HiHippo BM-500 CL, BB-500 CL User Manual
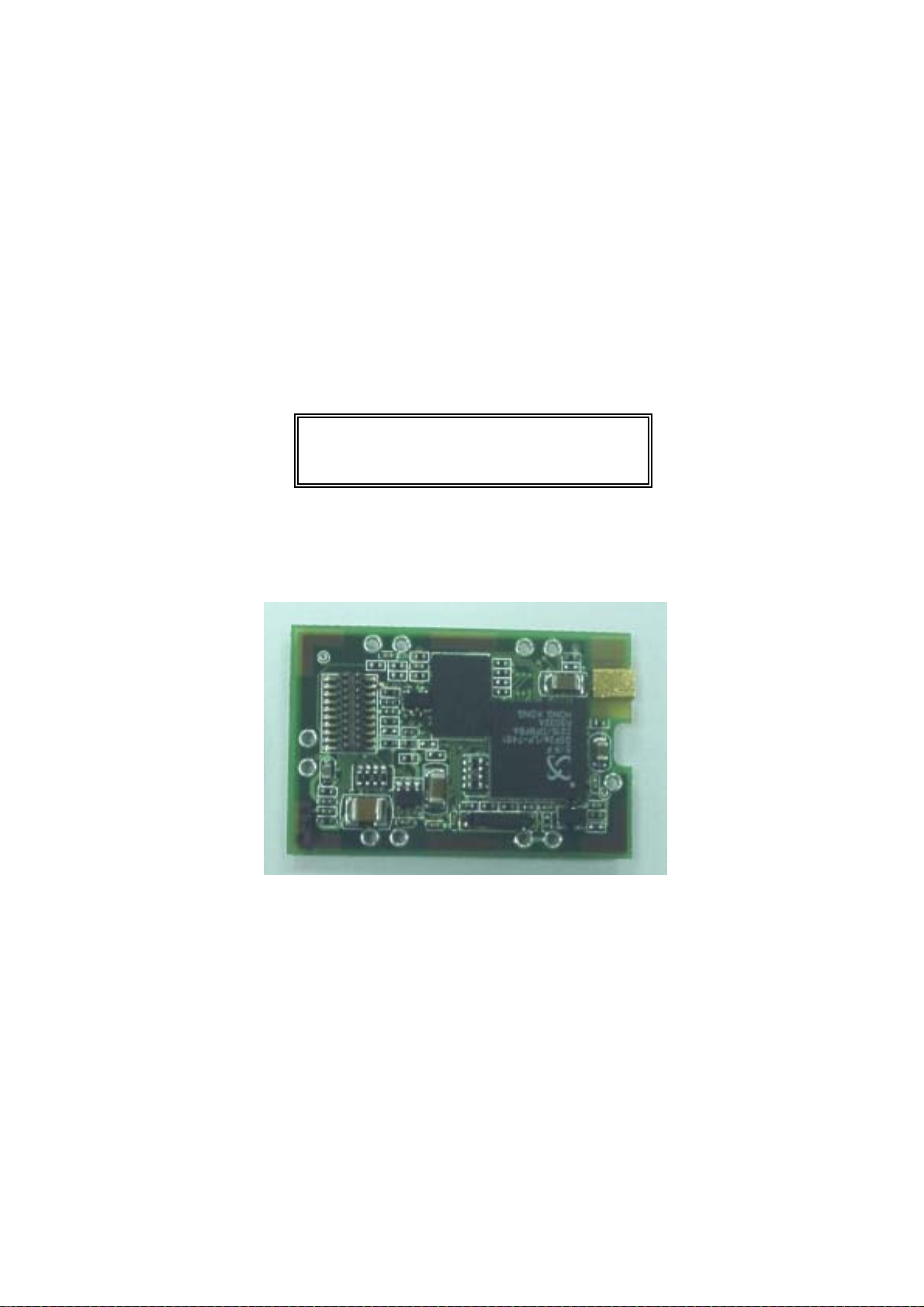
Rikaline GPS-21 / 21-LP
GPS Engine Board
User’s Guide
SiRF Star II V1.0 Oct 06, 2002
Rikaline Marketing Corp.
5F-1, 125, Roosevelt Road, Sec. 5, Taipei, Taiwan 116, R.O.C.
Phone: +886-2-2934-5456 Fax: +886-2-2934-4373
E-Mail: info@rikaline.com.tw Web: www.rikaline.com.tw
All Right Reserved

GPS-21 Operating Manual
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. Introduction
1.1 Overview
1.2 Features
1.3 Technical Specifications
2. Operational Characteristics
2.1 Initialization
2.2 Navigation
3. Hardware Interface
3.1 Connector
3.2 Pin Assignment
3.3 Trickle Power
3.4 Push-to-Fix Description
3.5 SRAM Data Backup Description
3.6 Mechanical Dimension
4. Software Interface
4.1 NMEA Transmitted Sentences
4.2 RTCM Received Data
5. Earth Datums
5.1 Earth Datums
5.2 Setting Syntax
6. Ordering Information
6.1 Product Options
6.2 Accessories
7. Warranty
………………………………………………………………………………………..
……………………………………………………………………………………..
……………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………..
……………………………………………………………….…
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………….……
………………………………………………………………………………….…
…..………..……………………………………………………….……
…………………………………………………………………………….…
…………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………….…
……………………………………………………..…
…………………………………………………………………..
……………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………….…
………………………………………………………………………..…
………………………………………………………………….…………
………………………………………………………………………….………
………………………………………………………………………………………………
Rikaline
3
3
3
3
5
5
5
6
6
6
8
9
9
10
12
12
15
16
16
17
18
18
18
18
Rikaline Marketing Corp.
Tel: ++886 2 2934 5456 Fax: ++886 2 2934 4373 E-Mail: info@rikaline.com.tw
5F-1, 125, Roosevelt Road, Sec. 5, Taipei, Taiwan 116
2
web: www.rikaline.com.tw

GPS-21 Operating Manual
Rikaline
1. Introduction
1.1 Overview
The Rikaline GPS-21 GPS Engine Board is designe d based on SiRF Star II Architecture with low
power consumption, small size and easy integrated for a broad spectrum of OEM system applications.
GPS-21 meets strict needs such as car navigation, mapping, surveying, security, agriculture and so on. Only
clear view of sky and certain power supply are necessary to the unit. It communicates with other electronic
utilities via compatible dual-channel through RS-232 or TTL and saves critical satellite data by built–in
backup memory. The Trickle-Power allows the unit operates a fraction of the time and Push-to-Fix permits
user to have a quick position fix even though the receiver usually stays off.
The GPS-21-LP utilizes the latest SiRF technology for applications where the power consumption is more
critically required.
1.2 Features
The GPS-21 provides a host of features that make it easy for integration and use.
1.
SiRF Star II chipset with embedded ARM7TDMI CPU available for customized applications in
firmware.
2. High performance receiver tracks up to 12 satellites while providing first fast fix and low power
consumption.
3. Differential capability utilizes real-time RTCM corrections producing 1-5 meter position accuracy.
4. Compact design ideal for applications with minimal space.
5. A rechargeable battery sustains internal clock and memory. The battery is recharged during normal
operation.
6. User initialization is not required.
7. Dual communication channels and user selectable baud rates allow maximum interface capability and
flexibility.
8. Optional communication levels, RS-232 and TTL meet ordinary application and new fashions of
connecting PDA with TTL or RS-232 output.
9. FLASH based program memory: New software revisions upgradeable through serial interface.
10. Built-in WAAS and EGNOS demodulator.
1.3 Technical specifications
1.3.1 Physical Characteristics
Dimension: 36(L) x 24(W) x 6(H) mm
1.42"(L) x 0.95"(W) x 0.24"(H).
Weight: 7g
1.3.2 Environmental Characteristics
1) Operating temperature: -40oC to +85oC
2) Storage temperature: -55
-45oC to +80oC with battery
1.3.3 Electrical Characteristics
1.3.3.1 General:
1) Frequency: L1, 1,575.42MHz
2) C/A Code: 1.023MHz Chip Rate
3) Channels: 12
Rikaline Marketing Corp.
Tel: ++886 2 2934 5456 Fax: ++886 2 2934 4373 E-Mail: info@rikaline.com.tw
o
C to +100oC.
5F-1, 125, Roosevelt Road, Sec. 5, Taipei, Taiwan 116
web: www.rikaline.com.tw
3
GPS-21 Operating Manual
1.3.3.2 Power
GPS-21 5V Version
GPS-21 3.3V Version
TTL
Main Power
Supply Current
Backup Power
Backup Current
Packup Period
GPS-21-LP 5V Version
+5VDC±5% 3.3VDC±10%
170mA Typical 170mA Typical
+2.5V to 3.3V +2.5V to 3.3V
10µA Typical 10µA Typical
230hr (9.6 days) 230hr (9.6 days)
GPS-21-LP 3.3V Version
TTL
Main Power
Supply Current
Backup Power
Backup Current
Packup Period
1.3.3.3 Datum
WGS 84
+5VDC±5% 3.3VDC±10%
100mA Typical 95mA Typical
+2.5V to 3.3V +2.5V to 3.3V
10µA Typical 10µA Typical
230hr (9.6 days) 230hr (9.6 days)
1.3.4 Performance
1.3.4.1 Acquisition
1) Tracks up to 12 satellites.
2) Update rate: 1 second.
3) Acquisition time
Reacquisition 0.1 sec., averaged
Snap Start 3 sec, averaged
Hot start 8 sec., averaged
Warm start 38 sec., averaged
Cold start 45 sec., averaged
1.3.4.2
1.3.4.3 DGPS Accuracy (Differential GPS)
1.3.4.4 Dynamic Conditions
Position Accuracy: (Non Differential GPS)
Position 5-25 meter CEP without SA
Velocity 0.1 meters/second, without SA
Time 1 microsecond synchronized GPS time
Position 1 to 5 meter, typical
Velocity 0.05 meters/second, typical
Altitude 18,000 meters (60,000 feet) max
Velocity 515 meters / second (1,000 knots) max
Acceleration 4 G, max
Jerk 20 meters/second
3
, max
1.3.4.5 1PPS Pulse
Level TTL
Pulse Duration 100ms
Time Reference at the pulse positive edge
Measurements Aligned to GPS second, ± 1 microsecond
1.3.5 Interfaces
Rikaline Marketing Corp.
Tel: ++886 2 2934 5456 Fax: ++886 2 2934 4373 E-Mail: info@rikaline.com.tw
5F-1, 125, Roosevelt Road, Sec. 5, Taipei, Taiwan 116
Rikaline
TTL
TTL
web: www.rikaline.com.tw
4

GPS-21 Operating Manual
1.3.5.1 Interface
Two full duplex serial communication, RS-232 or TTL compatible level, with user selectable baud rate
(4800-Default, 9600, 19200, 38400).
1.3.5.2 Protocol Message
SiRF Binary – Position, Velocity, Altitude, Status and Control
NMEA 0183 Version 2.2 ASCII output -- GGA, GLL, GSA, GSV, RMC, ZDA and VTG.
1.3.5.2 DGPS Protocol
Real-time Differential Correction input (RTCM SC-104 version 2.00 message types 1, 5 and 9).
Rikaline
2. Operational characteristics
2.1 Initialization
As soon as the initial self-test is complete, the GPS-21 begins the process of satellite acquisition and
tracking automatically. Under normal circumstances, it takes approximately 45 seconds to achieve a position
fix, 38 seconds if ephemeris data is known. After a position fix has been calculated, information about valid
position, velocity and time is transmitted over the output channel.
The GPS-21 utilizes initial data, such as last stored position, date, time and satellite orbital data, to
achieve maximum acquisition performance. If significant inaccuracy exists in the initial data, or the orbital
data is obsolete, it may take more time to achieve a navigation solution. The GPS-21 Auto-locate feature is
capable of automatically determining a navigation solution without intervention from the host system.
However, acquisition performance can be improved when the host system initializes the GPS-21 in the
following situation:
1) Moving further than 500 kilometers.
2) Failure of data storage due to the inactive internal memory battery.
2.2 Navigation
After the acquisition process is complete, the GPS-21 sends valid navigation information over
output channels. These data include:
1) Latitude/longitude/altitude
2) Velocity
3) Date/time
4) Error estimates
5) Satellite and receiver status
The GPS-21 sets the default of auto-searching for real-time differential corrections in RTCM SC-104
standard format, with the message types 1, 5, or 9. It accomplishes the satellite data to generate a differential
(DGPS) solution. The host system, at its option, may also command the GPS-21 to output a position
whenever a differential solution is available.
Rikaline Marketing Corp.
Tel: ++886 2 2934 5456 Fax: ++886 2 2934 4373 E-Mail: info@rikaline.com.tw
5F-1, 125, Roosevelt Road, Sec. 5, Taipei, Taiwan 116
5
web: www.rikaline.com.tw
GPS-21 Operating Manual
3. Hardware interface
3.1 Connectors
3.1.1 Antenna Connector
MCX, RSMA
3.1.2 Interface Connector
20-Pin and 10-Pin straight header, 2mm pitch
3.2 Pin Assignment of Connector
Table 1-1 Pin list of the 20-Pin Digital Interface Connector (CN1)
Pin
Name Type Description
Number
1 ANT_PWR PWR Antenna DC Voltage (note 4)
2 VCC_5V PWR +5 DC Power Input (note 5)
3 BAT PWR Backup Battery (note 3)
4 VCC_3V PWR +3.3V DC Power Input (note 6)
5 PBRES
6 GPIO3
7 GPIO7
8 GPIO6
9 GPIO5
10 GPIO10
11 TXA
12 RXA
13 GPIO13
14 TXB O Serial Data Output B
15 RXB I Serial Data Input B
16 NO USE Reserve
17 BOOTSEL I Booting Mode Select
18 GND PWR Ground
19 TIMEMARK/GPIO9 I/O 1PPS Time Mark Output (note 2)
20 ALT/GPIO15 I/O Alternative output (note 1)
I
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
O
I
I/O
Rikaline
Push Button Reset Input. Active Low
SW dependent functions (note 2)
SW dependent functions (note 2)
SW dependent functions (note 2)
SW dependent functions (note 2)
SW dependent functions (note 1)
Serial Data Output A
Serial Data Input A
SW dependent functions (note 1)
Note: 1) Pulled high (VCC/VDD) through on-board 100K Ohm resister.
2) Pulled low (GND) through on-board 100K Ohm resister.
3) Maximum voltage is 1.9V
4) If the module is build-in antenna power type, the pin is no used.
5) If the module is 3.3V type, the pin is no used.
6) If the module is 5V type, the pin in no used.
Table 1-2 Pin list of the 10-Pin Digital Interface Connector (JP1)
Pin Number Name Description
1 GPIOF SW dependent functions (note 1)
Rikaline Marketing Corp.
Tel: ++886 2 2934 5456 Fax: ++886 2 2934 4373 E-Mail: info@rikaline.com.tw
5F-1, 125, Roosevelt Road, Sec. 5, Taipei, Taiwan 116
6
web: www.rikaline.com.tw
 Loading...
Loading...