Features
Operating voltage: 2.4V~5.0V
·
Programmable tone melody generator
·
ADPCM or m-law PCM, PCM synthesis
·
Wide range of sampling rate for voice
·
synthesis
Minimum sampling rate step: 100Hz
·
Voice melody mixed output
·
Programmable 2 channels of melody mixed
·
output
Programmable 2 channels of voice mixed
·
output
13 kinds of melody beats
·
Applications
High-end educational leisure products
·
Alert and warning systems
·
General Description
The HT84XXX family is a series of programma
ble speech synthesizers and tone generators designed for user-defined voice and melody
applications. It provides various sampling
rates and beats, tone levels, tempos for the
speech synthesizer and melody generator. The
HT84XXX series has two built-in high quality,
current type D/A outputs with 16 levels of volume control. The user¢s commands enable the
user to program the powerful custom function
HT84XXX
Magic Voice
5 octaves of tone level and 18 tempos
·
16 levels of digital volume control
·
Two current type D/A outputs
·
Eight programmable I/O pins
·
Four programmable input pins
·
Provides 36 sec to 384 sec of voice capacity
·
Timer controller
·
Voice fill-in function
·
Powerful user-defined functions
·
Power-on initial setting
·
28-pin SKDIP package
·
Speech synthesizers and sound effect
·
generators
such as to build-in a tiny controller. The Magic
-
TM
Voice
similar to arithmetic operation, logic operation,
branch decision, random counter, and a programmable timer. The Magic Voice
are suitable for versatile voice and sound effect
applications.
The HT84XXX Magic Voice
mat
provides various operational functions
TM
TM
supported.
TM
TM
series
is Easy For-
ROM Selection Table
The HT84XXX series provides various voice capacity as shown below:
Part No. HT84036 HT84072 HT84144 HT84192 HT84384
ROM 768Kb 1536Kb 3072Kb 4096Kb 8192Kb
Voice
Length
Note: The voice capacity is based on a sampling rate of 21Kb/s
Magic VoiceTMis a trademark of Holtek Semiconductor Inc.
Easy Format
TM
is a trademark of Grow With Me, Inc.
36 sec 72 sec 144 sec 192 sec 384 sec
1 April 26, 2000
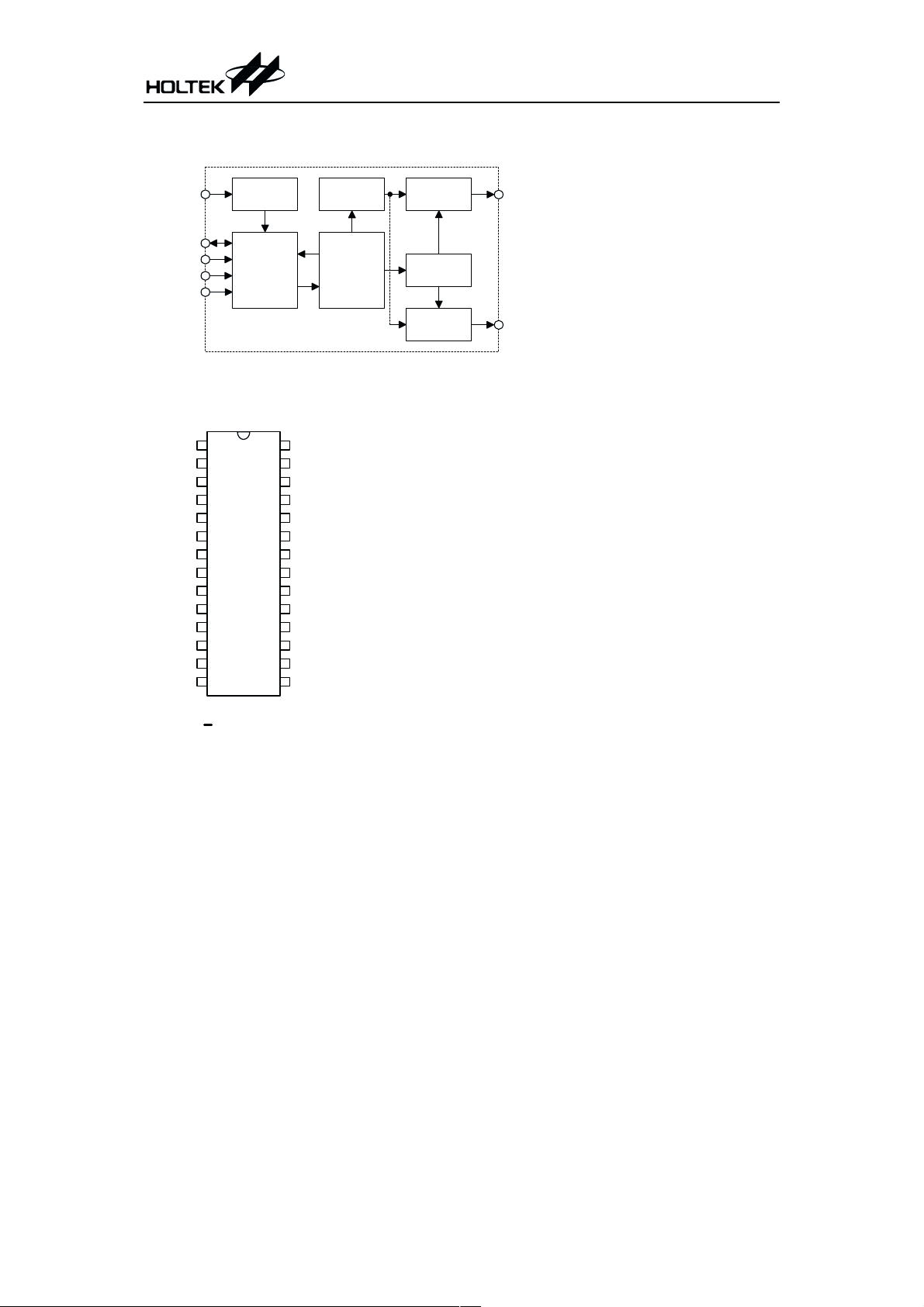
Block Diagram
HT84XXX
OSC
PB0~PB7
PA0~PA3
VDD
VSS
Tim e Base
G enerator
D ecoder
I/O
C ontroller
Pin Assignment
1
NC
2
NC
3
NC
4
NC
5
NC
6
VDD
PB7
PB6
PB5
PB4
PB3
PB2
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
AUD 0
AUD 1
&
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
OSC
VSS
VSS
PA0
PA1
PA2
PA3
PB0
PB1
Tone/M elody
Generator
DATA
& User
In struction
ROM
C u rre n t T y p e
D/A Output
Speech
Synthesizer
C u rre n t T y p e
D/A Output
AUD 0
AUD 1
HT84XXX
28 S K D IP
2 April 26, 2000
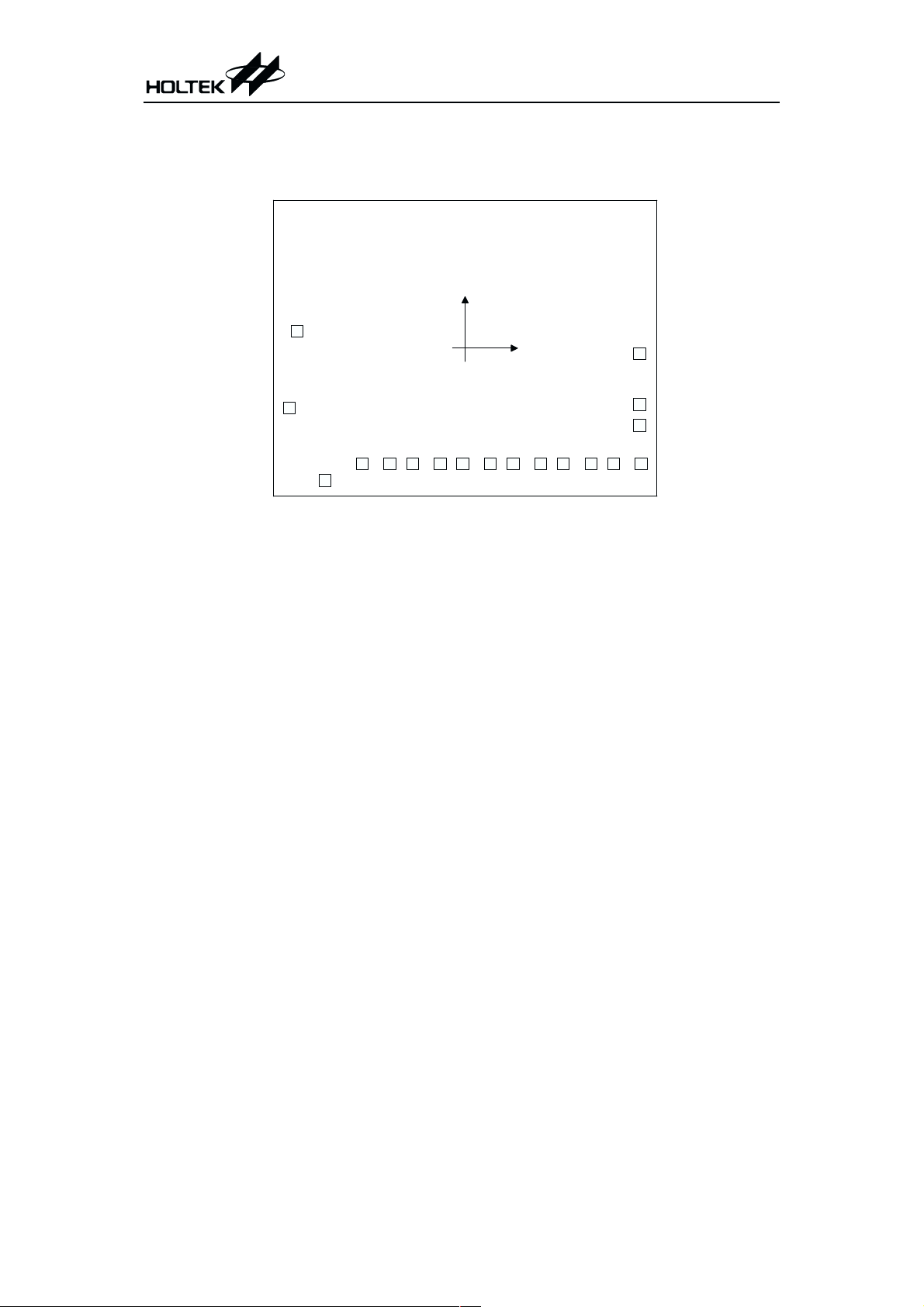
Pad Assignment
HT84036
VDD
AUD 0
HT84XXX
1
(0 , 0 )
OSC
18
17
VSS
VSS
7168
AUD 1
PB7
PB6
PB5
PB3
PB4
Chip size: 2735 ´ 2105 (mm)
102113124
9
PB2
PB1
PB0
135 146
PA3
PA2
15
PA0
PA1
2
* The IC substrate should be connected to VSS in the PCB layout artwork.
3 April 26, 2000
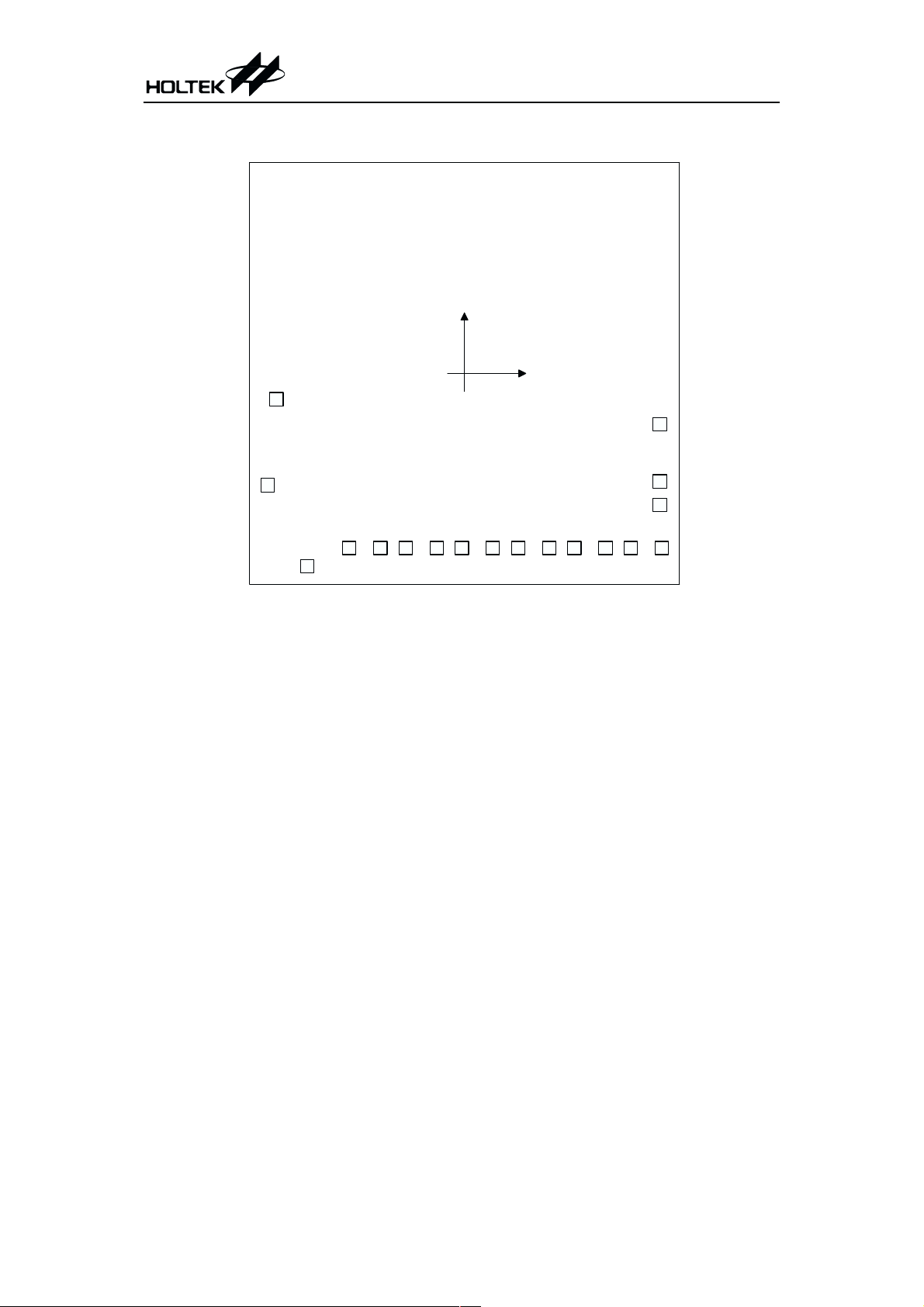
HT84072
HT84XXX
(0 , 0 )
VDD
AUD 0
1
18
17
4
AUD 1
PB7
PB6
6157168
PB5
PB4
9
10211312
PB3
PB2
PB1
Chip size: 2735 ´ 2645 (mm)
13514
PA3
PB0
2
PA2
PA0
PA1
* The IC substrate should be connected to VSS in the PCB layout artwork.
OSC
VSS
VSS
4 April 26, 2000
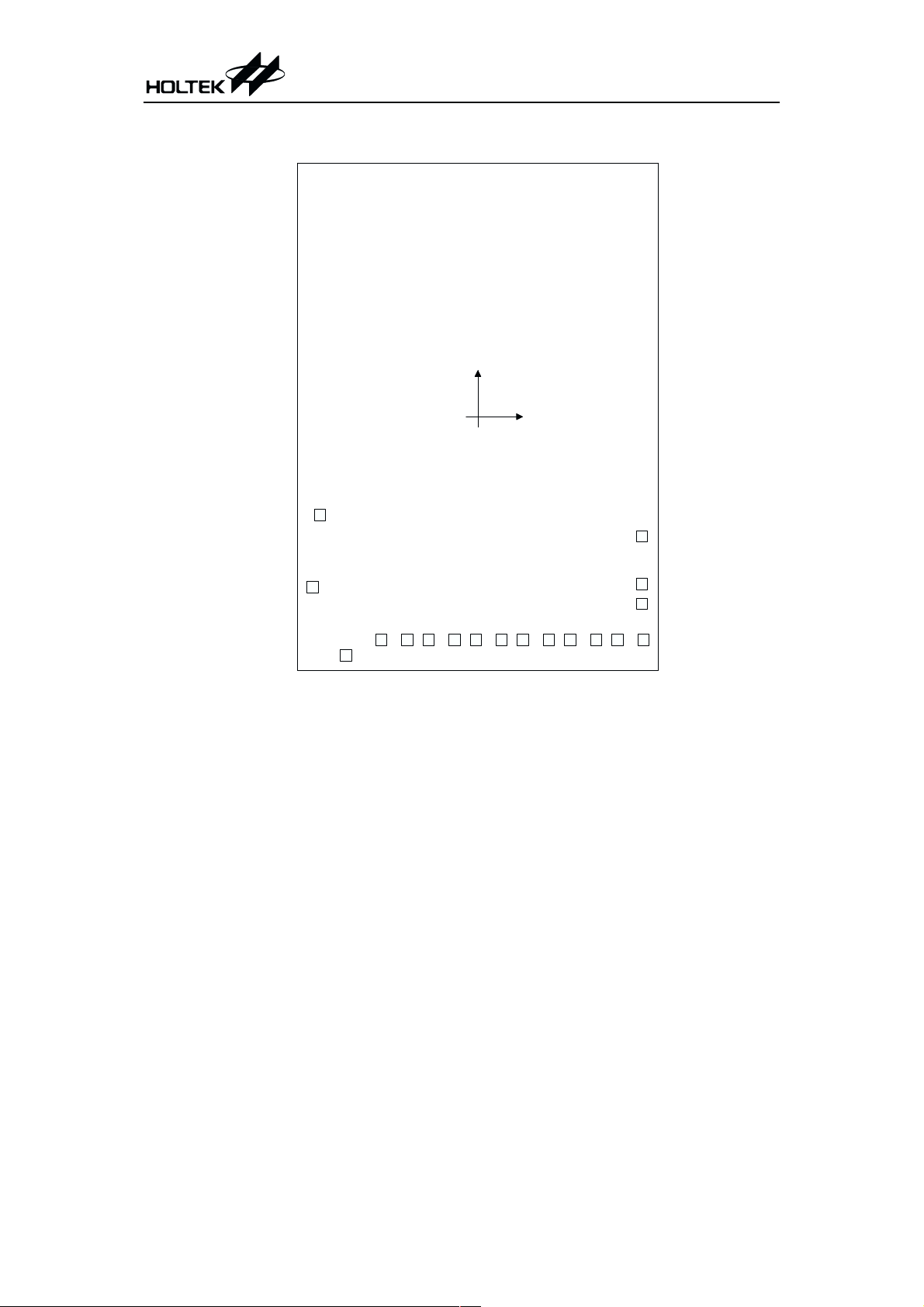
HT84144
VDD
HT84XXX
(0 , 0 )
1
OSC
18
AUD 0
7168179
AUD 1
PB7
PB5
PB6
PB3
PB4
Chip size: 2735 ´ 3735 (mm)
102113124135 146
PA1
PA2
PB1
PB2
PA3
PB0
2
VSS
VSS
15
PA0
* The IC substrate should be connected to VSS in the PCB layout artwork.
5 April 26, 2000
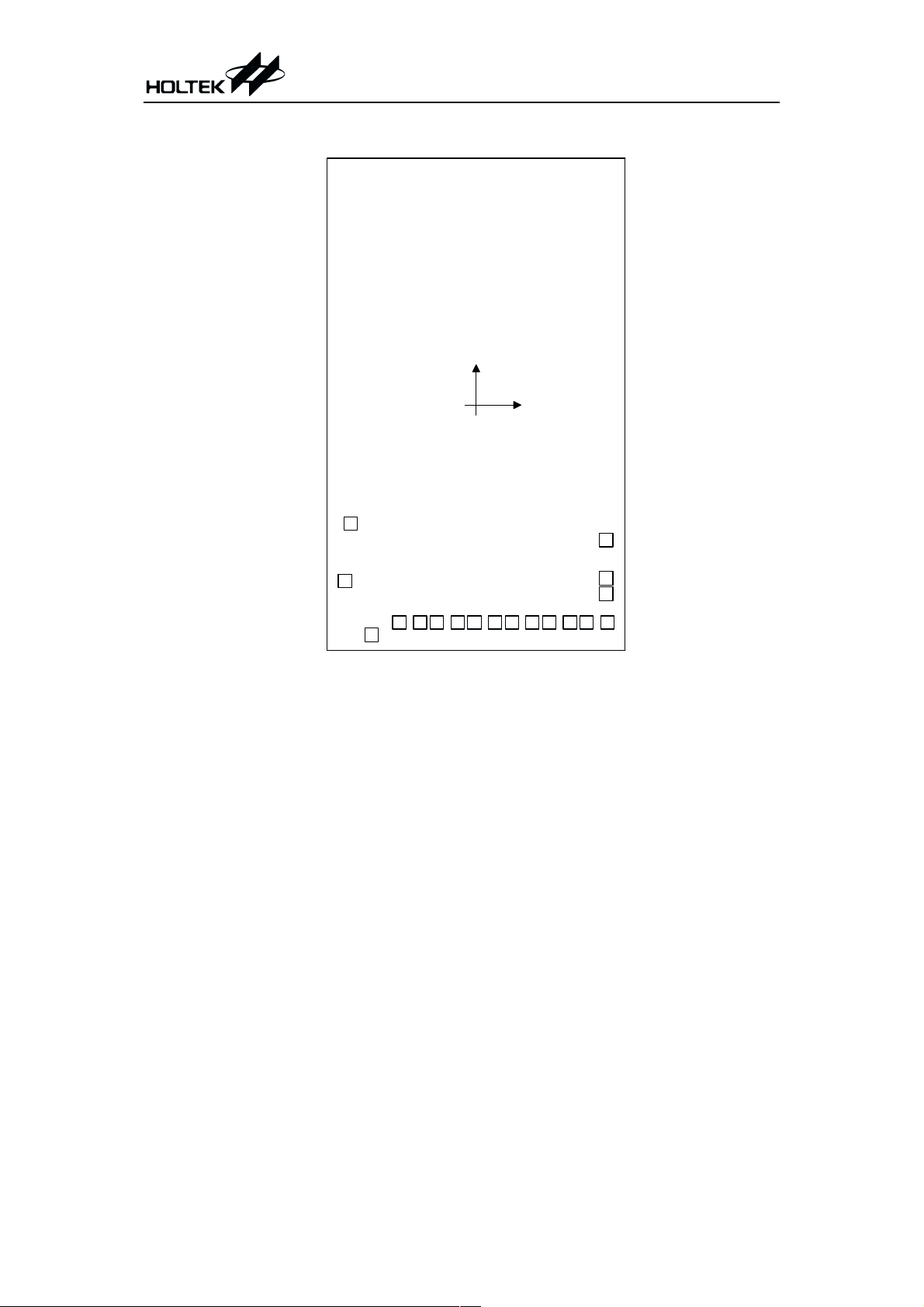
HT84192
HT84XXX
(0 ,0 )
VDD
AUD 0
1
2
3
AUD 1
5146157168
PB6
PB7
PB3
PB5
PB4
Chip size: 2735 ´ 4460 (mm)
18
OSC
VSS
17
VSS
11
10
9
PB2
12413
PA1
PA2
PA3
PB1
PB0
2
PA0
* The IC substrate should be connected to VSS in the PCB layout artwork.
6 April 26, 2000
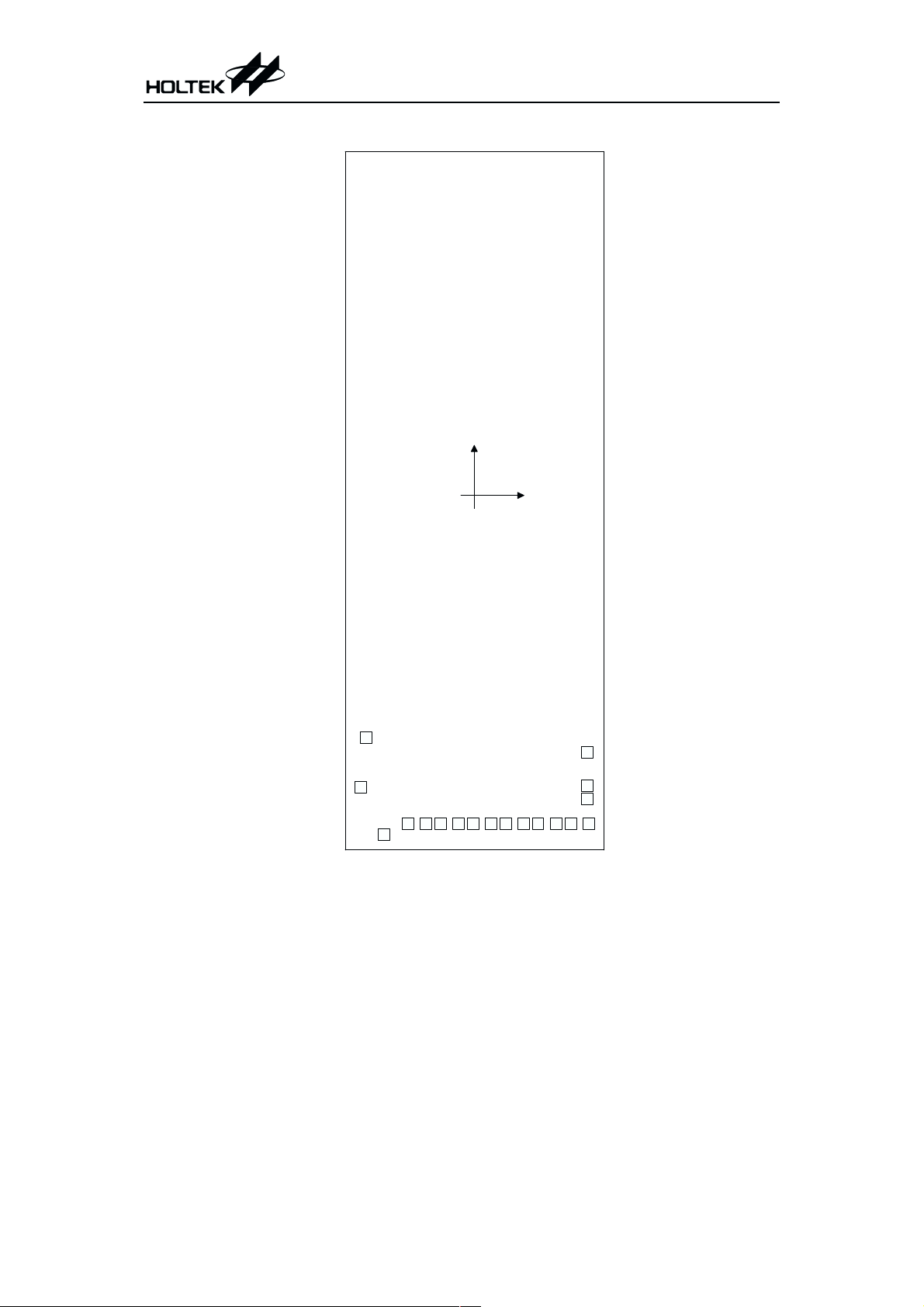
HT84384
HT84XXX
(0 , 0 )
VDD
AUD 0
1
2
7
8179
5
3
AUD 1
6
PB5
PB6
PB7
10
PB1
PB2
PB3
PB4
Chip size: 2740 ´ 7350 (mm)
11
PB0
12413
PA3
2
PA2
OSC1
18
VSS
16
VSS
14
15
PA0
PA1
* The IC substrate should be connected to VSS in the PCB layout artwork.
7 April 26, 2000
Pad Coordinates
HT84XXX
HT84036
Pad No. X Y Pad No. X Y
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9 169.35
HT84072
Pad No. X Y Pad No. X Y
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9 169.35
-1125.31
-1177.49 -398.79
-939.68 -884.61
-689.05 -774.24
-503.45 -774.24
-352.65 -774.24
-167.05 -774.24
-16.25 -774.24
-1125.31 -155.26
-1177.49 -668.79
-939.68 -1154.61
-689.05 -1044.24
-503.45 -1044.24
-352.65 -1044.24
-167.05 -1044.24
-16.25 -1044.24
114.74 10 320.15
11 505.75
12 656.55
13 842.15
14 992.95
15 1178.55
16 1167.43
17 1167.53
-774.24
-1044.24
18 1167.53
10 320.15
11 505.75
12 656.55
13 842.15
14 992.95
15 1178.55
16 1167.43
17 1167.53
18 1167.53
Unit: mm
-774.24
-774.24
-774.24
-774.24
-774.24
-774.24
-517.18
-377.08
-35.96
Unit: mm
-1044.24
-1044.24
-1044.24
-1044.24
-1044.24
-1044.24
-787.18
-647.08
-305.96
HT84144
Pad No. X Y Pad No. X Y
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9 169.35
-1125.31 -700.26
-1177.49 -1213.79
-939.68 -1699.61
-689.05 -1589.24
-503.45 -1589.24
-352.65 -1589.24
-167.05 -1589.24
-16.25 -1589.24
-1589.24
10 320.15
11 505.75
12 656.55
13 842.15
14 992.95
15 1178.55
16 1167.43
17 1167.53
18 1167.53
8 April 26, 2000
Unit: mm
-1589.24
-1589.24
-1589.24
-1589.24
-1589.24
-1589.24
-1332.18
-1192.08
-850.96
HT84XXX
HT84192
Pad No. X Y Pad No. X Y
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9 169.35
HT84384
Pad No. X Y Pad No. X Y
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9 172.85
-1125.31 -1062.76
-1177.49 -1576.29
-939.68 -2062.11
-689.05 -1951.74
-503.45 -1951.74
-352.65 -1951.74
-167.05 -1951.74
-16.25 -1951.74
-1951.74
-1121.81 -2507.96
-1173.99 -3021.49
-936.18 -3507.31
-685.55 -3396.94
-499.95 -3396.94
-349.15 -3396.94
-163.55 -3396.94
-12.75 -3396.94
-3396.94
10 320.15
11 505.75
12 656.55
13 842.15
14 992.95
15 1178.55
16 1167.43
17 1167.53
18 1167.53
10 323.65
11 509.25
12 660.05
13 845.65
14 996.45
15 1182.05
16 1170.93
17 1171.03
18 1171.03
Unit: mm
-1951.74
-1951.74
-1951.74
-1951.74
-1951.74
-1951.74
-1694.68
-1554.58
-1213.46
Unit: mm
-3396.94
-3396.94
-3396.94
-3396.94
-3396.94
-3396.94
-3139.88
-2999.78
-2658.66
Pin Description
Pin No. Pin Name I/O
1~5,
24~28
6 VDD
7 AUD0 O
8 AUD1 O
15~9 PB1~PB7 I/O
16 PB0 I/O
NC
Internal
Connection
¾¾
¾¾
PMOS
Open Drain
PMOS
Open Drain
Pull-high or
CMOS
Pull-high or
CMOS
Description
No connection
Positive power supply
Audio output for driving an external transistor
Audio output for driving an external transistor
Bidirectional I/O pins
Can be optioned as trigger inputs or LED outputs
Bidirectional I/O pins
Can be optioned as CDS interface with internal
Schmitt trigger input
9 April 26, 2000
HT84XXX
Pin No. Pin Name I/O
20~17 PA0~PA3 I
21, 22 VSS
Internal
Connection
Wake-up
Pull-high
¾¾
Description
Trigger inputs
Can also be configured as wake-up inputs
Negative power supply, ground
Built-in RC oscillator
23 OSC I
¾
An oscillator resistor is connected between OSC and
VSS
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Supply Voltage.................................-0.3V to 6V
Input Voltage .................V
-0.3V to VDD+0.3V
SS
Note: These are stress ratings only. Stresses exceeding the range specified under ²Absolute Maxi
mum Ratings² may cause substantial damage to the device. Functional operation of this device
at other conditions beyond those listed in the specification is not implied and prolonged expo
sure to extreme conditions may affect device reliability.
Electrical Characteristics
Symbol Parameter
V
I
STB
I
DD
I
OL
I
O
f
SYS
DD
Operating Voltage
Standby Current 3V No load, system HALT
Operating Current 3V
PB0~PB7 Sink Current 3V
Max. AUD1 and AUD2
Output Current
System Frequency 3V
V
DD
¾¾
3V
Storage Temperature.................-50°Cto125°C
Operating Temperature ..............-20°Cto70°C
Test Conditions
Min. Typ. Max. Unit
Conditions
No load, f
V
=0.3V
OL
=0.6V
V
OH
=240kW
R
OSC
SYS
2.4
=4MHz
-1.5 -2 ¾
3.6 4.0 4.4 MHz
¾
¾
¾
13
58mA
46
Ta=25°C
5.2 V
mA
mA
¾
mA
-
-
10 April 26, 2000

Functional Description
The Magic VoiceTMseries is a series of program
mable speech synthesizers and melody genera
tors. It provides various sampling rates and
beats, tone levels, tempos for speech synthe
sizer and melody generator. For voice synthe
sizer, the Magic Voice
6-bit m-law PCM and 4-bit ADPCM synthesis.
In HT84XXX series, a mixed output of two
channels PCM synthesis is allowed but only
one channel ADPCM synthesis is allowed. For
melody generator, the Magic Voice
a tone melody and PCM melody generator and
two channels mixed output for the whole series.
The Magic Voice
mable I/O pins and 4 programmable input pins
along with powerful user¢s command. The
user¢s instructions are employed to develop
new and customized functions for a wide vari
ety of innovative applications.
Speech and melody analysis
The speech and melody sources of the Magic
TM
Voice
can be recorded and edited from the PC
sound card and media tools. Holtek¢s CAD tools
first load a speech source file as .WAV or .PCM
format, then transfer the speech file as PCM,
LOG-PCM or ADPCM format, and finally save
it to the internal mask ROM by changing a
layer of the mask. The PCM format generates a
higher sound quality whereas the ADPCM format brings about a longer recording capacity.
The melody source can either be in the .MID or
in the .MLD format.
The .MID file is the standard format of the windows media tools. The .MLD file is a text for
mat. After the .MID file is compiled, the .MLD
file is automatically generated.
The Magic Voice
compression format of the voice .WAV and
.PCM file: AD4, PCM8, m-law PCM.
Current type D/A output
The HT84XXX series supply two high accuracy
current type D/A output pins for audio output.
The output volume is changeable from 0 to 15
digital levels by writing a value to the VOL
TM
provides 8-bit PCM,
TM
TM
series build-in 8 program
TM
can support the following
supports
UME_n (n=1 or 2) registers. The D/A pins are
PMOS open drain structure and ouput synthe
sized signals for driving a speaker through an
external NPN transistor when the chip is ac
tive. However, it becomes floating when the
chip is in the standby state. An 8050 type tran
sistor with h
=150 is recommended for the
FE
output driver of the D/A output pin.
Melody/Tone generator
The HT84XXX family has a built-in mel
ody/tone generator. The generator can generate
13 different kinds of melody beats, 5 octaves of
tone level, 18 tempos, and 2 channels mixed
output. Of these components, the melody tempo
is changeable and generates sound effects by
writing a control value to the TEMPO register.
The chip provides the following 18 tempos, 13
beats, and 5 octaves for user¢s programming.
·
18 tempos (Beats/Min.)
68 78 82 93 100 105
109 114 119 125 132 139
147 156 179 192 227 310
·
13 beats
1
24,112,18,16,14,13,12,23,34,
·
5 octaves
43,3
1,
2
2,
C1~B1, C2~B2, C3~B3, C4~B4, C5~B5
PCM/ADPCM synthesizer
The HT84XXX family contains a PCM and
ADPCM synthesizer. The synthesizer offers a
wide range of sampling rates from 4kHz to
24kHz for PCM synthesis and 4kHz to 16kHz
for ADPCM synthesis. The sampling rate of the
synthesizer can be changed by writing a control
value to the sampling rate register. It also sup
ports a small variety of 100Hz. For a higher
performance sound quality, the PCM coding is
required. But for a longer recording capacity,
the ADPCM coding is recommended.
-
HT84XXX
-
-
-
-
-
11 April 26, 2000

HT84XXX
The capability of the voice sampling rate for
various voice compression format.
f
OSC
PCM8
m-law
PCM
AD4
4M 12kHz 11kHz 8kHz
5M 15kHz 14kHz 10kHz
6M 18kHz 16kHz 12kHz
8M 24kHz 22kHz 16kHz
Oscillator configuration
The HT84XXX series provides an RC oscillator
for the system clock. The system oscillator
stops in the standby state so as to reduce power
consumption.
For the oscillator circuit, an external resistor is
required between OSC and VSS. The oscillator
frequency is typically 4MHz for an external re
sistor of 240kW. The RC type of oscillator offers
the most cost-effective solution, although the
frequency of the oscillation may vary with tem
perature and the chip itself due to process vari
ation.
R
OSC
f
OSC
4M
5M
6M
8M
HT84EVA HT84P00 IC
180kW 240kW 240kW
150kW 210kW 210kW
120kW 180kW 180kW
91kW 150kW 150kW
Mask options
The following options have to be defined to en
sure a proper system functioning:
·
Pull-high resistor: 33kW/98kW (3V)
·
-
Keydebounce time: 0ms~255ms(f
OSC
-
-
-
=4MHz)
12 April 26, 2000

Application Circuits
Basic application
HT84XXX
8050
8050
8050
8050
8050
8050
V
V
DD
R
OSC
DD
R
OSC
EASY 4-1
VDD
AUD0
AUD1
OSC
VSS
EASY 12
VDD
AUD0
AUD1
OSC
VSS
PA0
PA1
PA2
PA3
PB7
PB6
PB5
PB4
PB3
PB2
PB1
PB0
PA0
PA1
PA2
PA3
PB7
PB6
PB5
PB4
PB3
PB2
PB1
PB0
TR1
TR2
TR3
TR4
OUT7
OUT6
OUT5
OUT4
OUT3
OUT2
OUT1
TR1
TR2
TR3
TR4
OUT5
OUT4
OUT3
OUT2
OUT1
TR5
TR6
TR7
TR8
TR9
TR10
TR11
TR12
EASY 4
V
DD
VDD
AUD0
AUD1
OSC
R
OSC
VSS
EASY 8
V
DD
VDD
AUD0
AUD1
OSC
R
OSC
VSS
PA0
PA1
PA2
PA3
PB7
PB6
PB5
PB4
PB3
PB2
PB1
PB0
PA0
PA1
PA2
PA3
PB7
PB6
PB5
PB4
PB3
PB2
PB1
PB0
TR1
TR2
TR3
TR4
OUT8
OUT7
OUT6
OUT5
OUT4
OUT3
OUT2
OUT1
TR1
TR2
TR3
TR4
OUT6
OUT5
OUT4
OUT3
OUT2
OUT1
8050
TR5
TR6
TR7
TR8
8050
13 November 8, 1999

HT84XXX
8050
8050
V
8050
V
8050
DD
R
OSC
DD
R
OSC
EASY 16
VDD
AUD 0
AUD 1
OSC
VSS
EASY 20
VDD
AUD 0
AUD 1
OSC
VSS
PA0
PA1
PA2
PA3
PB7
PB6
PB5
PB4
PB3
PB2
PB1
PB0
PA0
PA1
PA2
PA3
PB7
PB6
PB5
PB4
PB3
PB2
PB1
PB0
TR1
TR2
TR3
TR4
OUT4
OUT3
OUT2
OUT1
TR1
TR2
TR3
TR4
OUT3
OUT2
OUT1
TR5
TR6
TR7
TR8
TR5
TR6
TR7
TR8
TR9
TR10
TR11
TR12
TR9
TR10
TR11
TR12
TR13
TR14
TR15
TR16
TR13
TR14
TR15
TR16
TR17
TR18
TR19
TR20
14 April 26, 2000

HT84XXX
8050
8050
V
8050
V
8050
DD
R
OSC
DD
R
OSC
EASY 24
VDD
AUD 0
AUD 1
OSC
VSS
EASY 28
VDD
AUD0
AUD1
OSC
VSS
PA0
PA1
PA2
PA3
PB7
PB6
PB5
PB4
PB3
PB2
PB1
PB0
PA0
PA1
PA2
PA3
PB7
PB6
PB5
PB4
PB3
PB2
PB1
PB0
TR1
TR2
TR3
TR4
OUT2
OUT1
TR1
TR2
TR3
TR4
OUT1
TR5
TR6
TR7
TR8
TR5
TR6
TR7
TR8
TR9
TR10
TR11
TR12
TR9
TR10
TR11
TR12
TR13
TR14
TR15
TR16
TR13
TR14
TR15
TR16
TR17
TR18
TR19
TR20
TR17
TR18
TR19
TR20
TR21
TR22
TR23
TR24
TR21
TR22
TR23
TR24
TR25
TR26
TR27
TR28
15 April 26, 2000

HT84XXX
8050
8050
8050
8050
V
V
DD
R OSC
DD
R OSC
EASY 32
VDD
AUD0
AUD1
OSC
VSS
EASY 64
VDD
AUD0
AUD1
OSC
VSS
TR1
PA0
TR2
PA1
TR3
PA2
TR4
PA3
PB7
PB6
PB5
PB4
PB3
PB2
PB1
PB0
PA3
PA2
PA1
PA0
TR1
TR9
PB6
TR17
PB5
TR25 TR26 TR27 TR28 TR29 TR 30 TR31
PB4
TR33 TR34 TR35 TR36 TR37 TR 38 TR39
PB3
TR41 TR42 TR43 TR44 TR45 TR 46 TR47
PB2
TR49 TR50 TR51 TR52 TR53 TR 54 TR55
PB1
TR57 TR58 TR59 TR60 TR61 TR 62 TR63
PB0
TR5
TR6
TR7
TR8
TR2
TR10
TR18 TR19 TR20 TR21 TR22 TR 23
TR9
TR10
TR11
TR12
TR3
TR11
TR13
TR14
TR15
TR16
TR4
TR12
TR17
TR18
TR19
TR20
TR5
TR13
TR21
TR22
TR23
TR24
TR6
TR14
TR25
TR26
TR27
TR28
TR7
TR15
TR29
TR30
TR31
TR32
TR8
TR16
TR24
TR32
TR40
TR48
TR56
TR64
PB7
Note: In Easy 64 mode, only falling edge trigger can be used in input state
In Easy 64 mode, the path command ²TRn?L:pathname² and ²TRn?H:pathname² are
invalid
16 April 26, 2000

Push-pull amplifilter application
47mF
47mF
V
8050
8550
V
8050
8550
HT84XXX
DD
IN P U T 1
VDD
AUD0
470
W
DD
AUD1
OSC
470
W
PA0
IN P U T 2
PA1
IN P U T 3
PA2
IN P U T 4
PA3
OUT8
PB7
OUT7
PB6
OUT6
PB5
OUT5
PB4
OUT4
PB3
OUT3
PB2
OUT2
PB1
OUT1
PB0
VSS
R
OSC
OP amplifilter application
To P ow er
Am p
To P ow er
Am p
10k
10k
W
V
DD
IN P U T 1
VDD
0.1mF
AUD0
W
560
W
0.1mF
AUD1
560
W
OSC
PA0
IN P U T 2
PA1
IN P U T 3
PA2
IN P U T 4
PA3
OUT8
PB7
OUT7
PB6
OUT6
PB5
OUT5
PB4
OUT4
PB3
OUT3
PB2
OUT2
PB1
OUT1
PB0
VSS
R
OSC
17 April 26, 2000

Application Notes
HT84XXX
Easy Format
TM
The syntax of the Easy FormatTMconsists of four major parts. They are format and audio file decla
ration part, input states declaration part, output states declaration part and path command part.
The architecture of the Easy Format
EASY n
; Comment
; Format and audio file declaration part
TM
program is shown as follows:
....
Stereo/Mono ; Two AUD output or single AUD output
INPUT STATES ; Input states declaration part
....
OUTPUT STATES ; Output states declaration part
....
PATHS ; Path command part
....
Note: Easy Format
TM
is a trademark of Grow With Me, Inc.
Format and voice/melody file declaration
In this area the format and audio file declaration are used to define the number of input and output
as well as declare the audio format.
Syntax: EASY n
The EASY n command is used to define the maximum number of trigger input in the application circuit. The alphanumeric n represents the number of trigger input where n has the choice from 4 to 64
with a scale 4. However, the determination of trigger input reflects the number of output. The relation of the number of I/O is shown in the following table.
EASY n TRn OUTn
-
EASY 4 TR1, TR2, TR3, TR4 OUT1, OUT2, ...., OUT7
EASY 8 TR1, TR2, ...., TR8 OUT1, OUT2, ...., OUT6
EASY 12 TR1, TR2, ...., TR12 OUT1, OUT2, ...., OUT5
EASY 16 TR1, TR2, ...., TR16 OUT1, OUT2, ...., OUT4
EASY 20 TR1, TR2, ...., TR20 OUT1, OUT2, OUT3
EASY 24 TR1, TR2, ...., TR24 OUT1, OUT2
EASY 28 TR1, TR2, ...., TR28 OUT1
EASY 32 TR1, TR2, ...., TR32
EASY 64 TR1, TR2, ...., TR64
* refer to the application circuit
18 April 26, 2000

HT84XXX
Syntax:
voice_file/compression_method
melody_file
tone_file
The source audio files must be included in your Easy program. The audio files include the voice files
with the extended name .PCM or .WAV, the melody files with .MID or .MLD format and the tone files
with Holtek¢s .HT8 format. The compression methods of voice files have three options such as m-law
PCM, PCM8 and AD4.
Example:
voice1.wav/pcm8 ; #0 voice files declaration
voice2.pcm/ad4 ; #1
melody1.mid ; #2 melody files declaration
melody2.mld ; #3
tone1.ht8 ; #4 tone files declaration
Stereo/Mono:
The audio output selection. If the audio output is declared as ²Stereo², the channel
1 voice will output via AUD1 and the channel 2 voice will output via AUD2. If the
audio output isdeclared as ²Mono², the channel 1 and channel 2 voices will mixedly
output via AUD1 and AUD2 is invalid. The default declaration is ²Mono². The au
dio file compressed by AD4 cannot output through channel 2. If the melody file out
puts through channel 2, the melody file cannotinclude anychannel 1 instructions.
-
-
Input states declaration
Syntax:
INPUT STATES
; TRn ....
statename: [rising_edge_path][/falling_edge_path] ....
The bracket [ ] is denoted as optional existence. If the path is assigned as ²X², the input trigger signal
is ignored. Unassigned trigger paths will automatically be assigned as ²X². When TRn detects a rising edge or a falling edge signal, the path name of the rising edge path or falling edge path will be exe
cuted. The statename and path label can be any name defined by the user. The ²/² denotes the falling
edge path. The maximum number of statename are 256 and the maximum number of different pathname
are 128.
Example:
INPUT STATES ; input states declaration
; TR1 TR2 TR3
Run: P12Start /P13Stop P14Go/P15Pause
where ²Run² denotes the input statename and ²P12Start², ²/P13Stop², ²P14Go² and ²/P15Pause² are
all pathnames. When a rising edge signal triggers the TR1, then the path of P12Start will be exe
cuted. And if a falling edge signal triggers the TR1, then the signal is ignored, etc.
19 April 26, 2000
-
-

HT84XXX
Output states declaration
Syntax:
OUTPUT STATES
; OUTn ....
statename: OutputMode ....
The possible output mode are listed and described on the following table. The maximum number of
output state are 256.
Output Mode Description
X
H
L
P+
P-
SP+
SP-
Example:
OUTPUT STATES ; output states declaration
; OUT1 OUT2
SirenOn: P+ L
Set OUTn to input mode with pull-high resistor
Set the output pins to logic high
Set the output pins to logic low
Send a (+) pulse train to output pins
Send a (-) pulse train to output pins
Send a plus single pulse to output pins
Send a minus single pulse to output pins
where ²SirenOn² denotes the output statename. Executing ²SirenOn² in the path command will send
a positive pulse train to PB0 and send a logic low to PB1.
Path command definition
Syntax:
PATHS
pathname: path command ....
The pathname is defined according to the user¢s desire. The elements of the path command are listed
and described on the following table. Each path equation consists of many path commands and each
command is separated by one or more space. In order to increase the program readability if the path
commands exceed the screen display you can break the path command to the next line and put the
symbol ²&² in front of the new line.
20 April 26, 2000

Path_Command Description
Input statename To active input state
Output statename To active output state
Pathname To execute the specified path
VAR=pathname Define the variable path
VAR To execute the variable path
Volume_1=n Define the volume 1 value (n=0~15)
Volume_2=n Define the volume 2 value (n=0~15)
Samplerate_1=n Define the sampling rate 1 value
Samplerate_2=n Define the sampling rate 2 value
Delay(n) To delay n (min=0.1s) (n=0.1~65), f
OSC
=4MHz
TRn?H:pathname If TRn is logic High, then the pathname is executed.
TRn?L:pathname If TRn is logic Low, then the pathname is executed.
Flashrate=n
FlashrateT=n
FlashrateV=n
Set the output pulse rate to ²n² pulses per second, where n can be
assigned as 1, 2, 3, ..., 12
Set the output pulse rate after the melody tempo,
n=1, 2, 3, ..., 12
Set the output pulse rate after the volume,
n=1, 2, ..., 12
END Enter power down mode
Mi=PB Read Port B to Mi
STOP1 Stop the sound of channel 1 playback
STOP2 Stop the sound of channel 2 playback
Mi=data Set the contents of Mi to be data
Mi=Mj Set the contents Mi to be Mj
Mi(bn)=1 or 0 Set bit bn to be 1 or 0, bn=0~7
Mi=Mj+data Add immediate data with Mj to Mi
Mi=Mi+Mj Add Mi with Mj to Mi
Mi=Mj.AND.data And immediate data with Mj to Mi, data=0~255
Mi=Mj.OR.data OR immediate data with Mj to Mi, data=0~255
Mi=Mj.XOR.data XOR immediate data with Mj to Mi, data=0~255
Mi?data:pathname If Mi=data then pathname is executed
Mi?Mj:pathname If Mi=Mj then pathname is executed.
Mi(bn)?1:pathname
Mi(bn)?0:pathname
If the bit bn of Mi is ²1² then the pathname is executed.
If the bit bn of Mi is ²0² then the pathname is executed.
HT84XXX
21 April 26, 2000

HT84XXX
Path_Command Description
Path1 is executed when Mi=1;
Mi:[Path1, Path2,
Path3, .... Pathn]
Random(Mi) Get a random code and put it to Mi
Timert: timer_path Initial the timer. If time out then timer_path is executed, t=0.1~65 sec.
TimerON Start the timer counter
TimerOFF Stop timer counter
n*soundfile, n*#N or
#N
[n*soundfile] or
[repeat *soundfile]
Wait
Note: The n of TRn ranges from 1 to 32
²Volume_1=15² is equal to ²Volume=15²
²Samplerate_1=4000² is equal to ²Samplerate=4000², ²4000² means that the sampling rate is
4kHz.
The Mi, Mj are working registers (i, j=0, 1, 2, ..., 10), the M0~M4 are dedicated for users, the
others are shared with VAR and Timer command.
Register Command Comment
M0~M4
M5, M6 VAR If the VAR instruction is used, the M5, M6 will be invalid.
M7~M10 Timer
Example:
EASY 4
INPUT STATES
; TR1 TR2 TR3 TR4
start: /P1 X X X
Path2 is executed when Mi=2;
....
Pathn is executed when Mi=n
Play the soundfile n times
#N is the N¢th soundfile which is defined in the audio file declaration part.
The starting number is 0
Play the soundfile n times or repeatedly via channel 2 and simultaneously
execute the next path command.
Stop executing the next path command until the channel 2 soundfile is
terminated.
¾
Normal register
If the Timer instruction are used, the M7~M10 will be invalid.
PATHS
POWERON: start END
where ²POWERON² is a reserved pathname and provides the initial setting. When the power is
turned on, a falling edge trigger in TR1 is accepted and others are all ignored.
22 April 26, 2000

Application 1 ¾ One shot, nonretriggerable
EASY 4
voice.wav/pcm8 ;#0 sound file declaration
INPUT STATES
; TR1 TR2 TR3 TR4
state1: /path1 X X X
busy: X X X X
PATHS
POWERON: state1 END
path1: busy 1*voice state1 END
TR1
AUD
Application 2 ¾ One shot, retriggerable by itself
EASY 4
voice.wav/pcm8 ;#0 sound file declaration
INPUT STATES
; TR1 TR2 TR3 TR4
state1: /path1 X X X
HT84XXX
PATHS
POWERON: state1 END
path1: 1*voice END
TR1
AUD
23 April 26, 2000

Application 3 ¾ One shot, retriggerable by the other pin only
EASY 4
voice1.wav/pcm8 ;#0 sound file declaration
voice2.wav/pcm8 ;#1
voice3.wav/pcm8 ;#2
voice4.wav/pcm8 ;#3
INPUT STATES
; TR1 TR2 TR3 TR4
state0: /path1 /path2 /path3 /path4
state1: X /path2 /path3 /path4
state2: /path1 X /path3 /path4
state3: /path1 /path2 X /path4
state4: /path1 /path2 /path3 X
PATHS
POWERON: state0 END
path1: state1 #0 state0 END
path2: state2 #1 state0 END
path3: state3 #2 state0 END
path4: state4 #3 state0 END
HT84XXX
TR1
TR2~TR 4
AUD
#0 #0 #(1~3)
24 April 26, 2000

Application 4 ¾ Level hold, retriggerable by the other pin only
EASY 4
voice1.wav/pcm8 ;#0 sound file declaration
voice2.wav/pcm8 ;#1
voice3.wav/pcm8 ;#2
voice4.wav/pcm8 ;#3
INPUT STATES
; TR1 TR2 TR3 TR4
state0: /path1 /path2 /path3 /path4
state1: path11 /path2 /path3 /path4
state2: /path1 path11 /path3 /path4
state3: /path1 /path2 path11 /path4
state4: /path1 /path2 /path3 path11
PATHS
POWERON: state0 END
path1: state1 #0 path1
path2: state2 #1 path2
path3: state3 #2 path3
path4: state4 #3 path4
path11: state0 END
HT84XXX
TR1
TR2~TR 4
AUD
#0 #0 #(1~3)
#0
25 April 26, 2000

Application 5 ¾ LED output, direct mode
EASY 4
voice1 .wav/pcm8 ;#0 sound file declaration
INPUT STATES
; TR1 TR2 TR3 TR4
state0: /path1 X X X
OUTPUT STATES
;OUT 1 2
alarm: P+ L
standby: L H
turnoff: X X
PATHS
POWERON: state0 flashrate=6Hz END
path1: alarm #0 standby delay(2) turnoff END
Application 6 ¾ LED output matrix mode
EASY 4
INPUT STATES
; TR1
state0: /path0
OUTPUT STATES
; OUT1 OUT2 OUT3 OUT4 OUT5 OUT6 OUT7
LED1: P+ L L L H H H
LED2: L P+ L L H H H
LED3: L L P+ L H H H
LED4: P+ L L H L H H
LED5: L P+ L H L H H
LED6: L L P+ H L H H
LED7: P+ L L H H L H
LED8: L P+ L H H L H
LED9: L L P+ H H L H
LED10: P+ L L H H H L
LED11: L P+ L H H H L
LED12: L L P+ H H H L
turnoff: X X X X X X X
HT84XXX
26 April 26, 2000

PATHS
POWERON: state0 M0=0 flashrate=3Hz END
path0: M0=M0+1
& M0:[P1,P2,P3,P4,P5,P6,P7,P8,P9,P10,P11,P12]
P1: LED1 delay(2) turnoff END
P2: LED2 delay(2) turnoff END
P3: LED3 delay(2) turnoff END
P4: LED4 delay(2) turnoff END
P5: LED5 delay(2) turnoff END
P6: LED6 delay(2) turnoff END
P7: LED7 delay(2) turnoff END
P8: LED8 delay(2) turnoff END
P9: LED9 delay(2) turnoff END
P10: LED10 delay(2) turnoff END
P11: LED11 delay(2) turnoff END
P12: M0=0 LED12 delay(2) turnoff END
HT84XXX
27 April 26, 2000

HT84XXX
Application 7 ¾ Police car
This is a full program application example to demonstrate how Easy Format handles a complicated
design requirement. All the work is to be done on a single page.
START ACCEL SIR EN BR AKE
L1 L2
There are four input trigger buttons and two output pins to drive two LEDs.
·
BUTTON #1: Turn ON (START) or OFF the engine.
·
BUTTON #2: Gas pedal to give ACCELERATION sound from idle and then keep on at a steady
running sound.
·
BUTTON #3: SIREN sound On/Off: toggle ON and toggle Off.
·
BUTTON #4: BRAKE, triggers deceleration sound and then brings the car to idle.
·
LEDs OUTPUTs: Blinks in opposite phase when the Siren sound is on. That is when one light is on,
the other light is off in an alternating pattern.
·
TIME OUT REQUIREMENTS: every sound needs to be automatically shut down after a specified
period if no more trigger signal is received.
Easy Format
TM
application example: Police Car flow chart
ID L E
P12STA R T P 25S IR E N O N
P21STA R T
P13AC C E L
RUN
P32BR A K EP23AC C E L
P53SIR E N O N
P53SIR E N O F F
SIREN+RUNSTOP
P41SIR E N O F F
P14SIR E N O N P 54B R A K E
P45AC C E L
SIREN
28 April 26, 2000

EASY 4
**********************************************************************
;* voice file define
**********************************************************************
StartSnd.wav/ad4
IdleSnd.wav/ad4
AccelSnd.wav/ad4
RunSnd.wav/ad4
DecelSnd.wav/ad4
SirenSnd.wav/ad4
SiRunSnd.wav/ad4
*********************************************************************
;* I/O States
*********************************************************************
INPUT STATES
; TR1 TR2 TR3 TR4
; Start Accel Siren Brake
StopCar: /P12Start /P13Accel /P14SirenOn X
Idle: /P21Start /P23Accel /P25SirenOn X
Run: X X /P35SirenOn /P32Brake
Siren X /P45Accel /P41SirenOff X
SirenRun X X /P53SirenOff /P54Brake
HT84XXX
OUTPUT STATES
; OUT1 OUT2
SirenOn: P+ P-
SirenOff: H H
*********************************************************************
;* Paths
*********************************************************************
Paths
POWERON: StopCar SirenOff FLASHRATE=6Hz END
P12Start: Idle 1*StartSnd 10*IdleSnd PowerDown
P21Start: StopCar END
P13Accel: Run 2*IdleSnd 1*AccelSnd 20*RunSnd
& PowerDown
29 April 26, 2000

P14SirenOn: Siren SirenOn 10*SirenSnd PowerDown
P41SirenOff: StopCar SirenOff END
P23Accel: Run 1*AccelSnd 20*RunSnd PowerDown
P32Brake: Idle 1*DecelSnd 10*idleSnd PowerDown
P25SirenOn: 1*AccelSnd SirenRun SirenOn 10*SiRunSnd PowerDown
P35SirenOn: SirenRun SirenOn 10*SiRunSond PowerDown
P53SirenOff: SirenOff Run 20*RunSnd PowerDown
P45Accel: P25SirenOn
P54Brake: 1*DecelSnd Siren SirenOn 10*SirenSnd
& PowerDown
PowerDown: SirenOff StopCar End
HT84XXX
30 April 26, 2000

HT84XXX
Holtek Semiconductor Inc. (Headquarters)
No.3 Creation Rd. II, Science-based Industrial Park, Hsinchu, Taiwan, R.O.C.
Tel: 886-3-563-1999
Fax: 886-3-563-1189
Holtek Semiconductor Inc. (Taipei Office)
5F, No.576, Sec.7 Chung Hsiao E. Rd., Taipei, Taiwan, R.O.C.
Tel: 886-2-2782-9635
Fax: 886-2-2782-9636
Fax: 886-2-2782-7128 (International sales hotline)
Holtek Semiconductor (Hong Kong) Ltd.
RM.711, Tower 2, Cheung Sha Wan Plaza, 833 Cheung Sha Wan Rd., Kowloon, Hong Kong
Tel: 852-2-745-8288
Fax: 852-2-742-8657
Copyright ã 2000 by HOLTEK SEMICONDUCTOR INC.
The information appearing in this Data Sheet is believed to be accurate at the time of publication. However, Holtek
assumes no responsibility arising from the use of the specifications described. The applications mentioned hereinare
used solely for the purpose of illustration and Holtek makes no warranty or representation that such applications
will be suitable without further modification, nor recommends the use of its products for application that may pres
ent a risk to human life due to malfunction or otherwise. Holtek reserves the right to alter its products without prior
notification. For the most up-to-date information, please visit our web site at http://www.holtek.com.tw.
31 April 26, 2000
-
 Loading...
Loading...