Page 1

HITACHI
SJ100 Series Inverter
Quick Reference Guide
• Single-phase Input 200V Class
• Three-phase Input 200V Class
• Three-phase Input 400V Class
Hitachi Industrial Equipment Systems Co., Ltd.
Manual No. NB5821XD • Dec. 2003
Page 2
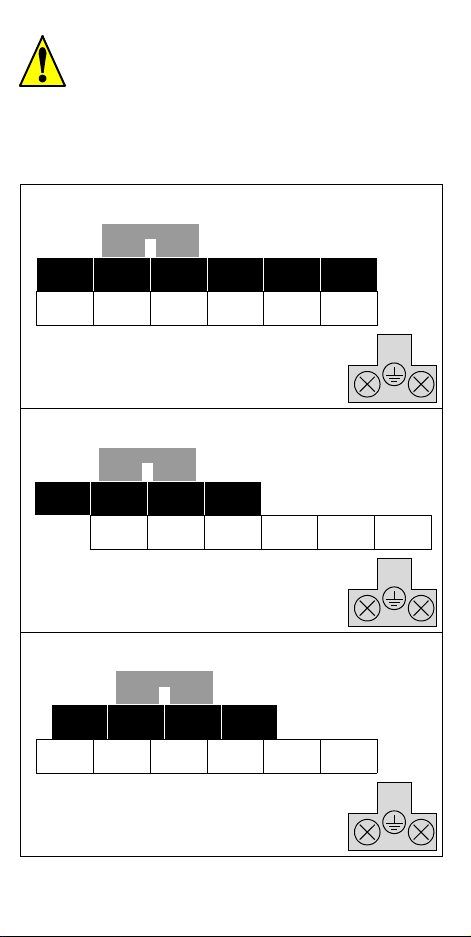
Caution: Be sure to read the SJ100 Inverter Manual and
follow its Cautions and Warnings for the initial product
installation. This Quick Reference Guide is intended for
reference use by experienced users in servicing existing
installations.
Power Circuit Terminals
–002NFE/NFU, –004NFE/NFU, –005NFE
Jumper
RB +1 + –
L1 L2 N/L3 U/T1 V/T2 W/T3
Chassis
Ground
–007 to 022NFE/NFU, –037LFU, 004 to 040HFE/HFU
Jumper
RB +1 + –
L1 L2 N/L3 U/T1 V/T2 W/T3
Chassis
Ground
–055LFU, –075LFU, 055HFE/HFU, 075HFE/HFU
Jumper
RB +1 + –
L1 L2 N/L3 U/T1 V/T2 W/T3
Chassis
Ground
1
Page 3
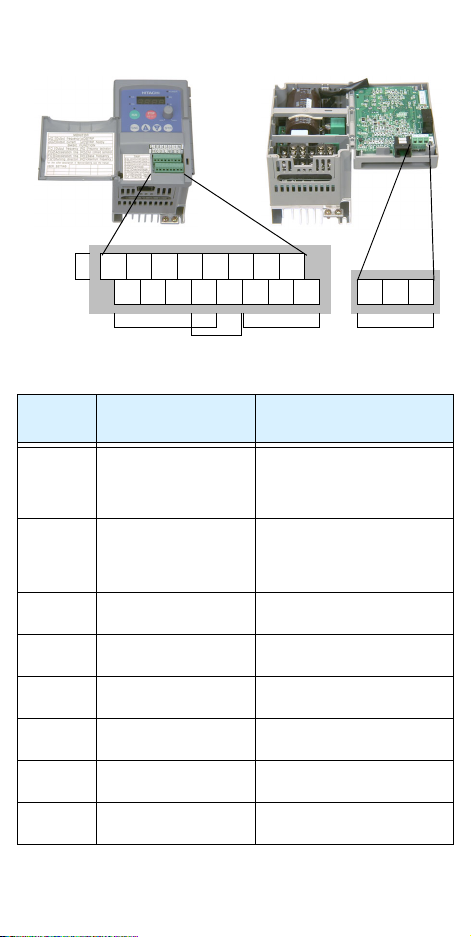
Control Circuit Terminals
Logic
inputs
Te rm in a l
Name
L
6 5 4 3 2 1
H O OI
Analog
inputs
FM
L
Analog
outputs
Description Ratings and Notes
CM2
outputs
P24
12 11
Logic
AL0 AL1 AL2
Alarm
relay
P24 +24V for logic inputs 24VDC supply, 30 mA max.
(Notes: Do not use for
network power
Do not short to terminal L)
1, 2, 3, 4,
L (top
row)
11, 12 Discrete logic outputs 50 mA max. ON current,
CM2 Common for logic
L (bottom
row)
Intelligent (program-
5, 6
mable) discrete logic
inputs
GND for logic inputs Sum of input 1 to 6 currents
27VDC max. (use P24 or an
external supply referenced to
terminal L), 4.7kΩ input
impedance
(Note: Do not ground)
27 VDC max. OFF voltage
outputs
FM PWM output 0 to 10VDC, 1 mA max.,
Common for analog
inputs
OI Analog input, current 4 to 19.6 mA range, 20 mA
100 mA max for sum of
terminals 11 and 12 currents
50% duty cycle
Sum of OI, O, and H
currents (return)
nominal
2
Page 4
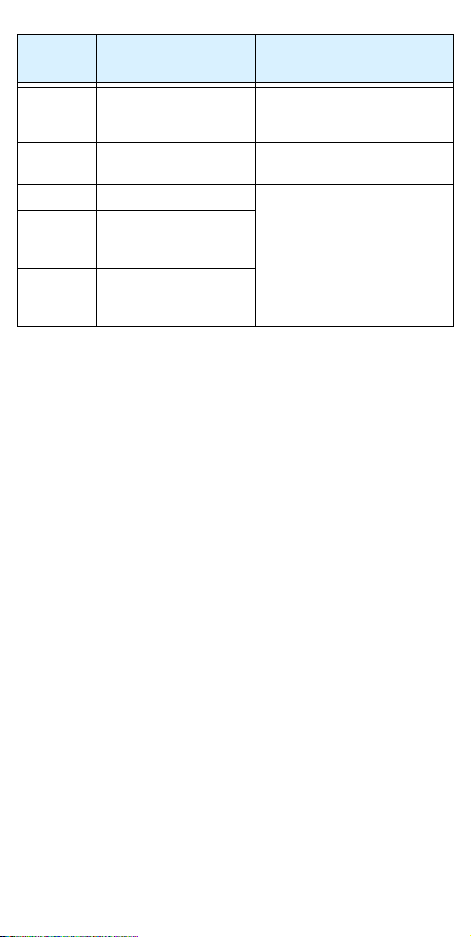
Te rm in a l
Name
Description Ratings and Notes
O Analog input, voltage 0 to 9.6 VDC range, 10VDC
nominal, 12VDC max., input
impedance 10 kΩ
H +10V analog reference 10VDC nominal, 10 mA
AL0 Relay common contact
AL1 Relay contact,
normally closed
during RUN
AL2 Relay contact,
normally open during
RUN
max.
Contact rating
Max resistive load = 250VAC,
2.5A; 30VDC 3A;
Max inductive load = 250VAC,
0.2A; 30VDC 0.7A
Minimum load = 5VDC 100mA,
100VAC 10mA
3
Page 5
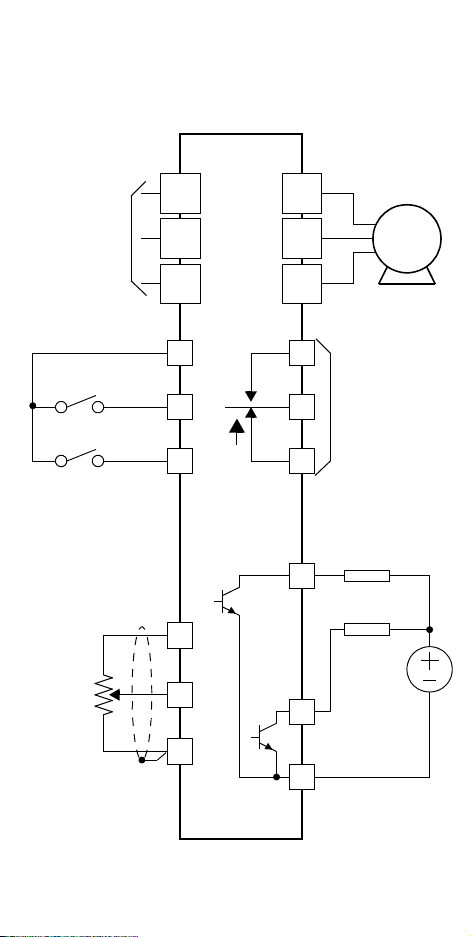
Basic Wiring Diagram
The following wiring diagram shows the power and motor connections for basic operation. The optional signal input wiring supports
external Fwd and Rev Run command, and a speed potentiometer.
SJ100
From 3-phase
power input
source (See
specifications
label on inverter
for details)
Inputs:
Forwa rd
Reverse
Analog reference
External
speed
reference
pot.
Analog common
R
(L1)
S
(L2)
T
(N/L3)
P24
1
2
H
O
L
U
(T1)
V
(T2)
W
(T3)
AL1
Alarm contacts,
AL0
AL2
Open collector
outputs:
Run signal
12
arrival signal
11
CM2
Motor
1 Form C
Load
Load
Frequency
Logic output
common
4
Page 6
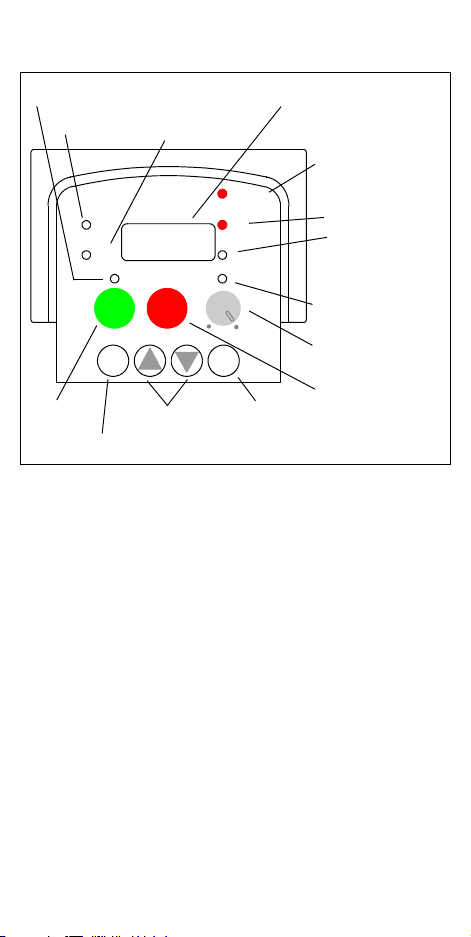
Inverter Keypad Operation
Run Key Enable LED
Run/Stop LED
RUN
PRG
RUN
FUNC.
Run Key
Up/Down Keys
Function Key
Parameter Display
Program/Monitor LED
HITACHI
50.0
STOP
RESET
MIN
2
1
STR
POWER
Hz
A
MAX
Store Key
Powe r L ED
Display Units LEDs
Hertz
Amperes
Potentiometer
Enable LED
Potentiometer
Stop/Reset Key
• Run/Stop LED – ON when the inverter output is ON and the
motor is developing torque, and OFF when the inverter output is
OFF (Stop Mode).
• Program/Monitor LED – ON when the inverter is ready for
parameter editing (Program Mode). It is OFF when the parameter
display is monitoring data (Monitor Mode).
• Run Key Enable LED – ON when the inverter is ready to
respond to the Run key, OFF when the Run key is disabled.
• Run Key – Press this key to run the motor (the Run Enable LED
must be ON first). Parameter F_04, Keypad Run Key Routing,
determines whether the Run key generates a Run FWD or Run
REV command.
• Stop/Reset Key – Press this key to stop the motor when it is
running (uses the programmed deceleration rate). This key will
also reset an alarm which has tripped.
(continued, next page...)
5
Page 7

• Potentiometer – Allows an operator to directly set the motor
speed when the potentiometer is enabled for output frequency
control.
• Potentiometer Enable LED – ON when the potentiometer is
enabled for value entry.
• Parameter Display – A 4-digit, 7-segment display for parame-
ters and function codes.
• Display Units: Hertz/Amperes – One of these LEDs will be ON
to indicate the units associated with the parameter display.
• Power LED – ON when the power input to the inverter is ON.
• Function Key – This key is used to navigate through the lists of
parameters and functions for setting and monitoring parameter
values.
• Up/Down Keys – Use these keys alternately to move up or down
the lists of parameter and functions shown in the display, and to
increment/decrement values.
• Store Key – When the unit is in Program Mode and the operator
has edited a parameter value, press the Store key to write the new
value to the EEPROM.
6
Page 8
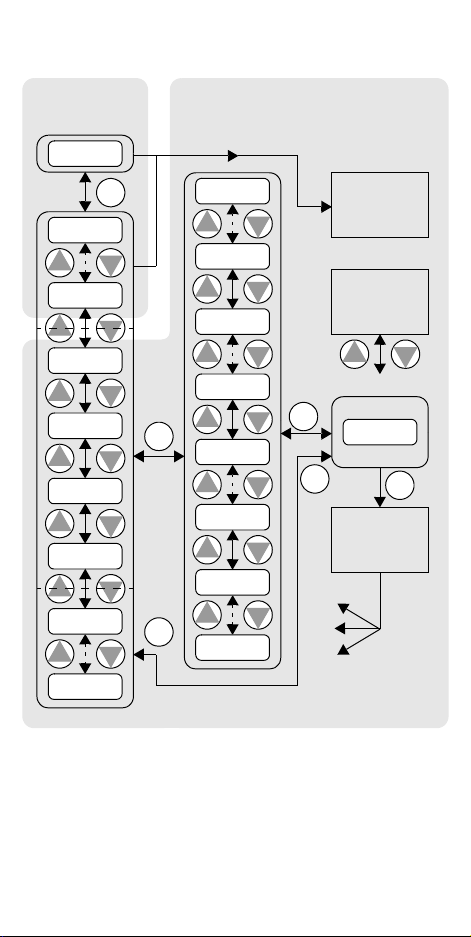
Keypad Navigation Map
Monitor Mode Program Mode
Display data
o.0
FUNC.
d
09
1
2
d
01
1
2
H––
1
2
C––
1
2
b
––
1
2
A––
1
2
F04
1
2
Select Parameter Edit Parameter
powerdown
h34
1
2
h01
1
2
c91
1
2
c01
92
01
FUNC.
2
FUNC.
2
2
1
FUNC.
b
1
b
1
A98
1
FUNC.
2
A01
F01
Store as
powerup
default
Increment/
decrement
value
1
2
Edit
123.4
STR
Write data
to
EEPROM
Return to
parameter list
7
Page 9

Powerup Test
The Powerup Test procedure uses minimal parameter settings to run
the motor. The procedure describes two alternative methods for
commanding the inverter: via the inverter keypad, or via the logic
terminals.
• Check power input and motor output wiring (see page 4 diagram).
• If using logic terminals for testing, verify correct wiring on [P24],
[FW], [H], [O], and [L] (bottom row) per the diagram on page 4.
• Reverse [RV] input wiring (defaults to terminal [2]) is optional.
Step Description Via Keypad
1 Set speed command
source setting
2 Set Run FW command
source
3 Set Run REV command
source
4 Set motor base freq. A_03 = 60
5 Set motor poles
(2 / 4 / 6 / 8)
6 Set keypad display to
monitor freq.
Perform safety check Disconnect load from motor
7 Turn keypad pot.
8 Run Forward command Press Run key Turn ON the
9 Increase speed Rotate keypad
10 Decrease speed Rotate keypad
11 Stop motor Press Stop key Turn OFF the
12 Run Reverse command
(optional)
13 Stop motor — Turn OFF the
A_01 = 00
(keypad pot.)
A_02 = 02
(Run key)
— C_02 = 01,
H_04 = 4 (default), change only if
your motor is different
Access D_01, press Func key, display
will show
0.0
to MIN position
pot. CW dir.
pot. CCW dir.
— Turn ON the [RV]
Via Logic
Te rm in a ls
A_01 = 01,
[H–O–L] input
A_02 = 01,
[FW] input
[RV] input
Ensure voltage on
[O]—[L] terminals= 0V
[FW] terminal
Increase voltage
at [O]
Decrease voltage
at [O]
[FW] terminal
terminal
[RV] terminal
8
Page 10

Error Codes
The SJ100 series inverters will trip on over-current, over-voltage,
and under-voltage to protect the inverter. The motor output turns
OFF, allowing the motor to free-run to a stop. Press the Stop/Reset
key to reset the inverter and clear the error.
Basic Error Codes
Error
Code
E01
E02
E03
E04
E05
E06
E07
E08
E09
E10
E11
Name Probable Cause(s)
Over current event while
at constant speed
Over current event during
deceleration
Over current event during
acceleration
Over current event for
other conditions
Overload protection • Motor overload is detected by the
Braking resistor overload • Regenerative braking resistor
Over voltage protection • DC bus voltage exceeds a threshold,
EEPROM error • Built-in EEPROM memory experi-
Under-voltage error • DC bus voltage decreased enough to
CT error
(current transformer)
CPU error • Built-in CPU had internal error
• Inverter output was short-circuited
• Motor shaft is locked
• Load is too heavy
• A dual-voltage motor is wired
incorrectly
Note: The SJ100 will over current trip
at nominally 200% of rated current
• DC braking power(A_54) set too
high
• Current transformer / noise error
electronic thermal function
exceeds the usage time or usage ratio
due to regenerative energy from motor
enced noise, high temperature, etc.
cause a control circuit fault
• High electrical noise near inverter
• A fault occurred in the built-in CT
E22
External trip • [EXT] input signal detected
E12
USP (Unattended Start
E13
Protection)
Ground fault • A ground fault was detected
E14
• When (USP) was enabled, an error
occurred when power was applied
while a Run signal was present
between the inverter output and the
motor. This feature protects the
inverter, and does not protect humans.
9
Page 11

Error
Code
E15
E21
E35
---
Name Probable Cause(s)
Input over-voltage • Input voltage was higher than the
Inverter thermal trip • Inverter internal temperature is
Thermistor • Thermistor input, [THM] and [L], is
Under-voltage (brownout) with output shutoff
specified value, 60 sec. after powerup
above the threshold
over the temp. threshold
• Low input voltage caused the
inverter to turn OFF the motor output
and try to restart. If unsuccessful, a
trip occurs.
Error Trip Conditions
Use function code D_08 to access the error trip conditions for the
current error as shown in the table below. Use the Up and Down
arrow keys to scroll through the trip condition parameters.
Step Display
1. Access D_08
2. Press Function Key If no error:
d 08
_ _ _
If error exists:
Exx
(error code)
3. Press Up/Dn key (if
error exists)
Output frequency at
trip point:
10.0
Motor current at trip
1
point:
0.025
2
DC bus voltage at trip
point:
189.8
10
Page 12

Restoring Factory Default Settings
Action Display Function/Parameter
1
FUNC.
Press , or as
needed.
FUNC.
Press .
Press/hold until...
Press . If setting is
correct, then skip next step.
1
FUNC.
b --
2
b 01
b 85
02
“B” Group selected
First “B” Group parameter
Country code for
initialization selected
00 = Japan
01 = Europe
02 = United States
To change country code, press
FUNC.
Press .
2
Press .
FUNC.
Press .
1
Press .
STR
Press .
1
Press/hold , , and
2
Press/hold (STOP) for
3 seconds, then release.
Now release the all keys
together, only after “D_00”
display begins blinking.
FUNC.
. Do not release yet.
STOP
RESET
b 85
b 84
00
01
b 84
b 84
d 00
EU
USA
JP
Initialization is complete.
d 01
1
2
or to set; to store.
Country code for
initialization selected
Initialization function
selected
0 = disable initialization,
clear trip history only
1 = enable initialization
Initialization now
enabled to restore all
defaults
First part of key sequence
Final part of special
sequence, “D_00” is
flashing
Default parameter
country code shown
during initialization
Function code for output
frequency monitor shown
STR
11
Page 13

Note: After initializing the inverter, use the Powerup Test
on page 8 to get the motor running again.
Parameter Tables
“D” Group: Monitoring Functions
Func.
Code
D_01 Output frequency monitor Hz
D_02 Output current monitor A
D_03 Rotation direction monitor —
D_04 Process variable (PV), PID feedback monitor %
D_05 Intelligent input terminal status —
D_06 Intelligent output terminal status —
D_07 Scaled output frequency monitor
(output frequency x B_86 scale factor)
D_08 Trip event monitor —
D_09 Trip history monitor —
Name / Description Units
Forward
Stop Reverse
Direction
ON
OFF
2 14365
Terminal Numbers
ON
OFF
12 11AL
Terminal Numbers
User-
defined
12
Page 14

Trip History Navigation Map
Monitor Mode
Display data
o.0
FUNC.
1
2
d
08
1
2
d
09
1
2
FUNC.
FUNC.
FUNC.
Error
exists?
Ye s
E07
1
60.0
1
4.0 0
1
270.0
(n-1)
Error
exists?
Ye s
E03
FUNC.
No
Error code
2
Output frequency
at trip point
2
Motor current
at trip point
2
DC bus voltage
at trip point
No
No error
____
No
history
____
FUNC.
(n-2)
Error
exists?
Ye s
E05
FUNC.
13
No
No
history
____
FUNC.
Page 15

Parameter tables for user-settable functions follow these conventions:
• Some parameters have 2nd motor equivalents, indicated by the
x2xx parameter codes in the left-most column.
• Some parameters specify an option code. Where applicable, the
options codes will be in a bulleted list in the Name/Description
column.
• The default values apply to all models unless otherwise noted for
each parameter... –FE (Europe) / – FU (U.S.) / –FR (Japan).
• Some parameters cannot be edited during Run Mode, and certain
Software Lock settings (B_31) can prohibit all edits. If in doubt,
place the inverter in Stop Mode or consult the inverter manual for
details.
“F” Group: Main Profile Parameters
Func.
Code
F_01 Output frequency setting 0.0
F_02 Acceleration (1) time setting 10.0
F202 Acceleration (1) time setting, 2nd motor 10.0
F_03 Deceleration (1) time setting 10.0
F203 Deceleration (1) time setting, 2nd motor 10.0
F_04 Keypad Run key routing
Name / Description
•00Forward •01Reverse
“A” Group: Standard Functions
Func.
Code
A_01 Frequency source setting
Name / Description
• 00 Keypad potentiometer
• 01 Control terminal
• 02 Function F_01 setting
–FE / –FU /
01 / 01 / 00
14
Default
Val ue
00
Default
Val ue
–FR
Set
Val ue
Set
Val ue
Page 16

Default
Func.
Code
A_02 Run command source setting
A_03/
A203
A_04/
A204
A_11 O/OI–L input active range start
A_12 O/OI–L input active range end frequency 0
A_13 O/OI–L input active range start voltage 0
A_14 O/OI–L input active range end voltage 100
A_15 O/OI–L input start frequency enable
A_16 External frequency filter time constant 8
A_20/
A220
A_21
A_22
A_23
A_24
A_25
A_26
A_27
A_28
A_29..
..A_35
A_38 Jog frequency setting 1.0
A_39 Jog stop mode
A_41/
A241
A_42/
A242
Name / Description
• 01 Input terminal FW or RV (assignable)
• 02 Run key on keypad, or digital
operator
Base frequency setting 50.0 / 60.0 /
Maximum frequency setting 50.0 / 60.0 /
frequency
• 00 Use A_11 starting value)
• 01 Use 0 Hz
Multi-speed frequency setting 0
Multi-speed frequency settings
(for both motors)
• 00 Free-run stop, jogging disabled
during motor run
• 01 Controlled deceleration, jogging
disabled during motor run
• 02 DC braking to stop, jogging
disabled during motor run
Torque boost method selection
• 00 Manual torque boost
• 01 Automatic torque boost
Manual torque boost value 11
Val ue
–FE / –FU /
01 / 01 / 02
0 / 0 / 5
0 / 0 / 10
0 / 0 / 15
0 / 0 / 20
0 / 0 / 30
0 / 0 / 40
0 / 0 / 50
0 / 0 / 60
0 / 0 / 0
0 / 0 / 0
–FR
60.0
60.0
0
01
00
00
Set
Val ue
15
Page 17

Default
Func.
Code
A_43/
A243
A_44/
A244
A_45 V/f gain setting 100
A_51 DC braking enable
A_52 DC braking frequency setting 0.5
A_53 DC braking wait time 0.0
A_54 DC braking force during deceleration 0
A_55 DC braking time for deceleration 0.0
A_61 Frequency upper limit setting 0.0
A_62 Frequency lower limit setting 0.0
A_63
A_65
A_67
A_64
A_66
A_68
A_71 PID Enable
A_72 PID proportional gain 1.0
A_73 PID integral time constant 1.0
A_74 PID derivative time constant 0.0
A_75 PV scale conversion 1.00
A_76 PV source setting
A_81 AVR function select
A_82 AVR voltage select 230/230/200
A_92/
A292
Name / Description
Manual torque boost frequency adjustment
V/f characteristic curve selection
• 00 V/f constant torque
• 01 V/f variable torque
• 02 Sensorless vector control
• 00 Disable • 01 Enable
Jump (center) frequency setting 0.0
Jump (hysteresis) frequency width
setting
• 00 PID operation OFF
• 01 PID operation ON
• 00 [OI] terminal (current input)
• 01 [O] terminal (voltage input)
• 00 AVR enabled • 01 AVR disabled
• 02 AVR enabled except during decel
Acceleration (2) time setting 15.0
Val ue
–FE / –FU /
–FR
10.0
02
00
0.5
00
00
02 / 00 / 02
400/460/400
Set
Val ue
16
Page 18

Func.
Code
A_93/
A293
A_94/
A294
A_95/
A295
A_96/
A296
A_97 Acceleration curve selection
A_98 Deceleration curve selection
Name / Description
Deceleration (2) time setting 15.0
Select method to switch to Acc2/Dec2
profile
• 00 2CH input from terminal
• 01 transition frequency
Acc1 to Acc2 frequency transition point 0.0
Dec1 to Dec2 frequency transition point 0.0
• 00 Linear • 01 S-curve
• 02 U-shape • 03 Reverse
U-shape
• 00 Linear • 01 S-curve
• 02 U-shape• • 03 Reverse
U-shape
–FE / –FU /
“B” Group: Fine-tuning Functions
Func.
Code
B_01 Selection of automatic restart mode
B_02 Allowable under-voltage power failure
B_03 Retry wait time before motor restart 1.0
Name / Description
• 00 Alarm output after trip, automatic
restart disabled
• 01 Restart at 0Hz
• 02 Resume operation after frequency
matching
• 03 Resume previous freq. after freq.
matching, then decelerate to stop and
display trip info
time
–FE / –FU /
Default
Val ue
–FR
00
00
00
Default
Val ue
–FR
00
1.0
Set
Val ue
Set
Val ue
17
Page 19

Default
Func.
Code
B_12/
B212
B_13/
B213
B_21 Overload restriction operation mode
B_22 Overload restriction setting Rated
B_23 Deceleration rate at overload restriction 1.0
B_31 Software lock mode selection
B_81 [FM] terminal analog meter adjustment 80
B_82 Start frequency adjustment 0.5
B_83 Carrier frequency setting 5.0 / 5.0 /
B_84 Initialization mode (parameters or trip
B_85 Country code for initialization
B_86 Frequency scaling conversion factor 1.0
B_87 STOP key enable
B_88 Restart mode after FRS
Name / Description
Level of electronic thermal setting Rated
Electronic thermal characteristic
• 00 Reduced torque • 01 Const. torque
• 00 Disabled
• 01 Enabled for accel and constant
speed
• 02 Enabled for constant speed only
• 00 Low-level access, [SFT] blocks
edits
• 01 Low-level access, [SFT] blocks
edits (except F_01 and Multi-speed
parameters)
• 02 No access to edits
• 03 No access to edits except F_01 and
Multi-speed parameters
history)
• 00 Trip history clear
• 01 Parameter initialization
• 00 Japan version • 01 Europe
version
•02US version
• 00 Enable • 01 Disable
• 00 Restart from 0Hz
• 01 Restart from frequency detected
from actual speed of motor
Val ue
–FE / –FU /
–FR
current of
each inverter
01 / 01 / 00
01
current
x 1.25
01
12.0
00
01 / 02 / 00
00
00
Set
Val ue
18
Page 20

Default
Func.
Code
B_89 Data select for digital operator OPE-J
B_90 Dynamic braking usage ratio 0.0
B_91 Stop mode selection 00
B_92 Cooling fan control
Name / Description
• 01 Output frequency (D_01)
• 02 Output current (D_02)
• 03 Motor direction (D_03)
• 04 PID PV feedback (D_04)
• 05 Input states for input terminals
(D_05)
• 06 Output states for output terminals
(D_06)
• 07 Scaled output frequency (D_07)
• 00 Fan always ON
• 01 Fan ON during Run, OFF during
Stop
Val ue
–FE / –FU /
–FR
01
00
“C” Group: Intelligent Terminal Functions
Set
Val ue
Func.
Code
C_01 Terminal [1] function Nineteen option
C_02 Terminal [2] function 01
C_03 Terminal [3] function 02 / 16 / 02
C_04 Terminal [4] function 03 / 13 / 03
C_05 Terminal [5] function 18 / 09 / 09
C_06 Terminal [6] function 09 / 18 / 18
C_11 Terminal [1] active
C_12 Terminal [2] active
C_13 Terminal [3] active
state
state
state
Name / Description
codes available
(see page 22)
• 00 Normally
open [NO]
• 01 Normally
closed [NC]
Default
Val ue
–FE / –FU /
–FR
00
00
00
00
19
Set
Val ue
Page 21

Default
Func.
Code
C_14 Terminal [4] active
C_15 Terminal [5] active
C_16 Terminal [6] active
C_21 Terminal [11] function Six option
C_22 Terminal [12] function 00
C_24 Alarm relay terminal
C_23 [FM] signal selection Three option
C_31 Terminal [11] active
C_32 Terminal [12] active
C_33 Alarm relay terminal
C_41 Overload level setting Rated
C_42 Frequency arrival setting for accel 0.0
C_43 Arrival frequency setting for decel 0.0
C_44 PID deviation level setting 3.0
C_81 O input span calibration Factory
C_82 OI input span calibration
C_91 Debug mode enable
C_92 Core monitor address (reserved) 0000
C_93 Core monitor date (reserved) —
C_94 Core set address (reserved) D001
C_95 Core set date (reserved) 00
Name / Description
state
state
state
function
state (–FU)
Reserved (–FE / –FR) 00 / — / 00
state (–FU)
Terminal [11] active
state (–FE / –FR)
active state
• 00 Display • 01 No display
• 00 Normally
open [NO]
01 Normally
closed [NC]
codes available
(see page 22)
codes available
(see page 23)
• 00 Normally
open (NO)
• 01 Normally
closed (NC)
Val ue
–FE / –FU /
–FR
00 / 01 / 00
00
00
01
05
00
— / 00 / —
— / 00 / —
00 / — / 00
01
current of
inverter
calibrated
00
Set
Val ue
20
Page 22

“H” Group: Motor Constants Functions
Func.
Code
H_01 Auto-tuning Setting
H_02/
H202
H_03/
H203
H_04/
H204
H_05/
H205
H_06/
H206
H_20/
H220
H_21/
H221
H_22/
H222
H_23/
H223
H_24/
H224
H_30/
H230
H_31/
H231
H032/
H232
H_33/
H233
H_34/
H234
Name / Description
• 00 Auto-tuning OFF
• 01 Auto-tune (measure motor resis-
tance and inductance, without rotating)
• 02 Auto-tune (rotate motor)
Motor data selection
• 00 Standard motor data
• 01 Auto-tuning data
• 02 Adaptive tuning data
Motor capacity Factory set
Motor poles setting
• 2 poles • 4 poles
• 6 poles • 8 poles
Motor speed constant 20
Motor stabilization constant 100
Motor constant R1 Inverter
Motor constant R2 Inverter
Motor constant L Inverter
Motor constant I
Motor Constant J Inverter
Auto-tuned motor constant R1 Inverter
Auto-tuned motor constant R2 Inverter
Auto-tuned motor constant L Inverter
Auto-tuned motor constant I
Auto-tuned motor constant J Inverter
0
0
Default
–FE / –FU /
Inverter
Inverter
Val ue
–FR
00
00
4
rating
rating
rating
rating
rating
rating
rating
rating
rating
rating
Set
Val ue
21
Page 23

Intelligent Input Terminal Listing
Symbol Code Input Terminal Name
FW 00 Forward Run/Stop
RV 01 Reverse Run/Stop
CF1 02 Multi-speed select, Bit 0 (LSB)
CF2 03 Multi-speed select, Bit 1
CF3 04 Multi-speed select, Bit 2
CF4 05 Multi-speed select, Bit 3 (LSB)
JG 06 Jogging
DB 07 External DC braking
SET 08 Set (select) second motor data
2CH 09 2-stage accel and decel
FRS 11 Free-run stop
EXT 12 External trip
USP 13 Unattended start protection
SFT 15 Software lock
AT 16 Analog input voltage/current sel.
RS 18 Reset inverter
PTC 19 PTC thermistor thermal protection
UP 27 Remote control Up func.
DWN 28 Remote control Down func.
Intelligent Output Terminal Listing
Symbol Code Input Terminal Name
RUN 00 Run signal
FA1 01 Freq. arrival type 1 – constant speed
FA2 02 Freq. arrival type 2 – over-frequency
OL 03 Overload advance notice signal
OD 04 Output deviation for PID control
AL 05 Alarm signal
22
Page 24

Analog Input Configuration
The following tables show the parameter settings required for various analog input signal types.
[AT] External Frequency Command Input
OFF [O] — [L]
ON [OI] — [L]
(not assigned to any input
terminal)
Summation of [O] — [L] and [OI] — [L]
Analog Output Function Listing
The following table shows all three functions available for assignment to the analog output terminal:
• Terminal [FM], option set by C_23
Option
Code
Function
Name
00 Output
frequency
01 Output
current
02 Digital output
frequency
Description
Actual motor speed,
represented by PWM
signal
Motor current (% of
maximum rated output
current), represented by
PWM signal
Output frequency 0 to max. freq. in Hz
Corresponding
Signal Range
0 to max. freq. in Hz
0 to 200%
Auto-tuning Procedure
The SJ100 auto-tuning feature calibrates the inverter to the parameters of a specific motor such as winding resistance and reactance.
For optimum sensorless vector control, it is important to auto-tune
during the initial installation, and after replacing either the motor or
the inverter.
Auto-tuning requires that you configure the inverter for SLV control
(set A_44 = 02). Then you can perform the auto-tuning procedure,
which is detailed in the SJ100 Inverter Instruction Manual.
23
 Loading...
Loading...