Page 1

User Manual
Installation
Dragon PTN
Interface Module PTN-4-GC-LW/PTN-4-GCB-LW
Interface Module PTN-4-GC-LW/PTN-4-GCB-LW Technical Support
Release 02 11/2018 https://hirschmann-support.belden.com
Page 2

The naming of copyrighted trademarks in this manual, even when not specially indicated, should not
be taken to mean that these names may be considered as free in the sense of the trademark and
tradename protection law and hence that they may be freely used by anyone.
© 2018 Hirschmann Automation and Control GmbH
Manuals and software are protected by copyright. All rights reserved. The copying, reproduction,
translation, conversion into any electronic medium or machine scannable form is not permitted,
either in whole or in part. An exception is the preparation of a backup copy of the software for your
own use.
The performance features described here are binding only if they have been expressly agreed when
the contract was made. This document was produced by Hirschmann Automation and Control GmbH
according to the best of the company's knowledge. Hirschmann reserves the right to change the
contents of this document without prior notice. Hirschmann can give no guarantee in respect of the
correctness or accuracy of the information in this document.
Hirschmann can accept no responsibility for damages, resulting from the use of the network
components or the associated operating software. In addition, we refer to the conditions of use
specified in the license contract.
You can get the latest version of this manual on the Internet at the Hirschmann product site
(www.doc.hirschmann.com).
Hirschmann Automation and Control GmbH
Stuttgarter Str. 45-51
72654 Neckartenzlingen
Germany
2 Interface Module PTN-4-GC-LW/PTN-4-GCB-LW
Release 02 11/2018
Page 3

Contents
1. INTRODUCTION ........................................................................................................... 5
1.1 General ................................................................................................. 5
1.2 Manual References ............................................................................... 5
2. MODULE DESCRIPTION ................................................................................................ 6
2.1 Front Panel ........................................................................................... 6
2.1.1 Insert/Remove Module into/from Node ................................................... 7
2.1.2 LEDs ............................................................................................................ 7
2.1.3 Connectors ................................................................................................. 8
2.2 Functional Operation ............................................................................ 9
2.2.1 Media Module for Ethernet: Interfacing to a LAN or WAN Network ........ 9
2.2.2 Ethernet Service ...................................................................................... 10
2.2.3 Voice Service ............................................................................................ 11
2.2.4 I/O with the Central Switching Module (=CSM) ...................................... 11
2.2.5 Synchronization / Clock Distribution / Network Timing .......................... 11
2.2.6 EFM-F IEEE 802.3ah (=Ethernet in the First Mile – Fiber) (future) .......... 11
2.2.7 MPLS-TP Compliancy ............................................................................... 11
2.2.8 PoE (=Power Over Ethernet) on 4-GC-LW ............................................... 12
2.2.9 Smart SFP ................................................................................................. 13
2.2.10 Storm Control on Ethernet LAN Port ....................................................... 14
2.2.11 BPDU Guard on Ethernet LAN Port ......................................................... 15
2.2.12 MRP (=Media Redundancy Protocol) Support ........................................ 15
2.3 Onboard Interfaces ............................................................................. 16
2.3.1 Straps ....................................................................................................... 16
2.3.2 Rotary DIP Switches ................................................................................. 16
3. MODULE SPECIFICATIONS .......................................................................................... 17
3.1 General Specifications ........................................................................ 17
3.2 Other Specificiations .......................................................................... 17
3.3 Ordering Information ......................................................................... 17
4. ABBREVIATIONS ........................................................................................................ 18
List of figures
Figure 1 Front Panel ...................................................................................................................... 6
Figure 2 RJ45 Ethernet port ........................................................................................................... 8
Figure 3 General Example: LAN/WAN ........................................................................................... 9
Figure 4 Detailed Example: Interfacing to a LAN or WAN Network ............................................ 10
Figure 5 PoE Example .................................................................................................................. 13
Figure 6 SDH/SONET over Dragon PTN via Smart SFPs ............................................................... 14
Figure 7 MRP: General Example .................................................................................................. 15
Figure 8 4-GC-LW/4-GCB-LW: Side View ..................................................................................... 16
Figure 9 Hardware Edition ........................................................................................................... 16
Interface Module PTN-4-GC-LW/PTN-4-GCB-LW 3
Release 02 11/2018
Page 4

List of Tables
Table 1 Manual References ........................................................................................................... 6
Table 2 LED Indications In Boot Operation ................................................................................... 7
Table 3 LED Indications in Normal Operation ............................................................................... 7
Table 4 RJ45 Ethernet port: Pin Assignments ............................................................................... 8
Table 5 Synchronization / Clock Distribution / Network Timing Overview ................................. 11
Table 6 Other Specifications ........................................................................................................ 17
4 Interface Module PTN-4-GC-LW/PTN-4-GCB-LW
Release 02 11/2018
Page 5
1. INTRODUCTION
1.1 General
This document is valid as of Dragon PTN Release 4.0DR.
This document describes the 4-GC-LW and 4-GCB-LW interface module (=IFM). The 4-GC-LW
supports PoE whereas the 4-GCB-LW not. These IFMs provide four 1Gbps LAN/WAN ports on
the front panel (LAN = Local Area Network; WAN = Wide Area Network). Port 1 is a gigabit
combo port (SFP/RJ45) whereas ports 2, 3 and 4 are 1 gigabit RJ45 ports. Each individual port
can be configured as either LAN or WAN port via HiProvision (=Dragon PTN Management
System). By default, each port is configured as WAN port. On the 4-GC-LW IFM, these RJ45
ports can deliver PoE (=Power Over Ethernet) as well. 4-GC-LW refers to ‘4 ports – Gigabit
Combo port – LAN WAN’.
Verify the 'Dragon PTN Bandwidth Overview' manual (Ref. [100] in Table 1) to see in which
node and IFM slot this IFM can be used.
Main supported features:
Gigabit Ethernet Ports:
1 x Combo (one of the two options below):
1 x RJ45 (Cu, electrical): 10/100/1000BASE-T;
1 x SFP (Fiber, optical): 1000BASE-X / Smart SFP;
3 x RJ45 (Cu, electrical): 10/100/1000BASE-T;
Synchronization
SyncE;
PTP IEEE 1588v2 (=Precision Time Protocol);
on 4-GC-LW: PoE IEEE 802.3at ;
Smart SFP;
LAN or WAN function selectable per port;
(future) EFM-F IEEE 802.3ah (=Ethernet in the first Mile – Fiber);
E-Tree in an Ethernet Service;
MRP (=Media Redundancy Protocol) Support.
1.2 Manual References
Table 1 is an overview of the manuals referred to in this manual. ‘&’ refers to the language
code, ‘*’ refers to the manual issue. All these manuals can be found in the HiProvision
(=Dragon PTN Management System) Help function.
Interface Module PTN-4-GC-LW/PTN-4-GCB-LW 5
Release 02 11/2018
Page 6
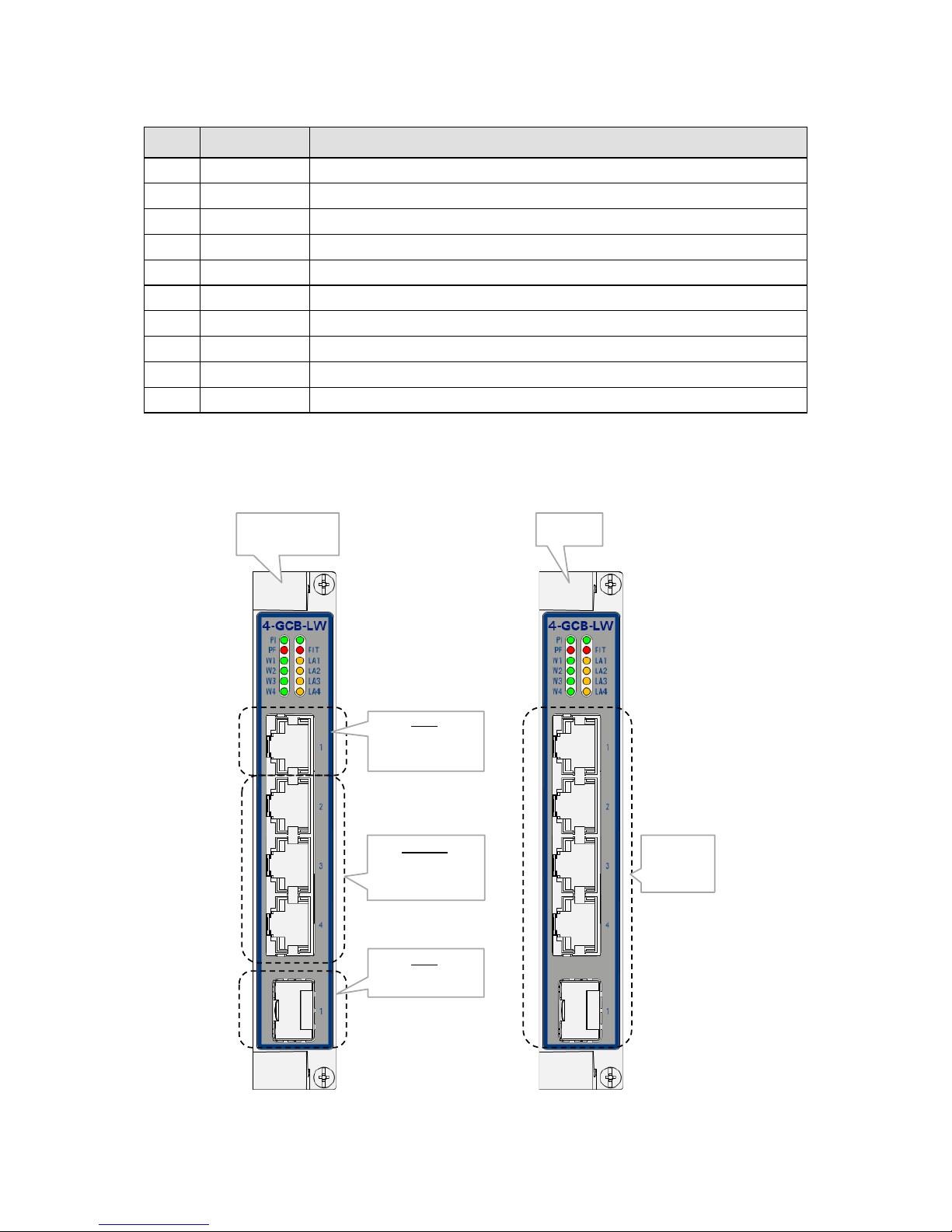
Table 1 Manual References
Ref.
Number
Title
[1]
DRA-DRM821-&-*
Dragon PTN and HiProvision Operation
[2]
DRA-DRM801-&-*
Dragon PTN Installation and Operation
[3]
DRA-DRM802-&-*
Dragon PTN Aggregation Nodes: PTN2210, PTN2209, PTN2206, PTN1104
[4]
DRA-DRM803-&-*
Dragon PTN Switching Module: PTN-CSM310-A
[5]
DRA-DRM808-&-*
Dragon PTN Interface Module: PTN-1-10G-LW
[6]
DRA-DRM817-&-*
Dragon PTN Interface Module: PTN-4-GO-LW
[7]
DRA-DRM819-&-*
Dragon PTN Interface Module: PTN-8-FXS
[8]
DRA-DRM811-&-*
Dragon PTN TRMs (Transmit Receive Modules: SFP, XFP)
[9]
DRA-DRM810-&-*
Dragon PTN General Specifications
[100]
DRA-DRM828-&-*
Dragon PTN Bandwidth Overview
2. MODULE DESCRIPTION
2.1 Front Panel
Figure 1 Front Panel
Port 2 ,3,4:
gigabit Ethernet port
RJ45
(including PoE)
Port1:
Gigabit Ethernet
combo port
RJ45, includes PoE
Same as
4-GC-LW but
without PoE
Port1:
Gigabit Ethernet
combo port: SFP
4-GC-LW
(HW Edition > 8)
4-GCB-LW
6 Interface Module PTN-4-GC-LW/PTN-4-GCB-LW
Release 02 11/2018
Page 7

2.1.1 Insert/Remove Module into/from Node
See ‘Dragon PTN Installation and Operation Manual’ Ref.[2].
2.1.2 LEDs
The meaning of the LEDs depends on the mode of operation (= boot or normal) in which the
4-GC-LW/4-GCB-LW module currently is running. After plugging in the module or rebooting
it, the module turns into the boot operation, see Table 2. After the module has gone through
all the cycles in the table below (=rebooted successfully), the module turns into the normal
operation, see LEDs in Table 3.
Table 2 LED Indications In Boot Operation
Cycle
PI
PF
FLT
Spare LED
W[1..4]
LA[1..4]
1
x
---
Slow blinking
---
---
---
2
x
---
Fast blinking
---
---
---
3
x
---
---
---
---
---
4
x
--- x --- x ---
5
x
---
---
--- x ---
x : LED is lit / --- : LED is not lit
The sub cycle times may vary. The entire boot cycle time [15] takes approximately 3 minutes.
Table 3 LED Indications in Normal Operation
LED
Color
Status
PI (=Power Input)
Not lit, dark
+12V power input to the board not OK
Green
+12V power input to the board OK
PF (=Power Failure)
Not lit, dark
power generation on the board itself is OK
Red
power generation on the board itself is erroneous
FLT (=FauLT)
Not lit, dark
no other fault or error situation, different from PF, is active on the module
Red
a fault or error situation, different from PF, is active on the module
W<port n°>
Not lit, dark
The link on port<port n°> is a LAN link
Green
The link on port<port n°> is a WAN link
LA<port n°>
Normal SFP or RJ45
Not lit, dark
The link on port<port n°> is down
Yellow lit
The link on port<port n°> is up, no activity
Yellow blinking
The link on port<port n°> is up, with activity
Smart SFP (see §2.2.9)
Not lit, dark
The port is administratively down or no service programmed on this port
Yellow blinking
A service is programmed on this port.
CAUTION: The link status and link activity to the SDH/SONET network cannot be
derived from this LA LED, instead it must be derived from the Smart SFP
status/alarms information in HiProvision.
Interface Module PTN-4-GC-LW/PTN-4-GCB-LW 7
Release 02 11/2018
Page 8

2.1.3 Connectors
This module has following ports:
Port1 = Combo Ethernet port: A ‘Combo’ port is a double Ethernet port with an electrical
(RJ45) and optical (SFP) port. Only one of the two ports can be active at the same time,
either the RJ45 or the SFP port. If an SFP link comes up on the SFP, the SFP link has
always priority over a possible RJ45 link. An RJ45 link on this port can only become active
if no link comes up on the SFP. If for example no SFP link is up, and the RJ45 brings up the
link first, the RJ45 port will become active. If an SFP link comes up later on, the SFP port
will become the active one and the RJ45 port will be deactivated. The SFPs that can be
used for this port can be found in Ref. [8] in Table 1.
RJ45: 10/100/1000 Gigabit Ethernet copper port, see figure and table below;
SFP: 100/1000 Gigabit Ethernet fiber port / Smart SFP;
NOTE: The behavior described above counts for both SFP and Smart SFPs;
Port2, 3, 4 = RJ45 Ethernet port: 10/100/1000Base-T Gigabit Ethernet copper port. Use
CAT5E shielded cables for 10/100Base-T and CAT6 shielded cables for 1000Base-T to
connect these ports.
Table 4 RJ45 Ethernet port: Pin Assignments
Pin No.
Signal 100/100Base-T
Signal 1000Base-T
1
Transmit output (+)
DA+ 2 Transmit output (-)
DA- 3 Receive input (+)
DB+ 4 ---
DC+ 5 ---
DC-
6
Receive input (-)
DB-
7
---
DD+ 8 ---
DD-
Figure 2 RJ45 Ethernet port
1
8
8 Interface Module PTN-4-GC-LW/PTN-4-GCB-LW
Release 02 11/2018
Page 9

2.2 Functional Operation
The 4-GC-LW/4-GCB-LW performs following major tasks:
2.2.1 Media Module for Ethernet: Interfacing to a LAN or WAN Network
WAN ports interconnect nodes within the Dragon PTN network (MPLS-TP) whereas LAN
ports interconnect the nodes with their applications.
Each Ethernet front port can be configured individually as LAN or a WAN port in HiProvision.
By default, each port is configured as WAN port. A LAN port talks Ethernet and a WAN port
talks MPLS-TP. As a result, the node can serve as an edge node (or LER = Label Edge Router)
where traffic is received on a LAN port, mapped into pseudowire and forwarded to the
correct label switched path on a WAN port.
When the module needs a WAN port configuration, typically combo port 1 will be used for
this because this port offers an SFP port which can be used to cover larger distances over
fiber within the WAN. The other ports can also be configured as WAN port, but these ports
must be hooked up to a copper cable via RJ45, which leads to shorter distances.
For a configured application service, the node can operate as a:
LER = Label Edge Router or access node: The node is located on the edge between the
LAN and WAN. The node converts Ethernet into MPLS-TP and vice versa;
LSR = Label Switching Router: The node is fully located in the WAN. The node has no end-
points for the configured application service, it only forwards MPLS-TP traffic via label
switched paths;
Figure 3 General Example: LAN/WAN
LER LER
LAN WAN LAN
router
router
HiProvision PC
(=Dragon PTN Man agement)
Dragon PTN MPLS-TP
Network
Drago n PTN Node
LSR
LSR
LSR
Interface Module PTN-4-GC-LW/PTN-4-GCB-LW 9
Release 02 11/2018
Page 10

Figure 4 Detailed Example: Interfacing to a LAN or WAN Network
2.2.2 Ethernet Service
a. General
The 4-GC-LW/4-GCB-LW IFM access or end-points communicate over the Dragon PTN
network via an Ethernet service. This service must be configured via HiProvision. This service
can operate port or VLAN based. An optional E-Tree can be configured as well on this
Ethernet service.
b. Port Based / VLAN Based
Port based: Use this mode if all the traffic on a port must be transported transparently in
one and the same service;
VLAN based/VLAN ID: Use this mode if each VLAN (ID) on a port must have its own
service. Ethernet packets with the configured VLAN ID will be forwarded in this service,
other VLAN IDs and untagged packets will be dropped. This behavior can be overruled by
a more advanced VLAN processing in the ‘VLAN Tagging/Untagging’ feature in
HiProvision. This feature also supports VLAN translation which replaces VLAN ID ‘x’ into
VLAN ID ‘y’.
c. E-Tree
An E-Tree is a rooted (not routed) point-to-multipoint partial service within a programmed
Ethernet service. E-Tree can be used as a security precaution to separate different customers
(=leafs) using the same Ethernet service while accessing one or more ISPs (=roots).
When an E-Tree is used, each service endpoint is designated as either leaf or root. A leaf can
only communicate with a root. A root can communicate with all the roots and leafs.
CSM
CSM310-A
IFC1
4-GC-LW
WAN: MPLS-TP (on fiber, copper) between Dragon PTN nodes
LAN: Ethernet (on copper) external devices
IFC2
4-GC-LW
CSM
CSM310-A
IFC2
4-GC-LW
LAN1
LAN2
LAN3
Switch
ETH
MPLS-TP
WAN (via SFP on fiber)
Dragon PTN No de Dragon PTN No de
Switch
ETH
MPLS-TP
10 Interface Module PTN-4-GC-LW/PTN-4-GCB-LW
Release 02 11/2018
Page 11

2.2.3 Voice Service
The 4-GC-LW/4-GCB-LW IFM ports can be configured in the Ethernet part of the Voice
service. See Ref. [1] and Ref.[7] in Table 1 for more information on the Voice service.
2.2.4 I/O with the Central Switching Module (=CSM)
The 4-GC-LW/4-GCB-LW module receives traffic (Ethernet or MPLS-TP) via its front panel
ports and forwards this to the CSM via the backplane. The CSM does all the processing on
this data (synchronization, CRC checks, conversions, switching…). The resulting data will be
forwarded via the backplane to one of the IFMs in the node.
2.2.5 Synchronization / Clock Distribution / Network Timing
The Dragon PTN network provides a number of mechanisms to perform synchronization /
clock distribution / network timing. The CSM makes sure that all the included IFMs in the
node are synchronized. See the table below for an overview of the mechanisms that are
supported on the 4-GC-LW/4-GCB-LW module.
It means that the front ports of the 4-GC-LW/4-GCB-LW module can be used to recover a
clock from an incoming data stream and redistribute this clock via an outgoing data stream;
Table 5 Synchronization / Clock Distribution / Network Timing Overview
Mechanism
Domain
What is
Synchronized?
Purpose
SyncE
Network wide
Clock Frequency
Distribute a synchronous clock, based on a PRC (=Primary
Reference Clock), network wide over all the nodes that need
it.
PTP IEEE 1588v2
Network wide
Timestamping
A protocol to synchronize real-time clocks (timestamping) in
Dragon PTN network elements and/or connected devices.
a. SyncE (=Synchronous Ethernet)
See the manuals in Ref.[1] and Ref.[4], [4b] for more detailed information.
b. PTP IEEE 1588v2 (=Precision Time Protocol)
See the HiProvision manual in Ref.[1] for more detailed information.
2.2.6 EFM-F IEEE 802.3ah (=Ethernet in the First Mile – Fiber) (future)
Future planned.
2.2.7 MPLS-TP Compliancy
See the CSM manual in Ref.[4], [4b].
Interface Module PTN-4-GC-LW/PTN-4-GCB-LW 11
Release 02 11/2018
Page 12

2.2.8 PoE (=Power Over Ethernet) on 4-GC-LW
NOTE: An NSM-A and 4-GC-LW are required to deliver PoE. NSM-B and 4-GCB-LW do not
support PoE.
PoE is a technology that allows a Powered Device (=PD, e.g. IP telephones, IP cameras etc.)
to receive power from ‘Power Sourcing Equipment’ (=PSE, e.g. the Dragon PTN node). An
example with PoE on/off can be found in Figure 5.
Dragon PTN nodes are able to deliver PoE when one (or two) external PoE PSU(s) is (are)
connected to the NSM via the PoE connectors. A possible external PoE PSU and how to
connect it can be found in the manual Ref.[3], [3b] see Table 1.
The PD receives power in parallel to data, over the existing CAT-5 Ethernet infrastructure.
PoE integrates data and power on the same cable, it keeps the structured cabling safe and
does not interfere with concurrent network operation.
PoE delivers a minimum of 48V of DC power over shielded/unshielded twisted-pair wiring for
terminals consuming less than 25.5 Watts of power.
Before the power is delivered to a connected device, a protocol measures whether that
device is a PoE device and how much power it needs (power classification). If required, the
necessary power will be delivered by the PSE with a maximum of 32 Watts per port.
PoE is supported on all the electrical RJ45 ports of the 4-GC-LW module. All these ports can
deliver power according to the 802.3af (PoE) and 802.3at (PoE+) standard.
Via HiProvision it is possible to enable/disable PoE per port and to verify which ports in each
node are PoE enabled;
Power management is supported, i.e. the Dragon PTN node decides in an intelligent way
which PoE ports will get power and which ones will not. There are a lot of possible scenarios
in which power management must tune its delivered power on each port. Some
configuration/status parameters in HiProvision used by power management are:
External PoE PSU power;
Available power budget;
Power Priority / Port Priority;
Power Class (class 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 configured and detected);
Power management also offers PoE diagnostics in HiProvision.
12 Interface Module PTN-4-GC-LW/PTN-4-GCB-LW
Release 02 11/2018
Page 13

Figure 5 PoE Example
2.2.9 Smart SFP
Smart SFP is a hot-pluggable optical transceiver that converts incoming STM/OC frames from
a fiber-optic SDH/SONET network into Ethernet frames at the 4-GC-LW/4-GCB-LW front port
1 or vice versa for outgoing frames. As a result, Dragon PTN allows to transparently transport
synchronous digital bit streams from an SDH/SONET network via the 4-GC-LW/4-GCB-LW
IFMs.
Smart SFPs must be used in a point-to-point port based Ethernet service over Dragon PTN.
The Smart SFP has an optional security feature onboard which allows to secure the point-topoint connection to only two dedicated MAC addresses. This can be done via setting the
Destination MAC Address in HiProvision for the Smart SFPs. Furthermore, the Smart SFPs
need some extra Quality of Service settings in HiProvision, see Ref. [1] in Table 1.
For clocking/synchronization, SyncE must be configured in the nodes that have Smart SFPs
plugged in.
Smart SFPs also generate appropriate alarms, e.g. Loss of Signal, Loss of Frame etc.
NOTE: Smart SFP is also called TSoP (Transparent Sonet/SDH over Packet).
NOTE: The supported Smart SFPs and speeds can be found in Ref. [8] in Table 1.
NOTE: SFPs are typically used on WAN ports whereas Smart SFPs are used on LAN ports.
External PoE PSUs:
AC/DC: 942 235-001
DC/DC: 942 235-002
56 VDC
56 VDC
PoE Connector Cable
942 256-105
4-GC-LW
PoE
NSM
PoE ON
Power
PoE OFF
Data
PoE Power & Data
External PSUs
Interface Module PTN-4-GC-LW/PTN-4-GCB-LW 13
Release 02 11/2018
Page 14

Figure 6 SDH/SONET over Dragon PTN via Smart SFPs
2.2.10 Storm Control on Ethernet LAN Port
NOTE: Storm Control is not relevant/supported on WAN Ports;
A traffic storm is the growing of excessive network traffic due to Ethernet packets flooding
the LAN. Such a storm can for example occur because of a data loop in the network due to
no or misconfiguration of MSTP. These storms degrade the network performance and must
be avoided whenever possible.
The storm control feature:
is an extra protection against these traffic storms;
can be configured on the IFM ports;
limits the amount of unlearned received data (Unicast, Broadcast, Multicast) on the LAN
port ingress or input side;
limits the amount of transmitted data (all data) on the LAN port egress or output side;
Data that exceeds the configured limitations will be dropped. As a result, a possible data
storm cannot overload the node processor or the node will limit outgoing data.
See Ref. [1] in Table 1 for more configuration information in HiProvision.
Dragon PTN MPLS-TP
Network
4-GC-LW:
Smart SFP on
Port1 (LAN)
STM/OC
Frames
STM/OC
Frames
SDH/SONET
Network
4-GC-LW:
Smart SFP on
Port1 (LAN)
SDH/SONET
Network
14 Interface Module PTN-4-GC-LW/PTN-4-GCB-LW
Release 02 11/2018
Page 15

2.2.11 BPDU Guard on Ethernet LAN Port
NOTE: BPDU Guard is not relevant/supported on WAN Ports;
BPDU Guard (=Bridge Protocol Data Unit) is a LAN port property or feature that:
shuts down the LAN port when a BPDU packet enters this port;
sends out dummy BPDU packets.
As a result, this feature or IFM:
protects the network against possible loops created via this IFM, although this IFM does
not support MSTP;
protects a running MSTP protocol somewhere else in the Dragon PTN network from
external MSTP influences via this LAN port, e.g. root bridge protection etc...
See Ref. [1] in Table 1 for more configuration information in HiProvision.
2.2.12 MRP (=Media Redundancy Protocol) Support
The MRP is a protocol (IEC 62439-2) especially designed for industrial applications which
need a predictable fail-over time. This protocol can only be used in a ring-topology network
and makes sure that the ring network stays loop-free. MRP does in ring networks what
spanning tree does in meshed networks but with much faster convergence times. The ring
has one selected MR Manager (MRM) and a number of MR Clients (MRC). The two Dragon
PTN nodes act as MRC. See Ref. [1] in Table 1 for more configuration information in
HiProvision.
Figure 7 MRP: General Example
Dragon P TN
MPLS-TP N etwork
Drag on PTN Node
MRP Access Ring
HiProvision
Access switches
running MRP
MRP Access Ring
MRC
MRC MRM MRC
MRM interrupting the loop
by blocki ng the port
MRC
MRC
Monitored Li nk
MRP
Entry Node +
Ring port
MRP
Entry Node +
Ring port
Dragon P TN
MPLS-TP N etwork
Interface Module PTN-4-GC-LW/PTN-4-GCB-LW 15
Release 02 11/2018
Page 16

2.3 Onboard Interfaces
Figure 8 4-GC-LW/4-GCB-LW: Side View
2.3.1 Straps
No user relevant straps. The straps J3, J9 and J17 in Figure 8 are straps for service engineers
only! These straps MUST NOT BE CHANGED, leave them with the default settings as
indicated in Figure 8.
2.3.2 Rotary DIP Switches
a. Hardware Edition
The Hardware Edition (labeled as CARD_ID) is set in decimal code using rotary switches S2 to
S3 (S3 = most significant). It can be read out as well via HiProvision. This edition has been
factory set and MUST NOT BE CHANGED!
Example: Setting S3=’0’ and S2=’5’ indicates Hardware Edition ‘5’ (dec).
Figure 9 Hardware Edition
Hardware
Edition
16 Interface Module PTN-4-GC-LW/PTN-4-GCB-LW
Release 02 11/2018
Page 17

3. MODULE SPECIFICATIONS
3.1 General Specifications
For general specifications like temperature, humidity, EMI ... see Ref.[9] in Table 1.
3.2 Other Specificiations
Table 6 Other Specifications
Description
Value
Weight
4-GC-LW: 0.25 kg / 0.6 lb
4-GCB-LW: 0.18 kg / 0.4 lb
MTBF
4-GC-LW: 80 years at 25°C/77°F
4-GCB-LW: pending
Power Consumption
6W (measured at 25°C/77°F, with data transport)
Module Size
width: 20.32 mm / 0.8 inches
height: 126 mm / 4.96 inches
depth: 195 mm / 7.68 inches
3.3 Ordering Information
PTN-4-GC-LW: 942 236-001;
PTN-4-GCB-LW: 942 236-008.
Interface Module PTN-4-GC-LW/PTN-4-GCB-LW 17
Release 02 11/2018
Page 18

4. ABBREVIATIONS
BPDU
Bridge Protocol Data Unit
CE
Conformité Européenne
CSM
Central Switching Module
EFM-F
Ethernet in the First Mile Over Point-to-Point Fiber
EMI
Electromagnetic Interference
FLT
Fault
IEC
International Electrotechnical Commission
IEEE
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
IETF
Internet Engineering Task Force
IFM
InterFace Module
ISP
Internet Service Provider
LAN
Local Area Network
LER
Label Edge Router
LSR
Label Switching Router
LVD
Low Voltage Directive
MIB
Management Information Base
MRC
Media Redundancy Clients
MRM
Media Redundancy Manager
MRP
Media Redundancy Protocol
MSTP
Multiple Spanning Tree
MTBF
Mean Time Between Failures
PD
Powered Device
PF
Power Failure
PI
Power Input
PoE
Power Over Ethernet
PSC
Protection State Coordination
PSE
Power Source Equipment
PSU
Power Supply Unit
PTN
Packet Transport Network
PTP
Precision Time Protocol
SNMP
Simple Network Management Protocol
SyncE
Synchronous Ethernet
TSoP
Transparent Sonet/SDH over Packet
18 Interface Module PTN-4-GC-LW/PTN-4-GCB-LW
Release 02 11/2018
Page 19

WAN
Wide Area Network
Interface Module PTN-4-GC-LW/PTN-4-GCB-LW 19
Release 02 11/2018
 Loading...
Loading...