Page 1

USER’S GUIDE
CGN RESIDENTIAL CABLE MODEM
VERSION 2.0 - FEBRUARY 2012
Page 2

ABOUT THIS USER’S GUIDE
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
2
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
ABOUT THIS USER’S
GUIDE
INTENDED AUDIENCE
This manual is intended for people who want to configure the CGN’s features via its
Graphical User Interface (GUI).
HOW TO USE THIS USER’S GUIDE
This manual contains information on each the CGN’s GUI screens, and describes
how to use its various features.
Use the Introduction (page 12) to see an overview of the topics covered in this
manual.
Use the Table of Contents (page 7), List of Figures (page 10) and List of Tables
(page 11) to quickly find information about a particular GUI screen or topic.
Use the Index (page 112) to find information on a specific keyword.
Use the rest of this User’s Guide to see in-depth descriptions of the CGN’s
features.
RELATED DOCUMENTATION
Quick Installation Guide: see this for information on getting your CGN up and
running right away. It includes information on system requirements, package
contents, the installation procedure, and basic troubleshooting tips.
Online Help: each screen in the CGN’s Graphical User Interface (GUI) contains
a Help button. Click this button to see additional information about configuring
the screen.
Page 3
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
3
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
DOCUMENT CONVENTIONS
This User’s Guide uses various typographic conventions and styles to indicate
content type:
Bulleted paragraphs are used to list items, and to indicate options.
1 Numbered paragraphs indicate procedural steps.
NOTE: Notes provide additional information on a subject.
Warnings provide information about actions that could harm you or your
device.
Product labels, field labels, field choices, etc. are in bold type. For example:
Select UDP to use the User Datagram Protocol.
A mouse click in the Graphical User Interface (GUI) is denoted by a right angle
bracket ( > ). For example:
Click Settings > Advanced Settings.
means that you should click Settings in the GUI, then Advanced settings.
A key stroke is denoted by square brackets and uppercase text. For example:
Press [ENTER] to continue.
CUSTOMER SUPPORT
For technical assistance or other customer support issues, please consult your Hitron
representative.
3
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
ABOUT THIS USER’S GUIDE
Page 4

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
4
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
DEFAULT CREDENTIALS
The CGN’s default login credentials are as follows. For more information, see
Logging into the CGN on page 22.
Table 1: Default Credentials
Username cusadmin
Password password
Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies. All rights reserved. All trademarks and
registered trademarks used are the properties of their respective owners.
DISCLAIMER: The information in this User’s Guide is accurate at the time of writing.
This User’s Guide is provided “as is” without express or implied warranty of any kind.
Neither Hitron Technologies nor its agents assume any liability for inaccuracies in this
User’s Guide, or losses incurred by use or misuse of the information in this User’s
Guide.
4
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
ABOUT THIS USER’S GUIDE
Page 5

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
5
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
COMPLIANCES
FCC INTERFERENCE STATEMENT
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B
digital device pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to
provide reasonable protection against radio interference in a commercial
environment.
This equipment can generate, use and radiate radio frequency energy and, if not
installed and used in accordance with the instructions in this manual, may cause
harmful interference to radio communications.
Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause interference, in
which case the user, at his own expense, will be required to take whatever measures
are necessary to correct the interference. If this equipment does cause harmful
interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the
equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one
of the following measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the
receiver is connected.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
The device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the
following two conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2)
this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may
cause undesired operation.
FCC Caution: Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party
responsible for compliance could void the user’s authority to operate this equipment.
IEEE 802.11b or 802.11g operation of this product in the U.S.A is firmware-limited to
channels 1 through 11.
IMPORTANT NOTE:
5
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
COMPLIANCES
Page 6

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
6
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement:
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an
uncontrolled environment. This equipment should be installed and operated with
minimum distance 20cm between the radiator & your body.
This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other
antenna or transmitter.
The availability of some specific channels and/or operational frequency bands are
country dependent and are firmware programmed at the factory to match the
intended destination. The firmware setting is not accessible by the end user.
Note to CATV System Installer - The cable distribution system should be grounded
(earthed) in accordance with ANSI/NFPA 70, the National Electrical Code (NEC), in
particular Section 820.93, Grounding of Outer Conductive Shield of a Coaxial Cable.
107 SMCD3G3-CCR 4-Port Gateway Administrator Manual
6
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
COMPLIANCES
Page 7

TABLE OF CONTENTS
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
7
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
About This User’s Guide ................................................................ 2
Compliances .................................................................................... 5
Table of Contents ............................................................................ 7
List of Figures ............................................................................... 10
List of Tables ................................................................................. 11
Introduction ................................................................................... 12
1.1 CGN Overview .................................................................................. 12
1.1.1 Key Features ............................................................................ 13
1.2 Hardware Connections ...................................................................... 14
1.3 LEDs ................................................................................................. 17
1.4 IP Address Setup .............................................................................. 20
1.4.1 Manual IP Address Setup ......................................................... 21
1.5 Logging into the CGN ........................................................................ 22
1.6 GUI Overview .................................................................................... 23
1.7 Resetting the CGN ............................................................................ 24
Status ............................................................................................. 26
2.1 Cable Overview ................................................................................. 26
2.1.1 DOCSIS .................................................................................... 26
2.1.2 IP Addresses and Subnets ....................................................... 27
2.1.2.1 IP Address Format ........................................................... 27
2.1.2.2 IP Address Assignment .................................................... 27
2.1.2.3 Subnets ............................................................................ 28
2.1.3 DHCP ........................................................................................ 29
2.1.4 DHCP Lease ............................................................................. 30
2.1.5 MAC Addresses ........................................................................ 30
Page 8

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
8
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
2.1.6 Routing Mode ........................................................................... 31
2.1.7 Configuration Files .................................................................... 31
2.1.8 Downstream and Upstream Transmissions .............................. 31
2.1.9 Cable Frequencies .................................................................... 31
2.1.10 Modulation .............................................................................. 32
2.1.11 TDMA, FDMA and SCDMA .................................................... 32
2.2 The System Info Screen .................................................................... 33
2.3 The Initialization Screen .................................................................... 37
2.4 The CM Status Screen ...................................................................... 38
2.5 The Password Screen ....................................................................... 41
2.6 The Capability Screen ....................................................................... 42
WAN/LAN ....................................................................................... 45
3.1 WAN/LAN Overview .......................................................................... 45
3.1.1 WAN and LAN .......................................................................... 45
3.1.2 LAN IP Addresses and Subnets ............................................... 46
3.1.3 DNS and Domain Suffix ............................................................ 46
3.1.4 Debugging (Ping and Traceroute) ............................................ 46
3.2 The IP Screen ................................................................................... 47
3.3 The Shared Media Screen ................................................................ 50
3.4 The Debug Screen ............................................................................ 51
3.5 The Backup Screen ........................................................................... 52
Firewall ........................................................................................... 54
4.1 Firewall Overview .............................................................................. 54
4.1.1 Firewall ..................................................................................... 54
4.1.2 Intrusion detection system ........................................................ 55
4.1.3 Ping ........................................................................................... 55
4.1.4 MAC Filtering ............................................................................ 55
4.1.5 IP Filtering ................................................................................. 55
4.1.6 Port Forwarding ........................................................................ 56
4.1.7 Port Triggering .......................................................................... 56
4.1.8 DMZ .......................................................................................... 56
4.2 The Firewall Options Screen ............................................................. 56
4.3 The Filter Setting Screen .................................................................. 57
8
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page 9

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
9
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
4.3.1 Adding or Editing an IP Filtering Rule ....................................... 63
4.4 The Forwarding Screen ..................................................................... 65
4.4.1 Adding or Editing a Port Forwarding Rule ................................ 67
4.5 The Port Triggering Screen ............................................................... 69
4.5.1 Adding or Editing a Port Triggering Rule .................................. 71
4.6 The DMZ Screen ............................................................................... 72
Parental Control ............................................................................ 74
5.1 Parental Control Overview ................................................................ 74
5.1.1 Website Blocking ...................................................................... 74
5.2 The Website Blocking Screen ........................................................... 75
5.3 The Scheduling Screen ..................................................................... 77
5.4 The Email / Syslog Alert Screen ....................................................... 79
Wireless ......................................................................................... 83
6.1 Wireless Overview ............................................................................ 83
6.1.1 Wireless Networking Basics ..................................................... 83
6.1.2 Architecture ............................................................................... 83
6.1.3 Wireless Standards ................................................................... 84
6.1.4 Service Sets and SSIDs ........................................................... 84
6.1.5 Wireless Security ...................................................................... 85
6.1.5.1 WPS ................................................................................. 85
6.1.6 WMM ........................................................................................ 86
6.2 The Setup Screen ............................................................................. 86
6.3 The Access Control Screen .............................................................. 93
6.4 The Advanced Screen ....................................................................... 95
6.4.1 Configuring WMM Parameters ............................................... 103
Troubleshooting .......................................................................... 107
...................................................................................................... 109
FCC STATEMENT ........................................................................ 110
Index ............................................................................................. 112
9
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page 10

LIST OF FIGURES
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
10
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 1: Application Overview ...........................................................................13
Figure 2: Hardware Connections ........................................................................15
Figure 3: LEDs ....................................................................................................18
Figure 4: Login ....................................................................................................23
Figure 5: GUI Overview ......................................................................................24
Figure 6: The Status > System Info Screen ........................................................34
Figure 7: The Status > Initialization Screen ........................................................37
Figure 8: The Status > CM Status Screen ..........................................................39
Figure 9: The Status > Password Screen ...........................................................42
Figure 10: The Status > Capability Screen .........................................................43
Figure 11: The WAN/LAN > IP Screen ...............................................................48
Figure 12: The WAN/LAN > Shared Media Screen ............................................51
Figure 13: The WAN/LAN > Debug Screen ........................................................52
Figure 14: The WAN/LAN > Backup Screen .......................................................53
Figure 15: The Firewall > Firewall Options Screen .............................................57
Figure 16: The Firewall > Filter Setting Screen ..................................................59
Figure 17: The Firewall > Filter Settings > Add/Edit Screen ...............................63
Figure 18: The Firewall > Forwarding Screen .....................................................65
Figure 19: The Firewall > Forwarding > Add/Edit Screen ...................................67
Figure 20: The Firewall > Port Triggering Screen ...............................................69
Figure 21: The Firewall > Port Triggering > Add/Edit Screen .............................71
Figure 22: The Firewall > DMZ Screen ...............................................................73
Figure 23: The Parental Control > Web Site Blocking Screen ............................75
Figure 24: The Parental Control > Scheduling Screen .......................................78
Figure 25: The Parental Control > Email / Syslog Alert Screen ..........................79
Figure 26: Add Target Email Address .................................................................81
Figure 27: The Wireless > Setup Screen ............................................................87
Figure 28: WPS PIN ............................................................................................89
Figure 29: The Wireless > Access Control Screen .............................................93
Figure 30: The Wireless > Advanced Screen .....................................................96
Figure 31: The Wireless > Advanced > WMM Configuration Screen ...............103
Page 11

LIST OF TABLES
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
11
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
LIST OF TABLES
Table 1: Default Credentials ................................................................................4
Table 2: Hardware Connections ........................................................................16
Table 3: LEDs ....................................................................................................18
Table 4: GUI Overview .......................................................................................24
Table 5: Private IP Address Ranges ..................................................................28
Table 6: IP Address: Decimal and Binary ..........................................................28
Table 7: Subnet Mask: Decimal and Binary .......................................................29
Table 8: The Status > System Info Screen ........................................................35
Table 9: The Status > CM Status Screen ..........................................................39
Table 10: The Status > Password Screen .........................................................42
Table 11: The Status > Capability Screen .........................................................43
Table 12: The WAN/LAN > IP Screen ...............................................................48
Table 13: The WAN/LAN > Shared Media Screen ............................................51
Table 14: The WAN/LAN > Debug Screen ........................................................52
Table 15: The LAN > Backup Screen ................................................................53
Table 16: The Firewall > Firewall Options Screen .............................................57
Table 17: The Firewall > Filter Setting Screen ...................................................60
Table 18: The Firewall > Filter Settings > Add/Edit Screen ...............................64
Table 19: The Firewall > Forwarding Screen .....................................................65
Table 20: The Firewall > Forwarding > Add/Edit Screen ...................................68
Table 21: The Firewall > Port Triggering Screen ...............................................69
Table 22: The Firewall > Port Triggering > Add/Edit Screen .............................71
Table 23: The Firewall > DMZ Screen ...............................................................73
Table 24: The Parental Control > Web Site Blocking Screen ............................76
Table 25: The Parental Control > Scheduling Screen .......................................78
Table 26: The Parental Control > Email / Syslog Alert Screen ..........................80
Table 27: The Wireless > Setup Screen ............................................................87
Table 28: The Wireless > Access Control Screen .............................................94
Table 29: The Wireless > Advanced Screen .....................................................97
Table 30: The Wireless > Advanced > WMM Configuration Screen ................103
Page 12

INTRODUCTION
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
12
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
1
INTRODUCTION
This chapter intoduces the CGN and its GUI (Graphical User Interface). It contains
the following sections:
CGN Overview on page 12
Hardware Connections on page 14
LEDs on page 17
IP Address Setup on page 20
Logging into the CGN on page 22
GUI Overview on page 23
Resetting the CGN on page 24
1.1 CGN OVERVIEW
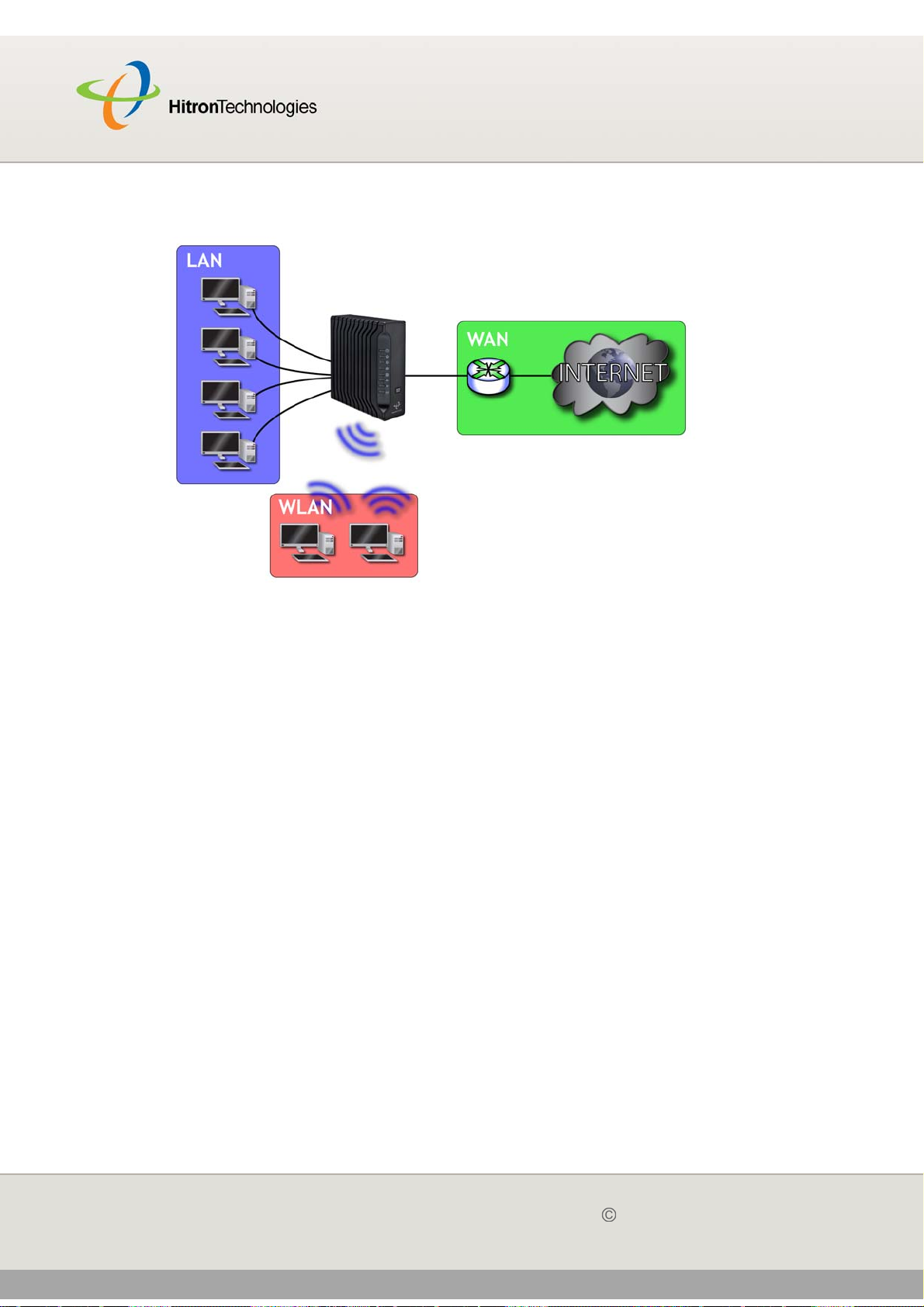
Your CGN is a NAT-capable cable modem and wireless access point that allows you
to connect your computers, wireless devices, and other network devices to one
another, and to the Internet via the cable connection.
Computers with a wired connection to the CGN are on the Local Area Network (LAN),
computers with a wireless connection to the CGN are on the Wireless Local Area
Network (WLAN) and the CGN connects to the service provider over the Wide Area
Network (WAN).
Page 13
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
13
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Figure 1: Application Overview
1.1.1 KEY FEATURES
The CGN provides:
Internet connection to cable modem service via CABLE port (F-type RF
connector)
Local Area Network connection via four 10/100/1000 Mbps (megabits per
second) Ethernet ports
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) for devices on the LAN
LAN troubleshooting tools (Ping and Traceroute)
IEEE 802.11b/g/n wireless MIMO (Multiple-In, Multiple-Out) networking, allowing
speeds of up to 300Mbps
Wireless security: WEP, WPA-PSK and WPA2-PSK encryption, Wifi Protected
Setup (WPS) push-button and PIN configuration, MAC filtering,
Wired security: stateful inspection firewall with intrusion detection system, IP and
MAC filtering, port forwarding and port triggering, De-Militarized Zone (DMZ)
and event logging
Parental control: scheduled website blocking and access logs
13
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
INTRODUCTION
Page 14

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
14
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Settings backup and restore
Secure configuration interface, accessible by Web browser
1.2 HARDWARE CONNECTIONS
This section describes the CGN’s physical ports and buttons.
14
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
INTRODUCTION
Page 15

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
15
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Figure 2: Hardware Connections
15
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
INTRODUCTION
Page 16

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
16
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Table 2: Hardware Connections
WPS PBC Press this button to begin the WiFi Protected Setup
(WPS) Push-Button Configuration (PBC) procedure.
Press the PBC button on your wireless clients in the
coverage area within two minutes to enable them to join
the wireless network.
See WPS on page 85 for more information.
Reset Use this button to reboot or reset your CGN.
Press the button and hold it for less than five seconds
to reboot the CGN. The CGN restarts, using your
existing settings.
Press the button and hold it for more than five
seconds to delete all user-configured settings and
restart the CGN using its factory default settings. See
Resetting the CGN on page 24 for more information
on resetting the CGN.
NOTE: Unless you previously backed-up the CGN’s
configuration settings prior to resetting the CGN,
the settings cannot be recovered.
USB The CGN provides one USB 2.0 host port, allowing you
to plug in a USB flash disk for mounting and sharing
through the LAN interfaces via the Samba protocol
(network neighborhood).
The CGN supports the following Windows file systems:
FAT16
FAT32
NTFS
USB devices must not drain more than 500mA
from the USB port. USB devices requiring
more than 500mA should be provided with
their own power source(s).
LAN1 Use these ports to connect your computers and other
LAN2
LAN3
LAN4
network devices, using Category 5 or 6 Ethernet cables
with RJ45 connectors.
16
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
INTRODUCTION
Page 17

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
17
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Table 2: Hardware Connections
CABLE Use this to connect to the Internet via an F-type RF
cable.
POWER Cable modem is plugged in to an electrical outlet and is
and receiving power.
1.3 LEDS
This section describes the CGN’s LEDs (lights).
17
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
INTRODUCTION
Page 18

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
18
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Figure 3: LEDs
Table 3: LEDs
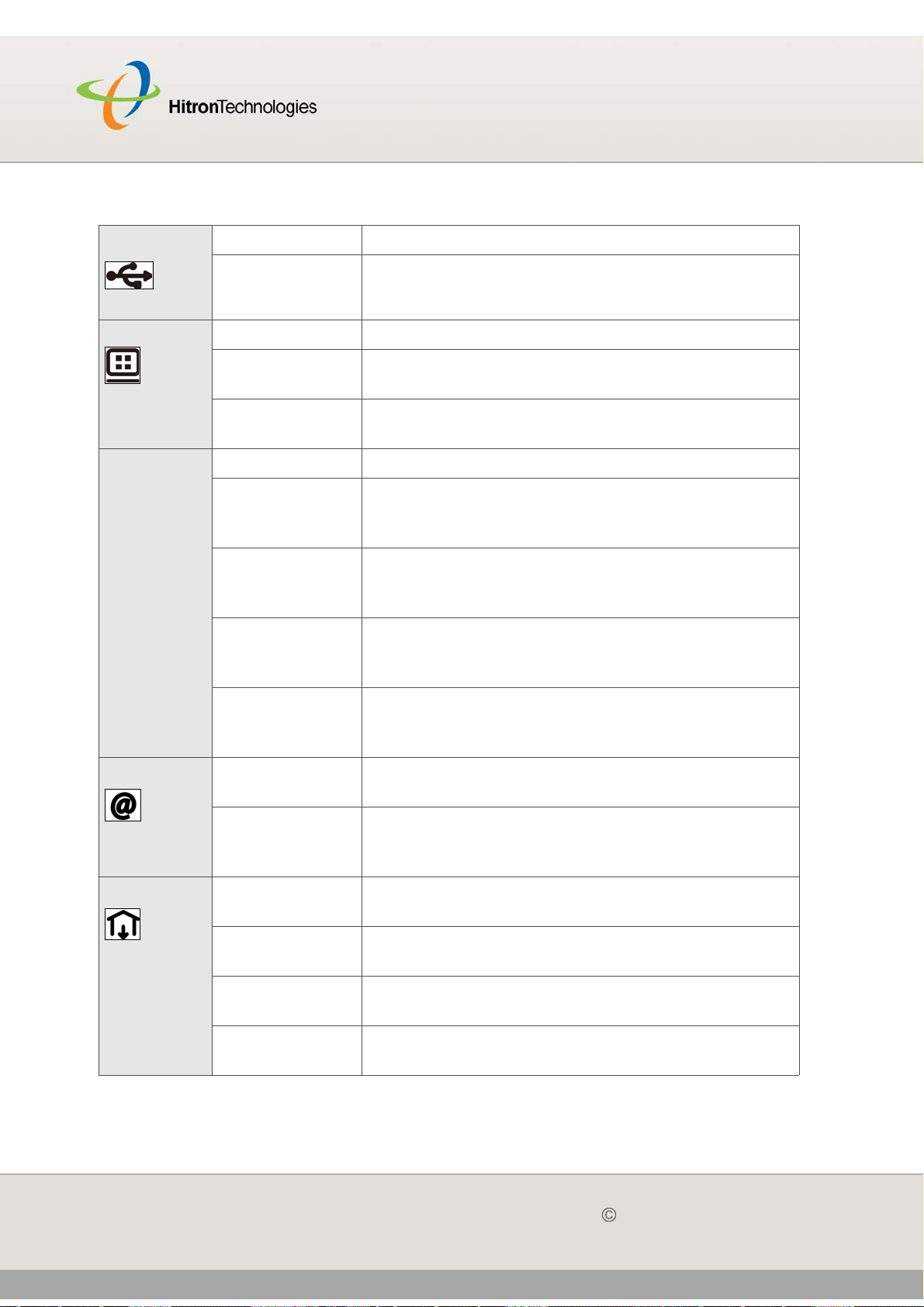
LED STATUS DESCRIPTION
WPS Off The WPS is not enabled.
Green, steady The WPS is enabled.
Red, blinking Error: Some error occurred which was not related to
security, such as failed to find any partner or
protocol prematurely aborted.
Session Overlap Detected: Protocol detected
overlapping operation could be a security risk.
Orange, blinking The protocol is searching for a partner, connecting,
or exchanging network parameters
WIRELESS Off The wireless network is not enabled.
Green, steady The wireless network is enabled, and no data is
being transmitted or received over the wireless
network.
Green, blinking The wireless network is enabled, and data is being
transmitted or received over the wireless network.
18
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
INTRODUCTION
Page 19
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
19
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Table 3: LEDs
USB Off The CGN is not linked up USB.
Green, steady The CGN has successfully linked up USB.
LAN/ Front Off No device is connected to the LAN port.
Green, blinking A device is connected to the LAN port via a
Ethernet link, and is transmitting or receiving data.
Green, steady A device has successfully connected to the LAN
port via a Ethernet link.
LAN/ Back Off No device is connected to the relevant LAN port.
Green, blinking A device is connected to the relevant LAN port via a
Fast Ethernet (10/100Mbps) link, and is transmitting
or receiving data.
Green, steady A device is connected to the relevant LAN port via a
Fast Ethernet (10/100Mbps) link, but is not
transmitting or receiving data.
Blue, blinking A device is connected to the relevant LAN port via a
Gigabit Ethernet (1000Mbps) link, and is
transmitting or receiving data.
Blue, steady A device is connected to the relevant LAN port via a
Gigabit Ethernet (1000Mbps) link, but is not
transmitting or receiving data.
Status Green, Blinking The CGN’s cabl e modem is registering with the
service provider’s CMTS.
Green The CGN’s cable modem has successfully
registered with the service provider and is ready for
data transfer.
US Green, blinking The CGN is searching for an upstream frequency
on the CABLE connection.
Green, steady The CGN has successfully located and locked onto
an upstream frequency on the CABLE connection.
Blue, steady The CGN is engaged in channel bonding on the
upstream connection.
Off There is no upstream activity on the CABLE
connection.
19
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
INTRODUCTION
Page 20
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
20
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
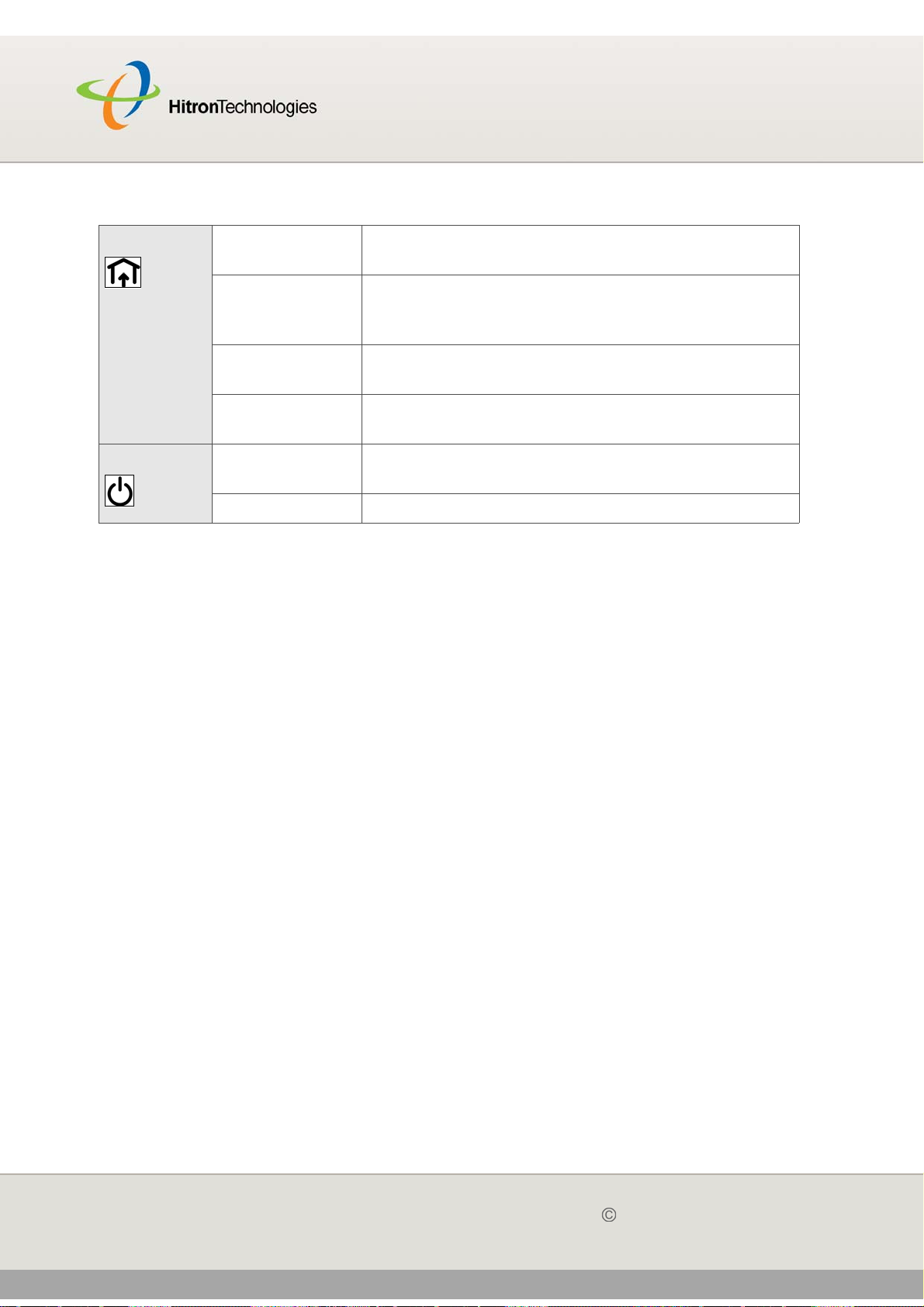
Table 3: LEDs
DS Green, blinking The CGN is searching for a downstream frequency
on the CABLE connection.
Green, steady The CGN has successfully located and locked onto
a downstream frequency on the CABLE
connection.
Blue, steady The CGN is engaged in channel bonding on the
downstream connection.
Off There is no downstream activity on the CABLE
connection.
Power Green Cable modem is plugged in to an electrical outlet
and is and receiving power
Off The CGN is not receiving power.
When you turn on the CGN, the LEDs light up in the following order:
Power
US
DS
Status
The ETH 1~4 LEDs light up as soon as there is activity on the relevant port, and
the WIRELESS LED lights up once the wireless network is ready.
USB
WIRELESS
1.4 IP ADDRESS SETUP
Before you log into the CGN’s GUI, your computer’s IP address must be in the same
subnet as the CGN. This allows your computer to communicate with the CGN.
NOTE: See IP Addresses and Subnets on page 27 for background information.
The CGN has a built-in DHCP server that, when active, assigns IP addresses to
computers on the LAN. When the DHCP server is active, you can get an IP address
automatically. The DHCP server is active by default.
20
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
INTRODUCTION
Page 21

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
21
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
If your computer is configured to get an IP address automatically, or if you are not
sure, try to log in to the CGN (see Logging into the CGN on page 22).
If the login screen displays, your computer is already configured correctly.
If the login screen does not display, either the CGN’s DHCP server is not active
or your computer is not configured correctly. Follow the procedure in Manual IP
Address Setup on page 21 and set your computer to get an IP address
automatically. Try to log in again. If you cannot log in, follow the manual IP
address setup procedure again, and set a specific IP address as shown. Try to
log in again.
NOTE: If you still cannot see the login screen, your CGN’s IP settings may have
been changed from their defaults. If you do not know the CGN’s new address,
you should return it to its factory defaults. See Resetting the CGN on page
24. Bear in mind that ALL user-configured settings are lost.
1.4.1 MANUAL IP ADDRESS SETUP
By default, your CGN’s local IP address is 192.168.0.1. If your CGN is using the
default IP address, you should set your computer’s IP address to be between
192.168.0.2 and 192.168.0.254.
NOTE: If your CGN DHCP server is active, set your computer to get an IP address
automatically in step 5. The CGN assigns an IP address to your computer.
The DHCP server is active by default.
Take the following steps to manually set up your computer’s IP address to connect to
the CGN:
NOTE: This example uses Windows XP; the procedure for your operating system
may be different.
1 Click Start, then click Control Panel.
2 In the window that displays, double-click Network Connections.
3 Right-click your network connection (usually Local Area Connection) and click
Properties.
4 In the General tab’s This connection uses the following items list, scroll
down and select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP). Click Properties.
21
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
INTRODUCTION
Page 22

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
22
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
5 You can get an IP address automatically, or specify one manually:
If your CGN’s DHCP server is active, select Get an IP address
automatically.
If your CGN’s DHCP server is active, select Use the following IP address.
In the IP address field, enter a value between 192.168.0.2 and
192.168.0.254 (default). In the Subnet mask field, enter 255.255.255.0
(default).
NOTE: If your CGN is not using the default IP address, enter an IP address and
subnet mask that places your computer in the same subnet as the CGN.
6 Click OK. The Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) window closes. In the Local Area
Connection Properties window, click OK.
Your computer now obtains an IP address from the CGN, or uses the IP address that
you specified, and can communicate with the CGN.
1.5 LOGGING INTO THE CGN
Take the following steps to log into the CGN’s GUI.
NOTE: You can log into the CGN’s GUI via the wireless interface. However, it is
strongly recommended that you configure the CGN via a wired connection on
the LAN.
1 Open a browser window.
2 Enter the CGN’s IP address (default 192.168.0.1) in the URL bar. The Login
screen displays.
22
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
INTRODUCTION
Page 23
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
23
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Figure 4: Login
3 Enter the Username and Password. The default login username is cusadmin,
and the default password is password.
NOTE: The Username and Password are case-sensitive; “password” is not the same
as “Password”.
4 Click Login. The System Info screen displays (see The System Info Screen on
page 33).
1.6 GUI OVERVIEW
This section describes the CGN’s GUI.
23
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
INTRODUCTION
Page 24

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
24
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Figure 5: GUI Overview
Table 4: GUI Overview
Primary
Navigation Bar
Secondary
Navigation Bar
Main Window Use this section to read information about your CGN’s
Each item in the Primary Navigation Bar has its own chapter in this User's Guide;
items in the Secondary Navigation Bar have their own section within a chapter.
Use this section to move from one part of the GUI to another.
Use this section to move from one related screen to another.
configuration, and make configuration changes.
1.7 RESETTING THE CGN
When you reset the CGN to its factory defaults, all user-configured settings are lost,
and the CGN is returned to its initial configuration state.
There are two ways to reset the CGN:
Press the RESET button on the CGN, and hold it in for ten seconds or longer.
24
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
INTRODUCTION
Page 25

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
25
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Click WAN/LAN > Backup. In the screen that displays, click the Factory Reset
button.
The CGN turns off and on again, using its factory default settings.
NOTE: Depending on your CGN’s previous configuration, you may need to re-
configure your computer’s IP settings; see IP Address Setup on page 20.
25
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
INTRODUCTION
Page 26

STATUS
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
26
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
2
STATUS
This chapter describes the screens that display when you click Status in the toolbar.
It contains the following sections:
Cable Overview on page 26
The System Info Screen on page 33
The Initialization Screen on page 37
The CM Status Screen on page 38
The Password Screen on page 41
The Capability Screen on page 42
2.1 CABLE OVERVIEW
This section describes some of the concepts related to the Cable screens.
2.1.1 DOCSIS
The Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification (DOCSIS) is a
telecommunications standard that defines the provision of data services) Internet
access) over a traditional cable TV (CATV) network.
Your CGN supports DOCSIS version 3.0.
Page 27

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
27
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
2.1.2 IP ADDRESSES AND SUBNETS
Every computer on the Internet must have a unique Internet Protocol (IP) address.
The IP address works much like a street address, in that it identifies a specific
location to which information is transmitted. No two computers on a network can have
the same IP address.
2.1.2.1 IP ADDRESS FORMAT
IP addresses consist of four octets (8-bit numerical values) and are usually
represented in decimal notation, for example 192.168.1.1. In decimal notation, this
means that each octet has a minimum value of 0 and a maximum value of 255.
An IP address carries two basic pieces of information: the “network number” (the
address of the network as a whole, analogous to a street name) and the “host ID”
(analogous to a house number) which identifies the specific computer (or other
network device).
2.1.2.2 IP ADDRESS ASSIGNMENT
IP addresses can come from three places:
The Internet Assigned Numbers Agency (IANA)
Your Internet Service Provider
You (or your network devices)
IANA is responsible for IP address allocation on a global scale, and your ISP assigns
IP addresses to its customers. You should never attempt to define your own IP
addresses on a public network, but you are free to do so on a private network.
In the case of the CGN:
The public network (Wide Area Network or WAN) is the link between the cable
connector and your Internet Service Provider. Your CGN’s IP address on this
network is assigned by your service provider.
27
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
STATUS
Page 28

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
28
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
The private network (in routing mode - see Routing Mode on page 31) is your
Local Area Network (LAN) and Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN), if
enabled. You are free to assign IP addresses to computers on the LAN and
WLAN manually, or to allow the CGN to assign them automatically via DHCP
(Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol). IANA has reserved the following blocks
of IP addresses to be used for private networks only:
Table 5: Private IP Address Ranges
FROM... ...TO
10.0.0.0 10.255.255.255
172.16.0.0 172.31.255.255
192.168.0.0 192.168.255.255
If you assign addresses manually, they must be within the CGN’s LAN subnet.
2.1.2.3 SUBNETS
A subnet (short for sub-network) is, as the name suggests, a separate section of a
network, distinct from the main network of which it is a part. A subnet may contain all
of the computers at one corporate local office, for example, while the main network
includes several offices.
In order to define the extent of a subnet, and to differentiate it from the main network,
a subnet mask is used. This “masks” the part of the IP address that refers to the main
network, leaving the part of the IP address that refers to the sub-network.
Each subnet mask has 32 bits (binary digits), as does each IP address:
A binary value of 1 in the subnet mask indicates that the corresponding bit in the
IP address is part of the main network.
A binary value of 0 in the subnet mask indicates that the corresponding bit in the
IP address is part of the sub-network.
For example, the following table shows the IP address of a computer (192.168.1.1)
expressed in decimal and binary (each cell in the table indicates one octet):
Table 6: IP Address: Decimal and Binary
192 168 0 1
11000000 10101000 00000000 00000001
28
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
STATUS
Page 29

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
29
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
The following table shows a subnet mask that “masks” the first twenty-four bits of the
IP address, in both its decimal and binary notation.
Table 7: Subnet Mask: Decimal and Binary
255 255 255 0
11111111 11111111 11111111 00000000
This shows that in this subnet, the first three octets (192.168.1, in the example IP
address) define the main network, and the final octet (1, in the example IP address)
defines the computer’s address on the subnet.
The decimal and binary notations give us the two common ways to write a subnet
mask:
Decimal: the subnet mask is written in the same fashion as the IP address:
255.255.255.0, for example.
Binary: the subnet mask is indicated after the IP address (preceded by a forward
slash), specifying the number of binary digits that it masks. The subnet mask
255.255.255.0 masks the first twenty-four bits of the IP address, so it would be
written as follows: 192.168.1.1/24.
2.1.3 DHCP
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, or DHCP, defines the process by which IP
addresses can be assigned to computers and other networking devices
automatically, from another device on the network. This device is known as a DHCP
server, and provides addresses to all the DHCP client devices.
In order to receive an IP address via DHCP, a computer must first request one from
the DHCP server (this is a broadcast request, meaning that it is sent out to the whole
network, rather than just one IP address). The DHCP server hears the requests, and
responds by assigning an IP address to the computer that requested it.
If a computer is not configured to request an IP address via DHCP, you must
configure an IP address manually if you want to access other computers and devices
on the network. See IP Address Setup on page 20 for more information.
By default, the CGN is a DHCP client on the WAN (the CATV connection). It
broadcasts an IP address over the cable network, and receives one from the service
provider. By default, the CGN is a DHCP server on the LAN; it provides IP addresses
to computers on the LAN which request them.
29
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
STATUS
Page 30

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
30
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
2.1.4 DHCP LEASE
“DHCP lease” refers to the length of time for which a DHCP server allows a DHCP
client to use an IP address. Usually, a DHCP client will request a DHCP lease
renewal before the lease time is up, and can continue to use the IP address for an
additional period. However, if the client does not request a renewal, the DHCP server
stops allowing the client to use the IP address.
This is done to prevent IP addresses from being used up by computers that no longer
require them, since the pool of available IP addresses is finite.
2.1.5 MAC ADDRESSES
Every network device possesses a Media Access Control (MAC) address. This is a
unique alphanumeric code, given to the device at the factory, which in most cases
cannot be changed (although some devices are capable of “MAC spoofing”, where
they impersonate another device’s MAC address).
MAC addresses are the most reliable way of identifying network devices, since IP
addresses tend to change over time (whether manually altered, or updated via
DHCP).
Each MAC address displays as six groups of two hexadecimal digits separated by
colons (or, occasionally, dashes) for example 00:AA:FF:1A:B5:74.
NOTE: Each group of two hexadecimal digits is known as an “octet”, since it
represents eight bits.
Bear in mind that a MAC address does not precisely represent a computer on your
network (or elsewhere), it represents a network device, which may be part of a
computer (or other device). For example, if a single computer has an Ethernet card
(to connect to your CGN via one of the LAN ports) and also has a wireless card (to
connect to your CGN over the wireless interface) the MAC addresses of the two
cards will be different. In the case of the CGN, each internal module (cable modem
module, Ethernet module, wireless module, etc.) possesses its own MAC address.
30
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
STATUS
Page 31

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
31
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
2.1.6 ROUTING MODE
When your CGN is in routing mode, it acts as a gateway for computers on the LAN to
access the Internet. The service provider assigns an IP address to the CGN on the
WAN, and all traffic for LAN computers is sent to that IP address. The CGN assigns
private IP addresses to LAN computers (when DHCP is active), and transmits the
relevant traffic to each private IP address.
NOTE: When DHCP is not active on the CGN in routing mode, each computer on the
LAN must be assigned an IP address in the CGN’s subnet manually.
When the CGN is not in routing mode, the service provider assigns an IP address to
each computer connected to the CGN directly. The CGN does not perform any
routing operations, and traffic flows between the computers and the service provider.
Routing mode is not user-configurable; it is specified by the service provider in the
CGN’s configuration file.
2.1.7 CONFIGURATION FILES
The CGN’s configuration (or config) file is a document that the CGN obtains
automatically over the Internet from the service provider’s server, which specifies the
settings that the CGN should use. It contains a variety of settings that are not present
in the user-configurable Graphical User Interface (GUI) and can be specified only by
the service provider.
2.1.8 DOWNSTREAM AND UPSTREAM TRANSMISSIONS
The terms “downstream” and “upstream” refer to data traffic flows, and indicate the
direction in which the traffic is traveling. “Downstream” refers to traffic from the
service provider to the CGN, and “upstream” refers to traffic from the CGN to the
service provider.
2.1.9 CABLE FREQUENCIES
Just like radio transmissions, data transmissions over the cable network must exist
on different frequencies in order to avoid interference between signals.
The data traffic band is separate from the TV band, and each data channel is
separate from other data channels.
31
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
STATUS
Page 32

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
32
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
2.1.10 MODULATION
Transmissions over the cable network are based on a strong, high frequency periodic
waveform known as the “carrier wave.” This carrier wave is so called because it
“carries” the data signal. The data signal itself is defined by variations in the carrier
wave. The process of varying the carrier wave (in order to carry data signal
information) is known as “modulation.” The data signal is thus known as the
“modulating signal.”
Cable transmissions use a variety of methods to perform modulation (and the
“decoding” of the received signal, or “demodulation”). The modulation methods
defined in DOCSIS 3 are as follows:
QPSK: Quadrature Phase-Shift Keying
QAM: Quadrature Amplitude Modulation
QAM TCM: Trellis modulated Quadrature Amplitude Modulation
In many cases, a number precedes the modulation type (for example 16 QAM). This
number refers to the complexity of modulation. The higher the number, the more data
can be encoded in each symbol.
NOTE: In modulated signals, each distinct modulated character (for example, each
audible tone produced by a modem for transmission over telephone lines) is
known as a symbol.
Since more information can be represented by a single character, a higher number
indicates a higher data transfer rate.
2.1.11 TDMA, FDMA AND SCDMA
Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA), Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA)
and Synchronous Code Division Multiple Access (SCDMA) are channel access
methods that allow multiple users to share the same frequency channel.
TDMA allows multiple users to share the same frequency channel by splitting
transmissions by time. Each user is allocated a number of time slots, and
transmits during those time slots.
FDMA allows multiple users to share the same frequency channel by assigning a
frequency band within the existing channel to each user.
32
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
STATUS
Page 33

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
33
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
SCDMA allows multiple users to share the same frequency channel by assigning
a unique orthogonal code to each user.
2.2 THE SYSTEM INFO SCREEN
Use this screen to see general information about your CGN’s hardware, its software,
and its connection to the Internet.
NOTE: Most of the information that displays in this screen is for troubleshooting
purposes only. However, you may need to use the MAC Address information
when setting up your network.
Click Status > System Info. The following screen displays.
33
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
STATUS
Page 34

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
34
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Figure 6: The Status > System Info Screen
34
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
STATUS
Page 35
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
35
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 8: The Status > System Info Screen
Device Information
System Time This displays the current date and time.
System Uptime This displays the number of days, hours, minutes and
seconds since the CGN was last switched on or rebooted.
Model Name This displays the device’s model name.
SW Version This displays the version number of the software that
controls the CGN.
HW Version This displays the version number of the CGN’s physical
hardware.
RF MAC This displays the Media Access Control (MAC) address of
the CGN’s RF module. This is the module that connects to
the Internet through the CATV connection.
Serial Number This displays a number that uniquely identifies the device.
RG Status This displays whether or not the CGN is in Residential
Gateway (RG) mode.
When the CGN is in Residential Gateway mode, ON
displays. When the CGN is not in Residential Gateway
mode, OFF displays.
Wifi Status This displays whether or not the CGN’s wireless network
is active.
When the CGN’s wireless network is active, ON displays.
When the CGN’s wireless network is not active, OFF
displays.
NAT Status This displays whether or not the CGN’s Network Address
Translation (NAT) feature is active.
When NAT is active, ON displays. When NAT is not active,
OFF displays.
DHCP Status This displays whether or not the CGN’s DHCP server is
active.
When the DHCP server is active, ON displays. When the
DHCP server is not active, OFF displays.
Firewall Status This displays whether or not the CGN’s firewall is active.
When the firewall is active, ON displays. When the firewall
is not active, OFF displays.
35
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
STATUS
Page 36

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
36
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Table 8: The Status > System Info Screen (continued)
WAN Information
WAN Address This field displays the CGN’s IP address on the WAN
(Wide Area Network) interface.
Subnet Mask This field displays the CGN’s WAN subnet mask.
Gateway Address This field displays the address of the device on the WAN
to which the CGN is connected.
DNS Server This field displays the Domain Name Servers that the
CGN uses to resolve domain names into IP addresses.
Uptime This displays the number of hours, minutes and seconds
that the CGN has been connected to another device over
the WAN interface.
Traffic Count This displays the number of bytes received and sent on
the WAN interface.
Wireless Information
SSID This displays the wireless network’s Service Set Identifier.
This is the name of the wireless network, to which wireless
clients connect.
Wireless Mode This displays the type of wireless network that the CGN is
using.
Channel This displays the wireless channel on which the CGN is
transmitting and receiving.
Security Type This displays the type of security the CGN’s wireless
network is currently using.
Cipher type This displays the type of encryption that the wireless
network’s security is using:
TKIP displays if it is using the Temporal Key Integrity
Protocol.
AES displays if it is using the Advanced Encryption
Standard.
TKIP and AES displays if it allows clients using either
encryption type to connect to the CGN.
SSID MAC This displays the Media Access Control (MAC) address of
the wireless module, to which wireless clients connect.
LAN Status
MAC Address This displays the Media Access Control (MAC) address of
the CGN’s Ethernet module. This is the module to which
you connect through the LAN ports.
36
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
STATUS
Page 37

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
37
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Table 8: The Status > System Info Screen (continued)
Private LAN IP
Address
Subnet Mask This displays the CGN’s LAN subnet mask.
Uptime This displays the number of hours, minutes and seconds
Traffic Count This displays the number of bytes received and sent on
This displays the IP address of the CGN’s Ethernet
module. This is the IP address you use to connect with the
CGN’s admin interface via the LAN ports.
that the CGN has been connected to another device over
the LAN interface.
the LAN interface.
2.3 THE INITIALIZATION SCREEN
This screen displays the steps successfully taken to connect to the Internet over the
CABLE connection.
Use this screen for troubleshooting purposes to ensure that the CGN has
successfully connected to the Internet; if an error has occurred you can identify the
stage at which the failure occurred.
NOTE: This screen displays when you first log in to the CGN.
Click Status > Initialization. The following screen displays.
Figure 7: The Status > Initialization Screen
37
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
STATUS
Page 38

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
38
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
For each step:
Process displays when the CGN is attempting to complete a connection step.
Success displays when the CGN has completed a connection step.
2.4 THE CM STATUS SCREEN
Use this screen to discover information about:
The nature of the upstream and downstream connection between the CGN and
the device to which it is connected through the CABLE interface.
IP details of the CGN’s WAN connection.
You can also configure the CGN’s downstream center frequency.
Click Status > CM Status. The following screen displays.
38
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
STATUS
Page 39
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
39
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
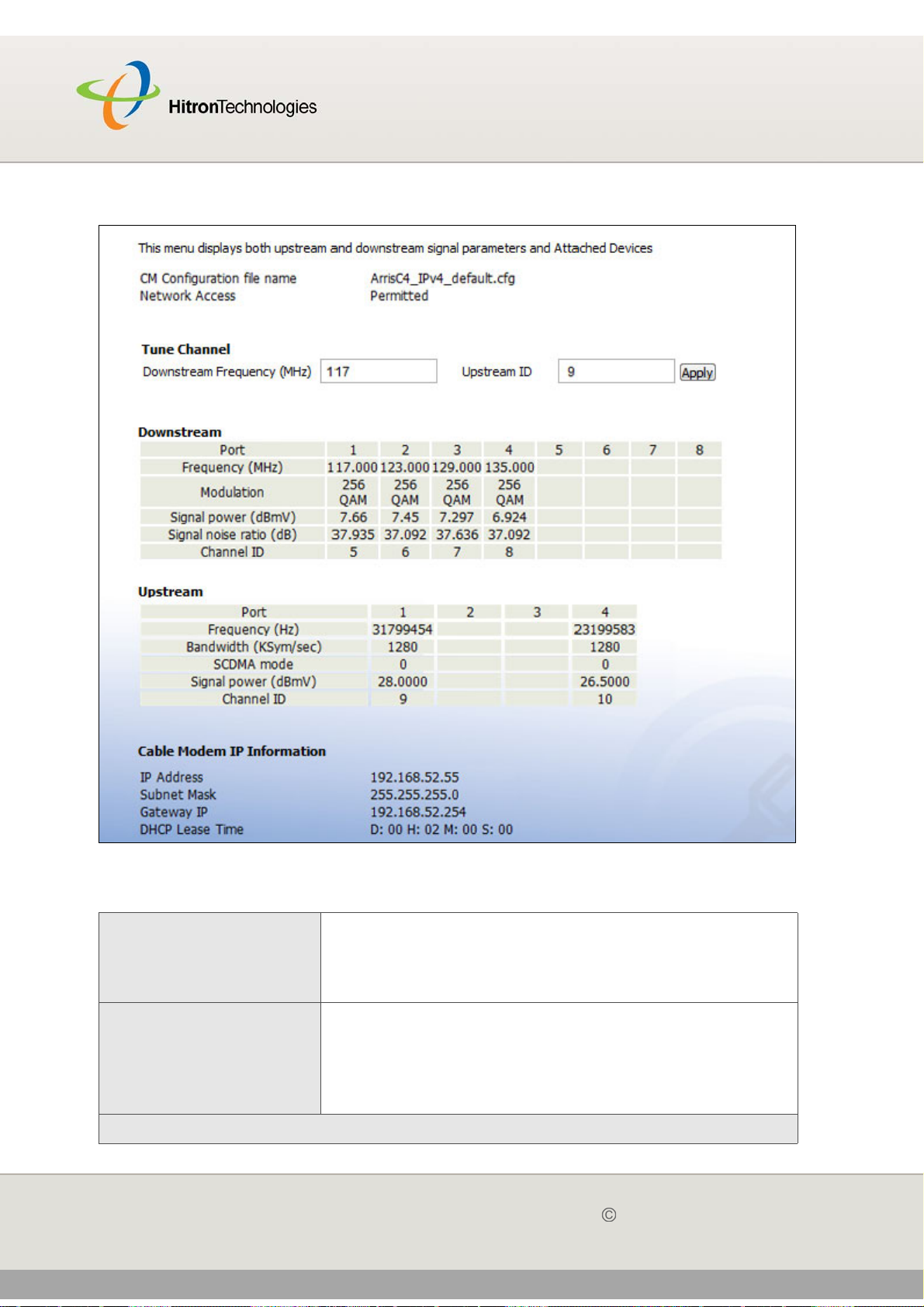
Figure 8: The Status > CM Status Screen
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 9: The Status > CM Status Screen
CM Configuration File
Name
This displays the name of the configuration file that the
CGN downloaded from your service provider. This file
provides the CGN with the service parameter data that it
needs to perform its functions correctly.
Network Access This displays whether or not your service provider allows
you to access the Internet over the CABLE connection.
Permitted displays if you can access the Internet.
Denied displays if you cannot access the Internet.
Tune Channel
39
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
STATUS
Page 40

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
40
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Table 9: The Status > CM Status Screen (continued)
Downstream Frequency This displays the center frequency in Megahertz (MHz)
at which the CGN connects over the CABLE interface.
If you want the CGN to use a different center frequency,
enter it in the field and click Apply.
NOTE: Do not change the frequency unless you have a
good reason to do so.
Upstream ID This displays the ID number of the channel on which the
upstream signal is to be transmitted. When an upstram
connection cannot be made on the specified channel,
the CGN attempts to connect on the next channel.
If you want the CGN to attempt to connect on a different
channel, enter it in the field and click Apply.
NOTE: Do not change the channel unless you have a
good reason to do so.
Downstream
NOTE: The downstream signal is the signal transmitted to the CGN.
Frequency (MHz) This displays the actual frequency in Megahertz (MHz)
of each downstream data channel to which the CGN is
connected.
Modulation This displays the type of modulation that each
downstream channel uses.
Signal Power (dBmV) This displays the power of the signal of each
downstream data channel to which the CGN is
connected, in dBmV (decibels above/below 1 millivolt).
Signal Noise Ratio
(dB)
This displays the Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) of each
downstream data channel to which the CGN is
connected, in dB (decibels).
Upstream
NOTE: The upstream signal is the signal transmitted from the CGN.
Frequency (Hz) This displays the frequency in Herz (Hz) of each
upstream data channel to which the CGN is connected.
Bandwidth (KSym/
sec)
This displays the bandwidth of each upstream data
channel to which the CGN is connected (in thousands of
symbols per second).
40
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
STATUS
Page 41
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
41
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Table 9: The Status > CM Status Screen (continued)
SCDMA Mode This displays the Synchronous Code Division Multiple
Access (SCDMA) mode of each channel on which the
upstream signal is transmitted.
Signal Power (dBmV) This displays the transmitted power of the signal of each
upstream data channel to which the CGN is connected,
in dBmV (decibels above/below 1 millivolt).
Channel ID This displays the ID number of each channel on which
the upstream signal is transmitted.
Cable Modem IP Information
IP Address This displays the CGN’s WAN IP address. This IP
address is automatically assigned to the CGN
Subnet Mask This displays the CGN’s WAN subnet mask.
Gateway IP This displays the IP address of the device to which the
CGN is connected over the CABLE interface.
DHCP Lease Time This displays the time that elapses before your device’s
IP address lease expires, and a new IP address is
assigned to it by the DHCP server.
2.5 THE PASSWORD SCREEN
Use this screen to change the password with which you log in to the CGN.
NOTE: If you forget your password, you will need to reset the CGN to its factory
defaults.
Click Status > Password. The following screen displays.
41
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
STATUS
Page 42

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
42
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Figure 9: The Status > Password Screen
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 10: The Status > Password Screen
Enter Current Password Enter the password with which you currently log into the
CGN
Enter New Password Enter and re-enter the password you want to use to log
Re-enter New Password
into the CGN.
Password Idle Time Enter the number of minutes of inactivity after which you
should be automatically logged out of the CGN. Once
this period elapses, you will need to log in again.
Apply Click this to save your changes to the fields in this
screen.
Cancel Click this to return the fields in this screen to their last-
saved values without saving your changes.
Help Click this to see information about the fields in this
screen.
2.6 THE CAPABILITY SCREEN
Use this screen to enable or disable the CGN’s residential gateway and Universal
Plug n Play (UPnP) functions.
Disabling the residential gateway feature sets the unit to use bridge mode only. Use
this mode when your network is already using another router.
42
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
STATUS
Page 43

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
43
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Click Status > Capability. The following screen displays.
Figure 10: The Status > Capability Screen
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 11: The Status > Capability Screen
Residential Gateway
function
Select the checkbox to enable the CGN’s residential
gateway features, or deselect the checkbox to disable
them.
UPnP Select the checkbox to enable the CGN’s Universal Plug
n Play features, or deselect the checkbox to disable
them.
HNAP Select the checkbox to enable the CGN’s Home
Network Administration Protocol features, or deselect
the checkbox to disable them.
USB Select the checkbox to enable the CGN’s USB media
sharing capability, or deselect the checkbox to disable
them.
NOTE: This option is available to logged-in MSO users
only.
When you select this checkbox and apply your changes,
the CGN reboots. Once it has successfully rebooted, the
WAN/LAN > Shared Media screen displays in the
cusadmin user interface.
Apply Click this to save your changes to the fields in this
screen.
Cancel Click this to return the fields in this screen to their last-
saved values without saving your changes.
Help Click this to see information about the fields in this
screen.
43
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
STATUS
Page 44

44
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
44
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
STATUS
Page 45

WAN/LAN
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
45
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
3
WAN/LAN
This chapter describes the screens that display when you click WAN/LAN in the
toolbar. It contains the following sections:
WAN/LAN Overview on page 45
The IP Screen on page 47
The Shared Media Screen on page 50
The Debug Screen on page 51
The Backup Screen on page 52
3.1 WAN/LAN OVERVIEW
This section describes some of the concepts related to the WAN/LAN screens.
3.1.1 WAN AND LAN
A Local Area Network (LAN) is a network of computers and other devices that usually
occupies a small physical area (a single building, for example). Your CGN’s LAN
consists of all the computers and other networking devices connected to the LAN 1~4
ports. This is your private network (in routing mode - see Routing Mode on page 31).
The LAN is a separate network from the Wide Area Network (WAN). In the case of
the CGN, the WAN refers to all computers and other devices available on the cable
connection.
By default, computers on the WAN cannot identify individual computers on the LAN;
they can see only the CGN. The CGN handles routing to and from individual
computers on the LAN.
Page 46

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
46
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
3.1.2 LAN IP ADDRESSES AND SUBNETS
IP addresses on the LAN are controlled either by the CGN’s built-in DHCP server
(see DHCP on page 29), or by you (when you manually assign IP addresses to your
computers).
For more information about IP addresses and subnets in general, see IP Addresses
and Subnets on page 27.
3.1.3 DNS AND DOMAIN SUFFIX
A domain is a location on a network, for instance example.com. On the Internet,
domain names are mapped to the IP addresses to which they should refer by the
Domain Name System. This allows you to enter “www.example.com” into your
browser and reach the correct place on the Internet even if the IP address of the
website’s server has changed.
Similarly, the CGN allows you to define a Domain Suffix to the LAN. When you enter
the domain suffix into your browser, you can reach the CGN no matter what IP
address it has on the LAN.
3.1.4 DEBUGGING (PING AND TRACEROUTE)
The CGN provides a couple of tools to allow you to perform network diagnostics on
the LAN:
Ping: this tool allows you to enter an IP address and see if a computer (or other
network device) responds with that address on the network. The name comes
from the pulse that submarine SONAR emits when scanning for underwater
objects, since the process is rather similar. You can use this tool to see if an IP
address is in use, or to discover if a device (whose IP address you know) is
working properly.
Traceroute: this tool allows you to see the route taken by data packets to get
from the CGN to the destination you specify. You can use this tool to solve
routing problems, or identify firewalls that may be blocking your access to a
computer or service.
46
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
WAN/LAN
Page 47

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
47
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
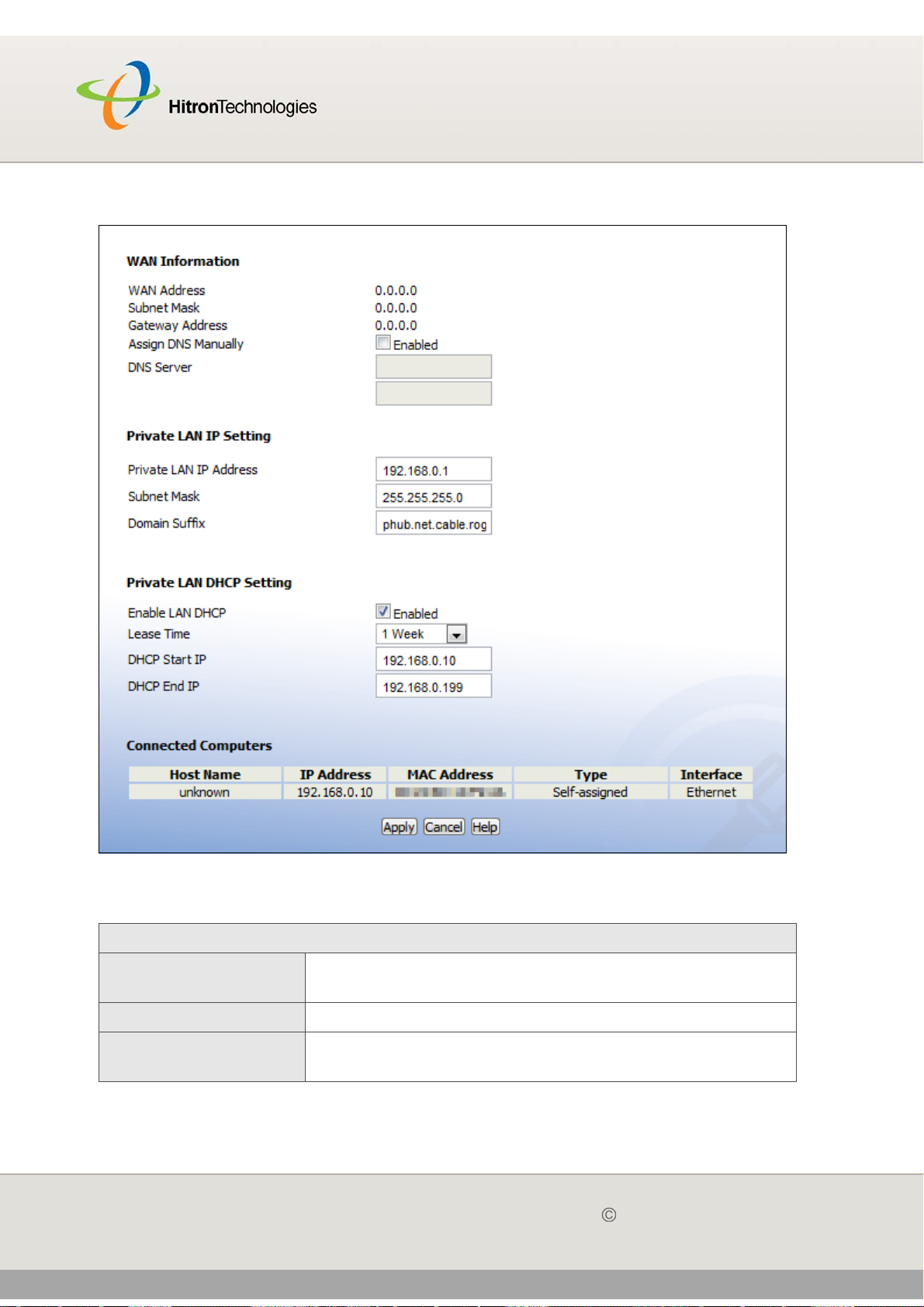
3.2 THE IP SCREEN
Use this screen to:
View information about the CGN’s connection to the WAN
Enable or disable manual DNS assignment
Define DNS servers for manual DNS assignment
Configure the CGN’s LAN IP address, subnet mask and domain suffix
Configure the CGN’s internal DHCP server
Define how the CGN assigns IP addresses on the LAN
See information about the network devices connected to the CGN on the LAN.
Click WAN/LAN > IP. The following screen displays.
47
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
WAN/LAN
Page 48
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
48
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Figure 11: The WAN/LAN > IP Screen
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 12: The WAN/LAN > IP Screen
WAN Information
WAN Address This field displays the CGN’s IP address on the WAN
(Wide Area Network) interface.
Subnet Mask This field displays the CGN’s WAN subnet mask.
Gateway Address This field displays the address of the device on the WAN
to which the CGN is connected.
48
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
WAN/LAN
Page 49

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
49
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Table 12: The WAN/LAN > IP Screen (continued)
Assign DNS
Manually
Select the checkbox to enable manual DNS server
assignment, and enter the DNS servers that you want
to use in the DNS Server fields below.
Deslect the checkbox to disable manual DNS server
assignment. The CGN uses the DNS servers assigned
automatically when it receives an IP address over the
WAN.
It is strongly recommended that you do not enable manual
DNS server assignment unless you have good reason to
do so.
DNS Server These fields display the Domain Name Servers that the
CGN uses to resolve domain names into IP addresses.
If you selected the Assign DNS Manually checkbox,
enter the DNS servers that you want to use in these fields.
Private LAN IP Setting
IP Address Use this field to define the IP address of the CGN on the
LAN.
Subnet Mask Use this field to define the LAN subnet. Use dotted
decimal notation (for example, 255.255.255.0).
Domain Suffix Use this field to define the domain that you can enter into a
Web browser (instead of an IP address) to reach the CGN
on the LAN.
It is suggested that you make a note of your device’s
Domain Suffix in case you ever need to access the
CGN’s GUI without knowledge of its IP address.
Private LAN DHCP Setting
Enable LAN DHCP Select this if you want the CGN to provide IP addresses to
network devices on the LAN automatically.
Deselect this if you already have a DHCP server on your
LAN, or if you wish to assign IP addresses to your
computers and other network devices manually.
Lease Time Use this field to define the time after which the CGN
renews the IP addresses of all the network devices
connected to the CGN on the LAN (when DHCP is
enabled).
DHCP Start IP Use this field to specify the IP address at which the CGN
begins assigning IP addresses to devices on the LAN
(when DHCP is enabled).
49
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
WAN/LAN
Page 50
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
50
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Table 12: The WAN/LAN > IP Screen (continued)
DHCP End IP Use this field to specify the IP address at which the CGN
stops assigning IP addresses to devices on the LAN
(when DHCP is enabled).
NOTE: Devices requesting IP addresses once the DHCP
pool is exhausted are not assigned an IP address.
Connected Computers
Host Name This displays the name of each network device connected
on the LAN.
IP Address This displays the IP address of each network device
connected on the LAN.
MAC Address This displays the Media Access Control (MAC) address of
each network device connected on the LAN.
Type This displays whether the device’s IP address was
assigned by DHCP (DHCP-IP), or self-assigned.
Interface This displays whether the device is connected on the LAN
(Ethernet) or the WLAN (Wireless(x), where x denotes
the wireless mode; b, g or n).
Apply Click this to save your changes to the fields in this screen.
Cancel Click this to return the fields in this screen to their last-
saved values without saving your changes.
Help Click this to see information about the fields in this screen.
3.3 THE SHARED MEDIA SCREEN
Use this screen to manage and share data stored on devices connected to the CGN’s
USB port. The CGN provides one USB 2.0 host port, allowing you to plug in a USB
flash disk for mounting and sharing through the LAN interfaces via the Samba
protocol (network neighborhood).
NOTE: This screen is not available unless a logged-in MSO admin user previously
enabled the USB option in the Status > Capability screen; see The
Capability Screen on page 42 for more information.
Click WAN/LAN > Shared Media. The following screen displays.
50
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
WAN/LAN
Page 51

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
51
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Figure 12: The WAN/LAN > Shared Media Screen
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 13: The WAN/LAN > Shared Media Screen
Group ID Specify the name of the Network Neighborhood
workgroup whose users may access the shared media
on the USB device.
No. This field displays the index number of the connected
USB device.
When no USB device is connected, no number displays
in this column.
Name This field displays the identifying name of the connected
USB device.
When no USB device is connected, no name
displays in this column.
When a USB device is connected, click its Name to
view the files on the device. These files are shared
with the relevant user group (defined in the Group ID
field).
Apply Click this to save your changes to the fields in this
screen.
Refresh Click this to reload the information in this screen. Do this
if you connect or disconnect a device from the USB port
and the information in this screen does not update
automatically.
Help Click this to see information about the fields in this
screen.
3.4 THE DEBUG SCREEN
Use this screen to perform ping and traceroute tests on IP addresses or URLs.
51
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
WAN/LAN
Page 52

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
52
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Click WAN/LAN > Debug. The following screen displays.
Figure 13: The WAN/LAN > Debug Screen
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 14: The WAN/LAN > Debug Screen
IP/URL Enter the IP address or URL that you want to test.
Method Select the type of test that you want to run on the IP/
URL that you specified.
Run Click this to perform the test.
Help Click this to see information about the fields in this
screen.
3.5 THE BACKUP SCREEN
Use this screen to back up your CGN’s settings to your computer, to load settings
from a backup you created earlier, to reboot your CGN, or to return it to its factory
default settings.
Click WAN/LAN > Backup. The following screen displays.
52
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
WAN/LAN
Page 53

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
53
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Figure 14: The WAN/LAN > Backup Screen
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 15: The LAN > Backup Screen
Backup/Restore Setting
Backup Settings
Locally
Restore Settings
Locally
Click this to create a backup of all your CGN’s settings
on your computer.
Use these fields to return your CGN’s settings to those
specified in a backup that you created earlier.
Click Choose File to select a backup, then click
Restore to return your CGN’s settings to those specified
in the backup.
Reboot/Factory Reset
Reboot Click Reboot to restart your CGN.
Factory Reset Click Factory to return your CGN to its factory default
settings.
NOTE: When you do this, all your user-configured
settings are lost, and cannot be retrieved.
Help Click this to see information about the fields in this
screen.
53
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
WAN/LAN
Page 54

FIREWALL
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
54
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
FIREWALL
This chapter describes the screens that display when you click Firewall in the
toolbar. It contains the following sections:
Firewall Overview on page 54
The Firewall Options Screen on page 56
The Filter Setting Screen on page 57
The Forwarding Screen on page 65
The Port Triggering Screen on page 69
The DMZ Screen on page 72
4
4.1 FIREWALL OVERVIEW
This section describes some of the concepts related to the Firewall screens.
4.1.1 FIREWALL
The term “firewall” comes from a construction technique designed to prevent the
spread of fire from one room to another. Similarly, your CGN’s firewall prevents
intrusion attempts and other undesirable activity originating from the WAN, keeping
the computers on your LAN safe. You can also use filtering techniques to specify the
computers and other devices you want to allow on the LAN, and prevent certain traffic
from going from the LAN to the WAN.
Page 55

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
55
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
4.1.2 INTRUSION DETECTION SYSTEM
An intrusion detection system monitors network activity, looking for policy violations,
and malicious or suspicious activity. The CGN’s intrusion detection system logs all
such activity to the Firewall > Local Logs screen.
4.1.3 PING
The CGN allows you to use the ping utility on the LAN (in the WAN/LAN > Debug
screen) and also on the WAN (in the Firewall > Firewall Options screen). For more
information, see Debugging (Ping and Traceroute) on page 46.
4.1.4 MAC FILTERING
Every networking device has a unique Media Access Control (MAC) address that
identifies it on the network. When you enable MAC address filtering on the CGN’s
firewall, you can set up a list of MAC addresses, and then specify whether you want
to:
Deny the devices on the list access to the CGN and the network (in which case
all other devices can access the network)
or
Allow the devices on the list to access the network (in which case no other
devices can access the network)
4.1.5 IP FILTERING
IP filtering allows you to prevent computers on the LAN from sending certain types of
data to the WAN. You can use this to prevent unwanted outgoing communications.
Specify the IP address of the computer on the LAN from which you want to prevent
communications, and specify the port range of the communications you want to
prevent. The CGN discards outgoing data packets that match the criteria you
specified.
55
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
FIREWALL
Page 56

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
56
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
4.1.6 PORT FORWARDING
Port forwarding allows a computer on your LAN to receive specific communications
from the WAN. Typically, this is used to allow certain applications (such as gaming)
through the firewall, for a specific computer on the LAN. Port forwarding is also
commonly used for running a public HTTP server from a private network.
You can set up a port forwarding rule for each application for which you want to open
ports in the firewall. When the CGN receives incoming traffic from the WAN with a
destination port that matches a port forwarding rule, it forwards the traffic to the LAN
IP address and port number specified in the port forwarding rule.
NOTE: For information on the ports you need to open for a particular application,
consult that application’s documentation.
4.1.7 PORT TRIGGERING
Port triggering is a means of automating port forwarding. The CGN scans outgoing
traffic (from the LAN to the WAN) to see if any of the traffic’s destination ports match
those specified in the port triggering rules you configure. If any of the ports match, the
CGN automatically opens the incoming ports specified in the rule, in anticipation of
incoming traffic.
4.1.8 DMZ
In networking, the De-Militarized Zone (DMZ) is a part of your LAN that has been
isolated from the rest of the LAN, and opened up to the WAN. The term comes from
the military designation for a piece of territory, usually located between two opposing
forces, that is isolated from both and occupied by neither.
4.2 THE FIREWALL OPTIONS SCREEN
Use this screen to turn firewall features on or off. You can enable or disable the
CGN’s intrusion detection system, and allow or prevent responses to ICMP requests
from the WAN.
Click Firewall > Firewall Options. The following screen displays.
56
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
FIREWALL
Page 57

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
57
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Figure 15: The Firewall > Firewall Options Screen
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 16: The Firewall > Firewall Options Screen
Firewall
Select this to turn the firewall on.
Deselect this to turn the firewall off.
NOTE: It is strongly recommended that you enable the
CGN's firewall unless LAN protection is provided
by another device or software.
Intrusion Detection
System
Ping on WAN Interface
Apply Click this to save your changes to the fields in this
Cancel Click this to return the fields in this screen to their last-
Help Click this to see information about the fields in this
Select this to turn the intrusion detection system off.
Deselect this to turn the intrusion detection system
on.
Select this to prevent responses to ICMP requests
originating from the WAN.
Select this to allow responses to ICMP requests
originating from the WAN.
screen.
saved values without saving your changes.
screen.
4.3 THE FILTER SETTING SCREEN
Use this screen to configure Media Access Control (MAC) address filtering on the
LAN, and to configure IP filtering.
57
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
FIREWALL
Page 58

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
58
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
NOTE: To configure MAC address filtering on the wireless network, see The Access
Control Screen on page 93.
You can set the CGN to allow only certain devices to access the CGN and the
network, or to deny certain devices access.
NOTE: To see a list of all the computers connected to the CGN on the LAN, click the
Connected Computers button in the Firewall > IP Filtering, Forwarding,
Port Triggering or Firewall Options screens.
You can turn IP filtering on or off, and configure new and existing IP filtering rules.
Click Firewall > Filter Setting. The following screen displays.
58
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
FIREWALL
Page 59
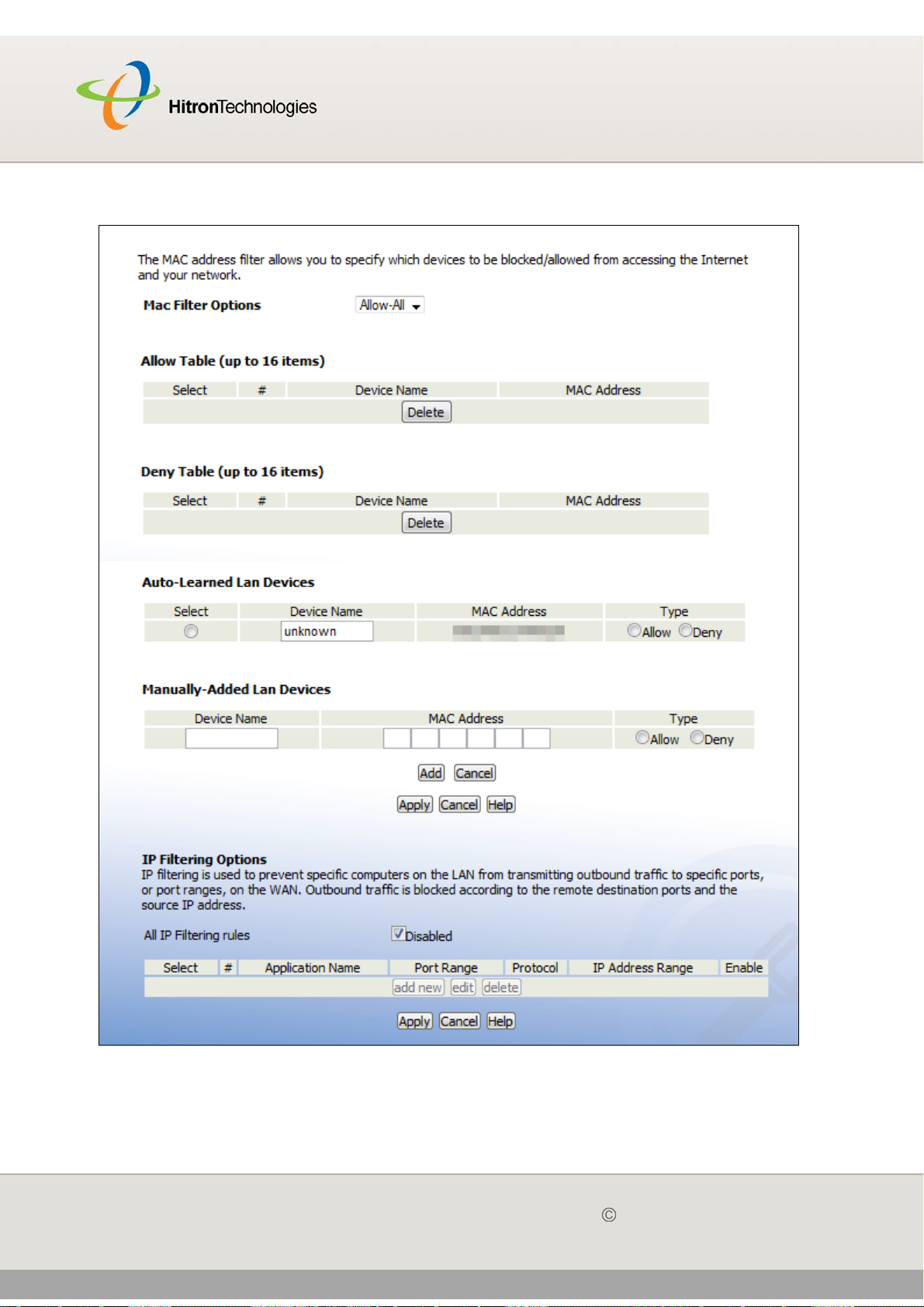
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
59
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Figure 16: The Firewall > Filter Setting Screen
59
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
FIREWALL
Page 60

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
60
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 17: The Firewall > Filter Setting Screen
MAC Filter Options
MAC Filter Options Use this field to control whether the CGN performs MAC
filtering.
Select Allow-All to turn MAC filtering off. All devices
may access the CGN and the network.
Select Allow to permit only devices with the MAC
addresses you set up in the Allow Table to access the
CGN and the network. All other devices are denied
access.
Select Deny to permit all devices except those with the
MAC addresses you set up in the Deny Table to
access the CGN and the network. The specified
devices are denied access.
Allow Table (up to 16 Items)
# This displays the index number assigned to the permitted
device.
Device Name This displays the name you gave to the permitted device.
MAC Address This displays the MAC address of the permitted device.
Delete Select a permitted device’s radio button ( ) and click this
to remove the device from the list. The device may no
longer access the CGN and the network.
NOTE: Make sure you do not delete your management
computer from the list; if you do so, you will need
to log back in from another computer, or reset the
CGN.
Deny Table (up to 16 Items)
# This displays the index number assigned to the denied
device.
Device Name This displays the name you gave to the denied device.
MAC Address This displays the MAC address of the denied device.
Delete Select a denied device’s radio button ( ) and click this to
remove the device from the list. The device may now
access the CGN and the network.
Auto-Learned LAN Devices
60
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
FIREWALL
Page 61

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
61
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Table 17: The Firewall > Filter Setting Screen (continued)
Device Name This displays the name of each network device that has
connected to the CGN on the LAN. To change the name
assigned to a device, edit it in the relevant field.
MAC Address This displays the MAC address of each network device
that has connected to the CGN on the LAN.
Type Use this field to specify the list to which you want to add
the device.
Select Allow to add the device to the Allow Table.
Select Deny to add the device to the Deny Table.
Manually-Added LAN Devices
Device Name Enter the name to associate with a network device that
you want to permit or deny access to the CGN and the
network.
NOTE: This name is arbitrary, and does not affect
functionality in any way.
MAC Address Specify the MAC address of the network device that you
want to permit or deny access to the CGN and the
network.
Type Use this field to specify the list to which you want to add
the device.
Select Allow to add the device to the Allow Table.
Select Deny to add the device to the Deny Table.
Add Click this to add the device to the list you specified.
Cancel Click this to clear the Manually-Added LAN Devices
fields.
Apply Click this to save your changes to the fields in the Mac
Filter tables.
Cancel Click this to return the fields in the Mac Filter tables to
their last-saved values without saving your changes.
Help Click this to see information about the fields in this screen.
IP Filtering Options
61
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
FIREWALL
Page 62

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
62
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Table 17: The Firewall > Filter Setting Screen (continued)
All IP Filtering Rules Use this to turn IP filtering on or off.
Deselect the checkbox to enable IP filtering.
Select the checkbox to disable IP filtering (default).
NOTE: You can add, edit or delete IP filtering rules only
when this checkbox is deselected.
Select Select an IP filtering rule’s radio button ( ) before
clicking Edit or Delete.
# This displays the arbitrary identification number assigned
to the IP filtering rule.
Application Name This displays the arbitrary name you assigned to the rule
when you create it.
Port Range This displays the start and end values of the ports to which
communications from the specified IP addresses is not
permitted.
Protocol This displays the type of communications that are not
permitted:
TCP displays if communications via the Transmission
Control Protocol are not permitted.
UDP displays if communications via the User
Datagram Protocol are not permitted.
TCP/UDP displays if communications via the
Transmission Control Protocol and the User Datagram
Protocol are not permitted.
IP Address Range This displays the start and end IP address from which
communications to the specified ports are not permitted.
Enable Use this field to turn each IP filtering rule on or off.
Select this checkbox to enable the IP filtering rule.
Deselect this checkbox to disable the IP filtering rule.
Add New Click this to define a new IP filtering rule. See Adding or
Editing an IP Filtering Rule on page 63 for information on
the screen that displays.
Edit Select an IP filtering rule’s radio button ( ) and click this
to make changes to the rule. See Adding or Editing an IP
Filtering Rule on page 63 for information on the screen
that displays.
62
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
FIREWALL
Page 63

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
63
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Table 17: The Firewall > Filter Setting Screen (continued)
Delete Select an IP filtering rule’s radio button ( ) and click this
to remove the rule. The deleted rule’s information cannot
be retrieved.
Apply Click this to save your changes to the fields in the IP
Filtering Options section.
Cancel Click this to return the fields in the IP Filtering Options
section to their last-saved values without saving your
changes.
Help Click this to see information about the fields in this screen.
4.3.1 ADDING OR EDITING AN IP FILTERING RULE
To add a new IP filtering rule, click Add in the Firewall > Filter Setting screen’s
IP Filtering Options section.
To edit an existing IP filtering rule, select the rule’s radio button ( ) in the
Firewall > Filter Setting screen’s IP Filtering Options section and click the
Edit button.
NOTE: Ensure that the Disabled checkbox is deselected in order to add or edit IP
filtering rules.
The following screen displays.
Figure 17: The Firewall > Filter Settings > Add/Edit Screen
63
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
FIREWALL
Page 64
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
64
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 18: The Firewall > Filter Settings > Add/Edit Screen
Application Name Enter a name for the application that you want to block.
NOTE: This name is arbitrary, and does not affect
functionality in any way.
Port Range Use these fields to specify the target port range to which
communication should be blocked.
Enter the start port number in the first field, and the end
port number in the second field.
To specify only a single port, enter its number in both
fields.
Protocol Use this field to specify whether the CGN should block
communication via:
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
User Datagram Protocol (UDP)
Both TCP and UDP.
NOTE: If in doubt, leave this field at its default (Both).
IP Address Range Use these fields to specify the range of local computers’
IP addresses from which communications should be
blocked.
Enter the start IP address in the first field, and the end IP
address in the second.
To specify only a single IP address, enter it in both fields.
Connected Computers Click this to see a list of the computers currently
connected to the CGN on the LAN.
Back Click this to return to the Firewall > Filter Settings
screen without saving your changes to the IP filtering
rule.
Apply Click this to save your changes to the fields in this
screen.
Cancel Click this to return the fields in this screen to their last-
saved values without saving your changes.
Help Click this to see information about the fields in this
screen.
64
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
FIREWALL
Page 65

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
65
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
4.4 THE FORWARDING SCREEN
Use this screen to configure port forwarding between computers on the WAN and
computers on the LAN. You can turn port forwarding on or off and configure new and
existing port forwarding rules.
Click Firewall > Forwarding. The following screen displays.
Figure 18: The Firewall > Forwarding Screen
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 19: The Firewall > Forwarding Screen
All Port Forwarding Rules Use this field to turn port forwarding on or off.
Select the checkbox to enable port forwarding.
Deselect the checkbox to disable port forwarding.
Select Select a port forwarding rule’s radio button ( ) before
clicking Edit or Delete.
# This displays the arbitrary identification number
assigned to the port forwarding rule.
Application Name This displays the arbitrary name you assigned to the rule
when you created it.
65
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
FIREWALL
Page 66

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
66
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Table 19: The Firewall > Forwarding Screen (continued)
Port Range These fields display the ports to which the rule applies:
The Public field displays the incoming port range.
These are the ports on which the CGN received
traffic from the originating host on the WAN.
The Private field displays the port range to which the
CGN forwards traffic to the device on the LAN.
Protocol This field displays the protocol or protocols to which this
rule applies:
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
User Datagram Protocol (UDP)
Transmission Control Protocol and User Datagram
Protocol (TCP/UDP)
Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE)
Encapsulating Security Protocol (ESP)
IP Address This displays the IP address of the computer on the LAN
to which traffic conforming to the Public Port Range
and Protocol conditions is forwarded.
Enable Use this field to turn each port forwarding rule on or off.
Select this checkbox to enable the port forwarding
rule.
Deselect this checkbox to disable the port forwarding
rule.
Add New Click this to define a new port forwarding rule. See
Adding or Editing a Port Forwarding Rule on page 67 for
information on the screen that displays.
Edit Select a port forwarding rule’s radio button ( ) and
click this to make changes to the rule. See Adding or
Editing a Port Forwarding Rule on page 67 for
information on the screen that displays.
Delete Select a port forwarding rule’s radio button ( ) and
click this to remove the rule. The deleted rule’s
information cannot be retrieved.
Apply Click this to save your changes to the fields in this
screen.
66
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
FIREWALL
Page 67
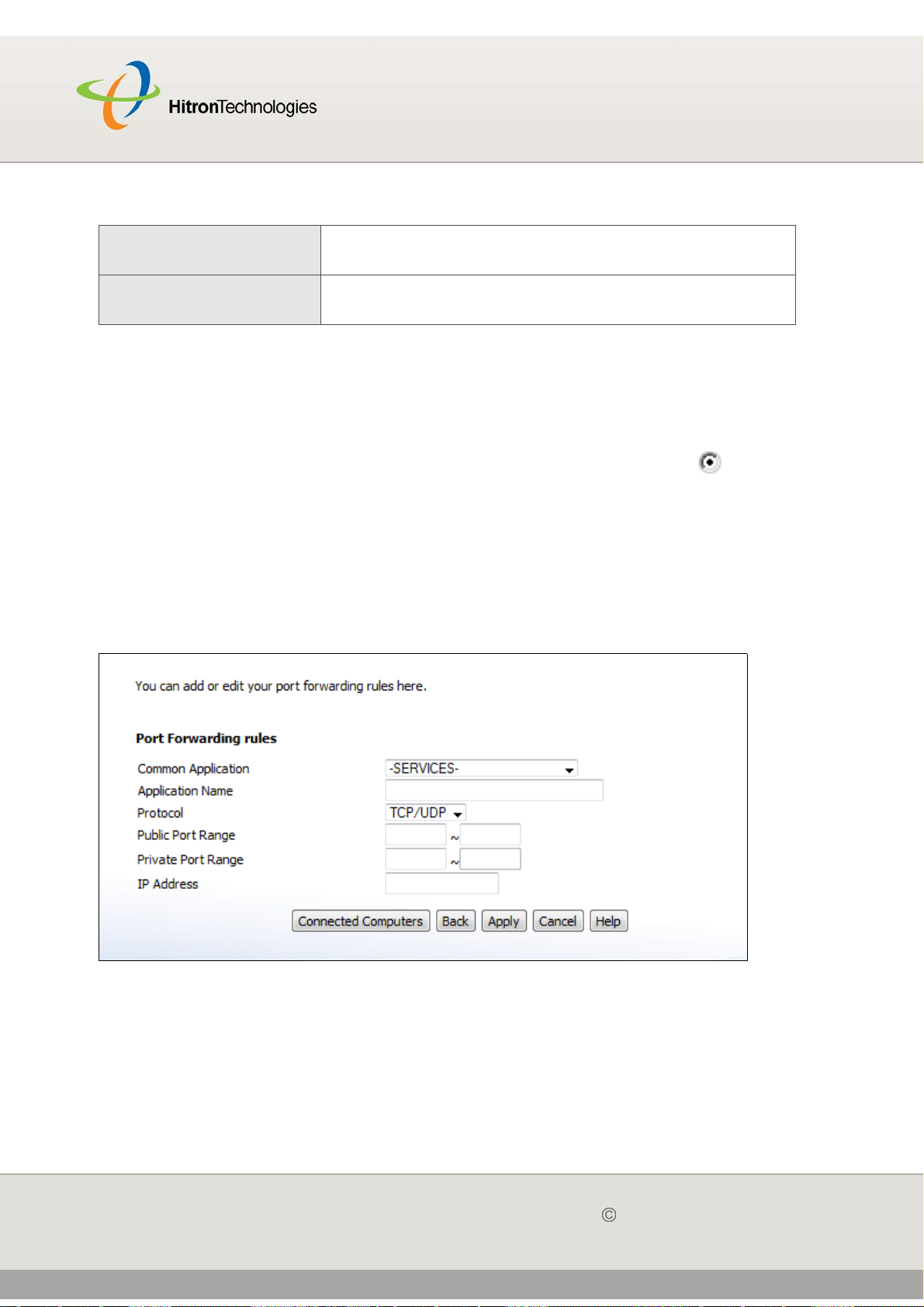
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
67
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Table 19: The Firewall > Forwarding Screen (continued)
Cancel Click this to return the fields in this screen to their last-
saved values without saving your changes.
Help Click this to see information about the fields in this
screen.
4.4.1 ADDING OR EDITING A PORT FORWARDING RULE
To add a new port forwarding rule, click Add in the Firewall > Forwarding
screen.
To edit an existing port forwarding rule, select the rule’s radio button ( ) in the
Firewall > Forwarding screen and click the Edit button.
NOTE: Ensure that the Disabled checkbox is disabled in order to add or edit port
forwarding rules.
The following screen displays.
Figure 19: The Firewall > Forwarding > Add/Edit Screen
67
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
FIREWALL
Page 68

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
68
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 20: The Firewall > Forwarding > Add/Edit Screen
Application Name Enter a name for the application for which you want to
create the rule.
NOTE: This name is arbitrary, and does not affect
functionality in any way.
Public Port Range Use these fields to specify the incoming port range.
These are the ports on which the CGN received traffic
from the originating host on the WAN.
Enter the start port number in the first field, and the end
port number in the second field.
To specify only a single port, enter its number in both
fields.
Private Port Range Use these fields to specify the ports to which the
received traffic should be forwarded.
Enter the start port number in the first field. The number
of ports must match that specified in the Public Port
Range, so the CGN completes the second field
automatically.
Protocol Use this field to specify whether the CGN should forward
traffic via:
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
User Datagram Protocol (UDP)
Transmission Control Protocol and User Datagram
Protocol (TCP/UDP)
Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE)
Encapsulating Security Protocol (ESP)
NOTE: If in doubt, leave this field at its default (TCP/
UDP).
IP Address Use this field to enter the IP address of the computer on
the LAN to which you want to forward the traffic.
Connected Computers Click this to see a list of the computers currently
connected to the CGN on the LAN.
Back Click this to return to the Firewall > Forwarding screen
without saving your changes to the port forwarding rule.
68
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
FIREWALL
Page 69

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
69
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Table 20: The Firewall > Forwarding > Add/Edit Screen
Apply Click this to save your changes to the fields in this
screen.
Cancel Click this to return the fields in this screen to their last-
saved values without saving your changes.
Help Click this to see information about the fields in this
screen.
4.5 THE PORT TRIGGERING SCREEN
Use this screen to configure port triggering. You can turn port triggering on or off and
configure new and existing port triggering rules.
Click Firewall > Port Triggering. The following screen displays.
Figure 20: The Firewall > Port Triggering Screen
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 21: The Firewall > Port Triggering Screen
All Port Triggering Rules Use this field to turn port triggering on or off.
Select the checkbox to enable port triggering.
Deselect the checkbox to disable port triggering.
Select Select a port triggering rule’s radio button ( ) before
clicking Edit or Delete.
# This displays the arbitrary identification number
assigned to the port triggering rule.
69
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
FIREWALL
Page 70
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
70
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Table 21: The Firewall > Port Triggering Screen
Application Name This displays the arbitrary name you assigned to the
rule when you created it.
Port Range These fields display the ports to which the rule applies:
The Trigger field displays the range of outgoing
ports. When the CGN detects activity (outgoing
traffic) on these ports from computers on the LAN, it
automatically opens the Target ports.
The Target field displays the range of triggered
ports. These ports are opened automatically when
the CGN detects activity on the Trigger ports from
computers on the LAN.
Protocol This displays the protocol of the port triggering rule.
Timeout (ms) This displays the time (in milliseconds) after the CGN
opens the Target ports that it should close them.
Enable Use this field to turn each port triggering rule on or off.
Select this checkbox to enable the port triggering
rule.
Deselect this checkbox to disable the port triggering
rule.
Add New Click this to define a new port triggering rule. See
Adding or Editing a Port Triggering Rule on page 71 for
information on the screen that displays.
Edit Select a port triggering rule’s radio button ( ) and click
this to make changes to the rule. See Adding or Editing
a Port Triggering Rule on page 71 for information on the
screen that displays.
Delete Select a port triggering rule’s radio button ( ) and click
this to remove the rule. The deleted rule’s information
cannot be retrieved.
Apply Click this to save your changes to the fields in this
screen.
Cancel Click this to return the fields in this screen to their last-
saved values without saving your changes.
Help Click this to see information about the fields in this
screen.
70
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
FIREWALL
Page 71

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
71
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
4.5.1 ADDING OR EDITING A PORT TRIGGERING RULE
To add a new port triggering rule, click Add in the Firewall > Port Triggering
screen.
To edit an existing port triggering rule, select the rule’s radio button ( ) in the
Firewall > Port Triggering screen and click the Edit button.
The following screen displays.
Figure 21: The Firewall > Port Triggering > Add/Edit Screen
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 22: The Firewall > Port Triggering > Add/Edit Screen
Application Name Enter a name for the application for which you want to
create the rule.
NOTE: This name is arbitrary, and does not affect
functionality in any way.
Trigger Port Range Use these fields to specify the trigger ports. When the
CGN detects activity on any of these ports originating
from a computer on the LAN, it automatically opens the
Target ports in expectation of incoming traffic.
Enter the start port number in the first field, and the end
port number in the second field.
To specify only a single port, enter its number in both
fields.
71
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
FIREWALL
Page 72

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
72
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Table 22: The Firewall > Port Triggering > Add/Edit Screen
Target Port Range Use these fields to specify the target ports. The CGN
opens these ports in expectation of incoming traffic
whenever it detects activity on any of the Trigger ports.
The incoming traffic is forwarded to these ports on the
computer connected to the LAN.
Enter the start port number in the first field, and the end
port number in the second field.
To specify only a single port, enter its number in both
fields.
Protocol Use this field to specify whether the CGN should activate
this trigger when it detects activity via:
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
User Datagram Protocol (UDP)
Transmission Control Protocol and User Datagram
Protocol (Both)
NOTE: If in doubt, leave this field at its default (Both).
Timeout (ms) Enter the time (in milliseconds) after the CGN opens the
Target ports that it should close them.
Connected Computers Click this to see a list of the computers currently
connected to the CGN on the LAN.
Back Click this to return to the Firewall > Forwarding screen
without saving your changes to the port forwarding rule.
Apply Click this to save your changes to the fields in this
screen.
Cancel Click this to return the fields in this screen to their last-
saved values without saving your changes.
Help Click this to see information about the fields in this
screen.
4.6 THE DMZ SCREEN
Use this screen to configure your network’s Demilitarized Zone (DMZ).
NOTE: Only one device can be on the DMZ at a time.
72
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
FIREWALL
Page 73

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
73
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Click Firewall > DMZ. The following screen displays.
Figure 22: The Firewall > DMZ Screen
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 23: The Firewall > DMZ Screen
Enable DMZ Host Use this field to turn the DMZ on or off.
Select the checkbox to enable the DMZ.
Deselect the checkbox to disable the DMZ.
Computers that were previously in the DMZ are now
on the LAN.
Connected Computers Click this to see a list of the computers currently
connected to the CGN on the LAN. To add a connected
computer to the DMZ, click its Add button and click
Apply in the screen that displays.
[...] IP Address [...] Enter the IP address of the computer that you want to
add to the DMZ.
Apply Click this to save your changes to the fields in this
screen.
Cancel Click this to return the fields in this screen to their last-
saved values without saving your changes.
Help Click this to see information about the fields in this
screen.
73
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
FIREWALL
Page 74

PARENTAL CONTROL
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
74
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
5
PARENTAL CONTROL
This chapter describes the screens that display when you click Parent Control in the
toolbar. It contains the following sections:
Parental Control Overview on page 74
The Website Blocking Screen on page 75
The Scheduling Screen on page 77
The Email / Syslog Alert Screen on page 79
5.1 PARENTAL CONTROL OVERVIEW
This section describes some of the concepts related to the Parental Control
screens.
5.1.1 WEBSITE BLOCKING
The Parental Control screens allow you to block access from computers on the LAN
to certain websites, or websites whose URLs (website addresses) contain the
keywords you specify.
You can also specify “trusted” computers, which should be exempted from website
blocking, and you can schedule website blocking so that it is only in effect at certain
times (evenings and weekends, for example).
Page 75
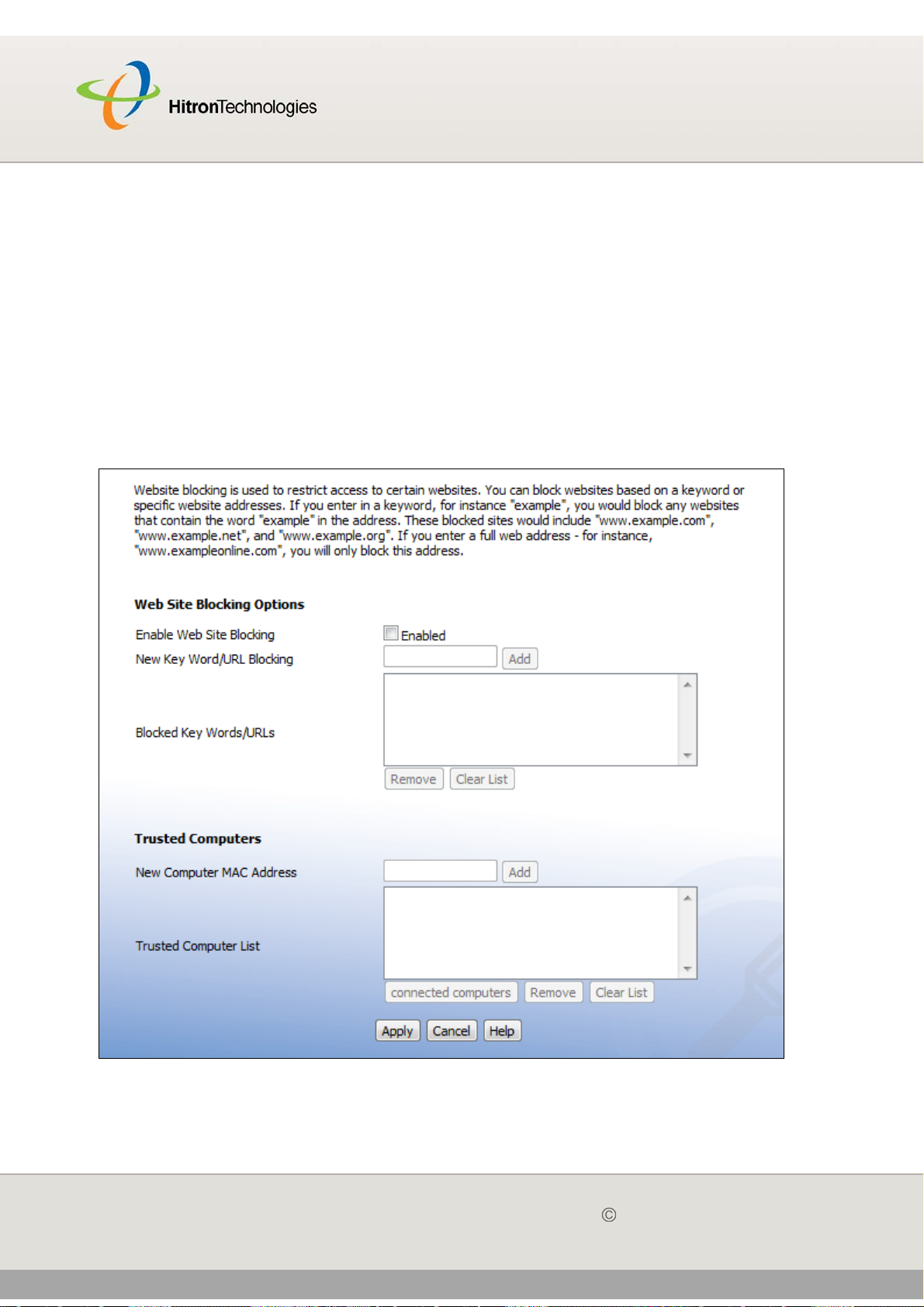
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
75
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
5.2 THE WEBSITE BLOCKING SCREEN
Use this screen to block access from the LAN to certain websites. You can also
specify trusted computers, which are not subject to the blocking filter.
NOTE: To apply the blocking filter only at certain times, use the Parental Control >
Scheduling screen.
Click Parental Control > Web Site Blocking. The following screen displays.
Figure 23: The Parental Control > Web Site Blocking Screen
75
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
PARENTAL CONTROL
Page 76

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
76
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 24: The Parental Control > Web Site Blocking Screen
Web Site Blocking Options
Enable Web Site
Blocking
New Key Word/URL
Blocking
Blocked Key Words/
URLs
Use this field to turn web site blocking on or off.
Select the checkbox to enable web site blocking.
Deselect the checkbox to disable web site blocking.
Use these fields to configure the websites to which users
on the LAN are denied access:
Enter a URL (for example, “www.example.com”) to
block access to that website only.
Enter a keyword (for example, “example”) to block
access to all websites that contain the keyword in
their URL (for example, “www.example.com”,
“www.example.org”, “www.someotherwebsite.com/
example” and so forth).
Click Add to add the URL or keyword to the Blocked
Key Words/URLs list.
This displays the list of websites and keywords to which
users on the LAN are denied access.
Select a URL or keyword and click Remove to delete
it from the list.
Click Clear List to delete all the URLs and keywords
from the list.
Trusted Computers
New Computer MAC
Address
Enter a computer’s Media Access Control (MAC)
address and click Add to include it in the trusted
computer list.
Trusted Computer
List
This displays a list of the computers which are exempt
from the website blocking filter, identified by their MAC
addresses.
Connected
Computers
Click this to see a list of the computers that are currently
connected to the CGN. To add a computer to the New
Computer MAC Address field, select its Add checkbox
and click Apply in the screen that displays.
Remove Select a computer’s MAC address from the Connected
Computers list and click this to delete it from the list.
76
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
PARENTAL CONTROL
Page 77

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
77
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Table 24: The Parental Control > Web Site Blocking Screen (continued)
Clear List Click this to delete all the computers’ MAC addresses
from the list.
Apply Click this to save your changes to the fields in this
screen.
Cancel Click this to return the fields in this screen to their last-
saved values without saving your changes.
Help Click this to see information about the fields in this
screen.
5.3 THE SCHEDULING SCREEN
Use this screen to control when the website blocking filter should be in effect.
NOTE: To configure the website blocking filter, use the Parent Control > Web Site
Blocking screen.
Click Parent Control > Scheduling. The following screen displays.
77
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
PARENTAL CONTROL
Page 78

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
78
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Figure 24: The Parental Control > Scheduling Screen
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 25: The Parental Control > Scheduling Screen
Days of the Week Select the days of the week on which you want the
website blocking filter to be in effect.
Time of Day Use these fields to control the time that the website
blocking filter should be in effect:
Select All Day to apply the website blocking filter at
all times.
To apply the website blocking filter only at certain
times of day, deselect All Day. Use the Start fields
to define the time that the filter should come into
effect, and use the End fields to define the time that
the filter should cease being in effect.
Apply Click this to save your changes to the fields in this
screen.
78
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
PARENTAL CONTROL
Page 79

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
79
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Table 25: The Parental Control > Scheduling Screen (continued)
Cancel Click this to return the fields in this screen to their last-
saved values without saving your changes.
Help Click this to see information about the fields in this
screen.
5.4 THE EMAIL / SYSLOG ALERT SCREEN
Use this screen to forward information to a target email address or system log each
time the firewall alert is triggered, and to define the time at which emails should be
sent and/or log entries created.
The firewall must be enabled for alerts to be triggered.
Click Parent Control > Email/Syslog Alert. The following screen displays.
Figure 25: The Parental Control > Email / Syslog Alert Screen
79
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
PARENTAL CONTROL
Page 80

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
80
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 26: The Parental Control > Email / Syslog Alert Screen
Mail Server Configuration Use this section to define the location of the transmitting
email server, and the email address from which admin
emails appear to originate.
SMTP Server
Address
Sender’s Email
Address
Mail Server
Authentication
Enter the address of the email server from which admin
emails should be sent.
Enter the email address from which admin emails
should appear to originate.
Use this section to enter the user credentials for the
defined email server.
User Name Enter the user name for your account on the defined
email server.
Password Enter the password associated with the above user
name.
80
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
PARENTAL CONTROL
Page 81

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
81
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Table 26: The Parental Control > Email / Syslog Alert Screen (continued)
Recipient List (up to 4
items)
Use this section to define up to four target email address
to which admin emails will be sent.
To enter a new target email address, click Add.
Enter the target email address’s Name and
Recipient’s Address in the fields that display, then
click Apply to save your changes. Alternatively, click
Cancel to return to the previous screen without
saving your changes.
Figure 26: Add Target Email Address
To make changes to an existing target email
address, select its radio button and click Edit. The
screen that displays is the same as the Add Target
Email Address screen.
To remove an email address, select its radio button
and click Delete. The email address is removed from
the list.
Syslog Server
Configuration
Syslog Server
Address
Use this section to define the server on which the
system log is stored.
Enter the address of the server on which the system log
is stored.
Alert Options Use this section to define the actions to be taken when
an intrusion event is detected.
When Intrusion is
Detected
Select Send Email to send an email to the list when
an intrusion event is detected.
Select Send Syslog to send an entry to the system
log when an intrusion event is detected.
Apply Click this to save your changes to the fields in this
screen.
81
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
PARENTAL CONTROL
Page 82

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
82
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Table 26: The Parental Control > Email / Syslog Alert Screen (continued)
Cancel Click this to return the fields in this screen to their last-
saved values without saving your changes.
Help Click this to see information about the fields in this
screen.
82
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
PARENTAL CONTROL
Page 83

WIRELESS
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
83
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
6
WIRELESS
This chapter describes the screens that display when you click Wireless in the
toolbar. It contains the following sections:
Wireless Overview on page 83
The Setup Screen on page 86
The Access Control Screen on page 93
The Advanced Screen on page 95
6.1 WIRELESS OVERVIEW
This section describes some of the concepts related to the Wireless screens.
6.1.1 WIRELESS NETWORKING BASICS
Your CGN’s wireless network is part of the Local Area Network (LAN), known as the
Wireless LAN (WLAN). The WLAN is a network of radio links between the CGN and
the other computers and devices that connect to it.
6.1.2 ARCHITECTURE
The wireless network consists of two types of device: access points (APs) and
clients.
The access point controls the network, providing a wireless connection to each
client.
Page 84

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
84
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
The wireless clients connect to the access point in order to receive a wireless
connection to the WAN and the wired LAN.
The CGN is the access point, and the computers you connect to the CGN are the
wireless clients.
6.1.3 WIRELESS STANDARDS
The way in which wireless devices communicate with one another is standardized by
the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). The IEEE standards
pertaining to wireless LANs are identified by their 802.11 designation. There are a
variety of WLAN standards, but the CGN supports the following (in order of adoption old to new - and data transfer speeds - low to high):
IEEE 802.11b
IEEE 802.11g
IEEE 802.11n
6.1.4 SERVICE SETS AND SSIDS
Each wireless network, including all the devices that comprise it, is known as a
Service Set.
NOTE: Depending on its capabilities and configuration, a single wireless access
point may control multiple Service Sets; this is often done to provide different
service or security levels to different clients.
Each Service Set is identified by a Service Set IDentifier (SSID). This is the name of
the network. Wireless clients must know the SSID in order to be able to connect to
the AP. You can configure the CGN to broadcast the SSID (in which case, any client
who scans the airwaves can discover the SSID), or to “hide” the SSID (in which case
it is not broadcast, and only users who already know the SSID can connect).
84
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
WIRELESS
Page 85

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
85
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
6.1.5 WIRELESS SECURITY
Radio is inherently an insecure medium, since it can be intercepted by anybody in the
coverage area with a radio receiver. Therefore, a variety of techniques exist to control
authentication (identifying who should be allowed to join the network) and encryption
(signal scrambling so that only authenticated users can decode the transmitted data).
The sophistication of each security method varies, as does its effectiveness. The
CGN supports the following wireless security protocols (in order of effectiveness):
WEP (the Wired Equivalency Protocol): this protocol uses a series of “keys” or
data strings to authenticate the wireless client with the AP, and to encrypt data
sent over the wireless link. WEP is a deprecated protocol, and should only be
used when it is the only security standard supported by the wireless clients.
WEP provides only a nominal level of security, since widely-available software
exists that can break it in a matter of minutes.
WPA-PSK (WiFi Protected Access - Pre-Shared Key): WPA was created to
solve the inadequacies of WEP. There are two types of WPA: the “enterprise”
version (known simply as WPA) requires the use of a central authentication
database server, whereas the “personal” version (supported by the CGN) allows
users to authenticate using a “pre-shared key” or password instead. While WPA
provides good security, it is still vulnerable to “brute force” password-guessing
attempts (in which an attacker simply barrages the AP with join requests using
different passwords), so for optimal security it is advised that you use a random
password of thirteen characters or more, containing no “dictionary” words.
WPA2-PSK: WPA2 is an improvement on WPA. The primary difference is that
WPA uses the Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) encryption standard
(which has been shown to have certain possible weaknesses), whereas WPA2
uses the stronger Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) in the Counter mode
with Cipher block chaining Message authentication code Protocol (CCMP),
which has received the US government’s seal of approval for communications
up to the Top Secret security level. Since WPA2-PSK uses the same pre-shared
key mechanism as WPA-PSK, the same caveat against using insecure or
simple passwords applies.
6.1.5.1 WPS
WiFi-Protected Setup (WPS) is a standardized method of allowing wireless devices
to quickly and easily join wireless networks, while maintaining a good level of
security. The CGN provides two methods of WPS authentication:
85
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
WIRELESS
Page 86

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
86
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Push-Button Configuration (PBC): when the user presses the PBC button on
the AP (either a physical button, or a virtual button in the GUI), any user of a
wireless client that supports WPS can press the corresponding PBC button on
the client within two minutes to join the network.
Personal Identification Number (PIN) Configuration: all WPS-capable
devices possess a PIN (usually to be found printed on a sticker on the device’s
housing). When you configure another device to use the same PIN, the two
devices authenticate with one another.
Once authenticated, devices that have joined a network via WPS use the WPA2
security standard.
6.1.6 WMM
WiFi MultiMedia (WMM) is a Quality of Service (QoS) enhancement that allows
prioritization of certain types of data over the wireless network. WMM provides four
data type classifications (in priority order; highest to lowest):
Voice
Video
Best effort
Background
If you wish to improve the performance of voice and video (at the expense of other,
less time-sensitive applications such as Internet browsing and FTP transfers), you
can enable WMM. You can also edit the WMM QoS parameters, but are disadvised
to do so unless you have an extremely good reason to make the changes.
6.2 THE SETUP SCREEN
Use this screen to configure your CGN’s basic wireless settings. You can turn the
wireless module on or off, select the wireless mode and channel, run WPS and
configure the wireless network’s SSID. You can also configure authentication and
encryption on your wireless network.
NOTE: It is strongly recommended that you set up security on your network;
otherwise, anyone in the radio coverage area can access your network.
86
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
WIRELESS
Page 87

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
87
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Click Wireless > Setup. The following screen displays.
Figure 27: The Wireless > Setup Screen
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 27: The Wireless > Setup Screen
Wireless Basic Settings
Wireless ON/OFF Use this field to turn the wireless network on or off.
Select ENABLE to turn the wireless network on.
Deselect DISABLE to turn the wireless network off.
87
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
WIRELESS
Page 88

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
88
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Table 27: The Wireless > Setup Screen (continued)
Wireless Mode Select the type of wireless network that you want to use:
11B/G Mixed: use IEEE 802.11b and 802.11n
11B Only: use IEEE 802.11b
11G Only: use IEEE 802.11g
11N Only: use IEEE 802.11n
11G/N Mixed: use IEEE 802.11g and 802.11N
11B/G/N Mixed: use IEEE 802.11b, 802.11g and
802.11N
NOTE: Only wireless clients that support the network
protocol you select can connect to the wireless
network. If in doubt, use 11B/G/N (default).
Channel Select the wireless channel that you want to use, or
select Auto to have the CGN select the optimum
channel to use.
NOTE: Use the Auto setting unless you have a specific
reason to do otherwise.
WPS ON/OFF Use this field to turn Wifi Protected Setup (WPS) on or
off.
Select ENABLE to turn WPS on.
Deselect DISABLE to turn WPS off.
88
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
WIRELESS
Page 89
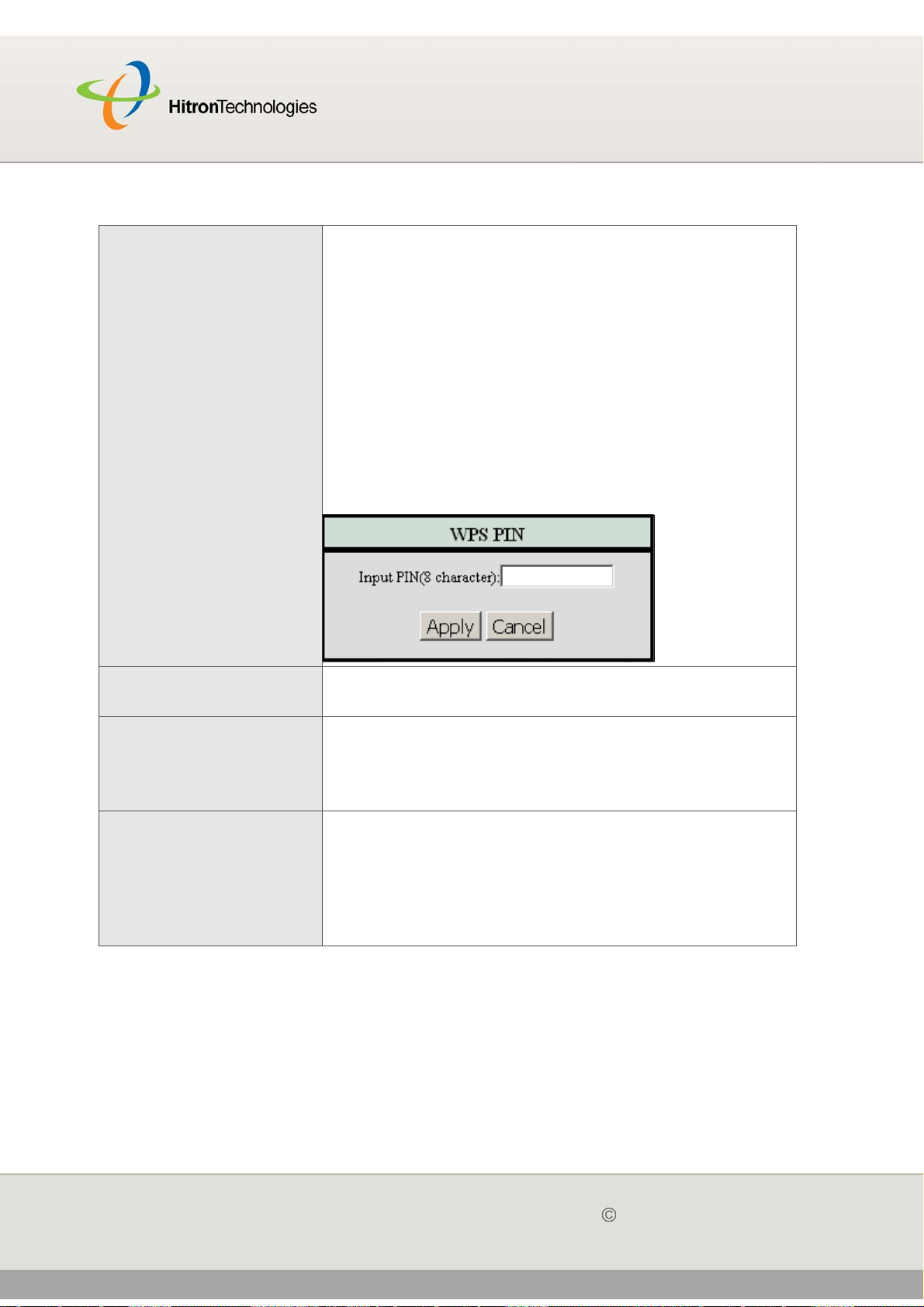
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
89
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Table 27: The Wireless > Setup Screen (continued)
Run WPS Use these buttons to run Wifi Protected Setup (WPS):
Click the PBC button to begin the Push-Button
Configuration process. You must then press the PBC
button on your client wireless devices within two
minutes in order to register them on your wireless
network.
Click the PIN button to begin the PIN configuration
process. In the screen that displays, enter the WPS
PIN that you want to use for the CGN, or the WPS
PIN of the client device you want to add to the
network.
Figure 28: WPS PIN
WPS Current Status This displays whether or not the CGN is using Wifi
Protected Setup.
SSID Setting This displays an entry for each of the CGN’s SSIDs.
NOTE: You may have additional BSSIDs, depending on
your contract with your service provider.
SSID Name Enter the name that you want to use for your wireless
network. This is the name that identifies your network,
and to which wireless clients connect.
NOTE: It is suggested that you change the SSID from its
default, for security reasons.
89
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
WIRELESS
Page 90
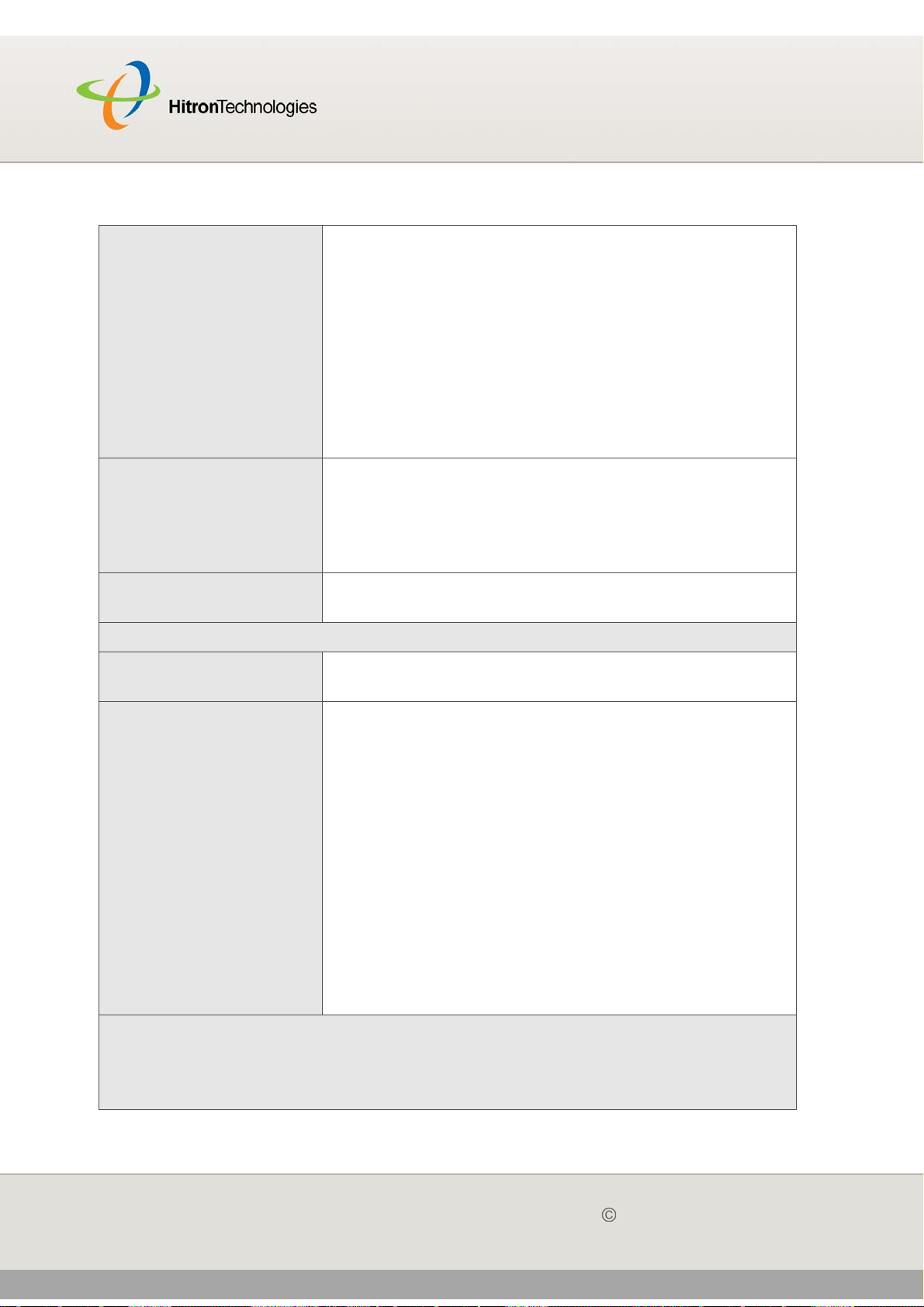
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
90
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Table 27: The Wireless > Setup Screen (continued)
Hidden Use this field to make your network visible or invisible to
other wireless devices.
Select the checkbox if you do not want the CGN to
broadcast the network name (SSID) to all wireless
devices in the coverage area. Anyone who wants to
connect to the network must know the SSID.
Deselect the checkbox if you want your network
name (SSID) to be public. Anyone with a wireless
device in the coverage area can discover the SSID,
and attempt to connect to the network.
In Service This field controls whether or not the SSID is in
operation.
NOTE: This field is user-configurable for the Primary
SSID only.
WMM Mode Select the checkbox if you want to apply Wifi MultiMedia
(WMM) Quality of Service (QoS) settings to this SSID.
Wireless Security
SSID Select the SSID for which you want to configure
security.
Security Mode Select the type of security that you want to use.
Select None to use no security. Anyone in the
coverage area can enter your network.
Select WEP to use the Wired Equivalent Privacy
security protocol.
Select WPA-Personal to use the WiFi Protected
Access (Personal) security protocol.
NOTE: Due to inherent security vulnerabilities, it is
suggested that you use WEP only if it is the only
security protocol your wireless clients support.
Under almost all circumstances, you should use
WPA-Personal.
WEP Settings
NOTE: These fields are only configurable when you select WEP from the Security
Mode list.
90
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
WIRELESS
Page 91

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
91
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Table 27: The Wireless > Setup Screen (continued)
WEP Key Length Use this field to specify the length of the security key
used to allow wireless devices to join the network. The
longer the key, the more secure it is.
Select 64-bit to use a ten-digit security key.
Select 128-bit to use a twenty-six-digit security key.
WEP Key 1~4 Use these fields to define the security keys that all
wireless devices on the network must use to join the
network.
The CGN supports up to four WEP keys, of which you
can select one as the default. You should input the
same four keys, in the same order, in your network’s
wireless clients. Your CGN and your wireless clients can
use different default keys, as long as all four keys are
present and in the same order. If your wireless client
supports only a single WEP key, use the CGN’s default
key.
Enter the keys in hexadecimal format (using the digits
0~9 and the letters A~F).
Default WEP Key Select the number of the security key that you want the
CGN to use as its default authentication key for
transmissions.
Authentication Select the authentication mode that you want to use:
Select Open System to allow wireless clients to
authenticate (identify themselves) to the CGN before
presenting their security credentials (WEP keys).
Select Shared Key to use the WEP key in the
authentication process. When a client wants to
associate, the CGN sends an unencrypted challenge
message. The client must use the WEP key to
encrypt the challenge message and return it to the
CGN, which then decrypts the message and
compares the result with its original message.
Open System authentication is the more secure of the
two authentication types, since while the Shared Key
system appears more robust, it is possible to derive
secure data by capturing the challenge messages.
Select Automatic to have the CGN choose the
authentication method.
91
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
WIRELESS
Page 92

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
92
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Table 27: The Wireless > Setup Screen (continued)
WPA_Personal
NOTE: These fields display only when you select WPA-Personal from the Security
Mode list.
WPA Mode Select the type of WPA security that you want to use:
Select WPA-PSK to use Wifi Protected Access (Pre-
Shared Key) mode
Select WPA2-PSK to use Wifi Protected Access 2
(Pre-Shared Key) mode
Select Auto (WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK) to allow
clients operating in either mode to connect to the
CGN.
Cipher Type Select the type of encryption that you want to use:
Select TKIP to use the Temporal Key Integrity
Protocol.
Select AES to use the Advanced Encryption
Standard.
Select TKIP and AES to allow clients using either
encryption type to connect to the CGN.
Group Key Update
Interval
Enter the frequency (in seconds) with which you want
the CGN to create new pre-shared keys, and issue them
to the wireless client.
Pre-Shared Key Enter the pre-shared key that you want to use for your
wireless network. You will need to enter this key into
your wireless clients in order to allow them to connect to
the network.
Pre-Authentication Use this field to allow pre-authentication (Enable) in
WPA2, or deny pre-authentication requests (Disable).
In preauthentication, a WPA2 wireless client can
perform authentication with other wireless access points
in its range when it is still connected to its current
wireless access point. This allows mobile wireless
clients to connect to new access points more quickly,
permitting more efficient roaming.
Apply Click this to save your changes to the fields in this
screen.
92
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
WIRELESS
Page 93

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
93
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Table 27: The Wireless > Setup Screen (continued)
Cancel Click this to return the fields in this screen to their last-
saved values without saving your changes.
Help Click this to see information about the fields in this
screen.
6.3 THE ACCESS CONTROL SCREEN
Use this screen to configure Media Access Control (MAC) address filtering on the
wireless network.
NOTE: To configure MAC address filtering on the wired LAN, see The Filter Setting
Screen on page 57.
You can set the CGN to allow only certain devices to access the CGN and the
network wirelessly, or to deny certain devices access.
Click Wireless > Access Control. The following screen displays.
Figure 29: The Wireless > Access Control Screen
93
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
WIRELESS
Page 94

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
94
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 28: The Wireless > Access Control Screen
MAC Filtering
SSID Select the SSID for which you want to configure wireless
access control.
NOTE: At the time of writing, the CGN supports a single
SSID.
MAC Filtering Mode Use this field to control whether the CGN performs MAC
filtering on the wireless network.
Select Allow-All to turn MAC filtering off. All devices
may access the CGN and the network wirelessly.
Select Allow to permit only devices with the MAC
addresses you set up in the Wireless Control List to
access the CGN and the network wirelessly. All other
devices are denied access.
Select Deny to permit all devices except those with
the MAC addresses you set up in the Wireless
Control List to access the CGN and the network
wirelessly. The specified devices are denied access.
Apply Click this to save your changes in the MAC filtering
section.
Wireless Control List (up to 16 Items)
# Index This displays the index number assigned to the
permitted or denied wireless device.
Device Name This displays the name you gave to the permitted or
denied wireless device.
MAC Address This displays the MAC address of the permitted or
denied wireless device.
Delete Select a permitted or denied wireless device’s radio
button ( ) and click this to remove the device from the
list. The device may no longer access the CGN and the
network.
Wireless Devices
Auto-Learned Wireless Devices
Device Name This displays the name of each network device that has
connected to the CGN on the wireless network.
94
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
WIRELESS
Page 95

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
95
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Table 28: The Wireless > Access Control Screen (continued)
MAC Address This displays the MAC address of each network device
that has connected to the CGN on the wireless network.
Add Select a device’s checkbox and click Add to add the
device to the Wireless Control List.
Manually-Added Wireless Devices
Device Name Enter the name to associate with a network device that
you want to permit or deny access to the CGN and the
network wirelessly.
NOTE: This name is arbitrary, and does not affect
functionality in any way.
MAC Address Specify the MAC address of the network device that you
want to permit or deny access to the CGN and the
network wirelessly.
Add Click this to add any Manually-Added Wireless
Devices, and Auto-Learned Wireless Devices with
their Add boxes checked, to the Wireless Control List.
Cancel Click this to return the fields in this screen to their last-
saved values without saving your changes.
Help Click this to see information about the fields in this
screen.
6.4 THE ADVANCED SCREEN
Click Wireless > Advanced. The following screen displays.
95
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
WIRELESS
Page 96

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
96
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Figure 30: The Wireless > Advanced Screen
96
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
WIRELESS
Page 97

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
97
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 29: The Wireless > Advanced Screen
Wireless Advanced Settings
BG Protection Mode Use this field to configure IEEE 802.11b/g protection.
Both 802.11b and 802.11g wireless communications
occur at the same radio frequencies. When the CGN is
wirelessly connected to 802.11b clients and 802.11g
clients simultaneously, the performance of the link to
802.11g clients can deteriorate due to the presence of
the 802.11b clients. Because 802.11b and 802.11g use
different modulation techniques, 802.11b clients do not
understand 802.11g’s Request To Send (RTS) and
Clear To Send (CTS) messages, which ensure that each
wireless device transmits only when other devices are
not transmitting.
When B/G protection is active, the CGN prevents
802.11b clients transmitting over 802.11g transmissions
by first transmitting an announcement (known as a CTS-
to-Self) to 802.11b clients, stating that it intends to
transmit to 802.11g clients.
Select Auto to have the CGN control whether B/G
protection is active or not.
Select Always-on to use B/G protection at all times.
Select Always-off to never use B/G protection.
97
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
WIRELESS
Page 98

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
98
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Table 29: The Wireless > Advanced Screen (continued)
IGMP Snooping Use this field to turn Internet Group Management
Protocol (IGMP) snooping on or off.
IGMP is used to manage multicast groups. In multicast
groups, data is transmitted to numerous IP addresses
simultaneously. This is the most efficient method of
providing the same data to many different recipients at
the same time, since each data packet needs to be sent
only once. Multicast groups are often used for Internet
TV and real-time streaming applications such as online
gaming.
IGMP snooping allows the CGN to “snoop” or listen in on
IGMP traffic, and to determine which computers on the
LAN belong to which IGMP groups. By keeping lists of
which computers belong to IGMP groups, the CGN can
send the IGMP data to only those computers that have
requested it, and can refrain from sending unsolicited
multicast data. This can improve your connection to
wireless clients.
Select Disable to turn IGMP snooping off.
Select Enable to turn IGMP snooping on.
WMM Configuration Click this to set up your Wifi Multimedia (WMM) Quality
of Service (QoS) settings. See Configuring WMM
Parameters on page 103 for information on the screen
that displays.
NOTE: Turn WMM on and off in the Wireless > Basic
Settings screen.
HT Physical Mode
98
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
WIRELESS
Page 99

Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
99
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Table 29: The Wireless > Advanced Screen (continued)
Operating Mode Use this field to configure how the CGN transmits in
IEEE 802.11n mode.
Mixed mode, on the other hand, allows 802.11a/b/g
stations to tell when 802.11n transmissions are
occurring, by transmitting RTS, CTS and CTS-to-Self
messages in a format the legacy stations can
understand. You should select this option if you have
802.11a/b/g stations in your networks, or if there are
other 802.11a/b/g networks in your area.
Green Field, also known is High Throughput (HT) mode,
assumes that there are no existing IEE 802.11a/b/g
stations using the same radio channel. In greenfield
mode, the 802.11a/b/g stations are unable to tell when
802.11n transmissions are occurring. You should select
this mode only if there are no 802.11a/b/g stations in
your network (or other networks in your location).
Otherwise these stations’ wireless transmissions will
interfere with your 802.11n transmissions. When no
802.11a/b/g stations are present, greenfield mode
allows greater wireless network speeds, because the
legacy messages (RTS, CTS and CTS-to-Self) do not
need to be sent.
Channel Bandwidth This field allows you to configure the width of the radio
channel the CGN uses to communicate with its wireless
clients (IEEE 802.11n only). Using the full 40MHz
bandwidth can double your data speed.
Select 20 to only use a 20 megahertz band.
Select 20/40 to use a 40 megahertz band when
possible, and a 20 megahertz band when a 40Mhz
band is unavailable.
99
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
WIRELESS
Page 100
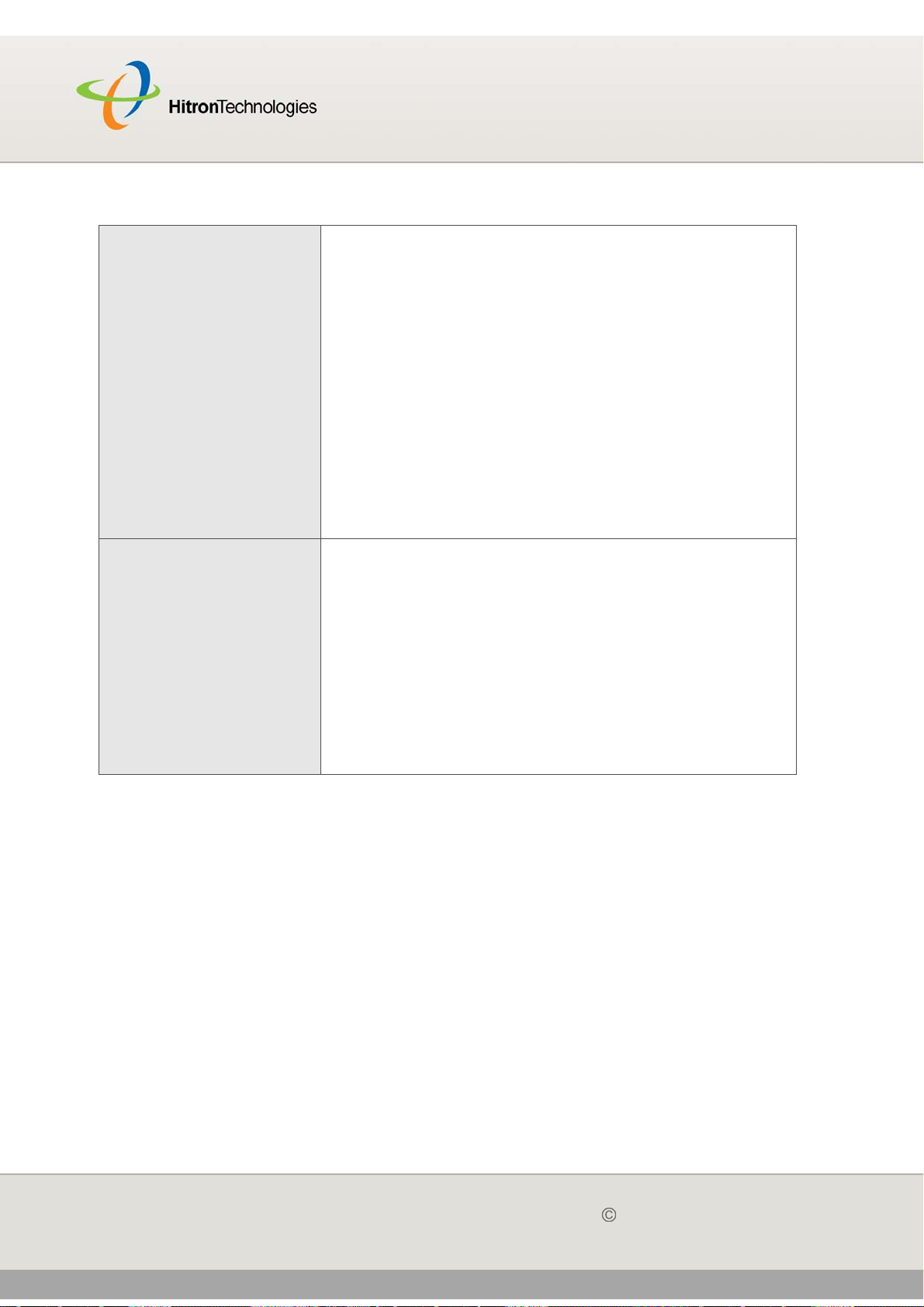
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
100
HITRON CGN USER’S GUIDE
Table 29: The Wireless > Advanced Screen (continued)
Guard Interval In 802.11n networks, the guard interval is the amount of
time that elapses between the transmission of symbols.
This is to prevent Inter-Symbol Interference, or ISI,
caused by echoes.
NOTE: In modulated signals, each distinct modulated
character (for example, each audible tone
produced by a modem for transmission over
telephone lines) is known as a symbol.
Select Long to use a long guard interval of 800
nanoseconds.
Select Short to use a short guard interval of 400
nanoseconds.
MCS Use this field to configure the Modulation and Coding
Scheme (MCS) that the CGN uses for IEEE 802.11n
transmissions.
The 802.11n protocol specifies 77 Modulation and
Coding Schemes. Each MCS refers to a combination of
a modulation technique, a coding rate, a guard interval,
and a certain number of spatial streams. The CGN
supports MCS 0~15, and 32.
Select the MCS that you wish to use for 802.11n
transmissions. If unsure, select Auto (default).
100
Version 2.0, February 2012. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
WIRELESS
 Loading...
Loading...