Page 1

INSTRUCTION MANUAL
For...は専用機種。複数の場合は「/」で区切る。不要の場合はとる。
形名を入力。 複数の場合は「/」で区切る。
3511-50
品名を入力。
LCR HiTESTER
Page 2

Page 3

Contents
Introduction i
Inspection i
Safety Notes ii
Notes on Use iv
Layout of This Manual v
Chapter 1 Product Overview 1
1.1 Product Overview 1
1.2 Product Features
1.3 Names and Functions of Parts
1.3.1 Front View 3
1.3.2 Operation Section Details 4
1.3.3 Rear View 5
1.3.4 Side View 6
Chapter 2 Before Starting Measurement 7
2.1 Connecting the Power Cord 7
2.2 Connecting the Test Leads
2.2.1 Establishing the Connections 9
2.3 Turning the Power On and Off 10
Chapter 3 Basic Functions 11
3.1 Choosing the Testing Parameters 11
3.2 Setting the Test Frequency
3.3 Setting the Test Signal Level
12
12
2
3
8
3.4 Setting the Testing Speed
3.5 Setting the Equivalent Circuit Mode
3.5.1 Equivalent Circuit Mode 14
3.6 Setting the Ranging 16
3.6.1 Test Range 16
3.6.2 Auto Range 20
3.6.3 Hold Range 20
3.7 Open Circuit Compensation 21
3.7.1 Performing Open Circuit Compensation 21
3.7.2 Open Circuit Compensation Error 22
3.7.3 Canceling Open Circuit Compensation 22
13
14
Page 4

3.8 Short Circuit Compensation 23
3.8.1 Performing Short Circuit Compensation 23
3.8.2 Short Circuit Compensation Error 25
3.8.3 Canceling Short Circuit Compensation 25
3.9 Setting the Trigger Signal 26
3.9.1 Setting the Trigger Mode 26
Chapter 4 Other Functions 27
4.1 Comparator Function 27
4.1.1 Operation Sequence 28
4.1.2 Setting the Upper and Lower Limits 28
4.1.3 Comparator Test Mode 30
4.2 Panel Save Function 31
4.2.1 Setting Panel Save 31
4.2.2 Aborting Panel Save 31
4.3 Panel Load Function 32
4.3.1 Setting Panel Load 32
4.3.2 Aborting Panel Load 32
4.4 Key Lock Function 33
4.4.1 Executing the Key Lock Function 33
4.4.2 Cancelling the Key Lock Function 33
4.5 Various Settings Made After Switching on Power 34
4.5.1 Setting Screen Flow After Power ON 34
4.5.2 Setting the Interface 35
4.5.3 Setting Beep 36
4.5.4 Executing System Reboot 37
4.6 Remote Function 38
4.6.1 Remote Mode 38
4.6.2 Cancelling the Remote Mode 38
4.7 The Residual Charge Protection Function 39
Chapter 5 Applications 41
5.1 Testing Using EXT I/O 41
5.1.1 The EXT I/O Connector 41
5.1.2 Pinouts for the EXT I/O Connector 42
5.1.3 Signal Lines for the EXT I/O Connector 43
5.1.4 Circuit Construction and Connections for the EXT I/O
Connector 45
5.1.5 Electrical Characteristics of the Output Signals 46
5.1.6 I/O Signal Timing 47
5.1.7 Time Taken for Testing 48
Page 5

5.2 Supplying DC Bias 50
5.2.1 How to Supply a DC Bias Voltage 51
5.2.2 How to Supply a DC Bias Current 52
5.3 9442 PRINTER (Option) 53
5.3.1 Preparation 53
5.3.2 Connection Method 55
5.3.3 Printing Results 56
5.4 Testing High Impedance Elements 57
5.5 Testing an Element in a Circuit
5.6 External Interference
5.6.1 Countermeasures Against Interference from
the Power Supply Line 59
5.6.2 Countermeasures Against Noise from
the Test Cables 60
58
59
Chapter6 RS-232C Interface 61
6.1 Overview 61
6.1.1 Introduction to the RS-232C Interface 61
6.1.2 Specifications 62
6.2 Connecting Method 63
6.2.1 Handshake 64
6.3 Operation 65
6.3.1 Communication Methods by the RS-232C 65
6.3.2 Message Format 66
6.3.3 Program Message 66
6.3.4 Response Messages 66
6.4 Headers 67
6.5 Data Formats
6.6 Delimiters
6.7 Separators
6.8 Abbreviation of Compound Commands
6.9 Output Queue
6.10 Input Buffer
6.11 Event Registers
6.12 Command Reference
6.12.1 Command Summary 74
68
69
69
70
71
71
72
74
6.13 Format of Command Explanations 76
6.14 Particular Commands
6.15 Commands Specific to the 3511-50
6.16 Initialization Items
6.17 Sample Programs
6.18 Troubleshooting
77
80
98
99
103
Page 6

Chapter 7 Maintenance, Adjustment, and Disposal 105
7.1 Maintenance and Servicing 105
7.2 How to Change the Power Supply Fuse and Change
the Power Supply Voltage
106
7.3 Shipping the Unit
7.4 Troubleshooting
7.5 Disposing of the Unit
109
109
110
Chapter 8 Specifications 113
8.1 General Specifications 113
8.2 Testing Parameters and Calculation Equations
8.3 Test Accuracy
116
118
Chapter 9 Options 121
Page 7
______________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Introduction
Thank you for purchasing the HIOKI "3511-50 LCR HiTESTER." To obtain
maximum performance from the product, please read this manual first, and
keep it handy for future reference.
i
A request
Inspection
Check the 3511-50 unit and the supplied accessories
We have tried to bring this manual as close to perfection as we could
achieve.
If perchance you find any unclear portions, mistakes, omissions, or the like,
we would be most obliged if you could please notify us of them via any
HIOKI agent, or directly.
When you receive the product, inspect it carefully to ensure that no damage
occurred during shipping. In particular, check the accessories, panel
switches, and connectors. If damage is evident, or if it fails to operate
according to the specifications, contact your dealer or Hioki representative.
Main unit
3511-50 LCR HiTESTER
Supplied accessories
(1) Instruction Manual
(2) Grounded three-core power cord (selected according to shipping destination)
(3) Spare fuse for power supply (according to voltage specification)
100 V, 120 V setting: 250 V F1.0AL 20 mm x 5mmdia.
220 V, 240 V setting: 250 V F0.5AL 20 mm x 5mmdia.
NOTE
No interface boards and no test cables are supplied with the unit as standard
equipment. You should order them separately, according to requirements.
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
Introduction
Page 8
ii
______________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Safety Notes
This manual contains information and warnings essential for safe operation
of the product and for maintaining it in safe operating condition. Before
using the product, be sure to carefully read the following safety notes.
This product is designed to conform to IEC 61010 Safety Standards,
WARNING
and has been thoroughly tested for safety prior to shipment. However,
mishandling during use could result in injury or death, as well as
damage to the product. Be certain that you understand the
instructions and precautions in the manual before use. We disclaim
any responsibility for accidents or injuries not resulting directly from
product defects.
The following symbols in this manual indicate the relative importance of
cautions and warnings.
WARNING
CAUTION
Safety symbols
The symbol printed on the product indicates that the user
should refer to a corresponding topic in the manual (marked with
the
In the manual, the symbol indicates particularly important
information that the user should read before using the product.
Indicates a grounding terminal.
Indicates AC (Alternating Current).
Indicates a fuse.
Indicates that incorrect operation presents a significant hazard that
could result in serious injury or death to the user.
Indicates that incorrect operation presents a possibility of injury to
the user or damage to the product.
symbol) before using the relevant function.
NOTE
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
Safety Notes
Advisory items related to performance or correct operation of the
product.
Page 9

iii
______________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Overvoltage Categories
This product conforms to the safety requirements for CAT II measurement
products.
To ensure safe operation of measurement products, IEC 60664 establishes
safety standards for various electrical environments, categorized as CAT I to
CAT IV, and called overvoltage categories. These are defined as follows.
CAT I Secondary electrical circuits connected to an AC electrical outlet
through a transformer or similar device.
CAT II Primary electrical circuits in equipment connected to an AC
electrical outlet by a power cord (portable tools, household
appliances, etc.)
CAT III Primary electrical circuits of heavy equipment (fixed installations)
connected directly to the distribution panel, and feeders from the
distribution panel to outlets.
CAT IV The circuit from the service drop to the service entrance, and to
the power meter and primary overcurrent protection device
(distribution panel).
Higher-numbered categories correspond to electrical environments with
greater momentary energy, so a measurement product designed for CAT III
environments can endure greater momentary energy than one designed for
CAT II. Using a measurement product in an environment designated with a
higher-numbered category than that for which the product is rated could
result in a severe accident, and must be carefully avoided.
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
Safety Notes
Page 10
iv
______________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Notes on Use
Follow these precautions to ensure safe operation and to obtain the full
benefits of the various functions.
WARNING
CAUTION
Before turning the product on, make sure the source voltage
matches that indicated on the product's power connector.
Connection to an improper supply voltage may damage the product
and present an electrical hazard.
To avoid electric shock and ensure safe operation, connect the
power cable to a grounded (3-contact) outlet.
Use this unit near the power supply socket.
The interior of the unit contains some components which are
subject to high voltage, and therefore dangerous. Absolutely do
not remove the cover panel.
Various connectors are present on the outside of the 3511-50. Never
connect any cable to any of these connectors without first turning off the
power supply and removing the power cord. Moreover, check the
connections carefully in order to avoid any chance of setting up a short
circuit etc..
In the event that the equipment malfunctions in any manner during use,
turn off the power immediately, and contact your dealer or HIOKI
representative.
Do not store or use the unit where it will be exposed to direct sunlight,
high temperatures, high humidity, or condensation. If exposed to such
conditions, the unit may be damaged, the insulation may deteriorate, and
the unit may no longer satisfy its specifications.
This product should be installed and operated indoors only, between 0
and 40
-10
The unit should always be stored in a range from -10 to 55 , 80% RH
or less.
Do not store or use the product where it could be exposed to direct
sunlight, high temperature or humidity, or condensation. Under such
conditions, the product may be damaged and insulation may deteriorate
so that it no longer meets specifications.
Do not drop the unit or subject it to severe shock. Doing so can cause
serious damage.
To avoid damage to the product, protect it from vibration or shock during
transport and handling, and be especially careful to avoid dropping.
and 35 to 80%RH. However, it can be safely operated down to
.
Warranty
HIOKI cannot be responsible for losses caused either directly or indirectly by
the use of the unit with other equipment, or if ownership is transferred to a
third party.
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
Notes on Use
Page 11

v
______________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Layout of This Manual
Chapter 1 Product Overview
Describes the product generally, and lists the parts and functions.
Chapter 2 Before Starting Measurement
How to connect the power cord etc., and important precautions before
operation.
Chapter 3 Basic Functions
Description of operating procedures and normal measurement functions
Chapter 4 Other Functions
Special functions.
Chapter 5 Detailed Description of Applications
Various testing applications.
Chapter 6 RS-232C Interface
General description of RS-232C and explanation of related commands.
Chapter 7 Maintenance, Adjustment, and Disposal
Chapter 8 Specifications
Chapter 9 Options
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
Layout of This Manual
Page 12

vi
______________________________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
Layout of This Manual
Page 13

1
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Chapter 1
1
2
1.1 Product Overview
The HIOKI 3511-50 LCR HiTESTER is capable of measuring the impedance
of various devices. With a wide range of test frequencies (from 120 Hz to 1
kHz), the 3511-50 offers high-speed, high-accuracy measurement
capabilities.
Product Overview
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
A
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
1.1 Product Overview
Page 14

2
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
1.2 Product Features
(1) Compact, lightweight single-function model
Streamlined to provide a single function for test frequencies 120 Hz and
1 kHz, the 3511-50 is compact and lightweight.
(2) High-speed measurement
The 3511-50 is capable of high-speed measurement: 5 ms at test frequency
1 kHz, and 13 ms at 120 Hz.
(3) Comparator function
On the 3511-50, comparator functions are standard. Different comparators
may be executed for two separate displayed parameters.
(4) LED display
Provides superior visibility.
(5) Two interfaces
The 3511-50 offers external I/O for sequencing and a standard RS-232C
interface. An optional 9518-01 GP-IB INTERFACE is also available.
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
1.2 Product Features
Page 15
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
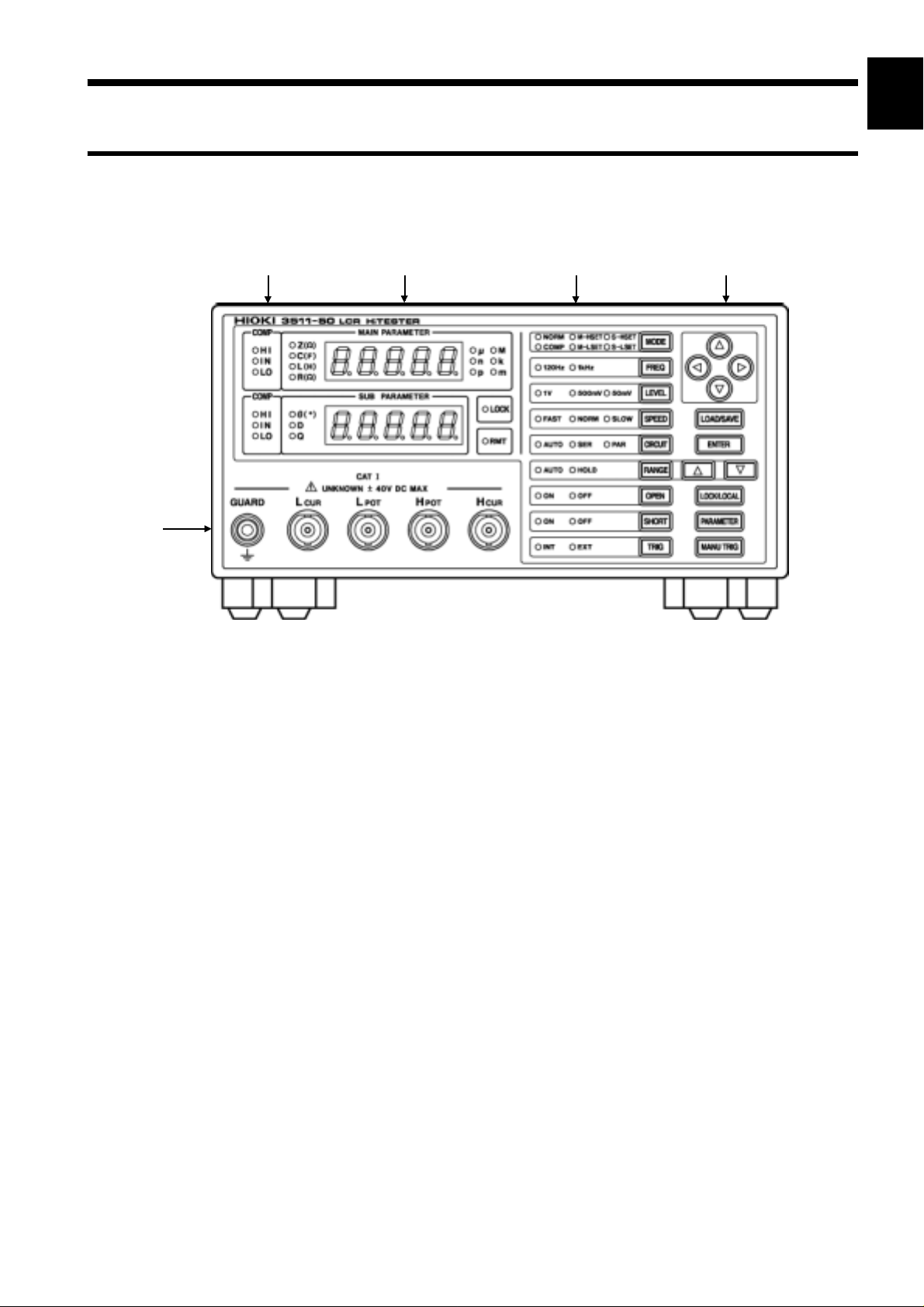
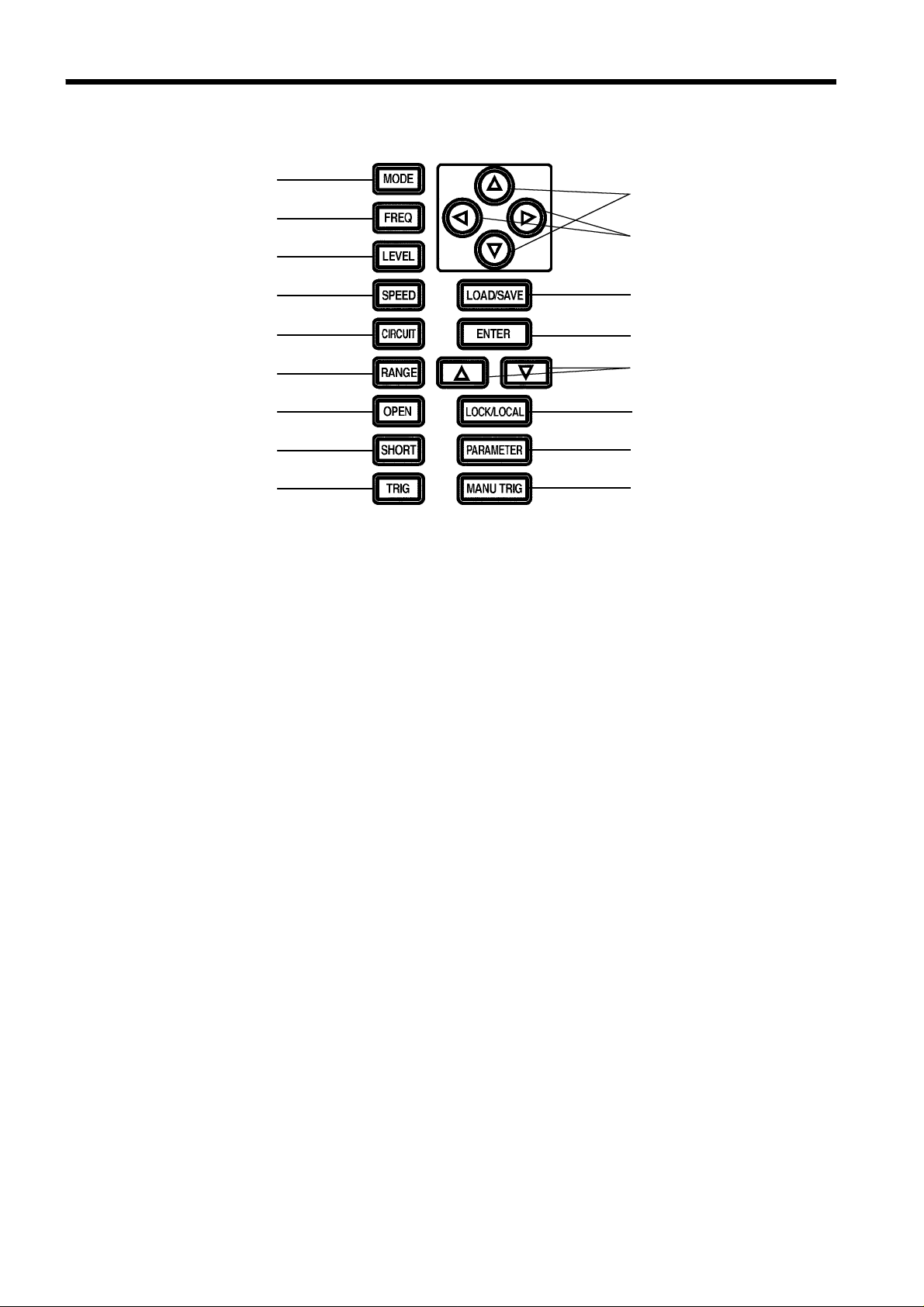
1.3 Names and Functions of Parts
3
1
1.3.1 Front View
3 1 2 4
5
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
1. Measurement display
Displays a testing parameter and corresponding measurement.
2. Status display
Displays current test conditions, presettings, and other information.
3. Comparator judgment display
Displays judgment in comparator mode.
4. Operation section
Use to set test conditions and to make other settings (see next page for more
information).
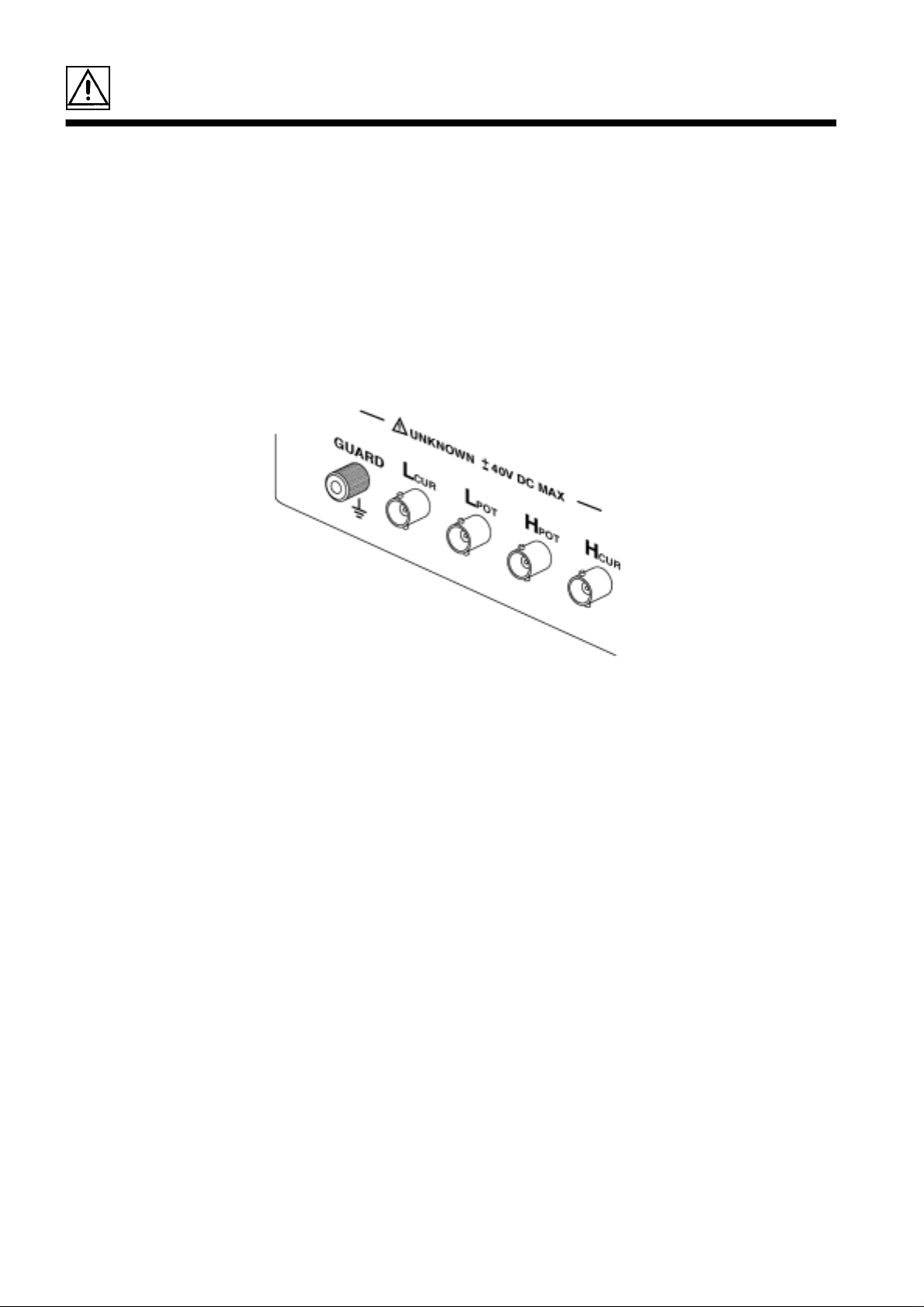
5. Test terminals
There are five test terminals:
H
: The test signal is supplied to this terminal.
CUR
H
: Detected voltage high terminal
POT
L
: Detected voltage low terminal
POT
L
: Test current detected terminal
CUR
GUARD: Guard terminal
These test terminals are designed according to the safety standard;
Pollution Degree 2, Overvoltage Category I.
9
10
11
12
13
14
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
1.3 Names and Functions of Parts
A
Page 16
4
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
1.3.2 Operation Section Details
1
17
2
16
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
15
14
13
12
11
10
1. Test mode selector key 10. Manual trigger key
2. Test frequency selector key 11. Testing parameter selector key
3. Test signal level selector key 12. LOCK/LOCAL key
4. Testing speed selector key 13. Test range selector key (up/down)
5. Equivalent circuit mode selector key 14. ENTER key
6. Test range selector key 15. LOAD/SAVE key
7. Open circuit compensation key 16. Digit selector key (left/right)
8. Short circuit compensation key 17. Count-setting key (up/down)
9. Trigger mode selector key
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
1.3 Names and Functions of Parts
Page 17
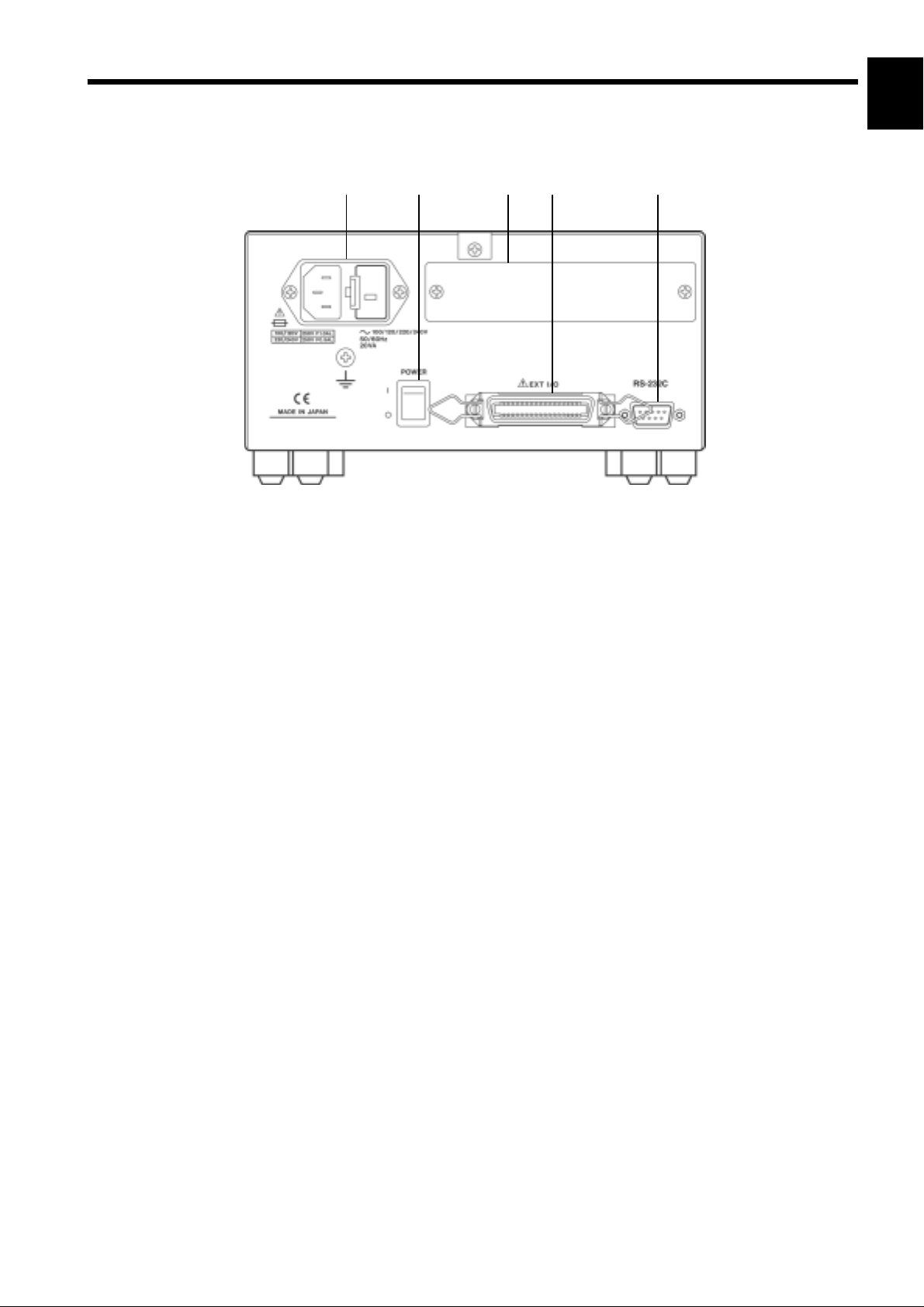
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
1.3.3 Rear View
5
1
12 34 5
1. Power input socket with voltage selector
Connect the supplied power cord here.
2. Power switch
Turns the power for the unit on and off.
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
3. Optional equipment interface
The optional 9518-01 GP-IB INTERFACE is connected here.
4. EXT I/O connector
For input of an external trigger signal and output of comparator results.
Compatible with sequencer connection.
5. RS-232C connector
Connect the RS-232C cable here.
9
10
11
12
13
14
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
1.3 Names and Functions of Parts
A
Page 18
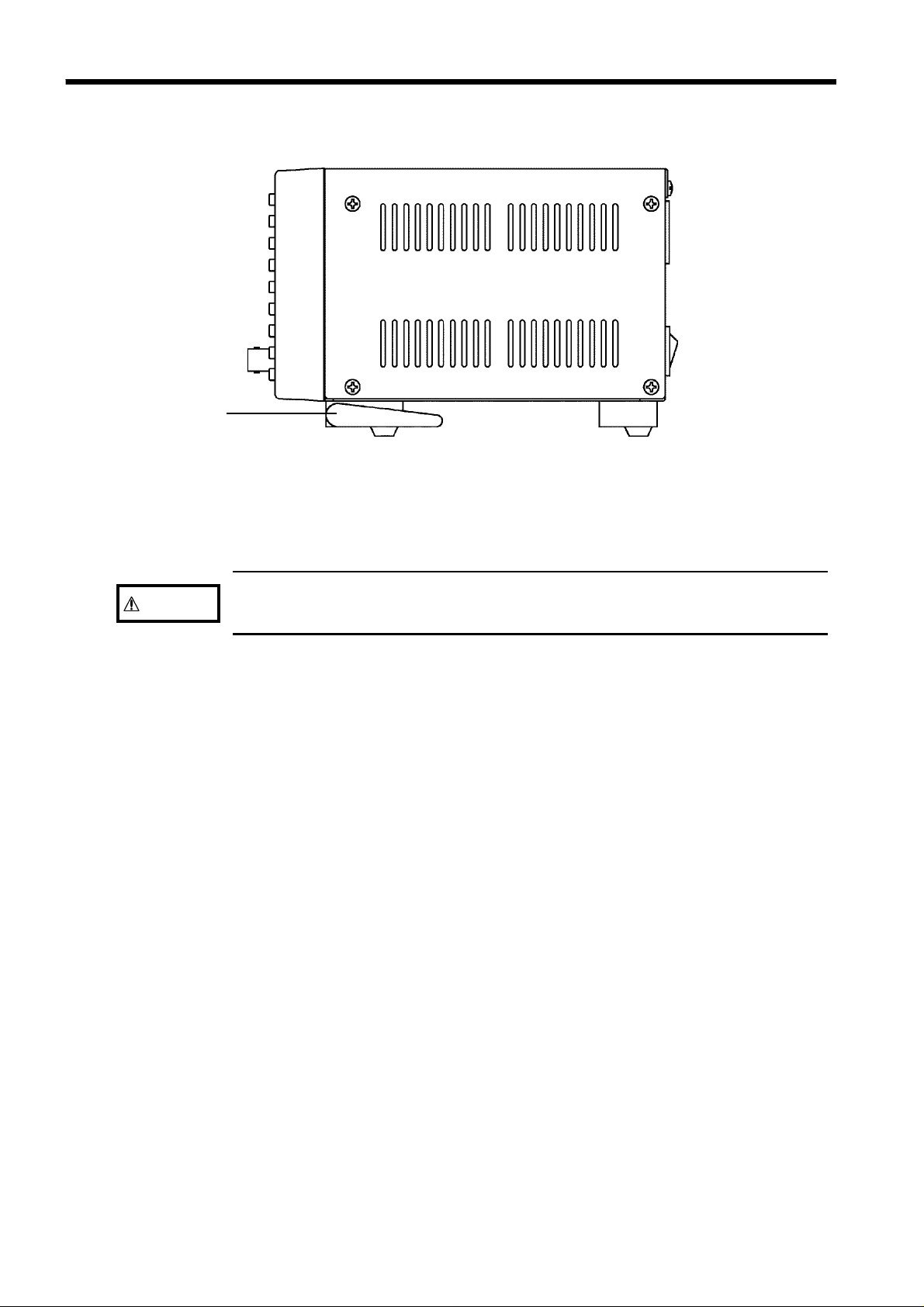
6
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
1.3.4 Side View
1
CAUTION
1. Stand
Do not apply strong downward pressure with the stand extended. Damage
to the stand will result.
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
1.3 Names and Functions of Parts
Page 19
7
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Chapter 2
1
2
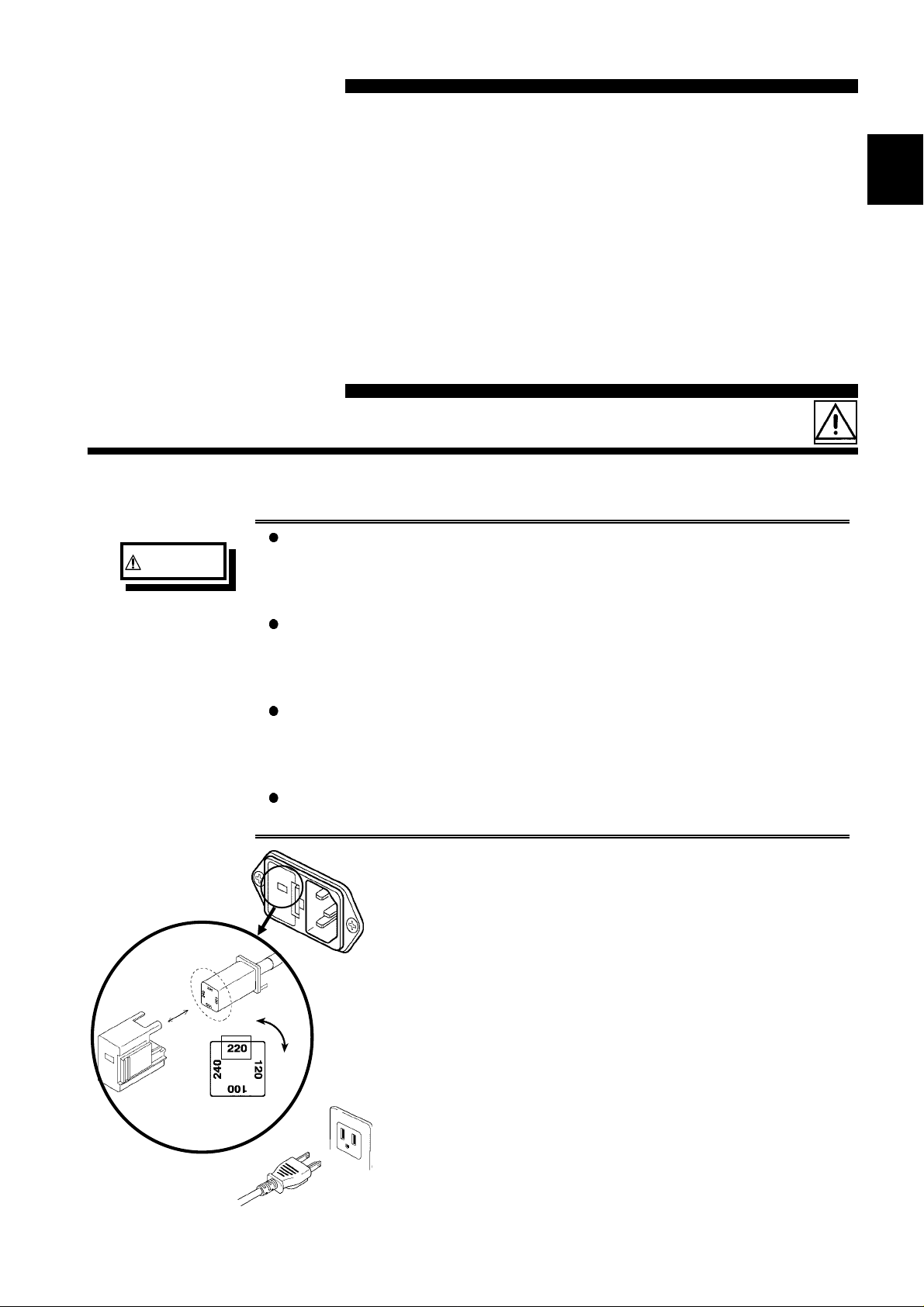
2.1 Connecting the Power Cord
When a 3511-50 unit is ordered, the supply voltage is set in
WARNING
the factory to the value specified, which can be 100 V, 120 V,
220 V, or 240 V.
The maximum rated power (with all options fitted) is 20 VA.
Before turning the product on, make sure the source voltage
matches that indicated on the product's power connector.
Connection to an improper supply voltage may damage the
product and present an electrical hazard.
The power supply voltage for this product is switchable. To
avoid electrical accidents, check that the voltage selector is
set correctly for the supply voltage you are using.
(For details, refer to Section 7.2)
To avoid electric shock and ensure safe operation, connect
the power cable to a grounded (3-contact) outlet.
Before Starting
Measurement
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
The power cord is connected according to the following
procedure.
1. Check that the main power switch of the unit is off.
2. Check that the power supply voltage is correct, and
connect the proper end of the power cord to the power
input socket (with voltage selector) at the rear of the unit.
3. Plug the other end of the power cord into the power
supply socket.
Grounding
Use the grounding type (three-wire) power cord supplied.
The unit will be grounded automatically.
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
2.1 Connecting the Power Cord
11
12
13
14
A
Page 20
8
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
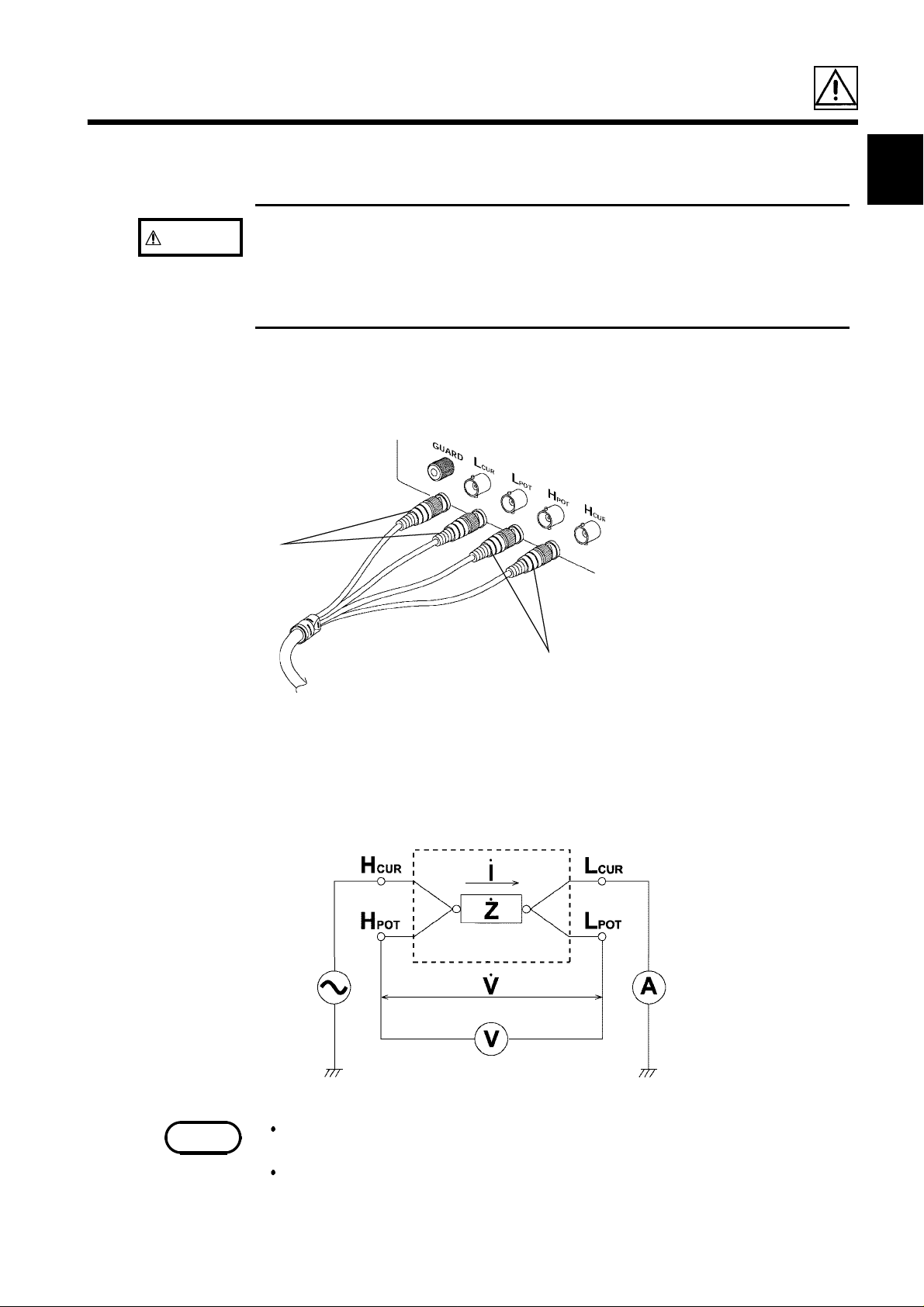
2.2 Connecting the Test Leads
The 3511-50 has five test terminals:
H
terminal (to which the test signal is supplied)
CUR
H
terminal (detected voltage high terminal)
POT
L
terminal (detected voltage low terminal)
POT
L
terminal (test current detected terminal)
CUR
GUARD terminal (connected to the chassis of the unit).
These test terminals are designed according to the safety standard;
Pollution Degree 2, Overvoltage Category I.
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
2.2 Connecting the Test Leads
Page 21
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
2.2.1 Establishing the Connections
9
1
2
CAUTION
The maxim um voltage whic h can be applied to the test terminals of t he
3511-50 unit is 40 V DC. If a DC voltage greater than this is applied
continuously, t he unit m ay be damaged.
For how to apply a DC bias voltage, refer to Section 5.2, " Supplying DC
Bias."
If using a test lead set supplied by HIOKI, connect the red leads to the H
terminal and to the H
terminal and to the L
Black
terminal, and connect the black leads to the L
POT
terminal.
POT
Red
CUR
3
4
CUR
5
6
7
8
NOTE
The unit is designed and adjusted for 75 Ω coaxial cable test leads. It is
best to use HIOKI test leads.
The connections to the article to be tested are as shown in the
following figure.
Test fixture
No test cables are included with the 3511-50 unit. They must be
purchased separately. For details, refer to Chapter 9, "Options."
If all four terminals are left floating, the numbers which appear on the
display are completely meaningless.
9
10
11
12
13
14
A
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
2.2 Connecting the Test Leads
Page 22

10
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
2.3 Turning the Power On and Off
How to turn the power on
Turn on the power switch on the rear panel. All LEDs on the front panel
light.
The test conditions will start off the same as they were when last the power
was turned off.
NOTE
NOTE
Wait for 60 minutes after turning on the power before starting testing, so as
to allow the unit to warm up fully.
How to turn the power off
Turn off the power switch on the rear panel. The test conditions will be
preserved.
Even if the power supply is interrupted because of a power failure or the
like, the test conditions (settings) will not be lost; when the power is turned
on again, the unit will return to its state just before the interruption.
This happens, however, in the normal test mode or comparator execution
mode only.
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
2.3 Turning the Power On and Off
Page 23
11
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Chapter 3
1
2
Basic Functions
3.1 Choosing the Testing Parameters
Z-θ Impedance (Ω) - Impedance phase angle ( )
C-D Static capacitance (F) - Loss coefficient (=tan δ)
L-D Inductance (H) - Loss coefficient (=tan δ)
L-Q Inductance (H) - Q factor
R Effective resistance (Ω)
As shown above, the 3511-50 permits five possible combinations of testing
parameters. Cycle through the combinations by repeatedly pressing .
Use the LED lamps to the left of the measurement display to check on
selected testing parameters.
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
NOTE
Check polarity via the impedance phase angle. Except for impedance phase
angle, all values are displayed as absolute values.
For details, refer to Section 8.2, "Testing Parameters and Calculation
Equations."
10
11
12
13
14
A
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
3.1 Choosing the Testing Parameters
Page 24
12
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
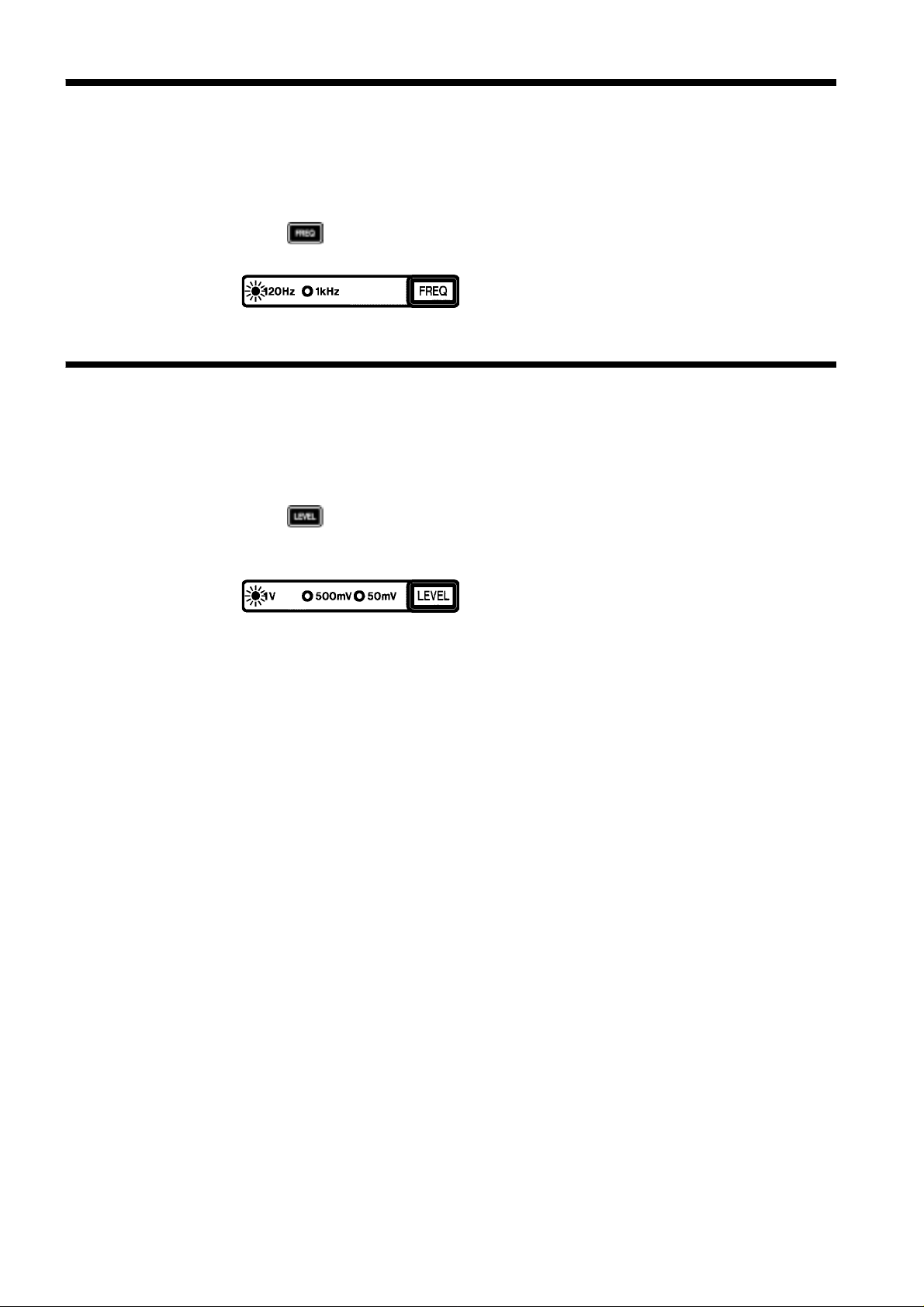
3.2 Setting the Test Frequency
For the 3511-50's test frequency, you may specify either 120 Hz or 1 kHz.
Procedure
Press to toggle between 120 Hz and 1 kHz. Use the LED lamp to the
left of the key to check on a set test frequency.
3.3 Setting the Test Signal Level
For the 3511-50's test signal level, you may specify 1 V, 500 mV or 50 mV.
Procedure
Press repeatedly to cycle through available settings: 1 V, 500 mV, and
50 mV. Use the LED lamp to the left of the key to check on a set test
signal level.
Precautions for changing test signal levels
The value of the test signal level may change according to the sample which
is being tested. During measurement, keep in mind that inductance is often
current-dependent.
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
3.2 Setting the Test Frequency
Page 25
13
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
3.4 Setting the Testing Speed
1
NOTE
For testing speed, select from one of the following three levels, depending on
the specific purpose. The slower the testing speed is, the more accurate are
the results.
FAST : Low accuracy testing is performed at high speed.
NORM : The speed used for normal testing
SLOW : High accuracy testing is performed slowly.
Procedure
Press repeatedly to cycle through available settings: FAST, NORM, and
SLOW. Use the LED lamp to the left of the key to check on a set testing
speed.
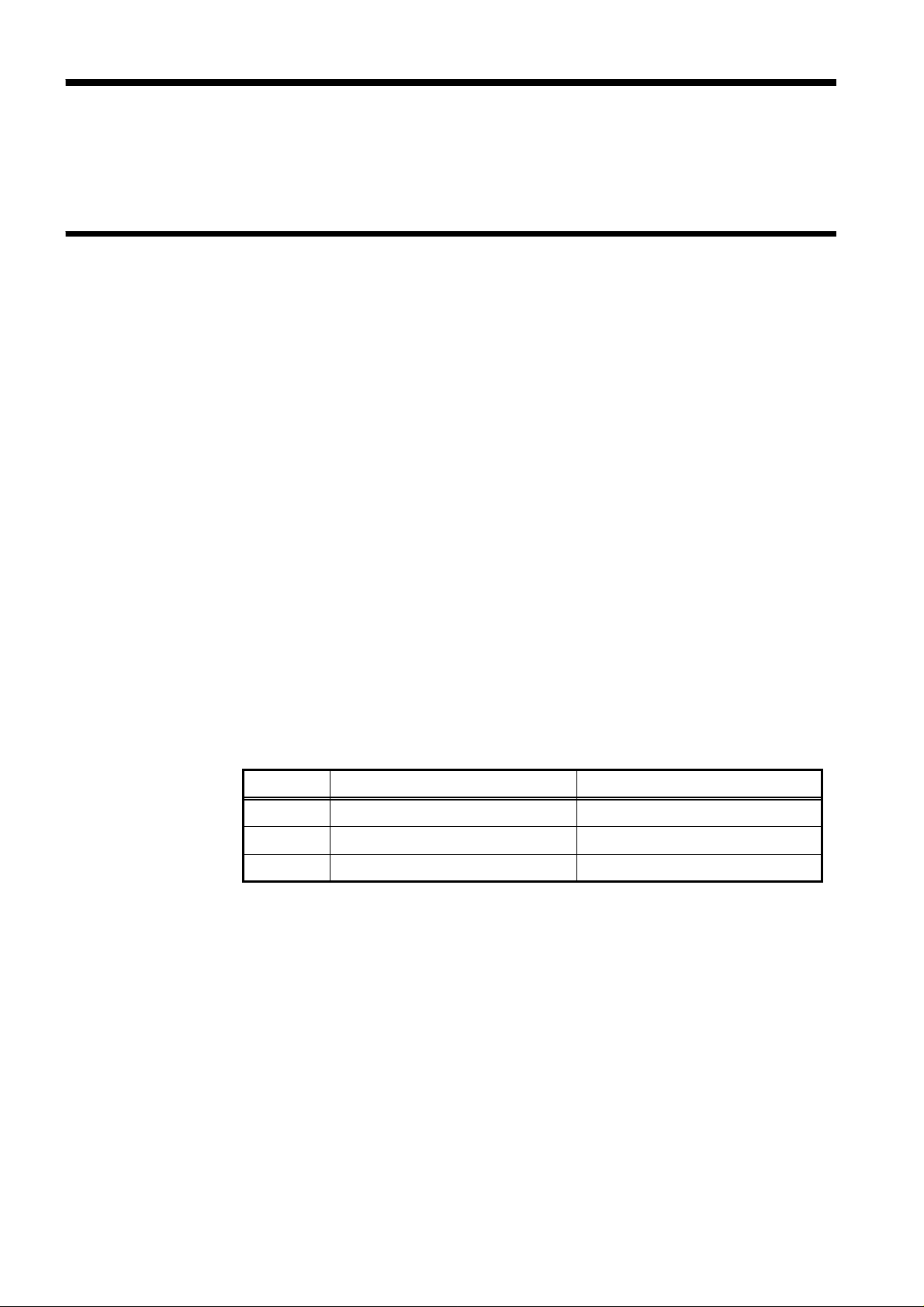
Testing speed
Test frequency FAST NORM SLOW
120 Hz 13 ms 90 ms 400 ms
1kHz 5ms 60 ms 300 ms
The testing time values above are for reference only, valid when Z-θ is
displayed and varying according to testing parameter setting conditions,
range mode, OPEN/SHORT compensation, and other conditions.
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
A
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
3.4 Setting the Testing Speed
Page 26
14
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
3.5 Setting the Equivalent Circuit Mode
You may set an equivalent circuit mode. Automatic selection is also
possible.
3.5.1 Equivalent Circuit Mode
The 3511-50 unit analyses the test sample in terms of a pure inductive
component (L), an equivalent circuit construction composed of a pure
capacitive component (C), and a pure resistive component (R), and
calculates as though these components were connected in series, or
alternatively connected in parallel. Therefore, it is possible for the user to
select either a series equivalent circuit mode or a parallel equivalent circuit
mode for this conceptual connection together of these L, C, and R
components.
When the impedance of the sample being tested is relatively high, the
parallel equivalent circuit mode should be selected manually, and when the
impedance of the sample being tested is relatively low, the series equivalent
circuit mode should be selected manually.
Generally, for a device such as an electrolytic capacitor or the like with a
high D value (i.e., a low Q value), the test values obtained when testing
using series equivalent circuit mode differ from those obtained when testing
using parallel equivalent circuit mode. The greater the resistance component
in the sample being tested, the more this difference in the test values
appears.
For example, the test values for capacitors of the same capacitance which
have different values of D in series equivalent circuit mode and in parallel
equivalent circuit mode may be as follows:
Series equivalent circuit mode
D=0 C C
D = 0.1 1.005C 0.995C
D = 0.5 1.118C 0.8944C
Parallel equivalent circuit mode
(Where C is the static capacitance)
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
3.5 Setting the Equivalent Circuit Mode
Page 27
15
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Therefore it is necessary for the user clearly to understand the setting of this
test mode, in order properly to assess test samples.
In general, parallel equivalent circuit mode should be used for elements
which have relatively low capacitance and high impedance such as film
capacitors and ceramic capacitors, since parallel resistance can cause great
loss in this case; while series equivalent circuit mode should be used for
elements which have relatively high capacitance and low impedance such as
electrolytic capacitors, since series resistance can cause great loss in this
case.
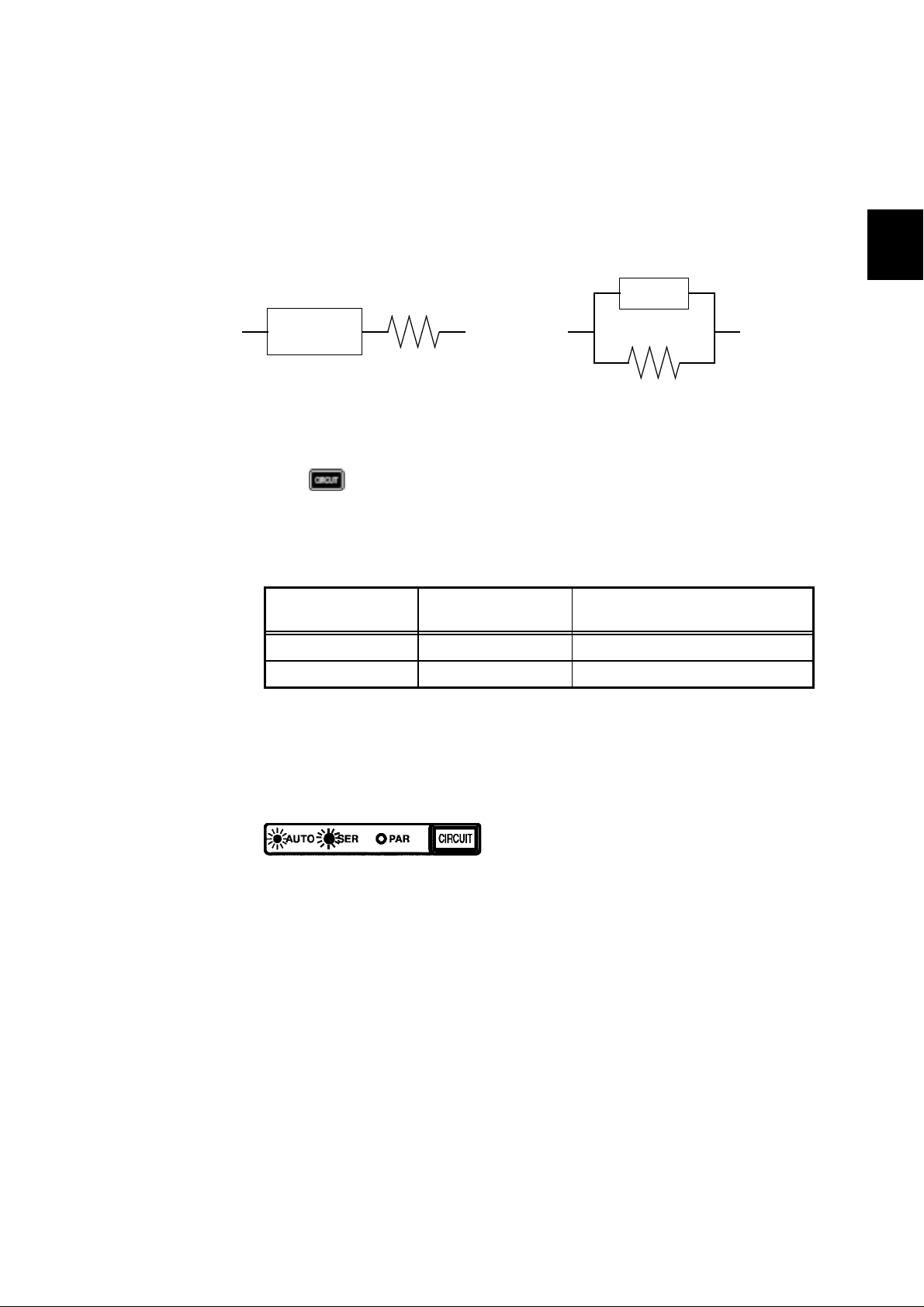
Series equivalent circuit Parallel equivalent circuit
Procedure
Press repeatedly to cycle through available settings: AUTO, SER, and
PAR.
AUTO : The series equivalent circuit mode or the parallel equivalent circuit
mode is selected automatically according to the following table,
following the measurement range.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Z,L,R-range number C-range number
1to5 6to10 Series equivalent circuit
6to10 1to5 Parallel equivalent circuit
SER : Series equivalent circuit mode
PAR : Parallel equivalent circuit mode
Use the LED lamp to the left of the key to check on a set equivalent circuit
mode.
The equivalent circuit mode is
set automatically.
8
9
10
11
12
13
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
3.5 Setting the Equivalent Circuit Mode
14
A
Page 28
16
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
3.6 Setting the Ranging
You may set a test range. Automatic selection is also possible.
3.6.1 Test Range
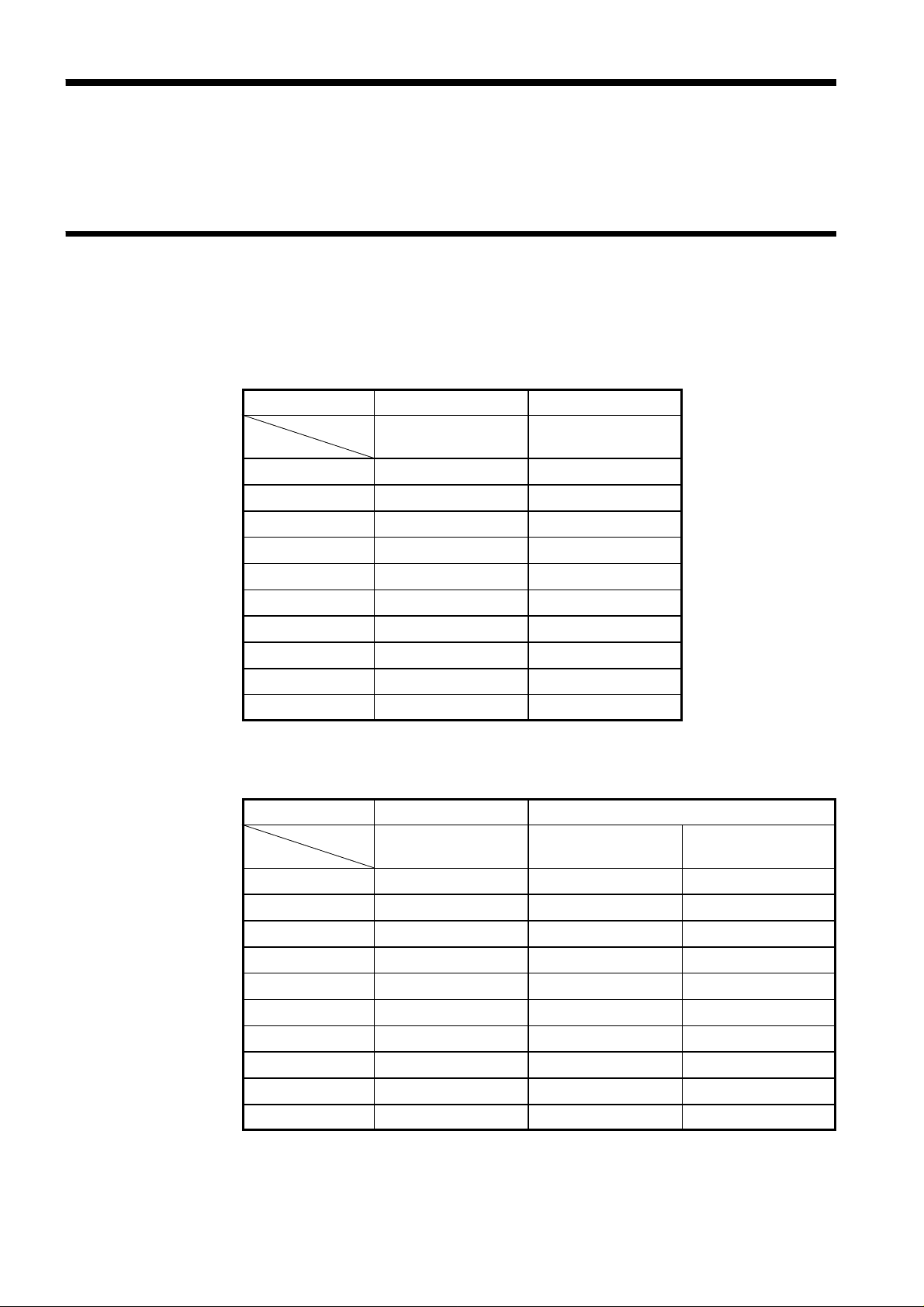
A test range is set, with impedance as a reference. The range numbers,
corresponding impedance ranges, and first parameter display ranges are as
follows:
Z-display range * R-display range
Frequency
Range number
10 009.00 to 200.00 MΩ 000.00 to 999.99 MΩ
9 0.9000 to 9.9999 MΩ 0.0000 to 9.9999 MΩ
8 090.00 to 999.99 kΩ 000.00 to 999.99 kΩ
7 09.000 to 99.999 kΩ 00.000 to 99.999 kΩ
6 0.9000 to 9.9999 kΩ 0.0000 to 9.9999 kΩ
5 090.00 to 999.99 Ω 000.00 to 999.99 Ω
4 09.000 to 99.999 Ω 00.000 to 99.999 Ω
3 0.9000 to 9.9999 Ω 0.0000 to 9.9999 Ω
2 0.0900 to 0.9999 Ω 0.0000 to 9.9999 Ω
1 0.0100 to 0.0999 Ω 0.0000 to 9.9999 Ω
Common to
120 Hz and 1 kHz
Common to
120 Hz and 1 kHz
*: Range of impedance which can be measured within the accuracy
guaranteed
Z-display range * L-display range
Frequency
Range number
10 009.00 to 200.00 MΩ 000.00 to 999.99 kH 00.000 to 99.999 kH
9 0.9000 to 9.9999 MΩ 00.000 to 99.999 kH 0.0000 to 9.9999 kH
8 090.00 to 999.99 kΩ 0.0000 to 9.9999 kH 000.00 to 999.99 H
7 09.000 to 99.999 kΩ 000.00 to 999.99 H 00.000 to 99.999 H
6 0.9000 to 9.9999 kΩ 00.000 to 99.999 H 0.0000 to 9.9999 H
5 090.00 to 999.99 Ω 0.0000 to 9.9999 H 000.00 to 999.99 mH
4 09.000 to 99.999 Ω 000.00 to 999.99 mH 00.000 to 99.999 mH
3 0.9000 to 9.9999 Ω 00.000 to 99.999 mH 0.0000 to 9.9999 mH
2 0.0900 to 0.9999 Ω 0.0000 to 9.9999 mH 000.00 to 999.99 µH
1 0.0100 to 0.0999 Ω 000.00 to 999.99 µH 00.000 to 99.999 µH
*: Range of impedance which can be measured within the accuracy guaranteed
Common to
120 Hz and 1 kHz
120 Hz 1 kHz
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
3.6 Setting the Ranging
Page 29
17
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Z-display range * C-display range
Frequency
Range number
10 009.00 to 200.00 MΩ 1 000.00 to 999.99 pF 00.000 to 99.999 pF
9 0.9000 to 9.9999 MΩ 2 0.0000 to 9.9999 nF 000.00 to 999.99 pF
8 090.00 to 999.99 kΩ 3 00.000 to 99.999 nF 0.0000 to 9.9999 nF
7 09.000 to 99.999 kΩ 4 000.00 to 999.99 nF 00.000 to 99.999 nF
6 0.9000 to 9.9999 kΩ 5 0.0000 to 9.9999 µF 000.00 to 999.99 nF
5 090.00 to 999.99 Ω 6 00.000 to 99.999 µF 0.0000 to 9.9999 µF
4 09.000 to 99.999 Ω 7 000.00 to 999.99 µF 00.000 to 99.999 µF
3 0.9000 to 9.9999 Ω 8 0.0000 to 9.9999 mF 000.00 to 999.99 µF
2 0.0900 to 0.9999 Ω 9 00.000 to 99.999 mF 0.0000 to 9.9999 mF
1 0.0100 to 0.0999 Ω 10 000.00 to 999.99 mF 00.000 to 99.999 mF
*: Range of impedance which can be measured within the accuracy guaranteed
NOTE
Common to
120 Hz and 1 kHz
If the impedance exceeds the measurement range, the first parameter display
is "UF" (underflow, i.e., impedance below the measurement range) or "OF"
(overflow, i.e., impedance above the measurement range), and the second
parameter display disappears.
Range number
Frequency
120 Hz 1 kHz
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
3.6 Setting the Ranging
A
Page 30
18
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
To measure a parameter other than Z - i.e., C, L, or R - determine an
appropriate range based on impedance. The following table presents
appropriate ranges for C and L when D is equal to or smaller than 0.1 and
those when θ is equal to or smaller than 6 .
Test range Z R
Frequency Common to
120Hzand1kHz
Range number Range Display range Range Display range
10 100 MΩ 200.00 MΩ 100 MΩ 200.00 MΩ
009.00 MΩ 009.10 MΩ
9 10 MΩ 9.9999 MΩ 10 MΩ 9.9000 MΩ
0.9000 MΩ 0.9100 MΩ
8 1MΩ 999.99 kΩ 1MΩ 990.00 kΩ
090.00 kΩ 091.00 kΩ
7 100 kΩ 99.999 kΩ 100 kΩ 99.000 kΩ
09.000 kΩ 09.100 kΩ
6 10 kΩ 9.9999 kΩ 10 kΩ 9.9000 kΩ
0.9000 kΩ 0.9100 kΩ
5 1kΩ 999.99 Ω 1kΩ 990.00 Ω
090.00 Ω 091.00 Ω
4 100 Ω 99.999 Ω 100 Ω 99.000 Ω
09.000 Ω 09.100 Ω
3 10 Ω 9.9999 Ω 10 Ω 9.9000 Ω
0.9000 Ω 0.9100 Ω
2 1 Ω 0.9999 Ω 1 Ω 0.9900 Ω
0.0900 Ω 0.0900 Ω
1 100 mΩ 0.0999 Ω 100 mΩ 0.0990 Ω
0.0100 Ω 0.0110 Ω
Common to
120Hzand1kHz
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
3.6 Setting the Ranging
Page 31

19
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Test range C L
Frequency 120 Hz 1kHz 120 Hz 1kHz
Range number Range Display range Range Display range Range Display range Range Display range
10 1F 999.99 mF 100 mF 99.999 mF 200 kH 200.00 kH 20 kH 20.000 kH
013.50 mF 01.600 mF 012.00 kH 01.450 kH
9 14.5 mF 14.500 mF 1.7 mF 1.7000 mF 13 kH 13.000 kH 1.55 kH 1.5500 kH
01.350 mF 0.1600 mF 01.200 kH 0.1450 kH
8 1.45 mF 1.4500 mF 170 µF 170.00 µF 1.3 kH 1.3000 kH 155 H 155.00 H
0.1350 mF 016.00 µF 0.1200 kH 014.50 H
7 145 µF 145.00 µF 17 µF 17.000 µF 130 H 130.00 H 15.5 H 15.500 H
013.50 µF 01.600 µF 012.00 H 01.450 H
6 14.5 µF 14.500 µF 1.7 µF 1.7000 µF 13 H 13.000 H 1.55 H 1.5500 H
01.350 µF 0.1600 µF 01.200 H 0.1450 H
5 1.45 µF 1.4500 µF 170 nF 170.00 nF 1.3 H 1.3000 H 155 mH 155.00 mH
0.1350 µF 016.00 nF 0.1200 H 014.50 mH
4 145 nF 145.00 nF 17 nF 17.000 nF 130 mH 130.00 mH 15.5 mH 15.500 mH
013.50 nF 01.600 nF 012.00 mH 01.450 mH
3 14.5 nF 14.500 nF 1.7 nF 1.7000 nF 13 mH 13.000 mH 1.55 mH 1.5500 mH
01.350 nF 0.1600 nF 01.200 mH 0.1450 mH
2 1.45 nF 1.4500 nF 170 pF 170.00 pF 1.3 mH 1.3000 mH 155 µH 155.00 µH
0.1350 nF 016.00 pF 0.1200 mH 014.50 µH
1 145 pF 145.00 pF 17 pF 17.000 pF 130 µH 130.00 µH 15.5 µH 15.500 µH
009.40 pF 00.940 pF 014.00 µH 01.600 µH
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
A
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
3.6 Setting the Ranging
Page 32

20
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Procedure
Press to toggle between AUTO and HOLD.
AUTO
HOLD
Use the LED lamp to the left of the key to check on a set test range.
3.6.2 Auto Range
The most suitable test range is set automatically. Useful when measuring an
unknown sample.
NOTE
Measurement requires more time.
3.6.3 Hold Range
Take measurements in the same range regardless of the value of the sample.
This is useful for high-speed measurement.
: The most suitable test range is set automatically.
: The test range is fixed, and mayonlybealteredmanually.
Procedures
(ei th er 1 o r 2 w il l do)
1. Press to set HOLD mode.
2. Press or . The range select key moves up or down.
As the range changes with or , the range number appears on the
measurement display for about a half-second, then returns to measurement
mode.
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
3.6 Setting the Ranging
Page 33

21
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
3.7 Open Circuit Compensation
With open circuit compensation, it is possible to reduce the influence of the
floating impedance of the test cables and thereby to enhance the accuracy of
measurement. It is effective for test samples whose impedance is relatively
high.
NOTE
With open circuit compensation set, compensated values for 120 Hz and 1
kHz are input. These are unrelated to test frequency setting conditions.
The testing accuracy specified in the specification of the 3511-50 unit
assumes that open circuit compensation and short circuit compensation is
being performed, as appropriate.
When you have changed the test cables, be sure to perform compensation
again. Correct test values will not be obtained if you go on testing using
the same old compensation values which were obtained before the cable
change.
Compensation is possible for the impedance range of 1 kΩ or greater.
3.7.1 Performing Open Circuit Compensation
Procedures
(1) Make sure that the HIGH and LOW leads are not contacted together.
NOTE
As closely as possible, route the test cable and set the probe-terminal
distance duri ng this procedure as if performing actual measurement.
Execute the guarding process. For the guarding process, refer to Section 5.4,
"Testing High Impedance Elements."
(2) Press . Begin compensation upon confirmation that the first
parameter measurement display (MAIN PARAMETER) is as shown.
The LED lamp flashes during open circuit compensation.
(3) If compensation ends properly, the unit beeps once and returns to normal
test mode.
(4) Refer to the LED lamp to the left of the key to check for normal
completion of open circuit compensation.
NOTE
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Open circuit compensation takes about 30 s.
3.7 Open Circuit Compensation
Page 34

22
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
If an error occurs during open circuit compensation, the unit beeps to notify
you of the error. An error message appears, as shown, and compensation is
aborted.
Press to return the unit to normal test mode.
NOTE
If an error occurs, when you return to normal test mode after aborting open
circuit compensation, the measurement value is not compensated for.
3.7.2 Open Circuit Compensation Error
The following are possible causes:
1. The circuit across HIGH and LOW terminals is not open.
2. The test cable is not connected correctly.
3. The impedance across the terminals does not reach 1 kΩ.
3.7.3 Canceling Open Circuit Compensation
Procedures
(1) Press with open circuit compensation ON. Open circuit
compensation is canceled. The value compensated for is not saved.
(2) The open circuit compensation will remain invalid until the
compensation data is deleted and another open circuit compensation is
performed.
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
3.7 Open Circuit Compensation
Page 35

23
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
3.8 Short Circuit Compensation
With short circuit compensation, i t is possible to reduce the influence of the
residual impedance of the test cables and thereby to enhance the accuracy of
measurement. It is effective for test samples whose impedance is relatively
low.
NOTE
With short circuit compensation set, compensated values for 120 Hz and 1
kHz are input. These are unrelated to test frequency setting conditions.
The testing accuracy specified in the specification of the 3511-50 unit
assumes that open circuit compensation and short circuit compensation is
being performed, as appropriate.
When you have changed the test cables, be sure to perform compensation
again. Correct test values will not be obtained if you go on testing using
the same old compensation values which were obtained before the cable
change.
Compensation is possible for the impedance range of 1 kΩ or less.
3.8.1 Performing Short Circuit Compensation
Procedures
(1) A shorting bar is used. This shorting bar is for short circuiting together
the ends of the test leads. Use an object whose impedance is as low as
possible.
Metallicplate
Possible
Metallic wire
Not possible
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
3.8 Short Circuit Compensation
Page 36

24
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
(2) Short circuit together the HIGH and LOW leads. In order to keep
external influences as low as possible, be sure to thrust the shorting bar
in all the way.
NOTE
NOTE
As closely as possible, route the test cable during this procedure as if
performing actual measurement.
(3) Press . Begin compensation upon confirmation that the first
parameter measurement display (MAIN PARAMETER) is as shown.
The LED lamp flashes during short circuit compensation.
(4) If compensation ends properly, the unit beeps once and returns to normal
test mode.
(5) Refer to the LED lamp to the left of the key to check for normal
completion of short circuit compensation.
Short circuit compensation takes about 30 s.
If an error occurs during short circuit compensation, the unit beeps to notify
you of the error. An error message appears, as shown, and compensation is
aborted.
Press to return the unit to normal test mode.
NOTE
If an error occurs, when you return to normal test mode after aborting short
circuit compensation, the measurement value is not compensated for.
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
3.8 Short Circuit Compensation
Page 37

25
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
3.8.2 Short Circuit Compensation Error
The following are possible causes:
1. The circuit across HIGH and LOW terminals is not short.
2. The test cable is not connected correctly.
3. The impedance across the terminals exceeds 1 kΩ.
3.8.3 Canceling Short Circuit Compensation
Procedures
(1) Press with short circuit compensation ON. Short circuit
compensation is canceled. The value compensated for is not saved.
(2) The short circuit compensation will remain invalid until the
compensation data is deleted an d another short circuit compensation is
performed.
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
3.8 Short Circuit Compensation
Page 38

26
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
3.9 Setting the Trigger Signal
The internal trigger or the external trigger can be set.
INT (Internal trigger mode):
Continuous testing is performed while automatically generating an internal
trigger signal.
EXT (External trigger mode):
A trigger signal is input from the outside either manually or automatically.
3.9.1 Setting the Trigger Mode
Press to toggle between INT and EXT. Use the LED lamp to the left
of the key to check on a set test frequency.
(1) Internal trigger mode
Testing is performed continuously.
(2) External trigger mode
Testing is performed with (manual trigger).
Press this key to perform testing once.
Testing is performed with a trigger from the EXT I/O connector TRIG
terminal.
When inputting the trigger signal through the interface:
Testing is performed once, when the "*TRG" command is transferred from
the interface. For details, see Chapter 6, "RS-232C Interface", or Chapter 6,
"Command Reference for 3511-50" of the Instruction Manual for the
optional 9518-01 GP-IB INTERFACE.
When inputting the trigger signal through the EXT I/O connector:
Testing is performed once, each time a negative sense pulse signal is
supplied to the EXT I/O connector on the rear panel of the 3511-50. For
details, refer to Section 5.1, "Testing Using EXT I/O."
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
3.9 Setting the Trigger Signal
Page 39

27
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Chapter 4
1
2
4.1 Comparator Function
With the upper and lower limits of the first and second parameters set, the
3511-50 compares measurements with the upper and lower limits and
produces a judgment (HI, IN, or LO)*, which is then displayed on the
comparator judgment display. Moreover, a corresponding signal can be
output via the EXT I/O connector on the rear panel of the 3511-50 unit.
* HI: exceeds the upper limit; IN: within upper and lower limits; LO: below the lower limit
You can set comparator upper and lower limits in the first and second
parameters, respectively. The judgment and the output of EXT I/O are
displayed for each parameter. The AND result of judgment for both first
and second parameters is also output from EXT I/O.
Other Functions
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
NOTE
If power is switched off in comparator test mode, switching on the 3511-50
again will start it in comparator test mode.
Switching off power in the upper or lower limit setting mode invalidates
the set upper or lower limit. If this occurs, the unit defaults to the
previous settings.
For parameters for which comparator judgment is unnecessary, the upper
and lower limits can be set to OFF. In such cases, the parameters set to
OFF are not compared for judgment.
Test conditions during comparator execution are as for normal test, with
one exception: the AUTO range is automatically switched to the HOLD
range.
10
11
12
13
14
A
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
4.1 Comparator Function
Page 40

28
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
4.1.1 Operation Sequence
Normal test mode
First parameter upper
limit setting mode
First parameter lower
limit setting mode
Second parameter
upper limit setting mode
Second parameter lower
limit setting mode
Comparator test mode
Set this among test conditions for executing a comparator.
Press .
Automatically switches the range setting to HOLD.
Use the COUNT setting key to set the upper limit.
Press to acknowledge and save the set value; then set the
lower limit.
Use the COUNT setting key to set the lower limit.
Press to acknowledge and save the set value; then set the
second parameter upper limit.
Use the COUNT setting key to set the upper limit.
Press to acknowledge and save the set value; then set the
lower limit.
Use the COUNT setting key to set the upper limit.
Press to acknowledge and save the set value.
If all upper and lower limits are OFF at this point, the system
switches to normal test mode. If setting upper and lower limits is
valid, the system switches to comparator test mode.
Press , and the system switches to normal test mode.
4.1.2 Setting the Upper and Lower Limits
(1) Press to enter a desired setting mode, for either the upper or lower
limit.
The current upper and lower limit settings are displayed in the status display
next to , and in the comparator judgment display.
Status display Comparator judgment
Conditions being
set
First parameter
upper limit
First parameter
lower limit
Second parameter
upper limit
Second parameter
lower limit
Set values are displayed at the following locations.
First parameter upper and lower limits : First parameter measurement
Second parameter upper and lower limits : Second parameter measurement
If the upper or lower limit value is set to OFF, the displayed setting will be
"-----." Upper or lower limit values set to OFF are not used for comparison
with a measurement.
"M-HSET" lights.
"M-LSET" lights.
"S-HSET" lights.
"S-LSET" lights.
display
"HI" lights to indicate the judgment
result for the first parameter.
"LO" lights to indicate the judgment
result for the first parameter.
"HI" lights to indicate the judgment
result for the second parameter.
"LO" lights to indicate the judgment
result for the second parameter.
display
display
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
4.1 Comparator Function
Page 41

29
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
NOTE
(2) Use the COUNT setting key to change the value digit by digit.
The value in the blinking digit may be altered. Navigate through the digits
with the keys, and through values with the keys.
To set the upper or lower limit to OFF, move the cursor to the left or right
end with
right extremes for 2 s or longer. The display changes to "-----." At the next
step, press to store the OFF setting.
Press the COUNT setting key when "-----" is displayed to redisplay the
former value.
Upper and lower limits are stored as counts displayed, regardless of test
conditions. As test conditions change, the absolute values indicated by
the counts change accordingly.
Use normal test conditions for comparator test conditions. Set upper and
lower limits only after setting test conditions for the comparator to be used
in normal test mode.For example, to set the upper limit to 0.999 µFwhen
test frequency is 120 Hz and test range is 1.45 µF in C-D display, enter
"09990."
(3) Press to store the setting, then move to the setting mode for the next
upper and lower limits.
If you press instead of , the mode switches to the next upper
and lower limit setting mode without recording the setting.
. Continue pressing if the cursor is at the left or
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
NOTE
The following verifications are not performed when upper and lower limits
are saved. Note that incorrect upper and lower limit settings will produce
incorrect judgments.
1. Is the set value within the parameter display range?
2. Is the relation between upper and lower limits correct?
The comparator judgments are made in the following order:
1. If the measured value is "OVER FLOW", HI is displayed, and the value
is "UNDER FLOW", LO is displayed.
2. Is the measured value greater than the lower limit or not? If not (NG
judgment result), then LO is displayed.
3. Is the measured value lower than the upper limit or not? If not (NG
judgment result), then HI is displayed.
4. If both 2 and 3 give an affirmative result, then IN is displayed.
No judgment is made if both upper and lower limits for a parameter are set
to OFF.
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
4.1 Comparator Function
A
Page 42

30
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
4.1.3 Comparator Test Mode
Upon completion of all upper and lower limit setting, if upper and lower
limit setting is not OFF, the system enters comparator measurement mode
and outputs a judgment each time a measurement is made, as a result of
comparison between the measurement and the upper or lower limit.
(1) Displaying judgment
Judgment for the first and second parameters is displayed in the comparator
judgment display.
For parameters for which upper and lower limit setting is OFF, no judgment
is displayed.
(2) Outputting judgment
Judgment (LO, IN, or HI) for the first and second parameters and the
AND result (valid when both parameters are IN) for both judgments are
output from EXT I/O. For details, refer to Section 5.1, "Testing Using
EXT I/O."
Comparator judgments (IN or NG) are indicated by a beep.
For more information on setting beeps to indicate judgment, see Section
4.5.3, "Setting Beep."
(3) Valid keys
In comparator test mode, test conditions cannot be changed, except for the
trigger setting. To change test conditions, press to switch to normal
test mode.
The following are valid keys and key functions:
Key Function
Moves to normal test mode.
Toggles the trigger setting between INT and EXT
Valid only when trigger setting is EXT Press this once to
permit one measurement.
Moves to the panel LOAD/SAVE screen. You can save
current test conditions or load previously saved test
conditions.
Switches key lock functions. Cancels remote mode.
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
4.1 Comparator Function
Page 43

31
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
4.2 Panel Save Function
1
The current test conditions may be saved to internal memory, up to a
maximum of 99 panels (or combinations) of test conditions.
All the set conditions are saved when panel save is performed, including
comparator upper and lower limits and OPEN/SHORT compensation values.
You can read saved measurement conditions later with the panel load
function.
4.2.1 Setting Panel Save
(1) Press repeatedly to cycle through available settings: panel load, panel
save and normal test (or comparator test) modes. For more information on
panel load mode, see Section 4.3, "Panel Load Function."
(2) Enter panel save mode and specify the panel number to save. In panel save
mode, only unsaved panel numbers are displayed. (The panel number at
shipment is "01.")
If all panels are used for the saving, when the panel mode is entered, "01"
appears.
COUNT
To overwrite a panel already in use, choose the panel number and correct.
Use the COUNT setting key to specify a panel number.
keys increase/decrease the value.
move the cursor to a digit to be set (up to two digits).
The LED for the digit under setting flashes.
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
NOTE
The set values must fall between 01 and 99.
(3) After specifying a panel number, press . The 3511-50 saves the test
conditions and reverts to normal or comparator test mode.
4.2.2 Aborting Panel Save
After specifying a panel number in panel save mode, press instead of
. The 3511-50 reverts to normal or comparator test mode without
performing the panel save.
NOTE
Under normal conditions of use, the average life of the backup battery for
the internal memory is about 6 years.
If the internal battery becomes exhausted, it is no longer possible to save
the test conditions. You should have the battery changed by an approved
HIOKI service facility (which is chargeable).
10
11
12
13
14
A
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
4.2 Panel Save Function
Page 44

32
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
4.3 Panel Load Function
You can read or load saved test conditions from internal memory.
4.3.1 Setting Panel Load
(1) Press repeatedly to cycle through available settings: panel load, panel
save and normal test (or comparator test) modes. For more information on
panel save mode, see Section 4.2, "Panel Save Function."
(2) Enter panel load mode and specify the panel number to load. Use the
COUNT setting key to specify a panel number. If no test condition is set, as
on shipment or reboot, "--" is displayed as a panel number. In this state, no
panel number can be set.
COUNT
The LED for the digit under setting flashes.
Each time a panel number is specified, the test conditions for the
corresponding panel are indicated by the LED lamp. You cannot select
panel numbers that are not panel-saved.
keys increase/decrease the value.
move the cursor to a digit to be set (up to two digits).
permit automatic specification of a panel number if it is panel-saved.
NOTE
The set values must fall between 01 and 99.
(3) After specifying a panel number, press . The 3511-50 loads the test
conditions and reverts to normal or comparator test mode.
4.3.2 Aborting Panel Load
After specifying a panel number in panel load mode, press instead of
. The 3511-50 moves to panel save mode without performing the
panel load. Press again. The 3511-50 reverts to normal or
comparator test mode.
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
4.3 Panel Load Function
Page 45

33
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
4.4 Key Lock Function
1
When the key lock is turned on, all key switches on the front panel are
disabled to protect settings.
4.4.1 Executing the Key Lock Function
Press for 2 s or longer. Use the LED lamp to the right of the second
parameter measurement display (SUB PARAMETER) to check on the key
lock condition.
NOTE
In the external trigger mode, the key lock does not apply to .The
external trigger can be activated manually.
The key lock function can be set only in normal or comparator test mode.
Note that, as long as is kept pressed, the key lock function is
activated and inactivated alternately.
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
4.4.2 Cancelling the Key Lock Function
Press for 2 s or longer. The LED lamp goes out to indicate that key
lock is canceled.
NOTE
Even if the power supply is interrupted, the key lock function is not
canceled.
9
10
11
12
13
14
A
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
4.4 Key Lock Function
Page 46

34
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
4.5 Various Settings Made After Switching o n Power
Enter settings for conditions related to system reboot (initialization of all test
conditions), interfaces, and beep sounds at comparator judgment immediately
after switching on power.
4.5.1 Setting Screen Flow After Power ON
With power turned on, screens are displayed in succession in the following
order:
1. All displays light.
2. Version information displayed
3. Interface setting
4. Beep sound setting
5. Test mode (normal test or comparator test)
To change a setting, press the COUNT setting key while screens 3 and 4 are
displayed. Press after screen 1 is displayed and before screen 2 is
displayed. The system reboot setting screen appears before screen 3 is
displayed.
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
4.5 Various Settings Made After Switching on Power
Page 47

35
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
4.5.2 Setting the Interface
You can print measurements by connecting an optional 9442 PRINTER to
the RS-232C interface. This is possible only with the EXT trigger.
Described below are procedures for switching the RS-232C interface settings
to settings appropriate for the 9442 PRINTER and PC connection.
1
2
NOTE
To use the RS-232C interface, remove the 9518-01 GP-IB INTERFACE
before switching on power. If you power on with the board (optional)
inserted in the optional board slot, the RS-232C setting screen will not
appear. Instead, the system will display "GP-iB" in the first parameter
measurement display, and the 3511-50 GP-IB address in the second
parameter measurement display.
Procedures
Once power has been switched on, the 3511-50 displays version information,
"rS232" in the first parameter measurement display and settings for the
RS-232C interface in the second parameter measurement display for
approximately 3 s.
Press the COUNT setting key as this information is displayed to switch the
display in the second parameter measurement display between "PC" and
"Print."
When connecting a PC and when not using the RS-232C interface, make
sure "PC" is displayed. When using a 9442 PRINTER, make sure that
"Print" is displayed.
Display in the first parameter
measurement display
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Display in the second
Setting
When connecting a PC
When not using the RS-232C
interface
When using a 9442
PRINTER
With a 9442 PRINTER, if no key input is made for approximately 3 s, the
current setting is acknowledged, and the screen switches to the next screen
(the "Beep sound setting" screen).
parameter measurement
display
10
11
12
13
14
A
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
4.5 Various Settings Made After Switching on Power
Page 48

36
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
4.5.3 Setting Beep
Set the beep to be sounded when a comparator judgment is made.
The following three modes are available:
1. No beep
2. Beeps when judgment of both first and second parameters is "IN."
3. Beeps when judgment of one of the first or second parameters is not "IN."
Procedures
After power is switched on, the system displays the "Interface setting." For
approximately 3 s, the system will display "bEEP" in the first parameter
measurement display and the desired beep sound setting in the second
parameter measurement display.
Press the COUNT setting key during this display. The indication in the
second parameter measurement display cycles through "oFF," "in" and
"Lo-Hi." If no key input occurs for 3 s, the current setting is acknowledged,
and the system enters measurement mode.
Display in the first parameter
measurement display
Setting
No beep
Beeps when judgment of both
first and second parameters
is "IN."
Beeps when judgment of one
of the first or second
parameters is not "IN."
Display in the second
parameter measurement
display
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
4.5 Various Settings Made After Switching on Power
Page 49

37
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
4.5.4 Executing System Reboot
All test conditi ons are initialized to the conditions i n force at shipment.
All measurement conditions include panel-saved conditions.
Procedures
Restart the 3511-50 while pressing . All displays will light, and in
approximately 1.5 s, the Section switches to the version information screen.
You can release the key when this occurs.
The 3511-50 displays version information, "rESEt" in the first parameter
measurement display and "no" in the second parameter measurement display.
Display in the first parameter
measurement display
Display in the second
Setting
parameter measurement
display
No system reboot
System reboot
Press the COUNT setting key to switch the display in the second parameter
measurement display between "no" and "YES." Press in either state.
Pressing in the "YES" state initializes all test conditions to the
conditions in force at shipment and switches the screen to "Interface setting."
The conditions in force at shipment are as follows:
Test mode Normal test mode
Test parameters |Z|-θ
Test frequency 1kHz
Test signal level 1V
Test speed NORM
Equivalent circuit mode AUTO
Test range AUTO
Open circuit
compensation
Short circuit
compensation
Trigger mode INT (Internal trigger)
Key lock function OFF
Beep sound setting OFF (when a comparator judgment is
Panel save All contents clear
Comparator Upper and lower limits for the first and
OFF
OFF
made)
second parameters both OFF
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
4.5 Various Settings Made After Switching on Power
Page 50

38
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
4.6 Remote Function
4.6.1 Remote Mode
External control via an interface will place the 3511-50 in remote mode
(remote control state), in which front panel key switch operations are
disabled.
Use the LED lamp to the right of the second parameter measurement display
(SUB PARAMETER) to check on the remote mode condition. This LED
lamp lights when the 3511-50 enters remote mode.
4.6.2 Cancelling the Remote Mode
Press to cancel the remote mode. The LED lamp goes out to
indicate that remote mode is canceled.
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
4.6 Remote Function
Page 51

39
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
4.7 The Residual Charge Protection Function
CAUTION
The quoted maximum voltage from which the unit c an be protected by
this f unct ion is f or reference purposes only, and is not a guaranteed
value. There may be danger of damage to the 3511-50 unit,
depending upon the operational circu m stances and upon how often
such charged capacitors are connected. In general, you should not
rely upon thi s protection function; be sure to discharge charged
capacitors properly before connecting them to the test terminals.
The residual charge protection function is for protection of the 351150 unit against the discharge of voltage present in c harged capacitors,
and is not capable of protecting the unit ag ai n s t DC vo l ta ge which is
constantly applied such as a superimposed DC voltage. (The
maximum volt age for supply to th e test termi n al s of the 35 11-50 unit
is 40 VDC.) If this is done, there is a danger of damage to the unit.
(For how to supply a DC bias voltage, refer to Secti on 5.2, " Supplying
DC Bi a s ".)
The 3511-50 has been enhanced by the incorporation of a residual charge
protection funct ion. If by mistake a charged capacitor is connected to the
test terminals, this function protects the internal circuitry of the unit from
discharge of such residual charge.
The maximum voltage from which the unit can be protected by this function
is determined from the capacitance value of the sample under test by the
following equation:
V: Voltage (volts) (maximum 400 VDC)
C: Capacitance (farads)
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
4.7 The Residual Charge Protection Function
Page 52

40
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
4.7 The Residual Charge Protection Function
Page 53

41
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Chapter 5
1
2
5.1 Testing Using EXT I/O
5.1.1 The EXT I/O Connector
This is a connector for output of comparator result signals, of a measurement
finished signal (
_______
(
INDEX
performing selection of the number of the panel to be loaded.
Connector used :
57RE-40360-730B (D29) (made by DDK)
Compatible connector:
57-30360 (solder cup connector without rib, made by DDK)
57-30360R (solder cup connector with rib, made by DDK)
RC30-36P (made by HIROSE ELECTRIC CO.,LTD.)
), and for input of an external trigger signal, and a signal for
______
EOM
Applications
), and of an analog measurement finished signal
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
18 1
36 19
EXT I/O Connector pin numbering (seen from 3511-50)
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
5.1 Testing Using EXT I/O
11
12
13
14
A
Page 54

42
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
5.1.2 Pinouts for the EXT I/O Connector
Pin number I/O Signal line name Pin number I/O Signal line name
1 IN
2 IN
3 IN
4 IN
5 IN
6 OUT
7 OUT
8 OUT
9 OUT
10 - Unused 28 - Unused
11 to 14 IN EXT DCV 29 to 32 OUT INT DCV
15 to 18 IN EXT COM 33 to 36 OUT INT GND
_____
TRIG
BCD01
BCD03
BCD11
BCD13
_____
M-IN
____
S-HI
_____
S-LO
______
INDEX
19 IN
20 IN
21 IN
22 IN
23 OUT
24 OUT
25 OUT
26 OUT
27 OUT
BCD00
BCD02
BCD10
BCD12
_____
M-HI
_____
M-LO
____
S-IN
____
AND
_____
EOM
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
5.1 Testing Using EXT I/O
Page 55

43
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
5.1.3 Signal Lines for the EXT I/O Connector
1
NOTE
All input and output signals excluding BCD 00 to 03, BCD 10 to 13, and the
power supply are all negative logic.
______
(1)
TRIG
When the 3511-50 is set to external trigger mode, a negative logic signal is
input from outside via this line. Testing is initiated once when this signal
goes low level.
(2) BCD00, BCD01, BCD02, BCD03
For the panel number to load, choose the ones digit.
When a trigger signal is input in external trigger mode, the panel chosen is
read and measurement begins.
(3) BCD10, BCD11, BCD12, BCD13
Choose the tens digit for the panel number to be loaded.
When a trigger signal is input in external trigger mode, the panel chosen is
read and measurement begins.
BCD Digit of 10 Digit of 1
BCD13 BCD12 BCD11 BCD10 BCD03 BCD02 BCD01 BCD00
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1
2 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0
3 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1
4 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0
5 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1
6 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0
7 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1
8 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0
9 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1
All other combinations are invalid.
Example: When reading panel 15, set "0001 0101."
*1 *2 *1: Digit of 10, *2: Digit of 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
NOTE
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Because the open state is "1", when specifying the panel number, be sure to set all
signals.
_____
(4)
M-HI
These lines output the comparator result for the first parameter.
_____
(5)
S-HI
These lines output the comparator result for the second parameter.
_____
(6)
AND
This line outputs the logical AND of the comparator results for the first
parameter and for the second parameter. This signal is output only if both
the comparator results are IN.
_____
,M-IN
_____
, S-IN
______
,M-LO
______
, S-LO
5.1 Testing Using EXT I/O
13
14
A
Page 56

44
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
________
(7)
INDEX
Output during analog measurement. When testing speed setting is FAST and
the range is HOLD, the sample can be changed after this signal is switched
off (i.e., after start-up edge).
NOTE
________
INDEX
AUTO range mode, the
If the testing speed is NORM or SLOW, the
times to execute analog measurement more than once.
When changing a sample via the
and measure in the HOLD range.
______
(8)
EOM
End of measurement signal.
(9) EXT DCV, EXT COM
These are terminals for supplying a power supply voltage from an external
device. This enables the 3511-50 unit to be connected to an external device
while maintaining the isolation. The range of power voltage which can be
connected is from 5 to 24 VDC.
(10) INT DCV, INT COM
These lines output +5 VDC and COM from the 3511-50 unit.
signal is output at each time of retest. If a measurement is made in
________
INDEX
signal may be output two or more times.
________
INDEX
________
INDEX
signal is output two or more
signal, set the testing speed to FAST
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
5.1 Testing Using EXT I/O
Page 57

45
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
5.1.4 Circuit Construction and Connections for the EXT I/O
Connector
1
2
CAUTION
Pull up resistors
4.7 kΩ (1/4 W)
The voltage of the external DC power supply to be connected to t he
EXT DCV and EXT COM ter m in al s should be f ro m 5 V to 24 V. Do
not supply DC voltage greater than 24 V. If you do, there is a danger
of damage to the unit.
Moreover, for driving the ci rcuitry, connect any device which is
capable of providing an output current of more than 200 mA.
The insulation of the signal lines is for eliminating mutual influences
between the signals. Any device which is connected to the 3511-50 unit
should always be properly protectively grounded. If proper connection to
a protective ground is not established, there is a danger of damage to
the insulation.
The circuit construction for the EXT I/O connector is shown in the figure.
Except for the power supply lines, all of the input and output signal lines are
insulated by photocouplers.
Internal DC power supply (5 V)
*
INT DCV
External DC power supply (5 V to 24 V)
EXT DCV
_____
M-HI
_____
M-IN
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Ground connection to
the chassis of the unit
4.7 kΩ (1/4 W)
* Can be connected when using the internal 5 V power supply.
Circuit construction
_____
EOM
______
TRIG
BCD00
External DC power supply (COM)
*
EXT COM
Internal DC power supply (COM)
INT GND
10
11
12
13
14
A
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
5.1 Testing Using EXT I/O
Page 58

46
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
NOTE
The internal DC power supply of 5 VDC is provided between INT DCV and INT
GND. The maximum current capacity is 100 mA. Do not connect any external
circuit whose current consumption is greater than 100 mA.
INT GND is grounded to the chassis of the 3511-50 unit.
The output signal low level output current is a maximum of 60 mA. If a
current greater than this is required, you should connect a transistor circuit
using a current amplifier driven by an external power source or the like
externally.
5.1.5 Electrical Characteristics of the Output Signals
The output signals are the collector outputs of the photocouplers, and are
connected to the external DC power supply (EXT DCV) via 4.7 kΩ pull-up
resistors provided internally to the 3511-50 unit.
The relationship between the external DC power supply voltage, the voltage
of the output signals, and the current, is as shown in the following table:
External DC
power supply
voltage
5V 5V 0.9 V 1.1 V 1.2 V
Output signals (internal pull-up resistors 4.7 kΩ)
Low level
High level
Output current
10 mA
Output current
40 mA
Output current
60 mA (max.)
12 V 12 V 0.9 V 1.1 V 1.2 V
24 V 24 V 0.9 V 1.1 V 1.2 V
Direct connection of a circuit whose input voltage VILis a maximum of 0.8
V or more is not possible.
In such a case, keep VILbelow 0.8 V by incorporating a transistor or a drive
capable buffer circuit or the like.
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
5.1 Testing Using EXT I/O
Page 59

47
_____
(
)
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
5.1.6 I/O Signal Timing
With the test conditions for testing by the comparator having been set (with
the trigger setting set to external trigger), when in this state a trigger signal
is input via the EXT I/O connector, or when the key is pressed, then
the decision result is output on the comparator result output signal line of
the EXT I/O connector.
An example of testing timing is as follows:
1
2
3
T1
TRIG
(Testing start signal)
T2
___
_______
_____
___
___
,IN
,LO
Symbol Meaning
T1
TRIG width (LOW)
Minimum time period that trigger signal is low
Previous decision result
INDEX
(Analog measurement in progress signal)
EOM
(Measurement finished signal)
HI
Comparator result output
T3
T4
T5
Decision result
Timing
(approximate)
100 µs
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
T2
T3
T4
T5
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
*1: With the panel load function, when a new panel number is loaded, the
*2: Reference value with the following conditions; test frequency:
From TRIG (LOW) to INDEX (LOW)
Time period from trigger to circuit response
INDEX width (LOW)
Minimum chucking time; chucking switching on INDEX
(HIGH) possible
EOM width (LOW)
Time period for testing
From EOM (HIGH) to TRIG (LOW)
Minimum time period from end of testing to next trigger
response time takes about 1 second.
1 kHz, testing speed:FAST, and when measuring |Z|.
5.1 Testing Using EXT I/O
500 µs*
1ms*
5ms*
1
2
2
0s
11
12
13
14
A
Page 60

48
(
)
(
)
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
5.1.7 Time Taken for Testing
The time taken for testing varies according to the test conditions. The
following values may be used for reference.
NOTE
These values are all for reference only. Do not rely upon them absolutely, because
the actual time taken for testing depends upon many operational conditions.
________
(1) Analog testing signal (INDEX
The output time (T3) of the analog testing signal (INDEX
)
________
) taken according
to the testing speed:
Measurements are averaged if the testing speed setting is NORM or SLOW.
________
The INDEX
signal is output for the number of times indicated in the table
below.
Testing speed
Test frequency
120 Hz 8.3 ms 1 17 ms 4 67 ms 5
1kHz 1ms 1 4ms 7 8ms 24
FAST NORM SLOW
T3
Number
of times
T3
Number
of times
T3
Number
of times
(2) Testing finished signal (EOM)
Use the following equation to obtain the output time of the testing finished
signal (EOM):
T4=(A)+(B)+(C)+(D)
(A) The time taken for testing for Z-θ display, normal test mode, open/short
circuit compensation off, and HOLD range:
Testing speed
Test frequency
120 Hz 13 ms 90 ms 400 ms
1kHz 5ms 60 ms 300 ms
FAST NORM SLOW
Allowance 2ms
(B) The time taken for calculation varies according to the display parameters:
Testing speed
Test frequency
120 Hz 0ms 1.5 ms 1.5 ms 1ms
1kHz 0ms 1.5 ms 1.5 ms 1ms
Z-θ C-D L-D/Q R
Allowance 2ms
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
5.1 Testing Using EXT I/O
Page 61

49
(
)
(
)
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
(C) The time taken for calculation varies according as to whether or not both
open circuit compensation and also short circuit compensation are
performed:
Open/short circuit compensation Calculation time
Open and/or short circuit
compensation performed
Not performed 0ms
Allowance 0.5 ms
(D) The time taken for calculation varies according as to whether or not the
comparator is operating:
Comparator operating Calculation time
Normal testing 0ms
When the comparator is operating 0.1 ms
Allowance 0.1 ms
1ms
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
5.1 Testing Using EXT I/O
14
A
Page 62

50
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
5.2 Supplying DC Bias
CAUTION
The maxim um voltage whic h can be applied to the test terminals of t he
3511-50 unit is 40 V DC. If a DC voltage greater than this is applied
continuously, t he unit m ay be damaged.
Supplying DC bias means that a DC voltage is supplied as a bias to a
sample for test whose characteristics are voltage dependent, such as an
electrolytic capacitor or a ceramic capacitor.
Further, a DC current can be supplied as a bias to a sample for test whose
characteristics are current dependent, s uch as a choke coil.
Since the 3511-50 unit has no DC bias input terminals, a DC bias must be
supplied in the manner described in the following sections.
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
5.2 Supplying DC Bias
Page 63

51
g
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
5.2.1 How to Supply a DC Bias Voltage
CAUTION
In order to avoid ele ctri c shock accident, be absolutely sure not to
touch the test terminals while the DC bias voltage is being supplied to
them.
If you disconnect the sample under test from the test terminals with
the DC bias voltage still being supplied, t hen the test sample is lef t
charged, which is very dangerous. In order to avoid electric shock
accident, be absolutely sure to discharge the test s am ple.
Do not short circuit between the clips of the test probes with the DC
bias voltage still being supplied. Doing so may damage the probes or
cause a short circuit accident.
To supply a DC bias voltage to a capacitor or the like, proceed as follows.
Use the optional 92 68 DC BIAS VOLTAGE UNIT.
For details on using the 926 8, refer to the Instruction Manual of the 9268.
(Depending on the test frequency, test signal level, and test range, the 9268
cannot be used.)
If the 9268 is not used, refer to the following.
3511-50
Capacitor
H
CUR
H
POT
Sample to be tested
L
CUR
C
Z
RorL(>>Z)
+
-
+
DC voltage
source
-
L
POT
GUARD
DC Bias Volta
e Circuit
Use a resistance (R) or inductance (L) which has a large enough impedance
with reference to the sample under test (Z).
Use a capacitor (C) which has a small enough impedance (i.e., a large
enough capacitance) with reference to the sample under test (Z).
Be careful about the polarity when connecting together the probes, the
sample to be tested, and the DC voltage source.
It takes a little time for the DC voltage which is being supplied to the
sample under test to reach the set voltage, so you should wait for a certain
stabilization time period (which depends upon the sample) before performing
testing. Be careful, because if you perform testing before this stabilization
time period has elapsed, the results will not be reliable.
After testing is completed, drop the voltage of the DC voltage source to
zero, and remove the sample under test from the probes after having
discharged any electric charge which may have built up.
If you have removed the sample under test from the probes without first
having discharged the accumulated electric charge, you should be careful to
do so immediately.
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
5.2 Supplying DC Bias
Page 64

52
↑
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
5.2.2 How to Supply a DC Bias Current
CAUTION
In order to avoid ele ctri c shock accident, be absolutely sure not to
touch the test terminals while the DC bias is being supplied to the m.
Do not short circuit between the clips of the test probes with the DC
bias st ill being supplied. Doing so may damage t he probes or cause
a short circuit accident.
To supply a DC bias, use the optional 9269 DC BIAS CURRENT UNIT.
For details on using the 926 9, refer to the Instruction Manual of the 9269.
(Depending on the test frequency, test signal level, and test range, the 9269
cannot be used.)
If the 9269 is not used, refer to the followings.
To supply a DC bias current to a transformer or a choke coil or the like,
construct an external bias cir cuit as follows. (For details, refer to JIS C-
6435.)
Choke coil
CH
Capacitor
C
+
DC current
+
-
source
Z
-
3511-50
H
CUR
H
POT
Sample to be tested
L
CUR
L
POT
DC Bias Current Circuit
Use a choke coil (CH) which has a large enough impedance with reference
to the sample under test (Z).
Use a capacitor (C) which has a small enough impedance (i.e., a large
enough capacitance) with reference to the sample under test (Z).
Be careful about the polarity when connecting together the probes, the
sample to be tested, and the DC current source.
Be careful not to magnetically saturate the choke coil (CH) with the DC bias
current.
It takes a little time for the DC current which is being supplied to the
sample under test to reach the set value, so you should wait for a certain
stabilization time period (which depends upon the value of the capacitor (C)
before performing testing. Be careful, because if you perform testing before
this stabilization time period has elapsed, the results will not be reliable.
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
5.2 Supplying DC Bias
Page 65

53
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
5.3 9442 PRINTER (Option)
The test values are printed out.
Use with the optional 9442 PRINTER, and 9444 CONNECTION CABLE.
5.3.1 Preparation
Use the 9442 PRINTER, the 9443* AC ADAPTER, and the 1196
RECORDING PAPER. To connect the main unit and printer, use the 9444
CONNECTION CABLE. (All are options.)
9442 DPU-414 Seiko Instruments Inc.
*9443-01 PW-4007-J1 Seiko Instruments Inc. (for Japan)
*9443-02 PW-4007-E1 Seiko Instruments Inc. (for EU)
*9443-03 PW-4007-U1 Seiko Instruments Inc. (for U.S.A.)
Setting the 9442 PRINTER communication conditions
Change the settings of the software dip switches (DIP SW) to use the 9442
for the 3511-50.
CAUTION
The 9442 is shipped with the function settings for use with the HIOKI
3166 CLAMP ON POWER HiTESTER. Before using, always change the
settings of the DIP switches.
For details on the operations and handling of the printer, refer to the
operation manual supplied to the printer.
For the printer, use the 1196 RECORDING PAPER (thermal paper, 10
rolls) or an equivalent.
(1) Turn off the power.
(2) Turn on the power while pressing the ON LINE button. Release the button after a
list of the current settings starts printing out.
(3) The print out of the current settings is followed by the prompt: "Continue? :Push
'On-line SW'", "Write?:Push 'Paper feed SW'". Press the ON LINE button to change
the settings.
(4) "Dip SW-1" is printed to make a settings for switch number 1 to 8 of DIP SW1.
Refer to the next table.
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
5.3 9442 PRINTER (Option)
Page 66

54
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Software DIP SW1
: Use these settings for the 3511-50
Switch No. Function ON (ON LINE) OFF (FEED)
1 Input method Parallel Serial
2 Printing speed High Low
3 Auto loading Enable Off
4 CR function
5
6
7 ON
8 ON
DIP SW setting
command
Printing density
(set to 100%)
To set to ON, press the ON LINE button once and to set to OFF, press the
FEED button once.
The setting is printed out after the ON LINE or FEED button is pressed to
allow to confirm the new setting. To change the settings, repeat from step
(1). When the setting for switch number 8 is made, the printer once again
prompts with "Continue? :Push 'On-line SW'", "Write?:Push 'Paper feed
SW'".
(5) Set the switch number 1 to 8 of DIP SW 2 and 3 in the same way from step (3)
referring to the following tables.
Software DIP SW2
Carriage return
and line feed
Enable Disable
Carriage return
OFF
Switch No. Function ON (ON LINE) OFF (FEED)
1 Print mode
2
3 Character type Ordinary characters Special characters
4 Zero font 0
5
6 ON
7 ON
8 ON
User-defined
characters back-up
International
character set
Normal printing
(40 columns)
Enable Disable
ON
Condensed printing
(80 columns)
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
5.3 9442 PRINTER (Option)
Page 67

55
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Software DIP SW3
Switch No. Function ON OFF
1 Data bit length 8bits 7bits
2 Parity permission None With parity
3 Parity condition Odd Even
4 Flow control H/W BUSY XON/XOFF
5
6 ON
7 ON
8 OFF
(6) After setting for the switch number 8 of DIP SW 3 is made, press the ON LINE or
FEED switch to complete settings. "Dip SW setting complete!!" is printed out.
5.3.2 Connection Method
WARNING
To avoid electrocution, turn off the power to all devices before
plugging or unplugging any cablesor peripherals.
(1) Set the 9442 PRINTER referring to Section 5.3.1, "Preparation."
(2) Connect the 9444 CONNECTION CABLE between the main unit and the printer.
OFF
Baud rate
(19200 bps)
3511-50 9442
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Frame
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Frame
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
5.3 9442 PRINTER (Option)
Page 68

56
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
5.3.3 Printing Results
When the external trigger is set, the test values are printed out after the test
is completed.
1. Normal test
2. Comparator operating
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
5.3 9442 PRINTER (Option)
Page 69

57
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
5.4 Testing High Impedance Elements
The measured value obtained when testing a high impedance element (such
as, for example, a resistor with resistance higher than 100 kΩ) is sometimes
unreliable, because such an element is vulnerable to the effects of external
interference and the like. In this case, reliable testing can be performed by
the use of guarding, that is, connecting a metallic plate to the GUARD
terminal and carrying out the measurement on the metallic plate.
Resin film
Metallic plate
When testing against a metallic plate, the surface of the plate should be
covered by a film of resin or the like, in order to prevent short circuiting
together the terminals.
When the open circuit compensation is performed always execute the
guarding process because of high impedance elements testing. If not, the
compensation values do not stabilize. It is not possible to obtain the reliable
measured value.
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
5.4 Testing High Impedance Elements
Page 70

58
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
5.5 Testing an Element in a Circuit
Test an element in a circuit after guarding.
Referring to the following figure, when measuring a resistance value for the
resistor R2, even if the tips of the two probes are contacted against the ends
of the resistor R2, considering the sum of the current flowing through the
resistor R2and the current flowing through the resistors R3and R4, what is
obtained is the resistance value for the parallel combination:
HL
R2R1
R4R3
NOTE
If as shown in the next figure a guard terminal is used, the current flowing
through the resistors R3(not flowing through R4) is absorbed by this guard
terminal, so that the resistance value for the resistor R2is accurately
measured.
HL
R2R1
R4R3
Guard terminal
The accuracy of measurement will not be improved in cases where for example
R
>> R
2
and R
3
As shown in the figure below, it is not possible to use this type of separation
process for testing of the impedance values of two resistors or other elements of
identical types which are connected in parallel, or for testing of the impedance
values of a coil and a capacitor which are connected in parallel.
is close to zero.
3
Two resistors in parallel
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
5.5 Testing an Element in a Circuit
Coil and capacitor in parallel
Page 71

59
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
5.6 External Interference
The 3511-50 is designed to be resistant to errors caused by interference from
the test cables or the power supply line. However, if the level of the
interference is particularly large, this can cause measurement errors or faulty
operation.
Refer to the examples given below for examples of countermeasures which
can be taken against interference which has caused faulty operation etc.
5.6.1 Countermeasures Against Interference from the Power
Supply Line
If noise is present in the power supply line, its influence can be moderated
by the following countermeasures:
(1) Grounding by using a protective ground wire
The 3511-50 unit is constructed so as to be provided with protective
grounding via the ground lead in the power cord.
This protective grounding serves the important function, not only of avoiding
the possibility of electric shock to the operator, but also of eliminating noise
from the power supply line by the provision of an internal filter.
Be sure to connect the 3511-50 unit to a properly 3-wire power supply
socket, using the grounded power cord which is supplied with the unit.
(2) Inserting a noise filter in the power supply line
Any excessive noise present in the power supply line can be suppressed by
purchasing a socket type noise filter (generally available commercially)
which can be inserted into the power supply socket, with the 3511-50 unit
connected to the output of the noise filter.
Various types of such socket type noise filters are readily available from
specialist manufacturers.
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
5.6 External Interference
Page 72

60
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
(3) Fitting an anti-interference ferrite core on the power cord
Pass the power cord through a commercially available anti-interference
ferrite core, and fix it on the power cord as close as possible to the AC
power inlet of the 3511-50 unit, so as to suppress noise from the power
supply line. Further benefit can often be obtained by fitting another antiinterference ferrite core on to the power cord at its other end, as close as
possible to the plug which connects to the power supply outlet.
Moreover, if the internal diameter of the ferrite core allows, winding the
power cord several times around the ferrite core may further reduce the
amount of noise. Various types of such anti-interference ferrite cores or
ferrite beads are readily available in the market from specialist
manufacturers.
5.6.2 Countermeasures Agai nst Noise from the Test Cables
If interference is producing noise in the test cables, its influence can be
moderated by the following countermeasure.
Fitting an anti-interference ferrite core on the test cables
Pass the test cables through a commercially available anti-interference ferrite
core, and fix it close to the test terminals, so as to suppress noise from the
test cables.
Moreover, if the internal diameter of the ferrite core allows, winding the test
cables several times around the ferrite core (as with the power cord as
described above) may further reduce the amount of noise.
Anti-interference ferrite core
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
5.6 External Interference
Page 73

61
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Chapter6
1
2
RS-232C Interface
6.1 Overview
6.1.1 Introduction to the RS-232C Interface
It is possible to control all the functions of the 3511-50 (except for powering
on and off) via the RS-232C bus.
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
A
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
6.1 Overview
Page 74

62
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
6.1.2 Specifications
Transfer system Start-stop synchronization
Baud rate 9600 bps
Data length 8bits
Parity None
Stop bits 1 bit
Delimiter CR+LF
Handshake hardware
Electrical
characteristic
Input voltage levels ON 5 V to 15 V
OFF -15 V to -5 V
Output voltage levels ON 5 V to 9 V
OFF 9 V to -5 V
RS-232C connector
The connector on the 3511-50 is for terminal (DTE). Connect the RS-232C
cable.
12345
6789
RS-232C interface connector pin assignments
(D-subminiature 9-pin male)
Signal assignments and explanation
Connector (Dsub)
pin number
1 --- --- Unused
2 BB(RxD) 104 Received Data
3 BA(TxD) 103 Transmitted Data
4 CD(DTR) 108/2 Data Terminal Ready
RS-232C CCITT
Circuit
Description
5 AB(GND) 102 Signal Ground
6 --- --- Unused
7 CA(RTS) 105 Request to Send
8 CB(CTS) 106 Clear to Send
9 --- --- Unused
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
6.1 Overview
Page 75

63
(
)
(
)
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
6.2 Connecting Method
1
2
WARNING
CAUTION
Example
In order to avoid electric shock, turn off the power to all devices
before plugging in or unplugging the RS-232C connector.
To avoid damage to the unit, do not short the connector and do
not input voltage to the connector.
Always fix the screws to connect the RS-232C cable.
When connecting the controller (DTE), use a cross cable which meets the
connector specifications of both sides of the 3511-50 and the controller.
Commands that contain data must be input in the specified data format.
Refer to Chapters 3 to 5 for details about the various functions.
When connecting to the controller using a D-subminiature 9-pin connector
BB(RxD)
BA(TxD)
CD(DTR)
AB(GND)
CA(RTS)
CB
CTS
3511-50
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Controller
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
BB(RxD)
BA(TxD)
CD(DTR)
AB(GND)
CA(RTS)
CB
CTS
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
SHELL
Specification: D-subminiature 9-pin female to D-subminiature 9-pin female
connectors, with "crossed" data connections
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
6.2 Connecting Method
11
12
13
14
A
Page 76

64
pty
A
(
)
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
6.2.1 Handshake
Buffer flow control
(1) Controls when receiving
When the receiving buffer is more than 85 % full, CA (RTS) is set to OFF
to indicate to the controller that the empty buffer capacity is low.
Processing of data in the buffer continues, and when the receiving buffer is
less than 25 % full, CA (RTS) is set to ON to indicate to the controller that
there is ample buffer capacity.
85 %
mount of input
buffer used
25 %
Buffer em
CA
RTS
ON
OFF
(2) Controlls when transmitting
When CB (CTS) is found to be OFF, transmission is suspended; it is found
to be ON transmission resumes.
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
6.2 Connecting Method
Page 77

65
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
6.3 Operation
1
6.3.1 Communication Methods by the RS-232C
In order to control the 3511-50 by the RS-232C, there are several kinds of
messages.
Of these, program messages are those received by the 3511-50 from the
computer, while response messages are those sent from the 3511-50 to the
computer.
Program messages
Messages
(1) Program messages
Program messages are command messages or query messages.
Command
making measurement condition settings or for reset or the like.
Example :FREQUENCY <data>
(Command message which sets the frequency)
・
Query
results of measurement, or the state of 3511-50 settings. A question mark
"?" is suffixed at the end of the command.
Example :FREQUENCY?
(Queries the current frequency)
messages are orders for controls of the 3511-50, such as for
messages are orders for responses relating to results of operation,
Response messages
2
3
4
Command messages
Query messages
5
6
7
8
9
(2) Response messages
It represents the response data for query messages from the 3511-50.
Example
(Current frequency is 1 kHz.)
:FREQUENCY 1000
Computer
3511-50Program messages
Response messages
10
11
12
13
14
A
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
6.3 Operation
Page 78

66
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
6.3.2 Message Format
The commands for the 3511-50 are as far as possible mnemonic.
Furthermore, all commands have a long form, and an abbreviated short form.
6.3.3 Program Message
The program message is made up from header and data portions.
Example Command message to set frequency to 1 kHz
:FREQUENCY 1000
1 2 3
1
Header portion
2
Space separating header portion and data portion.
3
Data portion (ASCII-format text or numeric values.
Some messages have no data portions...query messages, etc.)
A command header can be abbreviated. The whole command form is
referred to as the "long form" and the abbreviated form as the "short form."
In this manual, the short form is written in upper case letters, and then this
is continued in lower case letters so as to constitute the long form. Either of
these forms will be accepted during operation, but intermediate forms will
not be accepted. Further, during operation both lower case letters and upper
case letters will be accepted without distinction.
For "
FREQUENCY
short form) will be accepted. However, any one of "FREQU", or "FRE"is
wrong and will generate an error.
6.3.4 Response Messages
It represents the response message for query messages from the 3511-50.
Response messages generated by the 3511-50 are in long form and in upper
case letters.
Example
(Current frequency is 1 kHz.)
:FREQUENCY 1000
", either "
FREQuency
" (the long form) or "
FREQ
"(the
E
NOT
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
6.3 Operation
If an error occurs when the query message is received, the query does not produce
response message.
Page 79

67
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
6.4 Headers
1
(1) Program message headers
There are three types of header: simple headers, compound headers, and
particular headers.
Simple header
A header consisting of a single word beginning with a letter.
Examples
Compound header
A header consisting of a sequence of words separated by colons.
Examples
Partic ular hea der
A header beggining with an asterisk (*) to indicate t hat it is a part icular
command.
Examples
(2) Response message
Headers in response messages can be enabled or disabled by using the
"HEADer" command.
Example When frequency is set to 1 kHz:
:FREQUENCY?
(
Response message when headers are on.
:HEADer
:BEEPer:KEY, RANGe:AUTO
*
RST
Query message asking for the current setting of the frequency.
:FREQUENCY 1000
etc.
, etc.
etc.
2
3
4
5
6
7
)
8
1 2
Response message when headers are off.
(Data portion only)
1
Header portion
2
Data portion
1000
9
10
11
12
13
14
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
6.4 Headers
A
Page 80

68
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
6.5 Data Formats
The 3511-50 uses character string data and decimal numeric data, and the
type used varies according to the co mmand in question.
(1) Character data
Character string data must always begin with an alphabetic character, and
the characters following can be either alphabetic characters or numerals.
Although in character data either upper case letters or lower case letters are
accepted, response messages output by the 3511-50 are always in upper case
letters.
Example
:TRIGger inT
(2) Decimal data
The numeric data values are all represented in decimal, in three formats
identified as NR1, NR2 and NR3, and each of these can appear as either a
signed number or a n unsigned number. Unsigned numbers are taken as
positive. Further, if the accuracy of a numerical value exceeds the limit
which the 3511-50 can deal, it is rounded off (5 and above is rounded up; 4
and below is rounded down).
NR1 format: Integer data
Examples
+12, -23, 34
NR2 format: Fixed point numbers
Examples
+1.23, -23.45, 3.456
NR3 format: Floating point numbers.
Examples
+1E-2, -2.3E+4
The term "NRf format" includes all these three formats. When the 3511-50
is receiving it accepts NRf format, but when it is sending response messages
it utilizes whichever one of the formats NR1 to NR3 is indicated in the
specified command.
Examples
:RANGe +6.012
:RANGe 0.0006E4
:RANGe 6
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
6.5 Data Formats
Page 81

69
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
6.6 Delimiters
1
The term "delimiter" is used to refer to the following possibility for
separating data sequences.
The 3511-50 recognizes a carriage return plus linefeed (CR+LF) as
delimiters.
NOTE
The 3511-50 only begins to analyze a command after recognizing the delimiter.
6.7 Separators
(1) Message unit separator
A semicolon (;) is used as a message unit separator when it is desired to set
out several messages on a single line.
Example
NOTE
When messages are combined in this way, if a syntax error occurs, all
subsequent messages up to the next terminater will be ignored.
(2) Header separator
In a message which has a header and data, a space (represented by " " in
the examples) is used as the header separator to separate the header from the
data.
Example
:RANGe:AUTO ON;:BEEP:KEY ON ;*IDN?
:LEVel 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
(3) Data separator
If a message has several data items, commas (,) are required as data
separators for separating these data items from one another.
Example
:COMParator:FLIMit <lower limit> , <upper limit>
10
11
12
13
14
A
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
6.6 Delimiters
Page 82

70
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
6.8 Abbreviation of Compound Commands
When several compound commands have a common head portion (for
example, :BEEPer:KEY and :BEEPer:COMParator, etc.), then, when and
only when writing them directly following on from one another, this
common portion (:BEEPer: in this example) can be omitted from each
command except for the first one.
This common portion is called "the current path", by analogy with the
general concept of the current directory in the directory structure of UNIX or
MSDOS, and until it is cleared the analysis of following commands is
performed by deeming them to be preceded by the current path which has
been curtailed in the interests of brevity. This manner of using the current
path is shown in the following example:
Normal expression
Abbreviated expression
:BEEPer:KEY ON;:BEEPer:COMParator NG
:BEEPer: KEY ON;COMParator NG
This becomes the current path, an d can be
curtailed from t he following commands.
The current path is cleared when the power is turned on, when a colon (:)
appears at the start of a command, and when a delimiter is detected.
Messages with particular headers can be executed without relation to the
current path. Further, they have no effect upon the current path.
With the 3511-50, there are 5 possible current paths:
:BEEPer:
:COMParator:
:CORRection:
:RANGe:
:USER:
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
6.8 Abbreviation of Compound Commands
Page 83

71
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
6.9 Output Queue
Response messages accumulate in the output queue and are transmitted as
data and cleared.
The output queue is also cleared when the power is turned off and turned on
again.
The 3511-50 has an output queue of 300 bytes capacity. If the response
messages overflow this limit of 300 bytes, a query error is generated, and the
output queue is cleared.
6.10 Input Buffer
The 3511-50 has an input buffer of 300 bytes capacity. When more than
300 bytes of data are transmitted, when the buffer is full any subsequent
bytes received will be ignored.
(When the controller handshake setting is not the same as the 3511-50.)
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
6.9 Output Queue
Page 84

72
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
6.11 Event Registers
The 3511-50 includes three 8 bit event registers. It is possible to determine
the status of the unit by reading these registers.
The event register is cleared in the following situations:
When a "*CLS" command is executed.
When an event register query is executed. (*
When the unit is powered on.
(1) Standard event status register (SESR)
Standard event status register (SESR) bit assignments
ESR?, :ESR0?, :ESR1?
)
Bit 7
PON
Bit 6 Unused.
Bit 5
CME
Bit 4
EXE
Bit 3
DDE
Power on flag.
When the power is turned on, or on recovery from a power cut, this bit is set to 1.
Command error.
When a command which has been received contains a syntactic or semantic error, this
bit is set to 1.
The command is not supported by the 3511-50.
There is a mistake in a program header.
The number of data parameters is wrong.
The format of the parameters is wrong.
Execution error.
When for some reason a command which has been received cannot be executed, this
bit is set to 1.
The designated data value is outside the set range.
The designated data value is not acceptable.
Execution is impossible because some other function is being performed.
Device dependent error.
When a command cannot be executed due to some cause other than a command error,
a query error, or an execution error, this bit is set to 1.
Execution is impossible due to an abnormality inside the 3511-50.
During open or short circuit compensation, valid data cannot be obtained.
Query error.
Bit 2
QYE
Bit 1 Unused.
Bit 0 Unused.
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
6.11 Event Registers
This bit is set to 1 when a query error is detected by the output queue control.
When the data overflows the output queue.
When data in the output queue has been lost.
Page 85

73
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
(2) Event status registers 0 and 1 (ESR0 and ESR1)
Event Status Register 0 (ESR0) Bit Assignments
Bit 7
CEM
Bit 6
S
OF
Bit 5
SU
Bit 4
MOF
Bit 3
MUF
Bit 2
IDX
Bit 1
EOM
Bit 0 Unused
Compensation data measurement completed
Second parameter range overflow
Second parameter range underflow
F
First parameter range overflow
First parameter range underflow
Data sampling completed
Measurement completed
Event Status Register 1 (ESR1) Bit Assignments
Bit 7 Unused
Bit 6
AND
Bit 5
SLO
Bit 4
SIN
Bit 3
SHI
Bit 2
FLO
Bit 1
FIN
Bit 0
FHI
Logical product (AND) of comparison results (bit1, bit4)
Second parameter below lower limit
Second parameter within limits
Second parameter above upper limit
First parameter below lower limit
First parameter within limits
First parameter above upper limit
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
6.11 Event Registers
Page 86

74
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
6.12 Command Reference
6.12.1 Command Summary
Particular commands
Command Explanation
*CLS Clears event register. 77
*ESR? Queries standard event status register (SESR). 77
*IDN? Queries device ID. 77
*RST Device initialization. 78
*TRG Performs sampling once. 78
*TST? Queries the result of the self-test. 79
*WAI Waits until all execution is fully completed. 79
Specific commands
Command Function
Beep sound function
:BEEPer:COMParator
:BEEPer:COMParator?
:BEEPer:KEY
:BEEPer:KEY?
Equivalent circuit function
:CIRCuit
:CIRCuit?
:CIRCuit:AUTO
:CIRCuit:AUTO?
Comparator function
:COMParator
:COMParator?
:COMParator:FLIMit
:COMParator:FLIMit?
:COMParator:SLIMit
:COMParator:SLIMit?
Open and short circuit compensation function
:CORRection:DATA?
:CORRection:OPEN
:CORRection:OPEN?
:CORRection:SHORt
:CORRection:SHORt?
Sets the beep sound for the comparator.
Queries the beep sound for the comparator.
Sets the beep sound for key input.
Queries the beep sound for key input.
Sets the equivalent circuit mode.
Queries the equivalent circuit mode.
Sets the automatic equivalent circuit mode.
Queries the automatic equivalent circuit mode.
Enables and disables the comparator function. 83
Queries the comparator function enablement. 83
Sets the lower and upper limit values for the first parameter. 83
Queries the lower and upper limit values for the first parameter. 84
Sets the lower and upper limit values for the second parameter. 84
Queries the lower and upper limit values for the second parameter. 84
Queries the open and short circuit compensation values. 85
Enables and disables the open circuit compensation function. 85
Queries the open circuit compensation function enablement. 86
Enables and disables the short circuit compensation function. 86
Queries the short circuit compensation function enablement. 86
Ref
page
Ref
page
80
80
81
81
81
82
82
82
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
6.12 Comm an d Reference
Page 87

75
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Command Function
Communication error confirmation
:ERRor?
Queries the RS-232C error. 87
Event register
:ESR0?
:ESR1?
Queries event status register 0. 87
Queries event status register 1. 88
Test frequency function
:FREQuency
:FREQuency?
Sets the test frequency. 88
Queries the test frequency. 88
Headers
:HEADer
:HEADer?
Enables and disables headers for the response message. 89
Queries headers enablement. 89
Test signal level function
:LEVel
:LEVel?
Sets the test signal level. 89
Queries the test signal level. 90
Panel load function
:LOAD
Transfers the specified panel number. 90
Normal testings
:MEASure?
Queries the d a ta item. 91
Parameter settings
:PARAmeter
:PARAmeter?
Sets displayed parameters. 92
Queries displayed parameters. 92
Test range function
:RANGe
:RANGe?
:RANGe:AUTO
:RANGe:AUTO?
Sets test range. 93
Queries test range setting. 94
Sets the automatic test ranging. 94
Queries the automatic test range setting. 94
Panel saving function
:SAVE
:SAVE?
Saves the test conditions in specified panel number. 95
Queries the panel number in which data is saved. 95
Test speed function
:SPEEd
:SPEEd?
Sets the testing speed. 95
Queries the testing speed. 96
Trigger function
:TRIGger
:TRIGger?
Sets the type of trigger. 96
Queries the trigger setting. 96
ID function
:USER:IDENtity
:USER:IDENtity?
Sets the user ID. 97
Queries the user ID. 97
Ref
page
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
6.12 Comm an d Reference
Page 88

76
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
6.13 Format of Command Explanations
Syntax
<data>
Function
Example
Error
NOTE
Specifies the syntax for the command (a space is represented by " " in this syntax).
For a command that has parameters, specifies their format.
Specifies the function of the command.
These are simple examples of the use of the command.
Note that all transmission messages are expressed in a "short form."
Specifies what types of error may occur.
On the 3511-50, internal processing may involve a delay of 20 ms to 500 ms
maximum from command receipt to start of analysis.
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
6.13 Format of Com man d Explanations
Page 89

77
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
6.14 Particular Commands
*CLS
Clears the status byte register and the event registers.
Syntax *CLS
Function
Error
Clears all the event registers (SESR, ESR0, ESR1) associated with the bits of the status
byte register. Accordingly, also clears the status byte register.
This has no effect upon the output queue.
If the data parameters are set after this command, a command error occurs.
*ESR?
Queries the contents of the standard event status register (SESR).
Syntax *ESR?
Function
Example
Returns the contents of the standard event status register (SESR) as a numerical value in
NR1 format between 0 and 255, and then clears standard event status register.
No header is affixed to the response message.
Response
Bit 5 of SESR has been set to 1.
128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1
bit 7 bit 6 bit 5 bit 4 bit 3 bit 2 bit 1 bit 0
PON Unused CME EXE DDE QYE Unused Unused
32
Standard event status register (SESR)
Error
If the response message is longer than 300 bytes, a query error is generated.
*IDN?
Queries manufacturer's name, model name, and software version.
Syntax *IDN?
Function
Example
Error
The response consists of the name of the manufacturer of the unit, the model name, and
the software version.
No header is affixed to the response message.
First field Manufacturer's name
Second field Model name
Third field Fixed for fifty
Fourth field Software version
Response HIOKI,3511,50,V01.00
If the response message is longer than 300 bytes, a query error is generated.
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
6.14 Particular Commands
Page 90

78
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
*RST
Performs device initial setting.
Syntax *RST
Function
Resets the 3511-50. The items which are reset are listed below.
Test parameters
Test frequency
Test signal level
Test range
Equivalent circuit mode
Open circuit compensation
Short circuit compensation
Trigger setting
Test speed setting
Beep sound setting
Comparator
Panel save
Impedance (Z), phase angle (θ)
1kHz
1V
AUTO
AUTO
OFF
OFF
Internal trigger
NORMAL
ON for key input, OFF for comparator
Both first and second parameters
Upper and lower limit values: OFF
All contents clear
Error
If the data parameters are set after this command, a command error occurs.
*TRG
Issues external trigger.
Syntax *TRG
Function
Example
Error
In external trigger mode, performs measurement once.
Transmission :TRIGger EXTernal;
Executing this command in internal trigger mode generates an execution error.
If the data parameters are set after this command, a command error occurs.
Executing this command while the open or short circuit compensation is performed
generates an execution error.
*
TRG;:MEASure?
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
6.14 Particular Commands
Page 91

79
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
*TST?
Requests execution of, and queries the result of, the self test.
Syntax *TST?
Function
Example
Error
Performs the self test of the 3511-50, and returns the result thereof as a numerical value
in NR1 format between 0 and 3.
No header is affixed to the response message.
Bit 0: A ROM error occurred.
Bit 1: A RAM error occurred.
Bit 2: An I/O error occurred.
Bit 3: An interrupt error occurred.
Bits 4 to 7: Unused
Response 6
A RAM error (bit 1) and an I/O error (bit 2) h ave occurred.
If the response message is longer than 300 bytes, a query error occurs.
Executing this command while the open or short circuit compensation is performed
generates an execution error.
*WAI
Waits until all execution is fully completed.
Syntax *WAI
Function
Note
Example
Error
The unit goes into waiting state until the previous operation has been completed.
All of the specific commands are in any case sequential commands except the
:MEASure? query. Therefore, using this
:MEASure? query.
Transmission (If the frequency is set to 1 kHz)
When using the *WAI command
:FREQuency 120;*WAI;*TRG;:MEASure?
The response for :MEASure? is the test value at frequency of 120 Hz.
When not using the *WAI command
:FREQuency 120;*TRG;:MEASure?
The response for :MEASure? is the test value at frequency of 1 kHz.
If the data parameters are set after this command, a command error occurs.
WAI command has an effect upon only
*
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
6.14 Particular Commands
Page 92

80
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
6.15 Commands Specific to the 3511-50
:BEEPer:COMParator
Sets the beep sound for the comparator.
Syntax :BEEPer:COMParator
<data>
Function
Example
Error
IN/NG/OFF (character data)
Sets the beep sound produced when the comparator makes decisions.
IN: When the comparator result is within limits, a beep sound is emitted.
NG: When the comparator result is out of limits, a beep sound is emitted.
OFF: No beep sound is emitted.
Transmission :BEEPer:COMParator NG
When the value is out of limits, a beep sound is emitted.
If <data> is other than character data described above, an execution error occurs.
Executing this command while the open or short circuit compensation is performed
generates an execution error.
<data>
:BEEPer:COMParator?
Queries the beep sound for the comparator.
Syntax :BEEPer:COMParator?
<data>
IN/NG/OFF (character data)
Function
Example
Error
Returns the beep sound setting for when the comparator makes decision as character data.
IN: When the comparator result is within limits, a beep sound is emitted.
NG: When the comparator result is out of limits, a beep sound is emitted.
OFF: No beep sound is emitted.
Response
If headers are on :BEEPER:COMPARATOR NG
If headers are off NG
If the response message is longer than 300 bytes, a query error is generated.
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
6.15 Commands Specific to the 3511-50
Page 93

81
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
:BEEPer:KEY
Enables and disables the beep sound for key input.
Syntax :BEEPer:KEY
<data>
Function
Example
Error
ON/OFF (character data)
Sets the beep sound produced each time a key is pressed.
ON: A beep sound is emitted.
OFF: No beep sound is emitted.
Transmission :BEEPer:KEY ON
When a key is pressed, a beep sound is emitted.
If <data> is other than character data described above, an execution error occurs.
Executing this command while the open or short circuit compensation is performed
generates an execution error.
<data>
:BEEPer:KEY?
Queries the beep sound for key input.
Syntax :BEEPer:KEY?
<data>
Function
ON/OFF (character data)
Returns the beep sound setting for when a key is pressed as character data.
ON: A beep sound is emitted.
OFF: No beep sound is emitted.
Example
Error
Response
If headers are on :BEEPER:KEY ON
If headers are off ON
If the response message is longer than 300 bytes, a query error is generated.
:CIRCuit
Sets the equivalent circuit mode.
Syntax :CIRCuit
<data>
Function
Example
SER/PAR (character data)
Sets the equivalent circuit mode.
SER: Series equivalent circuit mode
PAR: Parallel equivalent circuit mode
Transmission :CIRCuit SER
The s
Error
If <data> is other than character data described above, an execution error occurs.
Executing this command while the open or short circuit compensation is performed
generates an execution error.
<data>
eries equivalent circuit mode is set.
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
6.15 Commands Specific to the 3511-50
Page 94

82
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
:CIRCuit?
Queries the equivalent circuit mode.
Syntax :BEEPer:KEY?
<data>
Function
Example
Error
SER/PAR (character data)
Returns the current equivalent circuit mode setting as char acter data.
SER: Series equivalent circuit mode
PAR: Parallel equivalent circuit mode
Response
If headers are on :CIRCUIT SER
If headers are off SER
If the response message is longer than 300 bytes, a query error is generated.
:CIRCuit:Auto
Sets the automatic equivalent circuit mode.
Syntax :CIRCuit:AUTO
<data>
Function
ON/OFF (character data)
Switches between automatic and manu al setting of equivalent circuit mode.
ON: Switches the automatic setting.
OFF: Switches the manual setting.
<data>
Example
Transmission ":CIRCuit:AUTO ON"
The equivalent circuit mode is switched to automatic selection (auto-ranging).
Error
If <data> is other than character data described above, an execution error occurs.
Executing this command while the open or short circuit compensation is performed
generates an execution error.
:CIRCuit:Auto?
Queries the automatic equivalent circuit mode.
Syntax :CIRCuit:AUTO?
<data>
Function
Example
Error
ON/OFF
Returns whether the equivalent circuit mode is automatically set as character data.
Response
If headers are on ":CIRCUIT:AUTO ON"
If headers are off "ON"
If the response message is longer than 300 bytes, a query error is generated.
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
6.15 Commands Specific to the 3511-50
Page 95

83
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
:COMParator
Enables and disables the comparator function.
Syntax :COMParator
<data>
Function
Example
ON/OFF (character data)
Turns the comparator function on and off.
Transmission :COMParator ON
<data>
The comparator function is turned on.
Error
If <data> is other than character data described above, an execution error occurs.
Executing this command while the open or short circuit compensation is performed
generates an execution error.
:COMParator?
Queries the comparator function enablement.
Syntax COMParator?
<data>
Function
Example
ON/OFF (character data)
Returns the current enablement st ate of the comparator function as character data.
Response
If headers are on :COMPARATOR ON
If headers are off ON
Error
If the response message is longer than 300 bytes, a query error is generated.
:COMParator:FLIMit
Sets the lower and upper limit values for the first comparator parameter.
Syntax :COMParator:FLIMit
<data>
Function
Example
<low> (lower limit value): OFF (character data) or numerical value in NR1 format
<high> (upper limit value): OFF (character data) or numerical value in NR1 format
Sets the lower and upper limit values for the first comparator parameter (i.e. the principal
measured value) as counts that are displayed on the screen.
The numerical value can be in NRf format, but rounding is performed for figures beyond
the last valid decimal place.
Transmission :COMParator:FLIMit 11234,12345
The lower limit value is set to 11234, and the upper limit value is set to 12345.
Error
If <data> is other than character data or numerical value described above, an execution
error occurs.
Executing this command while the open or short circuit compensation is performed
generates an execution error.
<low>,<high>
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
6.15 Commands Specific to the 3511-50
Page 96

84
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
:COMParator:FLIMit?
Queries the lower and upper limit values for the first comparator parameter.
Syntax :COMParator:FLIMit?
<data>
Function
Example
Error
OFF (character data) or numerical value in NR1 format
Returns the lower and upper limit values for the first comparator parameter as character
data or numerical value in order.
Response
If headers are on
If headers are off
If the response message is longer than 300 bytes, a query error is generated.
:COMPARATOR:FLIMIT 11234,12345
11234,12345
:COMParator:SLIMit
Sets the lower and upper limit values for the second comparator parameter.
Syntax COMParator: SLIMit:ABSolute
<data>
Function
<low> (lower limit value): OFF (character data) or numerical value in NR1 format
<high> (upper limit value): OFF (character data) or numerical value in NR1 format
Sets the lower and upper limit values for the second comparator parameter.
The numerical value can be in NRf format, but rounding is performed for figures beyond
the last valid decimal place.
<low>,<high>
Example
Transmission :COMParator:SLIMit 11234,12345
The lower limit value is set to 11234, and the upper limit value is set to 12345.
Error
If <data> is other than character data or numerical value described above, a command
error occurs.
Executing this command while the open or short circuit compensation is performed
generates an execution error.
:COMParator:SLIMit?
Queries the lower and upper limit values for the second comparator parameter.
Syntax COMParator:SLIMit?
<data>
Function
Example
Error
OFF (character data) or numerical value in NR1 format
Returns the lower and upper limit values for the second comparator parameter as
character data or numerical value in order.
Response
If headers are on :COMPARATOR:SLIMIT 11234,12345
If headers are off 11234,12345
If the response message is longer than 300 bytes, a query error occurs.
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
6.15 Commands Specific to the 3511-50
Page 97

85
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
:CORRection:DATA?
Queries the open circuit and short circuit compensation values.
Syntax :CORRection:DATA?
<data>
Function
Example
Residual impedance: Numerical value in NR3 format or OFF (character data)
Phase angle: Numerical value in NR2 format or OFF (character data)
Returns the open and short circuits compensation values in the current test frequency in
the following order.
<Residual impedance of short circuit compensation>
<Phase angle of short circuit compensation>
<Residual impedance of open circuit compensation>
<Phase angle of open circuit compensation>
When the compensation setting is OFF, returns the character data "OFF."
Response
If headers are on
If headers are off
:CORRECTION:DATA OFF,OFF,247.45E+06,-21.58
OFF,OFF,247.45E+06,-21.58
The short circuit compensation for the current test frequency is set to OFF, and
open circuit compensation is 247.45 MΩ, -21.58 .
Error
If the response message is longer than 300 bytes, a query error is generated.
:CORRection:OPEN
Enables and disables the open circuit compensation function.
Syntax :CORRection:OPEN
<data>
Function
Example
ON/OFF (character data)
Enables and disables the open circuit compensation function.
Specifying "ON" for <data> starts the reading of open circuit compensation data. Upon
completion of data reading, the open circuit compensation function is set to ON.
Transmission :CORRection:OPEN ON
The open circuit compensation function is set to ON.
Error
If <data> is other than character data described above, an execution error occurs.
Executing this command while the comparator fun ction is performed generates an
execution error.
<data>
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
6.15 Commands Specific to the 3511-50
Page 98

86
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
:CORRection:OPEN?
Queries the open circuit compensation function enablement.
Syntax :CORRection:OPEN?
<data>
Function
Example
ON/OFF (character data)
Returns the current enablement state of the open circuit compensation function as
character data.
ON: The open circuit compensation function has been set to on.
OFF: The open circuit compensation function has been set to off.
Response
If headers are on
If headers are off ON
:CORRECTION:OPEN ON
The open circuit compensation has been enabled.
Error
If the response message is longer than 300 bytes, a query error is generated.
:CORRection:SHORt
Enables and disables the short circuit compensation function.
Syntax :CORRection:SHORt
<data>
Function
ON/OFF (character data)
Enables and disables the short circuit compensation function.
<data>
Example
Transmission :CORRection:SHORt ON
The short circuit compensation function is enabled.
Error
If <data> is other than character data described above, an execution error occurs.
Executing this command while the comparator fun ction is performed generates an
execution error.
:CORRection:SHORt?
Queries the short circuit compensation function enablement.
Syntax :CORRection:SHORt?
<data>
Function
Example
ON/OFF (character data)
Returns the current enablement state of the short circuit compensation function as
character data.
ON: The short circuit compensation function has been set to on.
OFF: The short circuit compensation function has been set to off.
Response
If headers are on
If headers are off
:CORRECTION:SHORT ON
ON
The open circuit c ompensation function has been enabled.
Error
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
6.15 Commands Specific to the 3511-50
If the response message is longer than 300 bytes, a query error is generated.
Page 99

87
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
:ERRor?
Queries RS-232C communication condition errors.
Syntax :ERRor?
Function
<data>
Example
Error
Returns the value of RS-232C communication condition errors as a numerical value in
NR1 format from 0 to 7, and t hen clears RS-232C communication condition errors.
No header is prefixed to the response message.
Numerical data in NR1 format between 0 and 7
Response 4
An overrun error has occurred.
128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1
bit 7 bit 6 bit 5 bit 4 bit 3 bit 2 bit 1 bit 0
Unused Unused Unused Unused Unused Overrun
RS-232C communication condition errors register
If the response message is longer than 300 bytes, a query error is generated.
:ESR0?
Queries event status register 0.
Syntax ESR0?
error
Framing
error
Parity
error
Function
Example
Error
Returns the value of event status register 0 (ESR0) as a numerical value in NR1 format
between 0 and 255, and then clears event status register 0.
No header is prefixed to the response message.
Response 4
Bit 2 of ESR0 has been set to 1.
If the response message is longer than 300 bytes, a query error is generated.
128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1
bit 7 bit 6 bit 5 bit 4 bit 3 bit 2 bit 1 bit 0
CEM SOF SUF MOF MUF IDX EOM Unused
Event status register 0 (ESR0)
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
6.15 Commands Specific to the 3511-50
Page 100

88
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
:ESR1?
Queries event status register 1.
Syntax ESR1?
Function
Example
Error
Returns the value of event status register 1 (ESR1) as a numerical value in NR1 format
between 0 and 255, and then clears event status register 1.
No header is prefixed to the response message.
128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1
bit 7 bit 6 bit 5 bit 4 bit 3 bit 2 bit 1 bit 0
Unused AND SLO SIN SHI FLO FIN FHI
Event status register 1 (ESR1)
Response 64
Bit 6 of ESR1 has been set to 1.
If the response message is longer than 300 bytes, a query error is generated.
:FREQuency
Sets the test frequency.
Syntax FREQuency
<data>
Function
120/1000 (numerical data in NR1 format)
Sets the test frequency.
The numerical value can be in NRf format, but rounding is performed for figures beyond
the last valid decimal place.
<data>
Example
Transmission :FREQuency 1000
The test frequency is set to 1 kHz.
Error
If <data> is other than numerical value described above, an execution error occurs.
Executing this command while the open or short circuit compensation is performed
generates an execution error.
:FREQuency?
Queries the test frequency.
Syntax :FREQuency?
<data>
Function
Example
Error
120/1000 (numerical data in NR1 format)
Returns the current test frequency setting as a numerical value in NR1 format.
Response
If headers are on
If headers are off
The test frequency has been set to 1 kHz.
If the response message is longer than 300 bytes, a query error is generated.
:FREQUENCY 1000
1000
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
6.15 Commands Specific to the 3511-50
 Loading...
Loading...