HON HAI PRECISION IND J20H031 User Manual

J20H031
Wireless Access Point Module
802.11 a/b/g
User’s Manual

CHAPTER 1 ABOUT THE WIRELESS ACCE SS POINT MODULE..................3
INTRODUCTION ..........................................................................................................3
1-1
1-2
USING A WIRELESS LOCAL AREA NETWORK.............................................................. 3
1-3
FEA TURES AND REQUIREMENTS................................................................................. 4
CHAPTER 2 NETWORK CONFIGURING AND PLANNING.............................5
AD-HOC NETWORK....................................................................................................5
2-1
ACCESS POINT (INFRASTRUCTURE) NETWORK...........................................................6
2-2
CHAPTER 3 ATHEROS CLIENT UTILITY INSTALLATION.......................... 7
3-1
ATHEROS CLIENT UTILITY INSTALLATION..................................................................7
CHAPTER 4 ATHEROS CLIENT UTILITY (ACU) CONFIGURAT ION......... 10
4-1
ATHEROS CLIENT UTILITY ICON............................................................................... 10
CURRENT STATUS TAB ............................................................................................. 11
4-2
4-3
PROFILE MANAGEMENT........................................................................................... 13
CREATE OR MODIFY A PROFILE............................................................................. 14
4-3-1
4-3-2
SECURITY SETTINGS IN PROFILE MANAGEMENT .................................................. 16
ADVANCED SETTINGS IN PROFILE MANAGEMENT................................................. 20
4-3-3
DIAGNOSTIC TAB ..................................................................................................... 21
4-4
ACTION MENU......................................................................................................... 22
4-5
ENABLE/DISABLE RADIO...................................................................................... 22
4-5-1
ENABLE/DISABLE TRAY ICON...............................................................................22
4-5-2
CHAPTER 5 WIRELESS CONFIGURATION USING WINDOWS XP.................23
5-1
CONFIGURING YOUR WIRELESS NETWORKING SETTINGS........................................23
5-2
ADVANCED WIRELESS SETTINGS .............................................................................23
DISABLING THE RADIO ............................................................................................24
5-3
5-4
HELP AND SUPPORT INFORMATION...........................................................................24
APPENDIX A – A THEROS CLIENT UTILITY UNINSTALL PROCESS.............. 25
APPENDIX B - GLOSSARY.........................................................................................28
APPENDIX C –WIRELESS NOTICES....................................................................... 29

Chapter 1 About the Wireless Access Point Module
1-1 Introduction
The Wireless Access Point Module allows you to access Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs),
share a local printer and files with others in your network, access the Internet, and roam about the
office—wirelessly. This wireless Local Area Network solution is designed for both large and
small businesses, and it is scalable so that you can add users and new network features as your
networking needs grow.
The Wireless Access Point Module is a dual band WLAN device that allows for access to both
2.4GHz and 5GHz WLAN technologies. The Wire less Access Point Module will operate with at
a maximum data rate of 11Mbps with 802.11b (2.4GHz), 54Mbps with 802.11g (2.4GHz)
wireless networks and a maximum data rate of 54Mbps with 802.11a (5GHz) wireless networks.
The Wireless Access Point Module will automatically detect and seamlessly roam between
802.11b (2.4GHz), 802.11g (2.4GHz) and 802.11a (5GHz) wireless networks
1-2 Using a Wireless Local Area Network
A wireless LAN provides the same functionality of a wired network, but it eliminates the need to
install networking cables and other networking equipment. Not only is a wireless LAN easier to
deploy, but it also allows for mobility through “roaming.” For example the Wireless Access
Point Module can roam from a conference room to an office without being disconnected from the
network.

1-3 Features and Requirements
The Wireless Access Point Module includes the following features:
Wireless Features
• Support for the IEEE 802.11a standard
• Support for the IEEE 802.11b standard
• Operates within the 2.4-GHz band
• Operates within the 5GHz band
• Maximum data rate of up to 54 Mbps (802.11a/g)
• Maximum data rate of up to 11 Mbps (802.11b)
Interoperability
• WiFi certified at 5GHz to ensure wireless interoperability with other WiFi (802.11a)
certified devices.
• WiFi certified at 2.4GHz to ensure wireless interoperability with other WiFi (802.11b)
certified devices.
Security
• Cisco Client Extension compatibility (including LEAP)
• Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) encryption, operating with 64bit, 128bit or 152 bit
encryption
• AES-CCM Encryption support
• Support for Windows 802.1X supplicants
Chapter 2 Network Configuring and Planning
A wireless LAN can be configured for two different modes of operation. While each method has
its advantages, one may be better suited for your needs. Review the following configurations to
determine which mode is best for you.
• Ad-Hoc Network
• Access Point (Infrastructure) Network
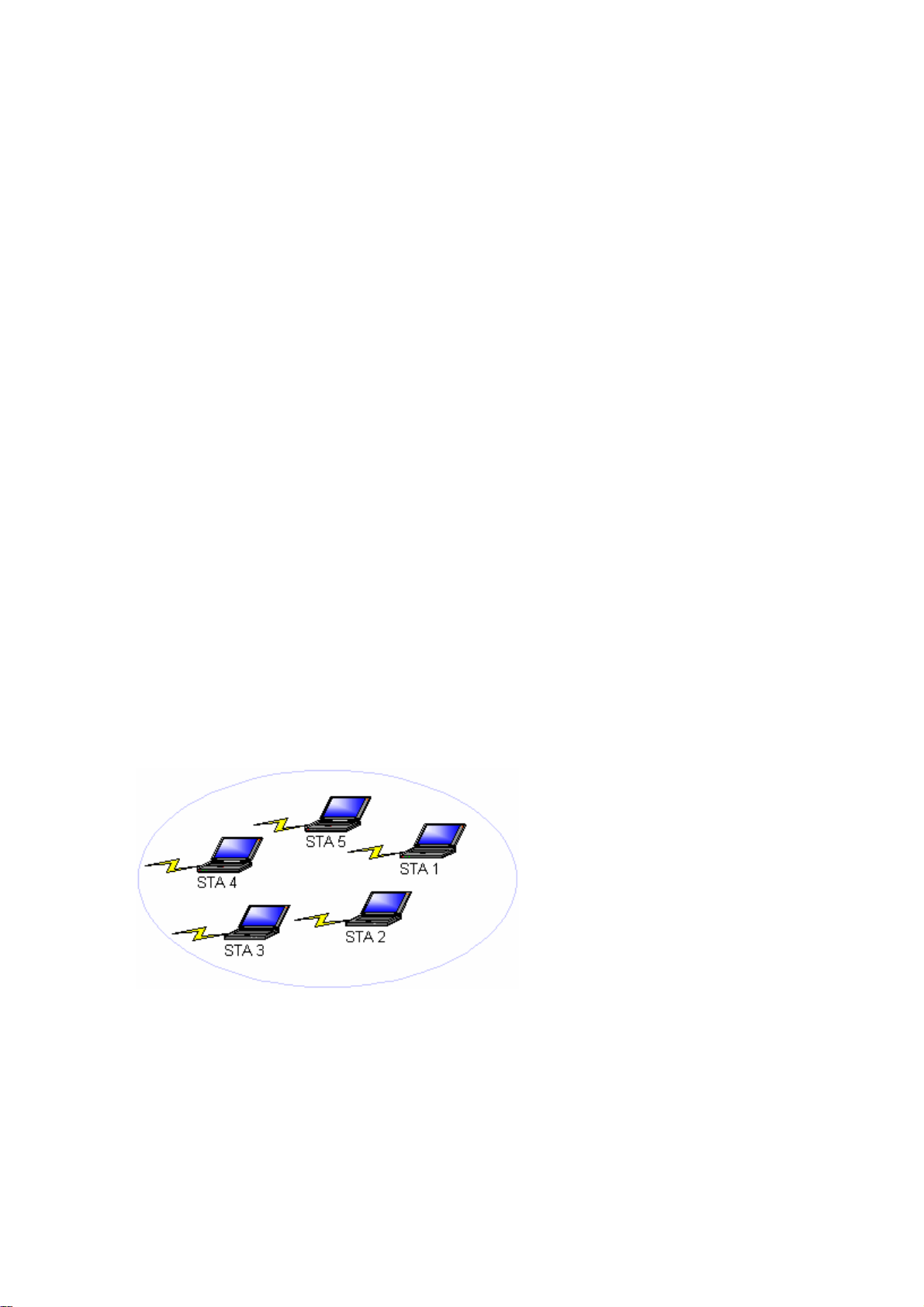
2-1 Ad-Hoc Network
An Ad-Hoc network is the simplest to deploy and is ideal for small offices. Ad-Hoc wireless
networks can be comprised of two or more wireless client configured to communicate with one
another. All Ad-hoc clients communicate directly with each other without using an access point
(AP). As a user on this type of network, you are able to quickly build up a wireless network in
order to share files with other employees, print to a shared office printer, and access the Internet
through a single shared connection.
Ad-hoc networking is cost effective, because no other devices components are needed (access
points, hubs or routers) in order to setup a network. However, with peer-to-peer Ad-Hoc
networking, your computer is only able to communicate with other nearby wireless clients.
Characteristics
Networked computers send data directly to each other
Advantages
• Simple setup
Cost efficiency
•
Disadvantages
Communication is limited to nearby wireless clients
Figure 2-1
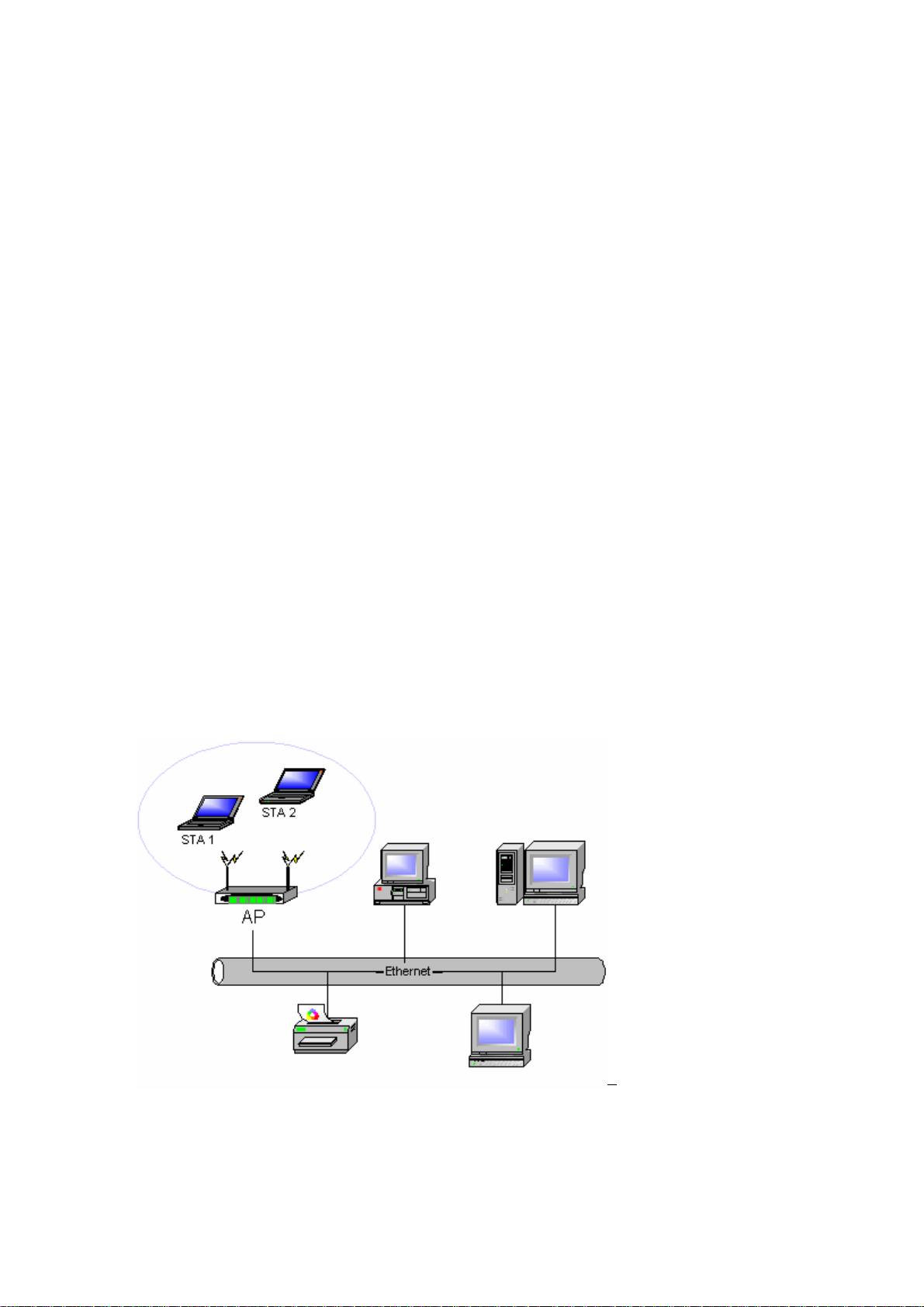
2-2 Access Point (Infrastructure) Network
An Access Point network is also referred to as an “Infrastructure” network. The key difference
between a wireless access point network and an Ad-Hoc network is the addition of one extra
element—the Access Point. The Access Point serves as the focal point for all data traffic on your
wireless network, optimally managing all wireless data transactions.
Additionally, the wireless Infrastructure can provide access to an existing wired LAN. This link
allows computers on the infrastructure wireless LAN to access the other wired LAN’s resources
and tools, including Internet access, email delivery, file transfer, and printer sharing.
Characteristics
Networked computers communicate with each other through a dedicated Access Point. All
data transmitted between the computers on this wireless LAN passes through the access
point.
Advantages
• Extended range: The access point extends the range of the wireless LAN. Each wireless
client computer can communicate with other computers equipped with wireless devices
that are within the range of the access point.
• Roaming: As you move throughout the building, the WLAN 802.11a/b/g device will
automatically search for an access point to use, ensuring continuous communication w ith
the wireless network.
• Network connectivity: An access point can provide wireless LAN access to an existing
wired network by bridging the two networks together. This gives users of the wireless
LAN access to corporate email, Internet, shared printers and files.
Disadvantages
Because this network mode offers more features, it requires additional components and setup
time to deploy
.
Figure 2-2
Chapter 3 Atheros Client Utility Installation
Note for Windows XP Users: The Windows XP operating system has a built-in feature
known as “Wireless Zero Configuration” which has the capability to configure and
control
Client utility will disable this Windows XP feature. For most Windows XP users, it is
recommended that they do not install the Atheros Client Utility . Installation of the
Atheros Client utility is only needed if your wireless LAN network requires Cisco Client
Extension or if you want to us e Atheros Client Utility instead of Windows XP Wireless
Zero configuration services.
3-1 Atheros Client Utility Installation
1. Begin installation by starting the software setup program according to the step described
below…
2. Click Next on the Software Setup “We lco me” dialog box.
the Wireless Access Point Module (See Chapter 5). Installing the Wireless LAN
• Windows 2000 – Double click the desktop icon labeled “Software Setup”.
• Windows XP - Choose Start\Programs\Software Setup
Figure 3-1
3. Scroll down and check the Box labeled, “Atheros Client Utility”.
4. Click on the Next button.
Figure 3-2
Figure 3-3
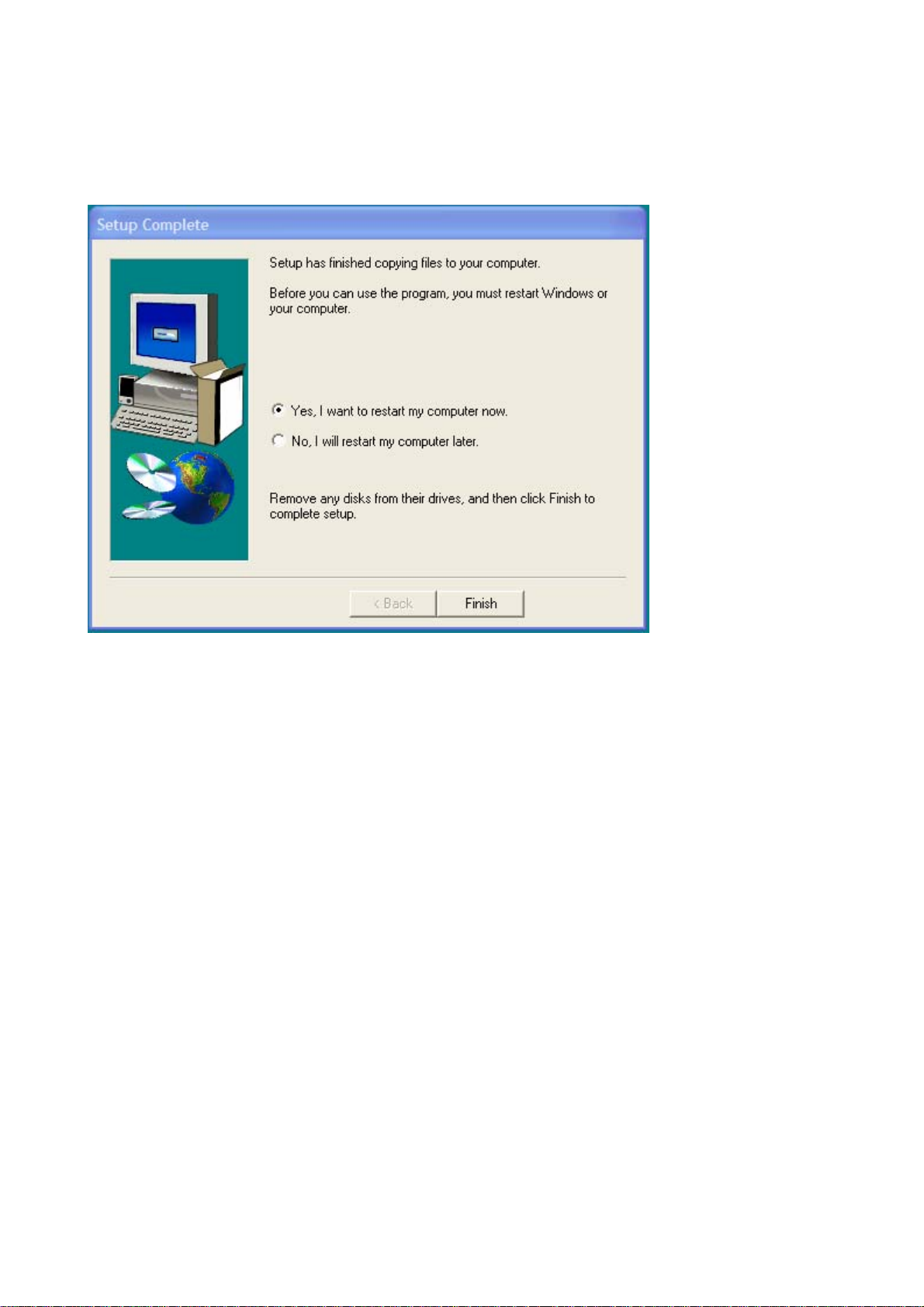
5. Congratulations! Atheros Client Utility has been installed successfully.
Please click ‘Finish’ to go to the next step.
Figure 3-4
6. The Atheros Client Utility will automatically be loaded each time your computer started. To access the
utility click on Atheros Client Utility icon in the system tray (Uninstall information can be found in
Appendix A)
 Loading...
Loading...