Page 1

Page 2
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Introduction .......................................................................................................................................................................2
General Safety Rules .....................................................................................................................................................3-4
Specific Safety Rules ..................................................................................................................................................... 4-5
Symbols ......................................................................................................................................................................... 6-7
Electrical ............................................................................................................................................................................8
Glossary of Terms ..............................................................................................................................................................9
Features ..................................................................................................................................................................... 10-12
Tools Needed ................................................................................................................................................................. 12
Loose Parts .................................................................................................................................................................... 13
Assembly ................................................................................................................................................................... 13-20
Operation ................................................................................................................................................................... 20-27
Adjustments .............................................................................................................................................................. 28-29
Maintenance ................................................................................................................................................................... 30
Parts Ordering/Service ...................................................................................................................................... Back Page
INTRODUCTION
This tool has many features for making its use more pleasant and enjoyable. Safety, performance, and dependability have
been given top priority in the design of this product making it easy to maintain and operate.
2
Page 3

GENERAL SAFETY RULES
WARNING:
Read and understand all instructions. Failure to follow
all instructions listed below, may result in electric shock,
fire and/or serious personal injury.
READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS
KNOW YOUR POWER TOOL. Read the operator’s manual
carefully. Learn the applications and limitations as well
as the specific potential hazards related to this tool.
G
UARD AGAI N S T EL E C TRICAL SHOC K BY
PREVENTING BODY CONTACT WITH GROUNDED
SURFACES. For example: pipes, radiators, ranges,
refrigerator enclosures.
KEEP GUARDS IN PLACE and in good working or
REMOVE
habit of checking to see that keys and adjusting wrenches
are removed from tool before turning it on.
K
EEP WORK AREA CLEAN. Cluttered areas and
benches invite accidents. DO NOT leave tools or pieces
of wood on the tool while it is in operation.
DO
not use power tools in damp or wet locations or expose
to rain. Keep the work area well lit.
K
EEP CH ILDRE N A N D V I SITO R S A WAY. All
visitors should wear safety glasses and be kept a safe
distance from work area. Do not let visitors contact
tool or extension cord while operating.
M
AKE WORKSHOP CHILDPROOF with padlocks,
master switches, or by removing starter keys.
DON’T
safer at the feed rate for which it was designed.
U
SE THE RIGHT TOOL. Do not force the tool or attachment
to do a job for which it was not designed.
USE
extension cord is in good condition. Use only a cord heavy
enough to carry the current your product will draw. An
undersized cord will cause a drop in line voltage resulting in
loss of power and overheating. A wire gauge size (A.W.G.)
of at least 14 is recommended for an extension cord 50
feet or less in length. If in doubt, use the next heavier
gauge. The smaller the gauge number, the heavier the
cord.
D
RESS PROPERLY. Do not wear loose clothing,
neckties, or jewelry that can get caught and draw you into
moving parts. Rubber gloves and nonskid footwear are
recommended when working outdoors. Also wear
protective hair covering to contain long hair.
ALWAYS WEAR SAFETY GLASSES WITH SIDE
S
HIELDS. Everyday eyeglasses have only impact-
resistant lenses, they are NOT safety glasses.
ADJUSTING KEYS AND WRENCHES. Form
NOT USE IN DANGEROUS ENVIRONMENTS. Do
FORCE THE TOOL. It will do the job better and
THE PROPER EXTENSION CORD. Make sure your
der.
SECURE
when practical, it is safer than using your hand and frees
both hands to operate the tool.
D
O NOT OVERREACH. Keep proper footing and
balance at all times.
M
AINTAIN TOOLS WITH CARE. Keep tools sharp
and clean for better and safer performance. Follow
instructions for lubricating and changing accessories.
D
ISCONNECT TOOLS. When not in use, before
servicing, or when changing attachments, blades, bits,
cutters, etc., all tools should be disconnected from power
source.
A
VOID ACCIDENTAL STARTING. Be sure switch is off
when plugging in any tool.
USE
operator’s manual for recommended accessories. The
use of improper accessories may result in injury.
NEVER
the tool is tipped.
CHECK
tool, a guard or other part that is damaged should be
carefully checked to determine that it will operate properly
and perform its intended function. Check for alignment
of moving parts, binding of moving parts, breakage of
parts, mounting and any other conditions that may affect
its operation. A guard or other part that is damaged must
be properly repaired or replaced by an authorized service
center to avoid risk of personal injury.
USE
a blade, cutter, or sanding spindle against the direction
or rotation of the blade, cutter, or sanding spindle only.
NEVER
THE POWER OFF. Don't leave tool until it comes to a
complete stop.
PROTECT
the cutting operation is dusty.
PROTECT
during extended periods of operation.
DO
yank it to disconnect from receptacle. Keep cord from
heat, oil, and sharp edges.
U
SE OUTDOOR EXTENSION CORDS. When tool
is used outdoors, use only extension cords with
approved ground connection that are intended for use
outdoors and so marked.
K
EEP BL A D ES C L EAN, SHA R P, AND WI T H
SUFFICIENT SET. Sharp blades minimize stalling
and kickback.
BLADE COASTS AFTER BEING TURNED OFF
WORK. Use clamps or a vise to hold work
RECOMMENDED ACCESSORIES. Consult the
STAND ON TOOL. Serious injury could occur if
DAMAGED PARTS. Before further use of the
THE RIGHT DIRECTION OF FEED. Feed work into
LEAVE TOOL RUNNING UNATTENDED. TURN
YOUR LUNGS. Wear a face or dust mask if
YOUR HEARING. Wear hearing protection
NOT ABUSE CORD. Never carry tool by the cord or
.
3
Page 4

GENERAL SAFETY RULES
NEVER USE IN AN EXPLOSIVE ATMOSPHERE.
Normal sparking of the motor could ignite fumes.
INSPEC T T OOL CORD S P ERIODICALLY. If
damaged, have repaired by a qualified service technician at
an authorized service facility. The conductor with insulation
having an outer surface that is green with or without yellow
stripes is the equipment-grounding conductor. If repair
or replacement of the electric cord or plug is necessary,
do not connect the equipment-grounding conductor to a
live terminal. Repair or replace a damaged or worn cord
immediately. Stay constantly aware of cord location and
keep it well away from the rotating blade.
INSPECT EXTENSION CORDS PERIODICALLY and
replace if damaged.
GROUND ALL TOOLS. If tool is equipped with three-
prong plug, it should be plugged into a three-hole electrical receptacle.
CHECK WITH A QUALIFIED ELECTRICIAN or service
personnel if the grounding instructions are not completely
understood or if in doubt as to whether the tool is properly
grounded.
USE ONLY CORRECT ELECTRICAL DEVICES: 3-wire
extension cords that have 3-prong grounding plugs and
3-pole receptacles that accept the tool's plug.
DO NOT MODIFY the plug provided. If it will not fit the
outlet, have the proper outlet installed by a qualified
electrician.
KEEP TOOL DRY, CLEAN, AND FREE FROM OIL AND
GREASE. Always use a clean cloth when cleaning. Never
use brake fluids, gasoline, petroleum-based products, or
any solvents to clean tool.
STAY ALERT AND EXERCISE CONTROL. Watch what
you are doing and use common sense. Do not operate
tool when you are tired. Do not rush.
DO
USE
BEFORE
BE
NEVER
N
D
WHEN
U
DOUBLE
NOT USE TOOL IF SWITCH DOES NOT TURN IT
ON AND OFF. Have defective switches replaced by an
authorized service center.
ONLY CORRECT BLADES. Do not use blades with
incorrect size holes. Never use blade washers or blade
bolts that are defective or incorrect. The maximum blade
capacity of your saw is 10 in.
MAKING A CUT, BE SURE ALL ADJUST-
MENTS ARE SECURE.
SURE BLADE PATH IS FREE OF NAILS. Inspect for
and remove all nails from lumber before cutting.
TOUCH BLADE or other moving parts during
use.
EVER START A TOOL WHEN ANY ROTATING
COM P O N E N T IS I N CON TA C T W I T H THE
WORKPIECE.
O NOT OPERATE A TOOL WHILE UNDER THE
IN FLU ENC E O F D RUG S, ALCOHOL, OR ANY
MEDICATION.
SERVICING use only identical replacement parts.
Use of any other parts may create a hazard or cause
product damage.
SE ONLY RECOMMENDED ACCESSORIES listed
in this manual or addendums. Use of accessories that
are not listed may cause the risk of personal injury.
Instructions for safe use of accessories are included
with the accessory.
CHECK ALL SETUPS. Make sure blade is tight
and not making contact with saw or workpiece before
connecting to power supply.
SPECIFIC SAFETY RULES
FIRMLY CLAMP OR BOLT the tool to a workbench or
table at approximately hip height.
KEEP
reach underneath work or in blade cutting path with hands
and fingers for any reason. Always turn the power off.
AL
to minimize risk of blade pinching and kickback. Saw may
slip, walk or slide while cutting long or heavy boards.
AL
possible.
BE
Never start the saw with the blade touching the
workpiece. Allow motor to come up to full speed
before starting cut.
M
FUNCTION) ARE LOCKED IN POSITION BEFORE
OPERATING YOUR SAW. Lock the miter table by securely
HANDS AWAY FROM CUTTING AREA. Do not
WAYS SUPPORT LONG WORKPIECES while cutting
WAYS USE A CLAMP to secure the workpiece when
SURE THE BLADE CLEARS THE WORKPIECE.
AKE SURE THE MITER TABLE AND SAW ARM (BEVEL
tightening the miter lock levers. Lock the saw arm (bevel
function) by securely tightening the bevel lock knob.
NEVER
END OF A CLAMPED WORKPIECE. NEVER hold onto or
bind the free scrap end of the workpiece in any operation.
If a work clamp and length stop are used together, they
must both be installed on the same side of the saw table to
prevent the saw from catching the loose end and kicking
up.
NEVER cut
STACK more than one workpiece on the saw table at a
time.
N
Always place the workpiece to be cut on the miter table
and position it firmly against the fence as a backstop.
Always use the fence.
4
USE A LENGTH STOP ON THE FREE SCRAP
more than one piece at a time. DO NOT
EVER PERFORM ANY OPERATION FREEHAND.
Page 5
SPECIFIC SAFETY RULES
NEVER hand hold a workpiece that is too small to be
clamped. Keep hands clear of the cutting area.
NEVER reach behind, under, or within three inches of the
blade
and its cutting path with hands and fingers for any
reason.
NEVER reach to pick up a workpiece, a piece of scrap,
or
anything else that is in or near the cutting path of the
blade.
A
VOI D AW KWA RD OPE RATI ONS AND H AND
POSITIONS where a sudden slip could cause your
hand to move into the blade. ALWAYS make sure you
have good balance. NEVER operate the miter saw
on the floor or in a crouched position.
NEVER stand or have any part of the body in line with
the path of the saw blade.
A
LWAYS release the power switch and allow the saw blade
to stop rotating before raising it out of the workpiece.
DO
IF
AL
NOT TURN THE MOTOR SWITCH ON AND OFF
RAPIDLY. This could cause the saw blade to loosen
and could create a hazard. Should this ever occur,
stand clear and allow the saw blade to come to a
complete stop. Disconnect your saw from the power
supply and securely retighten the blade bolt.
ANY PART OF THIS MITER SAW IS MISSING or
should break, bend, or fail in any way, or should any
electrical component fail to perform properly, shut off
the power switch, remove the miter saw plug from the
power source and have damaged, missing, or failed parts
replaced before resuming operation.
WAYS STAY ALERT! Do not allow familiarity (gained
from frequent use of the saw) to cause a careless mistake.
ALWAYS REMEMBER that a careless fraction of a second
is sufficient to inflict severe injury.
THE POWER SUPPLY CORD IS DAMAGED, it must
IF
be replaced only by the manufacturer or by an authorized
service center to avoid risk.
M
AKE SURE THE WORK AREA HAS AMPLE LIGHTING
to see the work and that no obstructions will interfere with
safe operation BEFORE performing any work using the
saw.
AL
WAYS TURN OFF THE SAW before disconnecting it
to avoid accidental starting when reconnecting to power
supply. NEVER leave the saw unattended while connected
to a power source.
TURN
a complete stop before moving workpiece or changing
settings.
THIS TOOL should have the following markings:
a) Wear eye protection.
b) Keep hands out of path of saw blade
c) Do not operate saw without guards in place.
d) Do not perform any operation freehand.
e) Never reach around saw blade.
f) Turn off tool and wait for saw blade to stop before
g) Disconnect power (or unplug tool as applicable)
h) No load speed.
AL
A
S
frequently and use to instruct other users. If you loan
someone this tool, loan them these instructions also.
OFF TOOL and wait for saw blade to come to
moving workpiece or changing settings.
before changing blade or servicing.
WAYS carry the tool only by the carrying handle.
VOID direct eye exposure when using the laser guide.
AVE T HESE INSTRU CTI ONS. Refer t o th em
WARNING:
Some dust created by power sanding, sawing, grinding, drilling, and other construction activities contains chemicals
known to cause cancer, birth defects or other reproductive harm. Some examples of these chemicals are:
• lead from lead-based paints,
• crystalline silica from bricks and cement and other masonry products, and
• arsenic and chromium from chemically-treated lumber.
Your risk from these exposures varies, depending on how often you do this type of work. To reduce your exposure to
these chemicals: work in a well ventilated area, and work with approved safety equipment, such as those dust masks
that are specially designed to filter out microscopic particles.
5
Page 6
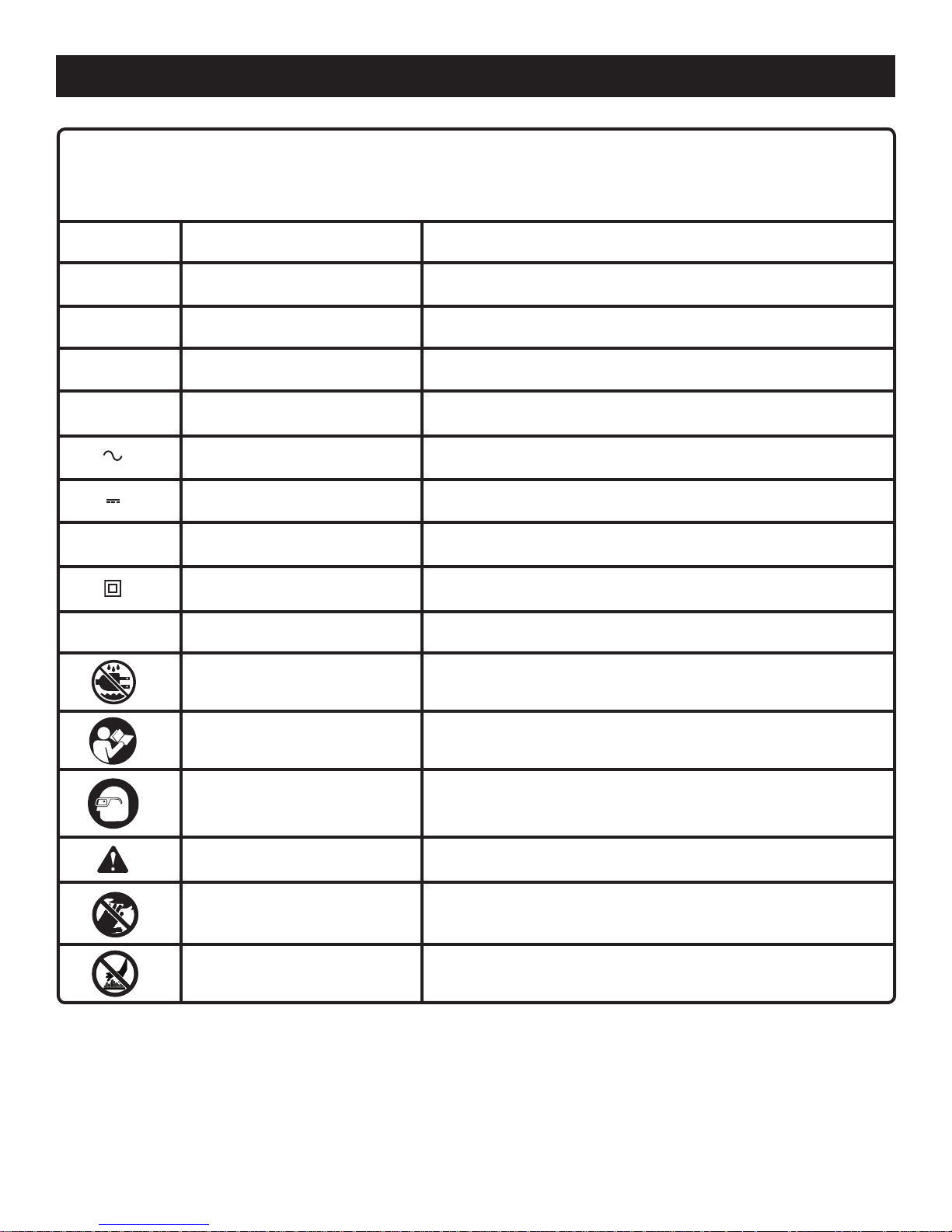
SYMBOLS
Some of the following symbols may be used on this tool. Please study them and learn their meaning. Proper
interpretation of these symbols will allow you to operate the tool better and safer.
SYMBOL NAME DESIGNATION/EXPLANATION
V V
A Amperes
Hz
W W
min Minutes
n
o
.../min
olts
Hertz
att
Alternating Current
Direct Current
No Load Speed
Class II Construction
Per Minute
Wet Conditions Alert
Voltage
Current
Frequency (cycles per second)
Power
Time
ype of current
T
Type or a characteristic of current
Rotational speed, at no load
Double-insulated construction
Revolutions, strokes, surface speed, orbits, etc., per minute
Do not expose to rain or use in damp locations.
Read The Operator’s Manual
Eye Protection
Safety Alert
No Hands Symbol
Hot Surface
To reduce the risk of injury, user must read and understand
operator’s manual before using this product.
Always wear safety goggles or safety glasses with side shields and,
as necessary, a full face shield when operating this product.
Precautions that involve your safety.
Failure to keep your hands away from the blade will result in
serious personal injury.
To reduce the risk of injury or damage, avoid contact with any
hot surface.
6
Page 7
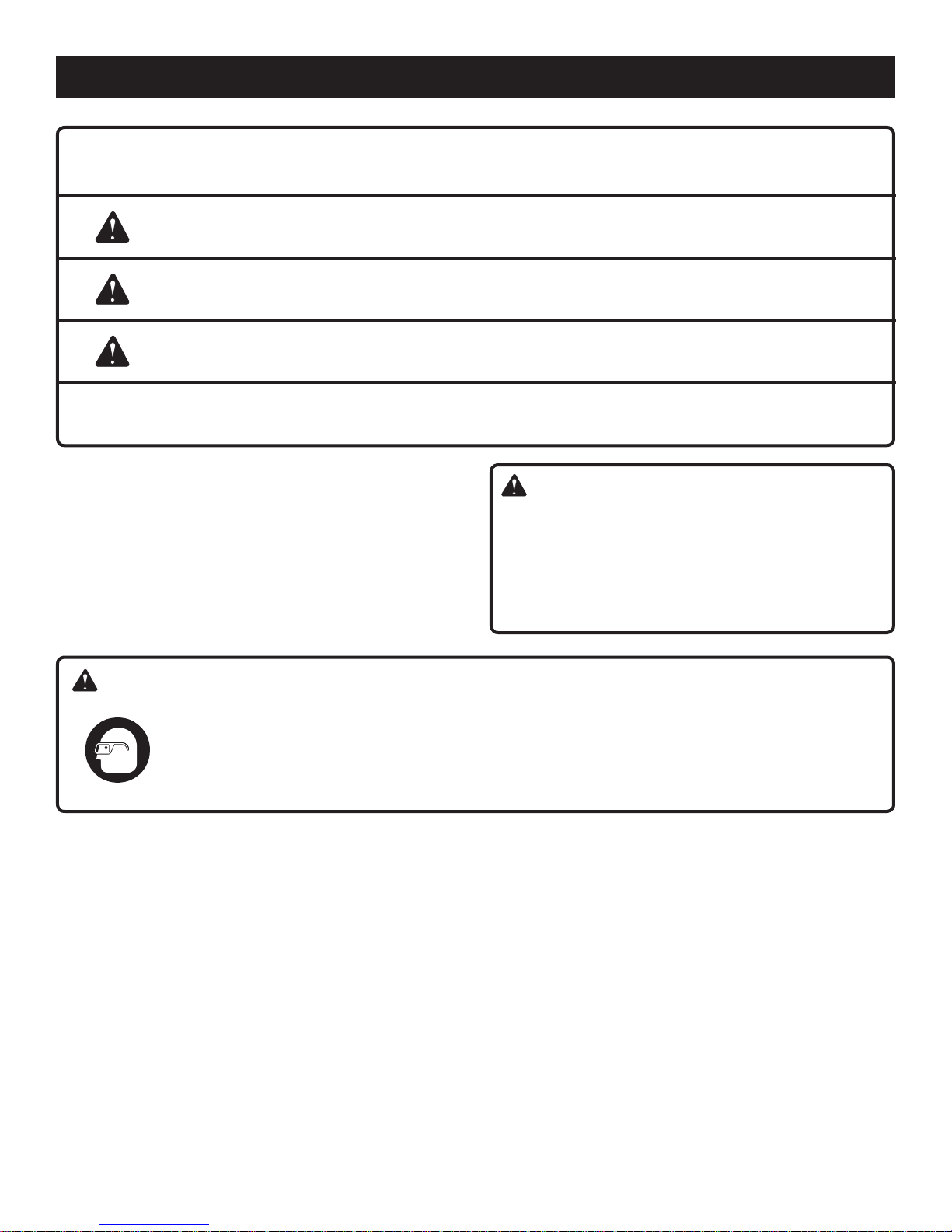
SYMBOLS
The following signal words and meanings are intended to explain the levels of risk associated with this product.
SYMBOL SIGNAL MEANING
DANGER:
WARNING:
CAUTION
CAUTION
Indicates an imminently hazardous situation, which, if not avoided, will result
in death or serious injury.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation, which, if not avoided, could result
in death or serious injury.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation, which, if not avoided, may result in
minor or moderate injury.
(Without Safety Alert Symbol) Indicates a situation that may result in property
damage.
SERVICE
Servicing requires extreme care and knowledge and should
be performed only by a qualified service technician. For
service we suggest you return the product to the nearest
AUTHORIZED SERVICE CENTER for repair. When servicing, use only identical replacement parts.
WARNING:
To avoid serious personal injury, do not attempt to use
this product until you read thoroughly and understand
completely the operator’s manual. If you do not understand the warnings and instructions in the operator’s
manual, do not use this product. Call customer service
for assistance.
WARNING:
The operation of any power tool can result in foreign objects being thrown into your eyes, which can
result in severe eye damage. Before beginning power tool operation, always wear safety goggles or
safety glasses with side shields and, when needed, a full face shield. We recommend Wide Vision
Safety Mask for use over eyeglasses or standard safety glasses with side shields. Always use eye
protection which is marked to comply with ANSI Z87.1.
SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS
7
Page 8
ELECTRICAL
EXTENSION CORDS
Use only 3-wire extension cords that have 3-prong grounding plugs and 3-pole receptacles that accept the tool’s plug.
When using a power tool at a considerable distance from the
power source, use an extension cord heavy enough to carry
the current that the tool will draw. An undersized extension
cord will cause a drop in line voltage, resulting in a loss of
power and causing the motor to overheat. Use the chart
provided below to determine the minimum wire size required
in an extension cord. Only round jacketed cords listed by
Underwriter’s Laboratories (UL) should be used.
**Ampere rating (on tool data plate)
0-2.0 2.1-3.4 3.5-5.0 5.1-7.0 7.1-12.0 12.1-16.0
Cord Length Wire Size (A.W.G.)
25' 16 16 16 16 14 14
50' 16 16 16 14 14 12
100' 16 16 14 12 10 —
**Used on 12 gauge - 20 amp circuit.
NOTE: A
When working with the tool outdoors, use an extension cord
that is designed for outside use. This is indicated by the
letters “WA” on the cord’s jacket.
Before using an extension cord, inspect it for loose or
exposed wires and cut or worn insulation.
WG = American Wire Gauge
WARNING:
Keep the extension cord clear of the working area.
Position the cord so that it will not get caught on lumber,
tools or other obstructions while you are working with a
power tool. Failure to do so can result in serious personal
injury.
SPEED AND WIRING
The no-load speed of this tool is approximately 4,500
rpm. This speed is not constant and decreases under a
load or with lower voltage. For voltage, the wiring in a
shop is as important as the motor’s horsepower rating. A
line intended only for lights cannot properly carry a power
tool motor. Wire that is heavy enough for a short distance
will be too light for a greater distance. A line that can
support one power tool may not be able to support two
or three tools.
GROUNDING INSTRUCTIONS
In the event of a malfunction or breakdown, grounding provides a path of least resistance for electric current to reduce
the risk of electric shock. This tool is equipped with an electric cord having an equipment-grounding conductor and a
grounding plug. The plug must be plugged into a matching
outlet that is properly installed and grounded in accordance
with all local codes and ordinances.
Do not modify the plug provided. If it will not fit the outlet,
have the proper outlet installed by a qualified electrician.
Improper connection of the equipment-grounding conductor
can result in a risk of electric shock. The conductor with
insulation having an outer surface that is green with or without yellow stripes is the equipment-grounding conductor. If
repair or replacement of the electric cord or plug is necessary, do not connect the equipment-grounding conductor
to a live terminal.
Check with a qualified electrician or service personnel if the
grounding instructions are not completely understood, or if
in doubt as to whether the tool is properly grounded.
Repair or replace a damaged or worn cord immediately.
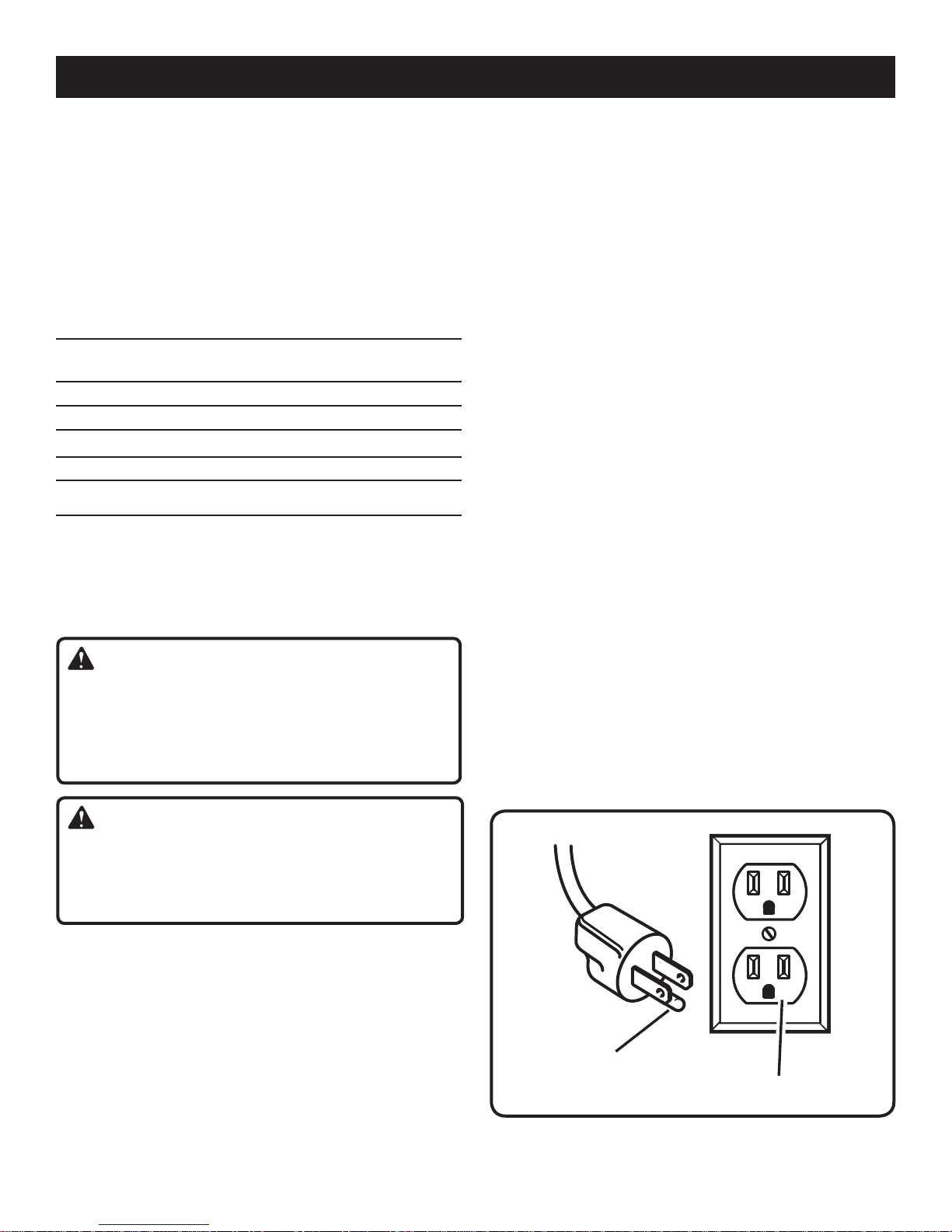
This tool is intended for use on a circuit that has an outlet
like the one shown in figure 1. It also has a grounding pin
like the one shown.
WARNING:
Check extension cords before each use. If damaged
replace immediately. Never use tool with a damaged cord
since touching the damaged area could cause electrical
shock resulting in serious injury.
ELECTRICAL CONNECTION
This tool is powered by a precision built electric motor. It
should be connected to a power supply that is 120 volts,
60 Hz, AC only (normal household current). Do not operate
this tool on direct current (DC). A substantial voltage drop
will cause a loss of power and the motor will overheat. If the
saw does not operate when plugged into an outlet, double
check the power supply.
GROUNDING
PIN
8
120V GROUNDED OUTLET
Page 9

GLOSSARY OF TERMS
Anti-Kickback Pawls (radial arm and table saws)
A
device which, when properly installed and maintained,
is designed to stop the workpiece from being kicked back
toward the front of the saw during a ripping operation.
Arbor
The shaft on which a blade or cutting tool is mounted.
Bevel Cut
A cutting operation made with the blade at any angle other
than 90° to the table surface.
Chamfer
cut removing a wedge from a block so the end (or part of
A
the end) is angled rather than at 90°.
Compound Cut
A cross cut made with both a miter and a bevel angle.
Cross Cut
A cutting or shaping operation made across the grain or the
width of the workpiece.
Cutterhead (planers and jointer planers)
rotating cutterhead with adjustable blades or knives. The
A
blades or knives remove material from the workpiece.
Dado Cut
A non-through cut which produces a square-sided notch or
trough in the workpiece (requires a special blade).
Featherboard
A device used to help control the workpiece by guiding
it securely against the table or fence during any ripping
operation.
FPM or SPM
per minute (or strokes per minute), used in reference
Feet
to blade movement.
Freehand
Performing a cut without the workpiece being guided by a
fence, miter gauge, or other aids.
Gum
A sticky
Heel
Alignment of the blade to the fence.
Kerf
The material removed by the blade in a through cut or the
slot produced by the blade in a non-through or partial cut.
Kickback
A hazard that can occur when the blade binds or stalls,
throwing the workpiece back toward operator.
Leading End
The end of the workpiece pushed into the tool first.
Miter Cut
A
to the blade other than 90°.
, sap-based residue from wood products.
cutting operation made with the workpiece at any angle
Non-Through Cuts
Any cutting operation where the blade does not extend
completely through the thickness of the workpiece.
Push Blocks (for jointer planers)
Device used to feed the workpiece over the jointer planer
cutterhead during any operation. This aid helps keep the
operator's hands well away from the cutterhead.
Push Blocks and Push Sticks (for table saws)
Devices
during cutting operations. A push stick (not a push block)
should be used for narrow ripping operations. These aids
help keep the operator's hands well away from the blade.
Pilot Hole (drill presses)
A small hole drilled in a workpiece that serves as a guide for
drilling large holes accurately.
Resaw
cutting operation to reduce the thickness of the workpiece
A
to make thinner pieces.
Resin
A sticky, sap-based substance that has hardened.
Revolutions Per Minute (RPM)
The number of turns completed by a spinning object in one
minute.
Ripping or Rip Cut
A cutting operation along the length of the workpiece.
Riving Knife/Spr
A metal piece, slightly thinner than the blade, which helps
keep the kerf open and also helps to prevent kickback.
Saw Blade Path
The area over, under, behind, or in front of the blade. As it
applies to the workpiece, that area which will be or has been
cut by the blade.
Set
The
set) outward from the face of the blade.
Snipe (planers)
Depression made at either end of a workpiece by cutter
blades when the workpiece is not properly supported.
Through Sawing
Any cutting operation where the blade extends completely
through the thickness of the workpiece.
Throw-Back
The throwing back of a workpiece usually caused by the
workpiece being dropped into the blade or being placed
inadvertently in contact with the blade.
W
The item on which the operation is being done.
Worktable
Surface where the workpiece rests while performing a
cutting, drilling, planing, or sanding operation.
used to feed the workpiece through the saw blade
eader/Splitter (table saws)
distance that the tip of the saw blade tooth is bent (or
orkpiece or Material
9
Page 10
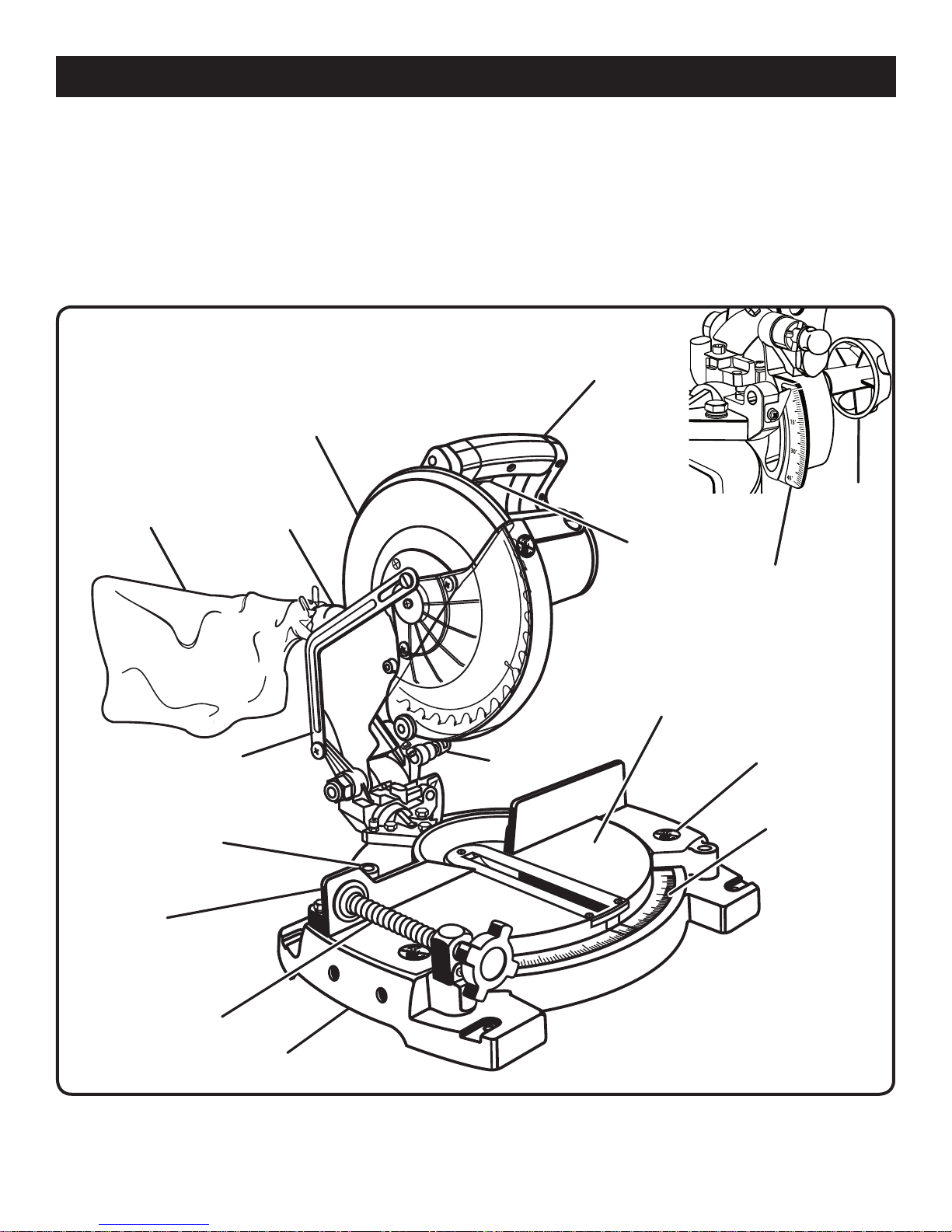
FEATURES
1
5
3
0
4
5
PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS
Blade Diameter. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 in.
Blade Arbor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5/8 in.
No Load Speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4,500 r/min. (RPM)
Input . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120 Volts, 60 Hz, AC Only, 12 Amps
Net Weight . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28 lbs.
UPPER BLADE
GUARD
DUST
BAG
DUST
GUIDE
Cutting Capacity with Miter at 0°/Bevel 0°:
Maximum nominal lumber sizes: ........................... 2 x 6
Cutting Capacity with Miter at 45°/Bevel 0°:
Maximum nominal lumber sizes: ...........................2 x 4
Cutting Capacity with Miter at 0°/Bevel 45°:
Maximum nominal lumber sizes: ...........................2 x 6
Cutting Capacity with Miter at 45°/Bevel 45°:
Maximum nominal lumber sizes: ...........................2 x 4
“D” HANDLE
BEVEL
LOCK
SWITCH
GER
TRIG
KNOB
BEVEL
SCALE
BLADE GUARD
LINKAGE
MITER
LOCK
LEVER
FENCE
WORK
CLAMP
BASE
LOCK PIN
MITER
ABLE
T
“NO HANDS”
LABEL
MITER
SCALE
Fig. 1
10
Page 11

FEATURES
KNOW YOUR COMPOUND MITER SAW
See Figure 1.
The safe use of this product requires an understanding of
the information on the tool and in this operator’s manual as
well as a knowledge of the project you are attempting. Before
use of this product, familiarize yourself with all operating
features and safety rules.
12 AMP MOTOR
Your saw has a powerful 12 amp motor with sufficient
power to handle tough cutting jobs. It is made with all ball
bearings, and has externally accessible brushes for ease
of servicing.
10 in. BLADE
A 10 in. saw blade is included with your compound miter saw.
It will cut materials up to 2 in. thick or 6 in. wide, depending
upon the angle at which the cut is being made.
MITER LOCK LEVERS
See Figure 2.
The miter lock levers securely lock the saw table at the
desired miter angles.
LOCK
UNLOCK
MITER LOCK
LEVERS
Fig. 2
SPINDLE LOCK BUTTON
See Figure 3.
A spindle lock button has been provided for locking the
spindle which keeps the blade in your saw from rotating.
Depress and hold the lock button while installing, changing,
or removing blade.
SWITCH TRIGGER
See Figure 4.
To prevent unauthorized use of your compound miter saw,
we suggest that you disconnect it from the power supply and
lock the switch in the off position. To lock the switch, install a
padlock (not included) through the hole in the switch trigger.
A lock with a long shackle up to 9/32 in. diameter may be
used. When the lock is installed and locked, the switch is
inoperable. Store the padlock key in another location.
SWITCH
GER
TRIG
SWITCH
TRIG
PADLOCK
GER
SPINDLE
LOCK BUTTON
Fig. 3
Fig. 4
11
Page 12

FEATURES
WARNING:
The operation of any saw can result in foreign objects
being thrown into your eyes, which can result in severe
eye damage. Before starting power tool operation, always
wear safety goggles or safety glasses with side shields
and a full face shield when needed. We recommend wide
vision safety mask for use over eyeglasses or standard
safety glasses with side shields.
BEVEL LOCK KNOB
The bevel lock knob securely locks your compound miter
saw at desired bevel angles. A positive stop adjustment
screw has been provided on each side of the saw arm.
These adjustment screws are for making fine adjustments
at 0° and 45°.
TOOLS NEEDED
ELECTRIC BRAKE
An electric brake has been provided to quickly stop blade
rotation after the switch is released.
FENCE
The fence on your compound miter saw has been provided
as a support to hold your workpiece securely against when
making all cuts.
SELF-RETRACTING LOWER BLADE GUARD
The lower blade guard is made of shock-resistant, seethrough plastic that provides protection from each side of
the blade. It retracts over the upper blade guard as the saw
is lowered into the workpiece.
The following tools (not included) are needed for making adjustments or installing the blade:
COMBINA
COMBINATION SQUARE
TION WRENCH (2)
10 mm, 14 mm
HEX KEY
5 mm
FRAMING SQUARE
PHILLIPS SCREWDRIVER
12
Fig. 5
Page 13

LOOSE PARTS LIST
The following items ar
Dust Bag
Work Clamp
DUST BAG
e included with your Compound Miter Saw:
Hex Key (6 mm)
Operator's Manual
HEX KEY
WORK CLAMP
Fig. 6
WARNING:
The use of attachments or accessories not listed might be hazardous and could cause serious personal injury.
ASSEMBLY
UNPACKING
This product has been shipped completely assembled.
Carefully lift saw from the carton and place it on a level
work surface.
Your saw has been shipped with the saw arm secured in
the
down position. To release the saw arm, push down
on the top of the saw arm, cut the tie-wrap, and pull out
on the lock pin. See Figure 10.
Lift the saw arm by the handle. Hand pressure should
r
emain on the saw arm to prevent sudden rise upon
release of the tie wrap.
Inspect the tool carefully to make sure no breakage or
damage occurr
ed during shipping.
Do not discard the packing material until you have carefully
inspected and satisfactorily operated the tool.
The saw is factory set for accurate cutting. After
a
ssembling it, check for accuracy. If shipping has
influenced the settings, refer to specific procedures
explained in this manual.
If any parts are damaged or missing, please call
1-800-525-2579 for assistance.
WARNING:
If any parts are damaged or missing do not operate this
tool until the parts are replaced. Failure to heed this warning could result in serious personal injury.
13
Page 14

WARNING:
ASSEMBLY
MOUNTING HOLES
See Figure 8.
Do not attempt to modify this tool or create accessories not recommended for use with this tool. Any such
alteration or modification is misuse and could result in a
hazardous condition leading to possible serious personal
injury.
WARNING:
Do not connect to power supply until assembly is
complete. Failure to comply could result in accidental
starting and possible serious personal injury.
WARNING:
Do not start the compound miter saw without checking
for interference between the blade and the miter fence.
Damage could result to the blade if it strikes the miter
fence during operation of the saw.
WARNING:
A rear bracket is included with this miter saw to prevent
tipping if the saw arm is released suddenly. Do not use
this saw before pulling the rear bracket out and securely
mounting the saw to a work surface.
WARNING:
Always make sure your compound miter saw is securely
mounted to a workbench or an approved workstand.
Failure to do so could result in an accident resulting in
possible serious personal injury.
Your compound miter saw should be permanently mounted
to a firm supporting surface such as a workbench. Four bolt
holes have been provided in the saw base for this purpose.
Each of the four mounting holes should be bolted securely
using 3/8 in. machine bolts, lock washers, and hex nuts (not
included). Bolts should be of sufficient length to accommodate
the saw base, lock washers, hex nuts, and the thickness of
the workbench.Tighten all four bolts securely.
The hole pattern for mounting to a workbench is shown in
figure 8. Carefully check the workbench after mounting to
make sure that no movement can occur during use. If any
tipping, sliding, or walking is noted, secure the workbench
to the floor before operating.
REAR BRACKET
See Figure 7.
The rear bracket is pushed into the base for shipping purposes.
to prevent tipping. Grasp the rear bracket with one hand and
pull on the bracket until it is fully extended.
Before usage, the rear bracket must be fully extended
TRACE HOLES
T THESE LOCATIONS FOR
A
HOLE PATTERN
BASE
BASE
REAR BRACKET
TRACE HOLES
AT THESE LOCATIONS FOR
HOLE PATTERN
MOUNTING SURF
ACE
Fig. 7
Fig. 8
14
Page 15

ASSEMBLY
WORK CLAMP
See Figure 9.
WARNING:
In some operations, the work clamp assembly may
interfere with the operation of the blade guard assembly.
Always make sure there is no interference with the blade
guard prior to beginning any cutting operation to reduce
the risk of serious personal injury.
The work clamp provides greater control by clamping the
workpiece to the fence or the saw table. It also prevents the
workpiece from creeping toward the saw blade. This is very
helpful when cutting compound miters.
Depending
workpiece, it may be necessary to use a C-clamp instead
of the work clamp to secure the workpiece prior to making
the cut.
T
o install the work clamp:
Place
saw table base.
Rotate the knob on the work clamp to move it in or out
as needed.
When using any clamp with the stop block, install the
clamp on the same side as the stop block. This will eliminate the possibility of trapping the workpiece, resulting in
the saw blade and workpiece kicking up. Failure to heed
this warning can result in serious personal injury.
TO INSTALL / REPLACE BLADE
See Figures 10 - 11.
A 10 in. blade is the maximum blade capacity of your saw.
Never use a blade that is too thick to allow outer blade
washer to engage with the flats on the spindle. Larger
blades will come in contact with the blade guards, while
thicker blades will prevent the blade screw from securing
the blade on the spindle. Either of these situations
could result in a serious accident and can cause serious
personal injury.
on the cutting operation and the size of the
the shaft of the work clamp in either hole on the
WARNING:
WARNING:
BASE
SA
BLADE
LOOSEN
TIGHTEN
BLADE
BOLT
W
OUTER
BLADE
W
ASHER
FLAT
WASHER
BLADE
BOLT
COVER
PHILLIPS
SCREW A
PHILLIPS
SCREW B
WORK
CLAMP
Fig. 9
LOWER
BLADE GUARD
FLA
T(S)
ON SPINDLE
INNER BLADE
WASHER
LOCK PIN
Fig. 10
WARNING
Failure to unplug your saw could result in accidental starting causing possible serious personal injury.
:
Unplug the saw.
Raise saw arm.
Rotate lower blade guard up and remove screws A and
Rotate the blade bolt cover up and back to expose
B.
the blade bolt.
15
Page 16

ASSEMBLY
Depress the spindle lock button and rotate the blade until
the spindle locks.
Using the hex key provided, loosen and remove the blade
bolt.
NOTE: The blade bolt has left-hand threads. Turn blade
bolt clockwise to loosen.
Remove outer blade washer and flat washer. Do
remove inner blade washer.
Wipe a drop of oil onto inner blade washer and outer
blade washer wher
e they contact the blade.
WARNING:
If inner blade washer has been removed, replace it before
placing blade on spindle. Failure to do so could cause an
accident since blade will not tighten properly.
Fit saw blade inside blade guard and onto spindle. The
blade teeth point downward at the front of saw as shown
in figure 10.
not
SPINDLE
LOCK
BUTTON
Fig. 11
CAUTION:
Always install the blade with the blade teeth and the arrow
printed on the side of the blade pointing down at the front
of the saw. The direction of blade rotation is also stamped
with an arrow on the upper blade guard.
Replace outer blade washer and flat washer. The double
“D” flats on the blade washers align with the flats on the
spindle.
Depress spindle lock button and replace blade bolt.
NOTE: The blade bolt has left-hand threads. Turn blade
bolt counter
Tighten blade bolt securely.
Replace the blade bolt cover.
Reinstall the phillips screws A and B securing the blade
bolt cover
clockwise to tighten.
. Tighten screws securely.
CAUTION:
Make sure the spindle lock button is not engaged
before reconnecting saw into power source. Never
engage spindle lock button when blade is rotating.
Your compound miter saw has been adjusted at the factory for making very accurate cuts. However, some of the
components might have moved out of alignment during
shipping. Also, over a period of time, readjustment will
probably become necessary due to wear. After unpacking
your saw, check the following adjustments before you begin
using saw. Make any readjustments that are necessary and
periodically check the parts alignment to make sure that
your saw is cutting accurately.
16
Page 17

ASSEMBLY
NOTE: Many of the illustrations in this manual show only por-
tions of your compound miter saw. This is intentional so that
we can clearly show points being made in the illustrations.
Never operate your saw without all guards securely in place
and in good operating condition.
SQUARING THE MITER TABLE TO THE
FENCE
See Figures 12 - 15.
Unplug your saw.
Push down on the saw arm and pull out the lock pin to
r
elease the saw arm.
Raise saw arm to its full raised position.
Loosen the miter lock levers.
Rotate the miter table until the pointer is positioned
°
at 0
.
Securely tighten the miter lock levers.
Lay a framing square flat on the miter table. Place one
leg
of the square against the fence. Place the other
leg of the square beside the throat plate in the miter table.
The edge of the square and the slot in the throat plate in
the miter table should be parallel as shown in figure 12.
If the edge of the framing square and the throat plate in
the
miter table are not parallel as shown in figures 13 and
14, adjustments are needed.
Using the hex key, loosen the socket head screws securing
the
fence. Adjust the fence left or right until the framing
square and throat plate are parallel.
Retighten the screws securely and recheck the fence-to-
table alignment.
FRAMING
SQUARE
VIEW OF MITER T
FRAMING
SQUARE
FENCE
THROAT PLATE
ABLE NOT SQUARE WITH FENCE,
ADJUSTMENTS ARE REQUIRED
FENCE
THROAT PLATE
MITER TABLE
MITER TABLE
Fig. 13
FRAMING
SQUARE
VIEW OF MITER T
FENCE
ABLE SQUARE WITH FENCE
CORRECTL
THROAT PLATE
Y ADJUSTED
MITER TABLE
Fig. 12
SOCKET HEAD
17
VIEW OF MITER TABLE NOT SQUARE WITH FENCE,
ADJUSTMENTS ARE REQUIRED
SCREW(S)
FENCE
SOCKET HEAD
SCREW(S)
Fig. 14
Fig. 15
Page 18

ASSEMBLY
SQUARING THE SAW BLADE TO THE FENCE
See Figures 16 - 19.
Unplug your saw.
Pull the saw arm all the way down and engage the lock
pin to hold the saw arm in transport position.
Loosen the miter lock levers.
Rotate the miter table until the pointer is positioned
Securely tighten the miter lock levers.
Lay a framing square flat on the miter table. Place one
NOTE: Make sure that the square contacts the flat part
The edge of the square and the saw blade should be
If the front or back edge of the saw blade angles away
Using a 14 mm wrench, loosen the hex head screws that
Rotate the mounting bracket left or right until the saw
Retighten the screws securely and recheck the blade-to-
°
at 0
.
leg of the square against the fence. Slide the other leg
of the square against the flat part of saw blade.
of the saw blade, not the blade teeth.
parallel as shown in figure 16.
from the square as shown in figures 17 and 18, adjustments are needed.
secure the mounting bracket to the miter table.
blade is parallel with the square.
fence alignment.
FENCE
BASE
BLADE
FENCE
BLADE
FRAMING
SQUARE
VIEW OF BLADE NOT SQUARE WITH FENCE,
ADJUSTMENTS ARE REQUIRED
Fig. 17
FENCE
BASE
VIEW OF BLADE
SQUARE WITH FENCE
FRAMING
SQUARE
BLADE
Fig. 16
BASE
FRAMING
SQUARE
VIEW OF BLADE NOT SQUARE WITH FENCE,
ADJUSTMENTS ARE REQUIRED
HEX HEAD
SCREW(S)
Fig. 18
MOUNTING
BRACKET
18
MITER
T
ABLE
Fig. 19
Page 19

ASSEMBLY
SQUARING THE BLADE TO THE MITER
TABLE
See Figures 20 - 23.
Unplug your saw.
Pull the saw arm all the way down and engage the lock
pin to hold the saw arm in transport position.
Loosen the miter lock levers.
Rotate the miter table until the pointer is positioned
at 0˚.
Securely tighten the miter lock levers.
Loosen bevel lock knob and set saw arm at 0˚ bevel (blade
set 90˚ to miter table). Tighten bevel lock knob.
Place a combination square against the miter table and
the flat part of saw blade.
NOTE: Make sure that the square contacts the flat part
of the saw blade, not the blade teeth.
Rotate the blade by hand and check the blade-to-table
alignment at several points.
The edge of the square and the saw blade should be
parallel as shown in figur
If the top or bottom of the saw blade angles away from
the
square as shown in figures 21 and 23, adjustments
are needed.
Using a 10 mm wrench or adjustable wrench, loosen the
lock
nut securing positive stop adjustment screw. Also
loosen bevel lock knob. See Figure 35.
Adjust positive stop adjustment screw to bring
saw blade into alignment with the squar
Retighten bevel lock knob. Next, retighten lock nut
securing
blade-to-table alignment.
NOTE:
squareness of the saw blade to the miter table at both 0˚
and 45˚ angles.
the positive stop adjustment screw. Recheck
The above procedure can be used to check blade
e 20.
e.
FENCE
COMBINATION
SQUARE
CORRECT VIEW OF BLADE SQUARE WITH MITER T
FENCE
COMBINATION
SQUARE
VIEW OF BLADE NOT SQUARE WITH MITER TABLE,
ADJUSTMENTS ARE REQUIRED
POSITIVE STOP
ADJUSTMENT
SCREW FOR
45° ANGLES
MITER
T
ABLE
MITER
T
ABLE
BLADE
ABLE
Fig. 20
BLADE
Fig. 21
LOCK
NUT(S)
Fig. 22
19
Page 20

ASSEMBLY
Your saw has two scale indicators, one on the bevel scale
and one on the miter scale. After squaring adjustments have
been made, it may be necessary to loosen the indicators
screws and reset them to zero.
FENCE
OPERATION
WARNING:
Do not allow familiarity with tools to make you careless. Remember that a careless fraction of a second is
sufficient to inflict serious injury.
WARNING:
Always wear safety goggles or safety glasses with side
shields when operating power tools. Failure to do so
could result in objects being thrown into your eyes
resulting in possible serious injury.
WARNING:
Do not use any attachments or accessories not
recommended by the manufacturer of this tool. The use
of attachments or accessories not recommended can
result in serious personal injury.
APPLICATIONS
You may use this tool for the purposes listed below:
Crosscutting wood and plastic
Crosscutting miters, joints, etc. for picture frames,
moldings, door casings, and fine joinery
Bevel cutting and compound cutting
NOTE:
operations, but for fine joinery cuts or cutting plastic, use
one of the accessory blades available from the dealer.
The blade provided is fine for most wood cutting
COMBINATION
SQUARE
VIEW OF BLADE NOT SQUARE WITH MITER T
ADJUSTMENTS ARE REQUIRED
MITER
ABLE
T
BLADE
ABLE,
Fig. 23
WARNING:
Before starting any cutting operation, clamp or bolt the
compound miter saw to a workbench. Never operate the
miter saw on the floor or in a crouched position. Failure to
heed this warning can result in serious personal injury.
WARNING:
To avoid serious personal injury, keep hands outside
the no hands zone, at least 3 in. from the blade. Never
perform any cutting operation freehand (without holding
workpiece against the fence). The blade could grab the
workpiece if it slips or twists.
WARNING:
To avoid serious personal injury, always tighten the miter
lock levers securely before making a cut. Failure to do
so could result in movement of the control arm or miter
table while making a cut.
20
Page 21

OPERATION
CUTTI N G W ITH YOUR COMP O U ND
MITER SAW
WARNING:
When using a work clamp or C-clamp to secure your
workpiece, clamp the workpiece on one side of the blade
only. The workpiece must remain free on one side of the
blade to prevent the blade from binding in workpiece. The
workpiece binding the blade will cause motor stalling and
kickback. This situation could cause an accident resulting
in possible serious personal injury.
WARNING:
NEVER move the workpiece or make adjustment to any
cutting angle while the saw is running and the blade is
rotating. Any slip can result in contact with the blade
causing serious personal injury.
TO CROSS CUT
See Figure 24.
A cross cut is made by cutting across the grain of the
workpiece. A straight cross cut is made with the miter table
set at the 0° position. Miter cross cuts are made with the
miter table set at some angle other than zero.
TO MITER CUT
Pull out and rotate the lock pin and lift saw arm to its full
height.
Loosen the miter lock levers.
Rotate the saw table until the pointer aligns with the
desired angle on the miter scale.
Tighten the miter lock levers securely.
Place the workpiece flat on the miter table with one edge
securely against the fence. If the board is warped, place
the convex side against the fence. If the concave edge
of a board is placed against the fence, the board could
collapse on the blade at the end of the cut, jamming the
blade.
STRAIGHT
CROSSCUT
Fig. 24
When cutting long pieces of lumber or molding, support
the
opposite end of the stock with a roller stand or with
a work surface level with the saw table.
Align cutting line on the workpiece with the edge of saw
blade.
Grasp the stock firmly with one hand and secure
it
against the fence or use the work clamp, or a C-clamp,
to secure the workpiece.
Before turning on the saw, perform a dry run of the cutting
operation
when the cut is made.
Grasp the saw handle firmly then squeeze the switch
trigger
maximum speed.
Slowly lower the blade into and through the workpiece.
Release the switch trigger and allow the saw blade to stop
otating before raising the blade out of workpiece. Wait
r
until the electric brake stops blade from turning before
removing the workpiece from the miter table.
just to make sure that no problems will occur
. Allow several seconds for the blade to reach
21
Page 22

1
5
3
0
4
5
OPERATION
TO BEVEL CUT
See Figures 25 - 26.
A bevel cut is made by cutting across the grain of the workpiece
with the blade angled to the workpiece. A straight bevel cut
is made with the miter table set at the zero degree position
and the blade set at an angle between 0° and 45°.
Pull out and rotate the lock pin and lift saw arm to its full
height.
Loosen the miter lock levers.
Rotate the saw table until the pointer aligns with zero on
the miter scale.
Tighten the miter lock levers securely.
Loosen the bevel lock knob and move the saw arm to the
left to the desired bevel angle.
Bevel angles can be set from 0° to 45°.
Align the indicator point for the desired angle.
Once the saw arm has been set at the desired angle,
securely tighten the bevel lock knob.
Place the workpiece flat on the miter table with one edge
securely against the fence. If the board is warped, place
the convex side against the fence. If the concave edge
of a board is placed against the fence, the board could
collapse on the blade at the end of the cut, jamming the
blade.
When cutting long pieces of lumber or molding, support
the opposite end of the stock with a roller stand or with
a work surface level with the saw table.
Align the cutting line on the workpiece with the edge of
saw blade.
Grasp the stock firmly with one hand and secure
it against the fence or use the work clamp, or a C-clamp,
to secure the workpiece.
Before turning on the saw, perform a dry run of the cutting
operation just to make sure that no problems will occur
when the cut is made.
Grasp the saw handle firmly then squeeze the switch
trigger. Allow several seconds for the blade to reach
maximum speed.
Slowly lower the blade into and through the workpiece.
Release the switch trigger and allow the saw blade to stop
rotating before raising the blade out of workpiece. Wait
until the electric brake stops blade from turning before
removing the workpiece from miter table.
MOUNTING
BRACKET
BEVEL CUT
INDICA
POINT
SCALE
Fig. 25
Fig. 26
TOR
22
Page 23

OPERATION
TO COMPOUND MITER CUT
A compound miter cut is a cut made using a miter angle and
a bevel angle at the same time. This type of cut is used to
make picture frames, cut molding, make boxes with sloping
sides, and for certain roof framing cuts.
To make this type of cut the control arm on the miter table
must be rotated to the correct angle and the saw arm must
be tilted to the correct bevel angle. Care should always be
taken when making compound miter setups due to the interaction of the two angle settings.
Adjustments of miter and bevel settings are interdependent
with one another. Each time you adjust the miter setting you
change the effect of the bevel setting. Also, each time you
adjust the bevel setting you change the effect of the miter
setting.
It may take several settings to obtain the desired cut. The
first angle setting should be checked after setting the second
angle, since adjusting the second angle affects the first.
Once the two correct settings for a particular cut have been
obtained, always make a test cut in scrap material before
making a finish cut in good material.
COMPOUND
MITER CUT
Fig. 27
TO MAKE A COMPOUND CUT
See Figures 27 - 28.
Pull out and rotate the lock pin and lift saw arm to its full
height.
Loosen the miter lock levers.
Rotate the saw table until the pointer aligns with the
desir
ed angle on the miter scale.
Tighten the miter lock levers secur
Loosen the bevel lock knob and move the saw arm to the
left to the desir
Bevel angles can be set from 0˚ to 45˚.
Once the saw arm has been set at the desired angle,
secur
ely tighten the bevel lock knob.
Recheck miter angle setting. Make a test cut in scrap
material.
Place the workpiece flat on the miter table with one edge
secur
ely against the fence. If the board is warped, place
the convex side against the fence. If the concave edge
of a board could collapse on the blade at the end of the
cut, jamming the blade.
When cutting long pieces of lumber or molding, support
the
opposite end of the stock with a roller stand or with
a work surface level with the saw table.
Align the cutting line on the workpiece with the edge of
saw blade.
G
rasp the stock firmly with one hand and secure
it against the fence or use the work clamp, or a C-clamp,
to secure the workpiece.
ed bevel angle.
ely.
°
X 45° COMPOUND MITER CUT
45
NOTE: When making a 45˚ left miter and a bevel angle
greater than 30˚, you must use a C-clamp to secure the
workpiece or move clamp to the right side of the base.
Before turning on the saw, perform a dry run of the cutting
operation
when the cut is made.
just to make sure that no problems will occur
Fig. 28
23
Page 24

0
OPERATION
Grasp the saw handle firmly then squeeze the switch
. Allow several seconds for the blade to reach
trigger
maximum speed.
Slowly lower the blade into and through the workpiece.
Release the switch trigger and allow the saw blade to stop
r
otating before raising the blade out of workpiece. Wait
until the electric brake stops blade from turning before
removing the workpiece from miter table.
LONG WORKPIECE
SUPPORT LONG WORKPIECES
See Figure 29.
Long workpieces need extra supports. Supports should be
placed along the workpiece so it does not sag. The support
should let the workpiece lay flat on the base of the saw and
work table during the cutting operation. Use the optional
work clamp or a C-clamp to secure the workpiece.
WORKPIECE
SUPPOR
TS
Fig. 29
24
Page 25

OPERATION
CUTTING COMPOUND MITERS
To aid in making the correct settings, the compound angle setting chart below has been provided. Since compound cuts
are the most difficult to accurately obtain, trial cuts should be made in scrap material, and much thought and planning
made, prior to making the required cut.
PITCH
OF SIDE
0°
5°
10°
15°
20°
25°
30°
35°
40°
45°
50°
55°
60°
65°
70°
75°
80°
85°
90°
4
M- 45.00°
B- 0.00°
M- 44.89°
B- 3.53°
M- 44.56°
B- 7.05°
M- 44.01°
B- 10.55°
M- 43.22°
B- 14.00°
M- 42.19°
B- 17.39°
M- 40.89°
B- 20.70°
M- 39.32°
B- 23.93°
M- 37.45°
B- 27.03°
M- 35.26°
B- 30.00°
M- 32.73°
B- 32.80°
M- 29.84°
B- 35.40°
M- 26.57°
B- 37.76°
M- 22.91°
B- 39.86°
M- 18.88°
B- 41.64°
M- 14.51°
B- 43.08°
M- 9.85°
B- 44.14°
M- 4.98°
B- 44.78°
M- 0.00°
B- 45.00°
5
M- 36.00°
B- 0.00°
M- 35.90°
B- 2.94°
M- 35.58°
B- 5.86°
M- 35.06°
B- 8.75°
M- 34.32°
B- 11.60°
M- 33.36°
B- 14.38°
M- 32.18°
B- 17.09°
M- 30.76°
B- 19.70°
M- 29.10°
B- 22.20°
M- 27.19°
B- 24.56°
M- 25.03°
B- 26.76°
M- 22.62°
B- 28.78°
M- 19.96°
B- 30.60°
M- 17.07°
B- 32.19°
M- 13.95°
B- 33.53°
M- 10.65°
B- 34.59°
M- 7.19°
B- 35.37°
M- 3.62°
B- 35.84°
M- 0.00°
B- 36.00°
NUMBER OF SIDES
6
M- 30.00°
B- 0.00°
M- 29.91°
B- 2.50°
M- 29.62°
B- 4.98°
M- 29.15°
B- 7.44°
M- 28.48°
B- 9.85°
M- 27.62°
B- 12.20°
M- 26.57°
B- 14.48°
M- 25.31°
B- 16.67°
M- 23.86°
B- 18.75°
M- 22.21°
B- 20.70°
M- 20.36°
B- 22.52°
M- 18.32°
B- 24.18°
M- 16.10°
B- 25.66°
M- 13.71°
B- 26.95°
M- 11.17°
B- 28.02°
M- 8.50°
B- 28.88°
M- 5.73°
B- 29.50°
M- 2.88°
B- 29.87°
M- 0.00°
B- 30.00°
7
M- 25.71°
B- 0.00°
M- 25.63°
B- 2.17°
M- 25.37°
B- 4.32°
M- 24.95°
B- 6.45°
M- 24.35°
B- 8.53°
M- 23.56°
B- 10.57°
M- 22.64°
B- 12.53°
M- 21.53°
B- 14.41°
M- 20.25°
B- 16.19°
M- 18.80°
B- 17.87°
M- 17.20°
B- 19.41°
M- 15.44°
B- 20.82°
M- 13.54°
B- 22.07°
M- 11.50°
B- 23.16°
M- 9.35°
B- 24.06°
M- 7.10°
B- 24.78°
M- 4.78°
B- 25.30°
M- 2.40°
B- 25.61°
M- 0.00°
B- 25.71°
8 9
M- 22.50°
B- 0.00°
M- 22.42°
B- 1.91°
M- 22.19°
B- 3.81°
M- 21.81°
B- 5.68°
M- 21.27°
B- 7.52°
M- 20.58°
B- 9.31°
M- 19.73°
B- 11.03°
M- 18.74°
B- 12.68°
M- 17.60°
B- 14.24°
M- 16.32°
B- 15.70°
M- 14.91°
B- 17.05°
M- 13.36°
B- 18.27°
M- 11.70°
B- 19.35°
M- 9.93°
B- 20.29°
M- 8.06°
B- 21.08°
M- 6.12°
B- 21.69°
M- 4.11°
B- 22.14°
M- 2.07°
B- 22.41°
M- 0.00°
B- 22.50°
M- 20.00°
B- 0.00°
M- 19.93°
B- 1.71°
M- 19.72°
B- 3.40°
M- 19.37°
B- 5.08°
M- 18.88°
B- 6.72°
M- 18.26°
B- 8.31°
M- 17.50°
B- 9.85°
M- 16.60°
B- 11.31°
M- 15.58°
B- 12.70°
M- 14.43°
B- 14.00°
M- 13.17°
B- 15.19°
M- 11.79°
B- 16.27°
M- 10.31°
B- 17.23°
M- 8.74°
B- 18.06°
M- 7.10°
B- 18.75°
M- 5.38°
B- 19.29°
M- 3.62°
B- 19.68°
M- 1.82°
B- 19.92°
M- 0.00°
B- 20.00°
10
M- 18.00°
B- 0.00°
M- 17.94°
B- 1.54°
M- 17.74°
B- 3.08°
M- 17.42°
B- 4.59°
M- 16.98°
B- 6.07°
M- 16.41°
B- 7.50°
M- 15.72°
B- 8.89°
M- 14.90°
B- 10.21°
M- 13.98°
B- 11.46°
M- 12.94°
B- 12.62°
M- 11.80°
B- 13.69°
M- 10.56°
B- 14.66°
M- 9.23°
B- 15.52°
M- 7.82°
B -16.26°
M- 6.34°
B- 16.88°
M- 4.81°
B- 17.37°
M- 3.23°
B- 17.72°
M- 1.62°
B- 17.93°
M- 0.00°
B- 18.00°
Each B (Bevel) and M (Miter) Setting is Given to the Closest 0.005°.
COMPOUND-ANGLE SETTINGS FOR POPULAR STRUCTURES
25
Page 26

OPERATION
CUTTING CROWN MOLDING
This compound miter saw does an excellent job of cutting
crown molding. In general, compound miter saws do a better
job of cutting crown molding than any other tool made.
In order to fit properly, crown molding must be compound
mitered with extreme accuracy.
The two contact surfaces on a piece of crown molding that
fit flat against the ceiling and the wall of a room are at angles
that, when added together, equal exactly 90˚. Most crown
molding has a top rear angle (the section that fits flat against
the ceiling) of 52˚ and a bottom rear angle (the section that
fits flat against the wall) of 38˚.
LAYING MOLDING FLAT ON THE MITER
TABLE
See Figure 30.
To use this method for accurately cutting crown molding for
a 90˚ inside or outside corner, lay the molding with its broad
back surface flat on the miter table and against the fence.
°
52
CEILING
When setting the bevel and miter angles for compound miters,
remember that the settings are interdependent; changing
one angle changes the other angle as well.
Keep in mind that the angles for crown moldings are very
precise and difficult to set. Since it is very easy for these
angles to shift, all settings should first be tested on scrap
molding. Also most walls do not have angles of exactly 90°,
therefore, you will need to fine tune your settings.
When cutting crown molding by this method the bevel angle
should be set at 33.85˚. The miter angle should be set at
31.62˚ either right or left, depending on the desired cut for
the application. See the chart below for correct angle settings
and correct positioning of crown molding on miter table.
The settings in the chart below can be used for cutting All
Standard (U.S.) crown molding with 52˚ and 38˚ angles. The
crown molding is placed flat on the miter table using the
compound features of the miter saw.
38
W
A
L
L
°
FENCE
TOP EDGE AGAINST FENCE =
LEFT SIDE, INSIDE CORNER
RIGHT SIDE, OUTSIDE CORNER
MITER TABLE
CROWN MOLDING FLAT ON MITER TABLE
INSIDE
CORNER
FENCE
BOTTOM EDGE AGAINST FENCE =
RIGHT SIDE, INSIDE CORNER
LEFT SIDE, OUTSIDE CORNER
MITER TABLE
OUTSIDE
CORNER
Fig. 30
26
Page 27

Bevel
Angle Type of Cut
Setting
Left side, inside corner
33.85˚
1. Top edge of molding against fence
2. Miter table set right 31.62˚
3. Save left end of cut
OPERATION
33.85˚
33.85˚
33.85˚
Right side, inside cor
1. Bottom edge of molding against fence
2. Miter table set left 31.62˚
3. Save left end of cut
Left side, outside corner
1. Bottom edge of molding against fence
2. Miter table set left 31.62˚
3. Save right end of cut
Right side, outside corner
1. Top edge of molding against fence
2. Miter table set right 31.62˚
3. Save right end of cut
ner
CUTTING WARPED MATERIAL
See Figures 31 - 32.
When cutting warped material, always make sure it is positioned on the miter table with the convex side against the
fence as shown in figure 31.
If the warped material is positioned the wrong way as shown
in figure 32, it will pinch the blade near the completion of
the cut.
WRONG
Fig. 32
WARNING:
To avoid a kickback and to avoid serious personal injury,
never position the concave edge of bowed or warped
material against the fence.
CLAMPING WIDE WORKPIECES
See Figure 33.
When cutting wide workpieces, such as 2 in. x 6 in., boards
should be clamped with a C-clamp as shown in figure 33.
RIGHT
WIDE
BOARD
Fig. 31
Fig. 33
27
Page 28

ADJUSTMENTS
WARNING:
Before performing any adjustment, make sure the tool is
unplugged from the power supply. Failure to heed this
warning could result in serious personal injury.
The compound miter saw has been adjusted at the
factory
components might have been jarred out of alignment during shipping. Also, over a period of time, readjustment will
probably become necessary due to wear. After unpacking
the saw, check the following adjustments before you begin
using saw. Make any readjustments that are necessary and
periodically check the parts alignment to make sure that the
saw is cutting accurately.
for making very accurate cuts. However, some of the
PIVOT ADJUSTMENTS
NOTE: These adjustments were made at the factory and
normally do not require readjustment.
TRAVEL PIVOT ADJUSTMENT
The saw arm should rise completely to the up position
by itself.
If the saw arm does not raise by itself or if there is play in
t
he pivot joints, have saw repaired at the nearest authorized
service center.
BEVEL PIVOT ADJUSTMENT
The compound miter saw should bevel easily by loosening
the bevel lock knob and tilting the saw arm to the left.
If movement is tight or if there is play in the pivot, have
saw r
epaired at the nearest authorized service center.
CAUTION:
Do not start the compound miter saw without checking
for interference between the blade and the throat plate.
Damage could result to the blade if it strikes the throat
plate during operation of the saw.
POSITIVE STOP
ADJUSTMENT
SCREW FOR
45° ANGLES
LOCK
NUT(S)
DEPTH STOP
See Figure 35.
The depth stop limits the blade’s downward travel. It allows
the blade to go below the miter table enough to maintain
full cutting capacities. The depth stop positions the blade
1/4 in. from the miter table support.
NOTE: The miter table support is located inside the miter
table.
The depth stop is factory set to provide maximum cutting capacity for the 10 in. blade provided with the saw.
Therefore, the saw with blade provided should never need
adjustments.
However, when the diameter of the blade has been reduced
due to sharpening, it may be necessary to adjust the depth
stop to provide maximum cutting capacity. Also, when a new
blade is installed, it is necessary to check the clearance of
the blade to the miter table support before starting the saw.
Make adjustments if needed.
Fig. 34
28
Page 29

1
5
3
0
4
5
ADJUSTMENTS
BEVEL
LOCK KNOB
POSITIVE STOP
ADJUSTMENT
SCREW FOR 0
°
ANGLES
DEPTH STOP
ADJUSTMENT
SCREW AND
HEX NUT
MITER
T
ABLE
THROAT
PLATE
DEPTH STOP ADJUSTMENTS
See Figure 35.
Unplug your saw.
WARNING:
Failure to unplug your saw could result in accidental starting causing possible serious personal injury.
To adjust the depth stop use a 10 mm wrench or adjustable
wrench and loosen the hex nut at the rear of the miter
saw arm.
Use a 5 mm hex key wrench to adjust the depth stop
adjustment
the screw counter-clockwise and raised by turning the
screw clockwise.
Lower the blade into the miter table. Check blade clearance
a
nd maximum cutting distance (distance from fence where
blade enters) to front of miter table slot.
Readjust if necessary.
Tighten the hex nut with a 10 mm wrench or adjustable
wr
ench.
To prevent the depth stop adjustment screw from turning
while
key wrench while tightening the hex nut.
screw. The saw blade is lowered by turning
tightening the hex nut, carefully hold it with the hex
LOCK NUT(S)
Fig. 35
29
Page 30

MAINTENANCE
WARNING:
When servicing, use only identical replacement parts.
Use of any other parts may create a hazard or cause
product damage.
WARNING:
Always wear safety goggles or safety glasses with side
shields during power tool operation or when blowing
dust. If operation is dusty, also wear a dust mask.
GENERAL MAINTENANCE
Avoid using solvents when cleaning plastic parts. Most
plastics are susceptible to damage from various types of
commercial solvents and may be damaged by their use. Use
clean cloths to remove dirt, dust, oil, grease, etc.
WARNING:
Do not at any time let brake fluids, gasoline, petroleumbased products, penetrating oils, etc., come in contact
with plastic parts. Chemicals can damage, weaken or
destroy plastic which may result in serious personal
injury.
BRUSH
CAP
BRUSH
ASSEMBLY
BRUSH
ASSEMBLY
BRUSH
CAP
Fig. 36
BRUSH REPLACEMENT
See Figure 36.
The saw has externally accessible brush assemblies that
should be periodically checked for wear.
Proceed as follows when replacement is required:
Unplug the saw.
Electric tools used on fiberglass material, wallboard, spackling
compounds, or plaster are subject to accelerated wear and
possible premature failure because the fiberglass chips and
grindings are highly abrasive to bearings, brushes, commutators, etc. Consequently, we do not recommended using this
tool for extended work on these types of materials. However,
if you do work with any of these materials, it is extremely
important to clean the tool using compressed air.
LUBRICATION
All of the bearings in this tool are lubricated with a sufficient
amount of high grade lubricant for the life of the unit under
normal operating conditions. Therefore, no further lubrication is required.
WARNING:
Failure to unplug the saw could result in accidental starting causing serious injury.
Remove brush cap with a screwdriver. Brush assembly is
spring loaded and will pop out when you remove brush
cap.
Remove brush assembly.
Check for wear. Replace both brushes when either has
less
than 1/4 in. length of carbon remaining. Do not
replace one side without replacing the other.
Reassemble using new brush assemblies. Make sure
curvatur
brush moves freely in brush tube.
Make sure brush cap is oriented correctly (straight) and
r
eplace.
Tighten brush cap securely. Do not overtighten.
e of brush matches curvature of motor and that
30
Page 31

NOTES
31
 Loading...
Loading...