Page 1

RocketRAID 404/454
User's Manual
Revision: 1.0
Date: Jan. 2004
HighPoint Technologies, Inc.
Page 2

Copyright
Copyright © 2004 HighPoint Technologies, Inc.. This document contains materials
protected by International Copyright Laws. All rights reserved. No part of this
manual may be reproduced, transmitted or transcribed in any form and for any
purpose without the express written permission of HighPoint.
Trademarks
Companies and products mentioned in this manual are for identification purpose
only. Product names or brand names appearing in this manual may or may not be
registered trademarks or copyrights of their respective owners.
Notice
Reasonable effort has been made to ensure that the information in this manual is
accurate. HighPoint assumes no liability for technical inaccuracies, typographical, or
other errors contained herein.
Backup your important data before using HighPoint's products and use at your
own risks. In no event shall HighPoint be liable for any loss of profits, or for
direct, indirect, special, incidental or consequential damages arising from any
defect or error in HighPoint's products or manuals.
Information in this manual is subject to change without notice and does not represent a commitment on the part of HighPoint.
Page 3

Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Chapter 1
Introduction
RAID Basics .............................................................................................. 1-1
IDE RAID .................................................................................................. 1-2
RocketRAID 404/454 ................................................................................. 1-3
Chapter 2
Adapter Installation
Adapter Layout ......................................................................................... 2-1
Hard Disk Connection ............................................................................... 2-1
Adapter Installation .................................................................................. 2-2
Verifying the Adapter's Installation ........................................................... 2-3
Driver Installation ...................................................................................... 2-4
Chapter 3
BIOS Configuration
Entering the BIOS Configuration Utility .................................................... 3-1
Creating a Disk Array ................................................................................ 3-2
Deleting Disk Arrays ................................................................................. 3-5
Add/Remove Spare ................................................................................... 3-6
Settings ..................................................................................................... 3-7
View ........................................................................................................... 3-8
Duplicate Critical RAID 1 array ................................................................. 3-9
Rebuilding a Broken RAID ........................................................................ 3-10
Chapter 4
RAID Administrator
Introduction .............................................................................................. 4-1
Installation ................................................................................................ 4-1
Getting Started .......................................................................................... 4-2
Using the Software .................................................................................... 4-4
i
Page 4

Table of Contents
Chapter 5
Trouble Shooting
Appendix A
Glossary
Appendix B
Contact Technical Support
ii
Page 5

Chapter 1
Introduction
This chapter will discuss the RAID-related background knowledge, as well
as the RocketRAID 404/454 ATA RAID solution.
Contents of this Chapter:
1.1 RAID Basics
1.2 IDE RAID
1.3 RocketRAID 404/454
Page 6
Introduction
1.1 RAID Basics
The term RAID is an acronym, and stands for Redundant Array of Independent Disks.
RAID is a method of combining several hard disk drives (physical disks) into one
logical unit (logical disk). This logical unit is referred to as the RAID array.
Arrays offer several advantages over standard, single-disk configurations - fault tolerance and/or higher data throughput (improved security and/or performance).
Hard disk drives can be combined into several different types of RAID arrays. These
different combinations are referred to as RAID levels.
Different RAID levels offer different advantages, depending upon the number of hard
disks used, and the security, cost, and performance requirements.
The most common types of RAID arrays include RAID 0, RAID 1, and RAID 5.
RAID 5 is a popular choice: it is a very cost-effective solution, and provides both
improved performance, and data security. It requires a minimum of three hard disk
drives. RAID 5 includes a rotating parity array, thus, all read and write operations can
be overlapped. RAID 5 arrays store parity information, but not redundant data.
There are also several types of combined-RAID levels, or hybrid arrays, such as RAID
1/0 (also known as RAID 10).
The table displayed below describes some of the more common types of RAID arrays,
the minimum number of hard drives required, and the benefits offered by each type
RAID level.
noitpircseD
0DIARgnipirtSataD2
1DIARgnirorriMksiD2
1DIAR
/
0
5DIAR
DOBJgninnapSksiD2
ytiraP
dnagnirorriM
gnipirtSataD
gnipirtSataD
gnitatoRhtiw
1-1
#muminiM
srevirDfo
4
3
stifeneB
ecnamrofrePtsehgiH
noitcetorpatadtuohtiw
hguorhtnoitcetorpataD
noitacilpudatad%001
htiwecnamrofreprehgiH
noitcetorpatad
ecnamrofreptsehgiH
noitcetorpatadhtiw
dnanoitcetorpatadoN
gnivorpmiecnamrofrep
ksidfoegasulluftub
yticapac
Page 7
Introduction
1.2 IDE RAID
RAID has long been associated with the SCSI hard disk bus interface, and was designed for use with high-end application systems. PC systems, and low-end business
applications were traditionally excluded from the benefits of RAID, do to the high cost,
and exclusivity associated with the SCSI interface.
IDE is an inexpensive and widely used hard disk bus interface, most commonly utilized
by PCs. Due to the explosion of the PC market in recent years, the IDE interface has
seen marked improvements in both performance and reliability, especially with the
emergence of the ATA100 and ATA133 standards.
This dramatic evolution of the IDE interface led to the development of IDE RAID (also
known as ATA RAID) technology.
IDE RAID is now widely available - many people can now take advantage of the
benefits of RAID, at a fraction of the cost of traditional SCSI systems.
The chart below compares IDE RAID to SCSI RAID, and provides the performance and
implementation costs of each interface:
DIAREDIDIARISCS
ecafretnI331ATAotICPISCS061artlUotICP
slennahCforebmuN21
sevirDforebmunmumixaM451
relortnoC
draC
ecirP001$994$
)pmr(nipS002700001
draH
evirD
yticapaCG04G33
ecirP
tuphguorhTataDmumixaMS/BM2*331S/BM061
sleveLDIARdetroppuSDOBJ,5,01,1,0DOBJ,5,3,01,1,0
021$005$
Note: The price may vary depending on different period and different market.
Due to the ideal combination of high-performance, security and affordability, IDE RAID
has been widely accepted by the market as a cost-effective RAID solution. The
HighPoint RocketRAID 404/454 is one of the best 4-channel ATA RAID solutions
available.
1-2
Page 8

Introduction
1.3 RocketRAID 404/454
Introduction to RocketRAID 404/454
As a four channel ATA133 RAID 5 adapter, the RocketRAID 404/454 supports up to
8 IDE hard disk drives, and provides multi level RAID support including RAID 0, 1,
10, 5 and JBOD. The RocketRAID 404/454 is a high quality, cost-effective solution
for all your storage needs.
Below are the main features and benefits of RocketRAID 404/454:
1. Supports four ATA channels and up to 8 hard disks
2. Supports up to ATA133 hard disks
3. Supports RAID 0, 1, 10, 5 and JBOD
4. Supports hot spare and hot swap
5.Bootable disk or disk array support
6. Error alarm and notification mechanism
7. Supports OSs like: Windows 9x/ME/NT4.0/2K/XP, Linux (Red Hat, SuSE, Turbo,
Caldera), and FreeBSD
8. Windows-based RAID configuration & management software tool (compatible
with BIOS)
9. Supports hard disk capacity over 137GB
High Performance and Data Security
The RocketRAID 404/454 can support multiple RAID arrays and provide parallel
disk/array access. With the RocketRAID 404/454 adapter's RAID 0 and 10 capabilities, data storage and retrieval is dramatically faster than single drive systems.
For RAID 1 and 10, the RocketRAID 404/454 provides disk mirroring. Hot spare
supports automatic array rebuild; and hot swap support swapping failed disks on
the fly and disk failure notification. These features provide a high level of security
and data protection against hard disk failures.
Expand the Computer's Data Storage with RocketRAID 404/454
adapter's mass storage capabilities
The RocketRAID 404/454 has four independent ATA channels and supports up to
eight IDE hard disk drives. It imposes no restrictions on hard disk capacity, and will
satisfy most of the business and personal applications.
1-3
Page 9

Chapter 2
Adapter Installation
This chapter will describe how to install the RocketRAID 404/454 adapter
into a computer, and how to properly attach hard drives to the adapter. Please
make sure to read through this chapter carefully before installing the adapter.
Contents of this Chapter:
2.1 Adapter Layout
2.2 Hard Disk Connection
2.3 Adapter Installation
2.4 Verifying the Adapter's Installation
2.5 Driver Installation
If you have any questions about the installation process, please contact our
technical support department.
Page 10
Adapter Installation
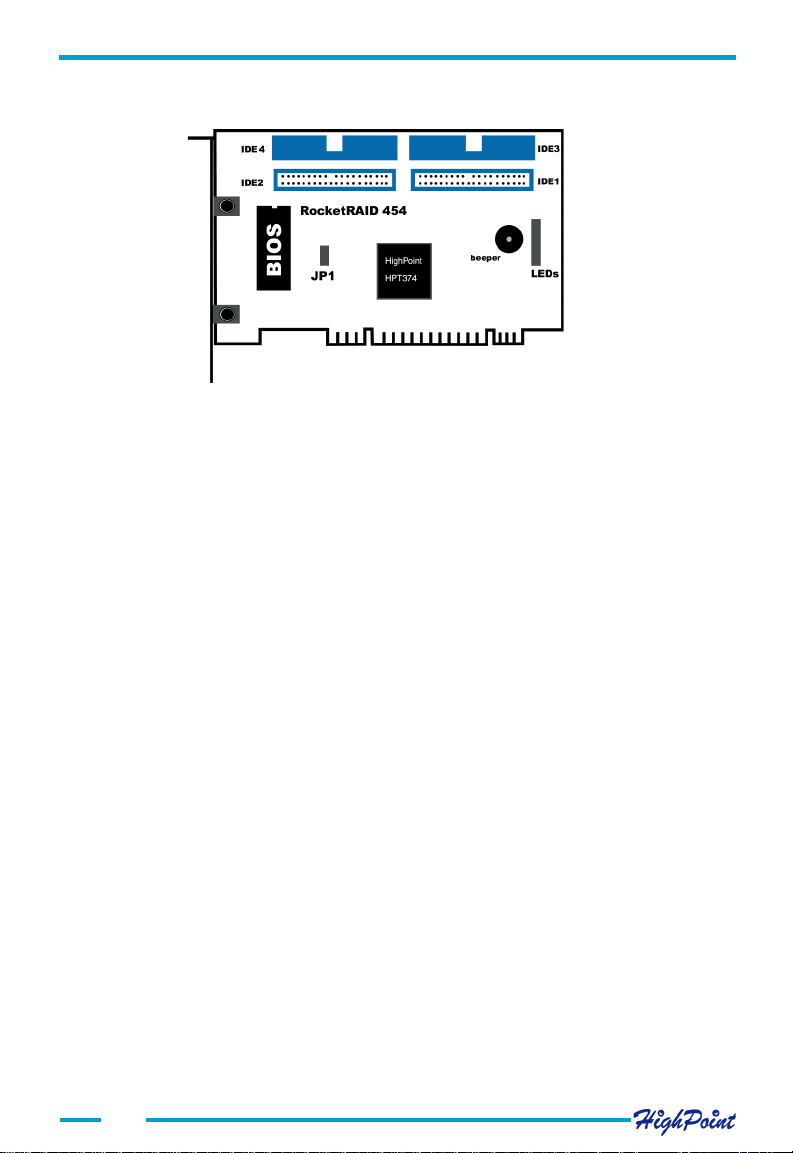
2.1 Adapter Layout
Adapter
Setting of JP1:
1-2 short connected : Disable loading configuration from adapter's BIOS, and
use the default on-chip configuration instead.
2-3 short connected: Enable loading configuration from adapter's BIOS.
The default setting of JP1 is 1-2 short connected. No need to change JP1 setting
after you got the adapter.
Note:
1. JP1's setting has nothing to do with updating BIOS. Either the JP1 is 1-2 shortconnected or 2-3 short-connected, user can update the BIOS by running the
program: LOAD.EXE contained in the driver diskette.
LEDs Connection:
The 8-pin LED is for LED connections. From top to bottom, there are 8 pins: 1-2 for
IDE1, 3-4 for ID 2, 5-6 for IDE3, and 7-8 for IDE4.
2.2 Hard Disk Connection
The following chart displays recommended drive configurations, based on the number
of drives and the type of RAID array being created.
Note:
1. "v" means it is better to connect hard disk at this position.
2. When connecting hard disk, pay much attention to its Master -Slave jumper
setting: if two hard disks are connected onto one IDE cable, then one disk must be
set as master while the other as slave.
Note: Some hard disks may work best if the jumpers are set to cable select, rather
than master/slave. Consult the drive's documentation for the manufacturer's
recommended settings.
2-1
Page 11
Adapter Installation
rebmuN
fo
sksiD
1v
2v v
3v v v
4vvvv
5vvvvv
6vvvvv v
7 vvv vvvv
8 vvvvvvvv
1EDI2EDI3EDI4DEI
yramirPevalSyramirPevalSyramirPevalSyramirPevalS
2.3 Adapter Installation
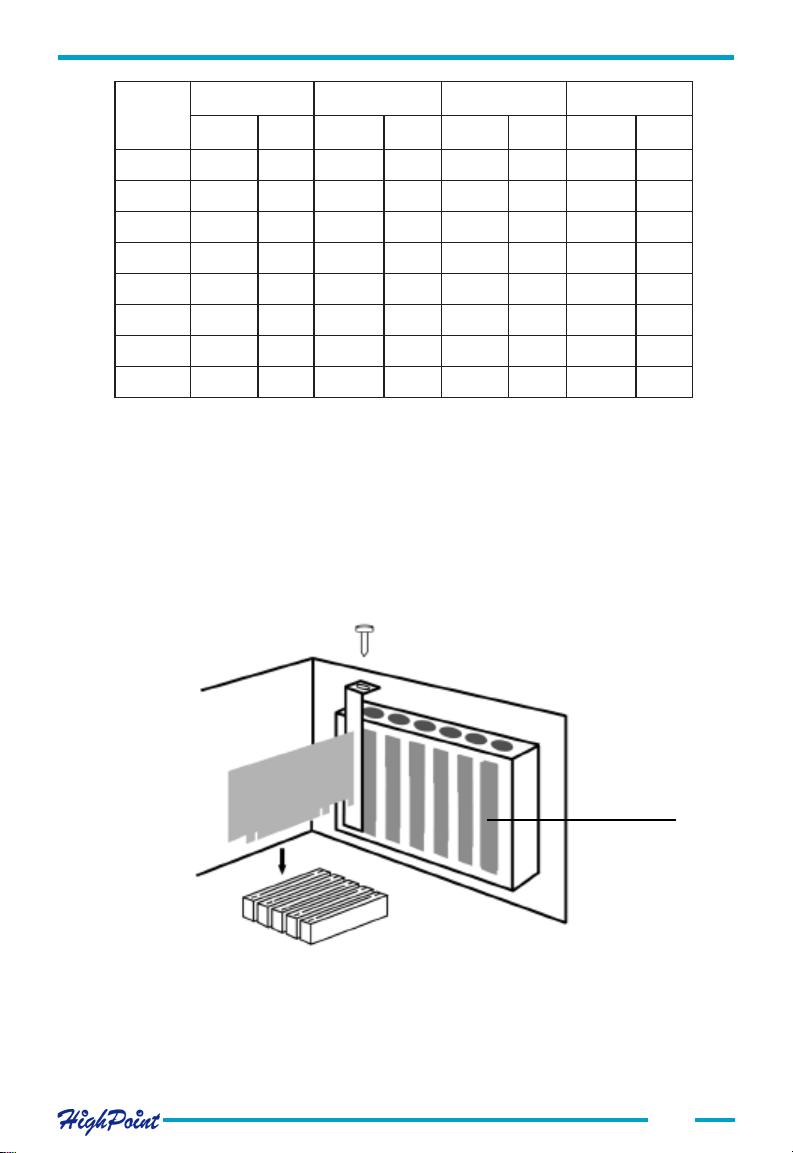
Follow these steps to install and connect hard disks to the host adapter.
1. Shut down the computer and unplug the power supply.
2. Please discharge static electricity from your body by touching a conductor.
3. Remove the corresponding card bracket from the back of the computer chassis.
4. Insert the RocketRAID 404/454 adapter steadily into a PCI slot on motherboard
and then settle it with screw.
Card Bracket
Adapter Installation
5. Set jumper of hard disks and settle them inside the computer chassis.
6. Connect hard disks to RAID adapter with IDE cables.
2-2
Page 12

Adapter Installation
Blue Connector
Cable Connection
7. Connect power supply connector to hard disk.
8. Replace the cover of computer chassis.
Note:
If multiple hard disks are attached to the host adapter, a powerful power supply is
needed in order to provide enough electricity for the system.
2.4 Verifying the Adapter's Installation
After installing the RocketRAID 404/454 host adapter, and connecting the hard disks
as required, the computer can be turned on. Please pay close attention to the information displayed on the screen while starting the computer. If the following information
is displayed (see the picture below), the RocketRAID 404/454 host adapter has been
successfully installed and recognized by the computer.
2-3
Page 13
Adapter Installation
Note:
1. If all of the connected hard disks are displayed on the screen, the disks have been
properly installed and recognized by the computer.
2.5 Driver Installation
After the RocketRAID 404/454 host adapter is installed and recognized by the computer, allow the operating system to boot. The host adapter's device driver must be
installed.
Windows 98/Me
Installation
After the operating system has booted, Windows will automatically detect the newly
installed adapter, and prompt the user to install it's driver. Follow these steps to install
the driver.
1. After the Add New Hardware Wizard window is displayed, press the Next button
until the following window appears:
2-4
Page 14
Adapter Installation
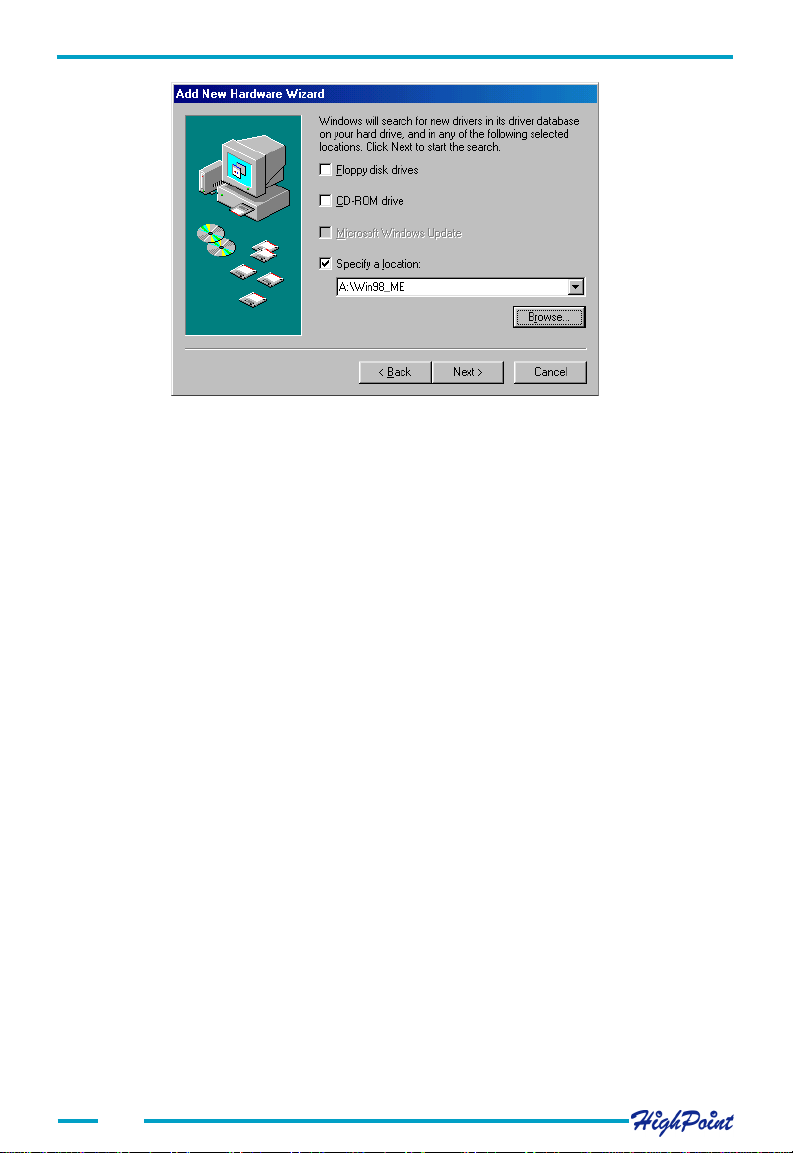
2. Insert the driver diskette, then select the Specify a location item, and type in the
driver location: A:\Win98_ME, then click on the Next button to continue.
(If the driver is located on a CD, make sure to input the correct path. For example:
D:\Driver\Win98_ME)
3. Confirm the following dialogue windows. Windows will then display a prompt to
restart the system. Select NO - do not restart the computer at this time.
4. Windows will then find a second device. Repeat steps 1 and 2, then click YES to
restart the computer.
Verify Installation
After installing the driver, and after Windows reboots:
1. Right-click on My Computer icon on desktop, and then select Properties item
from the popup menu.
2. From the popup window, activate Device Manager item, see next page.
2-5
Page 15
Adapter Installation
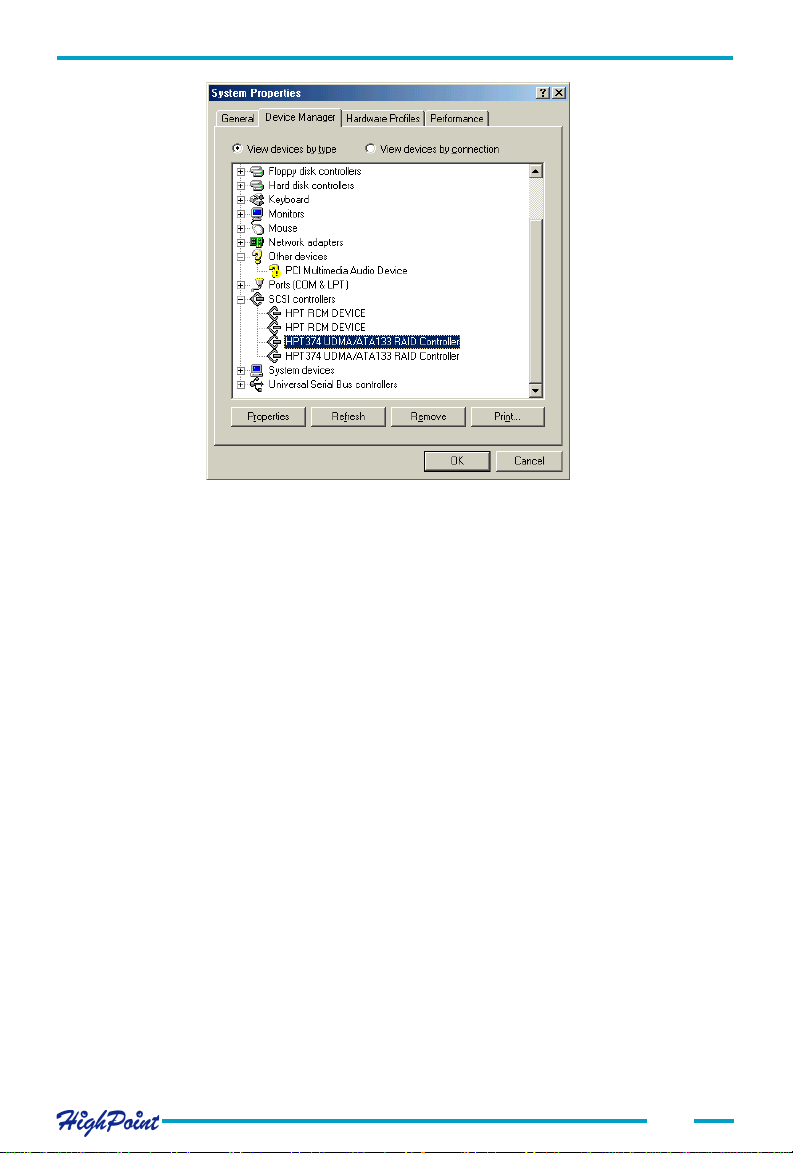
Double click the SCSI controllers entry. Four items should be displayed - two entries
for the HPT374 controller, and two entries for the RCM device. If any of these items is
not displayed, or any "?" or "!" marks are displayed near the device icons, the driver
had not been correctly installed. Delete these items, and reinstall the driver.
If all four items are properly displayed, the driver has been installed correctly.
Note:
1. If the system is not restarted after installing the driver, "!" marks may displayed
near the device entries.
Windows NT4.0
Installing the RocketRAID 404/454 driver for an existing Windows NT 4.0 system
1. Click Start-->Settings-->Control Panel, then double-click on the SCSI Adapters
icon.
2. A new window should be displayed - click on the Driver tab, then click on the Add
button.
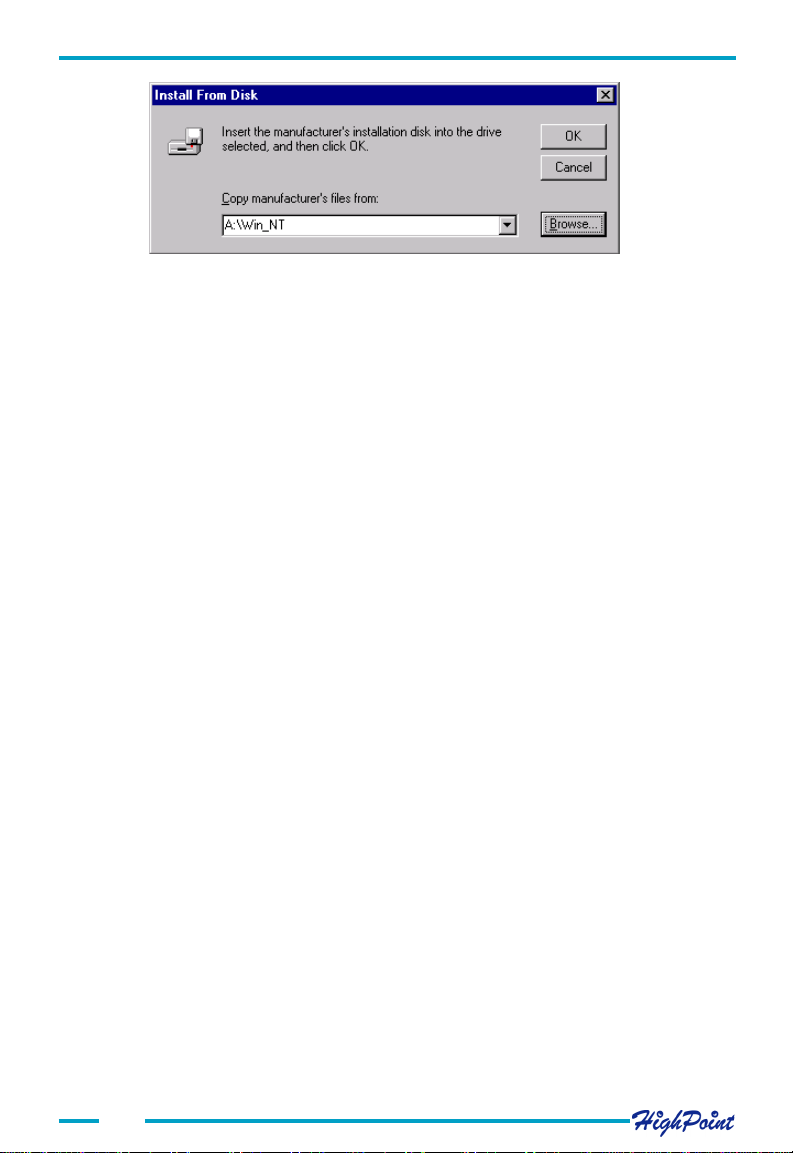
3. In the following window, click on the Have Disk...button. The following window
will appear (see the picture next page).
2-6
Page 16
Adapter Installation
4. Insert the driver diskette, and type in the path of driver location:
A :\Win_NT in the above window, then click OK. (If users install driver
from CD make sure input the correct path, for example D:\Driver\Win_NT)
5. Within the following window, select HPT374 UDMA/ATA133 RAID Controller
item, then click OK.
6. Confirm the following system prompts to finish the driver installation. When
installation is complete, restart the computer.
Installing the RocketRAID 404/454 driver during Windows NT 4.0 installation
1. Press F6 key when the installation program prompts Setup is inspecting your
computer's hardware configuration.
2. NT setup will then proceed normally. Later, NT setup will display a new window with
an option to press the "S" key to specify other devices. Please press the "S" key.
3. In the following window, select Other, then press the ENTER key to confirm.
4. Setup will then prompt you to insert the driver diskette. Insert the driver diskette,
and press ENTER to continue.
5. Next, select HPT374 UDMA/ATA133 RAID Controller for WinNT4.0, and press
ENTER to continue.
6. The following window will list the devices that will be installed. The HPT374 UDMA/
ATA133 RAID Controller should be included.
(If other devices need to be installed, please install them at this time. If all of the
devices have been installed, please proceed to the next step.)
7. Press ENTER to confirm the devices to be installed and continue the installation of
Windows NT4.0.
Verify Installation
After the driver has been installed and the computer is restarted:
1. Click Start-->Settings-->Control Panel, and then double-click on SCSI Adapters
icon.
2. Within the SCSI Adapters window, see next page.
2-7
Page 17
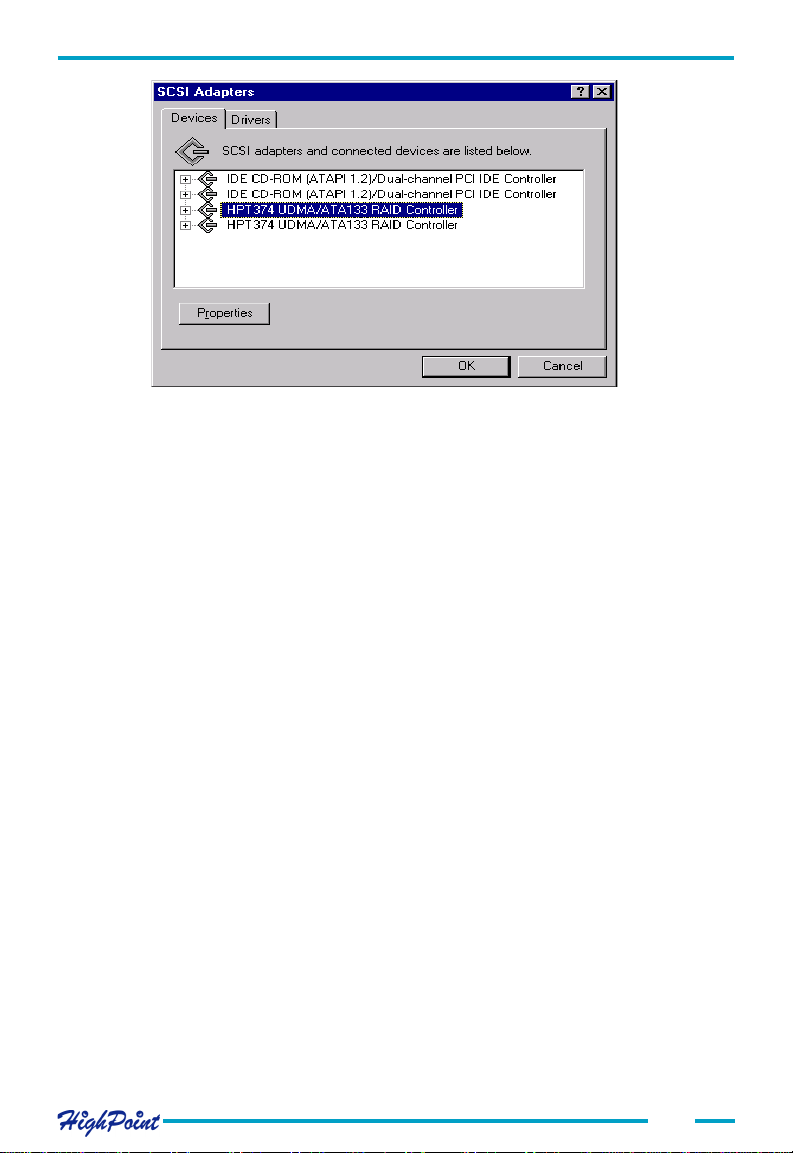
Adapter Installation
Make sure the HPT374 UDMA/ATA133 RAID Controller entries are displayed. This
indicates that the driver has been successfully installed. If these entries are not displayed, or any "?" or "!" marks are displayed near the device entries, the driver had not
been correctly installed. Delete these items, and reinstall the driver.
Windows 2000
Installing the RocketRAID 404/454 driver for an existing Windows 2000 system
After the operating system has booted, Windows 2000 will automatically detect the
newly installed adapter, and prompt the user to install it's driver. Follow these steps to
install the driver.
1. When the Found New Hardware Wizard window appears, click Next button to
continue, in the following window, please select Display a list ... and then click
Next to continue.
2. In the following window, select SCSI and RAID Controllers and then click
Next to continue.
3. In the following window, click Have Disk..., then Insert the driver diskette and
type in the driver location: A:\Win_2000, then click OK to continue. (If users
install driver from CD make sure input the correct path, for example
D:\Driver\Win_2000)
2-8
Page 18

Adapter Installation
4. In the following window, select HPT374 UDMA/ATA133 RAID Controller,
then click Next to continue.
5. Confirm the followup windows and click the Finish button to continue.
6. Next, Windows will find the HighPoint RCM device. Please confirm the Digital
Signature Not Found window when it appears, and restart the computer when
prompted.
Installing the RocketRAID 404/454 driver during Windows 2000 installation
(Recommend users copy the driver to a floppy diskette's root directory)
1. Booting from the CD-ROM - when the Windows 2000 Setup blue screen appears,
look towards the bottom of the screen. Windows will prompt you to press the F6 key
if you want to install a third part SCSI or RAID driver. Please press the F6 key at this
time.
2. The setup procedure will continue, and will later instruct you to press the "S" key to
specify additional adapters. Please press the "S" key at this time.
3. Then the setup program will prompt user to insert the driver diskette. Please
insert the driver diskette, then press ENTER to continue.
4. The following window will display several driver options. Please select the HPT374
UDMA/ATA133 RAID Controller for Windows 2000 option, and press ENTER to
continue.
5. The following window will list the devices that will be installed. The HPT374 UDMA/
ATA133 RAID Controller should be included.
(If other devices need to be installed, please install them at this time. If all of the
devices have been installed, please proceed to the next step.)
6. Press ENTER to continue Windows 2000 setup.
Verify Installation
After the driver has been installed, and the computer has been restarted:
1. Right-click My Computer icon, then select Properties item from the popup
menu.
2. In the popup window, select the Hardware item, then click on the Device Manager
button.
2-9
Page 19
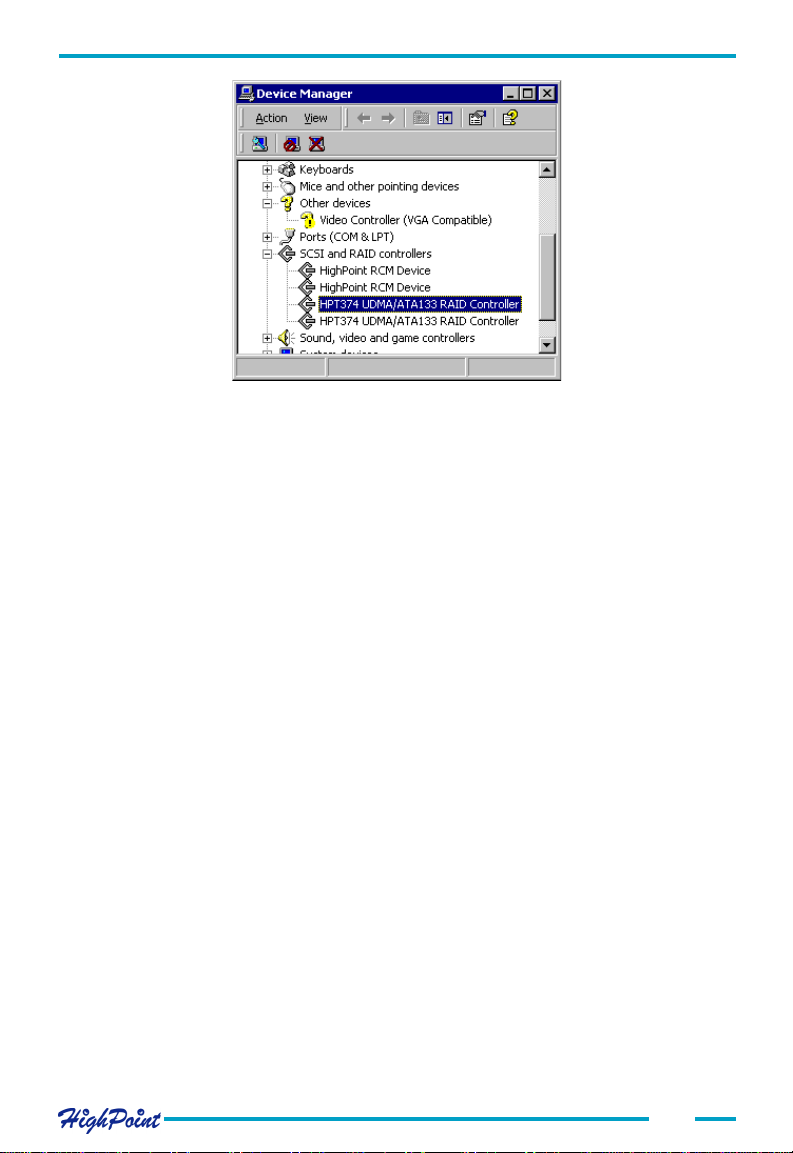
Adapter Installation
Make sure the correct HPT374 UDMA/ATA133 RAID Controller entries are displayed
(see the image above) . Four items should be displayed - two entries for the HPT374
controller, and two entries for the RCM device. If any of these items is not displayed,
or any "?" or "!" marks are displayed near the device icons, the driver had not been
correctly installed. Delete these items, and reinstall the driver.
If all four items are properly displayed, the driver has been installed correctly.
Windows XP
Installing the RocketRAID 404/454 driver for an existing Windows XP system
After the operating system has booted, Windows XP will automatically detect the
newly installed adapter, and prompt the user to install it's driver. Follow these steps to
install the driver.
1. When the Found New Hardware Wizard window appears, select Install from a
list or specify location(Advanced), and click Next to continue.
2. In the following window, please select Don' t search, I will choose the driver to
install, then click Next to continue.
3. In the following window of device list, please select SCSI and RAID controllers,
and then click Next to continue.
4. In the next window, click on Have Disk..., then type in the driver location:
A:\Win_XP into the following window, then click OK to continue.(If users install
driver from CD make sure input the correct path, for example
D:\Driver\Win_XP)
2-10
Page 20
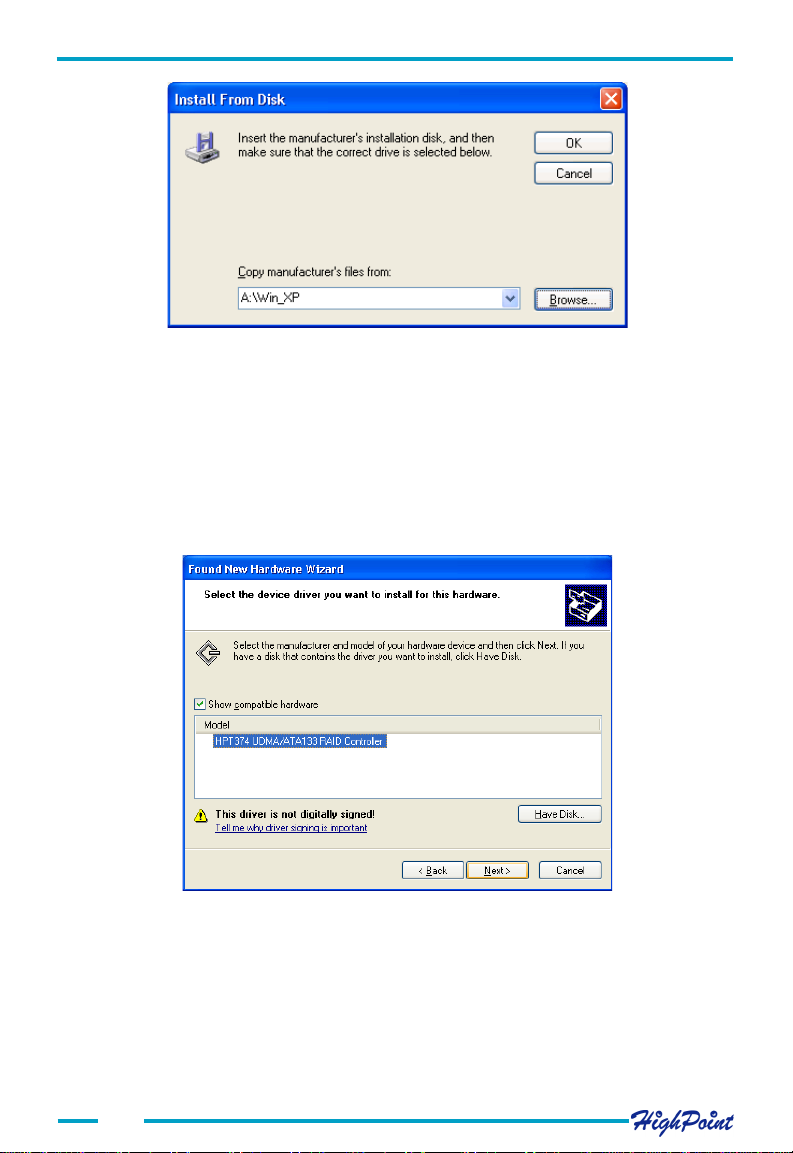
Adapter Installation
5. In the following window, select HPT374 UDMA/ATA133 RAID Controller,
then click Next to continue.
6. In the following window, click on Continue Anyway, then click Finish in the
following window.
7. Next, Windows will find the HighPoint RCM device. Please confirm the Digital
Signature Not Found window when it appears. Windows will then display a
prompt to restart the system. Select NO - do not restart the computer at this time.
Windows will then find a second device. Repeat steps 5 and 6, then click YES to
restart the computer.
Installing the RocketRAID 404/454 driver during Windows XP installation
(Recommend users copy the driver to a floppy diskette's root directory)
1. Booting from the CD-ROM - when the Windows XP Setup blue screen appears, look
towards the bottom of the screen. Windows will prompt you to press the F6 key if
you want to install a third part SCSI or RAID driver. Please press the F6 key at this
time.
2-11
Page 21

Adapter Installation
2. The setup procedure will continue, and will later instruct you to press the "S" key to
specify additional adapters. Please press the "S" key at this time.
3. Then the setup program will prompt user to insert the driver diskette. Please
insert the driver diskette, then press ENTER to continue.
4. The following window will display several driver options. Please select the HPT374
UDMA/ATA133 RAID Controller for Windows XP option, and press ENTER to
continue.
5. The following window will list the devices that will be installed. The HPT374 UDMA/
ATA133 RAID Controller should be included.
(If other devices need to be installed, please install them at this time. If all of the
devices have been installed, please proceed to the next step.)
6. Press ENTER to continue Windows XP setup.
Verify Installation
After the driver has been installed, and the computer has been restarted:
1. Right-click My Computer icon, then select Properties item from the popup
menu.
2. In the popup window, select Hardware tab and then click Device Manager
button.
Make sure the HPT374 UDMA/ATA133 RAID Controller entries are displayed (see
the image displayed above). This indicates that the driver has been successfully
installed. If these entries are not displayed, or any "?" or "!" marks are displayed near
the device entries, the driver had not been correctly installed. Delete these items, and
reinstall the driver.
2-12
Page 22

Chapter 3
BIOS Configuration Utility
The RocketRAID 404/454 includes a built-in BIOS configuration utility. This
utility provides options to configure and manage hard disks or disk arrays
connected to the RocketRAID 404/454 host adapter. The BIOS configuration utility is especially useful when arrays must be created before and OS is
installed.
Contents of this Chapter:
3.1 Entering the BIOS Configuration Utility
3.2 Creating a Disk Array
3.3 Deleting Disk Arrays
3.4 Add/Remove Spare
3.5 Settings
3.6 View
3.7 Duplicate Critical RAID 1 array
3.8 Rebuilding a Broken RAID array
Page 23

BIOS Configuration Utility
3.1 Entering the BIOS Configuration Utility
When the following information is displayed on the screen during bootup, press
Control+H to access the BIOS configuration utility.
The main interface of BIOS configuration utility is as below:
Main Menu:
Status:
Help: This column gives help information about the current selected item
This column lists all currently available operation commands.
This column lists all the hard disks and disk arrays connected to the
adapter. When this column is activated, user can select the target
device to perform a specific operation.
and the prompt on available operations.
3-1
Page 24

BIOS Configuration Utility
3.2 Creating a Disk Array
Follow these steps to create a disk array:
1. Within the Menu column of the main interface, use the arrow keys to highlight the
Create command and press ENTER. This will open a list of array modes (also
referred to as RAID levels). See the image below:
Use the arrow keys to highlight the array mode you wish to create, and press ENTER to
confirm the selection.
2. Within the Menu column of the main interface, use the arrow key to highlight
Array Name, and press ENTER. A dialogue box will appear (see the image below)
Name the array using the keyboard, and press ENTER to continue.
3. Within the Menu column of the Main interface, use the arrow key to highlight the
Select Devices option, and press ENTER. This will activate the Status column (see
the image below):
Highlight the disks that you wish to use, and press ENTER to select them. After all of
the disks have been selected, press the ESC key to return to the creation step menu.
4. When creating a RAID 0, 1/0, or 5 array, a block size must be selected. Within the
Menu column of the main interface, use the arrow keys to highlight the Block Size
option, and press ENTER. Select a block size from the pop-up list (see the image
next page):
3-2
Page 25

BIOS Configuration Utility
If user selected a RAID 1array, JBOD array in step 1, the Block Size is N/A, see
below:
5. Within the Menu column of the main interface, use the arrow keys to highlight the
Start Creation option, and press ENTER.
When creating RAID 0, 1/0 or JBOD array, simply use the arrow key to highlight the
Start Creation process and press ENTER. A warning message will then be displayed.
See the image below:
Please pay close attention to this warning. Press N to cancel, and press Y to continue.
When creating a RAID 1 (mirror) array, several options will be displayed: Create only,
or Create and Duplicate. The Create and Duplicate option will preserve the data on the
source disk 1) and will copy it to the mirror or target disk (disk 2).
Create only should only be used when stating from scratch - this option will not
preserve the data on either disk. See the image next page:
3-3
Page 26

BIOS Configuration Utility
A warning message will then be displayed. See the image below:
Please pay close attention to this warning. Press N to cancel, and press Y to proceed
with he duplication process.
When creating a RAID 5 array, several options will be displayed: Zero Build and No
Build. Zero Build will initialize the disk. Zero Build or No Build will start over if
interrupted, but No Build will create an array without initialization. See the image
below:
If the No Build option is selected, warning messages will be displayed. See the image
next page:
3-4
Page 27

BIOS Configuration Utility
Please pay close attention to this warning. Press N to cancel, and press Y to continue.
If Y is selected, another warning message will be displayed. See the image below:
Select Y to create the array, and N to cancel.
Warning:
Please pay close attention when warning message are displayed during step 5. When
creating RAID 0, 5 and JBOD arrays, selecting Y will destroy all data on the selected
disks.
3.3 Deleting Disk Arrays
Follow these steps to delete a disk array:
1. Within the Menu column of the main interface, use the arrow key to highlight the
Delete option, and press ENTER. The Status column will be activated. See the
image next page:
3-5
Page 28

BIOS Configuration Utility
Highlight the target disk array, and press ENTER to delete it.
2. A warning message will then appear. See the image below
Pay close attention to this warning. Press Y to delete the selected array, or press N to
cancel.
3.4 Add/Remove Spare
Follow these steps to add spare or delete spare from spare pool:
1. Within the Menu column of the main interface, use the arrow key to highlight the
Add/Remove Spare option, and press ENTER. The Status column will be activated.
See the image below:
Use the arrow keys to highlight the target disk, and press ENTER to add it to the spare
pool. To remove a disk from the spare pool, highlight it and press ENTER.
3-6
Page 29

BIOS Configuration Utility
2. After a disk has been added to the spare pool, it's status will be marked as Spare.
See the image below:
3.Repeat step 1 to add to or remove any additional disks from the spare pool.
Warning:
Adding a disk to the spare pool will delete all data on that disk.
See the image below:
Select Y to continue and N to cancel.
3.5 Settings
Follow these steps to set a disk or disk array:
1. Within the Menu column of the main interface, use the arrow key to highlight the
Select Settings option, and press ENTER. The following list will be displayed:
2. Use the arrow keys to select Set Boot Mark, and highlight the target disk or disk
array and press ENTER. This option will instruct this disk or array to act as the boot
unit, when motherboard has designated the RocketRAID 404/454 to act as the boot
device.
3-7
Page 30

BIOS Configuration Utility
3. Highlight the Remove Boot Mark to remove the boot designation from a selected
boot disk or disk array. Use the arrow keys to highlight the target disk or disk array
and press ENTER.
4. To change a disk or disk array's mode setting, use the arrow keys to highlight the
Device Mode option and press ENTER. This will display a series of possible mode
settings. See the image below:
5. To rename a disk array, use the arrow keys to highlight the Array Name option,
and press ENTER. This will open a dialogue box (see the image below).
Use the keyboard to create an array name, then press ENTER.
3.6 View
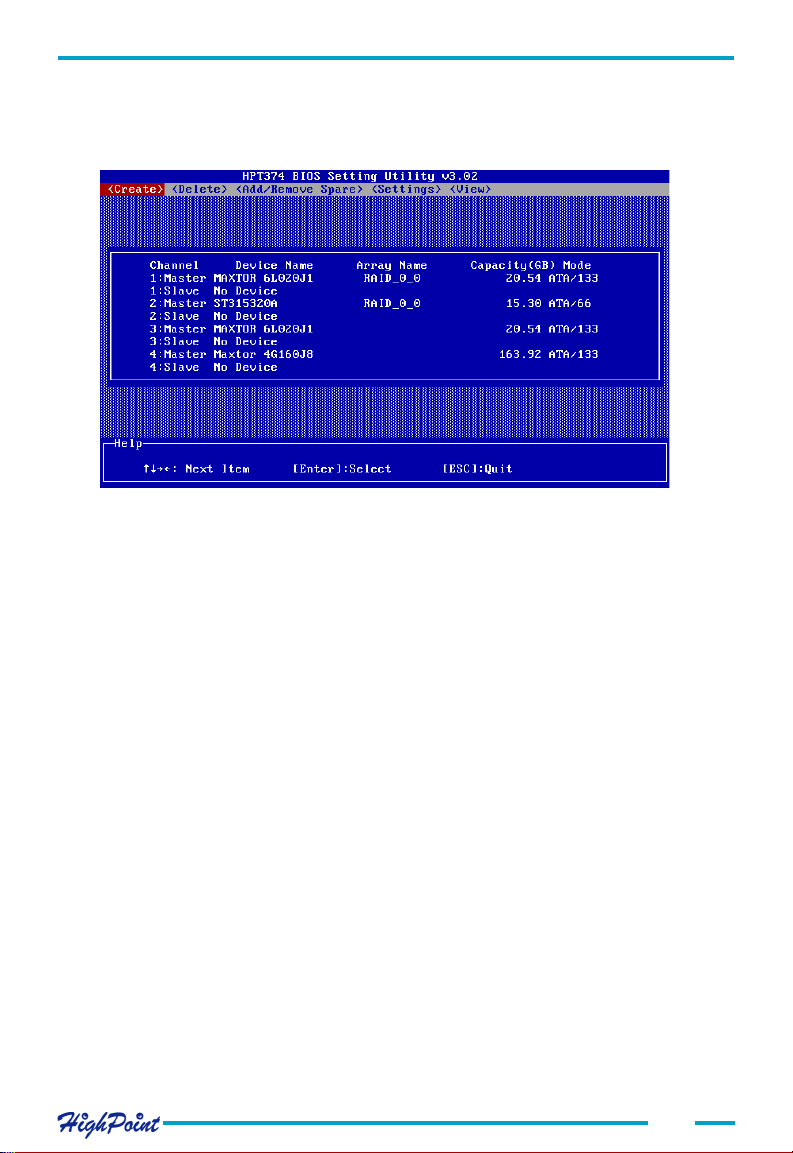
Follow these steps to view a disk or disk array:
1. Within the Menu column of the main interface, use the arrow key to highlight the
View option, and press ENTER. The following list will be displayed:
2. To view the Port information, use the arrow keys to highlight the Port option and
press ENTER. A new window will be displayed (see the image below):
3.To view Device information, use the arrow keys to highlight the Device option and
press ENTER. The following window will be displayed (see the image next page):
3-8
Page 31

BIOS Configuration Utility
4. To view information about a particular disk/RAID Array, use the arrow keys to
highlight the RAID array option, and press ENTER. The following window will be
displayed (see the image below):
5. To view information about logical drives, use the arrow keys to highlight the
Logical Drives option, and press ENTER. The following window will be displayed
(see the image below):
3.7 Duplicate Critical RAID 1 array
If a RAID 1 duplication procedure has been canceled, or any problem or fault that may
have lead to an inconsistency between the data on the source disk/disk array, and the
backup data on the target disk/disk array, is detected, the BIOS will display a warning
message during the computer's boot-up procedure. The faulty disk/disk array will be
marked as critical in the status column, and the BIOS will automatically prompt you to
duplicate the array to repair the inconsistency. See the image below:
3-9
Page 32

BIOS Configuration Utility
Select the Rebuild option to duplicate, or select Continue to boot to skip this procedure. The array can be repaired using after the operating system has booted, using the
RAID software (chapter 4 covers this subject).
3.8 Rebuilding a Broken RAID array
If the BIOS detects that a RAID 1 has been broken, when a spare disk is unavailable,
several options will be displayed. See the image below:
1. Power off
This command provides the option to power off the system and replace the failed disk
with a fresh unit. If the system does not support APM (advanced power management),
you must power down the computer manually. After replacing the failed disk, and
starting the system, access the BIOS configuration utility, and rebuild the damaged
array (see option 4 - Rebuild).
2. Destroy
This option is designed for use with RAID 1 arrays, and will delete the RAID relationship. The data on the surviving disk will be left intact.
3. Continue
This option will hide the broken array and continue to boot to the operating system.
4. Rebuild
This option will rebuild a damaged array using a fresh disk, and duplicate the data from
the surviving member of the original array to this fresh disk.
a) If this option is selected, the following window will be displayed:
3-10
Page 33

BIOS Configuration Utility
Highlight the target disk and press ENTER to select it.
b) The BIOS will then start the rebuild/duplication process. See the image below:
The ESC can be used to cancel the procedure anytime during the rebuild/duplication
process.
c) Continue to boot - this option will allow the BIOS to skip the rebuild option, and boot
into the operating system.
3-11
Page 34

Chapter 4
ATA RAID Software
This chapter discusses the HighPoint Storage Management Software.
Contents of this chapter:
4.1 Introduction
4.2 Installation
4.3 Getting Started
4.4 Using the Software
Page 35

ATA RAID Software
4.1 Introduction
The HighPoint Storage Management Software is comprised of two separate utilities:
HighPoint Storage Management Console and HighPoint Storage Management Service
To simplify this guide, we will refer to the HighPoint Storage Management Console as
the Management Console, and the HighPoint Storage Management Service as the
Management Service.
Additionally, the system that hosts the Management Console may be referred to as the
administrative system, and the system that hosts the Management Service may be
referred to as the remote system.
The Management Console can be installed to any computer, and is used to monitor and
control RAID configurations utilized by other computers (remote systems). From the
Management Console, you can monitor one or more of these remote systems. The
software can be used to create, monitor, delete, or modify various types of RAID
arrays, including RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 10 (1/0), RAID 5, and JBOD.
The Management Service is designed to run continually on computers that utilize one
or more HighPoint ATA RAID controller. It is designed to receive and carry out commands issued by the Management Console: logging events, executing scheduled tasks,
and creating or rebuilding RAID arrays.
4.2 Installation
Follow these steps to install the Serial ATA RAID software:
1. Insert the HighPoint ATA RAID Management Software setup floppy diskette 1
into your floppy drive, and double click the setup.exe icon to start the installation
procedure. When prompted, insert the remaining disks, and follow the
instructions displayed by the setup program.
2. Confirm the follow-up dialogue windows to finish the installation.
3. When installation is complete, restart the computer.
(Note: It is strongly recommended that you exit all windows programs before
running this Setup program.)
4. You can install both the Management Console, and the Management Service, to a
single computer, or install the Management Console to one computer, and the
Management Service to another computer (or several others). You can access the
Management Service through the Management Console software. See the image
next page:
4-1
Page 36

ATA RAID Software
4.3 Getting Started
With the Default option selected, the setup program will create a Program group.
Click on the Start button, then click the Programs selection and highlight the
HighPoint entry. The following items should be displayed:
HSM Service Manage For the administrative system
Management Consolve For the remote systems (or, any system
using a HighPoint RAID controller)
Uninstall... Uninstall the program
Small icons ( ) will be displayed towards the bottom right-hand corner of the
system's desktop (near the clock feature), to indicate that the software is running. See
the image below:
1. Starting the Management Service
Double click the small ( ) icon to open the main interface of the Management
Service:
4-2
Page 37

ATA RAID Software
The colored traffic lights represent the Service's status. The ( ) button can
be used to activate or disable the Server Side software. A green "light" indicates the
Software is active. A red "light" indicates the software is disabled.
2. Starting the Management Console
Double click the small ( ) icon to open the main interface of the Management
Console software. The main interface has five tabs: File, Configuration, Management,
View, and Help. Click on different tabs to activate different commands. See the image
below:
File: This tab includes four sub-tabs: Remote Control, Server
configuration, User Management, Password and Exit. Click the
Exit button to exit Serial ATA RAID software.
Mangement: This tab includes six sub-tabs: Array Management, Device
Management, Spare Management, Event Notification, Task
Schedule and Refresh. These sub-tabs will be introduced later.
4-3
Page 38

ATA RAID Software
View: This tab includes two sub-tabs: Event View, and Icon View. The
system will diplay the connection status of all the attached disks
or disk arrays. The Event View window will display all of the
events recorded while the software is running. The Icon View
window explains the functions of the various icons used by the
software.
Operation: This tab includes 5 sub-tabs: Add, Modify, Delete, Connect, and
Disconnect.
Help: Click on this tab to view the Help topics, or check information
about this version of the HighPoint Storage Management
software. The help feature summarizes the functions of this
software, and includes a topic search option.
4.4 Using the Software
The File tab
This software allows you to connect to remote computers that utilize HighPoint RAID
controllers, via an Internet connection. After verifying the system's name and password, the software can be used to monitor, repair or modify existing RAID arrays
utilized by the remote system. The software can also be used to modify user information, and the Management Service's configuration.
1. Remote Control
Click on the File tab, and select the Remote Control item from the menu. This will open
the Remote Control Window.
Adding a Connection
The Add button is used to add a new system to the Remote Control window. Systems
added to the Remote Control window automatically appear each time the program is
launched.
Click on the Add button from the Remote Control window, or select Add from the
Operation tab to add a new system. See the image below:
4-4
Page 39

ATA RAID Software
Enter the remote system's address, name and port information into the appropriate
fields, then click OK. Make sure the Address and Port information is correct - the
software will be unable to connect to the remote system if any information is left out.
Note: If you do not need to connect to a remote system, and only need to work with
arrays attached to the system you are working with, choose to add a new system, and
enter the following information into the appropriate fields:
System Address: 127.0.0.1
System Name: RAID (make sure that capital letters are used) - use "hpt" as the pass
word
System Port: 7402
Modifying a Connection
This option is used to modify a connection (the name and Port). First, select one of the
connections from the connections list, and then click the Modify button on the toolbar,
or click on the Operation tab and select the Modify option. This will open a new
window. See the image below:
After modifying the system name and system port information, click OK.
Note: The System Address information cannot be altered. In order to modify this item,
the connection must be deleted and recreated.
Deleting a Connection
This option will delete a connection from the connection list. Select one of the connections from the connection list, and click the Delete button on the toolbar, or Click on the
Operation tab and select the Delete option. Click OK to delete the selected connection
from the connection list. A warning message will be displayed. See next page:
4-5
Page 40

ATA RAID Software
Click on Y to delete the connection, or N to cancel this operation.
Note: Make sure the connection is not active - it must be disconnected before it can be
deleted from the connection list.
Connect to a Remote System
Click the Connect button on the tool bar, or click on the Operation tab and select the
Connect item from the menu. You can also double-click the desired connection from
the connection list to start this procedure. A new window will be displayed. See the
image below:
Click OK to connect to the selected system, and Cancel to cancel this operation.
Note: You can only connect to one remote system at a time. Be sure to close the
previous connection before attempting to connect to another system.
Disconnecting a Remote System
To disconnect from a remote system, click on the Disconnect button on the toolbar, or
click on the Operation tab, and select the Disconnect option. A new window will be
displayed. See the image below:
Click OK to disconnect from the remote system, or Cancel to cancel this operation.
4-6
Page 41

ATA RAID Software
2. Remote Server Configuration
Click on the File tab, and select the System Configuration option from the menu. A
new window will be displayed. See the image below:
You can modify the values of the System Port and Event Port fields.
System Port
When connecting to the remote system, make sure the port value is correct. The
default value is 7402 - this may have to be changed.
Event Port
The Management Console software retrieves event information through this port. The
default value is 7403 - make sure this value is not the same value used for the System
Port.
After setting the system configuration, you should close and restart the RAID software - this will ensure that the changes made will take effect.
3. User Management
Click on the File tab, and select User Management from the menu. This will open a new
window. See the image below:
4-7
Page 42

ATA RAID Software
The User Management displays information about all valid user accounts, and pro-
vides options to create, delete or modify user information.
Adding a user
Follow these steps to add a new user:
1) Click on the Add button, and enter a user name and password. Confirm this pass-
word, then click on the Next button. See the image below:
2) Click on the Privilege button, and select the appropriate security privileges. Click on
the Finish button. See the image below:
3) Once the new user has been successfully added, the user's entry will appear in the
User Management window.
4-8
Page 43

ATA RAID Software
Deleting a User
Highlight and select a user entry from the User Management window, and click on the
Delete button. The selected user will then be deleted.
Make sure the selected user is not connected to the remote computer - the Delete
option will be disabled if the user is connected to the system.
Set a User Password
Highlight and select a user entry from the User Management window, and click on the
Set Password button. You can also click on the File tab, then select the Password
option.
Changing a User's Password
Highlight and select a user entry from the User Management window, and click on the
Set Password button. You can also click on the File tab, then select the Password
option. Enter the new password and click the OK button to confirm. Click on the
Cancel to cancel the operation.
Changing a User's Privilege level
Highlight and select a user entry from the User Management window, and click on the
Privilege button. The following window will be displayed:
4-9
Page 44

ATA RAID Software
Make the appropriate changes and click the OK button to confirm. Click on the Cancel
button to cancel this operation.
The Management tab
The HighPoint Storage management Console software provides a variety of RAID
management features. These features are listed under the RAID Management menu
displayed under the main interface window. Sub-menus display additional information
about RAID configurations, and make management an simple task.
1. Array Management
Click on the Management tab, and select the Array Management option. This will
open a new window, which will display all of the logical drives attached to the RAID
controller. The logical drives are grouped according to physical disk. See the image
below:
4-10
Page 45

ATA RAID Software
Clicking on a drive icon to display information about this disk - the right side of the
screen will provide information about the physical disk, including the model, location,
transfer mode and capacity. Clicking on an array icon will provide information about
the selected array, including the name of the array, the RAID type or level, and capacity.
Creating an Array
If the Create Array option has been enabled under the Privilege settings, and enough
disks are available to create an array, click the Create button located on the toolbar.
You can also click on the Operation tab, and select the Create option. This will open
the Array Creation Wizard window.
Step 1:
Select the type of Array
Select the type of array you wish to create using the drop-down menu. If JBOD was
selected, you can jump directly to Step 4.
If any other type of array is selected, enter an array name, and click the Next button. If
you do not wish to name the array, leave the Array Name field blank, and click the Next
button.
If RAID 0, 10, or 5 was selected, proceed to step 3.
Step 2:
RAID 1 Creation Option:
If RAID 1 was selected, select from the following array options (see the image below):
1) Create Only
This option will create a RAID 1 array between the selected disks, but will not preserve
any of the data. The data on both disks will be lost.
2) Create and Duplicate
This option will create a RAID 1 array between the selected disks, and will copy the
data from the Source disk, to the Mirror (also referred to as the target) disk. All data that
was originally stored on the Mirror disk will be deleted.
4-11
Page 46

ATA RAID Software
Step 3:
Specify the Block Size
When creating a RAID 0 or 10 array, select the Block Size from the drop-down menu,
and click on the Next button. See the image below:
When creating a RAID 5 array, select the Block Size from the drop-down menu, and the
appropriate Creation Option. See the image next page:
4-12
Page 47

ATA RAID Software
1) Zero Build
Create and initialize data blocks with zero build parities - this will create the array and
initialize parity, but will delete all data from each of the hard disks. Use this option when
starting from scratch.
2) Scrub (build parity)
This will create an array and initialize parity using the existing data on the hard disks.
3) No Build
Create only - the parity function will not become active until the array is first used.
Step 4:
Select the array disks
Select the single disks from the Available Disks list, and add them to the Selected
Disks list using the ( ) button.
If you are creating a RAID 1 array, and have selected the Create and Duplicate option,
the disk which you select first will be the Source disk, and the disk you select second
will be the Mirror disk. Please make sure the size of Source disk bigger than Mirror disk.
If the the size of Source disk bigger than Mirror disk, the following window will appear.
Press OK to select Mirror disk again.
If you are creating a RAID 1 array, and have selected the Create Only option, the
source disk will be automatically selected for you.
4-13
Page 48

ATA RAID Software
After selecting the required disks, click on the Finish button to create the array.
Renaming an Array
Click on the Management tab, then select the Array Management option from the
menu. Select the array you wish to rename from the tree display, and click on the
Rename button found on the toolbar. You can also click on the Operation tab, and
select the Rename option. See the image below:
Enter a new name for the selected array, then click on the OK button. Click on the
Cancel button to cancel this operation.
Note: You can not rename arrays that are in the process of being duplicated, initialized,
rebuilt or verified.
Deleting an Array
Click on the Management tab, then select the Array Management option from the
menu. Select the array you wish to delete from the tree display, and click on the Delete
button found on the toolbar. You can also click on the Operation tab, and select the
Delete option. A warning message will be displayed. See next page:
4-14
Page 49

ATA RAID Software
Click Y to delete the selected array, or click N to cancel the operation.
Note: You can not delete arrays that are bootable or are in the process of being duplicated, initialized, rebuilt or verified.
Adding a Disk to an Array
Click on the Management tab, then select the Array Management option from the
menu. If an array is broken, you will have to add a new single disk to proceed with a
rebuild. Select the broken array, then click on the Add Disk button on the toolbar. You
can also click on the Operation tab, and select the Add Disk option.
If this menu option is disabled, then disks cannot be added to this particular array, or
the Add Disk Privilege has not been enabled.
When booting the computer, if one member disk of RAID 1, RAID 1/0 or RAID 5
array is broken, and there is a spare disk can be used to rebuild the broken array,
system will automatically use the spare disk to rebuild the broken array and then
replace data to the target disk, see below:
Press the OK button to rebuild the broken array, press Cancel to exit.
If you press the OK button ,the following window will appear, see next page:
4-15
Page 50

ATA RAID Software
Click OK to start the rebuild process, see below.
When the system detects a physical disk, a dialogue box will appear. Select a single
disk from the list, and add it to the broken array. Continue to add disks to the broken
array until the "broken" status changes. Once the status has changed, the system will
begin the auto-rebuild process. When the rebuild procedure is complete, please restart
the computer.
Verifying an Array
Click on the Management tab, then select the Array Management option from the
menu. Select the array you wish to verify, and click on the Verify button. You can also
click on the Operation tab, and select the verify option. Once the verify command has
been executed, refresh the software interface - a progress bar should appear.
If this menu option is disabled, then the array cannot be verified, or the Verify Disk
Privilege has not been enabled.
To abort the procedure, click on the Operation tab, and select the Abort option. This
will cancel the Verify procedure.
4-16
Page 51

ATA RAID Software
Rebuilding an Array
Click on the Management tab, then select the Device Management option from the
menu. Highlight the array that needs to be rebuilt, and click on the Rebuild Array
button. Broken RAID 5, RAID 1, or a sub-RAID 1 of a RAID 10 array can use this
feature.
If this menu option is disabled, then array cannot be rebuilt, or the Rebuild Array
Privilege has not been enabled.
To abort the procedure, click on the Operation tab, and select the Abort option. This
will cancel the Rebuild procedure.
Rescanning Devices
Click on the Management tab, then select the Device Management option from the
menu. Click on the Rescan Device button, or click on the Operation tab, and select the
Rescan Devices option. This will scan all of the physical devices attached to the RAID
controller.
3. Spare Pool
Click on the Management tab, then select the Device Management option from the
menu. Click on the Spare Pool button - this will open a new window. See the image
below:
4-17
Page 52

ATA RAID Software
Assign a disk to the spare pool
If you need to assign a spare disk to an important array, select the Assign to Dedicated
Array option. Disk arrays that can utilize the spare feature will be then be displayed,
and listed on the drop-down menu towards the right hand side of the array list. When
an array is selected, the Available Disks list section will display all the single, physical
disks attached to the RAID controller. The Array Spares list will display the physical
disks that have already been set to act as spare disks.
The procedure can be repeated to add or remove additional spare disks.
4. Event Notification
Click on the Management tab, then select the Event Notification item from the menu.
The E-mail Notification window will appear. When an event occurs, the system will
send an E-mail to the preset mailboxes.
E-mail notification setting
In order to send and receive email, you must first configure the SMTP server. Click the
Settings button on the toolbar, or click on the Operation tab and select the Settings
option. The E-mail notification-setting window will be displayed. See the image
below:
Check the Enable E-mail option, and fill out the Mail From, SMTP server, and Port
fields with the appropriate information. Click OK to complete this procedure. The
system does not support user-validated SMTP server.
Add Recipient
Click on the Add button found on the toolbar, or click on the Operation tab and select
the Add Recipient option. This will open the Add Recipient window.
See the image next page:
4-18
Page 53

ATA RAID Software
Enter an e-mail address, the recipient's name, and the notification options. Three types
of e-mail notification options are available: Information, Warning, and Error. You can
enable any number of these options. Click OK to confirm your selections.
Modify Recipient
Click on the Modify button located on the toolbar, or click on the Operation tab and
select the Modify Recipient option. This will open the Modify Recipient window.
Modify the desired fields, and click OK to confirm your selections.
Delete Recipient
Highlight a recipient, and click on the Delete button found on the toolbar, or click on
the Operation tab and select the Delete Recipient option. This will open the Delete
Recipient window. A warning message will be displayed. Click OK to delete the
recipient.
5. Task Management
Click on the Management tab, then select the Task Schedule Management item from
the menu. The following window will be displayed:
4-19
Page 54

ATA RAID Software
When an array needs to be regularly verified or rebuilt, you can create a new scheduled
task to automatically manage this procedure.
The Task Schedule list displays information about all added tasks. Double click one of
the task entries, or select one and click on the Details button to display detailed
information about the selected task. If the appropriate Privileges have been enabled,
you can add new tasks, and modify or delete existing tasks.
Adding a Task Schedule
There are two types of tasks that can be scheduled: Verify Array, or Rebuild Array. If
any arrays can be rebuild in the current system, click on the New button located on the
toolbar to open the New Task Schedule Wizard. See the image below:
Select the task type, and the target array from the drop-down menu. Then, click on the
Next button to continue.
4-20
Page 55

ATA RAID Software
The above window is used configure how often a particular task should be run. The
current time of the connected remote system is displayed at the top.
To add a new task:
1. Enter a name for the task. You can also use the default task name.
2. Set Frequency. If you want to add a task to rebuild an array, you can select Occur
one time option. If you want to add a task to verify an array, you can specify the
detailed occur time by daily, weekly or monthly.
3. Set the effective date for a task in the Duration option.
4. Check the Enable the task option to activate this task. If this option is unchecked,
then the system will never execute this scheduled task.
5. Click the Finish button. When a task has been added successfully, it will appear to
the task schedule list in the main window.
Modify Task Schedule
Select a task that you want to modify from the Task schedule list in the main
window, then click the Modify button on the toolbar. In the pop-up window you can
modify the task name and frequency the task occurs.
Delete Task Schedule
Select a task that you want to delete from the Task Schedule list displayed in the main
window, and click on the Delete button located on the toolbar.
If the array is deleted, all tasks assigned to the array will be deleted as well.
4-21
Page 56
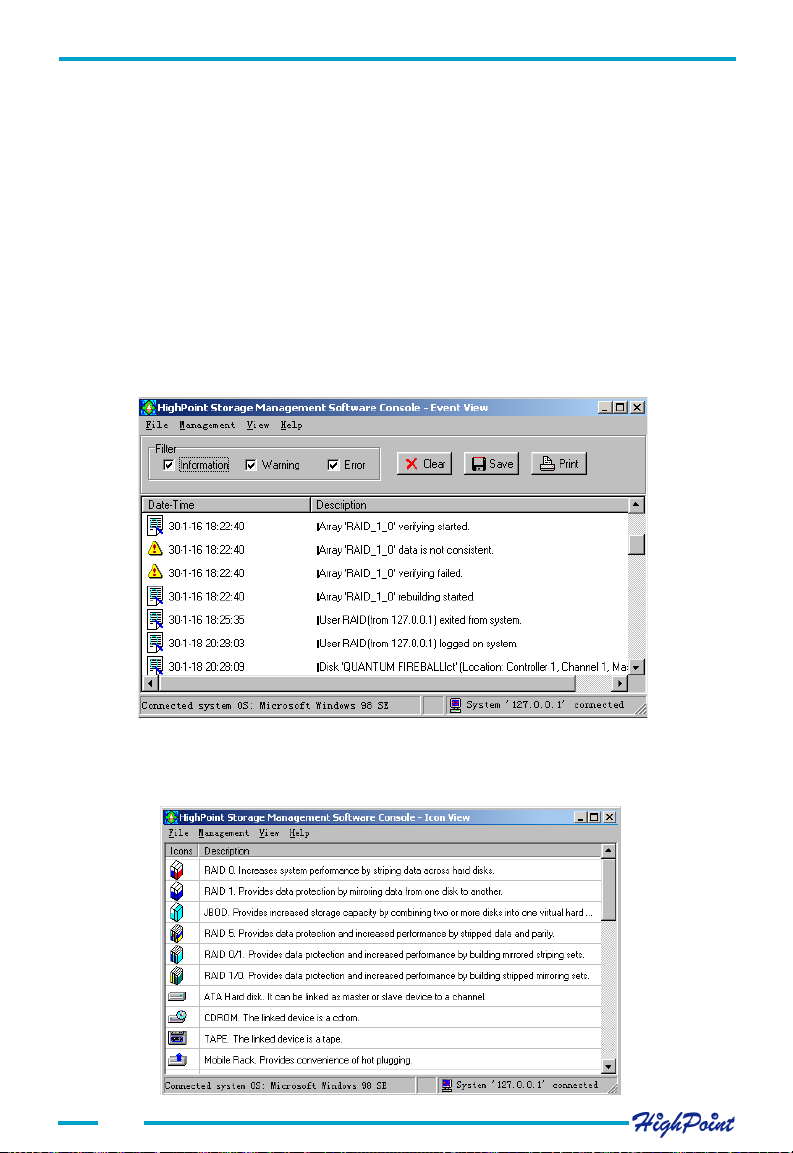
ATA RAID Software
The View tab
1. Event View
Click the View tab, and select the Event View option from the menu. This will display a
list of all the logged events of the remote system.
There are three types of logged events: Information, Warning, and Error.
Checking one of the Filter options will display all the selected type of events in
the following event View window.
Clicking the Clear button will clear all event View window in the event View
window and those stored on the remote system.
Clicking the Save button will save all of the events listed in the Event View
window as a plain text file.
Clicking the Print button will print all events listed in the event View window.
2. Icon View
Click the View tab, and select the Icon View option from the menu. A new window will
be displayed which shows the various event icons and their descriptions.
4-22
Page 57

Chapter 5
Trouble Shooting
Please refer to this chapter if you encounter any problems while using the
RocketRAID 404/454.
It provides answers to the most frequently asked questions, and solutions to
some of the more common problems associated with the host adapter.
Page 58

Trouble Shooting
1. The RocketRAID 404/454 adapter is not recognized by the
computer after inserting it into the PCI slot.
If the card is detected by the system the following screen will be displayed when the
computer is starting up:
If the above screen does not appear, the adapter is not recognized by the system.
Open the computer's chassis, and check for the following:
1) Whether or not the adapter has been securely installed into the PCI slot.
2) If necessary, try using another PCI slot.
After securing the adapter, replace the computer case and power on the system.
2. The hard disk connected to the host adapter is not detected.
After the RocketRAID 404/454 adapter is recognized by the system, the adapter's BIOS
will start to scan for hard disk drives. If drives are detected, the following information
will be displayed:
5-1
Page 59

Trouble Shooting
Please pay close attention to the information displayed by the BIOS - make sure all of
the hard disks attached to the controller are recognized by the BIOS.
If one or more of the hard disks are not recognized, open the computer's chassis and
check for the following:
1) Make sure the power cable for the hard drive is securely attached. If necessary, try
using another power cable.
2) Make sure the IDE cable is securely attached to the hard disk. If necessary, try using
another IDE cable.
3) If two hard disks are attached to the same cable, make sure the hard disk jumpers are
set correctly. Check the hard disk documentation for the manufacturer's recommended
jumper settings.
3.The hard disk mode is not correctly recognized by the host
adapter.
ATA 66/100/133 hard disks require special IDE cables. Make sure an ATA66/100/133
cable is used to attach the hard disks to the host adapter.
5-2
Page 60

Trouble Shooting
4. The operating system will not boot when the boot drive is attached to the host adapter.
In order to boot from a disk or disk array attached to the RocketRAID 404/454, certain
BIOS settings are required:
1) Make sure the motherboard's BIOS setup has set the host adapter as the first boot
device.
If the motherboard's BIOS setup does not list the host adapter as a boot option, use the
SCSI option.
2) Set the proper boot disk or disk array using the host adapter's BIOS (see Chapter 3
for more information).
5. What should I do if an array is reported as broken?
If an array is reported a broken, shutdown the system and make sure the power and IDE
cables are securely attached to the hard disks. If necessary, change the cables, then
power on the system. If the problem was related to a connection issue, this may restore
the array.
If the method described above does not work, the broken array was likely caused by a
hard disk error, or malfunction.
For RAID 1, 10, or 5 arrays, a new hard disk can be used to rebuild the broken array data will not be lost.
For RAID 0 or JBOD arrays, the array must be deleted, and recreated - all data on the
array will be lost. Please make sure to backup all important data stored on RAID 0 or
JBOD arrays.
5-3
Page 61

Appendix A
Appendix A
Glossary
Array
Also known as Disk Array, two or more hard disks combined together to appear as a
single device to the host computer.
RAID
Redundant Array of Independent Disks, it is a method of combining several hard
disks (physical disks) into one logical unit (logical disk), thus providing higher
performance and data redundancy.
RAID Levels
RAID levels refer to different array architectures (or methods of organizing a disk
array). Different RAID levels represent different performance level, security level and
cost.
Striping
Known as RAID 0, spread data over multiple disks to improve performance. It does
not provide data protection.
Mirroring
Known as RAID 1, which provides data protection by real-time and automatic
duplicating all data from a source disk to a mirror disk.
RAID 1/0
It is the combination of RAID 1 and RAID 0.
A-1
Page 62

Appendix A
RAID 5
RAID 5 includes a rotating parity array, thus, all read and write operations can be
overlapped. RAID 5 stores parity information but not redundant data. It requires at
least three disks to provide the most economic way to maximize data capacity with
faster transfer rate.
JBOD
JBOD is an acronym for Just a Bunch of Disks. It is used to refer to hard disks that
aren't configured according to RAID a subsystem of disk drives that improves
performance and fault tolerance. JBOD provides much more capacity (the sum of all
the disks). If there is more than a single physical disk (not member of an array and
not an ATAPI device or a removable disk), you can create a JBOD array.
Serial ATA
Serial ATA is an evolutionary replacement for the IDE ATA physical storage
interface.Serial ATA is scalable and will allow future enhancements to the computing
platform.
Broken Array
Disk array with a member disk failed. A broken RAID 1, RAID 5 or RAID 1/0 array
can still function with the remained normal disks, but a broken RAID 0 or JBOD will
no longer function.
Rebuild
The ability to use a new disk to replace the failed disk in a redundant disk array (say
mirror array, 1/0 array or 5 array), then to repair the broken disk array and recover all
the data on that failed disk.
Duplicate
The operation of duplicating user data to generate backup data within a RAID 1
array. Also known as Synchronize.
Spare Disk
A spare hard disk which can automatically be used to replace the failed member of a
redundant disk array and then automatically recover the redundant disk array
without intervention.
A-2
Page 63

Appendix A
Spare Pool
Logically the place where spare disks stay. When a disk is added into the spare pool,
it will become a spare disk.
Synchronize
Same as Duplicate.
A-3
Page 64

Appendix B
Appendix B
Contact Technical Support
If you encounter any problems or have any questions about the product, please make
sure to read through the manual.
Additional information about HighPoint products is available from our web site:
http://www.highpoint-tech.com
If the information provided by the manual and our web site are unable to answer your
questions or solve the problem, please contact our Technical Support department:
E-mail address:
support@highpoint-tech.com
B-1
Thank you for choosing our products!
Page 65

Fcc Part 15 Class B Radio Frequency Interference Statement
FCC Part 15 Class B Radio Frequency Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B
digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to
provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if
not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful
interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful
interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the
equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by
one or more of the following measures:
· Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
· Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
· Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which
the receiver is connected.
· Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Modifications not expressly approved by the manufacturer could void the user’ s
authority to operate the equipment under FCC rules.
This device complies with part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the
following two conditions: (1) this device may not cause harmful interference, and (2)
this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may
cause undesired operation.
European Union Compliance Statement
This Information Technology Equipment has been tested and found to comply with
the following European directives:
· European Standard EN55022 (1998) Class B
· European Standard EN55024 (1998)
 Loading...
Loading...