Honda Accord Lx 2003 Owner's Manual

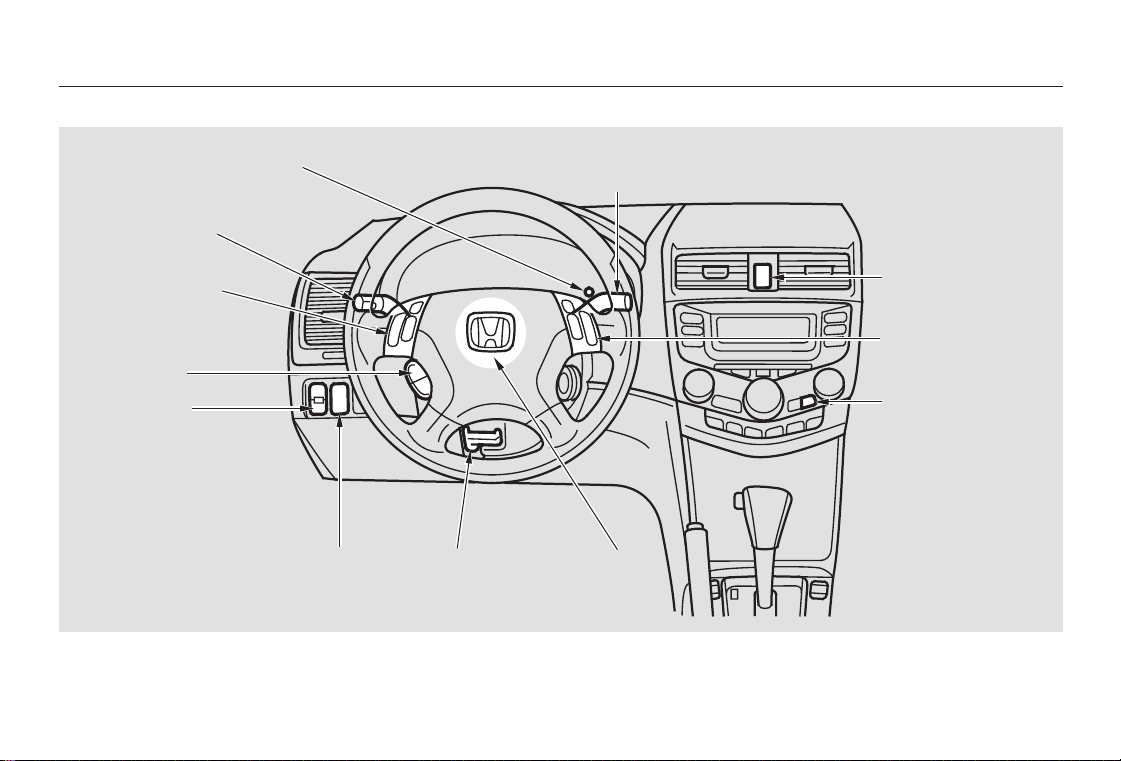
Your Car at a Glance
MIRROR CONTROLS
(P.101)
DOOR LOCK SWITCH
(P.79)
POWER WINDOW
SWITCHES
(P.96)
HAZARD WARNING LIGHTS (P.72)
AUDIO SYSTEM
DIGITAL CLOCK
(P.134, 150, 169)
(P.139, 156, 174)
HEATING/COOLING
CONTROLS
(P.112)
TRUNK RELEASE HANDLE/
FUEL FILL DOOR RELEASE
(P.84/204)
2
HOOD RELEASE
HANDLE
(P.206)
Your Car at a Glance
INSTRUMENT PANEL
BRIGHTNESS
(P. 69)
HEADLIGHTS/
TURN SIGNALS
(P. 68/70)
REMOTE AUDIO
CONTROLS
(P. 192)
VOICE CONTROL
SWITCHES
MOONROOF
SWITCH
(P. 100)
*
:
Only on cars equipped with Navigation System. Refer to the Navigation System Owner’s Manual.
*
TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM
(P. 232)
TILT/TELESCOPIC
ADJUSTMENT
(P. 73)
WINDSHIELD
WIPERS/WASHERS
(P. 70, 71/72)
HORN
HAZARD
WARNING LIGHTS
(P. 72)
CRUISE CONTROLS
(P. 195)
REAR WINDOW
DEFOGGER
(P. 72, 112, 125, 131)
3

4

Important Safety Precautions
You’ll find many safety
recommendations throughout this
section, and throughout this manual.
Therecommendationsonthispage
are the ones we consider to be the
most important.
Always Wear Your Seat Belt
A seat belt is your best protection in
all types of collisions. Airbags
supplement seat belts, but airbags
are designed to inflate only in a
moderate to severe frontal collision.
So even though your car is equipped
with airbags, make sure you and
your passengers always wear your
seat belts, and wear them properly.
(See page .)
Restrain All Children
Children are safest when they are
properly restrained in the back seat,
notthefrontseat.Achildwhoistoo
smallforaseatbeltmustbeproperly
restrained in a child safety seat. (See
page .)
6
15
21
Driver and Passenger Safety
Be Aware of Airbag Hazards Control Your Speed
While airbags can save lives, they
can cause serious or fatal injuries to
occupants who sit too close to them,
or are not properly restrained.
Infants, young children, and short
adults are at the greatest risk. Be
sure to f ollow all instructions and
warnings in this manual. (See page
.)
7
Don’t Drink and Drive
Alcohol and driving don’t mix. Even
one drink can reduce your ability to
respond to changing conditions, and
your reaction time gets worse with
every additional drink. So don’t drink
and drive, and don’t let your friends
drink and drive, either.
Excessive speed is a major factor in
crash injuries and deaths. Generally,
the higher the speed the greater the
risk, but serious accidents can also
occur at lower speeds. Never drive
faster than is saf e for current
conditions, regardless of the
maximum speed posted.
Keep Your Car in Safe Condition
Having a tire blowout or a
mechanical f ailure can be extremely
hazardous. To reduce the possibility
of such problems, check your tire
pressures and condition frequently,
and perform all regularly scheduled
maintenance. (See page .)
248

(3) (4)
(10)
(1)
(9)
(8)
(2)
Your Car’s Saf ety Features
Your car is equipped with many
features that work together to
protect you and your passengers
during a crash.
(7)
*
Some safety f eatures do not require
anyactiononyourpart.These
include a strong steel framework
that forms a safety cage around the
passenger compartment; f ront and
rear crush zones that are designed to
crumple and absorb energy during a
crash; a collapsible steering column;
(6)
(7)
(5)
(1) Safety Cage
(2) Crush Zones
(3) Seats and Seat-Backs
(4) Head Restraints
(5) Collapsible Steering Column
(6) Seat Belts
(7) Front Airbags
(8) Side Airbags
(9) Side Curtain Airbags
(10) Door Locks
If equipped:
(2)
(11) Seat Belt Tensioners
(11)
*
*
and seat belt tensioners that
automatically tighten the front seat
belts in the event of a crash.
CONTINUED
Driver and Passenger Safety
7

Your Car’s Saf ety Features
These safety features are designed
to reduce the severity of injuries in a
crash. However, you and your
passengers can’t take full advantage
of these safety features unless you
remain sitting in a proper position
always wear your seat belts
and
properly.
features can contribute to injuries if
they are not used properly.
8
In fact, some safety
Driver and Passenger Safety
Seat Belts
Foryoursafety,andthesafetyof
your passengers, your car is
equipped with seat belts in all seating
positions.
Your seat belt system also
includes a light on the
instrument panel to remind you and
your passengers to fasten your seat
belts.
Why Wear Seat Belts
Seat belts are the single most
effectivesafetydeviceforadultsand
larger children. (Infants and smaller
children must be properly restrained
in child seats.)
Not wearing a seat belt properly
increases the chance of serious
injury or death in a crash, even
though your car has airbags.
In addition, most states and all
Canadian provinces require you to
wear seat belts.
Not wearing a seat belt properly
increases the chance of serious
injury or death in a crash, even
if you have airbags.
Be sure you and your
passengers always wear seat
belts and wear them properly.
When properly worn, seat belts:
Keep you connected to the car so
you can take advantage of the car’s
built-in safety features.
Help protect you in almost every
type of crash, including frontal,
side, and rear impacts and
rollovers.
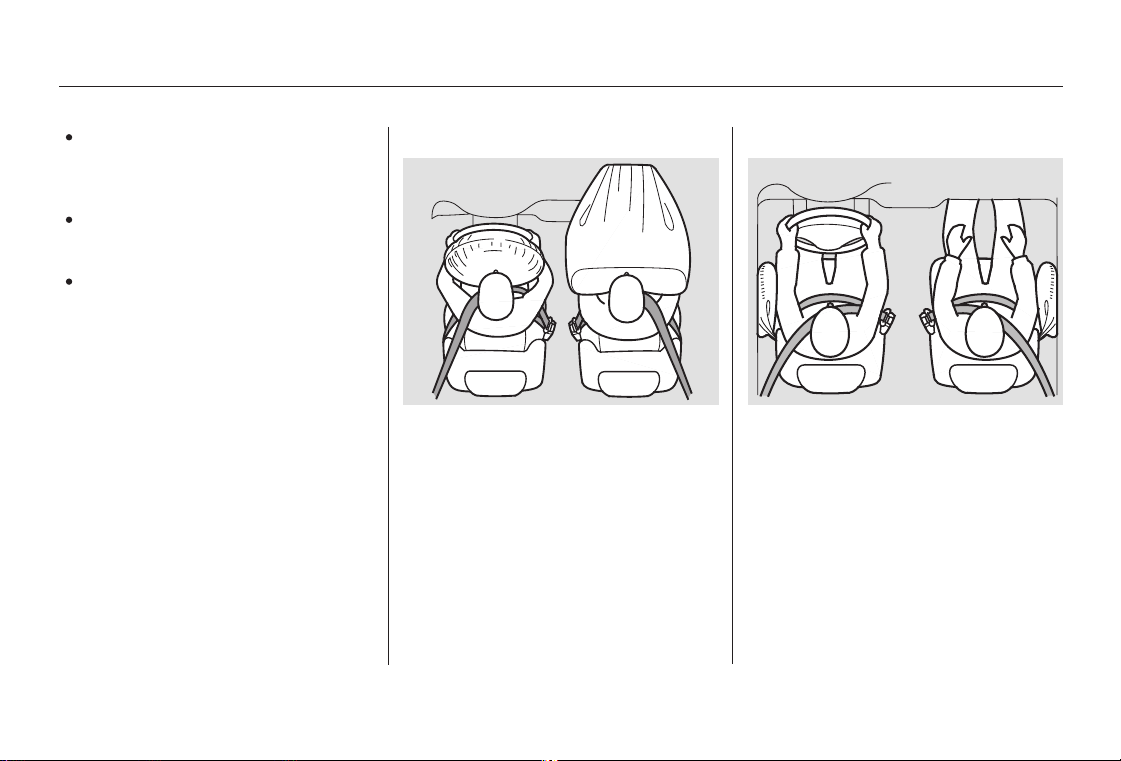
Your Car’s Saf ety Features
Help keep you from being thrown
against the inside of the car and
against other occupants.
Keep you from being thrown out
of the car.
Help keep you in a good position
should the airbags ever deploy. A
good position reduces the risk of
injury from an inf lating airbag, and
allows you to get the best
advantage from the airbag.
Of course, seat belts cannot
completely protect you in every
crash.Butinmostcases,seatbelts
can reduce your risk of serious
injury.
What you should do:
Always wear
your seat belt, and make sure you
wear it properly.
Airbags
Your car has a Supplemental
Restraint System (SRS) with f ront
airbags to help protect the heads and
chests of the driver and a front seat
passenger during a moderate to
severe f rontal collision.
Standard on V-6 and EX models.
Optional on the U.S. LX model
Your car also has side airbags to help
protect the upper torso of the driver
or a front seat passenger during a
moderate to severe side impact.
CONTINUED
Driver and Passenger Safety
9
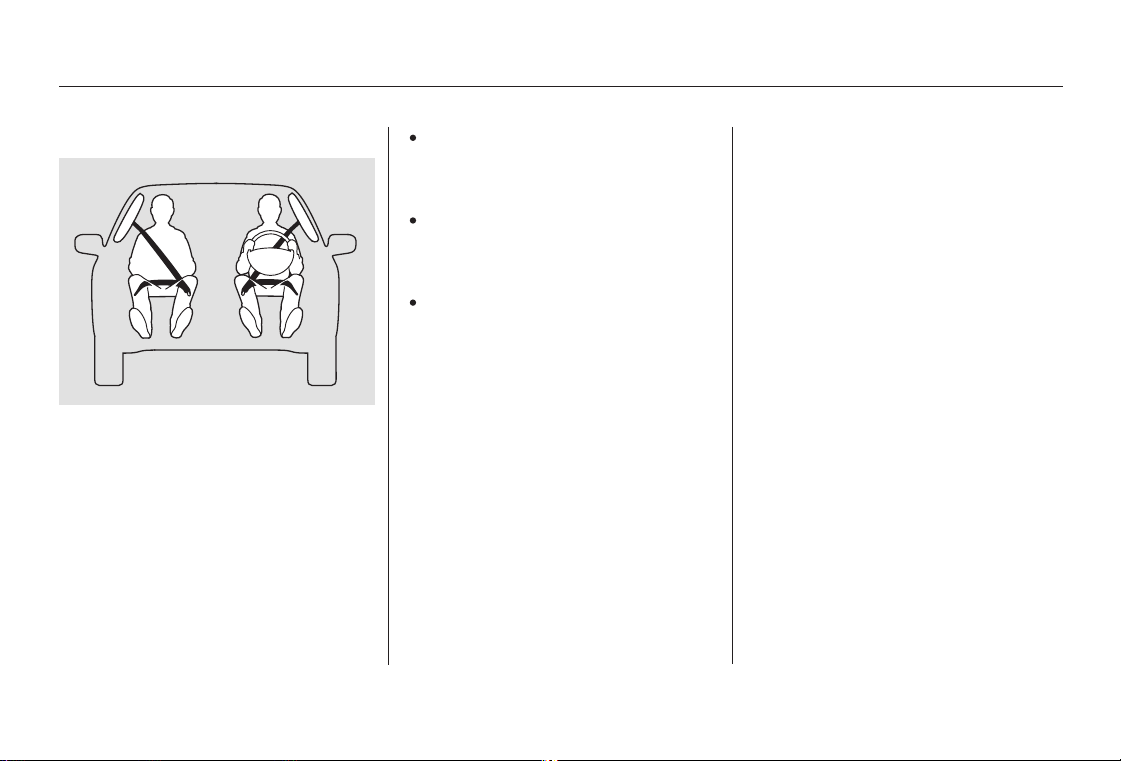
Your Car’s Saf ety Features
U.S. EX-V6 model, optional on Canadian
EX-V6 model
Your car also has side curtain
airbags. During a moderate to severe
side impact, side curtain airbags help
to protect the heads of the driver,
front seat passenger, and passengers
sitting in the outer rear seating
positions.
The most important things you need
to know about your airbags are:
10
Driver and Passenger Safety
Airbags do not replace seat belts.
They are designed to supplement
the seat belts.
Airbags off er no protection in rear
impacts, rollovers, or minor
frontal or side collisions.
Airbags can pose serious hazards.
To do their job, airbags must
inflate with tremendous force and
speed. So while airbags help save
lives, they can cause minor injuries,
or more serious or even fatal
injuries if occupants are not
properly restrained or sitting
properly.
What you should do:
Always wear
your seat belt properly, and sit
upright and as far back as possible
from the steering wheel or
dashboard.
Seats and Seat-Backs
Your car’s seats are designed to keep
you in a comfortable, upright
position so you can take full
advantage of the protection offered
by seat belts and the energy
absorbing materials in the seats.
How you adjust your seats and seatbacks can also affect your safety. For
example, sitting too close to the
steering wheel or dashboard
increases the risk of you or your
passenger being injured by striking
theinsideofthecar,orbyan
inflating airbag.
Reclining a seat-back too far reduces
the seat belt’s effectiveness and
increases the chance that the seat’s
occupant will slide under the seat
belt in a crash and be seriously
injured.
Your Car’s Saf ety Features
What you should do:
seats as far back as possible, and
keep adjustable seat-backs in an
upright position whenever the car is
moving.
Head Restraints
Head restraints can help protect you
from whiplash and other injuries. For
maximum protection, the back of
your head should rest against the
center of the head restraint.
Door Locks
Keeping your doors locked reduces
thechanceofbeingthrownoutof
the car during a crash. It also helps
prevent occupants from accidentally
opening a door and falling out, and
outsiders f rom unexpectedly opening
your doors.
Move the front
Pre-Drive Saf ety Checklist
To make sure you and your
passengers get the maximum
protection from your car’s saf ety
features, check the following each
time before you drive away:
All adults, and children who have
outgrown child safety seats, are
wearing their seat belts and
wearingthemproperly(seepage
).
15
Any infant or small child is
properly restrained in a child seat
inthebackseat(seepage ).
21
Frontseatoccupantsaresitting
upright and as far back as possible
from the steering wheel and
dashboard (see page ).
Seat-backs are upright (see page
).
14
Head restraints are properly
adjusted (see page ).
All doors are closed and locked
(see page ).
All cargo is properly stored or
secured (see page ).
12
Driver and Passenger Safety
13
15
214
11

Protecting Adults
The rest of this section gives more
detailed inf ormation about how you
can maximize your saf ety.
Remember, however, that no safety
system can prevent all injuries or
deaths that can occur in severe
crashes, even when seat belts are
properly worn and the airbags deploy.
12
Driver and Passenger Safety
Introduction
The f ollowing pages provide
instructions on how to properly
protect the driver and other adult
occupants.
These instructions also apply to
children who have outgrown child
seats and are large enough to wear
lap/shoulder belts. (See page for
important additional guidelines on
how to properly protect larger
children.)
Close and Lock the Doors
1.
After everyone has entered the car,
be sure the doors are closed and
locked.
36
Your car has a door monitor light on
the instrument panel to indicate
when a specific door is not tightly
closed.
For safety, locking the doors reduces
thechancethatapassenger,
especially a child, will open a door
while the car is moving and
accidentally fall out. It also reduces
thechanceofsomeonebeingthrown
out of the car during a crash.
For security, locked doors can
prevent an outsider from
unexpectedly opening a door when
you come to a stop.
See page for how to lock the
doors.
78

Protecting Adults
Adjust the Front Seats2.
Any driver who sits too close to the
steering wheel is at risk of being
seriously injured or killed by striking
the steering wheel or from being
struck by an inflating front airbag
during a crash.
To reduce the chance of injury, wear
your seat belt properly, sit upright
with your back against the seat, and
movetheseatawayfromthe
steering wheel to the farthest
distance that allows you to maintain
full control of the car.
The National Highway Traffic Safety
Administration and Transport
Canada recommend that drivers
adjust the seat so the center of the
chest is at least 10 inches away from
the center of the steering wheel. In
addition to adjusting the seat, you
can adjust the steering wheel in and
out (see page ).
Also make sure your front seat
passenger moves the seat as far to
the rear as possible.
73
Sitting too close to a front
airbag can result in serious
injury or death if the front
airbags inflate.
Always sit as far back from the
front airbags as possible.
Most shorter drivers can get f ar
enough away from the steering
wheel and still reach the pedals.
However, if you are concerned about
sitting too close, we recommend that
you investigate whether some type
of adaptive equipment may help.
Once your seat is adjusted correctly,
rock it back and forth to make sure
the seat is locked in position.
See page for how to adjust the
front seats.
87
Driver and Passenger Safety
13
Protecting Adults
Adjust the Seat-Backs3.
Adjust the driver’s seat-back to a
comfortable, upright position,
leaving ample space between your
chest and the airbag cover in the
center of the steering wheel. If you
sit too close to the steering wheel,
you could be injured if the front
airbag inflates.
14
Driver and Passenger Safety
A front passenger should also adjust
the seat-back to an upright position,
but as far from the dashboard as
possible. A passenger who sits too
close to the dashboard could be
injured if the front airbag inflates.
Reclining a seat-back so that the
shoulder part of the belt no longer
rests against the occupant’s chest
reduces the protective capability of
the belt. It also increases the chance
of sliding under the belt in a crash
and being seriously injured. The
farther a seat-back is reclined, the
greater the risk of injury.
Reclining the seat-back too far
can result in serious injury or
death in a crash.
Adjust the seat-back to an
upright position and sit well
back in the seat.
See page for how to adjust seatbacks.
87

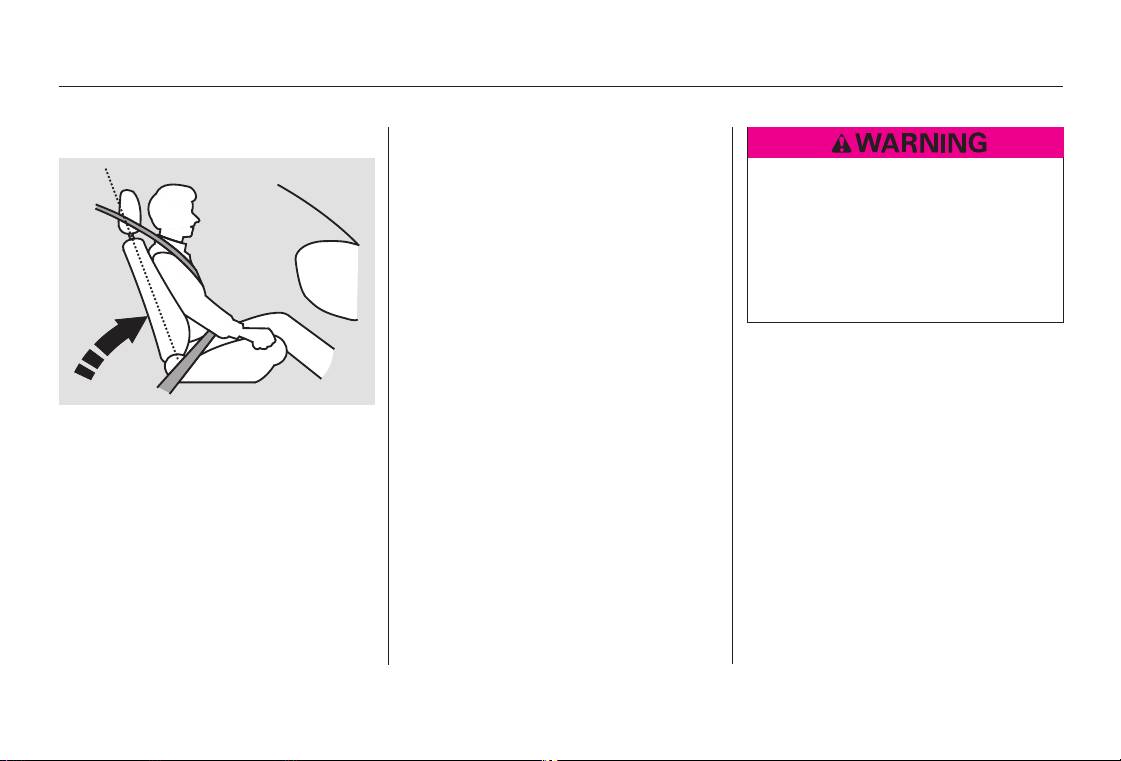
Protecting Adults
Adjust the Head Restraints Fasten and Position the Seat
4. 5.
Belts
Before driving, make sure everyone
with an adjustable head restraint has
properly positioned the head
restraint. The restraint should be
positioned so the back of the
occupant’s head rests against the
center of the restraint. A taller
person should adjust the restraint as
high as possible.
Improperly positioning head
restraints reduces their
effectiveness and you can be
seriously injured in a crash.
Make sure head restraints are
in place and positioned properly
before driving.
Properly adjusted head restraints
will help protect occupants from
whiplash and other crash injuries.
See page for how to adjust the
head restraints.
91
Insert the latch plate into the buckle,
then tug on the belt to make sure the
belt is securely latched. Also check
that the belt is not twisted, because a
twisted belt can cause serious
injuries in a crash.
CONTINUED
Driver and Passenger Safety
15
Protecting Adults
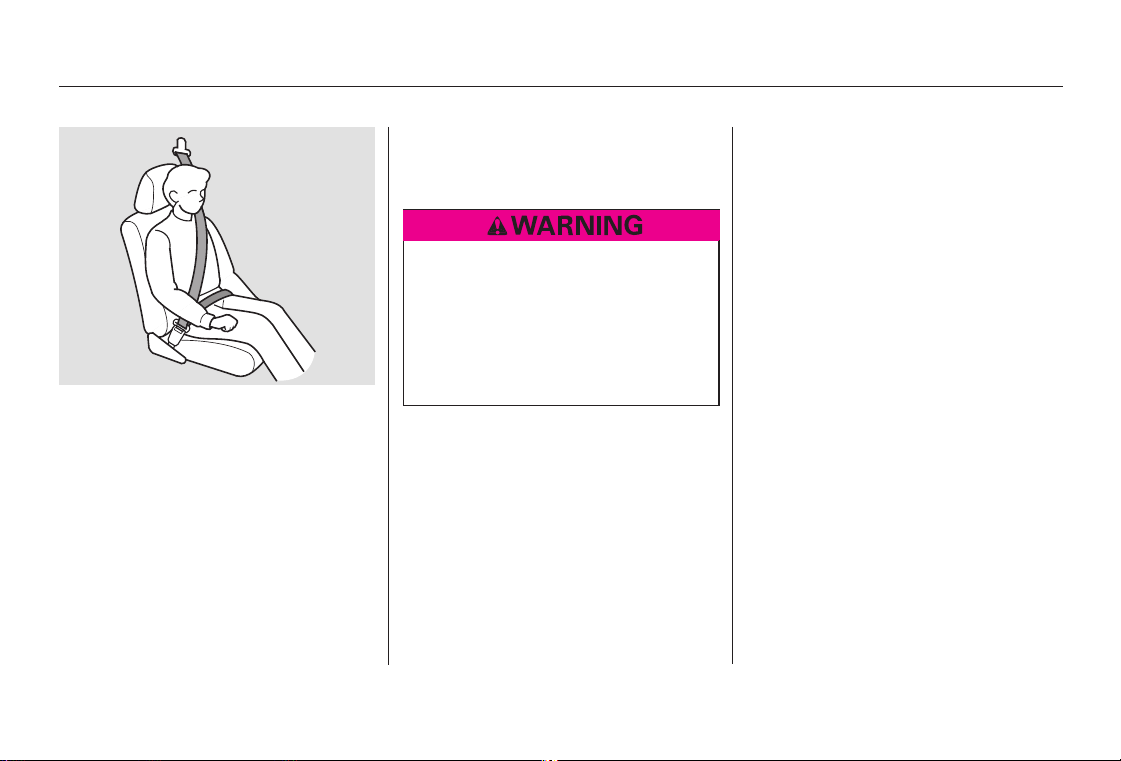
Position the lap part of the belt as
low as possible across your hips,
then pull up on the shoulder part of
the belt so the lap part fits snugly.
This lets your strong pelvic bones
take the force of a crash and reduces
the chance of internal injuries.
If necessary, pull up on the belt again
to remove any slack from the
shoulder part, then check that the
belt rests across the center of your
chest and over your shoulder. This
16
Driver and Passenger Safety
spreads the forces of a crash over
the strongest bones in your upper
body.
Improperly positioning the seat
belts can cause serious injury
or death in a crash.
Make sure all seat belts are
properly positioned before
driving.
If the seat belt touches or crosses
your neck, or if it crosses your arm
instead of your shoulder, you need to
adjust the seat belt anchor height.

Protecting Adults
RELEASE
BUTTONS
To adjust the height of a front seat
belt anchor, squeeze the two release
buttons and slide the anchor up or
down as needed (it has four
positions).
Never place the shoulder portion of a
lap/shoulder belt under your arm or
behind your back.
This could cause
very serious injuries in a crash.
If a seat belt does not seem to work
as it should, it may not protect the
occupant in a crash.
sit in a seat with an inoperative seat
belt.
Anyone using a seat belt that is
No one should
not working properly can be
seriously injured or killed. Have your
Honda dealer check the belt as soon
as possible.
See page for additional
42
information about your seat belt
system and how to take care of your
belts.
Driver and Passenger Safety
17

Protecting Adults
Adjust the Steering Wheel Maintain a Proper Sitting
6. 7.
Position
After all occupants have adjusted
their seats and put on seat belts, it is
very important that they continue to
sit upright, well back in their seats,
with their feet on the floor, until the
car is parked and the engine is off.
Sitting improperly can increase the
chance of injury during a crash. For
example, if an occupant slouches,
lies down, turns sideways, sits
forward, leans forward or sideways,
Adjust the steering wheel, if needed,
so that the wheel points toward your
chest, not toward your f ace.
Pointing the steering wheel toward
your chest provides optimal
protection from the airbag.
or puts one or both f eet up, the
chance of injury during a crash is
greatly increased.
In addition, an occupant who is out of
position in the front seat can be
seriously or f atally injured by
striking interior parts of the car, or
by being struck by an inflating front
airbag. Being struck by an inflating
side airbag can result in possibly
serious injuries.
Sitting improperly or out of
position can result in serious
injury or death in a crash.
Always sit upright, well back in
the seat, with your feet on the
floor.
See page for how to adjust the
steering wheel.
18
73
Driver and Passenger Safety

Protecting Adults
Remember, to get the best
protection from your car’s airbags
and other safety features, you must
sit properly and wear your seat belt
properly.
Advice for Pregnant Women
Because protecting the mother is the
best way to protect her unborn child,
a pregnant woman should always
wear a seat belt whenever she drives
or rides in a car.
Remember to keep the lap portion of
the belt as low as possible across
your hips.
Pregnant women should also sit
upright and as far back as possible
from the steering wheel or
dashboard. This will reduce the risk
of injuries to both the mother and
her unborn child that can be caused
by a crash or an inflating airbag.
Each time you have a check-up, ask
your doctor if it’s okay for you to
drive.
Driver and Passenger Safety
19
Protecting Adults
Additional Safety Precautions
Two people should never use the
same seat belt.
If they do, they
could be very seriously injured in a
crash.
Do not put any accessories on seat
belts.
Devices intended to improve
occupant comf ort or reposition the
shoulder part of a seat belt can
severely compromise the
protective capability of the seat
belt and increase the chance of
serious injury in a crash.
20
Driver and Passenger Safety
Do not place hard or sharp objects
between yourself and a front
airbag.
Carrying hard or sharp
objects on your lap, or driving with
a pipe or other sharp objects in
your mouth, can result in injuries
if your front airbag inflates.
Do not attach or place objects on
the front airbag covers.
Any object
attached to or placed on the covers
marked ‘‘SRS AIRBAG’’ in the
center of the steering wheel and
on top of the dashboard could
interfere with the proper operation
of the airbags. Or, if the airbags
inflate, the objects could be
propelled inside the car and hurt
someone.
On models with side airbags or
side curtain airbags, do not attach
hard objects on or near a front
door.
If a side airbag or a side
curtain airbag inflates, a cup
holder or other hard object
attached on or near the door could
be propelled inside the car and
hurt someone.
Keep your hands and arms away
from the airbag covers.
If your
hands or arms are close to the
airbag cover in the center of the
steering wheel or on top of the
dashboard, they could be injured if
the front airbag inflates.

Children depend on adults to protect
them. However, despite their best
intentions, many parents and other
adults may not know how to
properly
protect young passengers.
So if you have children, or if you ever
need to drive with a grandchild or
otherchildreninyourcar,besureto
read this section.
Children who are unrestrained
or improperly restrained can be
seriously injured or killed in a
crash.
Any child too small for a seat
belt should be properly
restrained in a child seat. A
larger child should be properly
restrained with a seat belt.
Protecting Children
All Children Must Be Restrained
Each year, many children are injured
or killed in car crashes because they
are either unrestrained or not
properly restrained. In fact, car
accidents are the number one cause
of death of children ages 12 and
under.
To reduce the number of child
deaths and injuries, every state and
Canadian province requires that
infants and children be restrained
whenever they ride in a car.
Anychildwhoistoosmalltoweara
seat belt should be properly
restrained in a child seat.
.)
A larger child should always be
restrained with a seat belt, and use a
booster, if needed.
(See page
(See page .)2636
CONTINUED
Driver and Passenger Safety
21

Protecting Children
Additional Precautions to Parents
Neverholdaninfantorchildon
your lap.
If you are not wearing a
seat belt in a crash, you could be
thrown forward into the
dashboard and crush the child.
child can be torn from your arms
during a crash. For example, if
your car crashes into a parked car
at 30 mph (48 km/h), a 20-lb
(9 kg) infant will become a 600-lb
(275 kg) force, and you will not be
able to hold on.
Never put a seat belt over yourself
and an infant or child.
During a
crash, the belt could press deep
into the child and cause very
serious injuries.
22
Driver and Passenger Safety
Children Should Sit in the Back
Seat
According to accident statistics,
children of all ages and sizes are
safer when they are restrained in the
back seat, not the f ront seat. The
National Highway Traffic Safety
Administration and Transport
Canada recommend that all children
ages 12 and under be properly
restrained in the back seat.
In the back seat, children are less
likely to be injured by striking hard
interior parts during a collision or
hard braking. Also, children cannot
be injured by an inflating airbag
when they ride in the back.
The Passenger’s Front Airbag
Poses Serious Risks to Children
Front airbags have been designed to
help protect adults in a moderate to
severe f rontal collision. To do this,
the passenger’s front airbag is quite
large, and it inflates with tremendous
speed.Ifyouarewearingaseatbelt,the
Infants
Never put a rear-f acing child seat in
the front seat of a car equipped with
a passenger’s airbag.
If the airbag
inflates, it can hit the back of the
child seat with enough force to kill or
very seriously injure an infant.

Protecting Children
Small Children
Placing a forward-f acing child seat in
the front seat of a car equipped with
a passenger’s f ront airbag can be
hazardous.
If the car seat is too far
forward, or the child’s head is
thrown f orward during a collision, an
inflating front airbag can strike the
child with enough force to kill or
very seriously injure a small child.
Larger Children
Children who have outgrown child
seats are also at risk of being injured
or killed by an inflating passenger’s
front airbag.
Whenever possible,
larger children should sit in the back
seat, in a booster seat if needed, and
be properly restrained with a seat
belt. (See page for important
36
information about protecting larger
children.)
U.S. Models
To remind you of the passenger’s
front airbag hazards, and that
children must be properly restrained
in the back seat, your car has
warninglabelsonthedashboardand
on the driver’s and front passenger’s
visors. Please read and follow the
instructions on these labels.
CONTINUED
Driver and Passenger Safety
23

Protecting Children
Canadian Models
To remind you of the f ront airbag
hazards, your car has warning labels
on the driver’s and front passenger’s
visors. Please read and follow the
instructions on these labels.
24
Driver and Passenger Safety
If You Must Drive with Several
Children
Your car has three seating positions
in the back seat where children can
be properly restrained.
If you ever have to carry more than
three children in your car:
Place the largest child in the front
seat, provided the child is large
enough to wear a seat belt
properly (see page ).
Move the car seat as far to the
rear as possible (see page ).3613
Have the child sit upright and well
backintheseat(seepage ).
Make sure the seat belt is properly
positioned and secured (see page
).
15
18
Protecting Children
If a Child Requires Close
Attention
Many parents say they prefer to put
an infant or small child in the front
passenger seat so they can watch the
child, or because the child requires
attention.
Placing a child in the front seat
exposes the child to hazards from
the passenger’s front airbag, and
paying close attention to a child
distracts the driver from the
important tasks of driving, placing
both of you at risk.
If a child requires physical attention
or frequent visual contact, we
strongly recommend that another
adult ride with the child in the back
seat. The back seat is far safer for a
child than the front.
Additional Safety Precautions
Use childproof door locks to
prevent children from opening the
doors.
Using this feature will
prevent children from opening the
doors and accidentally f alling out
(see page ).
Use the main power window
switch to prevent children from
opening the rear windows.
84
Using
this feature will prevent children
from playing with the windows,
which could expose them to
hazards or distract the driver (see
page ).
96
Do not leave children alone in your
car.
Leaving children without
adult supervision is illegal in most
states and Canadian provinces,
and can be very hazardous. For
example, infants and small
childrenleftinacaronahotday
can die from heatstroke. And
children left alone with the key in
the ignition can accidentally set
the car in motion, possibly injuring
themselves or others.
CONTINUED
Driver and Passenger Safety
25
Protecting Children
Lock all doors and the trunk when
your car is not in use.
Children
who play in cars can accidentally
get trapped inside the trunk and
be seriously injured or could die.
Teach your children not to play in
or around cars. Know how to
operate the emergency trunk
opener and decide if your children
should be shown how to use this
feature(seepage ).
Keep car keys/remote
transmitters out of the reach of
children.
Even very young
85
children learn how to unlock car
doors, turn on the ignition, and
openthetrunk,whichcanleadto
accidental injury or death.
26
Driver and Passenger Safety
General Guidelines for Using
Child Seats
The f ollowing pages give general
guidelines for selecting and installing
child seats for infants and small
children.
Selecting a Child Seat
To provide proper protection, a child
seat should meet three
requirements:
The child seat should meet safety
1.
standards.
The child seat should
meet Federal Motor Vehicle
Safety Standard 213 (FMVSS 213)
or Canadian Motor Vehicle Safety
Standard 213 (CMVSS 213). Look
for the manufacturer’s statement
of compliance on the box and seat.
2.
The child seat should be of the
proper type and size to fit the child.
Infants:
Childrenuptoaboutone
year old should be restrained in a
rear-f acing, reclining child seat. Only
a rear-facing seat provides the
proper support to protect an infant’s
head, neck, and back. See page
for additional information on
30
protecting infants.

Small Children:
A child who is too
large for a rear-facing child seat, and
who can sit up without support,
should be restrained in a forwardfacing child seat. See page for
33
additional inf ormation on protecting
small children.
3.
The child seat should fit the car
seating position (or positions)
whereitwillbeused.
Due to variations in the design of
child seats, car seats, and seat belts,
all child seats will not fit all car
seating positions.
However, Honda is confident that
one or more child seat models can fit
andbeproperlyinstalledinall
recommended seating positions in
your car.
Protecting Children
Before purchasing a child seat, we
recommend that parents test the
child seat in the specific car seating
position (or positions) where they
intend to use the seat. If a previously
purchased child seat does not fit, you
may need to buy a different one that
will fit.
CONTINUED
Driver and Passenger Safety
27
Protecting Children
Placing a Child Seat Front Passenger’s Seat
This page briefly summarizes
Honda’s recommendations on where
to place rear-facing and forwardfacing child seats in your car.
Airbags Pose Serious
Risks to Children
The passenger’s front airbag
inflates with enough force to kill
or seriously injure an infant in a
rear-facing child seat.
A small child in a forward-facing
child seat is also at risk. If the
carseatistoofarforward,or
the child’s head is thrown
forward during a collision, an
inflating front airbag can kill or
seriously injure the child.
If a small child must ride in the
front, follow the instructions
provided in this section.
Infants:
Never in the front seat, due
to the front airbag hazard.
Small children:
Not recommended,
due to the front airbag hazard. If a
small child must ride in front,
move the car seat to the rear-most
position and secure a front-facing
child seat with the seat belt. (see
page ).33
Back Seats
Infants:
Recommended positions.
Properlysecurearear-facing
child seat (see pages and ).
Small children:
Recommended
positions. Properly secure a frontfacing child seat (see pages and
).
40
30 40
33
28
Driver and Passenger Safety

Installing a Child Seat
After selecting a proper child seat,
and a good position to install the seat,
there are three main steps in
installing the seat:
Make sure the child seat is firmly
2.
secured.
After installing a child
seat, push and pull the seat
forward and f rom side to side to
verify that it is secure.
Protecting Children
If the child seat is not secure, try
installing it in a different seating
position, or use a different style of
child seat that can be firmly secured
in the desired seating position.
Properly secure the child seat to
1.
the car.
All child seats are
designed to be secured to the car
with the lap part of a lap/shoulder
belt. Some child seats can be
secured to the car’s LATCH
anchorage system instead. A child
whose seat is not properly secured
to the car can be endangered in a
crash. See pages , and for
31 34 40
instructions on how to properly
secure child seats in this car.
To provide security during normal
driving maneuvers as well as during
a collision, we recommend that
parents secure a child seat as f irmly
as possible.
However, a child seat does not need
to be ‘‘rock solid.’’ In some cars or
seating positions, it may be difficult
to install a child seat so that it does
not move at all. Some side-to-side or
back-and-f orth movement can be
expected and should not reduce the
child seat’s effectiveness.
Secure the child in the child seat.
3.
Make sure the child is properly
strappedinthechildseat
according to the child seat maker’s
instructions. A child who is not
properly secured in a child seat
canbethrownoutoftheseatina
crash and be seriously injured.
Storing a Child Seat
When you are not using a child seat,
either remove it and store it in a safe
place, or make sure it is properly
secured. An unsecured child seat can
be thrown around the car during a
crash or sudden stop and injure
someone.
Driver and Passenger Safety
29

Protecting Children
Protecting Infants
Child Seat Type
Only a rear-facing child seat provides
proper support for a baby’s head,
neck, and back. Infants up to about
one year of age must be restrained in
a rear-facing child seat.
Two types of seats may be used: a
seat designed exclusively for infants,
or a convertible seat used in the rearfacing, reclining mode.
30
Driver and Passenger Safety
Placing a rear-facing child seat
in the front seat can result in
serious injury or death if the
passenger’s front airbag inflates.
Always place a rear-facing child
seat in the back seat, not the
front.
We recommend that an infant be
restrained in a rear-facing child seat
until the infant reaches the seat
maker’s weight or height limit and is
able to sit up without support.
Rear-Facing Child Seat Placement
In this car, a rear-facing child seat
can be placed in any seating position
in the back seat, but not in the front
seat.
Never put a rear-f acing child seat in
the front seat.
If the passenger’s
front airbag inflates, it can hit the
back of the child seat with enough
force to kill or seriously injure an
infant. If an inf ant must be closely
watched, we recommend that
another adult sit in the back seat
with the baby.
Do not put a rear-f acing child seat in
a forward-facing position.
If placed
facing forward, an infant could be
very seriously injured during a
frontal collision.
Protecting Children
When properly installed, a rearfacing child seat may prevent the
driver or a front-seat passenger from
moving the seat as far back as
recommended (see page ). Or it
may prevent them f rom locking the
seat-back in the desired upright
position (see page ).
In either case, we recommend that
you place the child seat directly
behind the front passenger seat,
move the front seat as far forward as
needed, and leave it unoccupied. Or
you may wish to get a smaller child
seat that allows you to safely carry a
front passenger.
13
14
Rear-Facing Child Seat Installation
The lap/shoulder belts in the back
seats have a locking mechanism that
must be activated to secure a child
seat.
The f ollowing pages provide
instructions and tips on how to
secure a rear-facing child seat with
this type of seat belt.
If you have a child seat designed to
attach to the car’s LATCH
anchorage system, follow the
instructions on page .
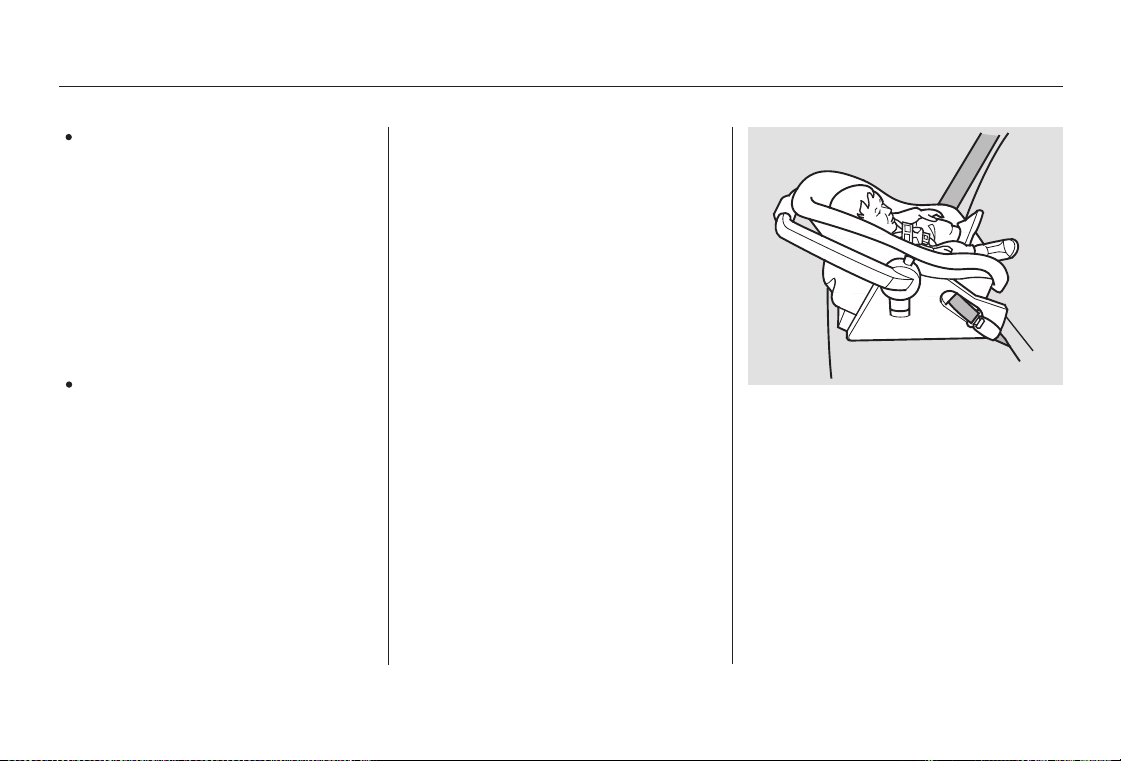
40
With the child seat in the desired
1.
back seating position, route the
belt through the child seat
according to the seat maker’s
instructions, then insert the latch
plate into the buckle.
CONTINUED
Driver and Passenger Safety
31
Protecting Children
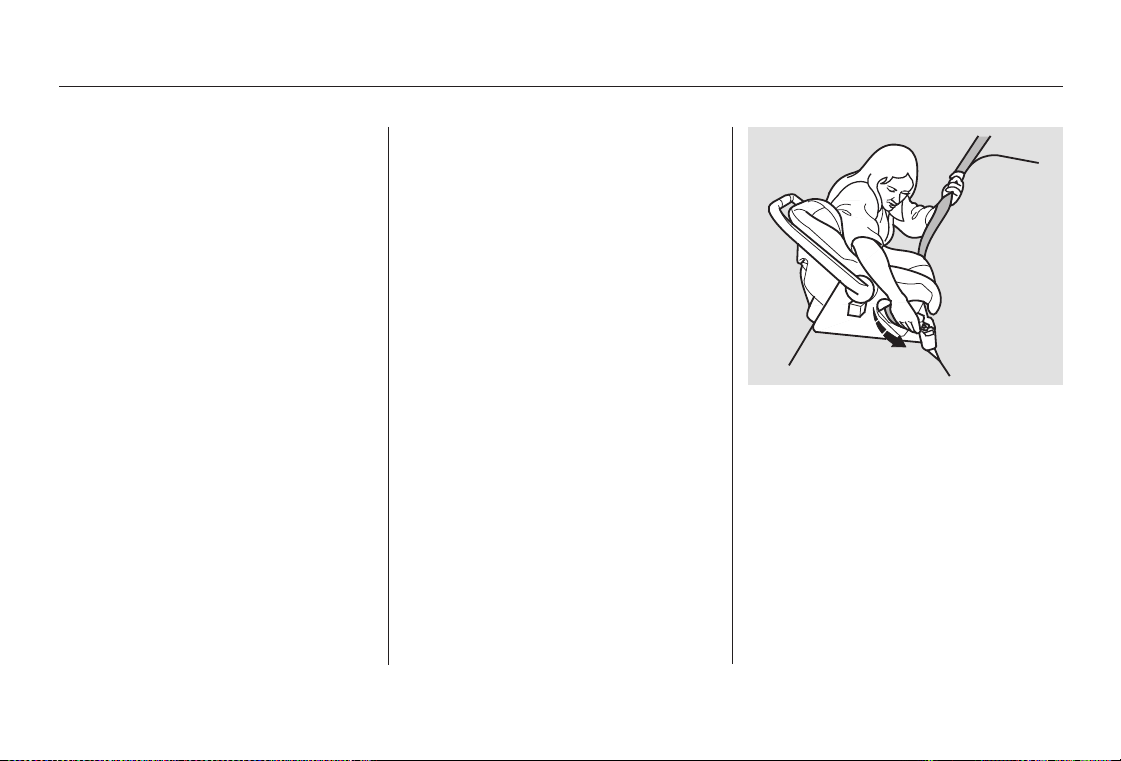
To activate the lockable retractor,
2.
slowly pull the shoulder part of the
belt all the way out until it stops,
then let the belt feed back into the
retractor (you might hear a
clicking noise as the belt retracts).
After the belt has retracted, tug on
3.
it. If the belt is locked, you will not
be able to pull it out. If you can pull
the belt out, it is not locked and
you will need to repeat these steps.
32
Driver and Passenger Safety
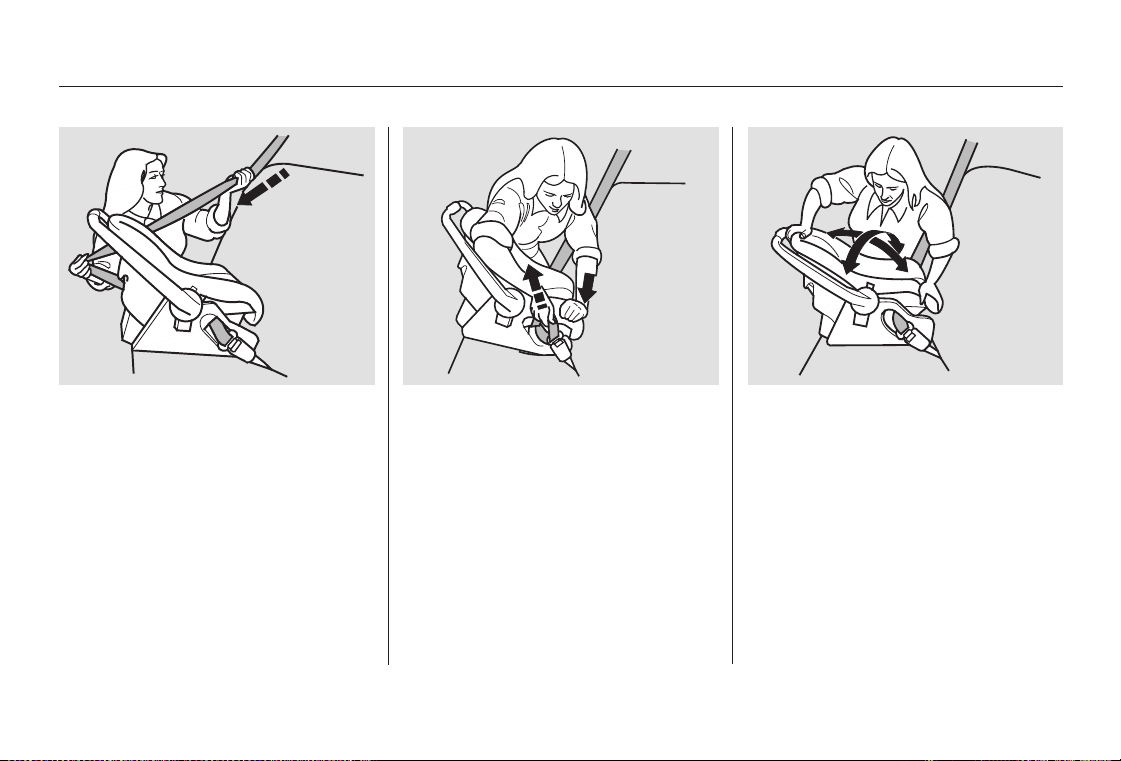
After confirming that the belt is
4. 5.
locked, grab the shoulder part of
the belt near the buckle and pull
up to remove any slack from the
lap part of the belt. Remember, if
the lap part of the belt is not tight,
the child seat will not be secure.
To remove slack, it may help to
putweightonthechildseat,or
push on the back of the seat, while
pulling up on the belt.
Push and pull the child seat
forward and f rom side to side to
verify that it is secure enough to
stay upright during normal driving
maneuvers. If the child seat is not
secure, unlatch the belt, allow it to
retract fully, then repeat these
steps.
To deactivate the locking
mechanism and remove a child seat,
unlatch the buckle, unroute the seat
belt, and let the belt fully retract.
 Loading...
Loading...