Page 1
HITACHI INVERTER
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
J300 SERIES
INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Three phase input 200/400V class
J300 U : USA version
After reading this manual, keep it at hand for future reference.
NB506XC
Hitachi, Ltd.
Tokyo Japan
Page 2
SAFETY
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
For the Best Results with J300 Series inverter, read this manual and all of the warning sign attached to
the inverter carefully before installing and operating it, and follow the instructions exactly. Keep this
manual handy for your quick reference.
Definitions and Symbols
A safety instruction (message) is given with a hazard alert symbol and a signal word;
WARNING or CAUTION. Each signal word has the following meaning throughout this manual.
This symbol means hazardous high voltage. It used to call your attention to
items or operations that could be dangerous to your and other persons operating this equipment.
Read these message and follow these instructions carefully.
This is the “Safety Alert Symbol.” This symbol is used to call your attention
to items or operations that could be dangerous to your or other persons operating this equipment. Read these messages and follow these instructions
carefully.
WARNING WARNING
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, can result in
serious injury or death.
CAUTION CAUTION
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, can result in
minor to moderate injury, or serious damage of product.
The matters described under CAUTION may, if not avoided, lead to
serious results depending on the situation. Important matters are described in
CAUTION (as well as WARNING), so be sure to observe them.
NOTE NOTE: Notes indicate an area or subject of special merit, emphasizing either
the product’s capabilities or common errors in operation or maintenance.
HAZARDOUS HIGH VOLTAGE
Motor control equipment and electronic controllers are connected to hazardous line voltages. When
servicing drives and electronic controllers, there might be exposed components with cases or protrusions
at or above line potential. Extreme care should be taken to protect against shock.
Stand on an insulating pad and make it a habit to use only one hand when checking components. Always
work with another person in case an emergency occurs. Disconnect power before checking controllers
or performing maintenance. Be sure equipment is properly grounded. Wear safety glasses whenever
working on an electronic controllers or rotating electrical equipment.
- i -
Page 3
PRECA UTIONS
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
WARNING: This equipment should be installed, adjusted and serviced by qualified electrical
maintenance personal familiar with the construction and operation of the equipment
and the hazards involved. Failure to observe this precaution could result in bodily injury.
WARNING : The user is responsible for ensuring that all driven machinery, drive train
mechanism not supplied by Hitachi, Ltd., and process line material are capable of safe operation
at an applied frequency of 150% of the maximum selected frequency range to the AC motor.
Failure to do so can result in destruction of equipment and injury to personnel should a single
point failure occur.
WARNING : For protection, install a leak breaker type with a high frequency circuit capable
of large currents to avoid an unnecessary operation. The ground fault protection circuit is not
designed to protect personal injury.
WARNING : HAZARD OF ELECTRICAL SHOCK. DISCONNECT INCOMING
POWER BEFORE WORKING ON THIS CONTROL.
AVERTISSEMENT : RISQUE DE CHOC ELECTRIQUE COUPER L'ALIMENTATION
AVANT LE DEPANNAGE DE CETTE COMMANDE.
WARNING : SEPARATE MOTOR OVERCURRENT, OVERLOAD AND OVER-
HEATING PROTECTION IS REQUIRED TO BE PROVIDED IN ACCORDANCE
WITH THE SAFETY CODES REQUIRED BY JURISDICTIONAL AUTHORITIES.
AVERTISSEMENT : LE MOTEUR DOIT ETRE MUNI D'UNE PROTECTION
DISTINCTE CONTRE LES SURINTENSITES, LA SURCHARGE ET LA
SURCHAUFFE,CONFORMEMENT AU CODE CANADIEN DE L'ELECTRICITE<
PREMIERE PARTIE.
CAUTION: These instructions should be read and clearly understood before working on J300
series equipment.
CAUTION: Proper grounds, disconnecting devices and other safety devices and their location
are the responsibility of the user and are not provided by Hitachi, Ltd.
CAUTION: Be sure to connect a motor thermal switch or overload device to the J300 series
controller to assure that the inverter will shut down in the event of an overload or an overheated
motor.
CAUTION: DANGEROUS VOLTAGE EXISTS UNTIL CHARGE LIGHT IS OFF.
ATTENTION: PRESENCE DE TENSIONS DANGEREUSES TANT QUE LE VOYANT
N'EST PAS ETEINT.
CAUTION: Rotating shafts and above ground electrical potentials can be hazardous. There-
fore, it is strongly recommended that all electrical work conform to the National Electrical Codes
and local regulations. Installation, alignment and maintenance should be performed only by
qualified personnel. Factory recommended test procedures, included in the instruction manual,
should be followed. Always disconnect electrical power before working on the unit.
- ii -
Page 4

NOTE : POLLUTION DEGREE 2
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
The inverter must be used in environment of the degree 2.
Typical constructions that reduce the possibility of conductive pollution are;
1) The use of an un-ventilated enclosure
2) The use of a filtered ventilated enclosure when the ventilation is fan forced that is,
ventilation is accomplished by one or more blowers within the enclosure that provide a
positive intake and exhaust.
NOTE : ENCLOSURE SIZE FOR 75 kW TO 110 kW
The inverter, 75kW to 110kW must be installed into an enclosure with dimmensions no
less than 183cm (72 in) by 183cm (72 in) by 60cm (24 in).
NOTE : ENCLOSURE SIZE FOR 132 kW AND BIGGER
The inverters, 132kW and bigger, are complied as recognizedcomponents.
Therse devices are intended for use in an overall ecclosure with an internal ambient of
40 degree C for variable torque rating or 50 degree C for constant torque rating maximum.
End product temperature testing should be conducted to verify sufficient forced air ventilation
is provided to maintain this ambient in room ambient of 10-40 degree C.
Based upon component level testing , end product temperature testing may be conducted at
any convenient room ambient in the rangeof 20-40 dwgree C, unless the room ambient in the
intended application exceeds 40degree C, in which case testing should be conducted at the
elevated ambient.
Enclosure internal ambient temperature should be measured above the drive on to the upper
left or right side. Temperature measurments on the drive itself should not be necessary.
NOTE : SET OF MOTOR CAPACITY AND POLES (A1, A2)
When data does not match a capacity of connected motor , it may cause unstaible motor
operation. Set proper motor capacity (kW) and motor poles even under V/F control mode.
- iii -
Page 5
Revision History Table
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
No. Revision Contents
The Date Operation
of Issue Manual No.
1 Page iii : Pollution degree Aug. 1997 NB506XA
Page 2-1 : Description of inverter model
Page4-2 : Change of note
Page 5-8, 5-9 : Addition of 750 to 1100H
Page 5-10 : Terminal description
Page 11-1,11-2,11-3 : addition of 750 to 1100H
2 Page iii : Enclosure size Feb. 1998 NB506XB
Page 4-1 : Enclosure size, page 7-5; note 3,
Page 7-11: F8 boost value in VP1 to 3
Page 7-15: A0 note for boost value
Page 12-13: additio of note 1
Page A25-A31: addition of line for set value
Page A-33: deletion of A-93 on clause
3 Page iii: note for 132 kW to 220 kW is added Feb. 1999 NB506XC
Page 2-1: added 132 to 220kW
Page 4-1; note for 132 kW to 220 kW is added
page 4-2: note,note1 corrected 110kW->260kW
page 5-8: added 1320 to 2200H in table
Page 5-10: terminal layout corrected
Page7-5: corrected monitor d3 39 to 99
Page7-18: A10, addition of 1320 to 2200H
Page 11-1,2,3: added 1320 to 2200H
- iv -
Page 6

TABLE OF CONTENTS
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Page
1. SAFETY PRECAUTIONS .......................................................................................... 1-1
2. INSPECTION UPON UNPACKING ........................................................................ 2-1
3. APPEARANCE AND NAMES OF PARTS ............................................................. 3-1
4. INSTALLATION .......................................................................................................... 4- 1
5. WIRING ......................................................................................................................... 5-1
6. OPERATION ................................................................................................................. 6-1
7. OPERATION OF THE DIGITAL OPERATOR ...................................................... 7- 1
8. PROTECTION FUNCTIONS ..................................................................................... 8 -1
9. TROUBLESHOOTING ............................................................................................... 9-1
10. MAINTENANCE AND INSPECTION ..................................................................... 10-1
11. STANDARD SPECIFICATIONS .............................................................................. 11-1
12. FUNCTIONS WHEN USING THE OPTIONAL REMOTE OPERATOR .......... 12-1
13. SERVICE ....................................................................................................................... 13-1
APPENDIX 1 ....................................................................................................................... A- 1
APPENDIX 2 ....................................................................................................................... A-15
APPENDIX 3 ....................................................................................................................... A-19
APPENDIX 4 ....................................................................................................................... A-20
APPENDIX 5 ....................................................................................................................... A-21
APPENDIX 6 ....................................................................................................................... A-24
APPENDIX 7 ....................................................................................................................... A-25
APPENDIX 8 ....................................................................................................................... A-32
- v -
Page 7
1. SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
1. Installation
CAUTION
* Be sure to install the unit on flame resistant material such as metal.
Otherwise, there is a danger of fire.
* Be sure not to place anything inflammable in the vicinity.
Otherwise, there is a danger of fire.
* Be sure not to let the foreign matter enter such as cut wire refuse, spatter
from welding, iron refuse, wire, dust, etc.
Otherwise, there is a danger of fire.
* Be sure to install it in a place which can bear the weight according to
the specifications in the text (4. Installation).
Otherwise, it may fall and there is a danger of injury.
* Be sure to install the unit on a perpendicular wall which is not subject
to vibration.
Otherwise, it may fall and there is a danger of injury.
* Be sure not to install and operate an inverter which is damaged or parts
of which are missing.
Otherwise, there is a danger of injury.
* Be sure to install it in a room which is not exposed to direct sunlight
and is well ventilated. Avoid environments which tend to be high in
temperature, high in humidity or to have dew condensation, as well as
places with dust, corrosive gas, explosive gas, inflammable gas,
grinding-fluid mist, salt damage, etc.
Otherwise, there is a danger of fire.
* Be sure that the wall surface is a nonflammable material, such as steel
plate.
............ p. 4-1
........... p. 4-1
........... p. 4-1
........... p. 4-1
........... p. 4-1
........... p. 4-1
........... p. 4-1
........... p. 4-2
2. Wiring
WARNING
* Be sure to ground the unit.
Otherwise, there is a danger of electric shock and/or fire.
* Wiring work shall be carried out by electrical experts.
Otherwise, there is a danger of electric shock and/or fire.
* Implement wiring after checking that the power supply is off.
It might incur electric shock and/or fire.
* After installing the main body, carry out wiring.
Otherwise, there is a danger of electric shock and/or injury.
* Wait until DC bus voltage is discharged after power supply is turned
off.
Otherwise, there is a danger of electric shock.
1-1
............ p. 5-1
............ p. 5-1
............ p. 5-1
............ p. 5-1
............ p. 5-10
Page 8
CAUTION
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
* Make sure that the input voltage is:
Three phase 200 to 220 V/50 Hz, 200 to 230 V/60 Hz
Three phase 380 to 415 V/50 Hz, 400 to 460 V/60 Hz
* Be sure not to input a single phase to a 3 phase type.
Otherwise, there is a danger of fire.
* Be sure not to connect AC power supply to the output terminals
[U (T1), V (T2), W (T3)].
Otherwise, there is a danger of injury and/or fire.
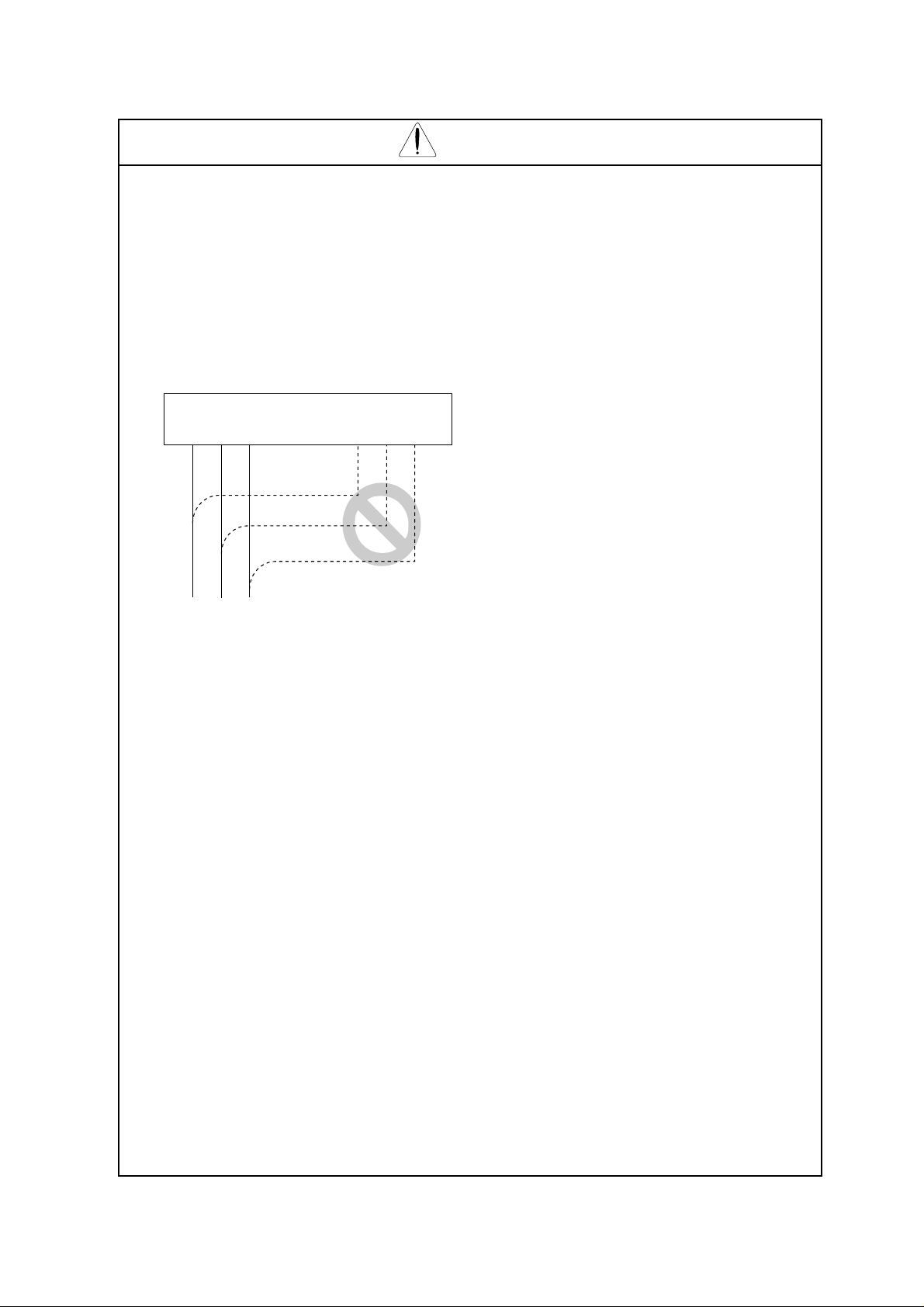
INPUT OUTPUT
Note)
(L1)
R S
Power supply
(L3) (T1) (T2) (T3)
(L2)
UVWT
............ p. 5-2
............ p. 5-2
............ p. 5-2
* Fasten the screws with the specified fastening torque. Check so that
there is no loosening of screws.
Otherwise, there is a danger of fire.
* Be sure to install an earth leakage breaker.
The ground fault protection is designed to detect current flowing to the
ground upon power on. This function is to protect the inverter, not
people. Install the earth leakage breaker to protect against the ground
fault on wires between the inverter and the motor. (Use a breaker that is
very sensitive to high frequency current so as not to cause malfunction.)
* Be sure to set the fuse(s) (the same phase as the main power supply)
in the operation circuit.
Otherwise, there is a danger of fire.
* As for motor leads, earth leakage breakers and electromagnetic
contactors, be sure to use the equivalent ones with the specified
capacity (rated).
Otherwise, there is a danger of fire.
* Connection to wiring terminal must be reliabily fixed with two means
of support.
............ p. 5-2
............ p. 5-2
............ p. 5-2
............ p. 5-2
............ p. 5-2
1-2
Page 9
CAUTION
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
External or remote over load protection required, if multiple motors to
be connected.
For models J300-450LFU and -550LFU only , connect to branch
circuit protected at maximum 300% of output current rating.
Suitable for use on a circuit capable of delivering not more than 10,000
rms symmetrical amperes,*** volts maximum,
(where *** = input voltage)
Alarm connection may contain harzordous live voltage even when
inverter is disconnected. In case of removing front cover for
maintenance or inspection, confirm that incoming power for alarm
connection is surely disconnected.
CAUTION
............ p. 5-4
............ p. 5-11
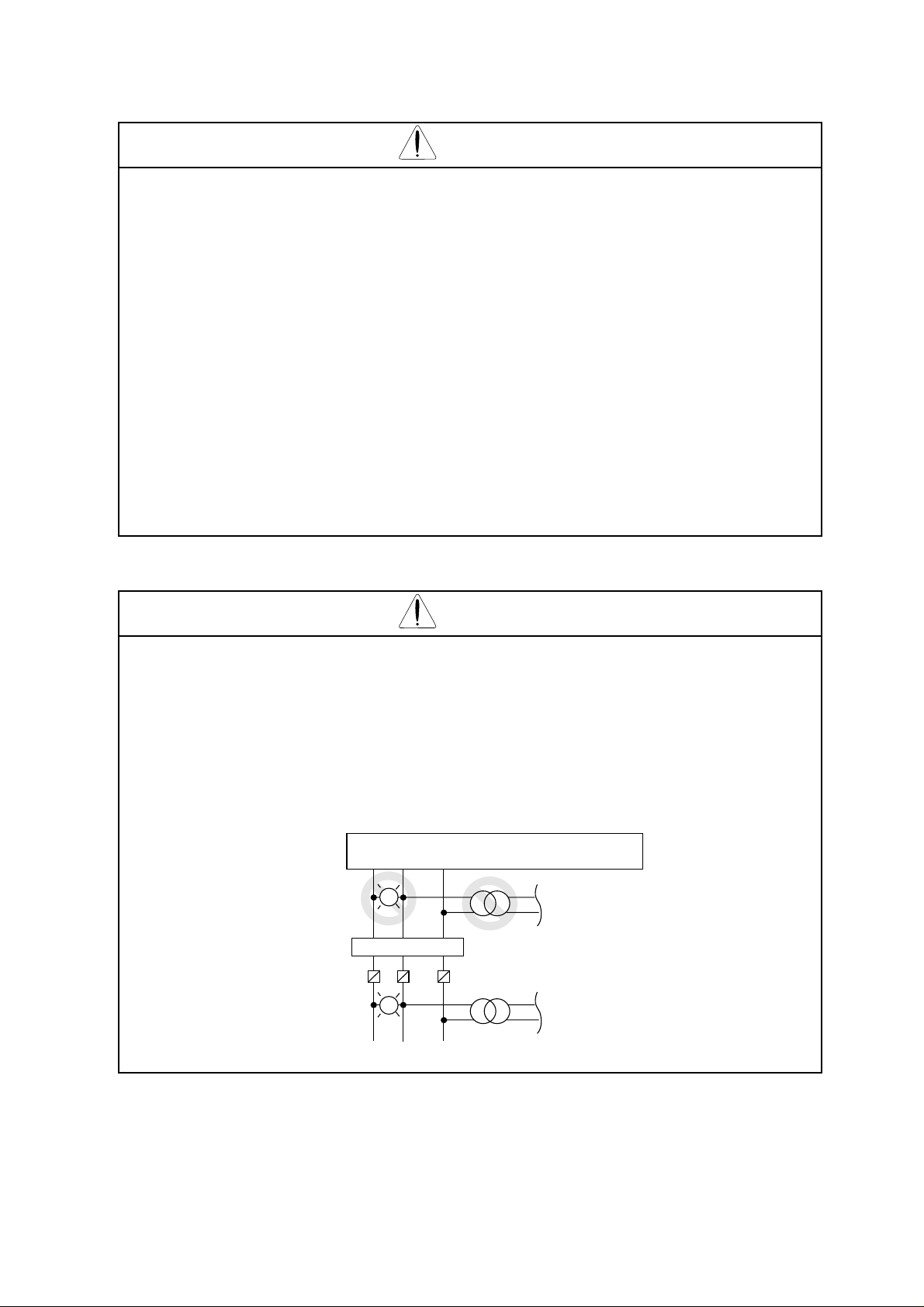
Input phase failure protection
(1) J300-U version inverter are provided with the phase failure protection on the power
supply.
(2) When a buzzer, lamp, noise filter or transformer is connected between the input power
terminals (L1, L2, L3) and input power fuses, input phase failure cannot be protected.
(L1) (L2) T(L3)
R S
L
Noise filter
Fuse
L
Power supply
(Bad example)
(Good example)
1-3
Page 10
3. Control and operation
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
WARNING
* Be sure to turn on the input power supply after mounting the surface
cover. While being energized, be sure not to remove the cover.
Otherwise, there is a danger of electric shock.
* Be sure not to operate the switches with wet hands.
Otherwise, there is a danger of electric shock.
* While the inverter is energized, be sure not to touch the inverter
terminals even during stoppage.
Otherwise, there is a danger of electric shock.
* If the re-try mode is selected, it may suddenly restart during the trip
stop. Be sure not to approach the machine. (Be sure to design the
machine so that personnel safety will be secured even if it restarts.)
Otherwise, there is a danger of injury.
* Even if the power supply is cut for a short period of time, it may restart
operation after the power supply is recovered if the operation command
is given. If it may incur danger to personnel, be sure to make a circuit
so that it will not restart after power recovery.
Otherwise, there is a danger of injury.
* The Stop Key is effective only when the function is set. Be sure to
prepare the Key separately from the emergency stop.
Otherwise, there is a danger of injury.
............ p. 6-1
............ p. 6-1
............ p. 6-1
............ p. 6-1
............ p. 6-1
............ p. 6-1
* After the operation command is given, if the alarm reset is conducted, it
will restart suddenly. Be sure to set the alarm reset after checking the
operation command is off.
Otherwise, there is a danger of injury.
* Be sure not to touch the inside of the energized inverter or to put a bar
into it.
Otherwise, there is a danger of electric shock and/or fire.
* The STOP/RESET key works only when a function is set. Prepare an
emergency switch separately. The use of the STOP/RESET key as an
emergency switch may cause an injury.
............ p. 6-1
............ p. 6-1
............ p. 7-1
1-4
Page 11

CAUTION
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
* Radiating fin and discharging resistor will have high temperature.
Be sure not to touch them.
Otherwise, there is a danger of getting burned.
* Low to high speed operation of the inverter can be easily set. Be sure
to operate it after checking the tolerance of the motor and machine.
Otherwise, there is a danger of injury.
* If a motor is operated at a frequency higher than 60Hz, be sure to check
the speeds of the motor and the machine with each manufacturer, and
after getting their consent, operate them.
Otherwise, there is a danger of machine breakage.
* Check the following before and during the test run.
Otherwise, there is a danger of machine breakage.
• Was the short-cut bar between +1 and + connected?
• Was the direction of the motor correct?
• Was the inverter tripped during acceleration or deceleration?
• Were the rpm and frequency meter correct?
• Were there any abnormal motor vibrations or noise?
• When overcurrent tripping or overvoltage tripping occurs during the
test run, increase the acceleration time or deceleration time.
............ p. 6-2
............ p. 6-2
............ p. 6-2
............ p. 6-3
4. Maintenance, inspection and part replacement
WARNING
* Be sure to turn off the power supply during maintenance and
inspection.
* After the power supply has been turned off, you must always wait 10
minutes so that DC bus capacitors can discharge then start maintenance
and inspection after the CHARGE lamp on the printed-circuit board has
gone out. (Immediately after the lamp has gone out, there will be a
residual voltage of about 50 V DC in the DC bus intermediate circuit.)
Perform the work after the CHARGE lamp has stopped flickering.
* Make sure that only qualified persons will perform maintenance,
inspection and part replacement. (Before starting the work, remove
metallic objects from your person (wristwatch, bracelet, etc.)
(Be sure to use tools protected with insulation.)
Otherwise, there is a danger of electric shock and/or injury.
........... p. 10-1
........... p. 10-1
........... p. 10-1
1-5
Page 12
CAUTION
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
* When removing connectors, never pull the wires. (Wires for cooling
fan and thermal relay)
Otherwise, there is a danger of fire due to wire breakage and/or injury.
5. Appendix
WARNING
* When the inverter stops due to a trip with retry mode selected, the
motor restarts suddenly. Stand clear of the machine. Otherwise, you
may be injured. (Design the machine in such a way that persons are
protected against a restart of the machine.)
* If the retry mode is selected, do not approach the inverter unnecessarily.
It will be restarted suddenly after it trips/stops. (Design the inverter so
that the safety can be assured even in such a restart.) Otherwise, bodily
injury will result.
........... p. 10-1
........... p. A-15
........... p. A-16
1-6
Page 13
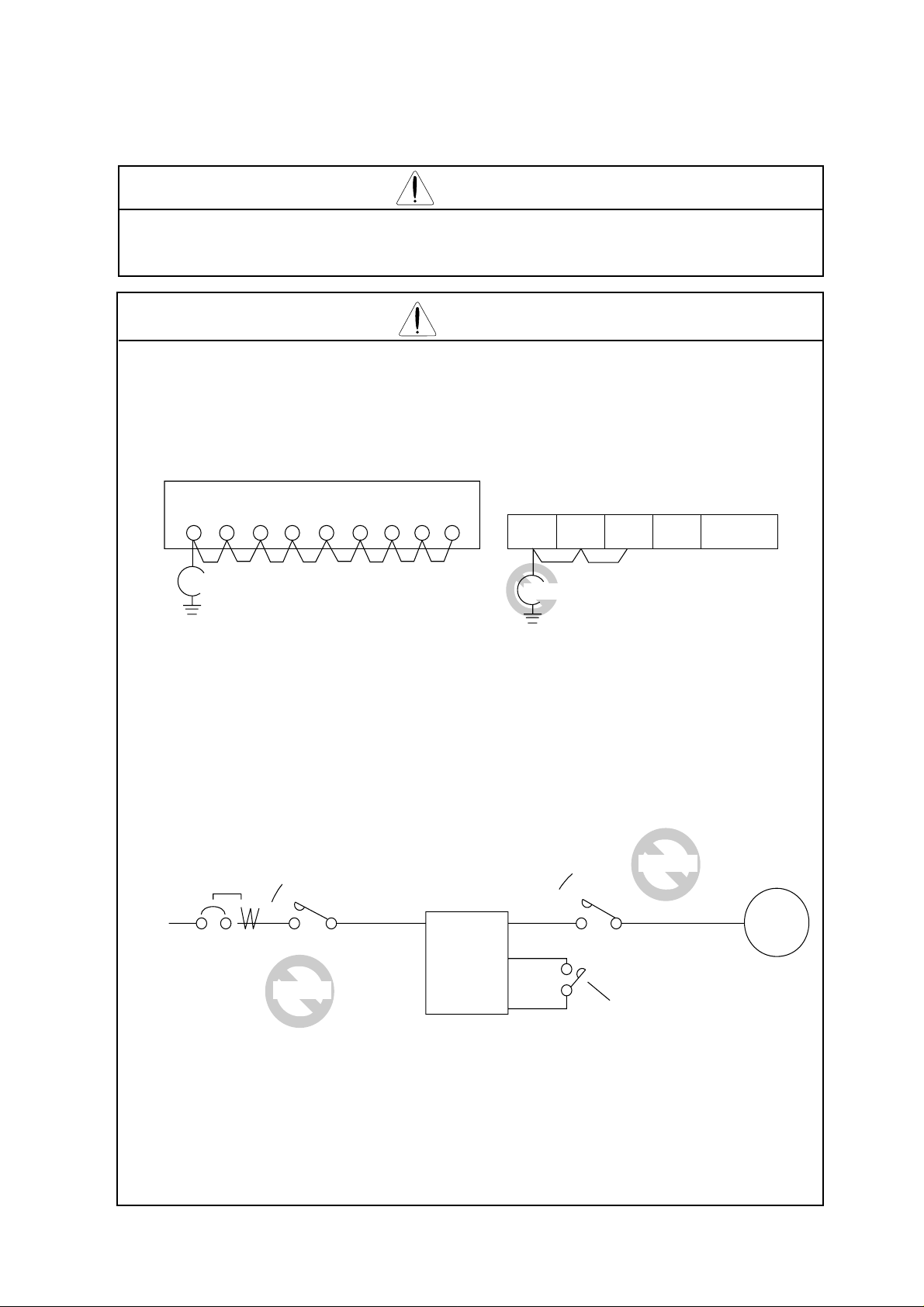
6. Others
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
WARNING
* Never modify the unit.
Otherwise, there is a danger of electric shock and/or injury.
CAUTION
* Withstand voltage tests and insulation resistance tests (megger tests) are executed
before the units are shipped, so that there is no need to conduct these tests before
operation.
When conducting megger tests as a part of daily inspection, be sure that these tests are
only executed between the main circuit and the ground. Do not execute megger tests
on the control circuit.
(L1) (L2) (L3) (RB) (+) (–) (T1) (T2)
R STRBPNUV
Megohm-meter
* Do not attach or remove wiring or connectors (including Digital operator and
(T3)
W
FW •••PLCP24FM
Megohm-meter
Remote operator) when power is applied. Also, do not check signals during
operation. Otherwise, a trip may occur or a failure may be caused. To stop the
operation, be sure to use an operation instruction (FW,REV.) Do not turn
power off within three minutes after it is turned on, or vice versa.
* Do not stop operation by switching off the electromagnetic(Mgo) contactors on
the primary or secondary sides of the inverter.To stop the operation, be sure to
use an operation instruction (FW,REV.) Do not turn power off within three
minutes after it is turned on, or vice versa. (Bad example)
Earth
Power
leakage
breaker
➤
➤
Mgo
(L1) (L2)
(L3) (T1) (T2) (T3)
R, S, T
U, V, W
➤
➤
ON,OFF
supply
INV
ON,OFF
FW
PV24
➤
Turn ON and OFF
(Good example)
When there has been an instantaneous power failure, and if an operation instruction
has been given, then the unit may restart operation after the power failure has ended. If
there is a possibility that such an occurrence may harm humans, then install an
electromagnetic contactor (Mgo) on the power supply side, so that the circuit does not
allow automatic restarting after the power supply recovers. If the optional remote
operator is used and the retry function has been selected, this will also cause automatic
restarting when an operation instruction has been input, so please be careful.
Motor
1-7
Page 14
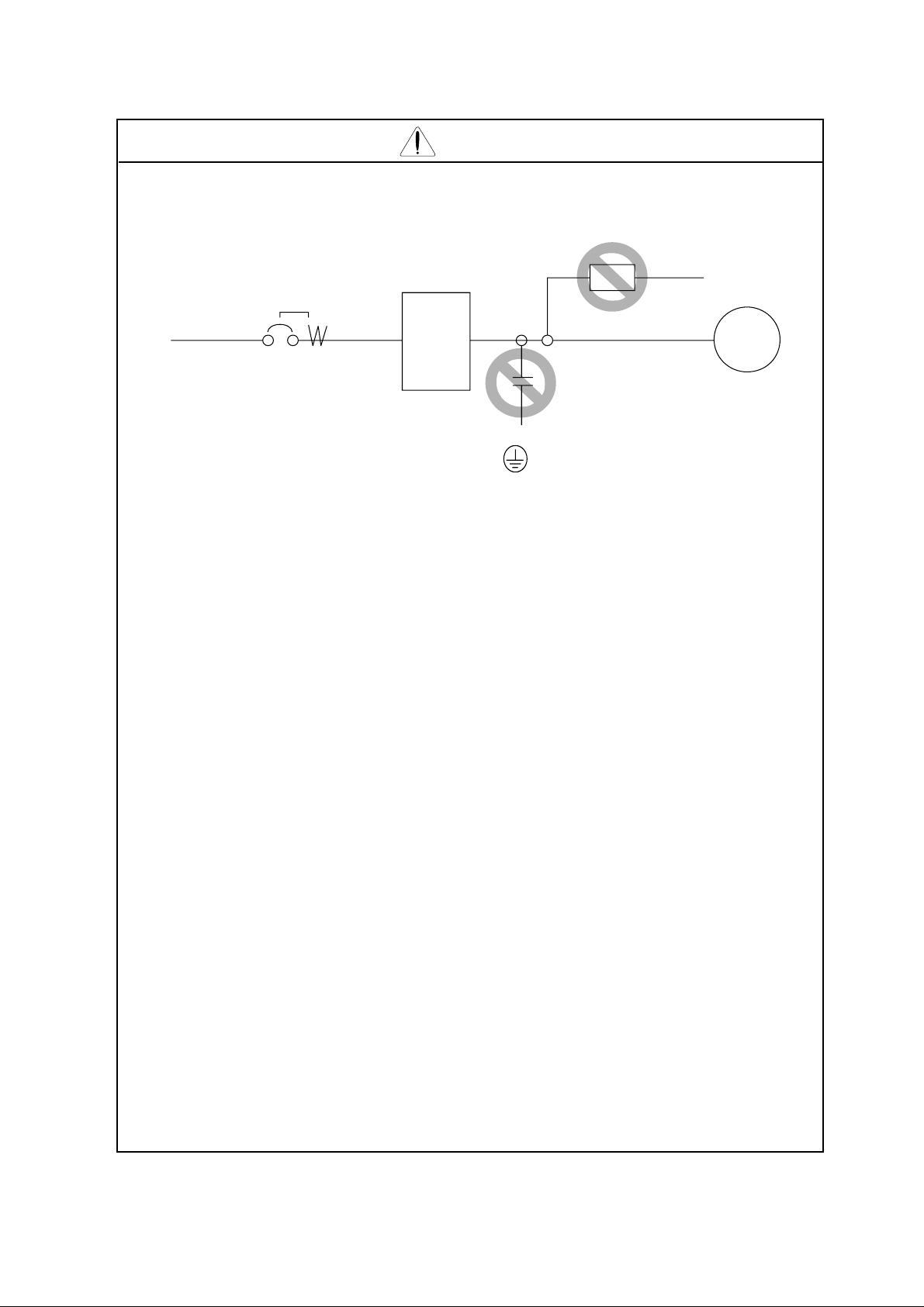
CAUTION
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
* Do not insert leading power factor capacitors or surge absorbers between the
output terminals of the inverter and the motor.
Earth
leakage
breaker
Power
supply
* Be sure to ground the grounding terminal, .
* When inspecting the unit, after turning the power supply off be sure to wait unitl
(L1)R,(L2)S,(L3)
T,
INV
(T1)U,(T2)V,(T3)
W,
Leading power factor capacitor
Surge absorber
Motor
the CHARGE lamp beside the control terminal is off before opening the cover.
(If the lamp is lit or still flickering, then the internal capacitor’s residual voltage is still
dangerous.)
* MOTOR TERMINAL SURGE VOLTAGE SUPPRESSION FILTER
(FOR THE 400 V CLASS)
In a system using an inverter of the voltage control PWM system, a surge voltage
caused by the cable constants such as the cable length (especially when the distance
between the motor and inverter is 10 m or more) and cabling method may occur at the
motor terminal.
A dedicated filter of the 400 V class for suppressing this surge voltage is available,
Please order one.
* PROTECTION AGAINST NOISE INTERFERENCE FROM INVERTER
The inverter uses many semiconductor switching elements such as transistors and
IGBTs. Thus, a radio set or measuring instrument located near the inverter is
susceptible to noise interference.
To protect the instruments from erroneous operation due to noise interference, they
should be installed well apart from the inverter. It is also effective to shield the whole
inverter structure.
Addition of an EMI filter on the input side of the inverter also reduces the effect of
noise from commercial power line on external devices.
Note that external dispersion of noise from the power line can be minimized by
connecting an EMI filter on the primary side of inverter.
1-8
Page 15
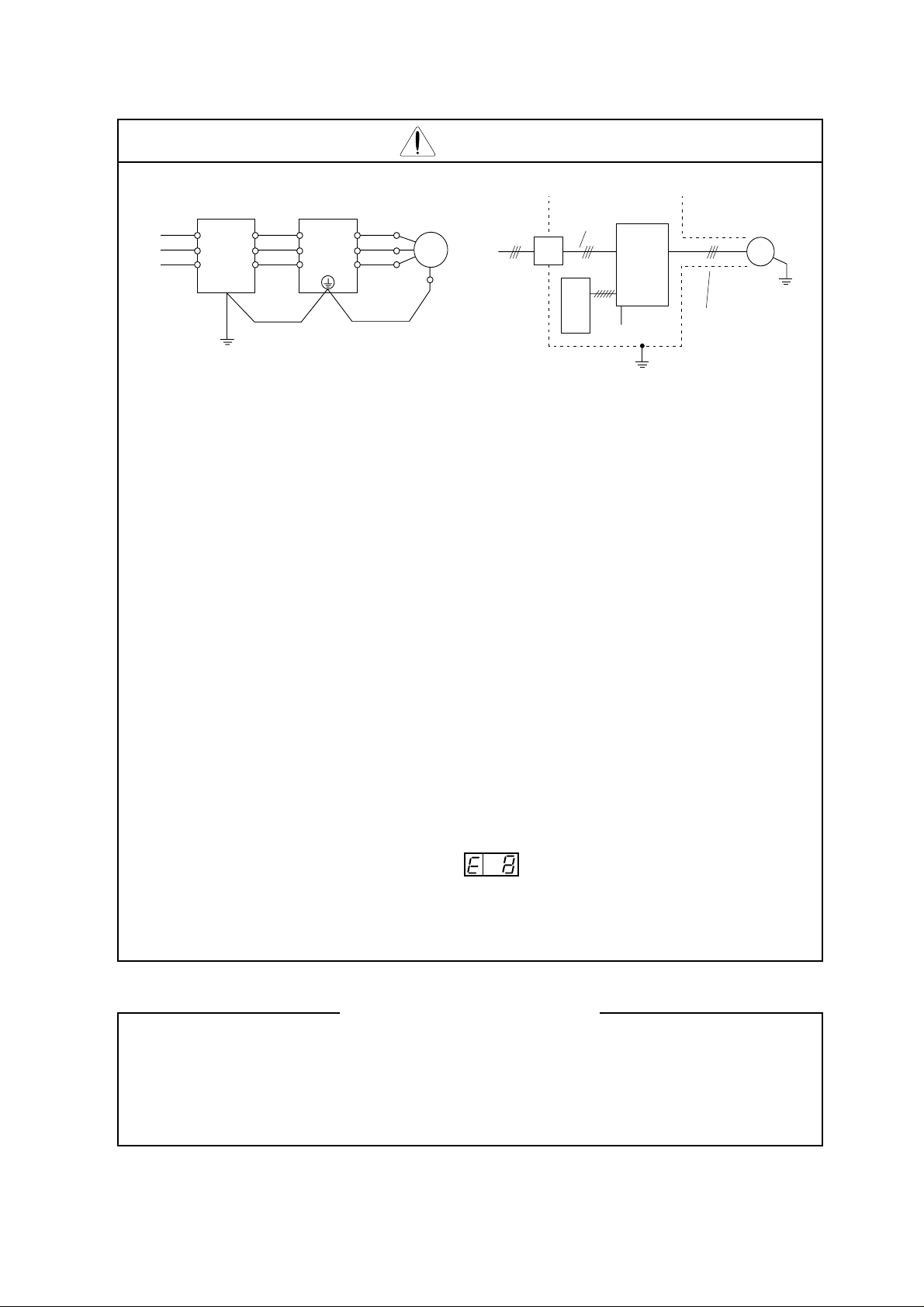
CAUTION
p
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
EMI filter Inverter
(T1)
U
R1
R2
S1
Power
source
* EFFECTS OF DISTRIBUTOR LINES ON INVERTERS
T1
S2
T2
L1(L1)
L2(L2)
L3(L3)
(T2)
V
(T3)
W
Motor
U
V
W
Terminal
for
grounding
Power
source
EMI
filter
Noise
➤
Inverter
➤
Remote
operator
Noise
Completely ground the shield made
of metal screen, enclosed panel, etc.
with as short a wire as
Piping
(to be grounded)
or shielded wire
In the cases below involving a general-purpose inverter, a large peak current flows on
the power supply side, sometimes destroying the converter module. Where such
situations are foreseen, or the paired equipment must be highly reliable, install an AC
reactor between the power supply and the inverter.
(A) The unbalance factor of the power supply is 3% or higher.
(B) The power supply capacity is at least 10 times greater than the inverter capacity
(and the power supply capacity, 500 kVA or more).
(C) Abrupt power supply changes are expected.
Motor
➤
Ground the
frame.
ossible.
Examples:
(1) Several inverters are interconnected with a short bus.
(2) A thyristor converter and an inverter are interconnected with a short bus.
(3) An installed phase advance capacitor opens and closes.
In cases (A), (B) or (C), we recommend installing an AC reactor of 3% (in a voltage
drop at rated current) with respect to the supply voltage on the power supply side.
* When occurring an EEPROM error ( ), be sure to confirm the setting
value again.
* When setting b contact to the reverse command ([REV] terminal), the inverter
state automatically. Do not set to b contact.
GENERAL CAUTION
In all the illustrations in this manual, covers and safety devices are occasionally
removed to describe the details. When the product is operated, make sure that the
covers and safety devices are placed as they were specified originally and operate it
according to the instruction manual.
1-9
Page 16
2. INSPECTION UPON UNPACKING
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Before installation and wiring, be sure to check the following:
• Make sure that there was no damage during transportation the unit.
• After unpacking the unit, make sure that the package contains one inverter and one operation manual
• Make sure that the product is the one you ordered by checking the specifications label on
the front of the cover.
Model abbreviation
(The example is for the J300-055HFE2)
Input power supply,
phase, and frequency
Production year
HITACHI
380-415V 3 Ph 50 Hz max:380-460V 3 Ph
400-460V 3 Ph 60 Hz Amps (CT) 13 A/(VT) 16 A
DATE
1995 J300U-055H251LMFG. NO.
Hitachi, Ltd.
INPUT
INVERTER
J300
(CT) 5.5kW(VT) 7.5kW
Made in Japan
055HFU
OUTPUT
NE15390
Contents of Specifications Label
If you discover any problems, contact your sales agent immediately.
Description of Inverter Model
J300 055 H F U
Version number
U : USA version
Structure type
F: with digital operator
Series name
(Semi-closed, open type)
Input voltage
L : Three phase 200V class
H : Three phase 400V class
Output voltage
Rated output current
Maximum applicable motor (4P kW)
Production number
and factory control symbol
Applicable motor capacity (4P.kW)
055: 5.5 kW
075: 7.5 kW
110: 11 kW
150: 15 kW
220: 22 kW
300: 30 kW
370: 37 kW
450: 45 kW
550: 55 kW
750: 75 kW
900: 90kW
1100: 110 kW
1320: 132 kW
1600: 160kW
2200: 220 kW
2-1
Page 17
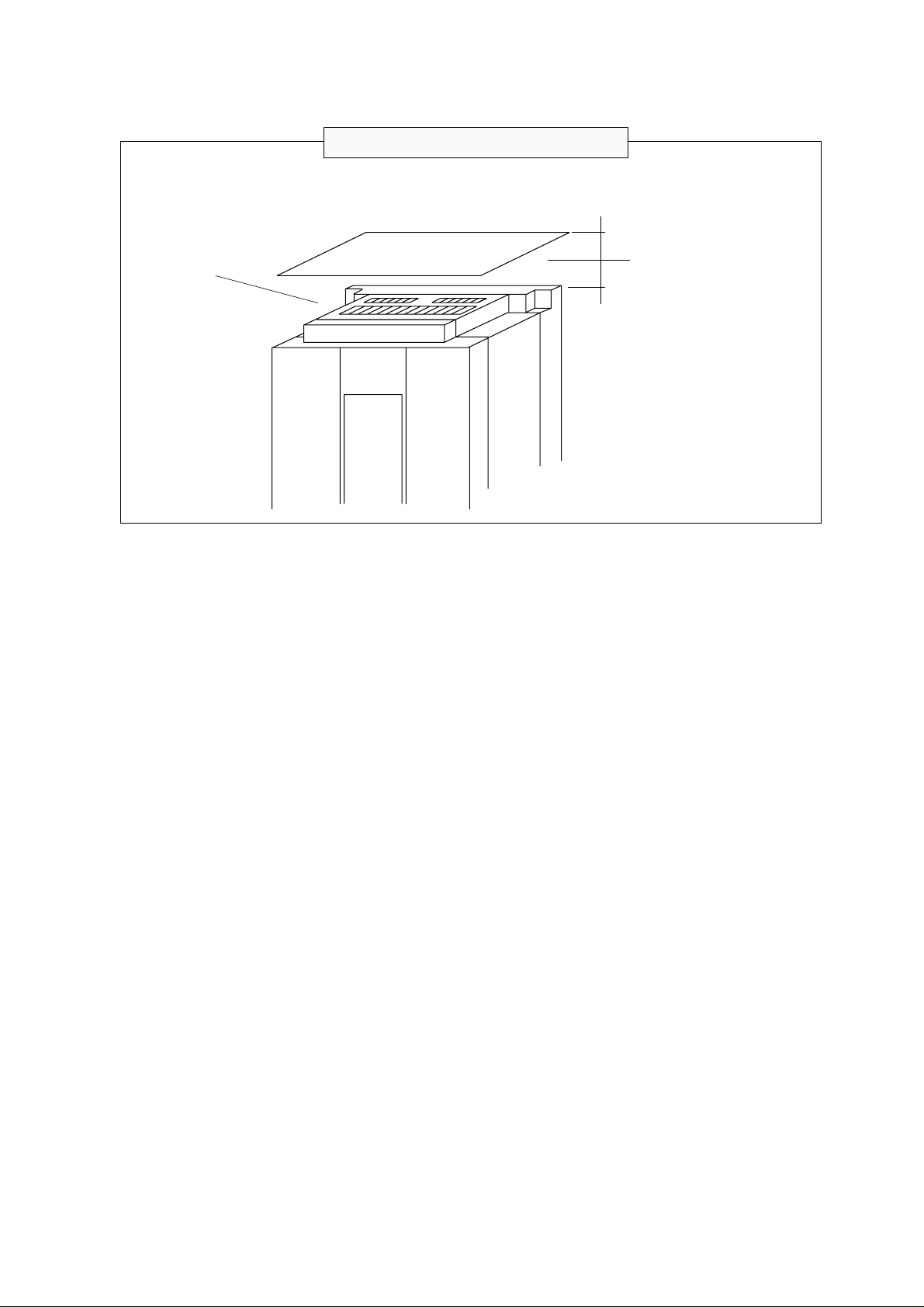
3. APPEARANCE AND NAMES OF PARTS
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
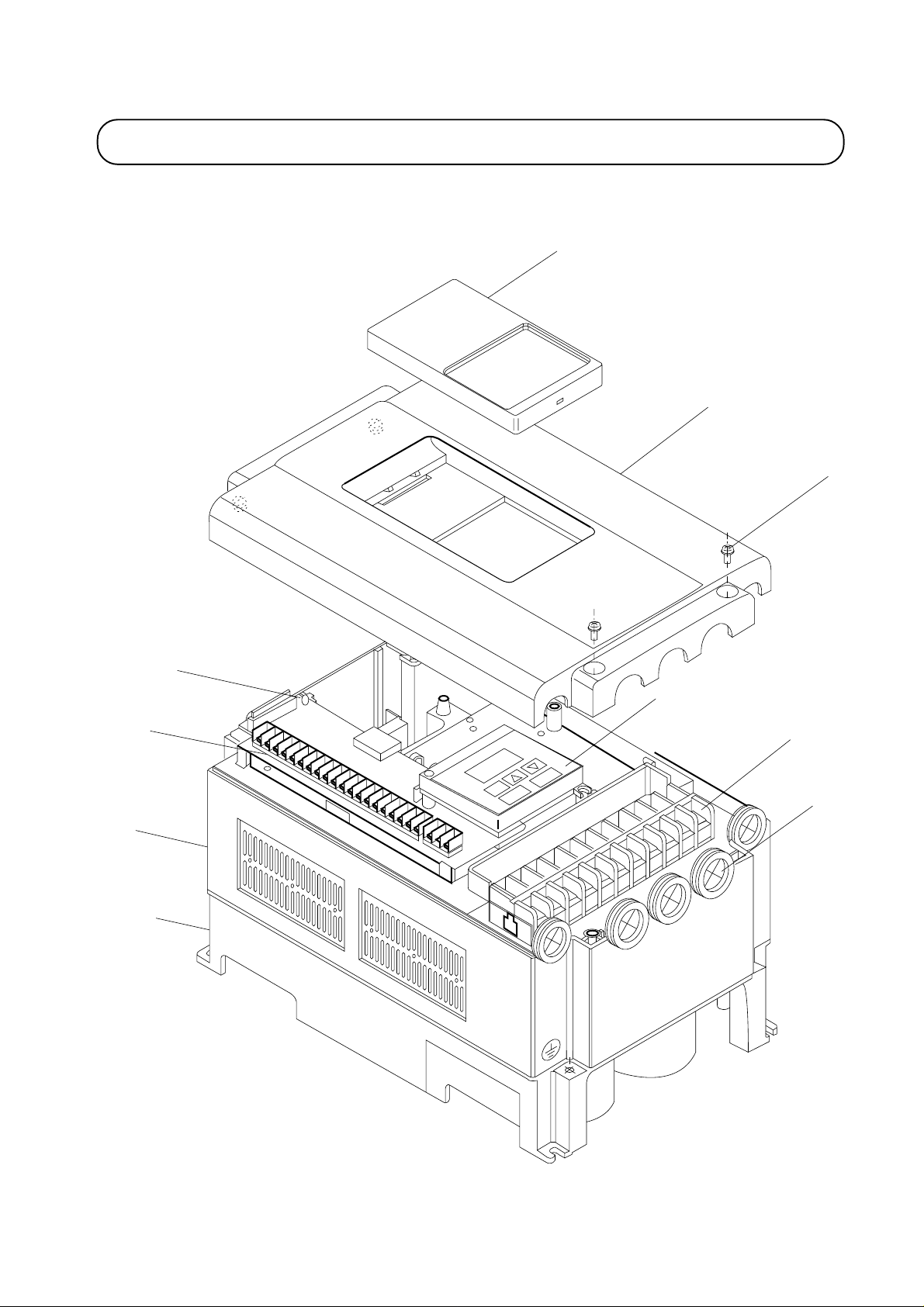
3.1 Names of Parts
Blind cover
Front cover
A set screw
Charge lamp
(LED)
Control circuit
terminals
Cover
Case
Digital
operator
Main circuit
terminals
Wiring
holes
3-1
Page 18
4. INSTALLATION
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
CAUTION
* Be sure to install the unit on flame resistant material such as metal.
Otherwise, there is a danger of fire.
* Be sure not to place anything inflammable in the vicinity.
Otherwise, there is a danger of fire.
* Be sure not to let the foreign matter enter such as cut wire refuse, spatter from welding,
iron refuse, wire, dust, etc.
Otherwise, there is a danger of fire.
* Be sure to install it in a place which can bear the weight according to the specifications
in the text (4. Installation).
Otherwise, it may fall and there is a danger of injury.
* Be sure to install the unit on a perpendicular wall which is not subject to vibration.
Otherwise, it may fall and there is a danger of injury.
* Be sure not to install and operate an inverter which is damaged or parts of which are
missing.
Otherwise, there is a danger of injury.
* Be sure to install it in a room which is not exposed to direct sunlight and is well
ventilated. Avoid environments which tend to be high in temperature, high in
humidity or to have dew condensation, as well as places with dust, corrosive gas,
explosive gas, inflammable gas, grinding-fluid mist, salt damage, etc.
Otherwise, there is a danger of fire.
NOTE : ENCLOSURE SIZE FOR 75 kW to 110kW
The inverters, 75kW to 110kW must be installed into an enclosure with dimmensions no
less than 183cm (72 in) by 183cm (72 in) by 60cm (24 in).
NOTE : ENCLOSURE SIZE FOR 132 kW AND BIGGER
The inverters, 132kW and bigger, are complied as recognizedcomponents.
Therse devices are intended for use in an overall ecclosure with an internal ambient of
40 degree C for variable torque rating or 50 degree C for constant torque rating maximum.
End product temperature testing should be conducted to verify sufficient forced air ventilation
is provided to maintain this ambient in room ambient of 10-40 degree C.
Based upon component level testing , end product temperature testing may be conducted at
any convenient room ambient in the rangeof 20-40 dwgree C, unless the room ambient in the
intended application exceeds 40degree C, in which case testing should be conducted at the
elevated ambient.
Enclosure internal ambient temperature should be measured above the drive on to the upper
left or right side. Temperature measurments on the drive itself should not be necessary.
4-1
Page 19
For cooling purposes, be sure that the inverter is installed vertically. In addition, be sure that it
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
is separated from other components and walls. If foreign matter is introduced into the interior
of the inverter, this may cause malfunctions, so make sure that no foreign matter can enter it.
➤
10 cm or more
➤
(30cm or more)
5 cm
➤
or
more
➤
➤
10 cm or more
➤
(30cm or more)
5 cm
➤
or
more
➤
(a) (b)
NOTE:
Install the inverter vertically.
Do not install it on the floor or horizontally.
( ) is for 75 to 260kW
Be sure to check the ambient temperature.
Flow of air
➤
➤
Wall
CAUTION
Be sure that the wall surface is a nonflammable
material, such as steel plate.
Place of installation Load characteristics Ambient temperature Applicable model
Within the enclosure
(NOTE 1)
Constant torque -10 to 50°C
Variable torque -10 to 40°C
All models
(NOTE 2)
NOTE 1: The inverter should be installed in a locked enclosure that meets the requirements in
IP4X.
The higher the ambient temperature inside the inverter, the shorter its life will be. If
a heat generating unit is used near the inverter, try to keep it as far away as possible.
Also, when installing the inverter in a box, be sure to carefully consider ventilation
and the dimensions.
NOTE 2: Each of inverters 22 kW to 260 kW must be installed in a locked enclosure.
4-2
Page 20
Precaution for installation and wiring
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
When executing the wiring work or another work, attach a cover on the vent hole (slit) on the top of the
inverter to prevent wire chips, weld spatters, iron scraps, or dust from falling into the inverter.
➤
15 cm or more
Vent hole
➤
Cover (a nonflammable
plate such as an iron plate)
➤
➤
4-3
Page 21
5. WIRING
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
WARNING
* Be sure to ground the unit.
Otherwise, there is a danger of electric shock and/or fire.
* Wiring work shall be carried out by electrical experts.
Otherwise, there is a danger of electric shock and/or fire.
* Implement wiring after checking that the power supply is off.
It might incur electric shock and/or fire.
* After installing the main body, carry out wiring.
Otherwise, there is a danger of electric shock and/or injury.
5-1
Page 22
CAUTION
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
* Make sure that the input voltage is:
Three phase 200 to 220 V/50 Hz, 200 to 230 V/60 Hz
Three phase 380 to 415 V/50 Hz, 400 to 460 V/60 Hz
* Be sure not to input a single phase to a 3 phase type.
Otherwise, there is a danger of fire.
* Be sure not to connect AC power supply to the output terminals
[U (T1), V (T2), W (T3)].
Otherwise, there is a danger of injury and/or fire.
INPUT OUTPUT
Note)
(L1)
R S
(L3) (T1) (T2) (T3)
(L2)
UVWT
Power supply
* Fasten the screws with the specified fastening torque. Check so that there is no
loosening of screws.
Otherwise, there is a danger of fire.
Be sure to install an earth leakage breaker.
* The ground fault protection is designed to detect current flowing to the ground upon
power on. This function is to protect the inverter,not people. Install the earth leakage
breaker to protect against the ground fault on wires between the inverter and the motor.
(Use a breaker that is very sensitive to high frequency current so as not to cause
malfunction.)
* Be sure to set the fuse(s) (the same phase as the main power supply)
in the operation circuit.
Otherwise, there is a danger of fire.
As for motor leads, earth leakage breakers and electromagnetic contactors, be sure to
use the equivalent ones with the specified capacity (rated).
Otherwise, there is a danger of fire.
5-2
Page 23
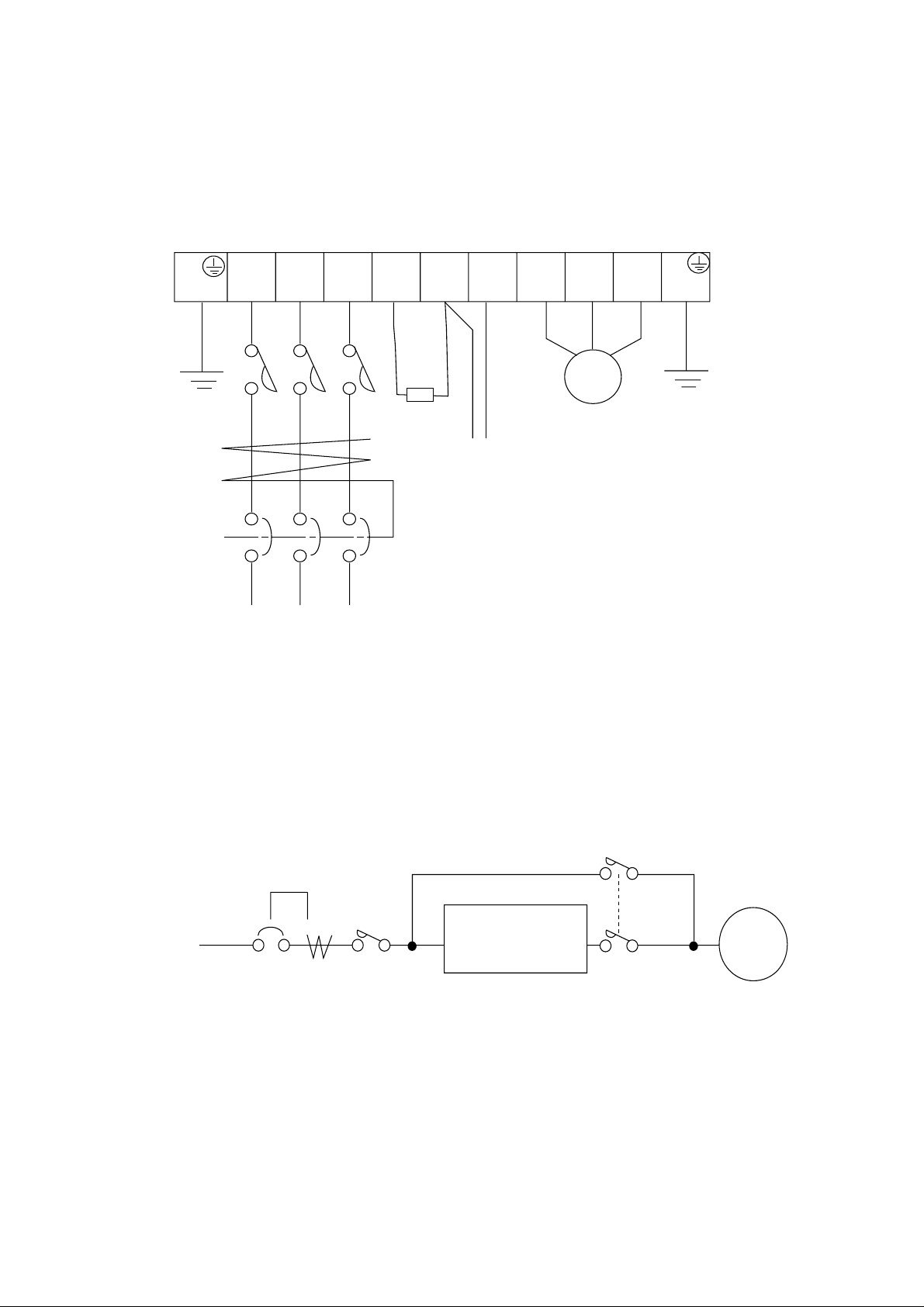
The terminal board will be exposed when the front cover or terminal cover (450L/HF,
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
550L/HF) is removed. Wire the inverter in this state.
5.1 Wiring the Power Supply and Motor
G
(PE)
R
(L1)S(L2)T(L3)
Power supply
RB
(RB)
Dynamic
braking
resistor
ELB
P
(+)N(-)U(T1)V(T2)W(T3)G(PE)
MOTOR
Braking Units
• The inverter will be damaged if the power supply is connected to the motor terminals
U(T1), V(T2) and W(T3), so be sure not to make any mistakes.
• If multiple motors are to be connected, be sure to attach a thermal relay to each motor.
NOTE 1: When changing the power supply of the motor between the inverter and commer-
cial power, be sure to install mechanically interlocked switches Mg1 and Mg2.
Mg1
ELB
Power
supply
Mg0
R (L1)
S (L2)
T (L3)
Inverter
(T1) U
(T2) V
(T3) W
Motor
Mg2
NOTE 2: Install an earth leakage breaker at the input of the inverter. (Select an earth leak-
age breaker whose sensitive current level is raised in high frequency range.)
When the cable length between the inverter and motor is long (more than 10 m),
the thermal relay may malfunction due to higher harmonics. Therefore, install an
AC reactor on the output side of the inverter or use a current sensor in place of the
thermal relay.
5-3
Page 24
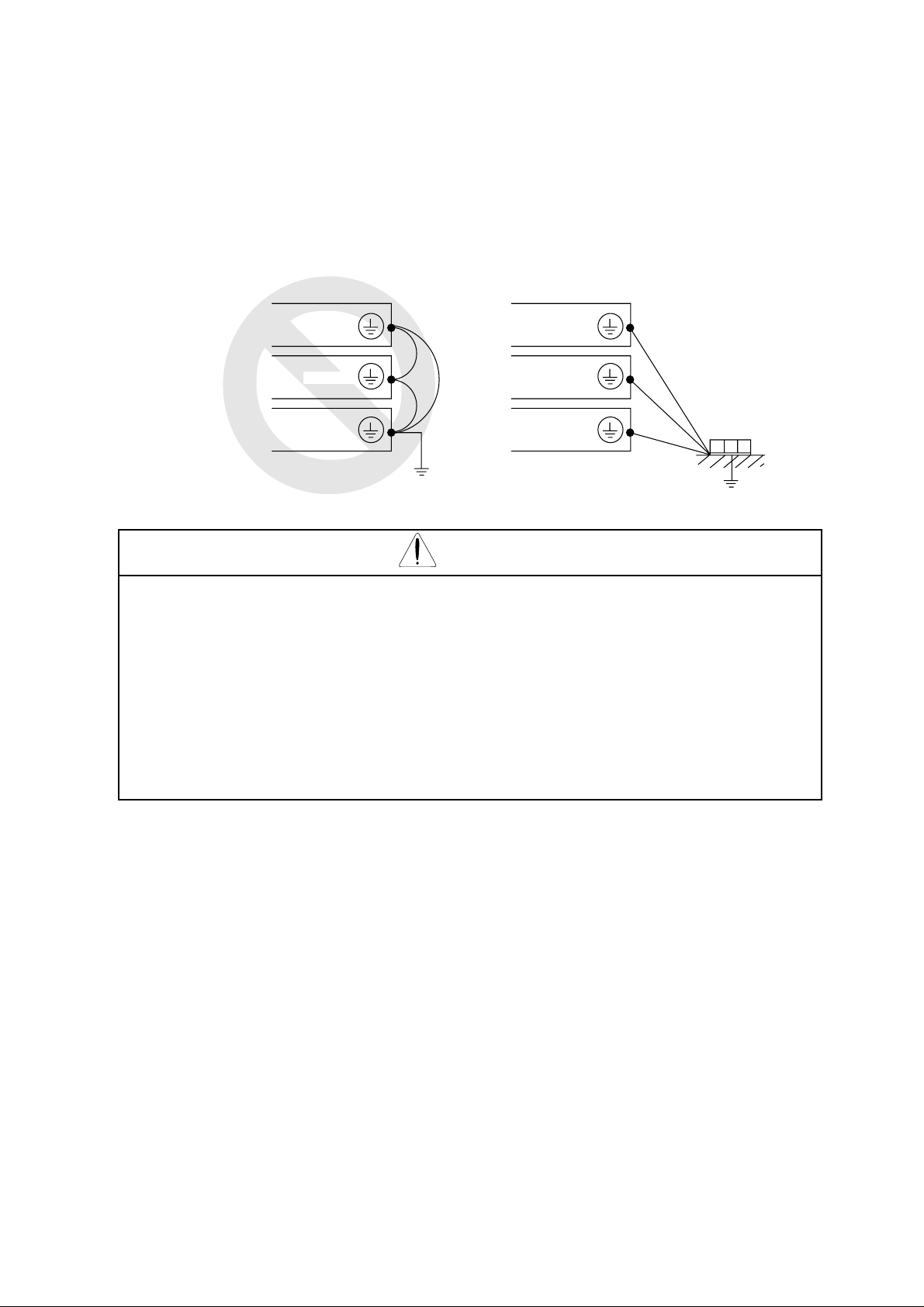
NOTE 3: Be sure that the specified grounding is carried out. Be sure to separate the unit’s
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
grounding pole from those of other heavy electric machinery, and avoid using
common grounding poles.
If multiple inverters are used, make sure that the grounding connections do not
create a loop.
Improper grounding Proper grounding
Inverter
Inverter
Inverter
Inverter
Inverter
Inverter
Grounding bolt
(at the site)
CAUTION
External or remote over load protection required, if multiple motors to be connected.
For models J300-450LFU and -550LFU only , connect to branch circuit protected at
maximum 300% of output current rating.
Suitable for use on a circuit capable of delivering not more than 10,000 rms
symmetrical amperes,*** volts maximum,
(where *** = input voltage)
5-4
Page 25

5.2 Wiring of Control Circuit Terminals
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
SINK TYPE wiring
(Factory settings)
FM CM1PLCP24FW87654321HOOILCM21211AL2 AL1 AL0
RY
RY
Input intelligent terminal
Frequency meter
Frequency setting
(500 Ω to 2 kΩ)
Current input
DC 4 to 20 mA
For output
Intelligent terminal
27 VDC 50 mA
50 mA max
Fault alarm
SOURCE TYPE wiring
FM CM1PLCP24FW87654321HOOILCM21211AL2 AL1 AL0
RY
RY
Input intelligent terminal
Frequency meter
Frequency setting
(500 Ω to 2 kΩ)
Current input
DC 4 to 20 mA
For output
Intelligent terminal
27 VDC 50 mA
50 mA max
NOTE 1: When an output intelligent terminal is used, be sure to install a surge absorbing
diode in parallel with the relay (RY). Otherwise, the surge voltage created when
the relay (RY) goes ON or OFF may damage the output intelligent terminal circuit.
Fault alarm
NOTE 2: Use a twisted and shielded wire for the signal line, and cut the shielded covering
as shown in the diagram below. Make sure that the length of the signal line is 20
meters or less.
5-5
Page 26
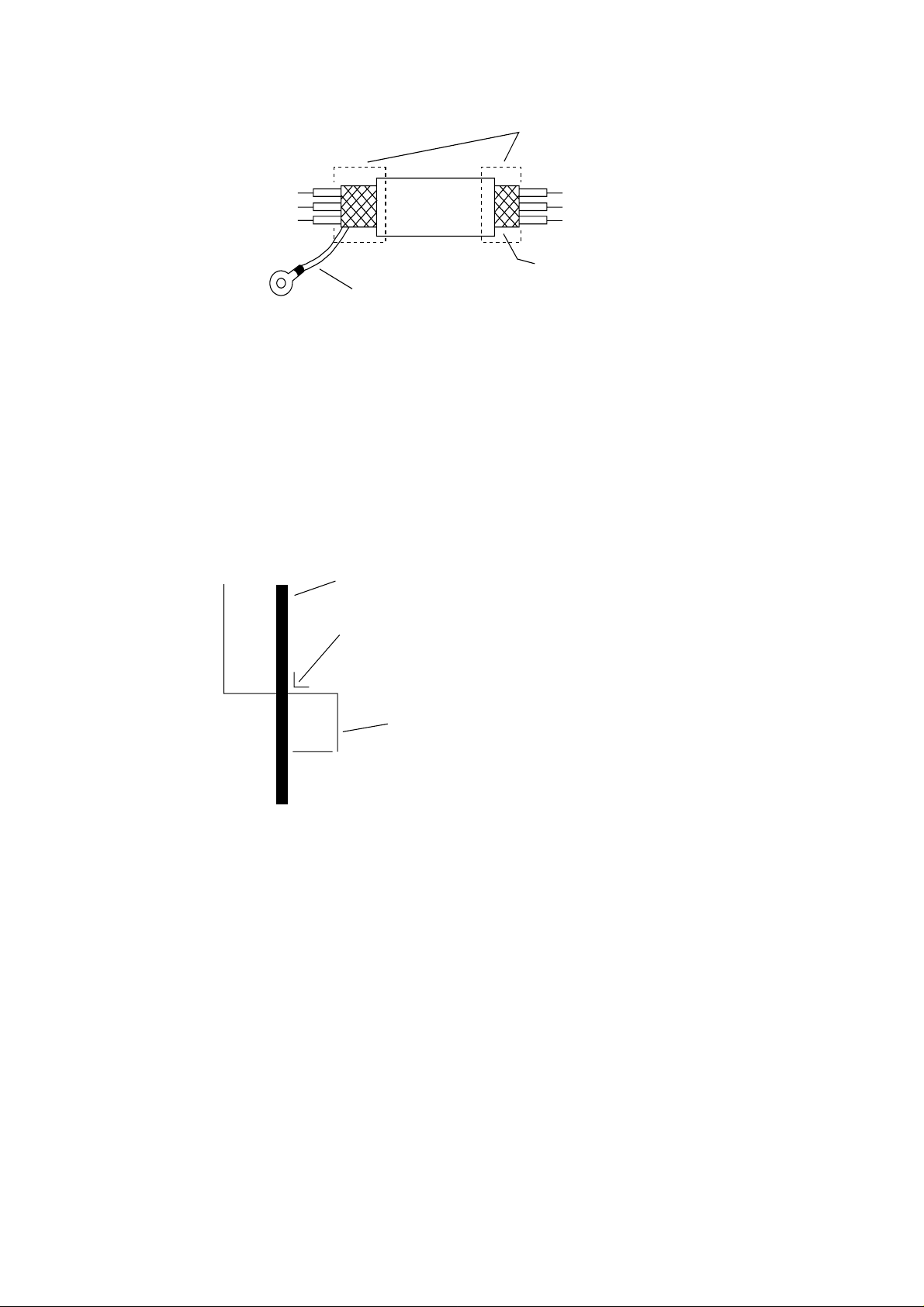
Insulate
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
➤
➤
➤
➤
No grounding necessary
Connect FG (frame ground) of the inverter.
NOTE 3: When the frequency setting signal is turned on and off with a contact, use a relay
which will not cause contact malfunctions, even with the extremely weak currents
and voltages, such as crossbar twin contacts, etc.
NOTE 4: Use relays which do not have contact defects at 24 V DC, 3 mA for the other
terminals.
NOTE 5: Separate the main circuit wiring from the relay control circuit wiring. If they must
cross, be sure that they cross at a right angle.
Main circuit power line
➤
(R, S, T, U, V, W, PP, P, RB, N, L1, L2, L3, T1, T2, T3, +, -, etc.)
Right angle
➤
➤
Signal input line
➤
➤
Separate by 10 cm or more.
(FM, CM1, PLC, P24, FW, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1,
H, O, OI, L, CM2, 12, 11, AL0, AL1, AL2)
NOTE 6: Do not short between the terminals H and L and between the terminals P24 and
CM1 of the control circuit.
NOTE 7: Insulate the common terminal L for frequency analog command input and the
common terminal (COMMON) of the peripheral equipment such as the sequencer
before starting use.
5-6
Page 27
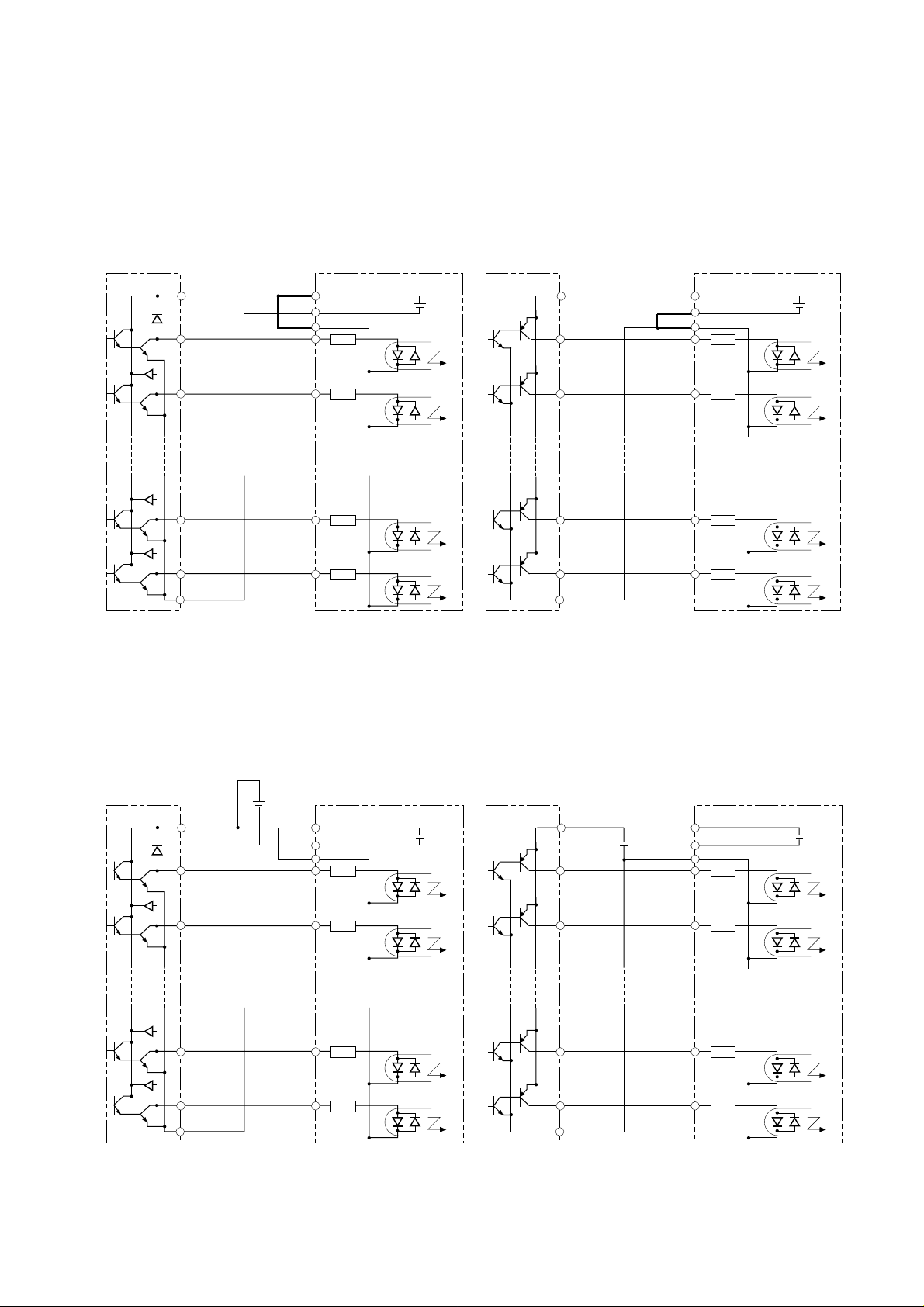
5.3 Connection to the Programmable Controller
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
(1) When the internal interface power source is used
① This is an example when the sink type transistor
output (open collector output) module of the
sequencer is connected
Note:
Make sure of the short-circuit bar or wire
between the terminals PLC and P24.
J300 series J300 series
S
1
P24
CM1
PLC
FW
+
24V DC
-
② This is an example when the source type
transistor output (open collector output)
module of the sequencer is connected
Note:
Make sure of the short-circuit bar or wire
between the terminals CM1 and PLC.
COM
1
P24
CM1
PLC
FW
+
24V DC
-
2
8
9
COM
YTR48 type output module
8
2
1
Inverter Inverter
(by Hitachi)
(2) When the external interface power source is used
① This is an example when the sink type transistor
output (open collector output) module of the
sequencer is connected
Note: Remove the short-circuit bar or wire between
the terminals CM1 and PLC or P24 and PLC.
+
24V DC
S
1
P24
CM1
PLC
FW
J300 series J300 series
+
24V DC
-
2
8
9
S
8
2
1
YTS48 type output module
(by Hitachi)
② This is an example when the source type
transistor output (open collector output)
module of the sequencer is connected
Note:
Remove the short-circuit bar or wire between
the terminals CM1 and PLC or P24 and PLC.
COM
+
24V DC
1
-
P24
CM1
PLC
FW
+
24V DC
-
2
8
9
COM
YTR48 type output module
(by Hitachi)
8
2
1
Inverter Inverter
YTS48 type output module
2
8
9
S
(by Hitachi)
Note: Be sure to turn the inverter on after the controller and external power source are turned on.
(Otherwise, the data in the inverter may be changed.)
5-7
8
2
1
Page 28
5.4 Wiring Equipment, Options (EMI filter, etc.)
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
➤
(200V class)
Inverter
model
J300-055LF
J300-075LF
J300-110LF
J300-150LF
J300-220LF
J300-300LF
J300-370LF
J300-450LF
J300-550LF
Constant torqe Variable torqe
Power
Motor
lines
output
R,S,T,U,V
(kW)
W,P,N
AWG 8
5.5
or more
AWG 6
7.5
or more
AWG 4
11
or more
AWG 3
15
22
30
37
45
55
or more
AWG 1/0
or more
AWG 3/0
or more
AWG 4/0
or more
300
or more
350
or more
Standard equipment
Power supply
➤
➤
ELB
Magnetic
contactor
Wiring (AWG or Kcmil)
Power
AWG 8
AWG 4
AWG 3
lines
External
resistor
RB1,2,3,
P,RB
10
or more
10
or more
Motor
output
(kW)
7.5
11
15
22
30
37
45
55
75
Power
lines
R,S,T,U,V
W,P,N
or more
AWG 6
or more
or more
or more
AWG 1/0
or more
AWG 3/0
or more
AWG 4/0
or more
300
or more
350
or more
Applicable equipment
Signal
lines
FM,CM1,PCL P24,AL0,AL1
FW,8,7,6,5,4,3 AL2
2,1,H,O,OL,L,
CM2,12,11
AWG 18
AWG 16
Shielded
or more
wire
When the
number of
shielded
wires to be
used is 11
or more,
the section
of each
shielded
wire
should be
AWG 20
Signal
lines
Earth leakage
breaker (ELB)
EX50C(30A)
EX50C(30A)
EX50C(50A)
EX60B(60A)
RX100(75A)
RX100(100A)
RX100(100A)
RX225(150A)
RX225(175A)
Electromagnetic
contactor
H20
H20
H25
H35
H50
H65
H80
H100
H125
(400V class)
Inverter
model
J300-055HF
J300-075HF
J300-110HF
J300-150HF
J300-220HF
J300-300HF
J300-370HF
J300-450HF
J300-550HF
J300-750HF
J300-900HF
J300-1100HF
J300-1320HF
J300-1600HF
J300-2200HF
Wiring
Constant torqe Variable torqe
Motor
output
(kW)
5.5
7.5
11
15
22
30
37
45
55
75
90
110
132
160
220
Power
lines
R,S,T,U,V
W,P,N
AWG 8
or more
AWG 8
or more
AWG 8
or more
AWG 6
or more
AWG 4
or more
AWG 4
or more
AWG 2
or more
AWG 1
or more
AWG 3/0
or more
300
or more
300
or more
350
or more
AWG 4 / 0
parallel
300
parallel
350
parallel
Motor
output
(kW)
7.5
11
15
22
30
37
45
55
75
90
110
132
160
220
260
Power
lines
R,S,T,U,V
W,P,N
AWG 8
or more
AWG 8
or more
AWG 8
or more
AWG 6
or more
AWG 4
or more
AWG 4
or more
AWG 2
or more
AWG 1
or more
AWG 3/0
or more
300
or more
300
or more
350
or more
AWG 4 / 0
parallel
300
parallel
parallel
350
Power
lines
External
resistor
RB1,2,3,
P,RB
10
or more
10
or more
Applicable equipment
Signal
lines
FM,CM1,PCL P24,AL0,AL1
FW,8,7,6,5,4,3 AL2
2,1,H,O,OL,L,
CM2,12,11
AWG 18
Shielded
or more
wire
When the
number of
shielded
wires to be
used is 11
or more,
the section
of each
shielded
wire
should be
AWG 20.
Signal
lines
AWG 16
Earth leakage
breaker (ELB)
EX50C(30A)
EX50C(30A)
EX50C(50A)
EX60B(60A)
RX100(75A)
RX100(100A)
RX100(100A)
RX225(150A)
RX225(175A)
RX225(225A)
RX225(250A)
RX400(350A)
RX400(400A)
RX600(600A)
RX600(600A)
Electromagnetic
contactor
H20
H20
H25
H35
H50
H65
H80
H100
H125
H150
H220
H250
H400
H600
H600
5-8
Page 29
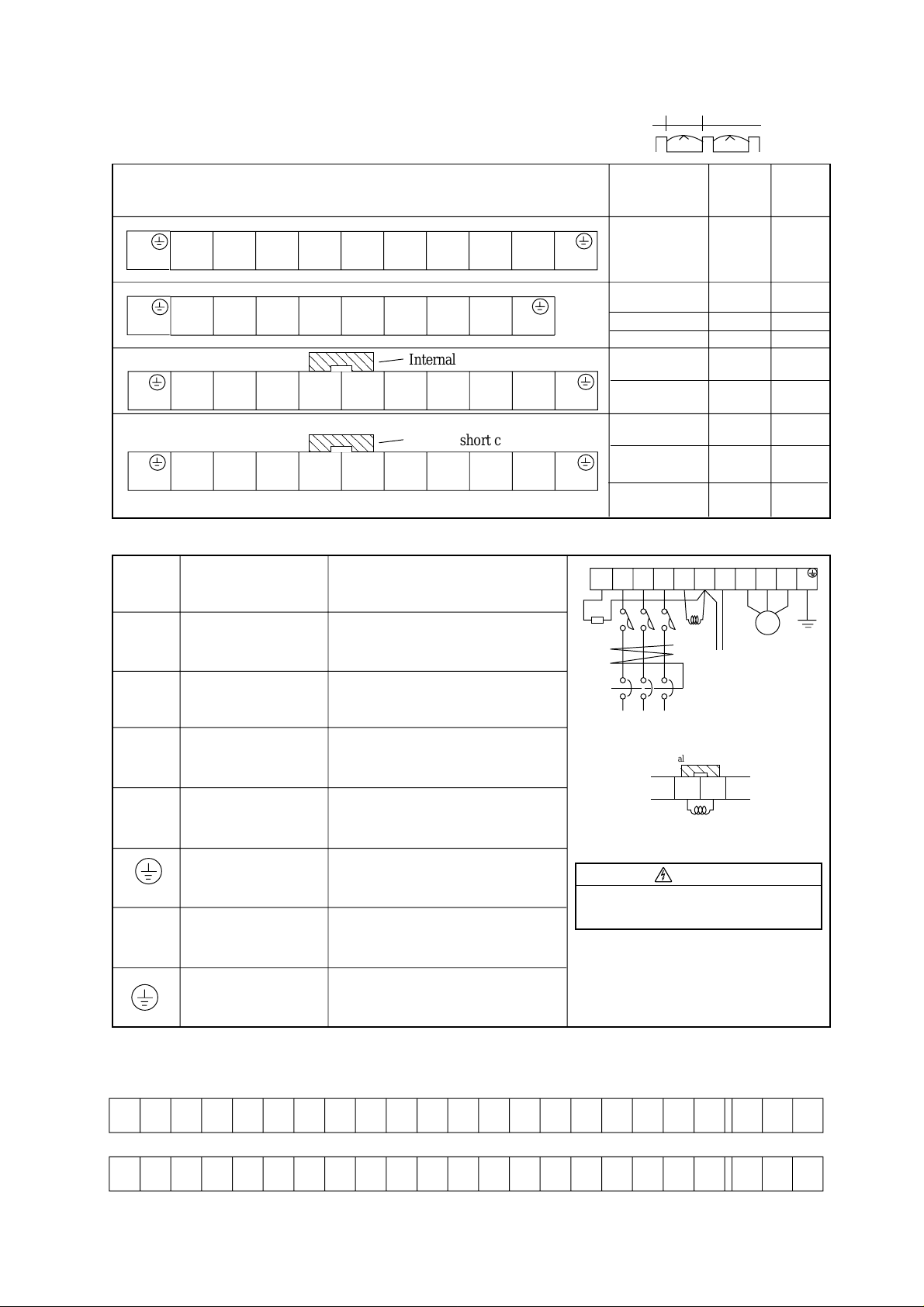
R
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
S
(L1)
(L2)T(L3)
Inverter
(T1)U(T2)V(T3)
IM
(+)
RB
W
Thermal
relay
Motor
➤
AC reactor for
➤
➤
P
➤
➤
➤
improving
the power factor
(ALI- L)
(ALI- H)
Radio noise filter
(Zero phase
reactor) (ZCL-A)
EMI filter for
inverter
(FFJ300- )
Regenerative
resistor
(RB - )
Radio noise filter
(Zero phase
reactor) (ZCL-A)
AC reactor for
reducing vibration
(ACL-L- )
(ACL-H- )
This part is used when the unbalance voltage ratio is 3%
or more and power supply is 500 kVA or more, and there
is a rapid change in the power supply.
It also improves the power factor.
Using the inverter may cause noise on the peripheral
equipment through the power lines.
This part reduces noise.
This part reduces common noise generated between
the power supply and the ground, as well as normal noise.
Put it in the primary side of inverter.
This part is used for applications that needs to increase
the brake torque of the inverter or to frequently turn on
and off and to run high inertia load.
This part reduces noise generated at the output of
the inverter.
(It is possible to use for both input and output.)
Running motors with the inverter generates vibration
greater than that with commercial power supply.
This part installed between the inverter and motor reduces
torque ripple.
When the cable length between the inverter and motor is
long, a countermeasure for a malfunction of the termal
relay is taken.
FunctionPart description
NOTE 1:
The applicable equipment is for Hitachi standard four pole squirrel-cage motor
NOTE 2: Be sure to consider the capacity of the circuit breaker to be used.
NOTE 3: Be sure to use bigger wires for power lines if the distance exceeds 20m.
NOTE 4: Be sure to use an grounding wire same size of power line or similar.
(*) Use AWG 16 wire for the alarm signal wire.
Classify the detective current of the earth leakage breaker depending on the total
distance between the inverter and the motor.
length
100 m and less
300 m and less
600 m and less
Detective current (mA)
30
100
200
NOTE 5:
NOTE 6:
When using CV wire and metal tube,
the leakage current is around 30 mA/km.
The leakage current becomes eight times
because IV wires have a high dielectric
constant. Therefore, use an one class
larger earth leakage breaker according
to the left table.
5-9
Page 30
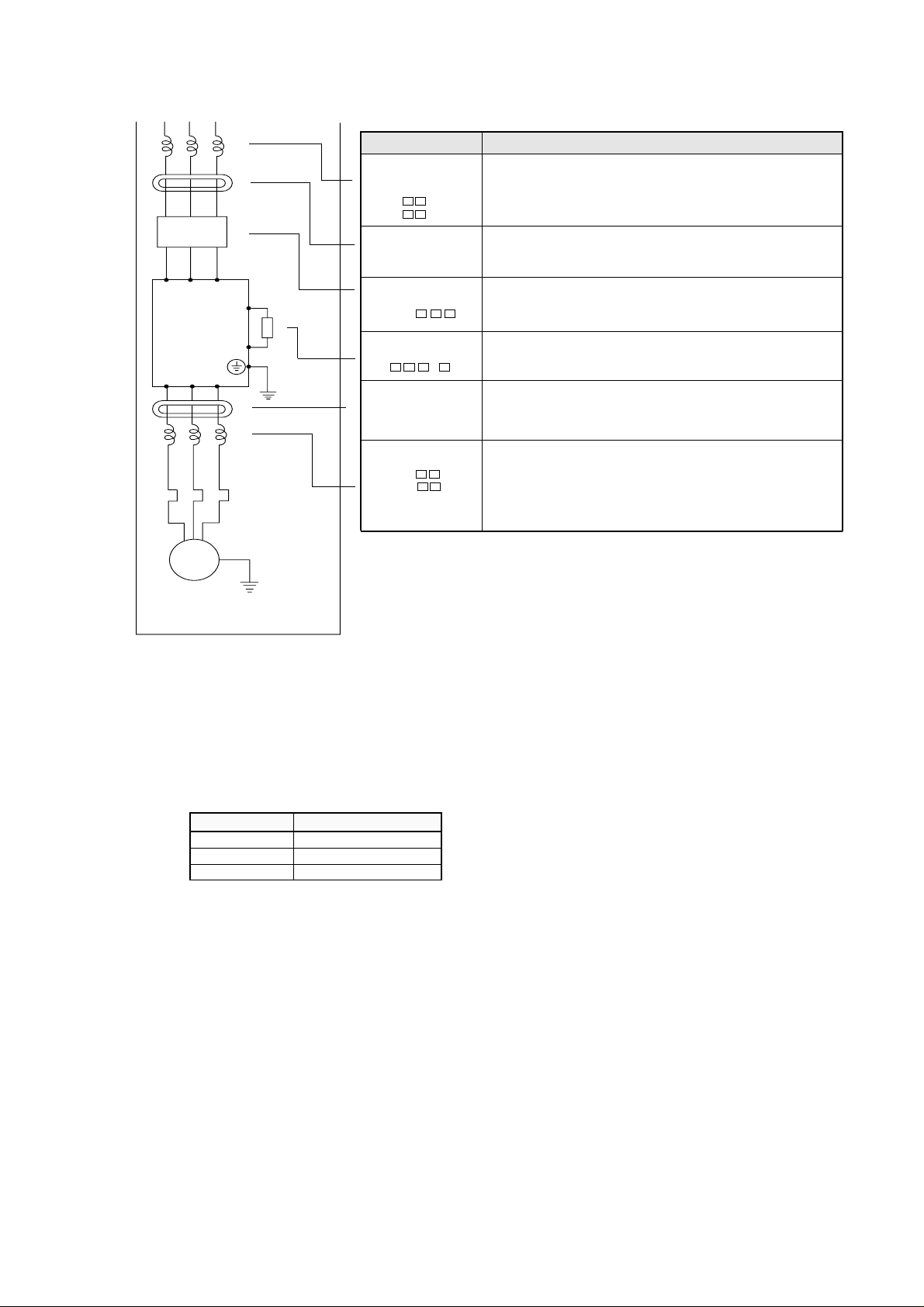
5.5 Terminal
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
(1) Main circuit terminal
➤
➤
Width
G
(PE)
G
(PE)
G
(PE)
G
(PE)
Main circuit
Terminal
symbol
R, S, T
(L1),(L2),(L3)
Terminal layout
R
(L1)
R
(L1)
S
(L2)
S
(L2)
RB
T
(L3)
(RB)
P
(+)N(Ð)U(T1)V(T1)W(T1)
T
(L3)P(+)N(Ð)U(T1)V(T1)W(T1)
Internal short circuit bar
R
(L1)
S
(L2)T(L3)PD(+1)P(+)N(Ð)U(T1)V(T1)W(T1)
Internal short circuit bar
R
(L1)
S
(L2)T(L3)PD(+1)P(+)N(Ð)U(T1)V(T1)W(T1)
Terminal description
Main power
Connect the power supply
Function
G
(PE)
G
(PE)
G
(PE)
G
(PE)
Braking
Type
055, 075LF
Screw
diameter
M5
055,075HF
011, 150LF
011, 150HF
220 to 370LF
450, 550LF
220 to 370HF
450, 550HF
750, 900HF
1100HF
M6
M8 23
M10
M6
M8 23
M10
M10 40
1320 to 2200HF M16 51
R
RB
(L1)S(L2)T(L3)PD(+1)P(+)N(-)U(T1)V(T2)W(T3)G(PE)
(RB)
resistor
DCL
Braking Units
Width
(mm)
13
17.5
35
17.5
35
MOTOR
U, V, W
(T1),(T2),(T3)
P, RB
(+),(RB)
P, N
(+),(-)
G
(PE)
PD
(+1)
Inverter output
External braking
resistor
Dynamic braking unit
Ground
External choke coil
Ground at case
Connect the motor
Connect a braking resistor (option)
* Only the 055LF/HF and 075LF/HF
are equipped RB terminals .
Connect a dynamic braking unit
(option)
Ground (connect grounding to avoid
electric shock)
Connect a choke coil (DCL) for
harmonics current reduction
Ground (connect grounding to avoid
electric shock)
Power supply
Remove the internal short circuit bar when
DCL is connected.
Wait until DC bus voltage is discharged after power
supply is turned off.
Otherwise, there is a danger of electric shock.
ELB
Internal short circuit bar
PD
(+1)P(+)
DCL
WARNING
(2) Control circuit terminal
The intelligent I/O terminals 1 to 8 and 11 and 12 are initialized as shown below at factory before shipment.
FM CM1 PLC P24 FW REV CF1 USP CH1 FRS JG AT RS H O OI L CM2 RUN FA1 AL2 AL1 AL0
↑↑ ↑↑↑↑↑↑ ↑↑
FMCM1PLCP24FW87654321HOOILCM21211AL2AL1AL0
5-10
Page 31

Control circuit
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Input
monitor
signal
Terminal
symbol
FM
CM1
PLC
P24
FW
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
Terminal description and function
Frequency monitor
Common for monitor
Common terminal for the external power
source of the sequencer (PLC)
Internal power source for the frequency
monitor and intelligent input terminal
Forward operation
Intelligent input terminal 8
Intelligent input terminal 7
Intelligent input terminal 6
Intelligent input terminal 5
Intelligent input terminal 4
Intelligent input terminal 3
Intelligent input terminal 2
Intelligent input terminal 1
Standard setting of
intelligent terminal
Reverse operation
REV
CF1 Multistage speed
(First stage)
USP Prevention function of
restart upon power on.
CH1 2 stage acc./dec.
FRS Free run input signal
JG Jogging
AT Current input selection
RS Reset
(NOTE 1)
Remarks
Dry contact
Close: ON (run)
Open: OFF (stop)
Min. ON time:
20 ms or more
Note:
If the power is turned
on when the input
terminals 1 to 5 are
kept on, all the data
stored in the inverter
is initialized.
Therefore, never turn
the power on in such
a state.
Frequency
command
input
Output
signal
Fault alarm
output
NOTE1:
H
O
OI
L
CM2
12
11
AL0
AL1
AL2
Power supply for frequency command
Voltage frequency command
Current frequency command
Common for frequency command
Common for intelligent output terminal
Intelligent output signal 12
Intelligent output signal 11
Normal: AL0-AL1 close
Abnormal, Power off:
AL1AL2
CAUTION
Alarm connection may contain hazardous live voltage even when inverter is disconnected.
In case of removing flont cover for maintenance or inspection, confirm that incoming power
for alarm connection is surely disconnected.
AL0-AL1 open
AL0
RUN
FA1
Run signal
Frequency arrival signal
Contact rating
250 VAC 2.5 A (Resistor load)
0.2 A (cos¿=0.4)
30 VDC 3.0 A (Resistor load)
0.7 A (cos¿=0.4)
10 VDC
0-5 VDC (nominal), 0-10 VDC
(nominal)(Input impedance 30 kΩ)
DC 4-20 mA (nominal)
Input impedance 250Ω
27 VDC
50 mA max
Min 100 VAC
10 mA
5 VDC
100 mA
Terminal RS can use only contact a (normally open). It cannot use contact b (normally closed).
5-11
Page 32

5.6 Control Circuit Terminals
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Terminal symbol Terminal name Description
FM Monitor terminal Analog: Output frequency, current, torque
Digital: Output frequency x frequency converted value
(Set in the remote operator monitor mode), max. pulse: 3.6 kHz
CM1 Common terminal 1 Common terminal for the monitor terminal
PLC
P24
FW
REV Reverse run/stop
CF1 SW1
CF2 Multistage speed SW2
Internal interface common
Input signal power source
Forward run/stop terminal
Common terminal for the external power source of the sequencer
Internal power source for the contact input terminal and frequency
monitor terminal, 24 VDC.
Common for the FW terminal and intelligent input terminals
OUTPUT frequency
Forward
Reverse
SWF
ON
SWR
Frequency
(Hz)
First
speed
ON
Second
speed
Fourth (FS)
Third
speed
speed
CM1 PLC P24 FW 8 1
CM1
PLC P24 FW
•••••
SWR
SWF
(Source type)
876
Time
• When setting frequency,
connect P24 and 6 or 7
and set with digital
operator or .
CF3 SW3
(NOTE 1)
Switch
SW1
ON ON ON ON
SW2
SWF
ONON
ON
JG Jogging Jogging run
DB External DC braking DC braking input signal
STN Initialization Initialization (shipment status at factory) input
SET 2nd function The output frequency setting, base and maximum frequencies,
control method, motor constant, acceleration or deceleration time,
manual torque boost setting, and electronic thermal setting are
changed in batch.
CH1 Two-stage acceleration The acceleration or deceleration time or selection of two-stage
1 to 8
or deceleration accration or deceleration is changed by turning the contact ON.
FRS Free run stop The inverter stops and the motor stops free run
FRS functions when the contact is opened. (European version)
EXT External trip External trip input signal (The contact is open.)
USP Power-ON restart Restart prevention when the power is turned on in the RUN
prevention state (The contact is open.)
CS Commercial power source Switch signal from the commercial power source to inverter
switching drive (Note: When the terminal is used, a trip is also conceled.)
SFT Terminal software lock The data of all funcitons except for output frequency setting is
locked. See 12-9 [F-25].
AT Analog input command Analog input voltage-current switching (When the contact is ON,
current input signal to OI-L is acrive.)
RS Reset Trip or alarm signal is reset.
UP Remote control function, When the contact is turned ON, the operation is accelerated.
acceleration (Available only when the frequency command is sent
to the operator.)
DWN Remote control function, When the contact is turned ON, the operation is decelerated.
deceleration (Available the frequency command is sent to the operator.)
SWF SW1 SW2
1 2
5-12
Page 33

Terminal symbol Terminal name Description
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
H Frequency command power • Initialization of a voltage signal by an external command
terminal is between 0 and 10 VDC. (Switching from 0 to 5V is executed
by A48.) When inputting 4 - 20 mA, turn the input terminal at
ON.
O Frequency command
terminal (voltage command)
OI Frequency command
terminal (current command)
L Frequency command
common terminal
CM2 Common terminal 2 Common terminal for intelligent output terminal
FA1 Frequency arrival signal When each operator is used, and arrival signal can be
RUN Signal during run The transistor output is turned ON during running.
OTQ Over-torque signal The transistor output is turned ON when the torque is more
11 • 12
H O OI L
VRO
(500 Ω to 2 kΩ)
When a current is inputted from between OI and L and the value is 4 mA,
the output frequency may 0.6 Hz. If this occurs, set a value more than the
frequency which is outputted by [A 4] start frequency setting.
(NOTE 2)
outputted at an optional frequency.
(Outputted even during DC injection braking)
than the set value.
The set value can be changed by the remote operator.
Use this function only under the sensor less vector control.
HOOIL HOOIL
+- +-
DC0 to 10 V
DC0 to 5V
Input impedance 30 kΩ
DC4 to 20 mV
Input impedance 250 kΩ
AL0
Normal: AL0-AL1 close
Abnormal, Power off:
AL1 Fault alarm terminal
AL2 AL1 AL0
AL0-AL1 open
Contact rating
AL2
250 VAC
30 VDC
2.5 A (Resistor load)
0.2 A (Cosø=0.4)
3.0 A (Resistor load)
0.7 A (cosø=0.4)
Min 100Vac
10 mA
5 VDC
100 mA
NOTE 1: To set four or more multispeeds, use the CF3 terminal.
NOTE 2: When an inconvernience occurs in the above characteristics, adjust it using
and . The sum of both analog input signals is outputted
When selecting one of analog input current and voltage, make sure that the other
is not inputted.
5-13
Page 34

5.7 Terminal Connection Diagram
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Power supply
Three phase
power supply
ELB
EF
Mg
BSS
BSS
AX
AX
Mg
Inverter
Mg
P24
(T1) U
(T2) V
(T3) W
(+) P
➤
Motor
P
RB RB
AL1
AL1
Dynamic braking resistor
055, 075LF: RB1,RB2 or RB3
AL0
055, 075HF: RB2, two each in series.
AL1
Fault alarm signal
AL2
(Normal: AL0-AL1 ON)
11
12
RY
RY
R (L1)
S (L2)
T (L3)
P24
24 VDC
PLC
FW
8
7
.
.
.
.
.
1
FM
CM1
10 VDC
➤
3
H
➤
➤
➤
Frequency setter
500Ω to 2 kΩ
Current input
4 to 2\0 mA
2
➤
➤
1
➤
O
OI
L
➤
G
(PE)
NOTE 1: Common terminal for each terminal is different.
Terminal
name
Command CM1FMCM1 (P24)
FW, 8 to 1
*
H, O, OI
L
11, 12
CM2
*: P24 is for source type wiring.
NOTE 2: The regenerative resistor has a temperature sensor.
When it works, turn off power supply to the inverter
o set the deceleration time longer.
➤
CM2
24 VDC
Follow the timing shown as below
upon power on.
Grounding
Main circuit
power supply
(NOTE 4)
➤
➤
0.6 or more seconds
Operation
command
Output
frequency
Number of
revolutions
of motor
NOTE 3: When the operation command is input first
and the main circuit power is turned ON,
and direct start results and a trip occurs.
NOTE 4: Do not input the operation command
simultaneously when the main circuit
is turned on.
5-14
Page 35

6. OPERATION
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
6.1 Before Starting Operation
Prior to the test run, check the following.
WARNING
* Be sure to turn on the input power supply after mounting the surface cover. While
being energized, be sure not to remove the cover.
Otherwise, there is a danger of electric shock.
* Be sure not to operate the switches with wet hands.
Otherwise, there is a danger of electric shock.
* While the inverter is energized, be sure not to touch the inverter terminals even during
stoppage.
Otherwise, there is a danger of electric shock.
* If the re-try mode is selected, it may suddenly restart during the trip stop. Be sure not
to approach the machine. (Be sure to design the machine so that personnel safety will
be secured even if it restarts.)
Otherwise, there is a danger of injury.
* Even if the power supply is cut for a short period of time, it may restart operation after
the power supply is recovered if the operation command is given. If it may incur
danger to personnel, be sure to make a circuit so that it will not restart after power
recovery.
Otherwise, there is a danger of injury.
* The Stop Key is effective only when the function is set. Be sure to prepare the Key
separately from the emergency stop.
Otherwise, there is a danger of injury.
* After the operation command is given, if the alarm reset is conducted, it will restart
suddenly. Be sure to set the alarm reset after checking the operation command is off.
Otherwise, there is a danger of injury.
* Be sure not to touch the inside of the energized inverter or to put a bar into it.
Otherwise, there is a danger of electric shock and/or fire.
6-1
Page 36

CAUTION
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
* Radiating fin and discharging resistor will have high temperature. Be sure not to touch
them.
Otherwise, there is a danger of getting burned.
* Low to high speed operation of the inverter can be easily set. Be sure to operate it
after checking the tolerance of the motor and machine.
Otherwise, there is a danger of injury.
* If a motor is operated at a frequency higher than 60Hz, be sure to check the speeds of
the motor and the machine with each manufacturer, and after getting their consent,
operate them.
Otherwise, there is a danger of machine breakage.
Note:
(1) Make sure that the power lines (input power supply R(L1), S(L2) and T(L3), and output
terminals, U(T1), V(T2) and W(T3) are connected correctly.
(2) Make sure that there are no mistakes in the signal line connections.
(3) Make sure that the inverter case ( ) is grounded.
(4) Make sure that terminals other than those specified are not grounded.
(5) Make sure that the inverter is installed vertically on a wall, and a nonflammable material
such as a steel plate is used as a mounting surface.
(6) Make sure that there are no short-circuits caused by stray pieces of wire, solderless termi-
nals or other objects left from wiring work. Also, make sure that no tools have been left
behind.
(7) Make sure that the output wires are not short-circuited or grounded.
(8) Make sure that there are no loose screws or terminals.
(9) Make sure that the maximum frequency setting matches the machine specifications.
Be sure to refer to page 10-2 when conducting insulation resistance and withstand
voltage tests. Never test terminals other than those which are indicated.
6-2
Page 37

6.2 Test Run
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Check the following before and during the test run.
Otherwise, there is a danger of machine breakage.
• Was the direction of the motor correct?
• Was the inverter tripped during acceleration or deceleration?
• Were the SPEED (rpm) and frequency meter correct?
• Were there any abnormal motor vibrations or noise?
When overcurrent tripping or overvoltage tripping occurs during the test run, increase
the acceleration time or deceleration time.
Factory settings
CAUTION
Maximum frequency: 60 Hz
Forward operation
An example of a general connection diagram is shown below.
Operating with digital operator:
When setting frequency, run and stop
with digital operator.
(The same way as remote operator
(DOP) or copy with (DRW).)
Three
phase
power
supply
L1
L2
L3
ELB
*
R(L1)
S(L2)
T(L3)
FW
CM1
PLC
P24
8
1
H
O
OI
L
(PE)
Inverter
Digital
operator
G
(T1)U
(T2)V
(T3)W
RB
(+)
(-)
AL
AL
AL
CM
Ground
Dynamic braking
P
resistor
Daynamic
N
braking unit
0
Fault alarm signal
1
(Normal:
2
AL0-AL1: ON
Abnormal:
Power off:
11
AL0-AL1: OFF)
12
2
Frequency meter
Running from external command:
When setting frequency, run and stop
from external command (FW,RV Terminal.)
The following shows run from
the operation box (OPE-4MJ2,OPE-8MJ2)
Three
L1
phase
L2
power
L3
supply
Forward
run/stop
Reverse
run/stop
Frequency
setter
ELB
Operator
OPE-4MJ2
OPE-8MJ2
Inverter
Digital
operator
G
(T1)U
(T2)V
(T3)W
RB
(+)
(-)
AL
AL
AL
CM
Ground
Dynamic braking
P
resistor
Daynamic
N
braking unit
0
1
Fault alarm
2
signal
11
12
2
Motor
R(L1)
S(L2)
T(L3)
*
PLC
P24
FW
8
FM
CM1
H
H
O
O
OI
L
L
(PE)
*: For sink type wiring.
6-3
Page 38

Operating with digital operator: Runnign from external command:
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Procedure
(1) Turn on ELB to supply power to the inverter. Make sure that the POWER LED on the digital
operator turns ON.
(2) Press the
FUNC
key once to display .
(3) Press 2 of the digital operator four times to display .
(4) Press the
FUNC
key and then press the
2
(4) Press the
key to set . Press the
establish the data.
FUNC
key to
key to set . Press the
establish the data.
(5) Press the 1 key four times to display
.
(6) Press 1 of the digital operatort five times
to dispaly .
(7) Press the
so as to increase to frequency or the
FUNC
key and then the 1 key
2
(5) Press the 1 key four times to display
(6) Short the terminals FW and P24 (CM1*)
of the control terminal block.
(7) Apply a voltage between the terminals O
and L to start running.
key so as to decrease the frequency.
(When the 1or 2 key is pressed con-
tinuously, the frequency is changed continuously.)
When the
FUNC
key is pressed, is
displayed.
(8) Open the terminals FW and P24 (CM1*)
of the control terminal block to stop deceleration.
*: Symbols are indicated for Sink type wiring.
Refer to page 5-5.
FUNC
key and then press the
FUNC
2
key to
.
(8) Check the output frequerncy and rotation
direction. When the 1or 2 key is
pressed to display and then the
FUNC
key is pressed, the rotation direction
can be checked. indicates forward
rotation and
r
indicates reverse
rotation. When the rotation direction is
checked, press the
FUNC
key. When the
rotation direction cannot be found, operate
the equipment at a low frequency to check
the rotation direction.
(9) Presst the
RUN
key. The equipment
starts running.
(10) Press the
STOP/RESET
key. The equipment
decelerates and stops.
6-4
Page 39

• The failure alarm signal is generated from the terminal AL0 and AL1 when a failure hap-
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
pens. At this time the contents of the failure are displayed on the digital operator.
• Whether the alarm terminal output is to be turned on or off during normal run can be
selected by the extension function .
The alarm output terminals at initial setting are as follows (1).
The alarm output terminals are valiable as follows (2) by setting .
(1) Contact b
During normal operation
AL2 AL1 AL0
Contact Power Operation
b
(initial
setting)
Status
ON
Normal
ON
Abnormal Open Closed
OFF
Ñ
• Contact specification
250 VAC 2.5 A (Resistor load) 0.2 A (cos¿=0.4) 100 VAC 10 mA
30 VDC 3.0 A (Resistor load) 0.7 A (cos¿=0.4) 5 VDC 100 mA
Working voltage: Max. 50 V
At occurrence of an
alarm or power off
AL2 AL1 AL0 AL2 AL1 AL0
AL0-AL1 AL0-AL2
Closed Open
During normal operation
or at power off
Contact Power AL0-AL1 AL0-AL2
a
(2) Contact a
At occurrence of an alarm
Operation
Status
ON
Normal Open Closed
ON
Abnormal Closed Open
OFF
ÑOpen Closed
Open Closed
MinimumMaximum
AL2 AL1 AL0
• Saving the alarm signal
When an alarm signal is outputted, the alarm signal data is stored even if the input power is
turned off and the contents can be checked by turning the power on once again. However,
when the input power is turned off, the inverter control power is also turned off. As a
result, when the power is turned on next, the alarm contact output is reset (deleted). Therefore, when saving the alarm contact output, let the external sequence receive and save it
and then turn off the inverter input power.
• When the alarm contact output is set ON during normal run, a time delay occurs until the
contact is closed when the power is turned on. Therefore, when using the alarm contact
output, set a time delay of about 2 seconds when the power is turned on.
6-5
Page 40

Resetting (Any one of A, B and C is possible)
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
CM1 PLC P24 1
A) Turn control terminal 1 on. (In the
initialization at factory before shipment, intelligent input terminal 1 is
allocated to the reset RS terminal.)
When the internal interface power source
P24-CM1 is used (Source type wiring)
B) Press
operator. (This is effective only when
STOP/RESET
on the digital
an alarm occurs.)
CM1 PLC P24 1
C) Open the power receiving breaker of
the inverter, and make sure that the
Charge lamp on the control board
goes out. (See page 3-1.) Then, close
When the internal interface power source
the power receiving breaker.
P24-CM1 is used (Sink type wiring)
NOTE: When the control circuit terminal RS is used, never short-circuit RS-P24 (CM1*)
for four seconds or more. Otherwise, a communication error
R-ERROR COMM<2> may occur (Although the digital operator display is
, the inverter is normal). When the above error occurs, open the RS termi-
nal and press the operator key.
*: For sink type wiring
How to return to the initialization (state before shipment)
When returning the equipment to the initial state set at factory before shipment for some
reason, see page 7-14.
6-6
Page 41

7. OPERATION OF THE DIGITAL OPERATOR
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
The standard type digital operator is modified so as to be used easily by minimizing key operations. Data can be set simply.
7.1 Names of Parts
Monitor (LED display)
This display shows frequency, motor
current, motor revolution speed, and
Trip history
FUNC (Function) key
This key is used for changing
commands. When pressing
key after setting data and
parameter, they are automatically memorized.
FUNC.FUNC.
FUNC.
FUNC.FUNC.
RUNRUN
RUN
RUNRUN
RUN key
This key is used for starting. (When
terminal run is selected, this key does
not work.)
POWER Lamp
Power lamp of control
circuit
Up key, Down key
These keys are used to
STOP/STOP/
RESETRESET
STOP/
RESET
RESETRESET
STOP/STOP/
change data and increase
or decrease the frequency.
STOP/RESET key
This key is used for stopping the motor or
resetting errors.
(When either operator or terminal is selected, this key works. If the extension
function is used, this function is void.)
WARNING
l The STOP/RESET key works only when a function is set. Prepare an emergency switch separately.
The use of the STOP/RESET key as an emergency switch may cause an injury.
7.2 Operation Procedure
(Example that the frequency is set and the equipment starts running)
➤➤ ➤ ➤
Display after
power is turned
on
.
(Frequency
monitor)
Press the
key once.
Press the
key once.
FUNC
FUNC
Press the
1
key five times.
When selecting the monitor
mode, press and
1
2
Start
run
Press
Press the key once
and set the frequency by using
the and keys.
RUN
FUNC
1
2
.
➤➤ ➤➤
The frequency which is
set by the key is
stored.
FUNC
to display .
7-1
Page 42

7.3 Key Description
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Data display The key are used to select the code and change the data. When
2
1
Code display the 1 key is pressed once, the monitor mode is displayed
FUNC
.
UP/DOWN key first and then , , , •••• are one by one. If the
key is pressed once again when is displayed, the display is
returned to .
If an optional code is selected when is displayed and the
FUNC
key is pressed, the extension function mode can be selected.
[Function key] . . . This key allows the selection of commands and memorizes parameters.
When this key is pressed once in the state of , , the
data state is set. When the key is pressed once in the state of ,
the extension function code selection state is set.
.
➤
FUNC
2
➤
2
1
➤
.
➤
➤
FUNC
➤
1
.
FUNC
➤
Select the extension
function code.
2
1
➤
FUNC
➤
A setting method which
is the smame as that for
to is
used for the subsequent
screen transition.
1
RUN
STOP/RESET
[RUN key] . . . This key starts the run.
screen transition
screen transition
The set value of F4 determines a forward run or a reverse run.
[STOP/RESET key] . . . This key stops the run.
When a trip occurs, this key becomes the reset key.
7-2
Page 43

7.4 Explanation of Screen Display
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
• When the inverter is turned on, the latest display appears. However, when the display
unit for data of the commands F2 to F14 is turned off, the commands (F2 to F14) are
displayed. (d10 and d11 excluded)
• Data during running in any function mode or extension function mode can be displayed.
Even if data cannot be changed during running, data can be monitored.
• In each of the function modes , , , , and , data
can be changed even during running. In other function modes and extension function
modes, data cannot be set during running.
to to
RUN
Or data display
Running start
,
Code which can change data during running
➤
The display is left unchanged.
➤
FUNC
.
Data can be changed
even during running
7-3
Page 44

7.5 Transition of Each Code
g
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
<Monitor mode>
Output frequency
monitor
➤
➤
Motor revolution
speed monitor
➤
➤
Output current
monitor
➤
➤
Frequency converted
value monitor
➤
➤
Trip monitor
➤
➤
Trip history
monitor
➤
<Function mode>
➤
Output frequency
setting
➤
➤
➤
Running direction
setting
➤
➤
➤
Acceleration time
setting
➤
➤
Deceleration time
setting
➤
➤
Manual torque boost
setting
➤
➤
Run command,
frequency command
➤
➤
Analog meter
adjustment
➤
➤
Motor receiving
voltage
➤
➤
Extension function
setting
When the key is pressed once
FUNC
➤
to set the extension function, the
screen is changed to the extension
function code selection screen.
When a code is selected from the
codes to and the
key is pressed, the screen is
FUNC
changed to the relevant extension
function settig screen.
To extension function code setting
<Extension function mode>
➤
Control method setting
Motor capacity setting
Motor poles setting
Speed control response
constant setting
Start frequency adjustment
Maximum frequency
limiter setting
Minimum frequency
limiter setting
Jump frequency setting 1
Jump frequency setting 2
Jump frequency setting 3
Carrier frequency setting
Frequency command sampling
frequency setting
Multispeed first
speed setting
Multispeed second
speed setting
Multispeed third
speed setting
Electronic thermal level
adjustment
Electronic thermal
characteristic selection
Motor pole number setting
for motor speed monitor
External frequency setting
start
External frequency setting
end
Instantaneous restart
selection
Dynamic braking usage
ratio
Optional arrival frequency
for acceleration
Optional arrival frequency
for deceleration
Monitor signal selection
Frequency converted
value setting
Analog input selection
Frequency arrival signal
output method
Restarting after FRS
signal selection
Reduced voltage soft
start setting
Running mode
selection
Jogging frequency
setting
Base frequency
setting
Maximum frequency
setting
Maximum frequency
selection
Frequency command/
output frequency adjust
(O−L terminal)
Frequency command/
output frequency adjust
(OI−L terminal)
Selection of reset
terminal performance
P gain setting of PID
funciton
I gain setting of PID
function
D gain setting of PID
funciton
Selection of PID
funciton
Setting method of PID
reference value
Setting of PID
reference value
Auto tuning setting
Motor data selection
Ro-To option selection
Input terminal setting 1
Input terminal setting 2
Input terminal setting 3
Input termianl setting 4
Input terminal setting 5
Input terminal setting 6
Input terminal setting 7
Input terminal setting 8
Output terminal setting 11
Output terminal setting 12
Input terminal a and b
contact setting
Output terminal a and b
contact settin
7-4
Page 45

7.6 Digital Operator Initialization List
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
(1) Monitor mode, function mode
• The standard set value of each code number is displayed.
• The extension functions shown on page 7-6 can be set by the extension
function setting function.
isplay
order
1
2
Function name Type
Output frequency monitor
Motor revolution speed
monitor
3
Output current monitor
4
Frequency converted value
monitor
5
Trip Monitor
6
Trip history monitor
7
Output frequency setting
8
Running direction setting
9
Acceleration time setting 1
Monitor
Monitor
Monitor
Monitor
Monitor
Monitor
Set value
Set value
Set value
Code
display
d 0
d 1
d 2
d 3
d10
d11
F 2
F 4
F 6
Screen display
Settable
during
running
—
—
—
—
—
—
√
Not possible
√
Monitor/set value
0.00-9.99/10.0-99.9/100-400
0.00-9.99/10.0-99.9/100-600
0.0-999
0.00-9.99/10.0-99.9/100.-999.
100-999/ 10- 99
—
—
0.00-9.99/10.0-99.9/100-400
F/r (forward run/reverse run)
0.01-9.99/10.0-99.9/100-999
Initial
value
—
—
—
—
—
—
0.00
F
30.0
Settable
for 2nd
function
—
—
—
—
—
—
√
—
√
Set
value
10
Deceleration time setting 1
11
Manual torque boost setting
12
Runn command, frequency
command setting
13
Analog meter adjustment
14
Motor receiving voltage
15
Extension function setting
Set value
Set value
Set value
Set value
Set value
Set value
F 7
F 8
F 9
F10
F11
F14
√
√
Not possible
√
Not possible
Not possible
0.01-9.99/10.0-99.9/100-999
00-99
00-15
00-250
200-230/380-480
A 0-A99/C 0-C21
NOTE 3
NOTE 1
NOTE 2
30.0
11
03
172
230/460
A 0
NOTE 1: In the standard configuration, four values from 0 to 3 can be selected. When an
optional PC board is mounted, 16 values from 0 to 15 can be selected. Refer to
F-9.
NOTE 2: For the 200 V class, one of 200, 215, 220, and 230 can be selected.
For the 400 V class, one of 380, 400, 415, 440, 460 and 480 can be selected.
NOTE 3: Set torque boost in 70 to 90 when using VP1, VP2 or VP3 in V/F control mode.
√
√
—
—
—
—
7-5
Page 46

(2) Extension function mode
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
• Each function name and settable range to the extension function mode are shown
below.
• Set the extension function code to be changed by .
Display
order
1
Control method setting
2
Motor capacity setting
3
Motor poles setting
4
Speed control response constant setting
5
Start frequency adjustment
6
Maximum frequency limiter setting
7
Minimum frequency limiter setting
8
Jump frequency setting 1
9
Jump frequency setting 2
10
Jump frequency setting 3
11
Carrier frequency setting
12
Frequency command sampling frequency
13
Multispeed first speed setting
14
Multispeed second speed setting
15
Multispeed third speed setting
16
Electronic thermal level adjustment
17
Electronic thermal characteristic selection
18
Motor pole number setting for motor speed monitor
19
External frequency setting start
20
External frequency setting end
21
Instantaneous restart selection
22
Dynamic braking usage ratio
23
Optional arrival frequency for acceleration
24
Optional arrival frequency for deceleration
25
Monitor signal selection
26
Frequency converted value setting
27
Analog input selection
28
Frequency arrival signal output method
29
Restarting after FRS signal selection
30
Reduced voltage soft start setting
31
Running mode selection
32
Jogging freguency setting
33
Base frequency setting
34
Maximum frequency setting
35
Maximum frequency selection
Frequency command/output frequency adjust (O-L terminal)
36
Frequency command/output frequency adjust (OI-L terminal)
37
Selection of reset terminal performance
38
P gain setting of PID funciton
39
I gain setting of PID funciton
40
D gain settingof PID function
41
Selection of PID funciton
42
Setting method of PID reference value
43
Setting of PID reference value
44
Auto tuning setitng
45
Motor data selection
46
Ro-To option selection
47
Input terminal setting 1
48
Input terminal setting 2
49
Input terminal setting 3
50
Input terminal setting 4
51
Input terminal setting 5
52
Input terminal setting 6
53
Input terminal setting 7
54
Input terminal setting 8
55
Output terminal setting 11
56
Output terminal setting 12
57
Input terminal a and b contact setting
58
Output terminal a and b contact setting
59
Externsion function name
Code
display
A 0
A 1
A 2
A 3
A 4
A 5
A 6
A 7
A 8
A 9
A10
A11
A12
A13
A14
A23
A24
A25
A26
A27
A34
A38
A39
A40
A44
A47
A48
A49
A54
A58
A59
A61
A62
A63
A64
A80
A81
A86
A90
A91
A92
A94
A95
A96
A97
A98
A99
C 0
C 1
C 2
C 3
C 4
C 5
C 6
C 7
C10
C11
C20
C21
Settable
running
Screen display
during
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
0.00-9.99/10.0-99.9/100
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
0-3, 5-9, 11-16, 18-28
Ñ
0-3, 5-9, 11-16, 18-28
Ñ
0-3, 5-9, 11-16, 18-28
Ñ
0-3, 5-9, 11-16, 18-28
Ñ
0-3, 5-9, 11-16, 18-28
Ñ
0-3, 5-9, 11-16, 18-28
Ñ
0-3, 5-9, 11-16, 18-28
Ñ
0-3, 5-9, 11-16, 18-28
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Setting range Initial value
0-5
3.7 to 160
2/4/6/8
0.10-9.99
0-120 (400)
0-120 (400)
0-400
0-400
0-400
2.0-16.0
1-8
0-120 (400)
0-120 (400)
0-120 (400)
20-120
0-2
2 to 48
0-120 (400)
0-120 (400)
0-3
0.0-99.9/100
0-400
0-400
0-3
0.0-99.9
0-1
0-2
0-1
0-6
0-2
0-9.99
30-120 (400)
30-120 (400)
120/400
0-255
0-255
0, 1
0.1-0.5
0.0-15.0
0.0-100
0-4
0, 1
0.00-200
0-2
0-2
0-1
0-2
0-2
00-FF
00-07
0
4
2.00
0.50
0
0
0
0
0
(16.0)
8
0
0
0
100
1
4
0
0
0
(1.5)
0
0
0
1.0
1
0
1
6
0
1.00
60
60
120
Ñ
Ñ
0
1.0
1.0
0.0
0
0
0.00
0
0
0
18
16
5
11
9
13
1
0
0
1
00
04
Settable
for
2nd
function
√
√
√
√
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
√
√
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
√
√
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
√
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
Ñ
NOTE 1: The most applicable motor capacity of the inverter is set.
NOTE 2: The initial setting of each inverter is adjusted when shipping from the works.
Remarks
NOTE 1
See 7-18
See 7-21
Frequencies below
the start frequency
cannot be set.
NOTE 2
NOTE 2
Set
value
7-6
Page 47

7.7 Explanation of Modes
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
(1) Monitor mode contents
Monitor
mode
contents
The frequency outputted by the inverter is monitored.
The display is as shown below.
Contents and display
Display when stopped
.
Output
frequency
monitor
Motor
rotation
speed
monitor
A frequency between 0.01 Hz
and 9.99 Hz is displayed in units
of 0.01 Hz.
A frequency between 10.0 Hz
99.9 Hz is displayed in units
.
of 0.1 Hz.
A frequency between 100 Hz and
400 Hz is displayed in units of
➤
FUNC
FUNC
(1)
. .
➤
(2)
(3)
to
to
.
to
1 Hz.
The rotational frequency converted value of the frequency outputted by the inverter
is displayed.
(Note that the value is not the real rotational frequency of the motor.)
The converted value is displayed as shown below using "rotational frequency/100."
Display when stopped
.
The converted value is displayed
➤
FUNC
FUNC
(1)
. .
➤
(2)
(3)
to
to
.
to
in units of 0.01 (1 rpm).
From 1 to 999 rpm
The converted value is displayed
in units of 0.1 (10 rpm).
.
From 1000 to 9990 rpm
The converted value is displayed
in units of 1 (100 rpm).
From 10000 to 60000 rpm
NOTE: Motor pole number can be set by .
The current outputted by the inverter is monitored. The display is as shown below.
The output display accuracy is about ±10%.
Inverter output current: I
Monitor display current: I
Rated current of the inverter: I
I
MC
- I
M
I
R
A current between 0.1 and 99.9 A
is displayed in units of 0.1 A.
.
A current between 100 A and 999 A
is displayed in units of 1 A.
Output
current
monitor
➤
FUNC
FUNC
Display
when
.
➤
(2)
stopped
to
.
to
7-7
M
MC
R
× 100 ≤ ±10%
Page 48

Contents and display
Monitor
mode
contents
FUNC
➤
to
to
➤
(2)
The product of the value of frequency converted value setting (A47) and that of output frequency
(d0) is displayed on the monitor.
Frequency
converted
value
monitor
0.0 to 9.99
FUNC
➤
.
When a trip occurs, the cause of the trip is displayed in this code. As a general display,
the contents of the latest trip are displayed. Whenever the key is pressed, the content
of each is displayed.
Trip
monitor
.
➤ ➤
FUNC FUNC
➤
STOP/RESET
FUNC
NOTE 1: When there is no trip, is displayed.
NOTE 2: The above example of the voltage between P(+) and N(-) indicates 390 to 399 V.
NOTE 3: When the key is pressed after a trip occurs,
is displayed.
FUNC
➤
The causes of the last trip and the last trip but one are displayed. When the command is displayed
and the key is pressed, the trip cause is displayed.
Trip
history
monitor
➤
FUNC
➤
FUNC
NOTE 1: When there is not a trip history, is displayed.
Trip cause Trip current
Voltage between trips
P and N
(Note 2)
Cause of the last trip
FUNC
Cause of the last trip
but one
FUNC
NOTE 2: How to delete trip history data, see page 7-14.
..
.
(1)
10.00 to 99.99
to
to
(4)
100.00 to 999.99
(3)
1000.00 to 9999.99
to
(5)
10000.00 to 39960.00
..
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
7-8
Page 49

Methods for setting the output frequency are as follows:
Initial set value
①
Connect the multispeed terminal for setting the frequency to CM1.
(The relationship between multispeeds 1 to 7 and the control circuit terminals is as
shown below.)
NOTE 4: When setting to over 120 Hz, the changing over maximum frequency is necessary.
Remote operator or copy unit must be used.
②
Set an optional output frequency using the or key.
③
Press the key once to store the set output frequency.
NOTE 2: is displayed.
④
Press the key once. (Check whether the output frequency, which is set,
is displayed.)
⑤
By repeating (1) to (4), the output frequency in the multispeed mode can be set.
Whenever any data is changed, be sure to press the key before starting
the next setting. Note that when the key is not pressed, the data will
not be set.
(When the value is switched to 400 by F-30, an output frequency of up to 400 Hz
can be set.)
Control circuit terminal
Multispeed
Multispeed 1
Multispeed 2
Multispeed 3
Multispeed 4
Multispeed 5
Multispeed 6
Multispeed 7
ON OFF
OFF ON
ON ON
ON OFF
OFF ON
ON ON
OFF OFF
OFF
ON
1 2 3 (*1)
7
CF1
6
5
CF2 CF3
CM1
By initialization, the multispeed can be
set up to the third stage. When CF3 is set by
terminal allocation (in this case, intelligent
input terminal 5 is allocated), up to the 7th stage
can be set (set by the extension function mode
C4).
Intelligent input terminal allocation: C0 to C7
Set value: 3 (CF3)
*1:
1
2
FUNC
1
NOTE 3:
FUNC
FUNC
.
➤
➤
1
2
.
.
.
➤
➤
FUNC
FUNC
2
1
Output
frequency
setting
1. Digital operator
2. Control circuit terminal
(multistage speed command)
3. External analog input
(0 to 10 V, 0 to 5 V, 4 to 20 mA)
4. Remote operator
(new type, general purpose)
5. Optional PCB
Refer to this setting.
Refer to this setting.
Refer to page 6-2.
Refer to the explanation of each remote operator.
Refer to each optional PCB operation.
(1) Setting from the digital operator
A frequency between 0.01 Hz and 9.99 Hz is
set in units of 0.01 Hz.
A frequency between 10.0 Hz and 99.9 Hz is
set in units of 0.1 Hz.
A frequency between 100 Hz and 400 Hz is
set in units of 1 Hz.
(2) Setting from the control circuit terminal (multispeed setting)
When the or key is pressed continuously, the value is changed continuously.
The output frequency at the multispeed can be set as specified below. When the running
mode is the process stepping mode, switch it to the multistage speed mode by the remote operator.
Example of terminal connection
for sink type
Refer to page 5-5.
(2) Function mode
Contents and display
Monitor
mode
contents
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
7-9
Page 50

Monitor
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
mode
contents
Contents and display
Set the motor direction.
Running
direction
Set the motor direction when running by pressing the key.
RUN
NOTE: The setting during run is impossible.
FUNC
➤
FUNC
Initial set value
➤
Forward run
Reverse run
Switching can be done by pressing
the key.
2
1
7-10
Page 51

Monitor
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
mode
contents
Contents and display
Acceleration time 1
and 2
Deceleration time 1
and 2
Manual
torque
boost
setting
These commands set and display Acc. time and Dec. time .
➤
FUNC
1
Initial value
➤
2
➤
➤
1
.
➤
2
() )
FUNC
➤
(
Setting range
0.01 to 9.99s
10.0 to 99.9s
100 to 999s
Period
Every 0.01s
Every 0.1s
Every 1s
.
Acceleration time 2 and deceleration time 2 are set when CH1 is connected with P24.
•
•
When a time of more than 1,000 seconds is set by the remote operator,
is displayed on the digital operator.
Set torque boost
•
Motor torque can be adjusted to increase the output voltage when the starting torque
is not sufficient in V/F control. Pay attention not to cause the motor to burnout and
an inverter trip. Set boost value in 70 to 90 when using VP1, VP2 or VP3 in V/F control mode.
Setting is effective only when V/F control is selected.
•
Output
Setting method
FUNC
➤
2
➤
Initial value
➤
➤
2
➤
1
FUNC
➤
1
With the remote operator (DOP, DRW, HOP, or HRW),
point A in the torque boost graph can be changed within
the range of 0% to 50% with respect to the base frequency.
voltage
100%
About 11.8
A
➤
10
0 5 25 50 Hz
660
12
30
(V-Boost F 20.0% is set
with the remote operator.)
Output
frequency
7-11
Page 52

Monitor
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
mode
contents
Contents and display
Switching the run command and frequency command setting modes
Set the run command and frequency command sending destinations. The standard specification
selection range is from 00 to 03.
Run
commanding
method
Frequency
commanding
method
Initial value
➤
Set value
Run command to
Digital operator
Digital operator
Terminal block
Terminal block
Digital operator
Option 1
Option 1
Digital operator
Option 2
Option 2
Terminal block
Option 1
Terminal block
Frequency command to
Digital operator
Terminal block
Digital operator
Terminal block
Option 1
Digital operator
Option 1
Option 2
Digital operator
Option 2
Option 1
Terminal block
Option 2
Option 2
Option 1
Option 2
Terminal block
Option 2
Option 1
Setting method
➤
2
1
➤
FUNC
Initial value
➤
FUNC
➤
NOTE1: The run command and frequency command sending destinations can be set to any
of the terminal, operator, option 1, and option 2. Select the relevant set value.
NOTE2: When option 1 or option 2 is selected for "Run command to" and "Frequency command
to," the digital operator and terminal block cannot issue commands. Set option 1
or option 2 (set values - ) only for operation or frequency commands
from the optional PC board.
7-12
Page 53

Contents and display
Monitor
mode
contents
➤
➤
➤
➤
1
2
➤
1
2
FUNC
FUNC
➤
Analog
meter
adjustment
FM
CM1
PLC
P24
Adjust the analog meter connected to the frequency monitor
terminal. (Initial setting of the [FM] terminal: Analog frequency monitor)
When operation starts, t/T output between FM and CM1 terminals is
proportional to the output data. Adjust the meter so that it indicates
the maximum point when the output is at the maximum.
Initial value
When adjusting the analog meter furthermore, repeat the same operation.
Maximum level of analog meter
Frequency monitor:
Current monitor:
Torque monitor:
(A63 maximum frequency setting)
(200% of inverter rated current)
(200% of rated torque)
NOTE 1:
NOTE 2:
This function is valid only when the analog monitor is used.
(Freqency monitor, current monitor, torque monitor)
The adjusted value when the input terminal STN (initialization) is used is
the initial value.
Motor
receiving
voltage
setting
➤
FUNC
➤
FUNC
➤
1
➤
2
400 V class
Initial value
Set the motor receiving voltage. When the key is pressed once, the current set value
of the motor receiving voltage is displayed.
FUNC
Extension
function
setting
➤
FUNC
➤
FUNC
Select the item of each extension function. After setting, the display is returned to the code
display.
After data is changed, be sure to press the key to store it.
➤
➤
2
1
➤
FUNC
➤
➤
2
1
➤
Code selection
When the data is changed,
the display blinks.
(Set value storage wait state)
Code selection
When the key is pressed, the display stops
blinking and the data is stored.
FUNC
FUNC
Sink type wiring
Refer to page 5-3
➤
➤
➤
➤
t
T
Output =
t (variation)
T
➤
1
➤
2
200 V class
Initial value
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
7-13
Page 54

Returning to the initialization (State set at factory before shipment)
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
When returning the equipment to the initial state set at factory before shipment for some reason,
follow the following procedure.
1) Allocate STN (set value ) to one of the input intelligent terminals. (Use to
in the extension function mode to set the intelligent terminals.)
(However, cannot be used since resetting RS is initially set.)
2) Short-circuit the STN terminal and P24 (CM1*), then turn power off and on. (When the power is
turned off, do not turn it on again until the CHARGE lamp of the logic PCB goes off.)
3) Keep the STN terminal open for more than 6 seconds. (When keying, resetting, or turning power
off is performed within 6 seconds, the equipment may not be initialized.)
4) Turn the power off after more than 6 seconds. (When the power is turned off within 6 seconds,
the equipment may not be initialized.)
How to Delete Trip History Data ( , and )
To delete trip history data for some reason, follow the instructions shown below using the remote
operator (DOP or HOP) or copy unit (DRW or HRW).
1. Using the remote operator (DOP-OA) or copy unit (DRW-OA)
(1) Display
(2) Move the cursor to beneath the initial set values. Select CLR and store it.
INIT TCNT
(trip history count clear) or the function mode initial setting
F-38 INIT
1) Turn the power off once and then turn it on. or close the reset terminal RS-P24 (CM1*) for
approx. a second. By this, trip history data is deleted.
2) When trip history is deleted, data of [F-38] is set to [CNT]. Trip counting restarts.
2. Using high-performance remote operator (HOP-OJ) or high-performance copy unit
(HRW-OJ)
(1) Display [TCNT 0: CNT] (trip history count clear) or the function mode initial setting
[2-1 INIT].
(2) Enter a count clearing value [0: CLR] from the 10-key pad.
1) Turn the power off once and then turn it on. or close the reset terminal RS-P24 (CM1*) for
approx. a second. By this, trip history data is deleted.
2) When trip history is deleted, data of [2-1 INIT] is set to [CNT]. Trip counting restarts.
.
NOTE: Symbols * are indicated for Sink type wiring.
7-14
Page 55

(3) Extension function mode contents
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Extension
function
code
Set the control method. Select one of the following control codes.
Contents and display
Control
method
setting
FUNC
➤
FUNC
Initial value
➤
➤
2
➤
➤
2
➤
➤
2
➤
➤
2
➤
➤
2
➤
V
V/f control (VC)
Constant torque characteristics
1
f0
V
V/f control (VP1)
Reduced torque characteristics,
1.5 power
1
NOTE : set torque boost in 70 to 90.
f0
V
V/f control (VP2)
Reduced torque characteristics,
1.7 power
1
NOTE : set torque boost in 70 to 90
f0
V
V/f control (VP3)
Reduced torque characteristics,
2.0 power
1
NOTE : set torque boost in 70 to 90
f0
V
Sensorless vector control (SLV)
1
f0
V
Vector control with sensor (V2)
NOTE : Vector control INV only
(Feedback board is nesessary)
f0
Set the motor capacity and number of motor poles according to the motor to be used.
The maximum rating of the applicable 4-pole motor for each inverter
NOTE :
When the data does not match
that of the mootor, satisfactory
characteristics may not be
obtained during the sensorless
vector running.
The full performances may
not be demonstrated if the
rating of a motor used is tow or
less than the maximum
applicable rating when
the sensor-less vector function
is used.
The sensor-less vector operation is disabled when two or
more motors are running.
Set this data properly according
to the motor used if its rating is
not the same as the maximum
applicable rating in V/f
operation.
Motor
capacity,
motor poles
setting
is set initially.
FUNC
➤
FUNC
Motor capacity
.
➤
2
1
➤
➤
.
➤
2
1
➤
.
➤
2
1
➤
.
No. of motor poles
FUNC
➤
FUNC
➤
➤
2
2
1
➤
➤
1
➤
Initial
value
➤
2
1
➤
7-15
Page 56

Extension
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
function
code
Speed
control
response
constant
setting
Start
frequency
adjustment
Contents and display
Set the response speed (ASR system gain) between the inverter and motor. When increasing
or decreasing the current motor response speed, adjust the ASR system gain. When the set value is
decreased, the response speed is increased. When the set value is increased, the response speed is
decreased.
1
A constant between 0.01
and 9.99 is set in units of 0.01.
A constant between 10.0
.
and 99.9 is set in units of 0.1.
A constant between 100
FUNC
➤
FUNC
Initial value
➤
.
➤
.
➤
.
2
1
➤
➤
.
2
1
➤
➤
and 655 is set in units of 1.
2
Set the frequency for starting output of the inverter.
Set a frequency between 0.1 Hz and 9.99 Hz in units of 0.01 Hz.
Output voltage
V
Adjustment
range
➤
➤
FUNC
.
➤
2
➤
Initial value
➤
.
➤
2
➤
1
FUNC
➤
1
0
.
0.10 9.99
f
Maximum
frequency
When the start frequency is increased,
the acceleration or deceleration time is
decreased.
7-16
Page 57

Extension
,,
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
function
code
Contents and display
Set the limits of frequency setting within the start frequency adjustment range and
maximum frequency setting range. When a value beyond the limits is inputted from the operator,
it will not be stored. Even if a value beyond the limits is inputted as external analog input, the set
value will not be changed.
Frequency
upper,
lower
limiter
Maximum
frequency limiter
FUNC
➤
FUNC
Minimum
frequency limiter
FUNC
➤
FUNC
2
➤
2
➤
➤
1
➤
.
➤
1
➤
.
(400)
Initial value
(400)
Initial value
Setting example
(When an upper limit of 45 Hz and a lower
limit of 20 Hz are set)
Output frequency
(60 Hz)
Upper limiter
Lower limiter
45
20
➤
Settable range
➤
0
Frequency command
(F-SET)
NOTE: Setting conditions
0 Hz or upper limit ≥ lower limit
When 0 Hz is set, the limiters will not operate.
To avoid a resonance with the load, the frequencies at up to 3 points can be jumped. The setting
order and the execution order may be changed.
The frequency equivalent to the jump frequency setting width (± 0.5 Hz) (Note 1) cannot be set as
a jump frequency.
NOTE 1 : The jump frequency can be set by the remote operator.
NOTE 2 : As to the frequencies which are set by the jump frequency setting function, the set
frequencies are jumped but the output frequencies pass.
Jump
frequency
setting 1
Jump
frequency
setting 2
Jump
In the case
of jump frequency 1
frequency
setting 3
ff
➤
➤
➤
➤
➤
➤
➤
➤
00
Set frequency (V) Output frequency (V)
In the case
of jump frequency 2
1
In the case
of jump frequency 3
FUNC
➤
FUNC
2
Initial value
➤
➤
➤
.
7-17
Output
frequency
Deceleration
Setting example
Jump frequency 1: 10 Hz
Jump frequency 2: 30 Hz
Jump frequency 3: 45 Hz
Jump frequency width: 0.5 Hz
f
45
Adjustment range
30
10
0
➤
➤
➤
Acceleration
➤
➤
(V)
Speed command
frequency
➤
Frequency which
➤
jumps by 1.0 Hz
➤
➤
➤
➤
➤
0.5 Hz
0.5 Hz
Page 58

Extension
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
function
code
Carrier
frequency
setting
Frequency
command
sampling
frequency
setting
Contents and display
Set the switching frequency of the power module.
FUNC
(NOTE 1)
Initial value
➤
.
➤
2
➤
FUNC
➤
1
.
NOTE 1: The initial value of carrier frequency
varies with the inverter capacity.
Carrier frequency initial value
model type
055 to 150 L/HF
220 L/HF
300 to 370 L/HF
450 to 550 L/HF
750 to 1100HF
1320 to 2200HF
initial value
CT
16 kHz
12 kHz
10 kHz
6 kHz
3 kHz
2 kHz
VT
8 kHz
6 kHz
5 kHz
3 kHz
2 kHz
2 kHz
When VP1 to VP3 is selected,carrier
frequency is automatically changed to
VT.
Set the frequency commands (voltage frequency command (O-L terminal signal), current frequency
command (OI-L terminal signal), and the number of samplings.
NOTE: How to set
FUNC
Initial value
➤
➤
2
➤
FUNC
➤
1
The number of samplings is set to 1.
:
The reaction time becomes shorter, but
¥
the output frequency becomes likely to
¥
vary.
¥
¥
The number of samplings is set to 8.
:
The reaction time becomes longer, but
the output frequency becomes stable.
Multispeed
setting 1
Multispeed
setting 2
Multispeed
setting 3
Set the output frequency of each multispeed speed. When setting four or more speeds, refer to the
item of output frequency setting.
Example of the connection method
Refer to Page 5-5
(8)
(7)
CF1
(6)
CF2
In the case
of multispeed
setting 1
In the case of multispeed setting 2
In the case of multispeed setting 3
FUNC
➤
FUNC
2
➤
.
➤
➤
(400)
1
Initial value
FM CM1 PLC P24
Example of Multispeed setting
Multispeed
Multispeed 1
Multispeed 2
Multispeed 3
NOTE: When using four or more multispeed commands,
use the multispeed terminal (CF3) as an input terminal.
FW
REV
Control circuit
terminal
(7) CF1 (6) CF2
ON OFF
OFF ON
ON ON
7-18
Page 59

Extension
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
function
code
Contents and display
Set the electronic thermal level. Set the thermal level in accordance with the rated current of the
motor in units of 1 (%).
Adjustment level =
Motor rated current
Inverter rated current
100
Electronic
thermal
level
adjustment
Electronic
thermal
characteristic
selection
Setting method
FUNC
➤
2
➤
Initial value
➤
➤
2
➤
Time(s)
1
FUNC
➤
1
➤
20% 120%
➤
0
Inverter rated current
➤
20 100 150 200
Inverter current (A)
Select the electronic thermal characteristics. Set the thermal characteristics in accordance with
the load to be used. For free setting of set value 2, the current and frequency can be set by each
remote operator.
Set value Function
0 Constant torque characteristic
Initial value
Setting method
FUNC
➤
1 Reduced torque characteristic
2
➤
2
1
➤
Initial value
➤
2
1
➤
(Can be set by the remote operator)
FUNC
Free setting
➤
Constant torque
➤
characteristic
100
80
60
➤
➤
Reduced torque
characteristic
Output current (%)
0
5 20 60 120
(Each characteristic
at 60 Hz or more is 100%.)
➤
Output frequency (Hz)
➤
Set the pole number of motor to convert output frequency into motor rotation speed on monitor
.
➤
2
➤
Initial value
➤
➤
2
➤
Settable numbers
2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 24, 32, 36, 48
1
FUNC
➤
1
Motor
poles
setting
for motor
speed
monitor
mode funciton
Setting method
FUNC
7-19
Page 60

Contents and display
Extension
function
code
➤
➤
1
2
➤
FUNC
FUNC
➤
Instantaneous
restart
selection
Set value
Function
0 Alarm output after tripped
1 Deceleration stop at the time
of restart
2
Frequency matching start at the time
of restart ( Note 1)
Initial value
Setting method
Set the inverter retry method when a power error occurs.
Select the set value of the retry method to be used.
3
0 Hz start at the time of restart
NOTE 1:
NOTE 2:
When the base frequency is one of the following ones, frequency matching may restart at 0 Hz.
When the base frequency is 60 Hz: Driven at 40 Hz or less
When the base frequency is 50 Hz: Driven at 30 Hz or less
For other precautions, refer to Chapter 1, "Instantaneous stop restart" of Appendix 2.
Since the retry mode is selected, the equipment restarts for trips of overcurrent, overvoltage, or undervoltage.
For undervoltage, 16 retries (17th trip) are executed.
For overcurrent or overvoltage, 3 retries (fourth trip) are executed.
Do not use this function for a case that a fallen substance should be held by the machine brake when the motor
is in the free-run mode.
Initial value
Restart
selection
➤
➤
External
frequency
setting
start
External
Frequency
setting end
Set the frequency for starting output for an external frequency command (0 to 10 V, 0 to 5 V,
4 to 20 mA) and the frequency for ending output. When 0 Hz is set, this function will be canceled.
➤
➤
1
2
➤
FUNC
Initial value
Setting method
➤
FUNC
.
(400)
External frequency
setting start
External frequency
setting end
Same as A26
Output frequency (Hz)
Frequency
command
0 10 V
05 V
4 20 mA
NOTE 1:
NOTE 2:
NOTE 3:
NOTE 4:
The standard setting is 0 Hz.
In this case, the selected V/f
pattern is used for running.
When changing the V/f pattern
after A 26 (start) and A 27 (end)
are set, readjust A 26 (start) and
A 27 (end).
When A 26 (start) > A 27 (end)
is set and the frequency command
value is minimized (0 V or 4 mA),
the output frequency may be
lowered than the value which is
set by A 26 by 0.1 to 0.3 Hz.
The reason is that it is judged that
there is some frequency due to
noise on the signal line and it is a
normal operation.
The setting shown left is also
possible with F31 of the remote
operator.
60
30
50
Output
frequency
(Hz)
60
10 V
5V
20mA
0 8 V
04 V
4 16.8
2
1
7.2
Start setting
command (20%)
Frequency
command
End setting
command (80%)
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
7-20
Page 61

Contents and display
Extension
function
code
➤
➤
1
2
➤
FUNC
FUNC
➤
Dynamic
braking
usage ratio
Initial value
Setting method
Set the usage ratio (%) for 100 seconds of BRD.
When the BRD operation exceeds this setting,
the operation will be stopped.
➤
➤
➤
➤
➤
➤
➤
➤
➤
➤
1
2
.
.
t1 t2 t3
ON ON ON
BRD ON
T =
(t1 + t2 + t3)
100 seconds
100 seconds
100
Function contents
NOTE 1:
NOTE 2:
NOTE 3:
NOTE 4:
NOTE 5:
NOTE 6:
The internal BRD circuit is not mounted
in an inverter other than the types 055L/HF,
and 075L/HF.
When 0 % is set, the BRD will not be
operated.
When T exceeds the set value, the BRD
will be stopped.
When mounting an external BRD unit, set
the usage ratio to and remove the
external resistors.
The initial settings of 110-550L/HF
are 0.0%.
Conditions when using the external
resistor are shown in the table.
Model
055, 075HF
RB2, two each in series
(70 ohm or more)
Inverter requiring an external resistor
External
resistor
Usage ratio
Max. 10 (%)
NOTE 7: This function cannot be used for the inverter types 110 to 550L/HF which have no built-in BRD
(dynamic braking) circuit.
.
Arrival
optional
frequency
at acceleration
Arrival
optional
frequency
at deceleration
➤
➤
1
2
➤
FUNC
Initial value
Setting method
When frequency arrival signal output method 2 is selected, an output signal is outputted
at an optional frequency. When frequency arrival signal output method 1 is selected, an output
signal is outputted at an optional frequency or more. For acceleration and deceleration
, the frequency is set in units of 0.1 Hz (in units of 1 Hz for 100 Hz or more).
➤
➤
➤
➤
➤
➤
➤
➤
➤
➤
.
➤
➤
1
2
FUNC
Initial value
.
➤
➤
➤
In the case of optional
arrival frequency
of acceleration
In the case of optional
arrival frequency
of deceleration
At the time of acceleration, an output signal
is turned ON in a range from the set frequency
-0.5 Hz to the set frequency +1.5 Hz. At the
time of deceleration, an output signal is turned
ON in a range from the set frequency +0.5 Hz
to the set frequency -1.5 Hz.
Output
frequency
f
Output
signal
(FA1)
Running
time
60 ms60 ms
0.5 Hz
-1.5 Hz
1.5 Hz
-0.5 Hz
t
0
➤
➤
FUNC
FUNC
ON
➤
➤
setting
setting
055, 075LF
RB1 to RB3
(17 ohm or more)
Max. 10 (%)
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
7-21
Page 62

Extension
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
function
code
Contents and display
Select the output monitors signal at the control circuit terminal FM from
the table indicated below.
Monitor
signal
selection
Frequency
converted
value
setting
Setting method
FUNC
Set value
➤
Initial value
2
➤
1
➤
FUNC
➤
0 Analog output frequency monitor
1 Analog current monitor
2
3
Analog torque monitor (Note)
Digital output frequency monitor
Function
Initial value
Output monitor signal
Frequency monitor
Current monitor
Analog
Torque monitor
Output full-scale value
Maximum frequency
200% of the rated current
200% of the rated torque
NOTE: Use the analog torque monitor function only in the
sensorless state. Under the V/f control, an appropriate
value is outputted. The accuracy is ±20%
(a rough value).
Set a converted value for frequency converted value monitoring. The product of this setting and the
ouptut frequency (d0) is displayed as the value for the frequency converted value monitor (d3).
Setting method
FUNC
➤
.
➤
2
1
➤
.
FUNC
➤
Initial value
➤
2
1
➤
Analog
input
selection
.
Set the maximum voltage to be supplied between the terminals 0 and L.
HO01L HO01L
Setting method
FUNC
➤
2
➤
➤
Initial value
1
FUNC
➤
Initial value
VR0
(500 Ω to 2kΩ)
Terminal connection example
Set value
0 Max. 5 V input
1 Max. 10 V input
+Ð
DC0 TO 5V
DC0 TO 10V
Input impedance
30 kΩ
Function
7-22
Page 63

Extension
,,
,,
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
function
code
Contents and display
When selecting the frequency arrival signal at the output terminal, select the arrival signal output
method.
Frequency
arrival
signal
output
method
Setting method
➤
2
FUNC
➤
1
➤
FUNC
➤
Initial value
Set value
0
At the time of constant speed arrival
Function
1 Optionally set frequency or more
2
Only optionally set frequency
Set optional frequencies of set value 1 and set
value 2 by and .
NOTE 1: The frequency arrival signal
can be allocated only to one
of the intelligent output terminals.
It cannot be outputted to
an individual output terminal
for acceleration and deceleration.
NOTE 2: Selection of arrival signal output
method for relay option board (J-RY)
can be done by remote oprator and
F-48 funciton.
Initial
value
Output
frequency
(Hz)
Arrival
signal
Output
frequency
(Hz)
Arrival
signal
Output
frequency
(Hz)
Arrival
signal
0
0
0
0.5Hz
➤
➤
0.5Hz
➤
➤
➤
➤
0.5Hz
➤
➤
➤
➤
➤
➤
➤
➤
60 ms
setting
ON
➤
60 ms
setting
ON
60 ms
At the time of constant
:
speed arrival
ON
Optionally set frequency
:
or more
➤
1.5Hz
➤
➤
Only optionally set
:
0.5Hz
➤
➤
setting
frequency
ON
➤
60 ms
➤
1.5Hz
➤
Time
➤
➤
Time
➤
Time
➤
1.5Hzsetting setting
➤
1.5Hz
➤
➤
Select an operation after a free run stop.
2
Set value Function
0
1
f matching
0 start
Restarting
after FRS
signal
selection
Set and with the and keys.
1
Setting method
Initial value
FUNC
➤
➤
2
1
➤
➤
7-23
Initial value
Page 64

Extension
,
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
function
code
Contents and display
Adjust reduced voltage start.
Reduced
voltage
soft start
setting
Running
mode
selection
Jogging
frequency
setting
FUNC
Initial value
➤
➤
2
➤
FUNC
➤
1
¥
¥
¥
¥
NOTE: How to set
There is no reduced voltage. The rush
:
current at the start of the inverter is
increased but the motor reaction time is
decreased.
:
The effect of the reduced voltage is
large.
The rush current is reduced but the
motor reaction time is increased.
Select the running mode. Set the running mode to be used.
Setting method
FUNC
➤
2
➤
1
➤
FUNC
Initial value
➤
Set value
0
1 Energy conservation running mode
Fuzzy most suitable acceleration
2
Initial value
NOTE: When the fuzzy most suitable acceleration and deceleration are selected and the load inertia (motor shaft
conversion) is more than about 20 times of that of the individual motor, an overvoltage trip may occur.
If this occurs, reset the mode to the normal running mode. For other precautions, refer to "Precautions for
fuzzy most suitable acceleration and deceleration" of Appendix 1.
Function
Normal running mode
and deceleration mode
Set the running command so as to be inputted to the terminal.
(Set to or .)
Since jogging is a direct input operation and may be easily tripped, set the jogging frequency
to 5 Hz or less.
Setting method
FUNC
.
➤
2
➤
1
➤
.
FUNC
(REV)
(JG)
➤
CM1 FW 8 3
Initial value
➤
2
1
➤
.
NOTE:
No frequency can be set
between 0.01 Hz and 0.09 Hz.
SWFW
SWJG
Operation timing
SWJG
20 msec min
➤
➤
SWFW
Motor
rotation
No jogging operation is performed when the set value is smaller than the start frequency .
➤
Free run
The free run operation is performed immediately after
SWFW is turned OFF.
7-24
Page 65

Contents and display
Extension
function
code
➤
➤
➤
➤
1
2
➤
1
2
FUNC
FUNC
➤
Base
frequency
setting
Maximum
frequency
setting
,,,
,,,
Set the base frequency and maximum frequency.
Setting method
Initial value
Setting example
V
100%
0
60 Hz
f
V
100%
0
60 Hz 120 Hz
f
When the frequency is set so that the base
frequency is larger than the maximum
frequency, the base frequency is forced
to be made equal to the maximum
frequency at the start of running.
Freely setting range
➤
➤
V
100%
(A62) base frequency
and (A63) maximum
frequency: 60 Hz
(A62) base frequency: 60 Hz
(A63) maximum frequency:
120 Hz
NOTE 1:
NOTE 2:
When a frequency more than the base frequency 60 Hz
is used, the motor is not a general purpose motor but
a special motor. Therefore, the maximum applicable
motor set value is different.
When the kW display is the same, the inverter
capacity may be increased.
Set the base frequency according to the specifications
of the motor. When the base frequency is set to less
than 50 Hz, the motor may be burned.
0
400 Hz
f
120 Hz60 Hz30 Hz
(400)
(NOTE 3)
Adjust the relationship between the external frequency command and the inverter output frequency.
Frequency
command
output
frequency
adjust
(O-L, OI-L)
: Voltage command (O-L)
: Current command (OI-L)
This function is factory-set to the appropriate position. If this setting is changed unnecessarily, the
correct relationship between the external frequency command and output frequency is no longer
maintained. This will result in poor control performance. Adjust the setting of this function only
when the output frequency does not conform to the external command.
Adjustment method
Voltage command:
Current command:
Put voltage command (10V of 5V) to O-L terminal, and adjust unit
output frequency comes to maximum.
Put current command (4-20mH) to OI-L terminal, and adjust unit
output frequency comes to maximum.
Maximum
frequency
selection
➤
➤
1
2
FUNC
Select 120 Hz or 400 Hz as the upper limit that can be set in the maximum frequency setting (A63).
➤
➤
Initial value
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
7-25
Page 66

Extension
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
function
code
Selection
of reset
terminal
performance
Contents and display
Possible to select a performance of a release timing of alarm signal when giving reset signal
from [RS] terminal
FUNC
Initial value
➤
➤
2
➤
Set value
FUNC
➤
1
Reset signal
from [RS]
terminal
Alarm
output
Reset signal
from [RS]
terminal
Alarm
output
Performance
➤
➤
These functions are used to set PID control operation gains.
P (Proportional) gain, I (Integral)
gain, D (Differential) gain
Set each gain.
Setting method
P
I 0.0 to 15.0 s
D
Gain adjusting range
0.0 to 5.0
0 to 100.0
.
➤
FUNC
2
1
➤
FUNC
Proportional gain
setting
Integral
gain
setting
Differential
gain setting
PID
control
selection
➤
.
➤
Initial value
➤
2
1
➤
.
This function is used to control the PID functions incorporated in the inverter.
This function is also used to select a feed-back signal input and set a magnification of the integral
gain setting value.
For details of PID control, refer to "Appendix 8 PID Control Functions".
Setting method
FUNC
➤
2
➤
➤
Initial value
1
FUNC
➤
Setting
value
0
1
2
3
4
Feed-back signal
input terminal
Built-in PID function disabled.
Analog current (OI-L)
Analog voltage (O-L)
Analog current (OI-L)
Analog voltage (O-L)
I (Integral) gain
magnification
× 1
× 1
× 10
× 10
Note 1:
Note 2:
Set "0" for the use of a PID optional board.
Do not assign a feed-back signal input and an target frequency command
to the same terminal. If assigned, the PID function will be disabled.
7-26
Page 67

Contents and display
Extension
function
code
This function is used to set a target value level of PID controlling within 0 to 200%.
This function is valid when 0 is set for .
Target
value
setting
method
selection
This function is used to select a method to enter the target value for executing each PID function.
NOTE 1:
NOTE 2:
Set "1" when a PID optional board (J-PI) is used.
The value entered to the OS terminal of J-PI is assumed as the target value.
The target value at set "1" is O-L, OI-L input signal, setting or multispeed
setting.
Set value
Performance
Internal
target
value level
setting
➤
➤
1
➤
FUNC
FUNC
➤
2
Setting method
Initial value
0
1
The target value depends
on the level set value.
The target value is set using
the frequency setting
method.
➤
➤
1
➤
FUNC
FUNC
➤
2
Setting method
Initial value
If an analog voltage is entered as a feedback
value, the feedback voltage (0 to 10V)
corresponds to this target value level
setting (0 to 200%). In other words, if,
when 5V is entered as the target feedback
value of a sensor, it is converted to an
internal target value, set 100% as this
internal target value.
Select whether to start auto tuning as well as a mode. When 1 or 2 is set, auto tuning is started
during the first operation.
Auto
tuning
setting
➤
➤
➤
FUNC
2
Initial value
Motor
data
selection
1
Set value
0
1
2
Function
Auto tuning is not performed.
Normal measurement mode
(The motor runs.)
R1, R2, or L measurement mode
(The motor does not run.)
Initial
value
Select the motor constant used for sensorless vectror control (SLV).
Set value
0
1
2
Data used
Old Hitachi general-
purpose motor data
New Hitachi general
purpose motor data
(ÒThe MotorÓ)
Auto tuning data
Initial
value
(For details of auto tuning, see Appendix 1.)
➤
➤
1
➤
FUNC
FUNC
➤
2
Initial value
➤
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
7-27
Page 68

Extension
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
function
code
Ro-Toption
selection
Contents and display
Unusable
7-28
Page 69

Extension
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
function
code
to
Input
terminal
setting
1 to 8
Contents and display
A terminal function is allocated to each of the input intelligent terminals 1 to 8. When using a
function other than the standard set functions or changing the terminal order, set the function
for each terminal. The minimum input signal acceptance time of the input intelligent terminals is
about 20 ms.
Arrary of codes and intelligent terminals
Code Function name
Input terminal setting 1C 0
Input terminal setting 2
C 1
C 2
Input terminal setting 3
C 3 Input terminal setting 4
C 4 Input terminal setting 5
C 5 Input terminal setting 6
C 6 Input terminal setting 7
C 7 Input terminal setting 8
Setting method
Terminal
rating plate
Initial setting
118
216
35
411
59
613
71
80
PCB terminal array
FM
CM1
PLC
P24
FW
8
7
6
5
4
Input intelligent
terminal section
3
2
1
H
Press the key once for the terminal code to be set.
FUNC
The set values of the terminals which are set at present are displayed. Display the set value
of the terminal to be used from the function list indicated below by pressing the key
2
and and then press the key.
FUNC
The display is returned to the code display and the terminal function is changed.
Enter the set value of the terminal name
FUNC
➤
Setting example: The RS (reset) function is changed to the SFT (treminal software lock) function.
to be used bypressing the keys and .
1
2
➤
FUNC
Input terminal function list
Set value
0
1
2
3
5
6
7
8
9
Abbrevia-
tion
REV
CF1
CF2
CF3
JG
DB
STN
SET
CH1
Function name
Reverse
Multispeed 1
Multispeed 2
Multispeed 3
Jogging
External DC braking
Initialization
2nd function
2-stage acceleration and deceleration
Set value
11
12
13
14
15
16
18
27
28
Abbrevia-
tion
FRS
EXT
USP
CS
SFT
AT
RS
UP
DWN
Function name
Free run
External trip
USP function
Commercial power source switching
Terminal software lock
Analog input voltage/current switching
Reset
Remote operation function, acceleration
Remote operation function, deceleration
1
➤
Precautions for terminal setting
Same terminals cannot be set between and .
When moving a terminal name to another terminal, set another terminal which is not to be
ued at the setting source before inputting the set value to the setting destination and then
select the terminal name which is to be set at the setting destination.
7-29
Page 70

Extension
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
function
code
Contents and display
A terminal function is allocated to each of the output intelligent terminals 11 and 12. When using
a function other than the standard set functions or changing the terminal order, set the function for
each terminal.
Output
terminal
setting
11 and 12
Arrary of codes and intelligent terminals
Code Function name
Output terminal setting 11C10
Output terminal setting 12
C11
Terminal
rating plate
11 0
12 1
Initial
setting
PCB terminal array
CM2
12
11
Input terminal function list
Set value
0
1
2
Abbrevia-
tion
FA1
RUN
OTQ
Function name
Frequency arrival signal
Signal during running
Overtorque signal (Note)
AL2
AL1
AL0
The setting method is the same
as that of the input terminals
to .
NOTE: The torque of the overtorque signal can be set by the remote operator. The initial
values of motoring and regeneration are 100% torque. The overtorque signal can be
used only under the sensorless vector control.
Setting method
Press the key once for the terminal code to be set.
FUNC
The set values of the terminals which are set at present are displayed. Display the set value
of the terminal to be used from the function list indicated below by pressing the key
2
and and then press the key.
FUNC
The display is returned to the code display and the terminal function is changed.
1
Enter the set value of the terminal name
FUNC
to be used by pressing the keys and .
➤
1
2
➤
FUNC
Precautions for terminal setting
Same terminals cannot be set between and .
When moving a terminal name to another terminal, set another terminal which is not to be
ued at the setting source before inputting the set value to the setting destination and then
select the terminal name which is to be set at the setting destination.
➤
7-30
Page 71

Extension
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
function
code
Input
terminal
a and b
contact
setting
Contents and display
The input intelligent terminals 4 to 1 can be changed individually to the a contact or b contact
specification. Select the set value by pressing the keys and by combining the contacts
1
2
a and b with reference to the table indicated below.
Example: When the set value is A: Contact a: Input terminals 3, 1
Contact b: Input terminals 4, 2
Setting method
FUNC
Press the key 10 times.
➤
Select the contact specification with
reference to the table indicated below.
1
FUNC
➤➤
Initial setting
➤
Output
terminal
a and b
contact
setting
Initial value
➤
➤
Set the high
order to 0.
Set value
FEdCbA9876543210
bbbbbbbbaaaaaaaa
4
bbbbaaaabbbbaaaa
3
bbaabbaabbaabbaa
2
Input terminal
babababababababa
1
a: Contact a specification
(Shorted when power
is turned ON)
Contact b specification
b:
(Opened when power
is turned ON)
Input terminal a and b contacts function list
The output ingent terminal 11 and 12 and alarm output terminal can be changed idividually to the
a contact or b contact specification. Select the set value by pressing the keys and by
1
2
combining the contacts a and b with reference to the table indicated below.
Example: When the set value is : Alarm output: Contact b
Terminals 11 and 12: Contact b
Setting method
FUNC
Press the key 3 times.
➤
1
FUNC
➤➤
Initial setting
Initial value
➤
➤
Set the high
order to 0.
Set value
11
12
Output
terminal
Alarm
(NOTE)
76543210
babababa
bbaabbaa
bbbbaaaa
Output terminal code list
➤
Output terminals 11 and 12
a: Contact a specification
b:
NOTE: For details of the Alarm terminal, see page 6-5.
7-31
(Shorted when power
is turned ON)
Contact b specification
(Opened when power
is turned ON)
Page 72

8. PROTECTION FUNCTIONS
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
The J300 series inverters are equipped with protection functions against overcurrent,
overvoltage, and undervoltage which protect the inverter. If the protection functions are
engaged, the output is shut down, motor runs free and holds that condition until it is reset.
Description
Over current
protection
Overload
protection
(NOTE 1)
Braking
resistor overload
Overvoltage
protection
EEPROM error
(NOTE 2)
Undervoltage
protection
CT error Abnormality on built-in CT and the output of the inverter is cut off.
A currrent due to the alternating current CT between the power module
and output terminal {U(T1), V(T2), W(T3)} is detected.
When the motor is restricted or decelerated suddenly, a large current
flows through the inverter and causes a fault. Therefore, when an
abnormal current is detected by the alternating current CT and it exceeds
a specified value, the output is cut off. (An abnormal current is also
detected in the power module. Refer to , , , and .)
When a motor overload is detected by the electronic thermal function, the output
of the inverter is cut off.
When the braking time exceeds the satting by braking duty factor, an
overvoltage the output of the inverter is cut off.
When the converter voltage exceeds a certain level due to regenerative energy from
the motor, this protection function engages, and the output of inverter is cut off.
When the memory built in has problems due to noise or excessive temperature rise,
this protective function engages, and the output of inverter is cut off.
A decrease of the input voltage of an inverter results in improper function of the
control circuit. It also generates motor heat and causes low torque. Output is cut off
when the input voltage goes down to less than 150-160V/300-320V(200/400Vclass).
Contents
Display
Constant
speed
Dec.
Acc.
CPU error
External trip
USP error
Ground fault
protection
Input overvoltage
Instantaneous
power failure
(NOTE 4)
Malfunction or abnormality on built-in CPU and the output of the inverter is cut
off.
An abnormality signal from external equipment cuts off the output of the inverter.
(When external trip function is selected)
It indicates an error when power is turned on while the inverter is being run.
(When USP function is selected)
The inverter is protected by detection of ground faults between the inverter output
and the motor upon power on. There may be the possibility of power module failure.
When the input voltage is higher than the specified value, it is detected 100 seconds
after power is turned on and the output is cut off. However, when a voltage higher
than approx. 250 to 270 V (200V class),
500 to 530 V (400 V class) is inputted, it is higher than the rated value of the part
in use, so that the part may not be protected and damaged.
When an instantaneous power failure for more than 15 ms occurs, the output is cut
off. When the instantaneous power failure time is long, the fault signal is released.
Note that when restart is selected, the equipment restarts when the running
command remains.
8-1
Page 73

It is displayed when the reset signal is kept supplied or an error occurs between the digital operator
and inverter. When one of the keys , , and is pressed, it is recovered.
When it is not recovered, turn power on once again.
Display
Contents
__
1
2
FUNC
Description
Contents
Display
Optional
connection error
An error occurs in the optional connection (connector, etc.).
Option 1
Option 2
Optional
PCB error
An error message outputted from the optional PCB
Option 1
Option 2
Phase failure
protection error
When a phase failure is detected on the receiving side {R(L1), S(L2), T(L3)}
of the inverter, the output is cut off. (NOTE 3)
Power module
protection
The detector which is built in the power module operates.
When the output side of the inverter is shorted or the motor is
restricted, a large current flows through the inverter and causes a
fault. Therefore, when a current in the power module or an
abnormal temperature of the main device is detected and it
exceeds a specified value, the output is cut off.
Constant speed
Deceleration
Acceleration
Stop
If a trip occurs, press the RESET key or short the reset terminal RS-CM1 assigned as a control
circuit terminal after a delay of 10 seconds.
A trip can be cleared by pressing the RESET key or shorting the reset terminal RS-CM1 assigned
as a control circuit terminal. Resetting the power supply cannot clear a trip. (To reset the power supply is
to turn power off and turn it on again after the CHARGE lamp at the upper right corner of the control PC
board goes off.) Check again whether the set data is correct.
Power OFF during motor deceleration may cause an input phase failure error.
The instantaneous ride-thru period of 15ms may be shortend depending on the power supply voltage or load.
When the J-FB is installed, an error is displayed for each factor as shown below.
Encoder line break:
Overspeed:
Positioning error:
Thermistor line break:
Motor overheat:
Malfunction or banormality on built-in CPU of the option:
Other display
It is displayed when a data set value more than 3 digits in length (for example, 1000) is set.
__
It is displayed when power is turned off.
__
There is no trip history available.
__
This is not an abnormal operation because the instantaneous stop restart function is being performed.
(When 1 to 3 is selected by the extension function .)
The autotuning operation terminates normally.
The autotuning operation terminates abnormally.
__
Waiting due to insufficient voltage. After recovery, the original display appears.
__
_
_
_
__
NOTE 1:
NOTE 2:
NOTE 3:
NOTE 4:
NOTE 5:
NOTE 5
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
8-2
Page 74

9. TROUBLESHOOTING
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
9.1 Error Messages and Diagnosis
When the inverter goes wrong, it operates as indicated below. Find the cause and take
contermeasures.
Error Messages and Diagnosis
Circuit breaker (MCB)
Electromagnetic contactor (Mg)
Symptom
Thermal relay (THRY)
Display on the
digital operator
(display on the
LCD of the
remote operator)
Failure alarm relay
Cause
(explanation
of message)
How to reset
Check Countermeasure
(NOTE 1)
E01
(OC. Drive)
E02
(OC. Decel)
E03
(OC. Accel)
●
Overcurrent detected
by the AC CT while
the motor was running
at a constant speed
(overcurrent during
operation)
Overcurrent detected
●
by the AC CT during
motor deceleration
(overcurrent during
deceleration)
Overcurrent detected
●
by the AC CT during
motor acceleration
(overcurrent during
acceleration)
A
Check whether a load was
changed rapidly.
Check whether there is a
shorted output or ground
fault.
A
Check whether the speed
was decreased rapidly.
Check whether there is a
shorted output or ground
fault.
A
Check whether a load was
changed rapidly.
Check whether there is a
shorted output or ground
fault.
Check whether the start
frequency is too high.
Check whether the torque
boost is too high.
Check whether the motor is
locked.
Do not change loads
rapidly.
Check whether the output
lines or motor is shorted.
Set a longer deceleration
time.
Check whether the output
lines or motor is shorted.
Do not change loads
rapidly.
Check whether the output
lines or motor is shorted.
Lower the start frequency.
Lower the torque boost.
Check the motor or loads.
Overloaded inverter
E05
(Over. L)
NOTE 1: How to reset
A: Stop the inverter. Then, connect the <RS> and <CM1> control terminals or press the STOP/RESET key on
the operator.
B: Opeate the circuit breaker and electromagnetic contactor (turn the power on again).
C: Stop the inverter. Then, reset the thermal relay.
●
(operation under an
overload)
A
Check for an overload.
Check whether the
electronic thermal level is
correct. (Check whether the
level has been changed.)
9-1
Lower the load ratio.
Set an appropriate level.
Page 75

Circuit breaker (MCB)
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Electromagnetic contactor (Mg)
Symptom
Thermal relay (THRY)
Display on the
digital operator
(display on the
LCD of the
remote operator)
Failure alarm relay
Cause
(explanation
of message)
How to reset
Check Countermeasure
E06
(OL. BRD)
E07
(Over. V)
E08
(EEPROM)
E09
(Under. V)
●
The regenerative
braking time is longer
by the value set by
BRD%ED.
●
Overvoltage in the DC
smoothing circuit
EEPROM error
●
Defective power
●
supply (insufficient
voltage)
A
Check the braking resistor
use ratio set in A 38 .
A
Check whether the speed
was decreased rapidly.
Check whether the motor
was run from the load side.
Check whether there is a
ground fault.
A
Check whether there is a
large-noise source near the
inverter.
Check whether the ambient
temperature is too high.
A
Check whether the voltage
is lowered.
Check whether the MCB or
Mg has a poor contact.
•
Set a longer deceleration
time.
•
Set a larger operation
duty cycle.
•
Set A 38 to 0.0 .
Set a longer deceleration
time.
Do not use consecutive
regenerative loads.
Check whether the output
lines or motor is shorted.
Move the noise source
away.
Replace the cooling fan.
Check the power supply.
Replace the MCB or Mg.
E10
(CT)
E11
(CPU)
E12
(EXTERNAL)
E13
(USP)
CT error
●
CPU error
●
External trip
●
USP error
●
Check whether 10 or more
instantaneous power
outages within 100 ms
occurred in 10 minutes.
A
Check whether the CT is
defective.
A
Check whether there is a
large-noise source near the
inverter.
Check whether the inverter
is defective.
A
Check whether there was a
defective external unit
when the external trip
function was selected.
A
Check whether power was
turned on while the inverter
was running when the USP
function was selected.
Check the power supply.
Repair the CT.
Move the noise source
away.
Repair the inverter.
Eliminate the error from
the external unit.
Eliminate the error from
the external unit.
9-2
Page 76

Circuit breaker (MCB)
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Electromagnetic contactor (Mg)
Symptom
Thermal relay (THRY)
Display on the
digital operator
(display on the
LCD of the
remote operator)
Failure alarm relay
Cause
(explanation
of message)
How to reset
Check Countermeasure
E14
(GND. Flt)
E15
(OV. SRC)
E16
(Inst. P-F)
E17
(NG. OP1)
E18
(NG. OP2)
E19
(OP1)
Ground fault on the
●
output side of the
inverter
Excessive received
●
voltage
Defective power
●
supply (instantaneous
power outage)
Incorrectly connected
●
option-1 PC board
Incorrectly connected
●
option-2 PC board
Defective option-1 PC
●
board
Check the wiring between the
A
inverter and motor and also
check the motor for a ground
fault. (Use a megger.)
Check whether an
A
excessive voltage was
received during an
operation other than
deceleration.
Check whether the voltage
A
is lowered.
Check whether the MCB or
Mg has a poor contact.
Check the connectors and
A
other connections for
abnormal conditions.
Check the connectors and
A
other connections for
abnormal conditions.
Refer to the instruction
A
manual.
Correct the portions having
a ground fault.
•
Lower the voltage to be
received.
•
Reduces fluctuations of
the received voltage.
•
Install an AC reactor on
the input side.
Restore the power supply
to normal.
Replace the MCB or Mg.
Repair the defective
connections.
Repair the defective
connections.
Defective option-2 PC
E20
(OP2)
E24
(PH. Fail)
E31
(PM. Drive)
E32
(PM. Decel)
NOTE 1: The failures detectable in the power module are overcurrents, excessively hot main devices, and insufficient
voltages from the gate circuit power supply.
●
board
Defective power
●
supply (missing phase)
(NOTE 1) Failure detected
●
by a detector in the power
module while the motor
was running at a constant
speed, or excessive temperature rise in the inverter
(NOTE 1) Failure detected
●
by a detector in the power
module during motor
deceleration, or excessive
temperature rise in the
inverter
Refer to the instruction
A
manual.
Check the power supply
A
connections for abnormal
conditions.
Check whether the MCB or
Mg has a poor contact.
Check whether a load was
A
changed rapidly.
Check whether there is a
shorted output or ground
fault.
Check whether the speed
A
was decreased rapidly.
Check whether there is a
shorted output or ground
fault.
Repair the abnormal
portions.
Replace the MCB or Mg.
Do not change loads
rapidly.
Check whether the output
lines or motor is shorted.
Set a longer deceleration
time.
Check whether the output
lines or motor is shorted.
9-3
Page 77

Circuit breaker (MCB)
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Electromagnetic contactor (Mg)
Symptom
Thermal relay (THRY)
Display on the
digital operator
(display on the
LCD of the
remote operator)
Failure alarm relay
Cause
(explanation
of message)
How to reset
Check Countermeasure
E33
(PM. Accel)
E34
(PM. ERR)
(NOTE 1)
●
Failure detected by a
detector in the power
module during motor
acceleration, or
excessive temperature
rise in the inverter
(NOTE 1)
●
Failure detected by a
detector in the power
module while the motor
was stopping, or
excessive temperature
rise in the inverter
Check whether the speed was
A
increased rapidly.
Check whether a load was
changed rapidly.
Check whether there is a shorted
output or ground fault.
Check whether the start
frequency is too high.
Check whether the torque
boost is too high.
Check whether the motor is
locked.
Check whether the
A
installation is vertical and the
wall is a nonflammable wall
such as an iron plate.
Check whether the cooling fan
is running and the ambient
temperature is too high.
Check the internal power
supply.
Set a longer acceleration
time.
Do not change loads rapidly.
Check whether the output
lines or motor is shorted.
Lower the start frequency.
Lower the torque boost.
Check the motor or loads.
Check the installation.
Replace the cooling fan.
Repair the internal power
supply.
E60
(OP1 0)
to
Defective J-FB PC
●
board
Check the main devices.
A
Refer to the manual supplied
with the J-FB PC board.
Repair main devices.
E67
(OP1 7)
E70
(OP2 0)
to
Defective J-FB PC
●
board
A
Refer to the manual supplied
with the J-FB PC board.
E77
(OP2 7)
NOTE 1: The failures detectable in the power module are overcurrents, excessively hot main devices, and insufficient
voltages from the gate circuit power supply.
9-4
Page 78

Circuit breaker (MCB)
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Electromagnetic contactor (Mg)
Symptom
Thermal relay (THRY)
Display on the
digital operator
(display on the
LCD of the
remote operator)
Failure alarm relay
Cause
(explanation
of message)
How to reset
Check Countermeasure
●
●
●
—
—
—
—
—
Power outage
—
—
—
Check for an overload.
C
Check whether the thermal
relay is set to an appropriate
value.
Check whether there is a
B
short or ground fault in the
power supply.
Check whether the MCB
capacity is sufficient.
Check whether the inverter
module or converter module
is defective.
Check for a power outage.
B
Check whether the MCB or
Mg has a poor contact.
Lower the load ratio.
Set the thermal relay to an
appropriate value.
Remove the short or ground
fault.
Increase the MCB capacity.
Repair the inverter module or
converter module.
Restore the power supply to
normal.
Replace the MCB or Mg.
9-5
Page 79

9.2 Trouble shooting
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Symptom Probable cause Countermeasure
The
motor
will not
run.
The inverter
outputs
U(T1), V(T2)
and W(T3)
are not
supplying
voltage.
• Is power being supplied to terminals
R(L1), S(L2) and T(L3)?
If it is, the POWER lamp should be on.
• Is the display E ?
**
• Is the operation instruction RUN ON?
• Is terminal FW (or REV) connected to
terminal CM1?
• Has the frequency setter been turned on
by pushing key and then
2
key.
FUNC
1
• Are the printed-circuit board terminals
H, O and L connected to
the potentiometer?
• Are the terminals connected to the
external and internal interface power
source the terminal mode is selected?
• Has RS/FRS been left ON?
• Is the mode key setting correct?
• Check terminals R(L1), S(L2), T(L3), U(T1),
V(T2), and W(T3).
• Turn on the power supply.
• Press and check the content.
2
1
Then press the reset key.
• Set to ON.
• Connect terminal CM1 to terminal FW
(or REV) on the printed-circuit board.
(When the terminal mode is selected.)
• Push down keys and set.
• When terminal mode is selected, connect the
potentiometer to H, O, and L, and then set.
• In the case of the internal interface power
source, short the terminals P24 and PLC or
CM1 and PLC.
• In the case of the external interface power
source, turn the PLC terminal on.
• Release reset.
• Contact FRS.
• Read the explanation of the function mode
once again. (Page 7-12) F9 frequency/run
commanding method
The
direction
of the
motor is
reversed.
Inverter
outputs
U(T1), V(T2)
and W(T3)
are supplying
voltage.
The optional
remote
operator is
used.
(copy unit)
• Has the motor seized or is the load too
great?
• Are the remote operator and equipment
body switched coorrectly ?
• Is the setting of the DIP switch on the
back of the remote operator correct ?
• Are the connections of output terminals
U(T1), V(T2) and W(T3) correct?
• Is the phase sequence of the motor
forward or reverse in respect to U(T1),
V(T2) and W(T3)?
• Are the terminals on the printed-circuit
board correct?
• Release seizure or lighten the load.
• Test the motor independently.
• Check the operation of the optional remote
operator. (copy unit)
12 34
ON
OFF
1: OFF
2: ON (Same as VWA, J100)
• Make the connections according to the phase
sequence of the motor. (In general, forward
should be in the sequence: U(T1), V(T2)
and W(T3).)
• Short the FW terminal for forward rotation or
the intelligent input terminal 8 (the intelligent
input terminal 8 is allocated to run command
REV by initialization at factory before
shipment) for reverse rotation to the CM1
terminal (Sink type).
9-6
Page 80

Symptom Probable cause Countermeasure
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
The rpm
of the
motor
will not
increase.
The rpm
of the
motor
does not
match the
inverter.
The data
is
incorrect.
The data is
returned to
the initial
setting.
The data has
not changed.
After checking the wiring of
Replace the frequency setter.
the frequency setter, the rpm still
does not increase when the setter
is turned.
Are terminals 7 and CM1, terminal 6
and CM1 ON (Sink type)?
Turn off terminal 7 and 6. (When the
frequency and multistage speed are fixed at
a given frequency, the speed potentiometer
will be invalid.)
Is the load too great? Decrease the load.
When the load is too great, the limiting
function will be activated, so that
the rotational speed will be lower than
the setting.
Is the maximum frequency setting
Check the speed-change ratio.
correct?
Are the number of motor poles,
the gear ratio, and pulley ratio correct?
The STN terminal is turned ON and the
power is turned on.
The input terminals 1 to 5 are turned
Turn the STN terminal OFF.
Input the data again.
Replace the logic PCB.
ON and then power is turned on.
Was the power turned off without
pushing the key after the data
FUNC
Input the data and push the key once.
FUNC
The data
is not
changed.
Data copied
by the copy
unit
is not input.
Frequency
setting can
not be
changed.
Run and
stop can not
be done.
The data can
not be
changed.
2
was changed with keys.
1
The data is memorized upon power off.
Is the time from power OFF to ON less
than six seconds?
Is the power turned off for five seconds
or more after the display changed
from REMT to INV.
(HRW-OJ)
The change of the terminal mode and
digital operator mode were correct?
Is the input terminal SFT ON ?
Is the software lock mode set at MD2
or MD3 ?
Note: If software lock is ON because of
use with an explosion proof motor,
do not release the software locks.
Take six seconds or more when turning power
OFF and ON after changing the data.
Copy again and turn the power off five
seconds or more after copying.
Confirm the change in setting mode.
Turn the SFT terminal OFF.
Turn the switch OFF.
9-7
Page 81

Symptom Probable cause Countermeasure
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Overload
(Electronic
thermal
trip)
(Low
frequency
zone)
The input
voltage
trips.
Is the torque boost too high ?
Do the electronic thermal characteristics
match the set characteristics of the
motor ?
Is the input voltage high ?
Is the equipment stopped with the
inverter DC voltage increased after
sudden deceleration ?
Decrease the torque boost.
Reset the electronic thermal characteristics
and level.
Lower the input voltage.
Set a deceleration time which is a little longer.
Increase the AVR set value above the current
input voltage and lower the V gain by
the ratio.
9-8
Page 82

10. MAINTENANCE AND INSPECTION
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
10.1 Maintenance and Inspection Precautions
WARNING
* Be sure to turn off the power supply during maintenance and inspection.
* After the power supply has been turned off, you must always wait 10 minutes so that
DC bus capacitors can discharge then start maintenance and inspection after the
CHARGE lamp on the printed-circuit board has gone out. (Immediately after the lamp
has gone out, there will be a residual voltage of about 50 V DC in the DC bus
intermediate circuit.)
Perform the work after the CHARGE lamp has stopped flickering.
* Make sure that only qualified persons will perform maintenance, inspection and part
replacement. (Before starting the work, remove metallic objects from your person
(wristwatch, bracelet, etc.)
(Be sure to use tools protected with insulation.)
Otherwise, there is a danger of electric shock and/or injury.
CAUTION
* When removing connectors, never pull the wires. (Wires for cooling fan and thermal
relay)
Otherwise, there is a danger of fire due to wire breakage and/or injury.
• General precautions
Always keep the unit clean so that dust or other foreign matter does not enter the inverter.
Take special care in regard to breaking lines and connection mistakes. Firmly connect
terminals and connectors. Keep electronic equipment away from moisture and oil. Dust,
steel filings and other foreign matter can damage insulation, causing unexpected accidents,
so take special care.
10.2 Inspection Items
(1) Daily inspection
(2) Periodic inspection (Approximately once a year) See 10-3.
(3) Insulation resistance tests, withstand voltage tests
10-1
Page 83

Conduct these tests by short-circuiting the terminals as shown below, and by following the
Applied
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
conditions described.
• In regard to insulation resistance tests, measure the terminals below and the grounding at
500 VDC, and make sure that 5 Megohms or greater is indicated.
• Do not perform the withstand voltage test. When it should be done,
in regard to withstand voltage tests, supply the terminals below and the grounding with
1500 VAC (200 V class), 2000 VAC (400 V class) for one minute, and make sure that
there are no abnormalities.
• Do not conduct insulation resistance tests and withstand voltage tests for terminals other
than those indicated below.
• Increase or decrease the applied voltage for the withstand voltage test slowly and turn the
equipment 0 V again.
Bad example
(L1) (L2) (L3) (RB) (+) (-) (T1) (T2) (T3)
R
Megohm-meter
P
RBST UVW
N
voltage
Good example
Time Time
0.1 sec. or more 0.1 sec. or more
NOTE 1: If the inverter is used under high temperature and heavy load conditions, its operat-
ing life will be significantly reduced.
NOTE 2: If the inverter has been stored for three years or more, apply the following condi-
tions.
1) Apply 80% of the rated voltage of the capacitor for 1 hour at normal temperature.
2) Increase the voltage to 90% and apply it for 1 hour.
3) Apply the rated voltage for 5 hours.
NOTE 3: Precautions in handling printed-circuit boards.
When maintenance and inspection of printed-circuit boards is necessary, be sure to
follow the precautions below.
• Prevent damage caused by static electricity. The IGBT of the inverter module,
the MCUs and ICs on a printed-circuit board can be destroyed by static electricity, so be sure to ground work benches, soldering irons, and yourself before
working on a printed-circuit board.
10-2
Page 84

Daily Inspection and Periodic Inspection (1/3)
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
10-3
Inspection
location
Overall Ambient
Main
circuit
Inspection item Inspection content Inspection method Criteria
environment
Devices overall Check for abnormal
Power supply
voltage
Overall
Inspection cycle
Periodic
Daily
Check ambient temperature,
humidity, dust, corrosive
gases, oil mist, etc.
Visual and aural
vibrations and noise.
Check the input line voltage. Measure the voltage
(1) Insulation resistance test
(between main circuit
terminals and grounding
terminal)
(2) Check installation for
looseness.
(3) Check for evidence of
overheating in the various
components.
(4) Clean.
inspection.
between inverter
terminals R(L1),
S(L2) and T(L3).
(1) Increase tighting
Making a check
on the terque is
needed for the
increase tighten ing of the modules
such as a power
module, diode
module. Do not
execute increse
tightening with
no torque gauge
prepared.
(2) Tighten.
(3) Visual
inspection.
Ambient temperature
between -10 to +50˚C;
no icing.
Ambient humidity 20 to
90%; no dew condensation.
No abnormalities.
200 to 220 V, 50 Hz
200 to 230 V, 60 Hz
380 to 415 V, 50 Hz
400 to 460 V, 60 Hz
No abnormalities in (1) and
(2).
Tightening torque (kgf.cm)
• M3: 8 - 10
• M4: 12 - 15
• M5: 20 - 25
• M6: 25 - 30
• M8: 100 - 135
• M10: 150 - 200
Tightening torque for IPM
and Diode modules
(kgf.cm)
• M4: 10-15
• M5: 15-20
• M6: 20-25
Standard
replacement
period
__
__
Instruments
Thermometer
Hygrometer
Tester
500 V class
Megohm meter
Page 85

Daily Inspection and Periodic Inspection (2/3)
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
10-4
Inspection
location
Main
circuit
Inspection item Inspection content Inspection method Criteria
Terminal board No damage. Visual inspection No abnormalities.
Smoothing
capacitor
Relays (1) Check for stuttering noise
Resistors (1) Check for large cracks
Cooling fan (1) Check for abnormal
(1) Check for leaking
(2) Check for swelling
when operating
or changes in color
vibrations and noise
(2) Check for dust
Inspection cycle
Regularly
Periodic
Visual inspection of
(1) and (2).
(1) Aural inspec tion.
(1) Visual inspection. (1) No abnormalities.
(1) Rotate manually
with power off
and increase
tightening
(2) Visual inspection
No abnormalities in (1) and
(2).
(1) No abnormalities.
(1) Smooth rotation
(2) No abnormality
Standard
replacement
period
___ ___
5 years
(Note 1)
5 years
___
2 - 3 years
Instruments
___
___
___
___
Page 86

Daily Inspection and Periodic Inspection (3/3)
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
10-5
Inspection
location
Control
circuit
Display Digital operation
Inspection item Inspection content Inspection method Criteria
Operation check (1) Check the balance of the
Component
check,
including
printedcircuit
boards
panel
Overall (1) No abnormal odor or
Capacitor No fluid leakage or
output voltage of
individual phases when
operating the inverter
independently.
(2) Conduct a sequence
protection operation test,
and make sure that there
are no errors in the protec tion and display circuits.
changes in color.
(2) No significant corrosion.
deformation.
(1) No illegible display
(2) No lack of character
Inspection cycle
Regularly
Periodic
Standard
replacement
period
(1) Measure the
voltage between
the phases of
inverter output
terminals U, V,
and W.
(2) Simulate
operation of the
inverter protect ion circuit.
Visual inspection No abnormalities
Visual inspection 5 years
Visual inspection Normal operation
(1) Within 2% voltage
difference between
phases.
(2) Operate without any
abnormalities.
No abnormalities
Display can be read out.
__
___
(Note 1)
7 years
Instruments
___
___
___
___
(3) No blown out LEDs
Note 1. The life of the capacitor is affected by the ambient temperature. Refer to the ambient temperature - capaciitor life curve shown in Appendix 5.
Note 2. The inverter must be cleaned periodically. If dust accumulates on the fan and heat sink, it can cause overheating of the inverter.
Page 87

10.3 Measurement Method for I/O Voltage, Current, and Power
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
General measuring instruments for I/O voltage, current, and power are indicated below. The
voltage to be measured is the fundamental wave effective voltage and the power to be measured is the total effective value.
R
(L1)
Power
supply
S
(L2)
T
(L3)
Measurement
item
Supply voltage
E
1
Supply current
I
1
Supply power
W
1
I
R
E
R
I
S
E
S
T
I
E
T
Table 3 Parts to be measured
Parts to be
measured
Between R and S, S and
T, T and R (E
R, S, T (I
Between R and S, S and
T (W
11
R
)(IS)(IT)
)(W12)
R
)(ES)(ET)
R
W
11
General
S
purpose
U
V
I
U
E
I
V
inverter
W
12
T
W
E
I
W
E
Measuring instrument Remarks
Moving-iron type
voltmeter or rectifier
type voltmeter
Moving-iron type
ammeter
Electrodynamic type
wattmeter
Fundamental
wave effective
value
Total effective
value
Total effective
value
U-V
V-W
W-V
U(T1)
W
01
V
Motor
(T2)
W
02
W
(T3)
Reference
value
Supply power
factor
Pf
1
Output voltage
E
0
Output current
I
0
Output power
W
0
Output power
factor
Pf
0
Calculate the supply power factor from the measured supply voltage, E
supply current I
= × 100 (%)
Pf
1
Between U and V, V and
W, W and U
(E
U
)(EV)(EW)
U, V, W (I
Between U and V, V
and W
01
)(W02)
(W
and supply power W1.
1
W
1
3 E
1I1
Rectifier type
voltmeter
U
)(IV)(IW) Moving-iron type
ammeter
Electronic type
wattmeter
Total effective
value
Total effective
value
Total effective
value
,
1
Calculate the output power factor from the output voltage E, output current I,
and output power W.
W
3 E
0
0I0
Pf0= × 100(%)
NOTE 1: Use a meter indicating a fundamental wave effective value for voltage, and meters
indicating total effective values for current and power.
NOTE 2: The inverter output waveform is a distorted wave, and low frequencys may cause
errors. However, the measuring instruments and methods indicated above provide
comparatively accurate values.
NOTE 3: A tester (general purpose) may not be suited often to measurement of a distorted
wave.
10-6
Page 88

Measurement method for output voltage
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
(L1)
R
(L2)
S
(L3)
T
Fundamental wave effective value:
VAC=1.1×VDC
(T1)
U
(T2)
V
(T3)
W
Motor
Diode 600 V 0.1 A min.
(200 V class)
1000 V 0.1 A min.
(400 V class)
220 kΩ
2W
➤
VDC
300 V (200 V class)
600 V (400 V class)
moving-coil type
10-7
Page 89

11. STANDARD SPECIFICATIONS
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
11.1 Common Standarsd Specifications
Item
Input voltage
Model Name (Type)
Enclosure (NOTE 1)
Rated AC input power supply (V)
Rated output voltage (V) (NOTE 2)
Output frequency range (NOTE 3)
Frequency accuracy
Frequency setting resolution
Voltage/frequency characteristics
Acceleration/deceleration time
Starting torque (NOTE 4)
Description
200 V class 400 V class
1100
055LF075LF110LF150LF220LF300LF370LF450LF550LF055HF075HF110HF150
HF
Semienclosed
type (IP20)
Three-phase (3 wires), 200 to 220 or
200 to 230 V±10%, 50 or 60 Hz±5%
Three-phase, 200 to 230 V
(Corresponding to the input voltage)
Open type (IP00)
Semienclosed
type (IP20)
Three-phase (3 wires), 380 to 415 or
400 to 460 V±10%, 50 or 60 Hz±5%
Three-phase, 380 to 460 V
(Corresponding to the input voltage)
220
HF
300HF370
HF
750
550
450
HF
HF
HF
Open type (IP00)
900
HF
1320
HF
0.1 to 400 Hz
Digital command ±0.01% and analog command ±0.1% for the maximum
frequency command
Digital setting: 0.01 Hz/60 Hz, Analog setting: Maximum frequency/1000
V/f variable, high start torque, standard starting torque (constant torque,
reduced torque)
0.01 to 3000 seconds, acceleration and deceleration individually set
150% or more (1 Hz)
HF
1600
HF
2200
HF
Braking
torque
Input
signals
Dynamic braking
(NOTE 5)
Feedback to capacitor
Dynamic braking using
external resistor or unit
(BRD)
DC injection braking
Frequency
Digital operator
setting
External signals
Forward/
reverse
run,
stop
Digital operator
External signals FW (forward run command)/stop
Intelligent input terminal
About
20%
Braking resistor optional for 055 and
075L, use braking unit (BRD) for
220 to 550L.
About 10 to 20% About 20%
Braking resistor optional for 055 and
075H, use braking unit (BRD) for
220 to 2200H.
About 10 to 15%
Operated at the DC braking frequency or by external input
Set by and
1
2
2 W 500 Ω to 2 kΩ potentiometer, 0 to 5 VDC (nominal),
0 to 10 VDC (nominal) (input impedance 30 kΩ), 4 to 20 mA (nominal)
(input impedance 250 Ω)
RUN / STOP (Only for forward run or reverse run, the function mode
should be switched.)
REV (reverse run command), FRS (free run stop command), CF1 to CF3
(multistage speed setting), USP (USP function), JG (jogging command),
CH1 (2-stage acceleration and deceleration), DB (external DB command),
RS(reset input), STN (initialization), SFT (software lock), AT (current input
selection), CS (commercial power source switching), SET (2nd setting
selection), EXT (external trip), UP (remote control, acceleration),
DOWN (remote control, deceleration)
Output
Intelligent output terminal FA1 (speed arrival signal), RUN (signal during run), OTQ (overtorque signal)
signals
Analog output frequency monitor (0 to 10 VDC full scale,1mA max.), digital
Frequency monitoring
frequency signal by remote operator, analog current monitor, analog torque
monitor
11-1
Page 90

Item Description
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Input voltage
Model Name (Type)
200 V class
055LF075LF110LF150LF220LF300LF370LF450LF550LF055HF075HF110HF150
HF
400 V class
300HF370
220
HF
HF
450
HF
550
HF
750
HF
900
HF
1100
HF
1320
HF
1600
HF
Fault alarm contact (AL0-AL1) OFF when an inverter alarm occurs
AVR function, data batch setting, V/F characteristic switching, curve
Other characteristics
acceleration and deceleration, upper and lower limiters, 8-stage speed,
start frequency fine adjustment, trip history monitor (up to three times
stored), fuzzeleration and deceleration, autotuning, etc.
Protection functions
Overcurrent, overvoltage, undervoltage, electronic thermal, abnormal
temperature, grounding current, overload restriction, etc.
Vibrations (NOTE 6)
5.9 m/S2 (0.6G) 10 - 55 Hz for 0550 to 075L /H
2.0 m/S2 (0.2G) 10 - 55 Hz for 220 to 550L and 220 to 1100H
General
specifi-
Operation location Altitude of 1000 m or less, indoors (free of corrosive gas and dust)
cations
Paint color
Regel gray No. 1 (Munsell 9.1Y 7.4/0.6 semigloss, cooling fan of aluminum
ground color)
Options Remote operator, copy unit, cable for digital operator, braking resistor, reactor
for improving power factor, noise filter for inverter, fitting for conduit tube
connection, fitting for removing cooling fins
Estimated mass (kg) 7.5
7.5 13 13 21 37 37 51 51 7.57.513 13 21 3636 46 46
70
70
80
130
130
2200
HF
130
NOTE 1:
NOTE 2:
NOTE 3:
NOTE 4:
NOTE 5:
NOTE 6:
Protective structure is based upon JEM1030-1977.
The output voltage will decrease if input voltage decreases.
Confirm with the motor manufacturer the motors maximum rpm when using a motor
running at frequency higher than 50/60 Hz.
When using the standard four-pole motor, select the high start torque (SLV) at the rated
voltage (200 V class: 200, 220, 230 V; 400 V calss:400, 415, 440, 460 V).
(For details, contact the dealer you purchased the product.)
Torque will be reduced when the base frequency exceeds 50/60 Hz.
The dynamic braking torque is about 70% for 055LF or about 60% for 075LF when one
of the 200 V class RB1 to RB3 (17Ω or more) is used at the shorttime rating or about
60% for 055HF or about 50% for 075HF when the 400 V class RB2 × 2 series
(70 Ω or more) is used.
According to the test method shown is JIS C 0911 (1984).
11-2
Page 91

11.2 Individual Specification (USA version (J300- LFU, HFU))
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Item
Input voltage
Model Name (Type)
Applicable
motor rating
Constant torque
(4P, max.
kW/HP)
(NOTE 1)
Variable torque
(NOTE 2)
Continuous
output
(kVA)
Constant
torque
Variable
torque
200 V
230 V
380 V
400 V
460 V
200 V
230 V
380 V
Description
200 V class 400 V class
055LF075LF110LF150LF220LF300LF370LF450LF550LF055HF075HF110HF150
5.5/
7.5/
15/
5.5/
7.5/1011/1515/
7.5
7.5/1011/1515/2022/3030/4037/5045/6055/7575/
20
22/
30
30/
40
37/5045/
60
55/
75
100
7.5
7.5/
10
11/
10
15
11/1515/
20
8.3 11 16 22 33 42 50 63 76
10 13 18 25 38 48 58 73 88
8.6
10.5
15 21 32 38 49 59 72
9.0 11 16 22 33 40 52 6276
9 12182537475671
11 14 21 29 43 54 65 82
10.412.7
86
99
9.6
18 25 38 466072
11.8
17 24 36 43 55 66 82
300HF370
220
HF
HF
22/3030/
20
40
22/3030/4037/5045/
HF
37/
50
60
450
HF
45/
60
55/
75
750
550
HF
HF
75/
55/
100
75
90/
75/
120
100
89
94
108124166
88
103
1100
900
HF
HF
110/
90/
150
120
110/
132/
150
200
103 137
108144
118
158
1320
1600
HF
HF
132/
160/
200
250
160/
220/
250
300
158 207
166 218
191 251
199 250
2200
HF
220/
300
260/
350
250
263
303
286
Rated output
current (A)
Carrier
frequency
(Hz)
Overload
current
capacity
General
specifications
NOTE 1:
NOTE 2:
NOTE 3:
NOTE 4:
NOTE 5:
Constant torque
Variable torque
(NOTE 3)
Constant torque
Variable torque
(NOTE 3)
Constant torque
Variable torque
(NOTE 3)
Ambient
temperature
CT
(NOTE 4)
VT
(NOTE 5)
Humidity
400 V
460 V
24 32 46 64 95
27 36 52 72
16
107
12
10.112.5
11.614.3
121145182 220
136 163 205 248 14.6
13 16 23 32 48 58 75 90
10 616 12
10
6
150%, for 1 minute
125%, for 1 minute
-10 to 50 degree C
-10 to 40 degree C
20 to 90% RH
18 25 37 45587086
21 29 43 52678099
18 26 36 54 65 84
16
16
12
12
10 6
10
110
101124
6
108
124
135
156180 240
118
143
156
3
2
209 263
166
191
241 303
208
240
302 380 435
315
2
2
The applicable motor is a Hitachi standard four-pole motor. When using another motor,
make sure that the rated motor current does not exceed the rated inverter current.
Applicable motor rating at variable torque is valid with the condition that output current
does not exceed the rating at variable torque.
When a V/F pattern (VP1, VP2, or VP3) for variable torque is selected (
for the digital operator or F04 for the remote operator), the setting data are automatically
changed by the inverter.
CT: Constant torque.
VT: Variable torque.
11-3
301
347
380
Page 92

12. FUNCTIONS WHEN USING THE OPTIONAL REMOTE OPERATOR
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
12.1 Connecting the remote operator
Be sure to turn the power supply off when connecting the connector.
High performance remote operator (HOP)
High performance copy unit (HRW)
Digital operator
Remote operator (DOP)
Copy unit (DRW)
(1) Insert the connector straight into the remote operator and inverter unit
printed-circuit board.
(2) Turn on the power supply.
(3) Make sure that the liquid crystal display of the remote operator is lit.
When the power supply of the inverter is turned on, FS000.0..... of the monitoring mode
will be displayed. If, however, any of the following is displayed when the inverter is
turned off, they will be displayed when power is turned on again.
• Frequency setting, multi-speed setting or other frequency displays, motor rotational
speed display, frequency conversion display, or output current display.
NOTE: When conflicting data is set, a warning WARN..... will be displayed. For 6 seconds
thereafter, do not perform the key operation, reset operation, running operation, power-OFF
operation. (Otherwise, a communication error may occur in the operator.)
12-1
Page 93

NOTE: See the operation manual of the remote operator for instructions.
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
In addition, see the following pages for details on its various functions. Set the dip-switches
mounted on the backside of the remote operator and copy unit as below.
When turned ON,
read out is inhibited.
If pushing down key with ON,
BPS
1234
1234
ON
OFF
"RD LOCK" is displayed.
Set as below (When setting status do not match model,
the correct function can not be attained.)
Switch
12
Model
J300 series
(Same as VWA, J100)
OFF ON
READ
Invalid
12-2
Page 94

12.2 Monitor mode
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Monitor mode list when the remote operator (DOP) and copy unit (DRW) are used
• Monitor mode initial values and display contents
Initial display contents, initialization, and change ranges are displayed
in the table indicated below.
Display
sequence
Monitor name Display content Initial value
Setting
range
: Setting can be changed
Y
during operation
: Setting can not be changed
N
during operation
: Display only
Setting and
change are
possible?
Remarks
1
Frequency setting
and output
frequency
Multistage-speed
setting and output frequency
Jogging frequency
setting
Expansion
multistage speed
Acceleration time
2
setting
Deceleration time
3
setting
Frequency setting
4
command
Operation command
5
1 2
FS0000.0 0.0Hz
1 2
TM 0.0 0.0Hz
1S0000.0 0.0Hz
2S0000.0 0.0Hz
3S0000.0 0.0Hz
JG0000.0 0.0Hz
4S0000.0 0.0Hz
7S0000.0 0.0Hz
ACC1 0030.00S
DEC1 0030.00S
F-SET-SELECT REM
F/R-SELECT REM
0.0 Hz
0.0 Hz
0.0 Hz
1.0 Hz
0.0 Hz
30.0S
30.0S
TRM
TRM
0 to 120
(400)
0 to 9.9
0 to 120
(400)
0.01 to
3000.00
0.01 to
3000.00
TRM/REM
OP1/OP2
TRM/REM
OP1/OP2
(1) displays the setting.
Y
(2) displays the output.
• is displayed
when run
instruction is ON.
F: Forward run
R: Reverse run
A trip occurs easily
Y
at 5 Hz or more.
• Valid when the mult istage speed terminal
3 is selected.
• The multistage speed
are displayed when
Y
the input terminal is
connected.
• For terminal setting,
refer to F-34 "Input
terminal setting".
Y
Y
REM: Setting from
N
the remote operator
TRM: Setting from the
N
inverter terminal
Motor pole count
6
setting and revolution speed monitor
Frequency converted
7
value setting and
converted value
RPM 4P 0RPM
/Hz01.0 0.00
4P
1.0
2 to 48
0 to 99.9
Y
Y
monitor
Current monitor
8
Torque monitor
9
10
NOTE 1: The terminal output when the digital output frequency monitor is set at the FM terminal of the control
Manual torque
boost adjustment
circuit is the "output frequency × frequency converted value". The upper limit of output is 3.6 kHz.
1 2
Im 0.0 A 0.0%
Torque 0%
V-Boost code <11>
11
0 to 99
Y
12-3
Synchronized speed
display
The arithmetic value
by the frequency
converted value is
displayed. (NOTE 1)
The (1) section depends
on the INV rated
current.
The (2) section
displays the rate to the
rated output current.
Page 95

Display
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
sequence
Monitor name Display content Remarks
Initial value
Setting
range
Setting and
change are
possible?
11
12
13
14
15
Display
sequence
16
17
Manual torque boost
frequency adjustment
Output voltage
gain adjustment
Jogging frequency
adjustment
Analog meter
adjustment
Terminal input
status monitor
V-Boost F 10.0%
V-Gain 100%
Jogging 1.00 Hz
ADJ 172
TERM LLLLLLLLL
Terminal
FW 7 5 3 1
• • •
8 6 4 2
10.0%
100%
1.0 Hz
172
0 to 50.0
20 to 100
0 to 9.99
0 to 250
When the terminal is ON: H
When the terminal is OFF: L
Y
Y
A trip occurs easily
Y
at 5 Hz or more.
Y
Monitor name Display content RemarksTrip cause, contents
Warning monitor Normal state
Alarm display Not occurred
Trip monitor
WARN #
WARN F1w>Fs
ERR1 #
ERR1 OVER. V
ERR1 31.0 Hz
ERR1 12.5 A
ERR1 787.0 Vdc
ERR1 RUN 0Y 10D
Frequency setting error
<Trip cause 1>
Trip cause
Output frequency when tripped
Output current when tripped
Voltage between P and N when
tripped
Cumulative years and months
when tripped
When the equipment is
normal, # is displayed.
When a value which is
larger than the upper or
smaller than the lower
limit is set, a warning
is displayed.
The message is
displayed on a priority
basis when an alarm
occurs.
Trip cause
Overvoltage trip
18
19
Total alarm count
Trip history monitor
Last trip contents
Contents of last
trip but one
ERROR COUNT 0
ERROR COUNT 25
ERR2 #
ERR2 OC.Accel
ERR2 5.0 Hz
ERR2 20.1 A
ERR2 580.0 Vdc
ERR2 RUN 0Y 7D
ERR3 #
ERR3 EXTERNAL
ERR3 0.0 Hz
ERR3 0.0 A
ERR3 560.0 Vdc
ERR3 RUN 0Y 1D
Total trip count
<Trip cause 2>
Trip cause
Output frequency when tripped
Output current when tripped
Voltage between P and N when
tripped
Cumulative years and months
when tripped
<Trip cause 3>
Trip cause
Output frequency when tripped
Output current when tripped
Voltage between P and N when
tripped
Cumulative years and months
when tripped
Not occurred
Not occurred
Trip cause
Overcurrent trip for
acceleration
Not occurred
Trip cause
External trip
12-4
Page 96

12.3 Function mode
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Function mode list when the remote operator is used
• Function mode initial values and display contents
Initial display contents, initialization, and change ranges are displayed in the table
indicated below.
Display
sequence
1 F-00 Base F-BASE 0060 Hz 60 Hz 30 to 120 (400) • When 120 Hz is switched to
2 F-01 Maximum F-MAX 0060 Hz 60 Hz 30 to 120 (400)
3 F-02 Start Fmin 0.50 Hz 0.5 Hz 0.1 to 9.9 • The equipment starts running
4 F-03 Motor input AVR AC 460 V 230/460 200,215,220,230 • The motor input voltage is set.
5 F-04 Control CONTROL VC V C VC, VP1, VP2, • VC, VP1, VP2, VP3:
6 F-05 Autotuning AUX AUTO NOR NOR NOR/AUT/NRT • At the first running after
NOTE 1: The motor constants R1, R2, L, M, J, Kp, Ti, and KPP vary with the capacity.
(Function mode 1) (Function mode 2)
Function Function Initialization display Initialization
No. name contents
frequency 400 Hz by F-30, a frequency
setting more than 120 Hz can be set.
frequency
setting
frequency at this set value.
adjustment
Input voltage /380,400,415
voltage setting 440,460,480
AVR AVRDEC OFF OFF ON/OFF • ON or OFF of the AVR
function function for deceleration
for is set. When dynamic
decelera- braking torque is necessary
tion for deceleration, OFF is set.
method VP3, SLV, V2 V/F characteristics
setting SLV:Sensorless vector control
Motor setting AUT/NRT is set, the
constant autotuning measurement
(NOTE 1) operation is executed.
Motor data AUX DATA NOR NOR NOR: Old Hitachi • The autotuning motor data
selection general purpose before starting autotuning
TMO: New measurement is data
Motor AUX K 005.50 kW
capacity
setting data.
Motor pole AUX P 4p 4p 2, 4, 6, 8 • The number of poles of the
count motor to be used is set.
setting
Motor AUX R1 1.004
constant
R1 setting
Motor AUX R2 0.776
constant
R2 setting
Motor AUX L 13.16 mH
constant
L setting
Rated capacity
of each inverter
Rated capacity
of each inverter
Rated capacity
of each inverter
Rated capacity
of each inverter
Setting, change
contents
Hitachi general equivalent to NOR.
purpose
AUT: Autotuning data
3.7 to 160 • Set a capacity smaller than the
0 to 65.535
0 to 65.535
0 to 655.35
Setting contents
V2:Sensor vector control
rated capacity as capacity
12-5
Page 97

Display
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
sequence
6 F-05 Motor AUX M 123.60 mH
7 F-06 Accelera- ACC 1 0030.00 s 30.00 s 0.01 to 3000 • When the fuzzy most
8 F-07 Decelera- DEC 1 0030.00 s 30.00 s 0.01 to 3000S • When the fuzzy most
(Function mode 1) (Function mode 2)
Function Function Initialization display Initialization
No. name contents
Rated capacity
Motor M setting
constant constant
Motor AUX J 0.44 kgm2Rated capacity
J setting
constant
Motor AUX Kp 002.00 2.0 0 to 100.00 • Smaller: High response
constant • Larger: Low response
Kp setting
Motor AUX Ti 00100 ms 100 ms 0 to 10000 • Set this item after the
constant feedback option PCB is
Ti setting installed.
Motor AUX KPP 001.00 1.0 0 to 100.00 • Set this item after the
constant feedback option PCB is
KPP setting installed.
Accelera- tion time suitable acceleration and
tion time setting deceleration (F-10) are set,
2-stage ACC 2 0015.00 s 15.00 s 0.01 to 3000 • The acceleration time can
acceleration be used when the input
time setting terminal CH1 is shorted.
Curve ACC LINE L L L (Linear), • The curve pattern is set for
pattern S (S curve), acceleration and
selection U (U curve), deceleration respectively.
for RU (reverse
acceleration U curve)
Accelera- ACC GAIN 02 2 (common to 1 to 10 • When the constant is set
tion and acceleration for one of acceleration and
deceleration and deceleration, it is common
curve deceleration) to both acceleration and
constant deceleration.
selection • See appendix 4.
Decelera- tion time suitable acceleration and
tion time setting deceleration (F-10) are set,
2-stage DEC 2 0015.00 s 15.00 s 0.01 to 3000S • The deceleration time can
deceleration be used when the input
time setting terminal CH1 is shorted.
Curve DEC LINE L L L (Linear), • The curve pattern is set for
pattern S (S curve), acceleration and deceleraselection U (U curve), tion respectively.
for RU (reverse
deceleration U curve)
Accelera- DEC GAIN 02 2 (common to 1 to 10 • When the constant is set
tion and acceleration for one of acceleration and
deceleration and decelera- deceleration, it is common
curve tion) to both acceleration and
constant deceleration.
selection • See appendix 4.
of each inverter phase.
of each inverter
Setting, change
contents
0 to 655.35 • Primary self inductance per
0 to 655.35 • Motor and machine inertia
Setting contents
the time displayed here is
invalid, though it can be
set.
• For input terminal
selection, refer to F-34
input terminal.
the time displayed here is
invalid, though it can be
set.
• For input terminal
selection, refer to F-34
input terminal.
12-6
Page 98

Display
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
sequence
9 F-08 Accelera- Fsp F 0000.0 Hz 0 Hz 0 to 400.0 • The frequency at which the
10 F-09 Pattern PARAM REM REM REM/ • The parameter setting com-
11 F-10
12 F-11 Multistage SPD 1 0000.00 Hz 0 Hz 0 to 120.0 (400) • The input terminal CF1 is set
(Function mode 1) (Function mode 2)
Function Function Initialization display Initialization
No. name contents
Accelera- tion stop acceleration operation is
tion halt frequency stopped temporarily is set.
setting
Accelera- Fsp TIME 00.0 s 0 s 0 to 60.0 • The time that the acceleration
tion stop is stopped temporarily at a
time setting certain frequency during
command- OP1/OP2 manding source is selected.
ing method (Option REM (each operator),
selection connected) OP1 (option 1), OP2 (option
Running
mode
Running RUN MODE NOR NOR NOR/OEN/ NOR: Normal running
mode GOD OEN: Energy conservation
selection running
Restarting RUN FRS ZST ZST fST/ZST fST: Restart after frequency
after FRS maching
signal ZST: 0 Hz start
selection
Multistage speed and used.
speed 1 speed
setting
Multistage SPD 2 0000.00 Hz 0 Hz 0 to 120.0 (400) • The input terminal CF2 is set
speed and used.
2-speed
setting
Multistage SPD 3 0000.00 Hz 0 Hz 0 to 120.0 (400) • The input terminals CF1 and
speed CF2 are set and used.
3-speed
setting
Multistage SPD 4 0000.00 Hz 0 Hz 0 to 120.0 (400) • The input terminals CF1 and
speed CF3 are set and used.
4-speed
setting
Multistage SPD 5 0000.00 Hz 0 Hz 0 to 120.0 (400) • The input terminals CF2 and
speed CF3 are set and used.
5-speed
setting
Multistage SPD 6 0000.00 Hz 0 Hz 0 to 120.0 (400) • The input terminals CF1, CF2,
speed and CF3 are set and used.
6-speed
setting
Multistage SPD 7 0000.00 Hz 0 Hz 0 to 120.0 (400) • The input terminal CF3 is set
speed and used.
7-speed
setting
Setting, change
contents
Setting contents
acceleration is set.
2)
GOD: Fuzzy most suitable
acceleration and
deceleration running
12-7
Page 99

Display
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
sequence
13 F-20 DC braking DCB SW O FF OFF ON/OFF • DC braking
14 F-21 Dynamic BRD-%ED 001.5% 1.5% 0 to 100.0 • The allowable usage ratio of
15 F-22 Allowable IPS TIME 1.0 s 1.0 s 0.3 to 25 s • When an instantaneous power
16 F-23 Electronic E-THM CHAR S UB SUB CRT/SUB/FRE • Electronic thermal
(Function mode 1) (Function mode 2)
Function Function Initialization display Initialization
No. name contents
DC selection ON: DC braking available
injection OFF: DC braking unavailable
braking DC braking DCB KIND LVL LVL LVL/EDG • DC braking method selection
type LVL: Level operation
selection EDG: Edge operation
DC braking DCB F 0000.5 Hz 0.5 Hz 0 to 400.0 Hz • The frequency at which the
frequency DC braking starts is set.
selection
DC braking DCB V-STA 00 0 0 to 20 • The DC braking force at start
force selec- is set.
tion
(at start)
DC braking DCB V-STP 00 0 0 to 20 • The DC braking force at stop
force selec- is set.
tion
(at stop)
DC braking DCB T-STA 000.0 s 0 s 0 to 600.0 • The DC braking time at start
time selec- is set.
tion
(at start)
DC braking DCB T-STP 000.0 s 0 s 0 to 600.0 • The DC braking time at stop
time selec- is set.
tion
(at stop)
DC braking DCB STOP-T 0.00 s 0 s 0 to 5.00 The output frequency is
output cut- lowered to the DC braking
off time frequency and the free run
adjustment time during execution of DC
braking the braking resistor for 100
setting seconds is set. (NOTE 1)
The
allowable power failure
usage time setting recovered is set.
ratio of Reclosing IPS WAIT 001.0 s 1.0 s 0.3 to 100.0 s • The waiting time until the
the
braking
resistor
for 100 recovered
seconds
is set.
Electronic thermal tic setting CRT: Constant
thermal
instantaneous
standby after
instantaneous
power failure
Instantaneous
power failure
restart FTP: Retry after frequency
selection matching is stopped
Trip selection
during stop failure occurs:
at under
voltage
characteristic
selection SUB: Reduced torque charac-
Electronic E-THM LEVEL 100% 100% 20 to 120%
thermal level
setting
IPS POWR ALM ALM ALM/FTP/ ALM: Alarm output
IPS TRIP OFF OF F ON/OFF When an instantaneous power
Setting, change
contents
RST/ZST ZST: 0 Hz start retry
Setting contents
braking is set.
failure occurs, the allowable
time until the power failure is
rerunning starts after an
instantaneous power failure
occurs and is recovered is set.
RST: Rerunning start retry
ON: Trip
OFF: Non-trip
torque characteristic
teristic
FRE: Free characteristic
characteris-
NOTE 1: Initial setting of usage ratio 1.5% 055-075L/HF 0% 110-550L/HF
12-8
Page 100

Display
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
sequence
16 F-23 Electronic E-THM A1 8.5A Rated capacity of 0 to 600.0 A
17 F-24 Overload OLOAD LEVEL125% 125% 50 to 150% Under the sensorless vector
18 F-25 Software S-LOCK MD1 MD1 MD0/MD1 MD0, MD1: Terminal software
(Function mode 1) (Function mode 2)
Function Function Initialization display Initialization
No. name contents
Electronic thermal each inverter
thermal
(NOTE 2) free setting
Overload restriction control, an overload is detected
restriction level setting from both the overload restric-
characteristic
current (1)
Electronic E-THM F1 0000 Hz Rated capacity of 0 to 400 Hz
thermal each inverter
characteristic
free setting
frequency (1)
Electronic E-THM A2 8.5A Rated capacity of 0 to 600.0 A
thermal each inverter
charac teristic
free setting
current (2)
Electronic E-THM F2 5 Hz Rated capacity of 0 to 400 Hz
thermal each inverter
characteristic
free setting
frequency (2)
Electronic E-THM A3 13.0 A Rated capacity of 0 to 600.0 A
thermal each inverter
characteristic
free setting
current (3)
Electronic E-THM F3 73 Hz Rated capacity of 0 to 400 Hz
thermal each inverter
characteristic
free setting
frequency (3)
Overload OLOAD CONST01.0 1.0 0.3 to 31.0 When the setting is 31.0 in SLV
restriction or V2 control mode, the
constant overload restriction has no
setting effect.
Valid OLOAD ACC ON O N ON: Valid for Even if the function is set to
selection acceleration OFF, the overload restriction is
for overload Keep the invalid only for the first
restriction function ON acceleration when the forward
acceleration for operation. and reverse run command is
lock MD2/MD3 lock (SFT)
selection MD2, MD3: Software lock
Setting, change
contents
Setting contents
tion and torque limiter.
turned on.
(NOTE 1)
NOTE 1: When MD0 is set and the input terminal SFT is turned ON, the data of all functions is locked. When MD2 is
set (stored), the data of all the functions is locked. During locking, no data can be changed. MD1, MD3
can set only the output frequency.
NOTE 2: Electronic thermal characteristic free setting current and frequency depends on the inverter rating.
12-9
 Loading...
Loading...