Hitachi DVP-303-U, DV-P-305-U Service manual

TK No.9003E
DV-P305U
SERVICE MANUAL
DV-P303U
CONTENTS
1. Precautions
2. Reference Information
3. Product Specification
4. Operating Instructions
5. Disassembly and Reassembly
6. Circuit Descriptions
7. Troubleshooting
8. Exploded Views
9. Replacement Parts List
10. Block Diagram
11. PCB Diagrams
12. Wiring Diagram
13. Schematic Diagrams
SPECIFICATIONS AND PARTS ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE FOR IMPROVEMENT
DVD PLAYER
2000March
Digital Media Products Division, Tokai
1-1
1. Precautions
1-1 Safety Precautions
1) Before returning an instrument to the customer,
always make a safety check of the entire
instrument, including, but not limited to, the
following items:
(1) Be sure that no built-in protective devices are
defective or have been defeated during servicing.
(1)Protective shields are provided to protect both
the technician and the customer. Correctly replace
all missing protective shields, including any
remove for servicing convenience.
(2)When reinstalling the chassis and/or other assembly in the cabinet, be sure to put back in place
all protective devices, including, but not limited to,
nonmetallic control knobs, insulating fish papers,
adjustment and compartment covers/shields, and
isolation resistor/capacitor networks. Do not
operate this instrument or permit it to be operated
without all protective devices correctly installed
and functioning.
(2) Be sure that there are no cabinet openings through
which adults or children might be able to insert
their fingers and contact a hazardous voltage. Such
openings include, but are not limited to,
excessively wide cabinet ventilation slots, and an
improperly fitted and/or incorrectly secured
cabinet back cover.
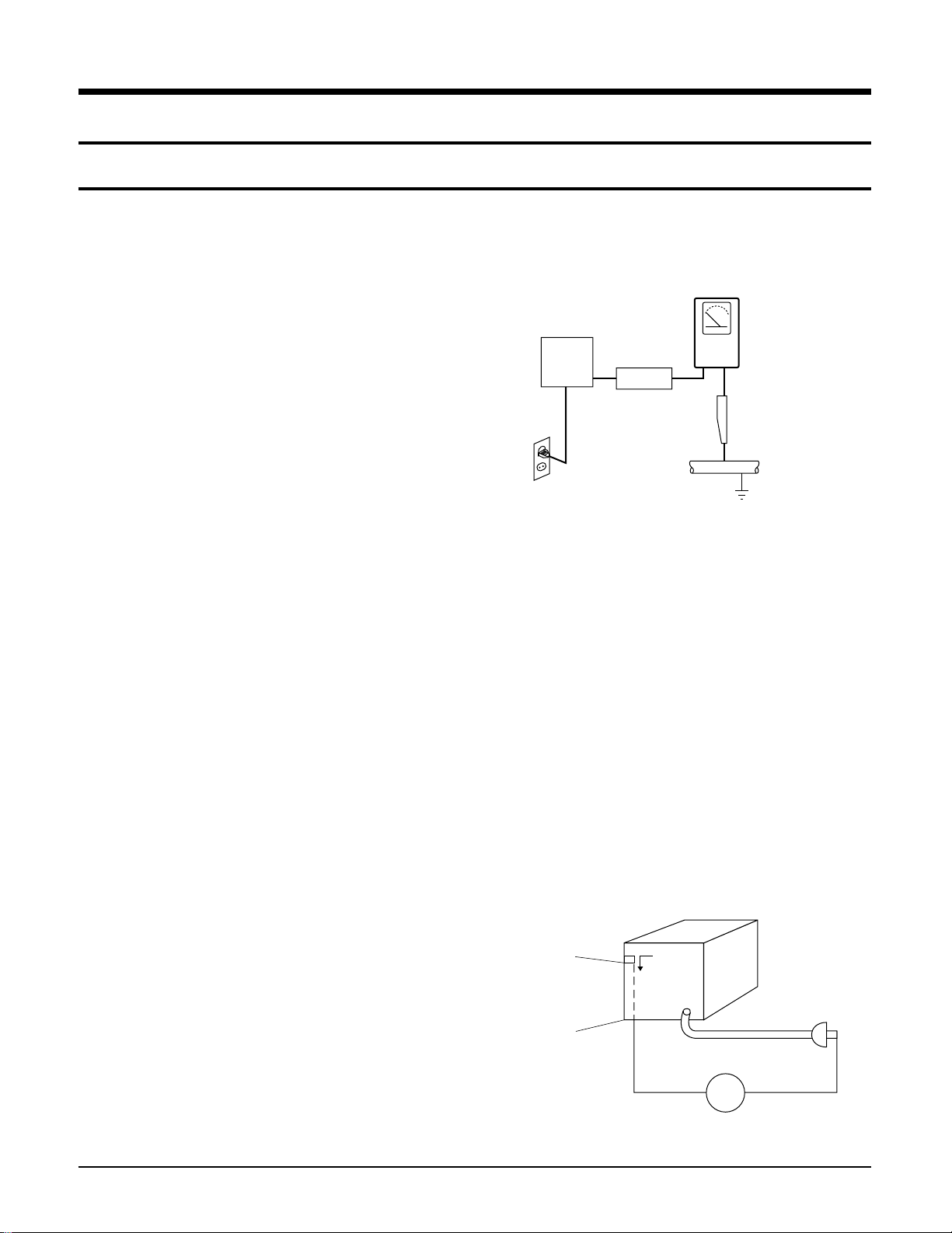
(3) Leakage Current Hot Check-With the instrument
completely reassembled, plug the AC line cord
directly into a 120V AC outlet. (Do not use a
isolation transformer during this test.) Use a
leakage current tester or a metering system that
complies with American National Standards
institute (ANSI) C101.1 Leakage Current for
Appliances and Underwriters Laboratories (UL)
1270 (40.7). With the instrument’s AC switch first
in the ON position and then in the OFF position,
measure from a known earth ground (metal water
pipe, conduit, etc.) to all exposed metal parts of the
instrument (antennas, handle brackets, metal
cabinets, screwheads, metallic overlays, control
shafts, etc.), especially any exposed metal parts
that offer an electrical return path to the chassis.
Any current measured must not exceed 0.5mA.
Reverse the instrument power cord plug in the
outlet and repeat the test. See Fig. 1-1.
Any measurements not within the limits specified
herein indicate a potential shock hazard that must
be eliminated before returning the instrument to
the customer.
Fig. 1-1 AC Leakage Test
(4) Insulation Resistance Test Cold Check-(1) Unplug
the power supply cord and connect a jumper wire
between the two prongs of the plug. (2) Turn on
the power switch of the instrument. (3) Measure
the resistance with an ohmmeter between the
jumpered AC plug and all exposed metallic
cabinet parts on the instrument, such as
screwheads, antenna, control shafts, handle
brackets, etc. When an exposed metallic part has a
return path to the chassis, the reading should be
between 1 and 5.2 megohm. When there is no
return path to the chassis, the reading must be
infinite. If the reading is not within the limits
specified, there is the possibility of a shock hazard,
and the instrument must be re-pared and
rechecked before it is returned to the customer. See
Fig. 1-2.
Fig. 1-2 Insulation Resistance Test
(READING SHOULD
NOT BE ABOVE
0.5mA)
EARTH
GROUND
DEVICE
UNDER
TEST
TEST ALL
EXPOSED METER
SURFACES
2-WIRE CORD
ALSO TEST WITH
PLUG REVERSED
(USING AC ADAPTER
PLUG AS REQUIRED)
LEAKAGE
CURRENT
TESTER
Antenna
Terminal
Exposed
Melal Part
ohm
ohmmeter

Precautions
1-2
2) Read and comply with all caution and safety related notes non or inside the cabinet, or on the
chassis.
3) Design Alteration Warning-Do not alter of add to
the mechanical or electrical design of this
instrument. Design alterations and additions,
including but not limited to, circuit modifications
and the addition of items such as auxiliary audio
output connections, might alter the safety
characteristics of this instrument and create a
hazard to the user. Any design alterations or
additions will make you, the service, responsible
for personal injury or property damage resulting
therefrom.
4) Observe original lead dress. Take extra care to
assure correct lead dress in the following areas:
(1) near sharp edges, (2) near thermally hot parts
(be sure that leads and components do not touch
thermally hot parts), (3) the AC supply, (4) high
voltage, and (5) antenna wiring. Always inspect in
all areas for pinched, out-of-place, or frayed wiring,
Do not change spacing between a component and
the printed-circuit board. Check the AC power cord
for damage.
5) Components, parts, and/or wiring that appear to
have overheated or that are otherwise damaged
should be replaced with components, parts and/ or
wiring that meet original specifications.
Additionally, determine the cause of overheating
and/or damage and, if necessary, take corrective
action to remove any potential safety hazard.
6) Product Safety Notice-Some electrical and
mechanical parts have special safety-related
characteristics which are often not evident from
visual inspection, nor can the protection they give
necessarily be obtained by replacing them with
components rated for higher voltage, wattage, etc.
Parts that have special safety characteristics are
identified by shading, an ( )or a ( )on
schematics and parts lists. Use of a substitute
replacement that does not have the same safety
characteristics as the recommended replacement
part might created shock, fire and/or other
hazards. Product safety is under review
continuously and new instructions are issued
whenever appropriate.

Precautions
1-3
1-2 Servicing Precautions
CAUTION : Before servicing Instruments covered
by this service manual and its supplements, read and
follow the Safety Precautions section of this manual.
Note : If unforseen circument create conflict between
the following servicing precautions and any of the
safety precautions, always follow the safety
precautions. Remember: Safety First.
1-2-1 General Servicing Precautions
(1) a. Always unplug the instrument’s AC power cord
from the AC power source before (1) re-moving
or reinstalling any component, circuit board,
module or any other instrument assembly, (2)
disconnecting any instrument electrical plug or
other electrical connection, (3) connecting a test
substitute in parallel with an electrolytic
capacitor in the instrument.
b. Do not defeat any plug/socket B+ voltage
interlocks with which instruments covered by
this service manual might be equipped.
c. Do not apply AC power to this instrument and
/or any of its electrical assemblies unless all
solid-state device heat sinks are correctly installed.
d. Always connect a test instrument’s ground lead
to the instrument chassis ground before
connecting the test instrument positive lead.
Always remove the test instrument ground lead
last.
Note : Refer to the Safety Precautions section ground
lead last.
(2) The service precautions are indicated or printed on
the cabinet, chassis or components. When
servicing, follow the printed or indicated service
precautions and service materials.
(3) The components used in the unit have a specified
flame resistance and dielectric strength.
When replacing components, use components
which have the same ratings. Components ientified by shading, by( ) or by ( ) in the circuit
diagram are important for safety or for the
characteristics of the unit. Always replace them
with the exact replacement components.
(4) An insulation tube or tape is sometimes used and
some components are raised above the printed
wiring board for safety. The internal wiring is
sometimes clamped to prevent contact with
heating components. Install such elements as they
were.
(5) After servicing, always check that the removed
screws, components, and wiring have been installed correctly and that the portion around the
serviced part has not been damaged and so on.
Further, check the insulation between the blades of
the attachment plug and accessible conductive
parts.
1-2-2 Insulation Checking Procedure
Disconnect the attachment plug from the AC outlet
and turn the power ON. Connect the insulation resistance meter (500V) to the blades of the attachment
plug. The insulation resistance between each blade of
the attachment plug and accessible conductive
parts(see note) should be more than 1 Megohm.
Note : Accessible conductive parts include metal
panels, input terminals, earphone jacks, etc.

Precautions
1-4
1-3 ESD Precautions
Electrostatically Sensitive Devices (ESD)
Some semiconductor (solid state) devices can be
damaged easily by static electricity.
Such components commonly are called Electrostatically Sensitive Devices(ESD). Examples of typical ESD
devices are integrated circuits and some field-effect
transistors and semiconductor chip components. The
following techniques should be used to help reduce
the incidence of component damage caused by static
electricity.
(1) Immediately before handling any semiconductor
component or semiconductor-equipped assembly,
drain off any electrostatic charge on your body by
touching a known earth ground. Alternatively,
obtain and wear a commercially available
discharging wrist strap device, which should be
removed for potential shock reasons prior to
applying power to the unit under test.
(2) After removing an electrical assembly equipped
with ESD devices, place the assembly on a
conductive surface such as aluminum foil, to
prevent electrostatic charge buildup or exposure of
the assembly.
(3) Use only a grounded-tip soldering iron to solder
or unsolder ESD devices.
(4) Use only an anti-static solder removal devices.
Some solder removal devices not classified as
“anti-static” can generate electrical charges
sufficient to damage ESD devices.
(5) Do not use freon-propelled chemicals. These can
generate electrical charges sufficient to damage
ESD devices.
(6) Do not remove a replacement ESD device from its
protective package until immediately before your
are ready to install it.(Most replacement ESD
devices are packaged with leads electrically
shorted together by conductive foam, aluminum
foil or comparable conductive materials).
(7) Immediately before removing the protective ma-
terials from the leads of a replacement ESD device,
touch the protective material to the chassis or
circuit assembly into which the device will be
installed.
CAUTION : Be sure no power is applied to the chassis or circuit, and observe all other safety
precautions.
(8) Minimize bodily motions when handling
unpackaged replacement ESD devices. (Otherwise
harmless motion such as the brushing together of
your clothes fabric or the lifting of your foot from a
carpeted floor can generate static electricity
sufficient to damage an ESD device).
Precautions
1-5
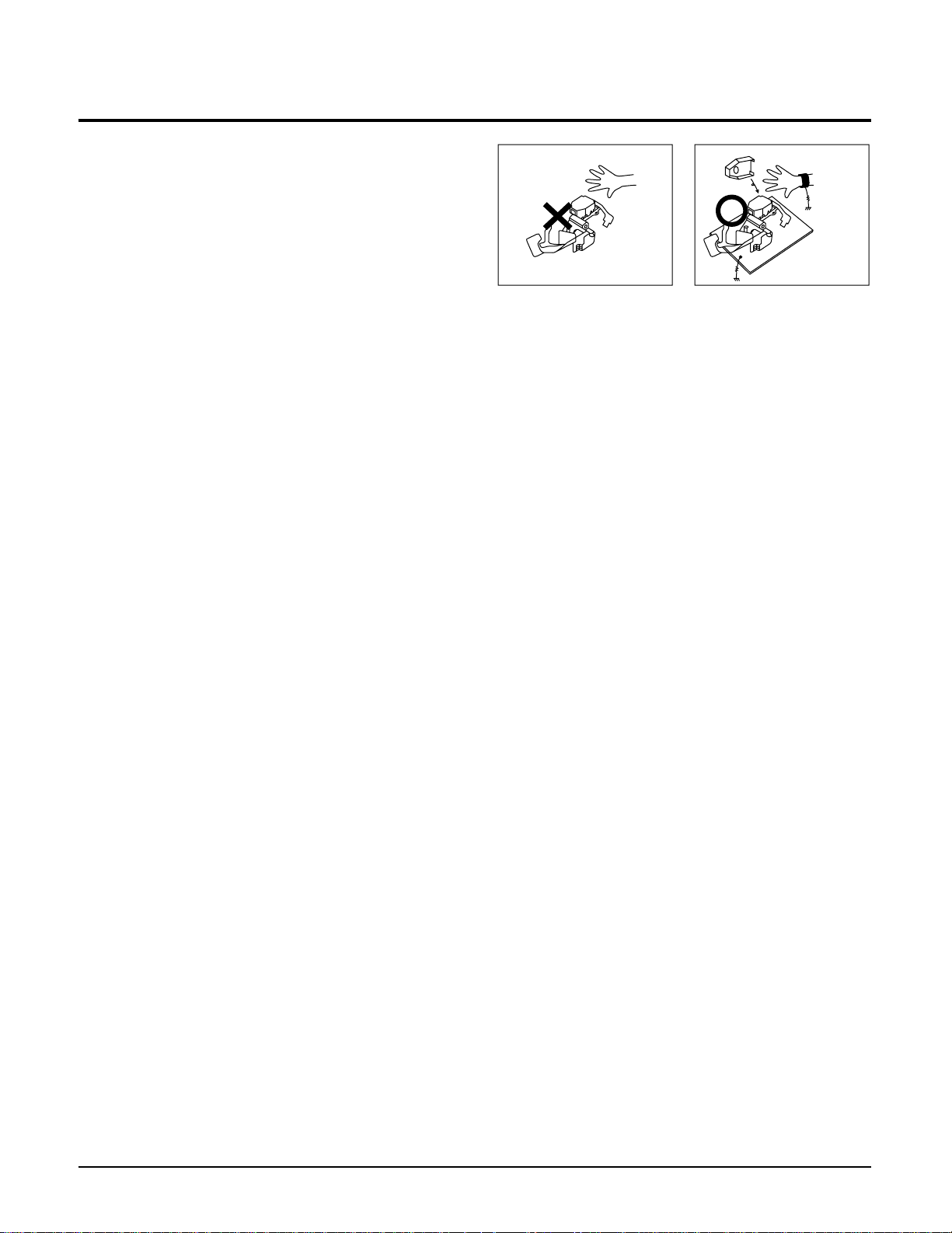
1-4 Handling the optical pick-up
The laser diode in the optical pick up may suffer
electrostatic breakdown because of potential static
electricity from clothing and your body.
The following method is recommended.
(1) Place a conductive sheet on the work bench (The
black sheet used for wrapping repair parts.)
(2) Place the set on the conductive sheet so that the
chassis is grounded to the sheet.
(3) Place your hands on the conductive sheet(This
gives them the same ground as the sheet.)
(4) Remove the optical pick up block
(5) Perform work on top of the conductive sheet. Be
careful not to let your clothes or any other static
sources to touch the unit.
•Be sure to put on a wrist strap grounded to the
sheet.
•Be sure to lay a conductive sheet made of copper etc.
Which is grounded to the table.
Fig.1-3
(6) Short the short terminal on the PCB, which is in-
side the Pick-Up ASS’Y, before replacing the PickUp. (The short terminal is shorted when the PickUp Ass’y is being lifted or moved.)
(7) After replacing the Pick-up, open the short
terminal on the PCB.
THE UNIT
WRIST-STRAP
FOR GROUNDING
1M
1M
CONDUCTIVE SHEET
Precautions
1-6
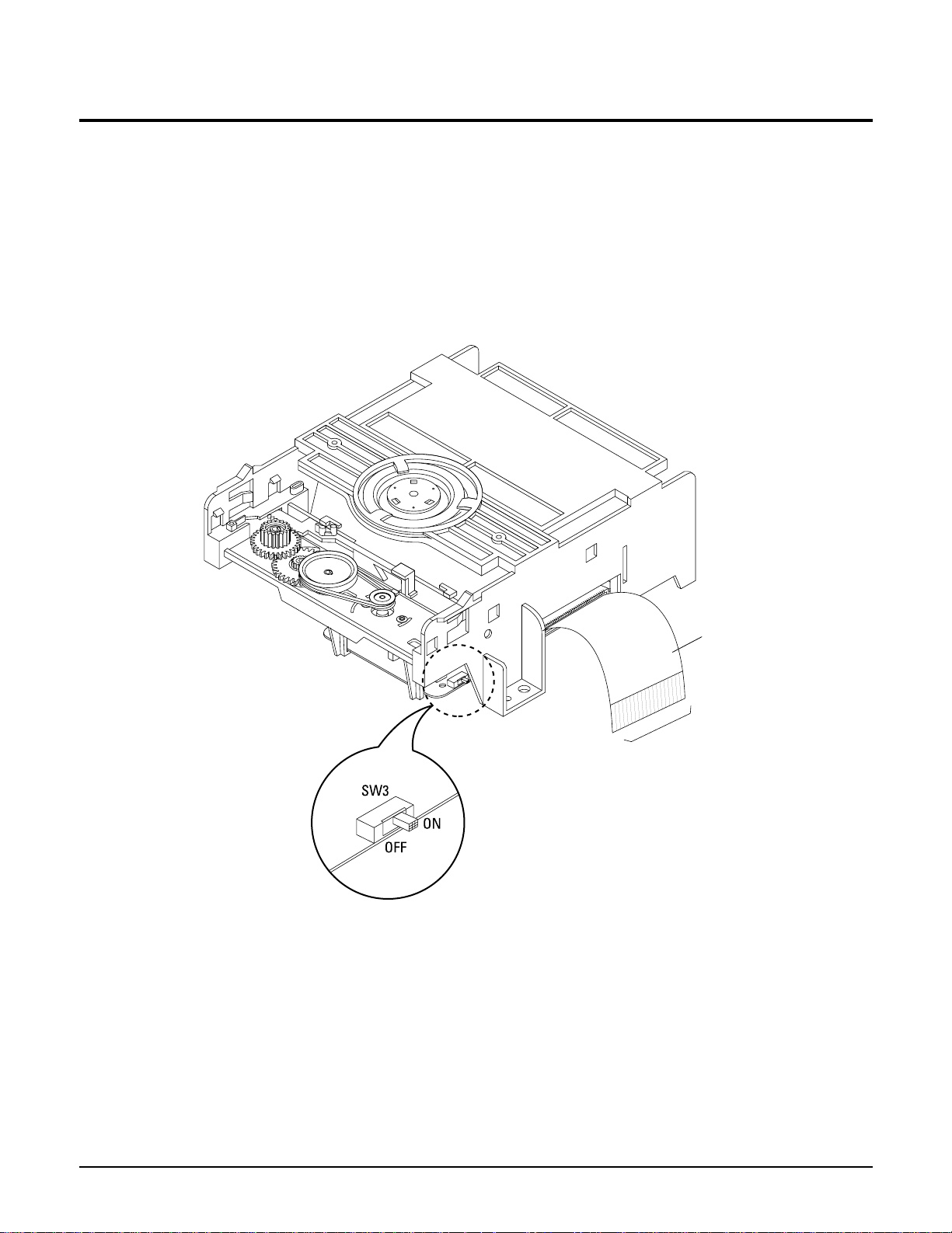
1-5 Pick-up disassembly and reassembly
1-5-1 Disassembly
1) Remove the power cable.
2) Switch SW3 on deck PCB to“OFF” before
removing the FPC.
( Inserted into Main PCB DCN1. See Fig. 1-4)
3) Disassemble the deck.
4) Disassemble the deck PCB.
1-5-2 Assembly
1) Replace the Pick-up.
2) Assemble the deck PCB.
3) Reassemble the deck.
4) Insert FPC into Main PCB DCN1 and switch SW3
on deck PCB to “ON”. (See Fig 1-4)
Note : If the assembly and disassembly are not done in correct sequence, the Pick-up may be damaged.
Fig. 1-4
FPC
TO MAIN PCB
(DCN1)
2-1
2. Reference Information
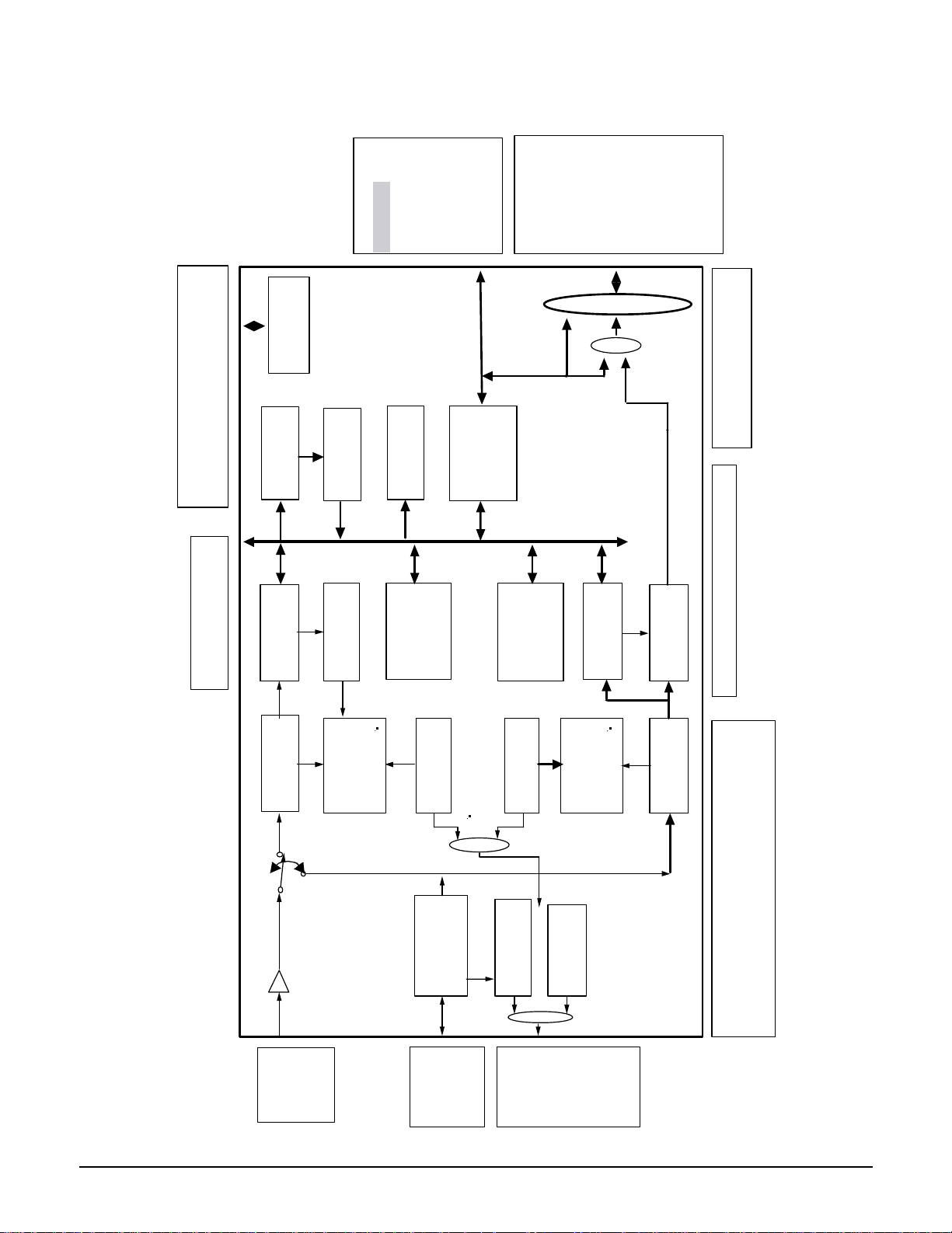
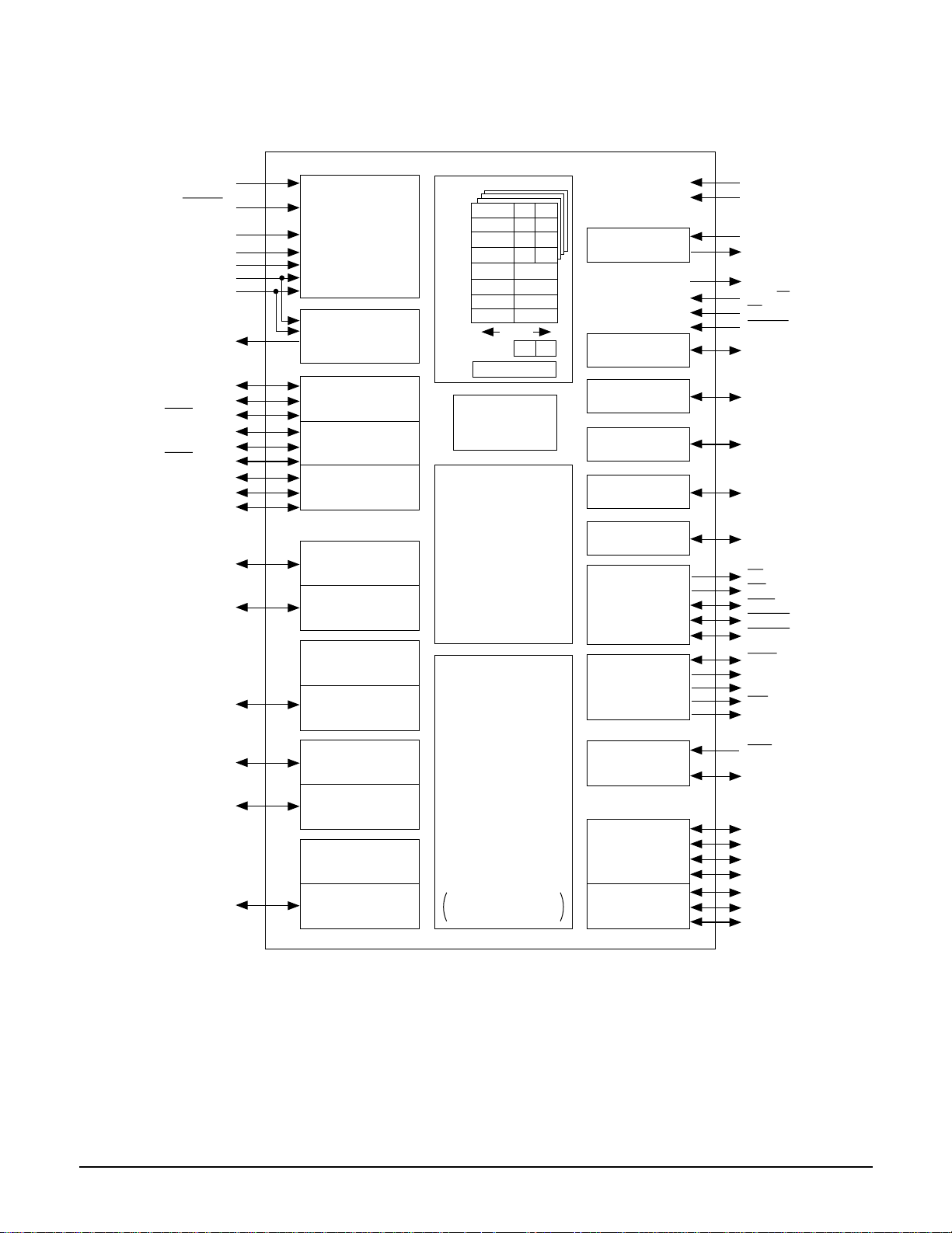
2-1 IC Dsecriptions
2-1-1 AIC1 (AK4393 ; Digital-to-Analog Converter)
Serial
Input
Interface
De-emphasis
Control
De-emphasis
Soft Mute
De-emphasis
Soft Mute
Left Channel
Right Channel
8X
Interpolator
8X
Interpolator
Multi-bit ˘•
Modulator
Multi-bit ˘•
Modulator
Switched
Capacitor Filter
Switched
Capacitor Filter
Control
Register
Double
Speed Select
Soft Mute
Power Down
Serial Data
Bit Clock
Left/Right Clock
Serial
Input Control
Clock Divider
Master Clock Clock Control
Left Output -
Left Output +
Right Output -
Right Output +
DVSS
DVDD
MCLK
PD
BICK
SD ATA
LRCK
SMUTE
DFS
DEM0
DEM1
DIF0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
DIF1
13
DIF2
CKS2
CKS1
CKS0
P/S
VCOM
AOUTL+
AOUTLAOUTR+
AOUTRAVSS
AVDD
VREFH
VREFL
BVSS
14
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
No. Pin Name I/O Pin Function and Description
1 DVSS - Digital Ground. Digital ground is 0V.
2 DVDD - Digital Supply. 3.3V or 5.0V nominal.
3 MCLK I Master Clock Input.
4 PD I Power-down and Reset. When low the AK4393 is in Power-down Mode and held in reset.
The AK4393 should always be reset after power-up.
5 BICK I Audio Serial Data Clock Input. A clock input of 64fs or more is recommended.
6
SD ATA I
Serial Data Input.
7 LRCK I Left/Right Clock Input. Defines the sampling rate, F
s
.
8 SMUTE
(or CS
)
I Soft Mute Input or Chip Select Input. If the P/S
pin (pin 25) is high, SMUTE controls the
soft mute function as follows:
- When SMUTE goes high, the soft mute cycle is initiated.
- When SMUTE goes low, the output mute is slowly released.
If the P/S
pin is low, SMUTE is the Chip Select Input for the Serial Control Mode. Chip
select is active when SMUTE is low.
9 DFS I Double Sampling Speed Input. When low, this pin defines the Normal Speed Mode, and
128 x F
s
oversampling is implemented. When high, the DFS pin defines the Double Speed
Mode, implemented with 64 x F
s
oversampling. This pin features an internal pull-down.
10 DEM0
(or CCLK)
I De-emphasis Enable #0 or Control Data Clock Input. If the P/S
pin (pin 25) is high,
DEM0 is used to select the De-emphasis Mode according to Table 3. If the P/S pin os low
DEM0 is the clock input for the Serial Control Mode.
11 DEM1
(or CDTI)
I De-emphasis Enable #1 or Control Data Input. If the P/S
pin (pin 25) is high, DEM1 is
used to select the De-emphasis Mode according to Table 3. If the P/S pin is low, DEM1 is
the control data input for the Serial Control Mode.
12 DIF0 I Digital Input Format Select #0.
13 DIF1 I Digital Input Format Select #1.
14 DIF2 I Digital Input Format Select #2.
15 BVSS - Substrate Ground Pin. Substrate ground is 0V.
16 VREFL I Low Level Voltage Reference Input. Normally connected to analog ground.
17 VREFH I High Level Voltage Reference Input. Normally connected to analog supply.
18 AVDD - Analog Supply. Analog supply is 5V nominal.
19 AVSS - Analog Ground. Analog ground is 0V.
20 AOUTR- O Right Channel Negative Output.
21 AOUTR+ O Right Channel Positive Output.
22 AOUTL- O Left Channel Negative Output.
23 AOUTL+ O Left Channel Positive Output.
24 VCOM O Common Voltage Output. Common voltage output is 2.6V nominal.
25 P/S
I Parallel/Serial Control Mode Select Input. If Low, the Serial Control Mode is
implemented. If High, the Parallel Control Mode is selected. This pin has an internal
pull-up.
26 CKS0 I Master Clock Select #0.
27 CKS1 I Master Clock Select #1.
28 CKS2 I Master Clock Select #2.
Reference Information
2-2
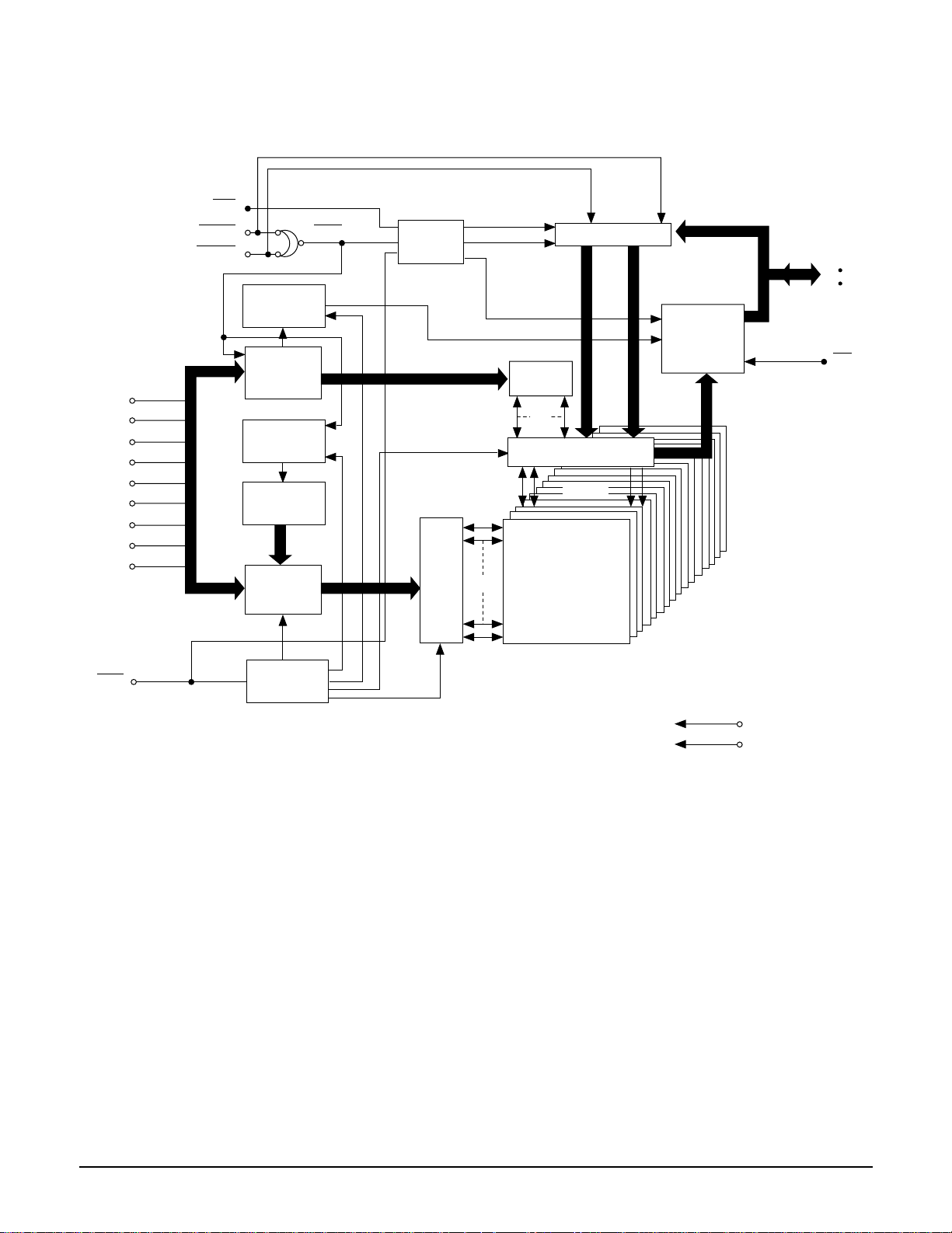
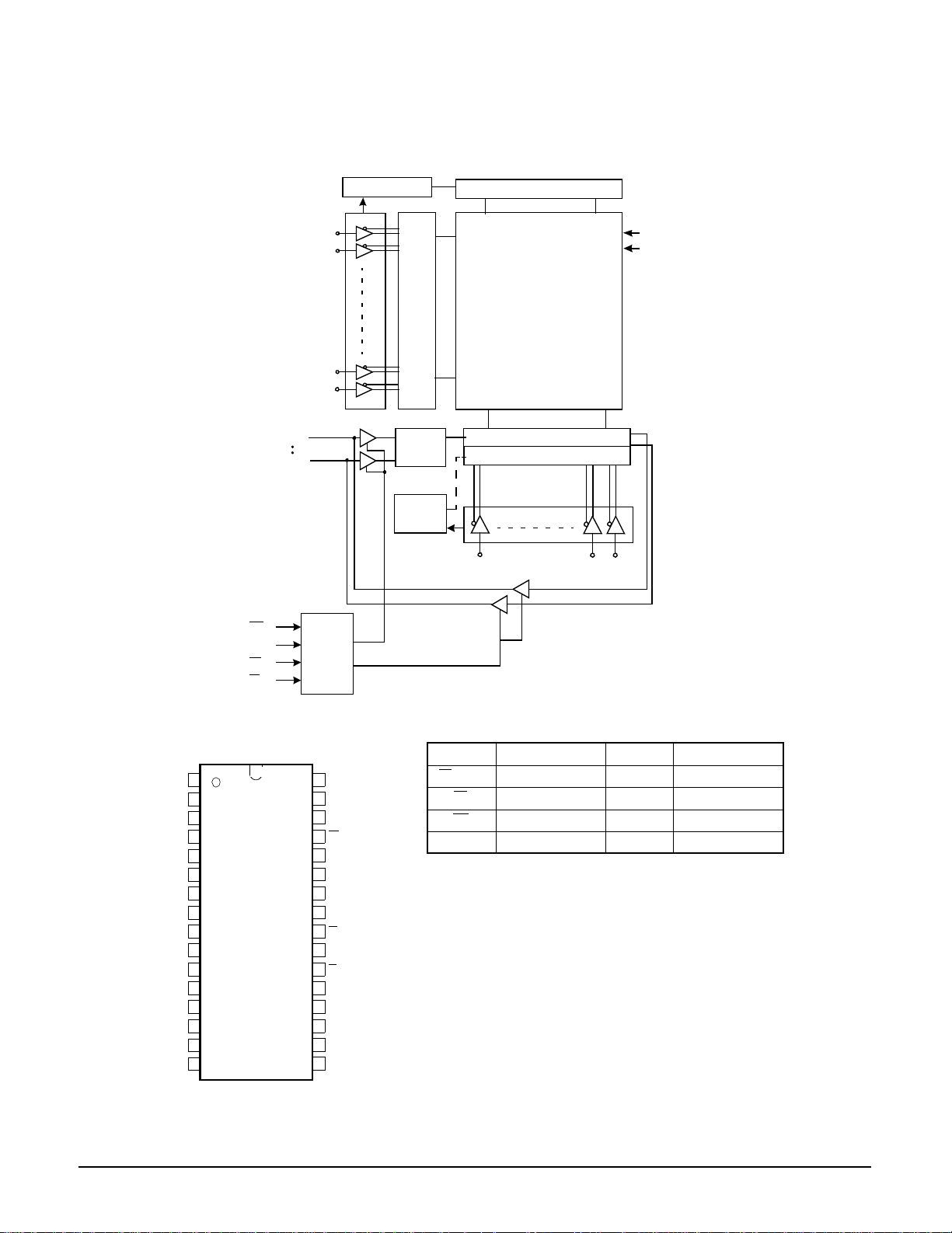
2-1-2 DIC1 (KS1453 ; Data Processor)
To DRAM
25 6K*16
DD[15:0]_BI
DAD R[8 :0]_ OUT
ZRAS_OUT
ZUCAS_OUT
ZLCAS_ OUT
ZOE[1:0]_OUT
ZWE[1:0]_OUT
To AV (13)
SDATA[ 0]_OU T/
CDATA
SDATA[ 1]_ OUT /LRC K
SDATA[2]_OUT/BCLK
SDATA[ 3]_OU T/C2PO
SDATA[ 4]_OU T/S Q DT
SDATA[ 5]_OU T/W FSY
SDATA[ 6]_OU T/S 0S1
SDATA[ 7]_BI /SQ CK
(32)
DATREQ_IN
TOS_ OUT
CSTROBE_OUT
DTER_OUT
DATACK_OUT
M
MICOM I/F
EDC
To MICOM (15)
MDAT[7:0]_BI, MRZA_IN, ZCS_IN, M WR_IN,
MRD_IN, ZIRQZD_OUT, ZWAIT_OUT, ZRST_IN
To RF (9)
PW MO[ 7:0 ]_OUT, BC AR Z_ IN
Descrambler
16-8
(6 ,4,3)
DEMOD
efmwr ID ECC
32BIT SR
Frame Sync
ECSY
DET/P ROT/INS
(6,4,3)
trans ID E CC
ECC
(2 08,19 2,17)
(1 82,17 2,11)
(17.57KHz )
VCO Timing
26.16MHz
&
RAM Control
Deinterleave
75Hz
676.08Hz
Generator
1 7 .5 8KH z= 2 6 .1 6M/1 488
7 .3 5KHz= 4 .3218M/588
DVDP,
SQ-VCD
V-CD,CD-DA
CIRC
(32,28,5)
(28,24,5)
Generator
VCO Timing
EFM
DEMOD
(7.35KHz )
Frame Sync
DET/P ROT/INS
CD-G
SUBCODE I/F
23BIT SR
M
Power(34)=VDD(11)+GND(23)
)
TE S T0_IN , TES T1_IN , TES T2_IN
Test Pin(3
M
WFCK 17.58/7.35KHz
RFCK 17.58/7.35KHz
X-tal & Timing
Generator
EFM I_IN
PL CK_IN
From
FG_IN
Servo (3)
X-tal (4)
XTI_ IN
XTO_OU T
CK33MI_IN
DVD CLV/CAV
To
CK33MO_OUT
CD CLV/CAV
M
Servo (6)
MON_OUT
MDP_OUT
MDS_OUT
FSW_OUT
PLLLOCK_
OUT
SERLOCK_
OUT
Monitor (9)
GFS_OU T, FRSYZ_OUT, TX_OUT , EFM O_OU T,
WFCK_OUT, RFCK_OUT, CK16M_OUT, DEMPHA_OUT
CLVLOCK_OUT
Reference Information
2-3
Notes
Notes
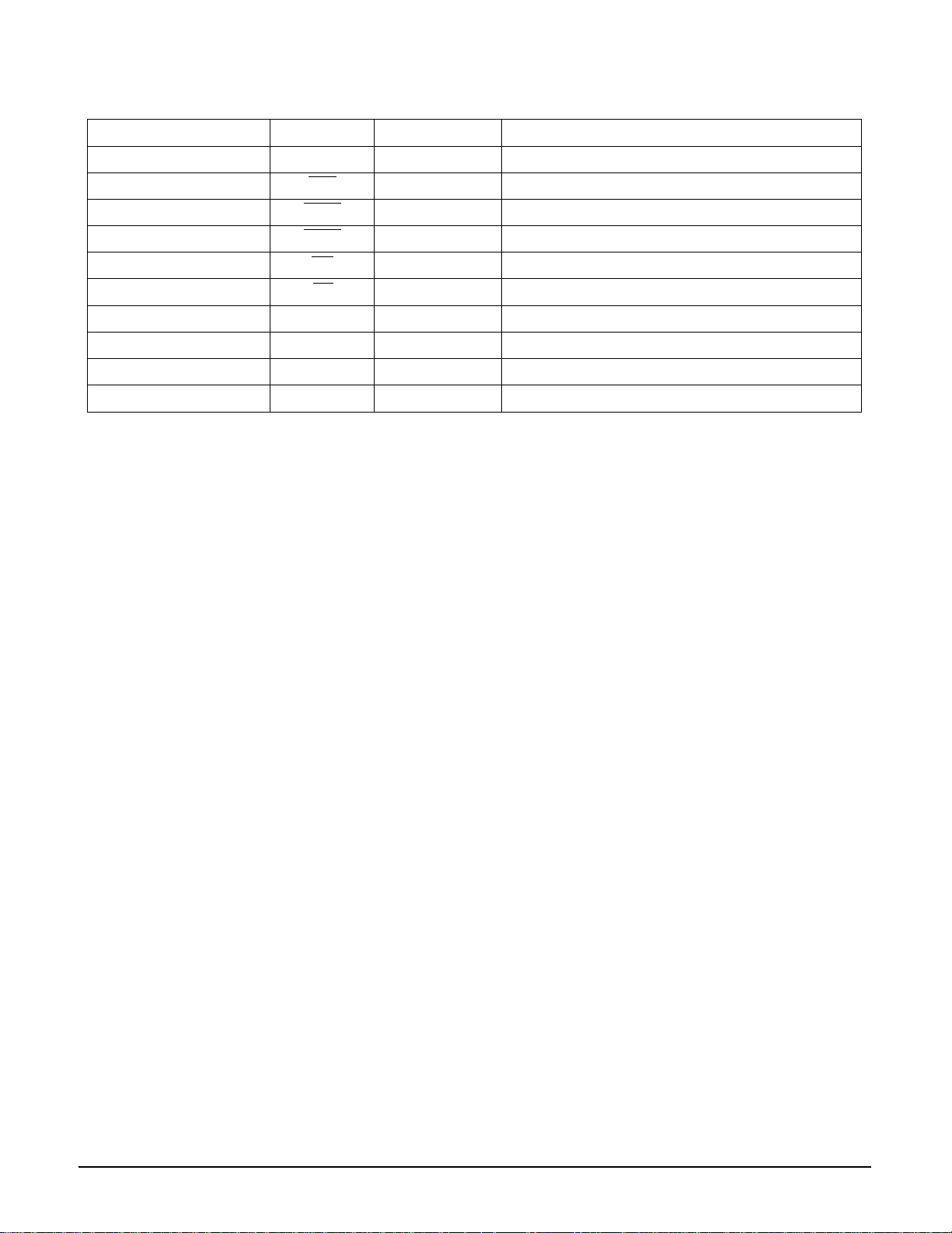
No. Pin Name Description I/O
65 SDATA5_OUT DVD Data/Subcode Frame Sync (WFSY) O AV Decoder
66 SDATA6_OUT DVD Data/Subcode Block Sync (S0S1) O AV Decoder
67 SDATA7_BI DVD Data/Subcode Serial Clock (SQCK) B AV Decoder
68 DVSS Digital GND (0 V)
69 CSTROBE_OUT Data Strobe (Clock) Output O AV Decoder
70 DATREQ_IN Data Request from A/V Decoder or ROM Decoder I AV Decoder
REGISTER H fi DATA) I MICOM
71 DTER_OUT DVD Data Error Output O AV Decoder
72 DVSS Digital GND (0 V)
73 PWMO7_OUT PWM Output Signal O RF
74 PWMO6_OUT PWM Output Signal O RF
75 PWMO5_OUT PWM Output Signal O RF
76 PWMO4_OUT PWM Output Signal O RF
77 DVDD Digital Power (+5 V)
78 PWMO3_OUT PWM Output Signal O RF
79 PWMO2_OUT PWM Output Signal O RF
80 PWMO1_OUT PWM Output Signal O RF
81 PWMO0_OUT PWM Output Signal O RF
82 DVSS Digital GND (0 V)
83 DVSS Digital GND (0 V)
84 DVSS Digital GND (0 V)
85 DVDD DIGITAL Power (+5 V)
86 DVDD DIGITAL Power (+5 V)
87 DVSS Digital GND (0 V)
88 DVSS Digital GND (0 V)
DRAM Address Bus
89 DVSS Digital GND (0 V)
93 GFS_OUT Good Frame Sync Detection State Output (OK at H) O Monitor
90 DVSS Digital GND (0 V)
91 FRSYZ_OUT Frame Sync Out O Monitor
92 TX_OUT Digital Out O Monitor
94 DVSS Digital GND (0 V)
95 CK33MI_IN System Clock Input for 33.8688 MHz I X-tal
96 CK33MO_OUT System Clock Output for 33.8688 MHz O X-tal
97 DVDD Digital Power (+5 V)
98 TEST0_IN Test Mode Selection Terminal I
99 TEST1_IN Test Mode Selection Terminal I
100 TEST2_IN Test Mode Selection Terminal I
101 EFMO_OUT EFM Out O Monitor
102 WFCK_OUT Write Frame Pulse O Monitor
103 RFCK_OUT Reference Frame Pulse O Monitor
104 PLCK_IN Phase Locked Clock I Servo
105 DVSS Digital GND (0 V)
106 PLLLOCK_OUT Lock Signal for PLL O Servo
107 CLVLOCK_OUT Lock Signal for CLV O Monitor
108 SERLOCK_OUT Lock Signal for SERVO O Servo
109 MDP_OUT Spindle Motor Phase Control Signal (3-STATE) O Servo
O DRAM
111 DVSS Digital GND (0 V)
110 MDS_OUT Spindle Motor Speed Control Signal (3-STATE) O Servo
112 DVSS Digital GND (0 V)
113 MON_OUT Spindle Motor Output Filter Switching Output O Servo
114 FG_IN Reference Signal for CAV I Servo
115 FSW_OUT Spindle Motor Output Filter Switching Output (3-STATE) O Servo
116 EFMI_IN EFM/EFM+ Signal Input I Servo
117 DVDD Digital Power (+5 V)
118 DVDD Digital Power (+5 V)
119 DVDD Digital Power (+5 V)
120 CK16M_OUT CK33Ms 2 Division Clock / 16.9344 MHz O Monitor
121 DEMPHA_OUT HIGH , when on Deemphasis O Monitor
122 BCARZ_IN BCA Input Signal I RF
123 DVSS Digital GND (0 V)
124 ZRST_IN Hardware Reset (Active Low) I MICOM
125 ZWAIT_OUT Micom Read / Write Access Wait (Wait at L) O MICOM
126 ZIRQZD_OUT Interrupt Request to Micom O MICOM
127 MRD_IN Micom Read Strobe (Active Low) I MICOM
128 MWR_IN Micom Write Strobe (Active Low) I MICOM
1 DVSS Digital GND (0 V)
2 ZCS_IN Chip Select (Active Low) I MICOM
No. Pin Name Description I/O Notes
4 DVSS Digital GND (0 V)
5 MDAT7_BI MICOM Data Bus B MICOM
6 MDAT6_BI MICOM Data Bus B MICOM
3 MRZA_IN Micom Register Select (L
7 MDAT5_BI MICOM Data Bus B MICOM
8 MDAT4_BI MICOM Data Bus B MICOM
9 MDAT3_BI MICOM Data Bus B MICOM
10 MDAT2_BI MICOM Data Bus B MICOM
11 MDAT1_BI MICOM Data Bus B M ICOM
12 MDAT0_BI MICOM Data Bus B MICOM
13 DVDD Digital Power (+5V)
14 XTI_IN System Clock Input for 26.16 MHz I XTAL
15 XTO_OUT System Clock Output for 26.16 MHz O XTAL
16 DVSS Digital GND (0 V)
17 DD15_BI DRAM Data Bus B DRAM
18 DD0_BI DRAM Data Bus B DRAM
19 DD14_BI DRAM Data Bus B DRAM
20 DD1_BI DRAM Data Bus B DRAM
21 DVSS Digital GND (0 V)
22 DD13_BI DRAM Data Bus B DRAM
23 DD2_BI DRAM Data Bus B DRAM
24 DD12_BI DRAM Data Bus B DRAM
25 DD3_BI DRAM Data Bus B DRAM
26 DVDD Digital Power (+5 V)
27 DD11_BI Digital Data Bus B DRAM
28 DD4_BI Digital Data Bus B DRAM
29 DD10_BI Digital Data Bus B DRAM
30 DD5_BI Digital Data Bus B DRAM
31 DVSS Digital GND (0 V)
32 DD9_BI DRAM Data Bus B DRAM
33 DD6_BI DRAM Data Bus B DRAM
34 DD8_BI DRAM Data Bus B DRAM
35 DD7_BI DRAM Data Bus B DRAM
36 DVSS Digital GND (0 V)
37 ZLCAS_OUT DRAM Low Column Address Strobe O DRAM
38 ZUCAS_OUT DRAM Upper Column Address Strobe O DRAM
39 ZWE1_OUT DRAM Write Enable 1 (8M ONLY) O DRAM
40 ZWE0_OUT DRAM Write Enable 0 (4M, 8M, 16M) O DRAM
41 ZOE1_OUT DRAM Output Enable 1 (16M MODE DADR9) O DRAM
46 DADR7_OUT DRAM Address Bus O DRAM
44 ZRAS_OUT DRAM Row Address Strobe O DRAM
45 DADR8_OUT
47 DVSS Digital GND (0 V)
42 DVDD Digital Power (+5 V)
43 ZOE0_OUT DRAM Output Enable 0 O DRAM
48 DADR0_OUT DRAM Address Bus O DRAM
49 DADR6_OUT DRAM Address Bus O DRAM
50 DADR1_OUT DRAM Address Bus O DRAM
51 DADR5_OUT DRAM Address Bus O DRAM
52 DADR2_OUT DRAM Address Bus O DRAM
53 DADR4_OUT DRAM Address Bus O DRAM
54 DADR3_OUT DRAM Address Bus O DRAM
55 DVSS Digital GND (0 V)
56 DVSS Digital GND (0 V)
57 TOS_OUT Top of Sector O AV Decoder
58 DATACK_OUT Data Acknowledge Signal Output O AV Decoder
59 DVDD DIGITAL Power (+5 V)
60 SDATA0_OUT DVD Data/CD Data Bit Stream (CDATA) O AV Decoder
61 SDATA1_OUT DVD Data/CD Data L/R Clock (LRCK) O AV Decoder
62 SDATA2_OUT DVD Data/CD Data Bit Clock (BLCK) O AV Decoder
63 SDATA3_OUT DVD Data/CD Data Error Flag (C2PO) O AV Decoder
64 SDATA4_OUT DVD Data/Subcode Serial Data (SQDT) O AV Decoder
Reference Information
2-4
2-1-3 DIC2 (KM416C254D ; CMOS 4M DRAM)
WE
CASL CAS
CASH
NO.2 CLOCK
GENERATOR
COLUMN
9
ADDRESS
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
D8
BUFFER
REFRESH
CONTROLLER
REFRESH
COUNTER
9
ROW.
ADDRESS
BUFFERS(9)
CONTROL
LOGIC
99
ROW
9
512
DECODER
DATA-IN BUFFER
COLUMN
DECODER
512
SENSE AMPLIFIERS
512x512x16
88
VO GATING
512x16
MEMORY
ARRAY
IO0
16
IO15
DATA-OUT
BUFFER
OE
16
RAS
NO.1CLOCK
GENERATOR
Vcc
Vss
Reference Information
2-5
PIN NO. SYM. TYPE DESCRITION
16~19, 22~26 A0~A8 Input Address Input
14 RAS Input Row Address Strobe
28 CASH Input Column Address Strobe/Upper Byte Control
29 CASL Input Column Address Strobe/Lower Byte Control
13 WE Input Write Enable
27 OE Input Output Enable
2~5, 7~10, 31~34, 36~39 I/O0~I/O15 Input/Output Data Input/Output
1, 6, 20 Vcc Supply Power, 5V
21, 35, 40 Vss Ground Ground
11, 12, 15, 30 NC - No Connect
Reference Information
2-6
2-1-4 MIC1 (TMP95C265 ; Main Micom)
AND~AN2
(PA0~PA2)
AN3/ADTRG
(PA3)
AN4~AN7
(PA4~PA7)
VREFH
VREFL
AVCC
AV55
DAOUT0,1
TxD0(P80)
RxD0(P81)
SCLK0/CT50(P82)
TxD1(P83)
RxD1(P84)
SCLK1/CT51(P85)
TxD2(P86)
RxD2(P87)
SCLK2/CT52(P57)
T10/INT(P70)
TO1(P71)
TO3/INT2(P72)
10BIT 8CH
A/D
CONVERTER
8BIT 2CH
A/D
CONVERTER
SERIAL I/O
(CH. 0)
SERIAL I/O
(CH. 1)
SERIAL I/O
(CH. 2)
8BIT TIMER
(TIMER 0)
8BIT TIMER
(TIMER 1)
8BIT TIMER
(TIMER 2)
8BIT TIMER
(TIMER 3)
900/H CPU
XWA
XBC
XDE
XHL
XIX
XIY
XIZ
XSP
WATCHDOG
W
BC
DE
H
32bit
SR
PC
TIMER
2KB ROM
IX
IY
IZ
SP
VCC [3]
A
L
F
OSC
PORT0
PORT1
PORT2
PORT3
PORT4
PORT5
CS/WAIT
CONTROLLER
(4-BLOCK)
VSS[3]
X1
X2
CLK
AM8/16
EA
RESET
(P00~P07)
D0~D7 *
(P10~P17)
D8~D15
(P20~P27)
A15~A23 *
(P30~P37)
A8~A15 *
(P40~P47)
A0~A7 *
RD(P50)*
WR(P51)*
HWR(P52)
BUSRQ(P53)
BUSAK(P54)
WAIT(P55)
C50(P60)
C51(P61)
C52(P62)
C53(P63)
T14/INT3(P73)
TO5(P74)
TO7/INT4(P75)
8BIT TIMER
(TIMER 4)
8BIT TIMER
(TIMER 5)
8BIT TIMER
(TIMER 6)
8BIT TIMER
(TIMER 7)
64KB ROM
Not included in
TMP95C265
INTERRUPT
CONTROLLER
16BIT TIMER
(TIMER 8)
16BIT TIMER
(TIMER 9)
NIMI
INTO(P56)
T18/INT5(P90)
T19/INT6(P91)
TO8(P92)
TO9(P93)
TIA/INT7(P94)
TIB/INT8(P95)
TOA/TOB(P96)
Reference Information
2-7
EPROM, SRAM ADDRESS
EPROM, SRAM ADDRESS
EPROM, SRAM ADDRESS
EPROM, SRAM ADDRESS
EPROM, SRAM ADDRESS
EPROM, SRAM ADDRESS
EPROM, SRAM ADDRESS
EPROM, SRAM ADDRESS
EPROM, SRAM, Zlva Adrs
EPROM, SRAM, Zlva Adrs
EPROM, SRAM, Zlva Adrs
EPROM, SRAM ADDRESS
EPROM, SRAM ADDRESS
EPROM, SRAM ADDRESS
EPROM, SRAM ADDRESS
EPROM, SRAM ADDRESS
EPROM, SRAM ADDRESS
EPROM, SRAM ADDRESS
EPROM, SRAM ADDRESS
EPROM, SRAM ADDRESS
51 D6 HAD6 Data6 I/0
NO PORT NAME ASSIGNED NAME DESCRIPTION TYPE REMARK
52 D7 HAD7 Data7 I/0
53 P10 CLSW Close Switch I DECK
54 P11 OPSW Open Swithc I DECK
55 P12 MTP8 Reserved I/0 0 NC
56 P13 MTP9 Reserved I/0 0 NC
57 P14 MTP10 Reserved I/0 0 NC
58 P15 MTP11 Reserved I/0 0 NC
0 74HCOO(5)
SERVO /RD Strobe Mask Signal
69 A18 HA18 Address 18 0
70 A17 HA17 Address 17 0
71 A16 HA16 Address 16 0
72 A15 HA15 Address 15 0
73 A14 HA14 Address 14 0
74 A13 HA13 Address 13 0
75 A12 HA12 Address 12 0
76 A11 HA11 Address 11 0
77 A10 HA10 Address 10 0
78 A9 HA9 Address 9 0
79 A8 HA8 Address 8 0
80 A7 HA7 Address 7 0
81 A6 HA6 Address 6 0
82 A5 HA5 Address 5 0
83 A4 HA4 Address 4 0
84 A3 HA3 Address 3 0
85 A2 HA2 Address 2 0
86 A1 HA1 Address 1(SERVO DAB) 0
87 A0 HA0 Address 0(DSP DAB) 0
65 P26/A22 MRP14 Reserved Address Port 0 NC
66 P25/A21 MRP15 Reserved Address Port 0 NC
67 P24/A20 MRP16 Reserved Address Port 0 NC
59 P16 MTP12 Reserved I/0 0 NC
60 P17 MTP13 Reserved I/0 0 NC
62 Vss DGND - GND
63 Vcc 5D - VCC
64 A23 HA23
61 AM8/16 AM8 Address Mode(H:8 BIT MODE) I VCC
68 A19 HA19 Address 19 0
88 /RD /RD /Read Strobe 0 /Read
I KS1452 (7)
Tracking Lock monitir from SERVO
89 /WR /WR /Write Strobe 0 /Write
90 P52 RSTB RF&Servo IC Reset 0 KS1461 (73), KS1452 (9)
91 Vss DGND - DGND
92 PA0 RFRP
I BA6849FP (20)
Spindle direcrion from SP Driver
93 PA1 TILTO Monitor signal I KS1452 (69)
94 PA2 MTP17 Reserved I I NC
95 PA3 SENSE SENSE monitor from SERVO I KS1452 (22)
96 PA4 FR
97 PA5 SLOCK LOCK monitor from DSP I KS1453 (108)
98 PA6 FOKB Focus lock monitor from RF I KS1461 (48)
99 PA7 RFO RF sum signal (Analog Lnput) I RFO
100 VREFH 5D A/D Ref Input (H) I 5D
1 VREFL DGND A/D Ref Input(L) I DGND
2 AVss DGND A/D Ref Input - DGND
NO PORT NAME ASSIGNED NAME DESCRIPTION TYPE REMARK
20MHz
0 Data Processor(KS1453)
0 fc/2
Data Processor(KS1453) Select
CLOCK OUTPUT (System Clock 2)
3 AVcc 5D A/D VCC Input - 5D
4 DAOUT0 MTP1 0 NC
5 DAOUT1 MPT2 0 NC
6 /NMI - PULL-UP I
7 P53 CSB D. Servo IC Chip Select 0 KS1452(10)
8 P54/BUSAK MTP3 0
9 /WAIT /MWAIT /Wait(ZiVA, DSP) I /MWait
10 P56 DVD/CD DVD/CD RF AGC Gain Select 0 RF(KS1461)
11 SCLK2 SCLK Serial Data Clock I FRONT
12 P80/TXD0 MD RF Contrl Data 0 KS1461(69)
13 P81/RXD0 STB RF Data Latch I/0 KS1461(71)
14 P82/SCLKO MC RF Control Clock 0 KS1461(70)
15 P83/TXD1 MTP5 0 NC
16 P84/RXD1 MTP6 0 NC
17 P85/SCLK1 MTP4 0 NC
18 TXD2 RXD Serial Data Output 0 FRONT
19 RXD2 TXD Serial Data Input I FRONT
20 CSO /CSO EPROM(M27C801) Select 0 EPROM(M27C801)
24 CLK CLK
21 CS1 /CS1 SRAM(KM681000) Select 0 SRAM(KM681000)
25 Vcc 5D - VCC
22 CS2 /DVD1CS AVDecoder(ZiVA4) Select 0 AVDecoder(ZiVA4)
23 CS3 /DSPCS
26 Vss GDND GND - GND
27 X1 X1 High Frequency OSC in I
28 X2 X2 High frequency OSC out 0
29 /EA /EA Internal ROM Less Mode I GND
30 /REST /MRST Master reset from FRONT I FRONT, IC
31 INT1 SRQ Interrupt from Front Micom I FRONT
32 P71 RRQ Request to Front Micom 0 FRONT
33 P72 SCL EEPROM CLOCK 0 KS24C020(6)
I DRIVER(FG, 2)
Interrupt from Spindle Motor FG
38 P91 ACT MUTE Driver IC MUTE(Actuator) 0 DRIVER(MUTE4, 37)
34 P73 SDA EEPROM DATA I/O 0 KS24C020(5)
35 P74 OPEN Tray Out Motor Control Output 0 DRIVER(0PIN-, 16)
39 P92 M/D MUTE Driver IC MUTE(Spindle) 0 DRIVER(MUTE3, 38)
36 P75 CLOSE Tray In Motor Control Output 0 DRIVER(0PIN-, 17)
37 INT5 FGINT
0 ZiVA-4(52)
AV Decoder Reset(Active H:4.0, L:4.1)
40 P93 ZRST DSP H/W reset 0 KS1453(124)
41 INT7 /DVDINT Interrupt from AV-DEC I INV(ZiVA-4(51))
42 INT8 /DSPINT Interrupt from DSP I INV(KS1453(126))
43 P96 ZIVA_RST
44 Vcc 5D
45 D0 HAD0 Data 0 I/0
46 D1 HAD1 Data 1 I/0
47 D2 HAD2 Data 2 I/0
48 D3 HAD3 Data 3 I/0
49 D4 HAD4 Data 4 I/0
50 D5 HAD5 Data 5 I/0

Reference Information
2-8
2-1-5 MIC2 (M27C801 ; 8Mbit (1Mbx8) UVEPROM and OTP EPROM)
LOGIC DIAGRAM
Vcc
A19
A16
A15
A12
A7
A6
A5
A4
A3
A2
A1
A0
Q0
Q1
Q2
Vss
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
20
8
A0-A19 A0-Q7
E
GVpp
Vss
TOP VIEW
Vcc
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
A18
A17
A14
A13
A8
A9
A11
GV
A10
E
Q7
Q6
Q4
Q4
Q3
PP
NAME
A0-A19
Q0-Q7
E
OVpp
Vcc
Vss
Data Outputs
FUNCTION
Address Inputs
Chip Enable
Output Enable/Program Supply
Supply Voltage
Ground
Reference Information
2-9
2-1-6 MIC3 (KM681000C ; CMOS 1M SRAM)
BLOCK DIAGRAM
CS1
CS2
WE
OE
I/O
I/O8
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A12
A13
A14
A15
A16
1
Control
logic
Clk gen.
Row
select
Data
cont
Data
cont
Precharge circuit.
VCC
VSS
Memory array
1024 rows
128· 8 columns
I/O Circuit
Column select
A0 A1 A2 A3 A9 A11A10
N.C
A16
A14
A12
A7
A6
A5
A4
A3
A2
A1
A0
I/O1
I/O2
I/O3
VSS
TOP VIEW
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
Name Function Name Function
VCC
32
A15
31
CS2
30
WE
29
28
A13
A8
27
A9
26
25
A11
24
OE
23
A10
22
CS
1
21
I/O8
20
I/O7
19
I/O6
18
I/O5
17
I/O4
CS1,CS2 Chip Select Inputs I/O1~I/O8 Data Inputs/Out-
OE
WE
0~A16 Address Inputs N.C No Connection
A
Output Enable Vcc Power
Write Enable Vss Ground

Reference Information
2-10
2-1-7 FIC1 (LC86P6232 ; Front Micom)
IR PLA
SIO 0
SIO 1
Timer 0
Timer 1
BUS
Interrupt Control
Stand-by Control
CF
Clock
RC
Generator
X’tal
Bus InterfaceBase Timer
Port 1
Port 7
Port 8
Port 2
BUS
ROM
PC
ACC
B Reg
C Reg
ALU
ADC
INT0-3
Noise Filter
Real Time
Service
XRAM
(128 bytes)
VFD Controller
High Voltage
Output
Port 3
Port 4
Port 5
PWM 1
PSW
RAR
RAM
Stack Pointer
PORT 0
Watch Dog Timer
Reference Information
2-11
51 S18 - SEG7 FLT SEGMENT CONTROL FLT
52 S19 - SEG8 FLT SEGMENT CONTROL FLT
NO PORT NAME TYPE ASSIGNED NAME DESCRIPTION REMARK
53 S20 - SEG9 FLT SEGMENT CONTROL FLT
54 S21 0 SEG10 FLT SEGMENT CONTROL FLT
55 S22 0 SEG11 FLT SEGMENT CONTROL FLT
56 S23 0 SEG12 FLT SEGMENT CONTROL FLT
57 S24 0 SEG13 FLT SEGMENT CONTROL FLT
58 S25 0 SEG14 FLT SEGMENT CONTROL FLT
59 S26 0 SEG15 FLT SEGMENT CONTROL FLT
60 S27 0 SEG16 FLT SEGMENT CONTROL FLT
61 S28 0 SEG17 FLT SEGMENT CONTROL FLT
62 S29 0 SEG18 FLT SEGMENT CONTROL FLT
63 S30 0 SEG19 FLT SEGMENT CONTROL FLT
64 S31 0 SEG20 FLT SEGMENT CONTROL FLT
65 P00 I MODE4 HARDWARE MODE SELECT MARKET CODE
66 P01 I MODE3 HARDWARE MODE SELECT MARKET CODE
67 P02 I MODE2 HARDWARE MODE SELECT MARKET CODE
68 P03 I MODE1 HARDWARE MODE SELECT MARKET CODE
69 P04 I MODE0 HARDWARE MODE SELECT MARKET CODE
70 P05 - TP10 NC
71 P06 - TP11 NC
72 P07 -- NC
73 P10/S0 0 0 TXD SERIAL DATA OUT SERIAL DATA OUT
74 P11/S1 0 I RXD SERIAL DATA IN SERIAL DATA IN
75 P12/SC K0 0 SCLK SERIAL CLOCK SERIAL CLOCK
76 P13/S0 1 - TP12 NC
77 P14/SI 1 - TP13 NC
78 P15/SC K1 - TP14 NC
79 P16/BU Z - TP15 NC
80 P17/PW MO - TP16 NC
81 P30 I S1 SHUTTLE DATA JOG/SHUTTLE
82 P31 I S2 SHUTTLE DATA JOG/SHUTTLE
83 P32 I S3 SHUTTLE DATA JOG/SHUTTLE
84 P33 I S4 SHUTTLE DATA JOG/SHUTTLE
85 P34 I J1 JOG DATA JOG/SHUTTLE
86 P35 I J2 JOG DATA JOG/SHUTTLE
87 P36 I AT VIDEO OUT SEL. VIDEO SELECT(OPEN)
88 P37 I AD VIDEO OUT SEL. VIDEO SELECT
89 VSS - +5V
90 VDD - GND
91 P40 0 RGBCTL SCART CONTROL SCART JACK
92 P41 0 SCON_B SCART CONTROL SCART JACK
93 P42 - TP28 NC
94 P43 0 WIDE SCART CONTROL SCART JACK
95 P44 0 SRQ request to main micom NC
96 P45 0 SAVE POWER SAVE MODE POWER
97 P46 0 AMUTE1 REAR MUTE AUDIO
98 P47 0 AMUTE0 FRONT MUTE AUDIO
99 P50 0 LED STANDBY LED LED
100 P51 0 ON/OFF POWER ON/OFF CONTROL POWER
1 P52 0 MRST Front end reset RESET
2 PWM1 - TP1 NC
NO PORT NAME TYPE ASSIGNED NAME DESCRIPTION REMARK
3 P20 0 CS1 Chip Select 1 AK4393
4 P21 0 CCLK Control Data Clock AK4393/AK4356
5 P22 0 CDTI Control Data AK4393/AK4356
6 P23 0 CS2 Chip Select 2 AK4356
7 P24 0 DARST PD(Power Down) AK4393
8 P25 0 DARST 1 PD(Power Down) AK4356
9 P26 0 VMUTE0 BA7660 MUTE(VIC2) VIDEO(RESERVED)
10 P27 0 VMUTE1 BA7660 MUTE(VIC1) VIDEO(RESERVED)
11 TEST1 - TP4 NC
12 *RES I *RES Reset
13 XT1 - GND Low Frequency OSC in
14 XT2 - TP5 Low Frequency OSC out
15 VSS - GND
16 CF1 I - High Frequency OSC in
17 CF2 0 - High Frequency OSC out
18 VDD - VDD
19 ANO/P8 0 I ECHO_VR ECHO volume A/D input KARAOKE
20 AN1/P8 1 I MIC_DET MIC detect KARAOKE
21 AN2/P8 2 - TP19 NC
22 AN3/P8 3 I KEY0 KEY SCAN TACT SW
23 AN4/P8 4 I KEY1 KEY SCAN TACT SW
24 AN5/P8 5 I KEY2 KEY SCAN TACT SW
25 AN6/P8 6 - NC
26 AN7/P8 7 - NC
27 P70/IN TO I RRQ Request to Front Micom MAIN MICOM
28 P71/IN T1 - TP25 NC
29 P72/IN T2 - TP26 NC
30 P73/IN T3 I REMOCON REMOCON data in REMOCON EYE
31 S0/T0 0 GRID11 FLT GRID CONTROL FLT
32 S1/T1 0 GRID10 FLT GRID CONTROL FLT
33 S2/T2 0 GRID9 FLT GRID CONTROL FLT
34 S3/T3 0 GRID8 FLT GRID CONTROL FLT
35 S4/T4 0 GRID7 FLT GRID CONTROL FLT
36 S5/T5 0 GRID6 FLT GRID CONTROL FLT
37 S6/T6 0 GRID5 FLT GRID CONTROL FLT
38 S7/T7 0 GRID4 FLT GRID CONTROL FLT
39 S8/T8 0 GRID3 FLT GRID CONTROL FLT
40 S9/T9 0 GRID2 FLT GRID CONTROL FLT
41 S10/T10 0 GRID1 FLT GRID CONTROL FLT
42 S11/T11 0
43 S12/T12 0 SEG1 FLT SEGMENT CONTROL FLT
44 S13/T13 0 SEG2 FLT SEGMENT CONTROL FLT
45 S14/T14 0 SEG3 FLT SEGMENT CONTROL FLT
46 S15/T15 0 SEG4 FLT SEGMENT CONTROL FLT
47 VOD - +5V
48 VP - -28V
49 S16 0 SEG5 FLT SEGMENT CONTROL FLT
50 S17 0 SEG6 FLT SEGMENT CONTROL FLT
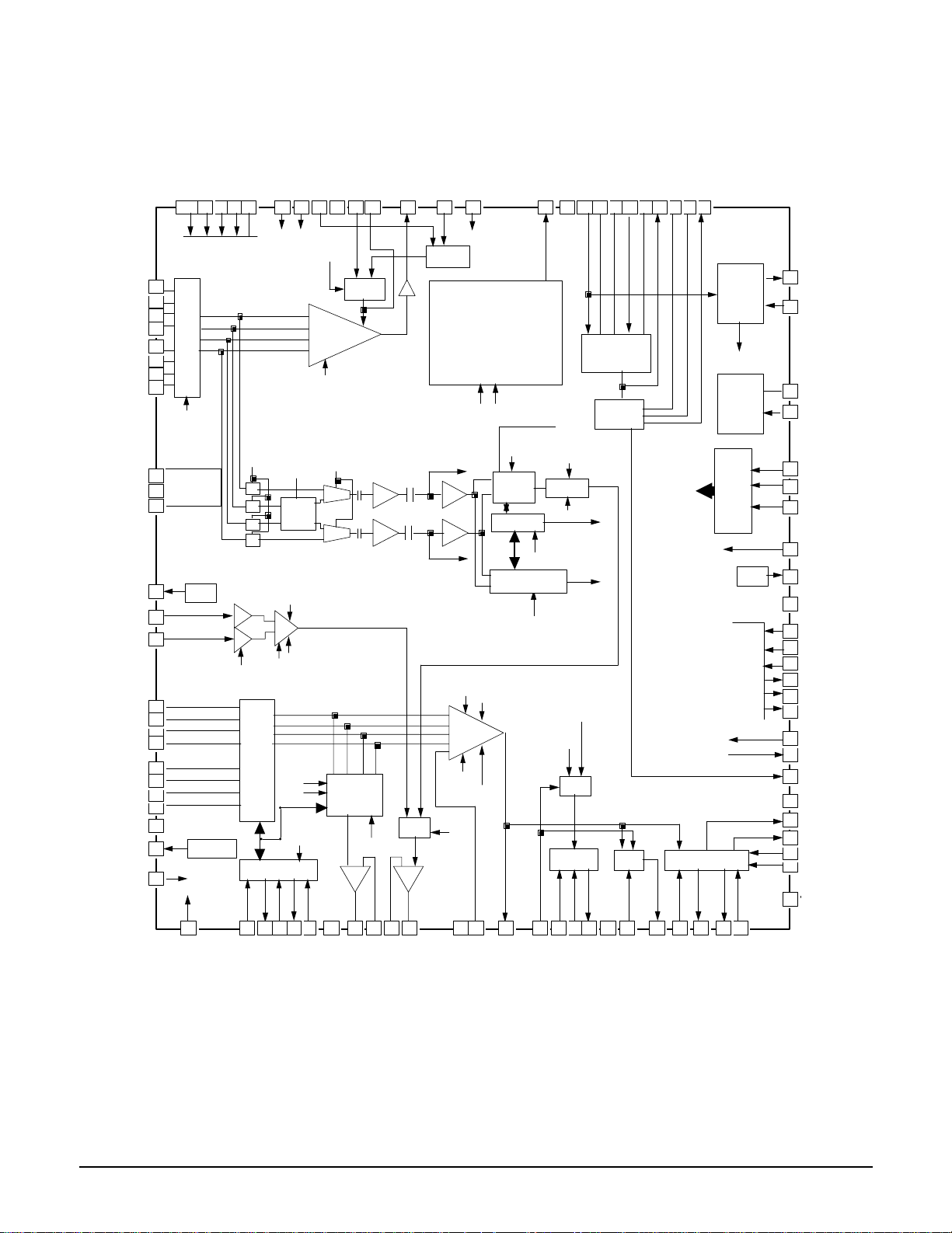
Reference Information
2-12
2-1-8 RIC1 (KS1461 ; RF Signal Processor)
ACD
BCD
CCD
DCD
ADVD
BDVD
CDVD
DDVD
RREFBF
RR EFEQ
RREF
VREFEQ
ADVD 1
BDVD 1
CDVD1
DDVD1
ACD1
BCD1
CCD1
DCD1
AVCC
VREF A
FOFST
VZOCTL
PLL F
EQF
100 98 94 92 89 8591 76848788 8293
to RF EQ
TUNING BLO CK
1
2
3
4
5
RF
MUX
A
B
C
D
6
7
8
CDR SEL( 00H )
9
VREF
GENERATOR
10
11
EQ VC
12
AMP
E
13
14
F
TBAL(01 H)
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
CDRS EL(00H )
ANALOG
VC AMP
25
AGCL EVEL
RDPF
EQG
AGCP
EQGND
AGCB
AGCI
97 959699 86
AGC-HOLD(00 H)
MUX
+
+
RF SUM
&AGC
+
+
GAIN_EQ(02 H)
DELAY_AB(07 H)
DELAY_C D(07H )
PLLC TL
DVCTL_SEL(02H)
D
D
D
D
GA _PLL DN (09 H )
GA _PLL DP (09 H)
GAIN_TE3(02H)
GCA
-
+
GCA
TEOFST(04H)
D1
C1
SUB
A1
RF
MUX
GAIN_FE(03 H)
FE_OFST(05H)
ALPC
B1
ga_RFSUM(08H)
GCA
MUX3
GCA
TE3B
OFSTHOLD
FE
LDONB (00 H)
+
FOFST
RFAGCO
AGCC
BCATH
EQIN
90
AGC_D ET
RF
Equali zer
S12
CD1
TE1RES
DELAY_SEL(00H)
PLL CTL
TBAL( 01H)
DPDEQ 1
+
+
+
+
OFSTHOLD
EQ
EQ
COM
COM
DPDEQ 2
CDR SEL( 00H )
OFSTHOLD
ABCD_ OFST(06H)
MUX
TESEL(00H )
-
-+
GAIN_ABCD(00H)
+
+
AB CD
+
SUM
+
-
DELA Y
TE1_LIMIT
Ab normal wav eform
Det ectio n c ircu it
DELAY_SEL(00H)
PLL CTL
ENV_SEL(02 H)
EQVCC
RFEQO
HOL D_CT L ( 0 8 H)
DPDMUTE
DPD_MUTE(02H)
SEOFHO LD
FL T _ CT L ( 0 0 H)
CAL_ENDB(02H)
PD,LPF
TEOFST( 04H)
PDLIMITRES
PD_L IMI T( 08 H)
FAUL TOUT
EQIN
MUX
ENVELOPE FOK DE FE CT
MROFST
83
CP1
CB1
RF RP
RFCT
MIRR
RFRPN
RFRP
CP2
CB2
80 77787981
&
CD1
S12
DVD1
DVD2
LDONB
FLT_CTL
CDRSEL
TESEL
AGC HOLD
TBAL
GAIN_TE3
ENV_ SE L
DVCTL_SEL
DPD_MUTE
GAIN_EQ
GAIN_FE
GAIN_AB CD
TE_OFST
FE_OFST
AB CD_OF ST
DELAY_CD
DELAY_AB
PDL IM I T
ga_RFSUM
HOLD_CTL
ga_PLLDP
ga_PLLDN
MIRRI
RFCT
BCA
BLOCK
BCA
AUTO
OFSTCTL
S/ I F
BLOCK
DPD
VC AMP
toDPD
BLOCK
75
BCAO
BCAI
74
73
RESET
72
OSC
71
STB
70
CLOCK
DATA
69
68
RREFDLY
VREFDPD
67
DPDGND
66
65
TE1RES
64
PL LCTL
63
DPDMUTE
62
FAULTOUT
DPDEQ2
61
DPDEQ1
60
59
TE3OFST
58
BCA
57
MIRR
56
DPDVCC
55
DFCT2
54
DFCT1
DFCTTH1
53
52
DFCTTH2
DVCC
51
31 42 43 4644 5026 27 40 41 47 4839 453428 32 3329 30 36 37 3835 49
LDODVD
PDVD
LDOCD
PDC D
OFSTH OLD
VREFLP_ BGI
AGND
FE
TEN
TE
FEN
ABCDN
PDL IMITRES
ABCDI
ABCD
ENVP
ENVB
FOKTH
DGND
ENV
DFCT_CP2
CC1
DFCT_CP1
FOKB
CC2
Reference Information
2-13
Pin
Pin Name I/O Description Related Block
No.
1 ACD I Optical main beam A, AC Coupling input terminals for CD of RF
2 BCD I Optical main beam B, AC Coupling input terminals for CD of RF
3 CCD I Optical main beam C, AC Coupling input terminals for CD of RF
4 DCD I Optical main beam D, AC Coupling input terminals for CD of RF
5 ADVD I Optical main beam A, AC Coupling input terminals for DVD of RF
6 BDVD I Optical main beam B, AC Coupling input terminals for DVD of RF
7 CDVD I Optical main beam C, AC Coupling input terminals for DVD of RF
8 DDVD I Optical main beam D, AC Coupling input terminals for DVD of RF
9 RREFBF - RF AMP I/O buffer bias resistance connection terminal RF AMP -
10 RREFEQ - RF EQ BIAS resistance connection terminal RF EQ -
11 RREF - Analog Block bias resistance connection terminal ANALOG -
12 VREFEQ - CAP connection terminal for RF EQ Center voltage EQ VC AMP -
13 E I CD Optical sub beam E input terminal for Servos TE 3B P/U
14 F I CD Optical sub beam F input terminal for Servos TE 3B P/U
15 ADVD1 I Optical main beam A input terminal for DVD of Servo block SERVO AMP P/U
16 BDVD1 I Optical main beam B input terminal for DVD of Servo block SERVO AMP P/U
17 CDVD1 I Optical main beam C input terminal for DVD of Servo block SERVO AMP P/U
18 DDVD1 I Optical main beam D input terminal for DVD of Servo block SERVO AMP P/U
19 ACD1 I Optical main beam A input terminal for CD of Servo block SERVO AMP P/U
20 BCD1 I Optical main beam B input terminal for CD of Servo block SERVO AMP P/U
21 CCD1 I Optical main beam C input terminal for CD of Servo block SERVO AMP P/U
22 DCD1 I Optical main beam D input terminal for CD of Servo block SERVO AMP P/U
23 AVCC P Power voltage input terminal for Analog Part ANALOG -
24 VREFA I/O CAP connection terminal for Analog Part center voltage
25 FOFST - CAP connection terminal (open) for Focus Auto Offsets FE AMP -
26 OFSTHOLD I On/Off terminal for Auto Offset Block.
27 VREFLP_BGI I Band gap voltage input block for ALPC ALPC -
28 LDODVD O
29 PDDVD I
30 LDOCD O
31 PDCD I
32 AGND P
33 FE O
34 FEN I
35 TEN I
36 TE O
37 PDLIMTRES -
38 ABCDN I
39 ABCD O
40 ABCDI I
41 ENVP -
42 ENVB -
43 ENV O
44 DGND P
45 FOKTH I
46 FOKB O
47 DFCT_CP1 -
48 DFCT_CP2 -
49 CC1 O
50 CC2 I
51 DVCC P
52 DFCTTH2 -
53 DFCTTH1 -
54 DFCT1 O
55 DFCT2 O
56 DPDVCC P
57 MIRR O
58 BCA O
block
block
block
block
block
block
block
block
Uses an external block
(L: Auto Offset Adjustments, H: Serial Offset Adjustments)
Optical Laser Diodes operation voltage output terminal for DVD
Optical Laser Monitor Diode voltage input terminal for DVD
Optical Laser Diode operating voltage output terminal for CD
Optical Laser Monitor Diode voltage input terminal for CD
Power GND terminal for Analog Part
FE AMP output terminal
Input terminal for selecting FE AMP Gain
Input terminal for selecting TE AMP Gain
TE AMP output terminal
Bias resistance terminal for PDLIMIT
ABCD AMP for selecting Gain (
ABCD AMP output terminal
ABCD AC Coupling input terminal for servo monitor
CAP connection terminal for selecting the RC value of Peak Hold
for detecting RF Envelopes
CAP connection terminal for selecting the RC value of Bottom
Hold for detecting RF Envelopes
RF Envelope Detect Output terminal
Power GND input terminal for digital circuits
Focus OK comparating level input terminal
Focus OK comparator output terminal (L: Focus OK)
Connection terminal for RC value of Peak Hold, for selecting the
maximum time for Servo signal
Connection terminal for RC value of Peak Hold, for selecting the
minimum defect time for PLL
Peak Hold Output terminal for selecting the minimum Defect time
for Defect
Peak Hold AC Coupling Input terminal for Defect
Power voltage input terminal for digital circuit
Resistance connection terminal for selecting the Defect Comparating Level for PLL
Resistance connection terminal for selecting the Defect Comparating Level for Servo
Defect output terminal for Servo
Defect output terminal for PLL
Power voltage input terminal for DPD TE
Mirror output terminal
BCA output terminal
- ) input terminal
PRE AMP P/U
PRE AMP P/U
PRE AMP P/U
PRE AMP P/U
PRE AMP P/U
PRE AMP P/U
PRE AMP P/U
PRE AMP P/U
ANA VC AMP SERVO
OFSTCTL MICOM
ALPC P/U
ALPC P/U
ALPC P/U
ALPC P/U
ANALOG -
FE AMP DSSP
FE AMP -
TE AMP -
TE AMP DSSP
DPD -
ABCD AMP -
ABCD AMP -
SERVO MONIT -
RF ENV -
RF ENV -
RF ENV DSSP
DIGITAL -
FOKB -
FOKB DSSP
DFCT -
DFCT -
DFCT -
DFCT -
DIGITAL -
DEFECT -
DEFECT -
DEFECT DSSP
DEFECT PLL
DPD -
MIRR DSSP
BCA DSP
Related
Part
Pin
Pin Name I/O Description Related Block
No.
59 TE3OFST -
60 DPDEQ1 O
61 DPDEQ2 O
62 FAULTOUT O
63 DPDMUTE I
64 PLLCTL I
65 TE1RES I
66 DPDGND P
67 VREFDPD O
68 RREFDLY -
69 DATA I
70 CLOCK I
71 STB I
72 OSC
73 RESET I
74 BCAI I
75 BCAO O
76 RFCT O
77 CB2 -
78 CP2 -
79 RFRP O
80 RFRPN I
81 MROFST I
82 CB1 -
83 CP1 -
84 MIRRI I
85 EQVCC P
86 RFEQ0 0
87 BCATH I
88 EQIN I
89 RFAGCO O
90 AGCC -
91 AGCI I
92 EQGND P
93 AGCLEVEL I
94 AGCB -
95 AGCP -
96 RDPF -
97 EQG I
98 EQF I
99 PLLF I
100 VZOCTL I
Cap connection terminal (open) for 3B TE Offset
DPD EQ (A+C) output terminal
DPD EQ (B+D) output terminal
DPD abnormal wave form output terminal (monitor)
DPD TE MUTE control terminal (H: Mute)
DPD TE PLL variable input terminal
DPD TE PLL variable bias resistance
Power GND input terminal for DPD TE
CAP connection terminal for DPD TE center voltage
Bias resistance connection terminal for Delay Block
Data input terminal
Clock input terminal
Data Enable input terminal
Input terminal for RC value of OSC, for Auto Offset Block
Reset input terminal (L: Reset) for Auto Offset Block
BCA Filter1
BCA Filter2
RF Ripple Center voltage output terminal for Mirror
CAP connection terminal of RC value of Bottom Hold, for RFCT
generation
CAP connection terminal of RC value of Peak Hold, for RFCT generation
RF Ripple Amp output terminal for Mirror
Input terminal for selecting RFRP Amp gain
RF Ripple Offset control terminal for Mirror
RC connection terminal of RC value of Bottom Hold, for RFRP
generation
RC connection terminal of RC value of Peak Hold, for RFRP generation
Input terminal for MIRR signal generation
Power voltage input signal for RF EQ
RF EQ output terminal
BCA Comparating Level control terminal
RFAGCO input terminal for RF EQ
RF AGC AMP output terminal
CAP connection terminal for time constant of AGC
AGC voltage input terminal while in AGC hold
Power GND input terminal for RF EQ
AGC Level control voltage input terminal (3.5 V) while in AGC hold
off
RC connection terminal for RC value of Bottom Hold, for RF AGC
RC connection terminal for RC value of Peak Hold, for RF AGC
Bias resistance connection terminal for selecting RF EQ frequency
RF EQ Boost Gain control voltage input terminal
RF EQ Peak Frequency control voltage input terminal
Wide-band PLL compatible RF EQ Peak Frequency Control terminal
RF EQ zero control terminal
Related
Related
3B TE AMP -
DPD -
DPD -
DPD -
DPD MICOM
DPD SERVO
DPD -
DPD -
DPD VC AMP -
Delay Block -
Serial Interface MICOM
Serial Interface MICOM
Serial Interface MICOM
Auto OFSTCTL -
Auto OFSTCTL MICOM
BCA -
BCA -
MIRROR DSSP
MIRROR -
MIRROR -
MIRROR DSSP
MIRROR -
MRROR -
MRROR -
MRROR -
MRROR -
RF EQ -
RF EQ PLL
BCA DSP
RFEQ,RFENV DSSP
RF AGC -
RF AGC -
RF AGC -
RF EQ -
RF AGC -
RF AGC -
RF AGC -
RF EQ -
RF EQ DSSP
RF EQ DSSP
RF EQ DSSP
RF EQ DSSP
Part
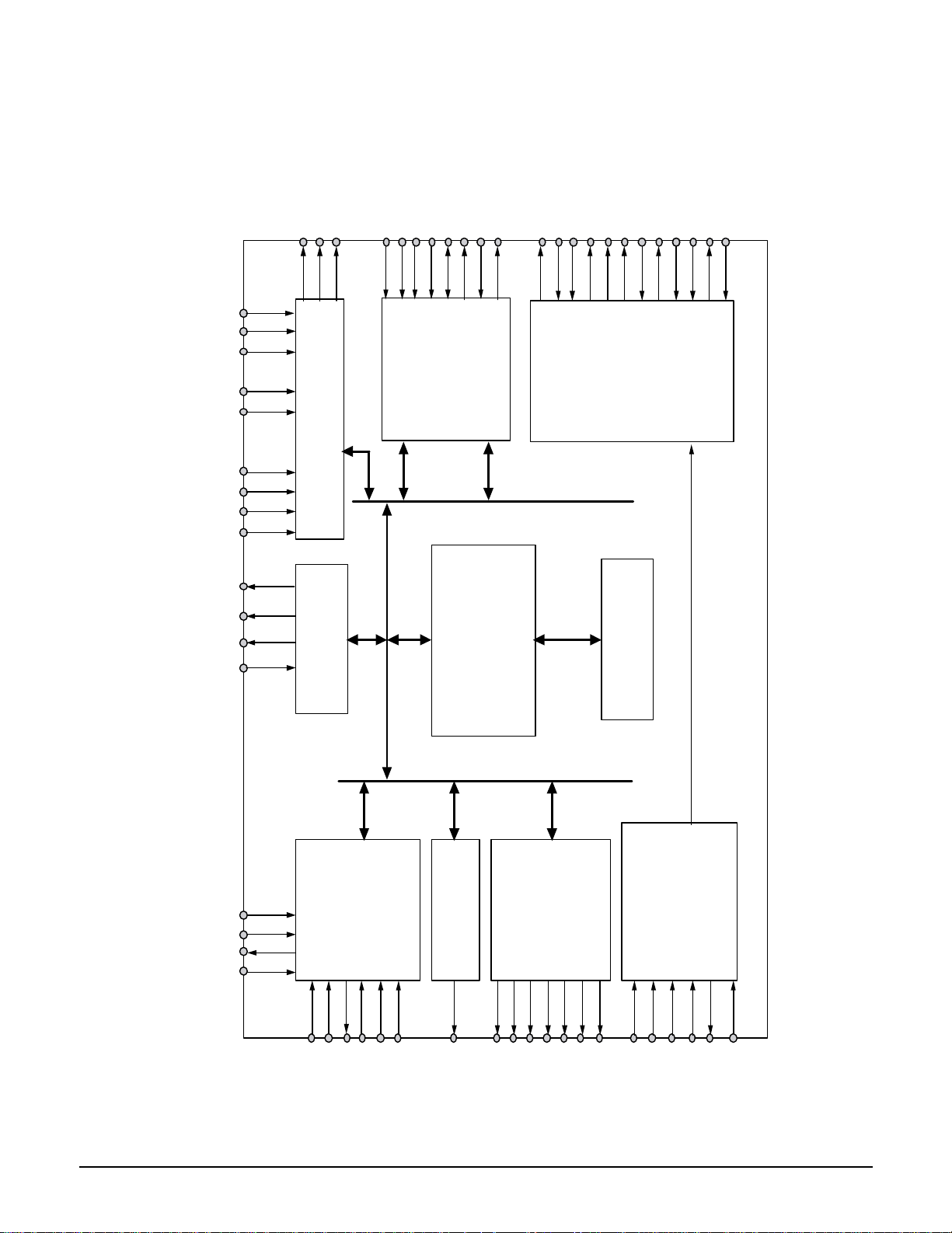
Reference Information
2-14
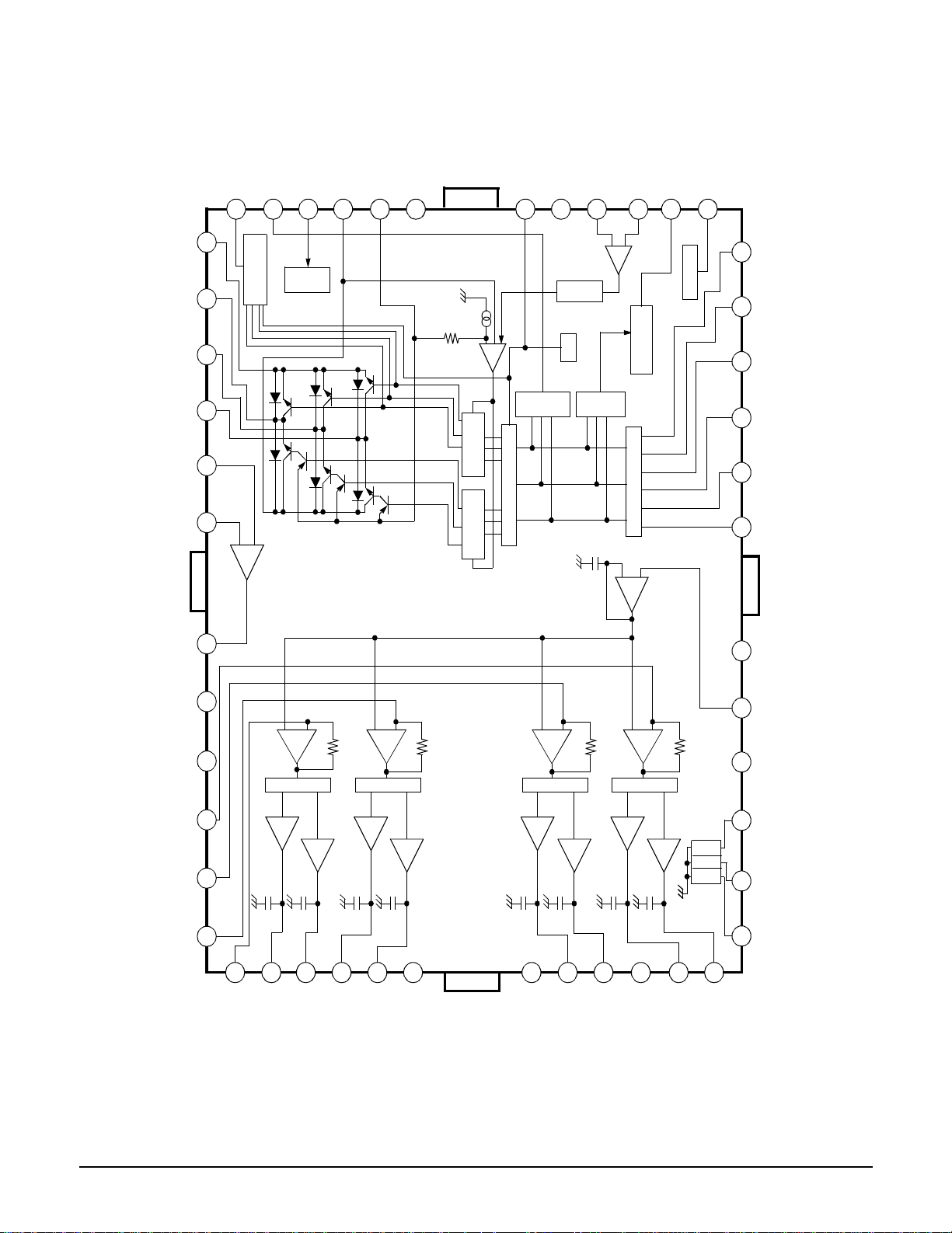
2-1-9 SIC1 (KS1452 ; Servo Processor)
FLKB
TLKB
LDONB
DIRC
PS1
SSTOP/PS0
DAB
CSB
MD ATA[7 :0 ]
MWRB
SENSE
MRDB
PSB
PLLLOCK
MDOUT[3:0]
RFD
PLCK
RVCO
VCT RL
EFM RTD
RPD
EQC TL
MAGIC0
INT 0_224
PLLHD
FDCTL
SMO N
LOCK
DFCT
FOKB
MIRR
TZCA
PHI 1
XOUT
XO
BLOCK
SYSCON
IN TE R FACE
RANGE PLL
WIDE CAPTURE
I/O IN TE R FACE B LOC K
XI
TIMI N G
GENER ATOR
FOR
DSP CORE
DIGIT AL SER VO
ROM
TEST
RSTB
TILTO
TILTI
A/D
BLOCK
CONVERTER
TRACK COU NTER
TE
ENV
VREF
TZCO
FE
SME
COUT
D/A
BLOCK
CONVERTER
SLD
TRD
SPD
FBAL
TBAL
DVCTL
FOD
EFM ASYMM ETRY
RFI
EFM I
ASY DVD
EFM
ASY CD
EFM OA
Reference Information
2-15
41 PVDD P PLL logic block VDD power supply pin
42 PLCK O PLCK
No Name I/O Description
43 PLLLOCK O Frequency lock detect output (H: lock, L: unlock)
44 EFMRTD O Latched EFM output signal
45 PVSS P PLL logic block VSS power supply pin
46 RVCO I Resistor pin for VCO gain
47 RFD I Gain adjust resister for frequency detector
48 RPD I Gain adjust resister for phase detector
49 VCTL I control voltage for VCO
50 MAGIC0 I Input for controlling hysteresis of the FD output (for testing)
51 EFMOA I EFM offset adjustment pin
52 TZCO O Tracking zero cross output pin
53 SVDD P Servo CPU VDD power supply pin
54 EQCTL O EQ control signal
55 EFMI I EFM signal for test
56 EFMO O EFM signal
57 LPFDVD I Asymmetric input signal for DVD
58 LPFCD I Asymmetric input signal for CD
59 RFI I Rf input signal
60 SVSS P Servo CPU VSS power supply pin
61 AVSS P Analog block VSS power supply pin
62 SME I Spindle error input pin
63 VREF I Reference voltage input pin
64 TE I Tracking error signal input pin
65 FE I Focus error signal input pin
66 ENV I RF envelope input pin
67 TILTI I TILT in (reserved)
68 AVDD P Analog block VDD power supply pin
69 TILTO O TILT out (reserved)
70 DVCTL O Depth variation control signal output pin
71 TBAL O Tracking balance signal output pin
72 FBAL O Focus balance signal output pin
73 SLD O Sled motor drive signal output pin
74 SPD O Spindle motor drive signal output pin
75 FOD O Focus actuator drive signal output pin
76 TRD O Tracking actuator drive signal output pin
77 TZCA I TE signal for tracking zero cross input pin
Direct jump control (for 1 track jump)
78 MDOUT0 O Mode data0 out controlled by micom
79 MDOUT1 O Mode data1 out controlled by micom
80 MDOUT2 O Mode data2 out controlled by micom
1 MDOUT3 O Mode data3 out controlled by micom
2 SSTOP/PS0PS1 I Limit switch/sled position sensor input pin0
3 PS1 I Sled motor position sensor input pin1
4 TEST I Test pin (L: normal H: test)
5 COUT O Counter clock
6 FLKB O Focus servo lock signal output pin
No Name I/O Description
7 TLKB O Tracking servo lock signal output pin
8 PSB I 0: 1 Bit, 1: 8 Bit
9 RSTB I System reset signal input pin
11 DAB I MICOM data/addrs select pin
10 CSB I MICOM chip select pin
12 MWRB I MICOM write clock signal input pin
13 MRDB I MICOM read clock signal input pin
14 MDATA0 I/O MICOM data pin0
15 MDATA1 I/O MICOM data pin1
16 MDATA2 I/O MICOM data pin2
17 MDATA3 I/O MICOM data pin3
18 MDATA4 I/O MICOM data pin4
19 MDATA5 I/O MICOM data pin5
20 MDATA6 I/O MICOM data pin6
21 MDATA7 I/O MICOM data pin7
22 SENSE O Internal status monitor pin
23 DVDD P Servo logic & ROM VDD power supply pin
24 XI I System clock signal input pin
25 XO O System clock signal output pin
26 XOUT O Clock out (33.9688MHz) to DSP
27 DVSS P Servo logic & ROM VSS power supply pin
28 SQCK O Clock output pin for subcode data read
29 SQSI I Subcode data input pin
30 SCOR I Timing detection input pin for subcode data read
34 FOKB I Focus OK signal input pin
35 FDCTL I PLL frequency detect control input pin
31 SMON I Motor ON signal input pin
32 LOCK I Lock signal input pin
33 DIRC I
36 LDONB O Laser diode ON signal output pin
37 DFCT I Defect detection signal input pin
38 MIRR I Mirror signal input pin
39 PLLHD I PLL hold signal from micom
40 INT0_224 O Servo interrupt monitor pin
Reference Information
2-16
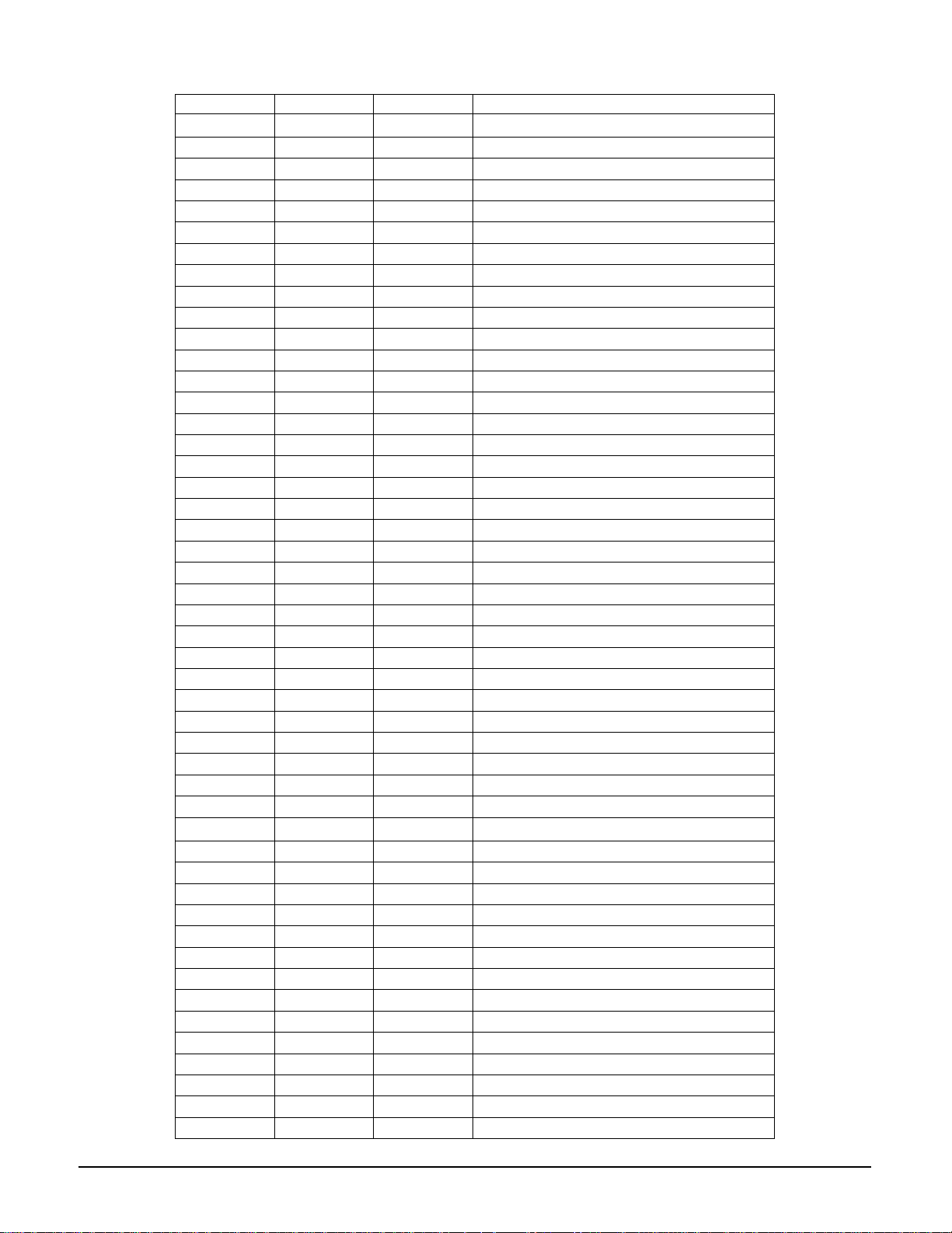
2-1-10 SIC4 (KA3017 ; Motor & Actuator Driver)
PWRGND
A3
A2
A1
OPIN +
OPIN
FIN (GND)
SB
DIR
SS
CS1
VM
13
Power
Save
-
+
Short vrake
14
15
16
17
-
18
FIN (GND)
SIGGND
-
+
Lower
Distributor
Upper
Distributor
PC1
VCC2
Absolute
Values
TSD
Direction
Detector
Direction select
EC
+
Detector
2P
ECR
-
FG
Comparator
Hall amp matrix
-
+
FG
VH
123654789101112
Hall bias
48
47
46
45
44
43
H3+
H3
-
H2+
-
H2
H1+
H1
-
FIN (GND)
OPOUT
VCC1
AVM 12
DI4
DI3
DI2
19
20
+
2P
DO3 +
-
+
AVM 3
2P
+
+
-
10k
-
2P
FIN (GND)
DO2 +
BTLPGND1
-
+
-
2P
DO1 +
10k
-
DO2
21
+
22
23
24
2P
25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36
-
DI1
DO1
-
+
+
2P
BTLPGND2
2P
-
-
DO3
10k
2P
42
BTLSGND
BIAS
41
10k
-
MUTE
MUTE
MUTE
-
DO4
DO4 +
40
39
38
37
AVM 4
MUTE12
MUTE3
MUTE4
Reference Information
2-17
No. Symbol I/O Description
1 VH I HALL BIAS
2 FG O FG SIGNAL OUTPUT
3 ECR I TORQUE CONTROL REFERENCE
4 EC I TORQUE CONTROL SIGNAL
5 VCC2 — SUPPLY VOLTAGE
6 PC1 — PHASE COMPENSATION CAPACITOR
7 SIGGND — SIGNAL GROUND
8VM— MOTOR SUPPLY VOLTAGE
9 CS1 I CURRENT SENSOR
10 S/S I START/STOP
11 DIR O 3-PHASE ROTATIONAL DIRECTION OUTPUT
12 SB I SHORT BRAKE
13 PWRGND — POWER GROUND
14 A3 O 3-PHASE OUTPUT 3
15 A2 O 3-PHASE OUTPUT 2
16 A1 O 3-PHASE OUTPUT 1
17 OPIN+ I OP AMP INPUT (+)
18 OPIN- I OP AMP INPUT (-)
19 OPOUT O OP AMP OUTPUT
20 VCC1 — SUPPLY VOLTAGE
21 AVM12 — BTL CH-1, 2 MOTOR SUPPLY VOLTAGE
22 DI4 I BTL DRIVE INPUT 4
23 DI3 I BTL DRIVE INPUT 3
24 DI2 I BTL DRIVE INPUT 2
25 DI1 I BTL DRIVE INPUT 1
26 DO1- O BTL DRIVE 1 OUTPUT (-)
27 DO1+ O BTL DRIVE 1 OUTPUT (+)
28 DO2- O BTL DRIVE 2 OUTPUT (-)
29 DO2+ O BTL DRIVE 2 OUTPUT (+)
30 BTLPGND1 — BTL POWER GROUND 1
31 BTLPGND2 — BTL POWER GROUND 2
32 DO3- O BTL DRIVE 3 OUTPUT (-)
33 DO3+ O
34 AVM3 — BTL CH3 MOTOR SUPPLY VOLTAGE
35 DO4- O BTL DRIVE 4 OUTPUT (-)
36 DO4+ O BTL DRIVE 4 OUTPUT (+)
37 MUTE4 I BTL DRIVE MUTE CH 4
38 MUTE3 I BTL DRIVE MUTE CH 3
39 MUTE12 I BTL DRIVE MUTE CH 1, 2
40 AVM4 — BTL CH 4 MOTOR SUPPLY VOLTAGE
41 BIAS — BTL BIAS VOLTAGE
42 BTLSGND — BTL DRIVE SIGNAL GROUND
43 H1- I HALL1(-) INPUT
44 H1+ I HALL1(+) INPUT
45 H2- I HALL2(-) INPUT
46 H2+ I HALL2(+) INPUT
47 H3- I HALL3(-) INPUT
48 H3+ I
BTL DRIVE 3 OUTPUT (+)
HALL3(+) INPUT
Reference Information
2-18
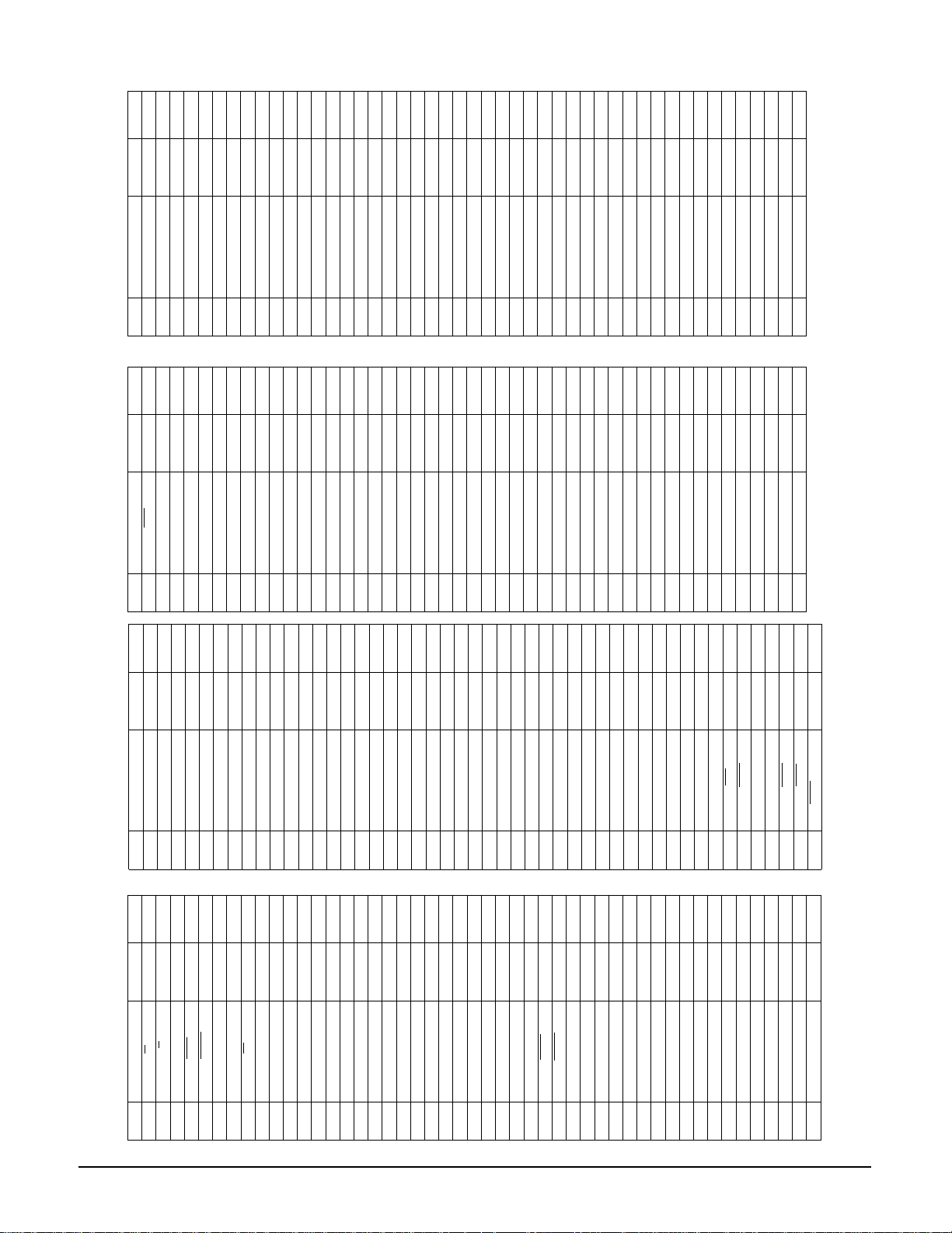
2-1-11 ZIC1 (ZIVA 4.1 ; A/V Decoder)
Video
Out
Audio
Interface
OSD
Decoder
Video
Digital
Encoder
Video
Mixer
Decoder
Subpicture
Decoder
MPEG Video
Digital
Audio
Decoder
CD-DA and LPCM
Dolby Digital Audio
Audio
Interface
DSP
Decoder
MPEG Audio
Digital Audio Input
Decoder
Memory
Controller
SDRAM
Interface
Host
Interface
Control Logic
Host
Interface
Program
CSS
SecureView
Descrambling
DVD/CD
Stream
Decoder
Bus Key
Authentication
Interface
(optional)
Reference Information
2-19
144 VSS_VIDEO ANALOG GND
145 Y/B/U 3.3V ANALOG O
146 VDD_DAC 3.3V ANALOG
147 VDD_VIDEO 3.3V ANALOG
148 NC No Connect O
149 VSS_DAC ANALOG GND
150 VSS_VIDEO ANALOG GND
151 C/R/V 3.3V ANALOG O
152 VDD_DAC 3.3V ANALOG
153 VDD_VIDEO 3.3V ANALOG
154 VSS_RREF ANA LOG GND
155 RREF 3.3V ANALOG O
156 VDD_RRE F 3.3V ANALOG
157 A_VSS GROUND
158 SYSCLK 3.3V I
159 VCLK 3.3V I
160 A_VDD 3.3V ANALOG
161 DVD-DATA0/CD-DATA 3.3V I
162 DVD-DATA1/CD-LRCK 3.3V I
163 DVD-DATA2/CD-BCK 3.3V I
164 DVD-DATA3/CD-C2P0 3.3V I
165 DVD-DATA4/CDG-SDATA 3.3V I
166 VSS GROUND
167 VDD_3.3 3.3V
168 DVD-DATA5/CDG-VFSY 3.3V I
169 DVD-DATA6/CDG-S0S1 3.3V I
170 DVD-DATA7/CDG-SCLK 3.3V I
171 VDACK 3.3V I
172 VREQUEST 3.3V O
173 VSTROBE 3.3V I
174 ERROR 3.3V I
175 VDD_3.3 3.3V
176 RESERVED GROUND
177 VDD_3.3 3.3V
178 VSS GROUND
179 NC No connect O
180 NC No connect O
181 NC No connect O
182 HADDR0 3.3V I
183 HADDR1 3.3V I
184 HADDR2 3.3V I
185 RESERVED 3.3V I
186 RESERVED 3.3V I
187 RESERVED 3.3V I
188 VSS GROUND
189 VDD_2.5 2.5V
Pin No. Pin Name I/O Voltage I/O Type
3.3V O
190 RESERVED 3.3V I
97 SD-BS
98 MADDR10 3.3V O
99 MADDR0 3.3V O
100 VDD _3.3 3.3V
101 VSS GROUND
102 MADDR1 3.3V O
103 MADDR2 3.3V O
104 MADDR3 3.3V O
105 RESERVED ANALOG GND
106 NC No connect O
107 NC No connect O
108 RESERVED 3.3V I
109 NC No connect O
110 RESERVED 3.3V I
111 RESERVED 3.3V ANALOG
112 RESERVED 3.3V I
113 DAI-LRCK 3.3V I/O
114 DAI-BCK 3.3V I/O
115 VDD _3.3 3.3V
116 VSS GROUND
117 DAI-DATA 3.3V I/O
118 DA-DATA3 3 .3V O
119 DA-DATA2 3 .3V O
120 DA-DATA1 3 .3V O
121 DA-DATA0 3 .3V O
122 DA-LRCK 3.3V O
123 VDD _3.3 3.3V
124 VSS GROUND
125 DA-XCK 3.3V I/O
126 DA-BCK 3.3V O
127 DA-IEC 3.3V O
128 VDD _2.5 2.5V
129 VSS GROUND
130 NC No Connect O
131 VSS_DAC ANALOG GND
132 VSS_VIDEO ANALOG GND
133 CVBS + sync 3.3V ANALOG O
134 VDD_DAC 3.3V ANALOG O
135 VDD_VIDEO 3 .3V ANALOG
136 NC N o Connect O
137 VSS_DAC ANALOG GND
138 VSS_VIDEO ANALOG GND
139 CVBS/G/Y 3.3V ANALOG O
140 VDD_DAC 3.3V ANALOG
141 VDD_VIDEO 3 .3V ANALOG
142 NC No Connect O
92 VDD_3.3 3.3V
93 VSS GROUND
143 VSS_DAC ANALOG GND
3.3V O
3.3V O
94 SD-RAS
95 SD-CS0
/MADDR11 3.3V O
96 SD-CS1
Pin No. Pin Name I/O Voltage I/O Type
3.3V O
3.3V O
49 PIO4 3.3V I/O
50 PIO5 3.3V I/O
51 PIO6 3.3V I/O
52 PIO7 3.3V I/O
53 MDATA0 3.3V I/O
54 MDATA1 3.3V I/O
55 VDD_3.3 3.3V
56 VSS GROUND
57 MDATA2 3.3V I/O
58 MDATA3 3.3V I/O
59 MDATA4 3.3V I/O
60 MDATA5 3.3V I/O
61 MDATA6 3.3V I/O
62 MDATA7 3.3V I/O
63 M DATA15 3.3V I/O
64 VDD_3.3 3.3V I/O
65 VSS GROUND I/O
66 M DATA14 3.3V I/O
67 VDD_2.5 2.5V
68 VSS GROUND
69 M DATA13 3.3V I/O
70 M DATA12 3.3V I/O
71 M DATA11 3.3V I/O
72 M DATA10 3.3V I/O
73 MDATA9 3.3V I/O
74 VDD_3.3 3.3V
75 VSS GROUND
76 MDATA8 3.3V I/O
77 LDQM 3.3V O
78 SD-CLK 3.3V O
79 CLKSEL 3.3V I
80 MADDR9 3.3V O
81 MADDR8 3.3V O
82 VDD_3.3 3.3V
83 VSS GROUND
84 MADDR7 3.3V O
85 MADDR6 3.3V O
86 MADDR5 3.3V O
Pin No. Pin Name I/O Voltage I/O Type
3.3V I
3.3V I
3.3V O, OD, PU
3.3V I
3.3V O, OD, PU
A3 3.3V O
3.3V I/O
3.3V I/O
87 VDD_2.5 2.5V
91 SD-CAS
88 VSS GROUND
89 MADDR4 3.3V O
90 MWE
2R/W
1RD
Pin No. Pin Name I/O Voltage I/O Type
3 VDD_3.3 3 .3V
4WAIT
5RESET
6 VSS GROUND
7 VDD_3.3 3 .3V
8INT
9 NC No Connect O
10 NC No Connect O
11 NC No Connect O
12 NC No Connect O
13 VDD_2. 5 2 .5V
14 VSS GROUND
15 NC No Connect O
16 NC No Connect O
17 NC No Connect O
18 NC No Connect O
19 VSS GROUND
20 VDD_3.3 3 .3V
21 VDATA0 3.3V O
22 VDATA1 3.3V O
23 VDATA2 3.3V O
24 VDAT
25 VDATA4 3.3V O
26 VDATA5 3.3V O
27 VDATA6 3.3V O
28 VDATA7 3.3V O
29 VSYNC
30 HSYNC
31 VSS GROUND
32 VDD_3.3 3 .3V
33 RESERVED 3 .3V I
34 RESERVED 3 .3V I
35 RESERVED 3 .3V I
36 VDD_2.5 2 .5V
37 VSS GROUND
38 RESERVED 3 .3V I
39 RESERVED 3 .3V I
40 RESERVED 3 .3V I
41 RESERVED 3 .3V I
42 RESERVED 3 .3V I
43 PIO0 3.3V I/O
44 VSS GROUND
45 VDD_3.3 3 .3V
46 PIO1 3.3V I/O
47 PIO2 3.3V I/O
48 PIO3 3.3V I/O
Reference Information
2-20
Pin No. Pin Name I/O Voltage I/O Type
Pin No. Pin Name I/O Voltage I/O Type
199 HDATA6 3.3V I/O
200 HDATA5 3.3V I/O
191 VSS GROUND
192 VDD _3.3 3.3V
3.3V I
201 HDATA4 3.3V I/O
202 HDATA3 3.3V I/O
203 HDATA2 3.3V I/O
204 VDD_3 .3 3.3V
205 VSS 3.3V
206 HDATA1 3.3V I/O
207 HDATA0 3.3V I/O
208 CS
193 RESERVED 3.3V I
194 RESERVED 3.3V I
195 RESERVED 3.3V I
196 RESERVED 3.3V I
197 HDATA7 3 .3V I/O
198 VSS GROUND
Reference Information
2-21
2-1-12 ZIC2/ZIC3 (KM416S1120D ; CMOS 16M SDRAM)
Data Input Register
Bank Select
CLK
ADD
Address Register
LCKE
LRAS LCBR LWE LDQM
CLK CKE CS
Refresh Counter
LRAS
Row Buffer
LCBR
Row Decoder Col. Buffer
LCAS LWCBR
Timing Register
RAS CAS WE L(U)DQM
512K x 16
512K x 16
Column Decoder
Latency & Burst Length
Programming Register
Sense AMP
Output BufferI/O Control
Pin Name Input Function
CLK System Clock Active on the positive going edge to sample all inputs.
CS
Chip Select
Disables or enables device operation by masking or enabling all inputs except
CLK, CKE and L(U)DQM
Masks system clock to freeze operation from the next clock cycle.
CKE Clock Enable
CKE should be enabled at least one cycle prior to new command.
Disable input buffers for power down in standby.
LWE
LDQM
DQi
VDD
DQ0
DQ1
V
SSQ
DQ2
DQ3
V
DDQ
DQ4
DQ5
SSQ
V
DQ6
DQ7
V
DDQ
LDQM
WE
CAS
RAS
CS
BA
A10/AP
A0
A1
A2
A3
V
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
DD
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
VSS
DQ15
DQ14
V
SSQ
DQ13
DQ12
V
DDQ
DQ11
DQ10
SSQ
V
DQ9
DQ8
V
DDQ
N.C/RFU
UDQM
CLK
CKE
N.C
A9
A8
A7
A6
A5
A4
V
SS
0 ~ A10/AP Address
A
BA Bank Select Address
RAS
CAS
WE
Row Address Strobe
Column Address Strobe
Write Enable
L(U)DQM Data Input/Output Mask
0 ~ 15 Data Input/Output Data inputs/outputs are multiplexed on the same pins.
DQ
DD/VSS Power Supply/Ground Power and ground for the input buffers and the core logic.
V
DDQ/VSSQ Data Output Power/Ground
V
N.C/RFU
No Connection/
Reserved for Future Use
Row / column addresses are multiplexed on the same pins.
Row address : RA
0 ~ RA10, column address : CA0 ~ CA7
Selects bank to be activated during row address latch time.
Selects bank for read/write during column address latch time.
Latches row addresses on the positive going edge of the CLK with RAS
Enables row access & precharge.
Latches column addresses on the positive going edge of the CLK with CAS
Enables column access.
Enables write operation and row precharge.
Latches data in starting from CAS
Makes data output Hi-Z, t
, WE active.
SHZ after the clock and masks the output.
Blocks data input when L(U)DQM active.
Isolated power supply and ground for the output buffers to provide improved noise
immunity.
This pin is recommended to be left No Connection on the device.
low.
low.

Reference Information
2-22
MEMO
3-1
3. Product Specifications
Power Requirements AC 120V, 60Hz
Power Consumption 17W
GENERAL
Weight 3.1kg
Dimensions W 430mm X D 280mm X 89mm
Operating Temperature Range +5˚C ~ +35˚C
Operating Humidity Range 10% to 75%
DVD Reading Speed : 3.49 m/sec
(Digital Versatile Disc)
Approx. Play Time (Single Sided, Single Layer Disc) : 135 min.
CD : 12Cm Reading Speed : 1.2 to 1.4 m/sec
DISC
(Compact Disc) Maximum Play Time : 74min.
CD : 8Cm Reading Speed : 1.2to 1.4 m/sec.
(Compact Disc) Maximum Play Time : 20min.
VCD : 12Cm
Reading Speed : 1.2 to 1.4 m/sec.
Maximum Play Time : 74min. (Video + Audio)
Composite Video 1 channel : 1.0Vp-p (75ohm load)
Y : 1.0Vp-p (75ohm load) ; DV-P305U Only
Video Output
Component Video Pr : 0.70Vp-p (75ohm load) ; DV-P305U Only
Pb : 0.70Vp-p (75ohm load) ; DV-P305U Only
S-Video
Luminance Signal : 1Vp-p (75ohm load)
Color Signal : 0.286Vp-p (75ohm load)
2 Channel L (1/L), R (2/R)
Audio Output
* Frequency Response
48kHz Sampling : 4Hz to 22kHz
96kHz Sampling : 4Hz to 44kHz
* S/N Ratio 115dB
* Dynamic Range 105dB
* Total Harmonic Distortion 0.003%
* : Nominal specification
 Loading...
Loading...