
High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 1 -
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
V 1.3
Overview of Characteristic
Support IEEE802.11b/g/n Wireless Standards
Based on Self-developed High Cost Effective MCU
Ultra-Low-Power for Battery Applications with Excellent Power Save Scheme
Support UART/SPI/PWM/GPIO Data Communication Interface
Support Work As STA/AP/AP+STA Mode
Support Smart Link Function (APP program provide)
Support Wireless and Remote Firmware Upgrade Function
Support WPS Function
Support Multi-TCP Link (5 Channel) Apllication
Support Soft Key Power Control
Support Internal/External Antenna Option
Single +3.3V Power Supply
Smallest Size: 23.1mm x 32.8mm x2.7mm
FCC/CE Certificated
HF-SH01
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 2 -
TABLE OF CONTENTS
LIST OF FIGURES .............................................................................................................................6
LIST OF TABLES............................................................................................................................... 7
HISTORY............................................................................................................................................8
1. PRODUCT OVERVIEW ...........................................................................................................9
1.1. General Description ............................................................................................................9
1.1.1 Device Features............................................................................................................. 9
1.1.2 Device Paremeters.......................................................................................................10
1.1.3 Key Application ............................................................................................................ 10
1.2. Hardware Introduction...................................................................................................... 11
1.2.1. Pins Definition.............................................................................................................. 11
1.2.2. Electrical Characteristics ..............................................................................................13
1.2.3. Mechanical Size...........................................................................................................14
1.2.4. On-board Chip Antenna ...............................................................................................14
1.2.5. External Antenna ......................................................................................................... 15
1.2.6. Evaluation Kit............................................................................................................... 15
1.2.7. Order Information.........................................................................................................17
1.3. Typical Application ........................................................................................................... 18
1.3.1. Hardware Typical Application ....................................................................................... 18
2. FUNCTIONAL DESCRI PTION .............................................................................................. 20
2.1. Wireless Networking......................................................................................................... 20
2.1.1. Basic Wireless Network Based On AP (Infrastructure)..................................................20
2.1.2. Wireless Network Based On AP+STA ..........................................................................20
2.2. Work Mode : Transparent Transmission Mode................................................................ 21
2.3. UART Frame Scheme........................................................................................................22
2.3.1. UART Free-Frame .......................................................................................................22
2.3.2. UART Auto-Frame .......................................................................................................22
2.4. Encryption......................................................................................................................... 23
2.5. Power Save Scheme .........................................................................................................23
2.6. Parameters Configuration ................................................................................................24
2.7. Firmware Update............................................................................................................... 24
2.8. GPIO/PWM Function ......................................................................................................... 25
2.9. SOCKET B Function ......................................................................................................... 26
2.10. Multi-TCP Link Connection ...........................................................................................26
3. OPERATION GUIDEL INE .....................................................................................................28
3.1. Configuration via Web Accessing....................................................................................28
3.1.1. Open Web Management Interface................................................................................ 28
3.1.2. System Page ...............................................................................................................28
3.1.3. Work Mode Page .........................................................................................................29
3.1.4. STA Setting Page......................................................................................................... 29
3.1.5. AP Setting Page...........................................................................................................30
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 3 -
3.1.6. Other Setting Page....................................................................................................... 31
3.1.7. Account Management Page ......................................................................................... 31
3.1.8. Upgrade Software Page ...............................................................................................32
3.1.9. Restart Page................................................................................................................ 32
3.1.10. Restore Page ...........................................................................................................32
3.2. HF-LPB100 Usage Introduction........................................................................................ 33
3.2.1. Software Debug Tools.................................................................................................. 33
3.2.2. Network Connection.....................................................................................................33
3.2.3. Default Parameter Setting ............................................................................................ 34
3.2.4. Module Debug..............................................................................................................34
3.3. Typical Application Examples..........................................................................................35
3.3.1. Wireless Control Application.........................................................................................35
3.3.2. Remote Management Application................................................................................. 36
3.3.3. Transparent Serial Port Application .............................................................................. 36
4. AT+INSTRUCTION INT RO DUCT ION...................................................................................37
4.1. Configuration Mode .......................................................................................................... 37
4.1.1. Switch to Configuration Mode.......................................................................................37
4.2. AT+ Instruction Set Overview........................................................................................... 38
4.2.1. Instruction Syntax Format.............................................................................................38
4.2.2. AT+ Instruction Set.......................................................................................................39
4.2.2.1. AT+E........................................................................................................................ 41
4.2.2.2. AT+WMODE ............................................................................................................41
4.2.2.3. AT+ENTM ................................................................................................................41
4.2.2.4. AT+TMODE..............................................................................................................42
4.2.2.5. AT+MID....................................................................................................................42
4.2.2.6. AT+VER................................................................................................................... 42
4.2.2.7. AT+RELD.................................................................................................................42
4.2.2.8. AT+FCLR ................................................................................................................. 43
4.2.2.9. AT+Z ........................................................................................................................ 43
4.2.2.10. AT+H .................................................................................................................... 43
4.2.2.11. AT+CFGRD .......................................................................................................... 43
4.2.2.12. AT+CFGWR.......................................................................................................... 43
4.2.2.13. AT+CFGFR...........................................................................................................44
4.2.2.14. AT+CFGTF ........................................................................................................... 44
4.2.2.15. AT+UART ............................................................................................................. 44
4.2.2.16. AT+ UARTF .......................................................................................................... 45
4.2.2.17. AT+ UARTFT........................................................................................................45
4.2.2.18. AT+ UARTFL ........................................................................................................45
4.2.2.19. AT+ UARTTE........................................................................................................45
4.2.2.20. AT+ SEND ............................................................................................................ 46
4.2.2.21. AT+ RECV ............................................................................................................ 46
4.2.2.22. AT+ PING ............................................................................................................. 46
4.2.2.23. AT+NETP ............................................................................................................. 46
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 4 -
4.2.2.24. AT+ MAXSK.......................................................................................................... 47
4.2.2.25. AT+ TCPLK........................................................................................................... 47
4.2.2.26. AT+ TCPTO.......................................................................................................... 48
4.2.2.27. AT+TCPDIS.......................................................................................................... 48
4.2.2.28. AT+SOCKB........................................................................................................... 48
4.2.2.29. AT+TCPDISB........................................................................................................ 49
4.2.2.30. AT+TCPTOB......................................................................................................... 49
4.2.2.31. AT+TCPLKB ......................................................................................................... 49
4.2.2.32. AT+SNDB ............................................................................................................. 50
4.2.2.33. AT+RCVB ............................................................................................................. 50
4.2.2.34. AT+WSSSID......................................................................................................... 50
4.2.2.35. AT+WSKEY .......................................................................................................... 50
4.2.2.36. AT+ WANN ........................................................................................................... 51
4.2.2.37. AT+ WSMAC ........................................................................................................51
4.2.2.38. AT+ WSLK............................................................................................................ 52
4.2.2.39. AT+ WSLQ............................................................................................................ 52
4.2.2.40. AT+WSCAN..........................................................................................................52
4.2.2.41. AT+ WSDNS.........................................................................................................52
4.2.2.42. AT+ LANN............................................................................................................. 53
4.2.2.43. AT+WAP............................................................................................................... 53
4.2.2.44. AT+WAKEY .......................................................................................................... 53
4.2.2.45. AT+WAMAC .........................................................................................................54
4.2.2.46. AT+WADHCP .......................................................................................................54
4.2.2.47. AT+WADMN .........................................................................................................54
4.2.2.48. AT+PLANG........................................................................................................... 55
4.2.2.49. AT+UPURL........................................................................................................... 55
4.2.2.50. AT+UPFILE........................................................................................................... 55
4.2.2.51. AT+UPWEB.......................................................................................................... 56
4.2.2.52. AT+UPCFG........................................................................................................... 56
4.2.2.53. AT+UPNVR........................................................................................................... 56
4.2.2.54. AT+UPAUTO ........................................................................................................56
4.2.2.55. AT+LOGSW..........................................................................................................57
4.2.2.56. AT+LOGPORT...................................................................................................... 57
4.2.2.57. AT+UPST ............................................................................................................. 57
4.2.2.58. AT+WEBU ............................................................................................................ 57
4.2.2.59. AT+MSLP ............................................................................................................. 58
4.2.2.60. AT+NTPRF ........................................................................................................... 58
4.2.2.61. AT+NTPEN........................................................................................................... 58
4.2.2.62. AT+NTPTM...........................................................................................................59
4.2.2.63. AT+WRMID........................................................................................................... 59
4.2.2.64. AT+RLDEN........................................................................................................... 59
4.2.2.65. AT+ASWD ............................................................................................................ 59
4.2.2.66. AT+MDCH ............................................................................................................ 60
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 5 -
4.2.2.67. AT+TXPWR .......................................................................................................... 60
5. PACKAGE INFORMATION ................................................................................................... 61
5.1. Recommended Reflow Profile.......................................................................................... 61
5.2. Device Handling Instruction (Module IC SMT Preparation)............................................. 61
5.3. Shipping Information ........................................................................................................62
APPENDI X A: HW REFERENCE DESI GN ..................................................................................63
APPENDI X B: CONTROL G PIO/PWM FUNCTION WITH NET WO RK COMMANDS ..............64
B.1 Network Command............................................................................................................... 64
B.2 Hexadecimal Network Command........................................................................................ 67
APPENDI X C: HTT P PROTOCOL TRANSFER ..........................................................................70
C.1. HTTP AT command.............................................................................................................. 70
C.1.1. AT+ HTTPURL.............................................................................................................70
C.1.2. AT+ HTTPTP ............................................................................................................... 70
C.1.3. AT+ HTTPPH............................................................................................................... 70
C.1.4. AT+ HTTPCN...............................................................................................................71
C.1.5. AT+ HTTPUA............................................................................................................... 71
C.1.6. AT+ HTTPDT...............................................................................................................71
C.2. HTTP Example ..................................................................................................................... 71
APPENDI X D: CONTACT INFORMATION .................................................................................. 73
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 6 -
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 1. HF-LPB100 View............................................................................................................. 11
Figure 2. HF-LPB100 Pins Map ......................................................................................................11
Figure 3. HF-LPB100 Mechanical Dimension..................................................................................14
Figure 4. HF-LPB100 PCB Symbol Size ......................................................................................... 14
Figure 5. Suggested Module Placement Region ............................................................................. 15
Figure 6. HF-LPB100 Evaluation Kit ............................................................................................... 16
Figure 7. HF-LPB100 Order Information ......................................................................................... 17
Figure 8. HF-LPB100 Hardware Typical Application........................................................................ 18
Figure 9. HF-LPB100 Basic Wireless Network Structure .................................................................20
Figure 10. HF-A11 AP+STA Network Structure ............................................................................. 21
Figure 11. Socket B function demo ............................................................................................... 26
Figure 12. Multi-TCP Link Data Transmition Structure...................................................................27
Figure 13. Open Web Management page......................................................................................28
Figure 14. System Web Page ....................................................................................................... 29
Figure 15. Work Mode Page ......................................................................................................... 29
Figure 16. STA Setting Page.........................................................................................................30
Figure 17. AP Setting Page........................................................................................................... 30
Figure 18. Other Setting Page.......................................................................................................31
Figure 19. Account Page............................................................................................................... 31
Figure 20. Upgrade SW page........................................................................................................32
Figure 21. Restart Page................................................................................................................32
Figure 22. Restore Page...............................................................................................................33
Figure 23. STA Interface Debug Connection .................................................................................33
Figure 24. AP Interface Debug Connection ...................................................................................34
Figure 25. “CommTools” Serial Debug Tools................................................................................. 34
Figure 26. “TCPUDPDbg” Tools Create Connection......................................................................34
Figure 27. “TCPUDPDbg” Tools Setting........................................................................................ 35
Figure 28. “TCPUDPDbg” Tools Connection .................................................................................35
Figure 29. Wireless Control Application......................................................................................... 35
Figure 30. Remote Management Application.................................................................................36
Figure 31. Transparent Serial Port Application ..............................................................................36
Figure 32. HF-LPB100 Default UART Port Parameters .................................................................37
Figure 33. Switch to Configuration Mode....................................................................................... 37
Figure 34. ”AT+H” Instruction for Help...........................................................................................38
Figure 35. Reflow Soldering Profile............................................................................................... 61
Figure 36. Shipping Information .................................................................................................... 62
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 7 -
LIST OF TABLES
Table 1 HF-LPB100 Module Technical Specifications....................................................................10
Table 2 HF-LPB100 Pins Definition ............................................................................................... 11
Table 3 HF-LPB100 External Antenna Parameters........................................................................15
Table 4 HF-LPB100 Evaluation Kit Interface Description ...............................................................16
Table 6 Standby Mode Status and Wake Up ..................................................................................23
Table 7 HF-LPB100 GPIO/PWM Pin Mapping Table .....................................................................25
Table 8 HF-LPB100 Web Access Default Setting .......................................................................... 28
Table 9 Error Code Describtion ..................................................................................................... 39
Table 10 AT+ Instruction Set List...................................................................................................39
Table 11 Reflow Soldering Parameter ............................................................................................. 61
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 8 -
HISTORY
Ed. V1.0 08-01-2013 First Version.
Ed. V1.1 09-10-2013 Update AT command.
Ed. V1.2 10-10-2013 Update AT command. Update PWM/GPIO function. Add HTTP protocol demo.
Add auto-frame function.
Ed. V1.3 10-18-2013 Update module view, add nReload Pin wireless upgrade and config description,
add nLink Pin wireless upgrade indication description.
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 9 -
1. PRODUCT OVERVIEW
1.1. General Description
The HF-LPB100 is a fully self-contained small form-factor, single stream, 802.11b/g/n Wi-Fi module,
which provide a wireless interface to any equipment with a Serial/SPI/USB interface for data
transfer.HF-LPB100 integrate MAC, baseband processor, RF transceiver with power amplifier in
hardware and all Wi-Fi protocol and configuration functionality and networking stack, in embedded
firmware to make a fully self-contained 802.11b/g/n Wi-Fi solution for a variety of applications.
The HF-LPB100 employs the world's lowest power consumption embedded architecture. It has been
optimized for all kinds of client applications in the home automation, smart grid, handheld device,
personal medical application and industrial control that have lower data rates, and transmit or receive
data on an infrequent basis.
The HF-LPB100 integrates all Wi-Fi functionality into a low-profile, 23.1x32.8x 2.7mm SMT module
package that can be easily mounted on main PCB with application specific circuits. Also, module
provides built-in antenna, external antenna option.
1.1.1 Device Features
Single stream Wi-Fi @ 2.4 GHz with support for WEP security mode as well as WPA/WPA2
Based on Self-developed High Cost Performance MCU
Ultra-low-power operation with all kinds of power-save modes.
Includes all the protocol and configuration functions for Wi-Fi connectivity.
Support STA/AP/AP+STA Mode
Support Smart Link Function
Support Wireless and Remote Firmware Upgrade Function
Support Max 6 Channel PWM/GPIO Output
Integrated chip antenna, antenna connector options.
Compact surface mount module 23.1mm x 32.8mm x 2.7mm.
Full IPv4 and IPv6 stack.
Low power RTOS and drivers.
FCC Certified.
RoHS and CE compliant.
Single supply – 3.3V operation.
HF-SH01
High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 10 -
1.1.2 Device Paremeters
Table 1 HF-LPB100 Module Technical Specifications
Class Item Parameters
Wireless
Parameters
Certification FCC/CE
Wireless standard 802.11 b/g/n
Frequency range 2.412GHz-2.484GHz
Transmit Power
802.11b: +16 +/-2dBm (@11Mbps)
802.11g: +14 +/-2dBm (@54Mbps)
802.11n: +13 +/-2dBm (@HT20, MCS7)
Receiver Sensitivity
802.11b: -93 dBm (@11Mbps ,CCK)
802.11g: -85 dBm (@54Mbps, OFDM)
802.11n: -82 dBm (@HT20, MCS7)
Antenna Option
External:I-PEX Connector
Internal:On-board PCB antenna
Hardware
Parameters
Data Interface
UART
SPI, PWM, GPIO
Operating Voltage 2.8~3.6V
Operating Current
Peak [Continuous TX]: ~200mA
Normal [WiFi ON/OFF, DTIM=100ms]:
Average. ~12mA, Peak: 200mA
Standby [WiFi Shutdown]: <200uA
Power Down Switch: <10uA
Operating Temp.
-40℃- 85℃
Storage Temp.
-45℃- 125℃
Dimensions and Size
23.1mm×32.8mm×2.7mm
Software
Parameters
Network Type STA /AP/STA+AP
Security Mechanisms WEP/WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK
Encryption WEP64/WEP128/TKIP/AES
Update Firmware Local Wireless, Remote
Customization
Web Page Upgrade
Support SDK for application develop
Network Protocol IPv4, TCP/UDP/FTP/HTTP
User Configuration
AT+instruction set. Android/ iOS
Smart Link APP tools
1.1.3 Key Application
Remote equipment monitoring
Asset tracking and telemetry
Security
Industrial sensors and controls
Home automation
Medical devices
HF-SH01
High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 11 -
1.2. Hardware Introduction
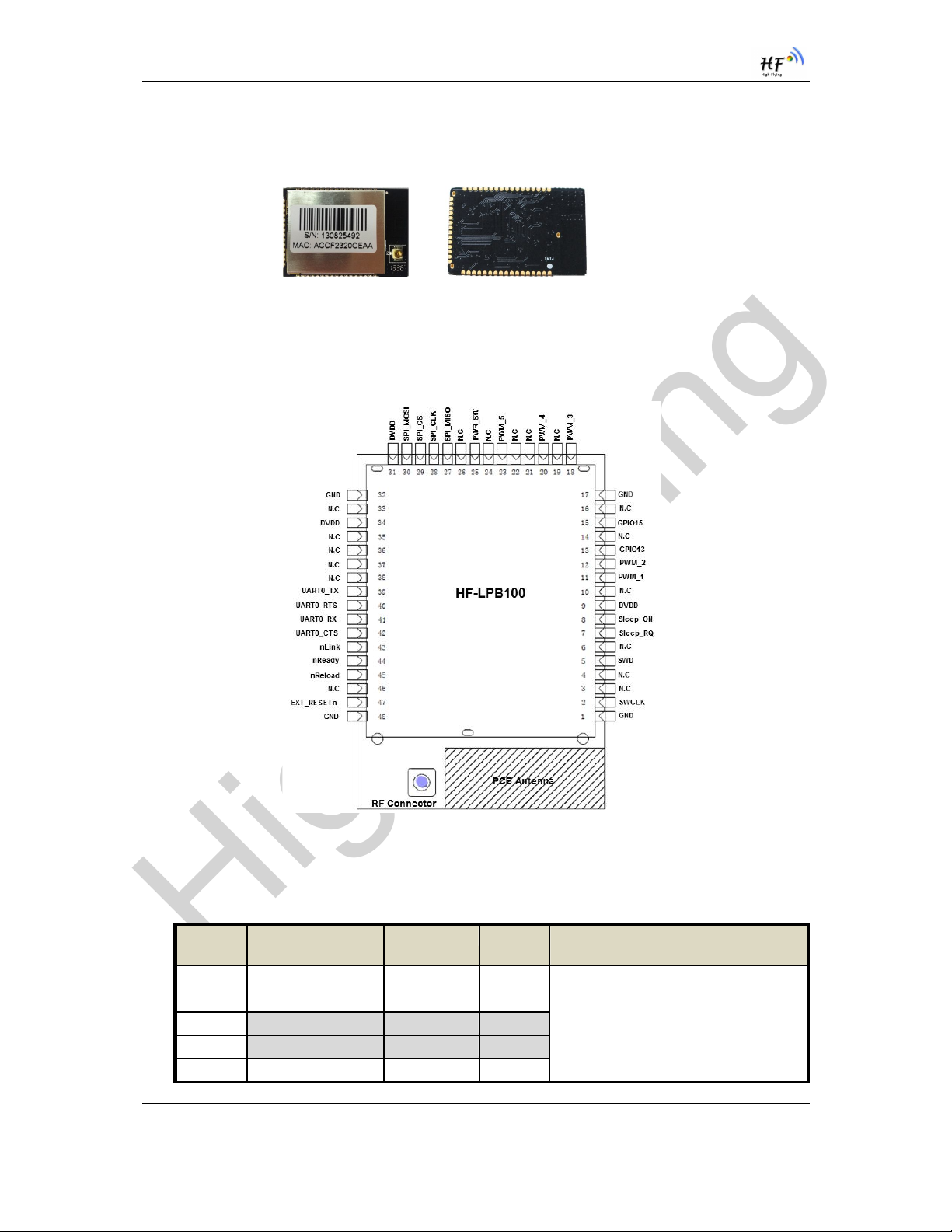
Figure 1. HF-LPB100 View
1.2.1. Pins Definition
Figure 2. HF-LPB100 Pins Map
Table 2 HF-LPB100 Pins Definition
Pin Describtion Net Name Signal
Type
Comments
1,17,32,48 Ground GND Power
2 Debug Pin SWCLK I, PD Debug functional pin,
No connect if not use.
3 NC
4 NC
5 Debug Pin SWD I/O,PU
HF-SH01
High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 12 -
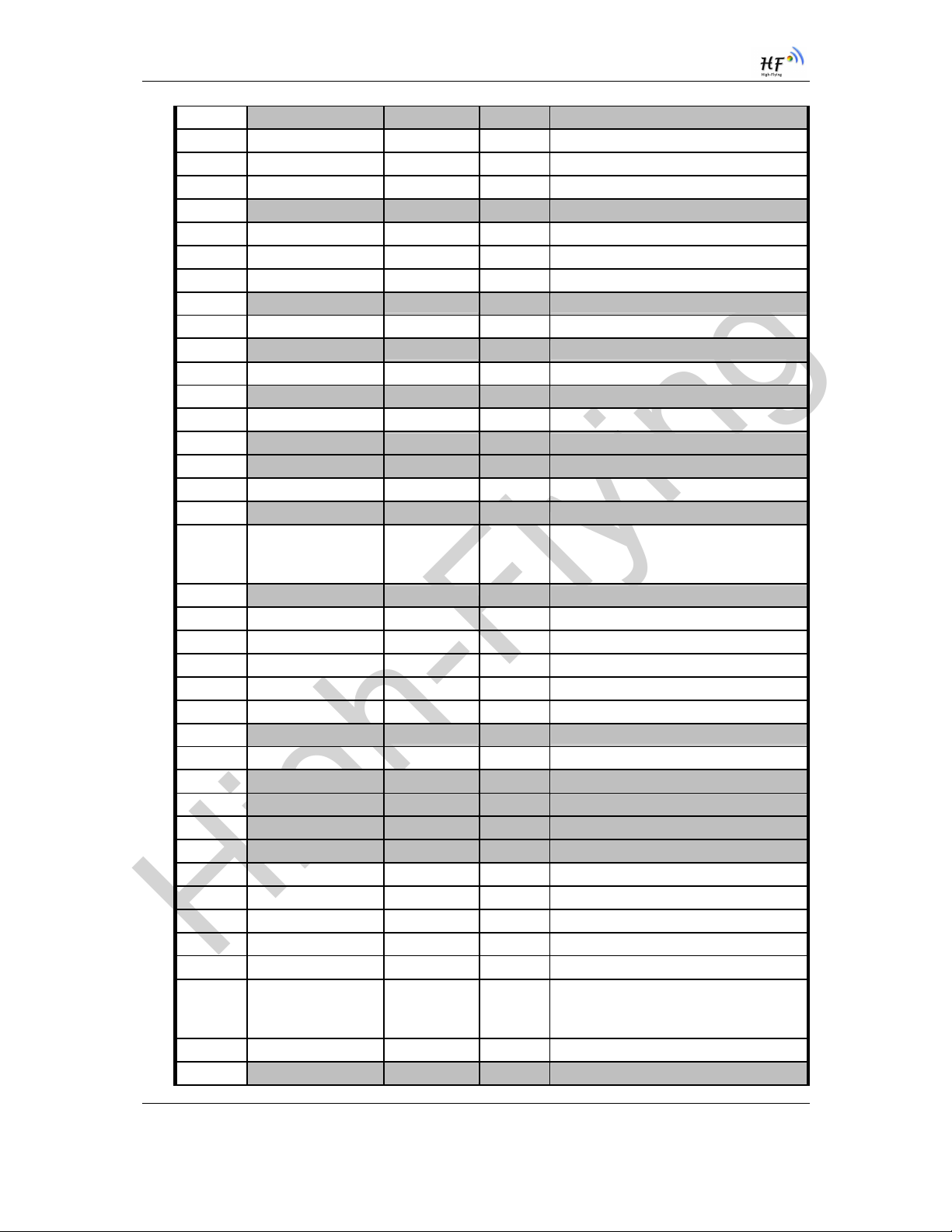
6 N.C No connect
7 GPIO Sleep_RQ I.PU GPIO7, No connect if not use.
8 GPIO Sleep_ON O GPIO8, No connect if not use.
9 +3.3V Power DVDD Power
10 N.C No connect
11 PWM/GPIO PWM_1 I/O GPIO11, No connect if not use.
12 PWM/GPIO PWM_2 I/O GPIO12, No connect if not use.
13 GPIO GPIO13 I/O GPIO13, No connect if not use.
14 N.C No connect
15 WPS/GPIO GPIO15 I/O GPIO15, WPS Function Pin.
16 N.C No connect
18 PWM/GPIO PWM_3 I/O GPIO18, No connect if not use.
19 N.C No connect
20 PWM/GPIO PWM_4 I/O GPIO20, No connect if not use.
21 N.C No connect
22 N.C No connect
23 GPIO PWM_5 I/O GPIO23, No connect if not use.
24 N.C No connect
25 Power Control
Switch
PWR_SW I,PU “0” – Power Down Mode(Lowest Power
Consumption)
“1” – Normal mode
26 N.C No connect
27 SPI Interface SPI_MISO I GPIO27, No connect if not use.
28 SPI Interface SPI_CLK I/O GPIO28, No connect if not use.
29 SPI Interface SPI_CS I/O GPIO29, No connect if not use.
30 SPI Interface SPI_MOSI O GPIO30, No connect if not use.
31 +3.3V Power DVDD Power
33 N.C No connect
34 +3.3 Power DVDD Power
35 N.C No connect
36 N.C No connect
37 N.C No connect
38 N.C No connect
39 UART0 UART0_TX O GPIO39, No connect if not use.
40 UART0 UART0_RTS I/O GPIO40, No connect if not use.
41 UART0 UART0_RX I GPIO41, No connect if not use.
42 UART0 UART0_CTS I/O GPIO42, No connect if not use.
43 Wi-Fi Status nLink O
Detailed functions see <Notes>
44 Module Boot Up
Indicator
nReady O “0” – Boot-up OK;
“1” – Boot-up No OK;
No connect if not use.;
45 Multi-Function nReload I,PU
Detailed functions see <Notes>
46 N.C No connect
HF-SH01
High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 13 -
47 Module Reset EXT_RESETn I,PU “Low” effective reset input.
<Notes>
nReload Pin (Button) function:
1. When this pin is set to “low” during module boot up, the module will enter wireless
firmware and config upgrade mode. This mode is used for customer manufacture.
(High-Flying will provide software tools for customer batch configuration and
upgrade firmware during mass production)
2. After module is powered up, short press this button ( “Low” < 3s ) to make the
module go into “Smart Link “ config mode, waiting for APP to set password and
other information.
3. After module is powered up, long press this button ( “Low” > 3s ) to make the
module recover to factory setting.
High-Flying strongly suggest customer fan out this pin to connector or button for
“Manufacture” and “ Smart Link” application.
nLink Pin (LED) function:
1. At wireless firmware and config upgrade mode , this LED used to indicate configure
and upgrade status.
2. At “Smart Link “ config mode, this LED used to indicate APP to finish setting.
3. At normal mode, it’s Wi-Fi link status indicator
High-Flying strongly suggest customer fan out this pin to LED.
1.2.2. Electrical Characteristics
Absolute Maximum Ratings:
Parameter Condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
Storage temperature range -45 125 °C
Maximum soldering temperature IPC/JEDEC J-STD-020 260 °C
Supply voltage 0 3.8 V
Voltage on any I/O pin 0 3.3 V
ESD (Human Body Model HBM) TAMB=25°C 2 KV
ESD (Charged Device Model, CDM) TAMB=25°C 1 KV
Power Supply & Power Consumption:
Parameter Condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
Operating Supply voltage 2.8 3.3 3.8 V
Supply current, peak Continuous Tx 200 mA
Supply current, IEEE PS DTIM=100ms 12 mA
Output high voltage Sourcing 6mA 2.8 V
Output low voltage Sinking 6mA 0.2 V
Input high voltage 2.2 V
Input low voltage 0.8 V
HF-SH01
High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 14 -
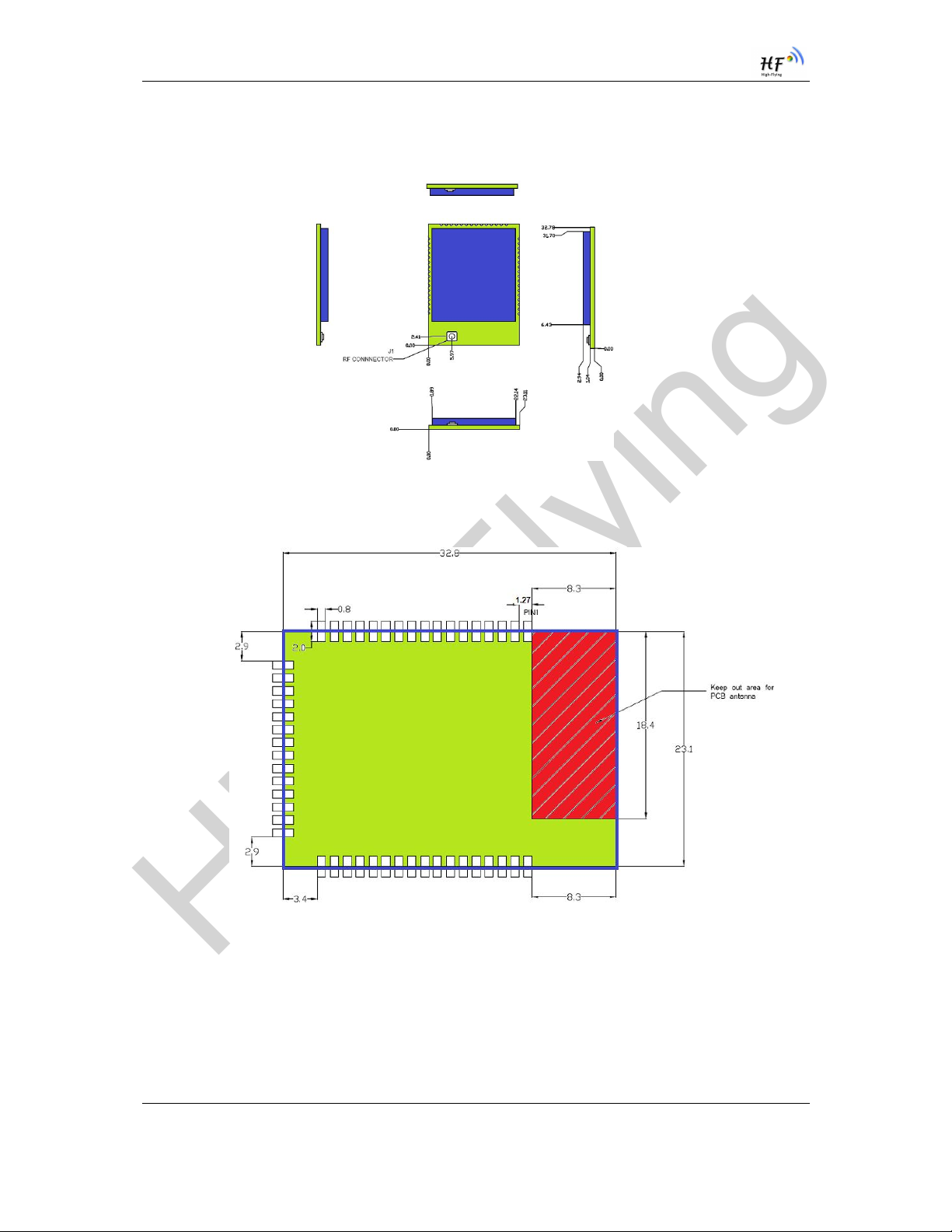
1.2.3. Mechanical Size
HF-LPB100 modules physical size (Unit: mm) as follows:
Figure 3. HF-LPB100 Mechanical Dimension
HF-LPB100 Module PCB symbol size (mm) as follows:
Figure 4. HF-LPB100 PCB Symbol Size
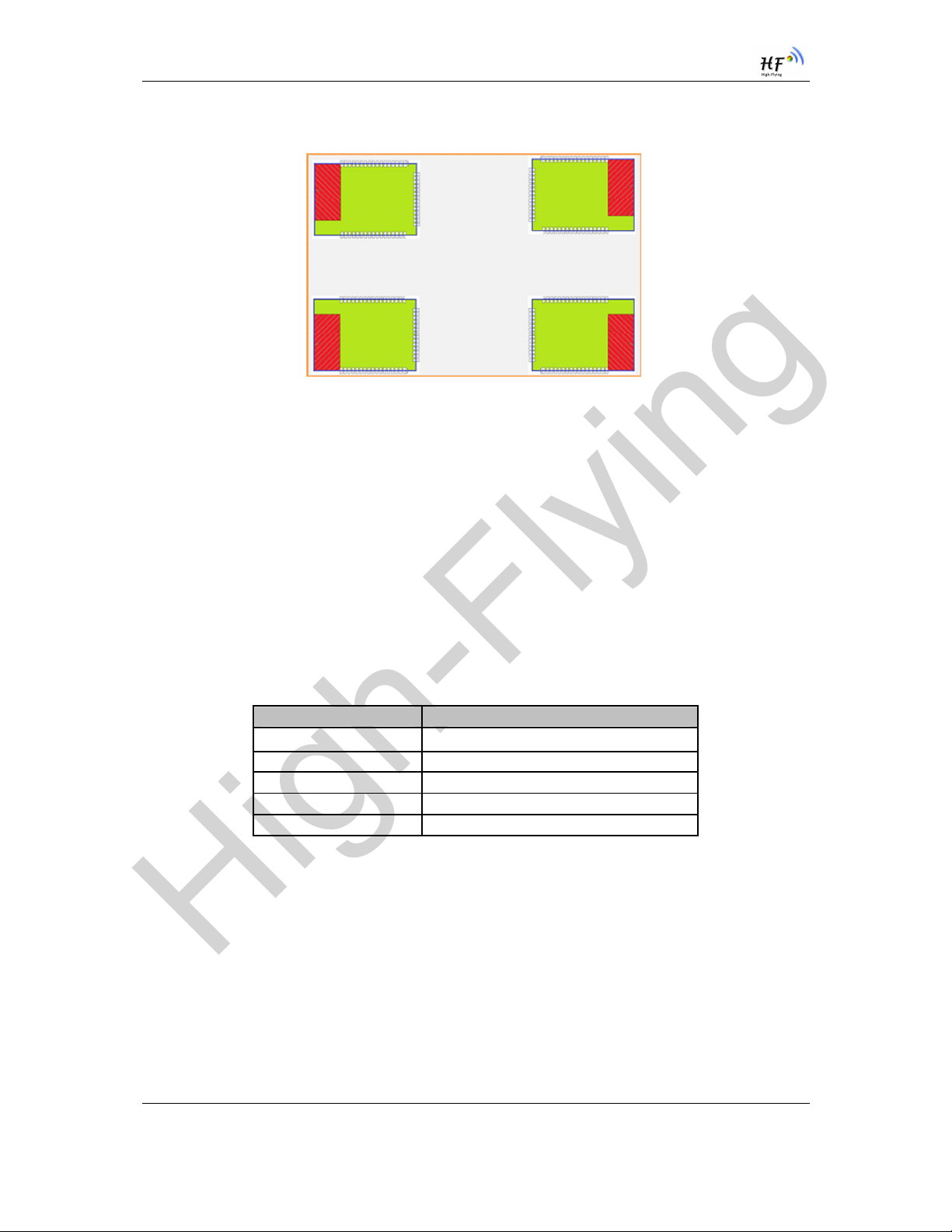
1.2.4. On-board Chip Antenna
HF-LPB100 module support internal on-board chip antenna option. When customer select internal
antenna, you shall comply with following antenna design rules and module location suggestions:
For customer PCB, RED color region (8.3x18.4mm) can’t put componet or paste GND net;
Antenna must away from metal or high components at least 10mm;
HF-SH01
High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 15 -
Antenna can’t be shieldedby any meal enclosure; All cover, include plastic, shall away from
antenna at least 10mm;
Figure 5. Suggested Module Placement Region
High-Flying suggest HF-LPB100 module better locate in following region at customer board, which to
reduce the effect to antenna and wireless signal, and better consult High-Flying technical people when
you structure your module placement and PCB layout.
1.2.5. External Antenna
HF-LPB100 module supports internal antenna and external antenna option for user dedicated
application.
If user select external antenna, HF-LPB100 modules must be connected to the 2.4G antenna
according to IEEE 802.11b/g/n standards.
The antenna parameters required as follows:
Table 3 HF-LPB100 External Antenna Parameters
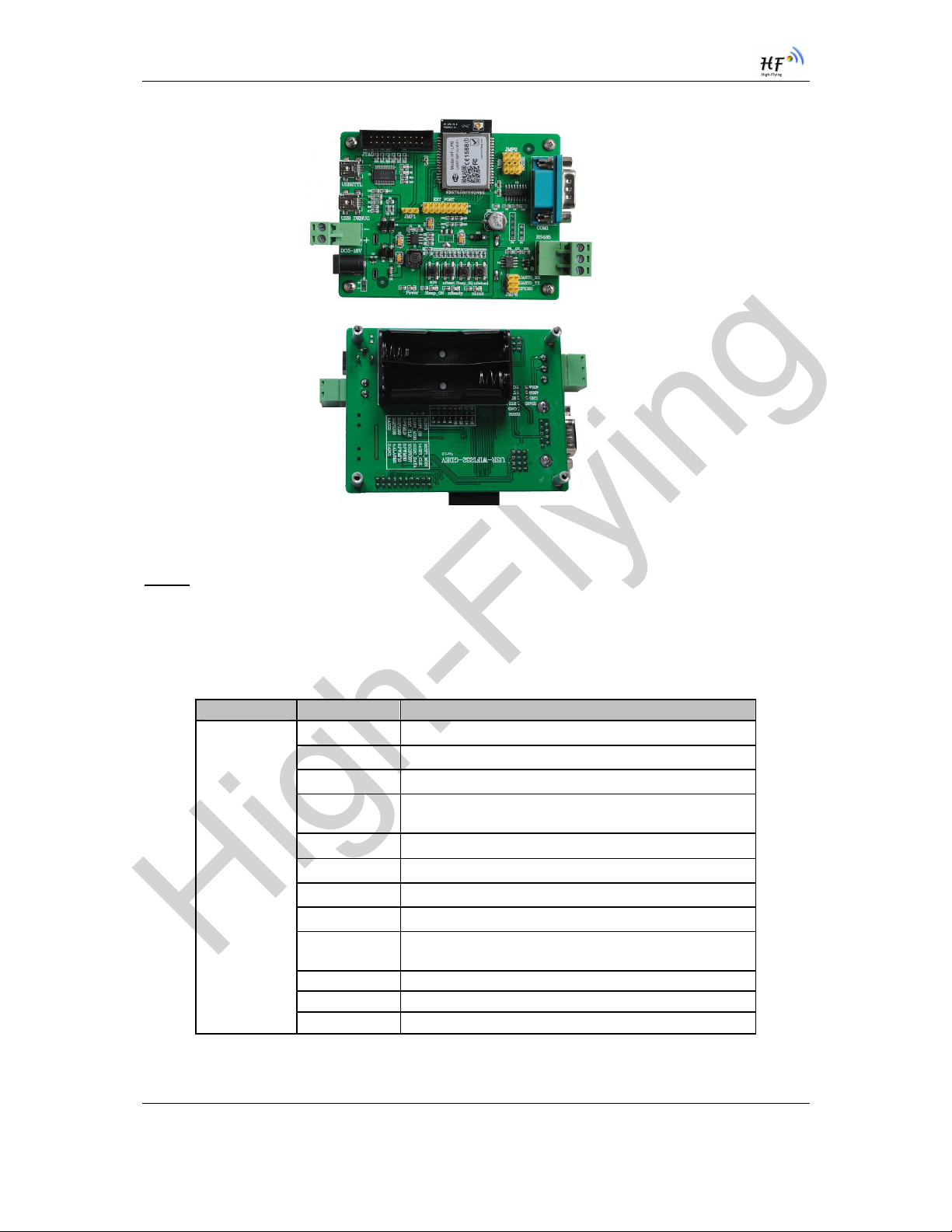
1.2.6. Evaluation Kit
High-Flying provides the evaluation kit to promote user to familiar the product and develop the detailed
application. The evaluation kit shown as below, user can connect to HF-LPB100 module with the RS-
232 UART, RS485, USB (Internal UART-USB convetor) or Wireless port to configure the parameters,
manage the module or do the some functional tests.
Item Parameters
Frequency range 2.4~2.5GHz
Impedance 50 Ohm
VSWR 2 (Max)
Return Loss -10dB (Max)
Connector Type I-PEX or populate directly
HF-SH01
High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 16 -
Figure 6. HF-LPB100 Evaluation Kit
Notes: User need download USB - UART port driver from High-Flying web or contact with technical
support people for more detail.
The external interface description for evaluation kit as follows:
Table 4 HF-LPB100 Evaluation Kit Interface Description
Function
Name Description
External
Interface
COM1 Main data/command RS-232 interface
RS485 Main data/command RS-485 interface
JTAG JTAG data debug interface (Not for user use)
USB2TTL
UART to USB debug interface. (For PC without
RS232, need load driver). Can be Power input.
USB DEBUG USB2.0 data interface.
DC Jack
DC jack for power in, 5~18V input.
DC5-18V DC jack for power in, 5~18V input.
BAT
2 Li-Battery Power Supply.
EXT PORT
HF-LPB100 GPIO function extend interface
connector
JMP1,JMP2 Reserved, No Jumper required.
JMP3 4Pin USB or RS232 Jumper. Left jump select USB.
JMP6 3Pin RS485 Jumper. No jump selects RS232.
HF-SH01
High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 17 -
1.2.7. Order Information
Base on customer detailed requirement, HF-LPB100 series modules provide different variants and
physical type for detailed application.
Figure 7. HF-LPB100 Order Information
LED
Power 3.3V Power Indicator
nLink
nLink -WiFi LINK Indicator
See 1.2.1
nReady
nReady – Module Bootup Ready Indicator
On (“low”)- Module bootup OK;
Off (“high”)- Mouule botup failed;
Twinkle- Remote Upgrade Ongoing;
Sleep_ON
Sleep_ON-Module asleep or awake Indicator
On (“low”)- Module in shundown(deep sleep) status;
Off (“high”)- Mouule in normal status;
Twinkle- Bootloader Upgrade Ongoing;
Button
nReset Used to reset the module.
nReload
Restore factory default configuration after push this
pin more than 3s.
See 1.2.1
WPS
WPS Button (Reserved, No Use)
Sleep_RQ
Pin Sleep Control button, more than 3s to put
module in standby mode.
HF-SH01
High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 18 -
1.3. Typical Application
1.3.1. Hardware Typical Application
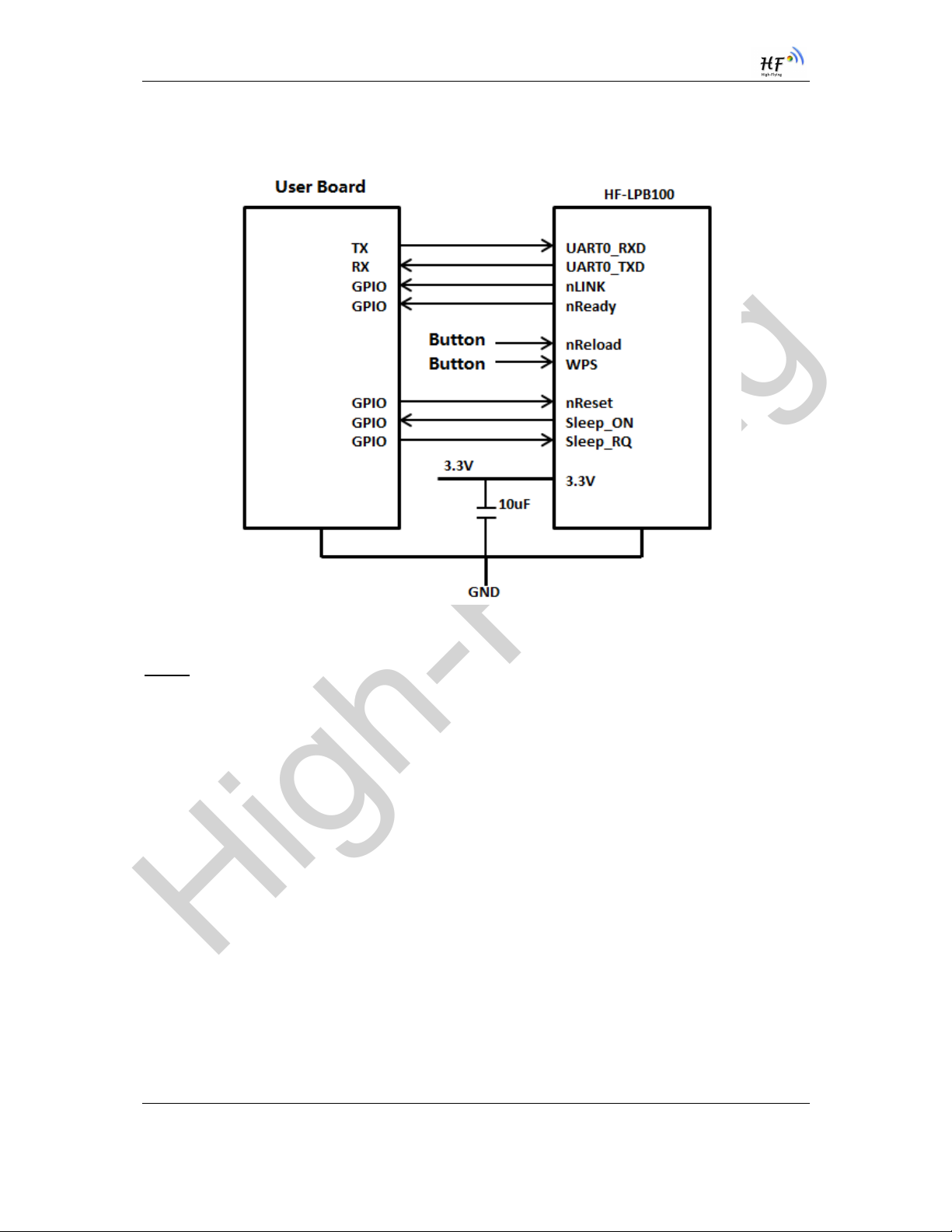
Figure 8. HF-LPB100 Hardware Typical Application
Notes:
nReset- Module hardware reset signal. Input. Logics “0” effective.
There is pull-up resister internal and no external pull-up required. When module power up or some
issue happened, MCU need assert nRST signal “0” at least 10ms, then set” 1” to keep module fully
reset.
nLink- Module WIFI connection status indication. Output.
(This pin is recommend to connect to LED, indicate status when the module in wireless
upgrade mode)
When module connects to AP (AP associated), this pin will output “0”. This signal used to judge if
module already at WiFi connection status. Thers is pull-up resister internal and no external pull-up
required. If nLink function not required, can leave this pin open.
nReady- Module boot up ready signal. Output. Logics “0” effective.
The module will output “0” after normal boot up. This signal used to judge if module finish boot up and
ready for application or working at normal mode. If nReady function not required, can leave this pin
open.
nReload- Module restore to factory default configuration.Input. Logics “0” effective.
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 19 -
(This pin is recommend to connect to button, is used to enter wireless upgrade mode)
User can de-assert nReload signal “0” more than 3s through button or MCU pin, then release, module
will restore to factory default configuration and re-start boot up process.. If nReload function not
required, can leave this pin open.
Sleep_RQ- Module Pin Sleep Control. Input.
The user should de-assert this pin low “0”, after 3’s assert to high ”1” to put the module to sleep status.
Also at the deep sleep/standby mode, user can de-assert this pin low “0”, after 1’s assert to high ”1” to
put the module to wake up the module. If Sleep_RQ function not required, can leave this pin open.
Sleep_ON- Module Pin Sleep Indicator. Output.
This pin is used to indicate that the module is asleep (Module output “0”) or awake (Module output “1”)
status. If user doesn't use pin sleep function, can leave this pin open.
UART0_TXD/RXD- UART port data transmit and receive signal.
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 20 -
2. FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
2.1. Wireless Networking
HF-LPB100 module can be configured as both wireless STA and AP base on network type. Logically
there are two interfaces in HF-LPB100. One is for STA, and another is for AP. When HF-LPB100
works as AP, other STA equipments are able to connect to wireless LAN via HF-LPB100 module.
Wireless Networking with HF-LPB100 is very flexible.
Notes:
AP: that is the wireless Access Point, the founder of a wireless network and the centre of the network
nodes. The wireless router we use at home or in office may be an AP.
STA: short for Station, each terminal connects to a wireless network (such as laptops, PDA and other
networking devices) can be called with a STA device.
2.1.1. Basic Wireless Network Based On AP (Infrastructure)
Infrastructure: it’s also called basic network. It built by AP and many STAs which join in.
The characters of network of this type are that AP is the centre, and all communication between STAs
is transmitted through the AP. The figure following shows such type of networking.
Figure 9. HF-LPB100 Basic Wireless Network Structure
2.1.2. Wireless Network Based On AP+STA
HF-LPB100 module support AP+STA network mode, means module support one AP interface and
one STA interface at the same time, as following figure,
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 21 -
Figure 10. HF-A11 AP+STA Network Structure
When module enables AP+STA function, Module’s STA interface can connect with router and connect
to TCP server in the network. At the same time, module’s AP interface is also active and permit
phone/PAD to connect through TCPB, then phone/PAD can control user device and and setting the
module parameters,
The advantage of AP+STA mode is:
Users can easily setting and track user device through Phone/PAD and not change the
orginal network setting.
Users can easily setting module’s parameters through WiFi when module works as STA
mode.
2.2. Work Mode : Transparent Transmission Mode
HF-LPB100 module support serial interface transparent transmission mode. The benefit of this mode
is achieves a plug and play serial data port, and reduces user complexity furthest. In this mode, user
should only configure the necessary parameters. After power on, module can automatically connect to
the default wireless network and server.
As in this mode, the module's serial port always work in the transparent transmission mode, so users
only need to think of it as a virtual serial cable, and send and receive data as using a simple serial. In
other words, the serial cable of users’ original serial devices is directly replaced with the module; user
devices can be easy for wireless data transmission without any changes.
The transparent transmission mode can fully compatible with user’s original software platform and
reduce the software development effort for integrate wireless data transmission.
The parameters which need to configure include:
Wireless Network Parameters
Wireless Network Name(SSID)
Security Mode
Encryption Key
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 22 -
TCP/UDP Linking Parameters
Protocol Type
Link Type(Server or Client)
Target Port ID Number
Target Port IP Address
Serial Port Parameters
Baud Rate
Data Bit
Parity (Check) Bit
Stop Bit
Hardware Flow Control
2.3. UART Frame Scheme
2.3.1. UART Free-Frame
HF-LPB100 support UART free-frame function. If user select open this function, module will check the
intervals between any two bytes when reciving UART data. If this interval time exceeds defined value
(50ms default), HF-LPB100 will think it as the end of one frame and transfer this free-frame to WiFi
port, or HF-LPB100 will receive UART data untill 1000 bytes, then transfer 1000 bytes frame to WiFi
port.
HF-LPB100’s default interval time is 50ms. User can also set this interval to fast (10ms) through AT
command. But user have to consider if user MCU can send UART data with 10ms interval ,or the
UART data may be divide as fragment.
Through AT command: AT+UARTTE=fash/normal, user can set the interval time: fast (10ms) and
normal (50ms).
2.3.2. UART Auto-Frame
HF-LPB100 support UART auto-frame function. If user select open this function and setting auto-
frame trigger length and auto-frame trigger time parameters, then module will auto framing the data
which received from UART port and transmitting to the network as pre-defined data structure.
Auto-frame trigger length: The fixed data length that module used to transmitting to the
network.
Auto-frame trigger time: After the trigger time, if UART port received data can’t reach auto-
frame trigger length, then module will transmitting available data to the network and bypass
the auto-frame trigger length condition.
Detailed UART auto-frame function can refer to AT+ instruction set “UARTF/UARTFT/UARTFL”
introduction.
HF-SH01
High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 23 -
2.4. Encryption
Encryption is a method of scrambling a message that makes it unreadable to unwanted parties,
adding a degree of secure communications. There are different protocols for providing encryption, and
the HF-LPB100 module supports following:
WEP
WPA-PSK/TKIP
WPA-PSK/AES
WPA2-PSK/TKIP
WPA2-PSK/AES
2.5. Power Save Scheme
HF-LPB100 module can work at two modes based on different power save scheme:
Normal (Active/Sleep) Mode - AP Associated, WiFi ON/OFF based on internal control
Standby Mode - Non AP Associated, WiFi Shut dwon
Normal (Active/Sleep) Mode Normal mode is no DTIM related (Default mode), module will monitor
the interval to Active/Sleep.
Standby Mode allows the WiFi circuitry to be powered down, which results in the lowest sleep current,
but at the expense of longer wake up times. This is due to the module associating with the access
point every time when it wakes up. The intent of this option is to allow for longer sleep times. Standby
mode can through AT+MSLP command or trigger “Sleep_RQ” pin to go in.
The standby mode status and wakeup method as follows: For standby mode, module provides two
wakes up options, user can select one or whole as the module wake up option. Refer to AT Instruction
(Power Management Instruction Set) for more detailed setting.
“Sleep_RQ” Pin Wake Up
“Reset” Pin Wake Up
Table 6 Standby Mode Status and Wake Up
Status Wake Up Method
Wi-Fi MCU Current UART GPIO Timeout AT Commond Reset Pin
Standby OFF OFF <80uA OFF Yes No No Yes
Sleep _RQ Pin Wake Up Option allows an external microcontroller to determine when HF-LPB100
should sleep and when it should wake by controlling the “Sleep_RQ” and “Sleep_ON” pin. at the
standby mode, user can de-assert this pin low “0”, after 1’s assert to high ”1” to put the module to
wake up the module. If user doesn't use pin sleep function, can leave this pin open.
Sleep _RQ Pin Wake Up Option allows an external microcontroller to de-assert “Reset” pin to low
“0” to reset the module.
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 24 -
2.6. Parameters Configuration
HF-LPB100 module supports two methods to configuration parameters: Web Accessing and
AT+instruction set.
Web accessing means users can configure parameters through Web browser. When HF-LPB100
module connected to wireless network, parameters configuration is done on a PC connected to the
same wireless network.
AT+instruction set configuration means user configure parameters through serial interface command.
Refer to “AT+instruction set” chapter for more detail.
2.7. Firmware Update
HF-LPB100 module supports two on-line upgrade methods:
Webpage Wi-Fi Upgrade
Remote Upgrade
Webpaged based Wi-Fiupgrade,please refer to 3.1.8 firmware upgrade page , user can upload
firmware file from PC to HF-LPB100.
HF-LPB100 module also support upgrade from remote HTTP server, keep module connects to AP
router before excuate remote HTTP upgrade. Remote upgrade have two methods: Direct Download
and Upgrade, Configure File Based Upgrade.
Configure File Based Upgrade
AT+UPURL command to set the remote directory which the configuration file located, such as
AT+UPURL=http://www.hi-flying.com/!admin/down/
Notes: The last ’/’ can’t be remove
AT+UPFILE command to set the configuration file name, such as AT+UPFILE=config.txt
AT+UPST command to start remote Application upgrade. After excuate this command, the module will
firstly download configuration file (“config.txt”), then download the upgrade file base on the URL
address listed in the configure file.
AT+UPWEB command to start remote Webpage upgrade. After excuate this command, the module
will firstly download configuration file (“config.txt”), then download the upgrade file base on the WEB
address listed in the configure file.
AT+UPCFG command to start remote Factory Config upgrade. After excuate this command, the
module will firstly download configuration file (“config.txt”), then download the upgrade file base on the
CFG address listed in the configure file.
AT+UPNVR command to start remote NVRAM Data upgrade. After excuate this command, the
module will firstly download configuration file (“config.txt”), then download the upgrade file base on the
NVR address listed in the configure file.
AT+UPAUTO command to start remote upgrade. After excuate this command, the module will firstly
download configuration file (“config.txt”), then download the upgrade file base on the URL,WEB,CFG
address listed in the configure file. It include the functions of AT+UPST,AT+UPWEB,AT+UPCFG.
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 25 -
General “config.txt” file format as following example:
[URL]=”http://10.10.100.100:80/lpb.bin”
[WEB]="http://10.10.100.100:80/web.bin"
[NVR]="http://10.10.100.100:80/nvram.dat"
[CFG]= "http://10.10.100.100:80/cfg.bin"
[URL]= the URL address of Application.
[WEB]=the URL address of Webpage
[NVR]= the URL address of NVRAM data
[CFG]= the URL address of Factory Parameter File
Direct Download and Upgrade
AT+UPURL command to set the remote directory and file name, such as:
AT+UPURL=http://www.hi-flying.com/!admin/down/,lpb.bin
After excuate this command, the module will directly download the “lpb.bin” file from remote directory
and start upgrade Application.
Notes: please contact with high-flying technical people before upgrade firmware, or maybe damage
the module and can’t work again.
2.8. GPIO/PWM Function
HF-LPB100 module can provide many GPIOs, which include max 6 PWM/GPIO control pins. User
devices can read/write GPIO/PWM pins status.
Table 7 HF-LPB100 GPIO/PWM Pin Mapping Table
When module works at PWM mode, PC and other devices can setup connection (TCP/UDP) through
WiFi, then read/write GPIO/PWM information through command data.
GPIO n OUT 0, Set GPIOn as output and output ‘0’, Response GPIO OK or GPIO NOK;
GPIO n OUT 1, Set GPIOn as output and output ‘1’, Response GPIO OK or GPIO NOK;
GPIO n GET, Read GPIOn pin status, Response +ok=1 or GPIO NOK
GPIO n SET, Save GPIOn set, Response GPIO OK or GPIO NOK
PWM n frequency duty, Set PWMn Channel output, Response GPIO OK or GPIO NOK
PWM n GET, Read PWMn Channel set, Response +ok=frequency duty or PWM NOK
PWM n SET, Save PWMn Channel set, Response PWM OK or PWM NOK
Notes: Please refer to Appendix B for details to use GPIO/PWM.
GPIO Configured Function Describtion
Default Setting Type
GPIO11 PWM/GPIO Channel PWM_1 GPIO11 I/O
GPIO12 PWM/GPIO Channel
PWM_2
GPIO12 I/O
GPIO15 GPIO Channel GPIO15 GPIO15
I/O
GPIO18 PWM/GPIO Channel PWM_3
GPIO18
I/O
GPIO20 PWM/GPIO Channel
PWM_4
GPIO20 I/O
GPIO23 GPIO Channel PWM_5 GPIO23 I/O
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 26 -
2.9. SOCKET B Function
HF-LPB100 support double socket communication, the socket B function is disabled by
default.
After the module is started, send command “AT+SOCKB” to set the connection parameter,
send command “AT+TCPDISB=on” to try to connect with TCP server, the module will stop
connecting after three failures. Send command “AT+TCPDISB=on” to make connection.
Send command “AT+TCPDISB=off” to close connection. Send command “AT+TCPLKB” to
inqure TCP connection.
Figure 11. Socket B function demo
2.10. Multi-TCP Link Connection
When HF-LPB100 module configured as TCP Server, it supports Multi-TCP link connection,
and maximum 5 TCP clients permit to connect to HF-LPB100 module. User can realize multiTCP link connection at each work mode.
Multi-TCP link connection will work as following structure:
Upstream: All dates from different TCP connection or client will be transmitted to the serial
port as a sequence.
Downstream: All data from serial port (user) will be duplicate and broadcast to every TCP
connection or client.
Detailed multi-TCP link data transmition structure as following figure:
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 27 -
Figure 12. Multi-TCP Link Data Transmition Structure
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 28 -
3. OPERATION GUIDELINE
3.1. Configuration via Web Accessing
When first use HF-LPB100 modules, user may need some configuration. User can connect to HF-
LPB100 module’s wireless interface with following default setting information and configure the
module through laptop.
Table 8 HF-LPB100 Web Access Default Setting
Parameters Default Setting
SSID HF-LPB100
IP Address 10.10.100.254
Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0
User Name Admin
Password Admin
3.1.1. Open Web Management Interface
Step 1: Connect laptop to SSID “HF-LPB100” of HF-LPB100 module via wireless LAN card;
Step 2: After wireless connection OK. Open Wen browser and access “http://10.10.100.254”;
Step 3: Then input user name and password in the page as following and click “OK” button.
Figure 13. Open Web Management page
The HF-LPB100 web management page support English and Chinese language. User can select
language environment at the top right corner and click “Apply” button.
The main menu include nine pages: “System”, “Work Mode”, “STA Setting”, “AP Setting”, “Other
Setting”, “Account”, “Upgrade SW”, “Restart”, “Restore”.
3.1.2. System Page
At this page, user can check current device’s important information and status such as: device ID
(MID), software version, wireless work mode and related Wi-Fi parameters.
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 29 -
Figure 14. System Web Page
3.1.3. Work Mode Page
HF-LPB100 module can works at AP mode to simplify user’s configuration, can also works at STA to
connect remote server through AP router. Also, it can configure at AP+STA mode which provide very
flexible application for customers.
Figure 15. Work Mode Page
3.1.4. STA Setting Page
User can push “Scan” button to auto search Wi-Fi AP router nearby, and can connect with associate
AP through some settings. Please note the encryption information input here must be fully same with
Wi-Fi AP router’s configration, and then it can link with AP correctly.
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 30 -
Figure 16. STA Setting Page
3.1.5. AP Setting Page
When user select module works at AP and AP+STA mode, then need setting this page and provide
wireless and network parameters. Most of the system support DHCP to achieve IP address, so we
suggest to “Enable” DHCP server in most applications.
Figure 17. AP Setting Page
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 31 -
3.1.6. Other Setting Page
HF-LPB100 usually works at data transparent transmission mode. At this mode, the user device which
connected with HF-LPB100 will connect and communicate with remote PC or server. At this page,
user need setting serial port communication parameters and defines TCP related protocal parameters.
Figure 18. Other Setting Page
3.1.7. Account Management Page
This page set web server’s user name and password.
Figure 19. Account Page
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 32 -
3.1.8. Upgrade Software Page
User can upgrade new software (firmware) version through Wi-Fi.
Figure 20. Upgrade SW page
3.1.9. Restart Page
Most of the settting and configuration can only effective after system restart. User shall restart after
finish all setting.
Figure 21. Restart Page
3.1.10. Restore Page
After module restore factory default setting, all user configuration profile will lose.
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 33 -
User can access http://10.10.100.254 to set again, and user name and password is “admin”. HF-
LPB100 will restore to AP mode for factory default setting.
Figure 22. Restore Page
3.2. HF-LPB100 Usage Introduction
3.2.1. Software Debug Tools
High-Flying use two common software tools debugging and applying HF-LPB100 module.
(User can also select other tools used to debug serial port).
Serial Debugging Software: ComTools
Ethernet Debugging Software: TCPUDPDbg
3.2.2. Network Connection
User can select two methods to connect HF-LPB100 module base on dedicated application.
Use HF-LPB100 STA interface. HF-LPB100 and debug PC2 connect to a wireless AP,
another PC1 (or user device) connect to HF-LPB100 module with serial port:
Figure 23. STA Interface Debug Connection
Use HF-LPB100 AP interface. Debug PC2 connect to HF-LPB100 through wireless
connection, another PC1 (or user device) connect to HF-LPB100 module with serial port.
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 34 -
Figure 24. AP Interface Debug Connection
3.2.3. Default Parameter Setting
Default SSID: HF-LPB100;
Deault security mode: open,none;
User UART parameter setting:115200,8,1,None;
Default network parameter setting:TCP,Server,8899,10.10.100.254;
Module IP address: dhcp,0.0.0.0,0.0.0.0,0.0.0.0;
3.2.4. Module Debug
PC1 open “CommTools” program, setting the same serial port parameters with HF-LPB100 module
and open serial port connection.
Figure 25. “CommTools” Serial Debug Tools
PC2 open “TCPUDPDbg” program, and create a new connection. If HF-LPB100 configured as Server
mode, “TCPUDPDbg” Tools shall create “Client “mode connection. Or otherwise, create a “Server”
mode connection.
Figure 26. “TCPUDPDbg” Tools Create Connection
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 35 -
Then setting the TCP/UDP connection parameters. Default as following:
Figure 27. “TCPUDPDbg” Tools Setting
Then, click “Create” button to create a connection.
Figure 28. “TCPUDPDbg” Tools Connection
Now, in transparent transmission mode, data can be transferred from “CommTools” program to
“TCPUDPDbg” program, or in reverse. You can see data in receiver side will keep same as in sender
side.
3.3. Typical Application Examples
3.3.1. Wireless Control Application
Figure 29. Wireless Control Application
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 36 -
For this wireless control application, HF-LPB100 works as Ad-Hoc mode. Module’s serial port
connects to user device. So, control agent (Smart phone for this example) can manage and control the
user device through the wireless connection with HF-LPB100 module.
3.3.2. Remote Management Application
Figure 30. Remote Management Application
For this remote management application, HF-LPB100 works as STA mode and connects to Internet
through wireless AP. Module configured as TCP Client and communicates with remote TCP server at
Internet. Module’s serial port connects to user device.
So, user device’s data or sampling information can send to remote TCP server for storage or
processing. Also remote TCP server can send command to control and manage the user device
through the wireless network.
3.3.3. Transparent Serial Port Application
For this transparent serial port application, two HF-LPB100 modules connect as below figures to build
up a transparent serial port connection. HF-LPB100 works as Ad-Hoc mode to connect each other.
Figure 31. Transparent Serial Port Application
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 37 -
4. AT+INSTRUCTION INTRODUCTION
4.1. Configuration Mode
When HF-LPB100 power up, it will default works as transparent transmission mode, then user can
switch to configuration mode by serial port command. HF-LPB100 UART default parameters setting as
below figure,
Figure 32. HF-LPB100 Default UART Port Parameters
In configuration mode, user can setting the module through AT+ instruction set, which cover all web
page setting function.
4.1.1. Switch to Configuration Mode
Two steps to finish switching from transparent transmission mode to configuration mode.
UART input “+++”, after module receive “+++”, and feedback “a” as confirmation.
UART input “a”, after module receive “a” and feedback “+ok” to go into AT+
instruction set configuration mode.
Figure 33. Switch to Configuration Mode
Notes:
1. When user input “+++” (No “Enter” key required), the UART port will display feedback information
“a”, and not display input information”+++” as above UART display.
2. Any other input or wrong step to UART port will cause the module still works as original mode
(transparent transmission).
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 38 -
AT+ Instruction Set Overview
User can input AT+ Instruction through hyper terminal or other serial debug terminal, also can program
the AT+ Instruction to script. User can also input “AT+H” to list all AT+ Instruction and description to
start.
Figure 34. ”AT+H” Instruction for Help
4.2.1. Instruction Syntax Format
AT+Instruction protocol is based on the instruction of ASCII command style, the description of syntax
format as follow.
Format Description
< >: Means the parts must be included
[ ]: Means the optional part
Command Message
AT+<CMD>[op][para-1,para-2,para-3,para-4…]<CR>
AT+: Prefix of command message;
CMD: Command string;
[op]: Symbol of command operator,
“=” : The command requires parameters input;
“NULL”: Query the current command parameters setting;
[para-n]: Parameters input for setting if required;
<CR>:”Enter” Key, it’s 0x0a or 0x0d in ASCII;
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 39 -
Notes: When input AT+Instruction, “AT+<CMD>” character will display capital letter automatic and
other parts will not change as you input.
Response Message
+<RSP>[op] [para-1,para-2,para-3,para-4…]<CR><LF><CR><LF>
+: Prefix of response message;
RSP: Response string;
“ok” : Success
“ERR”: Failure
[op] : =
[para-n]: Parameters if query command or Error code when error happened;
<CR>: ASCII 0x0d;
<LF>: ASCIII 0x0a;
Error Code
Table 9 Error Code Describtion
Error Code Description
-1 Invalid Command Format
-2 Invalid Command
-3 Invalid Operation Symbol
-4 Invalid Parameter
-5 Operation Not Permitted
4.2.2. AT+ Instruction Set
Table 10 AT+ Instruction Set List
Instruction Description
<null> NULL
Managment Instruction Set
E Open/Close show back function
WMODE Set/Query Wi-Fi work mode (AP/STA/APSTA)
ENTM Set module into transparent transition mode
TMODE Set/Query module data transfer mode
MID Query module ID information
VER Query module software version information
RELD Restore to factory default setting
FCLR Erase factory setting
Z Re-start module
H Help
Configure Parameters Instruction Set
CFGRD Batch Read User Configure Parameters
CFGWR Batch Write Configure Parameters
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 40 -
CFGFR Batch Read Factory Default Configure Parameters
CFGTF Copy User Parameters to Factory Default Parameters
UART Instruction Set
UART Set/Query serial port parameters
UARTFT Open/Close UART auto-frame function
UARTFT Set/Query UART auto-frame trigger time
UARTFL Set/Query UART auto-frame trigger length
UARTTE Set/Query UART free-frame triggerf time between two bytes
Command Mode Set
SEND Send Data at Command Mode
RECV Receive Data at Command Mode
Network Instruction Set
PING Network ”Ping” Instruction
NETP Set/Query network protocol parameters
MAXSK Set/Query TCP Client connection number
TCPLK Query if TCP link already build-up
TCPTO Set/Query TCP timeout
TCPDIS Open/Close TCP link
SOCKB Set/Query SOCKB parameters
TCPDISB Open/Close SOCKB TCP link
TCPTOB Set/Query SOCKB TCP timeout
TCPLKB Query if SOCKB TCP link already build-up
SNDB Send data to SOCKB in Command Mode
RCVB Receive data from SOCKB in Command Mode
Wi-Fi STA Instruction Set (Effective when module works as STA)
WSKEY Set/Query STA security parameters
WSSSID Set/Query associated AP SSID parameters
WANN Set/Query STA’s network parameters
WSMAC Set/Query STA’s MAC address
WSLK Query STA Wi-Fi link status
WSLQ Query STA Wi-Fi signal strength
WSCAN Scan AP
WSDNS Set/Query STA’s Static DNS server address
Wi-Fi AP Instruction Set (Effective when module works as AP)
LANN Set/Query AP’s network parameters
WAP Set/Query AP Wi-Fi parameters
WAKEY Set/Query AP security parameters
WAMAC Set/Query AP MAC address
WADHCP Set/Query AP DHCP Server status
WADMN Set/Query AP webpage domain name
Webpage Management Instruction Set
PLANG Set/Query Webpage Language Option
WEBU Set/Query Webpage User name and Code
Remote Upgrade Instruction Set
UPURL Set/Query remote upgrade URL address
UPFILE Set/Query remote upgrade configure file name
UPWEB Start remote web upgrade
UPCFG Start remote config file upgrade
UPNVR Start remote NVRAM data upgrade
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 41 -
UPAUTO Start remote upgrade
LOGSW Open/Close remote upgrade log
LOGPORT Set/Query UDP port of remote upgrade log
UPST Start remote Application upgrade
Power Management Instruction Set
MSLP Set/Query deep sleep/standby mode parameters
Network Time Set
NTPRF Set/Query time calibration interval
NTPEN Enable/Disable time calibration function
NTPTM Query time
Others Instruction Set
WRMID Set module ID
RLDEN Set/Query GPIO45 status
ASWD Set/Query WiFi configuration code
MDCH Set Wi-Fi Auto Switch Function
TXPWR Set/Query Wi-Fi Transmit Power
WIFI Config Tools don’t support “CFGRD” command yet。
4.2.2.1. AT+E
Function: Open/Close show back function;
Format:
AT+E<CR>
+ok<CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
When HF-LPB100 module firstly switch from transparent transmission to configuration mode, show
back status is open, input “AT+E” to close show back function, input“AT+E” again to open show back
function.
4.2.2.2. AT+WMODE
Function: Set/Query WIFI work mode;
Format:
Query Operation
AT+WMODE<CR>
+ok=<mode><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Set Operation
AT+ WMODE=<mode><CR>
+ok<CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
mode:Wi-Fi work mode
AP
STA
APSTA
4.2.2.3. AT+ENTM
Function: Set module into transparent transmition mode;
Format:
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 42 -
AT+ENTM<CR>
+ok<CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
When operate this command, module switch from configuration mode to transparent transmission
mode.
4.2.2.4. AT+TMODE
Function: Set/Query module data transfer mode.
Format:
Query Operation
AT+TMODE<CR>
+ok=<tmode><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Set Operation
AT+TMODE=<tmode><CR>
+ok<CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
tmode: data transfer mode, include:
throughput
cmd
pwm
4.2.2.5. AT+MID
Function: Query module ID information;
Format:
Query Operation
AT+MID<CR>
+ok=<module_id><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
module_id: Module ID information;
HF-LPB100;
Notes: User can set this parameter through AT+WRMID.
4.2.2.6. AT+VER
Function: Query module software version information;
Format:
Query Operation
AT+VER<CR>
+ok=<ver><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
ver: Module software version information;
4.2.2.7. AT+RELD
Function: module restore to factory default setting;
Format:
Set Operation
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 43 -
AT+ RELD<CR>
+ok=rebooting…<CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
When operate this command, module will restore to factory default setting and reboot.
4.2.2.8. AT+FCLR
Function: Erase factory setting;
Format:
Query Operation
AT+FCLR<CR>
+ok=<status><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
4.2.2.9. AT+Z
Function: Re-start module;
Format:
AT+ Z<CR>
4.2.2.10. AT+H
Function: Help;
Format:
Query Operation
AT+H<CR>
+ok=<command help><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
command help: command introduction;
4.2.2.11. AT+CFGRD
Function: Batch Read User Configure Parameters;
Format:
Query Operation
AT+CFGRD<CR>
+ok=<config><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
config: the first two bytes means the length of configuration parameters;
4.2.2.12. AT+CFGWR
Function: Batch Write User Configure Parameters;
Format:
Set Operation
AT+CFGWR=<config><CR>
+ok<CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
config: the first two bytes means the length of configuration parameters;
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 44 -
4.2.2.13. AT+CFGFR
Function: Batch Read Factory Default Configure Parameters;
Format:
Query Operation
AT+CFGFR<CR>
+ok=<config><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
config: the first two bytes means the length of configuration parameters;
4.2.2.14. AT+CFGTF
Function: Copy User Parameters to Factory Default Parameters;
Format:
Query Operation
AT+CFGTF<CR>
+ok=<status><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
status: feedback operation status;
4.2.2.15. AT+UART
Function: Set/Query serial port parameters;
Format:
Query Operation
AT+UART<CR>
+ok=<baudrate,data_bits,stop_bit,parity><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Set Operation
AT+UART=<baudrate,data_bits,stop_bit,parity><CR>
+ok<CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
baudrate:
300,600,1200,1800,2400,4800,9600,19200,38400,57600,115200,230400,
380400,460800.
data_bits:
8
stop_bits:
1,2
parity:
NONE
EVEN
ODD
Flowctrl: (CTSRTS)
NFC: No hardware flow control
FC: hardware flow control
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 45 -
4.2.2.16. AT+ UARTF
Function: Open/Close UART auto-frame function;
Format:
Query Operation
AT+ UARTF<CR>
+ok=<para><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Set Operation
AT+ UARTF=<para ><CR>
+ok<CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
para:
disable - Close auto-frame function;
enable - Open auto-frame function;
4.2.2.17. AT+ UARTFT
Function: Set/Query UART auto-frame trigger time;
Format:
Query Operation
AT+ UARTFT<CR>
+ok=<time><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Set Operation
AT+ UARTFT=<time ><CR>
+ok<CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
time: Range 100 ~10000; Unit: ms. Auto-frame trigger time
4.2.2.18. AT+ UARTFL
Function: Set/Query UART auto-frame trigger length;
Format:
Query Operation
AT+ UARTFL<CR>
+ok=<len><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Set Operation
AT+ UARTFL=<len ><CR>
+ok<CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
len: Range 8 ~1000; Unit: Byte. Auto-frame trigger length;
4.2.2.19. AT+ UARTTE
Function: Set/Query UART free-frame trigger time between two bytes;
Format:
Query Operation
AT+ UARTTE<CR>
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 46 -
+ok=<mode><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Set Operation
AT+ UARTTE=<mode><CR>
+ok<CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
mode:
fast: free-frame trigger time between two bytes is 10ms;
normal: free-frame trigger time between two bytes is 50ms;
4.2.2.20. AT+ SEND
Function: Send Data at Command Mode.
Format:
AT+SEND=<data_lenth><CR>
+ok<CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
data_lenth: Lenth of send data. Range: 0~1000 Byte
The UART port will wait 3 seconds for input after this command is sent OK. The data received
from UART port is sent to socket. If the interval of two bytes is more than 10ms, the data will be
sent instantly.
4.2.2.21. AT+ RECV
Function: Receive Data at Command Mode.
Format:
AT+RECV=<data_lenth><CR>
+ok=< data_lenth, data_content><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
data_lenth: Lenth of receive data. Range: 0~1000 Byte
data_content: contents of receive data.
If not receive any data in 3 second, then feedback +ok=0.
4.2.2.22. AT+ PING
Function: Network “PING” Instruction.
Format:
Set Operation
AT+ PING=<IP_address ><CR>
+ok=<sta><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
sta: feedback result
Success
Timeout
Unknown host
4.2.2.23. AT+NETP
Function: Set/Query network protocol parameters;
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 47 -
Format:
Query Operation
AT+NETP<CR>
+ok=<protocol,CS,port,IP><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Set Operation
AT+NETP=<protocol,CS,port,IP><CR>
+ok<CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
protocol:
TCP
UDP
CS: Network mode:
SERVER
CLIENT
Port: protocol port ID: Decimal digit and less than 65535
IP: Server’s IP address when module set as client
If set as UDP SERVER, the module will save the IP address and port of the latest UDP
packet received. The data will be sent to the saved IP address and port. If the module hasn’t
saved any IP address and port when power up. The data will be sent to the IP address and port
which is set by this command.
If set as UDP,CLIENT, the data will always be sent to the IP address and port set by this
command.
4.2.2.24. AT+ MAXSK
Function:Set/ Query TCP Client connection number.
Format:
Query Operation
AT+MAXSK<CR>
+ok=<num><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Set Operation
AT+MAXSK=<num><CR>
+ok<CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
num: TCP Client connection number. Range: 1~5. 5 is the default value it means
when the module work in TCP server , it accepts max 5 TCP client connect to it.
4.2.2.25. AT+ TCPLK
Function: Query if TCP link already build-up;
Format:
AT+TCPLK<CR>
+ok=<sta><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
sta.: if module already setup TCP link;
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 48 -
on: TCP link setup;
off: TCP link not setup;
4.2.2.26. AT+ TCPTO
Function: Set/Query TCP timeout;
Format:
Query Operation
AT+ TCPTO<CR>
+ok=<time><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Set Operation
AT+ TCPTO=<time ><CR>
+ok<CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
time: TCP timeout time.
<= 600, (600s);
>=0, (0 means no timeout);
Default, 300s;
4.2.2.27. AT+TCPDIS
Function: Open/Close TCP link;
Format:
Query Opera
AT+TCPDIS<CR>
+ok=<sta><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Set Operation
AT+ TCPDIS =<on/off><CR>
+ok<CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
When query, sta.: Feedback if TCP Client can be link,
On, TCP link close
off,TCP link on
When setting, “off” means close TCP link. After finish this command, module disconnect TCP
link and not connect again. “On” means open TCP link. After finish this command, module re-
connect TCP server right away.
4.2.2.28. AT+SOCKB
Function: Set/Query SOCKB parameters
Format:
Query Operation
AT+SOCKB<CR>
+ok=<protocol,port,IP><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Set Operation
AT+SOCKB=<protocol,port,IP><CR>
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 49 -
+ok<CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
Protocol: Protocol type:
TCP: Only for TCP Client
UDP
Port: Protocol Port in decimal, less than 65535
IP: Destination IP address, domain name is support
4.2.2.29. AT+TCPDISB
Function: Open/Close TCP_B connection
Format:
Query Operation
AT+TCPDISB<CR>
+ok=<sta><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Set Operation
AT+ TCPDISB =<on/off><CR>
+ok<CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
When setting, “off” means close TCP link. After finish this command, module disconnect TCP
link and not connect again. “On” means open TCP link. After finish this command, module re-
connect TCP server right away.
4.2.2.30. AT+TCPTOB
Function: Set/Query OperationTCP_B timeout
Format:
Query Operation
AT+ TCPTOB<CR>
+ok=<time><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Set Operation
AT+ TCPTOB=<time ><CR>
+ok<CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters
Time: TCP timeout
<= 600:600s
>=0:0 means no timeout
Default:300s
The module will not connect TCP_B after TCP timeout. The module will make connection
after another “TCPDIS” command.
4.2.2.31. AT+TCPLKB
Function:Query TCP_B connection status
Format:
AT+ TCPLKB<CR>
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 50 -
+ok=<sta><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
sta.: TCP_B connection status
on: TCP connected
off: TCP disconnected
4.2.2.32. AT+SNDB
Function: Send datas to SOCKB at Command Mode
Format:
AT+SNDB=<data_lenth ><CR>
+ok<CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
data_lenth: Lenth of send data. Range: 0~1000 Byte
The UART port will wait 3 seconds for input after this command is sent OK. The data received
from UART port is sent to socket. If the interval of two bytes is more than 10ms, the data will be
sent instantly.
4.2.2.33. AT+RCVB
Function: Receive datas from SOCKB at Command Mode
Format:
AT+RCVB=<data_lenth><CR>
+ok=< data_lenth, data_content><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
data_lenth: Lenth of receive data. Range: 0~1000 Byte
data_content: contents of receive data.
If not receive any data in 3 second, then feedback +ok=0.
4.2.2.34. AT+WSSSID
Function: Set/Query Wi-Fi associated AP SSID parameters.
Format:
Query Operation
AT+WSSSID<CR>
+ok=<ap’s ssid><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Set Operation
AT+ WSSSID=<ap’s ssid ><CR>
+ok<CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
ap’s ssid: AP’s SSID (Within 32 character);
4.2.2.35. AT+WSKEY
Function: Set/Query STA security parameters;
Format:
Query Operation
AT+WSKEY<CR>
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 51 -
+ok=<auth,encry,key><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Set Operation
AT+ WSKEY=< auth,encry,key><CR>
+ok<CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
auth: Authentication mode
OPEN
SHARED
WPAPSK
WPA2PSK
encry:Encryption algorithm
NONE: When “auth=OPEN”, effective
WEP: When “auth=OPEN” or “SHARED”, effective
TKIP: When ”auth= WPAPSK” or “WPA2PSK”, effective
AES: When “auth= WPAPSK” “WPA2PSK”, effective
key: password, ASCII code, shall less than 64 bit and greater than 8bit
4.2.2.36. AT+ WANN
Function: Set/Query STA network setting;
Format:
Query Operation
AT+WANN<CR>
+ok=<mode,address,mask,gateway><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Set Operation
AT+ WANN=< mode,address,mask,gateway ><CR>
+ok<CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
mode: STA’s IP network setting
static: Static IP
DHCP: Dynamic IP
address: STA IP address;
mask: STA subnet mask;
gateway: STA gateway address;
4.2.2.37. AT+ WSMAC
Function: Set/Query STA MAC address parameters;
Format:
Query Operation
AT+WSMAC<CR>
+ok=<mac_address><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Set Operation
AT+ WSMAC=<code,mac_address><CR>
+ok<CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 52 -
Parameters:
code: security code
8888 (default value)
Mac_address: STA MAC address, such as ACCF23FF1234
4.2.2.38. AT+ WSLK
Function: Query STA WiFi link status
Format:
Query Operation
AT+ WSLK<CR>
+ok=<ret><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
ret
”Disconnected”, if no WiFi connection;
”AP’ SSID(AP’s MAC” ), if WiFi connection available;
”RF Off”, if WiFi OFF;
4.2.2.39. AT+ WSLQ
Function: Query STA WiFi signal strength;
Format:
Query Operation
AT+ WSLQ<CR>
+ok=<ret><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
ret
”Disconnected”, if no WiFi connection;
”AP’s WiFi signal strength” , if WiFi connection available;
4.2.2.40. AT+WSCAN
Function: Scan AP;
Format:
AT+ WSCAN<CR>
+ok=<ap_site><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
ap_site: AP searched;
4.2.2.41. AT+ WSDNS
Function: Set/Query STA static DNS server address;
Format:
Query Operation
AT+WSDNS<CR>
+ok=<address><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Set Operation
AT+ WSDNS =<address><CR>
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 53 -
+ok<CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
address: STA’s DNS server address; Effective right away.
4.2.2.42. AT+ LANN
Function: Set/Query AP’s network parameters;
Format:
Query Operation
AT+LANN<CR>
+ok=<ipaddress,mask><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Set Operation
AT+ LANN=< ipaddress,mask><CR>
+ok<CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
ipaddress: AP’s IP address;
mask: AP’s net mask;
4.2.2.43. AT+WAP
Function: Set/Query AP Wi-Fi parameters;
Format:
Query Operation
AT+WAP<CR>
+ok=<wifi_mode,ssid,channel><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Set Operation
AT+ WAP =<wifi_mode,ssid,channel><CR>
+ok<CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
wifi_mode: Wi-Fi mode, include:
11B
11BG
11BGN (Default Value)
ssid:SSID at AP mode
channel: Wi-Fi channel selection:
AUTO
CH1~CH11; (Default CH1)
4.2.2.44. AT+WAKEY
Function: Set/Query AP Wi-Fi secruity parameters;
Format:
Query Operation
AT+WAKEY<CR>
+ok=<auth,encry,key><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Set Operation
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 54 -
AT+ WAKEY=< auth,encry,key><CR>
+ok<CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
auth: include
OPEN
WPA2PSK
Encry: include
NONE: When “auth=OPEN” available;
AES: When “auth=WPA2PSK” available;
key: security code, ASCII code, smaller than 64bit and bigger than 8 bit;
4.2.2.45. AT+WAMAC
Function: Query AP MAC address parameters;
Format:
Query Operation
AT+WAMAC<CR>
+ok=<mac_address><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
mac_address:AP’s MAC address;
Note: Module AP mode’s MAC address is related to STA mode’s MAC address. If user need
changeto others, please contact with high-flying technical people.
4.2.2.46. AT+WADHCP
Function: Set/Query AP DHCP server status;
Format:
Query Operation
AT+WADHCP<CR>
+ok=<status><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Set Operation
AT+ WADHCP=<status><CR>
+ok<CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
status:AP’s DHCP server function status:
on:DHCP Server Open;
off:DHCP Server Close:
4.2.2.47. AT+WADMN
Function: Set/Query AP webpage domain name;
Format:
Query Operation
AT+WADMN<CR>
+ok=<domain_name><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Set Operation
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 55 -
AT+ WADMN =<domain_name><CR>
+ok<CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
Domain_name: Webpage domain name (within 20 characters, can’t all numbers).
4.2.2.48. AT+PLANG
Function: Set/ Query webpage language option;
Format:
Query Operation
AT+ PLANG<CR>
+ok=<language> <CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Set Operation
AT+ PLANG=<language> <CR>
+ok<CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
language: webpage’s language
CN: Chinese Version (Default);
EN: English Version;
4.2.2.49. AT+UPURL
Function: Set/ Query remote upgrade URL address;
Format:
Query Operation
AT+ UPURL<CR>
+ok=<url> <CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Set Operation
AT+ UPURL=<url,filename> <CR>
+ok<CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
url: the upgrade file url address; the last charter shall be “/” (within 20 characters).
filename: the upgrade file name, it’s optional and not saved parameter. If provide
this file name here, the module will start upgrade right away;
4.2.2.50. AT+UPFILE
Function: Set/ Query remote upgrade configure file name;
Format:
Query Operation
AT+ UPFILE<CR>
+ok=<filename> <CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Set Operation
AT+ UPFILE=<filename> <CR>
+ok<CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 56 -
filename: the upgrade configure file name (within 20 characters).
4.2.2.51. AT+UPWEB
Function: Remote webpage upgrade
Format:
Query Operation
AT+UPWEB<CR>
+ok=<log><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
log: Some status print log from remote upgrade.
Note: After execute this command, the HF-LPB100 will automatic start upgrade Webpage base
on the setting of UPURL, UPFILE command contents;
4.2.2.52. AT+UPCFG
Function: Remote factory setting upgrade
Format:
Query Operation
AT+UPCFG<CR>
+ok=<log><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
log: Some status print log from remote upgrade.
Note: After execute this command, the HF-LPB100 will automatic start upgrade base on the
setting of UPURL, UPFILE command contents;
4.2.2.53. AT+UPNVR
Function: Remote NVRAM data upgrade
Format:
Query Operation
AT+UPNVR<CR>
+ok=<log><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
log: Some status print log from remote upgrade.
Note: After execute this command, the HF-LPB100 will automatic start upgrade base on the
setting of UPURL, UPFILE command contents;
4.2.2.54. AT+UPAUTO
Function: Remote Application, Webpage, factory setting upgrade
Format:
Query Operation
AT+UPAUTO<CR>
+ok=<log><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
log: Some status print log from remote upgrade.
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 57 -
Note: After execute this command, the HF-LPB100 will automatic start upgrade Application,
Webpage, factory setting base on the setting of UPURL, UPFILE command contents;
4.2.2.55. AT+LOGSW
Function: Open/Close remote upgrade logfile
Format:
Query Operation
AT+LOGSW<CR>
+ok=<status><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Set Operation
AT+LOGSW=<status><CR>
+ok<CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
status:
on: Open. The UART Port will print some upgrade status when upgrading. the
log file will be sent to UDP Port after successfully
off: Close.
4.2.2.56. AT+LOGPORT
Function: Set/Query remote upgrade UDP port of log file.
Format:
Query Operation
AT+LOGPORT<CR>
+ok=<port><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Set Operatioin:
AT+ LOGPORT =<port><CR>
+ok<CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
port: The remote upgrade UDP port of log file.
4.2.2.57. AT+UPST
Function: Start remote upgrade;
Format:
Query Operation
AT+ UPST<CR>
+ok=<log> <CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
log: feedback the status of remote upgrade;
Note: After execute this command, the HF-LPB100 will automatic start upgrade base on the
setting of UPURL, UPFILE command contents;
4.2.2.58. AT+WEBU
Function: Set/ Query webpage user name and password;
Format:
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 58 -
Query Operation
AT+ WEBU<CR>
+ok=<username,password> <CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Set Operation
AT+ WEBU=<username,password><CR>
+ok<CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
username: User Name, within 15 characters, not support empty.
password: password, within 15 characters, support empty.
4.2.2.59. AT+MSLP
Function: Set/Query deep sleep/standby mode parameters;
Format:
Query Operation
AT+ MSLP<CR>
+ok=<ret><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Set Operation
AT+ MSLP=<mode><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
ret:
normal: normal mode (100ms interval)
mode:
normal: normal mode (100ms interval)
standby: WiFi shut down mode
4.2.2.60. AT+NTPRF
Function: Set /Query time calibration interval
Format:
Query Operation
AT+ NTPRF<CR>
+ok=<num><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Set Operation
AT+ NTPRF=<num><CR>
+ok<CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
num:time calibration inverval,range:0~720, default:30 minutes, 10 minutes for
each step, set 0 means no time calibration automatically.
4.2.2.61. AT+NTPEN
Function: Enable/Disable time calibration function.
Format:
Query Operation
AT+ NTPEN<CR>
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 59 -
+ok=<status><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Set Operation
AT+ NTPEN=<status><CR>
+ok<CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
status:status of time calibration
on:Enable time calibration
off:Disable time calibration
4.2.2.62. AT+NTPTM
Function: Query network time
Format:
Query Operation
AT+ NTPTM<CR>
+ok=<time><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
time:networ time, for example: 2013-10-9 16:10:42 Wed,if it shows Not
Available means that the time calibration function is not enabled or the module
doesn’t connect to the internet.
4.2.2.63. AT+WRMID
Function: Set module ID;
Format:
Set Operation
AT+ WRMID=<wrmid> <CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
wrmid: set module’s ID (within 20 characters).
4.2.2.64. AT+RLDEN
Function: Set/Query GPIO45 function status
Format:
Query Operation
AT+RLDEN<CR>
+ok=<status><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Set Operation
AT+RLDEN=<status><CR>
+ok<CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
status: The status of module’s GPIO45(nReload) function
on: GPIO45 function (nReload) is enabled.
off: GPIO45 function is disabled
4.2.2.65. AT+ASWD
Function: Set/Query WiFi Configuration Password;
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 60 -
Format:
Query Operation
AT+ ASWD<CR>
+ok=<aswd> <CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Set Operation
AT+ ASWD=<aswd> <CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
aswd: WiFi Configuration Password (within 20 characters).
4.2.2.66. AT+MDCH
Function: Set Wi-Fi Auto Switch Function
Format:
Query Operation
AT+ MDCH<CR>
+ok=<mode> <CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Set Operation
AT+ MDCH=<mode> <CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
mode: Wi-Fi Auto Switch Mode
off: Disable Wi-Fi auto switch.
on: Enable Wi-Fi auto switch. When the module(STA mode) fail to connect to
router, it will switch to AP mode itself in one minute.
auto: Enable Wi-Fi auto detect function. The module will reset itself when
encounter any abnormal. The default time interval is 10 minutes.
3-120: unit: minute. Set the time interval to reset itself when abnormal.
4.2.2.67. AT+TXPWR
Function: Set/Query Wi-Fi Transmit Power, Real Transmit Power=Default Transmit
Power(16dBm) – [Setting Value] * 0.5dBm
Format:
Query Operation
AT+TXPWR <CR>
+ok=<num><CR>< LF><CR>< LF>
Set Operation
AT+TXPWR=<num><CR>
+ok<CR>< LF><CR>< LF>
Parameters:
num: [Setting Value]. The default is 0, it can be sent from 0 ~ 24. If set to 24, the
moudule transmit power will be at a minium of 4dBm. Reboot to make this setting
change valid. It will not restore to default if reload the module.
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 61 -
5. PACKAGE INFORMATION
5.1. Recommended Reflow Profile
Figure 35. Reflow Soldering Profile
Table 11 Reflow Soldering Parameter
Note: 1. Recommend to supply N2 for reflow oven.
2. N2 atmosphere during reflow (O2<300ppm)
5.2. Device Handling Instruction (Module IC SMT Preparation)
1. Shelf life in sealed bag: 12 months, at <30℃ and <60% relative humidity (RH)
2. After bag is opened, devices that will be re-baked required after last baked with window time
168 hours.
3. Recommend to oven bake with N2 supplied
4. Recommend end to reflow oven with N2 supplied
5. Baked required with 24 hours at 125+-5℃ before rework process for two modules, one is
new module and two is board with module
6. Recommend to store at ≦10% RH with vacuum packing
7. If SMT process needs twice reflow:
(1) Top side SMT and reflow (2) Bottom side SMT and reflow
Case 1: Wifi module mounted on top side. Need to bake when bottom side process over 168
hours window time, no need to bake within 168 hours
Case 2: Wifi module mounted on bottom side, follow normal bake rule before process
Note: Window time means from last bake end to next reflow start that has 168 hours space.
NO. Item Temperature (Degree)
Time(Sec)
1 Reflow Time Time of above 220
35~55 sec
2 Peak-Temp 260 max
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 62 -
5.3. Shipping Information
TRAY BOX
Size: 420*245*34 mm Size: 422*247*72 mm (inside)
CARTON
Size: 440*260*320 mm (inside)
Figure 36. Shipping Information
Note:
1 tray = 5*20pcs = 100 pcs
1 box = 2 trays = 2 * 100 pcs = 200pcs
1 carton = 4 boxes = 4 * 200 pcs = 800pcs
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 63 -
APPENDIX A: HW REFERENCE DESIGN
Detailed HF-LPB100 Evluation Board design source files, pls access High-Flying web download page
or contact with High-Flying technical support people to acquire.
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 64 -
APPENDIX B: CONTROL GPIO/PWM
FUNCTION WITH NETWORK COMMANDS
Send command data to control module’s GPIO, PWM port after make network connection with TCP or
UDP protocol. The status of GPIO won’t be changed if the module is reset
B.1 Network Command
B.1.1 GPIO <channel> OUT <value>
Function: Set GPIO Channel value temporarily.。
Parameters:
channel:GPIO Channel number, it can be 11、12、15、18、20、23(GPIO Pin
number)
value:GPIO Channel value,1(high voltage),0(low voltage)
Return Data:
GPIO OK: Command successful
GPIO NOK: Command failed
B.1.2 GPIO <channel> GET
Function: Query GPIO Channel value
Parameters:
channel: GPIO Channel number,it can be 11、12、15、18、20、23(GPIO Pin
number)
Return Data:
+ok=<value>
value:GPIO Channel value
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 65 -
GPIO NOK: Command failed
B.1.3 GPIO <channel> SET
Function: Save GPIO Channel setting
Parameters:
channel:GPIO Channel number,it can be 11、12、15、18、20、23(GPIO Pin
number)
Return Data:
GPIO OK: Command successful
GPIO NOK: Command failed
B.1.4 PWM <channel frequency duty>
Function: Set PWM Channel output temporarily
Parameters:
channel:PWM Channel number, it can be 11、12、18、20(GPIO Pin number)
frequency:PWM Channel frequency, it can be 500~60000
duty:PWM Channel duty, it can be 0~100.
Return Data:
PWM OK: Command successful
PWM NOK: Command failed
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 66 -
B.1.5 PWM <channel> GET
Function: Query PWM Channel output
Parameters:
channel: PWM Channel number,it can be 11、12、18、20(GPIO Pin number)
Return Data:
+ok=<frequency duty>
frequency:PWM Channel frequency
duty:PWM Channel duty
PWM NOK: Command failed
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 67 -
B.1.6 PWM <channel> SET
Function: Save PWM Channel setting
Parameters:
channel:PWM Channel number, it can be 11、12、18、20(GPIO Pin number)
Return Data:
PWM OK: Command successful
PWM NOK: Command failed
B.2 Hexadecimal Network Command
Send hexadecimal data to fastly read module’s port status.
B.2.1 Read all GPIO Channel
Send Data【0a】:
Return Data:【8a <value>】
value:bit0、bit1 represent GPIO15、GPIO23 value.
B.2.2 Reverse GPIO Channel value
Send Data【03 <channel> 】:
channel: GPIO Channel number, it can be 01、02(GPIO15、GPIO23)
Return Data:【83 <channel value>】
channel: GPIO Channel number, it can be 01、02(GPIO15、GPIO23)
value: GPIO Channel value, 0 or 1
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 68 -
B.2.3 Read All PWM Channel Frequency
Send Data:【30】:
Return Data:【b0 <value1 value2 value3 value4 value5 value6 value7 value8>】
value1: High byte of PWM Channel 0(GPIO11) frequency
value2: Low byte of PWM Channel 0(GPIO11) frequency
value3: High byte of PWM Channel 1(GPIO12) frequency
value4: Low byte of PWM Channel 1(GPIO12) frequency
value5: High byte of PWM Channel 2(GPIO18) frequency
value6: Low byte of PWM Channel 2(GPIO18) frequency
value7: High byte of PWM Channel 3(GPIO20) frequency
value8: Low byte of PWM Channel 3(GPIO20) frequency
B.2.4 Write PWM Channel Frequency
Send Data:【32 <channel value1 value2】:
channel: PWM Channel number
value1: High byte of PWM Channel frequency
value2: Low byte of PWM Channel frequency
Return Data:【b2 <channel value1 value2>】
Channel: PWM Channel number
value1: High byte of PWM Channel frequency
value2: Low byte of PWM Channel frequency
B.2.5 Read All PWM Channel Duty
Send Data:【20】:
Return Data:【a0 <value1 value2 value3 value4>】
value1: Duty of PWM Channel 0
value2: Duty of PWM Channel 1
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 69 -
value3: Duty of PWM Channel 2
value4: Duty of PWM Channel 3
B.2.6 Write PWM Channel Duty
Send Data:【22 <channel value1>】:
channel:PWM Channel number
value1: Duty of PWM Channel
Return Data:【a2 <channel value1>】
Channel:PWM Channel number
value1: Duty of PWM Channel
B.2.7 Save Present GPIO,PWM Setting
Send Data:【7a】:
Return Data:【fa】
B.2.8 Assert All GPIO Channel Low
Send Data:【04】:
Return Data:【84 00】
B.2.9 Assert All GPIO Channel High
Send Data:【05】:
Return Data:【85 01】
B.2.10 Read Resources of module
Send Data:【7e】:
Return Data:【fe <value1 value2 value3>】
value1: Module’s GPIO ouput pin number .
value2:Module’s GPIO input pin number
value3:Module’s PWM pin number
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 70 -
APPENDIX C: HTTP PROTOCOL TRANSFER
HF-LPB100 module support http data transfer in command mode. If any detailed HTTP protocol,
contact us and we may support customization.
C.1. HTTP AT command
C.1.1. AT+ HTTPURL
Function:Set /Query HTTP server IP address and Port Number.
Format:
Query Operation
AT+HTTPURL<CR>
+ok=<IP,Port><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Set Operation
AT+HTTPURL=<IP,Port><CR>
+ok<CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
IP:IP address.
Port:Port number.
C.1.2. AT+ HTTPTP
Function:Set /Query HTTP request type
Format:
Query Operation
AT+HTTPTP<CR>
+ok=<Type><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Set Operation
AT+HTTPTP=<Type><CR>
+ok<CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
Type:GET(default) or POST。
C.1.3. AT+ HTTPPH
Function:Set/Query HTTP protocol header path.
Format:
Query Operation
AT+HTTPPH<CR>
+ok=<Path><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Set Operation
AT+HTTPPH=<Path><CR>
+ok<CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 71 -
Parameters:
Path:Max length is 50 bytes.
C.1.4. AT+ HTTPCN
Function:Set/Query Connection of HTTP protocol header
Format:
Query Operation
AT+HTTPCN<CR>
+ok=<Connection><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Set Operation
AT+HTTPCN=<Connection><CR>
+ok<CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
Connection:Max length is 20 bytes.
C.1.5. AT+ HTTPUA
Function:Set/Query User-Agent of HTTP protocol header.
Format:
Query Operation
AT+HTTPUA<CR>
+ok=<Parameter><CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Set Operation
AT+HTTPUA=<Parameter><CR>
+ok<CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
Parameter:Max length is 20 bytes.
C.1.6. AT+ HTTPDT
Function: Send HTTP request or data.
Format:
Set Operation
AT+HTTPDT=<Data><CR>
+ok<CR>< LF ><CR>< LF >
Parameters:
Data:HTTP request data, send AT+HTTPDT directly if no data to be sent.
C.2. HTTP Example
HTTP parameter settings are as follows:
AT+HTTPURL=192.168.1.1,80 Set HTTP server address and port
AT+HTTPTP=POST Set HTTP request type
AT+HTTPPH=/abcd Set HTTP protocol header path
AT+HTTPCN= keep-alive Set HTTP Connection area
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 72 -
AT+HTTPUA= lwip1.3.2 Set HTTP User-Agent area
If send “AT+HTTPDT”, the data packet will be sent as the following instance including the two
new line:
POST /abcd HTTP/1.1
Connection:keep-alive
User-Agent:lwip1.3.2
Content-Length:0
Host:192.168.0.127:8999
If send AT+HTTPDT=abcd, the data packet will be sent as the following instance:
POST /abcd HTTP/1.1
Connection:keep-alive
User-Agent:lwip1.3.2
Content-Length:4
Host:192.168.0.127:8999
abcd
The data received from HTTP server will be output to serial port and end with “+ok”.
If the module hasn’t received data from HTTP server for 5 second, it will cut the TCP link with
HTTP server.
HF-SH01

High-Flying
Low Power WiFi Module User Manual
Shanghai High-Flying Electronics Technology Co., Ltd
www.hi-flying.com
- 73 -
APPENDIX D: CONTACT INFORMATION
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Address: Room.511/510, Building 7, No.365, Chuanhong Road, Pudong New Area,
Shanghai, China, 201202
Web:
www.hi-flying.com
Service Online: 400-189-3108
Sales Contact: sales@hi-flying.com
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
For more information about High-Flying modules, applications, and solutions, please visit our web site
http://www.hi-flying.com/en/
END OF DOCUMENT
© Copyright High-Flying, May, 2011
The information disclosed herein is proprietary to High-Flying and is not to be used by or disclosed to unauthorized persons
without the written consent of High-Flying. The recipient of this document shall respect the security status of the information.
The master of this document is stored on an electronic database and is “write-protected” and may be altered only by
authorized persons at High-Flying. Viewing of the master document electronically on electronic database ensures access to
the current issue. Any other copies must be regarded as uncontrolled copies.
HF-SH01

FCC STATEMENT
1. This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions:
(1) This device may not cause harmful interference.
(2) This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause
undesired operation.
2. Changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance could
void the user's authority to operate the equipment.
NOTE: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital
device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference in a residential installation.
This equipment generates uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and
used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications.
However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this
equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be
determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the
interference by one or more of the following measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is
connected.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled
environment. This equipment should be installed and operated with minimum distance 20cm
between the radiator & your body
 Loading...
Loading...