
HD155121F
RF Transceiver IC for GSM and PCN Dual band cellular systems
ADE-207-265A (Z)
2nd Edition
May 1999
Description
The HD155121F is a RF transceiver IC for GSM and PCN dual band cellular systems, and integrates most
of the low power silicon functions of a transceiver. The HD155121F incorporates two bias circuits for RF
LNAs, two first mixers, a second mixer, a programmable gain amplifier, and an IQ demodulator for the
receiver, and an IQ modulator and offset PLL for the transmitter. Also, on chip are dividers for the phase
splitter. Moreover the HD155121F includes control circuits to implement power saving modes. These
functions can operate down to 2.7 V and are housed in a 48-pin LQFP SMD package.
Hence the HD155121F can form a small size transceiver handset for dual band by adding a dual PLL
frequency synthesizer IC, power amplifiers and some external components.
The HD155121F is fabricated using a 0.6 µm double-polysilicon Bi-CMOS process.
Functions
Receiver(Rx)
• Low Noise Amplifier (LNA) bias circuit
• First mixer
• IF amplifier and second mixer
• Programmable Gain Amplifier (PGA)
• IQ demodulator with 90 degree phase splitter
Transmitter(Tx)
• IQ modulator with 90 degree phase splitter
• Offset PLL
Down converter
Phase comparator
TXVCO driver
Others
• IF dividers
• Power saving control circuit
• IFVCO

HD155121F
Features
• Highly integrated RF processing for hand-portables
• Operating supply voltage
VCC : 2.7 to 3.6 V
Phase comparator and TXVCO driver circuit : 2.7 to 5.25 V
• Current consumption
Rx mode (GSM) : 53 mA + LNA current
Rx mode (PCN) : 52 mA + LNA current
Tx mode (GSM) : 36 mA
Tx mode (PCN) : 37 mA
Idle mode :1 µA
• Operating temperature : –20 to +75 degree
• LQFP 48pin SMD (Low Profile Quad Flat Package)
• Wide operating frequencies
Rx RF GSM : 925 - 960 MHz
PCN : 1805 - 1880 MHz
1st IF : 225 MHz
2nd IF : 45 MHz
Tx RF GSM : 880 - 915 MHz
PCN : 1710 - 1785 MHz
IF GSM : 270 MHz
PCN : 135 MHz
• Offset PLL architecture for Transmitter
• High dynamic range Programmable Gain Amplifier (PGA)
2
Pin Arrangement
MIX1INB1
1
MIX1IN2
MIX1INB2
POONTX
POONRX2
POONRX1
MIX1OUTB
MIX1OUT
VCCMIX1
GNDMIX1
RFLOIN
VCCDIV
GNDDIV
373839404142434445464748
36
HD155121F
IFLO
MIX1IN1
RFOUT
RFIN1
RFIN2
VCCPLL
GNDPLL
VCOIN2
VCOIN1
VCCCOMP
PLLOUT
ICURAD
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
1413 24232221201918171615
QINB
QIN
IINB
IIN
VCCIQ
MODLB
(Top View)
GNDIQ
QOUTB
QOUT
IOUTB
IOUT
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
MIX2OB
BAND
IFVCOO
IFVCOI
VCCIF
GNDIF
IFIN
IFINB
LE
SDATA
CLK
MIX2O
3

HD155121F
Pin Description
Pin No. Pin Name Description
1 MIX1INB1 Negative input for Mixer1 (GSM)
2 MIX1IN1 Positive input for Mixer1 (GSM)
3 RFOUT Bias for the collector of LNA transistor
4 RFIN1 Bias for the base of LNA transistor (GSM)
5 RFIN2 Bias for the base of LNA transistor (PCN)
6 VCCPLL VCC for OPLL
7 GNDPLL GND for OPLL
8 VCOIN2 TxVCO signal input (PCN)
9 VCOIN1 TxVCO signal input (GSM)
10 VCCCOMP VCC for phase comparator
11 PLLOUT Current output to control and modulate the TxVCO
12 ICURAD Phase comparator output current setting
13 QINB Negative input of Q signal for modulator
14 QIN Positive input of Q signal for modulator
15 IINB Negative input of I signal for modulator
16 IIN Positive input of I signal for modulator
17 MODLB VCC for modulator load bias
18 VCCIQ VCC for IQ modulator and demodulator
19 GNDIQ GND for IQ modulator and demodulator
20 QOUTB Negative output of Q signal for modulator
21 QOUT Positive output of Q signal for modulator
22 IOUTB Negative output of I signal for modulator
23 IOUT Positive output of I signal for modulator
24 MIX2OB Negative output for Mixer2
25 MIX2O Positive output for Mixer2
26 CLK Clock for serial data
27 SDATA Serial data for Gain control
28 LE Load enable for serial data
29 IFINB Negative input for Mixer2
30 IFIN Positive input for Mixer2
31 GNDIF GND for Mixer2 and PGA
32 VCCIF VCC for Mixer2 and PGA
33 IFVCOI Base of IFVCO transistor
34 IFVCOO Emitter of IFVCO transistor
4

Pin Description (cont)
Pin No. Pin Name Description
35 BAND Band control (Low: GSM, High: PCN)
36 IFLO Output of IFVCO or Input of IF Local
37 GNDDIV GND for Divider and IFVCO
38 VCCDIV VCC for Divider and IFVCO
39 RFLOIN Input for RF Local
40 GNDMIX1 GND for Mixer1
41 VCCMIX1 VCC for Mixer1
42 MIX1OUT Positive output for Mixer1 (GSM/PCN)
43 MIX1OUTB Negative output for Mixer1 (GSM/PCN)
44 POONRX1 Power save control for LNA and Mixer1
45 POONRX2 Power save control for Mixer2, PGA and demodulator
46 POONTX Power save control for modulator and OPLL
47 MIX1INB2 Negative input for Mixer1 (PCN)
48 MIX1IN2 Positive input for Mixer1 (PCN)
HD155121F
5
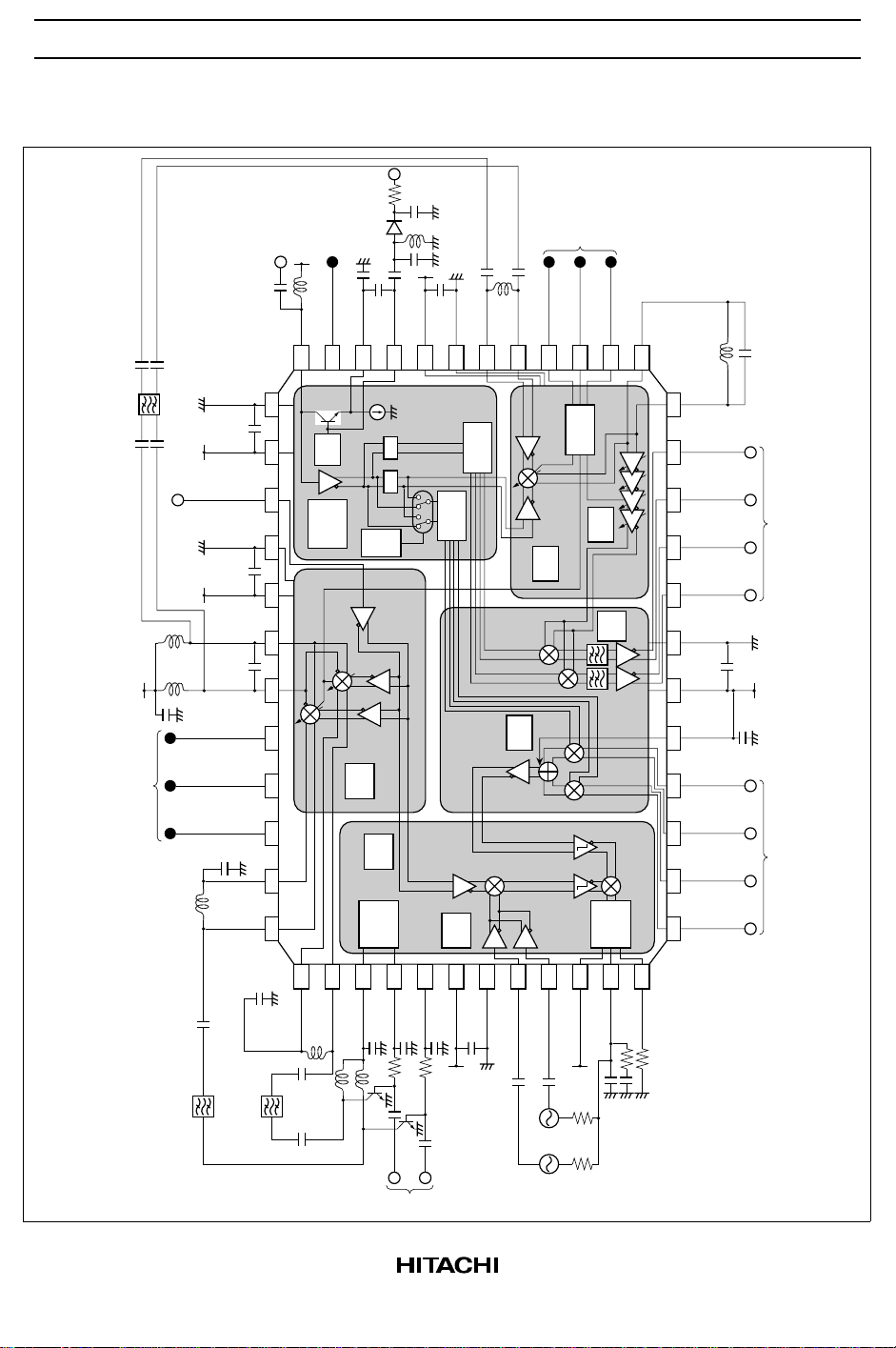
HD155121F
Block Diagram
Tune
GNDDIV
VCCDIV
1172MHz
(Rx: 1580MHz, Tx: 1575MHz)
from VCO
GNDMIX1
VCCMIX1
MIX1OUT
MIX1OUTB
POONRX1
POONRX2
RFLOIN
225MHz
(225MHz)
from
System controller
IFLO
BAND
IFVCOO
36
35
540
MHz
Vref
(IFVCO)
Vref
(Div.Rx)
(Div.Tx)
Vref
34
from
(Mix1)
IFVCOI
33
1/2 1/6
Band
SW
VCCIF
GNDIF
32
1/2
(1580/1575MHz) 1172MHz
GSM: 270MHz
225MHz
(225MHz)
IFIN
IFINB
31
30
1/2
(90deg)
(90deg)
45MHz
270MHz
(135MHz)
PCN: 135MHz
from System controller
LE
SDATA
CLK
29
28
27
26
Serial
interface
Vref
(PGA)
(IF)
Vref
(45MHz)
Vref
(Mod)
45MHz
(45MHz)
Vref
MIX2O
25
(Demod)
MIX2OB
23
IOUT
IOUTB
QOUT
QOUTB
GNDIQ
VCCIQ
MODB
IIN
45MHz
to Base bandfrom Base band
driver
ICURAD
IINB
QIN
13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 24
12
RICURAD
from System controller
POONTX
MIX1INB2
MIX1IN2 QINB
(1805MHz)
47 46 45 44 43 42 41 40 39 38 37
48
947MHz
1
2
MIX1IN1
MIX1INB1
Vref
(LNA)
LNA
Bias
circuit
3
4
RFIN1
RFOUT
947MHz
from Antenna
1172MHz
(1580/
1575MHz)
Vref
5
RFIN2
VCCPLL
(1805MHz)
(PLL)
6
7
VCOIN2
GNDPLL
(1710MHz)
8
270MHz
(135MHz)
9
VCOIN1
902MHz
Tx.VCO1Tx.VCO2
mode
Current
10
11
PLLOUT
VCCCOMP
6
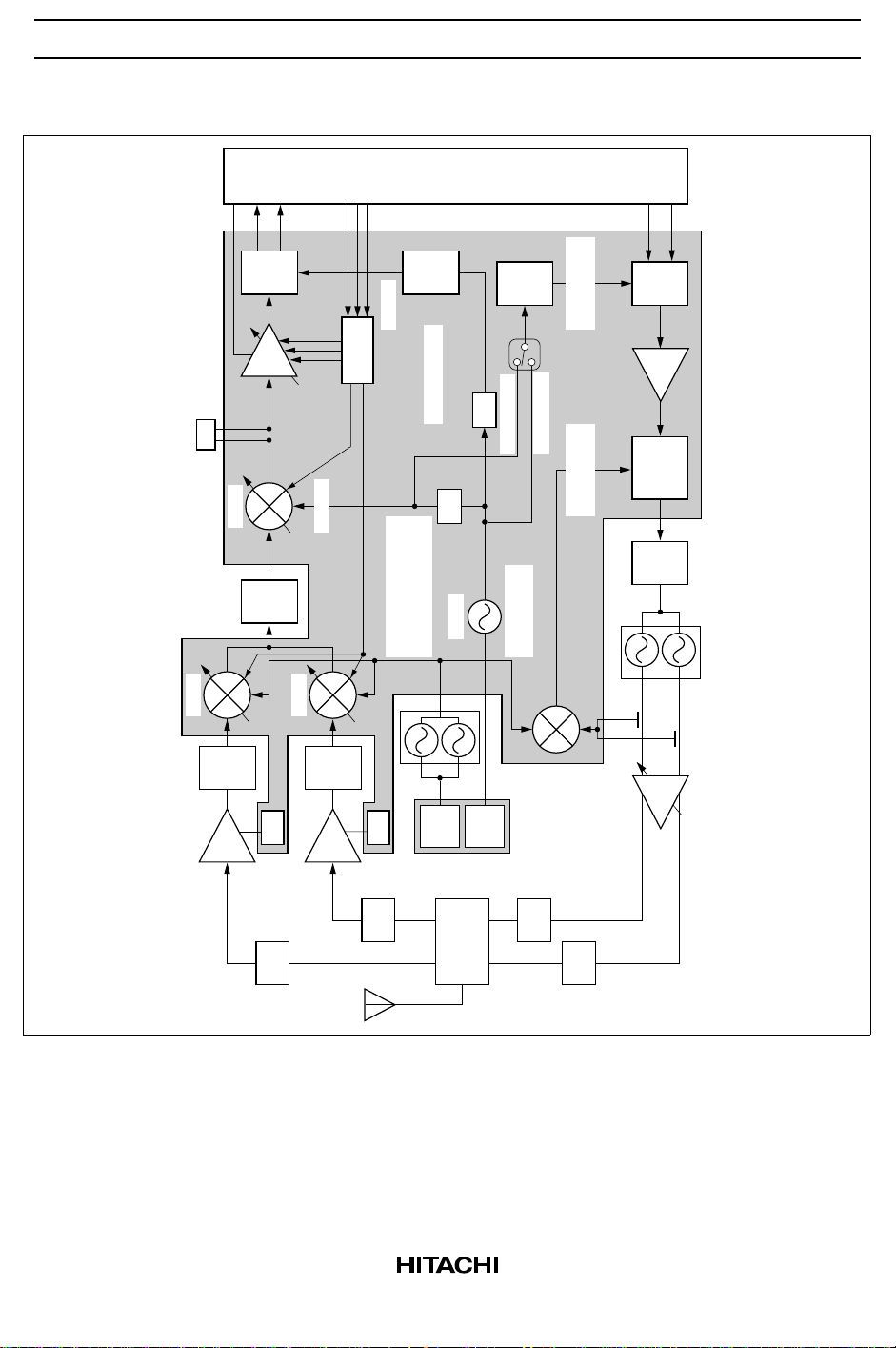
Configuration
HD155121F
B.B.
I
Q
Block
I
Q
LC
45 MHz
Mixer2
225 MHz
Mixer1
RF
SAW
LNA
925 to 960 MHz
filter
IF
I & Q
PGA
SAW
bias
RF
Demo.
filter
Mixer1
circuit
filter
270 MHz
RF
SAW
LNA
1805 to
1880 MHz
45 MHz
interface
Serial data
: 1150 to 1185 MHz
GSM
filter
bias
circuit
RF
filter
÷2
Shift
90 deg
HD155121F
÷2
: Rx. 1580 to 1655 MHz
/Tx. 1575 to 1650 MHz
PCN
RF VCO
PLL1
Dual
synth.
90 deg
÷6
PCN: 270 MHz
IFVCO
GSM: 540 MHz
PLL2
HD155017T
S/W
÷2
Shift
GSM: 270 MHz
PCN: 135 MHz
GSM: 540 MHz
GSM: 270 MHz
PCN: 135 MHz
PCN: 540 MHz
LPF
LPF
Mod
I & Q
Phase
Detector
filter
Loop
880 to 915 MHz
880 to 915 MHz
1710 to 1785 MHz
1710 to 1785 MHz
PA Module
7

HD155121F
Functional Operation
The HD155121F has been designed from system stand point and incorporated a large number of the circuit
blocks necessary in the design of a digital cellular handset.
Receiver Operation
The HD155121F incorporates two LNA bias circuits for external RF transistors, whose NF and power gain
can be better selected.
This circuit amplifies the RF signal after selection by the antenna filter before the signal enters the first
mixer section. The RF signal is combined with a local oscillator (LO) signal to generate a wanted first IF
signal in the 130 - 300 MHz range. The first mixer circuit uses a double-balanced Gilbert cell architecture,
which has open collector differential outputs. If, at 225 MHz, a 800 Ω LC load is connected to the mixer’s
outputs then a SSB NF of 9.0 dB (GSM), 9.1 dB (PCN) with a gain of 9.5 dB (GSM), 8.5 dB (PCN) is
realizable. The corresponding input compression point is –10.5 dBm (GSM), –12.5 dBm (PCN), which
allows the device to be used within a GSM and EGSM and PCN system.
A filter is used after the first mixer to provide image rejection and the conditioned signal is then passed
through an intermediate amplifier, before being down converted to a second IF in the range of 26 - 60
MHz.
The second mixer can generate a 45 MHz second IF, if a 270 MHz second local signal is used. The second
mixer also uses the Gilbert cell architecture, but with internal resistive differential outputs of 300 Ω. If
amplifier and second mixer has a SSB NF of 6.0 dB, a power gain of 13 dB and a input compression point
of –22 dBm. In order to improve the blocking characteristics of the device an external LC resonator across
the differential outputs of the second mixer is recommended.
First mixer and second mixer can switch the power gain. Switching gain step of first mixer is 12 dB, and
such step of second mixer is 16 dB.
The signal is then passed to the PGA circuit, which has a dynamic range of more than 80 dB (–42 dB - +56
dB typ.) and is controlled by digital serial data, which is generated by the microprocessor. This gain step is
2 dB.
The signal is then down converted by a demodulator to I and Q. Internal divider circuits convert the IFLO
signal to the same frequency as the second IF before passing this local signal through a phase splitter /
shifter in order to generate the in phase and quadrature phase IQ components. The phase accuracy of the
IQ demodulator is less than +/–1 degree and the amplitude mismatch is less than +/–0.5 dB. In order to
accommodate different baseband interfaces the HD155121F IQ differential outputs have a voltage swing of
1.6 Vpp and DC offset of less than +/–60 mV. Within each output stage a second order Butterworth filter
(fc = 210 kHz) is used to improve the blocking performance of the device.
In order to allow flexibility in circuit implementation the HD155121F can configured to use either a singleended or balanced external circuitry and components.
8

HD155121F
Transmitter Operation
The transmitter chain converts differential IQ baseband signals to a suitable format for transmission by a
power amplifier.
The common mode voltage range of the modulator inputs is 0.8 V to 1.2 V and they have 2.0 Vpp
differential swing. The modulator circuit uses double-balanced mixers for the I and Q paths. The Local
signals are generated by dividing the IFLO signals by 2, and then passed to the modulator through a phase
splitter / shifter. The IF signals generated are then summed to produce a single modulated IF signal which
is amplified and fed into the offset PLL block. Carrier suppression due to the mixer circuit is better than 31
dBc. If the common mode DC voltage of the I and Q inputs is adjusted, carrier suppression is better than
40 dBc easily. Side band suppression is better than 35 dBc without adjustment.
Within the offset PLL block there are a down converter, a phase comparator and a VCO driver. The down
converter mixes the first local signal and the TXVCO signal to create a reference local signal for use in the
offset PLL circuit. The phase comparator and the VCO driver generate an error current, which is
proportional to the phase differential between the reference IF and the modulated IF signals. This current is
used in a second order loop filter to generate a voltage, which in turn modulates the TXVCO. In order to
optimize the PLL loop gain, the error current value can be modified by changing the value of an external
resistor - ICURAD. In order to accommodate various control range of TXVCOs, the offset PLL circuit has
been designed to operate with a supply voltage up to 5.25 V.
9

HD155121F
Operation Modes
The HD155121F has necessary control circuitry to implement the necessary states within the dual band
system. Also provided is a power saving mode which reduces the current consumption of the device by
powering down unnecessary function blocks. Three pins are assigned for power saving mode control,
POONRX1, POONRX2 and POONTX. Also one pin is assigned for switching operational band, BAND.
Table 1 shows the relationship between the pins and the required operating mode. These pins are
controlled by the system controller.
As per GSM requirements the Tx and Rx sections do not operate simultaneously. For the receiver there is a
calibration mode in which the LNA bias circuit and first mixer are switched off. During this period the
gain of the PGA can be adjusted. Also the DC offsets of the IQ demodulator are measured and
subsequently canceled.
In order to change between the Rx and Tx modes a state called “warm-up” is used to ensure that the local
signals are not unduly affected. This method of switching between Tx and Rx ensures that lock is achieved
first time.
Power saving is implemented through use of the idle mode. All function blocks of the HD155121F are
switched off until such time as the system controller commands the device to power up again.
Table 1 Operating Modes with Power Saving
Mode Receive Calibrate Warm-up Transmit Idle
Band GSM PCN — — GSM PCN —
POONRX1 (44) H H L L L L H
POONRX2 (45) H H H L L L L
POONTX (46) L L L L H H Don’t care
BAND (35) L H Don’t care Don’t care L H Don’t care
Rx block LNA bias (GSM) ON OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF
LNA bias (PCN) OFF ON OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF
1st Mixer (GSM) ON OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF
1st Mixer (PCN) OFF ON OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF
2nd Mixer ON ON ON OFF OFF OFF OFF
PGA ON ON ON OFF OFF OFF OFF
I/Q demodulator ON ON ON OFF OFF OFF OFF
Tx block Offset PLL OFF OFF OFF OFF ON ON OFF
I/Q modulator OFF OFF OFF OFF ON ON OFF
Oscillator IF VCO ON ON ON ON ON ON OFF
block Divider (Rx) ON ON ON OFF OFF OFF OFF
Divider (Tx) OFF OFF OFF OFF ON ON OFF
1st local buffer ON ON ON ON ON ON OFF
IF local buffer ON ON ON ON ON ON OFF
Total current 53 mA 52 mA 34 mA 9.0 mA 36 mA 37 mA 1 µA
10

HD155121F
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Any stress in excess of the absolute maximum ratings can cause permanent damage to the HD155121F.
Item Symbol Rating Unit
Power supply voltage (V
Power supply voltage (V
Pin voltage V
Maximum power dissipation P
Operating temperature Topr –20 to +75 °C
Storage temperature Tstg –55 to +125 °C
)VCC–0.3 to +4.0 V
CC
)V
CCCOMP
CCCOMP
T
T
–0.3 to +5.5 V
–0.3 to VCC+0.3 (4.0 Max) V
400 mW
11

HD155121F
CCCO
Electrical Characteristics
DC Specifications (VCC = 3 V, Ta = 25°C unless otherwise specified.)
Item Mode Min Typ Max Unit Test Condition Note
Power supply voltage (VCC) 2.7 3.0 3.6 V
Power supply voltage (V
Power supply current (Rx.) GSM — 53.0 74.0 mA VCC = 3.0V, V
Power supply current (Tx.) GSM — 36.0 50.0 mA VCC = 3.0V, V
Power supply current (Warm-up) — 9.0 12.5 mA VCC = 3.0V, V
Power saving mode supply current — 1.0 10.0 µAVCC = 3.0V, V
Power up time (Rx.) — 1.5 5.0 µsec from PS mode 1
Power up time (Tx.) — 0.2 0.5 µsec from PS mode 1
Power on control voltage range
(POONRX1, POONRX2, POONTX)
Power off control voltage range
(POONRX1, POONRX2, POONTX)
I/Q common-mode output voltage 1.15 1.35 1.55 V
I/Q maximum output swing
(Single ended)
I/Q output DC offset voltage –60 0 60 mV VIOUTDC – VIOUTBDC,
I/Q common-mode input voltage 0.8 1.0 1.2 V 1
I/Q input swing (Single ended) 0.8 1.0 1.2 Vp-p VIIN, VIINB, VQIN, VQINB 1
Serial data VH (CLK, SDATA, LE) 2.3 — — V
Serial data VL (CLK, SDATA, LE) — — 0.8 V
Band control VH (BAND) 2.3 — — V
Band control VL (BAND) — — 0.8 V
Input current
(POONRX1, POONRX2, POONTX,
BAND, CLK, SDATA, LE)
Note: 1. These values are not tested in mass production.
2. Power supply current does not include the LNA bias current.
) 2.7 3.0 5.25 V
CCCOMP
PCN — 52.0 73.0 mA Mixer1, 2 = Gain1,
PCN — 37.0 52.0 mA
2.3 — — V
— — 0.8 V
0.8 1.06 — Vp-p VIOUT, VIOUTB,
–10 0 10 µA
= 3.0V, 2
CCCOMP
PGA = bitNo26
= 3.0V 2
CCCOMP
= 3.0V 2
CCCOMP
= 3.0V
MP
High level = VCC, Low level = 0V
at mode control pin and serial
data pin (POONRX1, RX2, TX,
BAND, CLK (no clock signal),
SDATA, LE)
VQOUT, VQOUTB
VQOUTDC, VQOUTBDC
2
12

HD155121F
AC Specifications (VCC = 3 V, Ta = 25°C unless otherwise specified.)
• LNA Bias circuit specifications
Item Mode Min Typ Max Unit Test Condition Note
LNA transistor bias current GSM 4.7 5.6 — mA
PCN 4.7 5.6 — mA
Frequency GSM 925 — 960 MHz 1
PCN 1805 1880 MHz
Power gain GSM — 19.4 — dB RF = 940 MHz 1
PCN — 13.4 — dB RF = 1842 MHz
Noise figure GSM — 1.6 — dB RF = 940 MHz 1
PCN — 1.6 — dB RF = 1842 MHz
3rd order input intercept point GSM — –6.0 — dBm 1
PCN — –2.0 — dBm
3rd order output intercept point GSM — 13 — dBm 1
PCN — 11 — dBm
1dB input compression point GSM — –14.5 — dBm 1
PCN — –9.5 — dBm
1dB output compression point GSM — 3.9 — dBm 1
PCN — 2.9 — dBm
Output (RF) Z GSM — 50 — Ω Output (GSM RF) 1
PCN — 50 — Ω Output (PCN RF)
Input (RF) Z GSM — 50 — Ω Input (GSM RF) 1
PCN — 50 — Ω Input (PCN RF)
Note: 1. These AC characteristics are shown for reference only and do not form part of the HD155121F
component specification.
13

HD155121F
• Mixer1 specifications (Differential output load between pin42 and pin43 = 800 Ω)
Item Mode Min Typ Max Unit Test Condition Note
Frequency (RF) GSM 925 — 960 MHz 1
PCN 1805 — 1880 MHz
Frequency (LO) GSM 1125 — 1260 MHz 1
PCN 1505 — 1680 MHz
Frequency (IF) — 200 225 300 MHz 1
RFLO input level — –8.0 — — dBm
Conversion gain 1 GSM 6.5 9.5 12.5 dB RF = 940MHz, LO = 1165MHz, IF = 225MHz 2
PCN 5.5 8.5 11.5 dB RF = 1842MHz, LO = 1617MHz, IF = 225MHz
Conversion gain 2 GSM –5.5 –2.5 0.5 dB RF = 940MHz, LO = 1165MHz, IF = 225MHz 2
PCN –6.5 –3.5 –0.5 dB RF = 1842MHz, LO = 1617MHz, IF = 225MHz
Noise figure 1 GSM — 9.0 10.5 dB RF = 940MHz, LO = 1165MHz, IF = 225MHz 1, 2
PCN — 9.1 10.6 dB RF = 1842MHz, LO = 1617MHz, IF = 225MHz
Noise figure 2 GSM — 15.0 16.5 dB RF = 940MHz, LO = 1165MHz, IF = 225MHz 1, 2
PCN — 16.0 17.5 dB RF = 1842MHz, LO = 1617MHz, IF = 225MHz
3rd order input
intercept point 1
3rd order input
intercept point 2
3rd order output
intercept point 1
3rd order output
intercept point 2
1dB input GSM –12.5 –10.5 — dBm RF = 940MHz, LO = 1165MHz, IF = 225MHz 2
compression point 1 PCN –14.5 –12.5 — dBm RF = 1842MHz, LO = 1617MHz, IF = 225MHz
1dB input GSM –8.5 –6.5 — dBm RF = 940MHz, LO = 1165MHz, IF = 225MHz 2
compression point 2 PCN –10.5 –8.5 — dBm RF = 1842MHz, LO = 1617MHz, IF = 225MHz
1dB output GSM –4.0 –2.0 — dBm RF = 940MHz, LO = 1165MHz, IF = 225MHz 1, 2
compression point 1 PCN –7.0 –5.0 — dBm RF = 1842MHz, LO = 1617MHz, IF = 225MHz
1dB output GSM –12.0 –10.0 — dBm RF = 940MHz, LO = 1165MHz, IF = 225MHz 1, 2
compression point 2 PCN –15.0 –13.0 — dBm RF = 1842MHz, LO = 1617MHz, IF = 225MHz
Note: 1. These values are not tested in mass production.
2. The loss (2.2 dB) of test circuit at Mixer1 output is calculated.
GSM –3.0 –1.0 — dBm RF1 = 940.8MHz, RF2 = 941.6MHz,
LO = 1165MHz, IF = 225MHz
PCN –6.0 –4.0 — dBm RF1 = 1842.8MHz, RF2 = 1843.6MHz,
LO = 1617MHz, IF = 225MHz
GSM 1.0 3.0 — dBm RF1 = 940.8MHz, RF2 = 941.6MHz,
LO = 1165MHz, IF = 225MHz
PCN –3.0 –1.0 — dBm RF1 = 1842.8MHz, RF2 = 1843.6MHz,
LO = 1617MHz, IF = 225MHz
GSM 6.5 8.5 — dBm RF1 = 940.8MHz, RF2 = 941.6MHz,
LO = 1165MHz, IF = 225MHz
PCN 2.5 4.5 — dBm RF1 = 1842.8MHz, RF2 = 1843.6MHz,
LO = 1617MHz, IF = 225MHz
GSM –1.5 0.5 — dBm RF1 = 940.8MHz, RF2 = 941.6MHz,
LO = 1165MHz, IF = 225MHz
PCN –6.5 –4.5 — dBm RF1 = 1842.8MHz, RF2 = 1843.6MHz,
LO = 1617MHz, IF = 225MHz
1, 2
1, 2
1, 2
1, 2
14

HD155121F
• Mixer2 specifications
Item Mode Min Typ Max Unit Test Condition Note
Frequency (IF1) 200 225 300 MHz 1
Frequency (LO2) 240 270 360 MHz LO2 = IFLO/2 1
Frequency (IF2) 40 45 60 MHz 1
IFLO input level –10 — — dBm
Conversion gain 1 10.5 13.0 15.5 dB IF1 = 225MHz, IFLO = 540MHz, IF2 = 45MHz 2
Conversion gain 2 –5.5 –3.0 –0.5 dB IF1 = 225MHz, IFLO = 540MHz, IF2 = 45MHz 2
Noise figure 1 — 6.0 7.5 dB IF1 = 225MHz, IFLO = 540MHz, IF2 = 45MHz 1, 2
Noise figure 2 — 12.0 13.5 dB IF1 = 225MHz, IFLO = 540MHz, IF2 = 45MHz 1, 2
3rd order input
intercept point 1
3rd order input
intercept point 2
3rd order output
intercept point 1
3rd order output
intercept point 2
1dB input
compression point 1
1dB input
compression point 2
1dB output
compression point 1
1dB output
compression point 2
Isolation 50 — — dB between Mixer1 output and Mixer2 input 1, 2
Note: 1. These values are not tested in mass production.
2. The loss (3.6 dB) of test circuit at Mixer2 output is calculated.
–15.0 –13.0 — dBm IF1 = 225.8MHz, IF2 = 226.6MHz,
LO = 540MHz, 2ndIF = 45MHz
–11.0 –9.0 — dBm IF1 = 225.8MHz, IF2 = 226.6MHz,
LO = 540MHz, 2ndIF = 45MHz
–2.0 0.0 — dBm IF1 = 225.8MHz, IF2 = 226.6MHz,
LO = 540MHz, 2ndIF = 45MHz
–14.0 –12.0 — dBm IF1 = 225.8MHz, IF2 = 226.6MHz,
LO = 540MHz, 2ndIF = 45MHz
–24.0 –22.0 — dBm IF1 = 225MHz, IFLO = 540MHz, IF2 = 45MHz 2
–21.0 –19.0 — dBm IF1 = 225MHz, IFLO = 540MHz, IF2 = 45MHz 2
–12.0 –10.0 — dBm IF1 = 225MHz, IFLO = 540MHz, IF2 = 45MHz 1, 2
–24.0 –22.0 — dBm IF1 = 225MHz, IFLO = 540MHz, IF2 = 45MHz 1, 2
1, 2
1, 2
1, 2
1, 2
15

HD155121F
• PGA and IQ Demodulator specifications (terminated by 10 kΩ at IQ demodulator output)
Item Mode Min Typ Max Unit Test Condition Note
Input frequency 40 45 60 MHz 1
Gain range — 98 — dB 1
Gain linearity –0.8 — 0.8 dB (in any 20dB window) 1
Gain step — 2 — dB 1
Noise figure 1 — 10.9 14 dB IF2 = 45MHz, bitNo46 1, 2
Noise figure 2 — 21.2 24 dB IF2 = 45MHz, bitNo26 1, 2
Noise figure 3 — 53.4 60 dB IF2 = 45MHz, bitNo6 1, 2
Gain 1 47.0 51.5 56.0 dB IF2 = 45MHz, bitNo46 2
Gain 2 7.0 11.5 16.0 dB IF2 = 45MHz, bitNo26 2
Gain 3 –33.0 –28.5 –24.0 dB IF2 = 45MHz, bitNo6 2
i/p CP 1 –70.5 –66 — dBm IF2 = 45MHz, bitNo46 2
i/p CP 2 –37 –34 — dBm IF2 = 45MHz, bitNo26 2
i/p CP 3 –14 –11 — dBm IF2 = 45MHz, bitNo6 2
IQ phase accuracy — 0.2 1.0 deg. Baseband = 67.7kHz
IQ amplitude mismatch — 0.1 0.5 dB Baseband = 67.7kHz 2
Output DC offset voltage 0 — | 60 | mV | IOUT–IOUTB | and
| QOUT–QOUTB |
Load out = 10kΩ
IQ maximum output swing
(Single ended)
I/Q common mode
output voltage
Note: 1. These values are not tested in mass production.
2. The loss (3.6 dB) of test circuit at PGA input is calculated.
0.8 1.06 — Vp-p Baseband = 67.7kHz
IOUT, IOUTB,
QOUT, QOUTB
Load out = 10kΩ
1.15 1.35 1.55 V
16

HD155121F
• IQ Modulator and Offset PLL specifications (IFLO is supplied by signal generator equipment)
Item Mode Min Typ Max Unit Test Condition Note
Frequency (RF) GSM 880 — 915 MHz 1
PCN 1710 — 1785 MHz
Frequency (LO) GSM 1150 — 1185 MHz 1
PCN 1530 — 1665 MHz
Frequency (IF) GSM — 270 — MHz
PCN — 135 — MHz
RFLO input level –8 — — dBm
IFLO input level –20 –10 — dBm
VCOIN1 & VCOIN2 input level –25 –15 –10 dBm 1
Carrier suppression ratio 31 40 — dBc All ‘1’ GMSK (Differential encode: off)
(Baseband = 67.7kHz)
Side-band suppression ratio 35 40 — dBc I/Q input swing = 1.0Vp-p,
I/Q common mode
input voltage = 1.0Vdc
Phase accuracy GSM — 1.0 2.5 RMS 200kHz BW 1
GSM — 3.0 7.5 peak 200kHz BW
PCN — 1.0 2.4 RMS 200kHz BW
PCN — 3.0 7.0 peak 200kHz BW
Modulation spectrum GSM — –34.0 — dB 200kHz offset 1
PCN — –34.5 — dB 30kHz bandwidth
Spectrum analyzer condition GSM — –68.0 — dB 400kHz offset 1
Detector mode: positive peak PCN — –67.0 — dB 30kHz bandwidth
GSM — –71.0 — dB 600kHz to 1.8MHz offset 1
PCN — –70.0 — dB 30kHz bandwidth
GSM — –71.5 — dB 1.8MHz to 3MHz offset 1
PCN — –72.0 — dB 100kHz bandwidth
GSM — –74.0 — dB 3MHz to 6MHz offset 1
PCN — –74.0 — dB 100kHz bandwidth
GSM — –76.0 — dB 6MHz upward offset 1
PCN — –76.0 — dB 100kHz bandwidth
Isolation of the 1st local input to
TxVCO input
IQ input swing (Single ended) 0.8 1.0 1.2 Vp-p IIN, IINB, QIN, QINB 1
I/Q common mode input voltage 0.8 1.0 1.2 V IIN, IINB, QIN, QINB 1
PLLOUT output current ratio — 1:0.5 — IPLLOUT GSM : IPLLOUT PCN 1
Phase detector
offset current ratio
Note: 1. These values are not tested in mass production.
— 43 — dB 1
0.30 0.35 0.45 offset current / output current
IIN = 1.5V (DC), IINB = 0.5V (DC)
QIN = 1.5V (DC), QINB = 0.5V (DC)
1
17

HD155121F
• IQ Modulator and Offset PLL specifications (IFLO is supplied by signal generator equipment) (cont)
Item Mode Min Typ Max Unit Test Condition Note
Tx noise
in Rx band
Lock up time GSM — 35 80 µsec 1
Note: 1. These values are not tested in mass production.
• IFVCO specifications
Item Mode Min Typ Max Unit Test Condition
Bias current 0.9 2.0 2.5 mA
GSM — –155.1 — dBc/Hz 925MHz to 935MHz
- 10MHz up from Txband
GSM — –164.1 — dBc/Hz 935MHz to 960MHz
- 20MHz up from Txband
PCN — –156 — dBc/Hz 1805MHz - 20MHz up from Txband
PCN — –162 — dBc/Hz 1850MHz - 65MHz up from Txband
PCN — 65 80 µsec
1
18
 Loading...
Loading...