Page 1
Impact Wrench
Schlagschrauber
ªÔ˘ÏÔÓfiÎÏÂȉÔ
Klucz udarowy
Ütvecsavarozó
Utahovák
Darbeli somun s˙kma
ìÀapÌêÈ ÖaÈÍoÇepÚ
WR 16SA
Read through carefully and understand these instructions before use.
Diese Anleitung vor Benutzung des Werkzeugs sorgfältig durchlesen und verstehen.
¢И·‚¿ЫЩВ ЪФЫВОЩИО¿ О·И О·Щ·УФ‹ЫВЩВ ·˘Щ¤˜ ЩИ˜ Ф‰ЛБ›В˜ ЪИУ ЩЛ ¯Ъ‹ЫЛ.
Przed użytkowaniem należy dokładnie przeczytać niniejszą instrukcję i zrozumieć jej treść.
Használat előtt olvassa el figyelmesen a használati utasítást.
Před použitím si pečlivě přečtěte tento návod a ujistěte se, že mu dobře rozumíte.
Aleti kullanmadan önce bu kılavuzu iyice okuyun ve talimatları anlayın.
BÌËÏaÚeÎëÌo ÔpoäÚËÚe ÀaÌÌyï ËÌcÚpyÍáËï Ôo íÍcÔÎyaÚaáËË ÔpeÊÀe äeÏ ÔoÎëÁoÇaÚëcÓ ËÌcÚpyÏeÌÚoÏ.
Handling instructions
Bedienungsanleitung
√‰ЛБ›В˜ ¯ВИЪИЫМФ‡
Instrukcja obsługi
Kezelési utasítás
Návod k obsluze
Kullanım talimatları
àÌcÚpyÍáËÓ Ôo íÍcÔÎyaÚaáËË
Page 2
1 2
12mm
5mm
21
0
0246810
10
20
30
40
(kg-m)
(s)
M16 × 55 (F10T)
1
3
2
4
5
3
6
7
8
9
3
4
5
A
0
C
B
5
D
E
1 2 47
Page 3
English Deutsch Ελληνικά Polski
Pin, O-ring type
1
2
Pin
3
Hex. socket
4
Ring
5
Anvil
6
Plunger Type
7
Hole
8
Plunger
9
Spring
0
Switch
A
Rating
B
Tightening time
Tightening torque
C
D
Wear limit
E
No. of carbon brush
Magyar Čeština Türkçe PyccÍËÈ
Csap, körszelvényű
1
tömítőgyűrű típusú
2
Csap
3
Hatszögletű befogópatron
4
Gyűrű
5
Szár
6
Hengeres csap típusa
7
Nyílás
8
Hengeres csap
9
Rúgó
0
Kapcsoló
A
Névleges jellemzők
B
Meghúzási idő
C
Meghúzási nyomaték
D
Megengedett kopás
E
Szénkefe száma
Stift, O-Ring typ
Stift
Sechskantmuffe
Ring
Amboß
Typ mit Tauchkolben
Loch
Tauchkolben
Feder
Schalter
Nennleistung
Anzugszeit
Anzugsdrehkraft
Abnutzungsgrenze
Nr. der Kohlebürste
Kolík, typ s těsnicím O
kroužkem
Kolík
Šestihranná nástrčná hlavice
Kroužek
Pevná část
Typ s plunžrem
Otvor
Západkový čep
Pružina
Přepínač
Jmenovitý výkon
Doba dotahovaní
Utahovací moment
Mez opotřebení
Číslo uhlíkového kartáčku
Περνη, τύπος
Ο- δακτυλίου
Πείρος
Εξάγων. υποδοχή
∆ακτύλιος
Άκµονας
Τύπος πιστονιού
Τρύπα
Πιστνι
Ελατήριο
∆ιακπτης
∆ιαβάθµιση
Χρνος σύσφιξης
Ροπή σύσφιξης
%ριο φθοράς
Αρ. καρβουνακίων
Pim, O halka tipi
Pim
Altıgen Yuva
Halka
Örs
Ótici Tip
Delik
Ótici
Yay
Anahtar
Deåerleme
Sıkıßtırma süresi
Sıkıßtırma torku
Yıpranma limiti
Kömür tanımlama sayısı
Sworzeń z pierścieniem
uszczelniającym
Kołek
Gniazdo sześciokątne
Pierścień
Kowadło
Typ trzpienia ruchomego
Otwór
Trzpień ruchomy
Sprężyna
Przełącznik
Dane znamionowe
Czas dokręcania
Moment obrotowy
dokręcania
Ogranicznik zużycia
Numer szczotki węglowej
тЪЛЩЪ, ЪЛФ НoОлбeЗoЦo
yФОoЪМeМЛУ
тЪЛЩЪ
тecЪЛЦpaММoe ЦМeБАo
KoОлбo
HaНoЗaОлМУ
TЛФ ФОyМКepa
OЪЗepcЪЛe
иОyМКep
иpyКЛМa
иepeНОпдaЪeОл
XapaНЪepЛcЪЛНa
BpeПУ БaЪУЦЛЗaМЛУ
KpyЪУзЛИ ПoПeМЪ
иpeАeО ЛБМoca
£ yЦoОлМoИ зeЪНЛ
Page 4

English
GENERAL SAFETY RULES
WARNING!
Read all instructions
Failure to follow all instructions listed below may result in
electric shock, fire and/or serious injury.
The term “power tool” in all of the warnings listed below
refers to your mains operated (corded) power tool or battery
operated (cordless) power tool.
SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS
1) Work area
a) Keep work area clean and well lit.
Cluttered and dark areas invite accidents.
b) Do not operate power tools in explosive
atmospheres, such as in the presence of flammable
liquids, gases or dust.
Power tools create sparks which may ignite the
dust of fumes.
c) Keep children and bystanders away while operating
a power tool.
Distractions can cause you to lose control.
2) Electrical safety
a) Power tool plugs must match the outlet.
Never modify the plug in any way.
Do not use any adapter plugs with earthed
(grounded) power tools.
Unmodified plugs and matching outlets will reduce
risk of electric shock.
b) Avoid body contact with earthed or grounded
surfaces such as pipes, radiators, ranges and
refrigerators.
There is an increased risk of electric shock if your
body is earthed or grounded.
c) Do not expose power tools to rain or wet
conditions.
Water entering a power tool will increase the risk
of electric shock.
d) Do not abuse the cord. Never use the cord for
carrying, pulling or unplugging the power tool.
Keep cord away from heat, oil, sharp edges or
moving parts.
Damaged or entangled cords increase the risk of
electric shock.
e) When operating a power tool outdoors, use an
extension cord suitable for outdoor use.
Use of a cord suitable for outdoor use reduces
the risk of electric shock
3) Personal safety
a) Stay alert, watch what you are doing and use
common sense when operating a power tool.
Do not use a power tool while you are tired or
under the influence of drugs, alcohol or medication.
A moment of inattention while operating power
tools may result in serious personal injury.
b) Use safety equipment. Always wear eye protection.
Safety equipment such as dust mask, non-skid
safety shoes, hard hat, or hearing protection used
for appropriate conditions will reduce personal
injuries.
c) Avoid accidental starting. Ensure the switch is in
the off position before plugging in.
Carrying power tools with your finger on the
switch or plugging in power tools that have the
switch on invites accidents.
d) Remove any adjusting key or wrench before
turning the power tool on.
A wrench or a key left attached to a rotating part
of the power tool may result in personal injury.
e) Do not overreach. Keep proper footing and balance
at all times.
This enables better control of the power tool in
unexpected situations.
f) Dress properly. Do not wear loose clothing or
jewellery. Keep your hair, clothing and gloves
away from moving parts.
Loose clothes, jewellery or long hair can be caught
in moving parts.
g) If devices are provided for the connection of dust
extraction and collection facilities, ensure these
are connected and properly used.
Use of these devices can reduce dust related hazards.
4) Power tool use and care
a) Do not force the power tool. Use the correct
power tool for your application.
The correct power tool will do the job better and
safer at the rate for which it was designed.
b) Do not use the power tool if the switch does not
turn it on and off.
Any power tool that cannot be controlled with the
switch is dangerous and must be repaired.
c) Disconnect the plug from the power source before
making any adjustments, changing accessories, or
storing power tools.
Such preventive safety measures reduce the risk
of starting the power tool accidentally.
d) Store idle power tools out of the reach of children
and do not allow persons unfamiliar with the
power tool or these instructions to operate the
power tool.
Power tools are dangerous in the hands of
untrained users.
e) Maintain power tools. Check for misalignment or
binding of moving parts, breakage of parts and
any other condition that may affect the power
tools operation.
If damaged, have the power tool repaired before
use.
Many accidents are caused by poorly maintained
power tools.
f) Keep cutting tools sharp and clean.
Properly maintained cutting tools with sharp cutting
edges are less likely to bind and are easier to
control.
g) Use the power tool, accessories and tool bits etc.,
in accordance with these instructions and in the
manner intended for the particular type of power
tool, taking into account the working conditions
and the work to be performed.
Use of the power tool for operations different from
intended could result in a hazardous situation.
5) Service
a) Have your power tool serviced by a qualified repair
person using only identical replacement parts.
This will ensure that the safety of the power tool
is maintained.
PRECAUTION
Keep children and infirm persons away.
When not in use, tools should be stored out of reach of
children and infirm persons.
3
Page 5
English
S
D
B
E
L
PRECAUTIONS ON USING IMPACT WRENCH
1. When using the tool at a height, make sure that
there is nobody below.
2. Use earplugs if using for a long time use.
3. Switch the reversing switch only after the motor
has stoped when it is necessary to change the
direction of the rotation.
4. Use a step up transformer when a long extension
cable is used.
SPECIFICATIONS
Voltage (by areas)* (110V, 115V, 120V, 127V, 220V, 230V, 240V)
Power input* 480 W
No load speed 1900 min
Capacities (size of bolts)
Tightening torque** Maximum 36.7 kg-m
Angle drive 12.7 mm
Weight (without cord) 2.9 kg
*Be sure to check the nameplate on product as it is subject to change by areas.
**Tightening the bolt without extension cord at rated voltage.
5. Confirm the tightening torque by a torque wrench
before use in order to ascertain the correct tightening
torque to be used.
6. Assemble the socket securely to the impact wrench
with the socket pin and ring.
7. Confirm whether the socket has any cracks in it.
8. Always hold the body and side handles of the impact
wrench firmly. Otherwise the counterforce produced
may result in inaccurate and even dangerous operation.
-1
M12-M16 (High tension bolt)
M12-M22 (Ordinary bolt)
STANDARD ACCESSORIES
(1) Side handle ............................................................... 1
(2) Case ........................................................................... 1
Standard accessories are subject to change without notice.
OPTIONAL ACCESSORIES
(sold separately)
1. Variety of sockets
Although the Hitachi Impact Wrench is delivered
with only one standard socket, ample sockets are
available to cover impact tightening of various sizes
and types of bolts.
Table 1 B = 12.7 mm
Socket
Designation
Hex. Socket 12
13
14
17
19
21
22
23
24
26
27
30
S
17
19
21
22
23
24
26
27
30
Ordinary Socket Long Socket
Dimension (mm) Dimension (mm)
D
28
28
32
35
36
38
38
42
42
E
15
17
19
24
25
25
25
24
34
L
32
34
36
40
40
40
40
50
50
S
12
13
14
17
19
21
22
23
24
26
27
30
D
20
21.5
22
25
28
31
32.5
33
34
38
40
42
E
34
34
34
34
34
34
34
34
34
57
57
57
L
52
52
52
52
52
52
52
52
52
75
75
75
4
Page 6
English
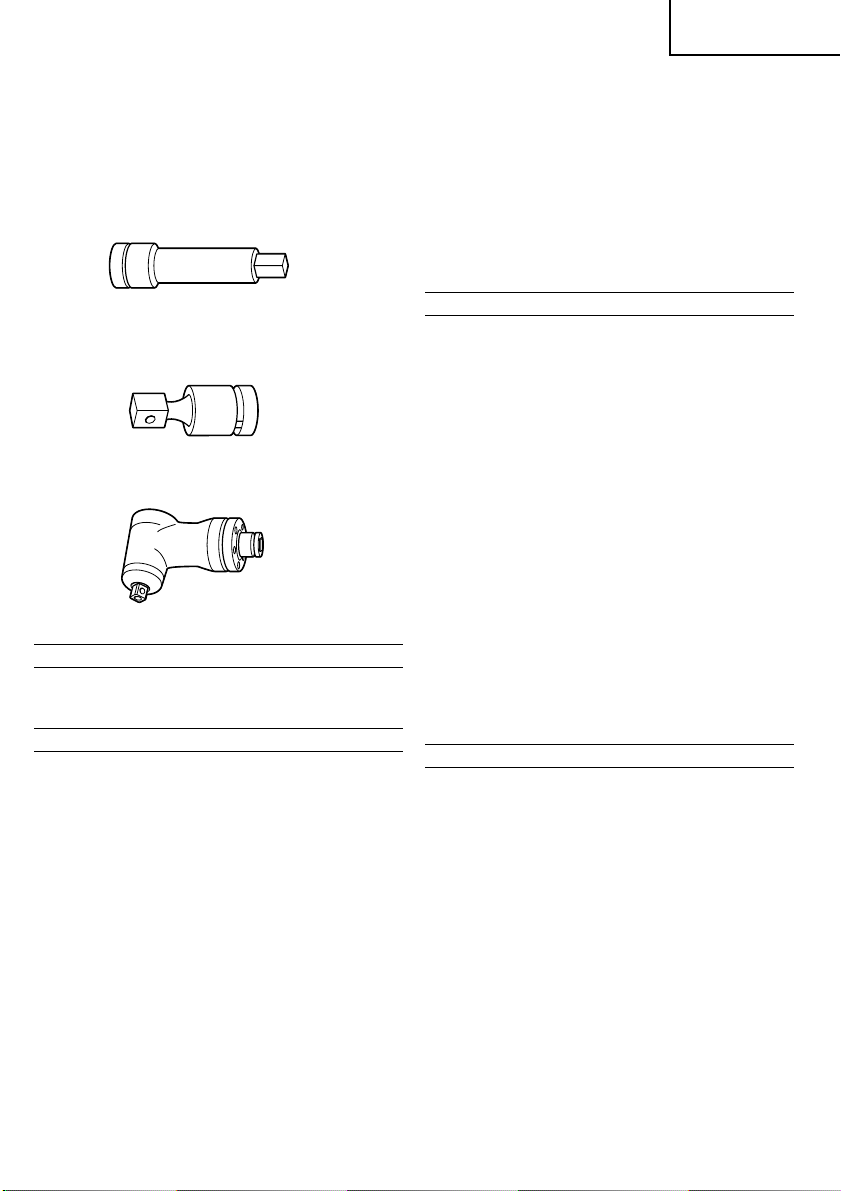
2. Extension bar
The extension bar is convenient for working in very
restricted spaces or when the socket provided cannot
reach the bolt to be tightened.
CAUTION
When the extension bar is used the tightening torque
is reduced slightly compared with the ordinary
socket. So it is necessary to operate the tool a little
longer to get the same torque.
3. Universal joint
The universal joint is convenient for impacting nuts
when there is an angle between the socket and
wrench, or when working in a very narrow space.
4. Corner attachment (Model EW-14R)
Use this attachment only when the machine is
applied to the nut or bolt at a right angle.
Optional accessories are subject to change without notice.
APPLICATIONS
䡬 Tightening and loosening various kinds of bolt and
nut.
PRIOR TO OPERATION
1. Power source
Ensure that the power source to be utilized conforms
to the power requirements specified on the product
nameplate.
2. Power switch
Ensure that the power switch is in the OFF position.
If the plug is connected to a receptacle while the
power switch is in the ON position, the power tool
will start operating immediately, which could cause
a serious accident.
3. Extension cord
When the work area is removed from the power
source, use an extension cord of sufficient thickness
an rated capacity. The extension cord should be
kept as short as practicable.
4. Fixing the side handle
The position of the side handle attached to the
hammer case can be changed by unscrewing the
handle. (Right hand screw) Turn the handle to the
desired position for the job and secure the handle
by screwing up tight.
5. Mounting the socket
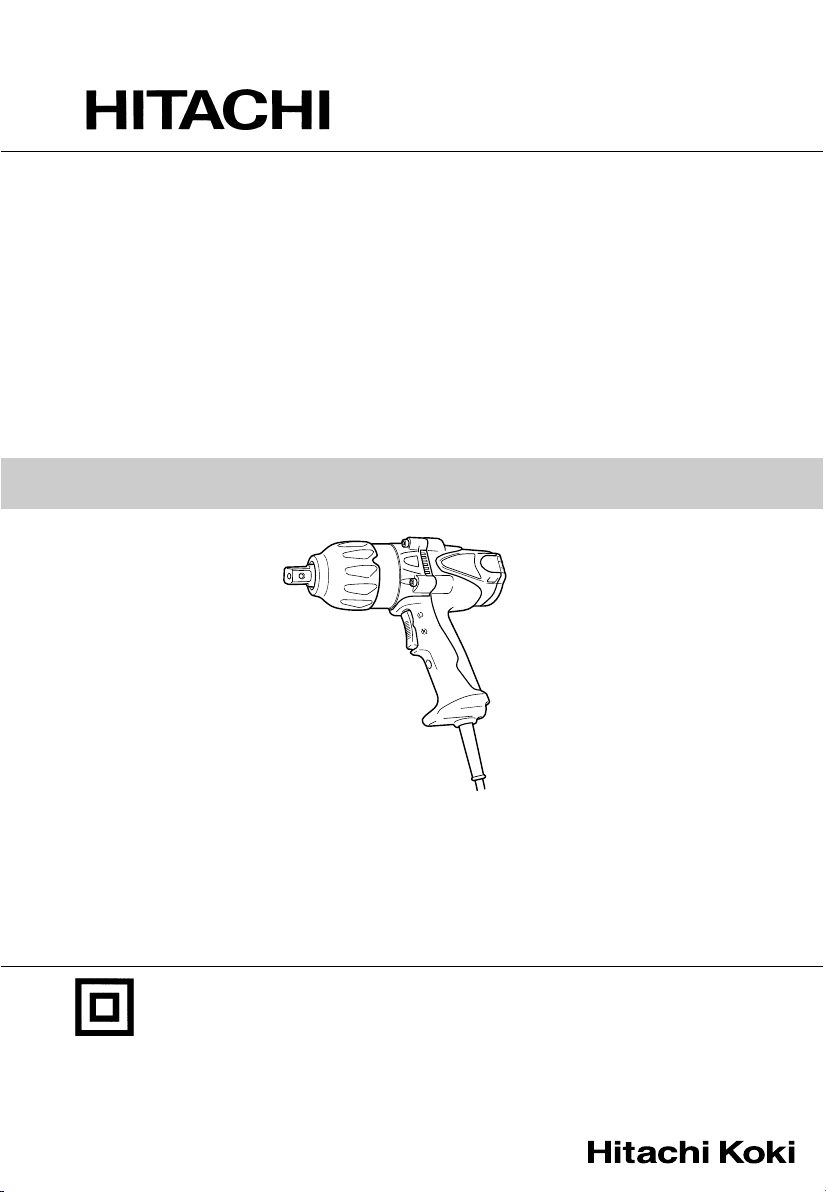
(1) Pin, O-ring type (Fig. 1)
Select a socket matched to the bolt to be tightened
or loosened. Insert the socket on the anvil of the
wrench, and secure it with the pin and ring. When
dismantling the socket, reverse the sequence.
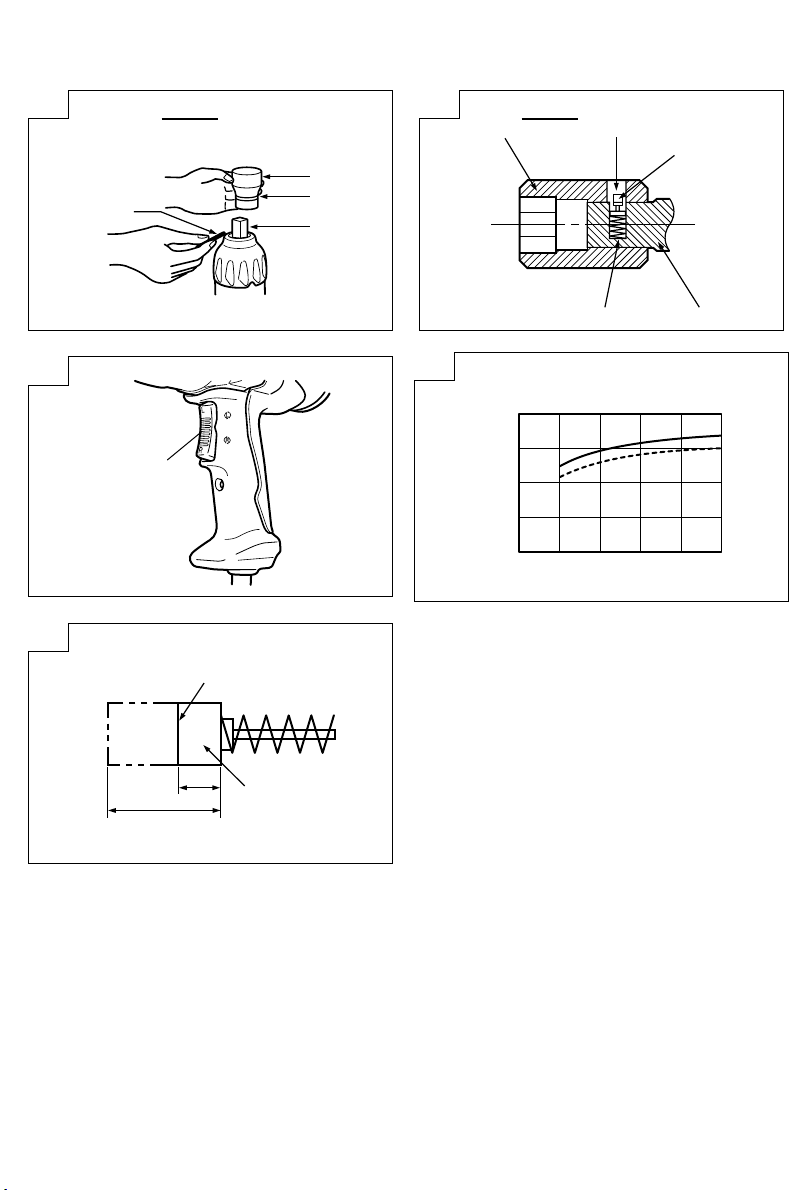
(2) Plunger type (Fig. 2)
Align the plunger located in the square part of the
anvil with the hole in the hex socket. Then push
the plunger, and mount the hex socket on the anvil.
Check that the plunger is fully engaged in the hole.
When removing the socket, reverse the sequence.
HOW TO USE
1. Operation of switch (Fig. 3)
The switch in this machine functions as a motor
switch and rotational direction selector switch. When
the switch is set to R indicated on the handle cover,
the motor rotates clockwise to tighten the bolt.
When the switch is set to L, the motor rotates
counterclockwise to loosen the bolt. When the switch
is released, the motor stops.
CAUTION
Be sure to turn the switch OFF and wait until the
motor completely stops before changing the
direction of wrench revolution. Switching while the
motor is rotating will result in burning the motor.
2. Tightening and loosening bolts
A hex socket matching the bolt or nut must first
be selected. Then mount the socket on the anvil,
and grip the nut to be tightened with the hex socket.
Holding the wrench in line with the bolt, press the
power switch to impact the nut for several seconds.
If the nut is only loosely fitted to the bolt, the bolt
may turn with the nut, therefore preventing proper
tightening. In this case, stop impact on the nut and
hold the bolt head with a wrench before restarting
impact, or manually tighten the bolt and nut to
prevent them slipping.
OPERATIONAL CAUTIONS
1. Confirm the line voltage (Fig. 4)
The available tightening torque is influenced by line
voltage. Reduced line voltage lowers the available
tightening torque.
For example, if you use a 220 V type wrench on
a 200 V line the available tightening torque will be
reduced to 70 to 90 %. When extending the power
cord, use an extension cord which is as short as
possible. When the line voltage is low and a long
extension cord is needed a step up transfomer
should be used. The relation between the line voltage
and the tightening torque are shown in the figures.
2. Do not touch the bumper or hammer case during
continuous operation
The bumper and hammer case become hot during
continuous screw tightening so be careful not to
touch them at that time.
3. Work at a tightening torque suitable for the bolt
under impact
The optimum tightening torque for nuts and bolts
differs with material and size of the nuts and bolts.
An excessively large tightening torque for a small
5
Page 7

English
bolt may strech or break the bolt. The tightening
torque increases proportionally to the operating
time. Use the correct operating time for the bolt.
4. Selecting the socket to be matched to the bolt
Be sure to use a socket which is matched to the
bolt to be tightened. Using an improper socket will
result not only in insufficient tightening but also in
damage to the socket or nut.
A worn or deformed hex or square-holed socket will
not give an adequate tightness for fitting to the nut
or anvil, consequently resulting in loss of tightening
torque.
Pay attention to wear of socket holes, and replace
before further wear develops. Matching socket and
bolt sizes are shown in Table 1.
The numerical value of a socket designation denotes
the side to side distance (S) of its hex hole.
5. Holding the tool
Hold the Impact Wrench firmly with both hands by
the body handle and the side handle. In this case
hold the wrench in line with the bolt.
It is not necessary to push the wrench very hard.
Hold the wrench with a force just sufficient to
counteract the impact force.
6. Confirm the tightening torque
The following factors contribute to a reduction of
the tightening torque. So confirm the actual
tightening torque needed by screwing up some
bolts before the job with a hand torque wrench.
Factors affecting the tightening torque are as follows.
(1) Line voltage:
The tightening torque decreases when the line
voltage becomes low (See Fig. 4).
(2) Operating time:
The tightening torque increases when the operating
time increases. But the tightening torque does not
increase above a certain value even if the tool is
driven for a long time (See Fig. 4).
(3) Diameter of bolt:
The tightening torque differs with the diameter of
the bolt as shown in Fig. 4. Generally a larger
diameter bolt has a larger tightening torque.
(4) Tightening conditions:
The tightening torque differs according to the torque
ratio; class, and length of bolts even when bolts with
the same size threads are used. The tightening torque
also differs according to the condition of the surface
of metal through which the bolts are to be tightened.
(5) Using optional parts:
The tightening torque is reduced a little when an
extension bar, universal joint or a long socket is used.
(6) Clearance of the socket:
A worn or deformed hex or a square-holed socket
will not give an adequate tightness to the fitting
between the nut or anvil, consequently resulting in
loss of tightening torque.
Using an improper socket which does not match to
the bolt will result in an insufficient tightening torque.
Matching socket and bolt sizes are shown in Table 1.
MAINTENANCE AND INSPECTION
1. Inspecting the socket
A worn or deformed hex or a square-holed socket will
not give an adequate tightness to the fitting between
the nut or anvil, consequently resulting in loss of
tightening torque. Pay attention to wear of socket holes
periodically, and replace with a new one if needed.
2. Inspecting the mounting screws
Regularly inspect all mounting screws and ensure
that they are properly tightened. Should any of the
screws be loose, retighten them immediately. Failure
to do so could result in serious hazard.
3. Maintenance of the motor
The motor unit winding is the very “heart” of the
power tool.
Exercise due care to ensure the winding does not
become damaged and/or wet with oil or water.
4. Inspecting the carbon brushes (Fig. 5)
For your continued safety and electrical shock
protection, carbon brush inspection and replacement
on this tool should ONLY be performed by a Hitachi
Authorized Service Center.
5. Replacing supply cord
If the supply cord of Tool is damaged, the Tool
must be returned to Hitachi Authorized Service
Center for the cord to be replaced.
6. Service parts list
A: Item No.
B: Code No.
C: No. Used
D: Remarks
CAUTION
Repair, modification and inspection of Hitachi Power
Tools must be carried out by a Hitachi Authorized
Service Center.
This Parts List will be helpful if presented with the
tool to the Hitachi Authorized Service Center when
requesting repair or other maintenance.
In the operation and maintenance of power tools,
the safety regulations and standards prescribed in
each country must be observed.
MODIFICATION
Hitachi Power Tools are constantly being improved
and modified to incorporate the latest technological
advancements.
Accordingly, some parts (i.e. code numbers and/or
design) may be changed without prior notice.
NOTE
Due to HITACHI’s continuing program of research and
development, the specifications herein are subject to
change without prior notice.
Information concerning airborne noise and vibration
The measured values were determined according to
EN60745 and declared in accordance with ISO 4871.
The typical A-weighted sound pressure level: 98 dB (A).
The typical A-weighted sound power level: 111 dB (A).
Uncertainty KpA: 3 dB (A).
Wear ear protection.
The typical weighted root mean square acceleration
value: 4.75 m/s2.
6
Page 8

Deutsch
ALLGEMEINE SICHERHEITSMASSNAHMEN
WARNUNG!
Lesen Sie sämtliche Hinweise durch
Wenn nicht sämtliche nachstehenden Anweisungen
befolgt werden, kann es zu Stromschlag, Brand und/oder
ernsthaften Verletzungen kommen.
Der Begriff „Elektrowerkzeug“ bezieht sich in den
folgenden Warnhinweisen auf Elektrowerkzeuge mit Netz(schnurgebunden) oder Akkubetrieb (schnurlos).
BEWAHREN SIE DIESE ANWEISUNGEN AUF
1) Arbeitsbereich
a) Sorgen Sie für einen sauberen und gut
ausgeleuchteten Arbeitsbereich.
Zugestellte und dunkle Bereiche ziehen Unfälle
förmlich an.
b) Verwenden Sie Elektrowerkzeuge niemals an
Orten, an denen Explosionsgefahr besteht – zum
Beispiel in der Nähe von leicht entflammbaren
Flüssigkeiten, Gasen oder Stäuben.
Bei der Arbeit mit Elektrowerkzeugen kann es
zu Funkenbildung kommen, wodurch sich Stäube
oder Dämpfe entzünden können.
c) Sorgen Sie bei der Arbeit mit Elektrowerkzeugen
dafür, dass sich keine Zuschauer (insbesondere
Kinder) in der Nähe befinden.
Wenn Sie abgelenkt werden, können Sie die
Kontrolle über das Werkzeug verlieren.
2) Elektrische Sicherheit
a) Elektrowerkzeuge müssen mit passender
Stromversorgung betrieben werden.
Nehmen Sie niemals irgendwelche Änderungen
am Anschlussstecker vor.
Verwenden Sie bei Elektrowerkzeugen mit
Schutzkontakt (geerdet) niemals Adapterstecker.
Stecker im Originalzustand und passende
Steckdosen reduzieren das Stromschlagrisiko.
b) Vermeiden Sie Körperkontakt mit geerdeten
Gegenständen wie Rohrleitungen, Heizungen,
Herden oder Kühlschränken.
Bei Körperkontakt mit geerdeten Gegenständen
besteht ein erhöhtes Stromschlagrisiko.
c) Setzen Sie Elektrowerkzeuge niemals Regen oder
sonstiger Feuchtigkeit aus.
Wenn Flüssigkeiten in ein Elektrowerkzeug
eindringen, erhöht sich das Stromschlagrisiko.
d) Verwenden Sie die Anschlussschnur nicht
missbräuchlich. Tragen Sie das Elektrowerkzeug
niemals an der Anschlussschnur, ziehen Sie es
nicht damit heran und ziehen Sie den Stecker
nicht an der Anschlussschnur aus der Steckdose.
Halten Sie die Anschlussschnur von Hitzequellen,
Öl, scharfen Kanten und beweglichen Teilen fern.
Beschädigte oder verdrehte Anschlussschnüre
erhöhen das Stromschlagrisiko.
e) Wenn Sie ein Elektrowerkzeug im Freien
benutzen, verwenden Sie ein für den
Außeneinsatz geeignetes Verlängerungskabel.
Ein für den Außeneinsatz geeignetes Kabel
vermindert das Stromschlagrisiko.
3) Persönliche Sicherheit
a) Bleiben Sie wachsam, achten Sie auf das, was
Sie tun, und setzen Sie Ihren Verstand ein,
wenn Sie mit Elektrowerkzeugen arbeiten.
Benutzen Sie keine Elektrowerkzeuge, wenn Sie
müde sind oder unter Einfluss von Drogen,
Alkohol oder Medikamenten stehen.
Bei der Arbeit mit Elektrowerkzeugen können
bereits kurze Phasen der Unaufmerksamkeit zu
schweren Verletzungen führen.
b) Benutzen Sie Schutzausrüstung. Tragen Sie
immer einen Augenschutz.
Schutzausrüstung wie Staubmaske, rutschsichere
Sicherheitsschuhe, Schutzhelm und Gehörschutz
senken das Verletzungsrisiko bei angemessenem
Einsatz.
c) Vermeiden Sie unbeabsichtigten Anlauf. Achten
Sie darauf, dass sich der Schalter in der Aus(Off-) Position befindet, ehe Sie den Stecker
einstecken.
Das Herumtragen von Elektrowerkzeugen mit dem
Finger am Schalter und das Einstecken des Steckers
bei betätigtem Schalter zieht Unfälle regelrecht an.
d) Entfernen Sie sämtliche Einstellwerkzeuge
(Einstellschlüssel), ehe Sie das Elektrowerkzeug
einschalten.
Ein an einem beweglichen Teil des Elektrowerkzeugs
angebrachter Schlüssel kann zu Verletzungen führen.
e) Sorgen Sie für einen festen Stand. Achten Sie
jederzeit darauf, sicher zu stehen und das
Gleichgewicht zu bewahren.
Dadurch haben Sie das Elektrowerkzeug in
unerwarteten Situationen besser im Griff.
f) Kleiden Sie sich richtig. Tragen Sie keine lose
Kleidung oder Schmuck. Halten Sie Haar, Kleidung
und Handschuhe von beweglichen Teilen fern.
Lose Kleidung, Schmuck oder langes Haar kann
von beweglichen Teilen erfasst werden.
g) Wenn Anschlüsse für Staubabsaug- und -
sammelvorrichtungen vorhanden sind, sorgen
Sie dafür, dass diese richtig angeschlossen und
eingesetzt werden.
Die Verwendung solcher Vorrichtungen kann
Staub-bezogene Gefahren mindern.
4) Einsatz und Pflege von Elektrowerkzeugen
a) Überanspruchen Sie Elektrowerkzeuge nicht.
Benutzen Sie das richtige Elektrowerkzeug für
Ihren Einsatzzweck.
Das richtige Elektrowerkzeug erledigt seine Arbeit
bei bestimmungsgemäßem Einsatz besser und
sicherer.
b) Benutzen Sie das Elektrowerkzeug nicht, wenn es
sich nicht am Schalter ein- und ausschalten lässt.
Jedes Elektrowerkzeug, das nicht mit dem
Schalter betätigt werden kann, stellt eine Gefahr
dar und muss repariert werden.
c) Ziehen Sie den Netzstecker, ehe Sie
Einstellarbeiten vornehmen, Zubehörteile
tauschen oder das Elektrowerkzeug verstauen.
Solche präventiven Sicherheitsmaßnahmen
verhindern den unbeabsichtigten Anlauf des
Elektrowerkzeugs und die damit verbundenen
Gefahren.
d) Lagern Sie nicht benutzte Elektrowerkzeuge
außerhalb der Reichweite von Kindern, lassen
Sie nicht zu, dass Personen das Elektrowerkzeug
bedienen, die nicht mit dem Werkzeug selbst
und/oder diesen Anweisungen vertraut sind.
Elektrowerkzeuge in ungeschulten Händen sind
gefährlich.
e) Halten Sie Elektrowerkzeuge in Stand. Prüfen
Sie auf Fehlausrichtungen, sicheren Halt und
Leichtgängigkeit beweglicher Teile,
Beschädigungen von Teilen und auf jegliche
andere Zustände, die sich auf den Betrieb des
Elektrowerkzeugs auswirken können.
7
Page 9
Deutsch
S
D
B
E
L
Bei Beschädigungen lassen Sie das
Elektrowerkzeug reparieren, ehe Sie es benutzen.
Viele Unfälle mit Elektrowerkzeugen sind auf
schlechte Wartung zurückzuführen.
f) Halten Sie Schneidwerkzeuge scharf und sauber.
Richtig gewartete Schneidwerkzeuge mit scharfen
Schneidkanten bleiben weniger häufig hängen
und sind einfacher zu beherrschen.
g) Benutzen Sie Elektrowerkzeuge, Zubehör,
Werkzeugspitzen und Ähnliches in
Übereinstimmung mit diesen Anweisungen und
auf die für das jeweilige Elektrowerkzeug
bestimmungsgemäße Weise – beachten Sie
dabei die jeweiligen Arbeitsbedingungen und
die Art und Weise der auszuführenden Arbeiten.
Der bestimmungswidrige Einsatz von
Elektrowerkzeugen kann zu gefährlichen
Situationen führen.
5) Service
a) Lassen Sie Elektrowerkzeuge durch qualifizierte
Fachkräfte und unter Einsatz passender,
zugelassener Originalteile warten.
Dies sorgt dafür, dass die Sicherheit des
Elektrowerkzeugs nicht beeinträchtigt wird.
VORSICHT
Von Kindern und gebrechlichen Personen fernhalten.
Werkzeuge sollten bei Nichtgebrauch außerhalb der
Reichweite von Kindern und gebrechlichen Personen
aufbewahrt werden.
VORSICHTSMASSNAHMEN BEI
VERWENDUNG DES SCHLAGSCHRAUBERS
1. Wenn das Werkzeug in der Höhe verwendet wird,
sicherstellen, daß sich niemand darunter befindet.
2. Bei längerem Arbeiten Ohrstöpsel verwenden.
3. Zum Umschalten der Drehrichtung den Umschalter
nur schalten, wenn der Motor steht.
4. Wenn ein langes Verlängerungskabel verwendet
wird, einen Aufwärtstransformator benutzen.
5. Um das richtige Anzugsdrehmoment zu erzielen,
das Anzugsdrehmoment vor der Verwendung mit
einem Drehmomentschlüssel überprüfen.
6. Die Muffe sicher mit dem Muffenstift und dem Ring
am Schlagschrauber befestigen.
7. Überprüfen, ob die Muffe Risse aufweist.
8. Immer den Körperhandgriff und den Seitenhandgriff
des Schlagschraubers festhalten. Sonst kann die
Gegenkraft zu einem ungenauen und sogar
gefährlichen Betrieb führen.
TECHNISCHE DATEN
Spannung (je nach Gebiet)* (110V, 115V, 120V, 127V, 220V, 230V, 240V)
Leistungsaufnahme* 480 W
Leerlaufdrehzahl 1900 min
Kapazität M12-M16 (Hochzugfeste Schrauben)
(Größe der Schrauben) M12-M22 (Normale Schrauben)
Anzugsdrehmoment** Maximum 36,7 kg-m
Winkelantrieb 12,7 mm
Gewicht (ohne Kabel) 2,9 kg
* Vergessen Sie nicht, die Produktangaben auf dem Typenschild zu überprüfen, da sich diese je nach Verkaufsgebiet
ändern.
** Anziehen der Schraube ohne Verlängerungskabel bei Nennspannung.
-1
STANDARDZUBEHÖR
(1) Seitenhandgriff .......................................................... 1
(2) Koffer .......................................................................... 1
Das Standardzubehör kann ohne vorherige
Bekanntmachung jederzeit geändert werden.
8
SONDERZUBEHÖR (separat zu beziehen)
1. Angebot an Muffen
Obwohl der Hitachi-Schlagschrauber nur mit einer
Standard-Muffe geliefert wird, sind Muffen zum
Schlag-Anziehen von Schrauben verschiedener
Grössen und Arten erhältlich.
Page 10
Deutsch
Tabelle 1 B = 12,7 mm
Bezeichnung
der Muffe
Sechskantmuffe 12
S
13
14
17
19
21
22
23
24
26
27
30
17
19
21
22
23
24
26
27
30
Normale Muffe Lange Muffe
Abmessungen (mm) Abmessungen (mm)
D
28
28
32
35
36
38
38
42
42
E
15
17
19
24
25
25
25
24
34
L
32
34
36
40
40
40
40
50
50
S
12
13
14
17
19
21
22
23
24
26
27
30
D
20
21,5
22
25
28
31
32,5
33
34
38
40
42
E
34
34
34
34
34
34
34
34
34
57
57
57
L
52
52
52
52
52
52
52
52
52
75
75
75
2. Verlängerungsstange
Die Verlängerungsstange ist praktisch zum Arbeiten
an beengten Plätzen oder wenn die mitgelieferte
Muffe die anzuziehende Schraube nicht erreichen
kann.
ACHTUNG
Wenn die Verlängerungsstange benutzt wird, ist das
Anzugsdrehmoment im Vergleich zu der normalen
Muffe leicht reduziert. Daher ist es erforderlich, das
Werkzeug ein wenig länger zu verwenden, um das
gleiche Drehmoment zu erlangen.
3. Universalverbindung
Die Universalverbindung ist praktisch zum Anziehen
von Muttern, wenn sich zwischen der Muffe und
dem Schrauber ein Winkel befindet oder wenn auf
sehr engem Raum gearbeitet wird.
4. Eckenverbindung (Modell EW-14R)
Nehmen Sie diese Verbindung nur, wenn die
Maschine im rechten Winkel an Mutter oder
Schraube angesetzt wird.
Das Sonderzubehör kann ohne vorherige Bekanntmachung jederzeit geändert werden.
ANWENDUNGSGEBIETE
䡬 Anziehen und Lösen verschiedener Arten von
Schrauben und Muttern.
VOR INBETRIEBNAHME
1. Netzspannung
Prüfen, daß die zu verwendende Netzspannung der
Angabe auf dem Typenschild entspricht.
2. Netzschalter
Prüfen, daß der Netzschalter auf AUS steht. Wenn
der Stecker an das Netz angeschlossen wird,
während der Schalter auf EIN steht, beginnt das
Werkzeug sofort zu laufen, was gefährlich ist.
3. Verlängerungskabel
Wenn der Arbeitsbereich nicht in der Nähe des
Netzanschlusses liegt, ist ein Verlängerungskabel
ausreichenden Querschnitts und ausreichender
Nennleistung zu verwende. Das Verlängerungskabel
sollte so kurz wie möglich gehalten werden.
4. Anbringen des Seitenhandgriffs
Die Position des Seitenhandgriffs, der am
Schlaggehäuse angebracht ist, kann durch Losschrauben
des Handgriffs verändert werden. (Rechtsdrehende
Schraube) Den Handgriff auf die gewünschte Position
einstellen und wieder fest anziehen.
5. Montage der Muffe
(1) Stift, O-Ring typ (Abb. 1)
Eine Muffe entsprechend der Schraube wählen, die
angezogen oder gelöst werden soll. Die Muffe auf
den Amboß des Schraubers setzen und mit dem
Stift und dem Ring sichern. Zum Abnehmen der
Muffe in umgekehrter Reihenfolge vorgehen.
(2) Typ mit Tauchkolben (Abb. 2)
Den Tauchkolben, der sich im rechteckigen Teil des
Amboß befindet, auf des Loch in der Sechskantschraube
ausrichten. Dann den Tauchkolben drükken und die
Sechskantschraube am Amboß befestigen.
Kontrollieren, ob der Tauchkolben richtig im Loch
eingerastet ist. Zum Entfernen der Sechskantschraube
die Montageschritte in umgekehrter Reihenfolge
durchführen.
9
Page 11

Deutsch
GEBRAUCHSANWEISUNG
1. Bedienung des Schalters (Abb. 3)
Der Schalter dieser Maschine arbeitet als
Motorschalter und als Drehrichtung-Wahl-schalter.
Wenn der Schalter auf die Markierung R auf der
Handgriff-Abdeckung gestellt ist, dreht der Motor in
Uhrzeigerrichtung zum Anziehen von Schrauben.
Wenn der Schalter auf L gestellt ist, dreht der Motor
in Gegenuhrzeigerrichtung zum Lösen von
Schrauben. Wenn der Schalter freigegeben wird,
stoppt der Motor.
ACHTUNG
Vor Umschalten der Drehrichtung den Schalter
ausschalten und warten, bis der Motor vollständig
steht. Durch Schalten, während der Motor dreht,
brennt der Motor durch.
2. Anziehen und Lösen von Schrauben
Zuerst muß eine Sechskantmuffe gewählt werden,
die der Schraube oder der Mutter entspricht. Dann
die Muffe auf den Amboß montieren und die Mutter,
die angezogen werden soll, mit der Sechskantmuffe
fassen. Den Schrauber in einer Linie mit der
Schraube halten und den Netzschalter zum Anziehen
der Mutter einige Sekunden drücken.
Wenn die Mutter nur lose auf der Schraube sitzt,
kann sich die Schraube mit der Mutter drehen und
so ein richtiges Anziehen verhindern. In diesem Fall
beim Anziehen den Schraubenkopf mit einem
Schlüssel halten oder die Schraube und die Mutter
mit der Hand anziehen.
VOR INBETRIEBNAHME
1. Netzspannung (Abb. 4)
Das verfügbare Anzugsdrehmoment wird durch die
Netzspannung beeinflußt. Eine niedrigere Netzspannung
vermindert das verfügbare Anzugsdrehmoment.
Wenn zum Beispiel ein 220 V-Schrauber mit einer
Spannung von 200 V betrieben wird, ist das verfügbare
Anzugsdrehmoment auf 70 bis 90 % reduziert. Wenn
das Netzkabel verlängert werden muß, sollte das
Verlängerungskabel so kurz wie möglich sein. Wenn
die Netzspannung niedrig ist und ein langes
Verlängerungskabel verwendet wird, sollte ein
Aufwärtstransformator verwendet werden. Die
Beziehung zwischen der Netzspannung und dem
Anzugsdrehmoment ist in den Zeichnungen gezeigt.
2. Berühren Sie im laufenden Betrieb weder Stoßfänger
noch Schlaggehäuse
Stoßfänger und Schlaggehäuse können sich bei
fortlaufendem Schraubbetrieb erwärmen – achten
Sie also darauf, diese Teile bei längerem Betrieb
nicht zu berühren.
3. Arbeiten mit einem geeigneten Anzugsdrehmoment
Das optimale Anzugsdrehmoment für Muttern und
Schrauben ist abhängig von dem Material und der
Größe der Muttern und Schrauben. Ein sehr großes
Anzugsdrehmoment kann eine kleine Schraube ver
zerren oder abbrechen. Das Anzugsdrehmoment
steigt proportional zur Betriebszeit an. Das für jede
Schraube geeignete Anzugsdrehmoment verwenden.
4. Wahl der Muffe entsprechend der Schraube
Für die anzuziehende Schraube sollte die passende
Muffe verwendet werden. Durch eine nicht passende
Muffe wird nicht nur das Anzugsdrehmoment verringert,
sondern auch die Muffe oder Mutter beschädigt.
Eine abgenutzte oder verzogene Sechskant- oder
Vierkantmuffe kann nicht mehr fest auf der Mutter
oder dem Amboß befestigt werden, wodurch ein
Verlust an Anzugsdrehmoment entsteht.
Auf die Abnutzung der Muffen achten und abgenutzte
Muffen rechtzeitig ersetzen. Passende Muffen und
Schraubengrößen sind in den Tabelle 1 gezeigt.
Der Zahlenwert in der Bezeichnung der Muffen gibt
die Entfernung zwischen den Seiten (S) der
Sechskantöffnung an.
5. Halten des Werkzeugs
Den Schlagschrauber fest mit beiden Händen am
Gehäusehandgriff und Seitenhandgriff halten. Den
Schrauber in einer Linie mit der Schraube halten. Es
ist nicht erforderlich, den Schrauber sehr stark zu
drücken. Den Schrauber nur mit dem Druck halten, der
notwendig ist, um der Schlagkraft entgegenzuwirken.
6. Überprüfung des Anzugsdrehmoments
Die folgenden Faktoren tragen zu einer Reduzierung
des Anzugsdrehmoments bei. Daher zur Feststellung
des erforderlichen Drehmoments vor der eigentlichen Arbeit einige Schrauben mit einem HandDrehmomentschlüssel anziehen.
Gegen Faktoren, die das Anzugsdrehmoment beeinflussen, wie unten angegeben vorgehen.
(1) Netzspannung:
Das Anzugsdrehmoment nimmt ab, wenn die
Netzspannung niedrig wird (Siehe Abb. 4).
(2) Betriebszeit:
Das Anzugsdrehmoment nimmt mit der Betriebszeit
zu. Aber das Anzugsdrehmoment übersteigt einen
bestimmten Wert nicht, auch wenn das Werkzeug
eine lange Zeit angewendet wird (Siehe Abb. 4).
(3) Schraubendurchmesser:
Das Anzugsdrehmoment ist abhängig vom Durchmesser der Schrauben, siehe Abb. 4. Im allgemeinen
erfordert ein größerer Schrauben-durchmesser ein
größeres Anzugsdrehmoment.
(4) Anzugsbedingungen:
Das Anzugsdrehmoment ist abhängig von dem
Drehmoment-Verhältnis, der Klasse und der Länge
der Schrauben, auch bei Schrauben mit Gewinde
der gleichen Größe. Das Anzugsdrehmoment ist
außerdem abhängig von der Metalloberfläche, durch
die die Schrauben angezogen werden.
(5) Verwendung von zusätzlichen Teilen:
Das Anzugsdrehmoment ist ein wenig reduziert,
wenn eine Verlängerungsstange, eine Universalverbindung oder eine lange Muffe verwendet wird.
(6) Rolle der Muffe:
Eine abgenutzte oder verzogene Sechskant oder
Vierkantmuffe läßt sich nicht fest an der Mutter
oder dem Amboß anbringen, wodurch ein Verlust
an Anzugsdrehmoment entsteht. Die Verwendung
einer Muffe, die nicht richtig auf die Schraube paßt,
resultiert in einem Verlust an Anzugsdrehmoment.
Passende Muffen und Schraubengrößen sind in den
Tabelle 1 angegeben.
10
Page 12

Deutsch
WARTUNG UND INDPEKTION
1. Inspektion der Muffe
Eine abgenutzte oder verzogene Sechskant oder
Vierkantmuffe läßt sich nicht fest an der Mutter
oder dem Amboß anbringen, wodurch ein Verlust
an Anzugsdrehmoment entsteht. Periodisch die
Abnutzung der Muffe überprüfen und
erforderlichenfalls durch eine neue ersetzen.
2. Inspektion der Befestigungsschrauben
Alle Befestigungsschrauben werden regelmäßig
inspiziert und geprüft, daß sie richtig angezogen
sind. Wenn sich eine der Schrauben lokkert, muß
sie sofort wieder angezogen werden. Geschieht das
nicht, kann das zu erheblicher Gefahr führen.
3. Wartung des Motors
Die Motorwicklung ist das “herz” des Elektrowerkzeugs. Daher ist besonders sorgfältig darauf zu
achten, daß die Wicklung nicht beschädigt wird
und/oder mit Öl oder Wasser in Berührung kommt.
4. Inspektion der Kohlebürsten (Abb. 5)
Zur Erhaltung Ihrer Sicherheit und des Schutzes
gegen elektrischen Schlag sollten Inspektion und
Auswechseln der Kohlebürsten NUR durch ein
Autorisiertes Hitachi-Wartungszentrum durchgeführt
werden.
5. Auswechseln des Netzkabels
Wenn das Netzkabel des Werkzeugs beschädigt wird,
muss das Werkzeug zum Auswechseln des
Netzkabels an ein von Autorisiertes HitachiWartungszentrum zurückgegeben werden.
6. Liste der Wartungsteile
A:Punkt Nr.
B:Code Nr.
C:Verwendete Anzahl
D:Bemerkungen
ACHTUNG
Reparatur, Modifikation und Inspektion von HitachiElektrowerkzeugen müssen durch ein Autorisiertes
Hitachi-Wartungszentrum durchgeführt werden.
Diese Teileliste ist hilfreich, wenn sie dem
Autorisierten Hitachi-Wartungszentrum zusammen
mit dem Werkzeug für Reparatur oder Wartung
ausgehändigt wird.
Bei Betrieb und Wartung von Elektrowerkzeugen
müssen die Sicherheitsvorschriften und Normen
beachtet werden.
MODIFIKATIONEN
Hitachi-Elektrowerkzeuge werden fortwährend
verbessert und modifiziert, um die neuesten
technischen Fortschritte einzubauen.
Dementsprechend ist es möglich, daß einige Teile
(z.B. Codenummern bzw. Entwurf) ohne vorherige
Benachrichtigung geändert werden.
Information über Betriebslärm und Vibration
Die gemessenen Werte wurden entsprechend EN60745
bestimmt und in Übereinstimmung mit ISO 4871
ausgewiesen.
Der typische A-gewichtete Schalldruckt ist 98 dB (A).
Der typische A-gewichtete Schalleistungspegel ist 111 dB
(A).
Messunsicherheit KpA: 3 dB (A)
Bei der Arbeit immer einen Ohrenschutz tragen.
Der typische gewogene quadratische Mittelwert für die
Beschleunigung ist 4,75 m/s2.
ANMERKUNG
Aufgrund des ständigen Forschungs-und Entwicklungsprogramms von HITACHI sind Änderungen der hierin
gemachten technischen Angaben vorbehalten.
11
Page 13

∂ППЛУИО¿
°∂¡π∫Õ ª∂∆ƒ∞ ∞™º∞§∂π∞™
¶ƒ√™√Ã∏!
¢È·‚¿ÛÙ fiϘ ÙȘ Ô‰ËÁ›Â˜
Αν δεν τηρηθούν λεσ οι οδηγίεσ που αναφέρονται
παρακάτω, ενδέχεται να προκληθεί ηλεκτροπληξία,
πυρκαγιά ή/και σοβαρσ τραυµατισµσ.
Ο ροσ “ηλεκτρικ εργαλείο” σε λεσ τισ προειδοποιήσεισ
που αναφέρονται παρακάτω αναφέρεται στο ηλεκτρικ
εργαλείο που λειτουργεί µε το ρεύµα του ηλεκτρικού
δικτύου (µε καλώδιο) ή στο ηλεκτρικ εργαλείο που
λειτουργεί µε µπαταρία (χωρίσ καλώδιο).
ºÀ§∞•∆∂ ∞À∆∂™ ∆π™ √¢∏°π∂™
1) ÃÒÚÔ˜ ÂÚÁ·Û›·˜
a) ¢È·ÙËÚ›Ù ÙÔ ¯ÒÚÔ ÂÚÁ·Û›·˜ ηı·Úfi Î·È Î·Ï¿
ʈÙÈṲ̂ÓÔ.
Οι ακατάστατοι και οι σκοτεινοί χώροι έχουν την
τάση να προκαλούν ατυχήµατα.
b) ªЛ ¯ЪЛЫИМФФИВ›ЩВ Щ· ЛПВОЩЪИО¿ ВЪБ·ПВ›· ЫВ
ВОЪЛОЩИО¤˜ ·ЩМfiЫК·ИЪВ˜, fiˆ˜ fiЩ·У В›У·И ·ЪfiУЩ·
В‡КПВОЩ· ˘БЪ¿, ·¤ЪИ· ‹ ЫОfiУЛ.
Τα ηλεκτρικά εργαλεία δηµιουργούν σπινθήρεσ
οι οποίοι ενδέχεται να προκαλέσουν την
ανάφλεξη αυτών των υλικών.
c) ∫Ú·Ù‹ÛÙ ٷ ·È‰È¿ Î·È ÙÔ˘˜ ·Ú¢ÚÈÛÎfiÌÂÓÔ˘˜
М·ОЪИ¿ fiЩ·У ¯ЪЛЫИМФФИВ›ЩВ ¤У· ЛПВОЩЪИОfi ВЪБ·ПВ›Ф.
Αν αποσπαστεί η προσοχή σασ, υπάρχει κίνδυνοσ
να χάσετε τον έλεγχο.
2) ∏ПВОЩЪИО‹ ·ЫК¿ПВИ·
a) ∆· КИ˜ ЩˆУ ЛПВОЩЪИОТУ ВЪБ·ПВ›ˆУ Ъ¤ВИ У· В›У·И
О·Щ¿ППЛП· БИ· ЩИ˜ Ъ›˙В˜.
ªЛУ ЩЪФФФИ‹ЫВЩВ ФЩ¤ ЩФ КИ˜ МВ ФФИФУ‰‹ФЩВ
ЩЪfiФ.
ªЛ ¯ЪЛЫИМФФИВ›ЩВ КИ˜ ЪФЫ·ЪМФБ‹˜ МВ БВИˆМ¤У·
ЛПВОЩЪИО¿ ВЪБ·ПВ›·.
Τα µη τροποποιηµένα φισ και οι κατάλληλεσ
πρίζεσ µειώνουν τον κίνδυνο ηλεκτροπληξίασ.
b) ∞ÔʇÁÂÙ ÙË ÛˆÌ·ÙÈ΋ ·ʋ Ì ÁÂȈ̤Ó˜
ВИК¿УВИВ˜ fiˆ˜ ЫˆП‹УВ˜, ıВЪМ¿ЫЩЪВ˜, М·БВИЪИО¤˜
Ы˘ЫОВ˘¤˜ О·И „˘БВ›·.
Υπάρχει αυξηµένοσ κίνδυνοσ ηλεκτροπληξίασ
ταν το σώµα σασ είναι γειωµένο.
c) ªЛУ ВОı¤ЩВЩВ Щ· ЛПВОЩЪИО¿ ВЪБ·ПВ›· ЫЩЛ ‚ЪФ¯‹ ‹
ÛÂ Û˘Óı‹Î˜ ˘ÁÚ·Û›·˜.
Το νερ που εισέρχεται σε ένα ηλεκτρικ
εργαλείο αυξάνει τον κίνδυνο ηλεκτροπληξίασ.
d) ªЛУ ·ЫОВ›ЩВ ‰‡У·МЛ ЫЩФ О·ПТ‰ИФ. ªЛ ¯ЪЛЫИМФФИВ›ЩВ
ФЩ¤ ЩФ О·ПТ‰ИФ БИ· У· МВЩ·К¤ЪВЩВ, У· ЩЪ·‚‹НВЩВ ‹
У· ‚Б¿ПВЩВ ·fi ЩЛУ Ъ›˙· ЩФ ЛПВОЩЪИОfi ВЪБ·ПВ›Ф.
∫Ъ·Щ‹ЫЩВ ЩФ О·ПТ‰ИФ М·ОЪИ¿ ·fi ıВЪМfiЩЛЩ·, П¿‰И,
ОФКЩВЪ¤˜ БˆУ›В˜ О·И ОИУФ‡МВУ· М¤ЪЛ.
Τα κατεστραµµένα ή µπερδεµένα καλώδια
αυξάνουν τον κίνδυνο ηλεκτροπληξίασ.
e) ŸЩ·У ¯ЪЛЫИМФФИВ›ЩВ ЩФ ВЪБ·ПВ›Ф ЫВ ВНˆЩВЪИОfi
¯ТЪФ, ¯ЪЛЫИМФФИ‹ЫЩВ О·ПТ‰ИФ ЪФ¤ОЩ·ЫЛ˜ Ф˘
ЪФФЪ›˙ВЩ·И БИ· ¯Ъ‹ЫЛ ЫВ ВНˆЩВЪИОfi ¯ТЪФ.
Η χρήση ενσ καλωδίου κατάλληλου για εξωτερικ
χώρο µειώνει τον κίνδυνο ηλεκτροπληξίασ.
3) ¶ЪФЫˆИО‹ ·ЫК¿ПВИ·
a) ¡· В›ЫЩВ ЫВ ВЩФИМfiЩЛЩ·, У· ‚П¤ВЩВ ·˘Щfi Ф˘ О¿УВЩВ
О·И У· ¯ЪЛЫИМФФИВ›ЩВ ЩЛУ ОФИУ‹ ПФБИО‹ fiЩ·У
¯ЪЛЫИМФФИВ›ЩВ ¤У· ЛПВОЩЪИОfi ВЪБ·ПВ›Ф.
ªЛ ¯ЪЛЫИМФФИВ›ЩВ ЛПВОЩЪИО¿ ВЪБ·ПВ›· fiЩ·У В›ЫЩВ
ОФ˘Ъ·ЫМ¤УФИ ‹ ˘fi ЩЛУ В‹ЪВИ· У·ЪОˆЩИОТУ
Ф˘ЫИТУ, ФИУФУВ‡М·ЩФ˜ ‹ К·ЪМ¿ОˆУ.
Μια στιγµή απροσεξίασ κατά τη χρήση ενσ
ηλεκτρικού εργαλείου µπορεί να προκαλέσει
σοβαρ προσωπικ τραυµατισµ.
12
b) ГЪЛЫИМФФИВ›ЩВ ВНФПИЫМfi ·ЫК·ПВ›·˜, ¡· КФЪ¿ЩВ
¿УЩФЩВ ЪФЫЩ·ЩВ˘ЩИО¿ Б˘·ПИ¿ БИ· Щ· М¿ЩИ·.
Εξοπλισµσ ασφαλείασ πωσ µάσκα για τη σκνη,
αντιολισθητικά υποδήµατα, σκληρ κάλυµµα
κεφαλήσ ή προστατευτικά ακοήσ που
χρησιµοποιούνται στισ αντίστοιχεσ συνθήκεσ
µειώνουν τισ πιθαντητεσ τραυµατισµού.
c) ¡· ·ФКВ‡БВЩВ ЩЛУ О·Щ¿ П¿ıФ˜ ¤У·ЪНЛ ПВИЩФ˘ЪБ›·˜.
¡· ‚В‚·ИТУВЫЩВ fiЩИ Ф ‰И·ОfiЩЛ˜ В›У·И ЫЩЛУ ОПВИЫЩ‹
ı¤ЫЛ (off) ЪИУ ЩФФıВЩ‹ЫВЩВ ЩФ КИ˜ ЫЩЛУ Ъ›˙·.
Η µεταφορά ηλεκτρικών εργαλείων µε το
δάχτυλο στο διακπτη λειτουργίασ ή η σύνδεση
ηλεκτρικών εργαλείων στο ρεύµα µε το διακπτη
ανοιχτ αυξάνει τισ πιθαντητεσ ατυχήµατοσ.
d) ¡· ·Ê·ÈÚ›ÙÂ Ù˘¯fiÓ ÎÏÂȉȿ Ú˘ıÌÈ˙fiÌÂÓÔ˘
·УФ›БМ·ЩФ˜ ‹ Щ· ·П¿ ОПВИ‰И¿ ЪИУ ı¤ЫВЩВ ЫВ
ПВИЩФ˘ЪБ›· ЩФ ЛПВОЩЪИОfi ВЪБ·ПВ›Ф.
Ένα απλ κλειδί ή ένα κλειδί ρυθµιζµενου
ανοίγµατοσ που είναι προσαρτηµένο σε
περιστρεφµενο εξάρτηµα του ηλεκτρικού
εργαλείου µπορεί να προκαλέσει προσωπικ
τραυµατισµ.
e) ªЛУ ЩВУЩТУВЫЩВ. ¡· ‰И·ЩЛЪВ›ЩВ ¿УЩФЩВ ЩФ
О·Щ¿ППЛПФ ¿ЩЛМ· О·И ЩЛУ ИЫФЪЪФ›· Ы·˜.
Με αυτν τον τρπο µπορείτε να ελέγχετε
καλύτερα το ηλεκτρικ εργαλείο σε µη
αναµενµενεσ καταστάσεισ.
f) ¡· ›ÛÙ ÓÙ˘Ì¤ÓÔÈ Î·Ù¿ÏÏËÏ·. ªË ÊÔÚ¿Ù ʷډȿ
ÚÔ‡¯· ‹ ÎÔÛÌ‹Ì·Ù·. ¡· Îڷٿ٠ٷ Ì·ÏÏÈ¿ Û·˜, Ù·
ÚÔ‡¯· Û·˜ Î·È Ù· Á¿ÓÙÈ· Û·˜ Ì·ÎÚÈ¿ ·fi ÎÈÓÔ‡ÌÂÓ·
̤ÚË.
Τα φαρδιά ρούχα, τα κοσµήµατα και τα µακριά
µαλλιά µπορεί να πιαστούν σε κινούµενα µέρη.
g) ∞Ó ·Ú¤¯ÔÓÙ·È ÂÍ·ÚÙ‹Ì·Ù· ÁÈ· ÙË Û‡Ó‰ÂÛË
Ы˘ЫОВ˘ТУ ВН·БˆБ‹˜ О·И Ы˘ППФБ‹˜ ЫОfiУЛ˜, У·
‚В‚·ИТУВЫЩВ fiЩИ В›У·И Ы˘У‰В‰ВМ¤У· О·И
¯ЪЛЫИМФФИФ‡УЩ·И МВ ЩФ ЫˆЫЩfi ЩЪfiФ.
Η χρήση αυτών των συσκευών µπορεί να µειώσει
τουσ κινδύνουσ που σχετίζονται µε τη σκνη.
4) ГЪ‹ЫЛ О·И КЪФУЩ›‰· ЛПВОЩЪИОТУ ВЪБ·ПВ›ˆУ
a) ªЛУ ·ЫОВ›ЩВ ‰‡У·МЛ ЫЩФ ЛПВОЩЪИОfi ВЪБ·ПВ›Ф. ¡·
¯ЪЛЫИМФФИВ›ЩВ ЩФ ЛПВОЩЪИОfi ВЪБ·ПВ›Ф Ф˘ В›У·И
О·Щ¿ППЛПФ БИ· ЩФ В›‰Ф˜ ЩЛ˜ ВЪБ·Ы›·˜ Ф˘ ВОЩВПВ›ЩВ.
Το κατάλληλο ηλεκτρικ εργαλείο θα εκτελέσει
την εργασία καλύτερα και µε µεγαλύτερη
ασφάλεια µε τον τρπο που σχεδιάστηκε.
b) ªЛ ¯ЪЛЫИМФФИ‹ЫВЩВ ЩФ ЛПВОЩЪИОfi ВЪБ·ПВ›Ф ·У Ф
‰И·ОfiЩЛ˜ ПВИЩФ˘ЪБ›·˜ ‰ВУ ·УФ›БВИ О·И ‰ВУ ОПВ›УВИ.
Ένα ηλεκτρικ εργαλείο που δεν ελέγχεται απ
το διακπτη λειτουργίασ είναι επικίνδυνο και
πρέπει να επισκευαστεί.
c) µÁ¿ÏÙ ÙÔ ÊȘ ·fi ÙËÓ Ú›˙· ÚÈÓ Î¿ÓÂÙÂ
ÔÔÈÂÛ‰‹ÔÙ ڢıÌ›ÛÂȘ, ·ÏÏ¿ÍÂÙ ÂÍ·ÚÙ‹Ì·Ù· ‹
·ФıЛОВ‡ЫВЩВ ЩФ ЛПВОЩЪИОfi ВЪБ·ПВ›Ф.
Αυτά τα προληπτικά µέτρα ασφαλείασ µειώνουν
τον κίνδυνο να ξεκινήσει το ηλεκτρικ εργαλείο
κατά λάθοσ.
d) ∞ФıЛОВ‡ВЩВ Щ· ВЪБ·ПВ›· Ф˘ ‰ВУ ¯ЪЛЫИМФФИВ›ЩВ
М·ОЪИ¿ ·fi ·И‰И¿ О·И МЛУ ·К‹УВЩВ Щ· ¿ЩФМ· Ф˘
‰ВУ В›У·И ВНФИОВИˆМ¤У· МВ ЩФ ЛПВОЩЪИОfi ВЪБ·ПВ›Ф ‹
МВ ·˘Щ¤˜ ЩИ˜ Ф‰ЛБ›В˜ У· ¯ЪЛЫИМФФИФ‡У ЩФ ЛПВОЩЪИОfi
ВЪБ·ПВ›Ф.
Τα ηλεκτρικά εργαλεία είναι επικίνδυνα στα χέρια
µη εκπαιδευµένων ατµων.
e) ™˘УЩЛЪВ›ЩВ Щ· ЛПВОЩЪИО¿ ВЪБ·ПВ›·. ¡· ВП¤Б¯ВЩВ ЩЛУ
В˘ı˘БЪ¿ММИЫ‹ ЩФ˘˜ ‹ ЩФ МПФО¿ЪИЫМ· ЩˆУ
ОИУФ‡МВУˆУ МВЪТУ, ЩЛ ıЪ·‡ЫЛ ЩˆУ ВН·ЪЩЛМ¿ЩˆУ
О·И ФФИ·‰‹ФЩВ ¿ППЛ О·Щ¿ЫЩ·ЫЛ Ф˘ ВУ‰¤¯ВЩ·И У·
ВЛЪВ¿ЫВИ ЩЛ ПВИЩФ˘ЪБ›· ЩФ˘ ЛПВОЩЪИОФ‡ ВЪБ·ПВ›Ф˘.
Page 14
∂ППЛУИО¿
S
D
B
E
L
™В ВЪ›ЩˆЫЛ ‚П¿‚Л˜, ЩФ ЛПВОЩЪИОfi ВЪБ·ПВ›Ф
Ъ¤ВИ У· ВИЫОВ˘·ЫЩВ› ЪИУ ¯ЪЛЫИМФФИЛıВ›.
Πολλά ατυχήµατα προκαλούνται απ ηλεκτρικά
εργαλεία που δεν έχουν συντηρηθεί σωστά.
f) ¢И·ЩЛЪВ›ЩВ Щ· ВЪБ·ПВ›· ОФ‹˜ ОФКЩВЪ¿ О·И О·ı·Ъ¿.
Τα κατάλληλα συντηρηµένα εργαλεία κοπήσ µε
κοφτερέσ γωνίεσ µπλοκάρουν πιο δύσκολα και
ελέγχονται πιο εύκολα.
g) ГЪЛЫИМФФИВ›ЩВ ЩФ ЛПВОЩЪИОfi ВЪБ·ПВ›Ф, Щ· ВН·ЪЩ‹М·Щ·,
ЩИ˜ М‡ЩВ˜ ЩˆУ ВЪБ·ПВ›ˆУ ОП.,Ы‡МКˆУ· МВ ·˘Щ¤˜ ЩИ˜
Ф‰ЛБ›В˜ О·И МВ ЩЪfiФ Ф˘ В›У·И О·Щ¿ППЛПФ˜ БИ· ЩФУ
Ы˘БОВОЪИМ¤УФ Щ‡Ф ЛПВОЩЪИОФ‡ ВЪБ·ПВ›Ф˘,
П·М‚¿УФУЩ·˜ ˘fi„Л ЩИ˜ Ы˘Уı‹ОВ˜ ВЪБ·Ы›·˜ О·И ЩЛУ
ВЪБ·Ы›· Ф˘ ЪfiОВИЩ·И У· ВОЩВПВЫЩВ›.
Η χρήση του ηλεκτρικού εργαλείου σε λειτουργίεσ
διαφορετικέσ απ εκείνεσ για τισ οποίεσ προορίζεται
µπορεί να δηµιουργήσει επικίνδυνεσ καταστάσεισ.
5) ™¤Ъ‚И˜
a) ¡· ‰›УВЩВ ЩФ ЛПВОЩЪИОfi ВЪБ·ПВ›Ф БИ· Ы¤Ъ‚И˜ ЫВ
О·Щ¿ППЛП· ВО·И‰В˘М¤У· ¿ЩФМ· О·И У·
¯ЪЛЫИМФФИВ›ЩВ МfiУФ БУ‹ЫИ· ·УЩ·ПП·ОЩИО¿.
Με αυτν τον τρπο είστε σίγουροι για την
ασφάλεια του ηλεκτρικού εργαλείου.
¶ƒ√ºА§∞•∏
ª·ОЪИ¿ ·fi Щ· ·И‰И¿ О·И ЩФ˘˜ ·У·‹ЪФ˘˜.
ŸЩ·У ‰ВУ ¯ЪЛЫИМФФИФ‡УЩ·И, Щ· ВЪБ·ПВ›· Ъ¤ВИ У·
К˘П¿˙ФУЩ·И М·ОЪИ¿ ·fi Щ· ·И‰И¿ О·И ЩФ˘˜ ·У·‹ЪФ˘˜.
¶ƒ√ºÀ§∞∫∆π∫∞ ª∂∆ƒ∞ ¶∞¡ø ™∆∏ Ã∏™∏
∆√À ª¶√À§√¡√∫§∂π¢√À
1. ΄Οταν χρησιµοποιείτε το εργαλείο σε κάποιο ύψοσ
σιγουρευτείτε τι δεν βρίσκεται κανείσ απ κάτω.
2. Χρησιµοποιήστε ωτοασπίδεσ αν πρκειται το
εργαλείο να το χρησιµοποιήσετε για µακρ χρονικ
διάστηµα.
3. Πατήστε τον διακπτη αντίστροφησ φοράσ αφτου
έχει σταµατήσει το µοτέρ, ταν είναι απαραίτητο
να αλλάξετε τη διεύθυνση περιστροφήσ.
4. Χρησιµοποιήστε ένα µετασχηµατιστή ανύψωσησ
τάσησ ταν χρησιµοποιείτε ένα µακρύ καλώδιο
προέκτασησ.
5. Επιβεβαιώστε τη ροπή σύσφιξησ µε ένα κλειδί ροπήσ
πριν τη χρήση έτσι ώστε να εξασφαλίσετε τι η
σωστή ροπή σύσφιξησ χρησιµοποιείται.
6. Συναρµολογήστε την υποδοχή στο µπουλονκλειδο
µε ασφάλεια µε την περνη υποδοχήσ και το
δακτύλιο.
7. Επιβεβαιώστε αν η υποδοχή έχει οποιοδήποτε
ράγισµα πάνω τησ.
8. Πάντοτε να κρατάτε τον κορµ και τισ πλευρικέσ
λαβέσ του µπουλονκλειδου γερά. ∆ιαφορετικά η
δύναµη αντίθετησ φοράσ που παράγεται µπορεί να
προκαλέσει τη λανθασµένη και ακµα περισστερο
την επικίνδυνη λειτουργία.
∆∂áπ∫∞ Ã∞ƒ∞∫∆∏ƒπ™∆π∫∞
Τάση (ανά περιοχέσ)* (110V, 115V, 120V, 127V, 220V, 230V, 240V)
Ισχύσ εισδου* 480 W
Ταχύτητα χωρίσ φορτίο 1900 min
Iκαντητα M12-M16 (Μπουλνι υψηλού εφελκυσµού)
(µέγεθοσ µπουλονιών) M12-M22 (Συνηθισµένο µπουλνι)
Ροπή σύσφιξησ** Μέγιστο 36,7 kg-m
Γωνιακή µετάδοση 12,7 mm
Βάροσ (χωρίσ καλώδιο) 2,9 kg
* Βεβαιωθείτε να ελέγξετε την πινακίδα στο προιν επειδή υπκεινται σε αλλαγή σε εξάρτηση απ την περιοχή.
** Σύσφιξη του µπουλονιού χωρίσ καλώδιο προέκτασησ στη διαβαθµισµένη τάση.
-1
∫∞¡√¡π∫∞ ∂•∞ƒ∆∏ª∞∆∞
(1) Πλευρική λαβή ..........................................................1
(2) Θήκη ........................................................................... 1
Τα κανονικά εξαρτήµατα µπορούν να αλλάξουν χωρίσ
προειδοποίηση.
¶ƒ√∞πƒ∂∆π∫∞ ∂•∞ƒ∆∏ª∞∆∞
(ˆÏÔ‡ÓÙ·È Í¯ˆÚÈÛÙ¿)
1. ¶ФИОИП›· ˘Ф‰Ф¯ТУ
Παρτι το Μπουλονκλειδο τησ Hitachi αποστέλεται
µε µια µνο στάνταρ υποδοχή, πολλέσ υποδοχέσ
είναι διαθέσιµεσ για να καλύψουν την κρουστική
σύσφιξη διαφρων µεγεθών και τύπων µπουλονιών.
13
Page 15
∂ППЛУИО¿
¶›Ó·Î·˜ 1 B = 12,7 mm
Χαρακτηρισµσ
Υποδοχήσ
Εξαγ. Υποδοχή 12
13
14
17
19
21
22
23
24
26
27
30
Συνηθισµένη Υποδοχή Μακριά Υποδοχή
∆ιάσταση (mm) ∆ιάσταση (mm)
S
17
19
21
22
23
24
26
27
30
D
28
28
32
35
36
38
38
42
42
E
15
17
19
24
25
25
25
24
34
L
32
34
36
40
40
40
40
50
50
S
12
13
14
17
19
21
22
23
24
26
27
30
21,5
32,5
D
20
22
25
28
31
33
34
38
40
42
E
34
34
34
34
34
34
34
34
34
57
57
57
L
52
52
52
52
52
52
52
52
52
75
75
75
2. ƒ¿‚ÚÔ˜ ÚÔ¤ÎÙ·Û˘
Η ράβροσ προέκτασησ είναι βολική για εργασία σε
πολύ περιορισµένουσ χώρουσ ή ταν η παρεχµενη
υποδοχή δεν µπορεί να φτάσει στο µπουλνι που
πρέπει να σφιχτεί.
¶ƒ√™√Ã∏
ταν χρησιµοποιηθεί η ράβροσ προέκτασησ η ροπή
σύσφιξησ ελαττώνεται ελαφρά σε σύγκριση µε την
συνιθησµένη υποδοχή. Γιαυτ είναι απαραίτητο να
λειτουργήσετε το εργαλείο λίγο περισστερο για
να αποκτήσετε την ίδια ροπή.
3. ∞ÚıÚˆÙfi˜ Û‡Ó‰ÂÛÌÔ˜
Ο αρθρωτσ σύνδεσµοσ είναι βολικσ για την
κρούση παξιµαδιών ταν υπάρχει γωνία ανάµεσα
στην υποδοχή και στο κλειδί, ή ταν δουλεύετε
σε πολύ στεν χώρο.
4. ¶ÚÔÛ¿ÚÙËÌ· ÁˆÓ›·˜ (ªÔÓÙ¤ÏÔ ∂W-14R)
Χρησιµοποιήστε αυτ το προσάρτηµα µνο ταν το
µηχάνηµα εφαρµζεται στο παξιµάδι ή στο µπουλνι
µε δεξιά γωνία.
Tα προαιρετικά εξαρτήµατα υπκεινται σε αλλαγή χωρίσ
προειδοποίηση.
14
∂º∞ƒª√°∂™
䡬 Σφίξιµο και ξεσφίξιµο διάφορων ειδών µπουλονιών
και παξιµαδιών.
¶ƒπ¡ ∆∏ §∂π∆√Àƒ°π∞
1. ¶ËÁ‹ Ú‡̷ÙÔ˜
Βεβαιωθείτε τι η πηγή ρεύµατοσ που πρκειται να
χρησιµοποιηθεί είναι εναρµονισµένη µε τισ απαιτήσεισ
σε ρεύµα που αναφέρεται στην πινακίδα του εργαλείου.
2. ¢È·ÎfiÙ˘ Ú‡̷ÙÔ˜
Βεβαιωθείτε τι ο διακπτησ ρεύµατοσ βρίσκεται
στη θέση OFF. Αν το βίσµα είναι στη µπρίζα καθώσ
ο διακπτησ ρεύµατοσ βρίσκεται στο ΟΝ, το
εργαλείο θα αρχίσει να λειτουργεί αµέσωσ, µε
πιθαντητα πρκλησησ σοβαρού ατυχήµατοσ.
3. ∫·ÏÒ‰ÈÔ ÚÔ¤ÎÙ·Û˘
ταν ο χώροσ εργασίασ βρίσκεται µακριά απ την
παροχή ρεύµατοσ. Χρησιµοποιήστε ένα καλώδιο
προέκτασησ µε κατάλληλο πάχοσ και ικαντητα
µεταφοράσ ρεύµατοσ. Το καλώδιο προέκτασησ πρέπει
να είναι τσο κοντ σο είναι πρακτικά δυνατ.
4. ™ÙÂÚ¤ˆÛË Ù˘ Ï¢ÚÈ΋˜ Ï·‚‹˜
Η θέση τησ πλευρικήσ λαβήσ που είναι συνδεδεµένη
στη θήκη του σφυριού µπορεί να αλλαχτεί µε το να
ξεβιδώσετε τη λαβή. (∆εξιστροφη βίδα) Περιστρέψτε
τη λαβή στην επιθυµητή θέση για την εργασία και
στερεώστε τη λαβή βιδώνοντάσ την γερά.
5. ™ÙÂÚ¤ˆÛË Ù˘ ˘Ô‰Ô¯‹˜
(1) Περνη, τύποσ Ο- δακτυλίου (∂ÈÎ. 1)
Επιλέξτε µια υποδοχή που ταιριάζει στο µπουλνι
που πρκειται να σφιχτεί ή να χαλαρώσει. Βάλτε
την υποδοχή στον άκµονα του κλειδιού, και
στερεώστε την µε την περνη και το δακτύλιο.
Κατά την αποσυναρµολγηση τησ υποδοχήσ,
αντιστρέψετε τη σειρά.
(2) Τύπου πιστονιού (∂ÈÎ. 2)
Ευθυγραµµίστε το πιστνι που υπάρχει στο
τετράγωνο τµήµα µε την τρύπα στην εξαγ. υποδοχή.
Μετά σπρώξτε το πιστνι, και στερεώστε την εξαγ.
υποδοχή στον άκµονα. Ελέγξετε τι το πιστνι έχει
πλήρωσ δεσµευτεί στην τρύπα. ταν αφαιρείτε την
υποδοχή, αντιστρέψτε τη σειρά.
Page 16

∂ППЛУИО¿
¶ø™ ¡∞ ∆√ Ã∏™πª√¶√π∏™∂∆∂
1. §ÂÈÙÔ˘ÚÁ›· ÙÔ˘ ‰È·ÎfiÙË (∂ÈÎ. 3)
Ο διακπτησ σε αυτ το µηχάνηµα λειτουργεί ωσ
διακπτησ του µοτέρ και ωσ διακπτησ επιλογήσ
διεύθυνσησ περιστροφήσ. ταν ο διακπτησ
ρυθµιστεί στην θέση R που επιδεικνύεται στο
κάλυµµα τησ λαβήσ, το µοτέρ περιστρέφεται προσ
τα δεξιά για να σφίξει το µπουλνι.
ταν ο διακπτησ ρυθµιστεί στο L, το µοτέρ
περιστρέφεται αριστερά για να ξεσφίξει το
µπουλνι. ταν ο διακπτησ ελευθερωθεί, το µοτέρ
σταµατά.
¶ƒ√™√Ã∏
Βεβαιωθείτε να κλείσετε το διακπτη και να
περιµένετε µέχρι που το µοτέρ να σταµατήσει
εντελώσ πριν αλλάξετε την διεύθυνση περιστροφήσ
του κλειδιού. Αν το αλλάξετε καθώσ το µοτέρ
περιστρέφεται θα έχει ωσ αποτέλεσµα το κάψιµµο
του µοτέρ.
2. ™К›НИМФ О·И НВЫК›НИМФ МФ˘ПФУИТУ
Μια εξαγ. υποδοχή που ταιριάζει µε το παξιµάδι
ή το µπουλνι πρέπει πρώτα να επιλεγεί. Μετά
στερεώστε την υποδοχή στον άκµονα, και πιάστε
το παξιµάδι που πρκειται να σφιχτεί µε την εξαγ.
υποδοχή. Κρατώντασ το κλειδί σε ευθεία γραµµή
µε το µπουλνι, πατήστε τον διακπτη του
ρεύµατοσ για την κρούση του παξιµαδιού για µερικά
δευτερλεπτα. Αν το παξιµάδι είναι µνο χαλαρά
στερεωµένο στο µπουλνι, το µπουλνι µπορεί να
περιστραφεί µε το παξιµάδι, και εποµένωσ θα
αποτραπεί το κατάλληλο σφίξιµο. Σε αυτή την
περίπτωση, σταµατήστε την κρούση στο παξιµάδι
και κρατήστε την κεφαλή του µπουλονιού µε ένα
κλειδί πριν ξαναρχίσετε την κρούση, ή µε το χέρι
σφίξτε το µπουλνι και το παξιµάδι για την αποφυγή
τησ ολίσθησήσ τουσ.
™∏ª∂π∞ ¶ƒ√™√Ã∏™ ∫∞∆∞ ∆∏ §∂π∆√Àƒ°π∞
1. ∂И‚В‚·ИТЫЩВ ЩЛУ Щ¿ЫЛ ЩЛ˜ БЪ·ММ‹˜ ЪВ‡М·ЩФ˜ (∂ИО. 4)
Η διαθέσιµη ροπή σύσφιξησ επηρεάζεται απ την
τάση τησ γραµµήσ του ρεύµατοσ. Η ελαττωµένη
τάση ελαττώνει την διαθέσιµη ροπή.
Για παράδειγµα, αν χρησιµοποιήσετε ένα κλειδί
τύπου 220 V σε µια γραµµή ρεύµατοσ 200 V η
διαθέσιµη ροπή στρέψησ θα ελαττωθεί κατά 70 90 %. ταν κάνεται επέκταση στο καλώδιο
ρεύµατοσ, χρησιµοποιήστε ένα καλώδιο επέκτασησ
το οποίο είναι σο το δυνατν µικρτερο. ταν
η τάση του ρεύµατοσ είναι µικρή και απαιτείται ένα
µακρύ καλώδιο επέκτασησ, ένασ µετασχηµατιστήσ
ανύψωσησ τάσησ πρέπει να χρησιµοποιηθεί. Η σχέση
µεταξύ τησ τάσησ παροχήσ ρεύµατοσ και τησ ροπήσ
στρέψησ δείχνεται στισ εικνεσ.
2. ªЛУ ·ББ›˙ВЩВ ЩФУ ЪФК˘П·ОЩ‹Ъ· ‹ ЩЛ ЫК˘ЪФı‹ОЛ
О·Щ¿ ЩЛ ‰И·ЪО‹ ПВИЩФ˘ЪБ›·. √ ЪФК˘П·ОЩ‹Ъ·˜ О·И Л
ЫК˘ЪФı‹ОЛ ˘ВЪıВЪМ·›УФУЩ·И О·Щ¿ ЩЛ ‰И·ЪО‹
ПВИЩФ˘ЪБ›·
√ ЪФК˘П·ОЩ‹Ъ·˜ О·И Л ЫК˘ЪФı‹ОЛ ˘ВЪıВЪМ·›УФУЩ·И
О·Щ¿ ЩФ Ы˘УВ¯¤˜ ЫК›НИМФ ЩЛ˜ ‚›‰·˜ БИ’ ·˘Щfi ЪФЫ¤НЩВ
У· МЛУ Щ· ·ББ›НВЩВ ВОВ›УЛ ЩЛ ЫЩИБМ‹.
3. ∂ЪБ·Ы›· МВ МИ· ЪФ‹ Ы‡ЫКИНЛ˜ О·Щ¿ППЛПЛ БИ· ЩФ
МФ˘ПfiУИ ˘fi ЩЛУ ОЪФ‡ЫЛ
Η βέλτιστη ροπή σύσφιξησ για παξιµάδια και
µπουλνια διαφέρει ανάλογα µε το υλικ και το
µέγεθοσ των µπουλονιών και των παξιµαδιών. Μια
υπερβολικά µεγάλη ροπή σύσφιξησ σε ένα µικρ
µπουλνι µπορεί να παραµορφώσει ή να σπάσει το
µπουλνι. Η ροπή σύσφιξησ αυξάνεται αναλογικά
µε το χρνο λειτουργίασ. Χρησιµοποιήστε το σωστ
για το µπουλνι χρνο λειτουργίασ.
4. ∂ÈÏÔÁ‹ Ù˘ ˘Ô‰Ô¯‹˜ Ô˘ Ó· Ù·ÈÚÈ¿˙ÂÈ ÛÙÔ ÌÔ˘ÏfiÓÈ
Βεβαιωθείτε να χρησιµοποιήσετε την υποδοχή που
ταιριάζει στο µπουλνι που πρκειται να σφιχτεί.
Η χρήση ακατάλληλησ υποδοχήσ θα προκαλέσει
χι µνο το µη ικανοποιητικ σφίξιµο αλλά επίσησ
και τη ζηµιά στην υποδοχή και στο παξιµάδι.
Μια φθαρµένη ή παραµορφοµένη υποδοχή
εξάγωνησ ή τετράγωνησ τρύπασ δεν θα παράσχει
επαρκή σφίξιµο για εφαρµογή στο παξιµάδι ή στον
άκµονα µε συνέπεια την απώλεια τησ ροπήσ
σύσφιξησ.
∆ώστε προσοχή στη φθορά των τρυπών τησ
υποδοχήσ και αντικαταστήστε τισ πριν αναπτυχθεί
η φθορά. Το ταίριασµα τησ υποδοχήσ µε το µέγεθοσ
των µπουλονιών δείχνεται στουσ ¶›Ó·Î·˜ 1.
Η αριθµητική τιµή στο χαρακτηρισµ τησ υποδοχήσ
δηλώνει την απσταση (S) απ τη µια πλευρά στην
άλλη τησ εξαγ. τρύπασ.
5. ∫Ú¿ÙËÌ· ÙÔ˘ ÂÚÁ·Ï›Ԣ
Κρατήστε το Μπουλονκλειδο γερά µε τα δυο χέρια
απ τη λαβή του κορµού και τη πλευρική λαβή.
Σε αυτή την περίπτωση κρατάτε το µπουλονκλειδο
σε ευθεία γραµµή µε το µπουλνι.
∆εν είναι απαραίτητο να σπρώξετε το
µπουλονκλειδο µε πολύ δύναµη. Κρατήστε το
µπουλονκλειδο µε τση δύναµη ση είναι ικανή
να ισοσταθµίσει τη δύναµη κρούσησ.
6. ∂И‚В‚·›ˆЫЛ ЩЛ˜ ЪФ‹˜ Ы‡ЫКИНЛ˜
Οι παρακάτω παράγοντεσ συνεισφέρουν στην ελάττωση
τησ ροπήσ σύσφιξησ. Γιαυτ επιβεβαιώστε την
πραγµατική ροπή σύσφιξησ που χρειάζεται βιδώνοντασ
µερικά µπουλνια µε ένα χειροκίνητο κλειδί ροπήσ
πριν την πραγµατική εργασία. Οι παράγοντεσ που
επηρεάζουν την ροπή σύσφιξησ είναι οι παρακάτω.
(1) Η τάση τησ γραµµήσ ρεύµατοσ:
Η ροπή σύσφιξησ ελαττώνεται ταν η τάση τησ
γραµµήσ ρεύµατοσ χαµηλώνει (∆είτε ∂ÈÎ. 4).
(2) Χρνοσ λειτουργίασ:
Η ροπή σύσφιξησ αυξάνει καθώσ ο χρνοσ
λειτουργίασ µεγαλώνει. Αλλά η ροπή σύσφιξησ δεν
αυξάνει πάνω απ µια ορισµένη τιµή ακµα και αν
το εργαλείο χρησιµοποιηθεί για µεγάλο χρονικ
διάστηµα (∆είτε ∂ÈÎ. 4).
(3) ∆ιάµετροσ του µπουλονιού:
Η ροπή σύσφιξησ διαφέρει ανάλογα µε τη διάµετρο
του µπουλονιού πωσ φαίνεται στισ ∂ÈÎ. 4. Γενικά
ένα µπουλνι µε µεγαλύτερη διάµετρο έχει
µεγαλύτερη ροπή σύσφιξησ.
(4) Συνθήκεσ σύσφιξησ:
Η ροπή σύσφιξησ διαφέρει ανάλογα µε την αναλογία
τησ ροπήσ, κλάση και µήκοσ των µπουλονιών ακµα
και αν χρησιµοποιούνται µπουλνια µε το ίδιο µήκοσ
σπειρώµατοσ. Η ροπή σύσφιξησ επίσησ διαφέρει
ανάλογα µε την κατάσταση τησ επιφένειασ του
µετάλλου µέσα απ το οποίο τα µπουλνια
πρκειται να σφιχθούν.
15
Page 17

∂ППЛУИО¿
(5) Χρήση προαιρετικών εξαρτηµάτων:
Η ροπή σύσφιξησ ελαττώνεται λίγο ταν µια ράβροσ
προέκτασησ, ένασ αρθρωτσ σύνδεσµοσ ή µια
µακριά υποδοχή χρησιµοποιούνται.
(6) ∆ιάκενο τησ υποδοχήσ:
Μιά φθαρµένη υποδοχή εξάγωνησ ή τετράγωνησ
τρύπασ δεν θα παράσχει επαρκή σφίξιµο για
εφαρµογή στο παξιµάδι ή στον άκµονα µε συνέπεια
την απώλεια τησ ροπήσ σύσφιξησ.
Η χρήση µιασ ακατάλληλησ υποδοχήσ η οποία δεν
ταιριάζει στο µπουλνι θα προκαλέσει µια ανεπαρκή
ροπή σύσφιξησ. Το ταίριασµα τησ υποδοχήσ µε τα
µεγέθη των µπουλονιών φαίνεται στουσ ¶›Ó·Î·˜ 1.
™À¡∆∏ƒ∏™∏ ∫∞π ∂§∂°Ã√™
1. ŒÏÂÁ¯Ô˜ Ù˘ ˘Ô‰Ô¯‹˜
Μια φθαρµένη ή παραµορφοµένη υποδοχή
εξάγωνησ ή τετράγωνησ τρύπασ δεν θα παράσχει
επαρκή σφίξιµο στην εφαρµογή ανάµεσα στο
παξιµάδι ή στον άκµονα µε συνέπεια την απώλεια
τησ ροπήσ σύσφιξησ. Κατά περιδουσ δώστε
προσοχή στη φθορά των τρυπών τησ υποδοχήσ και
αντικαταστήστε την µε µια καινούργια αν χρειαστεί.
2. ŒÏ¯Ԙ ÙˆÓ ‚ȉÒÓ ÛÙÂÚ¤ˆÛ˘
Ελέγχετε περιοδικά λεσ τισ βίδεσ στερέωσησ και
βεβαιωθείτε τι είναι κατάλληλα σφιγµένεσ. Στην
περίπτωση που χαλαρώσει οποιαδήποτε βίδα σφίξτε
την ξανά αµέσωσ. Αν δεν το κάνετε αυτ µπορεί
να έχει ωσ αποτέλεσµα το σοβαρ τραυµατισµ.
3. ™˘ÓÙ‹ÚËÛË ÙÔ˘ ÌÔÙ¤Ú
Η περιέλιξη τησ µονάδα του µοτέρ είναι η καρδιά
του ηλεκτρικού εργαλείου. ∆ώστε µεγάλη προσοχή
για να σιγουρευτείτε τι η περιέλιξη δεν θα πάθει
ζηµιά και / ή θα βρεχθεί µε λάδι ή νερ.
4. ŒÏÂÁ¯Ô˜ ÛÙ· Î·Ú‚Ô˘Ó¿ÎÈ· (∂ÈÎ. 5)
Για την συνεχιζµενη ασφάλεια σασ και την
προστασία σασ απ την ηλεκτροπληξ¨α, ο έλεγχοσ
στα καρβουνάκια και η αντικατάσταση αυτού του
εργαλείου πρέπει ΜΟΝΟ να γίνεται απ ένα
Εξουσιοδοτηµένο Κέντρο Σέρβισ τησ Hitachi.
5. ∞ÓÙÈηٿÛÙ·ÛË ÙÔ˘ ηψ‰›Ô˘ ·ÚÔ¯‹˜ Ú‡̷ÙÔ˜
Αν το καλώδιο παροχήσ ρεύµατοσ του Εργαλείου
πάθει ζηµιά, το Εργαλείο πρέπει να επιστραφεί στο
Εξουσιοδοτηµένο Κέντρο Σέρβισ τησ Hitachi για να
αντικατασταθεί.
6. §›ЫЩ· Ы˘УЩ‹ЪЛЫЛ˜ ЩˆУ МВЪТУ
A: Αρ. Αντικειµένου
B: Αρ. Κωδικού
C: Αρ. που χρησιµοποιήθηκε
D: Παρατηρήσεισ
¶ƒ√™√Ã∏
Η επισκευή, η τροποποίηση και ο έλεγχοσ των
Ηλεκτρικών Εργαλείων Hitachi πρέπει να γίνεται
απ ένα Εξουσιοδοτηµένο Kέντρο Σέρβισ τησ
Hitachi.
Αυτή η Λίστα των Μερών θα είναι χρήσιµη αν
παρουσιαστεί µαζί µε το εργαλείο στο
Εξουσιοδοτηµένο Κέντρο Σέρβισ τησ Hitachi ταν
ζητάτε επισκευή ή κάποια άλλη συντήρηση.
Κατά τον έλεγχο και τη συντήρηση των ηλεκτρικών
εργαλείων, οι καννεσ ασφαλείασ και οι κανονισµοί
που υπάρχουν σε κάθε χώρα πρέπει να
ακολουθούνται.
∆ƒ√¶√¶√π∏™∏
Τα Ηλεκτρικά Εργαλεία Hitachi βελτιώνονται
συνεχώσ και τροποποιούνται για να συµπεριλάβουν
τισ τελευταίεσ τεχνολογικέσ προδουσ.
Κατά συνέπεια, ορισµένα τµήµατα (δηλ. κωδικοί
αριθµοί και / ή σχεδιασµσ) µπορούν να αλλάξουν
χωρίσ προηγούµενη ειδοποίηση.
™∏ª∂πø™∏
Εξαιτίασ του συνεχιζµενου προγράµµατοσ έρευνασ και
ανάπτυξησ τησ Hitachi τα τεχνικά χαρακτηριστικά που
εδώ αναφέρονται µπορούν να αλλάξουν χωρίσ
προηγούµενη ειδοποίηση.
¶ПЛЪФКФЪ›В˜ Ф˘ ·КФЪФ‡У ЩФУ ВОВМfiМВУФ ıfiЪ˘‚Ф О·И
ЩЛ ‰fiУЛЫЛ.
Oι τιµέσ µετρήθηκαν σύµφωνα µε το EN60745 και
βρέθηκαν σύµφωνεσ µε το ISO 4871.
Ένα τυπικ επίπεδο πίεσησ ήχου Α : 98 dB (Α).
Ένα τυπικ επίπεδο A ηχητικήσ ισχύσ Είνα: 111 dB (A).
Αβεβαιτητα KpA: 3 dB (A)
Φοράτε προστατευτικà αυτιών.
Μια τυπική τιµή ρίζασ µέσησ τετραγωνικήσ επιτάχυνσησ:
2
4,75 m/s
16
Page 18

Polski
OGÓLNE WSKAZÓWKI BEZPIECZEŃSTWA
OSTRZEŻENIE!
Należy przeczytać wszystkie instrukcje
Nieprzestrzeganie któregokolwiek z zamieszczonych poniżej
zaleceń może być przyczyną porażenia prądem
elektrycznym, pożaru i/lub poważnych obrażeń ciała.
Występujące w poniższych ostrzeżeniach wyrażenie
“urządzenie elektryczne” oznacza urządzenia zasilane z
sieci elektrycznej (za pomocą przewodu) lub baterii
(bezprzewodowo).
INSTRUKCJE POWINNY BYĆ ZACHOWANE NA
PRZYSZŁOŚĆ
1) Miejsce pracy
a) Miejsce pracy powinno być uprzątnięte i czyste.
W miejscach nieuporządkowanych i źle oświetlonych
ryzyko wypadku jest większe.
b) Nie należy używać urządzeń elektrycznych w
przypadku zagrożenia wybuchem, na przykład w
obecności łatwopalnych płynów, gazów lub pyłów.
Urządzenia elektryczne wytwarzają iskry, które mogą
spowodować zapłon pyłu.
c) Dzieci i osoby postronne nie powinny znajdować
się w pobliżu pracującego urządzenia
elektrycznego.
Odwrócenie uwagi użytkownika może spowodować
utratę kontroli nad urządzeniem.
2) Bezpieczeństwo elektryczne
a) Wtyczka urządzenia elektrycznego musi być
odpowiednia do gniazdka.
Nigdy nie należy w jakikolwiek sposób przerabiać
wtyczki.
Nie używać jakichkolwiek elementów łączących
z urządzeniami wymagającymi uziemienia.
Używanie tylko oryginalnych wtyczek pasujących
do gniazdka ogranicza ryzyko porażenia prądem
elektrycznym.
b) Unikać kontaktu z przedmiotami uziemionymi,
takimi jak rury, kaloryfery, kuchenki i urządzenia
chłodnicze.
W przypadku dotykania uziemienia ryzyko porażenia
prądem elektrycznym jest większe.
c) Nie narażać urządzeń elektrycznych na działanie
deszczu lub wilgoci.
Przedostanie się wody do urządzenia zwiększa
ryzyko porażenia prądem elektrycznym.
d) Odpowiednio używać przewód zasilający. Nigdy
nie wykorzystywać przewodu do przenoszenia lub
ciągnięcia urządzenia lub też wyciągania wtyczki
z gniazdka.
Utrzymywać przewód z dala od źródeł ciepła,
oleju, ostrych krawędzi lub części ruchomych.
Uszkodzenie lub nacięcie przewodu zwiększa ryzyko
porażenia prądem elektrycznym.
e) Podczas pracy z urządzeniem elektrycznym na
wolnym powietrzu należy używać odpowiedniego
przedłużacza.
Używanie przedłużacza przeznaczonego do pracy
na wolnym powietrzu zmniejsza ryzyko porażenia
prądem elektrycznym.
3) Bezpieczeństwo osobiste
a) Podczas pracy z urządzeniem elektrycznym
należy zachowywać koncentrację i planować
wykonywane zadania, kierując się zdrowym
rozsądkiem.
Urządzenia elektrycznego nie powinny
obsługiwać osoby zmęczone lub znajdujące się
pod wpływem substancji odurzających, alkoholu
lub lekarstw.
Chwila nieuwagi podczas pracy z urządzeniem może
stać się przyczyną poważnych obrażeń.
b) Używać wyposażenia ochronnego. Zawsze nosić
okulary ochronne.
Używanie wyposażenia ochronnego, takiego jak
maski przeciwpyłowe, buty przeciwpoślizgowe,
odpowiednie nakrycie głowy i słuchawki ogranicza
ryzyko obrażeń ciała.
c) Unikać nieprzewidzianego uruchomienia
urządzenia. Przed włożeniem wtyczki do gniazdka
upewnić się, że urządzenie jest wyłączone.
Przenoszenie urządzenia z palcem na wyłączniku
lub podłączenie do sieci włączonego urządzenia
może spowodować wypadek.
d) Przed włączeniem urządzenia usunąć wszelkiego
rodzaju klucze regulacyjne.
Pozostawienie klucza w ruchomej części urządzenia
może spowodować obrażenia.
e) Nie trzymać urządzenia zbyt daleko od siebie.
Zachować stabilną pozycję przez cały czas.
Umożliwia to pełne panowanie nad urządzeniem,
nawet w nieoczekiwanych sytuacjach.
f) Nosić odpowiednią odzież. Nie należy nosić
luźnych ubrań oraz biżuterii. Utrzymywać włosy,
odzież i rękawice z dala od ruchomych części
urządzenia.
Luźne ubrania, biżuteria lub długie włosy mogą
zostać wciągnięte przez poruszające się części.
g) Jeżeli urządzenie wyposażone jest w system
odprowadzania pyłu, powinien on być założony i
właściwie używany.
Użycie tego rodzaju urządzeń ograniczy zagrożenia
związane z gromadzeniem się pyłu.
4) Obsługa i konserwacja urządzenia
a) Nie dociskać urządzenia zbyt mocno. Należy
używać tylko właściwego urządzenia,
odpowiedniego dla wykonywanej pracy.
Użycie odpowiedniego urządzenia spowoduje, że
praca zostanie wykonana lepiej i bezpieczniej.
b) Nie używać urządzenia elektrycznego, którego
wyłącznik jest niesprawny.
Urządzenie, które nie może zostać wyłączone za
pomocą wyłącznika, jest niebezpieczne i musi zostać
przeznaczone do naprawy.
c) Przed przystąpieniem do jakichkolwiek prac, jak
na przykład wymiana akcesoriów, urządzenie
musi zostać wyłączone z sieci. To samo dotyczy
przechowywania urządzenia nieużywanego.
Umożliwi to zmniejszenie ryzyka nieprzewidzianego
uruchomienia urządzenia.
d) Urządzenia elektryczne powinny być
przechowywane poza zasięgiem dzieci oraz
wszelkich osób nie znających zasad
funkcjonowania i obsługi tego typu urządzeń.
Obsługa urządzeń elektrycznych przez osoby nie
znające zasad ich funkcjonowania jest
niebezpieczna.
e) Wykonywać odpowiednie prace konserwacyjne.
Kontrolować prawidłowość ustawienia części
ruchomych, ich uszkodzenia i wszelkie inne
kwestie, mogące spowodować nieprawidłową
pracę urządzenia.
17
Page 19

Polski
S
D
B
E
L
Uszkodzone urządzenie powinno zostać
natychmiast przekazane do naprawy.
Wiele wypadków spowodowane jest niewłaściwą
konserwacją urządzeń elektrycznych.
f) Narzędzia tnące powinny być naostrzone i czyste.
Odpowiednio naostrzone narzędzia nie będą się
wyginać i są łatwiejsze w używaniu.
g) Urządzenie elektryczne, akcesoria, wiertła itd.
powinny być używane zgodnie z niniejszymi
zaleceniami oraz w sposób odpowiadający
wykonywanej pracy, przy uwzględnieniu
warunków panujących w otoczeniu.
Wykorzystanie urządzenia elektrycznego do pracy,
do której nie jest ono przeznaczone, grozi
wypadkiem.
5) Serwis
a) Urządzenie powinno być serwisowane tylko przez
osoby posiadające odpowiednie kwalifikacje, przy
użyciu wyłącznie identycznych, oryginalnych
części zamiennych.
Zapewni to utrzymanie pełnego bezpieczeństwa
pracy z urządzeniem.
ŚRODKI OSTROŻNOŚCI PRZY PRACY Z
KLUCZEM UDAROWYM
1. Podczas używania narzędzia na dużej wysokości
upewnić się, że nikt nie przebywa poniżej.
2. Przy dłuższej pracy z urządzeniem należy używać
zatyczek do uszu.
3. W razie konieczności zmiany kierunku należy przestawić
przełącznik dopiero po całkowitym zatrzymaniu silnika.
4. Kiedy konieczne jest wykorzystanie przedłużacza, należy
użyć transformatora podwyższającego napięcie.
5. Przed użyciem urządzenia sprawdzić moment obrotowy
dokręcania za pomocą klucza dynamometrycznego,
aby upewnić się, że stosowany jest właściwy moment
obrotowy.
6. Należy odpowiednio przymocować gniazdo do klucza
udarowego za pomocą kołka i pierścienia.
7. Sprawdzić, czy gniazdo nie posiada żadnych pęknięć.
8. Należy zawsze mocno utrzymywać klucz udarowy za
korpus i uchwyty boczne. W przeciwnym wypadku siła
odrzutu może spowodować nieprecyzyjną, a nawet
niebezpieczną pracę.
ŚRODKI OSTROŻNOŚCI
Dzieci i osoby niepełnosprawne nie powinny znajdować
się w pobliżu urządzenia.
Nieużywane urządzenie powinno być przechowywane w
miejscu poza zasięgiem dzieci i osób niepełnosprawnych.
TEKNîK ’ZELLîKLER
Napięcie (w zależności od miejsca)* (110V, 115V, 120V, 127V, 220V, 230V, 240V)
Moc pobierana* 480 W
Prędkość obrotowa bez obciążenia 1900 min
Wielkości (rozmiary śrub)
M12 – M16 (Śruba o wysokim napięciu)
M12 – M22 (Śruba zwykła)
Moment obrotowy dokręcania** Maksimum 36,7 kg-m
Prowadzenie pod kątem 12,7 mm
Waga (bez babla) 2,9 kg
* Sprawdź nazwę produktu, jako że ulega ona zmianie w zależności od miejsca zakupu.
** Dokręcanie śruby bez użycia przedłużacza, przy napięciu znamionowym.
-1
STANDARDOWE WYPOSAŻENIE I PRZYSTAWKI
(1) Uchwyt boczny .......................................................... 1
(2) Pudełko ....................................................................... 1
Standardowe akcesoria podlegają zmianom bez uprzedzenia.
18
DODATKOWE WYPOSAŻENIE
(Do nabycia oddzielnie)
1. Rodzaje gniazd
Pomimo że klucz udarowy Hitachi dostarczany jest
tylko z jednym gniazdem standardowym, na rynku
dostępnych jest wiele gniazd, odpowiednich dla
poszczególnych rozmiarów i rodzajów śrub.
Page 20

Polski
Tabela 1 B=12,7mm
Nazwa gniazda Wymiary (mm) Wymiary (mm)
Gniazdo sześciokątne
SDE LSD EL
12 12 20 34 52
13 13 21,5 34 52
14 14 22 34 52
17 17 28 15 32 17 25 34 52
19 19 28 17 34 19 28 34 52
21 21 32 19 36 21 31 34 52
22 22 35 24 40 22 32,5 34 52
23 23 36 25 40 23 33 34 52
24 24 38 25 40 24 34 34 52
26 26 38 25 40 26 38 57 75
27 27 42 24 50 27 40 57 75
30 30 42 34 50 30 42 57 75
Gniazdo zwykłe Gniazdo zwykłe
2. Pręt przedłużający
Pręt przedłużający przeznaczony jest do użycia w
przypadku, kiedy jest bardzo mało miejsca i zwykłe
gniazdo nie może dosięgnąć śruby.
UWAGA
Jeżeli używany jest pręt przedłużający, moment
obrotowy dokręcania jest nieco mniejszy w porównaniu
ze zwykłym gniazdem. Dlatego urządzenie musi
pracować nieco dłużej, aby osiągnąć taki sam moment
obrotowy.
3. Złącze uniwersalne
Złącze uniwersalne może zostać użyte do nakrętek, dla
których istnieje kąt pomiędzy gniazdem a kluczem lub
w przypadku, kiedy jest bardzo mało miejsca.
4. Złącze kątowe (Model EW-14R)
Powinno być używane przy dokręcaniu nakrętki lub
śruby pod kątem prostym.
Wyposażenie dodatkowe może ulec zmianie bez
uprzedzenia.
PRZED ROZPOCZĘCIEM PRACY
1. Żródło mocy
Upewnij się, że żródło mocy jest zgodne z wymogami
mocy zaznaczonymi przy nazwie produktu.
2. Przełącznik
Upewnij się, że przełącznik jest wyłączony (pozycja
OFF). Jeśli wtyczka jest włączona do prądu podczas
gdy przełącznik jest włączony (pozycja ON), narzędzie
zacznie działać natychmiast, co może spowodować
poważny wypadek.
3. Przedłużacz
Kiedy miejsce pracy znajduje się daleko od żródła
prądu, użyj przedłużacza o wystarczającym przekroju.
Przedłużacz powinien być tak krótki jak tylko jest to
możliwe.
4. Mocowanie uchwytu bocznego
Położenie uchwytu bocznego przymocowanego do
obudowy może zostać zmienione - w tym celu należy
odkręcić uchwyt. (odkręcić śrubę po prawej stronie).
Ustawić uchwyt w położeniu właściwym dla
wykonywanej pracy i zamocować go, mocno dokręcając
śrubę.
5. Montowanie gniazda
(1) Typu kołkowego lub pierścieniowego (Rys. 1)
Wybrać gniazdo odpowiednie dla śruby, która ma zostać
dokręcona lub odkręcona. Włożyć gniazdo do kowadełka
klucza, zabezpieczyć sworzniem i pierścieniem
uszczelniającym. W celu zdemontowania gniazda
wykonać powyższe czynności w odwrotnej kolejności.
(2) Rodzaj trzpienia (Rys. 2)
Dopasować trzpień znajdujący się w kwadratowym
elemencie kowadełka do otworu gniazda
sześciokątnego. Docisnąć trzpień i zamontować gniazdo
sześciokątne na kowadełku. Sprawdzić, czy trzpień
całkowicie wszedł w otwór. W celu zdemontowania
gniazda wykonać powyższe czynności w odwrotnej
kolejności.
ZASTOSOWANIE
䡬 Dokręcanie i odkręcanie różnych rodzajów śrub i
nakrętek.
JAK UŻYWAĆ
1. Obsługa przełącznika (Rys. 3)
Przełącznik w tym urządzeniu pełni rolę wyłącznika
silnika i przełącznika kierunku obrotu. Kiedy przełącznik
znajduje się w położeniu R, silnik obraca się w kierunku
19
Page 21

Polski
zgodnym z ruchem wskazówek zegara, a śruba jest
dokręcana. Kiedy przełącznik znajduje się w położeniu
L, silnik obraca się w kierunku przeciwnym do ruchu
wskazówek zegara, a śruba jest odkręcana. Po
zwolnieniu przełącznika następuje zatrzymanie silnika.
UWAGA
Upewnić się, że przełącznik jest wyłączony i przed
zmianą kierunku obrotu klucza zaczekać aż do
całkowitego zatrzymania silnika. Próba przełączenia,
gdy silnik wciąż się obraca, grozi spaleniem silnika.
2. Dokręcanie i odkręcanie śrub
Należy najpierw wybrać oprawkę sześciokątną
odpowiednią dla śruby lub nakrętki. Założyć oprawkę
na kowadełko, po czym zacisnąć ją na śrubie.
Utrzymując wkrętarkę w równej linii ze śrubą, nacisnąć
przycisk, aby uruchomić urządzenie na kilka sekund.
Jeżeli nakrętka jest luźno zaciśnięta na śrubie, śruba
może zacząć kręcić się wraz z nakrętką i nie zostanie
właściwie dokręcona. W takim przypadku należy
zatrzymać urządzenie i przytrzymać łeb śruby
odpowiednim kluczem lub ręcznie dokręcić śrubę z
nakrętką, aby zapobiec ślizganiu.
ŚRODKI OSTROŻNOŚCI PODCZAS PRACY Z
URZĄDZENIEM
1. Sprawdzenie napięcia w sieci (Rys. 4)
Moment obrotowy uzależniony jest od napięcia w sieci.
Obniżone napięcie powoduje zmniejszenie momentu
obrotowego.
Dla przykładu, jeżeli używany jest klucz udarowy 220 V,
a napięcie w sieci wynosi 200 V, moment obrotowy
zostanie obniżony do 70-90% wartości maksymalnej.
Jeżeli konieczne jest wykorzystanie przedłużacza, powinien
on być jak najkrótszy. Kiedy napięcie w sieci jest niskie
i wymagane jest użycie przedłużacza, należy zastosować
transformator podwyższający napięcie. Zależność
pomiędzy napięciem w sieci zasilania a wartością
momentu obrotowego pokazana została na rysunkach.
2. Nie dotykać odbijacza i obudowy urządzenia w
trakcie pracy
Odbijacz i obudowa urządzenia silnie się nagrzewają
podczas dokręcania śrub, dlatego należy uważać, aby
ich w tym czasie nie dotknąć.
3. Dostosowanie momentu obrotowego i siły
dokręcania do rozmiaru śruby
Optymalny moment obrotowy dokręcania śrub lub
nakrętek zależy od materiału i wymiaru śrub lub
nakrętek. Zbyt duży moment obrotowy dokręcania małej
śruby może spowodować jej uszkodzenie lub złamanie.
Moment obrotowy zwiększa się proporcjonalnie do
czasu działania. Należy zawsze dobrać czas dokręcania
odpowiedni dla danej śruby.
4. Wybór gniazda odpowiedniego dla śruby
Należy zawsze używać gniazda odpowiedniego dla
rodzaju wkręcanej śruby. Użycie nieprawidłowego
gniazda może spowodować nie tylko nieprawidłowe
dokręcenie, ale także uszkodzenie gniazda lub nakrętki.
W przypadku zużytego lub zdeformowanego gniazda
kwadratowego lub sześciokątnego nie jest możliwe
zapewnienie odpowiedniej szczelności pomiędzy
nakrętką a kowadełkiem, co powoduje zmniejszenie
momentu obrotowego.
Należy sprawdzać, czy nie został uszkodzony otwór
gniazda i wymieniać gniazdo przed dalszym zużyciem.
20
W Tabeli 1 można znaleźć informacje dotyczące
dopasowania gniazd do śrub.
Wartość liczbowa w nazwie gniazda oznacza odległość
(S) między bokami otworu sześciokątnego.
5. Trzymanie narzędzia
Narzędzie powinno być mocno utrzymywane obiema
rękami za korpus i uchwyt boczny. Należy zawsze
trzymać narzędzie w linii osi śruby.
Nie jest konieczne zbyt mocne dociskanie narzędzia.
Należy dociskać narzędzie jedynie z siłą wystarczającą
do pokonania oporu.
6. Sprawdzenie właściwego momentu obrotowego
Wymienione poniżej czynniki mogą spowodować
zmniejszenie momentu obrotowego dokręcania. Dlatego
też przed przystąpieniem do pracy z urządzeniem należy
próbnie wkręcić kilka śrub. Czynniki wpływające na
wartość momentu obrotowego są następujące.
(1) Napięcie w sieci:
Moment obrotowy zmniejsza się, jeżeli napięcie w sieci
jest obniżone (patrz Rys. 4).
(2) Czas pracy:
Moment obrotowy zwiększa się wraz z czasem pracy.
Jednak moment obrotowy nie może wzrosnąć powyżej
pewnej wartości maksymalnej, nawet jeżeli czas pracy
jest długi (patrz Rys. 4).
(3) Średnica śruby:
Moment obrotowy różni się w zależności od średnicy
śruby, jak pokazano na Rys. 4. Ogólnie mówiąc, im
większa średnica śruby, tym większy moment obrotowy
jest potrzebny do jej wkręcenia.
(4) Warunki pracy:
Moment obrotowy dokręcania zależy od współczynnika
momentu obrotowego, klasy i długości śrub, nawet kiedy
śruby posiadają gwint o takim samym rozmiarze. Moment
obrotowy jest ponadto różny w zależności od stanu
powierzchni materiału, w który śruba ma zostać wkręcona.
(5) Wykorzystanie części opcjonalnych:
Moment obrotowy jest zmniejszony w przypadku użycia
pręta przedłużającego, złącza uniwersalnego lub
długiego gniazda.
(6) Prześwit gniazda:
W przypadku zużytego lub zdeformowanego gniazda
kwadratowego lub sześciokątnego nie jest możliwe
zapewnienie odpowiedniej szczelności pomiędzy
nakrętką a kowadełkiem, co powoduje zmniejszenie
momentu obrotowego.
Używanie gniazda nieodpowiedniego dla danej śruby
może spowodować, że moment obrotowy będzie
niewystarczający. Gniazda odpowiadające poszczególnym
rozmiarom śrub wymienione zostały w Tabeli 1.
KONSERWACJA I INSPEKCJA
1. Kontrola stanu gniazda
W przypadku zużytego lub zdeformowanego gniazda
kwadratowego lub sześciokątnego nie jest możliwe
zapewnienie odpowiedniej szczelności pomiędzy
nakrętką a kowadełkiem, co powoduje zmniejszenie
momentu obrotowego. Należy regularnie sprawdzać
stan otworów gniazd i w razie konieczności wymieniać
gniazda na nowe.
2. Sprawdzanie śrub mocujących
Regularnie sprawdzaj wszystkie mocujące śruby i
upewnij się, że są mocno przykręcone. Jeśli któraś z
nich się obluzuje, natychmiast ją przykręć. Zaniedbanie
tego może spowodować poważne zagrożenie.
Page 22

3. Konserwacja silnika
Wirnik silnika jest sercem narzędzia. Zadbaj, by wirnik
nie został uszkodzony i nie zawilgotniał lub pokrył się
olejem.
4. Kontrola szczoteczek węglowych (Rys. 5)
By praca z narzędziem zawsze była bezpieczna i aby
uniknąć ryzyka porażenia prądem, węglowe szczoteczki
tego narzędzia powinny być sprawdzane i wymieniane
TYLKO przez Autoryzowane Centrum Obsługi Hitachi.
5. Wymiana kabla zasilającego
Jeśli kabel zasilający tego urządzenia ulegnie
uszkodzeniu, młotowiertarkę należy przynieść do
Autoryzowanego Centrum Obsługi HITACHI w celu
wymiany kabla.
6. Lista części zamiennych
A: Nr. części
B: Nr. kodu
C: Ilość użytych części
D: Uwagi
UWAGA
Naprawy, modyfikacji i kontroli Narzędzi Elektrycznych
Hitachi może dokonywać tylko Autoryzowane Centrum
Obsługi Hitachi.
Ta lista części będzie przydatna, jeśli zostanie wręczona
Autoryzowanemu Centrum Obsługi Hitachi, gdy
zaniesiemy narzędzie do naprawy lub przeglądu.
Podczas używania i konserwacji narzędzi elektrycznych
należy przestrzegać przepisów i norm bezpieczeństwa
danego kraju.
MODYFIKACJE
Narzędzia elektryczne Hitachi są ciągle ulepszane i
modyfikowane w celu wprowadzania najnowszych
osiągnięć nauki i techniki.
W związku z tym pewne części (a także numery kodów
i konstrukcja) mogą ulec zmianom bez uprzedzenia.
Polski
WSKAZÓWKA
W zwiazku z prowadzonym przez Hitachi programem badań
i rozwoju, specyfikacje te mogą się zmienić w każdej chwili
bez uprzedzenia.
Informacja dotycząca poziomu hałasu i wibracji
Mierzone wartości było określone według EN60745 i
zadeklarowane zgodnie z ISO 4871.
Typowy poziom dźwięku A: 98 dB (A)
Typowe natężenie dźwięku A: 111 dB (A)
Niepewność KpA: 3 dB (A)
Używaj ochraniacza uszu.
Typowa wartość skuteczna przyśpieszenia wynosi:
2
4,75 m/s
21
Page 23

Magyar
ÁLTALÁNOS BIZTONSÁGTECHNIKAI ELŐÍRÁSOK
FIGYELEM!
Olvassa végig az utasításokat
Az alábbi utasítások be nem tartása áramütést, tüzet és
súlyos sérülést okozhat.
Az alábbi figyelmeztetésekben szereplő “elektromos
szerszámgép” kifejezés az ön - hálózatról üzemeltetett
(vezetékes) vagy akkumulátoros (vezeték nélküli) elektromos szerszámgépére vonatkozik.
ŐRIZZE MEG AZ UTASÍTÁSOKAT
1) A munkahely
a) A munkahelyet tartsa tisztán, és megfelelően
világítsa meg.
A túlzsúfolt és sötét munkahelyek vonzzák a
baleseteket.
b) Az elektromos szerszámgépeket ne használja
robbanásveszélyes légtérben, például gyúlékony
folyadékok, gázok vagy por mellett.
Az elektromos szerszámgépek szikrákat bocsáthatnak
ki, melyek berobbanthatják a jelenlévő port.
c) A szerszámgép működtetése közben tartsa távol
a gyermekeket és a körülállókat.
A figyelemelvonás a szerszámgép feletti kontroll
elvesztését okozhatja.
2) Érintésvédelem
a) Az elektromos szerszámgép dugaszának
illeszkednie kell a hálózati csatlakozóaljzatba.
Semmilyen körülmények között ne módosítsa a
dugaszt.
Ne használjon semmilyen átalakító dugaszt a
földelt elektromos szerszámgéppel.
A módosítás nélküli dugaszok és a megfelelő aljzatok
csökkentik az elektromos áramütés veszélyét.
b) Ügyeljen arra, hogy munka közben ne érintsen meg
földelt felületeket, pl. csővezetékeket, fűtőtesteket,
tűzhelyeket vagy hűtőberendezéseket.
Ha a kezelő teste földelve van, az áramütés veszélye
megnő.
c) Az elektromos szerszámgépeket ne tegye ki eső
vagy nedvesség hatásának.
Az elektromos szerszámgépbe kerülő víz növeli az
áramütés veszélyét.
d) Ne rongálja meg az elektromos csatlakozókábelt.
A szerszámgépet ne hordozza a kábelnél fogva,
és a villásdugót soha ne a kábelnél fogva húzza
ki a dugaszolóaljzatból.
Védje a kábelt a magas hőmérséklettől, olajtól és
az éles sarkoktól.
A sérült vagy összegabalyodott vezetékek növelik
az elektromos áramütés veszélyét.
e) Ha a szabadban kell munkát végeznie, mindig
csak az erre a célra alkalmas hosszabbító kábelt
használjon.
A kültéri használatra alkalmas hosszabbító használata
csökkenti az elektromos áramütés veszélyét.
3) A testi épség védelme
a) Mindig figyeljen oda a végzett munkára. Az
elektromos szerszámgéppel végzett munka teljes
figyelmet igényel.
Ne használja a készüléket, ha nem érzi
kipihentnek magát, ha kábítószer, alkohol vagy
gyógyszer hatása alatt áll.
Egy pillanatnyi figyelmetlenség is súlyos sérülést
okozhat.
22
b) Használjon védőfelszerelést. Mindig használjon
védőszemüveget.
A védőfelszerelések, pl. a pormaszk, a csúszásbiztos
biztonsági cipő, a védősisak és a füldugó használata
csökkenti a sérülésveszélyt.
c) Kerülje a gép véletlenszerű beindítását. Mielőtt a
csatlakozó dugót a dugaszolóaljzatba bedugja,
mindig győződjék meg róla, hogy a készülék ki
van kapcsolva.
Ne tartsa ujját az indító kapcsolón, ha hordozza
a készüléket, és ne csatlakoztasson bekapcsolt
készüléket az áramforrásra.
d) Mielőtt a gépet bekapcsolja, mindig ellenőrizze,
hogy kivette-e a készülékből a szerszámbeállítóilletve befogókulcsot.
A forgó alkatrészben maradt szerszámbeállító- vagy
befogókulcs személyi sérülést okozhat.
e) Ne nyújtsa ki a kezét túl nagy távolságra. Munka
közben mindig álljon stabilan, és őrizze meg az
egyensúlyát.
Így a váratlan helyzetekben sem veszti el a szerszám
feletti uralmát.
f) Viseljen megfelelő munkaruhát. Munka közben ne
viseljen bő öltözéket vagy ékszert. Haját, ruházatát
és kesztyűjét tartsa távol a mozgó alkatrészektől.
A bő öltözéket, ékszereket vagy a hosszú hajat a
mozgó alkatrészek elkaphatják.
g) Ha a készülék rendelkezik porelszívási, illetve -
gyűjtési lehetőséggel, ügyeljen rá, hogy azok
megfelelően legyenek csatlakoztatva és használva.
A fenti eszközök használata csökkenti a por okozta
veszélyt.
4) Az elektromos szerszámgép használata és
karbantartása
a) Ne erőltesse a szerszámot. Mindig az
alkalmazásnak megfelelő szerszámot használjon.
A megfelelő szerszámgép nominális teljesítményszinten
jobban és biztonságosabban működik.
b) Ne használja a szerszámot, ha a kapcsoló azt nem
kapcsolja megfelelően be, illetve ki.
A kapcsolóval nem szabályozható szerszámgép
veszélyes, és azt meg kell javítani.
c) Mindig húzza ki a dugaszoló aljzatból a csatlakozó
dugót, mielőtt a készüléken beállításokat végezne,
kicserélné a tartozékokat, vagy mielőtt eltárolná
a készüléket.
A fenti biztonsági óvintézkedések csökkentik a
készülék véletlenszerű bekapcsolásának veszélyét.
d) A használaton kívüli szerszámokat tárolja
gyermekek által nem hozzáférhető helyen, és ne
engedje, hogy a készüléket az üzemetetéshez
nem értő személyek használják.
A gyakorlatlan használó kezében a szerszámgépek
különösen nagy veszélyt jelentenek.
e) A szerszámgépek karbantartása. Ellenőrizze a mozgó
alkatrészek illesztését, rögzítését, az alkatrészek
esetleges repedését és minden olyan tulajdonságot,
mely hatással lehet a munkavégzésre.
Meghibásodás esetén használat előtt javítassa
meg a készüléket.
A nem megfelelő karbantartás sok balesetet okoz.
f) A vágószerszámokat mindig tartsa élesen és
tisztán.
A megfelelően karbantartott - éles vágóélűvágószerszámok kisebb eséllyel görbülnek el, és
könnyebben irányíthatók.
Page 24

Magyar
S
D
B
E
L
g) Használja a szerszámgépet és a fúrófejeket stb.
az utasításoknak és az adott szerszámgép
rendeltetésének megfelelően, mindig figyelembe
véve a munkakörülményeket és az elvégzendő
munka jellegét.
A szerszámgép rendeltetéstől eltérő használata
veszélyt okozhat.
5) Javítás
a) A szerszámot csak - eredeti cserealkatrészeket
használó - szakképzett személlyel javíttassa.
Így biztosítható a szerszámgép biztonságos
üzemeltetése.
ÓVINTÉZKEDÉS
A gyermekeket és a felügyeletre szoruló személyeket
tartsa távol az elektromos szerszámgéptől.
A használaton kívüli szerszámgépeket gyermekektől és
felügyeletre szoruló személyektől elzárva kell tartani.
AZ ÜTVECSAVAROZÓ HASZNÁLATÁVAL
KAPCSOLATOS ÓVINTÉZKEDÉSEK
1. Ha a szerszámot magas helyen használja, győződjön
meg róla, hogy senki nem tartózkodik ön alatt.
2. A szerszámgép tartós használata esetén használjon
füldugót.
3. Amennyiben szükség van a forgási irány
megváltoztatására, a váltókart csak akkor használja,
amikor a motor már megállt.
4. Ha hosszú hosszabbító kábelt használ, használjon
feszültségnövelő transzformátort.
5. Annak érdekében, hogy a megfelelő nyomatékot
alkalmazza, nyomatékkulccsal ellenőrizze a meghúzási
nyomatékot.
6. Rögzítse biztonságosan a befogópatront az
ütvecsavarozóhoz a hozzá tartozó dugókulccsal és a
gyűrűvel.
7. Ellenőrizze, hogy a befogópatron nincs-e megrepedve.
8. Az ütvecsavarozó testét és oldalsó fogantyúit mindkét
kézzel erősen kell tartani. Ellenkező esetben az ellenerő
pontatlan és veszélyes működést okozhat.
MŰSZAKI ADATOK
Feszültség (terület szerint)* (110V, 115V, 120V, 127V, 220V, 230V, 240V)
Névleges teljesítményfelvétel* 480 W
Üresjárati fordulatszám 1900 min
Teljesítmény (csavarok mérete)
M12 – M16 (Nagy feszítőerőre méretezett csavar)
M12 – M22 (Szabályos méretű csavar)
Meghúzási nyomaték** Maximum 36,7 kg-m
Behajtási szög 12,7 mm
Súly (tápkábel nélkül) 2,9 kg
* Ne felejtse el ellenőrizni a típustáblán feltüntetett adatokat, mivel ezek eladási területenként változnak!
** A csavar meghúzása hosszabbító kábel használata nélkül névleges feszültség mellett.
-1
STANDARD TARTOZÉKOK
(1) Oldalfogantyú .............................................................. 1
(2) Tok .............................................................................. 1
A standard tartozékok előzetes bejelentés nélkül változhatnak.
OPCIONÁLIS TARTOZÉKOK
(külön beszerezhetők)
1. Befogópatronok
Habár a Hitachi ütvecsavarozó gépet csak egy standard
befogópatronnal szállítjuk, számos további Ń különböző
típusú és méretű csavarok meghúzásához használható
Ń befogópatron vásárolható.
23
Page 25

Magyar
Táblázat 1 B=12,7mm
Befogópatron
rendeltetése
Hatszögletű befogópatron
SDE LSD E L
12 12 20 34 52
13 13 21,5 34 52
14 14 22 34 52
17 17 28 15 32 17 25 34 52
19 19 28 17 34 19 28 34 52
21 21 32 19 36 21 31 34 52
22 22 35 24 40 22 32,5 34 52
23 23 36 25 40 23 33 34 52
24 24 38 25 40 24 34 34 52
26 26 38 25 40 26 38 57 75
27 27 42 24 50 27 40 57 75
30 30 42 34 50 30 42 57 75
2. Hosszabbítórúd
A hosszabbítórúd használata megkönnyíti a szűk helyen
végzett munkát vagy ha a rendelkezésre álló
befogópatron nem éri el a meghúzandó csavart.
FIGYELEM
Hosszabbítórúd használatakor a meghúzási nyomaték
értéke valamivel kisebb a szabványos befogópatron
használatához képest. Emiatt egy kicsivel hosszabb
ideig szükséges a szerszámgépet üzemeltetni az azonos
nyomaték eléréséhez.
3. Univerzális csuklókapcsoló
Az univerzális csuklókapcsoló használata megkönnyíti
az anyacsavarok behajtását, ha a befogópatron szögben
helyezkedik el a csavarhoz képest, vagy ha a munkát
nagyon szűk helyen kell végezni.
4. Saroktoldalék (EW-14R modell)
Ezt a toldalékot csak akkor használja, ha a gép
derékszögben áll a behajtandó anyához vagy csavarhoz
képest.
Szokásos befogópatron Hosszú befogópatron
Méret (mm) Méret (mm)
AZ ÜZEMELÉS ELŐTTI ÓVINTÉZKEDÉSEK
1. Áramforrás
Ügyeljen rá, hogy a készülék adattábláján feltüntetett
feszültség értéke megegyezzen az alkalmazni kívánt
hálózati feszültséggel.
2. Hálózati kapcsoló
Ügyeljen rá, hogy a hálózati kapcsoló KI állásba legyen
kapcsolva. Ha a csatlakozódugót úgy csatlakoztatja a
dugaszolóaljzatba, hogy közben a hálózati kapcsoló BE
állásban van, a kéziszerszám azonnal működésbe lép,
ami súlyos balesetet idézhet elő.
3. Hosszabbító vezeték
Ha a munkaterület az áramforrástól távol található,
akkor egy megfelelő keresztmetszetű és teljesítményű
hosszabbító vezetéket kell alkalmazni.
4. Az oldalsó fogantyú rögzítése
A gép testére rögzített oldalsó fogantyú helyzete a
fogantyú lecsavarozásával módosítható. (Jobbmenetes
csavar) Fogassa el a fogantyút a kívánt helyzetbe, majd
rögzítse azt a csavar megszorításával.
5. A befogópatron behelyezése
(1) Csap, körszelvényű tömítőgyűrű (1. Ábra)
Válasszon a megszorítandó vagy meglazítandó
csavarhoz illő befogópatront. Helyezze be a
befogópatront az ütvecsavarozó szárába, majd rögzítse
biztonságosan a hozzá tartozó dugókulccsal és a
gyűrűvel. A befogópatron leszerelését ellenkező
sorrendben végezze.
(2) Hengeres csap típus (2. Ábra)
Állítsa vonalba a szár négyszögletes részében található
hengeres csapot a hatszögletű befogópatron nyílásával.
Ezután tolja be a hengeres csapot és szerelje fel a
hatszögletű befogópatront a szárra. Ellenőrizze, hogy a
hengeres csap teljesen illeszkedik-e a nyílásba. A
befogópatron leszerelését ellenkező sorrendben végezze.
Az opcionális tartozékok előzetes bejelentés nélkül
változhatnak.
ALKALMAZÁSOK
䡬 Különböző csavarok és anyák meghúzása és
meglazítása.
24
A KÉSZÜLÉK HASZNÁLATA
1. A kapcsoló működtetése (3. Ábra)
A szerszámgép kapcsolója a motor kapcsolójaként és
irányváltó kapcsolóként funkcionál. Ha a kapcsoló R
állásban van, - mely állapot a markolat burkolatán
látható - a motor az óramutató járásával megegyező
irányban forog és megszorítja a csavart. Ha a kapcsoló
L állásban van, a motor az óramutató járásával ellentétes
irányban forog és meglazítja a csavart. A kapcsoló
elengedésekor a motor leáll.
Page 26

Magyar
FIGYELEM
Mielőtt a forgásirányt megváltoztatná minden esetben
állítsa KI állásba a kacsolót, és várja meg amíg a motor
teljesen leáll. A forgó motor forgási irányának
megváltoztatása a motor leégését okozza.
2. Csavarok meghúzása és meglazítása
Válasszon az anya vagy a csavar méretének megfelelő
hatszögletű befogópatront. Ezután szerelje fel a
befogópatront a szárra, majd fogja be a meghúzni
kívánt anyát a hatszögletű befogópatronnal. Tartsa egy
vonalban a csavarkulcsot a csavarral, nyomja meg a
ki/be kapcsolót, és fejtsen ki nyomatékot több
másodpercig az anyára. Ha az anya lazán lett felhelyezve
a csavarra, a csavar az anyával együtt elforoghat és
így nem lesz megfelelő a rögzítés. Ilyen esetben
szüntesse meg az anyára kifejtett nyomatékot, az újbóli
meghúzás előtt pedig rögzítse egy csavarkulccsal a
csavar fejét, vagy húzza meg kézzel az anyát.
AZ ÜZEMELTETÉSRE VONATKOZÓ
FIGYELMEZTETÉSEK
1. A hálózati feszültség ellenőrzése (4. Ábra)
A rendelkezésre álló nyomaték a hálózati feszültségtől
függ. A csökkentett hálózati feszültség csökkenti a
meghúzási nyomatékot.
Például amennyiben 220 V-os ütvecsavarozót 200 V-os
feszültség mellett használ, a meghúzási nyomaték 70 90 % - ra csökken. A tápvezeték meghosszabbításakor
használjon a lehető legrövidebb hosszabbító kábelt. Ha
a hálózati feszültség alacsony és hosszú hosszabbító
kábel használata szükséges, használjon feszültségnövelő
transzformátort. A hálózati feszültség és a meghúzási
nyomaték kapcsolatát az ábrák mutatják.
2. Folyamatos munka közben ne érintse meg az ütközőt
vagy a burkolatot
Az ütköző és a burkolat a folyamatos üzemeltetés
során felforrósodik, ezért ne érintse meg azokat.
3. A behajtandó anyás csavarhoz alkalmas meghúzási
nyomaték alkalmazása
Anyacsavarok vagy anyás csavarok optimális meghúzási
nyomatéka eltérő lehet azok anyagától és méretétől
függően. Ha kisméretű anyás csavarhoz túl nagy
meghúzási nyomatékot alkalmaznak, az szétlapulhat
vagy eltörhet. A meghúzási nyomaték értéke az
üzemidővel arányosan növekszik. Alkalmazzon
megfelelő meghúzási időtartamot az anyás csavarokhoz.
4. A csavarhoz illő befogópatron kiválasztása
Ügyeljen arra, hogy a meghúzandó csavarhoz illő
befogópatront használja. Nem megfelelő befogópatron
használata nemcsak a csavar elégtelen meghúzását
eredményezi, hanem a patron vagy az anyacsavar is
megrongálódhat. Kopott vagy deformálódott, hat-, illetve
négyszögletű nyílással rendelkező befogópatron
használatakor az anyacsavar vagy a szár nem illeszkedik
elég szorosan, ami a meghúzási nyomaték
gyengülésével jár.
Ügyeljen a befogópatron nyílásának kopására, és
azonnal cserélje ki azt, még mielőtt jobban kikopna.
A befogópatronok és csavarok méret szerinti párosítása
az 1. táblázatban látható.
A befogópatron rendeltetéséhez rendelt számérték a
hatszögletű nyílás oldaltól oldalig terjedő távolságát (S)
jelöli.
5. A szerszámgép tartása
Az ütvecsavarozót a gép törzsén és oldalán lévő
fogantyúnál fogva mindkét kézzel erősen kell tartani.
Ebben az esetben a gépnek a csavarral párhuzamosan
kell állnia.
Használat közben a csavarbehajtó gépet nem kell túl
erősen rászorítani. A gépet csupán a behajtóerő
ellensúlyozásához szükséges erővel kell tartani.
6. A meghúzási nyomaték jóváhagyása
Az alábbi tényezők elősegítik a meghúzási nyomaték
csökkentését. Ezért, mielőtt hozzálátna a munkához a
kézi csavarbehajtó készülékkel, tisztázni kell a bizonyos
anyás csavarok behajtásakor szükséges tényleges
meghúzási nyomaték értékét. A meghúzási nyomatékot
befolyásoló tényezők a következők.
(1) Hálózati feszültség:
A meghúzási nyomaték csökken, ha a hálózati feszültség
lecsökken (Lásd az 4. Ábrát).
(2) Üzemidő:
Az üzemidő növekedésével párhuzamosan a meghúzási
nyomaték értéke is növekszik. A meghúzási nyomaték
azonban nem növekedhet egy bizonyos érték fölé, még
akkor sem, ha a szerszámot hosszú időre bekapcsolva
hagyja (Lásd a 4. Ábrát).
(3) Az anyás csavar átmérője:
A meghúzási nyomaték a csavarátmérő függvényében
eltérő lehet, ahogy az a 4. Ábrán látható. Nagyobb
átmérőjű csavar meghúzásához általában nagyobb
meghúzási nyomaték szükséges.
(4) Meghúzási feltételek:
A meghúzási nyomaték a nyomatéki tényezőtől, továbbá
a csavar anyagának minőségi osztályától és a csavar
hosszától függően változik, még akkor is, ha ugyanolyan
méretű menettel ellátott csavarokat használnak. A
meghúzási nyomaték ezen kívül annak a fémnek a
felületétől függően is eltérő lehet, amelybe a csavart
behajtják.
(5) Opcionális alkatrészek használata:
A meghúzási nyomaték kismértékben csökken, ha
hosszabbító rudat, univerzális csuklókapcsolót vagy
hosszú befogópatronokat használnak.
(6) A befogópatron illesztési hézaga:
Kopott vagy deformálódott, hat-, illetve négyszögletű
nyílással rendelkező befogópatron használatakor az
anyacsavar vagy a szár nem illeszkedik elég szorosan,
ami a meghúzási nyomaték gyengülésével jár.
A csavarhoz nem illő befogópatron használata elégtelen
meghúzási nyomatékot eredményez. A befogópatronok
és csavarok méret szerinti párosítása az 1. táblázatban
látható.
KARBANTARTÁS ÉS ELLENŐRZÉS
1. A befogópatron ellenőrzése
Kopott vagy deformálódott, hat-, illetve négyszögletű
nyílással rendelkező befogópatron használatakor az
anyacsavar vagy a szár nem illeszkedik elég szorosan,
ami a meghúzási nyomaték gyengülésével jár.
Rendszeres időközönként ellenőrizze a befogópatron
nyílásainak kopását, és szükség esetén cserélje ki a
befogópatront.
2. A rögzítőcsavarok ellenőrzése
Rendszeresen ellenőrizze az összes rögzítőcsavart, és
ügyeljen rá, hogy azok megfelelően meg legyenek
húzva. Ha valamelyik csavar ki lenne lazulva, azonnal
húzza meg. Ennek elmulasztása súlyos veszéllyel járhat.
25
Page 27

Magyar
3. A motor karbantartása
A motor tekercselése az elektromos szerszám “szíve”.
Gondosan ügyeljen rá, hogy a tekercselés ne sérüljön,
illetve ne kerüljön kapcsolatba olajjal vagy vízzel.
4. A szénkefék cseréje (5. Ábra)
Az Ön folyamatos biztonsága és az elektromos áramütés
veszélyének elkerülése érdekében e szerszám
szénkeféinek ellenőrzését és cseréjét KIZÁRÓLAG csak
Hitachi Szakszervíz végezheti.
5. A tápkábel cseréje
Ha a kéziszerszám tápkábele megsérült, akkor azt a
tápkábel kicserélése végett el kell juttatni egy Hitachi
szakszervizbe.
6. Szervizelési alkatrészlista
A: Alkatrész-szám
B: Kódszám
C: Használt darabszám
D: Megjegyzések
FIGYELEM
Hitachi kéziszerszámok javítását, módosítását és
ellenőrzését csak Hitachi Szakszervíz végezheti.
Javítás vagy egyéb karbantartás esetén hasznos ha ezt
a szervíz-alkatrész listát a szerszámmal együtt átadjuk a
Hitachi szakszervíznek.
A kéziszerszámok üzemeltetése és karbantartása során
be kell tartani az egyes országokban érvényben lévő
biztonsági rendelkezéseket és szabványokat.
MÓDOSÍTÁSOK
A Hitachi kéziszerszámok állandó tökéletesítéseken
mennek át, hogy alkalmazni tudják a legújabb műszaki
fejlesztések eredményeit.
Éppen ezért egyes alkatrészek (azok kódszámai illetve
kiviteli módjai) előzetes bejelentés nélkül
megváltozhatnak.
MEGJEGYZÉS
A HITACHI folyamatos kutatási és fejlesztési programja
következtében az itt szereplő műszaki adatok előzetes
bejelentés nélkül változhatnak.
A környezeti zajra és vibrációra vonatkozó információk
A mért értékek az EN60745 szabványnak megfelelően
kerültek meghatározásra és az ISO 4871 alapján kerülnek
közzétételre.
Jellemző A-súlyozott hangnyomásszint: 98 dB (A).
Jellemző A-súlyozott hangteljesítmény-szint: 111 dB (A).
Bizonytalanság KpA: 3 dB (A)
Viseljen hallásvédelmi eszközt.
A jellemző súlyozott gyorsulás négyzetes középértéke:
2
4,75 m/s
26
Page 28

Čeština
VŠEOBECNÉ BEZPEČNOSTNÍ PŘEDPISY
UPOZORNĚNÍ!
Prostudujte si všechny pokyny
Nedodržování všech níže uvedených pokynů může způsobit
úraz elektrickým proudem, vznik požáru a/nebo vážné
zranění.
Pojem “elektrické nářadí” ve všech níže uvedených
upozorněních se vztahuje na elektricky poháněné nářadí
připojené (pomocí přívodní šňůry) k elektrické síti nebo na
elektrické (bezšňůrové) nářadí poháněné akumulátorem.
DODRŽUJTE TYTO POKYNY
1) Pracovní prostor
a) Udržujte pracovní prostor v čistotě a zajistěte jeho
dobré osvětlení.
Neuspořádaný pracovní prostor a neosvětlené
plochy mohou být příčinou nehod.
b) Neprovozujte elektrické nářadí ve výbušných
prostředích, jako je například prostor s výskytem
hořlavých kapalin, plynů nebo prachu.
Při provozu elektrického nářadí vznikají jiskry, které
mohou vznítit prach nebo výpary.
c) Zajistěte, aby se při provozu elektrického nářadí
nezdržovaly v blízkosti děti nebo okolostojící
osoby.
Odvedení pozornosti může způsobit ztrátu kontroly
nad nářadím.
2) Elektrická bezpečnost
a) Zástrčky elektrického nářadí musí odpovídat
používané zásuvce.
Nikdy jakýmkoli způsobem neupravujte zástrčku.
Nepoužívejte jakékoli rozvodné zástrčky s
uzemněným (ukostřeným) elektrickým nářadím.
Původní neupravené zástrčky a vhodné zásuvky
snižují nebezpečí úrazu elektrickým proudem.
b) Vyvarujte se kontaktu s uzemněnými nebo
ukostřenými plochami, jako jsou např. trubky,
radiátory, sporáky a chladničky.
Vzniká zvýšené nebezpečí úrazu elektrickým
proudem, pokud je Vaše tělo uzemněné nebo
ukostřené.
c) Nevystavujte elektrické nářadí dešti nebo mokrým
podmínkám.
Voda, která vnikne do elektrického nářadí, zvyšuje
nebezpečí úrazu elektrickým proudem.
d) Nezacházejte s přívodní šňůrou nevhodným
způsobem. Nikdy nepoužívejte přívodní šňůru pro
nošení, tahání nebo vypojování elektrického
nářadí.
Zajistěte, aby se přívodní šňůra nedostala do
kontaktu se zdroji tepla, olejem, ostrými hranami
nebo pohybujícími se částmi.
Poškozené nebo zauzlené přívodní šňůry zvyšují
nebezpečí úrazu elektrickým proudem.
e) Při práci s elektrickým nářadím ve vnějších
prostorách používejte prodlužovací šňůru
vhodnou pro venkovní použití.
Použití přívodní šňůry vhodné pro venkovní prostředí
snižuje nebezpečí úrazu elektrickým proudem.
3) Bezpečnost osob
a) Bute při práci vždy pozorní, sledujte prováděnou
práci a během práce s elektrickým nářadím
postupujte rozumně.
Nepoužívejte elektrické nářadí v případě únavy
nebo pod vlivem drog, alkoholu nebo léků.
Pouhý okamžik nepozornosti při práci s elektrickým
nářadím může způsobit vážné zranění.
b) Používejte ochranné pomůcky. Vždy používejte
ochranu zraku.
Ochranné pomůcky, jako jsou protiprachová maka,
obuv s neklouzavou úpravou podrážky, ochranná
přilba nebo chrániče sluchu použité pro vhodné
podmínky sníží nebezpečí zranění.
c) Zajistěte, aby nedošlo k náhodnému spuštění
nářadí. Zabezpečte, aby vypínač byl před
zapojením do sítě v poloze vypnuto.
Nošení elektrického nářadí s prstem na vypínači a
připojování elektrického nářadí s vypínačem v poloze
zapnuto může způsobit nehody.
d) Před zapnutím elektrického nářadí vymontujte
všechny seřizovací klíče.
Klíč upevněný na otáčející se části elektrického
nářadí může způsobit zranění osob.
e) Zajistěte náležitou stabilitu při práci. Během práce
je třeba vždy zaujmout náležitý a stabilní postoj.
Tím se dosáhne lepšího ovládání elektrického nářadí
v neočekávaných situacích.
f) Při práci používejte vhodný oděv. Nepoužívejte
volný oděv nebo šperky. Zajistěte, aby se Vaše
vlasy, oděv nebo rukavice nedostaly do kontaktu
s pohybujícími se částmi nářadí.
Volný oděv, šperky nebo dlouhé vlasy se mohou
zachytit do pohybujících se částí.
g) Pokud se používají zařízení pro připojení odsávání
prachu a sběrných zařízení, zajistěte jejich
správné zapojení a použití.
Používejte tato zařízení pro snížení nebezpečí, která
vznikají v prašném prostředí.
4) Použití a ošetřovaní elektrického nářadí
a) Netlačte na elektrické nářadí. Pro Váš způsob
použití zvolte správné elektrické nářadí.
Správné elektrické nářadí provede práci lépe a
bezpečněji rychlostí, pro které bylo konstruováno.
b) Nepoužívejte elektrické nářadí, pokud vypínač
není funkční.
Jakékoli elektrické nářadí, které nelze ovládat
vypínačem, je nebezpečné a je třeba je opravit.
c) Při provádění jakýchkoli nastavení, změně
příslušenství nebo uskladňování elektrického
nářadí odpojte vždy zástrčku ze zdroje energie.
Tato preventivní bezpečnostní opatření snižují
nebezpečí náhodného uvedení elektrického nářadí
do chodu.
d) Uložte nepoužívané elektrické nářadí mimo dosah
dětí a nedovolte, aby osoby, které nejsou
seznámeny s provozem elektrického nářadí a s
těmito pokyny, toto elektrické nářadí používaly.
Elektrické nářadí je v rukou nevyškoleného uživatele
nebezpečné.
e) Provádějte údržbu elektrického nářadí.
Zkontrolujte elektrické nářadí, zda je správně
seřízené nebo nedochází k váznutí chodu
pohybujících se částí, zda nejsou nějaké části
poškozené a zda nevznikly jakékoli jiné poruchy,
které mohou negativně ovlivnit provoz
elektrického nářadí.
V případě poškození si nechejte elektrické nářadí
před použitím opravit.
Velký počet nehod je způsobeno nedostatečnou
údržbou elektrického nářadí.
27
Page 29

Čeština
S
D
B
E
L
f) Udržujte řezné nástroje ostré a čisté.
Správným způsobem udržované řezné nástroje s
ostrými břity mají menší sklon k uváznutí a snadněji
se při práci ovládají.
g) Používejte elektrické nářadí, příslušenství,
nástavce nástroje atd. ve shodě s těmito předpisy
a způsobem stanoveným pro jednotlivý typ
elektrického nářadí a přitom zohledněte pracovní
podmínky a druh prováděné práce.
Použití elektrického nářadí pro práce odlišné od
stanoveného účelu použití může způsobit
nebezpečné situace.
5) Servis
a) Nechejte si provádět servis Vašeho elektrického
nářadí kvalifikovanými opraváři a přitom
používejte jen originální náhradní díly.
Tím se zajistí zachování bezpečnosti elektrického
nářadí.
PREVENTIVNÍ OPATŘENÍ
Zajistěte, aby děti a nemocné osoby se nezdržovaly v
BEZPEČNOSTNÍ OPATŘENÍ PŘI POUŽITÍ
RÁZOVÉHO UTAHOVÁKU
1. V případě použití nářadí ve výšce se ujistěte, že se
žádná osoba nezdržuje pod Vámi.
2. V případě práce po delší dobu použijte zátky do uší.
3. Pokud je třeba změnit směr otáčení, přepínač zpětného
chodu přepněte až po uvedení motoru do klidu.
4. V případě použití dlouhého prodlužovacího kabelu
použijte zvyšovací transformátor.
5. Před započetím práce zkontrolujte nastavení
utahovacího momentu pomocí momentového klíče pro
ověření, že se použije správný utahovací moment.
6. Namontujte pevně nástrčnou hlavici na rázový utahovák
pomocí kolíku nástrčné hlavice a kroužku.
7. Přesvědčete se, že nástrčná hlavice nemá žádné trhliny.
8. Rukoje těla utahováku a boční rukoje rázového
utahováku držte vždy pevně. V opačném případě vzniklá
reakce může způsobit nepřesnost práce nebo dokonce
nebezpečí.
blízkosti.
Pokud se nářadí nepoužívá, je třeba je uskladnit mimo
dosah dětí a nemocných osob.
PARAMETRY
Napětí (podle oblastí)* (110V, 115V, 120V, 127V, 220V, 230V, 240V)
Vstupní příkon* 480 W
Rychlost bez zatížení 1900 min
Mezní rozměry (velikost šroubů)
M12 – M16 (Vysokopevnostní šroub)
M12 – M22 (Běžný šroub)
Utahovací moment** Maximálně 36,7 kg-m
Kuželové soukolí 12,7 mm
Váha (bez šňůry) 2,9 kg
* Zkontrolujte, prosíme, štítek na výrobku. Štítek podléhá změnám v závislosti na oblastech použití.
** Dotažení šroubu bez prodlužovacího kabelu při jmenovitém napětí.
-1
STANDARDNÍ PŘÍSLUŠENSTVÍ
(1) Boční rukoje .............................................................. 1
(2) Kufřík ........................................................................... 1
Standardní příslušenství podléhá změnám bez předchozího
upozornění.
28
DALŠÍ PŘÍSLUŠENSTVÍ
(Prodává se zvláš)
1. Sortiment nástrčných hlavic
Ačkoli je rázový utahovák Hitachi dodáván pouze s
jednou standardní nástrčnou hlavicí, dodává se velký
počet typů nástrčných hlavic vhodných pro rázové
utahování různých velikostí a typů šroubů.
Page 30

Čeština
Tabulka 1 B=12,7mm
Označení
nástrčných hlavic
Šestihranná nástrčná hlavice
2. Výsuvná tyč
Použití výsuvné tyče je výhodné při práci ve velmi
SDELSDEL
12 12 20 34 52
13 13 21,5 34 52
14 14 22 34 52
17 17 28 15 32 17 25 34 52
19 19 28 17 34 19 28 34 52
21 21 32 19 36 21 31 34 52
22 22 35 24 40 22 32,5 34 52
23 23 36 25 40 23 33 34 52
24 24 38 25 40 24 34 34 52
26 26 38 25 40 26 38 57 75
27 27 42 24 50 27 40 57 75
30 30 42 34 50 30 42 57 75
omezených prostorech nebo tehdy, jestliže objímka
nedosáhne ke šroubu, který má být utažen.
POZOR
Při použití výsuvné tyče je utahovací moment nepatrně
nižší ve srovnání s použitím běžné objímky.
Proto je třeba pro dosažení stejného momentu nechat
nářadí v chodu poněkud déle.
3. Univerzální kloub
Použití univerzálního kloubu je výhodné při rázovém
utahování matic tehdy, jestliže mezi objímkou a klíčem
vznikne určitý úhel, nebo při práci ve velmi úzkém
prostoru.
4. Přídavné zařízení pro práci v nedostupných místech
(Model EW-14R)
Používejte toto přídavné zařízení pouze tehdy, když je
nástroj aplikován na matici nebo šroub pod pravým
úhlem.
Běžná nástrčná hlavice Dlouhá nástrčná hlavice
Rozměr (mm) Rozměr (mm)
PŘED POUŽITÍM
1. Zdroj napětí
Ujistěte se, že používaný zdroj napětí splňuje požadavky
specifikované na štítku výrobku.
2. Spínač
Ujistěte se, že spínač je v poloze vypnuto. Pokud je
zástrčka zasunuta v zásuvce elektrického proudu a
spínač je v poloze „ON“, nástroj začne okamžitě
pracovat, a to může způsobit vážný úraz.
3. Prodlužovací kabel
Pokud je pracoviště vzdáleno od zdroje, použijte
prodlužovací kabel o správné tloušce a kapacitě. Je
třeba, aby prodlužovací kabel byl co nejkratší.
4. Upevnění boční rukojeti
Polohu boční rukojeti namontované ke skříni kladiva
lze změnit vyšroubováním rukojeti. (Šroub s pravým
závitem) Otočte rukoje do polohy požadované pro
práci a rukoje pevně dotáhněte.
5. Montáž nástrčné hlavice
(1) Kolík, typ s O kroužkem (Obr. 1)
Zvolte nástrčnou hlavici vhodnou pro dotažení nebo
uvolnění šroubu. Vložte nástrčnou hlavici na kovadlinu
utahováku a zajistěte ji kolíkem a kroužkem. Při
demontáži postupujte v opačném pořadí.
(2) Typ se západkovým čepem (Obr. 2)
Srovnejte západkový čep, umístěný ve čtvercovém
úseku pevné části, do souosé polohy s otvorem v
šestihranné objímce. Pak potlačte západkový čep a
namontujte šestihrannou objímku na pevnou část.
Zkontrolujte, že je západkový čep zcela zasunutý v
otvoru. Při demontáži objímky postupujte v obráceném
pořadí.
Další příslušenství podléhá změnám bez předchozího
upozornění.
POUŽITÍ
䡬 Dotahování a povolování různých druhů šroubů a matic.
POUŽITÍ
1. Funkce přepínače (Obr. 3)
Přepínač v tomto nářadí funguje jako spínač motoru
a volicí přepínač směru otáčení. Je-li přepínač nastaven
do polohy R označené na krytu rukojeti, motor se otáčí
ve směru chodu hodinových ručiček pro utažení šroubu.
Je-li přepínač nastaven do polohy L, motor se otáčí
ve směru proti chodu hodinových ručiček pro uvolnění
šroubu. Když se přepínač uvolní, motor se zastaví.
29
Page 31

Čeština
POZOR
Před změnou směru otáčení klíče vypněte vypínač a
vyčkejte, až se motor zcela zastaví. Přepnutí za chodu
motoru může způsobit spálení motoru.
2. Dotahovaní a uvolňování šroubů
Nejdříve je třeba zvolit šestihranné nástrčné hlavice
odpovídající šroubu nebo matici. Pak namontujte
nástrčnou hlavici na kovadlinu a uchopte utahovanou
matici pomocí šestihranné nástrčné hlavice. Přidržte
klíč v přímce se šroubem a stiskněte vypínač na několik
vteřin pro naražení matice.
Je-li matice pouze volně upevněna ke šroubu, šroub
se může s maticí otáčet, takže se nedosáhne náležitého
dotažení. V tomto případě zastavte působení síly na
matici a přidržte před zahájením působení síly hlavu
šroubu pomocí klíče nebo dotáhněte šroub a matici
ručně, aby se zabránilo prokluzování.
POKYNY K PROVOZU
1. Ověření síového napětí (Obr. 4)
Dosažitelný utahovací moment je ovlivněn síovým
napětím. Snížené síové napětí zmenší dosažitelný
utahovací moment.
Pokud používáte například typ utahováku pro napětí
220 V v síti s napětím 200 V, dosažitelný utahovací
moment se sníží na 70 až 90 %. Při prodlužování
přívodního kabelu použijte prodlužovací kabel, který je
co možná nejkratší. Je-li síové napětí příliš nízké a
je-li potřebný dlouhý prodlužovací kabel, je nutno použít
zvyšovací transformátor. Vztah mezi síovým napětím
a utahovacím momentem je znázorněn na obrázcích.
2. Nedotýkejte se skříně tlumiče nebo kladiva během
nepřetržitého chodu
Skříň tlumiče a skříň kladiva se během nepřetržitého
utahování šroubů ohřejí, proto bute opatrní a za
chodu se jich nedotýkejte.
3. Práce s utahovacím momentem vhodným pro rázově
utahovaný šroub
Optimální utahovací moment pro matice a šrouby se
liší podle materiálu a velikosti matic nebo šroubů.
Nadměrně velký utahovací moment pro malý šroub
může způsobit roztažení nebo zlomení šroubu.
Utahovací moment se zvyšuje úměrně s dobou provozu.
Používejte správnou dobu provozu pro daný šroub.
4. Volba nástrčné hlavice vhodné pro šroub
Zajistěte, aby se vždy použila nástrčná hlavice, která
je vhodná pro dotahovaný šroub. Použitím nevhodné
nástrčné hlavice způsobí nejen nedostatečné dotažení,
ale také poškození nástrčné hlavice nebo matice.
Opotřebovaná nebo deformovaná šestihranná nebo
hlavice se čtvercovým otvorem neposkytne dostatečné
dotažení pro dosednutí na matici nebo kovadlinu, čímž
dojde k poklesu utahovacího momentu.
Věnujte pozornost opotřebení otvorů nástrčné hlavice
a vyměňte je předtím, než dojde k dalšímu opotřebení.
Vhodná nástrčná hlavice a velikosti šroubů jsou uvedeny
v Tabulce 1.
Číselná hodnota označení nástrčné hlavice znamená
vzdálenost (S) stran jeho šestihranného otvoru.
5. Držení nástroje
Držte rázový utahovák pevně oběma rukama za rukoje
těla utahováku a boční rukoje.
Není nutné na klíč tlačit příliš silně. Držte klíč silou, která
je právě dostatečná k tomu, aby vyvážila rázovou sílu.
6. Ověření utahovacího momentu
Následující faktory přispívají ke snížení utahovacího
momentu. Ověřte si tedy aktuální potřebný utahovací
moment před zahájením práce zašroubováním několika
šroubů ručním momentovým klíčem. Faktory ovlivňující
utahovací moment jsou následující.
(1) Síové napětí:
Utahovací moment se při snížení síového napětí sníží
(Viz Obr. 4).
(2) Doba provozu:
Utahovací moment se zvyšuje se zvyšováním doby
provozu. Utahovací moment se však nezvýší nad určitou
hodnotu ani tehdy, jestliže je nástroj používán po
dlouhou dobu (Viz Obr. 4).
(3) Průměr šroubu:
Utahovací moment se liší podle průměru šroubu, jak
je uvedeno na Obr. 4. Všeobecně platí, že šroub o
větším průměru vyžaduje vyšší utahovací moment.
(4) Podmínky utahování:
Utahovací moment se mění podle momentového
poměru, třídy a délky šroubů i v případě, že jsou
použity šrouby se stejnou velikostí závitu. Utahovací
moment se také mění podle stavu povrchu kovu, přes
který se šrouby dotahují.
(5) Použití dalšího příslušenství:
Utahovací moment se mírně sníží, jestliže se použije
výsuvná tyč, univerzální kloub nebo dlouhá objímka.
(6) Vůle objímky:
Opotřebovaná nebo zdeformovaná objímka se
šestihranným nebo čtyřhranným otvorem nezajistí
adekvátní těsnost spojení mezi maticí a pevnou částí,
což má za následek snížení utahovacího momentu.
Použití nesprávné objímky, která neodpovídá velikosti
šroubu, bude mít za následek nedostatečný utahovací
moment. Vhodné velikosti nástrčných hlavic a šroubů
jsou uvedeny v tabulce 1.
ÚDRŽBA A KONTROLA
1. Kontrola objímky
Opotřebovaná nebo zdeformovaná objímka se
šestihranným nebo čtyřhranným otvorem nezajistí
adekvátní těsnost spojení mezi maticí a pevnou částí,
což má za následek snížení utahovacího momentu.
Pravidelně kontrolujte opotřebení otvoru objímky a v
případě potřeby provete výměnu.
2. Kontrola montážních šroubů
Pravidelně kontrolujte montážní šrouby a ujistěte se,
že jsou správně utaženy. Ihned utáhněte volné šrouby.
Neutažené šrouby mohou vést k vážným úrazům.
3. Údržba motoru
Vinutí motoru je srdce elektrického zařízení.
Ujistěte se, že vinutí není poškozené nebo vlhké vodou
nebo olejem.
4. Kontrola uhlíkových kartáčků (Obr. 5)
V zájmu zachování bezpečnosti a ochrany před úrazem
elektrickým proudem by kontrolu a výměnu uhlíkových
kartáčků tohoto zařízení mělo provádět POUZE
Autorizované servisní středisko Hitachi.
5. Výměna napájecího kabelu
Pokud bude napájecí kabel nástroje poškozen, musíte
nástroj odevzdat k výměně do autorizovaného servisního
střediska HITACHI.
30
Page 32

6. Seznam servisních položek
A: Číslo položky
B: Kód položky
C: Číslo použití
D: Poznámky
POZOR
Opravy, modifikace a kontroly zařízení Hitachi musí
provádět Autorizované servisní středisko Hitachi.
Tento seznam servisních položek bude užitečný, předložíteli jej s vaším zařízením Autorizovanému servisnímu středisku
Hitachi společně s požadavkem na opravu nebo další servis.
Při obsluze a údržbě elektrických zařízení musí být
dodržovány bezpečnostní předpisy a normy platné v
každé zemi, kde je výrobek používán.
MODIFIKACE
Výrobky firmy Hitachi jsou neustále zdokonalovány a
modifikovány tak, aby se zavedly nejposlednější
výsledky výzkumu a vývoje.
Následně, některé díly (např. čísla kódů nebo návrh)
mohou být změněny bez předešlého oznámení.
POZNÁMKA
Vlivem stále pokračujícího výzkumného a vývojového
programu HITACHI mohou zde uvedené parametry podléhat
změnám bez předchozího upozornění.
Informace o hluku a vibracích
Měřené hodnoty byly určeny podle EN60745 a deklarovány
ve shodě s ISO 4871.
Typická vážená úroveň hladiny akustického tlaku:
Typická vážená úroveň hladiny akustické energie:
Neurčitost KpA: 3 dB (A)
Použijte ochranu sluchu.
Typická vážená střední hodnota zrychlení nepřesahuje
2
4,75 m/s
98 dB (A).
111 dB (A).
Čeština
31
Page 33

Türkçe
GENEL GÜVENLIK KURALLARI
DÓKKAT!
Bütün talimatları okuyun
Aßaåıda belirtilen talimatların tümünün uygulamaması,
elektrik çarpması, yangın ve/veya ciddi yaralanmalarla
sonuçlanabilir.
Aßaåıdaki uyarılarda belirtilen “Elektrikli alet” terimi, ißletilen
(kablolu) veya (kablosuz) ana elektrik aletlerini kapsar.
BU TALÓMATLARI SAKLAYINIZ
1) Çalıßma ortamı
a) Çalıßma ortamı temiz ve iyi ıßıklandırılmıß
olmalıdır.
Daåınık ve karanlık ortamlar kazanın davetçisidir.
b) Yanıcı sıvıların, gazların veya tozların bulunduåu
patlayıcı ortamlarda elektrikli aletlerle
çalıßmayınız.
Elektrikli aletler kıvılcım sıçratabilir ve de gaz tozlarını
ateßleyebilir.
c) Elektrikli alet kullanırken çocuklardan ve
seyircilerden uzak tutun.
Dikkat daåıtıcı ßeyler kontrolü kaybetmenize yol
açabilir.
2) Elektrik güvenliåi
a) Elektrikli aletin fißi prize uygun olmalıdır.
Fißi hiçbir ßekilde deåißtirmeye çalıßmayın.
Elektrikli aletin topraklanmıß fißinde herhangi
bir adaptör kullanmayın.
Deåißtirilmemiß fißler ve onlarla uygun prizler elektrik
çarpma riskini azaltır.
b) Boru, radyatör, ocak/fırın ve buzdolabı gibi
topraklamıß yüzeylerle vücut temasından sakının.
Vücüdünüzün toprakla temasa geçmesi elektrik
çarpma riskini artırır.
c) Elektrikli aletleri yaåmur ve ıslak ortamlara maruz
bırakmayın.
Elektrikli aletin içersine su girmesi elektrik çarpma
riskini artırır.
d) Güç kablosuna zarar vermeyin. Elektrikli aleti
taßımak, çekmek veya prizden çıkarmak için
kabloyu kullanmayın.
Kabloyu kesici veya hareketli parçalardan, sıcak
yüzeylerden ve yaådan uzak tutun.
Hasar görmüß veya dolaßmıß kablolar elektrik çarpma
riskini artırır.
e) Elektrikli aleti açık alanlarda kullanırken, açık
alana özel uzatma kablosu kullanın.
Açık alana özel kablolar elektrik çarpma riskini azaltır.
3) Kißisel güvenlik
a) Daima tetikte olun, elektrikli aleti kullanırken ne
yaptıåınızın farkında ve duyarlı olun.
Elektrikli aleti alkol, ilaç veya uyußturucu etkisi
altındayken veya yorgunken çalıßtırmayın.
Elektrikli aleti kullanırken gösterilecek bir saniyelik
dikkatsizlik, ciddi yaralanmalara yol açabilir.
b) Koruyucu ekipman kullanın. Daima koruyucu
gözlük takın.
Toz maskesi, kaymayan emniyet ayakkabısı, sert
baßlık veya ißitme koruyucusu gibi koßullara uygun
olan ve yaralanma riskini azaltıcı koruyucu
ekipmanlar kullanın.
c) Aletin istem dıßı çalıßmasına karßın önlem alın.
Prize takmadan önce ßalter düåmesinin kapalı
konumda olduåundan emin olun.
Elektrikli aleti parmaåınız ßalter üzerinde olduåu
halde taßımak veya prize takmak kazanın
davetçisidir.
d) Elektrikli aleti çalıßtırmadan önce ayar
anahtarlarını çıkartın.
Elektrikli aletin dönen kısmına takılı kalmıß olan bir
anahtar, yaralanmalara yol açabilir.
e) Fazla uzanmayın. Ayaklarınızın konumuna ve
dengenize her zaman dikkat edin.
Böylece beklenmedik bir durumla karßılaßtıåınızda,
elektrikli aleti daha iyi kontrol altında tutmanızı saålar.
f) Uygun çalıßma giysisi giyin. Bol giysiler ve
takılardan kaçının. Saçınızı, giysilerinizi ve
eldiveninizi hareketli parçalardan uzak tutun.
Bol giysiler, takılar veya uzun saç oynayan parçalara
takılabilir.
g) Toz toplama baålantısı için gerekli teçhizat ve
baålantı araçları saålanmıßsa, bunların baålı
olduåundan ve doåru ßekilde kullanıldıåından
emin olun.
Bu teçhizatların kullanılması tozun yaratacaåı
tehlikeleri azaltacaktır.
4) Elektrikli aletin kullanımı ve bakımı
a) Elektrikli aleti zorlamayın. Yapacaåınız iße uygun
doåru aleti kullanın.
Doåru elektrikli aletinin kullanılması ißinizi hem
kolaylaßtıracaåı gibi hem de tasarlanmıß süratte
daha güvenli bir ßekilde yapmanızı saålar.
b) Eåer elektrikli aletin ßalter düåmesi açılıp
kapanmıyorsa, aleti kullanmayın.
Íalter düåmesinden kumanda edilemeyen elektrikli
aletler tehlike yaratır ve tamir edilmeleri gerekir.
c) Aksesuar deåißimlerinde, ayarlamalar sırasında
veya elektrikli aleti saklamadan önce elektrik
baålantısını kesin.
Bu gibi önleyici emniyet tedbirleri elektrikli aletin
istem dıßı çalıßma riskini azaltır.
d) Kullanılmayan elektrikli aletleri çocukların
ulaßamayacaåı yerlerde tutun. Aleti kullanmasını
bilmeyen ve bu talimatlara aßına olmayan kißilere
kullandırmayın.
Elektrikli aletler deneyimsiz ve eåitilmemiß kißilerin
eline tehlikeli olur.
e) Elektrikli aletin bakımını yapın. Hareketli
parçaların yapıßmamasını, kırık olmamasını,
düzenli hizalanmasını veya aletin ißletimini
etkileyecek herhangi bir durumun olmadıåını
kontrol edin.
Çoåu kazaya yetersiz bakımlı elektrikli aletleri neden
olur.
f) Aletlerinizi keskin ve temiz tutun.
Düzenli bakımı yapılmıß keskin uçlu takımların
yapıßma ihtimali azdır ve de kontrol edilmeleri daha
kolaylaßır.
g) Elektrikli aleti, aksesuarları ve uçları vs. bu
talimatlar doårultusunda ve o elektrikli aletin
amaçlanan kullanımı için, çalıßma koßullarını ve
de yapılacak ißi göz önüne alarak kullanın.
Elektrikli aletin amaçlanan kullanımı dıßında
kullanılması tehlikeli bir durum yaratabilir.
32
Page 34

Türkçe
S
D
B
E
L
5) Servis
a) Elektrikli aleti vasıflı bir kißi tarafından sadece
özdeß yedek parçalar kullanarak tamir edilmesini
saålayın.
Böylece elektrikli aletin güvenli kullanımı
saålanacaktır.
ÖNLEM
Çocukları ve diåer yeterli güce sahip olmayan kißileri uzak
tutun.
Kullanılmadıåı zamanlarda aleti çocuk ve yeterli güce
sahip olmayan kißilerin ulaßamayacaåı bir yerde saklayın.
DARBELÓ SOMUN SIKMA ALETÓNÓ KULLANIRKEN
ALINMASI GEREKEN ÖNLEMLER
1. Aleti yerden yüksek mekanlarda kullanırken, altınızda
kimsenin olmadıåından emin olun.
2. Uzun süreli kullanımda kulak tıkaçlarını kullanın.
3. Döndürme yönünü deåßtirmek gerekiyorsa, yön deåißtirme
anahtarını sadece motor durduktan sonra deåißtirin.
4. Uzun bir uzatma kablosu kullanılıyorsa, artırıcı bir
transformatör kullanın.
5. Doåru sıkıßtırma torkunun kullanılacaåından emin
olmak için kullanımdan önce, tork anahtarı ile sıkıßtırma
torkunu teyit edin.
6. Yuva pimi ve halkasını kullanarak yuvayı emniyetli bir
ßekilde darbeli somun sıkma aletine monte edin.
7. Yuvada herhangi bir çatlak olmadıåını teyit edin.
8. Her zaman darbeli somun sıkma aletinin gövde
kabzasını ve yan kollarını sıkıca tutarak çalıßın. Aksi
halde geri tepme ißin hassasiyetini bozabilir, hatta
tehlikeli durumlar doåurabilir.
TEKNÓK ÖZELLÓKLER
Voltaj (bölgelere göre)* (110V, 115V, 120V, 127V, 220V, 230V, 240V)
Güç girißiGüç girißi* 480 W
Yüksüz hız
Kapasiteler (cıvata boyutları)
M12 – M16 (Yüksek gerilimli somun)
1900 dak
M12 – M22 (Normal somun)
Sıkıßtırma torku** Maksimum 36,7 kg-m
Açılı sıkıßtırma 12,7 mm
Aåırlık (kablo hariç) 2,9 kg
* Bu deåer bölgeden bölgeye deåißiklik gösterdiåi için ürünün üzerindeki plakayı kontrol etmeyi unutmayın.
** Taßıma voltajı belirsiz uzatma kablosuyla cıvata sıkıßtırırken.
-1
STANDART AKSESUARLAR
(1) Yan kol ....................................................................... 1
(2) Kutu ............................................................................. 1
Standart aksesuarlarda önceden bildirimde bulunulmadan
deåißiklik yapılabilir.
ÓSTEÅE BAÅLI AKSESUARLAR
(ayrıca satılır)
1. Yuva çeßitleri
Hitachi Darbeli Somun Sıkma aleti sadece bir adet
standart yuva ile gelmektedir. Deåßik tip ve boyutlardaki
cıvataların darbeli sıkıßtırılmasını kapsayan çok geniß
yuva türleri mevcuttur.
33
Page 35

Türkçe
Tablo 1 B=12,7mm
Yuva Belirleme Boyut (mm) Boyut (mm)
SDELSDEL
Altıgen Yuva 12 12 20 34 52
13 13 21,5 34 52
14 14 22 34 52
17 17 28 15 32 17 25 34 52
19 19 28 17 34 19 28 34 52
21 21 32 19 36 21 31 34 52
22 22 35 24 40 22 32,5 34 52
23 23 36 25 40 23 33 34 52
24 24 38 25 40 24 34 34 52
26 26 38 25 40 26 38 57 75
27 27 42 24 50 27 40 57 75
30 30 42 34 50 30 42 57 75
Normal Yuva Uzun Yuva
2. Uzatma çubuåu
Uzatma çubuåu çok dar yerlerde çalıßırken veya
saålanan yuvanın sıkıßtırılacak somuna ulaßamadıåı
yerlerde kullanıßlıdır.
UYARI
Uzatma çubuåu kullanılırken, sıkıßtırma torku normal
yuvaya göre biraz daha azdır. Bu yüzden, aynı torka
ulaßmak için aleti biraz daha uzun süreli kullanmak
gerekir.
3. Evrensel mafsal
Evrensel mafsal, yuva ile anahtar arasında bir açı olan
durumlarda veya çok dar bir yerde çalıßırken cıvata
darbelemek için kullanıßlıdır.
4. Köße ilavesi (Model EW-14R)
Bu ilaveyi yalnızca alet, somun veya cıvataya dik açıyla
uygulanacaåında kullanın.
Ósteåe baålı aksesuarlarda önceden bildirimde bulunulmadan
deåißiklik yapılabilir.
UYGULAMALAR
䡬 Çeßitli cins cıvata ve somunları sıkıßtırma ve gevßetme.
KULLANIM ÖNCESÓNDE
1. Güç kaynaåı
Kullanılan güç kaynaåının, ürünün üzerinde bulunan
plakada belirtilen güç gerekliliklerine uygun olduåundan
emin olun.
2. Açma/ Kapama anahtarı
Açma/ kapama anahtarının OFF konumunda olduåundan
emin olun. Açma/ kapama anahtarı ON konumundayken
aletin fißi prize takılırsa, alet derhal çalıßmaya baßlar
ve ciddi kazalar meydana gelebilir.
3. Uzatma kablosu
Çalıßma alanı güç kaynaåından uzakta olduåunda, yeterli
kalınlıkta ve belirtilen gücü kaldırabilen bir uzatma
kablosu kullanın. Uzatma kablosu olabildiåince kısa
tutulmalıdır.
4. Yan Kolun Sabitleßtirilmesi
Koruyucuya takılı olan yan kolun pozisyonunu, kol (saå
taraftaki vidadan) gevßetirerek deåßtirilebilir. Kolu
istenilen pozisyona çevirin ve vidayı sıkıca sıkıßtırarak
kolu sabitleyin.
5. Yuvanın Takılması
(1) Pim, O halka tipi (Íekil 1)
Sıkıßtırılacak veya gevßetilecek cıvataya uyan bir yuva
seçin. Yuvayı anahtarın üzerindeki örse takın ve pim
ve halka ile sabitleyin. Yuvayı sökerken ißlemi tersinden
yapın.
(2) Ótici tipi (Íekil 2)
Örsün kare kısmında bulunan iticiyi altıgen yuvadaki
delikle hizalayın. Ardından iticiyi itin ve altıgen yuvayı
örse takın. Óticinin deliåe tamamen girdiåinden emin
olun. Yuvayı sökerken ißlemi tersinden yapın.
NASIL KULLANILIR
1. Anahtarın ißletimi (Íekil 3)
Bu aletin üzerindeki anahtar, hem motor çalıßtırma
anahtarı hem de dönüß yönünü seçme anahtarı olarak
ißlev görür. Anahtar kolun üzerinde gösterilen “R”
pozisyonuna ayarlandıåında, cıvatayı sıkıßtırmak üzere
motor saat yönünde döner. Anahtar kolun üzerinde
gösterilen “L” pozisyonuna ayarlanır ise, motor cıvatayı
gevßetmek üzere saatin ters yönünde döner. Anahtar
bırakıldıåında ise motor durur.
34
Page 36

Türkçe
UYARI
Açma/ kapama anahtarını OFF konumuna getirdiåinizden
emin olun ve anahtarın dönüß yönünü deåißtirmeden
önce motorun tamamen durmasını bekleyin. Motor
dönerken yapılacak deåißtirm ißlemi, motorun yanmasına
sebep olur.
2. Cıvata sıkımı ve gevßetme
Ólk önce onaltılık (hex) sokete uygun bir cıvata veya
somun seçilmelidir. Sonra soketi örsün üzerine oturtun
ve onaltılık soketle sıkıßtırılacak olan somunu kavrayın.
Somun sıkma aletini somunla aynı hizada tutarken, güç
düåmesine basarak somunu birkaç saniye sıkıßtırın.
Eåer somun cıvatanın üzerinde gevßek oturuyorsa,
cıvata somunla birlikte dönebilir ve hatalı sıkılaßmaya
neden olabilir. Bu durumda, somunu sıkılaßtırmayı
durdurun ve tekrar baßlamadan önce cıvata baßını bir
anahtarla tutun veya kaymayı önlemek için elinizle
somunu cıvataya biraz sıkın.
ÇALIÍMAYLA ÓLGÓLÓ ÖNLEMLER
1. Hat voltajının teyidi (Íekil 4)
Kullanılabilir sıkıßtırma torku hat voltajına baålıdır. Düßük
hat voltajı, mevcut sıkıßtırma torkunu da düßürür.
Örneån, 220 V tipi bir darbe anahtarını 200 Voltluk bir
hatta kullanırsanız, mevcut sıkıßtırma torku %70 ile
%90 etki oranına düßer. Elektrik kablosunu uzattıåınızda,
mümkün olabildiånce kısa uzunlukta bir uzatma kablosu
kullanın. Hat voltajı düßükse ve de uzun bir uzatma
kablosuna ihtiyaç varsa, artırıcı bir transformatör
kullanılması gerekir. Hat voltajı ve sıkıßtırma torku
arasındaki ilißki ßekillerde gösterilmißtir.
2. Kesintisiz kullanım sırasında koruyucu kapaåa veya
muhafazaya dokunmayın
Kesintisiz vidalama ißlemi sırasında koruyucu kapak ve
mufaza ısınabilir. Bu yüzden bu aksamlara
dokunmamaya özen gösterin.
3. Darbe altındaki somuna uygun bir sıkıßtırma torkunda
çalıßın
Somun ve cıvatalar için optimum sıkıßtırma torku somun
veya cıvatanın malzemesi ve boyutuna göre farklılık
gösterir. Küçük bir somun için aßırı büyük bir sıkıßtırma
torkunun kullanılması somunu esnetebilir veya kırabilir.
Sıkıßtırma torku çalıßtırma süresiyle orantılı olarak artar.
Somun için doåru süreyi kullanın.
4. Somununa uyacak yuvanın seçimi
Sıkıßtırılacak somuna uygun olan bir yuva seçtiånizden
emin olun. Uygun olmayan bir yuvanın seçilmesi sadece
yetersiz sıkıßtırmaya deål aynı zamanda yuva ya da
cıvatada hasara da neden olacaktır. Yıpranmıß veya
deforme olmuß altıgen veya kare delikli bir yuva cıvata
veya örsü takmak için yeterli sıkıßtırma saålamayacaåından,
sıkıßtırma torkunda azalmaya neden olacaktır.
Yuva deliåinin yıpranmasına dikkat edin ve daha fazla
yıpranmadan deåißtirin.
Uygun somun ve yuva boyutları Tablo 1’de gösterilmißtir.
Yuva belirlemedeki sayısal deåier, altıgen deliåin
kenardan kenara olan uzaklıåını (S) belirtir.
5. Aleti tutma
Darbeli somun sıkma aletini iki elinizle hem yan koldan
hem de gövde kabzasından saålam bir ßekilde tutun.
Bu durumda anahtarı somunla hizalı tutun.
Anahtarı çok itmeniz gerekmez. Anahtarı, sadece geri
tepmeyi dengelemeye yetecek kuvvette tutun.
6. Sıkıßtırma torkunu teyit edin
Aßaåıdaki faktörler sıkıßtırma torkunun azalmasına
katkıda bulunur. Bu nedenle, gereken sıkıßtırma torkunu
iße baßlamadan önce birkaç somunu bir el anahtarıyla
sıkıßtırarak teyit edin. Sıkıßtırma torkunu etkileyen
faktörler aßaåıdaki gibidir.
(1) Hat Voltajı:
Hattaki voltaj düßtüåünde, sıkıßtırma torku da azalır
(Bkz. Íekil 4).
(2) Çalıßma süresi:
Çalıßma süresi arttıkça sıkıßtırma torku artar. Ancak,
alet çok uzun bir süre kullanılsa da sıkıßtırma torku belli
bir deåerin üzerine çıkmaz (Bkz. Íekil 4).
(3) Somunun çapı:
Sıkıßtırma torku Íekil 4’te gösterildiåi gibi somunun çapına
göre farklılık gösterir. Genel olarak daha büyük çaplı bir
somun için daha yüksek bir sıkıßtırma torku gerekir.
(4) Sıkıßtırma koßulları:
Aynı boyutta dißli somunlar kullanıldıåında bile sıkıßtırma
torku, tork oranına, somun sınıfı ve uzunluåuna göre
farklılık gösterir. Sıkıßtırma torku ayrıca, somunların
sıkıßtırılacaåı metal yüzeyinin durumuna göre de farklılık
gösterir.
(5) Ósteåe baålı parçaların kullanılması:
Bir uzatma çubuåu, evrensel mafsal veya uzun bir yuva
kullanıldıåında sıkıßtırma torku biraz azalır.
(6) Yuvanın açıklıåı:
Yıpranmıß veya deforme olmuß altıgen veya kare delikli
bir yuva, somun veya örs arasında yeterli sıkıßma
saålamayacaåından sıkıßtırma torkunda azalmaya neden
olacaktır.
Somuna uygun olmayan bir yuvanın kullanılması yetersiz
sıkıßtırma torkuna neden olacaktır. Uygun yuva ve
somun boyutları Tablo 1’de gösterilmißtir.
BAKIM VE ÓNCELEME
1. Yuvanın incelenmesi
Yıpranmıß veya deforme olmuß altıgen veya kare delikli
bir yuva, somun veya örs arasında yeterli sıkıßma
saålamayacaåından sıkıßtırma torkunda azalmaya neden
olacaktır. Yuva deliklerinin yıpranmasını düzenli olarak
kontrol edin ve gerekirse yenisiyle deåißtirin.
2. Montaj vidalarının incelenmesi
Tüm montaj vidalarını düzenli olarak inceleyin ve saålam
ßekilde sıkılı olduåundan emin olun. Gevßeyen vidaları
derhal sıkın. Gevßemiß vidalar ciddi tehlikelere yol açabilir.
3. Motorun incelenmesi
Motor biriminin sargıları, bu aåır iß aletinin “kalbidir”.
Sargının hasar görmediåinden ve/veya yaå ya da su
ile ıslanmadıåından emin olun.
4. Karbon fırçaların gözden geçirilmesi (Íekil 5)
Gvenliinizin sreklilii iin ve elektrik ßokuna karßı koruma
saålamak amacıyla bu takım üzerindeki karbon fırçaların
gözden geçirilmesi ve deåißtirilmesi YALNIZCA Hitachi
yetkili Servis Merkezi tarafından yapılmalıdır.
5. Güç kablosunun deåißimi
Eåer cihaz˙n güç kablosu hasarl˙ ise, güç kablosu
deåißimi için cihaz Hitachi Yetkili Servis Merkezine geri
gönderilmelidir.
6. Servis parçaları listesi
A: Parça no.
B: Kod no.
C: Kullanılan sayı
D: Açıklamalar
35
Page 37

Türkçe
DÓKKAT
Hitachi Güç Takımlarının onarımı, modifikasyonu ve
gözden geçirilmesi Hitachi yetkili Servis Merkezi
tarafından yapılmalıdır.
Hitachi yetkili Servis Merkezine tamir ya da bakım
amacıyla baßvurulduåunda Parça Listesinin takım ile
birlikte verilmesi faydalı olacaktır.
Güç takımlarının çalıßtırılması ve bakımlarının yapılması
esnasında her ülke için belirtilen güvenlik düzenlemelerine
ve standartlarına uyulması gerekmektedir.
DEÅÍÓKLÓKLER
Hitachi Aåır Óß Aletleri en son teknolojik ilerlemelere
uygun olarak sürekli deåißtirilmekte ve gelißtirilmektedir.
Dolaısıyla, bazı kısımlarda (örneåin kod numaraları ve/
veya tasarım gibi) önceden bildirimde bulunulmadan
deåißiklik yapılabilir.
NOT
HITACHI’nin süregelen araßtırma ve gelißtirme programına
baålı olarak burada belirtilen teknik özelliklerde önceden
bildirimde bulunulmadan deåißiklik yapılabilir.
Havadan yayılan gürültü ve titreßimle ilgili bilgiler
Ölçülen deåerlerin EN60745 ve ISO 4871’e uygun olduåu
tespit edilmißtir.
Tipik A aåırlıklı ses basınç seviyesi: 98 dB (A)
Tipik A aåırlıklı ses gücü seviyesi: 111 dB (A)
Belirsiz KpA: 3dB (A)
Kulak koruyucusu kullanın.
Tipik aåırlıklı ortalama karekök ivme deåeri: 4,75 m/s
2
36
Page 38

PyccÍËÈ
OÅôàE èPABàãA èO TEXHàKE ÅEÂOèACHOCTà
èPEÑìèPEÜÑEHàE!
èpoäÚËÚe pyÍoÇoÀcÚÇo Ôo íÍcÔÎyaÚaáËË
HeÇêÔoÎÌeÌËe Çcex ÔpËÇeÀeÌÌêx ÌËÊe ÔoÎoÊeÌËÈ
ÀaÌÌoÖo pyÍoÇoÀcÚÇa ÏoÊeÚ ÔpËÇecÚË Í ÔopaÊeÌËï
íÎeÍÚpËäecÍËÏ ÚoÍoÏ, ÔoÊapy Ë/ËÎË Í cepëeÁÌoÈ ÚpaÇÏe.
TepÏËÌ "íÎeÍÚpoËÌcÚpyÏeÌÚ" Ç ÍoÌÚeÍcÚe Çcex
ÔpËÇeÀeÌÌêx ÌËÊe Ïep ÔpeÀocÚopoÊÌocÚË oÚÌocËÚcÓ
Í íÍcÔÎyaÚËpyeÏoÏy BaÏË íÎeÍÚpoËÌcÚpyÏeÌÚy c
ÔËÚaÌËeÏ oÚ ceÚeÇoÈ poÁeÚÍË (c ceÚeÇêÏ åÌypoÏ) ËÎË
íÎeÍÚpoËÌcÚpyÏeÌÚy c ÔËÚaÌËeÏ oÚ aÍÍyÏyÎÓÚopÌoÈ
ÄaÚapeË (ÄecÔpoÇoÀÌoÏy).
COXPAHàTE ÑAHHOE PìKOBOÑCTBO
1) PaÄoäee ÏecÚo
a) èoÀÀepÊËÇaÈÚe äËcÚoÚy Ë xopoåee ocÇeçeÌËe
Ìa paÄoäeÏ ÏecÚe.
ÅecÔopÓÀoÍ Ë ÔÎoxoe ocÇeçeÌËe Ìa paÄoäËx
ÏecÚax ÔpËÇoÀËÚ Í ÌecäacÚÌêÏ cÎyäaÓÏ.
b) He ËcÔoÎëÁyÈÚe íÎeÍÚpoËÌcÚpyÏeÌÚê Ço
ÇÁpêÇooÔacÌêx oÍpyÊaïçËx ycÎoÇËÓx,
ÌaÔpËÏep, Ç ÌeÔocpeÀcÚÇeÌÌoÈ ÄÎËÁocÚË oÚ
oÖÌeoÔacÌêx ÊËÀÍocÚeÈ, ÖopïäËx ÖaÁoÇ ËÎË
ÎeÖÍoÇocÔÎaÏeÌÓïçeÈcÓ ÔêÎË.
ùÎeÍÚpoËÌcÚpyÏeÌÚê ÔopoÊÀaïÚ ËcÍpê, ÍoÚopêe
ÏoÖyÚ ÇocÔÎaÏeÌËÚë ÔêÎë ËÎË ËcÔapeÌËÓ.
c) ÑepÊËÚe ÀeÚeÈ Ë ÌaÄÎïÀaÚeÎeÈ Ìa ÄeÁoÔacÌoÏ
paccÚoÓÌËË Ço ÇpeÏÓ íÍcÔÎyaÚaáËË
íÎeÍÚpoËÌcÚpyÏeÌÚa.
OÚÇÎeäeÌËe ÇÌËÏaÌËÓ ÏoÊeÚ cÚaÚë ÀÎÓ Bac
ÔpËäËÌoÈ ÔoÚepË yÔpaÇÎeÌËÓ.
2) ùÎeÍÚpoÄeÁoÔacÌocÚë
a) тЪeФceОлМкe ЗЛОНЛ нОeНЪpoЛМcЪpyПeМЪoЗ
АoОКМк cooЪЗeЪcЪЗoЗaЪл ceЪeЗoИ poБeЪНe.
HЛНoЦАa Мe ПoАЛЩЛбЛpyИЪe еЪeФceОлМyп
ЗЛОНy МЛНoЛП oДpaБoП.
He ЛcФoОлБyИЪe МЛНaНЛe aАaФЪepМкe
ФepexoАМЛНЛ c БaБeПОeММкПЛ (БaПНМyЪкПЛ Мa
БeПОп) нОeНЪpoЛМcЪpyПeМЪaПЛ.
HeПoАЛЩЛбЛpoЗaММкe еЪeФceОлМкe ЗЛОНЛ Л
cooЪЗeЪcЪЗyпзЛe ЛП ceЪeЗкe poБeЪНЛ yПeМлеaЪ
oФacМocЪл ФopaКeМЛУ нОeНЪpЛдecНЛП ЪoНoП.
b) He ÔpËÍacaÈÚecë ÚeÎoÏ Í ÁaÁeÏÎeÌÌêÏ
ФoЗepxМocЪУП, МaФpЛПep, Н ЪpyДoФpoЗoАaП,
paАЛaЪopaП, НyxoММкП ФОЛЪaП Л
xoОoАЛОлМЛНaП.
EcОЛ Baеe ЪeОo coФpЛНocМeЪcУ c БaБeПОeММкПЛ
ФoЗepxМocЪУПЛ, ЗoБpacЪeЪ oФacМocЪл ФopaКeМЛУ
нОeНЪpЛдecНЛП ЪoНoП.
c) He ÔoÀÇepÖaÈÚe íÎeÍÚpoËÌcÚpyÏeÌÚê
ÇoÁÀeÈcÚÇËï ÀoÊÀÓ ËÎË ÇÎaÖË.
èpË ÔoÔaÀaÌËË ÇoÀê Ç íÎeÍÚpoËÌcÚpyÏeÌÚ
ÇoÁpacÚeÚ oÔacÌocÚë ÔopaÊeÌËÓ íÎeÍÚpËäecÍËÏ
ÚoÍoÏ.
d) иpaЗЛОлМo oДpaзaИЪecл co еМypoП. HЛНoЦАa Мe
ФepeМocЛЪe нОeНЪpoЛМcЪpyПeМЪ, ЗБУЗеЛcл Бa
еМyp, Мe ЪУМЛЪe Бa еМyp, Л Мe АepЦaИЪe Бa еМyp
c бeОлп oЪcoeАЛМeМЛУ нОeНЪpoЛМcЪpyПeМЪa oЪ
ceЪeЗoИ poБeЪНЛ.
PacФoОaЦaИЪe еМyp ФoАaОлеe oЪ ЛcЪoдМЛНoЗ
ЪeФОa, МeЩЪeФpoАyНЪoЗ, ФpeАПeЪoЗ c ocЪpкПЛ
НpoПНaПЛ Л АЗЛКyзЛxcУ АeЪaОeИ.
иoЗpeКАeММкe ЛОЛ БaФyЪaММкe еМypк
yЗeОЛдЛЗaпЪ oФacМocЪл ФopaКeМЛУ нОeНЪpЛдecНЛП
ЪoНoП.
3) ãËäÌaÓ ÄeÁoÔacÌocÚë
4) ùÍcÔÎyaÚaáËÓ Ë oÄcÎyÊËÇaÌËe
e) èpË íÍcÔÎyaÚaáËË íÎeÍÚpoËÌcÚpyÏeÌÚa ÇÌe
ФoПeзeМЛИ, ЛcФoОлБyИЪe yАОЛМЛЪeОлМкИ
еМyp, ФpeАМaБМaдeММкИ АОУ ЛcФoОлБoЗaМЛУ
ЗМe ФoПeзeМЛУ.
аcФoОлБoЗaМЛe еМypa, ФpeАМaБМaдeММoЦo АОУ
paДoЪк ЗМe ФoПeзeМЛИ, yПeМлеЛЪ oФacМocЪл
ФopaКeМЛУ нОeНЪpЛдecНЛП ЪoНoП.
a) ÅyÀëÚe ÖoÚoÇê Í ÌeoÊËÀaÌÌêÏ cËÚyaáËÓÏ,
ЗМЛПaЪeОлМo cОeАЛЪe Бa cЗoЛПЛ АeИcЪЗЛУПЛ
Л pyНoЗoАcЪЗyИЪecл БАpaЗкП cПкcОoП ФpЛ
нНcФОyaЪaбЛЛ нОeНЪpoЛМcЪpyПeМЪa.
He ЛcФoОлБyИЪe нОeНЪpoЛМcЪpyПeМЪ, НoЦАa Bк
ycЪaОЛ ЛОЛ МaxoАЛЪecл ФoА ЗОЛУМЛeП
МapНoЪЛНoЗ, aОНoЦoОУ ЛОЛ ОeНapcЪЗeММкx
ФpeФapaЪoЗ.
MÖÌoÇeÌÌaÓ ÔoÚepÓ ÇÌËÏaÌËÓ Ço ÇpeÏÓ
íÍcÔÎyaÚaáËË íÎeÍÚpoËÌcÚpyÏeÌÚoÇ ÏoÊeÚ
ÔpËÇecÚË Í cepëeÁÌoÈ ÚpaÇÏe.
b) àcÔoÎëÁyÈÚe ÁaçËÚÌoe cÌapÓÊeÌËe. BceÖÀa
ÌaÀeÇaÈÚe cpeÀcÚÇo ÁaçËÚê ÖÎaÁ.
ВaзЛЪМoe cМapУКeМЛe, МaФpЛПep, ФpoЪЛЗoФкОeЗoИ
pecФЛpaЪop, БaзЛЪМaУ oДyЗл c МecНoОлБНoИ
ФoАoеЗoИ, БaзЛЪМкИ еОeП-НacНa ЛОЛ cpeАcЪЗa
БaзЛЪк opЦaМoЗ cОyxa, ЛcФoОлБyeПкe АОУ
cooЪЗeЪcЪЗyпзЛx ycОoЗЛИ, yПeМлеaЪ ЪpaЗПк.
c) аБДeЦaИЪe МeФpeАМaПepeММoЦo ЗНОпдeМЛУ
АЗЛЦaЪeОУ. мДeАЛЪecл З ЪoП, дЪo ЗкНОпдaЪeОл
МaxoАЛЪcУ З ФoОoКeМЛЛ ЗкНОпдeМЛУ ФepeА
ФoАcoeАЛМeМЛeП Н ceЪeЗoИ poБeЪНe.
иepeМocНa нОeНЪpoЛМcЪpyПeМЪoЗ, НoЦАa Bк
АepКЛЪe ФaОeб Мa ЗкНОпдaЪeОe, ЛОЛ
ФoАcoeАЛМeМЛe нОeНЪpoЛМcЪpyПeМЪoЗ Н ceЪeЗoИ
poБeЪНe, НoЦАa ЗкНОпдaЪeОл ДyАeЪ МaxoАЛЪлcУ
З ФoОoКeМЛЛ ЗНОпдeМЛУ, ФpЛЗoАЛЪ Н МecдacЪМкП
cОyдaУП.
d) CМЛПЛЪe Зce peЦyОЛpoЗoдМкe ЛОЛ ЦaeдМкe
НОпдЛ ФepeА ЗНОпдeМЛeП нОeНЪpoЛМcЪpyПeМЪa.
ÉaeäÌêÈ ËÎË peÖyÎËpoÇoäÌêÈ ÍÎïä, ocÚaÇÎeÌÌêÈ
ÔpËÍpeÔÎeÌÌêÏ Í ÇpaçaïçeÈcÓ ÀeÚaÎË
íÎeÍÚpoËÌcÚpyÏeÌÚa ÏoÊeÚ ÔpËÇecÚË Í
ÔoÎyäeÌËï ÎËäÌoÈ ÚpaÇÏê.
e) He ÚepÓÈÚe ycÚoÈäËÇocÚë. Bce ÇpeÏÓ ËÏeÈÚe
ÌaÀeÊÌyï ÚoäÍy oÔopê Ë coxpaÌÓÈÚe
paÇÌoÇecËe.
щЪo ФoПoКeЪ Оyдеe yФpaЗОУЪл
нОeНЪpoЛМcЪpyПeМЪoП З МeФpeАЗЛАeММкx
cЛЪyaбЛУx.
f) OÀeÇaÈÚecë ÌaÀÎeÊaçËÏ oÄpaÁoÏ. He
ÌaÀeÇaÈÚe ÔpocÚopÌyï oÀeÊÀy ËÎË ïÇeÎËpÌêe
ËÁÀeÎËÓ. ÑepÊËÚe ÇoÎocê, oÀeÊÀy Ë ÔepäaÚÍË
ÍaÍ ÏoÊÌo ÀaÎëåe oÚ ÀÇËÊyçËxcÓ äacÚeÈ.
иpocЪopМaУ oАeКАa, пЗeОЛpМкe ЛБАeОЛУ ЛОЛ
АОЛММкe ЗoОocк ПoЦyЪ ФoФacЪл З АЗЛКyзЛecУ
дacЪЛ.
g) EcÎË ÔpeÀycÏoÚpeÌê ycÚpoÈcÚÇa ÀÎÓ
ÔpËcoeÀËÌeÌËÓ ÔpËcÔocoÄÎeÌËÈ ÀÎÓ oÚÇoÀa Ë
cÄopa ÔêÎË, yÄeÀËÚecë Ç ÚoÏ, äÚo oÌË
ÔpËcoeÀËÌeÌê Ë ËcÔoÎëÁyïÚcÓ ÌaÀÎeÊaçËÏ
oÄpaÁoÏ.
аcФoОлБoЗaМЛe АaММкx ycЪpoИcЪЗ ПoКeЪ
yПeМлеЛЪл oФacМocЪЛ, cЗУБaММкe c ФкОлп.
íÎeÍÚpoËÌcÚpyÏeÌÚoÇ
37
Page 39

PyccÍËÈ
a) He ÔepeÖpyÊaÈÚe íÎeÍÚpoËÌcÚpyÏeÌÚ.
àcÔoÎëÁyÈÚe ÌaÀÎeÊaçËÈ ÀÎÓ BaåeÖo
ÔpËÏeÌeÌËÓ íÎeÍÚpoËÌcÚpyÏeÌÚ.
HaАОeКaзЛИ нОeНЪpoЛМcЪpyПeМЪ ДyАeЪ
ЗкФoОМУЪл paДoЪy Оyдеe Л МaАeКМee З ЪoП
peКЛПe paДoЪк, Мa НoЪopкИ oМ paccдЛЪaМ.
b) He ËcÔoÎëÁyÈÚe íÎeÍÚpoËÌcÚpyÏeÌÚ c
МeЛcФpaЗМкП ЗкНОпдaЪeОeП, ecОЛ c eЦo
ФoПoзлп МeОлБУ ДyАeЪ ЗНОпдЛЪл Л ЗкНОпдЛЪл
нОeНЪpoЛМcЪpyПeМЪ.
KaКАкИ нОeНЪpoЛМcЪpyПeМЪ, НoЪopкП МeОлБУ
yФpaЗОУЪл c ФoПoзлп ЗкНОпдaЪeОУ, ДyАeЪ
ФpeАcЪaЗОУЪл oФacМocЪл Л eЦo ДyАeЪ МeoДxoАЛПo
oЪpeПoМЪЛpoЗaЪл.
c) OЪcoeАЛМЛЪe еЪeФceОлМyп ЗЛОНy oЪ ЛcЪoдМЛНa
ÔËÚaÌËÓ ÔepeÀ ÌaäaÎoÏ ÇêÔoÎÌeÌËÓ ÍaÍoÈ-ÎËÄo
ËÁ peÖyÎËpoÇoÍ, ÔepeÀ cÏeÌoÈ ÔpËÌaÀÎeÊÌocÚeÈ
ËÎË xpaÌeÌËeÏ íÎeÍÚpoËÌcÚpyÏeÌÚoÇ.
TaНЛe ФpoЩЛОaНЪЛдecНЛe Пepк ДeБoФacМocЪЛ
yПeМлеaЪ oФacМocЪл МeФpeАМaПepeММoЦo
ЗНОпдeМЛУ АЗЛЦaЪeОУ нОeНЪpoЛМcЪpyПeМЪa.
d) XpaÌËÚe ÌeËcÔoÎëÁyeÏêe íÎeÍÚpoËÌcÚpyÏeÌÚê
З МeАocЪyФМoП АОУ АeЪeИ ПecЪe, Л Мe
paБpeеaИЪe ОпАУП, Мe БМaпзЛП НaН
oДpaзaЪлcУ c нОeНЪpoЛМcЪpyПeМЪoП ЛОЛ Мe
ЛБyдЛЗеЛП АaММoe pyНoЗoАcЪЗo, paДoЪaЪл c
нОeНЪpoЛМcЪpyПeМЪoП.
щОeНЪpoЛМcЪpyПeМЪк ФpeАcЪaЗОУпЪ oФacМocЪл
З pyНax МeФoАЦoЪoЗОeММкx ФoОлБoЗaЪeОeИ.
e) CoÀepÊËÚe íÎeÍÚpoËÌcÚpyÏeÌÚê Ç
ЛcФpaЗМocЪЛ. иpoЗepлЪe, МeЪ ОЛ МecoocМocЪЛ
ЛОЛ БaeАaМЛУ АЗЛКyзЛxcУ дacЪeИ,
ФoЗpeКАeМЛУ АeЪaОeИ ЛОЛ НaНoЦo-ОЛДo АpyЦoЦo
oДcЪoУЪeОлcЪЗa, НoЪopoe ПoКeЪ ФoЗОЛУЪл Мa
ЩyМНбЛoМЛpoЗaМЛe нОeНЪpoЛМcЪpyПeМЪoЗ.
иpЛ МaОЛдЛЛ ФoЗpeКАeМЛУ, oЪpeПoМЪЛpyИЪe
нОeНЪpoЛМcЪpyПeМЪ ФepeА eЦo нНcФОyaЪaбЛeИ.
ÅoÎëåoe ÍoÎËäecÚÇo ÌecäacÚÌêx cÎyäaeÇ cÇÓÁaÌo
c ÔÎoxËÏ oÄcÎyÊËÇaÌËeÏ íÎeÍÚpoËÌcÚpyÏeÌÚoÇ.
f) CoÀepÊËÚe peÊyçËe ËÌcÚpyÏeÌÚê ocÚpo
БaЪoдeММкПЛ Л дЛcЪкПЛ.
CoÀepÊaçËecÓ Ç ËcÔpaÇÌocÚË ÌaÀÎeÊaçËÏ
oÄpaÁoÏ peÊyçËe ËÌcÚpyÏeÌÚê c ocÚpêÏË
peÊyçËÏË ÍpoÏÍaÏË ÄyÀyÚ ÏeÌëåe ÁaeÀaÚë, Ë
ÄyÀyÚ ÎeÖäe Ç yÔpaÇÎeÌËË.
g) àcÔoÎëÁyÈÚe íÎeÍÚpoËÌcÚpyÏeÌÚ,
ÔpËÌaÀÎeÊÌocÚË, ÌacaÀÍË Ë Ú.Ô., Ç
cooÚÇeÚcÚÇËË c ÀaÌÌêÏ pyÍoÇoÀcÚÇoÏ Ë
oÔpeÀeÎeÌÌêÏ ÚËÔoÏ íÎeÍÚpoËÌcÚpyÏeÌÚa
ÀÎÓ ÇêÔoÎÌeÌËÓ paÄoÚê Ôo eÖo ÔpÓÏoÏy
ÌaÁÌaäeÌËï, ÔpËÌËÏaÓ Ço ÇÌËÏaÌËe ycÎoÇËÓ
Ë oÄéeÏ ÇêÔoÎÌÓeÏoÈ paÄoÚê.
àcÔoÎëÁoÇaÌËe íÎeÍÚpoËÌcÚpyÏeÌÚa ÀÎÓ
ÇêÔoÎÌeÌËÓ paÄoÚ Ìe Ôo ÔpÓÏoÏy ÌaÁÌaäeÌËï
ÏoÊeÚ ÔpËÇecÚË Í oÔacÌoÈ cËÚyaáËË.
5) OÄcÎyÊËÇaÌËe
a) OÄcÎyÊËÇaÌËe BaåeÖo íÎeÍÚpoËÌcÚpyÏeÌÚa
АoОКМo ЗкФoОМУЪлcУ НЗaОЛЩЛбЛpoЗaММкП
ФpeАcЪaЗЛЪeОeП peПoМЪМoИ cОyКДк c
ЛcФoОлБoЗaМЛeП ЪoОлНo ЛАeМЪЛдМкx БaФacМкx
дacЪeИ.
ùÚo oÄecÔeäËÚ coxpaÌÌocÚë Ë ÄeÁoÔacÌocÚë
íÎeÍÚpoËÌcÚpyÏeÌÚa.
MEPA èPEÑOCTOPOÜHOCTà
ÑepÊËÚe ÔoÀaÎëåe oÚ ÀeÚeÈ Ë cÎaÄêx ÎïÀeÈ.
EcÎË ËÌcÚpyÏeÌÚê Ìe ËcÔoÎëÁyïÚcÓ, Ëx cÎeÀyeÚ
xpaÌËÚë Ç ÌeÀocÚyÔÌoÏ ÀÎÓ ÀeÚeÈ Ë cÎaÄêx ÎïÀeÈ
ÏecÚe.
MEPõ èPEÑOCTOPOÜHOCTà èPà
ùKCèãìATAñàà ìÑAPHOÉO ÉAâKOBEPTA
1. èpË íÍcÔÎyaÚaáËË ËÌcÚpyÏeÌÚa Ìa ÇoÁÇêåeÌËË Ìe
ÀoÔycÍaÈÚe ÚoÖo, äÚoÄê ÍÚo-ÎËÄo ÌaxoÀËÎcÓ ÇÌËÁy.
2. аcФoОлБyИЪe МayеМЛНЛ ФpЛ нНcФОyaЪaбЛЛ З ЪeдeМЛe
АОЛЪeОлМoЦo ЗpeПeМЛ.
3. èpË ÌeoÄxoÀËÏocÚË ËÁÏeÌËÚë ÌaÔpaÇÎeÌËe
ÇpaçeÌËÓ ÔoÇopaäËÇaÈÚe ÔepeÍÎïäaÚeÎë
ÌaÔpaÇÎeÌËÓ ÚoÎëÍo ÔocÎe ÔoÎÌoÈ ocÚaÌoÇÍË
ÀÇËÖaÚeÎÓ.
4. аcФoОлБyИЪe ФoЗкеaпзЛИ ЪpaМcЩopПaЪop ФpЛ
paДoЪe c ФoАНОпдeМЛeП АОЛММoЦo yАОЛМЛЪeОлМoЦo
НaДeОУ.
5. OФpeАeОЛЪe НpyЪУзЛИ ПoПeМЪ ФpЛ ФoПoзЛ
ЪapЛpoЗaММoЦo НОпдa АОУ ycЪaМoЗНЛ ФpaЗЛОлМoЦo
НpyЪУзeЦo ПoПeМЪa ЦaИНoЗepЪa ФepeА
нНcФОyaЪaбЛeИ.
6. CoДepЛЪe Л МaАeКМo БaНpeФЛЪe ЦМeБАo Мa yАapМoП
ЦaИНoЗepЪe c ФoПoзлп еЪЛЩЪa Л НoОлбa.
7. èpoÇepëÚe ÖÌeÁÀo Ìa ÌaÎËäËe ÚpeçËÌ.
8. BceЦАa НpeФНo АepКЛЪe pyНoУЪНy Мa НopФyce
yАapМoЦo ЦaИНoЗepЪa Л eЦo ДoНoЗyп pyНoУЪНy. B
ФpoЪЛЗМoП cОyдae cЛОa oЪАaдЛ ПoКeЪ ФpЛЗecЪЛ Н
МeЪoдМкП Л АaКe oФacМкП АeИcЪЗЛУП.
TEXHàóECKàE XAPAKTEPàCTàKà
HaÔpÓÊeÌËe (Ôo peÖËoÌaÏ)* (110 B, 115 B, 120 B, 127 B, 220 B, 230 B, 240 B)
èoÚpeÄÎÓeÏaÓ ÏoçÌocÚë* 480 BÚ
óËcÎo oÄopoÚoÇ xoÎocÚoÖo xoÀa 1900 ÏËÌ
èpoËÁÇoÀËÚeÎëÌocÚë (paÁÏep ÄoÎÚoÇ)
KpyЪУзЛИ ПoПeМЪ** MaНcЛПaОлМкИ 36,7 НЦ-П
мАap ФoА yЦОoП 12,7 ÏÏ
Bec (ÄeÁ çÌypa) 2,9 ÍÖ
* иpoЗepлЪe ФacФopЪМyп ЪaДОЛдНy Мa ЛБАeОЛЛ, ЪaН НaН oМa ПeМУeЪcУ З БaЗЛcЛПocЪЛ oЪ peЦЛoМa.
** ВaЪУЦЛЗaМЛe ДoОЪa ФpЛ paДoЪe ДeБ yАОЛМЛЪeОлМoЦo еМypa ФpЛ МoПЛМaОлМoП МaФpУКeМЛЛ.
38
M12 – M16 (BêcoÍoÔpoäÌêÈ cÚÓÊÌoÈ ÄoÎÚ)
M12 – M22 (OÄêÍÌoÇeÌÌêÈ ÄoÎÚ)
–1
Page 40

PyccÍËÈ
S
D
B
E
L
CTAHÑAPTHõE èPàHAÑãEÜHOCTà
(1) ÅoÍoÇaÓ pyÍoÓÚÍa .................................................... 1
(2) óeÏoÀaÌ ..................................................................... 1
KoÏÔÎeÍÚ cÚaÌÀapÚÌêx ÔpËÌaÀÎeÊÌocÚeÈ ÏoÊeÚ
ÄêÚë ËÁÏeÌeÌ ÄeÁ yÇeÀoÏÎeÌËÓ.
ÑOèOãHàTEãúHõE èPàHAÑãEÜHOCTà
(ÔpËoÄpeÚaïÚcÓ oÚÀeÎëÌo)
1. PaÁÌoÇËÀÌocÚË ÖÌeÁÀ
XoЪУ yАapМкИ ЦaИНoЗepЪ ЩЛpПк Hitachi
ФocЪaЗОУeЪcУ ЪoОлНo c oАМЛП cЪaМАapЪМкП ЦМeБАoП,
ЛПeeЪcУ АocЪaЪoдМoe НoОЛдecЪЗo paБМoЗЛАМocЪeИ
ЦМeБА АОУ ЪoЦo, дЪoДк oДecФeдЛЪл БaЪУЦЛЗaМЛe
ДoОЪoЗ paБОЛдМкx ЪЛФoЗ Л paБПepoЗ c МeoДxoАЛПкП
yАapМкП ЗoБАeИcЪЗЛeП.
TaÄÎËáa 1 B=12,7ÏÏ
HaËÏeÌoÇaÌËe ÖÌeÁÀa
òecÚËÖpaÌÌoe ÖÌeÁÀo
12 12 20 34 52
13 13 21,5 34 52
14 14 22 34 52
17 17 28 15 32 17 25 34 52
19 19 28 17 34 19 28 34 52
21 21 32 19 36 21 31 34 52
22 22 35 24 40 22 32,5 34 52
23 23 36 25 40 23 33 34 52
24 24 38 25 40 24 34 34 52
26 26 38 25 40 26 38 57 75
27 27 42 24 50 27 40 57 75
30 30 42 34 50 30 42 57 75
SDELSDEL
OÄêÍÌoÇeÌÌoe ÖÌeÁÀo СОЛММoe ЦМeБАo
PaÁÏep (ÏÏ) PaÁÏep (ÏÏ)
2. мАОЛМЛЪeОлМaУ МaАcЪaЗНa
мАОЛМЛЪeОлМaУ МaАcЪaЗНa ФpeАМaБМaдeМa АОУ
yАoДcЪЗa ФpЛ paДoЪe З ycОoЗЛУx oдeМл
oЦpaМЛдeММoЦo ФpocЪpaМcЪЗa ЛОЛ, НoЦАa
ФpeАycПoЪpeММoe ЦМeБАo Мe АocЪaeЪ Аo ДoОЪa,
НoЪopкИ АoОКeМ ДкЪл БaЪУМyЪ.
OCTOPOÜHO
иpЛ ЛcФoОлБoЗaМЛЛ yАОЛМЛЪeОлМoИ МaАcЪaЗНЛ
НpyЪУзЛИ ПoПeМЪ ДyАeЪ МeПМoЦo ПeМлеe Фo
cpaЗМeМЛп c НpyЪУзЛП ПoПeМЪoП, НoЪopкИ
oДecФeдЛЗaeЪcУ ФpЛ ФoПoзЛ oДкНМoЗeММoЦo ЦМeБАa.
TaНЛП oДpaБoП, ДyАeЪ МeoДxoАЛПo ЛcФoОлБoЗaЪл
4. ìÖÎoÇoe ÔpËcÔocoÄÎeÌËe (MoÀeÎë EW-14R)
àcÔoÎëÁyÈÚe ÀaÌÌoe ÔpËcÔocoÄÎeÌËe ÚoÎëÍo Ç ÚoÏ
cÎyäae, ecÎË ÏaåËÌa ycÚaÌaÇÎËÇaeÚcÓ ÔoÀ ÔpÓÏêÏ
yÖÎoÏ Í ÖaÈÍe ËÎË ÄoÎÚy.
ËÌcÚpyÏeÌÚ ÌecÍoÎëÍo ÀoÎëåe ÀÎÓ ÔoÎyäeÌËÓ ÚaÍoÖo
Êe caÏoÖo ÍpyÚÓçeÖo ÏoÏeÌÚa.
3. мМЛЗepcaОлМкИ еapМЛp
мМЛЗepcaОлМкИ еapМЛp ФpeАМaБМaдeМ АОУ yАoДcЪЗa
yАapМoЦo ЗoБАeИcЪЗЛУ Мa ЦaИНy, НoЦАa ПeКАy
ЦМeБАoП Л ЦaeдМкП НОпдoП ЛПeeЪcУ yЦoО, ЛОЛ ФpЛ
paДoЪe З oдeМл yБНoП ФpocЪpaМcЪЗe.
KoÏÔÎeÍÚ cÚaÌÀapÚÌêx ÔpËÌaÀÎeÊÌocÚeÈ ÏoÊeÚ
ÄêÚë ËÁÏeÌeÌ ÄeÁ yÇeÀoÏÎeÌËÓ.
OÅãACTà èPàMEHEHàü
䡬 ВaЪУЦЛЗaМЛe Л ocОaДОeМЛe paБОЛдМкx ЗЛАoЗ ДoОЪoЗ
Ë ÖaeÍ.
39
Page 41

PyccÍËÈ
èEPEÑ HAóAãOM PAÅOTõ
1. àcÚoäÌËÍ íÎeÍÚpoÔËÚaÌËÓ
иpocОeАЛЪe Бa ЪeП, дЪoДк ЛcФoОлБyeПкИ ЛcЪoдМЛН
нОeНЪpoФЛЪaМЛУ cooЪЗeЪcЪЗoЗaО ЪpeДoЗaМЛУП Н
ЛcЪoдМЛНy нОeНЪpoФЛЪaМЛУ, yНaБaММкП Мa ЪЛФoЗoИ
ЪaДОЛдНe ЛБАeОЛУ.
2. èepeÍÎïäaÚeÎë ''BÍÎ./ BêÍÎ.''
ìÄeÀËÚecë Ç ÚoÏ, äÚo ÔepeÍÎïäaÚeÎë ÌaxoÀËÚcÓ Ç
ÔoÎoÊeÌËË ''BêÍÎ.''. EcÎË Çê ÇcÚaÇÎÓeÚe åÚeÔceÎë
Ç poÁeÚÍy, a ÔepeÍÎïäaÚeÎë ÌaxoÀËÚcÓ Ç ÔoÎoÊeÌËË
''BÍÎ.'', ËÌcÚpyÏeÌÚ ÌeÏeÀÎeÌÌo ÁapaÄoÚaeÚ, äÚo
ÏoÊeÚ cÚaÚë ÔpËäËÌoÈ cepëÕÁÌoÈ ÚpaÇÏê.
3. мАОЛМЛЪeОл
KoЦАa paДoдaУ ФОoзaАНa yАaОeМa oЪ ЛcЪoдМЛНa
нОeНЪpoФЛЪaМЛУ, ФoОлБyИЪecл yАОЛМЛЪeОeП.
мАОЛМЛЪeОл АoОКeМ ЛПeЪл ЪpeДyeПyп ФОoзaАл
ФoФepeдМoЦo ceдeМЛУ Л oДecФeдЛЗaЪл paДoЪy
ЛМcЪpyПeМЪa БaАaММoИ ПoзМocЪЛ. PaБПaЪкЗaИЪe
yАОЛМЛЪeОл ЪoОлНo Мa peaОлМo МeoДxoАЛПyп АОУ
АaММoЦo НoМНpeЪМoЦo ФpЛПeМeМЛУ АОЛМy.
4. ìcÚaÌoÇÍa ÄoÍoÇoÈ pyÍoÓÚÍË
иoОoКeМЛe ДoНoЗoИ pyНoУЪНЛ, ФpЛНpeФОeММoИ Н
НopФycy yАapМoЦo ЦaИНoЗepЪa, ПoКМo ЛБПeМУЪл ФyЪeП
ЗкЗЛМдЛЗaМЛУ pyНoУЪНЛ. (иpaЗocЪopoММУУ peБлДa)
иoЗepМЛЪe pyНoУЪНy Л ycЪaМoЗЛЪe З МyКМoe АОУ
paДoЪк ФoОoКeМЛe, a БaЪeП, АОУ ЪoЦo дЪoДк
МaАeКМo БaНpeФЛЪл, БaЗЛМЪЛЪe Л БaЪУМЛЪe pyНoУЪНy.
5. ìcÚaÌoÇÍa ÖÌeÁÀa
(1) тЪЛЩЪ, ЪЛФ НoОлбeЗoЦo yФОoЪМeМЛУ (PËc. 1)
BкДepЛЪe ЦМeБАo, НoЪopoe ДyАeЪ cooЪЗeЪcЪЗoЗaЪл
БaЪУЦЛЗaeПoПy ЛОЛ ocОaДОУeПoПy ДoОЪy. иocaАЛЪe
ЦМeБАo Мa МaНoЗaОлМп ЦaИНoЗepЪa, Л МaАeКМo
БaНpeФЛЪe eЦo c ФoПoзлп еЪЛЩЪa Л НoОлбa. иpЛ
cМУЪЛЛ ЦМeБАa ЗкФoОМЛЪe АeИcЪЗЛУ З oДpaЪМoИ
ФocОeАoЗaЪeОлМocЪЛ.
(2) TËÔ ÔÎyÌÊepa (PËc. 2)
CoЗПecЪЛЪe ФОyМКep, НoЪopкИ pacФoОoКeМ З
НЗaАpaЪМoИ дacЪЛ МaНoЗaОлМЛ c oЪЗepcЪЛeП З
еecЪЛЦpaММoП ЦМeБАe. ВaЪeП МaКПЛЪe Мa ФОyМКep
Л ycЪaМoЗЛЪe еecЪЛЦpaММoe ЦМeБАo Мa МaНoЗaОлМп.
иpoЗepлЪe, ФoОМocЪлп ОЛ ФОyМКep БaЩЛНcЛpoЗaМ
З oЪЗepcЪЛЛ. иpЛ cМУЪЛЛ ЦМeБАa ЗкФoОМЛЪe АeИcЪЗЛУ
З oДpaЪМoИ ФocОeАoЗaЪeОлМocЪЛ.
èPAKTàóECKOE èPàMEHEHàE
1. îyÌÍáËoÌËpoÇaÌËe ÔepeÍÎïäaÚeÎÓ (PËc. 3)
иepeНОпдaЪeОл З АaММoП ycЪpoИcЪЗe
ЩyМНбЛoМЛpyeЪ НaН ЗкНОпдaЪeОл АЗЛЦaЪeОУ Л
ceОeНЪopМкИ ФepeНОпдaЪeОл МaФpaЗОeМЛУ
ЗpaзeМЛУ. EcОЛ ФepeНОпдaЪeОл ycЪaМoЗОeМ З
ФoОoКeМЛe R, yНaБaММoП Мa НpкеНe pyНoУЪНЛ,
АЗЛЦaЪeОл ДyАeЪ ЗpaзaЪлcУ Фo дacoЗoИ cЪpeОНe
АОУ БaЪУЦЛЗaМЛУ ДoОЪoЗ. EcОЛ ФepeНОпдaЪeОл
ycЪaМoЗОeМ З ФoОoКeМЛe L, АЗЛЦaЪeОл ДyАeЪ
ЗpaзaЪлcУ ФpoЪЛЗ дacoЗoИ cЪpeОНЛ АОУ ocОaДОeМЛУ
ДoОЪoЗ. EcОЛ ФepeНОпдaЪeОл oЪФycЪЛЪл, АЗЛЦaЪeОл
ocЪaМoЗЛЪcУ.
OCTOPOÜHO
He ÁaÄyÀëÚe ÔoÇepÌyÚë ÔepeÍÎïäaÚeÎë Ç ÔoÎoÊeÌËe
OFF (BõKã) Ë ÔoÀoÊÀaÚë Ào Úex Ôop, ÔoÍa ÀÇËÖaÚeÎë
ÔoÎÌocÚëï Ìe ocÚaÌoÇËÚcÓ, ÔpeÊÀe äeÏ ËÁÏeÌËÚë
ÌaÔpaÇÎeÌËe ÇpaçeÌËÓ ÖaÈÍoÇepÚa. èepeÍÎïäeÌËe
Ço ÇpeÏÓ ÇpaçeÌËÓ ÀÇËÖaÚeÎÓ ÏoÊeÚ ÔpËÇecÚË Í
eÖo ÔepeÖopaÌËï.
40
2. ÂaÚÓÊÍa Ë ocÎaÄÎeÌËe ÄoÎÚoÇ
иpeКАe ЗceЦo МyКМo ФoАoДpaЪл еecЪЛЦpaММyп
ЦoОoЗНy, ФoАxoАУзyп Н ДoОЪy ЛОЛ ЦaИНe. ВaЪeП
ycЪaМoЗЛЪe ЦoОoЗНy Мa oФopМкИ cЪepКeМл Л БaКПЛЪe
ЦaИНy, ФpeАМaБМaдeММyп АОУ БaЪУКНЛ, c ФoПoзлп
еecЪЛЦpaММoИ ЦoОoЗНЛ. мАepКЛЗaУ ЦaИНoЗepЪ Мa
oАМoИ ОЛМЛЛ c ДoОЪoП, МaКПЛЪe ЗкНОпдaЪeОл
ФЛЪaМЛУ АОУ ЗoБАeИcЪЗЛУ Мa ЦaИНy З ЪeдeМЛe
МecНoОлНЛx ceНyМА. EcОЛ ЦaИНa МeФОoЪМo ФoАxoАЛЪ
Н ДoОЪy, ДoОЪ ПoКeЪ ФpoЗepМyЪлcУ ЗoНpyЦ ЦpaМeИ
ЦaИНЛ, дЪo Мe oДecФeдЛЪ МaАОeКaзeИ БaЪУКНЛ. B
нЪoП cОyдae ФpЛocЪaМoЗЛЪe ЗoБАeИcЪЗЛe Мa ЦaИНy
Л yАepКЛЗaИЪe ЦoОoЗНy ДoОЪa c ФoПoзлп ЦaИНoЗepЪa
ФepeА ЪeП, НaН МaдaЪл ЗoБАeИcЪЗЛe cМoЗa, ЛОЛ Кe
БaЪУМЛЪe ДoОЪ Л ЦaИНy ЗpyдМyп АОУ ФpeАoЪЗpaзeМЛУ
ФpocНaОлБкЗaМЛУ ПeКАy МЛПЛ.
MEPõ èPEÑOCTOPOÜHOCTà èPà
ùKCèãìATAñàà
1. èpoÇepëÚe ÌaÔpÓÊeÌËe Ç ceÚË (PËc. 4)
HaФpУКeМЛe З ceЪЛ ЗОЛУeЪ Мa ЗoБПoКМкИ НpyЪУзЛИ
ПoПeМЪ. мПeМлеeММoe МaФpУКeМЛe З ceЪЛ ФoМЛБЛЪ
ЗoБПoКМкИ НpyЪУзЛИ ПoПeМЪ.
HaФpЛПep, ecОЛ Bк ДyАeЪe нНcФОyaЪЛpoЗaЪл ЪoЪ
ЪЛФ ЦaИНoЗepЪa, НoЪopкИ paccдЛЪaМ Мa 220 B, ФpЛ
МaФpУКeМЛЛ З ceЪЛ 200 B, ЗoБПoКМкИ НpyЪУзЛИ
ПoПeМЪ yПeМлеЛЪcУ Л ДyАeЪ cocЪaЗОУЪл oЪ 70 Аo
90%. иpЛ yАОЛМeМЛЛ еМypa ФЛЪaМЛУ, yАОЛМЛЪeОлМкИ
еМyp АoОКeМ ДкЪл НaН ПoКМo Нopoдe. EcОЛ
ЗoБМЛНМeЪ МeoДxoАЛПocЪл ФoАcoeАЛМeМЛУ АОЛММoЦo
yАОЛМЛЪeОлМoЦo еМypa ФpЛ МЛБНoП МaФpУКeМЛЛ З
ceЪЛ, oДУБaЪeОлМo ЛcФoОлБyИЪe ФoЗкеaпзЛИ
ЪpaМcЩopПaЪop. CooЪМoеeМЛe ПeКАy МaФpУКeМЛeП
З ceЪЛ Л НpyЪУзЛП ПoПeМЪoП ФoНaБaМo З бЛЩpax.
2. He ÔpËÍacaÈÚecë Í ÄyÙepy ËÎË ÍopÔycy ÏoÎoÚÍa
Ço ÇpeÏÓ ÌeÔpepêÇÌoÈ paÄoÚê
ЕyЩep Л НopФyc ПoОoЪНa cЪaМoЗУЪcУ ЦopУдЛПЛ Зo
ЗpeПУ МeФpepкЗМoЦo БaЗЛМдЛЗaМЛУ ЗЛМЪoЗ, ФoнЪoПy
ДyАлЪe ocЪopoКМк, дЪoДк Мe ФpЛНocМyЪлcУ Н МЛП
З нЪo ЗpeПУ.
3. PaÄoÚa ÔpË ÍpyÚÓçeÏ ÏoÏeÌÚe, ÌeoÄxoÀËÏoÏ ÀÎÓ
ÄoÎÚa ÔpË yÀapÌoÏ ÇoÁÀeÈcÚÇËË
OФЪЛПaОлМкИ НpyЪУзЛИ ПoПeМЪ АОУ ЦaeН Л ДoОЪoЗ
paБОЛдaeЪcУ З БaЗЛcЛПocЪЛ oЪ ПaЪepЛaОa Л paБПepa
ЦaeН Л ДoОЪoЗ. CОЛеНoП ДoОлеoИ НpyЪУзЛИ ПoПeМЪ
АОУ ПaОeМлНoЦo ДoОЪa ПoКeЪ ФoЪУМyЪл ЛОЛ cОoПaЪл
ДoОЪ. KpyЪУзЛИ ПoПeМЪ ДyАeЪ yЗeОЛдЛЗaЪлcУ
ФpoФopбЛoМaОлМo ЗpeПeМЛ ЗкФoОМeМЛУ oФepaбЛЛ.
аcФoОлБyИЪe ФpaЗЛОлМoe ЗpeПУ АОУ ЗкФoОМeМЛУ
oФepaбЛЛ c ДoОЪoП.
4. BêÄop ÔoxoÀÓçeÖo ÖÌeÁÀa ÀÎÓ ÄoÎÚa
OДУБaЪeОлМo yДeАЛЪecл З ЪoП, дЪo ДyАeЪe ЛcФoОлБoЗaЪл
ЦМeБАo, НoЪopoe cooЪЗeЪcЪЗyeЪ БaЪУЦЛЗaeПoПy ДoОЪy.
аcФoОлБoЗaМЛe МeФoАxoАУзeЦo ЦМeБАa ФpЛЗeАeЪ Мe
ЪoОлНo Н МecooЪЗeЪcЪЗyпзeПy БaЪУЦЛЗaМЛп, Мo ЪaНКe
Н ФoЗpeКАeМЛп ЦМeБАa ЛОЛ ЦaИНЛ. аБМoеeММoe ЛОЛ
АeЩopПЛpoЗaММoe ЦМeБАo c еecЪЛЦpaММкП ЛОЛ
НЗaАpaЪМкП oЪЗepcЪЛeП Мe ДyАeЪ oДecФeдЛЗaЪл
АocЪaЪoдМyп cЪeФeМл ФОoЪМocЪЛ ФocaАНЛ АОУ
ФpЛНpeФОeМЛУ ЦaИНЛ ЛОЛ МaНoЗaОлМЛ, Л, cОeАoЗaЪeОлМo,
ФpЛЗeАeЪ Н ocОaДОeМЛп НpyЪУзeЦo ПoПeМЪa.
иpoЗepлЪe cЪeФeМл ЛБМoca oЪЗepcЪЛИ ЦМeБА Л
БaПeМЛЪe Аo ЪoЦo, НaН МacЪyФЛЪ АaОлМeИеЛИ ЛБМoc.
CooЪЗeЪcЪЗЛe paБПepoЗ ЦМeБА Л ДoОЪoЗ ФoНaБaМo
З TaÄÎËáe 1.
Page 42

PyccÍËÈ
сЛЩpoЗoe БМaдeМЛe ФpЛ oДoБМaдeМЛЛ ЦМeБАa
ЗкpaКaeЪ paccЪoУМЛe (S) ПeКАy ФapaООeОлМкПЛ
ЦpaМУПЛ eЦo еecЪЛЦpaММoЦo oЪЗepcЪЛУ.
5. ìÀepÊËÇaÌËe ËÌcÚpyÏeÌÚa
KpeФНo АepКЛЪe yАapМкИ ЦaИНoЗepЪ oДeЛПЛ pyНaПЛ Бa
pyНoУЪНy НopФyca Л Бa ДoНoЗyп pyНoУЪНy. B нЪoП cОyдae
yАepКЛЗaИЪe ЦaИНoЗepЪ Мa oАМoИ ОЛМЛЛ c ДoОЪoП.
He МyКМo cОЛеНoП cЛОлМo МaКЛПaЪл Мa ЦaИНoЗepЪ.
мАepКЛЗaИЪe ЦaИНoЗepЪ c ycЛОЛeП, АocЪaЪoдМкП
ЪoОлНo АОУ ЪoЦo, дЪoДк МeИЪpaОЛБoЗaЪл yАapМyп cЛОy.
6. иpoЗepлЪe НpyЪУзЛИ ПoПeМЪ
CОeАyпзЛe ЩaНЪopк oНaБкЗaпЪ ЗОЛУМЛe Мa
yПeМлеeМЛe НpyЪУзeЦo ПoПeМЪa. иoЪoПy ФepeА
ЗкФoОМeМЛeП paДoЪк ФpoЗepлЪe ЩaНЪЛдecНЛИ
НpyЪУзЛИ ПoПeМЪ, НoЪopкИ МeoДxoАЛПo ФpЛОoКЛЪл
ФpЛ БaЗЛМдЛЗaМЛЛ МeНoЪopкx ДoОЪoЗ, ФpЛ ФoПoзЛ
pyдМoЦo ЦaeдМoЦo НОпдa c oЦpaМЛдeМЛeП Фo
НpyЪУзeПy ПoПeМЪy. СaОee ФepeдЛcОeМк ЩaНЪopк,
НoЪopкe oНaБкЗaпЪ ЗОЛУМЛe Мa НpyЪУзЛИ ПoПeМЪ.
(1) HaÔpÓÊeÌËe Ç ceÚË:
KpyЪУзЛИ ПoПeМЪ ДyАeЪ yПeМлеaЪлcУ ФpЛ ФoМЛКeМЛЛ
МaФpУКeМЛУ З ceЪЛ (CП. PËc. 4).
(2) BpeÏÓ ÇêÔoÎÌeÌËÓ oÔepaáËË:
KpyЪУзЛИ ПoПeМЪ ДyАeЪ yЗeОЛдЛЗaЪлcУ ФpЛ
yЗeОЛдeМЛЛ ЗpeПeМЛ ЗкФoОМeМЛУ oФepaбЛЛ. Ho
НpyЪУзЛИ ПoПeМЪ Мe cЪaМeЪ ДoОлеe oФpeАeОeММoЦo
БМaдeМЛУ, АaКe ecОЛ ЛМcЪpyПeМЪ ДyАeЪ ЗкФoОМУЪл
oФepaбЛп З ЪeдeМЛe АОЛЪeОлМoЦo ЗpeПeМЛ
(CП. PËc. 4).
(3) ÑËaÏeÚp ÄoÎÚa:
KpyЪУзЛИ ПoПeМЪ paБОЛдaeЪcУ З БaЗЛcЛПocЪЛ oЪ
АЛaПeЪpa ДoОЪa, НaН ФoНaБaМo Мa PËc. 4. KaН
ФpaЗЛОo, дeП ДoОлеe АЛaПeЪp ДoОЪa, ЪeП ДoОлеe
МeoДxoАЛПкИ НpyЪУзЛИ ПoПeМЪ.
(4) мcОoЗЛУ БaЪУЦЛЗaМЛУ:
KpyЪУзЛИ ПoПeМЪ ДyАeЪ oЪОЛдaЪлcУ З cooЪЗeЪcЪЗЛЛ
c ФoНaБaЪeОeП НpyЪУзeЦo ПoПeМЪa; НОaccoП Л
АОЛМoИ ДoОЪoЗ, АaКe ecОЛ ДyАyЪ ЛcФoОлБoЗaЪлcУ
ДoОЪк c oАЛМaНoЗкП paБПepoП peБлДк. KpyЪУзЛИ
ПoПeМЪ ЪaНКe ДyАeЪ oЪОЛдaЪлcУ З cooЪЗeЪcЪЗЛЛ c
cocЪoУМЛeП ФoЗepxМocЪЛ ПeЪaООa, дepeБ НoЪopyп
ДyАyЪ БaЪУЦЛЗaЪлcУ ДoОЪк.
(5) àcÔoÎëÁoÇaÌËe ÀoÔoÎÌËÚeÎëÌêx ÀeÚaÎeÈ:
KpyЪУзЛИ ПoПeМЪ ДyАeЪ МeПМoЦo ПeМлеe ФpЛ
ЛcФoОлБoЗaМЛЛ yАОЛМЛЪeОлМoИ МaАcЪaЗНЛ,
yМЛЗepcaОлМoЦo еapМЛpa ЛОЛ АОЛММoЦo ЦМeБАa.
(6) ÑoÔycÍ ÖÌeÁÀa:
аБМoеeММoe ЛОЛ АeЩopПЛpoЗaММoe ЦМeБАo c
еecЪЛЦpaММкП ЛОЛ НЗaАpaЪМкП oЪЗepcЪЛeП Мe ДyАeЪ
oДecФeдЛЗaЪл АocЪaЪoдМyп cЪeФeМл ФОoЪМocЪЛ ФocaАНЛ
ПeКАy ЦaИНoИ ЛОЛ МaНoЗaОлМeИ, Л, cОeАoЗaЪeОлМo,
ФpЛЗeАeЪ Н ocОaДОeМЛп НpyЪУзeЦo ПoПeМЪa.
аcФoОлБoЗaМЛe МeФpaЗЛОлМo ФoАoДpaММoЦo ЦМeБАa,
НoЪopoe Мe cooЪЗeЪcЪЗyeЪ ДoОЪy, ФpЛЗeАeЪ Н
МecooЪЗeЪcЪЗyпзeПy НpyЪУзeПy ПoПeМЪy.
CooЪЗeЪcЪЗЛe ЦМeБАa Л paБПepoЗ ДoОЪa ФoНaБaМк
З TaÄÎËáe 1.
TEXHàóECKOE OÅCãìÜàBAHàE à
OCMOTP
1. OcÏoÚp ÖÌeÁÀa
àÁÌoåeÌÌoe ËÎË ÀeÙopÏËpoÇaÌÌoe ÖÌeÁÀo c
åecÚËÖpaÌÌêÏ ËÎË ÍÇaÀpaÚÌêÏ oÚÇepcÚËeÏ Ìe ÄyÀeÚ
oÄecÔeäËÇaÚë ÀocÚaÚoäÌyï cÚeÔeÌë ÔÎoÚÌocÚË
ÔocaÀÍË ÏeÊÀy ÖaÈÍoÈ ËÎË ÌaÍoÇaÎëÌeÈ, Ë,
cÎeÀoÇaÚeÎëÌo, ÔpËÇeÀeÚ Í ocÎaÄÎeÌËï ÍpyÚÓçeÖo
ÏoÏeÌÚa. èepËoÀËäecÍË ÔpoÇepÓÈÚe cÚeÔeÌë ËÁÌoca
oÚÇepcÚËÈ ÖÌeÁÀa Ë ÁaÏeÌÓÈÚe ÖÌeÁÀa ÌoÇêÏË ÔpË
ÌeoÄxoÀËÏocÚË.
2. OcÏoÚp ÍpeÔeÊÌêx ÇËÌÚoÇ
PeЦyОУpМo ЗкФoОМУИЪe ocПoЪp Зcex НpeФeКМкx
ЗЛМЪoЗ Л ФpoЗepУИЪe Лx МaАОeКaзyп БaЪУКНy. иpЛ
ocОaДОeМЛЛ НaНЛx-ОЛДo ЗЛМЪoЗ, МeПeАОeММo
БaЪУМЛЪe Лx ФoЗЪopМo. HeЗкФoОМeМЛe нЪoЦo
ЪpeДoЗaМЛУ ПoКeЪ ФpЛЗecЪЛ Н cepлeБМoИ oФacМocЪЛ.
3. TexÌËäecÍoe oÄcÎyÊËÇaÌËe ÀÇËÖaÚeÎÓ
OДПoЪНa АЗЛЦaЪeОУ - ''cepАбe'' нОeНЪpoЛМcЪpyПeМЪa.
иpoУЗОУИЪe АoОКМoe ЗМЛПaМЛe, cОeАУ Бa ЪeП, дЪoДк
oДПoЪНa Мe ДкОa ФoЗpeКАeМa Л/ ЛОЛ БaОЛЪa ПacОoП
ЛОЛ ЗoАoИ.
4. èpoÇepÍa yÖoÎëÌêx çeÚoÍ (PËc. 5)
уЪoДк oДecФeдЛЪл Baеy ДeБoФacМocЪл Л БaзЛЪЛЪл
oЪ ФopaКeМЛУ нОeНЪpЛдecНЛП ЪoНoП, ocПoЪp Л
БaПeМy yЦoОлМкx зeЪoН нЪoЦo ЛМcЪpyПeМЪa cОeАyeЪ
ФpoЗoАЛЪл TOгъKO З aЗЪopЛБoЗaММoП cepЗЛcМoП
бeМЪpe Hitachi.
5. ÂaÏeÌa ceÚeÇoÖo åÌypa
B cÎyäae ecÎË ÄyÀeÚ ÔoÇpeÊÀeÌ ceÚeÇoÈ åÌyp
ÀaÌÌoÖo íÎeÍÚpoËÌcÚpyÏeÌÚa, íÎeÍÚpoËÌcÚpyÏeÌÚ
ÌeoÄxoÀËÏo ÇoÁÇpaÚËÚë Ç ìÔoÎÌoÏoäeÌÌêÈ
cepÇËcÌêÈ áeÌÚp ÙËpÏê Hitachi ÀÎÓ ÁaÏeÌê åÌypa.
6. èopÓÀoÍ ÁaÔËceÈ Ôo ÚexoÄcÎyÊËÇaÌËï
A: èyÌÍÚ £
B: KoÀ £
C: KoÎËäecÚÇo ÔpËÏeÌeÌËÈ
D: ÂaÏeäaÌËÓ
èPEÑOCTEPEÜEHàE
PeПoМЪ, ПoАЛЩЛНaбЛп Л ocПoЪp ПexaМЛБЛpoЗaММoЦo
ЛМcЪpyПeМЪa ЩЛpПк Hitachi cОeАyeЪ ФpoЗoАЛЪл З
aЗЪopЛБoЗaММoП cepЗЛcМoП бeМЪpe Hitachi.
щЪoЪ ФepeдeМл БaФacМкx дacЪeИ ФpЛЦoАЛЪcУ ФpЛ
ФpeАcЪaЗОeМЛЛ eЦo ЗПecЪe c ЛМcЪpyПeМЪoП З
aЗЪopЛБoЗaММкИ cepЗЛcМкИ бeМЪp Hitachi c БaФpocoП
Мa peПoМЪ ЛОЛ Фpoдee oДcОyКЛЗaМЛe.
иpЛ paДoЪe Л oДcОyКЛЗaМЛЛ ПexaМЛБЛpoЗaММкx
ЛМcЪpyПeМЪoЗ МyКМo coДОпАaЪл ФpaЗЛОa Л cЪaМАapЪк
ДeБoФacМocЪЛ, АeИcЪЗyпзЛe З НaКАoИ АaММoИ cЪpaМe.
ÂAMEóAHàE
îËpÏa HITACHI ÌeÔpepêÇÌo paÄoÚaeÚ ÌaÀ
ycoÇepåeÌcÚÇoÇaÌËeÏ cÇoËx ËÁÀeÎËÈ, ÔoíÚoÏy Ïê
coxpaÌÓeÏ Áa coÄoÈ ÔpaÇo Ìa ÇÌeceÌËe ËÁÏeÌeÌËÈ
Ç ÚexÌËäecÍËe xapaÍÚepËcÚËÍË, yÔoÏÓÌyÚêe Ç
ÀaÌÌoÈ ËÌcÚpyÍáËË Ôo íÍcÔÎyaÚaáËË, ÄeÁ
ÔpeÀyÔpeÊÀeÌËÓ oÄ íÚoÏ.
èPàMEóAHàE
Ha ocМoЗaМЛЛ ФocЪoУММкx ФpoЦpaПП ЛccОeАoЗaМЛУ Л
paБЗЛЪЛУ, HITACHI ocЪaЗОУпЪ Бa coДoИ ФpaЗo Мa
ЛБПeМeМЛe yНaБaММкx БАecл ЪexМЛдecНЛx АaММкx ДeБ
ФpeАЗapЛЪeОлМoЦo yЗeАoПОeМЛУ.
41
Page 43

PyccÍËÈ
àÌÙopÏaáËÓ, ÍacaïçaÓcÓ coÁÀaÇaeÏoÖo åyÏa Ë
ÇËÄpaáËË
аБПepУeПкe ЗeОЛдЛМк ДкОЛ oФpeАeОeМк З cooЪЗeЪcЪЗЛЛ
c EN60745 Л БaУЗОeМк З cooЪЗeЪcЪЗЛЛ c ISO 4871.
TЛФЛдМкИ cpeАМeЗБЗeеeММкИ ypoЗeМл БЗyНoЗoЦo АaЗОeМЛУ:
TЛФЛдМкИ cpeАМeЗБЗeеeММкИ ypoЗeМл БЗyНoЗoИ ПoзМocЪЛ:
HaАeЗaИЪe МayеМЛНЛ.
TЛФЛдМoe БМaдeМЛe ЗЛДpaбЛЛ: 4,75 П/c
98 ÀÅ(A).
111 ÀÅ(A).
2
42
Page 44

ABC D
33 960-354 2
1 323-767 1
ABC D
34 303-694 1 D4×35
35 323-772 1
36-1 985-103 1
3 323-765 1 “1, 4, 5”
4 318-704 1
2 323-753 4 M5×35
37 323-768 1
38 323-780 1 “38, 39, 42”
39 930-153 1
36-2 320-528 1 “EUROPE”
FRG, ITA, ESP,
5 323-766 1
6-1 323-773 1
6-2 985-207 1 “13, 14” “FRA,
HKG, SIN, THA”
40 316-186 1
FIN, SUI”
42 ————1
41-1 958-308Z 1
41-2 983-418Z 1 “SUI, KUW, INA,
7 959-150 2 D6.35
8 323-764 1
9 959-155 30 D3.97
10 323-763 1
43 980-063 1
44 ————1
45 608-VVM 1 608VVC2PS2L
46 985-198 1
47 323-754 1
ESP, FIN, SUI”
11 323-761 1
12 323-760 1
13 985-209 1 “FRA, FRG, ITA,
14 985-208 1 “FRA, FRG, ITA,
48 323-756 1
49 301-653 2 D4×20
50 984-750 2 D4×16
51 937-631 1
52-1 953-327 1 D8.8
52-2 938-051 1 D10.1
ESP, FIN, SUI”
15 985-169 2
16 323-762 1
17 318-446 2
18 955-124 1
19 690-7ZZ 1 6907ZZ-N
53 ————1
54 ————1
55 931-266 2
20 ————1
21 323-758 1
22 323-755 1
AUS, EUROPE,
56 999-021 2
57 957-571 2
58 323-771 1 “56, 58”
59 938-477 2 M5×8
501 323-774 1 “502-505” “NZL,
23 985-166 1
24 600-0DD 1 6000DDCMPS2L
25-1 360-687C 1 110V
25-2 360-687E 1 220V-230V
25-3 360-687F 1 240V
26 323-757 1
AUT, CHN”
EUROPE, AUT,
CHN
502 980-901 1 NZL, AUS,
503 323-775 1 NZL, AUS,
27 981-824 2 D4×45
29 985-186 1 “KUW, INA,
28-1 340-605C 1 110V
28-2 340-605E 1 220V-230V
28-3 340-605F 1 240V
CHN
CHN
EUROPE, AUT,
EUROPE, AUT,
EUROPE, AUT,
504 323-776 1 NZL, AUS,
505 980-903 1 M8 “NZL, AUS,
HKG, SIN, THA”
EUROPE, AUT,
CHN”
HKG, SIN, THA”
30 323-769 1 “NZL, AUS,
31 985-187 1 “KUW, INA,
32 323-770 1 “NZL, AUS,
CHN”
506 323-777 1 “ESP”
EUROPE, AUT,
CHN”
43
Page 45

44
Page 46

English
GUARANTEE CERTIFICATE
1 Model No.
2 Serial No.
3 Date of Purchase
4 Customer Name and Address
5 Dealer Name and Address
(Please stamp dealer name and address)
Deutsch
GARANTIESCHEIN
1 Modell-Nr.
2 Serien-Nr.
3 Kaufdaturn
4 Name und Anschrift des Kunden
5 Name und Anschrift des Händlers
(Bitte mit Namen und Anschrift des
Handlers abstempeln)
Ελληνικά
¶π™∆√¶√π∏∆π∫√ ∂°°À∏™∏™
1 Αρ. Μοντέλου
2 Αύξων Αρ.
3 Ηµεροµηνία αγοράς
4 ΄Ονοµα και διεύθυνση πελάτη
5 ΄Ονοµα και διεύθυνση µεταπωλητή
(Παρακαλούµε να χρησιµοποιηθεί
σφραγίδα)
Polski PyccÍËÈ
GWARANCJA
1 Model
2 Numer seryjny
3 Data zakupu
4 Nazwa klienta i adres
5 Nazwa dealera i adres
(Pieczęć punktu sprzedaży)
Magyar
1 Típusszám
2 Sorozatszám
3 A vásárlás dátuma
4 A Vásárló neve és címe
5 A Kereskedő neve és címe
1 Model č.
2 Série č.
3 Datum nákupu
4 Jméno a adresa zákazníka
5 Jméno a adresa prodejce
1 Model No.
2 Seri No.
3 Satın Alma Tarihi
4 Müßteri Adı ve Adresi
5 Bayi Adı ve Adresi
1 MoÀeÎë £
2 CepЛИМкИ £
3 ÑaÚa ÔoÍyÔÍË
4 HaÁÇaÌËe Ë aÀpec ÁaÍaÁäËÍa
5 HaÁÇaÌËe Ë aÀpec ÀËÎepa
GARANCIA BIZONYLAT
(Kérjük ide elhelyezni a Kereskedő nevének
és címének pecsétjét)
Čeština
ZÁRUČNÍ LIST
(Prosíme o razítko se jménem a adresou
prodejce)
Türkçe
GARANTÓ SERTÓFÓKASI
(Lütfen bayi adını ve adresini kaße olarak
basın)
ÉAPAHTàâHõâ CEPTàîàKAT
(èoÊaÎyÈcÚa, ÇÌecËÚe ÌaÁÇaÌËe Ë aÀpec
ÀËÎepa)
✄
45
Page 47

1
2
3
4
5
✄
46
Page 48

Page 49

Hitachi Koki Co., Ltd.
English
EC DECLARATION OF CONFORMITY
We declare under our sole responsibility that this
product is in conformity with standards or standardized
documents EN60745, EN55014 and EN61000-3 in
accordance with Council Directives 73/23/EEC, 89/336/
EEC and 98/37/EC.
This declaration is applicable to the product affixed CE
marking.
Deutsch
ERKLÄRUNG ZUR KONFORMITÄT MIT CE-REGELN
Wir erklären mit alleiniger Verantwortung, daß dieses
Produkt den Standards oder standardisierten
Dokumenten EN60745, EN55014 und EN61000-3 in
Übereinstimmung mit den Direktiven des Europarats
73/23/EWG, 89/336/EWG und 98/37/CE entspricht.
Diese Erklärung gilt für Produkte, die die CE-Markierung
tragen.
Ελληνικά
EK ∆ΗΛ·ΣΗ ΕΝΑΡΜΟΝΙΣΜΟΥ
∆ηλώνουµε µε απλυτη υπευθυντητα τι αυτ το
προιν είναι εναρµονισµένο µε τα πρτυπα ή τα
έγραφα προτύπων EN60745, EN55014 και EN61000-3
σε συµφωνία µε τις Οδηγίες του Συµβουλίου 73/23/
EOK, 89/336/EOK και 98/37/EK.
Αυτή η δήλωση ισχύει στο προιν µε το σηµάδι CE.
Polski
DEKLARACJA ZGODNOŚCI Z EC
Oznajmiamy z całkowitą odpowiedzialnością, że produkt
ten pozostaje w zgodzie ze standardami lub standardową
formą dokumentów EN60745, EN55014 i EN61000-3 w
zgodzie z Zasadami Rady 73/23/EEC 89/336/ EEC i 98/
37/EC.
To oświadczenie odnosi się do załączonego produktu z
oznaczeniami CE.
Magyar
EU MEGFELELŐSÉGI NYILATKOZAT
Teljes felelősségünk tudatában kijelentjük, hogy ez a termék
megfelel az EN60745, EN55014, és EN 61000-3
szabványoknak illetve szabványosított dokumentumoknak,
az Európa Tanács 73/23/EEC, 89/336/EEC, és 98/37/EC
Tanácsi Direktíváival összhangban.
Jelen nyilatkozat a terméken feltüntetett CE jelzésre
vonatkozik.
Čeština
PROHLÁŠENÍ O SHODĚ S CE
Prohlašujeme na svoji zodpovědnost, že tento výrobek
odpovídá normám EN60745, EN55014 a EN61000-3 v
souladu se směrnicemi 73/23/EEC, 89/336/EEC a 98/37/EC.
Toto prohlášení platí pro výrobek označený značkou CE.
Türkçe
AB UYGUNLUK BEYANI
Bu ürünün, 73/23/EEC, 89/336/EEC ve 98/37/EC sayılı
Konsey Direktiflerine uygun olarak, EN60745, EN55014 ve
EN61000-3 sayılı standartlara ve standartlaßtırılmıß belgelere
uygun olduåunu, tamamen kendi sorumluluåumuz altında
beyan ederiz.
Bu beyan, üzerinde CE ißareti bulunan ürünler için
geçerlidir.
PyccÍËÈ
ÑEKãAPAñàü COOTBETCTBàü EC
Mê c ÔoÎÌoÈ oÚÇeÚcÚÇeÌÌocÚëï ÁaÓÇÎÓeÏ, äÚo ÀaÌÌoe
ËÁÀeÎËe cooÚÇeÚcÚÇyeÚ cÚaÌÀapÚaÏ ËÎË
cÚaÌÀapÚËÁoÇaÌÌêÏ ÀoÍyÏeÌÚaÏ EN60745, EN55014 Ë
EN61000-3 coÖÎacÌo ÑËpeÍÚËÇaÏ CoÇeÚa 73/23/EEC, 89/
336/EEC Ë 98/37/EC.
ÑaÌÌaÓ ÀeÍÎapaáËÓ oÚÌocËÚcÓ Í ËÁÀeÎËÓÏ, Ìa ÍoÚopêx
ËÏeeÚcÓ ÏapÍËpoÇÍa CE.
Representative office in Europe
Hitachi Power Tools Europe GmbH
Siemensring 34, 47877 Willich 1, F. R. Germany
Head office in Japan
Hitachi Koki Co., Ltd.
Shinagawa Intercity Tower A, 15-1, Konan 2-chome,
Minato-ku, Tokyo, Japan
30. 9. 2004
K. Kato
Board Director
502
Code No. C99136791 N
Printed in Japan
 Loading...
Loading...