Page 1
HITACHI INVERTER
SJ100 SERIES
SERVICE MANUAL
(ADJUSTMENT AND MAINTENANCE)
Model:
European Version
SJ100-002NFE to SJ100-022 NFE
SJ100-004HFE to SJ100-075 HFE
US Version
SJ100-002NFU to SJ100-022NFU
SJ100-004HFU to SJ100-075HFU
SJ100-037LFU
Japanese Version
SJ100-002LFR to SJ100-037LFR
SJ100-004HFR to SJ100-075HFR
After reading this manual, keep it at hand for future reference
Hitachi, Ltd.
NBS585XA
Tokyo Japan
Page 2

INDEX
‑i‑
1. Pre-operation Check
1-1. Check inverter model and Manufacturing number
1-2. Check inverter parameter and motor specification
2. Measurement of The Internal Voltage Supply
3. Trouble Shoot
3-1. Error messages - Possible Cause and Remedy
3-2. Analysis of Various Operating Problems That Do Not Trigger an Trip Message
3-3. How to Initialize the Data (FACTORY SETTING)
3-4. Error Message Comparison
3-5. Other Displays
3-6. Auto tuning under high incoming voltage
4. Ambient Condition of the Frequency Inverter (Temperature, Altitude)
4-1. Required Derating in case of 50deg., 55 deg. of Ambient Temperature
4-2. Required derating toward altitude
5. Level of Each Detection
5-1. DC Bus Voltage Detection Characteristics
5.2. Output Current Detection Characteristics
5.3. Motor Temperature Detection (PTC)
5.4. Over Temperature Detection of the Frequency Inverter
6. Measurement & Replacement of Subassemblies
6-1. Insulation Measurement
6-2. Power Components Measurements
7. Maintenance and Inspection Procedure
7-1. Precautions
7-2. Measurement of Mains Voltage, Current and Power
7-3. Maintenance of Parts
7-4. If you install replacement INV at site
8. Daily Inspection and Periodical Inspection
9. Image block diagram
10. Spare parts list
1-1
1-1
1-2
2-1
3-1
3-1
3-7
3-8
3-9
3-10
3-10
4-1
4-1
4-4
5-1
5-1
5-3
5-4
5-4
6-1
6-1
6-1
7-1
7-1
7-1
7-4
7-4
8-1
9-1
10-1
10-1. parts list
10-2. I/O board compatibility
10-3. O, OI terminal adjustment procedure (C81, C82)
10-4. kW setup procedure
10-5. I/O board schematic (circuit diagram)
10-1
10-13
10-14
10-15
10-16
Page 3
Revisions
Revision history table
No. Revision contents Date of issue Manual No.
-ⅰⅰ-
Page 4
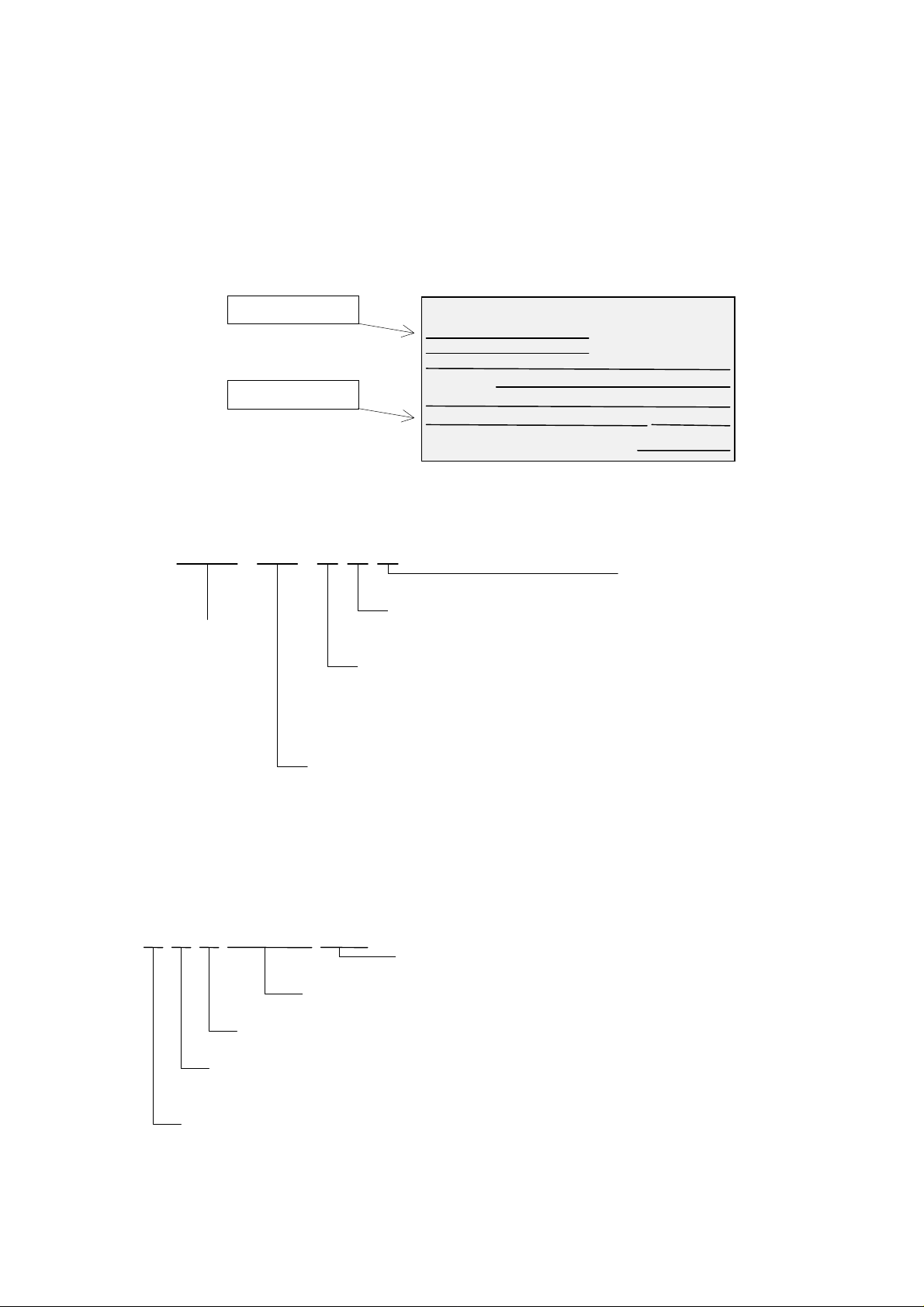
1. Pre-Operation Check
Before starting adjustment and maintenance, be sure to check the following specifications of the inverter
and the motor.
1.1 Check Inverter model and Manufacturing number (MFG No).
Inverter model
MFG No.
M odel : SJ100-015NFE
HP/kW : 2 / 1.5
Input/ E ntree:
Output/Sortie: 1-360Hz
MFG No. 78H T1129670060
Hitachi, Ltd.
HITACHI
50,60Hz
50,60Hz
200-240 V
200-240 V
200-240 V
MADE IN JAPAN
1Ph
3Ph
3Ph
Date: 9708
NE16452-6
16.0 A
9.3 A
7.1 A
You can find these information from the specification label which attached at the side cover of the unit.
(1) Description of the model name.
EF015 HSJ100
Version number
E: European version
Structure type
F: With operator
Input voltage class
N: Single/3 phase 20 0V class
L: 3 phase 200V class
H: 3 phase 400V class
U: US version
R: Japanese versionSeries name
(2) Description of MFG No.
T112967 0060H87
Revision of the inverter
Production Month
(1 - 9, 0:October, J:November, K:December)
Production year
(The unit digit of the year of grace. 7:1997, 8:1998, 9:1999, 0:2000)
Applicable motor kW
: 0.2kW002
: 0.4kW
004
: 0.55kW
005
: 0.75kW
007
: 1.1kW
011
: 1.5kW
015
Unique number
Production code
022
030
037
040
055
075
: 2.2kW
: 3.0kW
: 3.7kW
: 4.0kW
: 5.5kW
: 7.5kW
1-1
Page 5
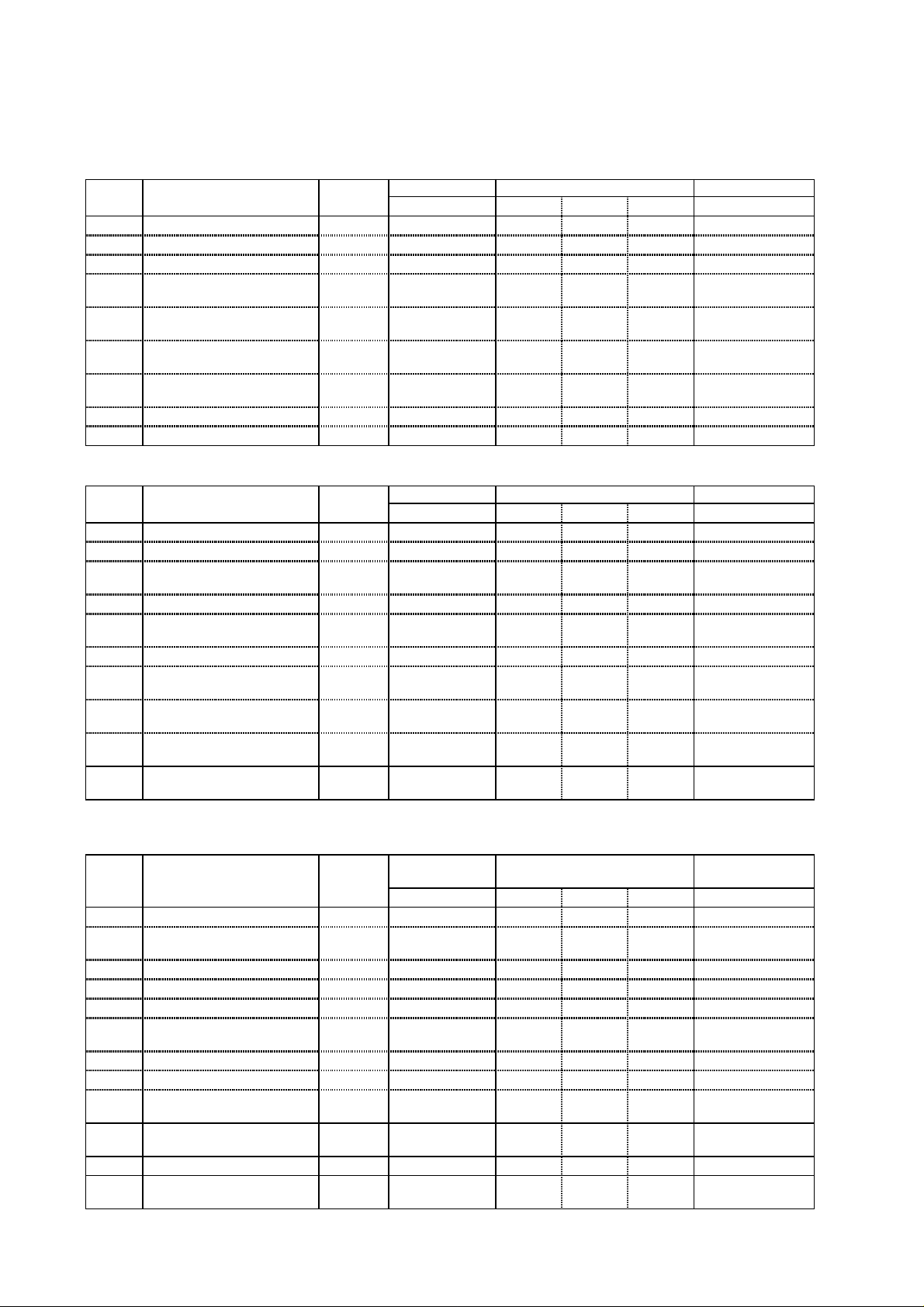
1.2 Check Inverter parameter and motor specification.
[1] Inverter specifications.
(1) Inverter specifications (Monitor mode)
Display Function name Category Screen display Initial Remarks
order Code display EU US JPN
1 Output frequency monitor Monitor d01 - - 2 Output current monitor Monitor d02 - - 3 Running direction monitor Monitor d03 - - 4 Feedback data of PID
control monitor
5 Intelligent input terminal
condition monitor
6 Intelligent output terminal
condition monitor
7 Output frequency
converted value monitor
8 Trip monitor Monitor d08 - - 9 Trip history monitor Monitor d09 - - -
(2) Inverter specifications (Basic function mode)
Display Function name Category Screen display Initial Remarks
Order Code display EU US JPN
1 Output frequency setting Set F01 0.0 0.0 0.0
2 Acceleration time 1 Set F02 10 10 10
- Acceleration time 1
(2nd setting)
3 Deceleration time 1 Set F03 10 10 10
- Deceleration time 1
4 Running direction setting Set F04 00 00 00
5 Extended function
6 Extended function
7 Extended function
8 Extended function
nd
setting)
(2
A group setting
B group setting
C group setting
H group setting
Note; “-“ means hidden display ;depends on 2nd setting selection.
Monitor d04 - - Monitor d05 - - Monitor d06 - - Monitor d07 - - -
Set F202 10 10 10
Set F203 10 10 10
Set A-Set B-Set C-Set H--
(3) Inverter specifications (Extended function mode : A group)
Displa
y
Order Code display EU US JPN
1 Frequency destination Set
2 Running command
3 Base frequency Set
- Base frequency(2nd setting) Set
4 Maximum frequency Set
- Maximum frequency(2
5 External freq. setting start S et
6 External freq. setting end Set
7 External freq. setting start
8 External freq. setting end
9 External freq. start pattern Set
10 Time constant of the filter
Function name Category Screen display Initial Remarks
destination
setting)
rate
rate
of analog input
A01
Set
nd
Set
Set
Set
Set
A02
A03
A203
A04
A204
A11
A12
A13
A14
A15
A16
01 01 00
01 01 02
50 60 60
50 60 60
50 60 60
50 60 60
000
000
000
100 100 100
01 01 01
888
1-2
Page 6
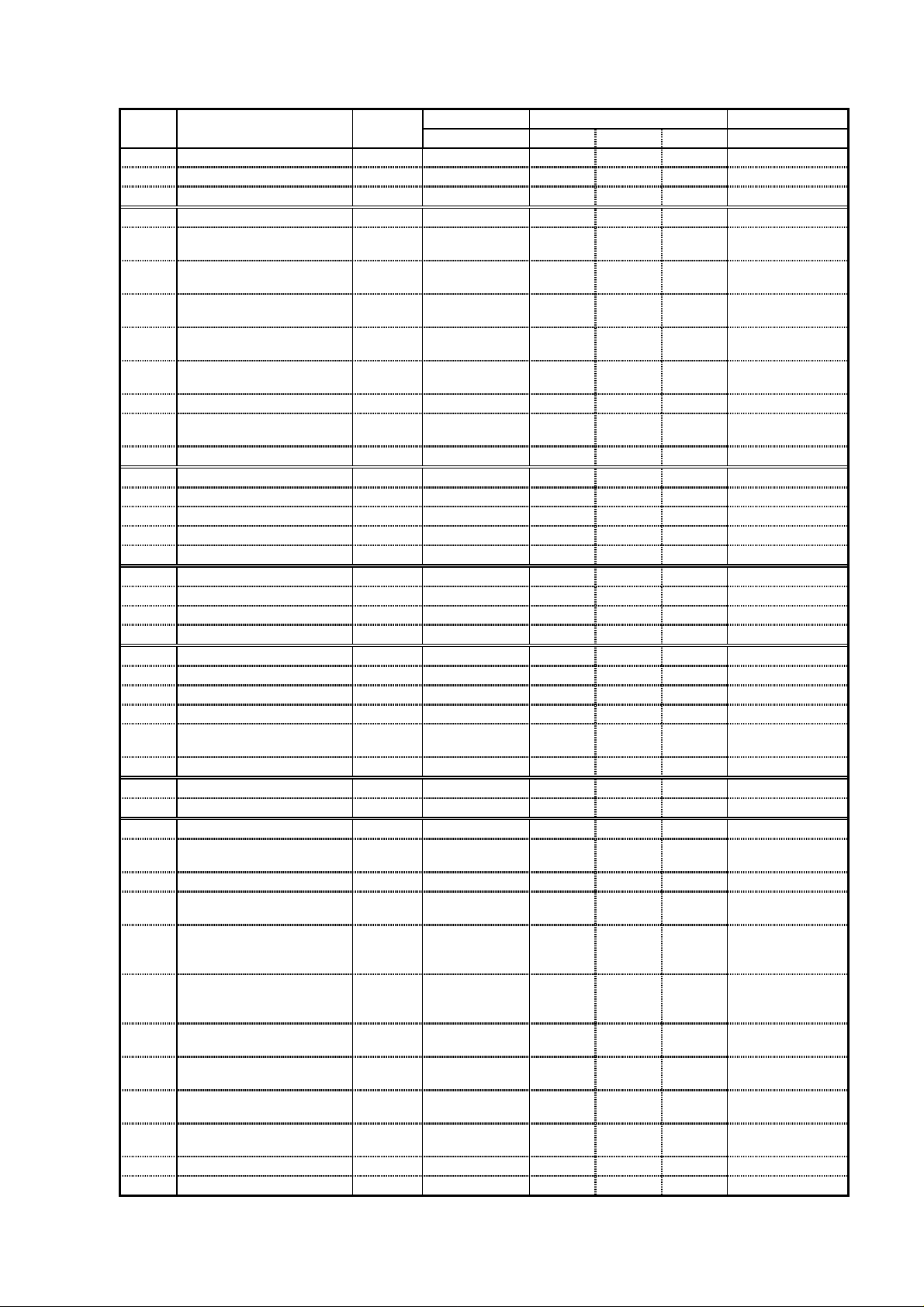
(3) Inverter specifications (Extended function mode : A group)
Display Function name Category Screen display Initial Remarks
Order Code display EU US JPN
11 Multi-speed 1 to 16 Set
12 Jogging frequency Set
13 Stop mode of jogging Set
14 Torque boost mode Set
- Torque boost mode(2
nd
A20 - A35
A38
A39
A41
A241
0 0 Note 1
1.0 1.0 1.0
00 00 00
00 00 00
00 00 00
setting)
15 Level of manual torque
Set
A42
11 11 11
boost
- Level of manual torque
boost (2
nd
setting)
16 Manual torque boost
Set
A242
A43
11 11 11
10.0 10.0 10.0
frequency
- Manual torque boost
A243
10.0 10.0 10.0
frequency (2nd setting)
17 V/f characteristics Set
- V/f characteristics(2
nd
A44
A244
00 00 00
00 00 00
setting)
18 V-gain Set
19 Selection of DC braking Set
20 DC braking frequency Set
21 DC braking waiting time Set
22 DC braking force Set
23 DC braking time Set
24 Frequency upper limiter Set
25 Frequency lower limiter Set
26 Jump frequency 1-3 Set
27 Jump frequency width 1-3 Set
28 Selection of PID control Set
29 P gain Set
30 I gain Set
31 D gain Set
32 Scale conversion of
Set
A45
A51
A52
A53
A54
A55
A61
A62
A63, A65, A67
A64, A66, A68
A71
A72
A73
A74
A75
100 100 100
00 00 00
0.5 0.5 0.5
0.0 0.0 0.0
000
0.0 0.0 0.0
0.0 0.0 0.0
0.0 0.0 0.0
0.0 0.0 0.0
0.5 0.5 0.5
00 00 00
1.0 1.0 1.0
1.0 1.0 1.0
0.0 0.0 0.0
1.0 1.0 1.0
PID control
33 Feedback destination Set
34 Selection of AVR function Set
35 AVR voltage Set
36 Second acceleration time Set
- Second acceleration
A76
A81
A82
A92
A292
00 00 00
02 02 02
230/400 230/460 200/400
15.0 15.0 15.0
15.0 15.0 15.0
time(2nd setting)
37 Second deceleration time Set
- Second deceleration
38 Method to use 2nd
time(2
nd
setting)
Set
A93
A293
A94
15.0 15.0 15.0
15.0 15.0 15.0
00 00 00
acceleration / deceleration
(Acc2 / Dec2)
- Method to use 2nd
acceleration / deceleration
(Acc2 / Dec2)(2
nd
setting)
39 Acc1 to Acc2 changing
Set
A294
A95
00 00 00
0.0 0.0 0.0
frequency
- Acc1 to Acc2 changing
A295
0.0 0.0 0.0
frequency(2nd setting)
40 Dec1 to Dec2 changing
Set
A96
0.0 0.0 0.0
frequency
- Dec1 to Dec2 changing
frequency(2
nd
setting)
41 Acceleration characteristic Set
42 Deceleration characteristic Set
A296
A97
A98
0.0 0.0 0.0
00 00 00
00 00 00
Note 1; A20;0, A21;5, A22;10, A23;15,A24;20, A25;30, A26;40, A27;50, A28; 60,A29--A35;0
1-3
Page 7
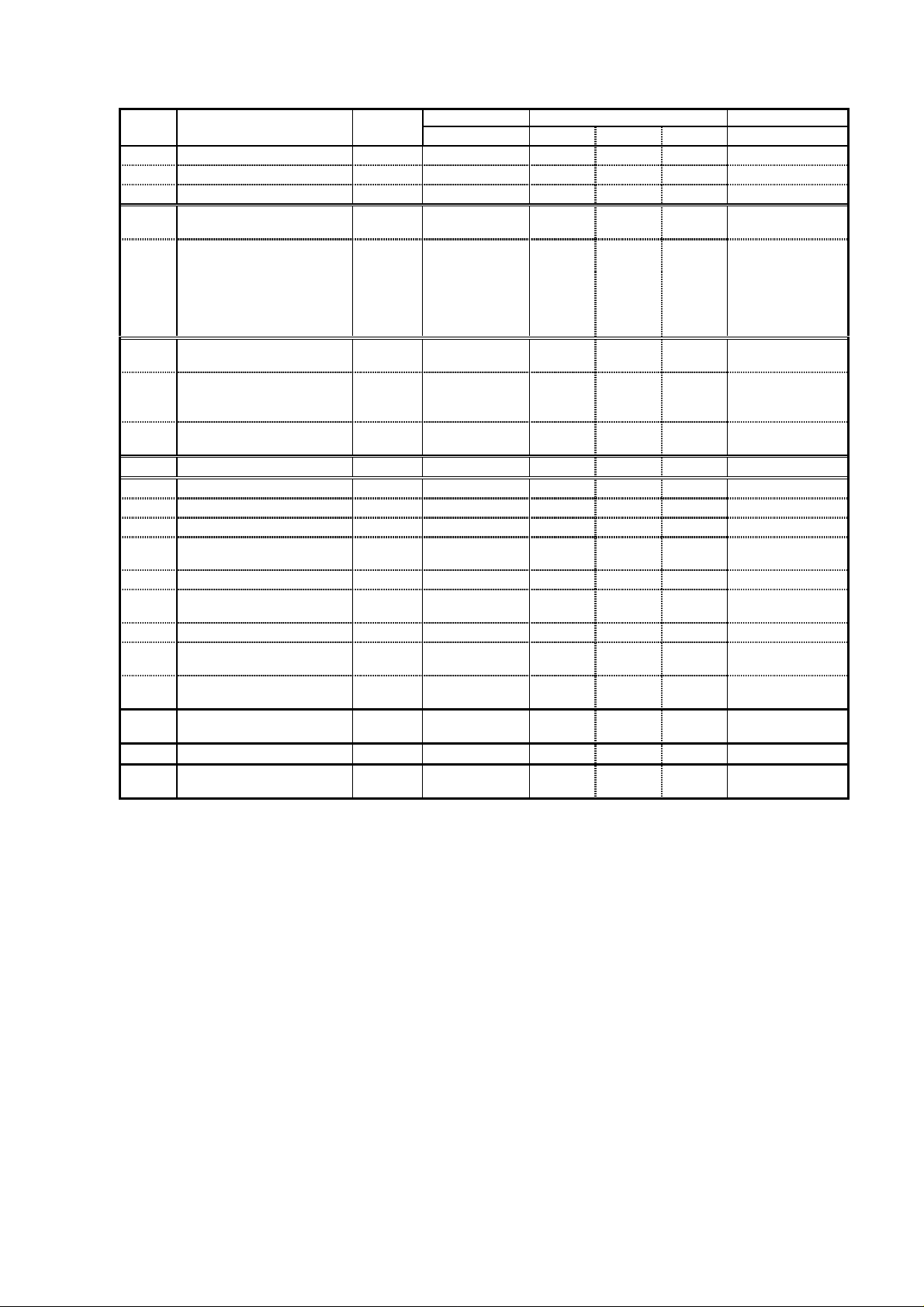
(4) Inverter specifications (Extended function mode : B group)
Display Function name Category Screen display Initial Remarks
Order Code display EU US JPN
1 Selection of restart mode Set B01 00 00 00
2 Allowable UV time Set B02 1.0 1.0 1.0
3 Retry waiting time Set B03 1.0 1.0 1.0
4 Electronic thermal level Set B12 note note note Rated current of
each inverter
- Electronic thermal level
(2
nd
setting)
5 Electronic thermal
characteristics
- Electronic thermal
characteristics (2
nd
setting)
6 Overload restriction
operation mode
7 Overload restriction level Set B22 note note note Rated current
8 Deceleration rate while
overload restriction
9 Selection of software lock Set B31 01 01 01
10 Analog meter adjustment Set B81 80 80 80
11 Start frequency adjustment Set B82 0.5 0.5 0.5
12 Carrier frequency Set B83 5 5 12
13 Data initialization or
Trip history clear
14 Initialization mode Set B85 01 02 00
15 Frequency converting
value
16 STOP key condition Set B87 00 00 00
17 Restart mode after FRS
invalid
18 Monitor contents
for OPE-J
19 Dynamic braking usage
ratio
20 Stopping mode selection Set B91 00 00 00
21 Cooling fan control
selection
Set B212 note note note Rated current of
each inverter
Set B13 01 01 00
Set B213 01 01 00
Set B21 01 01 01
* 1.25 for each
inverter
Set B23 1.0 1.0 1.0
Set B84 00 00 00
Set B86 1.0 1.0 1.0
Set B88 00 00 00
Set B89 01 01 01
Set B90 00 00 00
Set B92 00 00 00
1-4
Page 8
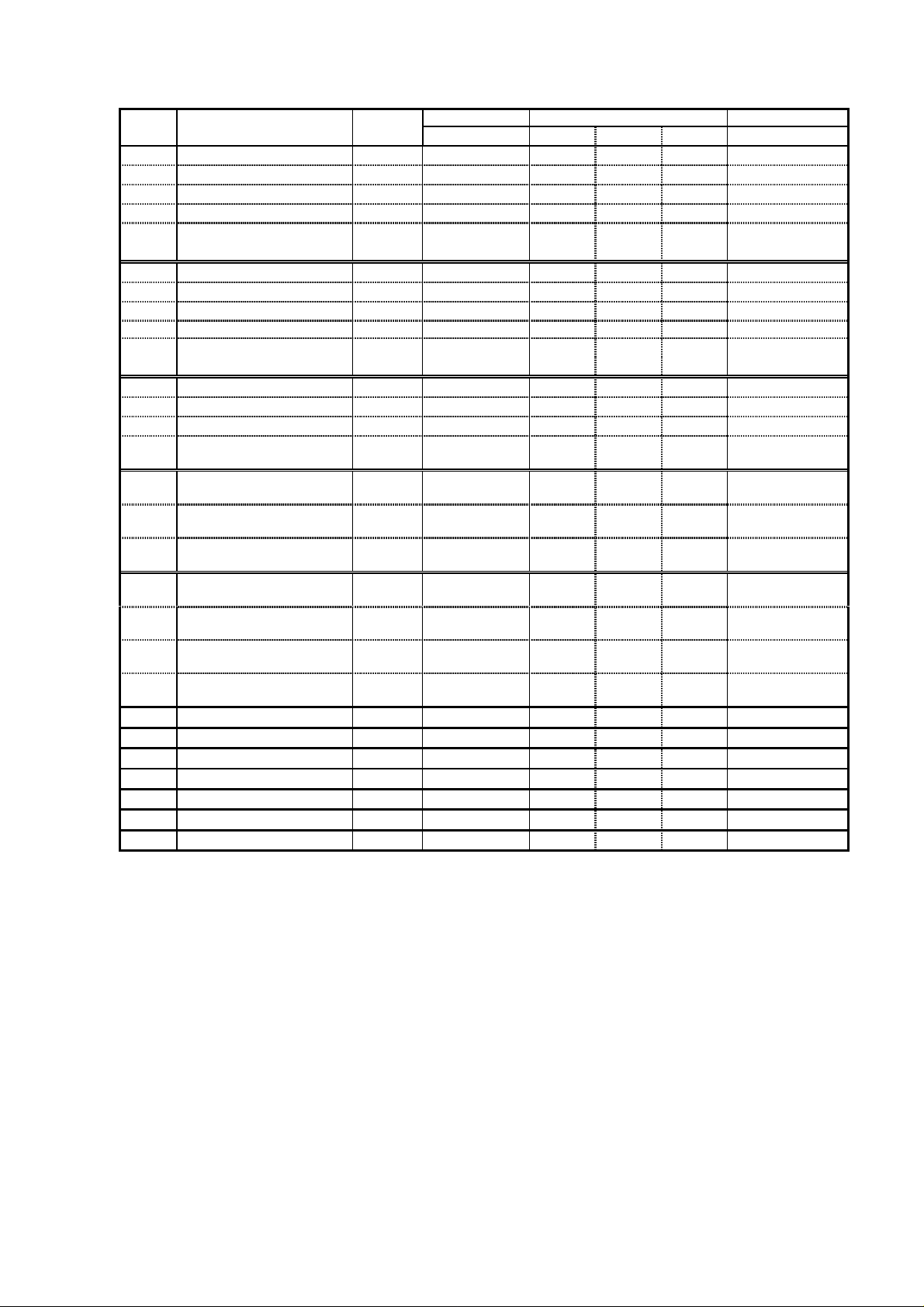
(5) Inverter specifications (Extended function mode : C group)
Display Function name Category Screen display Initial Remarks
Order Code display EU US JPN
1 Input terminal 1 assign Set C01 00 00 00
2 Input terminal 2 assign Set C02 01 01 01
3 Input terminal 3 assign Set C03 02 16 02
4 Input terminal 4 assign Set C04 03 13 03
5 Input terminal 5 assign Set C05 18 09 09
6 Input terminal 6 assign Set C06 09 18 18
7 Input terminal 1 condition Set C11 00 00 00
8 Input terminal 2 condition Set C12 00 00 00
9 Input terminal 3 condition Set C13 00 00 00
10 Input terminal 4 condition Set C14 00 01 00 Note 1
11 Input terminal 5 condition Set C15 00 00 00
12 Input terminal 6 condition Set C16 00 00 00
13 Output terminal 11 assign Set C21 01 01 01
14 Output terminal 12 assign Set C22 00 00 00
15 FM terminal condition set C23 00 00 00
16 Function of AL terminal
setting
17 Output terminal 11
condition
18 Output terminal 12
condition
19 AL output terminal
condition
20 Level of overload signal Set C41 note note note Rated current of
21 Arrival frequency
while acceleration
22 Arrival frequency
while deceleration
23 Level of deviation signal
under PID control
24 Analog input O adjustment Set C81 -- -- -25 Analog input OI adjustment Set C82 -- -- -26 Debug mode selection Set C91 00 00 00
27 Core monitor address Set C92 0000 0000 0000
28 Core monitor data Set C93 -- -- -29 Core set address Set C94 D0001 D000 D000
30 Core set data Set C95 -- -- --
Set C24 05 05 05
Set C31 00 00 00
Set C32 00 00 00
Set C33 01 01 01
each inverter
Set C42 0.0 0.0 0.0
Set C43 0.0 0.0 0.0
Set C44 3.0 3.0 3.0
Note 1
USP functi
on (NC) is allocated on US version and even another function such as CF1 is set, NO/NC
parameter is still the same. Therefore, please make sure the NO/NC parameter to suit the application.
1-5
Page 9
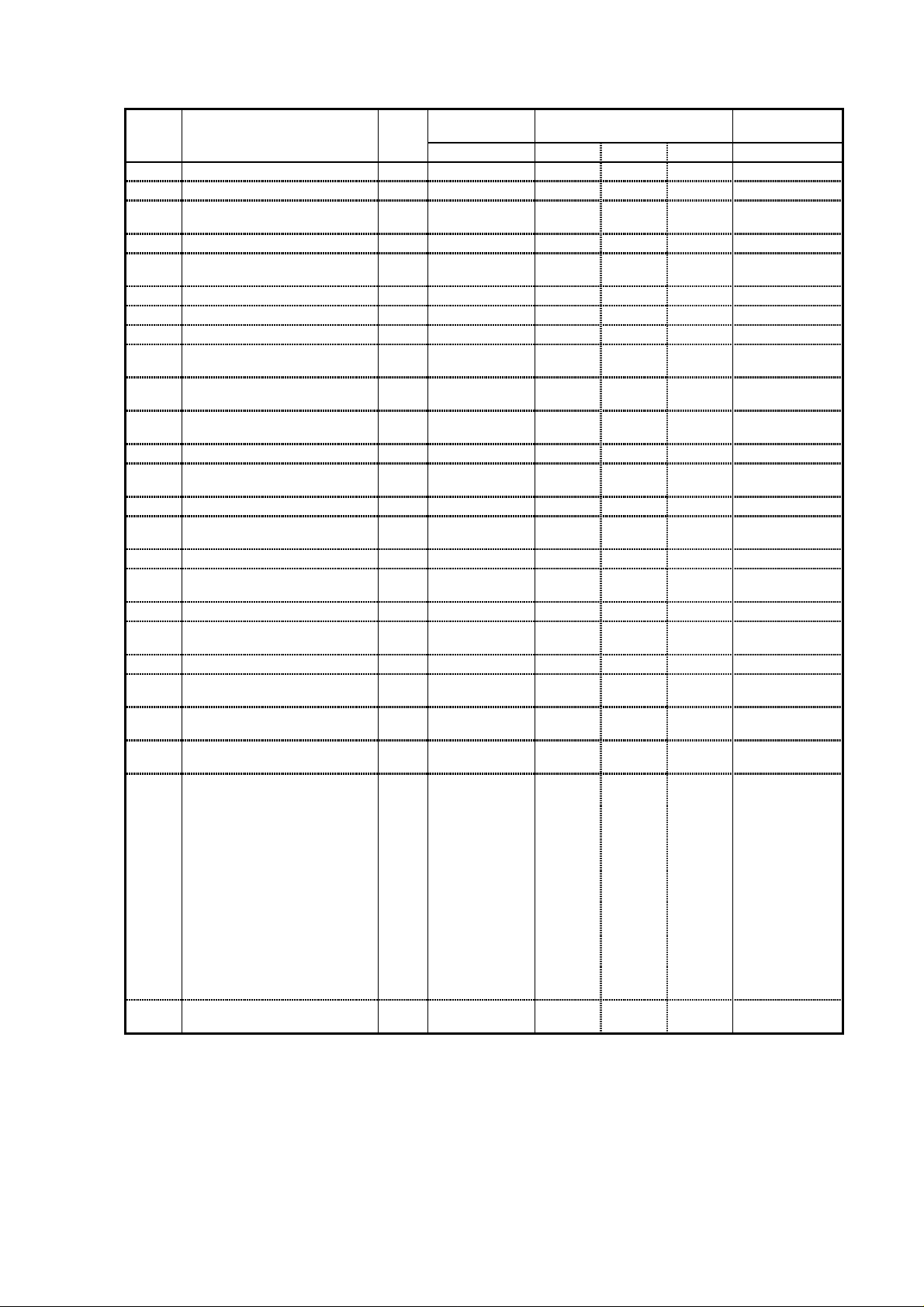
(6) Inverter specifications (Extended function mode : H group)
Display Function name CategoryScreen display Initial Remarks
Order Code display EU US JPN
1 Auto tuning setting Set H01 00 00 00
2 Motor data selection Set H02 00 00 00
- Motor data selection(2
setting)
3 Motor capacity setting Set H03 *3 *3 *3
- Motor capacity setting(2
setting)
Motor poles setting H04 4 4 4
Motor poles setting( 2nd setting) H204 4 4 4
4 Speed response setting Set H05 20 20 20
- Speed response setting(2
setting)
5 Motor stabilization constant
setting
- Motor stabilization constant
setting(2
nd
setting)
6 Motor constant R1 setting Set H20 *2 *2 *2
- Motor constant R1 setting(2
setting)
7 Motor constant R2 setting Set H21 *2 *2 *2
- Motor constant R2 setting(2
setting)
8 Motor constant L setting Set H22 *2 *2 *2
- Motor constant L setting(2
setting)
11 Motor constant Io setting H23 *2 *2 *2
- Motor constant Io setting(2
setting)
12 Motor constant J setting H24 *2 *2 *2
- Motor constant J setting(2
setting)
13 Motor constant R1(auto tuning
data)
- Motor constant R1(auto tuning
data,2nd setting
14 Motor constant R2(auto tuning
data)
- Motor constant R2(auto tuning
data,2
nd
setting
15 Motor constant L(auto tuning
data)
- Motor constant L(auto tuning
data,2
nd
setting
16 Motor constant Io(auto tuning
data)
- Motor constant Io(auto tuning
data,2
nd
setting
17 Motor constant J(auto tuning
data)
- Motor constant J(auto tuning
data,2
nd
setting
nd
nd
Set H202 00 00 00
Set H203 *3 *3 *3
nd
Set H205 20 20 20
Set H06 100 100 100
Set H206 100 100 100
nd
set H220 *2 *2 *2
nd
Set H221 *2 *2 *2
nd
nd
nd
Set H224 *2 *2 *2
H220 *2 *2 *2
H223 *2 *2 *2
*1 H30 *2 *2 *2
*1 H230 *2 *2 *2
*1 H31 *2 *2 *2
*1 H231 *2 *2 *2
*1 H32 *2 *2 *2
*1 H232 *2 *2 *2
*1 H33 *2 *2 *2
*1 H233 *2 *2 *2
*1 H34 *2 *2 *2
*1 H234 *2 *2 *2
*1; don’t change the data
*2 ; factory set
*3 ; specified by the capacity of each inverter
1-6
Page 10
[2] Motor specifications.
Output voltage
V
0
Motor MFG number
Output
frequency
Hz Hz
[3] Load conditions
Equipment name
Torque characteristics
kWMotor output
pMotor poles
rpmMotor rated rpm
AmpsRated current
VRated voltage
HzRated frequency
AmpsStarting current
secAcceleration ti me
NmRequired torque
secDeceleration time
Load inertia (J)
kgm
1-7/E
2
Variable speed range
Hz to
Hz
Page 11
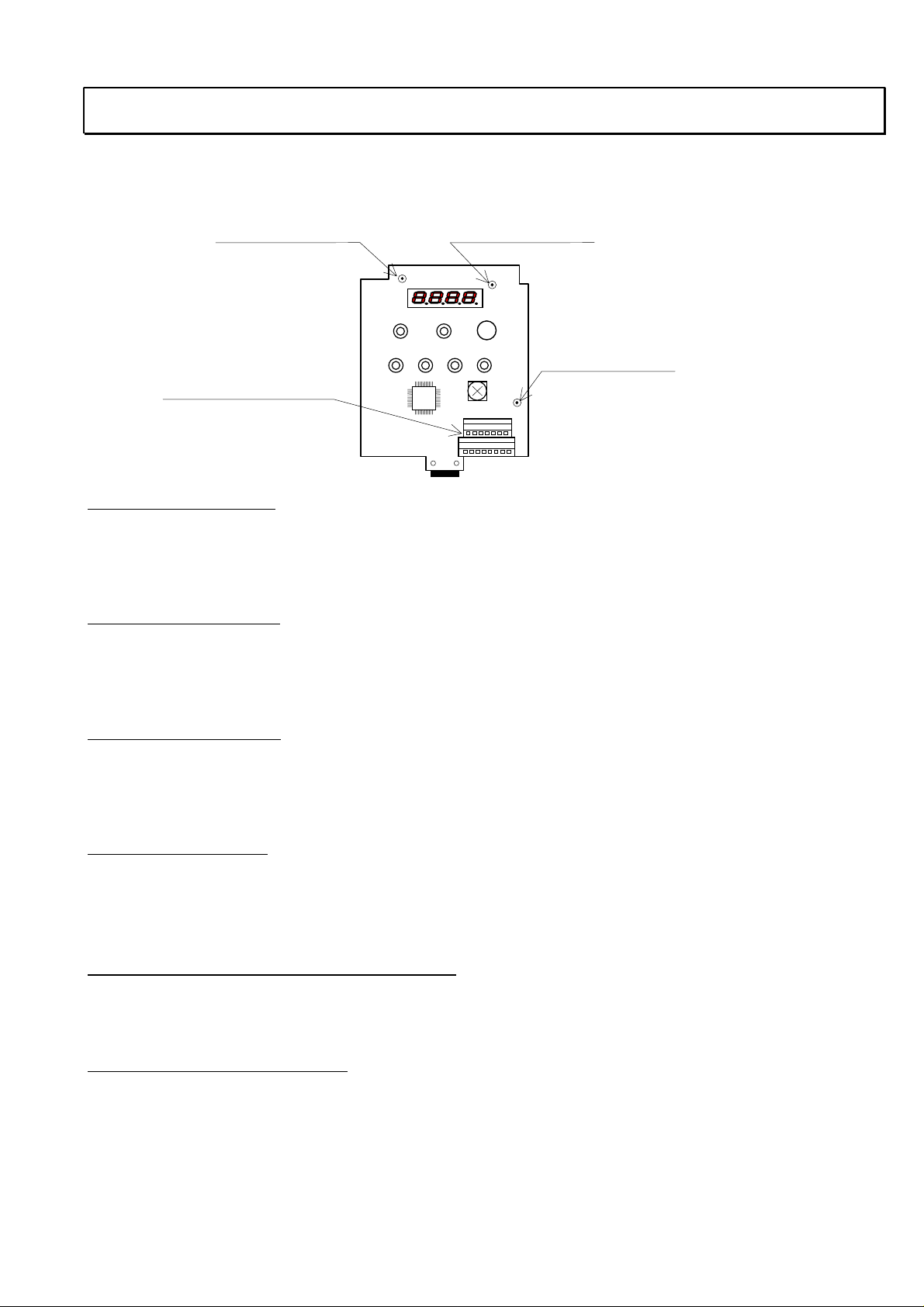
2. Measurement of the Internal Voltage Supply
There are PV5L, PV24L and NV12L internal DC voltage supplies. These supplies are isolated from the
main high voltage portion. And it is not possible to measure DC voltages at the non isolated portion.
Please make measurements for above mentioned voltages for the isolated portion.
Check pad of NV12 Check pad of PV24
Check pad of PV5
1 pin of TM2 is “L”common
PV5L supply voltage
Supplies 5V for I/O board.
Nominal voltage : min. 4.90Vdc to max. 5.20Vdc
Check PV5(address 1C) <- L
PV24L supply voltage
Supplies 24V to interface voltage supply, which is supplied to input terminals.
Nominal voltage : min. 21.60Vdc to max. 26.40Vdc
Check PV24(address 1A) <- L
NV12L supply voltage
Supplies -12Vdc to remote operator (DOP/DRW’s yellow back light ).
Nominal voltage : max. -10.80Vdc to min. -17.5Vdc
Check NV12(address 3A) <- L
“H” terminal voltage
Suppiles 10V to “H” terminal
Nominal voltage : min 9.5Vdc to max 11.5Vdc
<->
Check “H”
“L” with VR (1kohm)
“Potentiometer function on the front case
Set “A01” :”00”
<->
Monitor “F01” display 0
50(60) with clockwise and anti clockwise.
Cooling FAN voltage (PV24N)
Supplies 24V to cooling FAN .
Nominal voltage min 19. 9Vdc to max 27.2Vdc.
Check Red wire
<-
Black wire with the FAN.
Check the FAN working, direction(from down to up).
2-1/E
Page 12

3. Trouble Shoot
3-1. Error Messages - Possible Cause and Remedy:
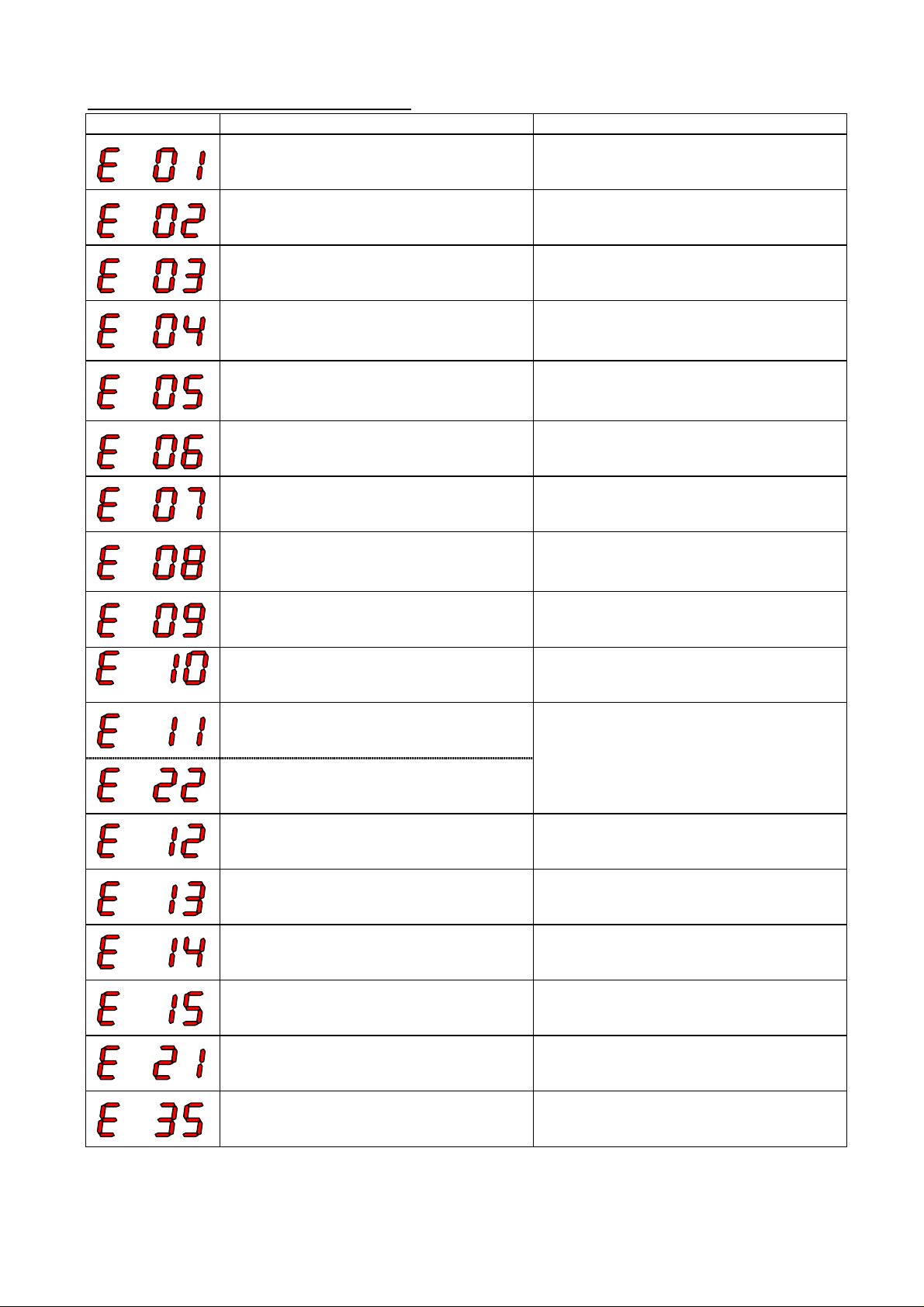
(1) Over current 1 (E 01, E 02, E 03, E 04)
Phenomena: Over current (CT or Rsh;gate driver IC) for each condition.
E 01 : Over current during constant speed operation.
E 02 : Over current during deceleration.
E 03 : Over current during acceleration.
E 04 : Over current at other condition than above mentioned.
(such as injection brake)
Cause: Load changed rapidly.
Remedy: Eliminate rapid changed in load.
Cause: Sort circuit or earth contact (ground fault) in the motor or the motor cable.
Remedy: Check with Megger. If the motor cable is disconnected from the inverter, the over
current should not be detected anymore.
Cause: A single-phase power failure (fuse, wire, ...) can cause a shutdown in certain
under load situations..
Remedy: Check all these mains phases and the mains fuses, preferably by comparison of
the three (two in case of single phase inverter) mains currents in a steady
operating state.
Cause: The motor is switched with a motor contactor during frequency inverter operation.
Remedy: Switching over the motor is inhibited.
Cause: Defect in the power component.
Remedy: Check the IGBT portion of ISPM.
Cause: Rapid acceler ation or deceleration.
Remedy: Set suitable acceleration or deceleration time.
Cause: St arting frequency is too high.
Remedy: Set starting frequency as low as possible.
Way to Reset: A
SJ100 has two kinds of detection; CT and Rsh. To resolve the detection at site, check the following
procedure.
1. Connect DOP/DRW.
2. Set F38 INIT DEBG ON. (to access debug mode)
3. Set F22 IPS POWR ALM mode, don’t set retry mode.
4. Test run and wait Over Current trip.
5. Set Core address “FBE4” if it’s 4kW or less.
5. Set Core address “FBE2” if it’s 5.5kW or above.
3-1
Page 13

Specimen ;
“CO FBE4 01 0000” ; under normal; 0Hz
“CO FBE4 15 0203” ; under over.C trip
“CO FBE4 15 C203” ; under OC.Drive trip.
“CO FBE4 15 4103” ; under OC.Accel trip
“FBE4” or “FBE2” is 1 byte data, the data is hex data. Example “4103”; “03” has no meaning.
Resolve “41”h bit by bit,
“41”h -> “0100 0001”b
if you found “xxxx xxx1” ; this means Over current detection from CT (CTU or CTW)
if you found “xxxx xx1x” ; this means Over current detection from Rsh
Standard operator is not available on this trouble shooting.
(2) Overload (E 05)
Phenomena: Overload (detected by CT) of the inverter.
This error can be reset 10 seconds after the E05 came out.
Cause: Motor load is heavy.
Remedy: Reduce the load and/or increase thermal level and/or use bigger capacity of
frequency inverter.
Cause: V- Boost value is high.
Remedy: Reduce V-Boost value or increase thermal level and/or use bigger capacity of
frequency inverter.
Cause: Set wrong value for electronic thermal level [b12] and/or electronic thermal
characteristic [b13].
Remedy: Set suitable value.
Cause: Set wrong value for the reactive current of the motor.
Remedy: Set suitable value. Reactive current value which should be input by function mode
is a value measured at 50Hz (60Hz) without load.
Way to Reset: A
(3) Braking Resistor Overload (over voltage) (E 06)
Phenomena: Over Voltage detection after BRD%ED was run out.
Cause: BRD select ion is not suitable.
Remedy: Check BRD %ED, BRD resistor ohm, BRD resistor W attage, BRD resistor wire,
machine inertial, operation cycle.
Way to Reset: A
3-2
Page 14

(4) Over voltage (E 07)
Phenomena: Over voltage at DC bus line of the frequency inverter.
Cause: Mains voltag e too high, mains voltage fluctuation or rapid mains voltage return
(choke energy leads to voltage increase).
Remedy: Make sure that mains voltage is within tolerance limits.
Cause: In case SJ100 is used in combination with a regenerative braking unit(ISPM)/
resistor but the regenerative braking unit(ISPM)/resistor does not function.
Remedy: Replace regenerative braking unit(ISPM)/resistor.
Cause: In case SJU100 is used in combination with a raking resistor but the braking
resistor cannot absorb the regenerative energy.
Remedy: Re-calculate and use suitable braking resistor.
Cause: Deceler ation time is too short.
Remedy: Make deceleration time longer, use braking unit (resistor), use bigger capacity of
frequency inverter.
Way to Reset: A
(5) Under voltage (E 09)
Phenomena: Under voltage at DC bus line of the frequency inverter.
Cause: The mains voltage is not available or not within the tolerance limits.
Remedy: Check all 3 (or 2) mains power supply voltage that it is within its specification.
Cause: T hyristor for smooth charging is defect and DC bus voltage drops while operation
due to current flows through smooth charging resistor.
Remedy: Change ISPM.
Cause: Period of instantaneous power failure is longer than the set value [b02], or DC bu s
voltage go down to its detecting level while instantaneous power failure.
Remedy: Get rid of the instantaneous power failure, evaluate the power supply system, set
bigger value for [b02].
Cause: O ne of the AC voltage is missing (applied only for 3 phase INV)
Remedy: Check AC line voltage , check the fuses.
Way to Reset: A
(6) EEPROM error (E 08)
Phenomena: Abnormal situation occurs at the memory portion of the frequency inverter due to
incoming noise etc..
Cause: I nfluenced by Electrical Magnetic Interference.
Remedy: Keep such noise source away from the frequency inverter.
Cause: Am bient temperature is too high.
Remedy: Take countermeasure against high ambient temperature.
3-3
Page 15

Cause: Re- power up the frequency inverter short time after power off. It is necessary to
keep several seconds after power off to memorize the current data at EEPROM. If
this time is too short, this storage performance cannot be done and leads to
EEPROM error.
Remedy: Keep certain time between power off and re-power up.
Cause: You didn’t wait 6 seconds or more at FACTORY SETTING.
Remedy: Please try FACTORY SETTING again.
Cause: RS t erminal was keeping “ON” at power off. (If RS is on, INV can not write the
correct data to EPROM at power off, next power on E08 will come out.)
Remedy: Please don’t use “RS” terminal “ON” at power off.
Cause: EEPRO M is def ect.
Remedy: Change unit.
After you reset the INV, please make sure the parameters espec ially maximum freq. / A cc /Dec
time / Low limit freq. to prevent any damage.
Way to Reset: A or Power off
(7) CT error (E 10)
Phenomena: When abnormality noise is near the INV or an abnormality (off set level is out of
spec.) occurs on built in CT.
Cause: I nfluenced by Electrical Magnetic Interference. (such as near contactor on/off)
Remedy: To Resolve if it’s influence, use another power line and don’t connect motor wires,
control wires. If no error comes out, resolve noise causes.
Cause: CT offset level failure
Remedy: To Resolve if it’s failure, use another power line and power on and check if E10
comes out at power on. If E10 came out , use (replace) another INV(ISPM).
Way to Reset: A or Power off
(8) CPU error (E 11, E 22)
Phenomena: Abnormal situation or malfunction of micro processor inside frequency inverter.
E 11 : CPU error from MCU inside core.
E 22 : CPU error from MCU on I/O board.
E22 is produced by MCU on I/O board and the causes is communication error between ISPM & M CU
on I/O board.
Cause: Cable ( between ISPM and I/O board)was cut. (E22)
Remedy: Replace the cable.
Cause: Dust s on the pins of CN2 on I/O board. (E22)
Remedy: Remove the dusts.
Cause: I nfluenced by Electrical Magnetic Interference.
Remedy: Keep such noise source away from the frequency inverter.
Cause: Am bient temperature is too high.
Remedy: Take countermeasure against high ambient temperature.
3-4
Page 16

Cause: Com ponent itself is defect.
Remedy: Replace ISPM (in case of E 11) or I/O board board (in case of E 12).
(9) External Trip (E 12)
Phenomena: Trip due to have inputted an external signal to “EXT” input terminal of the
frequency inverter.
Cause: Fault y external device or equipment gives frequency inverter a trip requirement
when external trip function (EXT) is selected.
Remedy: Evaluate external device or equipment which is connected to frequency inverter.
Way to Reset: A
(10) USP error (E 13)
Phenomena: Unexpected Start Protection. This error can occur when “USP” function is
selected.
Cause: Fr eq uency inverter trips when it is powered up with RUN command is given.
Remedy: Disable RUN command when power up the frequency inverter. Or disable USP
function if possible to the system.
Way to Reset: A or set RUN command off (stop)
(11) Ground fault error (E 14)
Phenomena: Earth contact in the motor or the motor cable or in the IGBT. Frequency inverter
detects this earth contact only at power up.
To resolve the causes , please power off and disconnect the motor wire at INV (UVW)terminal.
Cause: Ear th contact in the motor or the motor cable.
Remedy: Check the impedance between output portion(wire and motor) and earth.
Cause: Det e ct ion circuit /IGBT of the inverter is defect. If the m otor and t he mot or cable is
disconnected from the frequency inverter, the ground fault should not be detected
anymore.
Remedy: Please disconnect the motor and the motor cable.
If E14 comes out at power on, please replace the unit.
Way to Reset: Don’t reset.
(12) Over voltage at source (E 15)
Phenomena: High voltage at power source line. Frequency inverter cannot protect source over
voltage. If it is too high, frequency inverter will be damaged.
Cause: Sour ce voltage is too high.
Remedy: Check the source voltage continously.
Insert AC reactor at source lines.
Way to Reset: A
3-5
Page 17

(13) Over temperature (E 21)
Phenomena: Temperature sensor which located close to IGBT inside ISPM shows a too high
temperature.
Cause: Vent ilator blocked. (for models which has ventilator.)
Remedy: Check ventilator
Cause: The frequency inverter does not get enough cooling air.
Remedy: Check cabinet ventilation, air filters, and ventilation openings in the cabinet.
Way to Reset: A
(14) PTC error (E 35)
Phenomena: Resistance of motor thermistor is high. This error can occur when you select
“PTC” function.
Cause: Too much load of the motor.
Remedy: Reduce the load, use bigger motor.
Cause: Motor t hermist or is not connected while PTC function is selected.
Remedy: Disable PTC function when it is not used.
Cause: Char acteristics of the motor thermistor is not suitable. Frequency inverter gives
PTC error when the resistance value becomes more than 3k ohm +-10%.
Remedy: Use motor which has suitable thermistor for the inverter.
Or change thermistor characteristics of the thermistor by debug mode.
Way to Reset: A
Explanation of the way to reset.
A : Make close the terminals between RS and P24 (CM1 only for Japanese version) on the I/O board, or
press “STOP/RESET” key of the operator.
3-6
Page 18
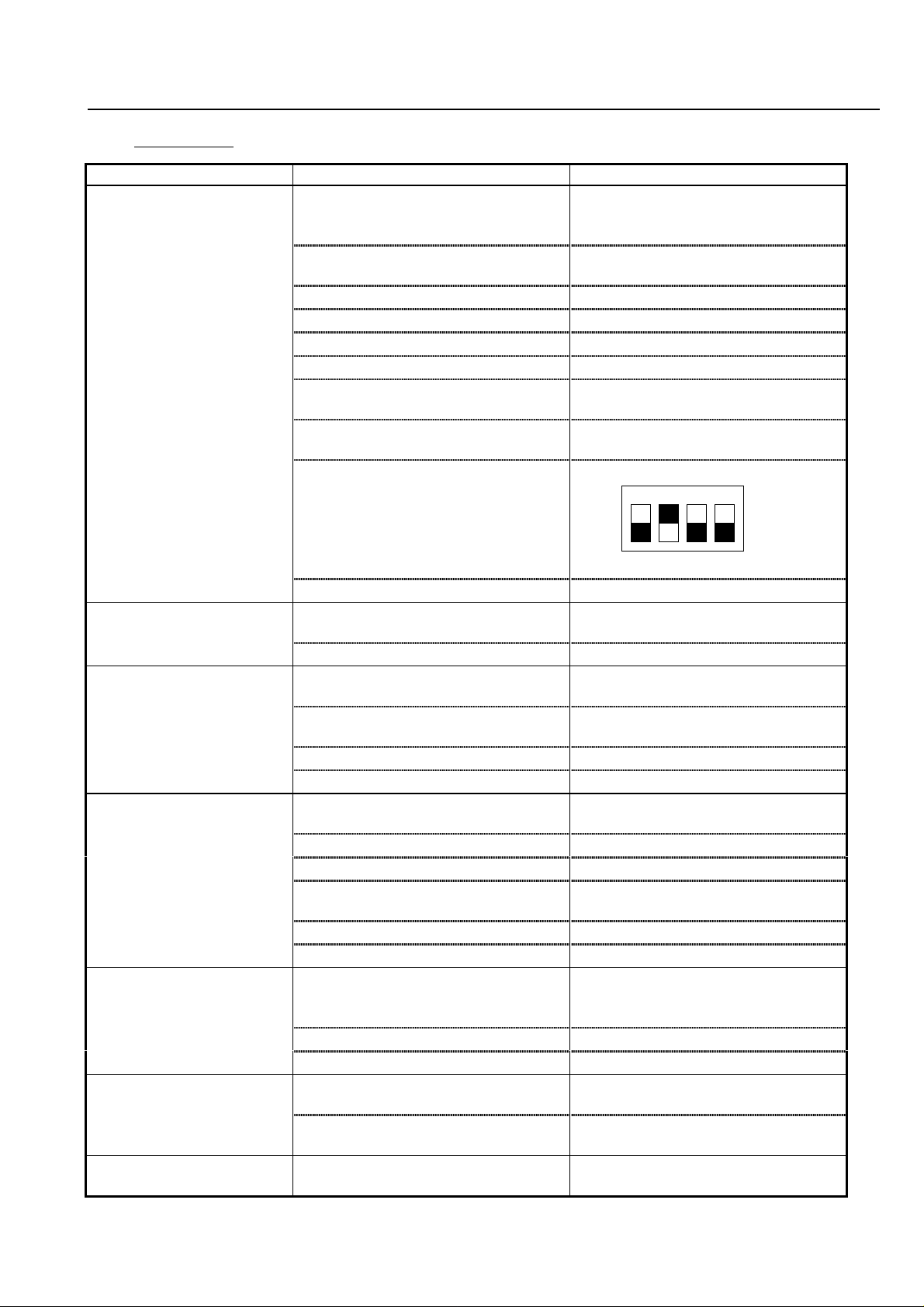
3-2. Analysis of Various Operating Problems That Do Not Trigger an Trip
message.
Problem Possible cause Remedy
The motor does not start Mode of frequency command [A01]
and/or Run command [A02] is not
proper
Incorrect power supply condition Check that the power supply is
Inverter is in trip mode Get rid of the trip cause
0 Hz of Multi-stage speed is given
FRS and/or RS is remaining Make FRS and RS invalid
0 Hz command is given
Each phase to phase voltage does
not balance. (out of +-3%)
Load is too heavy Decrease the load or use bigger
If you use DOP or DRW, DIP
switch selection of the operator is
incorrect.
Check each mode again
within its specification
Replace the unit
capacity of inverter and motor
Set as follows
Same as J300, J100,L100
Inverter Failure Replace the unit
Rotation direction is
opposite
Motor does not increase
speed
The inverter cannot be
programmed
Unstable rotation of the
motor
Data is not changed Forgot to press [STR] key Press [STR] key after changing
Cannot change data by
Copy Unit
Wiring of the mo tor cable is
incorrect (U, V, W)
Setting of [F04] is incorrect Check the setting
Motor load is too heavy
(Overload limitation)
External frequency set (VR) is out
of order
Frequency limiter [A61] is set Elim inat e fr equency limiter
Acceleration time is too short Set longer acceleration time
Software lock is selected [b31] Make software lock invalid
While INV running Stop the INV
RS or FRS command is given Make them invalid
Multi stage speed command is
given
Loose connection of DOP/DRW Connect DOP/DRW properly
Inverter is in trip mode Reset the inverter
Motor load is changing heavily Reduce t he motor load changing
Source voltage is changing Reduce the changing
Mechanical resonance Change output frequency
Turn main power off within 6
seconds after pressing [STR] key
Turn power off within 6 seconds
after started copying
Check the wiring of the motor
cable
Remove or decrease the motor
load
replace VR
Make inverter in stop mode
or use bigger capacity of inverter
and motor
data
Make sure to wait at least 6
seconds after [STR] key is pressed
Make sure to wait at least 6
seconds
3-7
Page 19
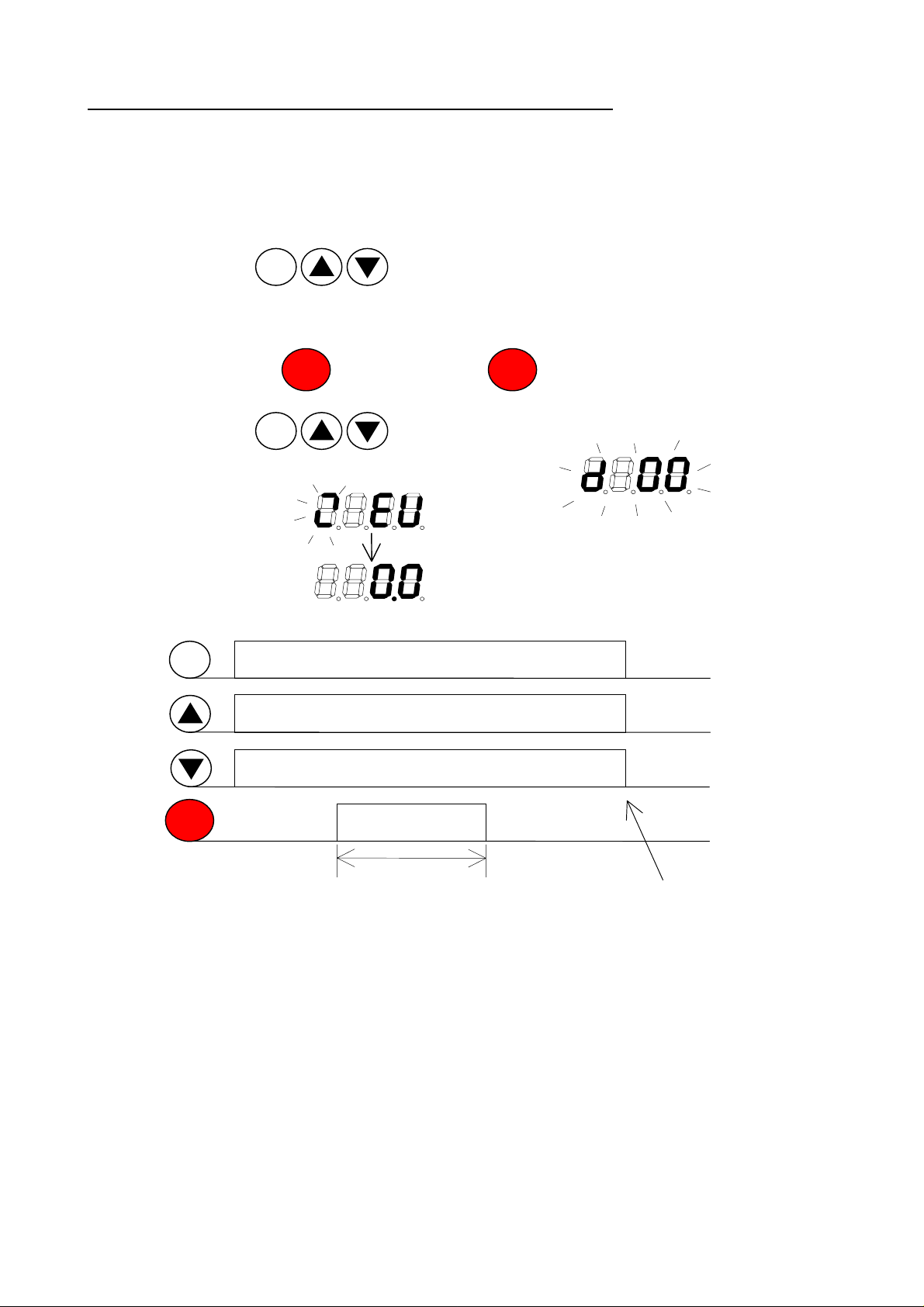
3-3. How to Initialize the Data (FACTORY SETTING)
1. Select the mode of initialization data to which you want to initialize by [b85].
Japanese version data -----> Set “00” and store
EU version data -----> Set “ 01” and store
US version data -----> Set “ 02” and store
2. Set [b84] to “01” to initialize and store.
3. Keep pressing keys at the same time.
FUNC.
2
1
(If front case is not closed by the screw, difficult to press 3keys.)
FUNC.
STOP
RESET
2
1
4. Additionally press key and release key approximately after one second.
5. Keep pressing keys until “d 00” will blink. (Approximately 2 seconds.)
STOP
RESET
6. Release all the keys after starts blinking.
Initializati on end
FUNC.
1
ON (press)
ON
2
STOP
RESET
ON
ON
1s or more
[c95] ; INV kW code
01;0.2kW , 02;0.4kW , 03;0.75kW (0.5 kW) , 04;1.5kW , 05;2.2kW ,
06;3.7kW(4.0kW) , 07;5.5kW, 08;7.5kW
Release after “d 00
started blinking
”
3-8
Page 20
3-4. Error Message comparison
Digital Panel DOP / DRW Contents
Over current while constant speed
OC. Drive
OC. Decel
OC. Accel
Over. C
Over. L
OL. BRD
driving (CT or gate driver IC)
Over current while deceleration (CT or
gate driver IC)
Over current while acceleration (CT or
gate driver IC)
Over current at other condition than
above(such as 0Hz,injection brake)
(CT or gate driver IC)
Over load
(Possible to reset after 10 seconds
has passed, detected by CT)
Over voltage after the BRD%ED
was run out. (DC bus)
Over voltage (DC bus)
Over. V
EEPROM error
EEPROM
(Check the parameters again if this
error occurred)
Under voltage (DC bus)
Under. V
CT
CPU 1
CPU 2
External
USP
GND Flt
OV. SRC
OH FIN
PTC
CT offset error such as external noise
or CT itself
CPU error
External error
USP error
Ground fault at power-on detected by
CT
Over voltage at source (DC bus)
(continuously 100sec while stop)
Over temperature (in the ISPM)
PTC error (only terminal 5 )
3-9
Page 21

3-5. Other Displays
Digital Panel Contents
- Reset terminal is ON
- During initialization (such as at power-on)
- Voltage is within UV level
- Power OFF
- During retry mode
- During initialization as EU settings
- During initialization as US settings
- During initialization as Japanese settings
- Erasing trip histories
- Copying with DRW,DRW-2
- When there is no data
(i.g. feedback data of PID, etc.)
Auto tuning was done.
Auto tuning was failed.
3-6. Auto tuning under high incoming voltage
If Auto tuning is not successful , try following procedure.
1. Set C91 “01” and press STR key. (to access debug mode)
2. Set H01 “01” and press STR key. (to do auto tuning)
3. If the SJ100 is 4kW or less, set C94 “fb82” and press STR key.
3. If the SJ100 is 5.5kW or above, set C94 “fb80” and press STR key.
4. Set C95 “0000” and press STR key.
5. Run command ON. (Run key or FW terminal) to get started Auto Tuning.
3-10/E
Page 22
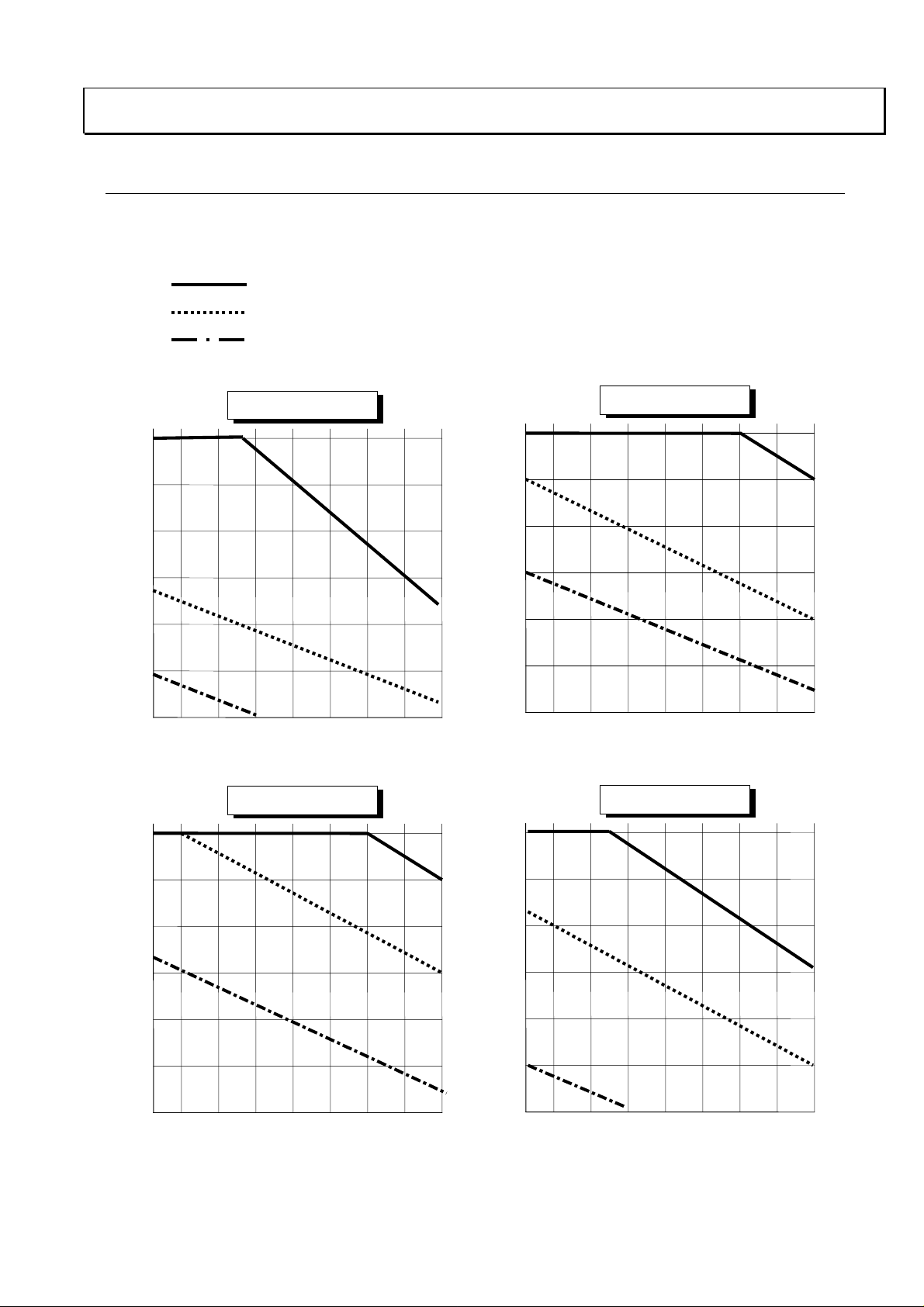
4. Ambient Condition of the Frequency Inverter
4-1. Required Derating in case of 50deg, 55deg of Ambient Temperature
Inverter ratings can be influenced by many factors. You can find in this section, the relation between
ambient temperature and output current (%) and carrier frequency.
Standard ratings in 40 degree C
Top cover removed condition in 50 degree C max.
Top cover removed condition in 55 degree C max.
% rate of output
current
100%
90%
80%
70%
Carrier frequency [kHz]
100%
SJ100-002NFE(U)
SJ100-007NFE(U)
% rate of output
current
100%
1614121086420.5
100%
SJ100-004NFE(U)
90%
80%
70%
1614121086420.5
Carrier frequency [kHz]
SJ100-015NFE(U)
90%
80%
70%
Carrier frequency [kHz]
90%
80%
70%
16
14121086420.5
Carrier frequency [kHz]
1614121086420.5
4-1
Page 23
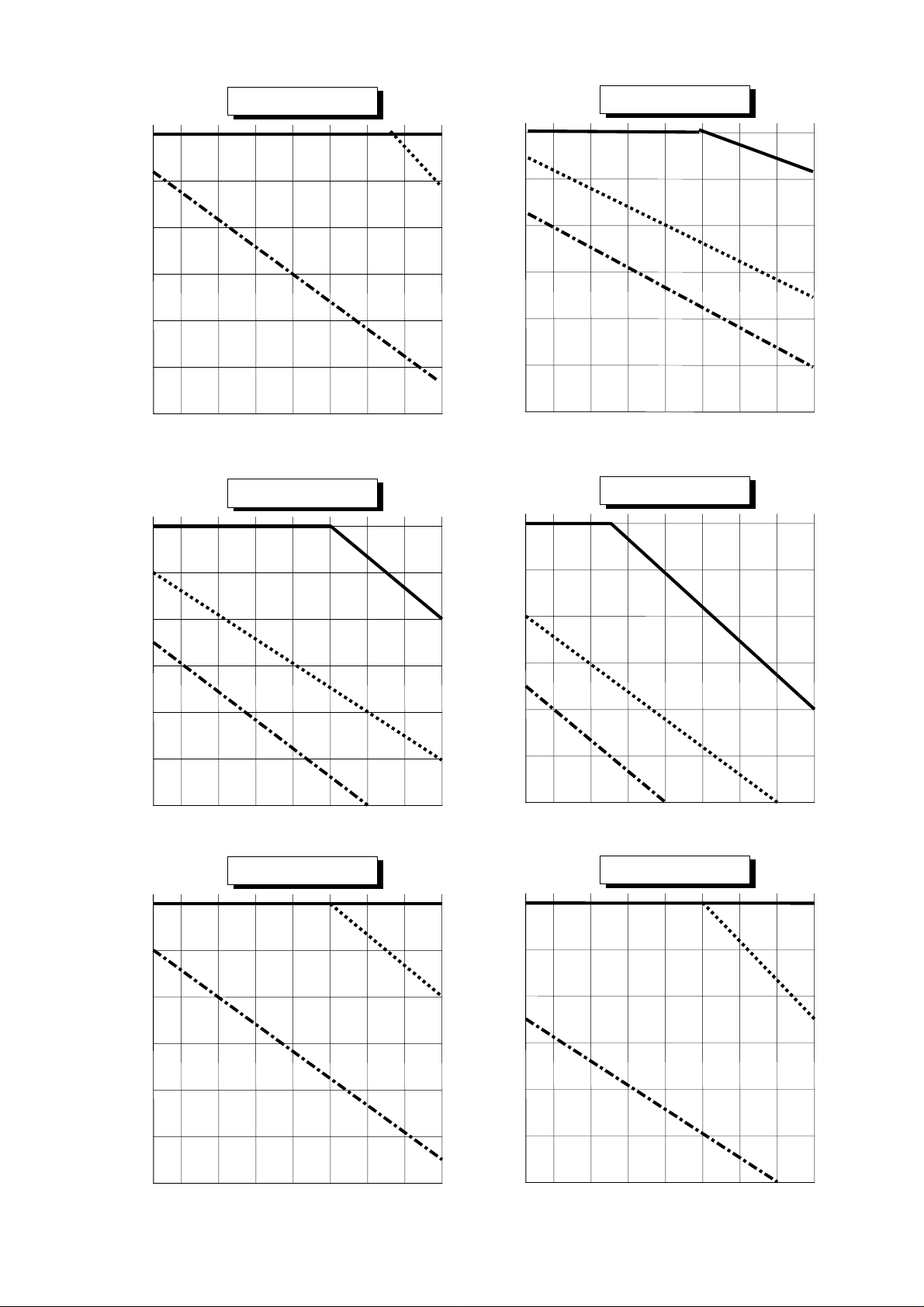
SJ100-022NFE(U)
SJ100-037LF(U)
100%
90%
80%
70%
100%
90%
Carrier frequency [kHz]
SJ100-004HFE(U)
100%
90%
80%
70%
60%
50%
1614121086420.5
40%
Carrier frequency [kHz]
1614121086420.5
SJ100-007HFE(U)
100%
90%
80%
70%
60%
50%
40%
100%
90%
80%
70%
Carrier frequency [kHz]
SJ100-015HFE(U)
80%
70%
60%
50%
1614121086420.5
40%
Carrier frequency [kHz]
1614121086420.5
SJ100-022HFE(U)
100%
90%
80%
70%
60%
50%
40%
Carrier frequency [kHz]
60%
50%
16
14121086420.5
40%
Carrier frequency [kHz]
1614121086420.5
4-2
Page 24

100%
90%
80%
70%
60%
50%
SJ100-040HFE(U)
40%
100%
90%
80%
70%
Carrier frequency [kHz]
SJ100-055LFU
Carrier frequency [kHz]
SJ100-055HFE(U)
16
14121086420.5
SJ100-075LFU
100%
90%
80%
1614121086420.5
70%
1614121086420.5
Carrier frequency [kHz]
SJ100-075HFE(U)
100%
90%
80%
70%
Carrier frequency [kHz]
4-3
100%
90%
80%
70%
1614121086420.5
Carrier frequency [kHz]
1614121086420.5
Page 25

4-2. Required derating toward altitude
100%
90%
80%
70%
1000
2000 3000 4000
Altitude [m]
Example of calculation
SJ100-007NFE (4 Amps) is installed at 2000m of altitude and 16kHz of carrier frequency.
Required derating of output frequency of this case will be as follows.
4 [Amps] * 90% * 95% = 3.4 [Amps]
Carrier frequency derating
Altitude frequency derating
<Note 1> When the top cover is removed for the high ambient temperature, inverter should be installed
in an enclosure of IP 4* (see EN60529) to comply with LVD directive.
<Note 2> If class B of EMC directive is required, carrier frequency must be set to 5kHz.
4-4/E
Page 26

5. Level of Each Detection
5-1. DC Bus Voltage Detection Characteristics
Frequency inverter has several detection characteristics for DC bus voltage as followings.
[1] 200V class
DC bus
voltage [Vdc]
400
Over voltage level
395V +- 20V
350
300
250
200
150
100
50
Trip
Reset
0
Trip
Actual DC bus
voltage
on
BRD on/off level
370V +-20V
Under voltage
recovering level
220V +- 10V
Under voltage
level
190V +- 10V
Trip
on
Display
example of
monitoring output
frequency
Over
voltage
trip
During
Under
voltage
OV.SRC level ; 375V +- 20V (continuously 100sec while stop)
BRD circuit has no hysterisys
5-1
Under
voltage
trip or
Waiting
for Retry
Page 27

[2] 400V class
DC bus
voltage [Vdc]
800
Over voltage level
790V +- 40V
700
600
500
400
300
200
100
0
Trip
Reset
Trip
Actual DC bus
voltage
Trip
on on
BRD on/off level
740V+-40V
Under voltage
recovering level
440V +- 20V
Under voltage
level
380V +- 20V
Display
example of
monitoring output
frequency
Over
voltage
trip
During
Under
voltage
Under
voltage
trip or
Waiting
for Retry
OV.SRC level ; 750V +- 40V (continuously 100sec while stop)
5-2
Page 28

5-2. Output Current Detection Characteristics
Frequency inverter has several detection characteristics for output current to protect IGBT from break
down, or to protect motor from over heat.
[1] Over current
Frequency inverter shuts off the output instantaneously when output current exceeds to 220%( 190)
of its rated current. (OC level is no link with Electronic thermal level)
e.g. Over current protection level of SJ100-015NFE (7.1 Amps of rated current) is
7.1 [Arms] * 200% = 14.2 [Arms] = 20.1 [A peak]
[2] Over load (Ele ctronic thermal pro te ction)
Frequency inverter shuts off the output when integration value of output current and time exceeds
specific value.
time
180s
No over load trip with
115% load
120s
60s
0
100%
% output current of the rated current of the frequency inverter
E-Thermal Level = [100]
Over Current trip
220%(-> 4kW)
190%(5.5kW ->)
150%, 60s
180%, 10s
220%(190%)150%
This Electronic thermal level can be changed from 50% to 120%. (Initial setting is 100%.)
time
180s
E-Thermal Level = [50]
120s
60s
150%, 60s
180%, 10s
0
50%
% output current of the rated current of the frequency inverter
100%
220%(190%)150%
5-3
Page 29

5-3. Motor Temperature Detection (PTC)
Frequency inverter has a motor temperature sensor input (PTC input : PTC resistor).
When the resistance value is more than 3k ohm +-10%, the frequency inverter trips with “E35”.
SJ100 inverter
U
V
W
L5(PTC)
Motor
PTC thermistor
Except Japanese version
5-4. Over Temperature Detection of the Frequency Inverter
Frequency inverter has a temperature detection against power devices of the main circuit. Frequency
inverter shuts down the output when temperature around IGBT comes up to 120 degree C.
5-4/E
Page 30

6. Measurement & Replacement of Subassemblies
6-1. Insulation Measurement
For SJ100 inverter,
do not perform insulation measurements
, otherwise MOV will be damaged.
(MOV; between R(L1)-G, S(L2)-G, T(L3)-G)
6.2. Power Components Measurements.
When checking the power components, the following procedure is recommended:
Clear voltage
!
W ait for capacitors discharge
!
Check capacitors for neutrality
!
Disconnect mains and motor wires
!
Test the diodes and IGBTs using a universal tester with a diode function.
!
Visual check is important for the ISPM, check the appearance such as smoke trace.
Note:
[1] DC BUS Measurement
Check “+” <- “ - ” voltage Zero.
In this test, the absolute values are not so important, since they depend strongly on the test
device used. The uniformity of the measured value is more important.
Resistance Measurement
From
+
To
-
Allowable Value
50kohm or more
P1, PD are located on the CB board / snubber board.
Check “+1” and “+” terminal are shorten by (copper) bar.
[2] Soft charge Resistor (RS) , Thyristor (THY) Measurement
Resistance Measurement
From
P1
PD
To
PD
P1
Allowable Value
15 to 25 ohm
(From P1 To PD From PD To P1 ;if RS was opened)
6-1
Page 31

[3] Rectifier Measurement
(Ll)
R
Each R(Ll), S(L2) and
(L2)
S
(L3)
T
This is to measure 6 rectifiers of the input side.
Resistance Measurement
From
R(Ll)
S(L2)
S(L2)
T(L3)
T(L3)
R(Ll)
R(Ll)
S(L2)
T(L3)
S(L2)
R(Ll)
T(L3)
S(L2)
R(Ll)
T(L3)
R(Ll)
S(L2)
T(L3)
To
-
P1PDTHY
Main circuit of SJ100
RS
Allowable Value
50kohm or more
50kohm or more
+1
+
+
Rsh
T(L3)
-
Each R(Ll), S(L2) and
50 ohm or less
T(L3)
Each R(Ll), S(L2) and
P1
50 ohm or less
T(L3)
P1
Each R(Ll), S(L2) and
50kohm or more
T(L3)
To make sure MOV, visual check of MOV is necessary on the ISPM.
CTU
U
V
W
CTW
If the result is out of its spec, replace the unit. ( relative check is important )
MOV(ZNR);ZNR1,ZNR2,ZNR3 are for phase to phase
MOV(ZNR);ZNR4,ZNR5,ZNR6 are for phase to ground
6-2
Page 32

[4] IGBT Measurement
Resistance Measurement
From
+
+
+
U
V
W
-
-
U
V
W
If the result is out of its spec, replace the unit.
Please note that this cannot cover 100% to find IGBT failure because if the power devices in failure,
To
U
V
W
+
+
+
U
V
W
-
-
-
Allowable Value
50kohm or more
50 ohm or less
50 ohm or less
50kohm or more
Rsh
DC current detecting
resistor (shunt resistor)
(Order of mili ohm)
sometimes you can find the failure in components while they are activated. (You cannot find the failure
while they are not activated.)
[5] Cooling FAN voltage circuit in the ISPM (PV 24N)
Check “b92” is preset “”00 (FAN to be worked) and disconnect the cooling FAN
Resistance Measurement
From
Pin(up) (Red)
Pin(up) (Black)
( relative check is important )
[6] Cooling FAN
Disconnect the cooling FAN and measure impedance of FAN circuit.
Resistance Measurement
From
Red wire
Black wire
( relative check is important )
[7] BRD(RB,+,-)
Disconnect BRD resistor.
Red wire, Black wire mean tester’s wires.
Resistance Measurement
+
Black wire
Red wire
(only reference)
Resistance Measurement
RB
Black wire
Red wire
(only reference)
Pin(down) (Black)
Pin(down) (Red)
To
To
Black wire
Red wire
RB
Red wire
Black wire
-
Red wire
Black wire
Allowable Value
20kohm or more
50ohm or less
Allowable Value
50kohm or less
100kohm or more
Allowable Value
100kohm - 400kohm
8ohm – 14ohm
Allowable Value
100kohm – 700kohm OL(initial charge)
2kohm – 4kohm
6-3/E
Allowable Value
Diode drop V
0.3 – 0.5
OL
Allowable Value
Diode drop V
OL
+
Page 33

7. Maintenance and Inspection Procedure
7-1. Precautions
(1) Maintenance and Inspection Precautions
Be sure to check the followings before starting maintenance and inspection because there is a
danger of electrical shock.
Display on the digital operation panel and POWER indication has been turned OFF.
!
The voltage between + and - is 15Vdc or lower.
!
Discharging resistor (500 ohm 30W for 200V class, 1k ohm 60W for 400V class) has been
!
connected between + and - terminals for 15 seconds or more after main power had turned off,
(2) General Precautions
Always keep the unit clean so that no dust nor other foreign materials come inside of the
!
frequency inverter.
Pay attention to broken lines and faulty connections. Firmly connect terminals and connectors.
!
Keep frequency inverter away from moisture and oil.
!
Dusts, steel filings, swarf , and other foreign materials can damage insulation and causing
!
unexpected accidents/failure. Please pay attention to them.
7-2. Measurement of Mains Voltage, Current and Power
General measuring instruments for mains voltage, current and power are shown in Table 7-1.
The voltage to be measured is the effective value of fundamental wave, and the power to be measured
is the total effective value.
(1) Measurement of output voltage
Moving iron type instrument does not show accurate values for measurement of the output voltage.
Make measurements according to the method shown in Fig. 7-3 (table 7-1) or using the circuit
indicated in Fig. 7-1 and 7-2.
Frequency
Inverter
U
V
W
2W
220kohm
Diode
600V 0.1A or above (200V class)
1000V 0.1A or above (400V class)
Fig. 7-1. Output voltage measurement circuit (with load)
Motor
+
-
Load
Fundamental wave
effective value : V
V
DC
Moving coil type DC Volt meter
300V (200V class)
600V (400V class)
AC
= VDC * 1.1
7-1
Page 34

When there is no motor connected to the inverter, please use additional resistor like Fig. 7-2. There
will be a voltage at output terminal even the frequency command is naught due to the lea kage current
of the semiconductor devices.
Frequency
Inverter
Additional resistor
5kohm 30W (200V class)
100W (400V class)
U
V
W
2W
220kohm
Diode
600V 0.1A or above (200V class)
1000V 0.1A or above (400V class)
Fig. 7-2. Output voltage measurement circuit (without motor)
+
-
Fundamental wave
effective value : V
V
DC
AC
Moving coil type DC Volt meter
= VDC * 1.1
300V (200V class)
600V (400V class)
(2) Measurement of Input voltage and Input / output current
Use moving iron type ampere meter. (Refer to Fig. 7-3 and Table 7-1.)
(3) Measurement of Input and output power
Use electrodynamics type watt meter for single phase use. Make measurements for all 3 phases is
case there is an unbalance in voltages and currents.
L1
L2
L3 / N
I
R
E
R
I
S
E
S
I
T
E
T
W
W
Fig. 7-3. Measurement Instruments
Frequency Inverter
L1
11
L2
12
L3 / N
U/T1
V/T2
W/T3
I
U
E
U-V
I
V
E
V-W
I
W
E
U-W
W
W
O1
Motor
O2
7-2
Page 35

Table 7-1 Measuring Instruments
Item
Suppl y voltage
E1
Supply current
I1
Supply power
W1
Supply power
Factor Pf1
Output voltag e
Eo
Output current
E
L1-L2
, E
Instruments
and E
L2-L3
L3-L1
Moving iron type voltmeter or
Type of Instrument
Rectifier type voltmeter
IL1, IL2 and I
W11 and W
L3
12
Moving iron type ammeter Total effective value
Electrodynamics wattmeter Total effective value
Calculate from above measured values E1, I1 and W1
W
1
Pf
=
E
, E
U-V
V-W
IU, IV and I
1
⋅⋅
3
EI
and E
W
11
W-U
100
(%)
×
According to Fig.7-1 and Fig.7-2 Total effective value
Moving iron type ammeter Total effective value
Remarks
Fundamental wave
effective value
Io
Output power
WO1 and W
O2
Electrodynamics wattmeter Total effective value
Wo
Output power
Calculate from above measured values Eo, Io and Wo
factor Pf2
W
1
Pf
=
O
3
EI
⋅⋅
OO
×
100
(%)
NOTE : Use a meter indicat ing a fundamental wave effective value for voltage, and meters indicating
total effective values for current and power.
7-3
Page 36

7-3. Maintenance of Parts
(1) Maintenance of printed circuit board (I/O board)
Printed circuit boards are maintenance free under normal applications except ALARAM relay
(hardware). However, in case which maintenance and inspection are necessary, pay attention to
the prevention of damage caused by static electricity as shown below.
* Prevent damage caused by static electricity
MCU and LSI on the printed circuit board can be destroyed by static electricity. Therefore be
sure to ground work benches, soldering irons and yourself before start working on a printed
circuit board.
(2) Maintenance of DC bus capacitor and cooling fan
We recommend that DC bus capacitors and cooling fans to be regularly replaced every three y ears
taking their lives into account. Please note that their life span shorten when they are used in high
temperatures and heavy loads.
Ambient
temperature (deg)
40
30
20
10
0
-10
7-4. If you install replacement INV at site
If you install replacement units at site, please preset the parameter by the panel or copy unit.
Capacitor Life Curve
210
Capacitor life time (year)
436587109
12 hours a day
operation
When the inverter is installed in a cabinet,
ambient temperature is the temperature in
the cabinet.
If you used the previous I/O board to replacement unit, the parameters are not changed.
Because parameters are memorized in the EEPROM on the control board on J100 /J300 series, and if
we used the previous control board to replacement unit at site to minimize the time. In case of
L100,SJ100 series, EEPROM is on the ISPM, even we replaced I/O board, the parameter is still the
same.
7-4/E
Page 37

8. Daily Inspection and Periodical Inspection
Inspection
point
8-1
Overall
Main
circuit
Item
Ambient
Environment
Devices overall Check for abnormal vibrations and
Power supply
voltage
Overall Check installation for looseness.
Terminal block No damage
DC bus
capacitor
Relay Check for stuttering noise when
Resistors Check for cracks or changes in color
Cooling fan Check for abnormal vibration and
Check ambient temperature,
humidity, dust, corrosive gas, oil mist,
etc.
noise.
Check voltage bet ween in put li nes .
Check for evidence of over heating in
the various components
Clean
Check for leaking liquid
Check for swelling
operation
noise
Check for dust
Contents
Cycle
daily
"
"
"
"
"
"
periodic
"
"
"
"
"
"
Method
Visual and aural
inspection
Measure the
voltage
between input
terminals
Tighten
Visual
inspection
Visual
inspection
Visual No abnormalities
inspection
Aural
inspection
Visual
inspection
-Rotate
manually while
power off
-Increase
tightening
Visual
inspection
Ambient temperature
: -10deg to 40deg,
no icing
No abnormalities.
Within its specification
Tightening torque
(except for terminal block)
M3: 0.5 - 0.6 N-m
M4: 0.98 - 1.3 N-m
No abnormalities
No abnormalities
No abnormalities
- Smooth rotation
- No abnormalities
Criteria
Standard
replacement
period
2 - 3 years
Instruments
Thermometer
Hygrometer
Tester
Tester
Page 38

8-2/E
Inspection
point
Control circuit
Display
Item
Operation check Check the balance of the output
voltage of each phase to phase
without motor.
Component
check including
PCB
Capacitors on
I/O board
Digital operation
panel
Perform a sequence protection
operation test and make sure that
there are no errors in the protection
and display circuits.
No abnormal odor nor changes in
color.
No significant corrosion.
No liquid leakage nor deformation.
- No illegible display
- No lack of character
- Segment failure of LEDs
Contents
Cycle
daily
"
"
periodic
"
"
"
"
Method
Measure the
output voltage
between U, V
and W
Simulate
operation of the
protection
circuit
Visual
inspection
Visual
inspection
Visual
inspection
Within 2% of voltage
difference between each
phases.
Operate without any
trouble
No abnormalities
No abnormalities
Normal operation.
Display is readable.
NOTE : 1. Life time of capacitor is affected by the ambient temperature. See Capacitor Life Curve in the following.
2. The frequency inverter must be cleaned periodically. If dust accumulates on the fan and heat sink, it can cause overheating.
3. See item 7-3 (2) for the life time of the capacitor.
Criteria
Standard
replacement
period
Instruments
See next
page
Page 39

9. Image block diagram
)
C
(LFU,NFE)
(1). IMAGE BLOCK DIAGRAM OF SJ100 INVERTER
*1
R(L1)
S(L2)
T(L3)
CORE INVERT ER
(IS PM)
CONVERTER
POW ER S UPPLY
DETECT V,I
DC REACTOR
(OPTION)
PD(+1)
RS
BRD resistor(option)
P(+)
+
SUB CO ND E N C ER BOAR D( HFx)
RB
N(-
B
Tr BR
I/O BLOCK
(I/O board)
MCU
+
+
INVERTER
U(T1)
V(T2)
W(T3)
OPERATION PANEL WITH
POTENTIOMETER
HITACHI
DRIVE CIRCUIT
SERIAL
COMMUNICATION
MCU
EEPROM
ISORATION
EMC DIRECTIVE COMPLIAN T WITH DEDICATED NOISE FILTER( OPTION)
Note; Main circuit capacitor CB; HFE,HFU; seri al connection.
; LFU,NFE; single connection.
COMMUNICATION
PORT
TERMINALS
US E R IN T E RFACE
REMORT OPERATOR
9-1/E
Page 40

Page 41

10-1. Spare Parts list
;
;
No
1 D 254858 2T004556 1 Key PAD (HITACHI)
2 D 254857 2T004372 4 Front case (S)
2 D 254855 1T001784 4 Front case (L)
3 D 254859 3T015677 7 Key cover
4 D 254864 4T013420 4 Volume KNOB
5 D 254863 4T013419 4 Top cover (S)
5 D 254865 4T013459 4 Top cover (L)
10-1
5 D 3T016369 4 Top cover (LL)
6 D 254856 2T004371 4 Case (S)
6 D 254854 1T001783 4 Case (M)
6 D 254853 1T001782 4 Case (L)
Class
.
Parts Code DWG.No. Parts Name Remarks Quantity Lot
For all models
SJ100-002-007LFR
SJ100-002-005NFE
SJ100-002,004NFU
SJ100-015-075LFR
SJ100-007-022NFE
SJ100-007-022NFU
SJ100-037-075LFU
SJ100-004-075HFR
SJ100-004-075HFE
For all models
For all models
SJ100-002-007LFR
SJ100-002-005NFE
SJ100-002,004NFU
SJ100-015-037LFR
SJ100-007-022NFE
SJ100-007-022NFU
SJ100-037LFU
SJ100-004-037HFR
SJ100-004-040HFE
SJ100-055,075LFU;HFE;HFU,LFR,HFR
SJ100-002-007LFR
SJ100-002-005NFE
SJ100-002,004NFU
SJ100-015,022LFR
SJ100-007,011NFE
SJ100-007NFU
SJ100-004-022HFR
SJ100-004-022HFE
SJ100-004-022HFU
SJ100-037LFR
SJ100-015,022NFE
SJ100-015,022NFU
SJ100-037LFU
SJ100-037HFR
SJ100-030,040HFE
SJ100-040HFU
HFU
HFU
110
110
110
110
110
110
110
110
110
110
110
Page 42

6 D 1T001858 4 C ase (LL)
,
;
;
7 D 254862 4T013417 4 Rear cover (S)
SJ100-055,075LFU;HFE;HFU,LFR,HFR
SJ100-002-007LFR
110
110
SJ100-002-005NFE
7 D 254860 3T015700 4 Rear cover (L)
SJ100-002
SJ100-015-037LFR
004NFU
110
SJ100-007-022NFE
SJ100-007-022NFU
SJ100-037LFU
SJ100-004-037HFR
HFU
110
110
7 D 3T016368 4 Rear cover (LL)
8 D 254861 3T015710 4 Condensor cover (L)
SJ100-004-040HFE
SJ100-055,075LFU;HFE;HFU,LFR,HFR
SJ100-037LFR
SJ100-015,022NFE
SJ100-015,022NFU
SJ100-037LFU ,037HFR
SJ100-030,040HFE
-
10-2
8 D 2T004495 4 Condensor cover (LL)
SJ100-055,075LFU;HFE;HFU,LFR,HFR
110
No
Class
.
Parts Code DWG.No. Pa rts Name Remarks Quantity Lot
9 C 254270 3T012518 2 Cooling fan(S)
9 C 254270 3T012518 2 Cooling fan(S)
9 D 254822 3T011924 4 Cooling fan(L)
10 D 254827 4T013337 1 ISPM-IO Cable (S)
10 254828 4T013337 4 ISPM-IO Cable (L)
11 --- 3T016869 3 ISPM (without PCB2)
11 -- 3T016870 3 ISPM (without PCB2)
11 -- 3T016871 3 ISPM (without PCB2)
11 -- 3T016872 3 ISPM (without PCB2)
SJ100-015,022LFR;HFR
SJ100-015,022HFE;HFU
SJ100-055LFR;LFU
SJ100-075LFU,LFR
SJ100-022NFE;NFU
SJ100-037LFR;LFU;HFR
SJ100-030HFE
SJ100-040HFE
HFU
SJ100-002-037LFR
SJ100-002-022NFE;NFU
SJ100-037LFU
SJ100-004-037HFR
SJ100-004-040HFE;HFU
SJ100-055,075LFU,HFE;HFU,LFR,HFR
SJ100-002LFR;NFE;NFU
SJ100-004LFR;NFE;NFU,
SJ100-005NFE
SJ100-007LFR
SJ100-007NFE;NFU
SJ100-011NFE
13
23
13
110
110
11
11
11
11
Page 43

11 -- 3T016873 3 ISPM (without PCB2)
)
)
ge)
11 -- 3T016874 3 ISPM (without PCB2)
11 -- 3T016875 3 ISPM (without PCB2)
11 -- 3T017100 2 ISPM (without PCB2)
11 -- 3T017101 2 ISPM (without PCB2)
11 -- 3T016876 2 ISPM (without PCB2)
11 -- 3T016877 2 ISPM (without PCB2)
11 -- 3T016878 2 ISPM (without PCB2
-
11 -- 3T016879 2 ISPM (without PCB2
11 -- 3T016880 2 ISPM (without PCB2) SJ100-037HFR
SJ100-015LFR;NFE;NFU
SJ100-022LFR;NFE;NFU
SJ100-037LFR;LFU
SJ100-055LFR;LFU
SJ100-075LFR;LFU
SJ100-004HFR;HFE;HFU
SJ100-007HFR;HFE;HFU
SJ100-015HFR;HFE;HFU 1 1
SJ100-022HFR;HFE;HFU 1 1
11
11
11
11
11
11
11
11
SJ100-030HFE
SJ100-040HFE;HFU
11 -- 3T017102 2 ISPM (without PCB2)
11 -- 3T017103 2 ISPM (without PCB2)
12 254890 4T013548 1 RS(soft charge resistor)
SJ100-055HFR;HFE;HFU
SJ100-075HFR;HFE;HFU
SJ100-002--022NFE;NFU
11
11
110
SJ100-037,055LFU
SJ100-002-055LFR
SJ100-004--055HFE;HFU,HFR
12 254890 4T013548 1 RS(soft charge resistor)
13 -- 4T013438 1 Copper bar
13 -- 4T013439 1 Copper bar
SJ100-075HFE;HFU;LFU,LFR,HFR
SJ100-002-007LFR
SJ100-002,004NFE;NFU,005NFE
SJ100-015-037LFR
210
110
110
SJ100-007--022NFE,NFU
SJ100-007--022NFU,037LFU
SJ100-004-037HFR
SJ100-004--040HFE;HFU
14 -- SJ100L I/O board
14 -- SJ100EUL I/O board SJ100-002--022NFE;NFU
SJ100-002-037LFR;HFR
11
SJ100-037LFU
SJ100-004--040HFE;HFU
14 -- SJ100UL
(only label
chan
I/O board
(from ’99 Oct. production)
SJ100-002-022NFU,037LFU
SJ100-004-040HFU
11
14 -- SJ100075L I/O board SJ100-055,075LFR;HFR 1 1
14 --- SJ100075EUL I/O board SJ100-055,075LFU;HFE;HFU 1 1
Page 44

15 -- CB470 Capacitor board SJ100-037HFR,030HFE
,
SJ100-040HFE
HFU
11
15 -- CB68X4H Capacitor board SJ100-055HFR,HFE,HFU 1 1
15 -- CB68X6H Capacitor board
16 -- SJCB180A PCB2
16 -- SJCB330A PCB2
16 -- SJCB680A PCB2
16 -- SJCB470B2 PCB2
16 -- SJCB680B2 PCB2
16 -- SJCB2330A PCB2
16 --- SJCB2680A PCB2
16 --- SJCB560B2 PCB2
10-4
16 --- SJCB470B2T PCB2
16 --- SJCB680B2T PCB2
16 -- L100SB055L PCB2
16 -- L100SB075L PCB2
16 -- SJCB180B4 PCB2
16 --- SJCB270B4 PCB2
16 --- SJCB470B4 PCB2
16 --- SJCB680B4 PCB2
16 --- SJCB470B4T PCB2
SJ100-075HFR,HFE;HFU
SJ100-002LFR
SJ100-004LFR
SJ100-007LFR
SJ100-015LFR
SJ100-022LFR;011NFE
SJ100-002NFE;NFU
SJ100-004NFE;NFU, 005NFE
SJ100-007NFE;NFU
SJ100-015NFE;NFU, 037LFR;LFU
SJ100-022NFE;NFU
SJ100-055LFR;LFU
SJ100-075LFR;LFU
SJ100-004HFR;HFE;HFU
SJ100-007HFR;HFE;HFU
SJ100-015HFR;HFE;HFU
SJ100-022HFR;HFE;HFU
SJ100-037HFR,030HFE
11
11
11
11
11
11
11
11
11
11
11
11
11
11
11
11
SJ100-040HFE,HFU
16 --- L100SB055H PCB2
16 --- L100SB075H PCB2
SJ100-055HFR;HFE;HFU
SJ100-075HFR;HFE;HFU
11
11
Page 45

Note No.10 4T013337 3 i s usable for 4T01337 4. The difference is t he length.
No.13 The copper bar is used between ISPM and heatsink.
C/H version is applied US version except key pad/kn ob/ cover/case etc.
This spare parts list will be changed without notice. To get latest spare parts list, please conta ct to sales office.
This service manual may not be revised if the spare parts list was revised.
-
Page 46

No. Parts name Quantity
1 Keypad 1
2 Front case (L) 1
3Key cover 1
4 Volume knob 1
5 Top cover (S) 1
6 Case (S) 1
7 Rear cover (S) 1
10-6
10 ISPM – IO cable (S) 1
11 ISPM 1
12 RS 1
14 I/O board 1
16 PCB2 1
SJ100-002NFE
002NFU
004NFE
004NFU
005NFE
Page 47

No. Parts name Quantity
1 Keypad 1
2 Front case (L) 1
3Key cover 1
4 Volume knob 1
5 Top cover (L) 1
6 Case (M) 1
7 Rear cover (L) 1
10-7
10 ISPM – IO cable (L) 1
11 ISPM 1
12 RS 1
14 I/O board 1
16 PCB2 1
SJ100-004HFE
004HFU
007NFE
007NFU
011NFE
Page 48

No. Parts name Quantity
1 Keypad 1
2 Front case (L) 1
3Key cover 1
4 Volume knob 1
5 Top cover (L) 1
6 Case (M) 1
7 Rear cover (L) 1
10-8
8 Cooling fan (L) 1
10 ISPM – IO cable (L) 1
11 ISPM 1
12 RS 1
14 I/O board 1
16 PCB2 1
SJ100-007HFE
007HFU
015HFE
015HFU
022HFE
022HFU
Page 49

No. Parts name Quantity
1 Keypad 1
2 Front case (L) 1
3Key cover 1
4 Volume knob 1
5 Top cover (L) 1
6 Case (L) 1
7 Rear cover (L) 1
10-9
8 Condensor cover 1
10 ISPM – IO cable (L) 1
11 ISPM 1
12 RS 1
14 I/O board 1
15 Capacitor board 1
16 PCB2 1
SJ100-015NFE
015NFU
Page 50

No. Parts name Quantity
1 Keypad 1
2 Front case (L) 1
3Key cover 1
4 Volume knob 1
5 Top cover (L) 1
6 Case (L) 1
7 Rear cover (L) 1
8 Condensor cover 1
10-10
9 Cooling fan (L) 1
10 ISPM – IO cable (L) 1
11 ISPM 1
12 RS 1
14 I/O board 1
15 Capacitor board 1
16 PCB2 1
SJ100-022NFE
022NFU
030HFE
037LFU
040HFE
040HFU
Page 51

10-11
No. Parts name Quantity
1 Keypad 1
2 Front case (L) 1
3Key cover 1
4 Volume knob 1
5 Top cover (LL) 1
6 Case (LL) 1
7 Rear cover (LL) 1
8 Condensor cover (LL) 1
9 Cooling fan (S) 1
10 ISPM – IO cable (L) 1
11 ISPM 1
12 RS 1
14 I/O board 1
15 Capacitor board 1
16 PCB2 1
SJ100-055LFU
055HFU
075HFU
055HFE
075HFE
055LFE
Page 52

10-12
No. Parts name Quantity
1 Keypad 1
2 Front case (L) 1
3Key cover 1
4 Volume knob 1
5 Top cover (LL) 1
6 Case (LL) 1
7 Rear cover (LL) 1
8 Condensor cover (LL) 1
9 Cooling fan (S) 2
10 ISPM – IO cable (L) 1
11 ISPM 1
12 RS 1
14 I/O board 1
15 Capacitor board 1
16 PCB2 1
SJ100-075LFU
075LFE
Page 53

10-2. I/O board compatibility
V: available - : not available
board
I/O
SJ100EUL "C","D","H" V - - - -
SJ100EUL "E","F","G","H" - V - - SJ100075EUL "A" - - V - SJ100L "C","D","H" - - - V SJ100075L "A" - - - - V
Name “R
evision
”
002NFE-022NFE
037LFE
004HFE-040HFE
002NFR-022NFU
037LFU
004HFU-040HFU
055HFE,075HFE
055LFU,075LFU
055HFU,075HFU
002LFR-037LFR
004HFR-037HFR
055LFR,075LFR
055HFR,075HFR
Note;
"SJ100xxxEUx" ; "SOURCE type" on the control terminal(different from SINK).
"SJ100xxxL" ; "SINK type" on the control terminal.(different from SOURCE)
kW setup is not necessary such as J100 , J300 series for I/O board if I/O board was replaced.
There is no compatibility between L100 series and SJ100 series.
10-13
Page 54

10-3. O,OI terminal adjustment procedure
If you need the fine adjustment with out F31 IN EX%S, IN EX%E function(DOP/DRW), or A group A13,A14
function (on standard panel), refer to following procedure.
At first, stop the SJ100, and erase the INV trip (error) to change parameters.
O terminal adjus tment
Supply the DC10 [V] and if the freq. Setting(F01) is not enough max freq. , increase “C81” value and press
the “STR” key and check the result. If the freq. Setting (F01) is not enough, continue the above procedure.
OI terminal adjustment
Supply the DC20 [mA] and if the freq. Setting(F01) is not enough max freq. , increase “C82” value and press
the “STR” key and check the result. If the freq. Setting (F01) is not enough, continue the above procedure.
If the data was added, the freq. setting will be increased. ( concept is as same as J100,J300)
“C81” and “C82” are possible to preset while INV running.
10-14
Page 55

10-4. kW setup procedure
To set up kW, we advise you not to use DOP/DRW !, use only standard panel.
Meaning
set C91 "01" ; Debug on
set C94 "D000" ; kW address
set C95 "xx" ; kW code
set B84 "01" ; to execute FACTORY SETTING
Try FACTORY SETTING
Check B12' display (F-23 E-THM LVL)
B12's display table
kW | 200V | 400V
002 | 1.40 | ---004 | 2.60 | 1.50
005,007 | 4.00 | 2.50
011,015 | 7.10 | 3.80
022 | 10.00 | 5.50
030,040 | 15.90 | 8.60
055 | 24.0 | 13.0
075 | 32.0 | 16.0
kW code table (common L100/SJ100)
xx | kW
01 | 002
02 | 004
03 | 005,007
04 | 011,015
05 | 022
06 | 030,040
07 | 055
08 | 075
In case of L100, SJ100, it automatically detects it's voltage class with hardware in the ISPM, voltage class
setup is not necessary.
10-15
Page 56

Page 57

Page 58

Page 59

Page 60

Page 61

Page 62

Page 63

Page 64

Page 65

Page 66

Page 67

Page 68

Page 69

Page 70

Page 71

Page 72

Page 73

Page 74

Page 75

End of page
 Loading...
Loading...