HIT HD66420TAO Datasheet

1
HD66420
(RAM-Provided 160 Channel 4-Level Grey Scale Driver for Dot
Matrix Graphics LCD)
Description
The HD66420 drives and controls a dot matrix graphic LCD(Liquid Crystal Display) using a bit-mapped
method. It provides a highly flexible display through its on-chip display RAM, in which each two bits of
data can be used to turn on or off one dot on LCD panel with four-level grey scale.
A single HD66420 can display a maximum of 160x80 dots using its powerful display control functions. It
can display only eight lines out of eighty lines. This function realize low power consumption because high
voltage for driving LCD is not needed.
An MPU can access HD66420 at any time, because the MPU operations are asynchronous with the
HD66420’s system clock and display operation.
Its low-voltage operation at 2.2 to 5.5V and standby function provides low power dissipation, making the
HD66420 suitable for small portable device applications.
Features
• Built-in bit-mapped display RAM: 25.6kbits (160 × 80 × 2 bits)
• Grey scale display: PWM four-level grey scale can be selected from 32 levels
• Grey scale memory management: Packed pixel
• Partial display: Eight-lines data can be displayed in any place
• An 80-system MPU interface
• Power supply voltage for operation : 2.2V to 5.5V
• Power supply voltage for LCD : 13 V max.
• Selectable multiplex duty ratio: 1/8, 1/32, 1/64, 1/80
• Built-in oscillator: external resister
• Low power consumption:
55µA typ. 80µA max. during display
0.1µA typ. 5µA max. during standby
• Circuits for generating LCD driving voltage : Contrast control, Operational amplifier, and Resistive
dividers
• Internal resistive divider: programmable bias rate
• 32-level programmable contrast control

HD66420
2
• Wide range of instructions reversible display, display on/off, vertical display scroll, blink, reversible
address, read-modify-write mode
• Package: TCP
Ordering Information
Type No. Package
HD66420TA0 TCP
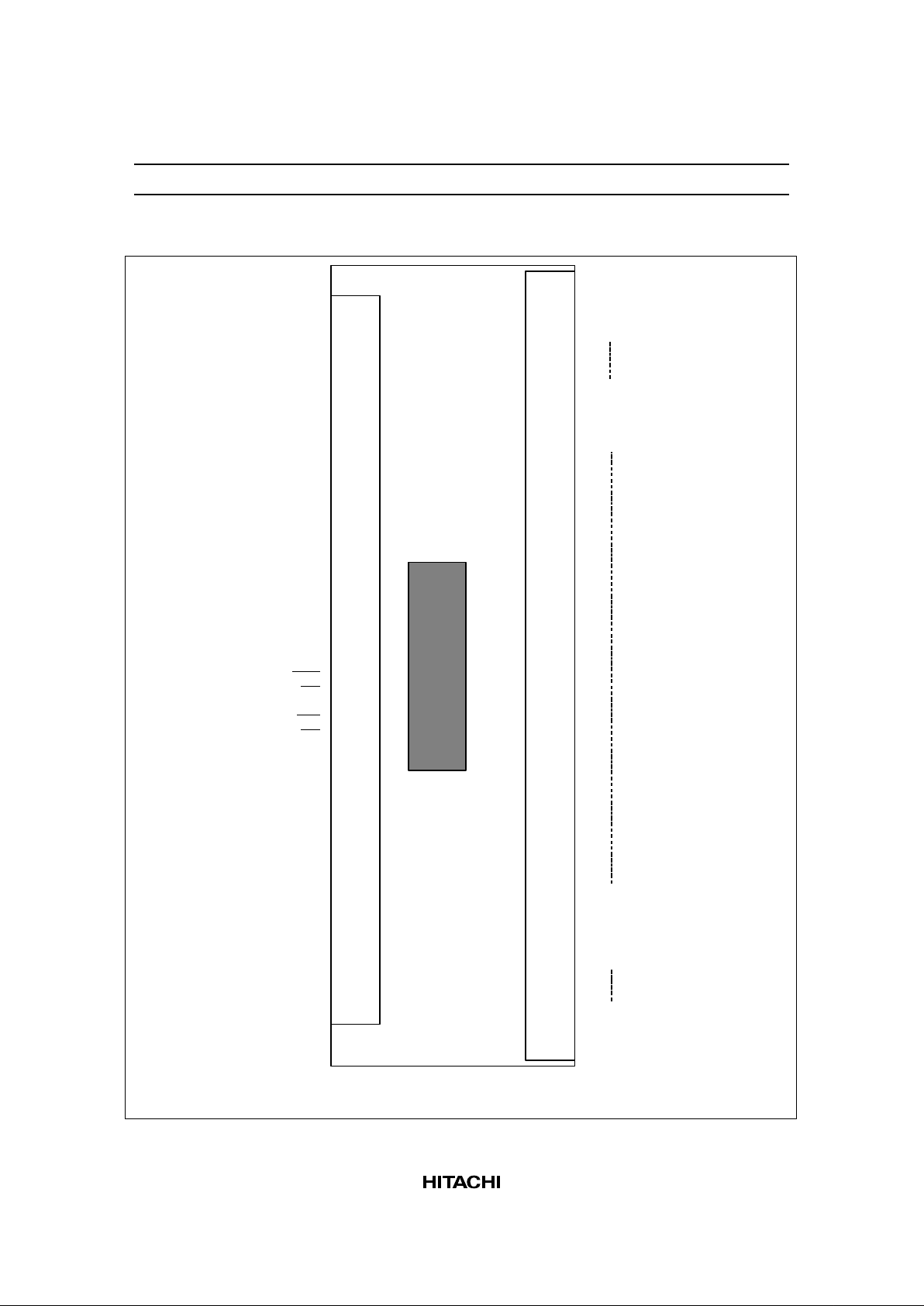
HD66420
3
Pin Arrangement
Note: This figure is not drawn to a scale
COM80
COM79
COM78
COM41
SEG160
SEG159
SEG158
COM40
SEG3
SEG2
SEG1
COM39
COM3
COM2
COM1
I/O,Power supply pins
LCD drive signal output pins
GND1
VLCD1
VCC1
V5O
V4O
V3O
V2O
V1O
GREF
IREFM
IREFP
VLCD2
VLCD3
VCC2
GND2
GND3
VCC3
OSC1
OSC2
OSC
CO
DCON
CL1
FLM
M
M/S
RES
CS
RS
WR
RD
VCC4
GND4
DB0
DB1
DB2
DB3
DB4
DB5
DB6
DB7
VCC5
GND5
VCC6
VLCD4
GND6

HD66420
4
Pin Description
Pin Name
Number of
Pins I/O Connected to Description
V
CC
1–6,
GND1–6
12 — Power supply VCC: +2.2V to +5.5V, GND: 0V
VLCD1–4 4 — Power supply Power supply to LCD driving circuit
V1O, V2O,
V3O, V4O,
V5O
5 — V1 to V5 of
HD66420
Several levels of power to the LCD driving outputs.
Master HD66420 outputs these levels to the slave
HD66420.
OSC 1 I Oscillator
resister or
Must be connected to external resister when using R-C
oscillation. When using an external clock, it must be
OSC1,
OSC2
2 I/O
external clock input to the OSC terminal.
CO 1 O OSC of Slave
HD66420
Clock output
DCON 1 O External DC/DC
convertor
Controls on/off switch of external DC/DC convertor
CL1 1 I/O CL1 of
HD66420
Line clock
FLM 1 I/O FLM of
HD66420
Frame signal
M 1 I/O M of HD66420 Converts LCD driving outputs to AC
M/S 1 I VCC or GND Specifies master/slave mode.
RES 1 I — Reset the LSI internally when drive low.
CS 1 I MPU Select the LSI, specifically internal registers (index and
data registers) when driven low.
RS 1 I MPU Select one of the internal registers; select the index
register when driven low and data registers when driven
low.
WR 1 I MPU Inputs write strobe; allows a write access when driven
low.
RD 1 I MPU Inputs read strobe; allows a read access when driven
low.
DB7 to DB0 8 I/O MPU 8-bits three-state bidirectional data bus; transfer data
between the HD66420 and MPU through this bus.
SEG1 to
SEG160
160 O LCD Output column drive signals
COM1 to
COM80
80 O LCD Output row drive signals
IREFP 1 — V
CC
Power supply for internal operation amplifier
IREFM 1 — External resistor Bias current for internal operational amplifier
GREF 1 — GND Power supply for internal operation amplifier

HD66420
5
Resister List
Index
Reg.Bits Data bits
CS RS 4 3 2 1 0 Register Name R/W 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
1 – ––––– –
0 0 – – – – – IR Index register W IR4 IR3 IR2 IR1 IR0
0 1 0 0 0 0 0 R0 Control register 1 W RMW DISP STBY PWR AMP REV HOLT ADC
0 1 0 0 0 0 1 R1 Control register 2 W BIS1 BIS0 WLS GRAY DTY1 DTY0 INC BLK
0 1 0 0 0 1 0 R2 X address register W XA5 XA4 XA3 XA2 XA1 XA0
0 1 0 0 0 1 1 R3 Y address register W YA6 YA5 YA4 YA3 YA2 YA1 YA0
0 1 0 0 1 0 0 R4 Display RAM access register R/W D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
0 1 0 0 1 0 1 R5 Display start line register W ST6 ST5 ST4 ST3 ST2 ST1 ST0
0 1 0 0 1 1 0 R6 Blink start line register W BSL6 BSL5 BSL4 BSL3 BSL2 BSL1 BSL0
0 1 0 0 1 1 1 R7 Blink end line register W BEL6 BEL5 BEL4 BEL3 BEL2 BEL1 BEL0
0 1 0 1 0 0 0 R8 Blink register 1 W BK0 BK1 BK2 BK3 BK4 BK5 BK6 BK7
0 1 0 1 0 0 1 R9 Blink register 2 W BK8 BK9 BK10 BK11 BK12 BK13 BK14 BK15
0 1 0 1 0 1 0 R10 Blink register 3 W BK16 BK17 BK8 BK9
0 1 0 1 0 1 1 R11 Partial display block register W PB3 PB2 PB1 PB0
0 1 0 1 1 0 0 R12 Gray scale palette 1 (0, 0) W GP14 GP13 GP12 GP11 GP10
0 1 0 1 1 0 1 R13 Gray scale palette 2 (0, 1) W GP24 GP23 GP22 GP21 GP20
0 1 0 1 1 1 0 R14 Gray scale palette 3 (1, 0) W GP34 GP33 GP32 GP31 GP30
0 1 0 1 1 1 1 R15 Gray scale palette 4 (1, 1) W GP44 GP43 GP42 GP41 GP40
0 1 1 0 0 0 0 R16 Contrast control register W CM1 CM0 CC4 CC3 CC2 CC1 CC0
0 1 1 0 0 0 1 R17 Reserved –
0 1 1 0 0 1 0 R18 Reserved –
0 1 1 0 0 1 1 R19 Reserved –
0 1 1 0 1 0 0 R20 Reserved –
0 1 1 0 1 0 1 R21 Reserved –
0 1 1 0 1 1 0 R22 Reserved –
0 1 1 0 1 1 1 R23 Reserved –
0 1 1 1 0 0 0 R24 Reserved –
0 1 1 1 0 0 1 R25 Reserved –
0 1 1 1 0 1 0 R26 Reserved –
0 1 1 1 0 1 1 R27 Reserved –
0 1 1 1 1 0 0 R28 Reserved –
0 1 1 1 1 0 1 R29 Reserved –
0 1 1 1 1 1 0 R30 Reserved –
0 1 1 1 1 1 1 R31 Reserved –

HD66420
6
RMW
RMW = 1: Read-modify-write mode; Address is incremented only after write access
RMW = 0: Address is incremented after both write and read access
DISP
DISP = 1: Display on
DISP = 0: Display off
STBY
STBY = 1:Internal operation and power circuit halt; display off
STBY = 0: Normal operation
PWR
PWR = 1: Output ‘High’ from DCON
PWR = 0: Output ‘Low’ from DCON
AMP
AMP = 1: OP amp enable
AMP = 0: OP amp disable
REV
REV = 1: Reverse display
REV = 0: Normal display
HOLT
HOLT = 1: Internal operation stops, Oscillator works
HOLT = 0: Internal operation starts
ADC
ADC = 1: Data in X address H’0 is output from SEG160
ADC = 0: Data in X address H’0 is output from SEG1
BIS1, 0
BIS1, 0 = (1,1): 1/6 LCD drive levels bias ratio
BIS1, 0 = (1,0): 1/7 LCD drive levels bias ratio
BIS1, 0 = (0,1): 1/8 LCD drive levels bias ratio
BIS1, 0 = (0,0): 1/9 LCD drive levels bias ratio
WLS
WLS = 1: 6-bit data is valid
WLS = 0: 8-bit data is valid
GRAY
GRAY = 1: Grayscale palette is available(gray scales can be selected from 32-levels)
GRAY = 0: Grayscale palette is not available(4-gray scales fixed)

HD66420
7
DTY1, 0
DTY1, 0 = (1,1): 1/8 display duty cycle - Partial display
DTY1, 0 = (1,0): 1/32 display duty cycle
DTY1, 0 = (0,1): 1/64 display duty cycle
DTY1, 0 = (0,0): 1/80 display duty cycle
INC
INC = 1: X address is incremented for each access
INC = 0: Y address is incremented for each access
BLK
BLK = 1: Blink function is used
BLK = 0: Blink function is not used

HD66420
8
Block Diagram
RD
WR CS
RS
DB7
-DB0
OSC
RES
OSC2
V3O
V2O
V5O
V4O
VLCD
FLM M CL1
CO
DCON
V1O
OSC1
M/S
Column Driver
Y Decoder
X Decoder
Row
Counter
320 x 80bit
Display memory
Level Shifter
Data Latch2
Data Latch1
COM1 COM40 SEG1 SEG160COM41 COM80
X Address Counter
Start Line Register
Attribute
Comparator
Blink End Line Register
Blink Start Line Register
Control Register
MPU Interface
Display Line
Counter
Row Driver
Oscillator
LCD driver power supply,
Contrast control
Y Address Counter
Data Buffer
Timing
Generator
Grey scale selector
Grey scale
palette
320
160
Level Shifter
Grey
scale
pattern
Generator
Contrast Control Register
Decoder
320
320
Row Driver
Level Shifter
I/O control
Blink Registers
MPX

HD66420
9
System Description
The HD66420 can display a maximum of 160 × 80 dots (ten 16x16-dot characters × 5 lines) four-level gray
scale or four colour LCD panel. Four levels of gray scale can be selected from 32-levels, so the appropriate
4-level gray scale can be displayed.
The HD66420 can reduce power dissipation without affecting display because data is retained in the
display RAM even during standby modes. An LCD system can be configured simply by attaching external
power supply, capacitors and resistors (figure 1) since the HD66420 incorporates power circuits.
COM1 to
COM40
HD66420
LCD panel
MPU
8
SEG1 to
SEG160
CS
RS
RD
WR
DB7 to DB0
COM41 to
COM80
DC/DC
Convertor
Figure 1 System Block Diagram

HD66420
10
MPU Interface
The HD66420 can interface directly to an MPU through an 8-bit data bus or through an I/O port (figure 2).
The MPU can access the HD66420 internal registers independently of internal clock timing.
The index register can be directly accessed but the other registers (data registers) cannot. Before accessing
a data register, its register number must be written to the index register. Once written, the register number is
held until it is rewritten, enabling the same register to be consecutively accessed without having to rewrite
to the register number for each access. An example of a register access sequence is shown in figure 3.
C0
C1
C2
C3
A0 - A7
CS
RS
RD
WR
DB0 - DB7
H8/325 HD66420
8
a) Interface through Bus
A15 - A0
A0
RD
WR
D0 - D7
CS
RS
RD
WR
DB0 - DB7
Z80 HD66420
8
b) Interface through I/O Port
decoder
Figure 2 8-Bit MPU Interface Examples

HD66420
11
RD
WR
DB7 to
DB0
Write index
register
RS
CS
Write data
register
Write index
register
Read data
register
Read data
register
Data
Data Data Data Data Data
Write data
register
Figure 3 8-Bit Data Transfer Sequence

HD66420
12
LCD Driver Configuration
Row and column outputs: The HD66420 outputs row signals from both sides. In any case, each output’s
function is fixed; COM1 to COM80 output row signals and SEG1 to SEG160 output column signals.
Dot-matrix Display
40-channel
row output
160-channel column
output
40-channel
row output
Row outputs from
both sides of LCD
160 × 80
HD66420
COM41 to
COM80
COM1 to
COM40
SEG1 to SEG160
Figure 4 Common outputs from both sides

HD66420
13
Column Address Inversion According to LCD Driver Layout: The HD6420 can always display data in
address H’0 on the top left of an LCD panel regardless of where it is positioned with respect to the panel.
This is because the HD66420 can invert the positional relationship between display RAM addresses and
LCD driver output pins by inverting RAM addresses. Specifically, the HD66420 outputs data in address
H’0 from SEG1 when the ADC bit in control register 1 is 0, and from SEG160 otherwise. Here, the scan
direction of row output is also inverted according to the situation as shown in figure 6. Note that addresses
and scan direction are inverted when data is written to the display RAM, and thus changing the ADC bit
after data has been written has no effect. Therefore. hardware control bits such as ADC must be set
immediately after reset is canceled, and must not be set while data is being displayed.
COM1
COM40LCD panel
COM80
COM41
b) ADC = 1
SEG1
SEG2
SEG3
SEG158
SEG159
SEG160
SEG157
SEG156
SEG155
SEG154
SEG153
COM80
COM41
COM1
COM40
a) ADC = 0
H’0
SEG1
SEG2
SEG3
SEG4
SEG5
SEG6
SEG7
SEG8
SEG158
SEG159
SEG160
LCD panel
H’1
HD66420
HD66420
H’0 H’1
Figure 5 LCD Driver Layout and RAM addresses : 1/80 Duty cycle
Table 1 Scanning Direction and RAM Address
DTY1 DTY0 ADC COMMON SEGMENT
0 0 0 COM1 → COM40, COM80 → COM41 H’00 → SEG1
1 COM41 → COM80, COM40 → COM1 H’00 → SEG160
1 0 COM1 → COM32, COM80 → COM49 H’00 → SEG1
1 COM49 → COM80, COM32 → COM1 H’00 → SEG160
1 0 0 COM1 → COM16, COM80 → COM65 H’00 → SEG1
1 COM65 → COM80, COM16 → COM1 H’00 → SEG160
1 0 8 COM depend on R11 H’00 → SEG1
1 8 COM depend on R11 H’00 → SEG160

HD66420
14
Multi-LSI Operation
Using multiple HD66420s provides the means for extending the number of display dots. Note the following
items when using the multi-LSI operation.
(1) The master LSI and the slave LSI must be determined; the M/S pin of the master LSI must be set high
and the M/S pin of the slave LSI must be set low.
(2) The master LSI supplies the FLM, M, CL1 and clock signals to the slave LSI via the corresponding
pins, which synchronizes the slave LSI with the master LSI.
(3) All control bits of slave LSI must be set with the same data with that of the master LSI.
(4) All LSIs must be set to LCD off in order to turn off the display.
(5) The standby function of slave LSI must be started up first, and that of the master LSI must be
terminated first.
(6) The power supply circuit of slave LSI stop working, so V1 to V5 levels are supplied from the master
LSI. If the internal power supply circuit can not drive two LSIs, use an external power supply circuit.
Figure 6 shows the configuration using two HD66420s and table 2 lists the differences between master and
slave modes.
Dot-matrix Display
40-channel
row output
160-channel
column output
40-channel
row output
320 x 80
HD66420
(Master)
160-channel
column output
HD66420
(slave)
CL1FLMM CL1FLMM OSCCOOSC OSC1 CO OSC1
Open
V1O to
V5O
V1O to
V5O
Figure 6 Configuration Using Two HD66420s

HD66420
15
Table 2 Comparison between Master and Slave Modes
Item Master Mode Slave Mode
Pin M/S Must be set high Must be set low
OSC Oscillation is active Oscillation is active
CO Output High-Z
FLM, M, CL1 Output signals Input signals
Registers R0, R2 to R15 Valid Valid
R1: BIS1, 0 Valid Invalid
R1: other Valid Valid
R16 Valid Invalid
Power supply circuit Valid Invalid

HD66420
16
Display RAM Configuration and Display
The HD66420 incorporates a bit-mapped display RAM. It has 320 bits in the X direction and 80 bits in the
Y direction. The 320 bits are divided into forty 8-bit groups. As shown in figure 6, data written by the MPU
is stored horizontally with the MSB at the far left and the LSB at the far right. The consecutive two bits
control one pixel of LCD, this means that one 8-bits data contains data which controls four pixels.
The ADC bit of control register 1 can control the positional relationship between X addresses of the RAM
and LCD driver output (figure 7). Specifically. the data in address H’0 is output from SEG1 when the ADC
bit in control register 1 is 0, and from SEG160 otherwise. Here, data in each 8-bit group is also inverted.
Because of this function, the data in X address H’0 can be always displayed on the top left of an LCD panel
with the MSB at the far left regardless of the LSI is positioned with respect to the panel. In this case, DB7,
DB5, DB3 and DB1 are more significant bit in consecutive two bits.
SEG1
SEG2
SEG3
SEG4
11100100
00011011
Y0
Y1
D
B
7
D
B
1
LCD panel
Display RAM
SEG157
SEG158
DEG159
SEG160
11100100
00011011
Y0
Y1
D
B
7
D
B
0
LCD panel
Display RAM
D
B
6
D
B
4
D
B
5
D
B
2
D
B
3
D
B
1
D
B
6
D
B
5
D
B
4
D
B
3
D
B
2
D
B
0
(a) ADC = 0 (b) ADC = 1
SEG160 SEG1
Figure 7 Display RAM Data and Display
 Loading...
Loading...