SERVICE MANUAL
MANUEL D'ENTRETIEN
WARTUNGSHANDBUCH
CAUTION:
Before servicing this chassis, it is important that the service technician read the “Safety
Precautions” and “Product Safety Notices” in this service manual.
SM0065
42PMA225EZ
Data contained within this Service
manual is subject to alteration for
improvement.
ATTENTION:
Avant d’effectuer l’entretien du châassis, le technicien doit lire les «Précautions de sécurité»
et les «Notices de sécurité du produit» présentés dans le présent manuel.
VORSICHT:
Vor Öffnen des Gehäuses hat der Service-Ingenieur die „Sicherheitshinweise“ und „Hinweise
zur Produktsicherheit“ in diesem Wartungshandbuch zu lesen.
Les données fournies dans le présent
manuel d’entretien peuvent faire l’objet
de modifications en vue de perfectionner
le produit.
Die in diesem Wartungshandbuch
enthaltenen Spezifikationen können sich
zwecks Verbesserungen ändern.
SPECIFICATIONS AND PARTS ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE FOR IMPROVEMENT
Colour Television
September 2004

TABLE OF CONTENTS
INTRODUCTION.......................................................................................................................................1
1.
2. MULTI STANDARD SOUND PROCESSOR ............................................................................................1
3. VIDEO SWITCH TEA6415........................................................................................................................1
4. AUDIO AMPLIFIER STAGE WITH TDA8928ST ......................................................................................1
5. POWER SUPPLY (SMPS)........................................................................................................................1
6. MICROCONTROLLER..............................................................................................................................2
7. SERIAL ACCESS CMOS 4K x 8 (32K bit) EEPROM 24C32A .................................................................2
8. CLASS AB STEREO HEADPHONE DRIVER TDA1308..........................................................................2
9. IC DESCRIPTIONS AND INTERNAL BLOCK DIAGRAM........................................................................2
9.1. TEA6415C .............................................................................................................................................3
9.1.1. General Description .....................................................................................................................3
9.1.2. Features ........................................................................................................................................3
9.1.3. Pinning..........................................................................................................................................3
9.2. 24C32A..................................................................................................................................................3
9.2.1. Features ........................................................................................................................................3
9.2.2. Description....................................................................................................................................4
9.2.3. Pin Function table........................................................................................................................4
9.2.4. Functional Descriptions..............................................................................................................5
9.3. LM317....................................................................................................................................................5
9.3.1. General Description .....................................................................................................................5
9.3.2. Features ........................................................................................................................................5
9.4. ST24LC21 .............................................................................................................................................5
9.4.1. Description....................................................................................................................................5
9.4.2. Features ........................................................................................................................................5
9.4.3. Pin connections ...........................................................................................................................6
9.5. TLC7733................................................................................................................................................6
9.5.1. Description....................................................................................................................................6
9.6. 74LVC257A ...........................................................................................................................................7
9.6.1. Features ........................................................................................................................................7
9.6.2. Description....................................................................................................................................7
9.6.3. Pin Description.............................................................................................................................7
9.7. 74LVC14A .............................................................................................................................................7
9.7.1. Features ........................................................................................................................................7
9.7.2. Applications..................................................................................................................................7
9.7.3. Description....................................................................................................................................7
9.7.4. Pin Description.............................................................................................................................8
9.8. TEA6420................................................................................................................................................8
9.8.1. Features ........................................................................................................................................8
9.8.2. Description....................................................................................................................................8
9.9. LM1086..................................................................................................................................................8
9.9.1. Description....................................................................................................................................8
9.9.2. Features ........................................................................................................................................8
9.9.3. Applications..................................................................................................................................9
9.9.4. Connection Diagrams..................................................................................................................9
9.10. LM1117 ..............................................................................................................................................9
9.10.1. General Description .................................................................................................................9
9.10.2. Features.....................................................................................................................................9
9.10.3. Applications..............................................................................................................................9
9.10.4. Connection Diagrams ..............................................................................................................9
9.11. DS90C385 .......................................................................................................................................10
9.11.1. General Description ...............................................................................................................10
9.11.2. Features...................................................................................................................................10
9.11.3. Pin Description .......................................................................................................................10
9.12. MSP34X1G ......................................................................................................................................12
9.12.1. Introduction.............................................................................................................................12
9.12.2. Features...................................................................................................................................13
9.12.3. Pin connections......................................................................................................................13
i
Plasma TV Service Manual 11/01/2005

TDA1308..........................................................................................................................................15
9.13.
9.13.1. General Description ...............................................................................................................15
9.13.2. Features...................................................................................................................................15
9.13.3. Pinning.....................................................................................................................................16
9.14. PI5V330 ...........................................................................................................................................16
9.14.1. General Description ...............................................................................................................16
9.15. AD9883A..........................................................................................................................................16
9.15.1. General Description ...............................................................................................................16
9.15.2. Features...................................................................................................................................16
9.15.3. Pin Descriptions .....................................................................................................................17
9.16. SAA7118E .......................................................................................................................................19
9.16.1. General Description ...............................................................................................................19
9.16.2. Features...................................................................................................................................20
9.16.3. Pinning.....................................................................................................................................21
9.17. TPS72501 ........................................................................................................................................25
9.17.1. General Description ...............................................................................................................25
9.17.2. Features...................................................................................................................................25
9.18. TSOP1836 .......................................................................................................................................26
9.18.1. Description..............................................................................................................................26
9.18.2. Features...................................................................................................................................26
9.19. PCF8591..........................................................................................................................................26
9.19.1. General Description ...............................................................................................................26
9.19.2. Features...................................................................................................................................26
9.19.3. Pinning.....................................................................................................................................27
9.20. PW1231 ...........................................................................................................................................27
9.20.1. General Description ...............................................................................................................27
9.20.2. Features...................................................................................................................................27
9.20.3. Applications............................................................................................................................28
9.21. PW181 .............................................................................................................................................28
9.21.1. General Description ...............................................................................................................28
9.21.2. Features...................................................................................................................................28
9.21.3. Applications............................................................................................................................29
9.22. SIL151B ...........................................................................................................................................29
9.22.1. General Description ...............................................................................................................29
9.22.2. Features...................................................................................................................................29
9.23. SDRAM 4M x 16 (MT48LC4M16A2TG-75) .....................................................................................29
9.23.1. General Description ...............................................................................................................29
9.23.2. Features...................................................................................................................................30
9.23.3. Pin Descriptions .....................................................................................................................30
9.24. FLASH 8MBit ...................................................................................................................................32
9.24.1. Description..............................................................................................................................32
9.24.2. Features...................................................................................................................................32
10. SERVICE MENU SETTINGS..................................................................................................................33
10.1. display menu....................................................................................................................................33
10.2. calibration menu...............................................................................................................................35
deinterlacer menu...........................................................................................................................................36
10.3. Service menu factory reset values...................................................................................................38
11. BLOCK DIAGRAM ..................................................................................................................................39
12. CIRCUIT DIAGRAMS .............................................................................................................................47
ii
Plasma TV Service Manual 11/01/2005

1. INTRODUCTION
42” Plasma TV is a progressive TV control system with built-in de-interlacer and scaler. It uses a
852*480 panel with 16:9 aspect ratio. The TV is capable of operation in PAL, SECAM, NTSC (playback)
colour standards and multiple transmission standards as B/G, D/K, I/I’, and L/L´ including German and
NICAM stereo. Sound system output is supplying 2x10W (10%THD) for stereo 8! speakers. The
chassis is equipped with many inputs and outputs allowing it to be used as a center of a media system.
It supports following peripherals:
2 SCART’s with all of them supporting full SCART features including RGB input
1 AV inputs. (CVBS+ Stereo Audio)
1 SVHS input
1 Streeo Headphone output
1 D-Sub 15 PC input
1 DVI input
1 Stereo audio input for PC/DVI
Other features include, Picture-In-Picture (PIP) , Picture-And-Picture (PAP) .
2. MULTI STANDARD SOUND PROCESSOR
The MSP34x1G family of single-chip Multistandard Sound Processors covers the sound processing of
all analog TV-Standards worldwide, as well as the NICAM digital sound standards. The full TV sound
processing, starting with analog sound IF signal-in, down to processed analog AF-out, is performed on
a single chip.
These TV sound processing ICs include versions for processing the multichannel television sound
(MTS) signal conforming to the standard recommended by the Broadcast Television Systems
Committee (BTSC). The DBX noise reduction, or alternatively, Micronas Noise Reduction (MNR) is
performed alignment free. Other processed standards are the Japanese FM-FM multiplex standard
(EIA-J) and the FM Stereo Radio standard.
Current ICs have to perform adjustment procedures in order to achieve good stereo separation for
BTSC and EIA-J. The MSP34x1G has optimum stereo performance without any adjustments.
3. VIDEO SWITCH TEA6415
In case of three or more external sources are used, the video switch IC TEA6415 is used. The main
function of this device is to switch 8 video-input sources on the 6 outputs.
Each output can be switched on only one of each input. On each input an alignment of the lowest level
of the signal is made (bottom of sync. top for CVBS or black level for RGB signals).
Each nominal gain between any input and output is 6.5dB.For D2MAC or Chroma signal the alignment
is switched off by forcing, with an external resistor bridge, 5VDC on the input. Each input can be used
as a normal input or as a MAC or Chroma input (with external Resistor Bridge). All the switching
possibilities are changed through the BUS. Driving 75ohm load needs an external resistor. It is possible
to have the same input connected to several outputs.
4. AUDIO AMPLIFIER STAGE WITH TDA8928ST
The TDA8928ST is a switching power stage for high efficiency class-D audio power amplifier system.
With this power stage a compact 2x10 W Self Oscillating Digital Amplifier System (SODA) can be built,
operating with high efficiency and very low dissipation. No heat sink is required. The system operates
over a wide supply voltage range from ±7.5 V to ±30 V and consumes a very low quiescent current.
5. POWER SUPPLY (SMPS)
The DC voltages required at various parts of the chassis are provided by an SMPS transformer
controlled by the IC MC44608, which is designed for driving, controlling and protecting switching
transistor of SMPS. The transformer generates 145V for FBT input, +/-14V for audio amplifier, 5V and
3.3V stand by voltage and 33V, 12V and 5V supplies for other different parts of the chassis.
An optocoupler is used to control the regulation of line voltage and stand-by power consumption. There
is a regulation circuit in secondary side. This circuit produces a control voltage according to the
changes in 145V DC voltage, via an optocoupler (TCET1102G) to pin3 of the IC.
During the switch on period of the transistor, energy is stored in the transformer. During the switch off
period energy is fed to the load via secondary winding. By varying switch-on time of the power
1
Plasma TV Service Manual 11/01/2005

transistor, it controls each portion of energy transferred to the second side such that the output voltage
remains nearly independent of load variations.
6. MICROCONTROLLER
The microprocessor is embedded inside PW181 chip which also handles scaling, frame rate conversion
and OSD generation. The on-chip 16-bit microprocessor is a Turbo x86-compatible processor core with
on-chip peripherals (timers, interrupt controller, 2-wire serial master/slave interface, UART, I/O ports,
and more). Special peripherals such as Infrared (IR) pulse decoders and a digital pulse width modulator
(PWM) are also included. There are two independent 2-wire serial master/slave interface modules that
can be multiplexed to control up to five 2-wire serial ports. The slave 2-wire interface is designed for
HDCP use only (and requires the use of HDCP Image Processors). On-chip RAM of up to 64 Kbytes is
available. A complete microprocessor system can be implemented simply by adding external ROM. The
on-chip processor can be disabled to allow external processor control of all internal functions.
7. SERIAL ACCESS CMOS 4K x 8 (32K bit) EEPROM 24C32A
The Microchip Technology Inc. 24C32A is a 4K x 8 (32K bit) Serial Electrically Erasable PROM. It has
been developed for advanced, low power applications such as personal communications or data
acquisition. The 24C32A also has a page-write capability of up to 32 bytes of data. The 24C32A is
capable of both random and sequential reads up to the 32K boundary. Functional address lines allow
up to eight 24C32A devices on the same bus, for up to 256K bits address space. Advanced CMOS
technology and broad voltage range make this device ideal for low-power/low-voltage, non-volatile code
and data applications.
8. CLASS AB STEREO HEADPHONE DRIVER TDA1308
The TDA1308 is an integrated class AB stereo headphone driver contained in a DIP8 plastic package.
The device is fabricated in a 1 mm CMOS process and has been primarily developed for portable digital
audio applications.
9. IC DESCRIPTIONS AND INTERNAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
TEA6415C
24C32
LM317T
ST24LC21
TLC7733
74LVC257A
74LVC14A
TEA6420D
LM1086
LM1117
DS90C385
TL431
MSP3411G
TDA7265
TDA1308
PI5V330
AD9883A
SAA7118E
TPS72501
TSOP1836
PCF8591
PW1231
PW181
SIL151B
SDRAM 4M x 16 (MT48LC4M16A2TG-75)
FLASH
2
Plasma TV Service Manual 11/01/2005

9.1.
TEA6415C
9.1.1. General Description
The main function of the IC is to switch 8 video input sources on 6 outputs. Each output can be
switched on only one of each input. On each input an alignment of the lowest level of the signal is made
(bottom of synch. top for CVBS or black level for RGB signals). Each nominal gain between any input
and output is 6.5dB. For D2MAC or Chroma signal the alignment is switched off by forcing, with an
external resistor bridge, 5 V
DC on the input. Each input can be used as a normal input or as a MAC or
Chroma input (with external resistor bridge). All the switching possibilities are changed through the
BUS. Driving 75" load needs an external transistor. It is possible to have the same input connected to
several outputs. The starting configuration upon power on (power supply: 0 to 10V) is undetermined. In
this case, 6 words of 16 bits are necessary to determine one configuration. In other case, 1 word of 16
bits is necessary to determine one configuration.
9.1.2. Features
• 20MHz Bandwidth
• Cascadable with another TEA6415C (Internal address can be changed by pin 7 voltage)
• 8 Inputs (CVBS, RGB, MAC, CHROMA,)
• 6 Outputs
• Possibility of MAC or chroma signal for each input by switching-off the clamp with an external resistor
bridge
• Bus controlled
• 6.5dB gain between any input and output
• 55dB crosstalk at 5 MHz
• Fully ESD protected
9.1.3. Pinning
1. Input : Max : 2Vpp, Input Current: 1mA, Max : 3mA
2. Data : Low level : -0.3V Max: 1.5V,
High level : 3.0V Max : Vcc+0.5V
3. Input : Max : 2Vpp, Input Current: 1mA, Max : 3mA
4. Clock : Low level : -0.3V Max: 1.5V,
High level : 3.0V Max : Vcc+0.5V
5. Input : Max : 2Vpp, Input Current: 1mA, Max : 3mA
6. Input : Max : 2Vpp, Input Current: 1mA, Max : 3mA
7. Prog
8. Input : Max : 2Vpp, Input Current: 1mA, Max: 3mA
9. Vcc : 12V
10. Input : Max : 2Vpp, Input Current: 1mA, Max : 3mA
11. Input : Max : 2Vpp, Input Current: 1mA, Max : 3mA
12. Ground
13. Output : 5.5Vpp, Min: 4.5Vpp
14. Output : 5.5Vpp, Min: 4.5Vpp
15. Output : 5.5Vpp, Min: 4.5Vpp
16. Output : 5.5Vpp, Min: 4.5Vpp
17. Output : 5.5Vpp, Min: 4.5Vpp
18. Output : 5.5Vpp, Min: 4.5Vpp
19. Ground
20. Input : Max: 2Vpp, Input Current : 1mA, Max : 3mA
9.2.
24C32A
9.2.1. Features
• Voltage operating range: 4.5V to 5.5V
- Maximum write current 3 mA at 5.5V
3
Plasma TV Service Manual 11/01/2005

- Standby current 1 mA typical at 5.0V
• 2-wire serial interface bus, I
2CTM
compatible
• 100 kHz and 400 kHz compatibility
• Self-timed ERASE and WRITE cycles
• Power on/off data protection circuitry
• Hardware write protect
• 1,000,000 Erase/Write cycles guaranteed
• 32-byte page or byte write modes available
• Schmitt trigger filtered inputs for noise suppression
• Output slope control to eliminate ground bounce
• 2 ms typical write cycle time, byte or page
• Up to eight devices may be connected to the same bus for up to 256K bits total memory
• Electrostatic discharge protection > 4000V
• Data retention > 200 years
• 8-pin PDIP and SOIC packages
• Temperature ranges
- Commercial (C): 0°C to 70°C
- Industrial (I): -40°C to +85°C
- Automotive (E): -40°C to +125°C
9.2.2. Description
The Microchip Technology Inc. 24C32A is a 4K x 8 (32K bit) Serial Electrically Erasable PROM. It has
been developed for advanced, low power applications such as personal communications or data
acquisition. The 24C32A also has a page-write capability of up to 32 bytes of data. The 24C32A is
capable of both random and sequential reads up to the 32K boundary. Functional address lines allow
up to eight 24C32A devices on the same bus, for up to 256K bits address space. Advanced CMOS
technology and broad voltage range make this device ideal for low-power/low-voltage, non-volatile code
and data applications. The 24C32A is available in the standard 8-pin plastic DIP and both 150 mil and
200 mil SOIC packaging.
9.2.3. Pin Function table
Name Function
A0, A1, A2 User Configurable Chip Selects
Vss Ground
SDA Serial Address/Data I/O
SCL Serial Clock
WP Write Protect Input
Vcc +4.5V to 5.5V Power Supply
4
Plasma TV Service Manual 11/01/2005

9.2.4. Functional Descriptions
The 24C32A supports a Bi-directional 2-wire bus and data transmission protocol. A device that sends
data onto the bus is defined as transmitter, and a device receiving data as receiver. The bus must be
controlled by a master device which generates the Serial Clock (SCL), controls the bus access, and
generates the START and STOP conditions, while the 24C32A works as slave. Both master and slave
can operate as transmitter or receiver but the master device determines which mode is activated.
9.3.
LM317
9.3.1. General Description
The LM117/LM217/LM317 are monolithic integrated circuit in TO-220, ISOWATT220, TO-3 and D
2
PAK packages intended for use as positive adjustable voltage regulators.
They are designed to supply more than 1.5A of load current with an output voltage adjustable over a
1.2 to 37V range.
The nominal output voltage is selected by means of only a resistive divider, making the device
exceptionally easy to use and eliminating the stocking of many fixed regulators.
9.3.2. Features
• Output voltage range: 1.2 to 37V
• Output current In excess of 1.5A
• 0.1% Line and Load Regulation
• Floating Operation for High Voltages
• Complete Series of Protections: Current Limiting, Thermal Shutdown And Soa Control
ST24LC21
9.4.
9.4.1. Description
The ST24LC21 is a 1K bit electrically erasable programmable memory (EEPROM), organized by 8 bits.
2
This device can operate in two modes: Transmit Only mode and I
C bidirectional mode. When powered,
the device is in Transmit Only mode with EEPROM data clocked out from the rising edge of the signal
2
applied on VCLK. The device will switch to the I
applied on SCL pin. The ST24LC21 can not switch from the I
C bidirectional mode upon the falling edge of the signal
2
C bidirectional mode to the Transmit Only
mode (except when the power supply is removed). The device operates with a power supply value as
low as 2.5V. Both Plastic Dual-in-Line and Plastic Small Outline packages are available.
9.4.2. Features
• 1 million Erase/Write cycles
• 40 years data retention
• 2.5V To 5.5V single supply voltage
• 400k Hz compatibility over the full range of supply voltage
• Two wire serial interface I
2
C bus compatible
• Page Write (Up To 8 Bytes)
• Byte, random and sequential read modes
• Self timed programming cycle
• Automatic address incrementing
• Enhanced ESD/Latch up
• Performances
5
Plasma TV Service Manual 11/01/2005
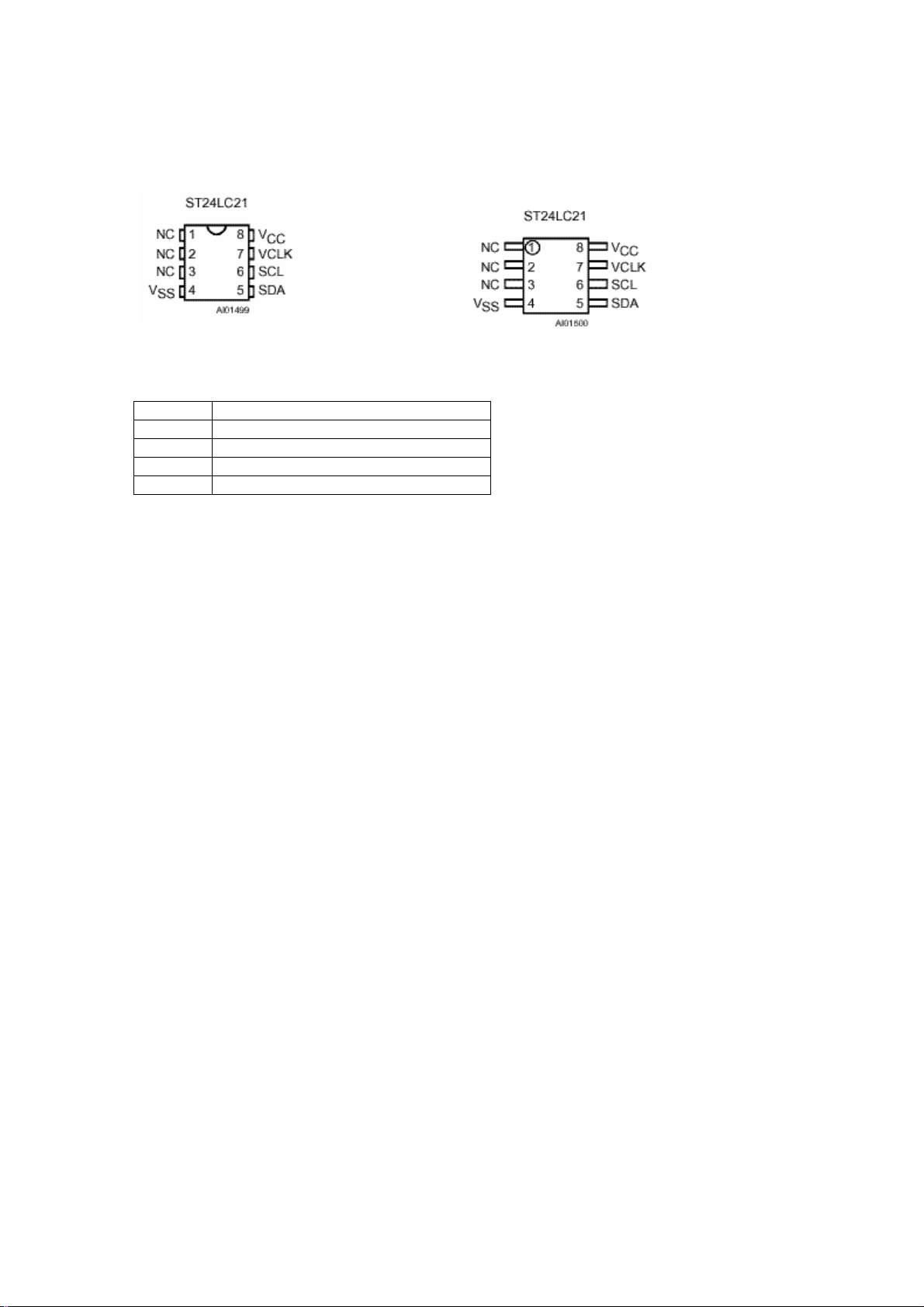
9.4.3. Pin connections
DIP Pin connections CO Pin connections
NC: Not connected
Signal names
SDA Serial data Address Input/Output
SCL Serial Clock (I2C mode)
Vcc Supply voltage
Vss Ground
VCLK Clock transmit only mode
9.5.
TLC7733
9.5.1. Description
The TLC77xx family of micro power supply voltage supervisors is designed for reset control, primarily in
microcomputer and microprocessor systems.
During power-on, RESET is asserted when V
reaches 1 V. After minimum V
DD
(. 2 V) is established,
DD
the circuit monitors SENSE voltage and keeps the reset outputs active as long as SENSE voltage
I(SENSE)
)
(V
remains below the threshold voltage. An internal timer delays return of the output to the inactive state to
ensure proper system reset. The delay time, t
= 2.1 x 10 4 x CT
t
d
, is determined by an external capacitor:
d
Where
is in farads
C
T
is in seconds
t
d
The TLC77xx has a fixed SENSE threshold voltage set by an internal voltage divider. When SENSE
voltage drops below the threshold voltage, the outputs become active and stay in that state until
SENSE voltage returns above threshold voltage and the delay time, t
, has expired.
d
In addition to the power-on-reset and under voltage-supervisor function, the TLC77xx adds power-down
control support for static RAM. When CONTROL is tied to GND, RESET will act as active high. The
voltage monitor contains additional logic intended for control of static memories with battery backup
during power failure. By driving the chip select (CS) of the memory circuit with the RESET output of the
TLC77xx and with the CONTROL driven by the memory bank select signal (CSH1) of the
microprocessor (see Figure 10), the memory circuit is automatically disabled during a power loss. (In
this application the TLC77xx power has to be supplied by the battery.)
The TLC77xxQ is characterized for operation over a temperature range of –40°C to 125°C, and the
TLC77xxI is characterized for operation over a temperature range of –40°C to 85°C.
6
Plasma TV Service Manual 11/01/2005
9.6.
74LVC257A
9.6.1. Features
Wide supply voltage range of 1.2 to 3.6 V
In accordance with JEDEC standard no. 8-1A
CMOS lower power consumption
Direct interface with TTL levels
Output drive capability 50 _ transmission lines at 85°C
5 Volt tolerant inputs/outputs, for interfacing with 5 Volt logic
9.6.2. Description
The 74LVC257A is a high-performance, low-power, low-voltage, Si-gate CMOS device and superior to
most advanced CMOS compatible TTL families.
Inputs can be driven from either 3.3V or 5.0V devices. In 3-State operation, outputs can handle 5V. This
feature allows the use of these devices as translators in a mixed 3.3V/5V environment.
The 74LVC257A is a quad 2-input multiplexer with 3-state outputs, which select 4 bits of data from two
sources and are controlled by a common data select input (S). The data inputs from source 0 (1l 0 to 4l
0 ) are selected when input S is LOW and the data inputs from source 1 (1l 1 to 4l 1 ) are selected
when S in HIGH. Data appears at the outputs (1Y to 4Y) in true (non-inverting) form from the selected
inputs. The 74LVC257A is the logic implementation of a 4-pole, 2-position switch, where the position of
the switch is determined by the logic levels applied to S. The outputs are forced to a high impedance
OFF-state when OE is HIGH.
9.6.3. Pin Description
PIN NUMBER SYMBOL DESCRIPTION
1 S Common data select input
2, 5, 11, 14
3, 6, 10, 13
1|
1|
to 4|
0
to 4|
1
Data inputs from source 0
0
Data outputs from source 1
1
4,7,9,12 1Y to 4Y 3-State multiplexer outputs
8 GND Ground (0V)
15 OE 3-State output enable input (active LOW)
16 Vcc Positive supply voltage
9.7. 74LVC14A
9.7.1. Features
• Wide supply voltage range of 1.2 to 3.6 V
• In accordance with JEDEC standard no. 8-1A
• Inputs accept voltages up to 5.5 V
• CMOS low power consumption
• Direct interface with TTL levels
9.7.2. Applications
• Wave and pulse shapers for highly noisy environments
• Astable multivibrators
• Monostable multivibrators
9.7.3. Description
The 74LVC14A is a high-performance, low power, low-voltage Si-gate CMOS device and superior to
most advanced CMOS compatible TTL families.
Inputs can be driven from either 3.3 V or 5 V devices. This feature allows the use of these devices as
translators in a mixed 3.3 V/5 V environment.
The 74LVC14A provides six inverting buffers with Schmitt-trigger action. It is capable of transforming
slowly changing input signals into sharply defined, jitter-free output signals.
7
Plasma TV Service Manual 11/01/2005

9.7.4. Pin Description
PIN NUMBER SYMBOL DESCRIPTION
1, 3, 5, 9, 11, 13 1A – 6A Data inputs
2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12 1Y – 6Y Data outputs
7 GND Ground (0V)
14 Vcc Positive supply voltage
9.8.
TEA6420
9.8.1. Features
• 5 Stereo Inputs
• 4 Stereo Outputs
• Gain Control 0/2/4/6db/Mutefor Each Output
• Cascadable (2 Different Addresses)
• Serial Bus Controlled
• Very Low noise
• Very Low distortion
9.8.2. Description
The TEA6420 switches 5 stereo audio inputs on 4 stereo outputs.
2
All the switching possibilities are changed through the I
C bus.
9.9.
LM1086
9.9.1. Description
The LM1086 is a series of low dropout positive voltage regulators with a maximum dropout of 1.5V at
1.5A of load current. It has the same pin-out as National Semiconductor’s industry standard LM317.
The LM1086 is available in an adjustable version, which can set the output voltage with only two
external resistors. It is also available in five fixed voltages: 2.5V, 2.85V, 3.3V, 3.45V and 5.0V. The fixed
versions integrate the adjust resistors. The LM1086 circuit includes a zener trimmed band-gap
reference, current limiting and thermal shutdown.
9.9.2. Features
• Available in 2.5V, 2.85V, 3.3V, 3.45V, 5V and Adjustable Versions
• Current Limiting and Thermal Protection
• Output Current 1.5A
• Line Regulation 0.015% (typical)
• Load Regulation 0.1% (typical)
8
Plasma TV Service Manual 11/01/2005

9.9.3. Applications
• SCSI-2 Active Terminator
• High Efficiency Linear Regulators
• Battery Charger
• Post Regulation for Switching Supplies
• Constant Current Regulator
• Microprocessor Supply
9.9.4. Connection Diagrams
TO-220 TO-263
Top View
10094802
10094804
Top View
9.10. LM1117
9.10.1. General Description
The LM1117 is a series of low dropout voltage regulators with a dropout of 1.2V at 800mA of load
current. It has the same pin-out as National Semiconductor’s industry standard LM317. The LM1117 is
available in an adjustable version, which can set the output voltage from 1.25V to 13.8V with only two
external resistors. In addition, it is also available in five fixed voltages, 1.8V, 2.5V, 2.85V, 3.3V, and 5V.
The LM1117 offers current limiting and thermal shutdown. Its circuit includes a zener trimmed bandgap
reference to as-sure output voltage accuracy to within ±1%. The LM1117 series is available in SOT223, TO-220, and TO-252 D-PAK packages. A minimum of 10µF tantalum capacitor is required at the
output to improve the transient response and stability.
9.10.2. Features
• Available in 1.8V, 2.5V, 2.85V, 3.3V, 5V, and Adjustable Versions
• Space Saving SOT-223 Package
• Current Limiting and Thermal Protection
• Output Current 800mA
• Line Regulation 0.2% (Max)
• Load Regulation 0.4% (Max)
• Temperature Range
— LM1117 0°C to 125°C
— LM1117I -40°C to 125°C
9.10.3. Applications
• 2.85V Model for SCSI-2 Active Termination
• Post Regulator for Switching DC/DC Converter
• High Efficiency Linear Regulators
• Battery Charger
• Battery Powered Instrumentation
9.10.4. Connection Diagrams
SOT-223
Top
View
TO-220
Top
View
9
TO-252
Top
View
Plasma TV Service Manual 11/01/2005

9.11. DS90C385
9.11.1. General Description
The DS90C385 transmitter converts 28 bits of LVCMOS/LVTTL data into four LVDS (Low Voltage
Differential Signalling) data streams. A phase-locked transmit clock is transmitted in parallel with the
data streams over a fifth LVDS link.
Every cycle of the transmit clock 28 bits of input data are sampled and transmitted. At a transmit clock
frequency of 85 MHz, 24 bits of RGB data and 3 bits of LCD timing and control data (FPLINE,
FPFRAME, DRDY) are transmitted at a rate of 595 Mbps per LVDS data channel. Using an 85 MHz
clock, the data throughput is 297.5 Mbytes/sec. Also available is the DS90C365 that converts 21 bits of
LVCMOS/LVTTL data into three LVDS (Low Voltage Differential Signalling) data streams. Both
transmitters can be programmed for Rising edge strobe or falling edge strobe through a dedicated pin.
A Rising edge or Falling edge strobe transmitter will interoperate with a Falling edge strobe Receiver
(DS90CF386/DS90CF366) without any translation logic.
The DS90C385 is also offered in a 64 ball, 0.8mm fine pitch ball grid array (FBGA) package which
provides a 44 % reduction in PCB footprint compared to the TSSOP package. This chipset is an ideal
means to solve EMI and cable size problems associated with wide, high-speed TTL interfaces.
9.11.2. Features
• 20 to 85 MHz shift clock support
• Best–in–Class Set & Hold Times on TxINPUTs
• Tx power consumption <130 mW (typ) @85MHz Grayscale
• Tx Power-down mode <200µW (max)
• Supports VGA, SVGA, XGA and Dual Pixel SXGA.
• Narrow bus reduces cable size and cost
• Up to 2.38 Gbps throughput
• Up to 297.5 Megabytes/sec bandwidth
• 345 mV (typ) swing LVDS devices for low EMI
• PLL requires no external components
• Compatible with TIA/EIA-644 LVDS standard
• Low profile 56-lead or 48-lead TSSOP package
• DS90C385 also available in a 64 ball, 0.8mm fine pitch ball grid array (FBGA) package
9.11.3. Pin Description
DS90C385 MTD56 (TSSOP) Package Pin Description-FPD Link Transmitter
Pin Name I/O No. Description
TxIN
TxOUT+
TxOUT-
TxCLKIN
R_FB
TxCLK OUT+
TxCLK OUT-
PWR DOWN
Vcc
GND
PLL Vcc
PLL GND
LVDS Vcc
LVDS GND
I 28
O 4
O 4
I 1
I 1
O 1
O 1
I 1
I 3
I 4
I 1
I 2
I 1
I 3
TTL level input. This includes: 8 Red, 8 Green, 8 Blue, and 4 control lines —FPLINE,
FPFRAME and DRDY (also referred to as HSYNC, VSYNC, Data Enable).
Positive LVDS differentiaI data output.
Negative LVDS differential data output.
TTL Ievel clock input. Pin name TxCLK IN.
Programmable strobe select
Positive LVDS differential clock output.
Negative LVDS differential clock output.
TTL level input. Assertion (low input) TRI-STATES the outputs, ensuring low current at
power down.
Power supply pins for TTL inputs.
Ground pins for TTL inputs.
Power supply pin for PLL.
Ground pins for PLL.
Power supply pin for LVDS outputs.
Ground pins for LVDS outputs.
10
Plasma TV Service Manual 11/01/2005

DS90C385SLC SLC64A Package Pin Description-FPD Link Transmitter
Pin Name I/O No. Description
TxIN
TxOUT+
TxOUT-
TxCLKIN
R_FB
TxCLK OUT+
TxCLK OUT-
PWR DOWN
Vcc
GND
PLL Vcc
PLL GND
LVDS Vcc
LVDS GND
NC
I 28
O 4
O 4
I 1
I 1
O 1
O 1
I 1
I 3
I 5
I 1
I 2
I 2
I 4
6
TTL level input.
Positive LVDS differentiaI data output.
Negative LVDS differential data output.
TTL Ievel clock input. The rising edge acts as data strobe. Pin name TxCLK IN.
Programmable strobe select. HIGH = rising edge, LOW = falling edge.
Positive LVDS differential clock output.
Negative LVDS differential clock output.
TTL level input. Assertion (low input) TRI-STATES the outputs, ensuring low
current at power down.
Power supply pins for TTL inputs.
Ground pins for TTL inputs.
Power supply pin for PLL.
Ground pins for PLL.
Power supply pin for LVDS outputs.
Ground pins for LVDS outputs.
Pins not connected.
11
Plasma TV Service Manual 11/01/2005

9.12. MSP34X1G
MSP3411G
Multistandard Sound Processor Family
9.12.1. Introduction
The MSP 34x1G family of single-chip Multistandard Sound Processors covers the sound processing of
all analog TV-Standards worldwide, as well as the NICAM digital sound standards. The full TV sound
processing, starting with analog sound IF signal-in, down to processed analog AF-out, is performed on
a single chip. Figure shows a simplified functional block diagram of the MSP 34x1G.
The MSP 34x1G has all functions of the MSP 34x0G with the addition of a virtual surround sound
feature.
Surround sound can be reproduced to a certain extent with two loudspeakers. The MSP 34x1G
includes the Micronas virtualizer algorithm “3D-PANORAMA” which has been approved by the Dolby
1)
Laboratories for with the "Virtual Dolby Surround" technology. In addition, the MSP 34x1G includes the
“PAN-ORAMA” algorithm.
These TV sound processing ICs include versions for processing the multichannel television sound
(MTS) signal conforming to the standard recommended by the Broadcast Television Systems
Committee (BTSC). The DBX noise reduction, or alternatively, Micronas Noise Reduction (MNR) is
performed alignment free.
Other processed standards are the Japanese FM-FM multiplex standard (EIA-J) and the FM Stereo
Radio standard.
Current ICs have to perform adjustment procedures in order to achieve good stereo separation for
BTSC and EIA-J. The MSP 34x1G has optimum stereo performance without any adjustments.
The MSP 34x1G has built-in automatic functions: The IC is able to detect the actual sound standard
automat-ically (Automatic Standard Detection). Furthermore, pilot levels and identification signals can
be evaluated internally with subsequent switching between mono/stereo/bilingual; no I
2 C interaction is
necessary (Automatic Sound Selection).
Source Select
2
S bus interface consists of five pins:
I
2
S_DA_IN1, I2S_DA_IN2: For input, four channels (two channels per line, 2*16 bits) per sampling
1. I
cycle (32 kHz) are transmitted.
2
S _DA_OUT: For output, two channels (2*16 bits) per sampling cycle (32 kHz) are transmitted.
2. I
2
S _CL: Gives the timing for the transmission of I2S serial data (1.024 MHz).
3. I
2
S _WS: The I2S _WS word strobe line defines the left and right sample.
4. I
12
Plasma TV Service Manual 11/01/2005

9.12.2. Features
• 3D-PANORAMA virtualizer (approved by Dolby Laboratories) with noise generator
• PANORAMA virtualizer algorithm
• Standard Selection with single I
2
C transmission
• Automatic Sound Selection (mono/stereo/bilingual),
• Automatic Carrier Mute function
• Interrupt output programmable (indicating status change)
• Loudspeaker / Headphone channel with volume, balance, bass, treble, loudness
• AVC: Automatic Volume Correction
• Subwoofer output with programmable low-pass and complementary high-pass filter
• 5-band graphic equalizer for loudspeaker channel
• Spatial effect for loudspeaker channel, processing of all deemphasis filtering
• Two selectable sound IF (SIF) inputs
• Four Stereo SCART (line) inputs, one Mono input; two Stereo SCART outputs
• Complete SCART in/out switching matrix
• Two I
2
S inputs; one I2S output
• Automatic Standard Detection of terrestrial TV standards
• Demodulation of the BTSC multiplex signal and the SAP channel
• Alignment free digital DBX noise reduction
• BTSC stereo separation (MSP 3441G also EIA-J) significantly better than specification
• SAP and stereo detection for BTSC system
• Demodulation of the FM-Radio multiplex signal
9.12.3. Pin connections
NC = not connected; leave vacant
LV = if not used, leave vacant
OBL = obligatory; connect as described in circuit diagram
DVSS: if not used, connect to DVSS
AHVSS: connect to AHVSS
Pin No. Pin Name Type
PLCC
68-pin
1 16 14 9 8 ADR_WS OUT LV ADR word strobe
2 - - - - NC LV Not connected
3 15 13 8 7 ADR_DA OUT LV ADR Data Output
4 14 12 7 6 I2S_DA_IN1 IN LV I2S1 data input
5 13 11 6 5 I2S_DA_OUT OUT LV I2S data output
6 12 10 5 4 I2S_WS IN/OUT LV I2S word strobe
7 11 9 4 3 I2S_CL IN/OUT LV I2S clock
8 10 8 3 2 I2C_DA IN/OUT OBL I2C data
9 9 7 2 1 I2C_CL IN/OUT OBL I2C clock
10 8 - 1 64 NC LV Not connected
11 7 6 80 63 STANDBYQ IN OBL Stand-by (low-active)
12 6 5 79 62 ADR_SEL IN OBL I2C bus address select
13 5 4 78 61 D_CTR_I/O_0 IN/OUT LV D_CTR_I/O_0
14 4 3 77 60 D_CTR_I/O_1 IN/OUT LV D_CTR_I/O_1
15 3 - 76 59 NC LV Not connected
16 2 - 75 58 NC LV Not connected
17 - - - - NC LV Not connected
18 1 2 74 57 AUD_CL_OUT OUT LV
19 64 1 73 56 TP LV Test pin
20 63 52 72 55 XTAL_OUT OUT OBL Crystal oscillator
21 62 51 71 54 XTAL_IN IN OBL Crystal oscillator
22 61 50 70 53 TESTEN IN OBL Test pin
23 60 49 69 52 ANA_IN2+ IN
24 59 48 68 51 ANA_IN- IN
25 58 47 67 50 ANA_IN1+ IN LV IF input 1
PSDIP
64-pin
PSDIP
52-pin
PQFP
80-pin
PLQFP
64-pin
Connection
(if not used)
AVSS via
56 pF/LV
AVSS via
56 pF/LV
Short Description
Audio clock output
(18.432 MHz)
IF Input 2 (can be left
vacant, only if IF input 1 is
also not in use)
IF common (can be left
vacant, only if IF input 1 is
also not in use)
13
Plasma TV Service Manual 11/01/2005
26 57 46 66 49 AVSUP OBL Analog power supply 5V
- - - 65 - AVSUP OBL Analog power supply 5V
- - - 64 - NC LV Not connected
- - - 63 - NC LV Not connected
27 56 45 62 48 AVSS OBL Analog ground
- - - 61 - AVSS OBL Analog ground
28 55 44 60 47 MONO_IN IN LV Mono input
- - - 59 - NC LV Not connected
29 54 43 58 46 VREFTOP OBL
30 53 42 57 45 SC1_IN_R IN LV SCART 1 input, right
31 52 41 56 44 SC1_IN_L IN LV SCART 1 input, left
32 51 - 55 43 ASG1 AHVSS Analog Shield Ground 1
33 50 40 54 42 SC2_IN_R IN LV SCART 2 input, right
34 49 39 53 41 SC2_IN_L IN LV SCART 2 input, left
35 48 - 52 40 ASG2 AHVSS Analog Shield Ground 2
36 47 38 51 39 SC3_IN_R IN LV SCART 3 input, right
37 46 37 50 38 SC3_IN_L IN LV SCART 3 input, left
38 45 - 49 37 ASG4 AHVSS Analog Shield Ground 4
39 44 - 48 36 SC4_IN_R IN LV SCART 4 input, right
40 43 - 47 35 SC4_IN_L IN LV SCART 4 input, left
41 - - 46 - NC LV or AHVSS Not connected
42 42 36 45 34 AGNDC OBL Analog reference voltage
43 41 35 44 33 AHVSS OBL Analog ground
- - - 43 - AHVSS OBL Analog ground
- - - 42 - NC LV Not connected
- - - 41 - NC LV Not connected
44 40 34 40 32 CAPL_M OBL Volume capacitor MAIN
45 39 33 39 31 AHVSUP OBL Analog power supply 8V
46 38 32 38 30 CAPL_A OBL Volume capacitor AUX
47 37 31 37 29 SC1_OUT_L OUT LV SCART output 1, left
48 36 30 36 28 SC1_OUT_R OUT LV SCART output 1, right
49 35 29 35 27 VREF1 OBL Reference ground 1
50 34 28 34 26 SC2_OUT_L OUT LV SCART output 2, left
51 33 27 33 25 SC2_OUT_R OUT LV SCART output 2, right
52 - - 32 - NC LV Not connected
53 32 - 31 24 NC LV Not connected
54 31 26 30 23 DACM_SUB OUT LV Subwoofer output
55 30 - 29 22 NC LV Not connected
56 29 25 28 21 DACM_L OUT LV Loudspeaker out, left
57 28 24 27 20 DACM_R OUT LV Loudspeaker out, right
58 27 23 26 19 VREF2 OBL Reference ground 2
59 26 22 25 18 DACA_L OUT LV Headphone out, left
60 25 21 24 17 DACA_R OUT LV Headphone out, right
- - - 23 - NC LV Not connected
- - - 22 - NC LV Not connected
61 24 20 21 16 RESETQ IN OBL Power-on-reset
62 23 - 20 15 NC LV Not connected
63 22 - 19 14 NC LV Not connected
64 21 19 18 13 NC LV Not connected
65 20 18 17 12 I2S_DA_IN2 IN LV I2S2-data input
66 19 17 16 11 DVSS OBL Digital ground
- - - 15 - DVSS OBL Digital ground
- - - 14 - DVSS OBL Digital ground
67 18 16 13 10 DVSUP OBL Digital power supply 5V
- - - 12 - DVSUP OBL Digital power supply 5V
- - - 11 - DVSUP OBL Digital power supply 5V
68 17 15 10 9 ADR_CL OUT LV ADR clock
Reference voltage IF A/D
converter
14
Plasma TV Service Manual 11/01/2005
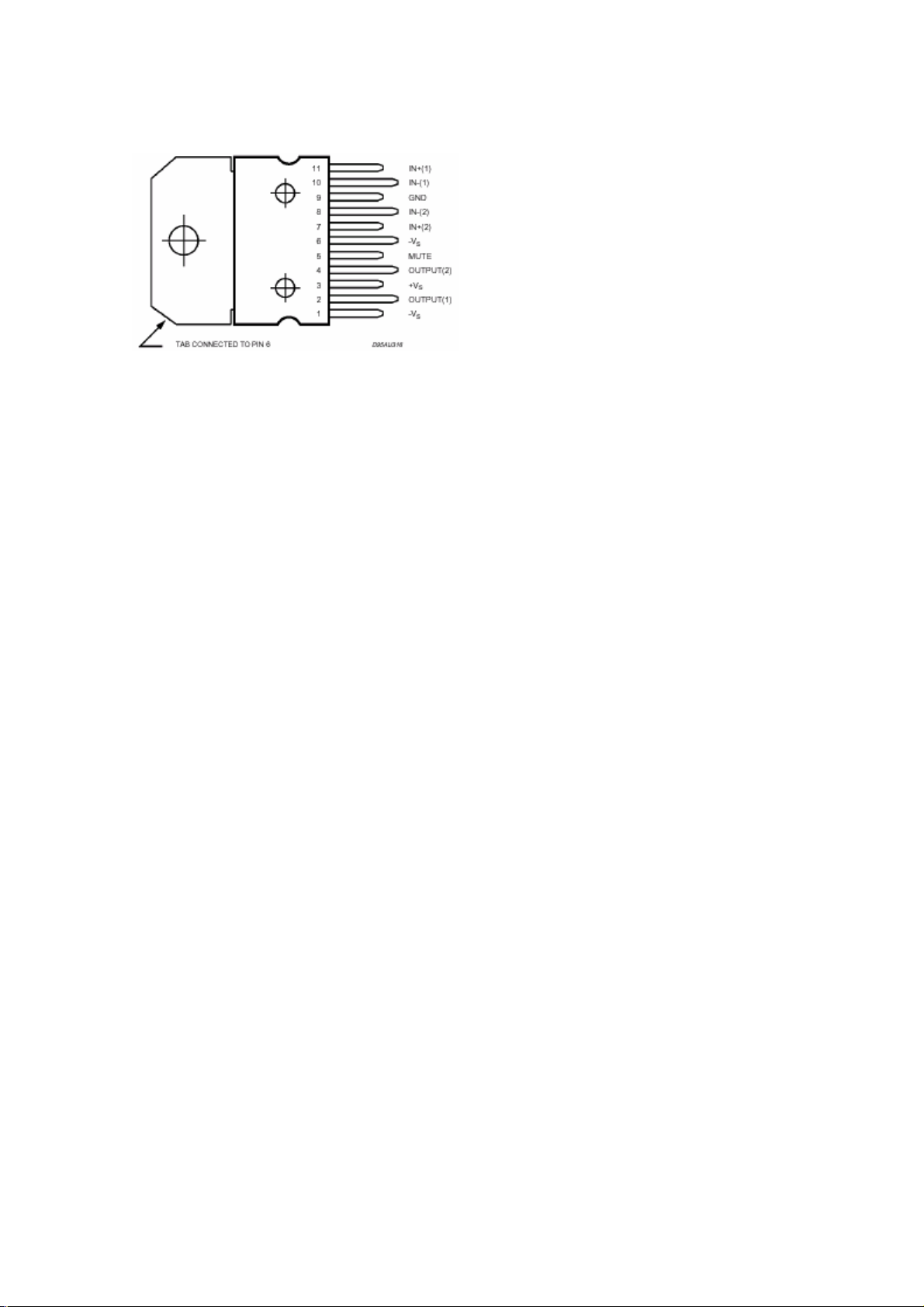
9.13. TDA1308
9.13.1. General Description
The TDA1308 is an integrated class AB stereo headphone driver contained in an SO8 or a DIP8 plastic
package. The device is fabricated in a 1 mm CMOS process and has been primarily developed for
portable digital audio applications. It gets its input from two analog audio outputs (DACA_L and
DACA_R) of MSP 34x0G. The gain of the output is adjustable by the feedback resistor between the
inputs and outputs.
9.13.2. Features
Wide temperature range
•
• No switch ON/OFF clicks
• Excellent power supply ripple rejection
• Low power consumption
• Short-circuit resistant
• High performance
• high signal-to-noise ratio
• High slew rate
• Low distortion
• Large output voltage swing.
15
Plasma TV Service Manual 11/01/2005

9.13.3. Pinning
SYMBOL PIN DESCRIPTION
OUTA 1 Output A
INA(neg) 2 Inverting input A
INA(pos) 3 Non-inverting input A
VSS 4 Negative supply
INB(pos) 5 Non-inverting input B
INB(neg) 6 Inverting input B
OUTB 7 Output B
VDD 8 Positive supply
9.14. PI5V330
9.14.1. General Description
The PI5V330 is well suited for video applications when switching composite or RGB analog. A picturein-picture application will be described in this brief. The pixel-rate creates video overlays so two or more
pictures can be viewed at the same time. An inexpensive NTSC titler can be implemented by
superimposing the output of a character generator on a standard composite video background.
9.15. AD9883A
9.15.1. General Description
The AD9883A is a complete 8-bit, 140 MSPS, monolithic analog interface optimized for capturing RGB
graphics signals from personal computers and workstations. Its 140 MSPS encode rate capability and
full power analog bandwidth of 300 MHz supports resolutions up to SXGA (1280 × 1024 at 75 Hz).
The AD9883A includes a 140 MHz triple ADC with internal 1.25 V reference, a PLL, and programmable
gain, offset, and clamp control. The user provides only a 3.3 V power supply, analog input, and Hsync
and COAST signals. Three-state CMOS outputs may be powered from 2.5 V to 3.3 V.
The AD9883A’s on-chip PLL generates a pixel clock from the Hsync input. Pixel clock output
frequencies range from 12 MHz to140 MHz. PLL clock jitter is 500 ps p-p typical at 140 MSPS. When
the COAST signal is presented, the PLL maintains its output frequency in the absence of Hsync. A
sampling phase adjustment is provided. Data, Hsync, and clock output phase relationships are
maintained. The AD9883A also offers full sync processing for composite sync and sync-on-green
applications. A clamp signal is generated internally or may be provided by the user through the CLAMP
input pin. This interface is fully programmable via a 2-wire serial interface.
Fabricated in an advanced CMOS process, the AD9883A is provided in a space-saving 80-lead LQFP
surface-mount plastic package and is specified over the –40.˚C to +85. ˚C temperature range.
9.15.2. Features
• Industrial Temperature Range Operation
• 140 MSPS Maximum Conversion Rate
• 300 MHz Analog Bandwidth
• 0.5 V to 1.0 V Analog Input Range
• 500 ps p-p PLL Clock Jitter at 110 MSPS
• 3.3 V Power Supply
• Full Sync Processing
• Sync Detect for Hot Plugging
• Midscale Clamping
• Power-Down Mode
• Low Power: 500 mW Typical
• 4:2:2 Output Format Mode
• APPLICATIONS
• RGB Graphics Processing
• LCD Monitors and Projectors
• Plasma Display Panels
• Scan Converters
• Microdisplays
• Digital TV
16
Plasma TV Service Manual 11/01/2005

9.15.3. Pin Descriptions
Complete Pinout list
Pin Type Mnemonic Function Value Pin No.
Inputs RAIN
GAIN
BAIN
HSYNC
VSYNC
SOGIN
CLAMP
COAST
Outputs Red [7:0]
Green [7:0]
Blue [7:0]
DATACK
HSOUT
VSOUT
SOGOUT
References REF BYPASS
MIDSCV
FILT
Power Supply VD
VDD
PVD
GND
Control SDA
SCL
A0
Analog Input for Converter R
Analog Input for Converter G
Analog Input for Converter B
Horizontal SYNC Input
Vertical SYNC Input
Input for Sync-on-Green
Clamp Input (External CLAMP Signal) PLL
COAST Signal Input
Outputs of Converter Red, Bit 7 is the MSB
Outputs of Converter Green, Bit 7 is the MSB
Outputs of Converter Blue, Bit 7 is the MSB
Data Output Clock
HSYNC Output (Phase-Aligned with DATACK)
VSYNC Output (Phase-Aligned with DATACK)
Sync-on-Green Slicer Output
Internal Reference Bypass
Internal Midscale Voltage Bypass
Connection for External Filter Components for
Internal PLL
Analog Power Supply
Output Power Supply
PLL Power Supply
Ground
Serial Port Data I/O
Serial Port Data Clock (100 kHz Maximum)
Serial Port Address Input 1
0.0 V to 1.0 V
0.0 V to 1.0 V
0.0 V to 1.0 V
3.3 V CMOS
3.3 V CMOS
0.0 V to 1.0 V
3.3 V CMOS
3.3 V CMOS
3.3 V CMOS
3.3 V CMOS
3.3 V CMOS
3.3 V CMOS
3.3 V CMOS
3.3 V CMOS
3.3 V CMOS
1.25 V 58
3.3 V
3.3 V
3.3 V
0 V
3.3 V CMOS
3.3 V CMOS
3.3 V CMOS
54
48
43
30
31
49
38
29
70–77
2–9
12–19
67
66
64
65
37
33
39, 42,
45, 46,
51, 52,
59, 62
11, 22,
23, 69,
78, 79
26, 27,
34, 35
1, 10,
20, 21,
24, 25,
28, 32,
36, 40,
41, 44,
47, 50,
53, 60,
61, 63,
68, 80
57
56
55
Pin Function Descriptions:
Pin Name Function
OUTPUTS
HSOUT
VSOUT
SOGOUT
Horizontal Sync Output
A reconstructed and phase-aligned version of the Hsync input. Both the polarity
and duration of this output can be programmed via serial bus registers. By
maintaining alignment with DATACK and Data, data timing with respect to
horizontal sync can always be determined.
Vertical Sync Output
A reconstructed and phase-aligned version of the video Vsync. The polarity of this
output can be controlled via a serial bus bit. The placement and duration in all
modes is set by the graphics transmitter.
Sync-On-Green Slicer Output
This pin outputs either the signal from the Sync-on-Green slicer comparator or an
unprocessed but delayed version of the Hsync input. See the Sync Processing
Block Diagram (Figure 12) to view how this pin is connected. (Note: Besides slicing
off SOG, the output from this pin gets no other additional processing on the
17
Plasma TV Service Manual 11/01/2005

SERIAL PORT (2-WIRE)
SDA
SCL
A0
DATA OUTPUTS
RED
GREEN
BLUE
DATA CLOCK OUTPUT
DATACK
INPUTS
RAIN
GAIN
BAIN
HSYNC
VSYNC
SOGIN
CLAMP
AD9883A. Vsync separation is performed via the sync separator.)
Serial Port Data I/O
Serial Port Data Clock
Serial Port Address Input 1
For a full description of the 2-wire serial register and how it works, refer to the 2Wire Serial Control Port section.
Data Output, Red Channel
Data Output, Green Channel
Data Output, Blue Channel
The main data outputs. Bit 7 is the MSB. The delay from pixel sampling time to
output is fixed. When the sampling time is changed by adjusting the PHASE
register, the output timing is shifted as well. The DATACK and HSOUT outputs are
also moved, so the timing relationship among the signals is maintained. For exact
timing information, refer to Figures 7, 8, and 9.
Data Output Clock
This is the main clock output signal used to strobe the output data and HSOUT into
external logic. It is produced by the internal clock generator and is synchronous
with the internal pixel sampling clock. When the sampling time is changed by
adjusting the PHASE register, the output timing is shifted as well. The Data,
DATACK, and HSOUT outputs are all moved, so the timing relationship among the
signals is maintained.
Analog Input for Red Channel
Analog Input for Green Channel
Analog Input for Blue Channel
High impedance inputs that accept the Red, Green, and Blue channel graphics
signals, respectively. (The three channels are identical, and can be used for any
colours, but colours are assigned for convenient reference.) They accommodate
input signals ranging from 0.5 V to 1.0 V full scale. Signals should be ac-coupled to
these pins to support clamp operation.
Horizontal Sync Input
This input receives a logic signal that establishes the horizontal timing reference
and provides the frequency reference for pixel clock generation. The logic sense of
this pin is controlled by serial register 0EH Bit 6 (Hsync Polarity). Only the leading
edge of Hsync is active; the trailing edge is ignored. When Hsync Polarity = 0, the
falling edge of Hsync is used. When Hsync Polarity = 1, the rising edge is active.
The input includes a Schmitt trigger for noise immunity, with a nominal input
threshold of 1.5 V.
Vertical Sync Input
This is the input for vertical sync.
Sync-on-Green Input
This input is provided to assist with processing signals with embedded sync,
typically on the Green channel. The pin is connected to a high speed comparator
with an internally generated threshold. The threshold level can be programmed in
10 mV steps to any voltage between 10 mV and 330 mV above the negative peak
of the input signal. The default voltage threshold is 150 mV. When connected to an
ac-coupled graphics signal with embedded sync, it will produce a noninverting
digital output on SOGOUT. (This is usually a composite sync signal, containing
both vertical and horizontal sync information that must be separated before
passing the horizontal sync signal to Hsync.) When not used, this input should be
left unconnected. For more details on this function and how it should be
configured, refer to the Sync-on-Green section.
External Clamp Input
This logic input may be used to define the time during which the input signal is
clamped to ground. It should be exercised when the reference dc level is known to
be present on the analog input channels, typically during the back porch of the
graphics signal. The CLAMP pin is enabled by setting control bit Clamp Function to
1, (register 0FH, Bit 7, default is 0). When disabled, this pin is ignored and the
clamp timing is determined internally by counting a delay and duration from the
18
Plasma TV Service Manual 11/01/2005

COAST
REF BYPASS
MIDSCV
FILT
POWER SUPPLY
VD
VDD
PVD
GND
trailing edge of the Hsync input. The logic sense of this pin is controlled by Clamp
Polarity register 0FH, Bit 6. When not used, this pin must be grounded and Clamp
Function programmed to 0.
Clock Generator Coast Input (Optional)
This input may be used to cause the pixel clock generator to stop synchronizing
with Hsync and continue producing a clock at its current frequency and phase.
This is useful when processing signals from sources that fail to produce horizontal
sync pulses during the vertical interval. The COAST signal is generally not
required for PC-generated signals. The logic sense of this pin is controlled by
Coast Polarity (register 0FH, Bit 3). When not used, this pin may be grounded and
Coast Polarity programmed to 1, or tied HIGH (to VD through a 10 k resistor) and
Coast Polarity programmed to 0. Coast Polarity defaults to 1 at power-up.
Internal Reference BYPASS
Bypass for the internal 1.25 V band gap reference. It should be connected to
ground through a 0.1 µF capacitor. The absolute accuracy of this reference is
±4%, and the temperature coefficient is ±50 ppm, which is adequate for most
AD9883A applications. If higher accuracy is required, an external reference may
be employed instead.
Midscale Voltage Reference BYPASS
Bypass for the internal midscale voltage reference. It should be connected to
ground through a 0.1 µF capacitor. The exact voltage varies with the gain setting
of the Blue channel.
External Filter Connection
For proper operation, the pixel clock generator PLL requires an external filter.
Connect the filter shown in Figure 6 to this pin. For optimal performance, minimize
noise and parasitics on this node.
Main Power Supply
These pins supply power to the main elements of the circuit. They should be
filtered and as quiet as possible.
Digital Output Power Supply
A large number of output pins (up to 25) switching at high speed (up to 110 MHz)
generates a lot of power supply transients (noise). These supply pins are identified
separately from the VD pins so special care can be taken to minimize output noise
transferred into the sensitive analog circuitry. If the AD9883A is interfacing with
lower voltage logic, V DD may be connected to a lower supply voltage (as low as
2.5 V) for compatibility.
Clock Generator Power Supply
The most sensitive portion of the AD9883A is the clock generation circuitry. These
pins provide power to the clock PLL and help the user design for optimal
performance. The designer should provide quiet, noise-free power to these pins.
Ground
The ground return for all circuitry on-chip. It is recommended that the AD9883A be
assembled on a single solid ground plane, with careful attention given to ground
current paths.
9.16. SAA7118E
9.16.1. General Description
The SAA7118E is a video capture device for applications at the image port of VGA controllers. Philips
X-VIP is a new multistandard comb filter video decoder chip with additional component processing,
providing high quality, optionally scaled, video.
The SAA7118E is a combination of a four-channel analog pre-processing circuit including source
selection, anti-aliasing filter and ADC, an automatic clamp and gain control, a Clock Generation Circuit
(CGC), a digital multistandard decoder containing two-dimensional chrominance/luminance separation
by an adaptive comb filter and a high performance scalar, including variable horizontal and vertical up
and downscaling and a brightness, contrast and saturation control circuit.
19
Plasma TV Service Manual 11/01/2005

It is a highly integrated circuit for desktop video and similar applications. The decoder is based on the
principle of line-locked clock decoding and is able to decode the colour of PAL, SECAM and NTSC
signals into ITU 601 compatible colour component values. The SAA7118E accepts CVBS or S-video
(Y/C) as analog inputs from TV or VCR sources, including weak and distorted signals as well as
baseband component signals Y-P
-PR or RGB. An expansion port (X-port) for digital video
B
(bidirectional half duplex, D1 compatible) is also supported to connect to MPEG or video phone codec.
At the so called image port (I-port) the SAA7118E supports 8 or 16-bit wide output data with auxiliary
reference data for interfacing to VGA controllers.
The target application for the SAA7118E is to capture and scale video images, to be provided as digital
video stream through the image port of a VGA controller, for capture to system memory, or just to
provide digital baseband video to any picture improvement processing.
9.16.2. Features
Video acquisition/clock
• Up to sixteen analog CVBS, split as desired (all of the CVBS inputs optionally can be used to convert
e.g. Vestigial Side Band (VSB) signals)
• Up to eight analog Y + C inputs, split as desired
• Up to four analog component inputs, with embedded or separate sync, split as desired
• Four on-chip anti-aliasing filters in front of the Analog-to-Digital Converters (ADCs)
• Automatic Clamp Control (ACC) for CVBS, Y and C (or VSB) and component signals
• Switchable white peak control
• Four 9-bit low noise CMOS ADCs running at twice the oversampling rate (27 MHz)
• Fully programmable static gain or Automatic Gain Control (AGC), matching to the particular signal
properties
• On-chip line-locked clock generation in accordance with “ITU 601”
• Requires only one crystal (32.11 or 24.576 MHz) for all standards
• Horizontal and vertical sync detection.
Video decoder
• Digital PLL for synchronization and clock generation from all standards and non-standard video
sources e.g. consumer grade VTR
• Automatic detection of any supported colour standard
• Luminance and chrominance signal processing for PAL B, G, D, H, I and N, combination PAL N, PAL
M, NTSC M, NTSC-Japan, NTSC 4.43 and SECAM
• Adaptive 2/4-line comb filter for two dimensional chrominance/luminance separation, also with VTR
signals
– Increased luminance and chrominance bandwidth for all PAL and NTSC standards
– Reduced cross colour and cross luminance artefacts
• PAL delay line for correcting PAL phase errors
• Brightness Contrast Saturation (BCS) adjustment, separately for composite and baseband signals
• User programmable sharpness control
• Detection of copy-protected signals according to the macrovision standard, indicating level of
protection
• Independent gain and offset adjustment for raw data path.
Component video processing
• RGB component inputs
-PR component inputs
• Y-P
B
• Fast blanking between CVBS and synchronous component inputs
• Digital RGB to Y-C
-CR matrix.
B
Video scalar
• Horizontal and vertical downscaling and up scaling to randomly sized windows
• Horizontal and vertical scaling range: variable zoom to 1/64 (icon) (note: H and V zoom are restricted
by the transfer data rates)
• Anti-alias and accumulating filter for horizontal scaling
• Vertical scaling with linear phase interpolation and accumulating filter for anti-aliasing (6-bit phase
accuracy)
• Horizontal phase correct up and downscaling for improved signal quality of scaled data, especially for
compression and video phone applications, with 6-bit phase accuracy (1.2 ns step width)
20
Plasma TV Service Manual 11/01/2005

• Two independent programming sets for scalar part, to define two ‘ranges’ per field or sequences over
frames
• Field wise switching between decoder part and expansion port (X-port) input
• Brightness, contrast and saturation controls for scaled outputs.
Vertical Blanking Interval (VBI) data decoder and slicer
• Versatile VBI-data decoder, slicer, clock regeneration and byte synchronization e.g. for World
Standard Teletext (WST), North-American Broadcast Text System (NABTS), close caption, Wide
Screen Signalling (WSS) etc.
Audio clock generation
• Generation of a field-locked audio master clock to support a constant number of audio clocks per
video field
• Generation of an audio serial and left/right (channel)
Digital I/O interfaces
• Real-time signal port (R port), inclusive continuous line-locked reference clock and real-time status
information supporting RTC level 3.1 (refer to document “RTC Functional Specification” for details)
• Bidirectional expansion port (X-port) with half duplex functionality (D1), 8-bit Y-C
-CR
B
– Output from decoder part, real-time and unscaled
– Input to scalar part, e.g. video from MPEG decoder (extension to 16-bit possible)
• Video image port (I-port) configurable for 8-bit data (extension to 16-bit possible) in master mode (own
clock), or slave mode (external clock), with auxiliary timing and handshake signals
• Discontinuous data streams supported
• 32-word ´ 4-byte FIFO register for video output data
• 28-word ´ 4-byte FIFO register for decoded VBI-data output
• Scaled 4 :2 :2, 4 :1 :1, 4 :2 :0, 4 :1 :0 Y-C
-CR output
B
• Scaled 8-bit luminance only and raw CVBS data output
• Sliced, decoded VBI-data output.
Miscellaneous
• Power-on control
• 5 V tolerant digital inputs and I/O ports
• Software controlled power saving standby modes supported
• Programming via serial I 2 C-bus, full read back ability by an external controller, bit rate up to 400
kbits/s
• Boundary scan test circuit complies with the “IEEE Std. 1149.b1 - 1994”
• BGA156 package.
9.16.3. Pinning
SYMBOL PIN TYPE DESCRIPTION
XTOUT A2 O crystal oscillator output signal; auxiliary signal
XTALO A3 O 24.576 MHz (32.11 MHz) crystal oscillator output; not
connected if TTL clock input of XTALI is used
V
A4 P ground for crystal oscillator
SS(xtal)
TDO A5 O test data output for boundary scan test; note 2
XRDY A6 O task flag or ready signal from scaler, controlled by XRQT
XCLK A7 I/O clock I/O expansion port
XPD0 A8 I/O LSB of expansion port data
XPD2 A9 I/O MSB - 5 of expansion port data
XPD4 A10 I/O MSB - 3 of expansion port data
XPD6 A11 I/O MSB - 1 of expansion port data
TEST1 A12 I/pu do not connect, reserved for future extensions and for testing:
scan input
TEST2 A13 I/pu do not connect, reserved for future extensions and for testing:
scan input
AI41 B1 I analog input 41
TEST3 B2 O do not connect, reserved for future extensions and for testing
V
XTALI B4 I input terminal for 24.576 MHz (32.11 MHz) crystal oscillator
B3 P Supply voltage for crystal oscillator
DD(xtal)
or connection of external oscillator with TTL compatible
21
Plasma TV Service Manual 11/01/2005

square wave clock signal
TDI B5 I/pu test data input for boundary scan test; note 2
TCK B6 I/pu test clock for boundary scan test; note 2
XDQ B7 I/O data qualifier for expansion port
XPD1 B8 I/O MSB - 6 of expansion port data
XPD3 B9 I/O MSB - 4 of expansion port data
XPD5 B10 I/O MSB - 2 of expansion port data
XTRI B11 I X-port output control signal, affects all X-port pins (XPD7 to
XPD0, XRH, XRV, XDQ and XCLK), enable and active
polarity is under software control (bits XPE in subaddress
83H)
TEST4 B12 O do not connect, reserved for future extensions and for testing:
scan output
TEST5 B13 NC do not connect, reserved for future extensions and for testing
TEST6 B14 NC do not connect, reserved for future extensions and for testing
VSSA4 C1 P ground for analog inputs AI4x
AGND C2 P analog ground
TEST7 C3 NC do not connect, reserved for future extensions and for testing
TEST8 C4 NC do not connect, reserved for future extensions and for testing
V
C5 P Digital supply voltage 1 (peripheral cells)
DDD1
TRST C6 I/pu test reset input (active LOW), for boundary scan test (with
internal pull-up); notes 2, 3 and 4
XRH C7 I/O horizontal reference I/O expansion port
V
C8 P Digital supply voltage 2 (core)
DDD2
V
C9 P Digital supply voltage 3 (peripheral cells)
DDD3
V
C10 P Digital supply voltage 4 (core)
DDD4
XPD7 C11 I/O MSB of expansion port data
TEST9 C12 NC do not connect, reserved for future extensions and for testing
TEST10 C13 NC do not connect, reserved for future extensions and for testing
TEST11 C14 I/pu do not connect, reserved for future extensions and for testing:
scan input
AI43 D1 I analog input 43
AI42 D2 I analog input 42
AI4D D3 I differential input for ADC channel 4 (pins AI41 to AI44)
V
D4 P analog supply voltage for analog inputs AI4x (3.3 V)
DDA4
V
D5 P Digital ground 1 (peripheral cells)
SSD1
TMS D6 I/pu test mode select input for boundary scan test or scan test;
note 2
V
D7 P Digital ground 2 (core; substrate connection)
SSD2
XRV D8 I/O vertical reference I/O expansion port
V
D9 P Digital ground 3 (peripheral cells)
SSD3
V
D10 P Digital ground 4 (core)
SSD4
V
D11 P Digital ground 5 (peripheral cells)
SSD5
V
D12 P Digital supply voltage 5 (peripheral cells)
DDD5
TEST12 D13 I/pu do not connect, reserved for future extensions and for testing:
scan input
HPD0 D14 I/O LSB of host port data I/O, extended CB -CR input for
expansion port, extended C
-CR output for image port
B
AI44 E1 I analog input 44
V
E2 P analog supply voltage for analog inputs AI4x (3.3 V)
DDA4A
AI31 E3 I analog input 31
V
E4 P ground for analog inputs AI3x
SSA3
HPD1 E11 I/O MSB - 6 of host port data I/O, extended CB -CR input for
expansion port, extended C
-CR output for image port
B
HPD3 E12 I/O MSB - 4 of host port data I/O, extended CB -CR input for
expansion port, extended C
-CR output for image port
B
HPD2 E13 I/O MSB - 5 of host port data I/O, extended CB -CR input for
expansion port, extended CB -CR output for image port
HPD4 E14 I/O MSB - 3 of host port data I/O, extended CB -CR input for
expansion port, extended C
-CR output for image port
B
AI3D F1 I/O differential input for ADC channel 3 (pins AI31 to AI34)
AI32 F2 I analog input 32
AI33 F3 I analog input 33
V
F4 P analog supply voltage for analog inputs AI3x (3.3 V)
DDA3
22
Plasma TV Service Manual 11/01/2005

V
F11 P Digital ground 6 (core)
SSD6
V
F12 P Digital supply voltage 6 (core)
DDD6
HPD5 F13 I/O MSB - 2 of host port data I/O, extended CB -CR input for
expansion port, extended C
-CR output for image port
B
HPD6 F14 I/O MSB - 1 of host port data I/O, extended CB -CR input for
expansion port, extended CB -CR output for image port
AI34 G1 I analog input 34
V
G2 P analog supply voltage for analog inputs AI3x (3.3 V)
DDA3A
AI22 G3 I analog input 22
AI21 G4 I analog input 21
V
G11 P Digital ground 7 (peripheral cells)
SSD7
IPD1 G12 O MSB - 6 of image port data output
HPD7 G13 I/O MSB of host port data I/O, extended CB -CR R input for
expansion port, extended C
-CR output for image port
B
IPD0 G14 O LSB of image port data output
AI2D H1 I differential input for ADC channel 2 (pins AI24 to AI21)
AI23 H2 I analog input 23
V
H3 P ground for analog inputs AI2x
SSA2
V
H4 P analog supply voltage for analog inputs AI2x
DDA2
IPD2 H11 O MSB - 5 of image port data output
V
H12 P Digital supply voltage 7 (peripheral cells)
DDD7
IPD4 H13 O MSB - 3 of image port data output
IPD3 H14 O MSB - 4 of image port data output
V
J1 P analog supply voltage for analog inputs AI2x
DDA2A
AI11 J2 I analog input 11
AI24 J3 I analog input 24
V
J4 P ground for analog inputs AI1x
SSA1
V
J11 P Digital ground 8 (core)
SSD8
V
J12 P Digital supply voltage 8 (core)
DDD8
IPD6 J13 O
IPD5 J14 O
MSB − 1 of image port data output
MSB − 2 of image port data output
AI12 K1 I analog input 12
AI13 K2 I analog input 13
AI1D K3 I differential input for ADC channel 1 (pins AI14 to AI11)
V
K4 P analog supply voltage for analog inputs AI1x (3.3 V)
DDA1
IPD7 K11 O MSB of image port data output
IGPH K12 O multi purpose horizontal reference output signal; image port
(controlled by subaddresses 84H and 85H)
IGP1 K13 O general purpose output signal 1; image port (controlled by
subaddresses 84H and 85H)
IGPV K14 O multi purpose vertical reference output signal; image port
(controlled by subaddresses 84H and 85H)
V
L1 P analog supply voltage for analog inputs AI1x (3.3 V)
DDA1A
AGNDA L2 P analog signal ground
AI14 L3 I analog input 14
V
L4 P Digital ground 9 (peripheral cells)
SSD9
V
L5 P Digital ground 10 (core)
SSD10
ADP6 L6 O MSB - 2 of direct analog-to-digital converted output data
(VSB)
ADP3 L7 O MSB - 5 of direct analog-to-digital converted output data
(VSB)
V
L8 P Digital ground 11 (peripheral cells)
SSD11
V
L9 P Digital ground 12 (core)
SSD12
RTCO L10 O/st/pd real-time control output; contains information about actual
system clock frequency, field rate, odd/even sequence,
decoder status, subcarrier frequency and phase and PAL
sequence; the RTCO pin is enabled via I
2
C-bus bit RTCE;
see notes 5, 6
V
L11 P Digital ground 13 (peripheral cells)
SSD13
ITRI L12 I/(O) image port output control signal, affects all input port pins
inclusive ICLK, enable and active polarity is under software
control (bits IPE in subaddress 87H); output path used for
testing: scan output
IDQ L13 O output data qualifier for image port (optional: gated clock
output)
23
Plasma TV Service Manual 11/01/2005

IGP0 L14 O general purpose output signal 0; image port (controlled by
subaddresses 84H and 85H)
AOUT M1 O analog test output (do not connect)
V
M2 P ground for internal Clock Generation Circuit (CGC)
SSA0
V
M3 P analog supply voltage (3.3 V) for internal clock generation
DDA0
circuit
V
M4 P
DDD9
V
M5 P
DDD10
ADP7 M6 O
ADP2 M7 O
V
M8 P
DDD11
V
M9 P
DDD12
RTS0 M10 O
V
M11 P
DDD13
AMXCLK M12 I
FSW M13 I/pd
ICLK M14 I/O
Digital supply voltage 9 (peripheral cells)
Digital supply voltage 10 (core)
MSB − 1 of direct analog-to-digital converted output data
(VSB)
MSB − 6 of direct analog-to-digital converted output data
(VSB)
Digital supply voltage 11 (peripheral cells)
Digital supply voltage 12 (core)
real-time status or sync information, controlled by
subaddresses 11H and 12H
Digital supply voltage 13 (peripheral cells)
audio master external clock input
fast switch (blanking) with internal pull-down inserts
component inputs into CVBS signal
clock output signal for image port, or optional
asynchronous back-end clock input
TEST13 N1 NC do not connect, reserved for future extensions and for testing
TEST14 N2 I/pu do not connect, reserved for future extensions and for testing
TEST15 N3 I/pd do not connect, reserved for future extensions and for testing
CE N4 I/pu chip enable or reset input (with internal pull-up)
LLC2 N5 O line-locked 1 ¤2 clock output (13.5 MHz nominal)
CLKEXT N6 I external clock input intended for analog-to-digital conversion
of VSB signals (36 MHz)
ADP5 N7 O MSB - 3 of direct analog-to-digital converted output data
(VSB)
ADP0 N8 O LSB of direct analog-to-digital converted output data (VSB)
SCL N9 I serial clock input (I 2 C-bus)
RTS1 N10 O real-time status or sync information, controlled by
subaddresses 11H and 12H
ASCLK N11 O audio serial clock output
ITRDY N12 I target ready input for image port data
TEST16 N13 NC do not connect, reserved for future extensions and for testing
TEST17 N14 NC do not connect, reserved for future extensions and for testing
TEST18 P2 I/O do not connect, reserved for future extensions and for testing
EXMCLR P3 I/pd
external mode clear (with internal pull-down)
LLC P4 O line-locked system clock output (27 MHz nominal)
RES P5 O reset output (active LOW)
ADP8 P6 O MSB of direct analog-to-digital converted output data (VSB)
ADP4 P7 O MSB - 4 of direct analog-to-digital converted output data
(VSB)
ADP1 P8 O MSB - 7 of direct analog-to-digital converted output data
(VSB)
INT_A P9 O/od I2C-bus interrupt flag (LOW if any enabled status bit has
changed)
SDA P10 I/O/od serial data input/output (I 2 C-bus)
AMCLK P11 O audio master clock output, up to 50% of crystal clock
ALRCLK P12 O/st/pd audio left/right clock output; can be strapped to supply via a
3.3 kW resistor to indicate
that the default 24.576 MHz crystal (ALRCLK = 0; internal
pull-down) has been replaced
by a 32.110 MHz crystal (ALRCLK = 1); see notes 5 and 7
TEST19 P13 I/pu do not connect, reserved for future extensions and for testing:
scan input
Notes
1. I = input, O = output, P = power, NC = not connected, st = strapping, pu = pull-up, pd = pull-down, od
= open-drain.
24
Plasma TV Service Manual 11/01/2005

2. In accordance with the “IEEE1149.1” standard the pads TDI, TMS, TCK and TRST are input pads
with an internal pull-up transistor and TDO is a 3-state output pad.
3. For board design without boundary scan implementation connect the TRST pin to ground.
4. This pin provides easy initialization of the Boundary Scan Test (BST) circuit. TRST can be used to
force the Test Access Port (TAP) controller to the TEST_LOGIC_RESET state (normal operation) at
once.
5. Pin strapping is done by connecting the pin to the supply via a 3.3 κΩ resistor. During the power-up
reset sequence the corresponding pins are switched to input mode to read the strapping level. For the
default setting no strapping
resistor is necessary (internal pull-down).
6. Pin RTCO operates as I 2 C-bus slave address pin; RTCO = 0 slave address 42H/43H (default);
RTCO = 1 slave address 40H/41H.
7. Pin ALRCLK: 0 = 24.576 MHz crystal (default; Philips order number 4322 143 05291); 1 = 32.110
MHz crystal
9.17. TPS72501
9.17.1. General Description
The TPS725xx family of 1-A low-dropout (LDO) linear regulators has fixed voltage options available that
are commonly used to power the latest DSPs, FPGAs, and microcontrollers. An adjustable option
ranging from 1.22 V to 5.5 V is also available. The integrated supervisory circuitry provides an active
low RESET signal when the output falls out of regulation. The no capacitor/any capacitor feature allows
the customer to tailor output transient performance as needed. Therefore, compared to other regulators
capable of providing the same output current, this family of regulators can provide a stand alone power
supply solution or a post regulator for a switch mode power supply.
These regulators are ideal for higher current applications. The family operates over a wide range of
input voltages (1.8 V to 6 V) and has very low dropout (170 mV at 1-A).
Ground current is typically 210 µA at full load and drops to less than 80 µA at no load. Standby current
is less than 1 µA.
Each regulator option is available in either a SOT223–5, D (TPS72501 only), or DDPAK package. With
a low input voltage and properly heatsinked package, the regulator dissipates more power and
achieves higher efficiencies than similar regulators requiring 2.5 V or more minimum input voltage and
higher quiescent currents. These features make it a viable power supply solution for portable, battery
powered equipment.
Although an output capacitor is not required for stability, transient response and output noise are
improved with a 10-µF output capacitor.
Unlike some regulators that have a minimum current requirement, the TPS725 family is stable with no
output load current. The low noise capability of this family, coupled with its high current operation and
ease of power dissipation, make it ideal for telecom boards, modem banks, and other noise sensitive
applications.
9.17.2. Features
• 1-A Output Current
• Available in 1.5-V, 1.6-V, 1.8-V, 2.5-V Fixed-Output and Adjustable Versions (1.2-V to 5.5-V)
• Input Voltage Down to 1.8 V
• Low 170-mV Dropout Voltage at 1 A (TPS72525)
• Stable With Any Type/Value Output Capacitor
• Integrated Supervisor (SVS) With 50-ms RESET Delay Time
• Low 210-µA Ground Current at Full Load (TPS72525)
• Less than 1-µA Standby Current
25
Plasma TV Service Manual 11/01/2005

• ±2% Output Voltage Tolerance over Line, Load, and Temperature (–40C to 125C)
• Integrated UVLO
• Thermal and Over Current Protection
• 5-Lead SOT223–5 or DDPAK and 8–Pin SOP (TPS72501 only) Surface Mount Package
9.18. TSOP1836
9.18.1. Description
The TSOP18.. – series are miniaturized receivers for infrared remote control systems. PIN diode and
preamplifier are assembled on lead frame, the epoxy package is designed as IR filter. Carrier frequency
for TSOP1836 is 36kHz.
The demodulated output signal can directly be decoded by a microprocessor. The main benefit is the
reliable function even in disturbed ambient and the protection against uncontrolled output pulses.
9.18.2. Features
• Photo detector and preamplifier in one package
• Internal filter for PCM frequency
• TTL and CMOS compatibility
• Output active low
• Improved shielding against electrical field disturbance
• Suitable burst length .6 cycles/burst
Special Features
• Small size package
• Enhanced immunity against all kinds of disturbance light
• No occurrence of disturbance pulses at the output
• Short settling time after power on (<200_s)
9.19. PCF8591
9.19.1. General Description
The PCF8591 is a single-chip, single-supply low power 8-bit CMOS data acquisition device with four
analog inputs, one analog output and a serial I
Three address pins A0, A1 and A2 are used for programming the hardware address, allowing the use of
up to eight devices connected to the I
2
C-bus without additional hardware. Address, control and data to
and from the device are transferred serially via the two-line bidirectional I
2
C-bus interface.
2
C-bus.
The functions of the device include analog input multiplexing, on-chip track and hold function, 8-bit
analog-to-digital conversion and an 8-bit digital-to-analog conversion. The maximum conversion rate is
given by the maximum speed of the I
2
C-bus.
9.19.2. Features
• Single power supply
• Operating supply voltage 2.5 V to 6 V
• Low standby current
26
Plasma TV Service Manual 11/01/2005

• Serial input/output via I 2 C-bus
• Address by 3 hardware address pins
• Sampling rate given by I 2 C-bus speed
• 4 analog inputs programmable as single-ended or differential inputs
• Auto-incremented channel selection
Analog voltage range from VSS to VDD
•
• On-chip track and hold circuit
• 8-bit successive approximation A/D conversion
• Multiplying DAC with one analog output.
9.19.3. Pinning
SYMBOL PIN DESCRIPTION
AINO 1 analog inputs (A/D converter)
AIN1 2
AIN2 3
AIN3 4
A0 5 hardware address
A1 6
A2 7
V
8 negative supply voltage
SS
SDA 9 I2C-bus data input/output
SCL 10 I2C-bus clock input
OSC 11 oscillator input/output
EXT 12 external/internal switch for oscillator input
AGND 13 analog ground
V
14 voltage reference input
REF
AOUT 15 analog output (D/A converter)
VDD 16 positive supply voltage
9.20. PW1231
9.20.1. General Description
The PW1231 is a high-quality; digital video signal processor that incorporates Pixelworks’ patented
deinterlacing, scaling, and video enhancement algorithms. The PW1231 accepts industry-standard
video formats and resolutions, and converts the input into any desired output format. The video
algorithms are highly efficient, providing excellent quality video.
The PW1231 Video Signal Processor combines many functions into a single device, including memory
controller, auto-configuration, and others. This high level of integration enables simple, flexible, costeffective solutions featuring fewer required components.
9.20.2. Features
• Built-In Memory Controller
• Motion-Adaptive Deinterlace Processor
• Intelligent Edge Deinterlacing
• Digital Colour/Luminance Transient Improvement (DCTI/DLTI)
• Interlaced Video Input Options, including NTSC and PAL
• Independent horizontal and vertical scaling
27
Plasma TV Service Manual 11/01/2005

• Copy Protection
• Two-Wire Serial Interface
9.20.3. Applications
For use with Digital Displays
• Flat-Panel (LCD, DLP) TVs
• Rear Projection TVs
• Plasma Displays
• LCD Multimedia Monitors
• Multimedia Projectors
9.21. PW181
9.21.1. General Description
The PW181 Image Processor is a highly integrated “system-on-a-chip” that interfaces computer
graphics and video inputs in virtually any format to a fixed-frequency flat panel display.
Computer and video images from NTSC/PAL to WUXGA at virtually any refresh rate can be resized to
fit on a fixed-frequency target display device with any resolution up to WUXGA. Video data from 4:3
aspect ratio NTSC or PAL and 16:9 aspect ratio HDTV or SDTV is supported. Multi-region, nonlinear
scaling allows these inputs to be resized optimally for the native resolution of the display.
Advanced scaling techniques are supported, such as format conversion using multiple programmable
regions. Three independent image scalars coupled with frame locking circuitry and dual programmable
colour lookup tables create sharp images in multiple windows, without user intervention.
Embedded SDRAM frame buffers and memory controllers perform frame rate conversion and
enhanced video processing completely on-chip. A separate memory is dedicated to storage of onscreen display images and CPU general purpose use.
Advanced video processing techniques are supported using the internal frame buffer, including motion
adaptive, temporal deinterlacing with film mode detection. When used in combination with the new
third-generation scalar, this advanced video processing technology delivers the highest quality video for
advanced displays.
Both input ports support integrated DVI 1.0 content protection using standard DVI receivers.
A new advanced OSD Generator with more colours and larger sizes supports more demanding OSD
applications, such as on-screen programming guides. When coupled with the new, faster, integrated
microprocessor, this OSD Generator supports advanced OSD animation techniques.
Programmable features include the user interface, custom start-up screen, all automatic imaging
features, and special screen effects.
9.21.2. Features
• Third-generation, two-dimensional filtering techniques
• Third-generation, advanced scaling techniques
• Second-generation Automatic Image Optimization
• Frame rate conversion
• Video processing
• On-Screen Display (OSD)
• On-chip microprocessor
• JTAG debugger and boundary scan
• Picture-in-picture (PIP)
28
Plasma TV Service Manual 11/01/2005

• Multi-region, non-linear scaling
• Hardware 2-wire serial bus support
9.21.3. Applications
• Multimedia Displays
• Plasma Displays
• Digital Television
9.22. SIL151B
9.22.1. General Description
The SiI 151B receiver uses Panel Link Digital technology to support high-resolution displays up to
SXGA (25-112MHz). This receiver supports up to true colour panels (24 bit/pixel, 16M colours) with
both one and two pixels per clock.
All Panel Link products are designed on a scaleable CMOS architecture, ensuring support for future
performance enhancements while maintaining the same logical interface. System designers can be
assured that the interface will be stable through a number of technology and performance generations.
Panel Link Digital technology simplifies PC and display interface design by resolving many of the
system level issues associated with high-speed mixed signal design, providing the system designer
with a digital interface solution that is quicker to market and lower in cost.
9.22.2. Features
• Low Power Operation: 201mA max. current consumption at 3.3V core operation
• Time staggered data output for reduced ground bounce and lower EMI
• Sync Detect feature for Plug & Display iMHot Plugginglo
• Cable Distance Support: over 5m with twisted-pair, fiber-optics ready
®
• Compliant with DVI 1.0 (DVI is backwards compatible with VESA
P&D TM and DFP)
• HSYNC de-jitter circuitry enables stable operation even when HSYNC contains jitter
• Low power standby mode
• Automatic entry into standby mode with clock detect circuitry
• Standard and Pb-free packages
9.23. SDRAM 4M x 16 (MT48LC4M16A2TG-75)
9.23.1. General Description
The Micron ® 64Mb SDRAM is a high-speed CMOS, dynamic random-access memory containing
67,108,864 bits. It is internally configured as a quad-bank DRAM with a synchronous interface (all
signals are registered on the positive edge of the clock signal, CLK). Each of the x4’s 16,777,216-bit
banks is organized as 4,096 rows by 1,024 columns by 4 bits. Each of the x8’s 16,777,216-bit banks is
organized as 4,096 rows by 512 columns by 8 bits. Each of the x16’s 16,777,216- bit banks is
organized as 4,096 rows by 256 columns by 16 bits.
Read and write accesses to the SDRAM are burst oriented; accesses start at a selected location and
continue for a programmed number of locations in a programmed sequence. Accesses begin with the
registration of an ACTIVE command, which is then followed by a READ or WRITE command. The
address bits registered coincident with the ACTIVE command are used to select the bank and row to be
accessed (BA0, BA1 select the bank; A0-A11 select the row). The address bits registered coincident
with the READ or WRITE command are used to select the starting column location for the burst access.
The SDRAM provides for programmable READ or WRITE burst lengths of 1, 2, 4, or 8 locations, or the
full page, with a burst terminate option. An auto precharge function may be enabled to provide a selftimed row precharge that is initiated at the end of the burst sequence.
The 64Mb SDRAM uses an internal pipelined architecture to achieve high-speed operation. This
architecture is compatible with the 2n rule of prefetch architectures, but it also allows the column
address to be changed on every clock cycle to achieve a high-speed, fully random access. Precharging
one bank while accessing one of the other three banks will hide the precharge cycles and provide
seamless, high-speed, random-access operation.
The 64Mb SDRAM is designed to operate in 3.3V memory systems. An auto refresh mode is provided,
along with a power-saving, power-down mode. All inputs and outputs are LVTTL-compatible.
29
Plasma TV Service Manual 11/01/2005

SDRAMs offer substantial advances in DRAM operating performance, including the ability to
synchronously burst data at a high data rate with automatic column-address generation, the ability to
interleave between internal banks in order to hide precharge time and the capability to randomly
change column addresses on each clock cycle during a burst access.
9.23.2. Features
• PC66-, PC100-, and PC133-compliant
• Fully synchronous; all signals registered on positive edge of system clock
• Internal pipelined operation; column address can be changed every clock cycle
• Internal banks for hiding row access/precharge
• Programmable burst lengths: 1, 2, 4, 8, or full page
• Auto Precharge, includes CONCURRENT AUTO PRECHARGE, and Auto Refresh Modes
• Self Refresh Modes: standard and low power
• 64ms, 4,096-cycle refresh
• LVTTL-compatible inputs and outputs
• Single +3.3V ±0.3V power supply
9.23.3. Pin Descriptions
PIN NUMBERS SYMBOL TYPE DESCRIPTION
38 CLK Input Clock: CLK is driven by the system clock. All SDRAM input
signals are sampled on the positive edge of CLK. CLK also
increments the internal burst counter and controls the output
registers.
37 CKE Input Clock Enable: CKE activates (HIGH) and deactivates (LOW)
the CLK signal. Deactivating the clock provides PRECHARGE
POWER-DOWN and SELF REFRESH operation (all banks
idle), ACTIVE POWER-DOWN (row active in any bank) or
CLOCK SUSPEND operation (burst/access in progress). CKE
is synchronous except after the device enters power-down and
self refresh modes, where CKE becomes asynchronous until
30
Plasma TV Service Manual 11/01/2005

after exiting the same mode. The input buffers, including CLK,
are disabled during power-down and self refresh modes,
providing low standby power. CKE may be tied HIGH.
19 CS# Input Chip Select: CS# enables (registered LOW) and disables
(registered HIGH) the command decoder. All commands are
masked when CS# is registered HIGH. CS# provides for
external bank selection on systems with multiple banks. CS# is
considered part of the command code.
16, 17, 18 WE#, CAS#,
RAS#
39 x4, x8: DQM
15, 39 x16: DQML,
DQMH
20, 21 BA0, BA1 Input Bank Address Inputs: BA0 and BA1 define to which bank the
23-26, 29-34, 22,
35
2, 4, 5, 7, 8, 10,
11, 13, 42, 44, 45,
47, 48, 50, 51, 53
2, 5, 8, 11, 44, 47,
50, 53
5, 11, 44, 50 DQ0-DQ3 x4: I/O Data Input/Output: Data bus for x4.
40 NC – No Connect: These pins should be left unconnected.
36 NC – Address input (A12) for the 256Mb and 512Mb devices
3, 9, 43, 49 VDDQ Supply DQ Power: Isolated DQ power on the die for improved noise
6, 12, 46, 52 VSSQ Supply DQ Ground: Isolated DQ ground on the die for improved noise
1, 14, 27 VDD Supply Power Supply: +3.3V ±0.3V.
28, 41, 54 VSS Supply Ground.
A0-A11 Input Address Inputs: A0-A11 are sampled during the ACTIVE
DQ0-DQ15 x16: I/O Data Input/Output: Data bus for x16 (4, 7, 10, 13, 42, 45, 48,
DQ0-DQ7 x8: I/O Data Input/Output: Data bus for x8 (2, 8, 47, 53 are NCs for
Input Command Inputs: WE#, CAS#, and RAS# (along with CS#)
define the command being entered.
Input Input/Output Mask: DQM is an input mask signal for write
accesses and an output enable signal for read accesses. Input
data is masked when DQM is sampled HIGH during a WRITE
cycle. The output buffers are placed in a High-Z state (twoclock latency) when DQM is sampled HIGH during a READ
cycle. On the x4 and x8, DQML (Pin 15) is a NC and DQMH is
DQM. On the x16, DQML corresponds to DQ0-DQ7 and
DQMH corresponds to DQ8-DQ15. DQML and DQMH are
considered same state when referenced as DQM.
ACTIVE, READ, WRITE or PRECHARGE command is being
applied.
command (row-address A0-A11) and READ/WRITE command
(column-address A0-A9 [x4]; A0-A8 [x8]; A0-A7 [x16]; with A10
defining auto precharge) to select one location out of the
memory array in the respective bank. A10 is sampled during a
PRECHARGE command to determine if all banks are to be
precharged (A10[HIGH]) or bank selected by BA0, BA1
(A1[LOW]). The address inputs also provide the op-code
during a LOAD MODE REGISTER command.
and 51 are NCs for x8; and 2, 4, 7, 8, 10, 13, 42, 45, 47, 48,
51, and 53 are NCs for x4).
x4).
immunity.
immunity.
31
Plasma TV Service Manual 11/01/2005

9.24. FLASH 8MBit
9.24.1. Description
The M29W800A is a non-volatile memory that may be erased electrically at the block or chip level and
programmed in-system on a Byte-by-Byte or Word-by-Word basis using only a single 2.7V to 3.6V V
CC
supply. For Program and Erase operations the necessary high voltages are generated internally. The
device can also be programmed in standard programmers.
The array matrix organization allows each block to be erased and reprogrammed without affecting other
blocks. Blocks can be protected against programming and erase on programming equipment, and
temporarily unprotected to make changes in the application. Each block can be programmed and
erased over 100,000 cycles.
Instructions for Read/Reset, Auto Select for reading the Electronic Signature or Block Protection status,
Programming, Block and Chip Erase, Erase Suspend and Resume are written to the device in cycles of
commands to a Command Interface using standard microprocessor write timings.
9.24.2. Features
• 2.7V to 3.6V Supply Voltage for Program, Erase and Read Operations
• Access Time: 80ns
• Programming Time: 10µs typical
• Program/Erase Controller (P/E.C.)
– Program Byte-by-Byte or Word-by-Word
– Status Register bits and Ready/Busy Output
• Security Protection Memory Area
• Instruction Address Coding: 3 Digits
• Memory Blocks
– Boot Block (Top or Bottom location)
– Parameter and Main blocks
• Block, Multi-Block and Chip Erase
• Multi Block Protection/Temporary Unprotection Modes
• Erase Suspend and Resume Modes
– Read and Program another Block during Erase Suspend
• Low Power Consumption
– Stand-by and Automatic Stand-by
• 100,000 Program/Erase Cycles per Block
• 20 Years Data Retention
– Defectivity below 1ppm/year
• Electronic Signature
– Manufacturer Code: 20h
– Top Device Code, M29W800AT: D7h
– Bottom Device Code, M29W800AB: 5Bh
32
Plasma TV Service Manual 11/01/2005

10. SERVICE MENU SETTINGS
All system, geometry and white balance alignments are performed in production service mode. Before
starting the production mode alignments, make sure that all manual adjustments are done correctly. To
start production mode alignments enter the MENU by pressing “M” button and then press the
I-II(13) button, mute(5), image size(3), ve pip(15) respectively. The following menu appears on the screen.
(see remote control button functions (page 38a)
There are 3 submenus in service menu. These are display, calibration and deinterlacer menus.
Press “◄/►” buttons to select a menu title and then “▲/▼” buttons to select a menu item and “◄/►”
or “OK” buttons to set the menu item to the desired option. To exit the service menu press “M” button.
Entire service menu parameters of Plasma TV are listed below.
display
blank color
panel
power on time
backlight on time
scart prescale
nicam prescale
black red green blue
0 852x480
33:5
33:0
Vestel V1.0.10 Release Build
25
32
down to change display settings
10.1. display menu
By pressing “◄/►” buttons select the first icon. display menu appears on the screen.
display
blank color
panel
power on time
backlight on time
scart prescale
nicam prescale
black red green blue
0 852x480
33:5
33:0
Vestel V1.0.10 Release Build
25
32
down to change display settings
blank colour
By pressing ‘’/’’ button, select blank colour. Press ‘’/’’ button to set the blank colour. The
options are: black, red, green and blue.
panel
Displays panel resolution
power on time
Displays total working time of the set
backlight on time
Displays total backlight on time of the set. (Not used for plasma displays)
33
Plasma TV Service Manual 11/01/2005

scart prescale
By pressing ‘’/’’ button, select scart prescal er. Press ‘’/’’ button to set the scart prescaler. Scart
prescale can be adjusted between 0 and 127.
nicam prescale
By pressing ‘’/’’ button, select nicam prescale r. Press ‘’/’’ button to set the nicam prescaler.
Nicam prescale can be adjusted between 0 and 127.
display
scart prescale
nicam prescale
fm/am prescale
subwoofer corner
subwoofer layer
agc adjustment
carrier mute enable disable
25
32
25
3
9
17
right/left to adjust scart prescale
fm/am prescale
By pressing ‘’/’’ button, select fm/am prescaler. Press ‘’/’’ button to set the fm/am prescaler.
Fm/am prescale can be adjusted between 0 and 127.
subwoofer corner
By pressing ‘’/’’ button, select subwoof er corner. Press ‘’/’’ button to set the subwoofer corner.
Subwoofer corner can be adjusted between 0 and 7.
subwoofer level
By pressing ‘’/’’ button, select subwoofer level. Press ‘’/’’ button to set the subwoofer level.
Subwoofer level can be adjusted between 0 and 32.
agc adjustment
Adjustment for automatic gain control of tuner. By pressing ‘’/’’ button, select agc adjustment.
Press ‘’/’’ button to set the agc adjustment. Agc adjustment can be adjusted between 0 and 31.
carrier mute
This option is not available for this model.
34
Plasma TV Service Manual 11/01/2005

10.2. calibration menu
By pressing “#/$” buttons select the second icon. calibration menu appears on the screen.
calibration
col o r te m p
R
G
B
vide o f orma t
col o rs p ac e
tes t patte rn
col o r c om po nen ts
sol i d f i el d le ve l
55 00K
none
75 00K 9300 K use r
6500 K
au t o
RGB
so lid c olor vert bar s
al l
red gree n b lue
33
33
33
33
do wn to chan ge cal. setting s, sc ro lling m en u
colour temp
By pressing ‘’/’’ button, select colour temp. Press ‘’/’’ button to set the colour temperature. The
options are: 5500K, 6500K, 7500K, 9300K and user.
R/G/B
By pressing ‘’/’’ button, select Red, Green or Blue. Press ‘’’’ button to increase the colour
temperature. Press ‘’’’ button to decrease the colour temperature. Colour temperature can be
adjusted between values 0 and 63.
video format
By pressing ‘’/’’ button, select video format. Press ‘’/’’ button to set the video format. The
options are: auto, ntsc, pal, secam and ntsc japan.
colour space
Displays the current colour space used. RGB, YPbPr SMPTE240, YPbPr REC709 and YCbCr
REC601.
test pattern
By pressing ‘’/’’ button, select test pattern. Press ‘’/’’ button to set the test pattern. The options
are: none, solid colour and vert bars.
calibration
colourspace
test pattern
colour components
solid field level
adc calibration
factory reset <ok> to activate
none
all
RGB
solid colour vert bars
red green blue
33
advertisement
on off
right/left to adjust item
35
Plasma TV Service Manual 11/01/2005

colour components
By pressing ‘’/’’ button, select colour components. Press ‘’/’’ button to set the colour
components. The options are: all, red, green and blue.
solid field level
By pressing ‘’/’’ button, select solid field level. Press ‘’’’ button to increase or ‘’’’ button to
decrease the solid field level. Solid field level can be adjusted between 0 and 64.
adc calibration
Not used for this model.
factory reset
By pressing ‘’/’’ button, select factory reset. Press “OK” button to return to the factory setting
values.
advertisement
When this item is made on, VESTEL advertisement is represented at certain time intervals.
deinterlacer menu
By pressing “#/$” buttons select the third icon. deinterlacer menu appears on the screen.
deinterlacer
blank expansion
dcti
dlti
luminance peaking
film mode
film mode speed
vof
off on
off on
off
off
on
on
131
64
3
down for deinterlacer settings, scrolling menu
blank expansion
By pressing ‘’/’’ button, select blank expansion. blank expansion can be set to on or off by
pressing ‘’/’’ button.
dcti
Digital colour transition improvement: By pressing ‘’/’’ button, select dcti. DCTI can be adjusted
between 0 and 255 by pressing ‘’/’’ button.
dlti
Digitial luma transition improvement: By pressing ‘’/’’ button, select dlti. DLTI can be adjusted
between 0 and 255 by pressing ‘’/’’ button.
luminance peaking
By pressing ‘’/’’ button, select luminance peaking. Luminance peaking can be set to on or off by
pressing ‘’/’’ button.
film mode
By pressing ‘’/’’ button, select film mode. Film mode speed can be set to on or off by pressing
‘’/’’ button.
36
Plasma TV Service Manual 11/01/2005

deinterlacer
vof
bad cut
nr threshold
noise reduction
lai level
sharpness
sparkle
off on
off on
low
high
40
2
10
255
right/left to adjust item
film mode speed
By pressing ‘’/’’ button, select film mod e speed. Film mode speed can be set to 0, 1, 2 or 3 by
pressing ‘’/’’ button.
vof
video on film. By pressing ‘’/’’ button, select vof. VOF can be set to on or off by pressing ‘’/’’
button.
bad cut
By pressing ‘’/’’ button, select bad cut. Bad cut can be set to on or off by pressing ‘’/’’ button.
nr threshold
By pressing ‘’/’’ button, select nr threshold. Nr threshold can be set to low or high by pressing
‘’/’’ button.
noise reduction
By pressing ‘’/’’ button, select noise reduction. Noise reduction can be adjusted between 0 and
255 by pressing ‘’/’’ button.
lai level
By pressing ‘’/’’ button, select lai level. Lai level can be set to 0, 1 or 2 by pressing ‘’/’’ button.
sharpness
By pressing ‘’/’’ button, select sharpness. Sharpness can be adjusted between 0 and 255 by
pressing ‘’/’’ button.
sparkle
By pressing ‘’/’’ button, select sparkle. Sparkle can be adjusted between 0 and 255 by pressing
‘’/’’ button.
37
Plasma TV Service Manual 11/01/2005

10.3. Service menu factory reset values
SERVICE MENU
BLANK COLOUR black
SCART PRESCALE 15
NICAM PRESCALE 32
DISPLAY
FM/AM PRESCALE 14
SUBWOOFER CORNER 5
SUBWOOFER LEVEL 32
AGC 16
COLOUR TEMPERATURE 6500
COLOUR TEMPERATURE-USER 6500
VIDEO FORMAT AUTO
CALIBRATION
COLOUR SPACE autodetected
TEST PATTERN none
COLOUR COMPONENTS all
SOLID FIELD LEVEL 33
INITIAL APS on
BLACK EXPANSION
DCTI
DLTI
LUMINANCE PEAKING
FILM MODE
FILM MODE SPEED
DEINTERLACER
VOF
BAD CUT
NR THRESHOLD
NOISE REDUCTION
LAI LEVEL
SHARPNESS
SPARKLE
These values are not
recorded, for this reason
they are adjusted to a
specified value.
38
Plasma TV Service Manual 11/01/2005

Remote Control Buttons
6285&( 3&
0
,,,
= Stand By
PC = PC Button
= Image Size
+=Volume Up
= Mute
OK = Okay / Freeze
= Cursor Right
= Cursor Down
= Cursor Left
= Cursor Up
M = Menu
- = Volume Down
I-II = Mono/Stereo - Dual A-B
= Not used on this model
= VE PIP (Not used on this model)
SOURCE = Source select
2.
38a

R
bit
bit
11. BLOCK DIAGRAM
GENERAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
AUDIO
DECODING
MSP34XX
MICRONAS
AUDIO/VIDEO/GRAPHICS IN/OUT
48dual
RGB
YUV
16-
bit
bit
PW1231
YUV
16-
24-
SAA7118E
VIDEO PROCESSOR
MAIN PICTURE
PHILIPS
SAA7118E
VIDEO PROCESSOR
PIP PICTURE
PHILIPS
SIL151 SILICON
IMAGE
DVI Rx
AD9883 ANALOG DEVICE
ADC
Plasma TV Service Manual 11/01/2005
MAIN BOARD
bit RGB
39
6 LAYER
RG
B
24-
PW181
MAIN_L,
MAIN_R,
24-
bit RGB
I2C
HS, VS,
DE, CLK
AUDIO AMPL. BOARD
2 -LAYER
AUDIO
AMPLIFIE
TPA3002D
DS090C385 LVDS
NATIONAL
Tx

A/V BOARD
6-
layer
TUNER & IF BLOCK
SC3_V_OUT
SC1_V_OUT
I2C
I2C
UV1316
Tuner 1
Philips
UV1316
Tuner 2
Philips
TO TEA6415
IF 1
PHILIPS
IF IC 1
TDA9886
TUN1_CVBS
TUN1_QSS1
VIDEO SWITCH
TO MSP3411G
AUDIO PROCESSOR
FOR MAIN SOUND
TO TEA6415 PIP
IF 2
PHILIPS
IF IC 2
TDA9886
TUN2_CVBS
TUN2_QSS2
VIDEO SWITCH
TO MSP3411G
AUDIO PROCESSOR
40
Plasma TV Service Manual 11/01/2005
FOR PIP SOUND

VIDEO MATRIXING
41
Plasma TV Service Manual 11/01/2005

AUDIO MATRIXING
42
Plasma TV Service Manual 11/01/2005


VIDEO & IMAGE PROCESSING
VxtoSAA7118_MP
SVIDEO1_C
SAA
7118
MP
SAA
7118
PIP
AD9883
SIL151
16-bit YUV
DE-INTERLACER
16-bit YUV
24-bit RGB
48-bit RGB
SCART1
SCART1
RGB,FB
RGB,FB
SCART2
SCART2
RGB,FB
RGB,FB
SVIDEO1_Y
TXT/CC_FB
TXT/CC_FB
TXT/CC_R
TXT/CC_R
TXT/CC_R
TXT/CC_G
TXT/CC_G
TXT/CC_G
TXT/CC_B
TXT/CC_B
TXT/CC_B
VxtoSAA7118_PIP
SVIDEO1_C
SVIDEO1_Y
SC_FB
PI5
PI5
V330
V330
SC_FB
SC_R
SC_R
SC_G
SC_G
SC_B
SC_B
PC_R_IN
PC_G_IN
PC_B_IN
PC_HS
PC_VS
DVI Input
PW1231
24-bit
RGB
ROM
VRGB
PW181
De-interlacer
FRC
Scaler
OSD
Gamma
Correction
GRGB
Progressive or
Interlaced
24-bit dual RGB,
HS, VS, DE,
PCLK, Par it y
44
Plasma TV Service Manual 11/01/2005

TELETEXT DECODING & PIN8 SWITCHING
TELETEXT
FROM VIDEO
SWITCH
CVBS_
SAA5264
for TELETEXT
PHILIPS
TXT/CC_FB
TXT/CC_R
TXT/CC_G
TXT/CC_B
INTO SAA7118
RGB/FB PORTS
SC1 PIN8SC1 PIN8
SC2 PIN8SC2 PIN8
PIN 8
I2C COMMUNICATION
SWITCHING
SC3 PIN8SC3 PIN8
PCF8591
SC4 PIN8SC4 PIN8
45
Plasma TV Service Manual 11/01/2005

INPUT & OUTPUTS
1. SCART 1 CVBS INPUT
2. SCART 2 CVBS INPUT
3. SCART 1 RGB FB INPUT
4. SCART 2 RGB FB INPUT
5. FAV IN
6. FRONT SVHS IN
7. VGA INPUT
Plasma TV Service Manual 11/01/2005
8. DVI INPUT
9. PC AUDIO INPUT
10. MAIN TUNER
11. PIP TUNER
46
1. SCART 1 CVBS OUT
2. SCART 2 CVBS OUT
3. AUDIO LINE OUT

12. CIRCUIT DIAGRAMS







(Not used on this model)



THE UPDATED PARTS LIST
FOR THIS MODEL IS
AVAILABLE ON ESTA

Hitachi, Ltd. Tokyo, Japan
International Sales Division
THE HITACHI ATAGO BUILDING,
No. 15 –12 Nishi Shinbashi, 2 – Chome,
Minato – Ku, Tokyo 105-8430, Japan.
Tel: 03 35022111
HITACHI EUROPE LTD,
Whitebrook Park
Lower Cookham Road
Maidenhead
Berkshire
SL6 8YA
UNITED KINGDOM
Tel: 01628 643000
Fax: 01628 643400
Email: consumer-service@hitachi-eu.com
HITACHI EUROPE GmbH
Munich Office
Dornacher Strasse 3
D-85622 Feldkirchen bei München
GERMANY
Tel: +49-89-991 80-0
Fax: +49-89-991 80-224
Hotline: +49-180-551 25 51 (12ct/min)
Email: HSE-DUS.service@hitachi-eu.com
HITACHI EUROPE srl
Via Tommaso Gulli N.39, 20147
Milano, Italia
ITALY
Tel: +39 02 487861
Tel: +39 02 38073415 Servizio Clienti
Fax: +39 02 48786381/2
Email: customerservice.italy@hitachi-eu.com
HITACHI EUROPE S.A.S
Lyon Office
B.P. 45, 69671 BRON CEDEX
FRANCE
Tel: +33 04 72 14 29 70
Fax: +33 04 72 14 29 99
Email: france.consommateur@hitachi-eu.com
HITACH EUROPE AB
Egebækgård
Egebækvej 98
DK-2850 Nærum
DENMARK
Tel: +45 43 43 6050
Fax: +45 43 60 51
Email: csgnor@hitachi-eu.com
Hitachi Europe Ltd
Bergensesteenweg 421
1600 Sint-Pieters-Leeuw
BELGIUM
Tel: +32 2 363 99 01
Fax: +32 2 363 99 00
Email: sofie.van.bom@hitachi-eu.com
www.hitachidigitalmedia.com
HITACHI EUROPE S.A.
364 Kifissias Ave. & 1, Delfon Str.
152 33 Chalandri
Athens
GREECE
Tel: 1-6837200
Fax: 1-6835964
Email: service.hellas@hitachi-eu.com
HITACHI EUROPE S.A.
Gran Via Carlos III, 86, planta 5
Edificios Trade - Torre Este
08028 Barcelona
SPAIN
Tel: +34 93 409 2550
Fax: +34 93 491 3513
Email: atencion.cliente@hitachi-eu.com
HITACHI Europe AB
Box 77 S-164 94 Kista
SWEDEN
Tel: +46 (0) 8 562 711 00
Fax: +46 (0) 8 562 711 13
Email: csgswe@hitachi-eu.com
HITACHI EUROPE LTD (Norway) AB
STRANDVEIEN 18
1366 Lysaker
NORWAY
Tel: 67 5190 30
Fax: 67 5190 32
Email: csgnor@hitachi-eu.com
HITACHI EUROPE AB
Neopoli / Niemenkatu 73
FIN-15140 Lahti
FINLAND
Tel : +358 3 8858 271
Fax: +358 3 8858 272
Email: csgnor@hitachi-eu.com
HITACHI EUROPE LTD
Na Sychrove 975/8
101 27 Pr aha 10 – Bohdalec
CZECH REPUBLIC
Tel: +420 267 212 383
Fax: +420 267 212 385
Email: csgnor@hitachi-eu.com
 Loading...
Loading...