MiniOCS (e.g., HE500OCSxxx, HE500RCSxxx) MAN0305
MAN0227
Other Useful References
CAN Networks MAN0799
Cscape Programming and Reference MAN0313
Wiring Accessories and Spare Parts Manual MAN0347
Email QSG MAN0923
February 8, 2010 Page 16 of 124 # 1018
Page 17
MAN0924-01-EN CH.3
CHAPTER 3: MECHANICAL INSTALLATION
Note: Each RX-371 OCS unit is shipped with an inbox datasheet. The datasheet is the first document
you need to refer to for model-specific information related to pin-outs, jumper settings, and other
key installation information. Visit our website to obtain datasheets, user documentation, an d updates.
3.1 Overview
The mechanical installation greatly affects the operation, safety and appearance of the system.
Information is provided to mechanically install the unit such as cut-out sizes, mounting procedures and
other recommendations for the proper mechanical installation of the unit.
3.2 Mounting Requirements
3.2.1 Mounting Procedures (Installed in a Panel Door)
Once the panel design has been completed using the criteria and suggestions in the following
sections, use the following steps to panel mount the RX-371 OCS.
1. Remove all connectors from the RX-371 OCS unit.
2. Make sure the gasket is installed on the RX-371 OCS and is free from dust and debris. Check
that the corners of the gasket are secure.
3. Pass the unit through the panel.
4. Insert each of the four (4) mounting clips into the slots in the RX-371 OCS case. One clip
should be installed on each corner. Lightly tighten each screw so the clip is held in place.
5. Tighten the screws on the clips such that the gasket is compressed against the panel.
001OCS001
001OCS002
Figure 3.1: Panel Mounting of RX-371 OCS
February 8, 2010 Page 17 of 124 # 1018
Page 18
CH. 3 MAN0924-01-EN
3.3. Mounting Orientation
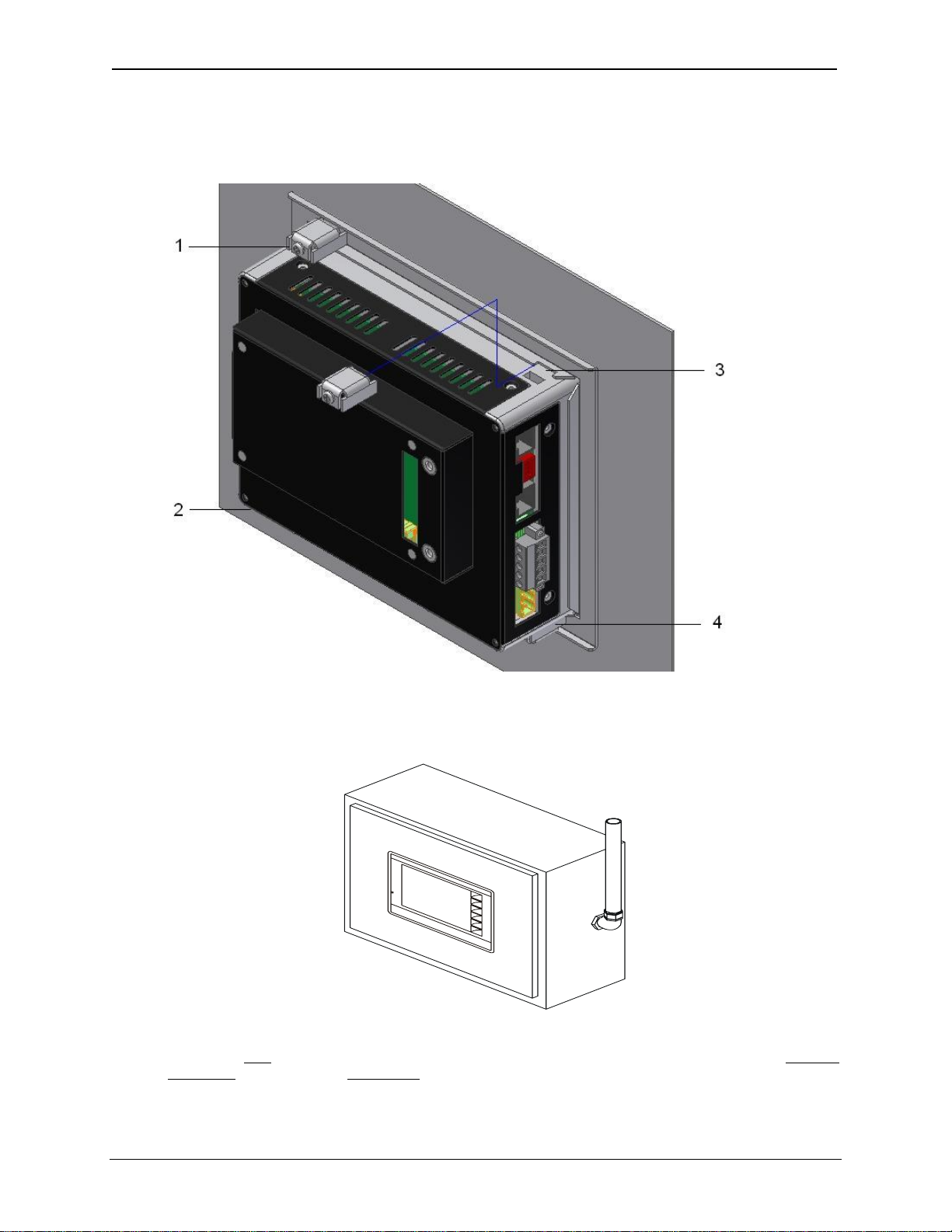
3.3.1 RX-371 Mounting Clip
Figure 3.2: RX-371 Mounting Clips (4 clips)
3.3.2 RX-371 Mounting Orientation
NOTE:
There are NO orientation restrictions on the RX. However, the above orientation provides for optimum
readability of the screen and ease of use of the keypad.
Figure 3.3: RX-371 Mounting orientation
001OCS001
February 8, 2010 Page 18 of 124 # 1018
Page 19
MAN0924-01-EN CH.3
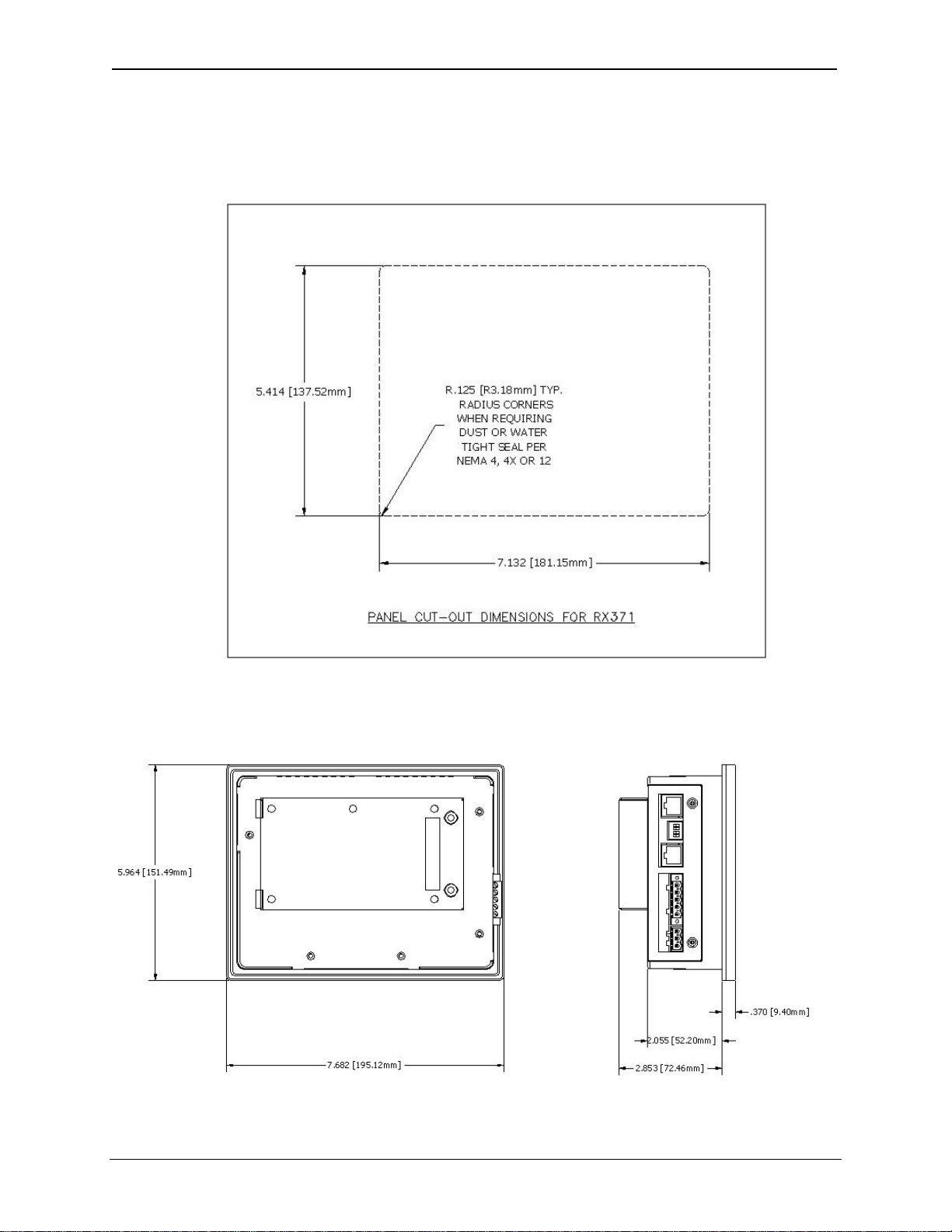
3.4 Panel Cut-Out
For installations requiring NEMA4X liquid and dust protection the panel cutout should be cut with a
tolerance of ± 0.005” (0.1 mm).
3.5 RX-371 Dimensions
Figure 3.4: Panel Cutout Tolerances
Figure 3.5: RX-371 Dimensions
February 8, 2010 Page 19 of 124 # 1018
Page 20
CH. 3 MAN0924-01-EN
3.6 Factors Affecting Panel Layout Design and Clearances
Warning: It is important to follow the requirements of the panel manufacturer and to follow
applicable electrical codes and standards.
The designer of a panel layout needs to assess the requirements of a particular system and to consider
the following design factors.
3.6.1 Clearance / Adequate Space
Install devices to allow sufficient clearance to open and close the panel door.
Table 3.1 – Minimum Clearance Requirements for Panel Box and Door
Minimum Distance between base of device and sides of
cabinet
2 inches (50.80mm)
Minimum Distance between base of device and wiring ducts 1.5 inches (38.10mm)
If more than one device installed in panel box (or on door):
Minimum Distance between bases of each device
4 inches between bases of each
device (101.60mm)
When door is closed:
Minimum distance between device and closed door
(Be sure to allow enough depth for RX-371 OCS)
2 inches (50.80mm)
3.6.2 Grounding
Warning: Be sure to meet the ground requirements of the panel manufacturer and also meet
applicable electrical codes and standards.
Panel box
: The panel box needs to be properly connected to earth ground to provide a good common
ground reference.
Panel door
: Tie a low impedance ground strap between the panel box and the panel door to ensure that
they have the same ground reference.
3.6.3 Temperature / Ventilation
Ensure that the panel layout design allows for adequate ventilation and maintains the specified ambient
temperature range. Consider the impact on the design of the panel layout if operating at the extreme
ends of the ambient temperature range. For example, if it is determined that a cooling device is required,
allow adequate space and clearances for the device in the panel box or on the p anel door.
3.6.4 Orientation
When panel-mounted, there are no orientation restrictions on the RX-371 OCS.
3.6.5 Noise
Consider the impact on the panel layout design and clearance requirements if noise suppression devices
are needed. Be sure to maintain an adequate distance between the RX-371 OCS and noisy devices
such as relays, motor starters, etc.
February 8, 2010 Page 20 of 124 # 1018
Page 21

MAN0924-01-EN CH.3
3.6.6 Shock and Vibration
The RX-371 OCS has been designed to operate in typical industrial environments that can inflict some
shock and vibration on the unit. For applications that can inflict excessive shock and vibration, use proper
dampening techniques or relocate the RX-371 OCS to a location that minimizes shock and / or vibration.
3.7 Panel Layout Design and Clearance Checklist
The following list provides highlights of panel layout design factors.
____Meets the electrical code and applicable standards for prope r grounding, etc.?
____Meets the panel manufacturer’s requirements for grounding, etc.?
____Is the panel box properly connected to earth ground? Is the panel door properly grounded? Has the
appropriate procedure been followed to properly ground the devices
in the panel box and on the
panel door?
____Are minimum clearance requirements met? Can the panel door be easily opened and closed? Is
there adequate space between device bases as well as the sides of the panel and wiring ducts?
____Is the panel box deep enough to accommodate the RX-371?
____Is there adequate ventilation? Is the ambient temperature range maintained? Are cooling or heating
devices required?
____Are noise suppression devices or isolation transformers required? Is there adequate distance
between the base of the RX-371 OCS and noisy devices such as relays or motor starters? Ensure
that power and signal wires are not
routed in the same conduit.
____Are there other requirements that impact the particular system, which need to be considered?
February 8, 2010 Page 21 of 124 # 1018
Page 22

CH.3 MAN0924-01-EN
NOTES
2/8/2010 Page 22 of 124 # 1018
Page 23
MAN0924-01-EN CH.4
CHAPTER 4: ELECTRICAL INSTALLATION
4.1 Initial Electrical Installation
Refer the datasheet that covers ports, connectors, wiring and pin outs. Visit our website
http://www.heapg.com/) to obtain latest documentation.
(
4.2 Grounding Definition
Ground: The term Ground is defined as a conductive connection between a circuit or piece of
equipment and the earth. Grounds are fundamentally used to protect an application from harmful
interference causing either physical damage such as by lightning or voltage transients or from circuit
disruption often caused by radio frequency (RF) interference.
4.3 Ground Specifications
Ideally, a ground resistance measurement from equipment to earth ground is 0 ohms. In reality it typically
is higher. The U.S. National Electrical Code (NEC) states the resistance to ground shall not
ohms. Horner APG recommends less than 15 ohms resistance from our equipment to ground.
Resistance greater than 25 ohms can cause undesirable or harmful interference to the device.
4.4 How to Test for Good Ground
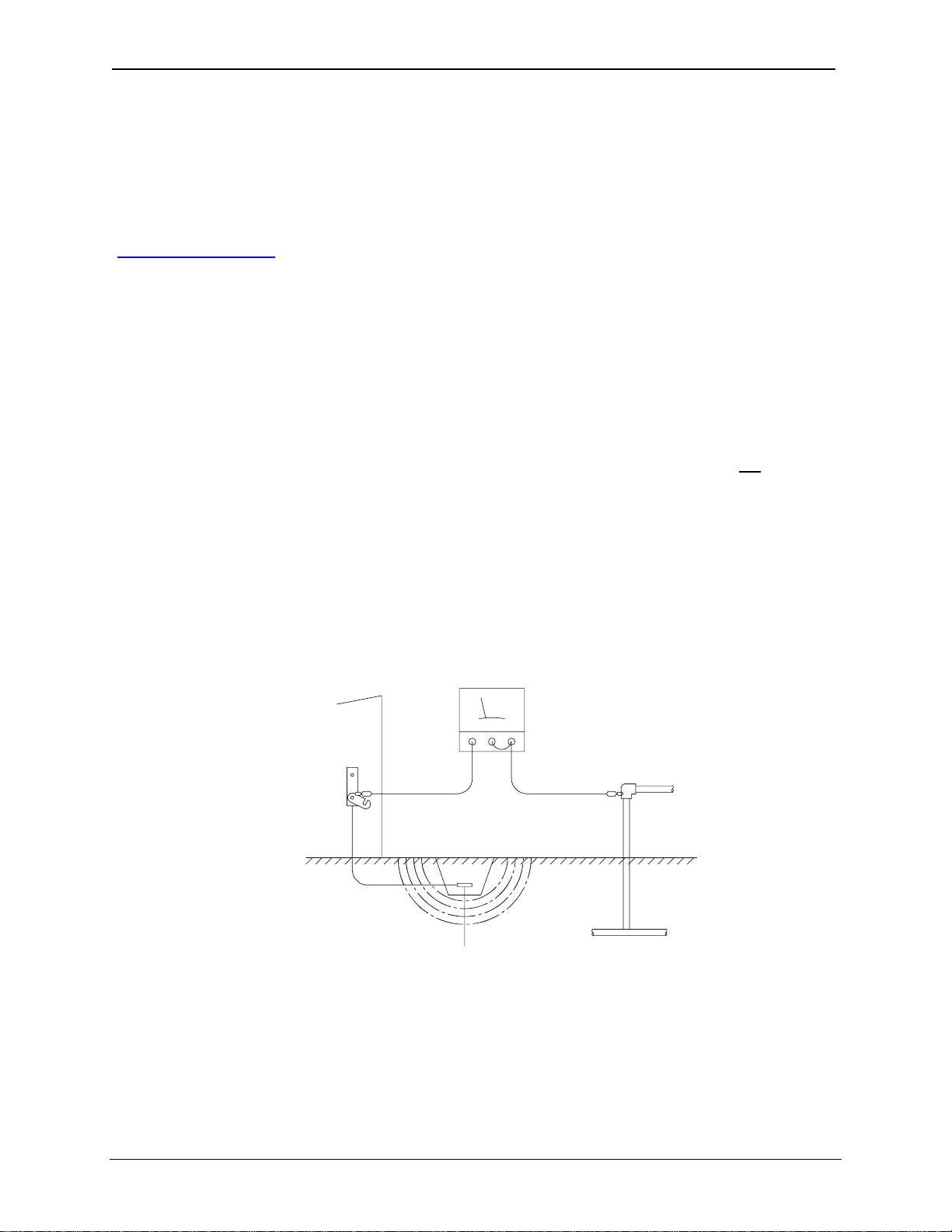
In order to test ground resistance, a Ground Resistance Tester must be used. A typical Ground
Resistance Meter Kit contains a meter, two or three wire leads, and two ground rods. Instructions are
supplied for either a two-point or three-point ground test.
Figure 4.1 shows a two-point ground connection test.
GROUND RESISTANCE ME TER
GROUND
DISCONNECTED
FROM SERVICE
GROUND ROD
METAL WATER PIPE OR
OTHER GOOD GROUND
Figure 4.1: Two-Point Ground Connection Test
exceed 25
February 8, 2010 Page 23 of 124 # 1018
Page 24
CH.4 MAN0924-01
(
)
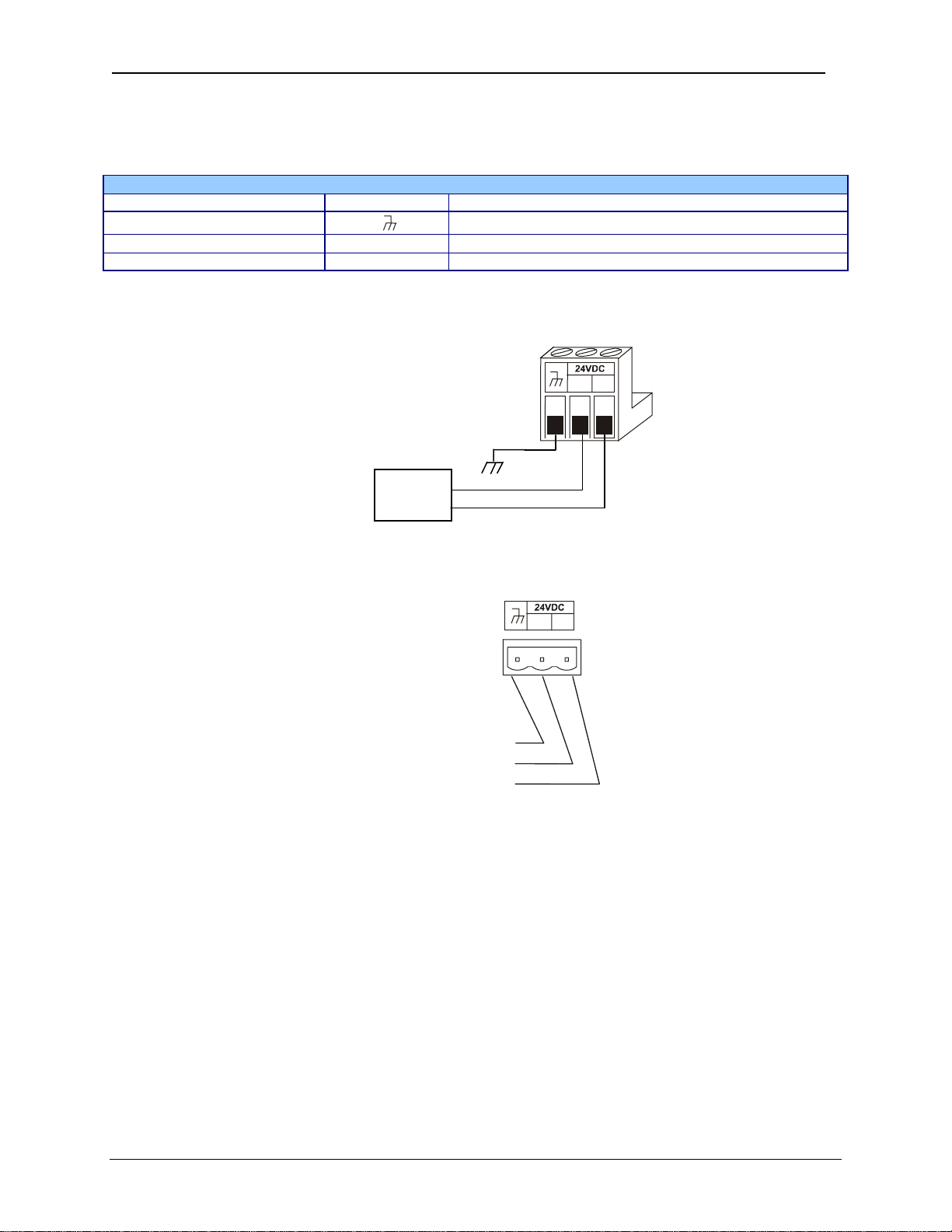
4.5 RX-371 Primary Power Port
Table 4.1 – Primary Power Port Pins
Pin Signal Description
1
2 0V Input power supply ground
3 +24V Input power supply positive voltage
Frame Ground
+
-
Power Connector
Power Up:
Connect to Earth Ground.
Apply 10 – 30 VDC.
Screen lights up.
Torque rating 4.5 - 7 Lb-In
0.50 – 0.78 N-m
10-30 VDC
supply
-
+
Figure 4.2: Power Connector (Primary Power Port)
+
-
PIN 1
PIN 2
PIN 3
Figure 4.3: Primary Power Port as Viewed looking at RX-371
February 8, 2010 Page 24 of 124 # 1018
Page 25
MAN0924-01-EN CH.5
CHAPTER 5: SERIAL COMMUNICATIONS
5.1 Overview
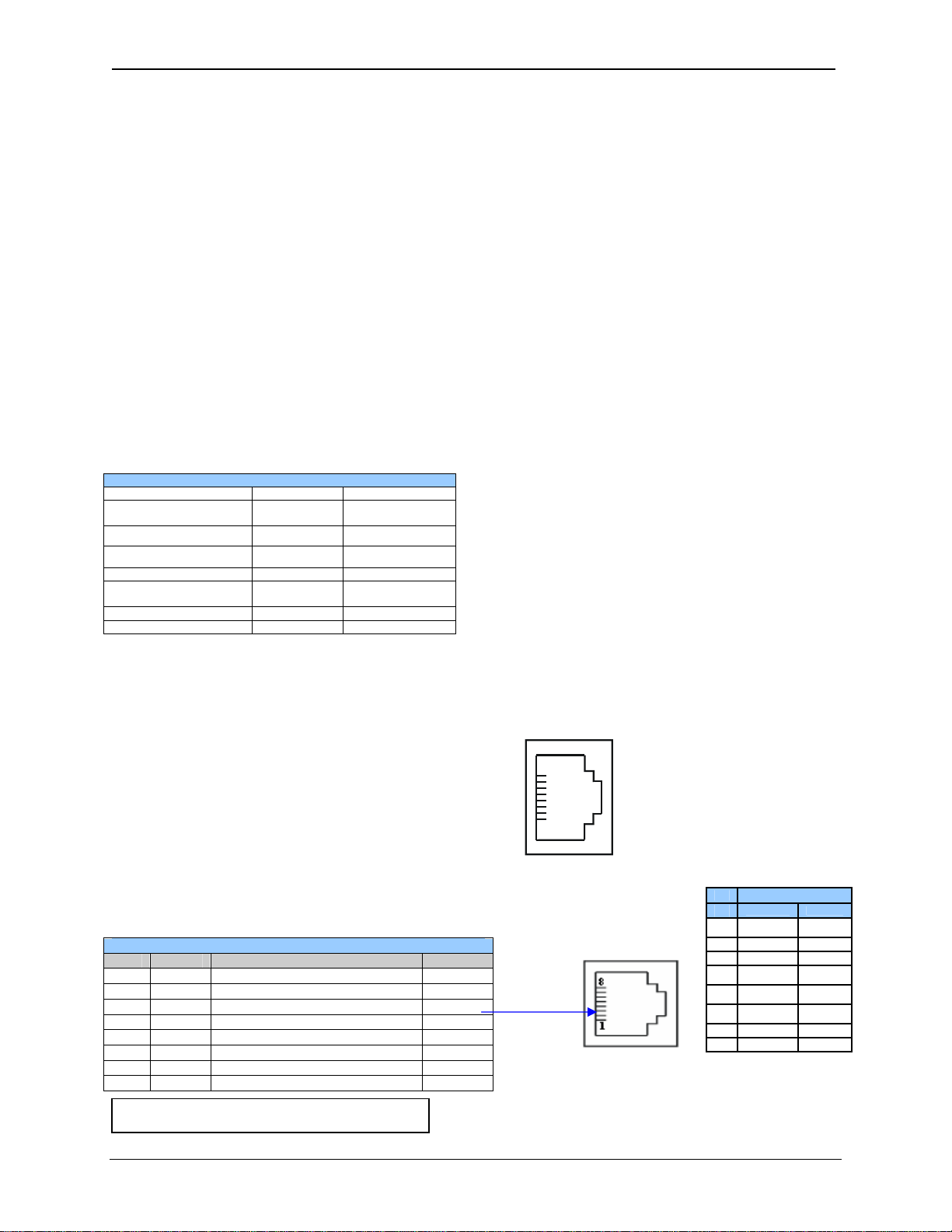
All RX-371 OCS models provide two serial ports, which are implemented with 8-pin modular RJ45
connectors, and are labeled MJ1 and MJ2. The MJ1 serial port is normally used (although MJ2 can now
be used as well) for RX-371 OCS programming by connecting it to the COM port of a PC running Cscape.
In addition, both MJ1 and MJ2 can be used for application-specific communication, using a variety of
standard data exchange protocols.
5.2 Port Descriptions
The MJ1 serial port contains both a half-duplex RS-485 interface and an RS-232 interface with RTS/CTS
handshaking.
The MJ2 serial port contains both a full-duplex RS-485 interface and an RS-232 interface with no
handshaking. Both the MJ1 and MJ2 RS-485 interfaces provide switchable termination and bias resistors
internally.
Functions Port 1 (MJ1) Port 2 (MJ2)
RS-232
Hardware Handshaking
Programming
Ladder function controlled 9 9
Serial Downloadable
Protocols
RS 485 Half duplex 9 9
RS485 Full duplex X 9
5.3 Wiring
Figure 5.1 along with Table 5.1and Table 5.2 show how the MJ1 and MJ2 serial port pins are assigned.
Pin Signal Signal Description Direction
1 RX/TX+ RS-485 Receive/Transmit Positive In/Out
2
3 CTS
4 RTS1 RS-232 Request to Send In
5 +5* +5 VDC 60mA max Out
6 0V Ground
7 TD1 RS-232 Transmit Data In
8 RD1 RS-232 Receive Data Out
• * +5 on RX-371 Rev E and later
• * +5 on all revisions XLt, XL6 and RX-371
Table 2 - Ports and Functions
9 9
9 X
9 9
9 9
Note: MJ1 and MJ2 look the
same but have different pin
assignments and functions.
Figure 5.1: MJ Serial Port Connector
Table 5.1 – MJ1 Serial Port Pin Assignments
RX/TX−
RS-485 Receive/Transmit Negative In/Out
1
RS-232 Clear to Send Out
8
1
Pin MJ1 Pins
Signal Direction
TXD OUT
8
RXD IN
7
0 V Ground
6
+5 60mA OUT
5*
RTS OUT
4
CTS IN
3
RX- / TX- IN / OUT
2
RX+ / TX+ IN / OUT
1
−
February 8, 2010 Page 25 of 124 # 1018
Page 26
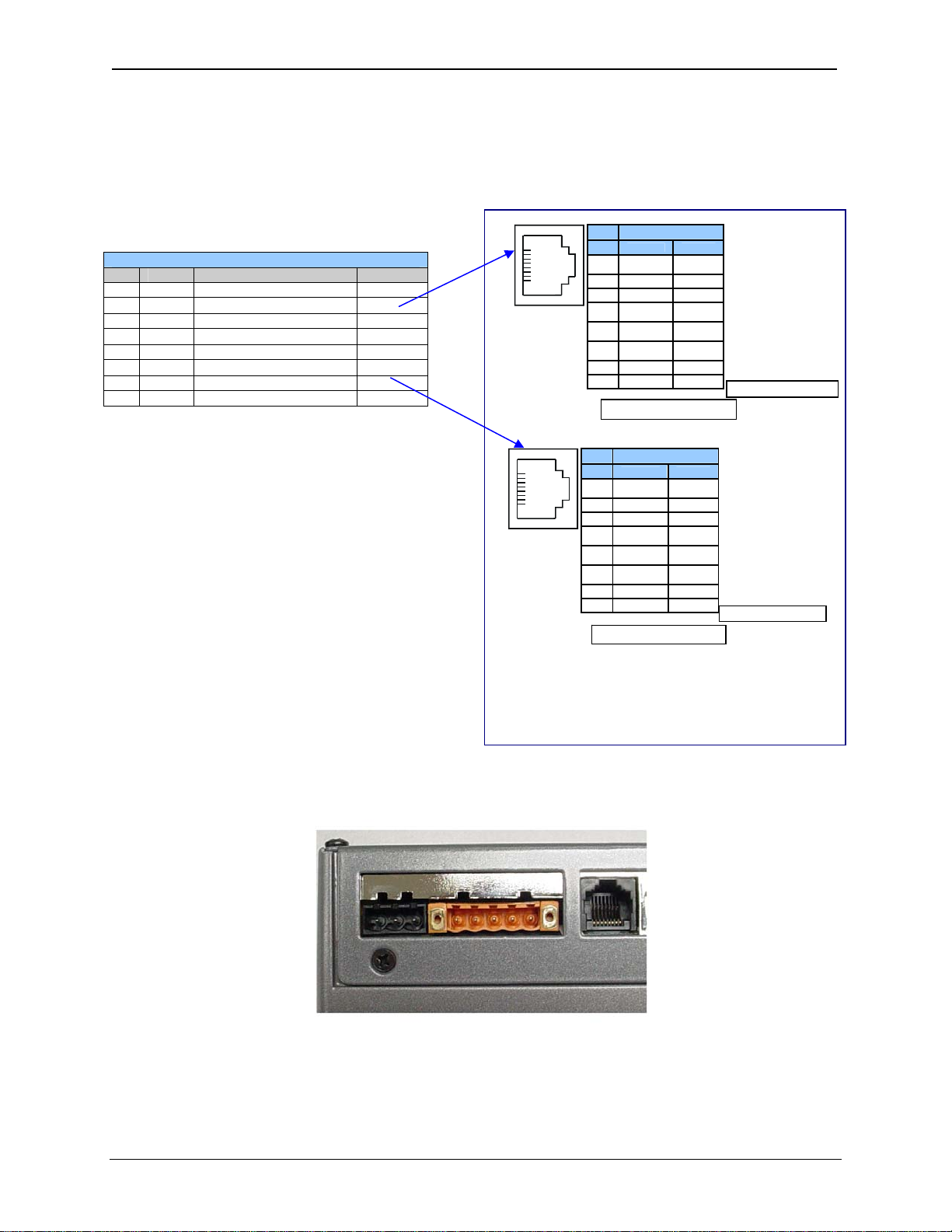
CH.5 MAN0924-01-EN
8
Signals are labeled for connection to a DTE device
Pin MJ2 Pins
Signal Direction
TXD OUT
8
RXD IN
7
0 V Ground
6
+5 60mA OUT
5*
TX- OUT
4
TX+ OUT
3
RX- IN
2
RX+ IN
1
MJ2 Full Duplex Mode
* +5Vdc 60mA Max
Table 5.2 – – MJ2 Serial Port Pin Assignments
Pin Signal Signal Description Direction
1 RX+ RS-485 Receive Positive In
2
RX−
RS-485 Receive Negative
In
3 TX+ RS-485 Transmit Positive Out
4
TX−
RS-485 Transmit Negative Out
5 +5* +5 VDC 60mA max Out
6 0V Ground
−
7 TD1 RS-232 Transmit Data In
8 RD1 RS-232 Receive Data Out
8
1
1
Pin MJ2 Pins
8
7
6
5*
4
3
2
1
MJ2 Half Duplex Mode
Signal Direction
TXD OUT
RXD IN
0 V Ground
+5 60mA OUT
TX- OUT
TX+ OUT
TX-/RX- IN/OUT
TX+/RX+ IN/OUT
* +5Vdc 60mA Max
MJ2 Pinouts in Full and Half Duplex Modes
Figure 5.2: MJ Serial Port Connectors
February 8, 2010 Page 26 of 124 # 1018
Page 27
MAN0924-01-EN CH.5
r
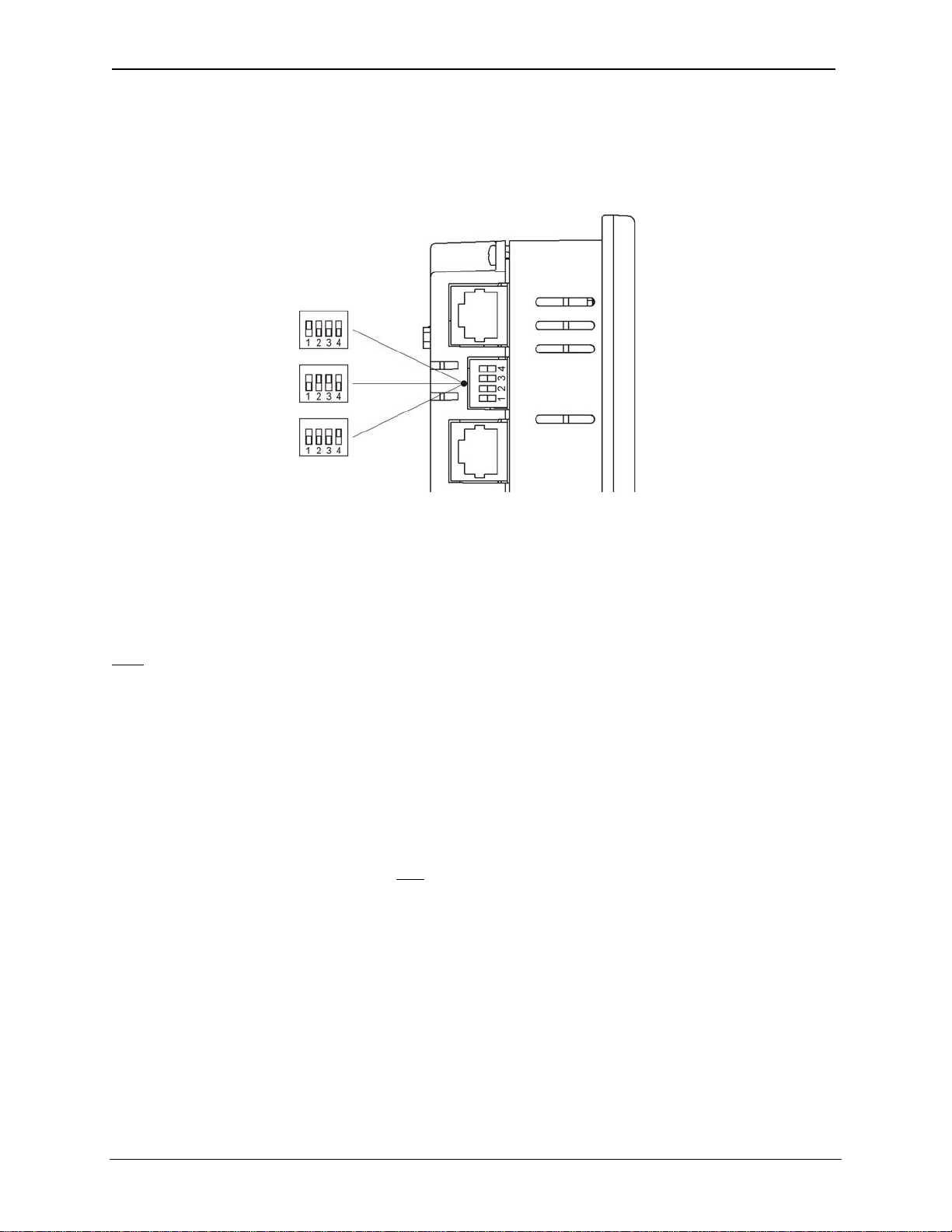
The DIP Switches are used fo
termination of the RS-485 ports. The
RX-371 is shipped un-terminated.
To terminate, select one of the DIP
Switches and configure it based upon
the option that is desired.
SW1 - ON enables MJ2 RS485 port
termination (121 Ohms).
OFF disables MJ2 RS485 port
termination.
SW2 & SW3 - ON places MJ2 RS485 port in
half-duplex mode.
OFF places MJ2 RS485 port in full-
duplex mode.
SW4 - ON enables MJ1 RS485 port
termination (121 Ohms).
OFF disables MJ1 RS485 port
termination.
5.4 RS-485 Termination
Proper RS-485 termination minimizes reflections and improves reliability.
Both serial ports allow an internal RS-485 termination resistor to be placed across pins 1 and 2 by DIP
Switch Setting.
the two devices physically located at the endpoints of the RS-485 network should be terminated.
Only
5.5 RS-485 Biasing
RS-485 biasing passively asserts a line-idle state when no device is actively transmitting, whic h is useful
for multi-drop RS-485 networking.
Both serial ports allow internal RS-485 bias resistors to be switched in, pulling pin 1 up to 3.3V and pulling
pin 2 down to ground. The Set Serial Ports item in the System Menu can be used to enable RS-485
biasing. Also, an application graphics screen that writes to %SR164 can do the same thing. Setting
%SR164.1 enables MJ1 biasing and setting %SR164.2 enables MJ2 biasing.
If biasing is used, it should be enabled in only
one of the devices attached to the RS-485 network.
5.6 Cscape Programming via Serial Port
The RX-371 OCS MJ1/MJ2 serial port supports CsCAN Programming Protocol. If a PC COM port is
connected to the RX-371 OCS MJ1/2 serial port, Cscape can access the RX-371 OCS for programming
and monitoring.
5.7 Ladder-Controlled Serial Communication
Using Serial Communication function blocks, both MJ1 and MJ2 support Generic, Modbus Master and
Modbus Slave Protocols. In addition, external modems can be connected and accessed using Init, Dial
and Answer Modem function blocks.
February 8, 2010 Page 27 of 124 # 1018
Page 28

CH.5 MAN0924-01-EN
5.8 Downloadable Serial Communication Protocols
Both MJ1 and MJ2 also support downloadable protocols, such as Allen Bradley DF1, CsCAN Master, GE
Fanuc SNP and Modbus Master.
Note: Refer download section of website for the list of latest supported protocols
http://www.heapg.com/Pages/TechSupport/Downloads.html)
(
February 8, 2010 Page 28 of 124 # 1018
Page 29

MAN0924-01-EN CH.6
CHAPTER 6: CAN COMMUNICATIONS
Note: For additional CAN information, refer to the CAN Networks manual (
6.1 Overview
All RX-371 OCS models provide a CAN networking port, which is implemented with a 5-pin connector.
The connector is labeled NET1.
MAN0799) on our website.
Figure 6.1: NET 1 Connector
Like the MJ1 serial port, the NET1 port can be used for RX-371 OCS programming by connecting it to the
CAN port of a PC running Cscape. The NET1 port also allows the RX-371 OCS to exchange global data
with other OCS/RCS controllers and to access remote Network I/O devices (SmartStix Modules).
6.2 Port Description
The RX-371 OCS NET1 port implements the ISO 11898-2 physical layer and the CAN 2.0A data link
layer standards. Also, since the NET1 port is powered by an internal isolated power supply, external
CAN power is not required.
6.3 CAN (NET1) Port Wiring
This section shows how the CsCAN port pins are assigned.
Note: The V+ connection is not
required on the RX-371 OCS.
The RX-371 OCS network port is
self-powered. Supporting devices
can require this connection, and
this pin can be used to land the
extra wire required for those
devices.
Figure 6.2: CsCAN Port Connector
February 8, 2010 Page 29 of 124 # 1018
Page 30
CH.6 MAN0924-01-EN
Table 6.1 – CsCAN Port Pin Assignments
Pin Signal Signal Description Direction
1 V- CAN Ground
−
2 CN_L CAN Data Low In/Out
3 SHLD Shield Ground
−
4 CN_H CAN Data High In/Out
5 NC No Connect
−
6.4 Cscape Programming via CAN
The NET1 port supports CsCAN Programming Protocol. If a PC has a CAN interface installed (via PCI
card or USB), and the PC CAN port is connected to the RX-371 OCS NET1 port, Cscape can access the
RX-371 OCS for programming and monitoring.
In addition, the RX-371 OCS supports single-point-programming of all OCS devices that are connected to
a CAN network. If the PC COM port is connected to the RX-371 MJ1 serial port, it can act as a passthrough gateway allowing Cscape to access all OCS devices that are attached to the CAN network.
6.5 Ladder-Controlled CAN Communication
Using Put and Get Network Words function blocks, the NET1 port can exchange digital and analog global
data with other OCS devices (nodes) attached to the CAN network.
In addition, Put and Get Network Heartbeat function blocks allow nodes on the CAN network to regularly
announce their presence and to detect the presence (or absence) of other nodes on the network.
6.6 Using CAN for I/O Expansion (Network I/O)
Connecting Network I/O devices (SmartStix Modules) to the NET1 port allows the RX-371 OCS I/O to be
economically expanded and distributed. A variety of SmartStix Modules are available for this purpose.
February 8, 2010 Page 30 of 124 # 1018
Page 31

MAN0924-01-EN CH. 7
CHAPTER 7: ETHERNET COMMUNICATION
7.1 Ethernet Module Protocols and Features
The following table describes the Ethernet Module Protocols and features supported by RX-371.
Protocol / Feature Protocol / Feature Description
ICMP Ping Internet Control Message Protocol
EGD (Peer) GE Fanuc Ethernet Global Data
SRTP Server GE Fanuc Service Request Transfer Protocol
CsCAN TCP Server Horner APG CsCAN over Ethernet
Modbus TCP Slave Modbus over Ethernet
Ethernet / IP Server ODVA CIP over Ethernet
FTP Server File Transfer Protocol
HTTP Server HyperText Transfer Protocol (W eb Server)
SMTP Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (Chapter 16)
7.2 Ethernet System Requirements
Full Ethernet functionality requires:
1. PC running Cscape Programming Software Version 8.7 with upgrade or later (for configuration).
2. OCS controller with inbuilt/onboard Ethernet port.
3. FTP & HTTP protocols.
7.3 Ethernet Module Specifications
Speeds 10 BaseT Ethernet (10-Mbps)
100 BaseTx Fast Ethernet (100-Mbps)
Modes Half or Full Duplex
Auto-Negotiation Both 10/100-Mbps and Half/Full Duplex
Connector Type Shielded RJ-45
Cable Type
(Recommended)
Port Auto MDI/MDI-X
7.4 Ethernet Module Configuration
Note: The following configuration is required for all applications regardless of the protocols used.
Additional configuration procedures must be performed for each protocol used (refer SUP0740 for details
on configuring individual protocol).
To configure the Ethernet Module, use Cscape Programming Software to perform the following steps
1. On the main Cscape screen, select the Controller menu and its I/O Configure sub-menu to
open the I/O Configuration dialog (Figure 7.1)
2. If configuring a different OCS Model than the one shown in the I/O Configuration dialog, click
on the topmost Config button, select the desired OCS Model, and then click OK
CAT5 (or better) UTP
February 8, 2010 Page 31 of 124 # 1018
Page 32

CH. 7 MAN0924-01-EN
Figure 7.1: I/O Configuration Dialog
3. Click the Config button to the right of the Ethernet Module, and then select the Module Setup
tab, revealing the Ethernet Module Configuration dialog as shown in figure 7.2
Figure 7.2: Ethernet Module Configuration
February 8, 2010 Page 32 of 124 # 1018
Page 33

MAN0924-01-EN CH. 7
4. Configure the Ethernet Module parameters as follows:
It has two parts 1. Register Usage and 2. Protocol Support
Register Usage:
i. IP Address: Enter the static IP Address for the Ethernet Module being configured.
Note: IP Addresses are entered as four numbers, each ranging from 0 to 255. These four
numbers are called octets and they are always separated by decimal points.
ii. Net Mask: Enter the Net Mask (sometimes called Subnet Mask) being used by all nodes on
the local network. Typical local networks use Class C IP Addresses, in which case the low
octet (rightmost number) is used to uniquely identify each node on the local network. In this
case, the default Net Mask value of 255.255.255.0 should be used.
iii. Gateway: Enter the IP Address of a Gateway Server on the local network that allows for
communication outside of the local network. To prevent the Ethernet Module from
communicating outside the local network, set the Default Gateway IP Address to 0.0.0.0 (the
default setting).
iv. Status Register: Enter an OCS Register reference (such as %R100) to indicate which 16-bit
OCS register will have the Ethernet Status word written to it. Table 3.1 shows how this
register value is formatted and explains the meaning of each bit in the Status Word.
Table 3.1 - Ethernet Status Word Register Format
High Byte Low Byte
Bit
16
Bit
15
Bit
14
Bit
13
Bit
12
Bit
11
Bit
Bit 9 Bit 8 Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit
10
1
0 0 Dup Spd 0 Rx Tx Link TCP Connections
Status Bit(s) Status Indication
Minimum Maximum
Status Values
0 Reserved Always 0
Dup Link Duplex (Auto-Negotiated) 0 = Half Duplex 1 = Full Duplex
Spd Link Speed (Auto-Negotiated) 0 = 10 Mbps 1 = 100 Mbps
Rx Receive State 0 = Inactive 1 = Active
Tx Transmit State 0 = Inactive 1 = Active
Link Link State 0 = Down 1 = Up
TCP Connections
Total Number of Active TCP Connections
(CsCAN, SRTP, Modbus, EIP, FTP, HTTP)
0 40
v. Version Register: Enter an OCS Register reference (such as %R101) to indicate which 16-
bit OCS register will have the Ethernet Firmware Version written to it. The value stored in the
Version Register is: (Ethernet Firmware Version * 100). For example, for Ethernet Firmware
Version 4.30, the Version register will contain 430.
For the Status and Version registers (if configured), the Direction settings are always
Only
vi. Use CAN ID for last Octet: The Use CAN ID for last Octet checkbox does not
affect Net
Mask, Gateway, Status or Version configuration. If the checkbox is checked then it behaves
as follows:
Read
February 8, 2010 Page 33 of 124 # 1018
Page 34

CH. 7 MAN0924-01-EN
A. If the IP Address Direction combo box is Read / Write, the Use CAN ID for last Octet
checkbox will be unchecked and grayed.
B. If the IP Address Direction combo box is empty or Read Only, the Use CAN ID for last
Octet checkbox will be ungrayed, and can then be unchecked or checked.
C. If the Use CAN ID for last Octet checkbox is checked, the unit’s 8-bit CAN Network ID
replaces the last (rightmost) octet of the Default IP Address, and the combined result
will be the unit’s IP Address. In this case, if the IP Address Register edit box contains a
valid OCS register, the indicated register will be loaded with the combined IP Address.
vii. Enhanced Configuration
To perform Enhanced Configuration, first check the Enhanced Configuration checkbox. In this
case, IP Address, Net Mask, Gateway, Status and Version can all be optionally
assigned to
OCS registers. By default, the register edit boxes are empty indicating that no registers are
assigned.
As with the IP Address register (described in the Standard Configuration section below), Net
Mask and Gateway register Directions can be set to Read Only or Read / Write
With Cscape 8.2 onwards, the ETN Module Configuration dialog has been enhanced
to support the following:
1. More easily expanded Protocol Support list for current and future
protocols.
2. Optional Enhanced Configuration:
a. Allows Net Mask and Gateway to be optionally read from or written
to OCS registers.
b. Allows all
OCS register assignments to be optional instead of
mandatory.
Ethernet Module Configuration Dialog Rules
The following rules describe how the new Ethernet Module Configuration Dialog is to be used:
I. The Enhanced Configuration checkbox will be unchecked and grayed if configuring an
ETN100 or ETN116 Module.
II. If the Enhanced Configuration checkbox is checked, Cscape will display an error
message and will abort an I/O Configuration download if:
A. Configuring an ETN200 or ETN300 Module with ETN Firmware < 4.35,
B. Configuring an OCS, RX or NX with Engine Firmwa re < 11.91.
III. If the Enhanced Conf iguration checkbox is unchecked, the dialog maintains backward
compatibility as follows:
A. The Net Mask and Gateway Register edit boxes will be empty and grayed.
B. The Net Mask and Gateway Direction combo boxes will be empty and grayed.
C. All other dialog objects function the same as in the Cscape 8.0b dialog, except
as follows:
1. The new IP Address Direction combo box replaces the old Get IP
from IP Addr Register checkbox. A Direction of Read Only, is
February 8, 2010 Page 34 of 124 # 1018
Page 35

MAN0924-01-EN CH. 7
equivalent to unchecked and a Direction of Read / Write is equivalent
to checked.
2. The new Protocol Support area contains a protocol list box showing
the protocols supported by the platform being configured. Each
protocol in the list box has a checkbox in front of it that can be checked
to enable the protocol. The single Config Selected Protocol button
applies to the protocol that is currently highlighted in the list box.
Standard Configuration
To perform Standard Configuration, simply leave the Enhanced Configuration
checkbox unchecked.
In this case, Net Mask and Gateway cannot
Address, Status and Version must
be assigned to OCS registers.
be assigned to OCS registers, while IP
Note that the assigned IP Address register’s Direction can set to Read only or Read
/ Write.
If the register is Read only, the Default IP Address becomes the unit’s IP Address and
is loaded into the assigned register, where it can be read by the application. (Note: In
this case, the low octet of the IP Address can be replaced with the unit’s CAN Network
ID, by checking the Use CAN ID for last Octet checkbox.)
If the register is Read / Write, the application should write an IP Address to the
assigned register, and this value will then be the unit’s IP Address. (In this case, the
Default IP Address is used only if communication is lost during an I/O configuration
download; otherwise the Default IP Address is ignored.)
Protocol Support:
The Protocol Support area contains a list of all the protocols supp orted by the platform being configured.
To activate a protocol, check its checkbox.
For protocols that require additional configuration, click on a listed protocol to select it and then click the
Configure Selected Protocol button. This will open a new dialog with configuration options for the
selected protocol (Detailed configuration of the protocols is explained in the corresponding chapters
below).
February 8, 2010 Page 35 of 124 # 1018
Page 36

CH. 7 MAN0924-01-EN
NOTE
February 8, 2010 Page 36 of 124 # 1018
Page 37

MAN0924-01-EN CH. 8
CHAPTER 8: REMOVABLE MEDIA
8.1 Micro SD Overview
All RX-371 OCS models provide a slot for a Micro SD memory card. The Removable Media manager is a
graphic object that allows viewing the filenames, size and dates of files and directories on a Micro SD
card. The operator can optionally change directories, delete files and format a new SD card. This object
also supplies status information such as color change on card OK, card full and card missing status. The
file view includes total card capacity and remaining free space.
8.1.1 Accessing Files with an RX-371 OCS
a. Insert a Micro SD card into the RX-371 OCS Micro SD slot.
b. If not formatted, use the Removable Media Manager object to format the card.
c. The RX-371 OCS ladder application program can read and write to the Micro SD card. The file
is saved as a .csv file, which is compatible with several PC applications such as Excel.
8.1.2 Accessing Files with a PC
a. Insert or connect the Micro SD memory card to the PC according to the manufacturer’s
instructions.
b. The PC typically sees the Micro SD card as a removable storage device like a small solid-state
hard drive. Files can be read from and written to the Micro SD card in the same way they are
read/written to a standard hard disk. The only file format that can be read or written by an OCS
application is a .csv (comma separated value) file.
8.2 Removable Media (RM) Function Blocks in Cscape
Note: For detailed information regarding RM function blocks and parameters, refer to the help file
in Cscape Software. Refer ‘USB Flash Media support for RM Functions’ for USB flash drive
access details.
The following RM functional blocks are available in Cscape Software. These function blocks will reference
- USB A Flash Drive when filename is pr efixed with ‘B:’.
a. Read RM csv
b. Write RM csv
c. Rename RM csv
d. Delete RM csv
e. Copy RM csv
- Micro SD when filename is prefixed with ‘A:’ or nothing OR
This function allows reading of a comma-separated value file from the Micro SD interface into the
controller register space.
This function allows writing of a comma-separated value file to the Micro SD interface from the
controller register space.
This function allows renaming a file on the RM card. The data in the file is not
changed.
This function allows deleting a file on the RM card.
This function allows copying a file on the RM card. The data in the file is not changed.
February 8, 2010 Page 37 of 124 # 1018
Page 38

CH. 8 MAN0924-01-EN
8.3 Configuring Removable Media Manager graphic object in Cscape
The Removable Media Manager is a graphic object that allows viewing filenames, size and dates of files,
and directories on a RM card. The operator can optionally change directories, delete files, and format new
RM cards. This object also supplies status information such as Color change on card OK, Card full, and
Card missing status. For additional information, refer Cscape Help File|Graphics|Removable Media.
8.4 Filenames used with the Removable Media (RM) Function Blocks
The RM function blocks support the flash with a DOS/Windows standard FAT-16 file system. All names
must be limited to the “8.3” format where the filename contains eight characters a period then a threecharacter extension.
The entire filename including any path must be less than or equal to 147 characters.
When creating filenames and directories it is sometimes desirable to include parts of the current date or
time. There are six special symbols that can be entered into a filename that are replaced by the OCS with
current time and date information.
Table 8.1 – Filename Special Symbols
Symbol Description Example
$Y
$M
$D
$h
$m
$s
Substitutes the current 2 digit year 2004 = 04
Substitutes the current month with a 2 digit code March = 03
Substitutes the current day 22
nd
= 22
Substitutes the current hour in 24 hour format 4 pm = 16
Substitutes the current minute 45 = 45
Substitutes the current second 34 = 34
Note that all the symbols start with the dollar sign ($) character. Date symbols are in upper case, time
symbols are in lower case.
The following are examples of the substituted time/date filenames:
Current date and time: March 1, 2004 3:45:34 PM
Filename: Data$M$D.csv = Data0301.csv
Filename: Year$Y\Month$M\aa$D_$h.csv = Year04\Month03\aa01_15.csv
Filename: Month_$M\Day_$D\$h_$m_$s.csv = Month_03\Day_01\15_45_34.csv
8.5 System Registers used with RM
%SR175 Status – This shows the current status of the RM interface.
%SR176 Free Space – This 32-bit register shows the free space on the RM card in bytes.
%SR178 Card Capacity – This 32-bit register shows the total card capacity in bytes.
Possible status values are shown in the table:
Table 8.2 – RM Status Values
0 RM interface OK
1 Card present but unknown format
2 No card in slot
3 Card present, but not supported
4 Card swapped before operation was complete
5 Unknown error
February 8, 2010 Page 38 of 124 # 1018
Page 39

MAN0924-01-EN CH.9
CHAPTER 9: SMARTSTACK I/O
Note: Because the configuration parameters are different for each SmartStack Module, refer to the data
sheet that is sent with the product and is specific
9.1 Configuration Procedures
Note: SmartStack Modules use Cscape Software for configuration. RX371 supports metal smartstack
modules and can connect upto 4 modules.
1. From the Main Menu, select Controller | I/O Configure.
Note: The look of the screen varies depending upon the type of controller that appears.
2. First, ensure that the desired controller is selected.
In this case, a different controller than the one shown on the screen might be desired. It is
necessary to select the desired controller, which is the RX-371. In this example configuration.
Continue with Step 2.
However, if you are satisfied with the controller selection, press a Base # tab. Go to Step 3
to the selected module.
Figure 9.1: Main Configuration I/O Screen
Note: The Auto Config System button can be pressed prior to selecting the desired controller and I/O.
By pressing the button, the current configuration from the local ID is uploaded and any current settings
are overwritten. A dialog box appears and indicates that settings will be deleted from currently configured
models. If OK, press Yes. Then press OK.
February 8, 2010 Page 39 of 124 # 1018
Page 40

CH.9 MAN0924-01-EN
Selecting a Different Controller
To select a different controller, ensure that the CPU Slots tab is pressed. Then, click on the slot or the
Config button. The Configure Controller screen appears.
Figure 9.2: Selecting a Controller
To select a different controller, click on the Family Type list box and select the controller series. Then
click on select Device Type list box and scroll down to select the desired controller. Then press OK. If
satisfied with the controller now selected, press Base # tab at the top of the screen. Then, go to Step 3.
Note: The Auto Config button can be pressed prior to selecting the desired controller. By pressing the
button, the settings are deleted from any controller that is physically connected to the PC.
February 8, 2010 Page 40 of 124 # 1018
Page 41

MAN0924-01-EN CH.9
3. The following screen appears. In this configuration example, I/O modules are going to be
selected and configured for Base 2.
Any Base can be selected. It is not necessary to select bases in a specific order.
The Main base contains the slots directly located on the back of the RX-371.
Figure 9.3: Main Base Screen appears with RX-371
Pressing the Auto Config Base button deletes any current settings from the configuration within Cscape,
and the I/O that is fitted to the target controller displayed. A Warning box appears and indicates that the
settings will be deleted from the configuration within Cscape. If OK, press Yes. Then press OK
.
Upon pressing the Base 2 tab, the following screen appears.
February 8, 2010 Page 41 of 124 # 1018
Page 42

CH.9 MAN0924-01-EN
Figure 9.4: Base 2 Selected
Double-click on a slot or press the Config button located next to the slot. The following screen appears.
Select a tab at the top of the screen, and then select an I/O module. (For this example, the DIQ611 is
going to be selected.) Press OK.
Figure 9.5: Selecting an I/O Module
February 8, 2010 Page 42 of 124 # 1018
Page 43

MAN0924-01-EN CH.9
4. The following screen appears.
Figure 9.6: Base 2 with an I/O Module Selected
The description and properties of the I/O module are provided. If satisfied with the selections, press OK.
Note: If a module already occupies a slot and a different module is desired, right-click on the slot and
press Replace. To leave a slot empty, right-click on the slot and press Delete. By right-clicking on a slot,
its configuration can be copied into another slot on the same base (or a different base) and pasted into a
new slot.
5. Click on the Config button of the I/O module that is placed in the slot, the Module Configuration
Screen appears. Two tabs are available for selection:
February 8, 2010 Page 43 of 124 # 1018
Page 44

CH.9 MAN0924-01-EN
Figure 9.7: I/O Map & Module Setup Tabs
a. I/O Map Tab
The I/O Map describes the I/O registers assigned to a specific I/O module. Although there are no userdefined parameters, the I/O Map can be viewed after
the SmartStack module is configured to review the
registers.
• Model number provides the part number.
• Description Describes the number of input and output channels and other key
Characteristics of the module.
• Type: Displays the register types assigned to the module.
• Starting Location: Denotes the starting location of the register type.
• Ending Location: Denotes the ending location of the register type.
• Number: Indicates the number of a particular register type.
Note: Do not
Type column (i.e., %I and %Q). The numbers do not
confuse the described number of input and output channels with the numbers found in the
necessarily match.
b. Module Setup
Module Setup for the I/O Selected in the above example (DIQ611) shows the output state on the
controller.
February 8, 2010 Page 44 of 124 # 1018
Page 45

MAN0924-01-EN CH.10
CHAPTER 10: SYSTEM SETTINGS AND ADJUSTMENTS
10.1 System Menu - Overview
The RX-371 controller has a built-in System Menu, which lets the user view system settings and make
adjustments. To start the System Menu, press the SYSTEM key (or set %SR3 to 1), which will display
the Main Menu with options as shown in
Menu item and press
Sub-Menus
to display the item’s Sub-Menu.
Network Ok? Yes
Network ID: 253
Network Baud: 125 KB
(Use ↓↑ to adjust)
Model: RX-371
Mode: Idle
Scan Rate (mS): 0.0
Lcl Net Use (%): 0.0
All Net Use (%): 0.0
Ladder Size: 2
Config Size: 8
Graphics Size: 8
String Size: 8
Bitmap Size: 8
Text Tbl Size: 8
Font Tbl Size: 8
Protocol Size: 8
SMS File Size: 8
Firmware Rev: 11.76
BIOS Rev: 0.12
FPGA Rev: 2.8
Self-Test: Ok
Logic Error: Ok
User Program: Ok
User Graphics: Ok
W-Dog Trips: 0
Net Errors: 0
Network State: Ok
Network ID: Ok
Dup Net ID: Ok
Clock Error: Ok
I/O System: Ok
Battery: Ok
Base Selected: CPU
Base Online? Yes
Slot 1:+I/O: FOX100*
Slot 2:+I/O: ETN300
Slot 3:+I/O: Empty
Slot 4: I/O: Empty
* FOX is not active in this product)
(
Figure 10.1. Then use the and keys to select a Main
Sub-Menus
Port 1:
(None Loaded)
Port 2:
(None Loaded)
Fkeys: Momentary
Sys-Fn enable: Yes
Main Menu
Set Network ID
Set Network Baud
View Status
View Diags
View I/O Slots
View Protocols
Set Fkeys Mode
Set Serial ports
Set Time/Date
Set Beeper
Set Screen
Removable Media
Fail-Safe System
Clone Unit
(Press ESC to
Exit)
Note: The RX display shows up
to 15 lines of text at a time. For
System Menu screens that
contain more than 15 lines of
text, use the ↓ and ↑ keys to
scroll the display.
Backup/Restore Data
Enable AutoRun
Enable AutoLoad
(ESC to exit)
Figure 10.1: System Menu
(Use ↓↑ to adjust)
MJ1 RS485 Bias: No
MJ2 RS485 Bias: No
(Use ↓↑ to adjust)
Time: 10:21:36
Date: 22-Jun-2006
Day: Thursday
(Use ↓↑ to adjust)
( each field )
Beeper enable: Yes
(Use ↓↑ to adjust)
Saver enable: No
Timeout (min): 15
Popup Status: Off
Update Time (mS): 5
Update time sets
the maximum time
used by graphics
in the logic scan.
Media Directory
Media Card Not Present
Directory Empty
Clone Unit
February 8, 2010 Page 45 of 124 # 1018
Page 46

CH.10 MAN0924-01-EN
10.2 System Menu – Navigation and Editing
As mentioned above, pressing the front panel SYSTEM key starts the System Menu. Then user can use
the following keys as per needs:
Æ To scroll up
Æ To scroll down
Æ To exit from the System Menu.
Æ Enter to display the item’s Sub-Menu.
A Sub-Menu generally shows a list of System Settings and their values. After opening a Sub-Menu, if any
of its System Settings are editable, the first System Setting that can be edited is highlighted. If desired,
and keys can be used to select a different System Setting to be edited.
the
At this point, either press ESC to exit the Sub-Menu (returning to the Main Menu) or press
highlighted System Setting. If
is pressed, the System Setting’s value will be highlighted, indicating that
to edit the
it is ready to be modified.
The arrow keys are used to edit System Settings that have just a few possible values. Each time the
arrow key is pressed, a new possible value is displayed. When the desired value appears, press the
Enter key to save it; otherwise, press the ESC key to cancel the edit.
The numeric keys are normally used to enter numeric System Settings. In addition, to edit a single
numeric digit, use the
or key to select the digit and then either press a numeric key or use or
to modify the digit. In any case, after entering the new desired value, press the Enter key to save it;
otherwise, press the ESC key to cancel the edit.
10.3 System Menu – Details
The following sections describe each of the Sub-Menus in detail.
Set Network ID
This Sub-Menu displays two System Settings of which only Network ID is editable.
Network Ok? Yes = CsCAN connected to a CAN network and functioning
Properly
No = Not ready to communicate on CAN network
February 8, 2010 Page 46 of 124 # 1018
Page 47

MAN0924-01-EN CH.10
Network ID: 1 to 253 = This node’s CsCAN Network ID; must be
unique on network
Set Network Baud
This Sub-Menu displays just one System Setting and it is editable.
Network Baud: 125 KB = 125 KBaud CAN network
250 KB = 250 KBaud CAN network
500 KB = 500 KBaud CAN network
1 MB = 1 MBaud CAN network
View OCS Status
The View OCS Status Sub-Menu displays up to 17 System Settings. Only the Mode System Setting is
editable.
Model: RXx71 x - indicates the size of the display
x – 3 = 5.7”; 4 = 8”; 5 = 10”; 6 = 12”
Mode: Idle = RX is in Idle mode
February 8, 2010 Page 47 of 124 # 1018
Page 48

CH.10 MAN0924-01-EN
DoIo = RX is in Do I/O mode
Run = RX is in Run mode
Scan Rate(mS): 0.0 = RX is not in Run mode
0.1 to 999.9 = Average number of mS for each ladder scan
Lcl Net Use (%): 0.0 to 100.0 = CAN network bandwidth % used by this RX node
All Net Use (%): 0.0 to 100.0 = CAN network bandwidth % used by all nodes
Ladder Size: x = Number of bytes in application ladder program
Config Size: x = Number of bytes in application I/O configuration
Graphics Size: x = Number of bytes in application graphic screens
String Size: x = Number of bytes in application string table
Bitmap Size: x = Number of bytes in application bitmaps
Text Tbl Size: x = Number of bytes in application text tables
Font Tbl Size: x = Number of bytes in application font tables
Protocol Size: x = Number of bytes in application downloaded protocols
SMS Size: x = Number of bytes in application SMS configuration
Firmware Rev: xx.yy = Current firmware version
BIOS Rev: x.y = Current BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) version
FPGA Rev: x.y = Current FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array)
version
Self-Test: Ok = All power-on self-tests passed
Fault = One or more power-on self-tests failed
View OCS Diags
The View OCS Diags Sub-Menu displays 11 System Diagnostics, none of which are editable. The first
two System Diagnostics are critical. If any of them indicate a Fault condition, the RX will not
enter or
remain in Run mode, and the problem must be investigated and corrected.
Logic Error: Ok = All executed ladder instructions are legal for loaded
Firmware
Fault = A ladder instruction not
supported by firmware was
Found
User Program: Ok = Ladder program and I/O configuration loaded
Successfully
Fault = Ladder program or I/O configuration not loaded or load
Failed
Following System Diagnostics are informational. If any of them indicate a Warning condition, the RX can
still enter and remain in Run mode, but the problem should be investigated and corrected.
February 8, 2010 Page 48 of 124 # 1018
Page 49

MAN0924-01-EN CH.10
User Graphics: Ok = Application graphics objects loaded successfully
Warn = Application graphics objects not loaded or load failed
W-Dog Trips: 0 = Watchdog timer has not tripped since the last power-up
x = Number of times watchdog timer has tripped
Net Errors: 0 = No CAN network bus-off errors have occurred
x = Number of CAN network bus-off errors that have occurred
Network State: Ok = At least one other node was found on the CAN network
Warn = No other nodes were found on the CAN network
Network ID: Ok = This node’s CAN Network ID was in the range 1 to 253
Warn = This node’s CAN Network ID was out of range at power-up
Dup Net ID: Ok = This node’s Network ID is unique on the CAN network
Warn = This node’s Network ID is duplicated in another node
Clock Error: Ok = Time and date have been set
Warn = Time and date need to be set
I/O System: Ok = I/O configuration matches the installed I/O and COM
modules
Warn = I/O configuration needs updating to match installed
Modules
Battery: Ok = Battery voltage level at an acceptable level
Warn = Battery voltage level below an acceptable level
February 8, 2010 Page 49 of 124 # 1018
Page 50

CH.10 MAN0924-01-EN
View I/O Slots
The View I/O Slots sub menu displays 6 System Settings, only one of which is editable.
Slot 1: I/O: FOX100 = FOX100 has been configured through Cscape*
Slot 2: I/O: ETN300 = ETN300 has been configured through Cscape
Slot 3: I/O: Empty = N/A
Slot 4: I/O: Empty = N/A
Base Selected: CPU = I/O on the CPU Base
Main = I/O on the Main Base (Smart Stack)
2-7 = I/O on the remote base (FOX hub / base)*
Base Online? Yes = Indicates no problems with fiber cables
No = Indicates a problem with fiber cables
* FOX is not active in this product
View Protocols
February 8, 2010 Page 50 of 124 # 1018
Page 51

MAN0924-01-EN CH.10
The View Protocols Sub-Menu displays two System Settings, none of which are editable.
As mentioned earlier, MJ1 (Port 1) and MJ2 (Port 2) serial ports support downloadable protocols. To
assign a downloadable protocol to a RX-371 serial port, select the Protocol Config item in Cscape’s
Program menu and then setup a protocol for Port 1 or Port 2 (or both of them).
In the View Protocols Sub-Menu, the currently downloaded protocol, if any, and its version number are
displayed for the respective port.
Port 1:
Protocol name = (None Loaded) or name of the protocol assigned to MJ1
Protocol version = Blank or ve rsion of the protocol assigned to MJ1
Port 2:
Protocol name = (None Loaded) or name of the protocol assigned to MJ2
Protocol version = Blank or ve rsion of the protocol assigned to MJ2
Set Fkeys
The Set Fkeys Sub-Menu displays two System Settings, both of which are editable.
Fkeys: Momentary (default) = %K1-5 bits go On/Off as F1-F5 are pressed / released
Toggle = %K1-5 bits toggle each time F1-F5 are pressed
SYS_Fn enable: Yes (default) = Reset and all clear, system functions enabled
No = Reset and all clear, system functions disabled
February 8, 2010 Page 51 of 124 # 1018
Page 52

CH.10 MAN0924-01-EN
Set Serial Ports
The Set Serial Ports Sub-Menu displays two System Settings, all of which are editable.
MJ1 RS485 Bias: No = MJ1 RS485 bias resistors are not
switched in
Yes = MJ1 RS485 bias resistors are switched in
MJ2 RS485 Bias: No = MJ2 RS485 bias resistors are not
switched in
Yes = MJ2 RS485 bias resistors are switched in
Set Time/Date
The Set Time/Date Sub-Menu displays three System Settings. Time and Date are editable, and Day is
automatically calculated from the Date setting. Note that Time and Date are split into three editable fields
each. Use
← or → to select a field and then use ↓ or ↑ to edit the field.
Time: 10:21:36 = Current time (hh:mm:ss in 24-hour format)
Date: 22-Jun-2006 = Current date (dd-md-yyyy)
Day: Thursday = Current day of week calculated from the Date setting
February 8, 2010 Page 52 of 124 # 1018
Page 53

MAN0924-01-EN CH.10
Set Beeper
The Set Beeper Sub-Menu displays one System Setting, which is editable
Beeper enable: Yes (default)= Enables beeper
No = Disables beeper (does NOT affect ladder access)
Set Screen
The Set Screen Sub-Menu displays four System Settings, all of which are editable
Saver enable: Yes = Enable screen saver
No (default) = Disable screen saver
Timeout (min): 5 - 1200 = Amount of time in minutes to expire with NO touch activity before
activating screen saver (black screen)
Popup Status: Off (default) = Disable popup status
Warning = Display popup status only if controller status changes to NOT Ok or
NOT Run mode.
ON = Display popup status on any controller status change.
Update Time (mS): 2 - 50 = Maximum amount of time to allow for graphics update per scan
February 8, 2010 Page 53 of 124 # 1018
Page 54

CH.10 MAN0924-01-EN
g
g
Removable Media
The Removable Media Sub-Menu displays the Removable Media Manager. After selecting Removable
Media from the Main Menu, one of four Sub-Menu screens will appear:
Media Directory
Media Card Not Present
Free bytes: Total bytes:
Del
Del
All
For
mat
Save
m
P
Esc
= No RM card has been installed in the
Memory slot
= RM card is installed and initialized, but
contains no files
Media Directory
FILENAM1.EXT 508 11-1-06 10:23a
Free bytes: 6382590 Total bytes: 63826944
Del
Del
All
For
mat
Save
P
m
Esc
= RM card is installed and initialized, and
it contains files.
Free bytes indicates the free space on
RM card in bytes.
Total bytes indicates the total capacity
of the card in bytes.
If the Removable Media Manager displays files or directories, as in the last example above, there are
several options available:
Del = Delete the highlighted file or directory
DelAll = Delete all files and directories
Format = Format the RM card
SavPgm = Save RX-371 application to DEFAULT.PGM
Esc = Cancel current operation (back up one screen)
If a directory name is highlighted, pressing Enter will switch to that directory showing its files and subdirectories. In a sub-directory, highlighting.. (dot dot) and pressing Enter will move up one directory.
February 8, 2010 Page 54 of 124 # 1018
Page 55

MAN0924-01-EN CH.10
Fail – Safe System
The Fail-Safe System is a set of features that allow an application to continue running in the event of
certain types of "soft" failures. These "soft" failures include:
• Battery power loss
• Battery-Backed Register RAM or Application Flash corruption due to, for example, an excessive
EMI event.
Selecting “Fail-Safe System” menu will open the following menu screen:
Selecting Backup/Restore Data displays the following screen in:
Backup = Copies Battery Backed RAM contents on to the onboard FLASH memory of the OCS.
Restore = Copies the backed up data from onboard FLASH to the battery backed RAM.
Clear Backup = The backup data will be erased from the onboard FLASH.
Exit = Goes back to previous menu.
February 8, 2010 Page 55 of 124 # 1018
Page 56

CH.10 MAN0924-01-EN
“Enable AutoRun” displays the following options which can be selected:
Enable AutoRun No = OCS will be in IDLE mode after AutoLoad or Automatic Restore.
Yes = OCS will be automatically placed into RUN mode after AutoLoad or
Automatic Restore.
“Enable AutoLoad” displays the following options which can be selected:
Enable AutoLoad No = Does not load AUTOLOAD.PGM automatically when application
program is absent or corrupted.
Yes = Loads AUTOLOAD.PGM file automatically from RM when application
program is absent or corrupted.
Clone Unit
‘Clone Unit’ feature allows the user to “clone” the OCS of the exact same model. This feature “clones”
application program and unit settings stored in Battery backed RAM of an OCS into the RM (refer
Removable Media
Chapter 8 for details on using RM). It can then be used to clone a different OCS (exact
same model).
February 8, 2010 Page 56 of 124 # 1018
Page 57

MAN0924-01-EN CH.10
This feature can be used for:
• Replacing an OCS by another unit of the same model.
• Duplicating or “clone” units without a PC.
Clone
Selecting “Clone Unit” menu will open the following menu screen:
Note: Free/Total – displays number of free and total bytes in Removable Media.
Selecting Make Clone brings up the screen below for the user:
After confirmation, the OCS will create two new files in the root directory of the Removable Media Drive
as shown below:
AUTOLOAD.PGM Application file
CLONE.DAT File having all unit settings and register values from Battery Backed RAM
February 8, 2010 Page 57 of 124 # 1018
Page 58

CH.10 MAN0924-01-EN
Load Clone
Selecting “Clone Unit” menu will open the following menu screen. Select “Load Clone”.
NOTE: For security enabled files, Load clone asks for password validation before loading the application.
10.4 Touch screen calibration
The touch screen is calibrated at the factory and rarely needs modification. However, if actual touch
locations do not appear to correspond with responding objects on the display, field adjustment is
available. To access the field adjustable touch screen calibration dialog, press and hold both the SYS and
F1 key for longer than 2 seconds and a dialog similar to figure 9.2 should appear. Thereafter, use a
plastic tip stylus and follow the dialog instructions.
Note that special system keys may be locked out from user access. If the SYS-F1 combination
does NOT respond, verify that the system menu’s Set Fkeys sub-menu’s parameter SYS_Fn is
enabled.
February 8, 2010 Page 58 of 124 # 1018
Page 59

MAN0924-01-EN CH.10
Figure 10.2: Touch Calibration Screen
February 8, 2010 Page 59 of 124 # 1018
Page 60

CH.10 MAN0924-01-EN
NOTES
February 8, 2010 Page 60 of 124 # 1018
Page 61

MAN0924-01-EN CH. 11
CHAPTER 11: USER INTERFACE
11.1 Overview
This chapter presents the user interface (or operator view) of the RX-371 and some of the model specific
characteristics of the RX-371 as compared to the rest of the OCS line. This chapter does NOT cover
building screens or using the CSCAPE graphics editor. For instructions on creating screens and using the
graphics editor, refer to the graphics editor help file.
The following aspects are discussed:
• Displaying and entering data
• Alpha-numeric data entry
• Navigating around screens
• Beeper acknowledgement
• Touch (slip) sensitivity
• Alarm log dialog
• RM dialog
• Run and OK status
• Screen Saver
• Dimmer
11.2 Displaying and entering Data
Figure 11.1: Example Screen
February 8, 2010 Page 61 of 124 # 1018
Page 62

CH.11 MAN0924-01-EN
Multiple objects are provided for displaying data such as virtual panel lights, push buttons, numeric value
displays, bar graphs, meters, graphs and animated bitmaps. On the RX-371, these graphical objects
(through ladder manipulation of attribute bits) can change color, flash or change visibility to attract
operator attention.
On objects that accept user input, the input is provided by touching the object or alternately changing an
OCS register (i.e. Function key registers). Objects that allow input generally have a raised 3D
appearance. An exception is the binary type objects, such as buttons, which are shown in a depressed
3D appearance when in the ON state. Objects that normally accept touch input may be disabled through
program control (through ladder manipulation of an attribute bit). If an object is disabled, the object’s
representation changes to a 2D appearance.
On objects that represent non-discrete information, more action may be required beyond that of simply
touching the object. For example, the slider object requires the operator to touch and slide the control in
the direction desired. Alternately, alpha-numeric entry objects invoke a pop-up alpha-numeric keypad for
additional user input. The alpha-numeric keypad is discussed below.
Note that if the numeric entry object displays >>>>>>>, the value is too big to display in the field or is
above the maximum for an editable field. Likewise, if the numeric entry object displays <<<<<<< in a
numeric field, the value is too small to display or is below the minimum for an editable field.
11.3 Alpha-numeric keypad
To allow entry of a specific number or text, several of the input objects invoke a pop-up alpha-numeric
keypad when the object is touched. An example of the alpha-numeric keypad invoked from a numeric
input object is shown in Figure 10.2. Once invoked, the operator may touch the appropriate keys to enter
a specific value. When entering a value, the alpha-numeric keypad is in one of two modes [new-value or
edit-value].
New-value mode
Generally, when the alpha-numeric keypad is first invoked, it is placed in new-value mode. Initially, the
alpha-numeric keypad displays the current value with all the digits being highlighted. Once the first digit is
entered, the current value is erased from the display and the new digit is placed in the first location.
Thereafter, no digits are highlighted and new digits are added to the rightmost position while the other
digits are shifted left.
Edit-value mode
Edit-value mode may be entered from the initial new-value mode by pressing either the left or right arrow
key before any digit key is pressed. The result will be a single character highlighted. The user may then
either touch a key to change the digit at the selected position or the up and down arrows may be used to
add or subtract (respectively) from the selected digit. The user may then use the left or right arrow keys to
select a new position.
February 8, 2010 Page 62 of 124 # 1018
Page 63

MAN0924-01-EN CH. 11
Figure 11.2: Alpha-numeric Keypad
Once the desired value is entered, pressing the Enter key moves that value into the object (and the
corresponding OCS register) and the alpha-numeric keypad disappears. Alternately, pressing the ESC
key any time before the Enter key cancels the operation, leaves the objects current value unchanged, and
the alpha-numeric keypad disappears.
Note: Each numeric entry object has a configured minimum and maximum value. If the operator enters a
value outside of the configured range, the new value is ignored when Enter is pressed and the current
object value is NOT changed.
Since the alpha-numeric keypad services several different graphical objects, certain keys on the alphanumeric keypad may be disabled (grayed) when the keypad is invoked for certain objects. The following
describes the alpha-numeric keypad variation based on object.
Numeric Object
When editing a numeric value, the [+/-] or the [.] key are disabled (grayed) if the object is NOT configured
for floating-point value or a signed value.
Password Object
When editing a password value, the arrow keys, [+/-], and the [.] keys are disabled. Additionally, overwrite
mode is disabled. When entering digits, the pop-up keypad hides the value by displaying ‘*’ alternately for
each digit.
ASCII Object
When editing an ASCII value, each press of the same key generates a different value. For example, the
[1 _QZ] key generates the following sequence:
<space>, Q, Z, q, z, 1, <repeat sequence>
The digit keys (except zero) sequence the corresponding 3 alphabetical characters first in upper case
followed by the same 3 characters in lower case followed by the corresponding numeric digit. Thereafter,
continued presses of the same key repeat the sequence.
February 8, 2010 Page 63 of 124 # 1018
Page 64

CH.11 MAN0924-01-EN
The [+/-] key generates the following mathematical character sequence:
+, -, *, /, =, (,), <repeat sequence>
The [.] key generates the following punctuation character sequence:
.,?, :, ;, ,,’ ,”, $, <repeat sequence>
Once the desired alpha-numeric character is obtained, use the left or right arrow to select a new position.
Alternately, pressing different key moves to the next position.
Text Table Object
When editing a Text Table Object, all the keys except the Up and Down arrow keys are grayed and
disabled. The next text selection is made by pressing either the Up or Down arrow.
Time/Date Object
When editing a Time/Date Table Object, all the keys except the Up, Down, Left and Right arrow keys are
grayed and disabled. The specific field (i.e. hour or minutes) is selected using the Left and Right arrows.
The value in the selected field is changed by pressing either the Up or Down arrow.
11.4 Screen Navigation
To allow the operator to change screens, a screen jump object is generally used. This object may be
visually represented as a 3-D button (responding to touch) or remain invisible and logically tied to an
OCS register. An optional system ICON may be configured for display along with the legend, which aids
in identifying the object as one that causes a screen change (shown below in figure 10.3)
Figure 11.3: Screen Jump Object (configured for a specific screen)
The RX-371 had the ability to store up to 8 screen jumps and then transverse back through those screens
when the desired operation is complete (useful for virtual menus). On OCS models that contain a front
panel ESC key, each press of the ESC key transverses back one screen; however, since the RX-371
does NOT have an ESC key on the front panel an alternate method is used. Screen jump objects on a
RX-371 may be configured to simulate an ESC key. Typically, screen jump objects simulating an ESC key
are labeled Back or Previous to indicate to the operator that it is possible to transverse back to a previous
screen.
February 8, 2010 Page 64 of 124 # 1018
Page 65

MAN0924-01-EN CH. 11
Figure 11.4: Screen Jump Object (configured to return to previous screen)
Note that changing the current displayed screen through use of a display coil in ladder logic clears the
screen jump queue.
11.5 Ladder Based Screen Navigation
Ladder logic can use several techniques to control screen navigation. Coils can be tied to %D registers to
make them screen coils. These coils have two modes, switch and alarm. If the ladder program energizes
an alarm display coil, the screen associated with this coil is displayed and overrides the normal user
screens. This is designed to show alarm conditions or to display other ladder-detected events. When the
text coil is de-energized, the previous screen that was being viewed before the alarm is returned.
The switch display coil switches to the associated screen when it is energized. Once it is de-energized
the screen remains until it is switched by the user or ladder.
Figure 11.5: Force and Switch Coils in Ladder Programming
There is also a system register that can be used to for control based screen navigation. %SR1 can be
read to determine the current screen or written to change the current screen.
Refer to the on-line help in Cscape for more information on control-based screen navigation.
11.6 Beeper Acknowledgement
The RX contains an internal beeper that provides an audible acknowledgment when an operator touches
a graphic object that accepts touch input. When the graphic object is enabled, a short 5ms tone is
emitted. When the graphic object is disabled, a longer 100ms tone is emitted to enounce that graphical
object is not currently accepting the touch input.
February 8, 2010 Page 65 of 124 # 1018
Page 66

CH.11 MAN0924-01-EN
If beep acknowledgement is not desired, the beeper function can be disabled from the system menu.
11.7 Touch (Slip) Sensitivity
Touch slip sensitivity is preset to meet most applications; however, adjustment is available to reduce the
sensitivity for touch release. That is, once a graphical object (button) is touched and held by a finger, the
default touch slip sensitivity allows for a slight slip of the finger on the graphical object before the RX-371
assumes touch been released (equates to approximately a quarter inch of movement with a stylus).
In some applications (such as jog buttons) where the operator is pushing a button for a period of time, the
amount of slip while holding a button pressed may exceed the default sensitivity. To increase the amount
of tolerable slip and prevent false releases of the button, the RX-371 allows adjustment of the allowable
slide up to 5x the default value.
To enable the touch (slip) sensitivity, first an OCS data register must be allocated through the Graphics
editor Configuration menu for Display Settings. Once a Touch Sensitivity register is assigned, that register
may be modified [range = 1(Low) to 5 (High)] to the desired slide amount. If a value outside the valid
range is entered in the touch sensitivity register, it is ignored and the last valid value is used.
11.8 Alarms
Alarm presentation to the operator is highly configurable and beyond the scope of this document to
describe fully. For more information refer to the graphics editor help file. This section presents a typical
configuration thereby providing an introductory description on what the operator should expect.
The alarm object is generally used to enunciate alarms to the operator. While the display characteristics
of this object is configurable, it is generally displayed as a button that changes colors to indicate the
highest state of the alarm(s) in the alarm group it is monitoring. The following indicates the priority of the
alarm states and the default colors associated with these states.
• Highest (Red) - Unacknowledged Alarms Exist
• - (Yellow) - Acknowledged Alarms Exist
• Lowest (Green) - No Alarms Exist
Figure 11.6: Alarm Object
To view, acknowledge and/or clear alarms, the operator must access the alarm viewer. This is
accomplished by touching an (enabled) alarm object. When accessed, the alarm viewer is displayed as
pop-up alarm viewer dialog similar to that shown in Figure 11.7.
February 8, 2010 Page 66 of 124 # 1018
Page 67

MAN0924-01-EN CH. 11
Figure 11.7: Alarm Viewer
The currently selected entry is indicated by a yellow highlight which can be moved up or down by
touching the arrow buttons or by directly touching an entry. If more entries exist than can fit on the page,
a scroll bar is displayed on the right side that also indicates the current relative position.
The current state of the displayed alarm is indicated by its color and optionally by an abbreviated indicator
after the date/time stamp (ALM, ACK, RTN). The operator can acknowledge an alarm by selecting it from
the list and touching the ACK button. The operator can also clear an alarm if that function is enabled in
the alarm object. If not enabled, the Clear buttons are grayed and do not respond to touch. Once view
operations are complete, simply touch the Esc button to remove the pop-up alarm viewer.
Note that OCS registers %SR181 and %SR182 are available for ladder use, which indicate presence of
unacknowledged or acknowledged alarm (respectively). The screen designer may implement these
registers to switch screens or activate the beeper to attract the operator’s attention.
11.9 Removable Media
The removable media object is generally used to inform the operator on the current state of the
removable media device and allow access to its file structure. The removable media object is displayed
as a button that changes colors to indicate the current state of the removable media device. The following
indicates the device states and the default colors associated with these states.
• Highest (Red) - Device Error
• - (Yellow) - Device Full (threshold adjustable)
• Lowest (Green) - Device OK
Figure 11.8: Removable Media Object
February 8, 2010 Page 67 of 124 # 1018
Page 68

CH.11 MAN0924-01-EN
To view and perform file operations, the operator must access the removable viewer. This is
accomplished by either touching an (enabled) removable media object or through the system menu.
When accessed, the removable media viewer is displayed as pop-up removable media dialog similar to
that shown in Figure 10.8.
Note that the removable media object can be configured to open the removable media viewer at a certain
directory complete with restrictions on transversing back up the file path. This may be used to restrict
operator access to non-critical files.
Figure 11.9: Removable media viewer
The currently selected entry is indicated by a yellow highlight which can be moved up or down by
touching the arrow buttons or by directly touching an entry. If more entries exist than can fit on the page,
a scroll bar is displayed on the right side that also indicates the current relative position.
File operations are accomplished by pressing the appropriate button at the bottom of the removable
media viewer. The configuration of the removable media object that invokes the removable media viewer
defines what buttons are enabled and available to the user. A button is grayed and does not respond to
touch if configured as disabled.
The (Enter) button (if enabled) performs certain operations based on the selected file’s type:
.. - change di splay to parent directory
<DIR> - change display to child directory
bmp, jpeg - display bitmap (if compatible format)
pgm - load applicat ion (if compatible model and version)
Alternately, the (enter) button can be configured to simply load the ASCII representation of the file path
(including the file name) to a group of OCS registers. That pathname can then be used by ladder for
opening and manipulating that file.
Once view operations are complete, simply touch the Esc button to remove the pop-up removable media
viewer.
If the removable media is used in an application, the removable media device requires changing by the
operator, and the application is attempting to write to the removable media when it is removed, the screen
designer should create objects that allow the operator to temporally halt access to the removable media.
This prevents corruption to the file system if the removable media is removed during a file write sequence.
The graphic objects should set OCS register %SR174.1 (when requesting the card be removed) and
February 8, 2010 Page 68 of 124 # 1018
Page 69

MAN0924-01-EN CH. 11
provide an indicator based on OCS register %SR174.2 (which indicates that it is safe to remove the
removable media).
Figure 11.10: Example application segment for safe removal of removable media
11.10 OK and Run Status
Since the RX-371 does not provide external LEDs for the Ok and Run status of the configuration
and ladder logic engine (respectively), an optional pop-up may be enabled to warn the user that
one of these two status indications has changed. When enabled in the system menu, a status
change is indicated as shown in figure10.11.
Figure 11.11: OK and RUN Status
To remove the popup, simply touch the OK button. If either the Ok or Run indicator is reset, the operator
may consult the system menu diagnostic screen to determine the problem.
February 8, 2010 Page 69 of 124 # 1018
Page 70

CH.11 MAN0924-01-EN
11.11 Screen Saver
The RX-371 screen backlight life is typically 5 years when in continuous use. If the application does not
require interaction with the RX-371 for long periods of time, the backlight life can be extended by using
the screen saver function. When enabled through the system menu, the backlight is shut off (screen goes
black) after a specified time of no touch activity on the screen. When the screen saver shuts off the
backlight, any operator touch on the screen or function keys reactivates the backlight.
Note that when the screen saver is active (backlight shut off), any initial touch activity on the screen (or
function key) to reactivate the backlight is otherwise ignored by the RX-371. Any additional touch activity
is also ignored by the RX-371 for approximately one second thereafter.
It is possible for the application to temporarily disable the screen saver by generating a positive transition
to %SR57.16 (coil only) at a rate faster than the screen saver timeout value. This may be desired while
waiting for alarm acknowledgement.
11.12 Screen Brightness
The RX-371 provides a feature that allows screen dimming for night operation. To enable this feature, the
application must access and control system register %SR57 (Display Backlight Brightness). Screen
brightness is continuously variable by driving %SR57 through the range of 100 (full bright) to 0 (full off). It
is left to the screen designer on if and how to present a Screen Brightness control to the user.
Note that backlight life may be shorted when screen is dimmed or screen brightness is varied on a
repetitive basis.
February 8, 2010 Page 70 of 124 # 1018
Page 71

MAN0924-01-EN CH. 12
CHAPTER 12: REGISTERS
12.1 RX-371 Resources
12.1.1 Overview
This section defines the resource limits that a programmer needs to know when writing a program using
the RX-371. The RX-371 combines operator interface (display and keypad), local and remote I/O (analog
and digital), networking, and controller, into a single product. In addition, the RX-371 has graphical
capabilities. The controller portion of the RX-371 products is programmed in ladder logic via the
Windows-based Cscape (Control Station Central Application Programming Environment) package.
12.1.2 Resource Limits
Table 12.1 Resource Limits
Resource RX-371
%S 1 bit
%SR 16 bit
%T 1 bit
%M 1 bit
%R 16 bit
%K 1 bit
%D 1 bit
%I 1 bit
%Q 1 bit
%AI 16 bit
%AQ 16 bit
%IG 1 bit
%QG 1 bit
%AIG 16 bit
%AQG 16 bit
Ethernet
CsCAN
Serial Ports
IDs Per CsCAN
Network
SmartStack
Modules
Keypad
Display Type
Display Size
Display Screen
Dimensions
Screen
Memory
Colors
User Screens
Objects Per
User Screen
Ladder Code
CsCAN, Ping, EGD, SRTP, Modbus TCP Master (Downloadable protocol) & Slave, Ethernet IP,
FTP, or HTTP @ 10 MBd or 100 MBd
125 kBd, 250 kBd, 500 kBd, or
2 RS-232 / RS-485 Ports. Software Selectable.
64 w/o repeat (253 w/ 3 repeaters)
5 user-defined Function keys and a System key
256
192
2048
2048
9999
5
1023
2048
2048
512
512
64 (Per ID)
64 (Per ID)
32 (Per ID)
32 (Per ID)
1 MBd
4 Main Slots
5.7” QVGA TFT
5.7”
320 x 240
2.75 MB
32,768
1023
50
256 kB
February 8, 2010 Page 71 of 124 # 1018
Page 72

CH. 12 MAN0924-01-EN
12.1.3 Resource Definitions
System Registers
System Registers (%S and %SR) are used to store general RX-371 status information. This
information is used internally, and is also available to the operator via the System Menu, using the
RX-371 display and keypad. The System Registers are also available for User Screens and can be
accessed by Ladder Code.
%S Registers
%S Registers are 1-bit memory locations containing system status information, which are
implemented as shown in
Table 12.2:
Table 12.2- %S Registers
Register Name Description
%S1
%S2
%S3
%S4
%S5
%S6
%S7
%S8
%S9
%S10
%S11
%S12
%S13
%S16
FST_SCN
NET_OK On if CsCAN Network is functioning properly
T_10MS On for 5 mS; Off for 5 mS
T_100MS On for 50 mS; Off for 50 mS
T_SEC On for 500 mS; Off for 500 mS
IO_OK On if SmartStack I/O is configured properly
ALW_ON Always On
ALW_OFF Always Off
PAUSING_SCN
RESUMED_SCN
IO_FORCED On if one or more I/O points are currently being forced
IO_FORCING On if I/O forcing is enabled
NET_IO_OK On if Network I/O (SmartStix) is functioning properly
Ethernet COM module is OK
On during the first scan after entering RUN mode
On during the last scan before Pause-N-Load
On during the first scan before Pause-N-Load
%SR Registers
%SR Registers are 16-bit memory locations, containing system status information, implemented as
shown in
Table 12.3.
Note: Where 2 %SRs are combined to make a 32-bit value, the lower numbered %SR is the low word,
while the higher numbered %SR is the high word.
Table 12.3- %SR Registers
Register Name Description Min Val Max Val
%SR1
%SR2
%SR3
%SR4
%SR5
%SR6
%SR7
%SR8
%SR9-10
%SR11-12
%SR 13-16
%SR17-18
%SR19-20
%SR21-22
%SR23
%SR 24-25
%SR26
%SR27
%SR28
%SR29
USER_SCR Current User Screen Number 1 1023
ALRM_SCR Current Alarm Screen Number (0=none) 0 1023
SYS_SCR Current System Screen Number (0=none) 0 14
SELF_TEST Bit-Mapped Self-Test Result 0 65535
CS_MODE Control Station Mode (0=Idle, 1=Do I/O, 2=Run) 0 2
SCAN_RATE Average Scan Rate ( / 10) - 1000
MIN_RATE Minimum Scan Rate ( / 10) - 1000
MAX_RATE Maximum Scan Rate ( / 10) - 1000
EDIT_BUF Data Field Edit Buffer 0 2
LADDER_SIZE Ladder Code Size 2 256K
Reserved - - IO_SIZE I/O Configuration Table Size 16 127K
NET_SIZE Network Configuration Table Size 34 1K
SD_SIZE Security Data Table Size - LADDER_CRC Ladder Code CRC 0 65535
Reserved - - IO_CRC I/O Configuration Table CRC 0 65535
NET_CRC Network Configuration Table CRC 0 65535
SD_CRC Security Data Table CRC 0 65535
NET_ID This Station’s Primary Network ID (CsCAN) 1 253
32
-1
February 8, 2010 Page 72 of 124 # 1018
Page 73

MAN0924-01-EN CH. 12
Table 12.3- %SR Registers
Register Name Description Min Val Max Val
%SR30
%SR31
NET_BAUD
NET_MODE
Network Baud Rate (CsCAN)
(0=125KB; 1=250KB; 2=500KB; 3=1MB)
Network Mode (0=network not
required; 1=network
required; 2=network optimized;
0 3
0 3
3=network required and optimized)
%SR32
%SR33
LCD_CONT LCD Display Contrast setting 0 255
FKEY_MODE Function Key Mode (0=Momentary; 1=Toggle) 0 1
RS232 Serial Protocol Mode
%SR34
%SR35-36
%SR37
%SR38
%SR39
%SR40
%SR41
%SR42
%SR43
%SR44
%SR45
%SR46
%SR47
%SR48
%SR49
%SR50
%SR51
%SR52
%SR53-54
%SR55
%SR56
%SR57
%SR58
%SR59-60
%SR61
%SR62
%SR63
%SR64
%SR65-76
%SR77-88
%SR89-100
%SR101-
112
%SR113114
%SR115116
%SR117-
118
%SR119120
%SR121-
122
%SR123-
124
SERIAL_PROT
SERIAL_NUM This Station’s 32-bit Serial Number 0 2
MODEL_NUM This Station’s Binary Mo del Number 0 65535
ENG_REV Firmware Rev Number ( / 100) 0000 9999
CPLD_REV BIOS Rev Number ( / 100) 000 255
FPGA_REV FPGA Image Rev Number ( / 10) 000 255
LCD_COLS Vertical Pixel Count
LCD_ROWS Horizontal Pixel Count
KEY_TYPE Keypad Type
RTC_SEC Real-Time-Clock Second 0 59
RTC_MIN Real-Time-Clock Minute 0 59
RTC_HOUR Real-Time-Clock Hour 0 23
RTC_DATE Real-Time-Clock Date 1 31
RTC_MON Real-Time-Clock Month 1 12
RTC_YEAR Real-Time-Clock Year 1996 2095
RTC_DAY Real-Time-Clock Day (1=Sunday) 1 7
NET_CNT Network Error Count 0 65535
WDOG_CNT Watchdog-Tripped Error Count 0 65535
BAD_LADDER Bad Ladder Code Error Index 0 65534
F_SELF_TEST Filtered Bit-Mapped Self-Test Result 0 65535
LAST_KEY Key Code of Last Key Press or Release 0 255
BAK_LITE
USER_LEDS User LED Control / Status 0 65535
Reserved - - NUM_IDS T his Station’s Number of Network IDs 1 253
NUM_IDS This Station’s Number of Network IDs 1 253
SS_BASE SmartStack I/O Base Selector 0 7
SS_STATUS SmartStack I/O Base Status 0 2
SS_INFO_1 SmartStack I/O Module #1 Information Structure - SS_INFO_2 SmartStack I/O Module #2 Information Structure - SS_INFO_3 SmartStack I/O Module #3 Information Structure - -
SS_INFO_4 SmartStack I/O Module #4 Information Structure - GOBJ_SIZE Graphics Object Table Size 8 256K
GSTR_SIZE Graphics String Table Size 8 128K
GBMP_SIZE Graphics Bitmap Table Size 4 256K
GTXT_SIZE Graphics Text Table Size 8 128K
GFNT_SIZE Graphics Font Table Size 8 256K
PROT_SIZE Protocol Table Size 16 64K
(0=Firmware Update (RISM); 1=CsCAN; 2=Generic
(Ladder- Controlled); 3=Modbus RTU; 4=Modbus
ASCII)
LCD Backlight Dimmer Register
0 = 0% On; 25=25% On; 100-255 = 100% On
0 4
32
-1
0 255
February 8, 2010 Page 73 of 124 # 1018
Page 74

CH. 12 MAN0924-01-EN
Table 12.3- %SR Registers
Register Name Description Min Val Max Val
%SR125
%SR126
%SR127
%SR128
%SR129
%SR130
%SR131174
%SR164.3
%SR164.4
%SR164.5
%SR164.6
%SR164.7
%SR164.8
%SR164.9
%SR164.10
%SR164.11
%SR164.12
165-174
%SR175
%SR176-
177
%SR178-
179
%SR180
%SR181
%SR182
%SR183
%SR184
%SR185
%SR186
%SR187
%SR188
%SR189
%SR190
%SR191
%SR192
GOBJ_CRC Graphics Object Table CRC 0 65535
GSTR_CRC Graphics String Table CRC 0 65535
GBMP_CRC Graphics Bitmap Table CRC 0 65535
GTXT_CRC Graphics Text T able CRC 0 65535
GFNT_CRC Graphics Font Table CRC 0 65535
PROT_CRC Protocol Table CRC 0 65535
Reserved - - Enable Automatic Restore Operation (Fail Safe)
Enable Backup (Fail Safe System)
Enable AUTORUN (Fail Safe)
Enable AUTOLOAD (Fail Safe)
Clear Backup trigger bit
Create Backup trigger bit
MAKE_CLONE trigger bit
LOAD_CLONE trigger bit
Reserved
Removable
Media
Removable
Media
Removable
Media
Reserved - - -
ALM_UNACK
ALM_ACT Active Alarm (high bit indicates what group #)
SYS_BEEP System Beep Enable (0=disabled; 1=enabled)
USER_BEEP Software configurable (0=OFF; 1=ON)
SCR_SAVER Screen Sav er Enabled (0=disabled; 1=enabled)
SCR_SA_TM Screen Saver Time in minutes (delay)
NET_USE Average Net Usage of all units on the CAN network
NET_MIN
NET_MAX
NT_TX_AVG Average Net Usage of this unit
NT_TX_MIN Minimum Net Usage of this unit
NT_TX_MAX Maximum Net Usage of this unit
Make Clone Fail (This bit goes high when Make /
Create clone fails)
Load Clone Fail (This bit goes high when Load
clone fails)
Current Removable Media interface status 0 6
Indicates free space on the Removable Media card
in bytes.
Indicates the total card capacity in bytes. 0 2
Unacknowledged Alarm (high bit indicates what
group #)
Minimum Net Usage of all units on the CAN
network
Maximum Net Usage of all units on the CAN
network
0 2
31
31
User Registers
User Registers (%T, %M, and %R) are used to store application-specific RX-371 data. This data can
be accessed via User Screens and/or by Ladder Code.
%T Register
A %T Register is a non-retentive
1-bit memory location used to store application-specific state
information.
%M Registers
A %M Register is a retentive
1-bit memory location used to store application-specific state
information.
February 8, 2010 Page 74 of 124 # 1018
Page 75

MAN0924-01-EN CH. 12
%R Registers
A %R Register is a retentive
16-bit memory location used to store application-specific values.
HMI Registers
HMI Registers (%K and %D) give the user access to the RX keypad and displ ay.
%K Registers
A %K Register is a non-retentive
1-bit memory location (contact), used to store the state of a
function key on the RX keypad. If the function keys are set for momentary mode, a function key’s
associated %K register will be ON as long as the function key is pressed. If the function keys are
set for toggle mode, a function key’s associated %K register will toggle each time the function key
is pressed.
%D Registers
A %D Register is a non-retentive
1-bit memory location (coil), which can be turned ON by
Ladder Code to cause the corresponding User or Alarm Screen to be displayed.
I/O Registers
%I Registers
A %I Register is a 1-bit memory location, which is normally used to store the state of one of the
digital inputs on board or associated with a SmartStack I/O module. When used in this way, %I
registers are non-retentive
inputs, are retentive
, and can be used just like %M registers.
. All extra %I registers, which are not associated with SmartStack
%Q Registers
A %Q Register is a non-retentive
1-bit memory location, which is normally used to store the
state of one of the digital outputs on board or associated with a SmartStack I/O module.
%AI Registers
A %AI Register is a 16-bit memory location, which is normally used to store the value of one of
analog inputs on board or associated with a SmartStack I/O module. When used in this way, %AI
registers are non-retentive
. All extra % AI registers, which are not associated with inputs, are
retentive, and can be, used just like %R registers.
%AQ Registers
A %AQ Register is a non-retentive
16-bit memory location, which is normally used to store the
value of one of the analog outputs on board or associated with a SmartStack I/O module.
Global Data I/O Registers
Global Data I/O Registers (%IG, %QG, %AIG and %AQG) give the user access to the CsCAN
Network Port’s Global I/O data. This data can be accessed via User Sc reens and/or by Ladder Code.
The CsCAN Network is based on the Bosch Control Area Network (CAN), and implements the
CsCAN Protocol which is designed to take maximum advantage of the global data broadcasting
capability of CAN. Using this network protocol, up to 64 nodes can be linked without repeaters, and
up to 253 nodes can be linked by using 3 repeaters. For more information regarding CsCAN Protocol,
refer to the CsCAN Protocol Specification document (MAN0799).
%IG Registers
A %IG Register is a retentive
digital state obtained from another node on the network.
%QG Registers
A %QG Register is a retentive
state to be sent as global data to another node on the network.
1-bit memory location, which is normally used to store a global
1-bit memory location, which is normally used to store a digital
February 8, 2010 Page 75 of 124 # 1018
Page 76

CH. 12 MAN0924-01-EN
%AIG Registers
A %AIG Register is a retentive
16-bit memory location, which is normally used to store a global
analog value obtained from another node on the network.
%AQG Registers
A %AQG Register is a retentive
16-bit memory location, which is normally used to store an
analog value to be sent as global data to another node on the network.
February 8, 2010 Page 76 of 124 # 1018
Page 77

MAN0924-01-EN CH. 13
CHAPTER 13: CSCAPE CONFIGURATION
13.1 Overview
RX-371 hardware is programmed with a Windows-based PC application called Cscape (HE500OSW232).
Please see the on-line help provided with Cscape for additional details.
13.2 Cscape Status Bar
When the RX-371 is connected to a PC using Cscape software a Status Bar appears at the bottom of the
screen. The Cscape Status Bar can be used to determine if communications have been established
between the RX-371 and the Cscape program. Components of the Cscape Status Bar are explained as
below.
Message Line -
The contents of
these messages
are context
sensitive. The
Message line can
be empty.
Current User -
indicates who is logged
(for security purposes).
Ready User: NONE HERX371-CsCAN (Model=) Equal Local :1 Target :2(R) [no forces] MOD
Controller Model - (Model Confirmation)
• Controller Model indicates the controller model for
which the program in Cscape is configured.
• (Model Confirmation) provides the following
indications:
• (Model=) - The actual Target Controller matches the
configured Controller Model and Network.
• (Model Not=) – The actual Target Controller does not
match the configured Controller Model and Network.
• (Model?) – there may have been a change since the
last time the Target Controller was compared to the
configured Controller Model and Network.
Equal Indicator – indicates whether the current program in Cscape is equal to the program
stored in the Target Controller.
• If Equal, the program in Cscape is the same as the program stored in the Target Controller.
• If Not Equal, the program in Cscape is not
Controller.
• If Unknown, there may have been a change since the last time the program in Cscape was
compared to the Target Controller.
Communications Status - indicates the current status of the
“pass through” Connector.
• Local: xx – indicates the Network ID of the RX to which the
• Ta rg et : yy( R ) – indicates the Network ID of the device with
the same as the program stored in the Target
File Modified Indicator - indicates that the file in
the selected window has been modified but has
not been saved.
Cscape program is physically connected through its serial
port. It can serve as a pass through device to other nodes
on the network.
which the Cscape program is exchanging data.
Note: The Local unit and Target unit can be the
same unit or they can be separate units.
The following are status indicators:
(R) – Running
(D) - Do I/O
(I) – Idle
(?) – Cscape is not communicating with the remote unit.
[no forces] – indicates no I/O has been forced.
February 8, 2010 Page 77 of 124 # 1018
Page 78

CH. 13 MAN0924-01-EN
13.3 Establishing Communications
The preferred method of communicating between Cscape and a RX-371 is via USB port. The RX-371
OCS can communicate with Cscape using USB to USB, USB to serial adapters, serial port
communications via MJ1 Port, onboard Ethernet Port, CAN (CsCAN) or modems. For communications
other than USB or the MJ1 port please refer to the manual which ships with the communications adapter
hardware being used for programming.
13.3.1 To connect RX-371 with USB port: (Preferred method)
Connect a PC’s (Personal Computer running a Windows Microsoft operating system) USB port via USB
cable to the USB mini B port on the RX-371 OCS.
The PC will detect a new device has been plugged into the USB port.
Figure 13.1: Front Panel and USB Programming Connector
February 8, 2010 Page 78 of 124 # 1018
Page 79

MAN0924-01-EN CH. 13
February 8, 2010 Page 79 of 124 # 1018
Page 80

CH. 13 MAN0924-01-EN
February 8, 2010 Page 80 of 124 # 1018
Page 81

MAN0924-01-EN CH. 13
Next, configure Cscape to use the correct communications port. This can be done using the Tools |
Editor Options | Communication Port dialog in Cscape. In order to find the Comm Port number that the
RX-371 is using, go to the PC’s Control Panel and System, System Properties, Hardware.
February 8, 2010 Page 81 of 124 # 1018
Page 82

CH. 13 MAN0924-01-EN
Next, go to the PC’s Device Manager and Ports.
February 8, 2010 Page 82 of 124 # 1018
Page 83

MAN0924-01-EN CH. 13
Note that, in this example, the RX-371 is on COM3. This COM number may vary from PC to PC.
Now that you know which COM port the RX-371 is plugged to, go to Cscape, Tools, Application Settings,
Communications, click on Configure button and then choose the correct COM port (in this example Com
5) in the Add Target dialog.
February 8, 2010 Page 83 of 124 # 1018
Page 84

CH. 13 MAN0924-01-EN
If communications are successful, the target indicator should show the mode of the controller Target:
yy(R) as shown in the status section above
Cscape Status Bar. (13.2)
If the controller is not communicating you may need to set the target ID of the controller in Cscape or on
the unit. The Target ID allows directing communications to a particular unit when multiple units are
connected via a CsCAN network. Units without CsCAN network ports respond to any network ID and do
require the ID to be configured.
not
To check or change the ID on the RX-371 OCS, press the system menu key.
The first item in the menu is Set Network ID. Pressing Enter allows you to view or modify the ID of the
unit.
February 8, 2010 Page 84 of 124 # 1018
Page 85

MAN0924-01-EN CH. 13
To change the Target ID of Cscape, use the Controller | Set Target Network ID dialog.
13.3.2 Communication via MJ1 Serial Port:
Start by configuring Cscape to use the correct communications port. This can be done using the Tools |
Editor Options | Communication Port dialog in Cscape.
Next connect the PC serial port to the port labeled MJ1 on the RX. The easiest way to interface between
the serial port and the units MJ1 port would be to use an HE500CBL300A. The HE500CBL300A is sold
separately.
If communications are successful, the target indicator should show the mode of the controller Target:
yy(R) as shown in the status section above.
If the controller is not communicating you may need to set the target ID of the controller in Cscape or on
the unit. The Target ID allows directing communications to a particular unit when multiple units are
connected via a CsCAN network. Units without CsCAN network ports respond to any network ID and do
require the ID to be configured.
not
To check or change the ID on the RX-371, press the UP and DOWN keys on the RX simultaneously to
enter the system menu. The first item in the menu is Set Netw ork ID . Pressing Enter allows you to view
or modify the ID of the unit.
To change the Target ID of Cscape, use the Controller | Set Target Network ID dialog.
13.3.2 Communicating via On Board Ethernet Port
From Cscape go to Controller -> I/O Configure and do auto configuration for the connected controller,
Click on Config of Ethernet & go to Module Setup.
February 8, 2010 Page 85 of 124 # 1018
Page 86

CH. 13 MAN0924-01-EN
In Module configuration dialog go to IP Address field enter unused IP Address and configure unused
registers in Register field & then click OK. Screen shot for the same as follows:
Download the configuration to Controller. Connect LAN cable to the Controller in default LAN Port.
From Cscape go to Tools -> Editor Options -> Communication Port -> configure. Select Ethernet and
enter IP address which is configured in the file. Select mode as Nx/Rx Series mode from drop down list.
The controller should get connected to Cscape. If communications are successful, the target indicator
should show the mode of the controller Target: yy(R) as shown in the status section above.
13.4 Models supported
Cscape 9.0 and beyond supports all the options offered in the RX-371. For the latest version of Cscape or
compatibility information,
contact Technical Support.
13.5 Configuration
An overview of configuration:
1.) Start the configuration by selecting the Controller | Hardware Configure menu item.
2.) If the RX-371 is connected to the PC press the Auto Config System button to automatically
detect the Base model, I/O and any communication options.
3.) If the RX is not
connected press the Config button to the right side top end of the screen. This
allows the base CPU to be selected.
4.) Select RX-371 from the type drop down box.
February 8, 2010 Page 86 of 124 # 1018
Page 87

MAN0924-01-EN CH. 13
5.) Once the RX-371 CPU is selected, pres s OK to exit the dialo g and configure the I/O.
6.) Once done configuring the I/O, OK out of configuration dialogs.
February 8, 2010 Page 87 of 124 # 1018
Page 88

CH. 13 MAN0924-01-EN
NOTES
February 8, 2010 Page 88 of 124 # 1018
Page 89

MAN0924-01-EN CH. 14
CHAPTER 14: FAIL–SAFE SYSTEM
14.1 Overview
The Fail-Safe System is a set of features that allow an application to continue running in the event of
certain types of "soft" failures. These "soft" failures include:
• Battery power loss
• Battery-Backed Register RAM or Application Flash corruption due to, for example, an excessive
EMI event.
The Fail-Safe System has the following capabilities:
• Manually backup the current Battery-Backed RAM Register Settings into Flash memory.
• Manually restore Register Settings from the values previously backed up in Flash to Battery-
Backed RAM.
• Detect corrupted Register Settings at power-up and then automatically restore them from Flash.
• Detect corrupted or empty application in Flash memory at power-up and then automatically load
the AUTOLOAD.PGM application file from Removable Media (Compact Flash or MicroSD).
• If an automatic Register Restore or Application Load occurs, the OCS can automatically be
placed in RUN mode
The fail-safe system can be accessed by going to the system menu of the controller. A new menu “FailSafe System” has been added at the end of the main system menu for this. Selecting “Fail- Safe System”
menu will open the following menu screen:
Figure 14.1: Fail Safe System Menu
14.2 Settings
To use the fail – safe feature, the user needs to do the following:
1. Backup the current Battery-Backed RAM Register contents in On-Board Flash memory using
System Menu options.
2. From Cscape, create AUTOLOAD.PGM for the application program using ‘Export to Removable
Media’.
3. Place the Removable Media with AUTOLOAD.PGM in the device.
4. Set the ‘Enable AutoLoad’ option in the device to YES.
February 8, 2010 Page 89 of 124 # 1018
Page 90

CH. 14 MAN0924-01-EN
5. Set the ‘Enable AutoRun’ option to YES if the controller needs to be placed in RUN mode
automatically after automatic restore of data or AutoLoad operation.
14.3 Backup / Restore Data
Selecting this option brings up a screen having four operations:
• Backup OCS Data.
• Restore OCS Data.
• Clear Backup Data.
• Exit
Figure 14.2: Backup / Restore Data
Backup OCS Data:
Figure 14.3: Backup Registers
When initiated, this will allow the user to manually copy Battery-Backed RAM contents on to the onboard
FLASH memory of the OCS. This will have the effect of backing up all the registers and controller settings
(Network ID, etc.) that would otherwise be lost due to a battery failure.
%SR164.4 is set to 1 when backup operation is performed.
February 8, 2010 Page 90 of 124 # 1018
Page 91

MAN0924-01-EN CH. 14
Restore OCS Data:
When initiated, this will allow the user to manually copy the backed up data from the onboard FLASH to
the Battery-Backed RAM.
A restore operation will be automatically initiated if a backup has been previously created and on powerup the Battery-Backed RAM registers fail their check.
The following process will be followed for restoring data:
• The controller will be placed in IDLE mode.
• Data will be copied from onboard FLASH to OCS Battery-Backed RAM
• The controller will reset.
• The controller will be put in RUN mode if the AutoRun setting is ‘Yes’ else it will remain in IDLE
mode.
%SR164.3 is set to 1 only when an automatic restore operation is performed - not on a manual one. This
bit is reset to 0 when a new backup is created.
Restoring of data can be manually performed by selecting RESTORE option from the Backup / Restore
Data menu. This will cause the controller to reset.
Figure 14.4: Restore OCS Data
Clear Backup Data:
When initiated, the backup data will be erased from the onboard Flash and no backup will exist.
%SR164.4 and %SR164.3 is reset to 0 when backed up data is erased.
February 8, 2010 Page 91 of 124 # 1018
Page 92

CH. 14 MAN0924-01-EN
Figure 14.5: Clear Backup Data
Exit: Goes back to the previous screen.
February 8, 2010 Page 92 of 124 # 1018
Page 93

MAN0924-01-EN CH. 14
The OCS follows the following sequence in execution of Automatic Restore:
Figure 14.6: Flow Chart for Automatic Restore
February 8, 2010 Page 93 of 124 # 1018
Page 94

CH. 14 MAN0924-01-EN
14.4 AutoLoad
Figure 14.7: AutoLoad Menu
This system menu option allows the user to specify whether the OCS automatically loads the application
AUTOLOAD.PGM located in Removable Media.
When the AutoLoad setting is enabled (set to YES), it can either be manually initiated or automatically
initiated at power-up.
The automatic initiation will happen only in the following two cases:
• When there is no application program in the OCS and a valid AUTOLOAD.PGM is available in the
removable media of the device.
• When the program residing in onboard memory is corrupted and a valid AUTOLOAD.PGM is
available in the removable media of the device.
AutoLoad can be manually initiated when the SYS-F3 key is pressed (OCS can be in any of the following
mode – Idle / Run / DOIO). This also requires a valid AUTOLOAD.PGM to be present in the removable
media of the device.
When the AutoLoad setting is not enabled (set to NO), OCS will be in IDLE mode and the application is
not loaded.
If the AUTOLOAD.PGM is security enabled, the user will be prompted to enter the password before
loading the application. The application will be loaded from the Removable media only after getting the
correct password.
%SR164.6 can be set to enable AutoLoad feature.
February 8, 2010 Page 94 of 124 # 1018
Page 95

MAN0924-01-EN CH. 14
The OCS follows the following sequence in execution of AutoLoad:
Figure 14.8: Flow Chart for AutoLoad
February 8, 2010 Page 95 of 124 # 1018
Page 96

CH. 14 MAN0924-01-EN
14.5 AutoRun
Figure 14.9: AutoRun Menu
This system menu option, when enabled (YES), allows the user to automatically place the OCS into RUN
mode after the AutoLoad operation or automatic Restore Data operation.
When the AutoRun setting is disabled (NO), the OCS remains in the IDLE mode after a Restore Data or
AutoLoad operation.
%SR164.5 can be set by putting the system into RUN mode automatically, once an AutoLoad has been
performed or an Automatic Restore has occurred.
If for any reason the AutoLoad-Run (Loading the AUTOLOAD.PGM automatically and OCS put in RUN
mode) sequence does not succeed, a pop-up message box saying "AUTO-LOAD-RUN SEQUENCE
FAILED" will be displayed. It will also show the reason for its failure. On acknowledging this message box
the AutoLoad-Run sequence will be terminated, controller will return to the first user-screen and will be
placed in IDLE mode.
February 8, 2010 Page 96 of 124 # 1018
Page 97

MAN0924-01-EN CH.15
CHAPTER 15: CLONE UNIT
15.1 Overview
‘Clone Unit’ feature allows the user to “clone” the OCS of the exact same model. This feature “clones”
application program and unit settings stored in Battery backed RAM of an OCS into the RM (refer
Removable Media
same model).
This feature can be used for:
• Replacing an OCS by another unit of the same model.
• Duplicating or “clone” units without a PC.
15.2 Clone
User needs to perform the following to Clone:
1. The ‘Clone Unit’ can be accessed by going to the ‘System Menu’ of the OCS. A new menu “Clone
Unit” has been added at the end of the main system menu as shown below:
Chapter 8 for details on using RM). It can then be used to clone a different OCS (exact
Figure 15.1: System Menu
2. Selecting “Clone Unit” menu will open the following menu screen:
Figure 15.2: Clone Unit Menu before Cloning
Note: Free/Total – displays number of free and total bytes in Removable Media.
February 8, 2010 Page 97 of 124 # 1018
Page 98

CH.15 MAN0924-01-EN
3. Make / Create Clone option enables user to duplicate / Clone application file, all unit settings and all
register values from Battery Backed RAM.
Selecting Make Clone brings up the screen below for the user:
Figure 15.3: Clone Unit Confirm Screen
After confirmation, the OCS will create two new files in the root directory of the Removable Media Drive
as shown below:
AUTOLOAD.PGM Application file
CLONE.DAT File having all unit settings and register values from Battery Backed RAM
Figure 15.4: Clone Unit Files
NOTE: Make/Create clone operation automatically includes the security in \AUTOLOAD.PGM file for
security enabled files.
February 8, 2010 Page 98 of 124 # 1018
Page 99

MAN0924-01-EN CH.15
4. Once the cloning is successful, OCS gives a message as below:
Figure 15.5: Cloning Status
Make/Create clone can also be triggered by setting %SR164.9 bit to “1” from Ladder program or graphics.
Once the operation is completed, this bit is made zero by the firmware. When Make clone operation is
triggered by this SR bit, it does not ask the user for confirmation for making clone. The success / failure of
the operation is also not notified on screen to the user.
In case of failure of “Make Clone” operation, %SR164.11 bit is set to “1” by the firmware and never reset.
NOTE: Backup of registers in flash memory is not performed by Clone Feature. If user desires, Backup
should be done as explained in
Chapter 14 (Fail Safe System).
15.3 Load Clone
This option loads the application, all unit settings and register values from Removable media to the
Battery backed RAM (Regardless of AutoLoad settings) and then resets the OCS for the settings to take
effect.
User needs to perform the following to Load Clone:
1. Select “Clone Unit” from main system menu of OCS as shown below:
Figure 15.6: System Menu
February 8, 2010 Page 99 of 124 # 1018
Page 100

CH.15 MAN0924-01-EN
2. Selecting “Clone Unit” menu will open the following menu screen. Select “Load Clone”.
Figure 15.7: Clone Unit Menu after Cloning
3. User needs to confirm Load Clone as shown below:
Figure 15.8: Load Clone Confirm Screen
4. After confirmation, all unit settings and register values will be loaded from Removable media to the
Battery backed RAM (Regardless of AutoLoad settings) and then OCS resets for the settings to take
effect.
NOTE: For security enabled files, Load clone asks for password validation before loading the application.
Load clone can also be triggered by setting %SR164.10 bit to “1” from Ladder program or graphics. Once
the operation is completed, this bit is made zero by the firmware. When Load clone operation is triggered
by this SR bit, it does not ask the user for confirmation for loading clone. The success / failure of the
operation is also not notified on screen to the user.
In case of failure of “Load Clone” operation, %SR164.12 bit is set to “1” by the firmware and never reset.
February 8, 2010 Page 100 of 124 # 1018
 Loading...
Loading...