HIT HD61202UFS, HCD61202U Datasheet

HD61202U
(Dot Matrix Liquid Crystal GraphicDisplay Column Driver)
ADE-207-273(Z)
'99.9
Rev. 0.0
Description
HD61202U is a column (segment) driver for dot matrix liquid crystal graphic display systems. It stores the
display data transferred from a 8-bit micro controller in the internal display RAM and generates dot matrix
liquid crystal driving signals.
Each bit data of display RAM corresponds to on/off state of a dot of a liquid crystal display to provide
more flexible than character display.
As it is internally equipped with 64 output drivers for display, it is available for liquid crystal graphic
displays with many dots.
The HD61202U, which is produced in the CMOS process, can complete portable battery drive equipment
in combination with a CMOS micro-controller, utilizing the liquid crystal display’s low power dissipation.
Moreover it can facilitate dot matrix liquid crystal graphic display system configuration in combination
with the row (common) driver HD61203U.
Features
• Dot matrix liquid crystal graphic display column driver incorporating display RAM
• RAM data direct display by internal display RAM
RAM bit data 1: On
RAM bit data 0: Off
• Display RAM capacity: 512 bytes (4096 bits)
• 8-bit parallel interface
• Internal liquid crystal display driver circuit: 64
• Display duty cycle
Drives liquid crystal panels with 1/32–1/64 duty cycle multiplexing
1

HD61202U
• Wide range of instruction function
Display data read/write, display on/off, set address, set display start line, read status
• Power supply: VCC: 2.7V~5.5V
• Liquid crystal display driving voltage: 8V to 16V
Ordering Information
Type No. Package
HD61202UFS 100-pin plastic QFP (FP-100A)
HD61202UTE 100-pin thin plastic QFP (TFP-100B)
HCD61202U Chip
2
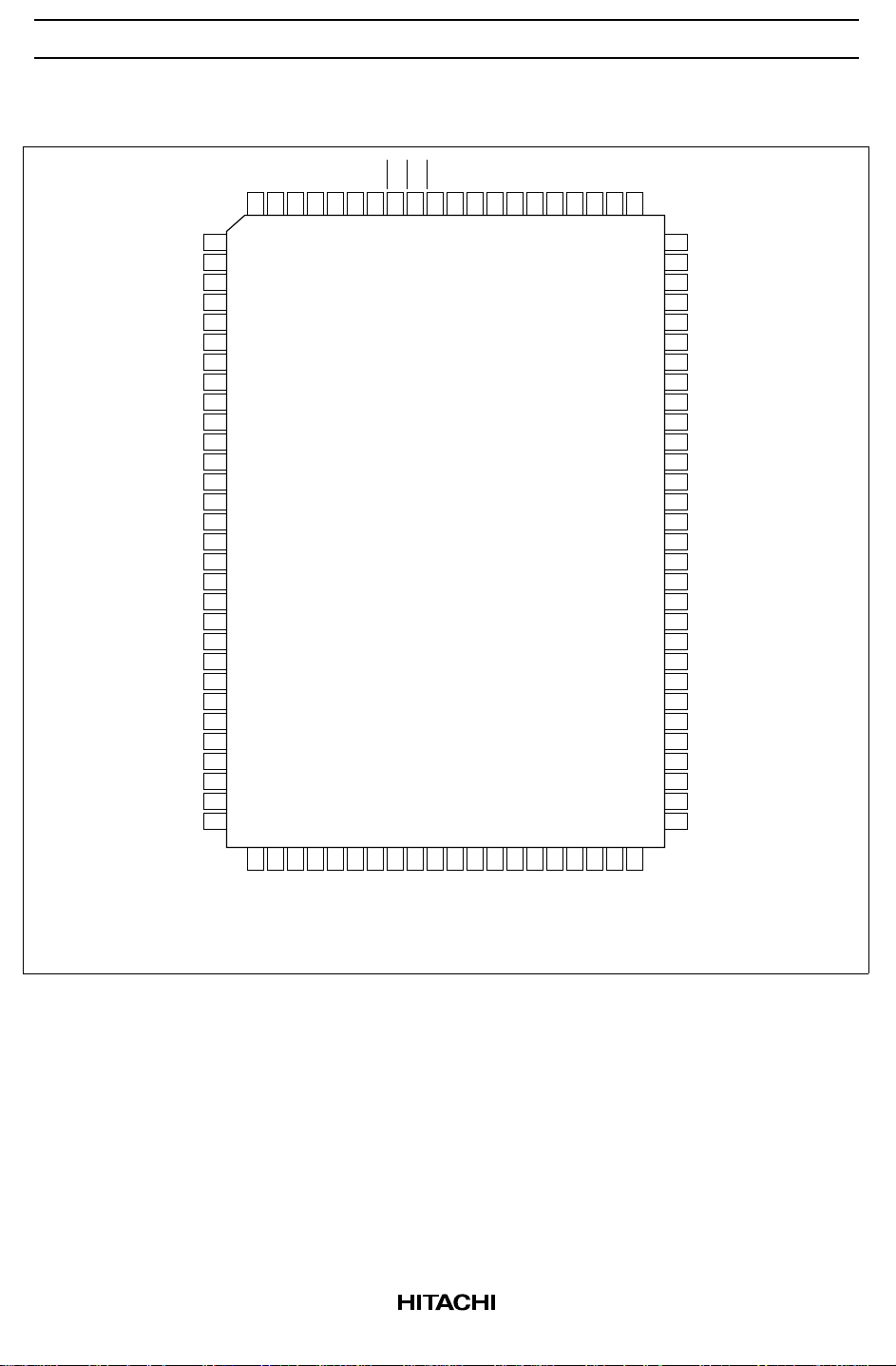
Pin Arrangement
(
)
HD61202U
ADC
V
V4R
V3R
V2R
V1R
V
EE2
Y64
Y63
Y62
Y61
Y60
Y59
Y58
Y57
Y56
Y55
Y54
Y53
Y52
Y51
Y50
Y49
Y48
Y47
Y46
Y45
Y44
Y43
FRMEø1ø2CL
99989796959493929190898887868584838281
100
1
2
M
3
CC
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31323334353637383940414243444546474849
D/I
R/W
RST
CS1
HD61202UFS
(FP-100A)
CS2
CS3NCNCNCDB7
DB6
DB5
DB4
DB3
DB2
80
79
78
77
76
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
DB1
DB0
GND
V4L
V3L
V2L
V1L
V
EE1
Y1
Y2
Y3
Y4
Y5
Y6
Y7
Y8
Y9
Y10
Y11
Y12
Y13
Y14
Y15
Y16
Y17
Y18
Y19
Y20
Y21
Y22
Y42
Y41
Y40
Y39
Y38
Y37
Y36
Y35
Y34
Y33
Y32
Y31
Y30
Y29
Y28
Y27
Y26
Y25
Y24
Y23
Top view
3
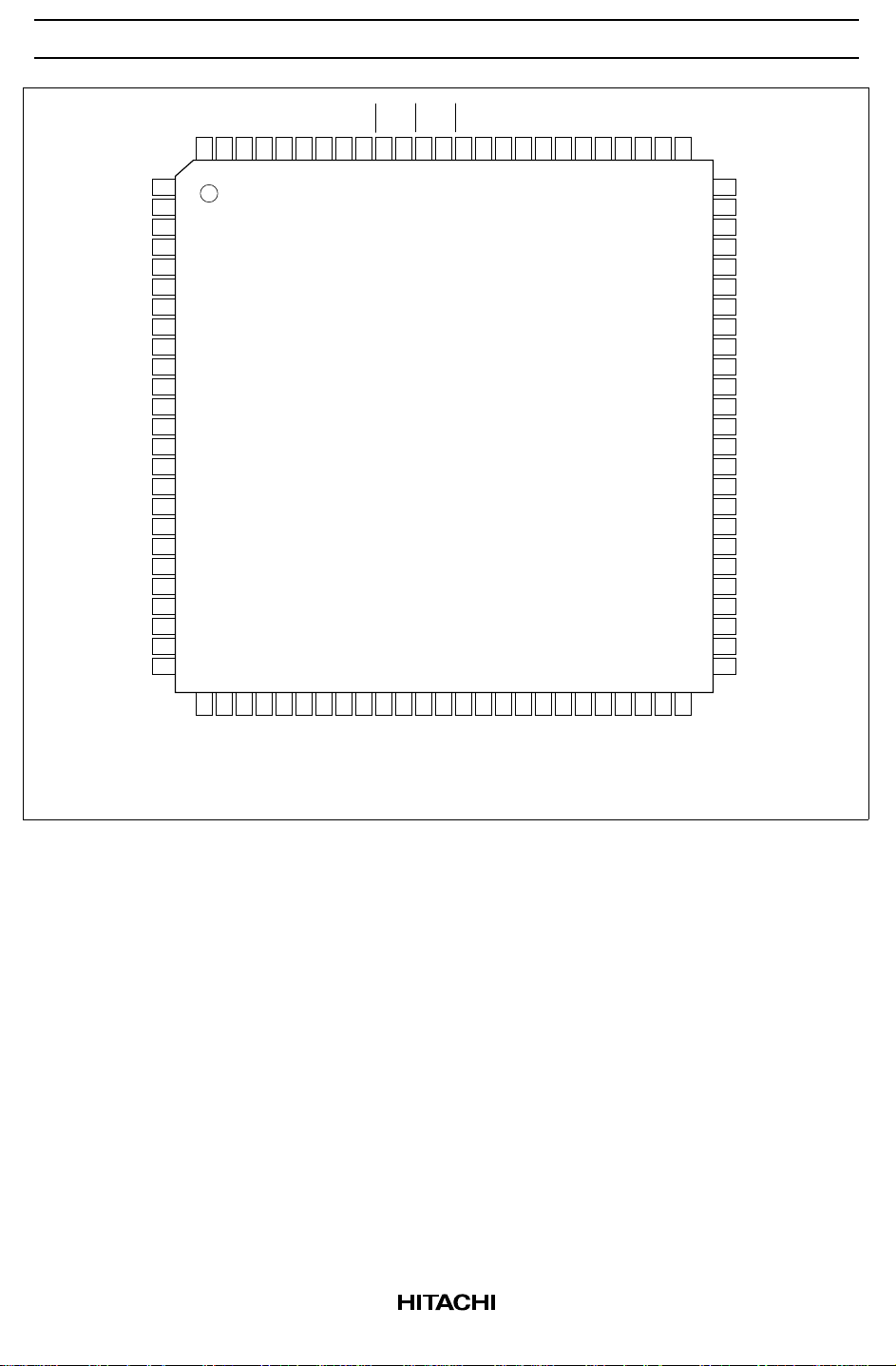
HD61202U
M
ADC
FRMEø1ø2CL
D/I
R/W
RSTNCCS1NCCS2
CS3NCDB7
DB6
DB5
DB4
DB3
DB2
DB1
DB0
GND
V
V4R
V3R
V2R
V1R
V
EE2
Y64
Y63
Y62
Y61
Y60
Y59
Y58
Y57
Y56
Y55
Y54
Y53
Y52
Y51
Y50
Y49
Y48
Y47
Y46
9998979695949392919089888786858483828180797877
100
1
CC
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26272829303132333435363738394041424344454647484950
HD61202UTE
(TFP-100B)
76
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
V4L
V3L
V2L
Y1L
V
EE1
Y1
Y2
Y3
Y4
Y5
Y6
Y7
Y8
Y9
Y10
Y11
Y12
Y13
Y14
Y15
Y16
Y17
Y18
Y19
Y20
Y45
Y44
Y43
Y42
Y41
Y40
Y39
Y38
Y37
Y36
Y35
Y34
Y33
(Top view)
Y32
Y31
Y30
Y29
Y28
Y27
Y26
Y25
Y24
Y23
Y22
Y21
4
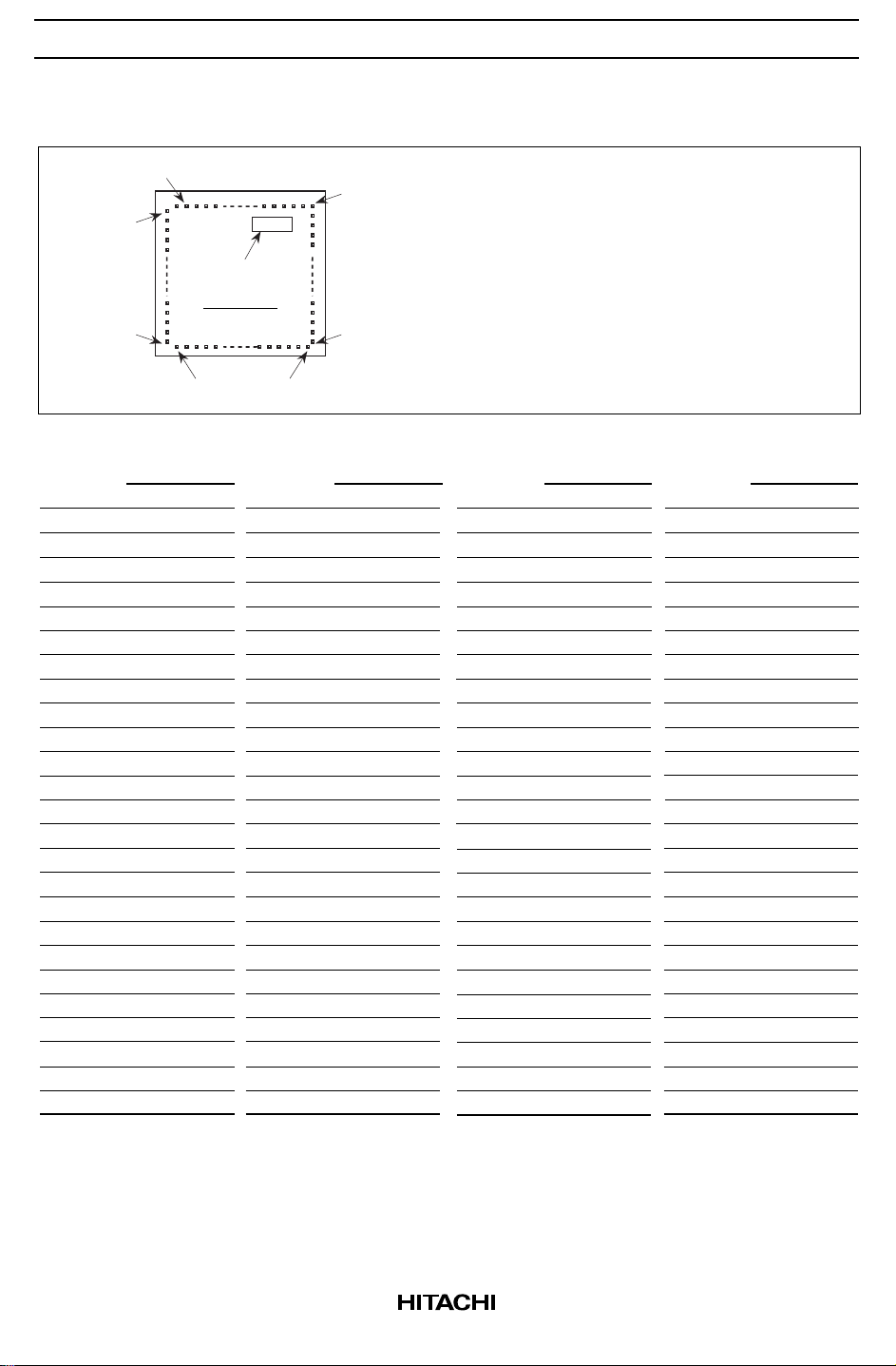
HCD61202U PAD Arrangement
HD61202U
NO.3
NO.27
No.1
CHIP CODE
HD61202U
No.28
No.53
NO.78
NO.54
HCD61202U Pad Location Coordinates
PAD
No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
PAD
Name
XY
–1493
ADC
–1649
M
V
–1789
CC
–1789
V4R
–1789
V3R
–1789
V2R
V1R
–1789
V
–1789
EE2
–1789
Y64
–1789
Y63
–1789
Y62
–1789
Y61
–1789
Y60
Y59
–1789
–1789
Y58
–1789
Y57
Y56
–1789
Y55
–1789
Y54
–1789
Y53
–1789
Y52
–1789
–1789
Y51
Y50
–1789
Y49
–1789
–1789
Y48
Coordinate
1756
1756
1689
1445
1293
1148
1011
869
721
591
461
331
201
–60
–190
–320
–450
–580
–710
–840
–970
–1100
–1230
–1369
71
PAD
No.
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
PAD
Name
Y47
Y46
Y45
Y44
Y43
Y42
Y41
Y40
Y39
Y38
Y37
Y36
Y35
Y34
Y33
Y32
Y31
Y30
Y29
Y28
Y27
Y26
Y25
Y24
Y23
Coordinate
XY
–1789
–1789
–1764
–1604
–1452
–1312
–1171
–976
–846
–716
–586
–456
–326
–196
–65
65
195
325
455
585
715
845
975
1170
1311
–1508
–1653
–1789
–1789
–1789
–1789
–1789
–1789
–1789
–1789
–1789
–1789
–1789
–1789
–1789
–1789
–1789
–1789
–1789
–1789
–1789
–1789
–1789
–1789
–1789
Chip Size : 4.08 × 4.08 mm
Coordinate : Pad Center
Origin : Chip center
Pad Size : 90 × 90 µm
EE1
Coordinate
XY
1452
1604
1764
1789
1789
1789
1789
1789
1789
1789
1789
1789
1789
1789
1789
1789
1789
1789
1789
1789
1789
1789
1789
1789
1789
PAD
No.
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
PAD
Name
Y22
Y21
Y20
Y19
Y18
Y17
Y16
Y15
Y14
Y13
Y12
Y11
Y10
Y9
Y8
Y7
Y6
Y5
Y4
Y3
Y2
Y1
V
V1L
V2L
2
–1789
–1789
–1789
–1654
–1507
–1369
–1230
–1100
–970
–840
–710
–580
–450
–320
–190
–60
71
201
331
461
591
721
1024
1153
1293
2
PAD
No.
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
PAD
Name
V3L
V4L
GND
DB0
DB1
DB2
DB3
DB4
DB5
DB6
DB7
NC
NC
NC
CS3
CS2
CS1
RST
R/W
D/I
CL
ø2
ø1
E
FRM
Coordinate
XY
1442
1789
1789
1590
1756
1789
1756
1495
1756
1335
1756
1176
1756
1016
1756
854
1756
694
1756
535
375
1756
1756
218
1756
62
1756
–94
–249
1756
1756
–405
1756
–560
1756
–716
1756
–871
–1027
–1182
–1338
1756
1756
1756
5
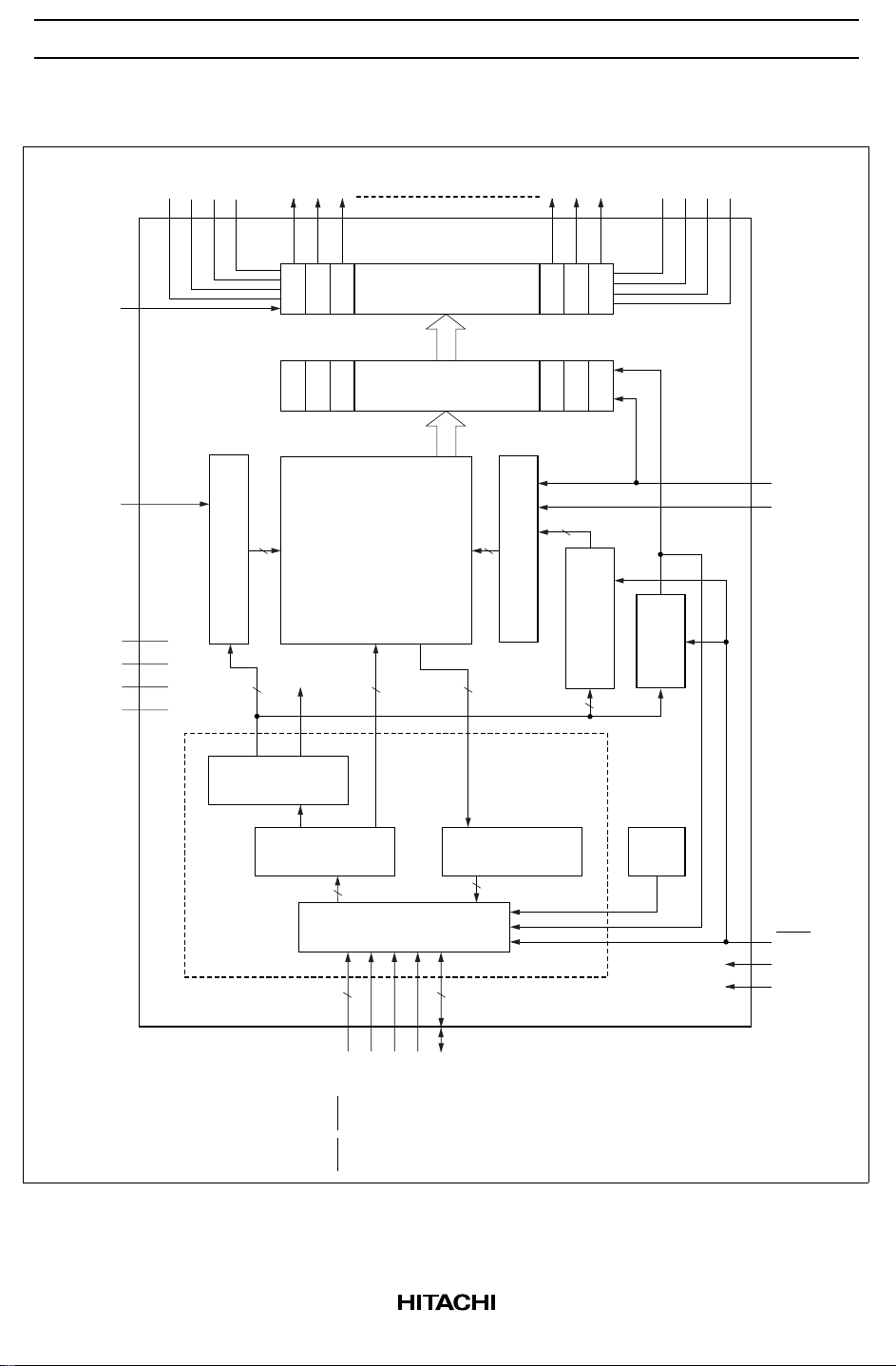
HD61202U
Block Diagram
V1L
V2L
V3L
V4L
Y1Y2Y3
Y62
Y63
Y64
V1R
V2R
V3R
V4R
ADC
V
CC
GND
V
EE1
V
EE2
1
M
1
9
XY address counter
9
Instruction
register
Liquid crystal display
2
3
driver circuit
Display data latch
2
3
4096 bit
Display data RAM
8
64 64
626364
626364
CL
6
8
6
Z address counter
line register
Display start
6
on/off
Display
FRM
Busy
flag
RST
ø1
ø2
Interface control
8
I/O buffer
3
D/I
R/W
CS1, CS2, CS3
Output registerInput register
8
8
E
DB0–DB7
6

Terminal Functions
HD61202U
Terminal
Name
V
CC
GND
V
EE1
V
EE2
V1L, V1R
V2L, V2R
V3L, V3R
V4L, V4R
CS1
CS2
CS3
Number of
Terminals I/O Connected to Functions
2 Power supply Power supply for internal logic.
Recommended voltage is:
GND = 0V
= 2.7 to 5.5V
V
CC
2 Power supply Power supply for liquid crystal display drive circuit.
Recommended power supply voltage is V
16V. Connect the same power supply to V
V
EE1
and V
are not connected each other in the LSI.
EE2
CC–VEE
and V
EE1
= 8 to
8 Power supply Power supply for liquid crystal display drive.
Apply the voltage specified depending on liquid crystals
within the limit of V
through VCC.
EE
V1L (V1R), V2L (V2R): Selection level
V3L (V3R), V4L (V4R): Non-selection level
Power supplies connected with V1L and V1R (V2L &
V2R, V3L & V3R, V4L & V4R) should have the same
voltages.
3 I MPU Chip selection.
Data can be input or output when the terminals are in the
following conditions:
Terminal name CS1 CS2 CS3
Condition L L H
EE2
.
E 1 I MPU Enable.
At write (R/W = low): Data of DB0 to DB7 is latched at
At read (R/W = high):Data appears at DB0 to DB7 while
R/W 1 I MPU Read/write.
R/W = High: Data appears at DB0 to DB7 and can be
read by the MPU.
When E = high, CS1, CS2 = low and
CS3 = high.
R/W = Low: DB0 to DB7 can accept at fall of E when
CS1, CS2 = low and CS3 = high.
D/I 1 I MPU Data/instruction.
D/I = High: Indicates that the data of DB0 to DB7 is
display data.
D/I = Low: Indicates that the data of DB0 to DB7 is
display control data.
the fall of E.
E is at high level.
7
HD61202U
Terminal
Name
ADC 1 I V
Number of
Terminals I/O Connected to Functions
/GND Address control signal to determine the relation between
CC
Y address of display RAM and terminals from which the
data is output.
ADC = High: Y1: H’0, Y64: H’63
ACD = Low: Y64: H’0, Y1: H’63
DB0–DB7 8 I/O MPU Data bus, three-state I/O common terminal.
M 1 I HD61203U Switch signal to convert liquid crystal drive waveform into
AC.
FRM 1 I HD61203U Display synchronous signal (frame signal).
Presets the 6-bit display line counter and synchronizes
the common signal with the frame timing when the FRM
signal becomes high.
CL 1 I HD61203U Synchronous signal to latch display data. The rising CL
signal increments the display output address counter and
latches the display data.
ø1, ø2 2 I HD61203U 2-phase clock signal for internal operation.
The ø1 and ø2 clocks are used to perform operations
(I/O of display data and execution of instructions) other
than display.
Y1–Y64 64 O Liquid crystal
display
Liquid crystal display column (segment) drive output.
The outputs at these pins are at the light-on level when
the display RAM data is 1, and at the light-off level when
the display RAM data is 0.
Relation among output level, M, and display data (D) is
as follows:
M
10
1010
V1 V3 V2 V4
RST 1 I MPU or
external CR
D
Output
level
The following registers can be initialized by setting the
RST signal to low level.
1. On/off register 0 set (display off)
2. Display start line register line 0 set (displays from line
0)
After releasing reset, this condition can be changed only
by instruction.
NC 3 Open Unused terminals. Don’t connect any lines to these
terminals.
Note: 1 corresponds to high level in positive logic.
8

HD61202U
Function of Each Block
Interface Control
I/O Buffer: Data is transferred through 8 data bus lines (DB0–DB7).
DB7: MSB (most significant bit)
DB0: LSB (least significant bit)
Data can neither be input nor output unless CS1 to CS3 are in the active mode. Therefore, when CS1 to
CS3 are not in active mode it is useless to switch the signals of input terminals except RST and ADC; that
is namely, the internal state is maintained and no instruction excutes. Besides, pay attention to RST and
ADC which operate irrespectively of CS1 to CS3.
Register: Both input register and output register are provided to interface to an MPU whose speed is
different from that of internal operation. The selection of these registers depend on the combination of R/W
and D/I signals (Table 1).
1. Input register
The input register is used to store data temporarily before writing it into display data RAM.
The data from MPU is written into input register, then into display data RAM automatically by internal
operation. When CS1 to CS3 are in the active mode and D/I and R/W select the input register as shown
in Table 1, data is latched at the fall of the E signal.
2. Output register
The output register is used to store data temporarily that is read from display data RAM. To read out the
data from the output register, CS1 to CS3 should be in the active mode and both D/I and R/W should be
1. With the read display data instruction, data stored in the output register is output while E is high
level. Then, at the fall of E, the display data at the indicated address is latched into the output register
and the address is increased by 1.
The contents in the output register are rewritten by the read display data instruction, but are held by
address set instruction, etc.
Therefore, the data of the specified address cannot be output with the read display data instruction right
after the address is set, but can be output at the second read of data. That is to say, one dummy read is
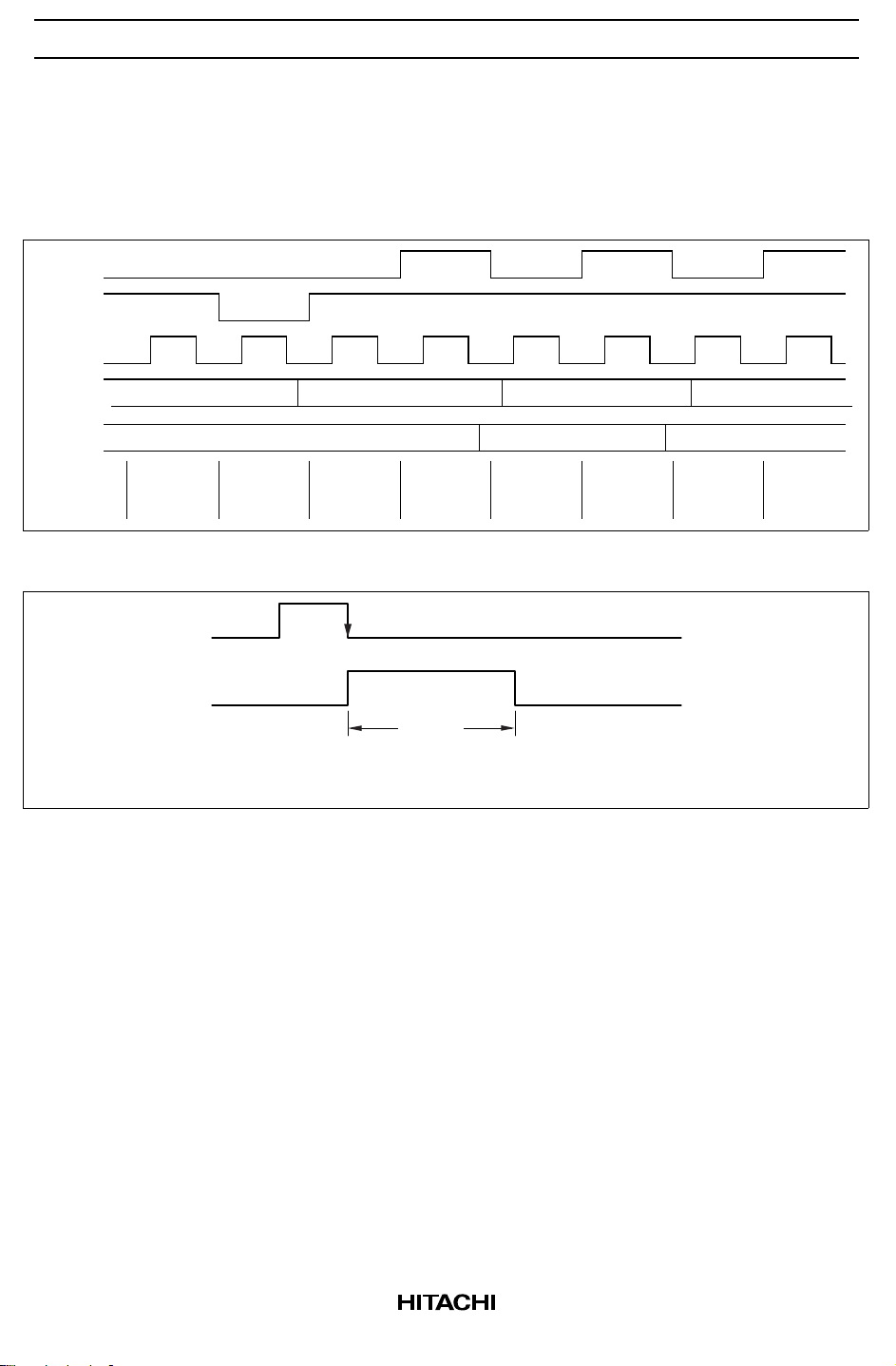
necessary. Figure 1 shows the MPU read timing.
Table 1 Register Selection
D/I R/W Operation
1 1 Reads data out of output register as internal operation (display data RAM →
output register)
1 0 Writes data into input register as internal operation (input register → display
data RAM)
0 1 Busy check. Read of status data.
0 0 Instruction
9
HD61202U
Busy Flag
Busy flag = 1 indicates that HD61202U is operating and no instructions except status read instruction can
be accepted. The value of the busy flag is read out on DB7 by the status read instruction. Make sure that the
busy flag is reset (0) before issuing instructions.
D/I
R/W
E
Address
Output
register
DB0–DB7
Busy
check
E
Busy
flag
Write
address N
f
CLK
N N + 1 N + 2
Busy
check
Read data
(dummy)
Figure 1 MPU Read Timing
T Busy
is ø1, ø2 frequency
Figure 2 Busy Flag
Data at address N Data at address N + 1
Busy
check
Read
data at
address N
1/f
≤ T Busy ≤ 3/f
CLK
Busy
check
CLK
Data read
address
N + 1
10
 Loading...
Loading...