Honda Power Equipment WDP30X, WDP20X User Manual


The engine exhaust from this product
contains chemicals known to the State
of California to cause cancer, birth
defects or other reproductive harm.
This owner’s manual is considered a permanent part of your
diaphragm pump. It must be available to all operators of the pump
and should remain with the pump if resold.
The information and specifications in this publication were in effect at
the time of approval for printing. American Honda Motor Co., Inc.
reserves the right to discontinue or change specifications or design at
any time without notice and without incurring any obligation whatever.
No part of this publication may be reproduced without written
permission.

INTRODUCTION
Congratulations on your selection of a Honda diaphragm pump. We
are certain you will be pleased with your purchase of one of the finest
pumps on the market.
We want to help you get the best results from your new pump and to
operate it safely. This manual contains the information on how to do
that; please read it carefully.
As you read this manual, you will find information preceded by a
-1 symbol. That information is intended to help you avoid
damage to your pump, other property, or the environment.
We suggest you read the warranty policy to fully understand its
coverage and your responsibilities of ownership. The warranty policy
is a separate document that should have been given to you by your
dealer.
When your pump needs scheduled maintenance, keep in mind that
your authorized Honda servicing dealer is specially trained in
servicing Honda pumps and is supported by the parts and service
divisions of American Honda. Your Honda dealer is dedicated to your
satisfaction and will be pleased to answer your questions and
concerns.
Best Wishes,
Power Equipment Division
American Honda Motor Co., Inc.
0 1998 American Honda Motor Co., Inc. - All Rights Reserved
1

INTRODUCTION
A FEW WORDS ABOUT SAFETY
Your safety, and the safety of others, are very important. And using
this pump safely is an important responsibility.
To help you make informed decisions about safety, we have provided
operating procedures and other information on labels and in this
manual. This information alerts you to potential hazards that could
hurt you or others.
Of course, it is not practical or possible to warn you about all the
hazards associated with operating or maintaining a pump. You must
use your own good judgment.
You will find important safety information in a variety of forms,
including:
l Safety Label - on the pump.
A
l Safety Messages - preceded by a safety alert symbol
one of three words: DANGER, WARNING, or CAUTION.
These signal words mean:
and
You WILL be KILLED or SERIOUSLY
HURT if you don’t follow instructions.
You CAN be KILLED or SERIOUSLY
HURT if you don’t follow instructions.
You CAN be HURT if you don’t follow
instructions.
l Safety Headings-such as IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION.
0 Safety Section -
l Instructions - how to use this pump correctly and safely.
such as PUMP SAFETY.
This entire book is filled with important safety information - please
read it carefully.
2

CONTENTS
Turn to the beginning of each chapter for a complete list of subjects.
PUMP SAFETY. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Important information about some specific hazards,
and what you can do to prevent injury.
L
CONTROLS . .
Identification of components and information about how
the controls work.
BEFORE OPERATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
How to prepare your pump and yourself before you
begin pumping.
OPERATION. .
Starting and stopping the engine, safe pumping
practices, and pumping tips.
TRANSPORTING . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
How to load and carry your pump safely
MAINTENANCE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
When and how to perform routine inspection, service,
and adjustments to keep your pump in good operating
condition.
TROUBLESHOOTING . .
What to check if you have a problem with your pump.
STORAGE...................................... 55
How to protect your pump from rust and corrosion, and
ensure that it will start easily when you want to use it again.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . ..*...................
17
53
9
SPECIFICATIONS.. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Specifications, dimensions, capacities, and other
technical information.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Additional information, Honda publications available to
you, and how to contact us if you have a question or a
warranty repair problem.
INDEX . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
QUICK REFERENCE INFORMATION . . . inside back cover
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . 71
3

-

PUMP SAFETY
This chapter explains what you need to know to operate your
diaphragm pump safely.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
Operator Responsibility
Pump Operation.
Refuel With Care
Hot Exhaust
Carbon Monoxide Hazards
SAFETY LABEL LOCATION
................................
................................
....................................
...........................
........................
........................
................
6
6
6
6
7
7
8
5

PUMP SAFETY
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
Honda WDP20X and WDP30X pumps are not designed to pump
drinking water. Pump only non-potable water, muddy water, and
water containing solids. Other uses can result in injury to the operator
or damage to the pump and other property.
Most accidents can be prevented if you follow all instructions in this
manual and on the pump. The most common hazards are discussed
below, along with the best way to protect yourself and others.
Opecator Responsibility
It is the operator’s responsibility to provide the necessary safeguards
to protect people and property. Know how to stop the pump quickly in
case of emergency. Understand the use of all controls and
connections. For your safety and the safety of others, keep all shields
in place when the engine is running.
Be sure that anyone who operates the pump receives proper
instruction. Do not let children operate the pump. Keep children, pets,
and bystanders away from the area of operation.
Pump Operation
Do not pump drinking water. Pumps are designed to only pump
non-potable water, muddy water, and water containing solids.
Pumping flammable liquids, such as gasoline or fuel oils, can result in
a fire or explosion, causing serious injury. Pumping sea water,
beverages, acids, chemical solutions, or any other liquid that
promotes corrosion can damage the pump.
Operate pump on a level surface. If engine is tilted, fuel may spill.
Refuel With Care
Gasoline is extremely flammable, and gasoline vapor can explode.
Refuel outdoors, in a well-ventilated area, with the engine stopped
and the pump on a level surface. Do not overfill the fuel tank. Never
smoke near gasoline, and keep other flames and sparks away.
Always store gasoline in an approved container. Make sure that any
spilled fuel has been wiped up before starting the engine.
6

I
Hot Exhaust
The muffler becomes very hot during operation and remains ,hot for a
while after stopping the engine. Be careful not to touch the muffler
while it is hot. Let the engine cool before transporting the pump or
storing it indoors.
To prevent fire hazards, keep the pump at least 3 feet (1 meter) away
from building walls and other equipment during operation. Do not
place flammable objects close to the engine.
Carbon Monoxide Hazards
Exhaust gas contains poisonous carbon monoxide. Avoid inhalation
of exhaust gas. Never run the engine in a closed garage or confined
area.
PUMP SAFETY
7
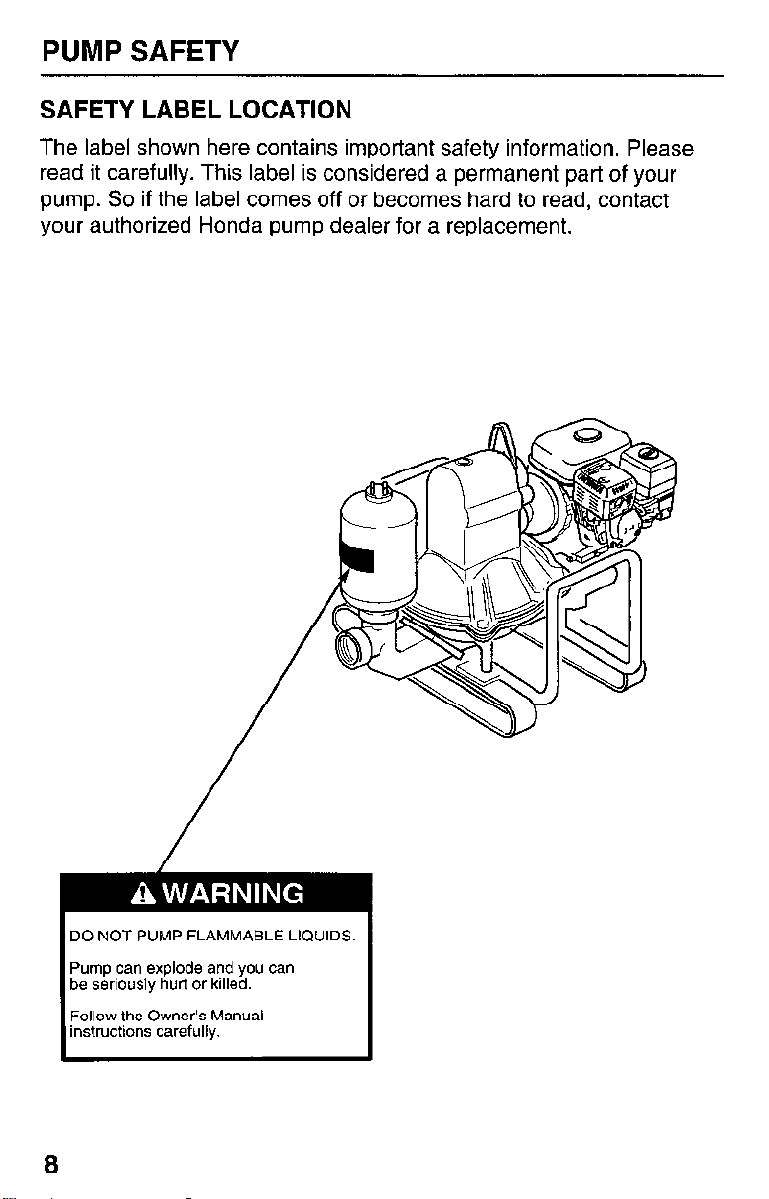
PUMP SAFETY
SAFETY LABEL LOCATION
The label shown here contains important safety information. Please
read it carefully. This label is considered a permanent part of your
pump. So if the label comes off or becomes hard to read, contact
your authorized Honda pump dealer for a replacement.
DO NOT PUMP FLAMMABLE LIQUIDS.
Pump can explode and you can
be seriously hurt or killed.
Follow the Owner’s Manual
instructions carefully.

CONTROLS
This chapter shows you the locations of controls and other important
parts of your pump, and tells you how the controls work.
COMPONENT IDENTIFICATION
DESCRIPTION OF CONTROLS.
Throttle Lever.
ChokeLever
FuelValveLever
Ignition Switch
Oil Alert” System
Recoil Starter.
...............................
.................................
.............................
...............................
.............................
...............................
....................
....................
10
11
11
11
11
12
12
12
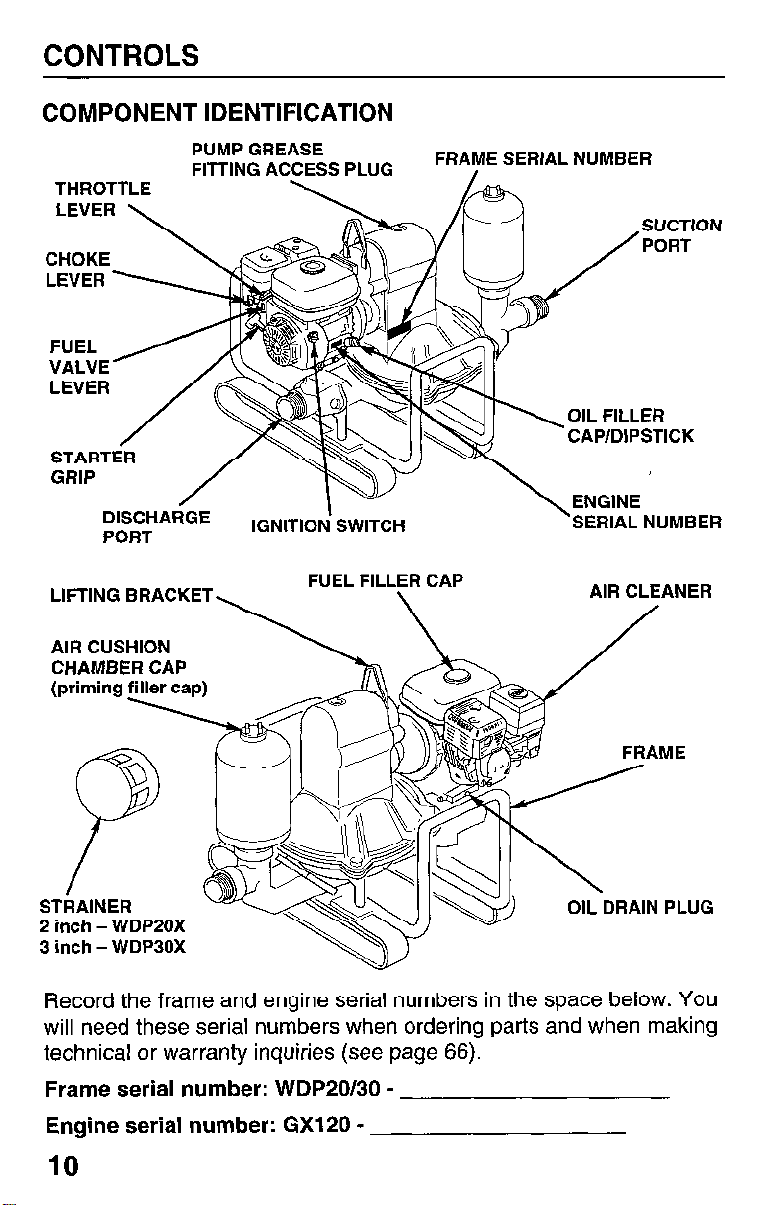
CONTROLS
COMPONENT IDENTIFICATION
THROTTLE
SERIAL NUMBER
CAP/DIPSTICK
SERIAL NUMBER
LIFTING BRACKET
AIR CUSHION
CHAMBER CAP
(priming yp)
STkAlNER
2 inch - WDPSOX
3 inch - WDP30X
FUEL FILLER CAP
AIR CLEANER
AME
OIL DRAIN PLUG
Record the frame and engine serial numbers in the space below. You
will need these serial numbers when ordering parts and when making
technical or warranty inquiries (see page 66).
Frame serial number: WDP20/30 -
Engine serial number: GX120 -
10
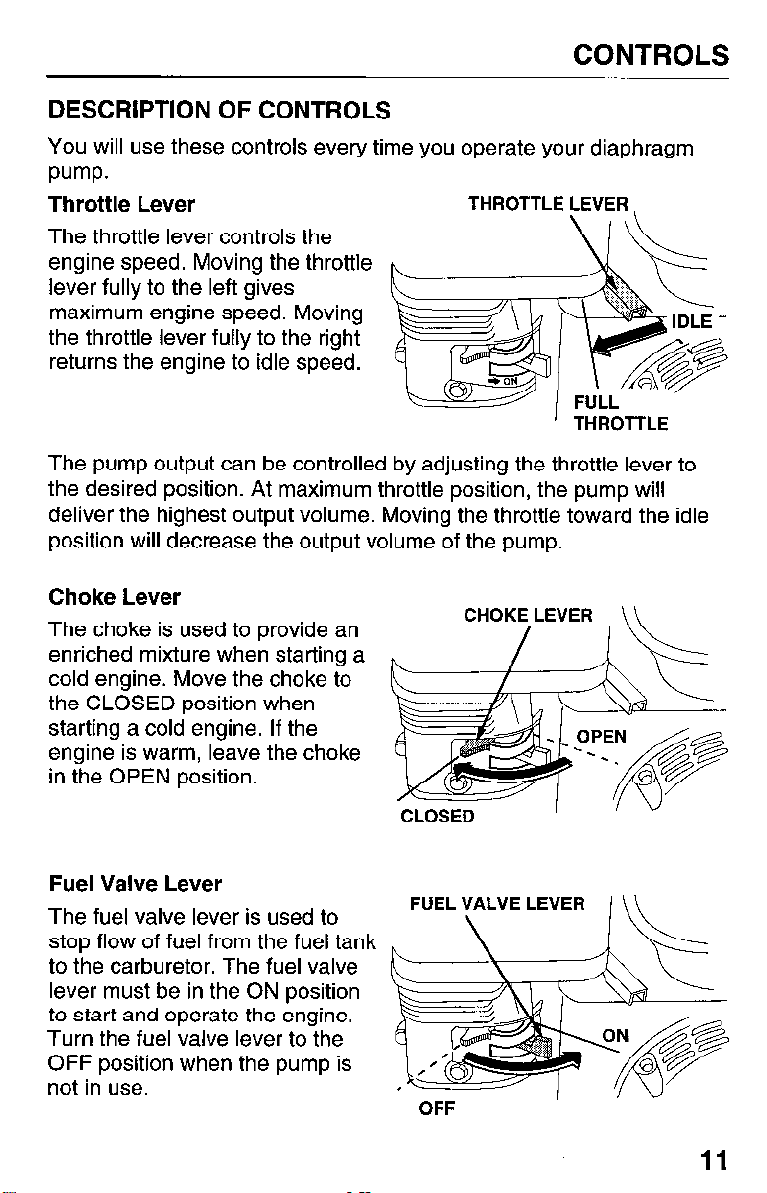
CONTROLS
DESCRIPTION OF CONTROLS
You will use these controls every time you operate your diaphragm
pump.
Throttle Lever
The throttle lever controls the
engine speed. Moving the throttle
lever fully to the left gives
maximum engine speed. Moving
the throttle lever fully to the right
returns the engine to idle speed.
The pump output can be controlled by adjusting the throttle lever to
the desired position. At maximum throttle position, the pump will
deliver the highest output volume. Moving the throttle toward the idle
position will decrease the output volume of the pump.
Choke Lever
The choke is used to provide an
enriched mixture when starting a
cold engine. Move the choke to
the CLOSED position when
starting a cold engine. If the
engine is warm, leave the choke
in the OPEN position.
Fuel Valve Lever
The fuel valve lever is used to
stop flow of fuel from the fuel tank
to the carburetor. The fuel valve
lever must be in the ON position
to start and operate the engine.
Turn the fuel valve lever to the
OFF position when the pump is
not in use.
CHOKE LEVER
/
FUEL VALVE LEVER
\
OFF
11
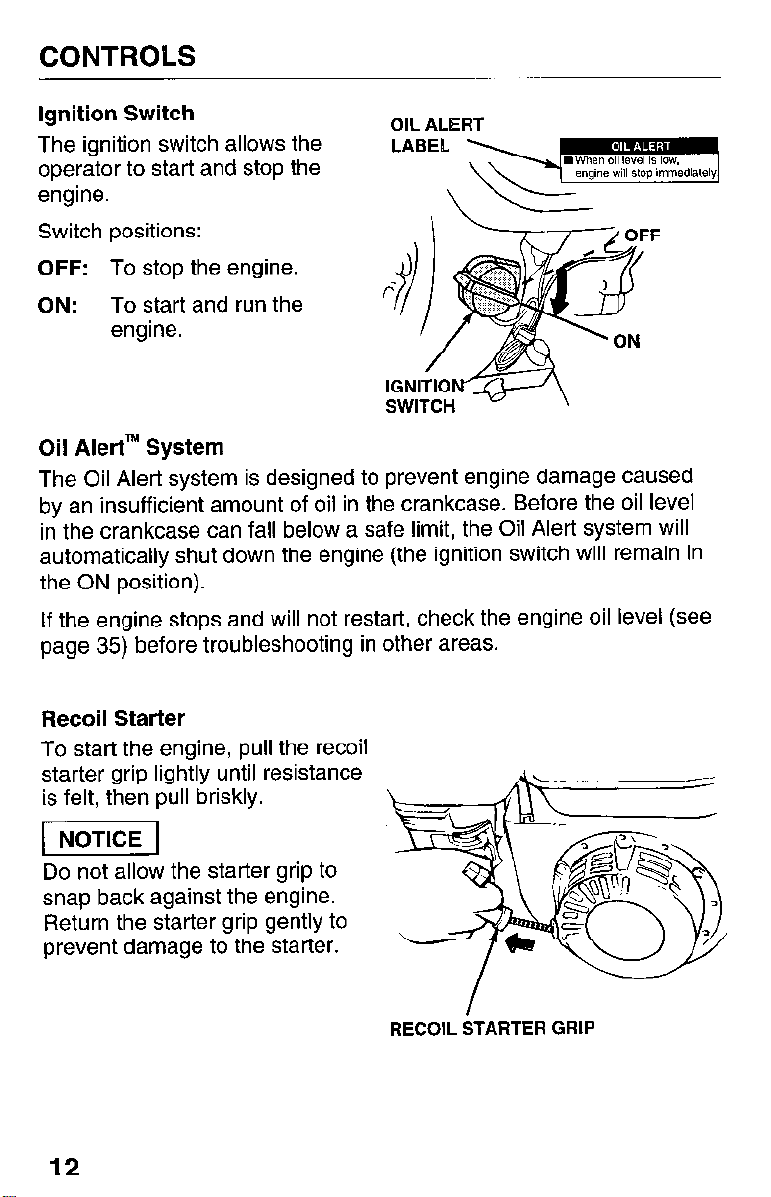
CONTROLS
Ignition Switch
The ignition switch allows the
operator to start and stop the
engine.
Switch positions:
OFF: To stop the engine.
ON: To start and run the
engine.
Oil AlertTM System
The Oil Alert system is designed to prevent engine damage caused
by an insufficient amount of oil in the crankcase. Before the oil level
in the crankcase can fall below a safe limit, the Oil Alert system will
automatically shut down the engine (the ignition switch will remain in
the ON position).
If the engine stops and will not restart, check the engine oil level (see
page 35) before troubleshooting in other areas.
OIL ALERT
Recoil Starter
To start the engine, pull the recoil
starter grip lightly until resistance
is felt, then pull briskly.
(
Do not allow the starter grip to
snap back against the engine.
Return the starter grip gently to
prevent damage to the starter.
12
RECOIL STARTER GRIP

This chapter tells you how to prepare your pump and yourself before
you begin pumping.
ARE YOU READY TO GET STARTED? ..... m ........ 14
Knowledge .................................... 14
IS YOUR PUMP READY TO GO? ................... 15
Check the General Condition of the Pump ........... 15
Check the Suction and Discharge Hoses ............ 16
Check the Engine .............................. 16
13

BEFORE OPERATION
ARE YOU READY TO GET STARTED?
Your safety is your responsibility. A little time spent in preparation will
significantly reduce your risk of injury.
Knowledge
Read and understand this manual. Know what the controls do and
how to operate them.
Familiarize yourself with the pump and its operation before you begin
pumping. Know what to do in case of emergencies.
Be sure of what you are pumping. This pump is designed to pump
only non-potable water, muddy water, and water containing solids.
14

BEFORE OPERATION
IS YOUR PUMP READY TO GO?
For your safety, and to maximize the service life of your equipment, it
is very important to take a few moments before you operate the pump
to check its condition. Be sure to take care of any problem you find,
or have your servicing dealer correct it, before you operate the pump.
Improperly maintaining this pump, or failing
to correct a problem before operation, could
cause a malfunction in which you could be
seriously injured.
Always perform a preoperation inspection
before each operation, and correct any
problem.
Exhaust gas contains poisonous carbon monoxide. Avoid inhalation
of exhaust gas. Never run the engine in a closed garage or confined
area.
1
To prevent fire hazards, keep the pump at least 3 feet (1 meter) away
from building walls and other equipment during operation. Do not
place flammable objects close to the engine.
Before beginning your preoperation checks, be sure the pump is on a
level surface and the ignition switch is in the OFF position.
Check the General Condition of the Pump
l Look around and underneath the pump for signs of oil or gasoline
leaks.
l Remove any excessive dirt or debris, especially around the engine,
muffler, and recoil starter.
l Look for signs of damage.
l Check that all nuts, bolts, screws, hose connectors and clamps are
tightened.
l Keep all shields in place while operating the pump.
15

BEFORE OPERATION
Check the Suction and Discharge Hoses
. Check the general condition of the hoses. Be sure the hoses are in
serviceable condition before connecting them to the pump.
Remember that the suction hose must be of reinforced
construction to prevent hose collapse.
l Check that the sealing washer in the suction hose connector is in
good condition (see page 21).
l Check that the hose connectors and clamps are securely installed
(see pages 21 & 22).
l Check that the strainer is in good condition and is installed on the
suction hose (see page 21). D
Check the Engine
l Check the oil level (see page 35). To avoid the inconvenience of
an unexpected shutdown by the Oil Alert system, always check the
engine oil level before startup.
l Check the air filter (see page 36). A dirty air filter will restrict air
flow to the carburetor, reducing engine and pump performance.
l Check the fuel level (see page 33). Starting with a full tank will help
to eliminate or reduce operating interruptions for refueling.
Remember, be sure to correct any problem you find, or have your
servicing dealer correct it, before you operate the pump.
16

OPERATION
This chapter tells how to operate your pump safely and effectively.
To safely realize the full potential of this pump, you need a complete
understanding of its operation and a certain amount of practice with
its controls.
Read this chapter completely before operating the pump. Take time
to familiarize yourself with the controls and how they operate. The
small amount of time spent in familiarization will reward you with
greater efficiency and reduced risk.
SAFE OPERATING PRECAUTIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
PUMP PREPARATION.. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Suction Hose Connection . . . . . . . , . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Discharge Hose Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . : . . . . . 22
PumpPriming . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
STARTING THE ENGINE. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
STOPPING THE ENGINE. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Emergency.................................... 25
Normal....................................... 25
17

OPERATION
SAFE OPERATING PRECAUTIONS
To safely realize the full potential of this pump, you need a complete
understanding of its operation and a certain amount of practice with
its controls.
Before operating the pump for the first time, please review the
IMPORTANT SAFETY /NFORMA.T/ON on page 6 and the chapter
tilted BEFORE OPERATION.
For you safety, avoid starting or operating the engine in an enclosed
area, such as a garage. Your engine’s exhaust contains poisonous
carbon monoxide gas which can collect rapidly in an enclosed area
and cause illness or death.
Do not pump drinking water. Pump only non-potable water, muddy
water, and water containing solids. Pumping flammable liquids, such
as gasoline or fuel oils, can result in a fire or explosion, causing
serious injury. Pumping sea water, beverages, acids, chemical
solutions, or any other liquid that promotes corrosion can damage the
pump-
18

OPERATION
Due to the pump diaphragm reciprocating motion, pump assembly
and hoses will move up and down and side-to-side during pumping.
This may cause the pump to walk or move around while pumping.
Depending on the surface conditions, pump hose length, and other
factors it may be necessary to anchor the pump to limit pump
movement. During operation, observe pump movement and anchor
the pump frame as necessary. To anchor the pump, attach anchored
tie down straps to the pump lift handles.
While pumping, the suction hose may move out of the pumping
source and the discharge hose may move away from the pumping
destination. It may also be necessary to anchor hose ends to prevent
hose movement.
If there is no one to monitor the pump during operation, it is advisable
to anchor the pump to prevent unexpected movement.
Pump total dynamic discharge head is 50 feet. Total dynamic
discharge head includes static discharge head (discharge vertical
height) and head loss due to friction. Head loss makes it impractical
for the static discharge head to exceed 25 feet. Pumping to a static
discharge head greater than 25 feet can damage pump.
This diaphragm pump should never be run with the discharge output
shut off or restricted.
piq
Pump case failure may result if the discharge output is shut off or
restricted. To avoid pump damage, do not restrict, shut off or
momentarily stop the fluid flow from the discharge hose.
A rigid pipe should never be used with a diaphragm pump. Flexible
hoses must be attached to the pump. The suction hose must be
noncollapsible. Never use hoses that are smaller than the suction or
discharge fittings. Example: 2 inch pump requires a 2 inch inside
diameter or greater hose and 3 inch pump requires a 3 inch inside
diameter or greater hose. Using rigid pipes or hoses that are too
small will cause severe damage to the diaphragm pump.
1 NOTICE 1
Due to pump movement during operation, connecting a rigid pipe to
the pump will cause pump damage. Always use flexible suction and
discharge hoses to prevent pump damage.
19
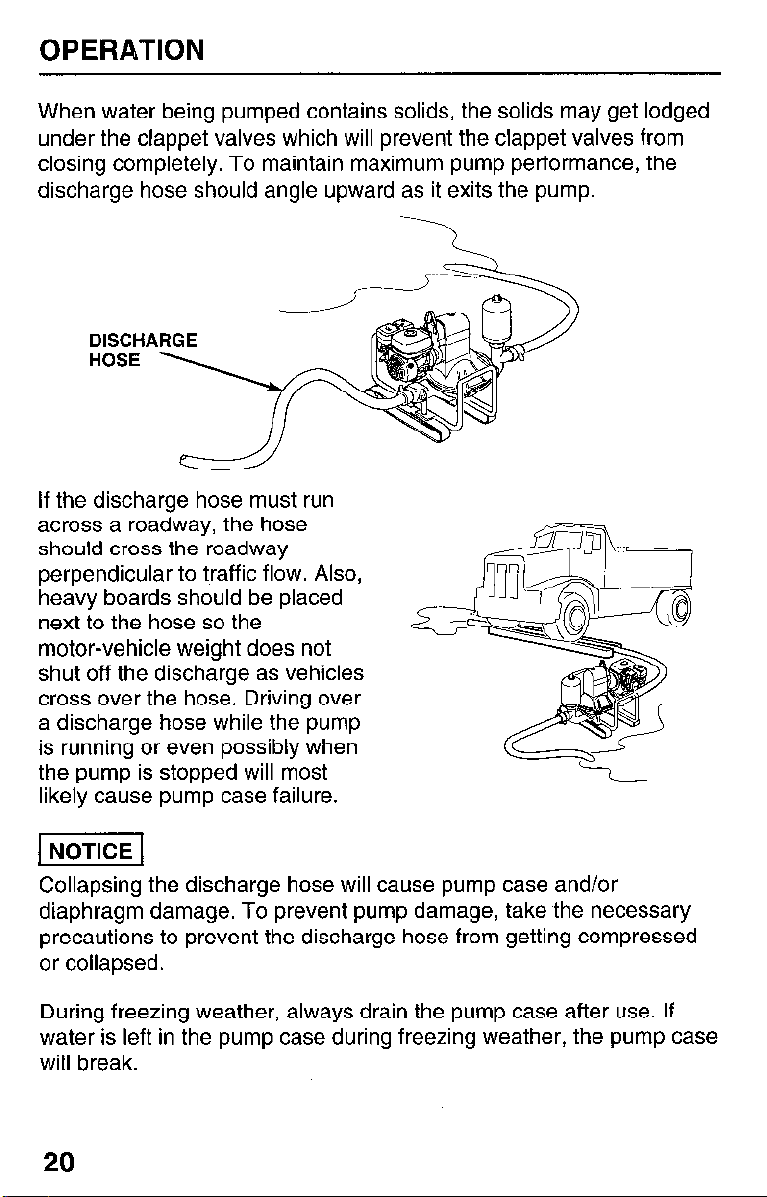
OPERATION
When water being pumped contains solids, the solids may get lodged
under the clappet valves which will prevent the clappet valves from
closing completely. To maintain maximum pump performance, the
discharge hose should angle upward as it exits the pump.
DISCHARGE
HOSE
If the discharge hose must run
across a roadway, the hose
should cross the roadway
perpendicular to traffic flow. Also,
heavy boards should be placed
next to the hose so the
motor-vehicle weight does not
shut off the discharge as vehicles
cross over the hose. Driving over
a discharge hose while the pump
is running or even possibly when
the pump is stopped will most
likely cause pump case failure.
Collapsing the discharge hose will cause pump case and/or
diaphragm damage. To prevent pump damage, take the necessary
precautions to prevent the discharge hose from getting compressed
or collapsed.
During freezing weather, always drain the pump case after use. If
water is left in the pump case during freezing weather, the pump case
will break.
20
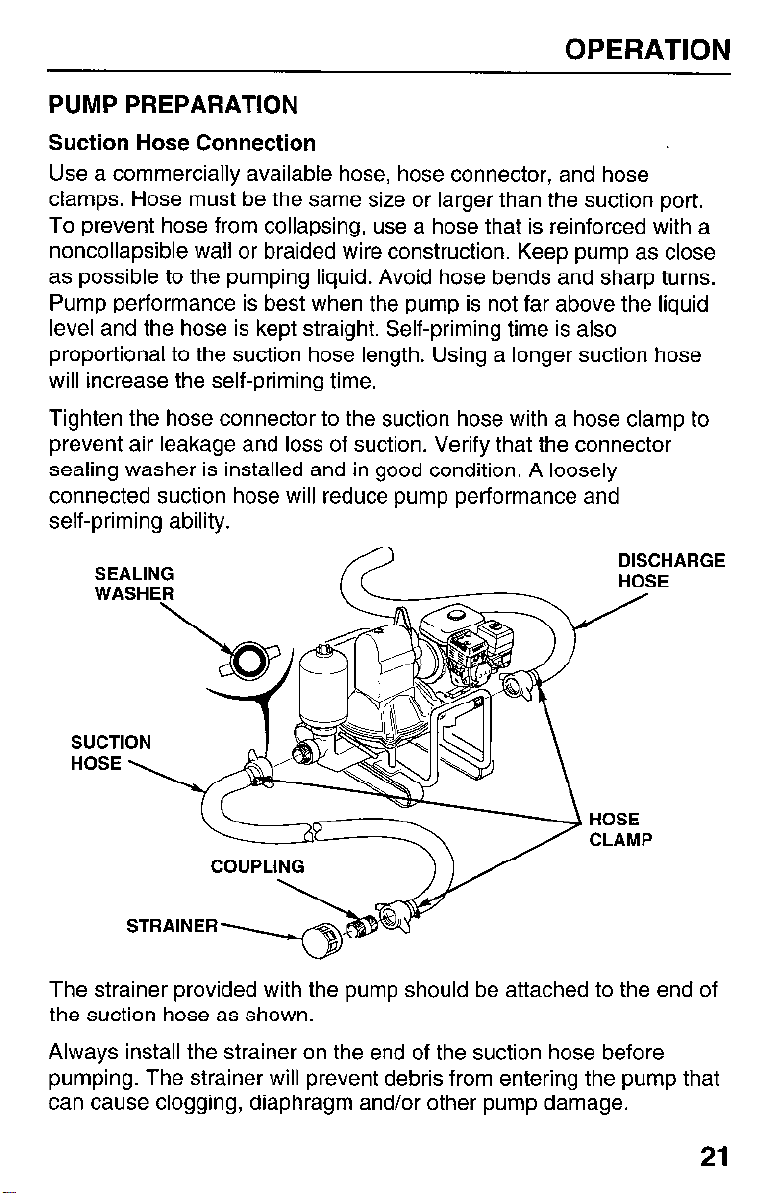
OPERATION
PUMP PREPARATION
Suction Hose Connection
Use a commercially available hose, hose connector, and hose
clamps. Hose must be the same size or larger than the suction port.
To prevent hose from collapsing, use a hose that is reinforced with a
noncollapsible wall or braided wire construction. Keep pump as close
as possible to the pumping liquid. Avoid hose bends and sharp turns.
Pump performance is best when the pump is not far above the liquid
level and the hose is kept straight. Self-priming time is also
proportional to the suction hose length. Using a longer suction hose
will increase the self-priming time.
Tighten the hose connector to the suction hose with a hose clamp to
prevent air leakage and loss of suction. Verify that the connector
sealing washer is installed and in good condition. A loosely
connected suction hose will reduce pump performance and
self-priming ability.
SEALING
WASHER
\
SUCTION
HoSE \
COUPLING
STRAINER~~
The strainer provided with the pump should be attached to the end of
the suction hose as shown.
Always install the strainer on the end of the suction hose before
pumping. The strainer will prevent debris from entering the pump that
can cause clogging, diaphragm and/or other pump damage.
\
cc_,,-, FE
DISCHARGE
21
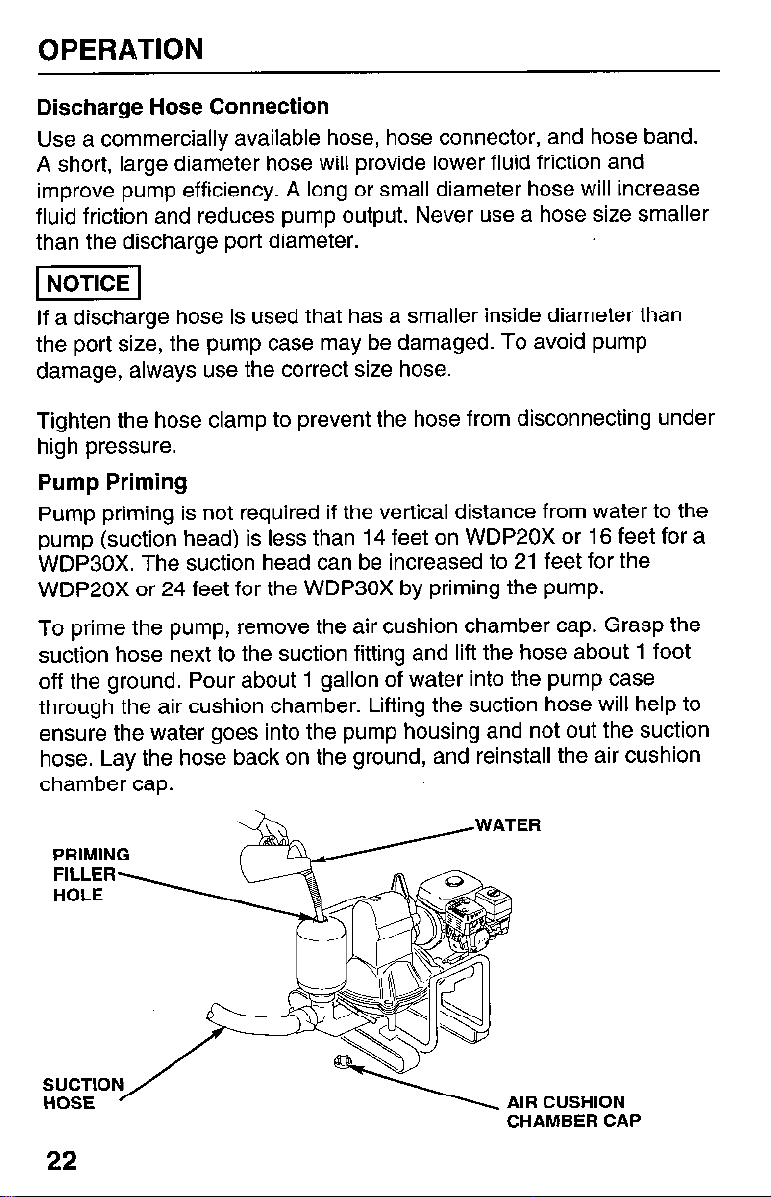
OPERATION
Discharge Hose Connection
Use a commercially available hose, hose connector, and hose band.
A short, large diameter hose will provide lower fluid friction and
improve pump efficiency. A long or small diameter hose will increase
fluid friction and reduces pump output. Never use a hose size smaller
than the discharge port diameter.
1 NOTICE 1
If a discharge hose is used that has a smaller inside diameter than
the port size, the pump case may be damaged. To avoid pump
damage, always use the correct size hose.
Tighten the hose clamp to prevent the hose from disconnecting under
high pressure.
Pump Priming
Pump priming is not required if the vertical distance from water to the
pump (suction head) is less than 14 feet on WDP20X or 16 feet for a
WDP30X. The suction head can be increased to 21 feet for the
WDP20X or 24 feet for the WDP30X by priming the pump.
To prime the pump, remove the air cushion chamber cap. Grasp the
suction hose next to the suction fitting and lift the hose about 1 foot
off the ground. Pour about 1 gallon of water into the pump case
through the air cushion chamber. Lifting the suction hose will help to
ensure the water goes into the pump housing and not out the suction
hose. Lay the hose back on the ground, and reinstall the air cushion
chamber cap.
PRIMING
CUSHION
CHAMBER CAP
 Loading...
Loading...