Page 1
Global Leader in Integrated Room Automation Systems
MODEVA Technical Reference Manual
Disclaimer
This document contains information that is the proprietary and confidential property of INNCOM
International Inc. By acceptance hereof, each recipient agrees to use the information contained
herein only for the purpose anticipated by INNCOM, and not to disclose to others, copy or reproduce,
any part hereof without the written consent of INNCOM. The recipient agrees to return this document
to INNCOM immediately upon request.
Content
1 MODEVA Product Overview ........................................................................................ 2
2 MODEVA System Block Diagram ................................................................................. 2
3 Touch User Interface ................................................................................................ 3
4 MODEVA Logic Board ................................................................................................ 4
4.1 RF capability ........................................................................................................... 5
4.2 S5-bus ................................................................................................................... 5
4.3 IR Tx and Rx ........................................................................................................... 5
5 Load Assembly ........................................................................................................ 5
5.1 Categories of Load Assembly Load Switching ................................................................ 5
5.2 Load Assembly Dimming ........................................................................................... 6
5.3 Air-Gap Switch ........................................................................................................ 7
5.4 Overload Protection .................................................................................................. 7
5.5 Load Assembly Parallel Power Supplies ........................................................................ 8
6 MODEVA System Technical Specification ...................................................................... 8
6.1 MODEVA/Load Assembly Current Consumption Characteristics ...................................... 10
7 Load Specifications ................................................................................................. 10
7.1 Single gang installation ........................................................................................... 10
7.2 Multigang Installation ............................................................................................. 11
8 Multigang Installation Derating Chart ........................................................................ 11
8.1 Actuator Ratings .................................................................................................... 11
9 Standard Wiring ..................................................................................................... 12
10 MODEVA User Interface Assembly Ordering Information .............................................. 13
11 MODEVA Load Assembly Ordering Information ........................................................... 15
11.1 Load Assembly Ordering Information ........................................................................ 15
12 Document Information and Revision History ............................................................... 16
Page 2

M O D E V A R e f e r e n c e M a n u a l P a g e 2 o f 16
Figure 1 MODEVA Triple Gang System
1 MODEVA Product Overview
The MODEVA™ system, an elegantly
designed, easy to use lighting, drapes, and
amenities control system, provides an
unrivaled guestroom management
experience. The MODEVA system allows
guest control of multiple loads from many
locations. MODEVA (comprising a logic
board and user interface), in combination
with the Load Assembly infrastructure (see
below), consists of user interfaces, low
voltage interfaces, wired and wireless
communications, dimmers, and switches
designed to operate within INNCOM’s
Integrated Room Automation System
(IRAS). The MODEVA system brings all
guestroom control features into a sleekly
designed unit housed in either a capacitive
glass or a more traditional keypad user
interface.
The MODEVA system was designed by the engineers at INNCOM International Inc., who pioneered Energy
Management Systems in the hotel industry long before “green” was a marketing concept. INNCOM is again
blazing a trail for enhanced guestroom controls with the MODEVA and Load Assembly system.
The MODEVA system brings an unmatched level of design flexibility by utilizing a “system in a box” approach.
Mixing a variety of individual components and actuators, the MODEVA system provides endless guestroom
control features and options that interoperate seamlessly with INNCOM’s e4 Smart Digital Thermostat for an
unparalleled energy management and lighting control platform. With the fully configurable user interface and
logic board, which allows the hotelier and the INNCOM design team to create a unique look and feel while
customizing functionality, the MODEVA system can meet nearly any design requirement conceived for the hotel
guestroom.
MODEVA itself contains all of the hardware components (including logic operations, radio communications, and
user interface functionality) necessary to operate as a low voltage controls interface within a thin (8mm thick)
assembly that rests outside of the wall box cavity. This brings an incredible advantage to MODEVA by allowing it
to be decoupled safely from the line power switching and dimming performed by the system’s Load Assembly
actuators. Since the MODEVA user interface is 12VDC powered and equipped with wired S5-bus
communications and a 2.4 GHz RF radio, it can be used as a standalone, low voltage controls interface for load
center style applications. This also frees the MODEVA from the mechanical confines of gang box dimensions.
Coupled with Load Assembly WBI actuators, the MODEVA becomes a complete load controlling system in the
gang box that can perform every function conceived for guestroom controls.
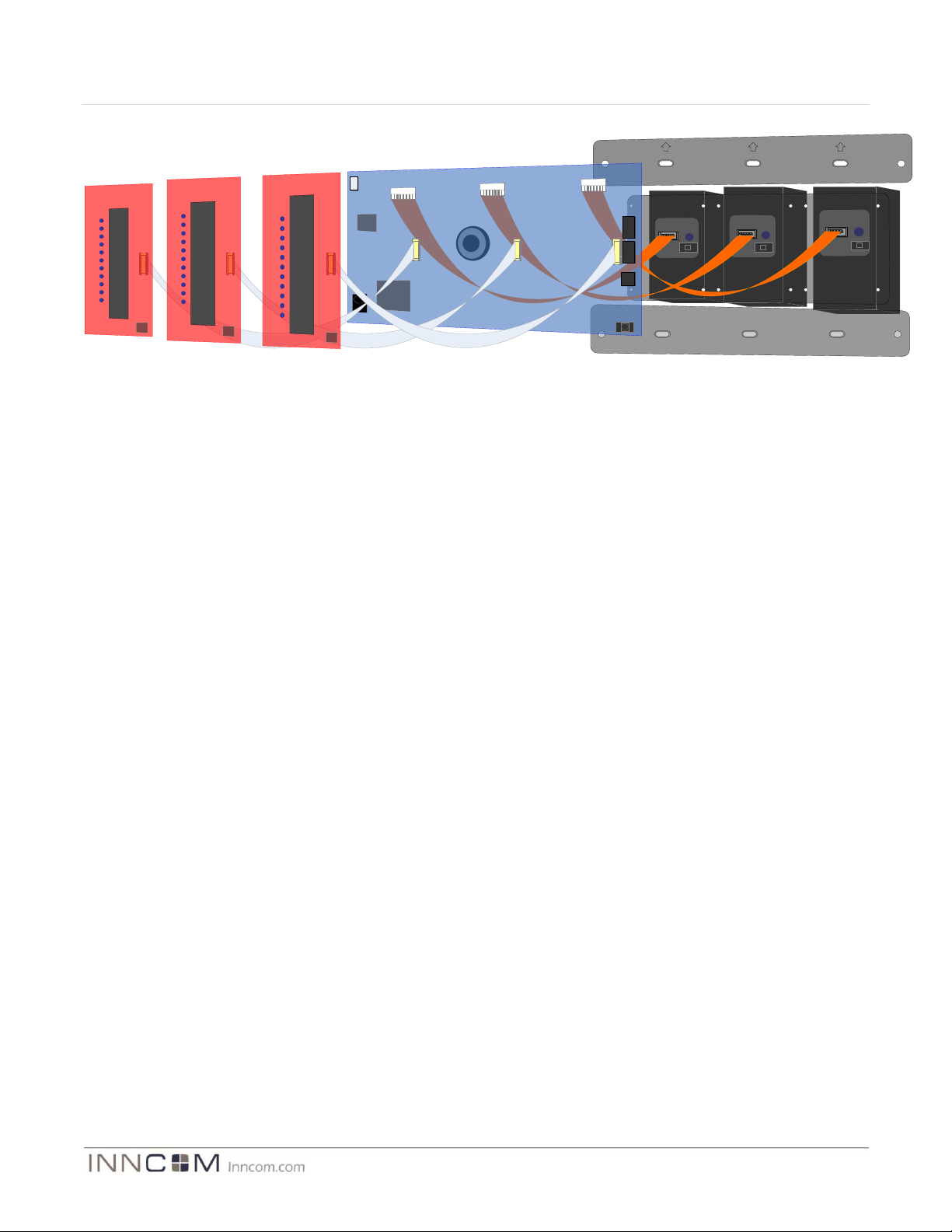
2 MODEVA System Block Diagram
The MODEVAI system comprises 3 segments: the mounting frame / touch user interface, the logic board, and the
Load Assembly components (mounting brackets and actuators). The exploded diagram below illustrates the high
level functionality of each of the 3 segments.
Page 3
M O D E V A R e f e r e n c e M a n u a l P a g e 3 o f 16
Service LED
and Switch
IR Rx
CPU
WBI Gang 1
WBI Gang 2
WBI Gang 3
Touch PCB
Interface 3
Touch PCB
Interface 1
Radio
Circuit
IR Tx
Touch PCB
Interface 2
GND
S5bus
12VDC
GS2 Interface 1
GS2 Interface 2
GS2 Interface 3
Speaker / Piezo
Touch Interface 1
Touch Interface 2
Touch Interface 3
Slider
Slider
Slider
LED Array
LED Array
LED Array
GS2 Logic Board
WBI Mounting Bracket and Actuators
Service LED
and Switch
Service LED
and Switch
GND
S5bus
12VDC
GND
S5bus
12VDC
12VDC Power
supply
Touch Interface
Figure 2 MODEVA System Block Diagram
Note the modular concepts that contribute to the flexibility in the MODEVA system. For instance, the triple gang
assembly uses three touch user interfaces with the same layout and mechanical dimensions but configured in four
different ways (refer to Figure 2 above and Figure 3 below). On the back end, the system’s three actuators can be
used as dimmers or as simple load switchers and can be arranged in any configuration that the application
requires. In between lies the logic board containing all logic and communications control required for nearly any
IRAS application.
3 Touch User Interface
The MODEVA touch user interface contains the touch sensors and indicator LEDs for system input and output. The
touch user interface can be fabricated with a specific geometry and sensor layout to accommodate multiple
applications (while also easing assembly and production) by designing only one touch user interface dimension that
is used for single gang, double gang, and triple gang assemblies.
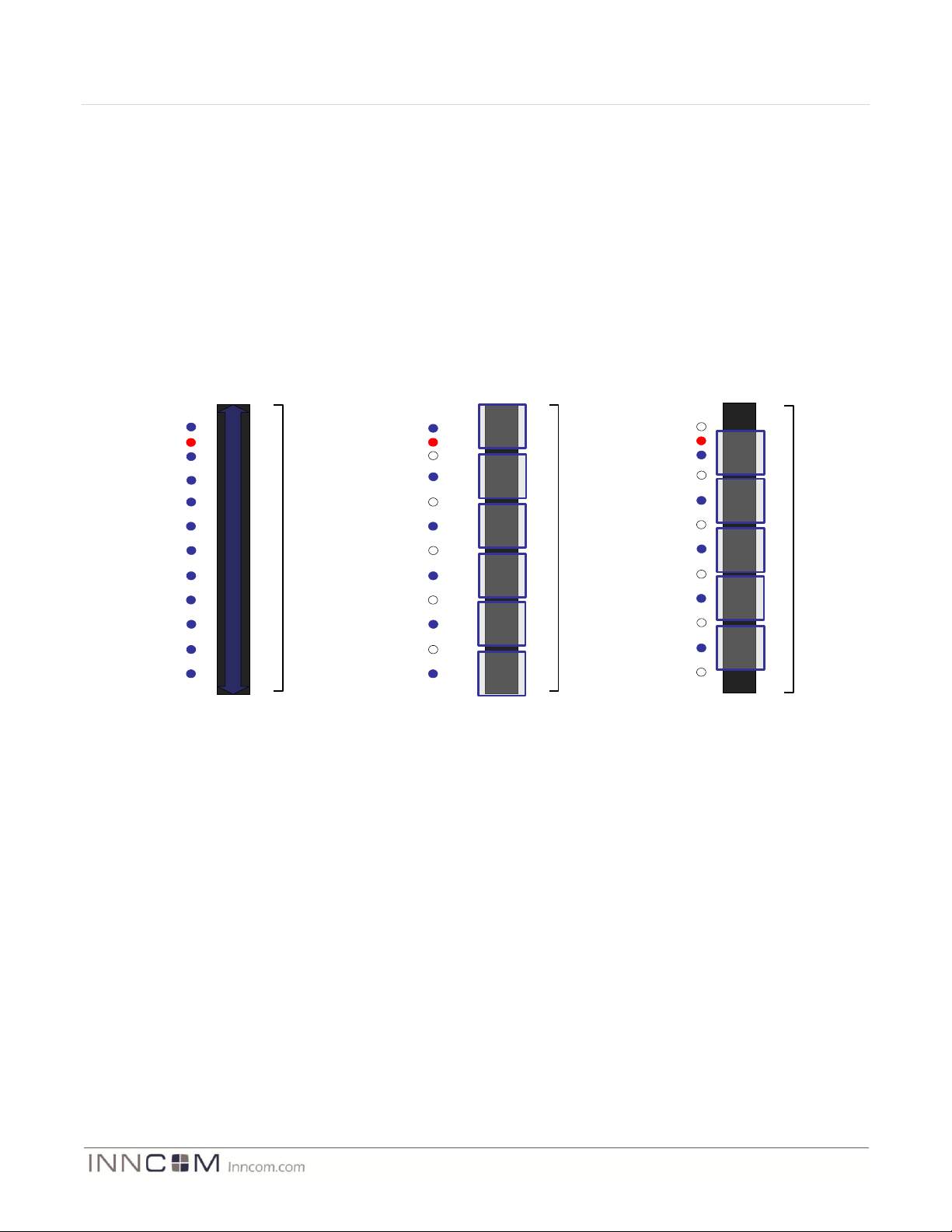
MODEVA incorporates a capacitive controller capable of detecting touch on up to 6 sensors or one single slider
per touch user interface. The sensors sense fields through any dielectric material such as glass or plastic up to
10mm thick. Each sensor can be tuned to a unique sensitivity level. INNCOM plans to provide a single touch user
interface layout at the product launch based on a single slider that can be configured in one of the four following
ways:
Basic Slider
0–255 levels of control operated by the slide of a finger across the glass in the up or down direction. This
slider array makes use of all 11 LEDs with the exception of the Red LED. This layout is optimal for slide
dimming a dimmable lighting load or as a drape control.
Five segmented slider layout
This layout segments the slider into five evenly distributed discrete sensor locations in software using a
unified hardware layout. In Figure 3 below, the five-segment layout makes use of the corresponding Blue
LEDs. In the five segment configuration, the LEDs change from array functionality to indicator
functionality. This layout is optimal where five or fewer functions (such as lighting control, amenities
such as Do Not Disturb and Make Up Room, and general purpose functionality) are required.
Six segmented slider layout
This layout segments the slider into six evenly distributed discrete sensor locations in software using a
unified hardware layout. In Figure 3, the six-sensor layout makes use of the corresponding Blue LEDs. In
the six-sensor configuration, the LEDs change from array functionality to indicator functionality. This
Page 4
M O D E V A R e f e r e n c e M a n u a l P a g e 4 o f 16
Input 5
Input 4
Input 3
Input 2
Input 1
Out 1
Out 2
Out 3
Out 4
Out 5
Out 6
Out 7
Out 8
Out 9
Out 10
Out 11
Out 12
Segmented Matrix
Discrete Input Range – 6
Key Configuration
0
255
Slider LED Array
Out 1
Out 2
Out 3
Out 4
Out 5
Out 6
Out 7
Out 8
Out 9
Out 10
Out 11
Out 12
Slider LED Array
Slider Matrix
Slider Array
0
255
Slider LED Array
Input 3
Input 1
Input 2
Input 4
Input 5
Input 6
Out 1
Out 2
Out 3
Out 4
Out 5
Out 6
Out 7
Out 8
Out 9
Out 10
Out 11
Out 12
Segmented Matrix
Discrete Input Range - 5
Key configuration
0
255
Figure 3 Slider Layout Configurations
layout is optimal where six or fewer functions (such as lighting control, amenities such as Do Not Disturb
and Make Up Room and general purpose functionality) are required. The Red LED is reserved for Do Not
Disturb functionality.
Proximity sensor layout
Optionally, a sensor on MODEVA can operate as a proximity sensor by increasing the proximity
sensitivity. This would be ideal for an application where the MODEVA assembly is backlighting text or
LED arrays located close to the nightstand or bed (see Backlighting below). When the unit is not in use,
the backlight LEDs can be dimmed to a very low level so as not to disrupt the guest’s sleep. When a hand
is waved in front of MODEVA, the unit would detect the motion and resume the backlight of the panel to
the normal bright levels or could even activate a nightlight.
Nightlight
MODEVA inputs and LEDs can be arranged to function as a nightlight/bath light by parsing the slider
into discrete inputs through software. Bright white LEDs and suppression of backlighting combine to
produce variable levels of illumination.
Backlighting
MODEVA touch user interface and front cover housings use LEDs and a housing material designed to
diffuse the backlight to an evenly illuminated glow. This can provide a subtle backlight feature to the
user interface that can illuminate text icons and other input information.
4 MODEVA Logic Board
The MODEVA logic board contains a 32-bit, 16Mhz microprocessor for all logic operations, system coordination, S5bus circuit, 2.4Ghz RF radio circuit, IR Tx, and Rx components for close proximity detection; it interfaces towards
the touch user interface and Load Assembly actuators. This is the brains and control center for the MODEVA system
designed to support nearly any application in the guestroom environment. The logic board is available in single,
double, and triple gang geometry. All features are available in each design; only the number of Load Assembly and
touch user interface interconnects changes based on the mechanical requirements. Because the MODEVA contains
Page 5
M O D E V A R e f e r e n c e M a n u a l P a g e 5 o f 16
Figure 4 Load Assembly Frame
all logic communications and interfacing capability, it can be used as a low-voltage remote control interface for load
center style applications.
4.1 RF capability
MODEVA shares the electrical design of the 0dB 2.4GHz 802.15.4 INNCOM TXR radio module by embedding the
radio components in the logic board. This sub-circuit has been specifically tuned for optimal performance for the
guestroom environment. Typically, the RF transceiver can expect to reach up to a 70ft radius in an indoor, urban
environment. MODEVA communicates on the standard INNCOM RF protocol, a proprietary encrypted protocol
that runs over the 802.15.4 platform stack. This is a shared protocol that is used by all other RF capable INNCOM
products. The protocol’s encryption method provides protection for the P5 frame being sent into the RF spectrum
and makes it very difficult to interpret the data and reuse it maliciously.
Note: RF performance can be degraded by pre existing environmental factors.
4.2 S5-bus
The logic board incorporates the most modern S5-bus circuit design, to support up to 15 S5-bus devices in a single
guestroom network segment.
4.3 IR Tx and Rx
MODEVA uses a low power IR transmitter and receiver to provide two functions: IR communications for TV and
A/V system control and proximity detection. This circuit is not to be confused with IR5 and cannot be used as a
wireless IR5 transceiver for IRAS and guestroom network purposes.
5 Load Assembly
The Load Assembly is the core of MODEVA system flexibility. The Load Assembly consists of mounting brackets
and WBI actuators that provide the mechanical platform and load bearing capability for the MODEVA system.
Each MODEVA (and each input located on the interface) can control any one of the individual actuators as part of
the Load Assembly located within the local gang box, or it can remotely control other actuators as part of the
guestroom network IRAS. This allows the designer to locate actuators with specifically designed functions
throughout the guestroom network and to have control over that actuator from any user interface in the
guestroom network. The MODEVA platform uses magnets located on the back side of the logic board that adhere
to the large flat metal surfaces of the Load Assembly brackets, allowing for screwless mounting that adds to the
aesthetic product design.
5.1 Categories of Load Assembly Load Switching
5.1.1 TRIAC Dimmer Power Supply
The TRIAC dimmer provides dimming control of
resistive light loads such as incandescent, halogen, and
TRIAC dimmable LEDs. The TRIAC dimmer can dim
100–120VAC loads up to 500W.
The TRIAC Actuator also provides a class-2, 12VDC
output used to power the MODEVA logic and touch
user interface and to provide connection and power for a
wired S5-bus IRAS network.
Page 6
M O D E V A R e f e r e n c e M a n u a l P a g e 6 o f 16
5.2.1 High-frequency noise
5.2.2 Low-frequency non-harmonics:
Caused by variable-speed motor drives, on-line UPS
systems.
Caused by signaling systems, power line carrier
communications.
5.1.2 MOSFET Dimmer Power Supply
The MOSFET dimmer is specifically designed to dim capacitive loads such as dimmable fluorescent
lamps and electronic ballast. Secondarily, it can also dim resistive loads such as incandescent, halogen,
and dimmable LEDs. The MOSFET dimmer is designed to dim 100–120VAC up to 350W.
The MOSFET Actuator also provides a class-2, 12VDC output used to power the MODEVA logic and touch
user interface and to provide connection and power for a wired S5-bus IRAS network.
5.1.3 Relay Switched Power Supply
The Relay power supply is specifically designed to switch capacitive, inductive, resistive, and general
purpose loads up to 500W.
The WBI Relay Actuator also provides a class-2, 12VDC output used to power the MODEVA logic and
touch user interface and to provide connection and power for a wired S5-bus IRAS network.
5.2 Load Assembly Dimming
With the MODEVA product offering, INNCOM presents a “lighting control system in a box” that provides a
multifaceted range of modular and component level flexibility competitors cannot offer. Because of this,
INNCOM’s lighting control hardware quality must be on par with or exceed the competitions’. To achieve the
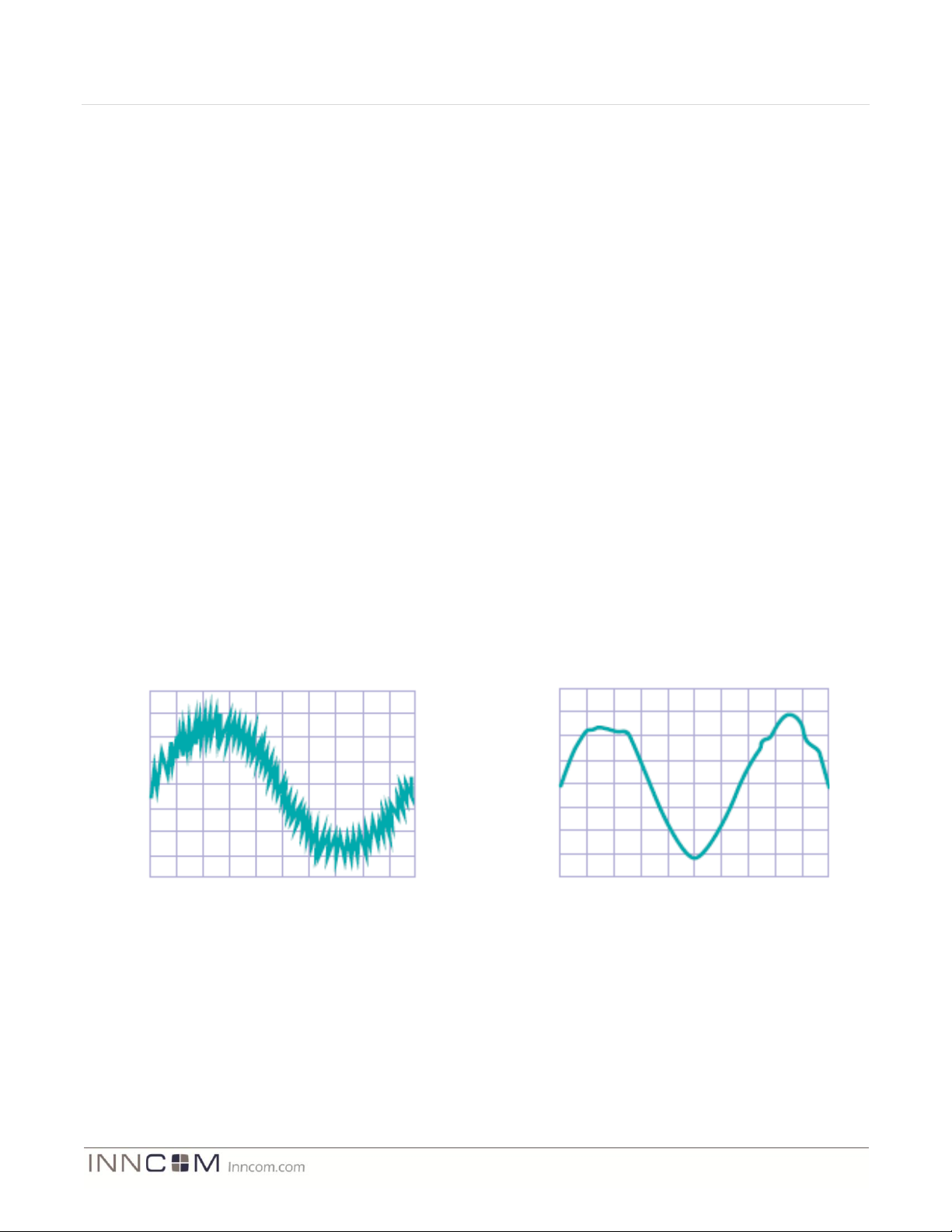
highest level of smooth dimming operation with both the MOSFET and TRIAC dimmers, a clean power line must
be available for the Load Assembly actuators. Corrupt zero crossing information will affect turn-on points and
turn-on time of the TRIAC and MOSFET dimmers, which ultimately affects dimming quality. Zero crossing
information and accurate line frequencies are a problem for dimming products because they are more sensitive to
line voltage problems. AC line evaluation to ascertain that it meets INNCOM’s minimum technical requirements
for dimming light loads is essential.
Typically, there are six different types of power line noise that can be found in the industrial commercial and
hotel environments:
Page 7

M O D E V A R e f e r e n c e M a n u a l P a g e 7 o f 16
5.2.3 Variable baseline frequency
5.2.4 Impulse noise
Caused by backup generators and small power grids.
Caused by switch arcing (loads switching on and off).
5.2.5 RMS voltage changes
5.2.6 Notch and low frequency noise
Caused by heavy load switching.
Caused by elevators and large industrial loads
TRIAC and MOSFET dimmers can withstand certain levels of any one kind of the noises listed above. However, if
any single noise is present at a high magnitude, or multiple noise conditions occur simultaneously, the poor
quality conditions on the line will result in poor quality dimming performance. INNCOM application
engineering, operations, and customer service need to be aware of these property conditions to ensure proper
operation of the MODEVA light dimmers. A site survey that includes the evaluation of the line voltage at each
property must be conducted.
5.3 Air-Gap Switch
The TRIAC and MOSFET Load Assemblies are equipped with an air gap switch (relay) to ensure that the load is
safely turned off and that there is no leakage current to the fixture during routine lamp maintenance. The air gap
switch engages each time the load is dimmed completely off under normal operation.
5.4 Overload Protection
If a MOSFET or TRIAC Dimmer is continuously overloaded, a thermal shut down will occur to protect the solid
state circuitry. This thermal shutdown temperature can be configured and monitored with INNCOM
configuration tool such as the PC-501.
The MOSFET Dimmer is equipped with an additional overload detection circuit that detects a catastrophic
overload / short and shuts down the dimmer to protect the solid state circuitry.
Page 8
M O D E V A R e f e r e n c e M a n u a l P a g e 8 o f 16
Hot
Neutral
120/240VAC
50/60Hz
Lighting Load
WBI Actuator 1
200mA
375mA550mA
WBI Actuator 2 WBI Actuator 3
12VDC
GND
R
Load
WBI MOSFET
Dimmer
WBI MOSFET
Dimmer
WBI MOSFET
Dimmer
Number of Load Assemblies
Nominal Voltage
Voltage at Maximum
Load
Output Rating
Single Actuator
+12VDC
+11.0VDC
200mA
Two Actuators
+12VDC
+11.0VDC
400mA
Three Actuators
+12VDC
+11.1VDC
600mA
Four Actuators
+12VDC
+11.1VDC
700mA
Five Actuators
+12VDC
+11.2VDC
800mA
Six Actuators
+12VDC
+11.2VDC
900mA
Mechanical Package
Length
Width
Height
American Single Gang
119mm
74mm
8.0mm
American Double Gang
119mm
124mm
8.0mm
American Triple gang
119mm
174mm
8.0mm
5.5 Load Assembly Parallel Power Supplies
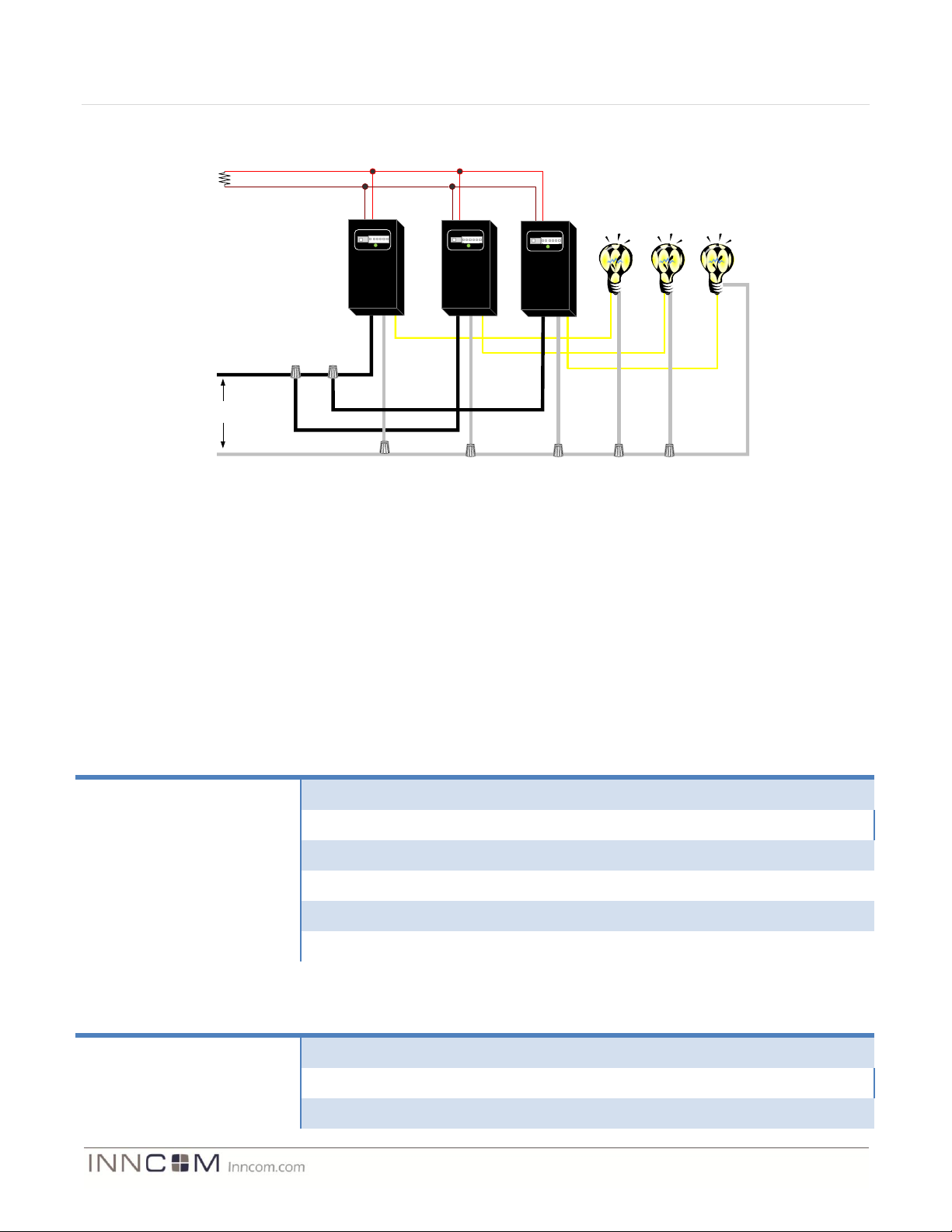
Figure 5 Parallel Power Supplies
The WBI actuators operate in parallel to supply a higher load capacity than that achievable by a single actuator.
The total output power of the actuators in parallel is based on the voltage specifications at maximum load versus
the output current at maximum load and a nominal recover time after a fold back condition occurs. Therefore, the
sum of paralleled power supplies is not simply I1 + I2 + I3= I max. However, aggregate power of the paralleled
supplies is greater than that available from a single source.
The benefit of this design is the ability to aggregate actuators into a system that permits load sharing without
concern for back feeding voltage that typically occurs when more than one supply is used. A triple ganged
MODEVA system can provide up to 550mA to power 12VDC S5-bus devices in the circuit. INNCOM
recommends the use of up to seven power supplies in any given network segment. A disadvantage is that a short
condition on any one of the actuators will drag all of the actuators into a fold-back state until the short condition
is resolved.
6 MODEVA System Technical Specification
Page 9

M O D E V A R e f e r e n c e M a n u a l P a g e 9 o f 16
Glass Touch Surface Area
Length
Width
Height
American Single Gang
115mm
70mm
2.0mm
American Double Gang
115mm
120mm
2.0mm
American Triple gang
115mm
170mm
2.0mm
Electrical Characteristics
Parameter
User Interface
Capacitive touch sensor / slider
Maximum # of inputs
1-6 sensor inputs, or 1 slider per gang
Alternate User Interface
Keypad—traditional mechanical switches
Communications
1. Wired S5-bus
2. 2.4Ghz RF
3. IR Infrared (not IR5)
Output Power
12VDC, up to 200mA*
Micro controller
16Mhz, 32-bit ARM based MCU
Page 10
M O D E V A R e f e r e n c e M a n u a l P a g e 10 o f 16
Device
Peak Current Consumption
Logic Board (basic)
50mA
Logic Board w/ 1mW Radio
60mA
Logic board with IR transceiver
70mA
Capacitive Touch PCBA (02-7060)
10mA(n x 3.5mA) (logic board current plus the number of LEDs)
Load Assembly Relay Actuator
35mA
Load Assembly TRIAC Actuator
35mA
Load Assembly MOSFET Actuator
35mA
Logic Board w/ 1mW Radio
60mA
=121mA (Peak Current Consumption)
Capacitive Touch PCBA (02-7060)
10mA(6 x 3.5mA)=31mA
MOSFET Actuator
30mA
Actuator
Ratings
Voltage
Frequency
Power / Amperes
Load Type
Relay Actuator
120-240 Vac
50/60 Hz
4.1 A
Resistive
120-240 Vac
50/60 Hz
4.1 A
General Purpose
120-240 Vac
50/60 Hz
500 W
Tungsten / ELV
120-240 Vac
50/60 Hz
250 VA
Electric Ballast
TRIAC Dimmer
120 Vac
60 Hz
2.9 A
Resistive
120 Vac
60 Hz
2.9 A
General Purpose
120 Vac
60 Hz
500 W
Tungsten / ELV
120 Vac
60 Hz
250 VA
Electronic Ballast
6.1 MODEVA/Load Assembly Current Consumption Characteristics
For example, a MODEVA assembly that
uses the capacitive touch PCBA for a 6 input / output user interface,
communicates wirelessly using the 2.4Ghz radio, and
uses the MOSFET dimmer to actuate a load
would have a peak current consumption figured as follows:
The total DC load rating of a single actuator is 200mA. Therefore, a single actuator has 80mA remaining to
provide 12VDC power to S5-bus devices.
7 Load Specifications
7.1 Single gang installation
The following table provides load ratings at absolute maximum based on the load type in a single gang wall box.
Page 11

M O D E V A R e f e r e n c e M a n u a l P a g e 11 o f 16
Actuator
Ratings
Voltage
Frequency
Power / Amperes
Load Type
MOSFET
Dimmer
120 Vac
60 Hz
2.9 A
Resistive
120 Vac
60 Hz
2.9 A
General Purpose
120 Vac
60 Hz
350 W
Tungsten / ELV
120 Vac
60 Hz
250 VA
Electronic Ballast
Actuator
Ratings
Voltage
Frequency
Power / Amperes
Load Type
TRIAC Dimmer
120 Vac
60 Hz
2.9 A
Resistive
120 Vac
60 Hz
2.9 A
General Purpose
120 Vac
60 Hz
400 W
Tungsten
120 Vac
60 Hz
250 VA
Electronic Ballast
MOSFET
Dimmer
120 Vac
60 Hz
2 A
Resistive
120 Vac
60 Hz
2 A
General Purpose
120 Vac
60 Hz
250 W
Tungsten
120 Vac
60 Hz
250 VA
Electronic Ballast
Actuator
Ratings
TRIAC Dimmer
Voltage
Frequency
Power /
Amperes
Load Type
120 Vac
60 Hz
2.9 A
Resistive
120 Vac
60 Hz
2.9 A
General Purpose
120 Vac
60 Hz
400 W
Tungsten
120 Vac
60 Hz
250 VA
Electronic Ballast
MOSFET
Dimmer
Voltage
Frequency
Power /
Amperes
Load Type
120 Vac
60 Hz
2 A
Resistive
120 Vac
60 Hz
2 A
General Purpose
7.2 Multigang Installation
The MODEVA and Load Assembly comes in single, double and triple gang configurations; the double and triple
gang assemblies may be any combination of relay, switches, MOSFET Dimmer or TRIAC Dimmer. The table
below provides the derated output based on the configuration.
8 Multigang Installation Derating Chart
8.1 Actuator Ratings
Page 12

M O D E V A R e f e r e n c e M a n u a l P a g e 12 o f 16
Actuator
Ratings
120 Vac
60 Hz
250 W
Tungsten
120 Vac
60 Hz
250 VA
Electronic Ballast
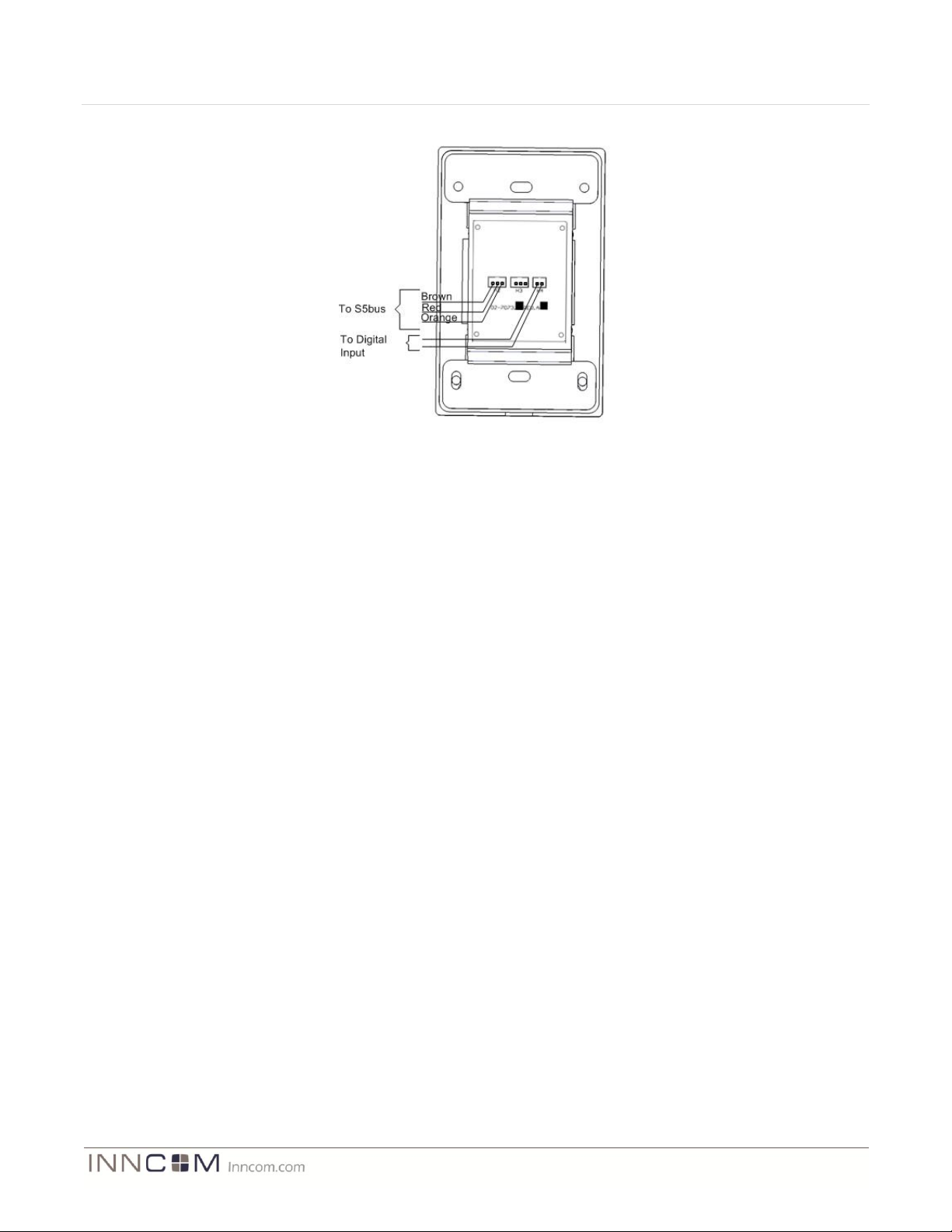
Figure 6 Single Gang Wiring Diagram
Brown
Red
Orange
To S5bus
To Digital
Input
To Digital Input
To Digital Input
Phase
120V 60Hz
Load
Load
Load
Neutral
Green
Yellow
Yellow
Yellow
White White White
Black Black Black
9 Standard Wiring
In Figure 6, the MODEVA and Load Assembly is configured for switching or dimming the level of AC power
delivered to a load, such as a Tungsten lighting load.
In Figure 7, the MODEVA and Load assembly is configured for switching or dimming the level of AC power
Figure 7 Double and Triple Gang Wiring Diagram
delivered to multiple loads, such as two or three tungsten lighting loads.
Page 13
M O D E V A R e f e r e n c e M a n u a l P a g e 13 o f 16
Figure 8 Single Gang Powered Remote Control
In the configuration shown in Figure 8, the MODEVA is used as a three-way switch to transmit S5bus or RF
signals to auxiliary INNCOM devices to manage in-room communications irrespective of the location of the
system devices. In this respect, the MODEVA provides remote control of auxiliary INNCOM devices.
In Figures 6, 7, and 8 each MODEVA is equipped with low voltage connections to provide +12VDC power to
other devices, communicate on the S5bus, or provide a digital input for a door switch.
10 FCC Statement
This device contains FCC ID: GTC027060TXR.
This device complies with part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) This
device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including
interference that may cause undesired operation.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part
15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference
when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate
radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause
harmful interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause
harmful interference, in which case the user will be required to correct the interference at his own expense.
Changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance could void the user's
authority to operate the equipment.
11 MODEVA User Interface Assembly Ordering Information
The MODEVA and Load Assembly are designed to be modular and can be completely independent of each other.
For instance, a double gang MODEVA user interface can be specified, while the system may only require a single
Load Assembly actuator. Therefore, the Ordering Part Numbers (OPN) for the MODEVA and Load Assembly are
separated. Both the MODEVA and Load Assembly are available in several operating ranges. The MODEVA OPN
is formed by a combination of the elements, as shown in the figure below:
Page 14

M O D E V A R e f e r e n c e M a n u a l P a g e 14 o f 16
03-7060
Assembly Part Number
03-7060 – Single Gang Assembly
03-7061 – Double Gang Assembly
03-7062 – Triple Gang Assembly
GHS1
Switch Model
Defined by project
R0
Frame Plate Color
WH = White
BK = Black
AL = Almond
XX = Custom Pantone Color
Radio
R0 = No Radio
R1 = Layer-1 Radio (02-9994.L1)
R2 = Layer-2 Radio (02-9894.L2- Not available)
R3 = Reserved for future application
R4 = Reserved for future application
R5= Reserved for future application
WH
Figure 9 User Interface Assembly Ordering Part Number
Examples:
03-7060.GHS1.R1.WH = MODEVA user interface assembly switch #1 designed for the Grand Hyatt New York
project that includes the CC2430 based radio circuit and a white framing plate. “GHS1” further defines the
attributes of the Touch User interface PCB model (ex. GS-765.XXX) in the following:
Number of capacitive touch keys or sliders
Locations of capacitive touch keys
Number of indicator LEDs
LED locations
LED colors
This information is found in the 03-7060.GHS1 Hardware Guide. Note that when a double and triple gang
assembly is designed (03-7062.xxx.xx.xx) it becomes more critical to refer to the hardware guide that defines the
touch user interface attributes for the left gang, center gang, and right gang. Again note that in a double and triple
gang assembly two and three touch user interface PCBA’s are required, but always only one logic board PCBA is
required.
03-7061.GHS2.R0.WH = A double gangMODEVA assembly configured for the Grand Hyatt Switch position #2
that does not include the CC2430 radio circuit, uses a white framing plate, and uses a GS-765.STD in the left
position, and a GS-765.NL01 in the right position. (See GS-765.STD and GS-765.NL01 hardware guide for specific
details of the touch user interface).
Page 15

M O D E V A R e f e r e n c e M a n u a l P a g e 15 o f 16
Assembly Part Number
03-7001 – Single Gang Assembly
03-7002 – Double Gang Assembly
03-7003 – Triple Gang Assembly
Actuator Type: Left Position (or Single Gang)
L – Low Voltage Adapter
0 - Relay Actuator
1 - Triac Actuator (400W dimmable)
2 - MOSFET Actuator (400W dimmable)
3 - Reserved for future application
4 - Reserved for future application
03-7 0 0 3
Actuator Type: Center Position (or Right in
Double Gang)
L – Low Voltage Adapter
0 - Relay Actuator
1 - Triac Actuator (dimmable)
2 - MOSFET Actuator (dimmable)
3 - Reserved for future application
4 - Reserved for future application
Actuator Type: Right Position
L – Low Voltage Adapter
0 - Relay Actuator
1 - Triac Actuator (dimmable)
2 - MOSFET Actuator (dimmable)
3 - Reserved for future application
4- Reserved for future application
2 0 1
12 MODEVA Load Assembly Ordering Information
12.1 Load Assembly Ordering Information
The Load Assembly system is available in several operating ranges but is based on the same fundamental
hardware platform. The ordering part numbers (OPN) are formed by a combination of the elements, as shown in
Figure 7 below.
Example:
03-7003.L01 = A triple gang MODEVA Load Assembly that includes a low voltage adapter in the left position, a
relay actuator in the center position and a TRIAC dimmer in the right position.
Figure 10 Load Assembly Ordering Part Number
Page 16

M O D E V A R e f e r e n c e M a n u a l P a g e 16 o f 16
Date
Changes
13-Oct-2009
First Draft
16-Oct-2009
Edited for content and composition
02-Mar-2010
Product information added and edited
09-Apr-2010
Updated Derating chart for UL
20-Apr-2010
Updated order guide to include radio option for logic components
18-Jun-2010
Update to reflect name changes; new ratings tables
07-Jul-2010
Replaced mechanical drawings of the brackets, label drawings, etc with
standard wiring drawings
23-Aug-2010
Updated FCC statement
13 Document Information and Revision History
Author Ryan Gardner
File \\Niantic\departments\R&D\Working Documents\Reference Manuals\MODEVA\Drafts
 Loading...
Loading...