Page 1

Communication Instruction Manual
IM3523
IM3533
IM3533-01
LCR METER
IM3570
IMPEDANCE ANALYZER
IM3590
CHEMICAL
IMPEDANCE ANALYZER
August 2012 Revised edition 4 IM3570A983-04 12-08H
Page 2

Page 3
Contents
Contents
i
1
Introduction.....................................................1
Safety Information..........................................1
Chapter 1 Specifications 3
1.1 RS-232C Specifications .........................3
1.2 GP-IB Specifications ..............................4
1.3 USB Specifications ................................4
1.4 LAN Specifications .................................4
Chapter 2 Model IM3570
Connection and
Setting 5
2.1 Overview of Communication ..................5
2.2 RS-232C Connection and Settings ........7
Connecting the RS-232C Cable ..............7
Setting RS-232C ......................................8
2.3 GP-IB Connection and Settings .............9
Connecting the GP-IB Cable ...................9
Setting GP-IB ...........................................9
2.4 USB Settings and Connection .............11
Setting USB ...........................................11
Connecting the USB Cable ....................12
2.5 LAN Settings and Connection ..............13
LAN Settings ..........................................13
Connecting a LAN Cable .......................18
2.6 Remote Mode ......................................19
3.4 RS-232C Connection and Settings
(when connected to the Z3001) ...........26
Connecting the RS-232C Cable ............ 26
Setting RS-232C ................................... 27
3.5 LAN Settings and Connection
(when connected to the Z3002) ...........29
LAN Settings ......................................... 29
Connecting a LAN Cable ...................... 33
3.6 Remote Mode .......................................34
Chapter 4 Model IM3533/
IM3533-01/ IM3590
Connection and
Setting 35
4.1 Overview of Communication ................35
4.2 USB Settings and Connection ..............37
Setting USB .......................................... 37
Connecting the USB Cable ................... 38
4.3 GP-IB Connection and Settings
(when connected to the Z3000) ...........39
Connecting the GP-IB Cable ................. 39
Setting GP-IB ........................................ 39
4.4 RS-232C Connection and Settings
(when connected to the Z3001) ...........41
Connecting the RS-232C Cable ............ 41
Setting RS-232C ................................... 42
4.5 LAN Settings and Connection
(when connected to the Z3002) ...........43
LAN Settings ......................................... 43
Connecting a LAN Cable ...................... 48
4.6 Remote Mode .......................................49
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Chapter 3 Model IM3523
Connection and
Setting 21
3.1 Overview of Communication ................21
3.2 USB Settings and Connection .............22
Setting USB ...........................................22
Connecting the USB Cable ....................23
3.3 GP-IB Connection and Settings
(when connected to the Z3000) ...........24
Connecting the GP-IB Cable .................24
Setting GP-IB .........................................24
Appendix A 1
Appendix 1 Checking the USB Virtual COM ..
Port.........................................A 1
Appendix 2 Checking RS-232C and USB
Communication in Windows...A 2
Appendix 3 Checking LAN Communication in
Windows.................................A 8
11
12
Appendix
Index
索
引
Page 4

ii
Contents
Page 5

1
Introduction
This instruction manual provides details on the communication interfaces of the IM3523, IM3533, IM3533-01
LCR Meter, IM3570 Impedance Analyzer and IM3590 Chemical Impedance Analyzer.
In this document, the "instrument" means the IM3523, IM3533, IM3533-01, IM3570 and IM3590.
Safety Information
This manual contains information and warnings essential for safe operation of the instrument and for maintaining it in safe operating condition. Be fo re u sing it, b e sure to ca re fully r ead the follo win g safe ty pr ecautio ns.
Safety Symbols
The following symbols in this manual indicate the relative importance of cautions and warnings.
Indicates that incorrect operation presents a significant hazard that could result in serious injury or death to the user.
Indicates that incorrect operation presents a possibility of injury to the user or damage to
the product.
Advisory items related to performance or correct operation of the product.
Notation
Symbols in this manual
Indicates the prohibited action.
p.
* Indicates that descriptive information is provided below.
[ ]
CURSOR
(Bold character)
Windows
Dialogue Dialogue box represents a Windows dialog box.
Indicates the location of reference information.
Menus, commands, dialogs, buttons in a dialog, and other names on the screen and the keys are
indicated in brackets.
Bold characters within the text indicate operating key labels.
Unless otherwise specified, “Windows” represents Windows 95, 98, Me, Widows NT4.0, Windows
2000, Windows XP, Windows Vista, or Windows 7.
Mouse Operation
Click: Press and quickly release the left button of the mouse.
Right-click: Press and quickly release the right button of the mouse.
Double click: Quickly click the left button of the mouse twice.
Drag:
While holding down the left button of the mouse, move the mouse and then release the left button
to deposit the chosen item in the desired position.
Page 6

2
Page 7
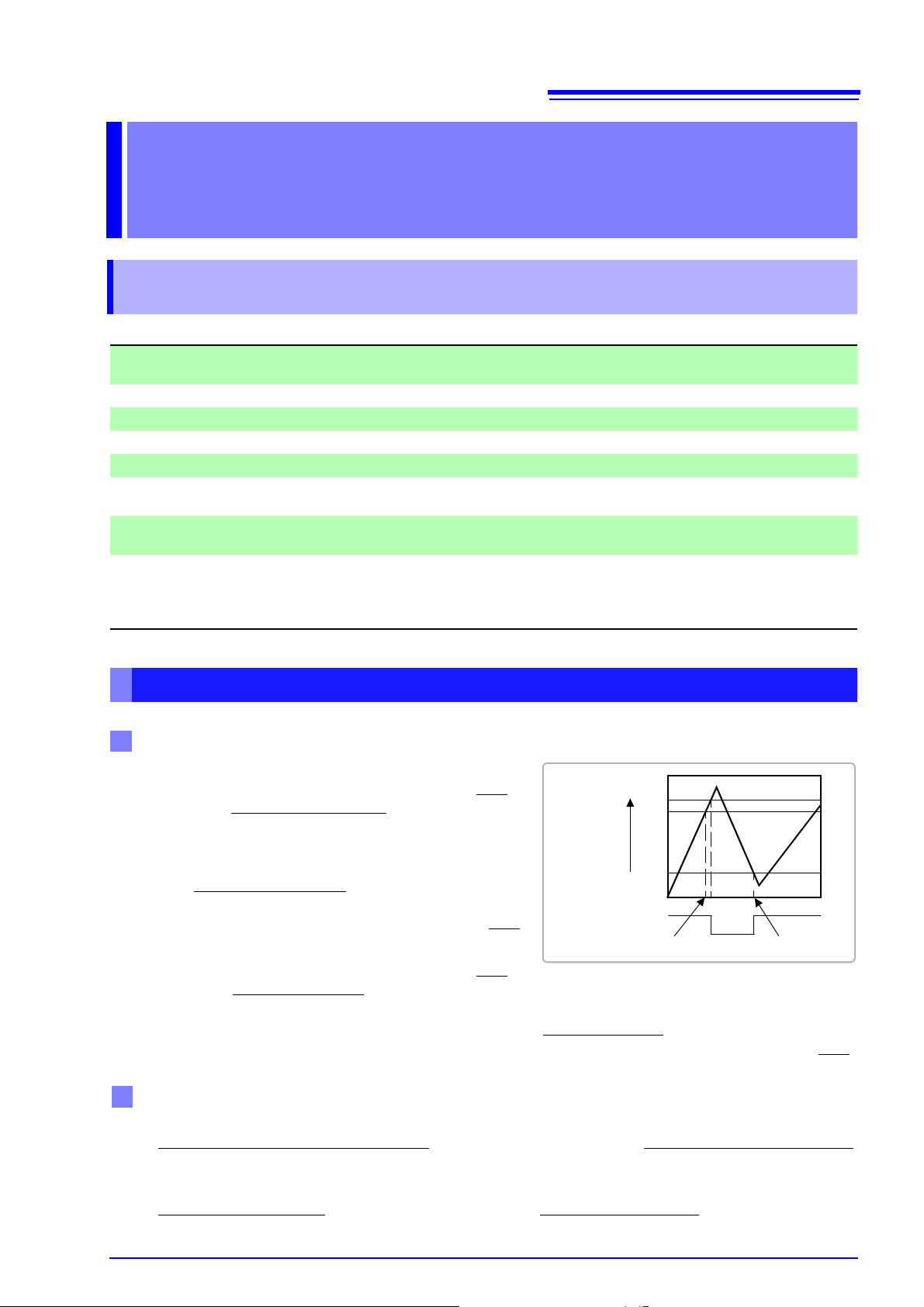
1.1
Control during Receiving
CA(RTS)
OFF
ON
25%
85%
Input Buffer
Usage
Amount
Buffer Space
75%
Send XOFF
Send XON
Control during Sending
RS-232C Specifications
3
Specifications Chapter 1
1.1 RS-232C Specifications
Transmission Method
Transmission Speed 9600 bps, 19200 bps, 38400 bps, 57600 bps
Data Bits 8 bits
Parity None
Stop bit 1 bits
Message terminator
(delimiter)
Flow control
Input voltage
Electrical
Specifications
level
Output voltage
level
Communication method: Full duplex
Synchronous method: Start-stop synchronization
CR+LF, CR
Hardware (RTS/CTS control), software (XON/XOFF control)
"Handshake (About Buffer Flow Control)" (p. 3)
5 to 15 V ........ON
-15 to -5 V ....... OFF
5 to 9 V ..........ON
-9 to -5 V ........ OFF
Chapter 1 Specifications
Handshake (About Buffer Flow Control)
When using hardware (RTS/CTS control):
• When the data in the receive buffer exceeds 85% of
the buffer, CA(RTS) is set to OFF
notified that there is not much space remaining in the
buffer.
• Processing of the data in the buffer continues, and
then CA(RTS) is set to ON
fied that there is sufficient remaining space in the buffer when the amount of data becomes less than 25%
When using software (XON/XOFF control):
• When the data in the receive buffer exceeds 75% of
the buffer, XOFF(13H) is sent
the buffer.
• Processing of the data in the buffer continues, and then XON(11H) is sent and the controller is notified
that there is sufficient remaining space in the buf fer when the amo unt of dat a becomes less than 25%
When using hardware (RTS/CTS control):
• When CB(CTS) is confirmed to be OFF, the sending of data is halted. When it is confirmed to be ON,
the sending of data is resumed.
When using software (XON/XOFF control):
• When XOFF is received, the sending of data is halted. When XON is received, the sending of data is
resumed.
and the controller is
and the controller is noti-
.
and the controller is notified that there is not much space remaining in
.
Page 8

4
1.2 GP-IB Specifications
1.2 GP-IB Specifications
SH1 Supports all source handshake functions.
AH1 Supports all acceptor handshake functions.
T6 Supports standard talker functions.
L4 Supports standard listener functions.
SR1 Supports all service request functions.
RL1 Supports all remote/local functions.
PP0 Parallel poll functions are not supported.
DC1 Supports all device clear functions.
DT1 Supports all device trigger functions.
C0 Controller functions are not supported.
Code used: ASCII code
Supports serial poll functions.
Talk only mode is not supported.
Supports the talker cancel function by MLA (My Listen Address).
Listener only mode is not supported.
Supports the listener cancel function by MTA (My Talk Address).
1.3 USB Specifications
Connector Series B receptacle
Compliance standard USB2.0 (Full Speed/High Speed)
No. of ports 1
Class Communication class
Supported OS Windows 2000, XP, Vista, 7
1.4 LAN Specifications
Connector RJ-45 connector × 1
Compliance standard IEEE 802.3-compliant Ethernet
Transfer system 10BASE-T/ 100BASE-TX Auto detected
Protocol TCP/IP
Function Command control
Page 9
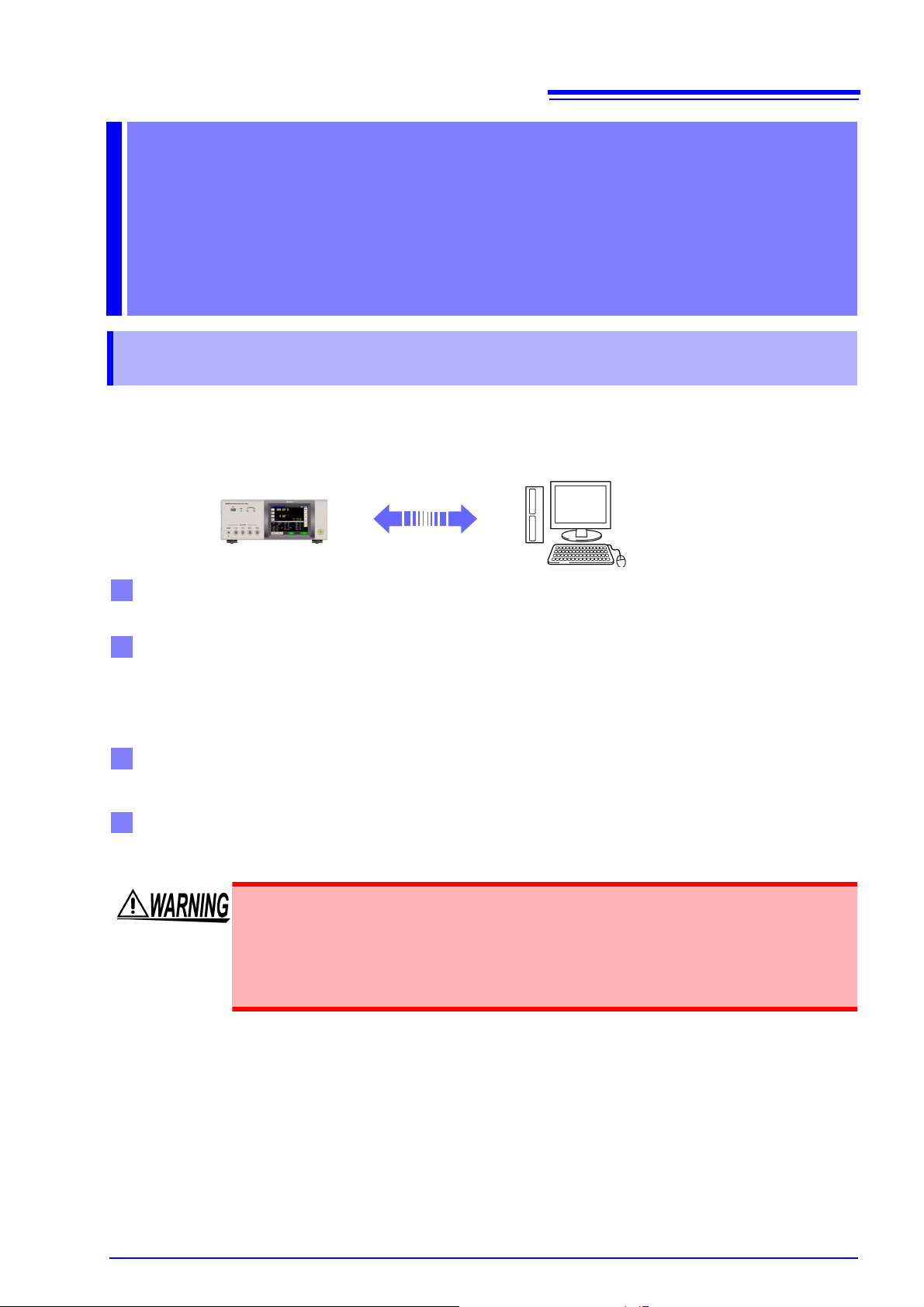
Model IM3570
RS-232C communication (p. 7)
GP-IB communication (p. 9)
USB communication (p. 11)
LAN communication (p. 13)
Connection and
2.1
Overview of Communication
5
Setting Chapter 2
2.1 Overview of Communication
You can control the instrument with communication commands from a computer via the GP-IB, RS-232C,
USB, and LAN interfaces.
There are the following four communication methods. To enable communication, the communication conditions need to be set on the instrument.
Printer can be connected to enable printing measurement values and screens.
• Commands common to IEEE-488-2 1987 (requirement) can be used.
• The instrument complies with the following standard. (Compliance standard: IEEE-488.1 1987)
• The instrument has been designed with reference to the following standard. (Reference standard:
IEEE-488.2 1987)
0
Chapter 2 Model IM3570 Connection and Setting
The instrument is communication class compatible.
Command control using the TCP/IP protocol is possible.
• Always turn both devices OFF when connecting and disconnecting an interface
connector. Otherwise, an electric shock accident may occur.
• To avoid damage to the instrument, do not short-circuit the terminal and do not
input voltage to the terminal.
• Failure to fasten the connectors properly may result is sub-specification performance or damage to the equipment.
Page 10
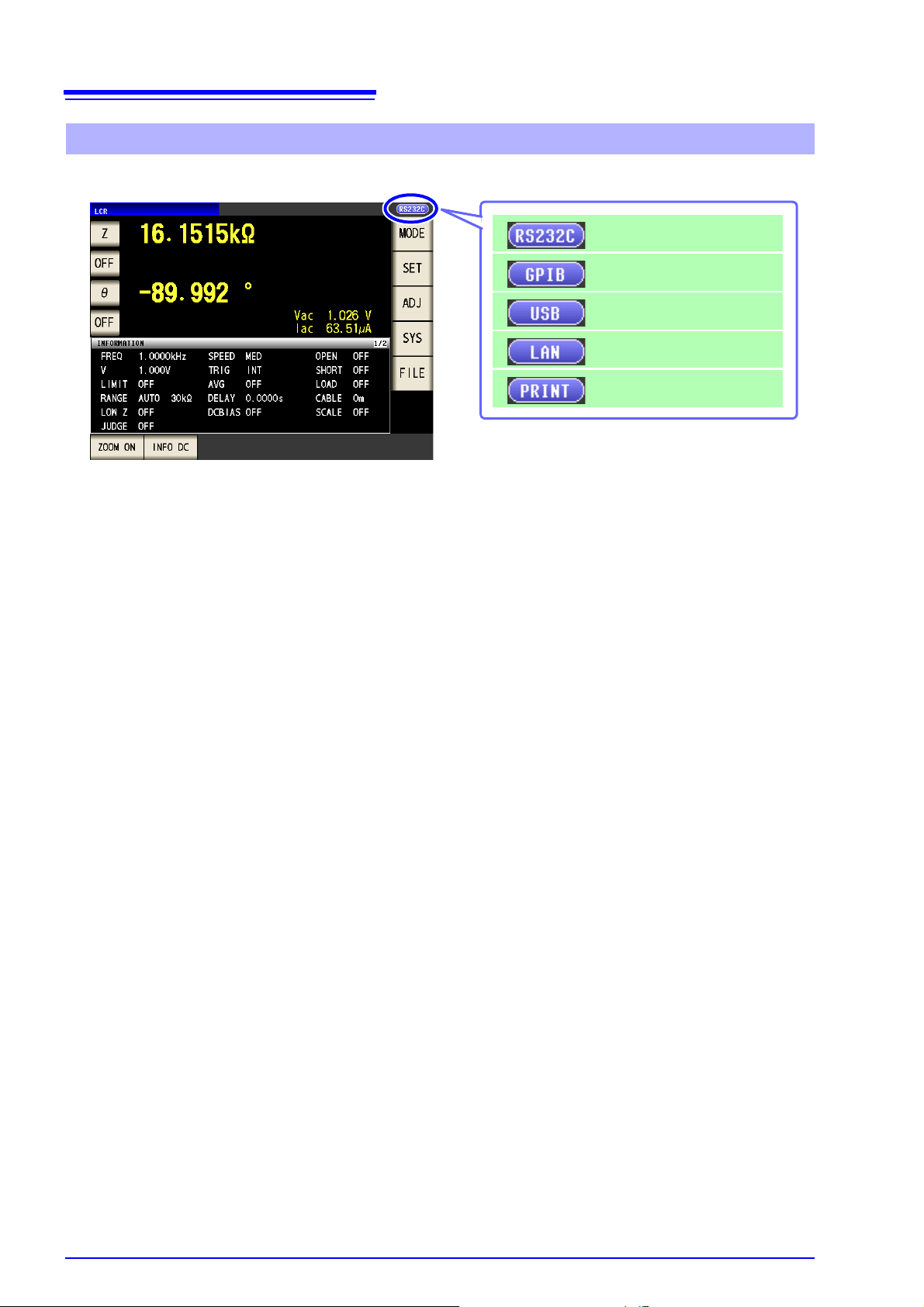
6
When RS-232C is set
When GP-IB is set
When USB is set
When LAN is set
When printer is set
2.1
Overview of Communication
Screen Displayed while Setting Interfaces
When you set an interface, the icon for the set interface is displayed on the right side of the screen.
Page 11
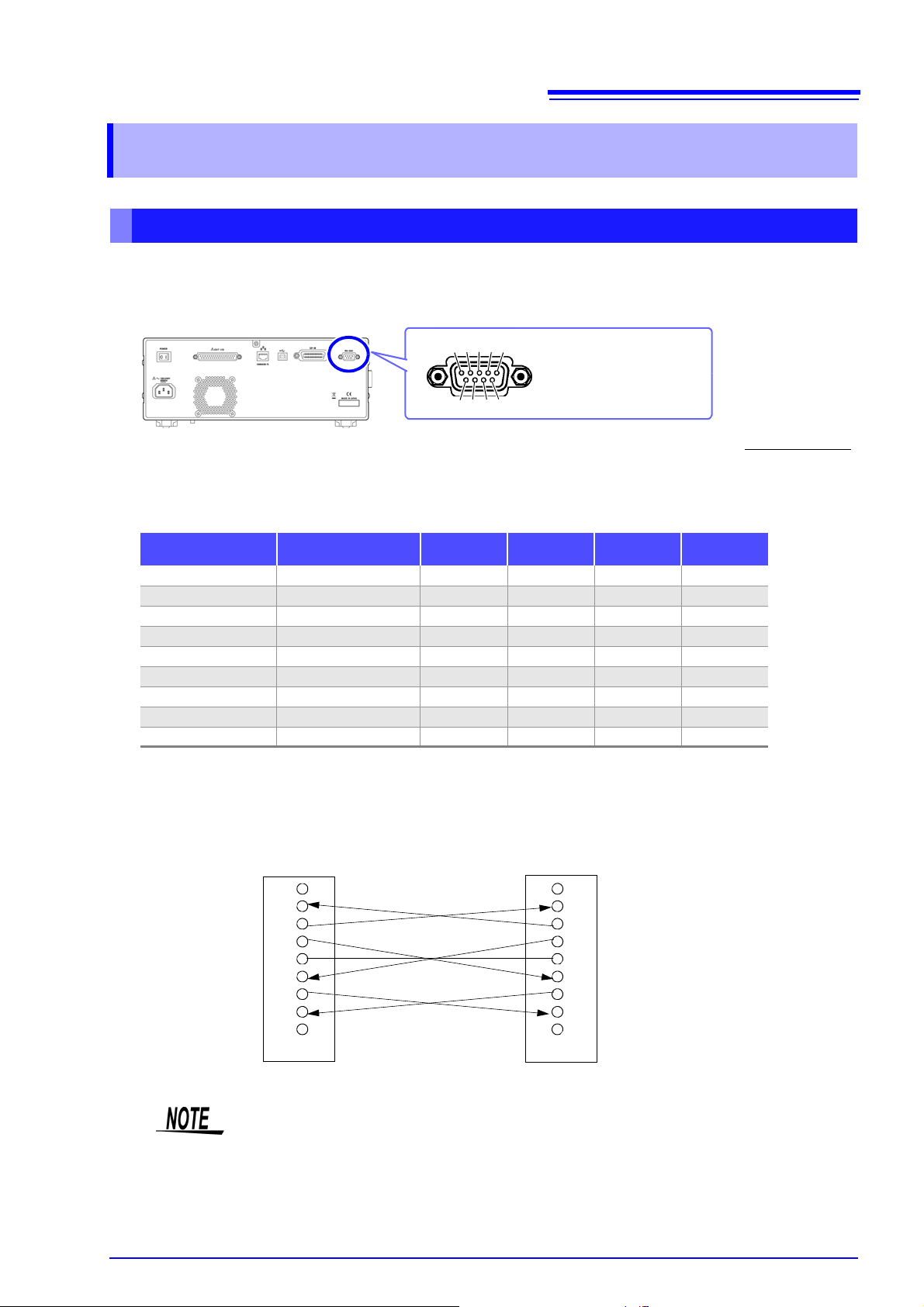
2.2
Male 9-pin D-sub
#4-40 attaching screws
To connect the instrument to a controller (DTE), use a crossover cable
compatible with the connectors on both the instrument and the controller.
The I/O connector is a DTE (Data Terminal Equipment) configuration.
6 7 8 9
1 2 3 4 5
IM3570
BB (RxD)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
BA (TxD)
CD (DTR)
AB (GND)
CA (RTS)
CB (CTS)
SHELL
BA (TxD)
CD (DTR)
AB (GND)
CA (RTS)
CB (CTS)
BB (RxD)
Controller (DOS/V PC)
RS-232C Connection and Settings
2.2 RS-232C Connection and Settings
Connecting the RS-232C Cable
7
Connect the RS-232C cable to the RS-232C connector.
(Recommended cable: 9637 RS-232C cable)
Connector (D-sub)
Pin No.
1Unused
2 Received Data 104 BB RD RxD
3 Transmitted Data 103 BA SD TxD
4 Data Terminal Ready 108/2 CD ER DTR
5 Signal Ground 102 AB SG GND
6 Unused
7 Request to Send 105 CA RS RTS
8 Clear to Send 106 CB CS CTS
9Unused
Interchange Circuit
Name
CCITT
Circuit No.
EIA
Abbreviation
JIS
Abbreviation
Chapter 2 Model IM3570 Connection and Setting
Common
Abbreviation
Example: Connecting to a DOS/V PC
Specification: D-sub 9-pin female and female connector, reverse connection
Hardware control will not work properly if you use a cable that has CA(RTS) and CB(CTS)
short-circuited.
Page 12

8
Procedure
LCR Measurement Screen
Interface Settings
You can configure the setting from any of mode, mode.
Press .
RS-232C Settings
Press to confirm the setting.
RS-232C Settings
Select the terminator setting.
CR+LF
CR
Select the baud rate setting.
Select the handshake setting.
No flow control
Hardware (RTS/CTS control)
Software (XON/XOFF control)
Hardware + software
2.2
RS-232C Connection and Settings
Setting RS-232C
Page 13

2.3
Recommended cable:
9150-02 GP-IB connection cable (2 m)
9151-04 GP-IB connection cable (4 m)
Procedure
LCR Measurement Screen
Interface Settings
You can configure the setting from any of mode, mode.
GP-IB Connection and Settings
2.3 GP-IB Connection and Settings
Connecting the GP-IB Cable
9
Connect the GP-IB cable to the GP-IB connector.
Setting GP-IB
Chapter 2 Model IM3570 Connection and Setting
Page 14

10
Press .
GPIB Setting
GPIB Setting
Use or to set the GP-IB address.
Select the terminator setting.
LF with EOI
LF with CR+EOI
Press to confirm the setting.
2.3
GP-IB Connection and Settings
Page 15
2.4
To connect the instrument to a computer the first time, a dedicated USB driver must be installed.
Before connecting the instrument to the computer, install the USB driver.
The USB driver can be downloaded from the bundled CD, or our web site.(http://www.hioki.c om)
The USB driver is compatible with the Windows XP (32-bit version), Windows Vista (32-bit, 64-bit
version), and Windows 7 (32-bit, 64-bit version) operating systems.
Procedure
LCR Measurement Screen
Interface Settings
You can configure the setting from any of mode, mode.
Press .
USB Setting
USB Settings and Connection
2.4 USB Settings and Connection
Setting USB
11
Chapter 2 Model IM3570 Connection and Setting
Page 16
12
USB Setting
Select the terminator setting.
CR+LF
CR
Press to confirm the setting.
USB cable
(commercially available product)
USB interface port of computer
Type B
2.4
USB Settings and Connection
Connecting the USB Cable
Connect a USB cable (commercially available USB cable) to the USB port of the instrument.
• To avoid faults, do not disconnect or reconnect the USB cable during instrument
operation.
• Connect the instrument and the computer to a common earth ground. Using different grounds could result in potential difference between the instrument and the
computer. Potential difference on the USB cable can result in malfunctions and
faults.
Page 17
2.5
• Make these settings before connecting to a network. Changing settings while connected can
duplicate IP addresses of other network devices, and incorrect address information may otherwise be presented to the network.
• The instrument does not support DHCP (automatic IP address assignment) on a network.
Setting Items
Network Environment Configuration
IP Address _________._________._________._________
Subnet Mask _________._________._________._________
Default Gateway _________._________._________._________
LAN Settings and Connection
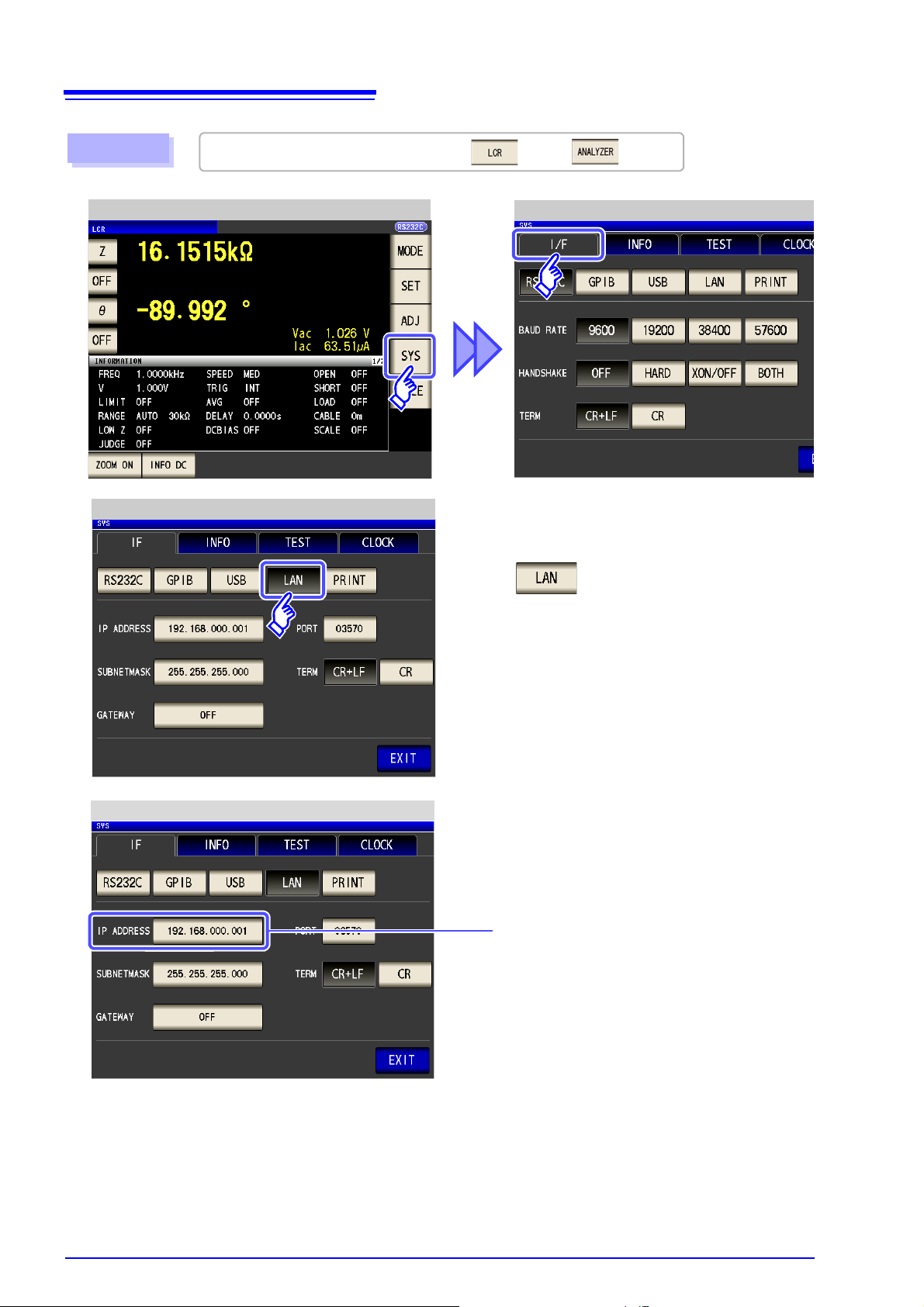
2.5 LAN Settings and Connection
LAN Settings
You can perform command control using the TCP/IP protocol.
Set the instrument to match your network environment in advance.
Identifies each device connected on a network.
IP address
Subnet mask
Default Gateway
Each network device must be set to a unique address.
The instrument supports IP version 4, with IP addresses indicated as four decimal octets, e.g.,
"192.168.0.1".
This setting is for separating the IP address into the network address that indicates the network and
the host address that indicates the instrument. On this instrument, the subnet mask is represented as
four decimal numbers separated by ". " such as "255.255.255.0."
When the computer and instrument are on different but overlapping networks (subnets), this IP address specifies the device to serve as the gateway between the networks.
If the computer and instrument are connected one-to-one, no gateway is used, and the instrument's
default setting "0.0.0.0" can be kept as is.
13
Chapter 2 Model IM3570 Connection and Setting
Example 1. Connecting the instrument to an existing network
When connecting the instrument to an existing network, the network settings need to be confirmed in
advance.
An IP address which is not the same as that of another network device needs to be assigned.
Confirm the following items with the network administrator, and write them down.
Example 2. Connecting multiple instruments to a single computer using a hub
When building a local network with no outside connection, the following private IP addresses are recommended.
Example of private IP address:
IP Address ...............Computer: 192.168.0.100
Instrument: 192.168.0.1, 192.168.0.2, 192.168.0.3...
(Set an IP address that differs from that of other network devices.)
Subnet Mask............255.255.255.0
Default Gateway ......OFF(0.0.0.0)
Example 3. Connecting one instrument to a single computer using the 9642 LAN Cable
The 9642 LAN Cable can be used with its supplied connection adapter to connect one instrument to one
computer, in which case the IP address is freely settable. Use the recommended private IP addresses.
IP Address ...............Computer: 192.168.0.100
Instrument: 192.168.0.1 (Set to a different IP address than the computer.)
Subnet Mask............255.255.255.0
Default Gateway ......OFF(0.0.0.0)
Page 18
14
Procedure
LCR Measurement Screen
Interface Settings
You can configure the setting from any of mode, mode.
Press .
LAN Settings
LAN Settings
Select the IP address.
2.5
LAN Settings and Connection
Page 19

2.5
IP address Settings
Use or to set the IP address.
Press to confirm the setting.
LAN Settings
Select the subnet mask.
128.000.000.000 255.128.000.000 255.255.128.000 255.255.255.128
192.000.000.000 255.192.000.000 255.255.192.000 255.255.255.192
224.000.000.000 255.224.000.000 255.255.224.000 255.255.255.224
240.000.000.000 255.240.000.000 255.255.240.000 255.255.255.240
248.000.000.000 255.248.000.000 255.255.248.000 255.255.255.248
252.000.000.000 255.252.000.000 255.255.252.000 255.255.255.252
254.000.000.000 255.254.000.000 255.255.254.000
255.000.000.000 255.255.000.000 255.255.255.000
(Initial setting)
Subnet mask Settings
Use or to set the subnet mask,
and press to confirm the setting.
Any of the following 30 subnet masks can be set for th e instrument.
LAN Settings and Connection
15
Chapter 2 Model IM3570 Connection and Setting
Page 20
16
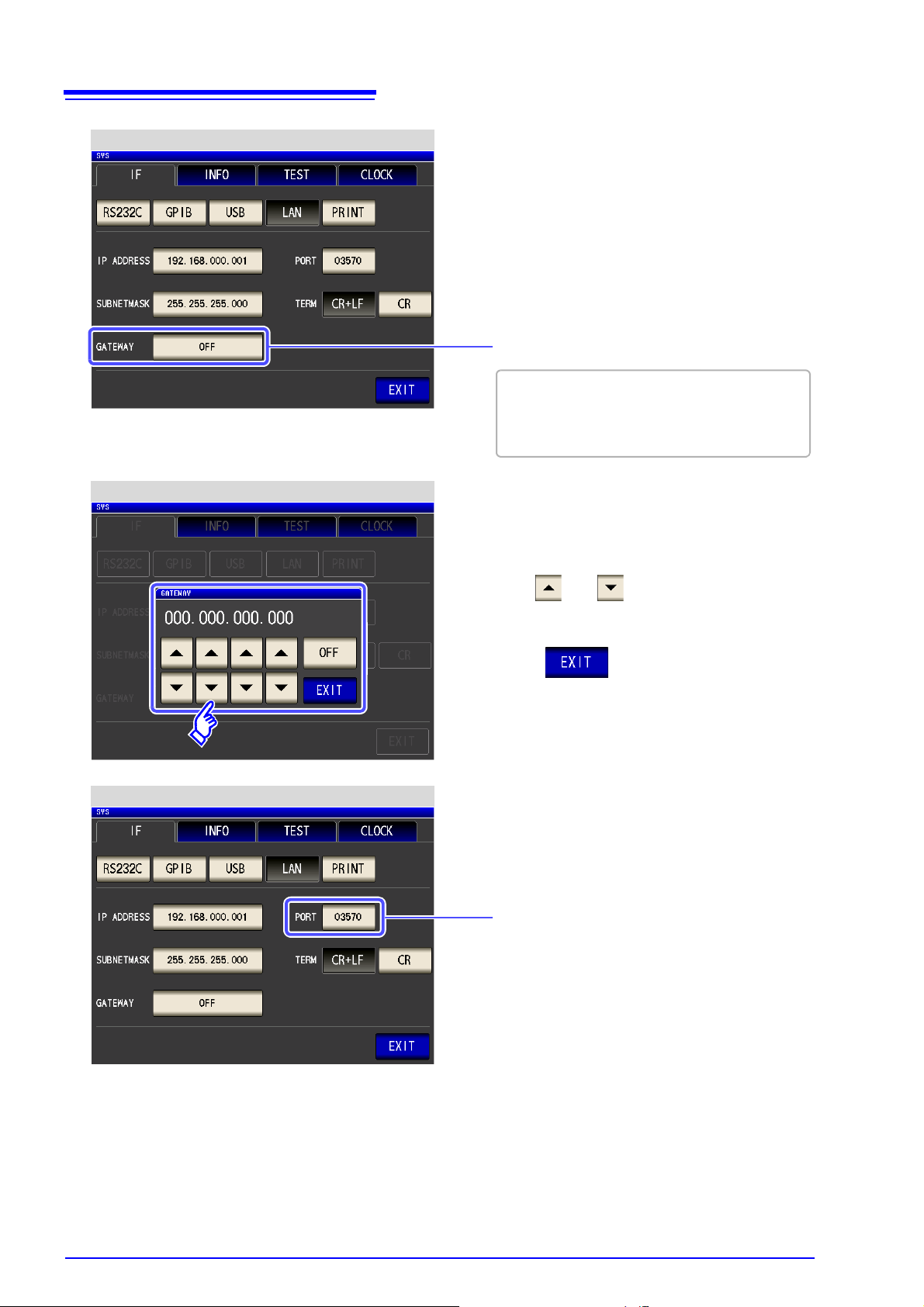
LAN Settings
Select the default gateway.
If the default gateway does not need to be set, for
example, when connecting the instrument and
computer on a one-to-one basis using a cross cable, leave this set to OFF.
Default gateway Settings
Use or to set the default gateway.
Press to confirm the setting.
LAN Settings
Select the port number.
2.5
LAN Settings and Connection
Page 21

2.5
Port number Settings
Use or to set the port number to
use for communication commands.
Press to confirm the setting.
Settable range : 1024 to 65535
LAN Settings
Select the terminator setting.
CR+LF
CR
Press to confirm the setting.
LAN Settings and Connection
17
Chapter 2 Model IM3570 Connection and Setting
Page 22

18
On: Performing communication with 100BASE.
Off: Performing communication with 10BASE.
Flashes when data is being exchanged.
SPEED LED
RX/TX LED
The MAC address of the LAN is displayed
below the serial number.
You can also check it on the instrument
screen.
See: "Checking the Version of the Instru-
ment" in the instruction manual.
LAN interface
Crossover adapter
Connecting with the 9642 LAN Cable and crossover adapter (sup plied with the 9642)
1
Connect the LAN Cable to the
crossover adapter.
Connect the crossover adapter to
the LAN interface on the instrument.
2
Connect the LAN Cable to the
100BASE-TX connector on the PC.
3
2.5
LAN Settings and Connection
Connecting a LAN Cable
Use a LAN cable to connect the instrument and computer.
Required items:
When connecting the instrument to an existing network (prepare any of the following):
• Straight-through Cat 5, 100BASE-TX-compliant Ethernet cable (up to 100 m, commercially available).
For 10BASE communication, a 10BASE-T-compliant cable may also be used.
• Hioki 9642 LAN Cable (option)
(A cross adapter cannot be used.)
When connecting one instrument to a single computer (prepare one of the following):
• 100BASE-TX-compliant cross-over cable (up to 100 m)
• 100BASE-TX-compliant straight-through cable with cross-over adapter (up to 100 m)
• Hioki 9642 LAN Cable (option)
When connecting the instrument to a single computer (connect the instrument to the computer)
Page 23

19
All of the keys except are disabled.
Remote Mode State
Procedure
Press to return to the normal state
(local state).
1
The measurement screen is redisplayed.
Local State
LCR Measurement Screen
2.6
Remote Mode
2.6 Remote Mode
When you connect a device to an interface and start communication, the mode becomes remote mode
(remote operation state) and the keys on the LCD are disabled.
Chapter 2 Model IM3570 Connection and Setting
Canceling Remote Mode
Page 24

20
2.6
Remote Mode
Page 25

Model IM3523
USB communication (p. 22)
GP-IB communication (when connected to the Z3000) (p. 24)
RS-232C communication (when connected to the Z3001) (p. 26)
LAN communication (when connected to the Z3002) (p. 29)
Connection and
3.1
Overview of Communication
21
Setting Chapter 3
3.1 Overview of Communication
You can contro l the instrument with communication commands from a computer via th e USB, GP-IB, RS232C and LAN interfaces.
There are the following four communication methods. To enable communication, the communication conditions need to be set on the instrument.
The instrument is communication class compatible.
• Commands common to IEEE-488-2 1987 (requirement) can be used.
• The instrument complies with the following standard. (Compliance standard: IEEE-488.1 1987)
• The instrument has been designed with reference to the following standard. (Reference standard:
IEEE-488.2 1987)
Chapter 3 Model IM3523 Connection and Setting
Printer can be connected to enable printing measurement values and screens.
Command control using the TCP/IP protocol is possible.
• Always turn both devices OFF when connecting and disconnecting an interface
connector. Otherwise, an electric shock accident may occur.
• To avoid damage to the instrument, do not short-circuit the terminal and do not
input voltage to the terminal.
• Failure to fasten the connectors properly may result is sub-specification performance or damage to the equipment.
Page 26

22
To connect the instrument to a computer the first time, a dedicated USB driver must be installed.
Before connecting the instrument to the computer, install the USB driver.
The USB driver can be downloaded from the bundled CD, or our web site. (http://www.hioki.com)
The USB driver is compatible with the Windows XP (32-bit version), Windows Vista (32-bit, 64-bit
version), and Windows 7 (32-bit, 64-bit version) operating systems.
The SYSTEM screen will be displayed.
Selected interface
Using the Z3000
Using the Z3001
Using the Z3002
When an option is connected
Select.
1
Select the terminator setting.
2
You will return to the measurement screen.
3.2
USB Settings and Connection
3.2 USB Settings and Connection
Setting USB
Open the SYSTEM screen.
1
Select USB as the interface.
The display will vary with the installed options.
2
Select the terminator setting.
3
4
Page 27
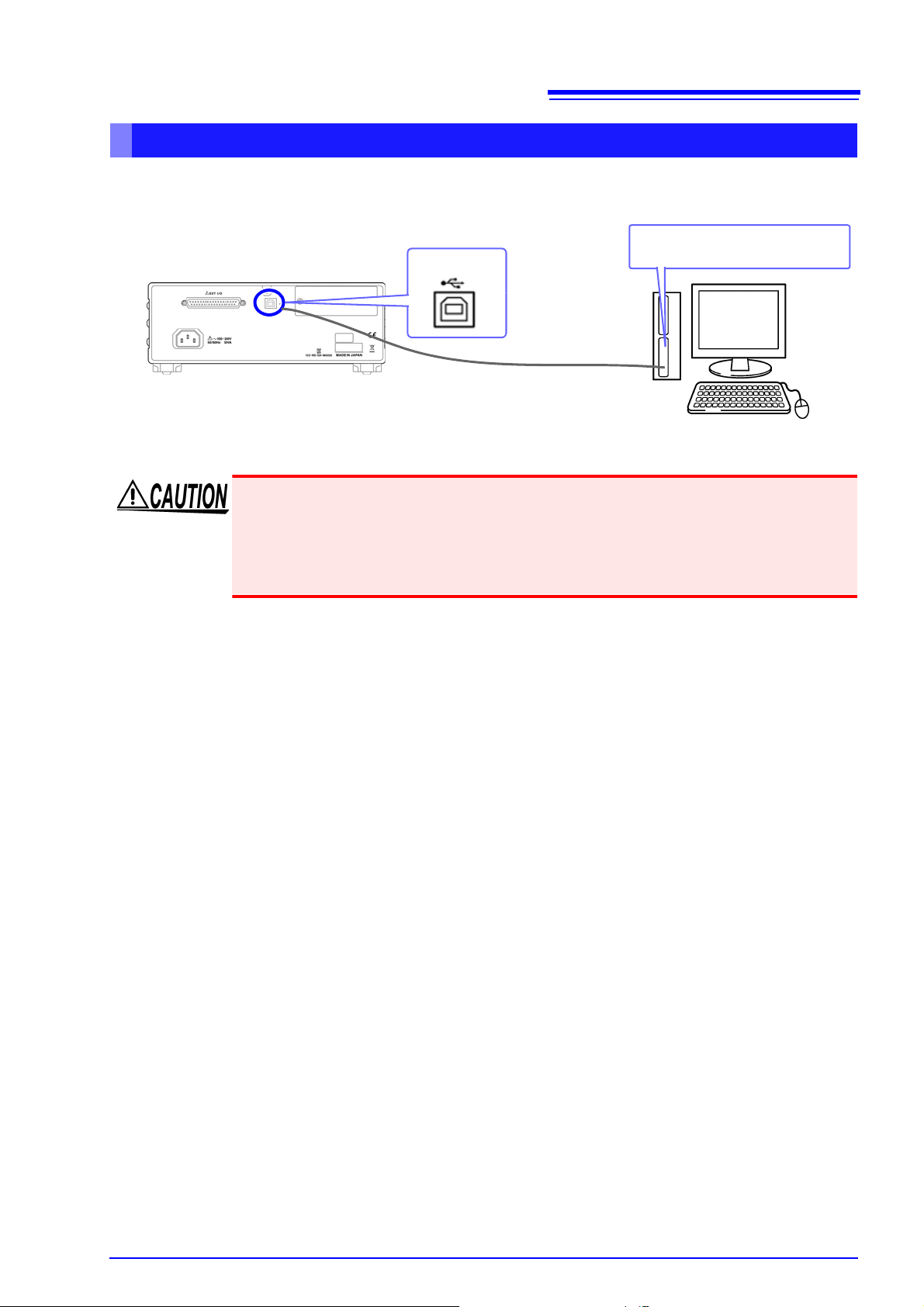
3.2
USB cable
(commercially available product)
Type B
USB interface port of computer
USB Settings and Connection
Connecting the USB Cable
Connect a USB cable (commercially available USB cable) to the USB port of the instrument.
• To avoid faults, do not disconnect or reconnect the USB cable during instrument
operation.
• Connect the instrument and the computer to a common earth ground. Using different grounds could result in potential difference between the instrument and the
computer. Potential difference on the USB cable can result in malfunctions and
faults.
23
Chapter 3 Model IM3523 Connection and Setting
Page 28

24
Recommended cable:
9150-02 GP-IB connection cable (2 m)
9151-04 GP-IB connection cable (4 m)
Open the SYSTEM screen.
Select.
1
Select GP-IB.
2
3.3
GP-IB Connection and Settings (when connected to the Z3000)
3.3 GP-IB Connection and Settings (when connected to the Z3000)
Connecting the GP-IB Cable
Connect the GP-IB cable to the GP-IB connector.
Setting GP-IB
Open the SYSTEM screen.
1
Select GP-IB as the interface.
2
Page 29

Select the terminator setting.
Select.
1
LF with CR+EOI
2
LF with EOI
Select.
1
Select the GP-IB address setting.
2
You will return to the measurement screen.
3
Set the GP-IB address.
Valid setting range: 0 to 30
4
3.3
GP-IB Connection and Settings (when connected to the Z3000)
25
Chapter 3 Model IM3523 Connection and Setting
5
Page 30

26
Male 9-pin D-sub
#4-40 attaching screws
To connect the instrument to a controller (DTE), use a crossover cable
compatible with the connectors on both the instrument and the controller.
The I/O connector is a DTE (Data Terminal Equipment) configuration.
6 7 8 9
1 2 3 4 5
IM3523
BB (RxD)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
BA (TxD)
CD (DTR)
AB (GND)
CA (RTS)
CB (CTS)
SHELL
BA (TxD)
CD (DTR)
AB (GND)
CA (RTS)
CB (CTS)
BB (RxD)
Controller (DOS/V PC)
3.4
RS-232C Connection and Settings (when connected to the Z3001)
3.4 RS-232C Connection and Settings (when connected to the Z3001)
Connecting the RS-232C Cable
Connect the RS-232C cable to the RS-232C connector.
(Recommended cable: 9637 RS-232C cable)
Connector (D-sub)
Pin No.
1 Unused
2 Received Data 104 BB RD RxD
3 Transmitted Data 103 BA SD TxD
4 Data Terminal Ready 108/2 CD ER DTR
5 Signal Ground 102 AB SG GND
6 Unused
7 Request to Send 105 CA RS RTS
8 Clear to Send 106 CB CS CTS
9 Unused
Interchange Circuit
Name
CCITT
Circuit No.
EIA
Abbreviation
Abbreviation
Example: Connecting to a DOS/V PC
Specification: D-sub 9-pin female and female connector, reverse connection
JIS
Common
Abbreviation
Hardware control will not work properly if you use a cable that has CA(RTS) and CB(CTS)
short-circuited.
Page 31

Setting RS-232C
Open the SYSTEM screen.
Select.
1
Select RS-232C.
2
Select.
1
Select the baud rate setting.
2
Select.
1
Select the terminator setting.
2
Open the SYSTEM screen.
1
Select RS-232C as the interface.
2
3.4
RS-232C Connection and Settings (when connected to the Z3001)
27
Chapter 3 Model IM3523 Connection and Setting
Select from the following baud rate setting.
9600, 19200, 38400, 57600
3
Select the terminator setting.
4
Page 32

28
Select.
1
Select the handshake setting.
2
OFF
No flow control
HARD
Hardware (RTS/CTS control)
XON/OFF
Software (XON/XOFF control)
BOTH
Hardware + software
You will return to the measurement screen.
3.4
RS-232C Connection and Settings (when connected to the Z3001)
Select the handshake setting.
5
6
Page 33

3.5
• Make these settings before connecting to a network. Changing settings while connected can
duplicate IP addresses of other network devices, and incorrect address information may otherwise be presented to the network.
• The instrument does not support DHCP (automatic IP address assignment) on a network.
Setting Items
Network Environment Configuration
IP Address _________._________._________._________
Subnet Mask _________._________._________._________
Default Gateway _________._________._________._________
LAN Settings and Connection (when connected to the Z3002)
3.5 LAN Settings and Connection (when connected to the Z3002)
LAN Settings
29
You can perform command control using the TCP/IP protocol.
Set the instrument to match your network environment in advance.
Identifies each device connected on a network.
IP address
Subnet mask
Default Gateway
Each network device must be set to a unique address.
The instrument supports IP version 4, with IP addresses indicated as four decimal octets, e.g.,
"192.168.0.1".
This setting is for separating the IP address into the network address that indicates the network and
the host address that indicates the instrument. On this instrument, the subnet mask is represented
as four decimal numbers separated by ". " such as "255.255.255.0."
When the computer and instrument are on different but overlapping networks (subnets), this IP address specifies the device to serve as the gateway between the networks.
If the computer and instrument are connected one-to-one, no gateway is used, and the instrument's
default setting "0.0.0.0" can be kept as is.
Example 1. Connecting the instrument to an existing network
When connecting the instrument to an existing network, the network settings need to be confirmed in
advance.
An IP address which is not the same as that of another network device needs to be assigned.
Confirm the following items with the network administrator, and write them down.
Chapter 3 Model IM3523 Connection and Setting
Example 2. Connecting multiple instruments to a single computer using a hub
When building a local network with no outside connection, the following private IP addresses are recommended.
Example of private IP address:
IP Address ...............Computer: 192.168.0.100
Instrument: 192.168.0.1, 192.168.0.2, 192.168.0.3...
(Set an IP address that differs from that of other network devices.)
Subnet Mask............255.255.255.0
Default Gateway ......OFF(0.0.0.0)
Example 3. Connecting one instrument to a single computer using the 9642 LAN Cable
The 9642 LAN Cable can be used with its supplied connection adapter to connect one instrument to one
computer, in which case the IP address is freely settable. Use the recommended private IP addresses.
IP Address ...............Computer: 192.168.0.100
Instrument: 192.168.0.1 (Set to a different IP address than the computer.)
Subnet Mask............255.255.255.0
Default Gateway ......OFF(0.0.0.0)
Page 34

30
Open the SYSTEM screen.
Select.
1
Select LAN.
2
Select.
1
Select the IP address.
2
3.5
LAN Settings and Connection (when connected to the Z3002)
Open the SYSTEM screen.
1
Select LAN as the interface.
2
Select the IP address.
3
Page 35

Select the subnet mask.
128.000.000.000 255.128.000.000 255.255.128.000 255.255.255.128
192.000.000.000 255.192.000.000 255.255.192.000 255.255.255.192
224.000.000.000 255.224.000.000 255.255.224.000 255.255.255.224
240.000.000.000 255.240.000.000 255.255.240.000 255.255.255.240
248.000.000.000 255.248.000.000 255.255.248.000 255.255.255.248
252.000.000.000 255.252.000.000 255.255.252.000 255.255.255.252
254.000.000.000 255.254.000.000 255.255.254.000
255.000.000.000 255.255.000.000 255.255.255.000
(Initial setting)
Any of the following 30 subnet masks can be set for th e instrument.
Select.
1
Select the subnet mask.
2
Select.
1
Select the default gateway.
2
Set the default gateway to OFF
(000.000.000.000).
If the default gateway does not need to be set, for example, whe n connecting the instrument and
computer on a one-to-one basis using a cross cable, leave this set to OFF.
Select.
1
Select the terminator setting.
2
4
3.5
LAN Settings and Connection (when connected to the Z3002)
31
Chapter 3 Model IM3523 Connection and Setting
Select the default gateway.
5
Select the terminator setting.
6
Page 36

32
Select.
1
Select the port number.
2
Revert the setting to the default
value.
You will return to the measurement
screen.
3.5
LAN Settings and Connection (when connected to the Z3002)
Select the port number.
Settable range : 1024 to 65535
7
8
Page 37

33
On: Performing communication with 100BASE.
Off: Performing communication with 10BASE.
Flashes when data is being exchanged.
SPEED LED
RX/TX LED
The MAC address of the LAN is displayed
below the serial number.
You can also check it on the instrument
screen.
See: "Checking the Version of the Instru-
ment" in the instruction manual.
LAN interface
Crossover adapter
Connecting with the 9642 LAN Cable and crossover adapter (sup plied with the 9642)
1
Connect the LAN Cable to the
crossover adapter.
Connect the crossover adapter to
the LAN interface on the instrument.
2
Connect the LAN Cable to the
100BASE-TX connector on the PC.
3
3.5
LAN Settings and Connection (when connected to the Z3002)
Connecting a LAN Cable
Use a LAN cable to connect the instrument and computer.
Required items:
When connecting the instrument to an existing network (prepare any of the following):
• Straight-through Cat 5, 100BASE-TX-compliant Ethernet cable (up to 100 m, commercially available).
For 10BASE communication, a 10BASE-T-compliant cable may also be used.
• Hioki 9642 LAN Cable (option)
(A cross adapter cannot be used.)
When connecting one instrument to a single computer (prepare one of the following):
• 100BASE-TX-compliant cross-over cable (up to 100 m)
• 100BASE-TX-compliant straight-through cable with cross-over adapter (up to 100 m)
• Hioki 9642 LAN Cable (option)
Chapter 3 Model IM3523 Connection and Setting
When connecting the instrument to a single computer (connect the instrument to the computer)
Page 38

34
Keys other than [F1] are disabled.
You will return to the measurement
screen.
You will return to the measurement
screen.
3.6
Remote Mode
3.6 Remote Mode
When you connect a device to an interface and start communication, the mode becomes remote mode
(remote operation state) and the keys on the LCD are disabled.
Remote status
Canceling Remote Mode
1
2
Page 39

4.1
USB communication (p. 37)
GP-IB communication (when connected to the Z3000) (p. 39)
RS-232C communication (when connected to the Z3001) (p. 41)
LAN communication (when connected to the Z3002) (p. 43)
Overview of Communication
Model IM3533/ IM3533-01/
IM3590 Connection and
35
Setting Chapter 4
4.1 Overview of Communication
You can contro l the instrument with communication commands from a computer via th e USB, GP-IB, RS232C and LAN interfaces.
There are the following four communication methods. To enable communication, the communication conditions need to be set on the instrument.
The instrument is communication class compatible.
• Commands common to IEEE-488-2 1987 (requirement) can be used.
• The instrument complies with the following standard. (Compliance standard: IEEE-488.1 1987)
• The instrument has been designed with reference to the following standard. (Reference standard:
IEEE-488.2 1987)
Chapter 4 Model IM3533/ IM3533-01/ IM3590 Connec-
Printer can be connected to enable printing measurement values and screens.
Command control using the TCP/IP protocol is possible.
• Always turn both devices OFF when connecting and disconnecting an interface
connector. Otherwise, an electric shock accident may occur.
• To avoid damage to the instrument, do not short-circuit the terminal and do not
input voltage to the terminal.
• Failure to fasten the connectors properly may result is sub-specification performance or damage to the equipment.
Page 40

36
When USB is set
When GP-IB is set
When RS-232C is set
When LAN is set
When printer is set
4.1
Overview of Communication
Screen Displayed while Setting Interfaces
When you set an interface, the icon for the set interface is displayed on the right side of the screen.
Page 41

4.2
To connect the instrument to a computer the first time, a dedicated USB driver must be installed.
Before connecting the instrument to the computer, install the USB driver.
The USB driver can be downloaded from the bundled CD, or our web site.(http://www.hioki.c om)
The USB driver is compatible with the Windows XP (32-bit version), Windows Vista (32-bit, 64-bit
version), and Windows 7 (32-bit, 64-bit version) operating systems.
You can configure the setting from any of mode, mode and mode.
Procedure
LCR Measurement Screen
Interface Settings
Using the Z3002
Using the Z3001
Press .
USB Setting
Using the Z3000
When an option is connected
USB Settings and Connection
4.2 USB Settings and Connection
Setting USB
The display will vary with the installed options.
37
Chapter 4 Model IM3533/ IM3533-01/ IM3590 Connec-
Page 42

38
USB Setting
Select the terminator setting.
CR+LF
CR
Press to confirm the setting.
USB cable
(commercially available product)
Type B
USB interface port of computer
4.2
USB Settings and Connection
Connecting the USB Cable
Connect a USB cable (commercially available USB cable) to the USB port of the instrument.
• To avoid faults, do not disconnect or reconnect the USB cable during instrument
operation.
• Connect the instrument and the computer to a common earth ground. Using different grounds could result in potential difference between the instrument and the
computer. Potential difference on the USB cable can result in malfunctions and
faults.
Page 43

4.3
Recommended cable:
9150-02 GP-IB connection cable (2 m)
9151-04 GP-IB connection cable (4 m)
You can configure the setting from any of mode, mode and mode.
Procedure
LCR Measurement Screen
Interface Settings
GP-IB Connection and Settings (when connected to the Z3000)
4.3 GP-IB Connection and Settings (when connected to the Z3000)
39
Connecting the GP-IB Cable
Connect the GP-IB cable to the GP-IB connector.
Setting GP-IB
Chapter 4 Model IM3533/ IM3533-01/ IM3590 Connec-
Page 44

40
Press .
GPIB Setting
GPIB Setting
Use or to set the GP-IB address.
Select the terminator setting.
LF with EOI
LF with CR+EOI
Press to confirm the setting.
4.3
GP-IB Connection and Settings (when connected to the Z3000)
Page 45

4.4
Male 9-pin D-sub
#4-40 attaching screws
To connect the instrument to a controller (DTE), use a crossover cable
compatible with the connectors on both the instrument and the controller.
The I/O connector is a DTE (Data Terminal Equipment) configuration.
6 7 8 9
1 2 3 4 5
IM3570
BB (RxD)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
BA (TxD)
CD (DTR)
AB (GND)
CA (RTS)
CB (CTS)
SHELL
BA (TxD)
CD (DTR)
AB (GND)
CA (RTS)
CB (CTS)
BB (RxD)
Controller (DOS/V PC)
RS-232C Connection and Settings (when connected to the Z3001)
4.4 RS-232C Connection and Settings (when connected to the Z3001)
41
Connecting the RS-232C Cable
Connect the RS-232C cable to the RS-232C connector.
(Recommended cable: 9637 RS-232C cable)
Connector (D-sub)
Pin No.
1Unused
2 Received Data 104 BB RD RxD
3 Transmitted Data 103 BA SD TxD
4 Data Terminal Ready 108/2 CD ER DTR
5 Signal Ground 102 AB SG GND
6 Unused
7 Request to Send 105 CA RS RTS
8 Clear to Send 106 CB CS CTS
9Unused
Interchange Circuit
Name
CCITT
Circuit No.
EIA
Abbreviation
JIS
Abbreviation
Chapter 4 Model IM3533/ IM3533-01/ IM3590 Connec-
Common
Abbreviation
Example: Connecting to a DOS/V PC
Specification: D-sub 9-pin female and female connector, reverse connection
Hardware control will not work properly if you use a cable that has CA(RTS) and CB(CTS)
short-circuited.
Page 46

42
Procedure
LCR Measurement Screen
Interface Settings
You can configure the setting from any of mode, mode and mode.
Press .
RS-232C Settings
Press to confirm the setting.
RS-232C Settings
Select the handshake setting.
No flow control
Hardware (RTS/CTS control)
Software (XON/XOFF control)
Hardware + software
Select the terminator setting.
CR+LF
CR
Select the baud rate setting.
4.4
RS-232C Connection and Settings (when connected to the Z3001)
Setting RS-232C
Page 47

4.5
• Make these settings before connecting to a network. Changing settings while connected can
duplicate IP addresses of other network devices, and incorrect address information may otherwise be presented to the network.
• The instrument does not support DHCP (automatic IP address assignment) on a network.
Setting Items
Network Environment Configuration
IP Address _________._________._________._________
Subnet Mask _________._________._________._________
Default Gateway _________._________._________._________
LAN Settings and Connection (when connected to the Z3002)
4.5 LAN Settings and Connection (when connected to the Z3002)
LAN Settings
43
You can perform command control using the TCP/IP protocol.
Set the instrument to match your network environment in advance.
Identifies each device connected on a network.
IP address
Subnet mask
Default Gateway
Each network device must be set to a unique address.
The instrument supports IP version 4, with IP addresses indicated as four decimal octets, e.g.,
"192.168.0.1".
This setting is for separating the IP address into the network address that indicates the network and
the host address that indicates the instrument. On this instrument, the subnet mask is represented as
four decimal numbers separated by ". " such as "255.255.255.0."
When the computer and instrument are on different but overlapping networks (subnets), this IP address specifies the device to serve as the gateway between the networks.
If the computer and instrument are connected one-to-one, no gateway is used, and the instrument's
default setting "0.0.0.0" can be kept as is.
Chapter 4 Model IM3533/ IM3533-01/ IM3590 Connec-
Example 1. Connecting the instrument to an existing network
When connecting the instrument to an existing network, the network settings need to be confirmed in
advance.
An IP address which is not the same as that of another network device needs to be assigned.
Confirm the following items with the network administrator, and write them down.
Example 2. Connecting multiple instruments to a single computer using a hub
When building a local network with no outside connection, the following private IP addresses are recommended.
Example of private IP address:
IP Address ...............Computer: 192.168.0.100
Instrument: 192.168.0.1, 192.168.0.2, 192.168.0.3...
(Set an IP address that differs from that of other network devices.)
Subnet Mask............255.255.255.0
Default Gateway ......OFF(0.0.0.0)
Example 3. Connecting one instrument to a single computer using the 9642 LAN Cable
The 9642 LAN Cable can be used with its supplied connection adapter to connect one instrument to one
computer, in which case the IP address is freely settable. Use the recommended private IP addresses.
IP Address ...............Computer: 192.168.0.100
Instrument: 192.168.0.1 (Set to a different IP address than the computer.)
Subnet Mask............255.255.255.0
Default Gateway ......OFF(0.0.0.0)
Page 48

44
You can configure the setting from any of mode, mode and mode.
Procedure
LCR Measurement Screen
Interface Settings
Press .
LAN Settings
LAN Settings
Select the IP address.
4.5
LAN Settings and Connection (when connected to the Z3002)
Page 49

4.5
IP address Settings
Use or to set the IP address.
Press to confirm the setting.
LAN Settings
Select the subnet mask.
128.000.000.000 255.128.000.000 255.255.128.000 255.255.255.128
192.000.000.000 255.192.000.000 255.255.192.000 255.255.255.192
224.000.000.000 255.224.000.000 255.255.224.000 255.255.255.224
240.000.000.000 255.240.000.000 255.255.240.000 255.255.255.240
248.000.000.000 255.248.000.000 255.255.248.000 255.255.255.248
252.000.000.000 255.252.000.000 255.255.252.000 255.255.255.252
254.000.000.000 255.254.000.000 255.255.254.000
255.000.000.000 255.255.000.000 255.255.255.000
(Initial setting)
Subnet mask Settings
Use or to set the subnet mask,
and press to confirm the setting.
Any of the following 30 subnet masks can be set for th e instrument.
LAN Settings and Connection (when connected to the Z3002)
45
Chapter 4 Model IM3533/ IM3533-01/ IM3590 Connec-
Page 50
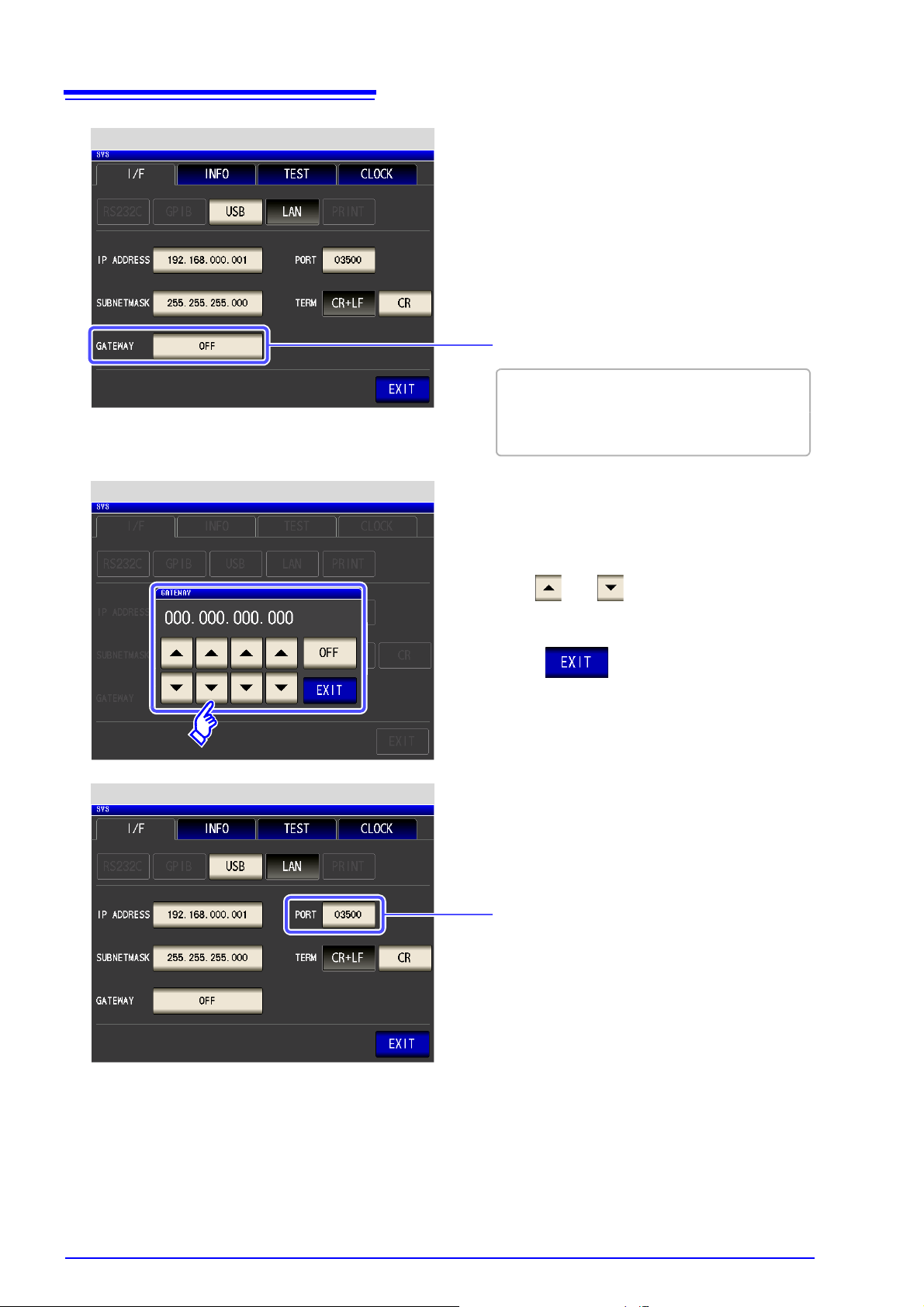
46
LAN Settings
Select the default gateway.
If the default gateway does not need to be set, for
example, when connecting the instrument and
computer on a one-to-one basis using a cross cable, leave this set to OFF.
Default gateway Settings
Use or to set the default gateway.
Press to confirm the setting.
LAN Settings
Select the port number.
4.5
LAN Settings and Connection (when connected to the Z3002)
Page 51

4.5
Port number Settings
Use or to set the port number to
use for communication commands.
Press to confirm the setting.
Settable range : 1024 to 65535
LAN Settings
Select the terminator setting.
CR+LF
CR
Press to confirm the setting.
LAN Settings and Connection (when connected to the Z3002)
47
Chapter 4 Model IM3533/ IM3533-01/ IM3590 Connec-
Page 52

48
On: Performing communication with 100BASE.
Off: Performing communication with 10BASE.
Flashes when data is being exchanged.
SPEED LED
RX/TX LED
The MAC address of the LAN is displayed
below the serial number.
You can also check it on the instrument
screen.
See: "Checking the Version of the Instru-
ment" in the instruction manual.
LAN interface
Crossover adapter
Connecting with the 9642 LAN Cable and crossover adapter (sup plied with the 9642)
1
Connect the LAN Cable to the
crossover adapter.
Connect the crossover adapter to
the LAN interface on the instrument.
2
Connect the LAN Cable to the
100BASE-TX connector on the PC.
3
4.5
LAN Settings and Connection (when connected to the Z3002)
Connecting a LAN Cable
Use a LAN cable to connect the instrument and computer.
Required items:
When connecting the instrument to an existing network (prepare any of the following):
• Straight-through Cat 5, 100BASE-TX-compliant Ethernet cable (up to 100 m, commercially available).
For 10BASE communication, a 10BASE-T-compliant cable may also be used.
• Hioki 9642 LAN Cable (option)
(A cross adapter cannot be used.)
When connecting one instrument to a single computer (prepare one of the following):
• 100BASE-TX-compliant cross-over cable (up to 100 m)
• 100BASE-TX-compliant straight-through cable with cross-over adapter (up to 100 m)
• Hioki 9642 LAN Cable (option)
When connecting the instrument to a single computer (connect the instrument to the computer)
Page 53

49
All of the keys except are disabled.
Remote Mode State
Procedure
Press to return to the normal state
(local state).
1
The measurement screen is redisplayed.
Local State
LCR Measurement Screen
4.6
Remote Mode
4.6 Remote Mode
When you connect a device to an interface and start communication, the mode becomes remote mode
(remote operation state) and the keys on the LCD are disabled.
Chapter 4 Model IM3533/ IM3533-01/ IM3590 Connec-
Canceling Remote Mode
Page 54

50
4.6
Remote Mode
Page 55

A1
Check
Check the COM number on the right of "HIOKI IM3570 Impedance Analyzer" po rt in the [Ports
(COM & LPT)] list.
• When the IM3523, IM3533, IM3533-01 and IM3590 : Check the COM number to the right of
"HIOKI USB Device" in the [Ports (COM & LPT)] list.
• When the IM3570 : Check the COM number to the right of "HIOKI IM3570 Impedance Analyzer" in the [Ports (COM & LPT)] list.
Click
Appendix 1 Checking the USB Virtual COM Port
Appendix
Appendix 1 Checking the USB Virtual COM Port
The instrument’s USB interface supports communications-class performance, allowing control operations on
par with RS-232C to be performed from a computer. When you connect the instrument to a computer and set
its interface to USB, it will be recognized as a virtual COM port on the computer.
Device Manager starts.
The procedure to start Device Manager differs depending on the version of the Windows operating system.
For details, refer to Help of the operating system.
Page 56

A2
Click
Click [Start Menu]
- [All Programs] - [Accessories] - [Communications] and [Hyper
Terminal].
Click
Click
Click [Yes].
Appendix 2 Checking RS-232C and USB Communication in Windows
Appendix 2 Checking RS-232C and USB Com-
munication in Windows
When using, for example, Visual Basic or PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) on a computer to perform
communication with a measuring instrument via RS-232C or USB, development at a later time will go
smoother if you use Hyper Terminal, which comes standard with Windows XP, to check communication.
The following describes the procedure up until performing communication using Hyper Terminal.
Hyper Terminal is not supplied with Windows Vista and Windows 7.
Start Hyper Terminal.
1
2
Set the Telnet program settings.
Page 57

3
2
Click
1
Enter the area code.
Enter the area code in [What area code (or city code) are you in now?].
1
Click [OK].
2
Click
Click [OK].
A3
Appendix 2 Checking RS-232C and USB Communication in Windows
Set the information for where you are now.
4
Set the phone and modem options.
Page 58

A4
1
Enter
2
Click
Enter a name in the [Name] field, and select any icon.
(The name and icon are used for the shortcut.)
1
Click [OK].
2
2
Click
1
Select a COM port in [Connect using].
Select a COM port in [Connect using].
1
Click [OK].
2
Appendix 2 Checking RS-232C and USB Communication in Windows
Set a name and icon.
5
6
Set the connection method.
Page 59

7
2
Click
1
Enter
Set the properties in accordance with the measuring instrument to be used.
(For the information, refer the instruct ion manu al of the m ea su rin g ins tru m en t to be use d .)
1
Click [OK].
2
Click
Click
Click
Click
A5
Appendix 2 Checking RS-232C and USB Communication in Windows
Set the properties of the COM port to be used.
8
9
The main screen of Hyper Terminal appears.
Select [Disconnect] from the [Call] menu.
Select [Properties] from the [File] menu.
The properties screen appears.
Page 60

A6
2
3
Click
1
Click
4
Click
Add check marks.
1
Click
Click [Settings] tab and then [ASCII Setup...].
1
Add check marks to [Send line ends with line feeds], [Echo typed characte rs locally], and
[Append line feeds to incoming line ends]
.
2
Click [OK] to close [ASCII Setup].
3
Click [OK].
4
Click
Appendix 2 Checking RS-232C and USB Communication in Windows
Set the ASCII settings.
10
Select [Call] from the [Call] menu to connect to the measuring instrument.
11
Preparation for communication is completed.
Page 61

12
Sent
Received
A7
Appendix 2 Checking RS-232C and USB Communication in Windows
Perform communication with the measuring instrument.
Send a character string to the measuring instrument.
The following shows an example of entering "*idn?" and then pressing the Enter key.
Communication has been established if there is a response from the measuring instrument.
In the following example, the "HIOKI,IM3570,V1.00" character string was received.
Page 62

A8
Click [Start Menu] - [All Programs] - [Accessories] - [Communications] and [Hyper Terminal].
Click
Click
2
Click
1
Enter a name
Enter a name in the [Name] field
1
Click [OK]. (You can enter any name.)
2
A [Connect To] dialog appears.
Appendix 3 Checking LAN Communication in Windows
Appendix 3 Checking LAN Communication in
Windows
You can use Hyper Terminal which comes standard with Windows XP to check LAN communication.
The following describes the procedure up until performing communication using Hyper Terminal.
Launch HyperTeminal.
1
Specify a connection name.
2
Page 63
3
2
Enter
1
Select the connection method
3
Click
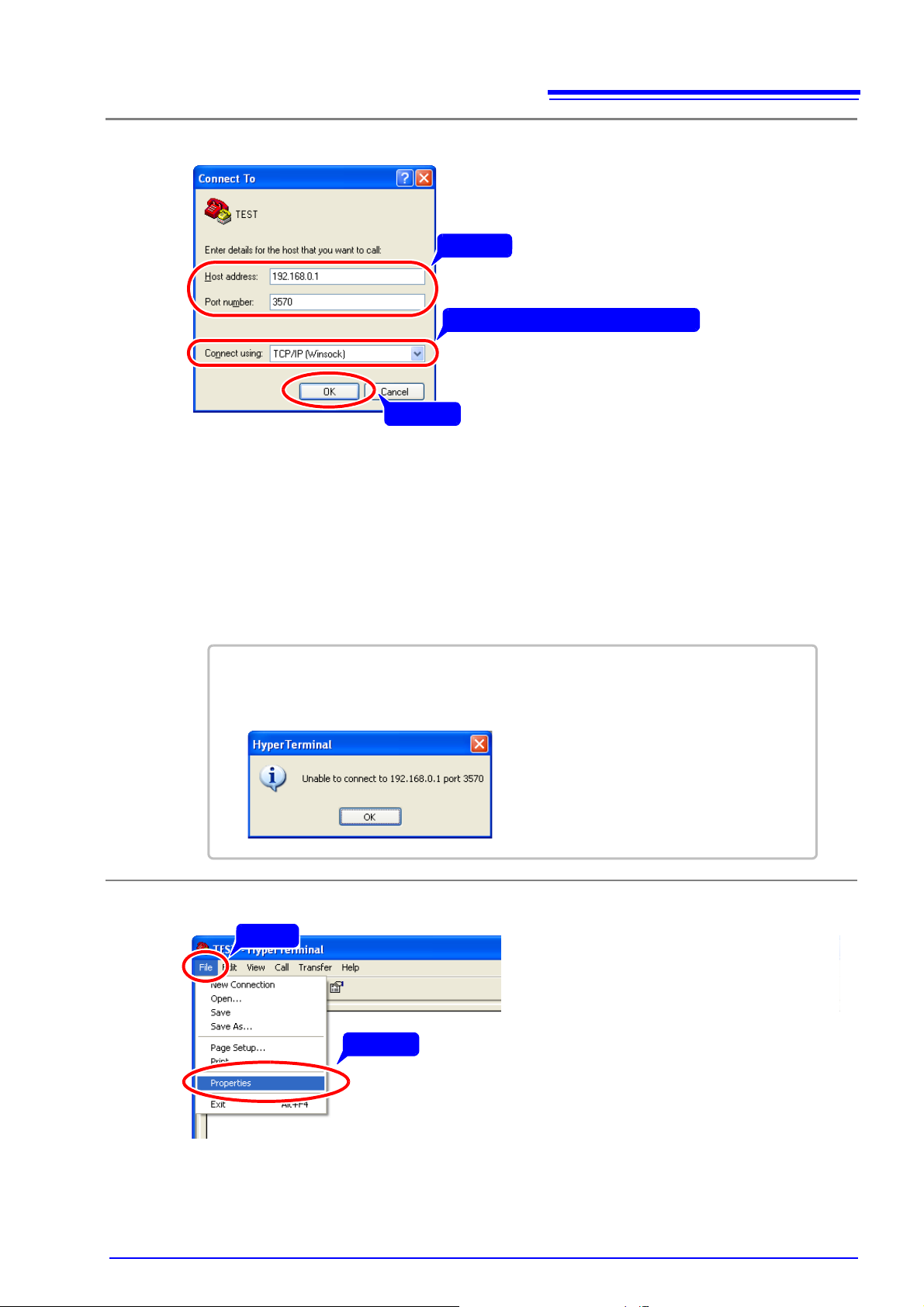
In [Connect using] select [TCP/IP (Winsock)].
1
•In [Host address], enter the IP address of the instrument.
• Enter the port number set on the instrument in the [Port number] field.
• The default port number is 3500 (for the IM3523, IM3533, IM3533-01 and IM3590) o r 3570
(for the IM3570).
See ”Select the IP address” IM3523(p. 30), IM3533/ IM3533-01(p. 44), IM3590(p. 44), IM3570(p. 14)
2
Click [OK].
3
If the following screen appears, there is a problem with the LAN settings.
Check that the LAN settings of the instrument and the IP address on the computer side
are correct.
1
Click
Click
Select [Properties] in the [File] menu.
1
The Properties dialog for the specified connection name appears.
A9
Appendix 3 Checking LAN Communication in Windows
Make the connection settings.
Make detailed connection settings.
4
Page 64

A10
2
3
Click
4
Click
1
Click
Add check marks.
1
Click
Click [Settings] tab and then [ASCII Setup...].
1
Add check marks to [Send line ends with line feeds], [Echo typed characters locally], and
[Append line feeds to incoming line ends].
2
Click [OK] to close [ASCII Setup].
3
Click [OK].
4
Sent
Received
Appendix 3 Checking LAN Communication in Windows
Perform communication with the measuring instrument.
5
Send a character string to the measuring instrument.
The following shows an example of entering "*idn?" and then pressing the Enter key.
Communication has been established if there is a response from the measuring instrument.
In the following example, the "HIOKI,IM3570,V1.00" character string was received.
Page 65

Page 66

 Loading...
Loading...