Page 1

HPE XP7 Fast Snap User Guide
Abstract
This guide provides information about how to configure and use Fast Snap to store snapshots
in an XP7 Storage system. This document is intended for system administrators and Hewlett
Packard Enterprise representatives and authorized service providers who install, configure,
and operate the XP7 Storage system.
Part Number: 858749-403
Published: January 2019
Edition: 18
Page 2

©
Copyright 2018 Hewlett Packard Enterprise Development LP
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for Hewlett Packard Enterprise products
and services are set forth in the express warranty statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be
construed as constituting an additional warranty. Hewlett Packard Enterprise shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or
omissions contained herein.
Confidential computer software. Valid license from Hewlett Packard Enterprise required for possession, use, or copying. Consistent
with FAR 12.211 and 12.212, Commercial Computer Software, Computer Software Documentation, and Technical Data for
Commercial Items are licensed to the U.S. Government under vendor's standard commercial license.
Links to third-party websites take you outside the Hewlett Packard Enterprise website. Hewlett Packard Enterprise has no control
over and is not responsible for information outside the Hewlett Packard Enterprise website.
Acknowledgments
Microsoft® and Windows® are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or other
countries.
Java® and Oracle® are registered trademarks of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
UNIX® is a registered trademark of The Open Group.
Page 3

Contents
Overview of Fast Snap............................................................................8
About Fast Snap........................................................................................................................... 8
Workflow for storing Fast Snap snapshot data...................................................................8
Components of Fast Snap............................................................................................................ 9
Fast Snap pairs................................................................................................................ 11
Volume components.........................................................................................................12
Snapshot tree components ............................................................................................. 13
Maximum number of Fast Snap pairs.............................................................................. 13
Consistency and snapshot groups................................................................................... 13
Snapshot Clones .............................................................................................................14
Snapshot trees and cascaded pairs ................................................................................14
Creating cascaded pairs.................................................................................................. 15
Volume differences between Fast Snap and Business Copy...........................................17
XP7 Storage software applications for Fast Snap............................................................20
How Fast Snap works................................................................................................................. 21
How Fast Snap uses pools and pool volumes................................................................. 21
Usage level rebalancing among parity groups................................................................. 21
How Fast Snap uses V-VOLs...........................................................................................22
How Fast Snap pairs are created.....................................................................................22
Using snapshot pairs (not cascaded) ..............................................................................23
Using cascaded pairs.......................................................................................................23
Workflow for creating groups and storing snapshot data using RAID Manager...............26
Methods of storing snapshot data.................................................................................... 28
Fast Snap pair restoration................................................................................................29
How Fast Snap pair status changes........................................................................................... 29
Fast Snap host access and pair status............................................................................ 31
Workflow for Fast Snap pair status changes....................................................................31
Copy threshold option and host server I/O performance for Fast Snap......................................33
Sharing Fast Snap volumes with other software applications.....................................................33
Sharing Fast Snap volumes that have Data Retention access attributes........................ 35
Sharing Fast Snap volumes with Auto LUN..................................................................... 38
Sharing Fast Snap volumes with Business Copy.............................................................38
Sharing Fast Snap volumes with Continuous Access Synchronous and Continuous
Access Journal.................................................................................................................41
Sharing Fast Snap volumes with High Availability........................................................... 44
Sharing Fast Snap volumes with Thin Provisioning and Thin Provisioning MF in a
single storage system.......................................................................................................53
Sharing Fast Snap volumes with Resource Partition....................................................... 54
Acronyms and abbreviations for XP7 Storage system software applications used in this
guide........................................................................................................................................... 54
Fast Snap system and planning requirements.................................. 55
Fast Snap system requirements................................................................................................. 55
Fast Snap licensed capacity requirements...................................................................... 55
Fast Snap shared memory requirements.........................................................................56
Fast Snap volume requirements...................................................................................... 56
Fast Snap data pool requirements................................................................................... 60
Fast Snap consistency group requirements.....................................................................61
Fast Snap snapshot group requirements......................................................................... 63
Contents 3
Page 4

Fast Snap planning requirements............................................................................................... 63
Calculating the number of Fast Snap pairs based on pair tables.....................................64
Calculating Fast Snap pairs based on the snapshot estimated manageable capacity.... 64
Calculating Fast Snap pairs based on cache management devices................................65
Calculating the number of cache management devices.................................................. 66
Calculating the Fast Snap pair capacity for THP pools....................................................66
Fast Snap cache management device requirements.......................................................68
Calculating and assigning pool capacity.......................................................................... 69
External Storage and external volumes used as pool-VOLs............................................71
Simultaneous processing of multiple Fast Snap pair tasks..............................................71
Pair operations when pairs are cascaded ....................................................................... 72
Pair operations when pairs are not cascaded.................................................................. 83
Pair operations when a P-VOL is shared by multiple S-VOLs......................................... 84
Data recovery and backup differences between Fast Snap and Business Copy.............85
Removing Fast Snap.................................................................................................................. 86
Configuring Fast Snap..........................................................................88
Prerequisites for configuring Fast Snap......................................................................................88
Workflow for configuring Fast Snap............................................................................................ 88
Workflow for creating and managing Fast Snap pairs......................................................89
Creating Fast Snap data pools.........................................................................................89
Selecting pool volumes.................................................................................................... 92
Pool creation and data drive type priority.........................................................................94
Workflow for registering virtual volumes..................................................................................... 95
Editing the SSID for virtual volumes ................................................................................95
Changing V-VOL settings.................................................................................................98
Creating V-VOLs for Fast Snap S-VOLs........................................................................100
Overview of using RAID Manager to run commands through in-band connections................. 108
Changing system options that affect Fast Snap performance.................................................. 108
Managing Fast Snap Pairs..................................................................112
Fast Snap pair tasks..................................................................................................................112
Checking Fast Snap pair status................................................................................................ 112
Reloading Fast Snap configuration information........................................................................ 112
Workflow for creating and managing Fast Snap pairs...............................................................113
Workflow for creating Fast Snap pairs using Remote Web Console.........................................113
Creating Fast Snap pairs using Remote Web Console.............................................................114
Selecting a pool as your primary volume........................................................................117
Example of creating complex Fast Snap pairs..........................................................................118
Pair operations for each consistency group.............................................................................. 119
Adding Fast Snap pairs to snapshot or consistency groups using RAID Manager........ 119
Workflow for defining Fast Snap pairs and defining them in snapshot or consistency
groups using Remote Web Console...............................................................................119
Storing snapshot data or cloning pairs........................................................................... 119
Splitting Fast Snap pairs to store snapshot data...................................................................... 120
Splitting Fast Snap pairs to store snapshot data using RAID Manager......................... 121
Workflow for storing snapshot data or clone pairs in consistency groups.................................121
Using consistency group pair-split with shared volumes................................................122
Restoring Fast Snap pairs........................................................................................................ 124
Failure during Fast Snap pair restore.............................................................................126
Restoring suspended Fast Snap pairs........................................................................... 126
Fast Snap pair resynchronization............................................................................................. 126
Pair resynchronization methods.....................................................................................126
Resynchronizing Fast Snap pairs.................................................................................. 127
4 Contents
Page 5

Assigning MU numbers to deleted snapshot data.................................................................... 127
Deleting snapshot data............................................................................................................. 128
Deleting Fast Snap pairs...........................................................................................................129
Accelerating the Fast Snap pair deletion process..........................................................130
Removing Fast Snap snapshot groups.......................................................................... 130
Assigning secondary volumes to Fast Snap pair snapshot data.............................................. 131
Assigning secondary volumes to snapshot data after creating new Fast Snap pairs.... 131
Assigning secondary volumes to snapshot data of existing Fast Snap pairs.................132
Releasing assignment of secondary volumes from Fast Snap pair snapshot data.................. 133
Changing assignment of secondary volumes to Fast Snap pair snapshot data....................... 134
Monitoring and maintaining Fast Snap.............................................136
Monitoring pair information....................................................................................................... 136
Viewing summary replication information.......................................................................136
Viewing local replication summary information.............................................................. 137
Viewing the number of pairs...........................................................................................139
Viewing the list of primary volumes................................................................................139
Viewing pair properties ..................................................................................................140
Fast Snap pair status definitions.................................................................................... 141
Viewing pair synchronization rates.................................................................................142
Monitoring consistency groups................................................................................................. 143
Viewing the number of consistency groups....................................................................143
Viewing the list of consistency groups............................................................................145
Viewing consistency group properties............................................................................145
Viewing Fast Snap pair task history..........................................................................................147
Fast Snap task code definitions..................................................................................... 149
Viewing licensed capacities...................................................................................................... 150
Viewing the number of cache management devices.................................................................150
Managing pools.........................................................................................................................151
Monitoring pool information............................................................................................151
Viewing used pool capacity ...........................................................................................153
Viewing formatted pool capacity and pool usage rates..................................................154
Increasing pool capacity.................................................................................................155
Decreasing pool capacity............................................................................................... 159
Editing the data pool warning threshold......................................................................... 163
Editing pool names.........................................................................................................165
Workflow for recovering blocked pools...........................................................................168
Workflow for decreasing pool capacity...........................................................................170
Managing virtual volumes......................................................................................................... 172
Editing virtual volume names......................................................................................... 172
Workflow for deleting V-VOLs specified for Fast Snap S-VOLs..................................... 174
Viewing snapshot data capacity ...............................................................................................175
Maintaining pairs during storage system maintenance.............................................................176
Switching off the power supply.......................................................................................176
Definition of failure.................................................................................................................... 177
Troubleshooting Fast Snap................................................................178
Overview................................................................................................................................... 178
Failures in a cascaded configuration........................................................................................ 178
Troubleshooting the source of SIM codes.................................................................................179
Troubleshooting pools, pairs, and volumes related to Fast Snap............................................. 179
Workflow for correcting pool-related failures (SIM = 601xxx, 602xxx, 604xxx,
605xxx, and 606xxx)...................................................................................................... 184
Workflow for fixing errors when SIMs related to cache management devices are reported..... 190
Contents 5
Page 6

Calculating the number of remaining cache management devices................................190
Workflow for fixing errors when pool-related SIMs are reported...............................................190
Completing SIMs ......................................................................................................................192
Automatic completion of SIMs........................................................................................192
Manually completing SIMs............................................................................................. 192
RAID Manager command reference for Fast Snap.......................... 194
Pair tasks using RAID Manager or Remote Web Console........................................................194
RAID Manager pair command results.......................................................................................195
Parameter ranges for RAID Manager options...........................................................................196
Troubleshooting with RAID Manager........................................................................................ 196
RAID Manager SSB2 codes...........................................................................................196
Notes on using Fast Snap primary volumes as Continuous Access Synchronous,
Business Copy, or Continuous Access Journal pair volumes........................................ 206
Fast Snap GUI windows and wizards................................................208
Replication window................................................................................................................... 208
Local Replication window..........................................................................................................211
View Pair Synchronization Rate window...................................................................................227
View Pair Properties window.....................................................................................................231
History window..........................................................................................................................238
Consistency Group Properties window..................................................................................... 240
Create FS Pairs wizard............................................................................................................. 244
Create FS Pairs window.................................................................................................244
Assign Secondary Volumes window.............................................................................. 253
Create FS Pairs confirmation window............................................................................ 260
Select Pool window...................................................................................................................267
Split Pairs wizard.......................................................................................................................269
Split Pairs window.......................................................................................................... 269
Split Pairs confirmation window..................................................................................... 272
Resync Pairs wizard..................................................................................................................274
Resync Pairs window..................................................................................................... 274
Resync Pairs confirmation window................................................................................ 277
Delete Pairs window................................................................................................................. 279
Edit Local Replica Options wizard............................................................................................ 281
Edit Local Replica Options window................................................................................ 281
Edit Local Replica Options confirmation window........................................................... 286
FS Pairs window....................................................................................................................... 287
Assign Secondary Volumes wizard...........................................................................................292
Assign Secondary Volumes window.............................................................................. 293
Assign Secondary Volumes confirmation window..........................................................299
Remove Secondary Volumes window.......................................................................................305
6 Contents
Websites.............................................................................................. 308
Support and other resources.............................................................309
Accessing Hewlett Packard Enterprise Support....................................................................... 309
Accessing updates....................................................................................................................309
Customer self repair..................................................................................................................310
Remote support........................................................................................................................ 310
Warranty information.................................................................................................................310
Regulatory information.............................................................................................................. 311
Page 7

Documentation feedback...........................................................................................................311
Contents 7
Page 8
Overview of Fast Snap
About Fast Snap
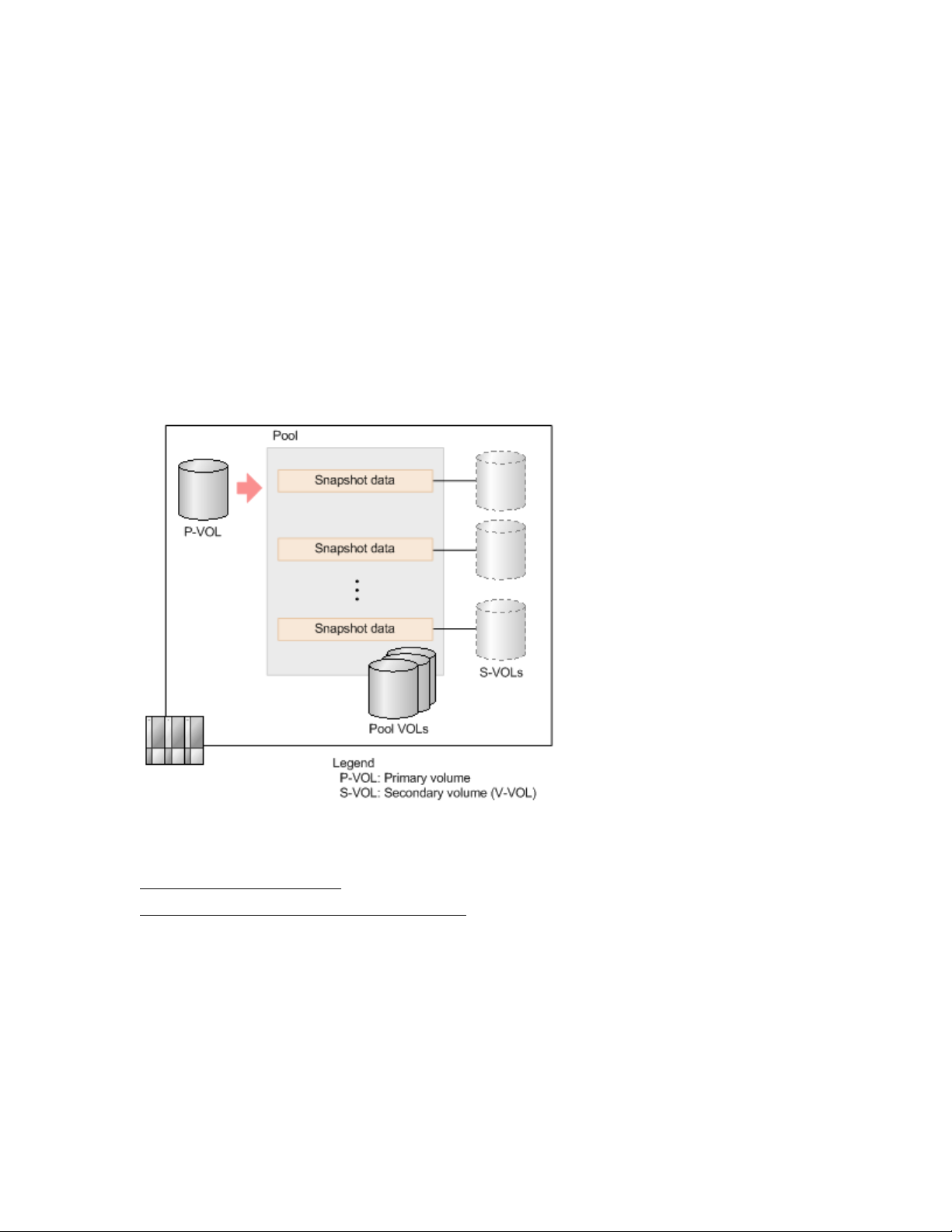
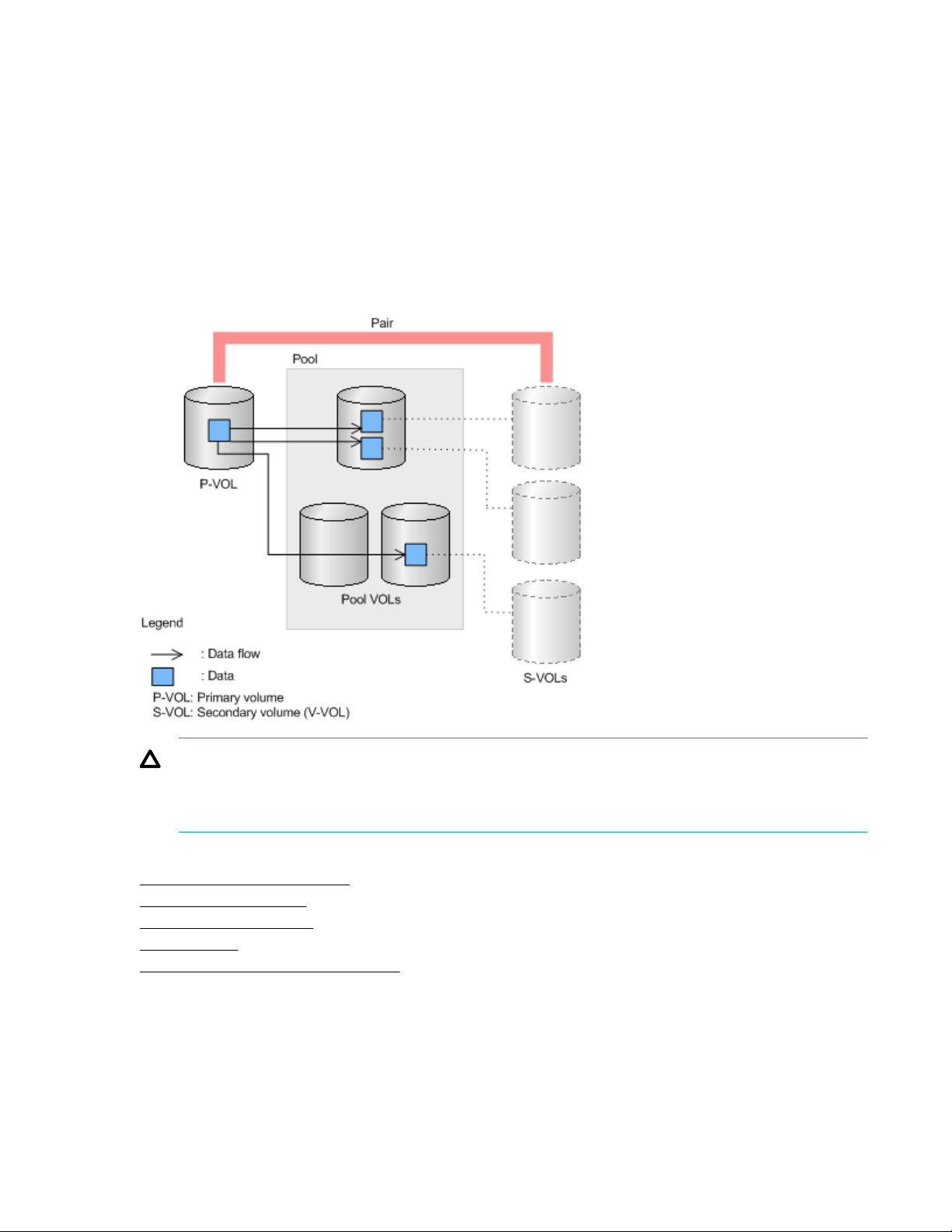
To store snapshot data, you create a pair with a logical volume functioning as the P-VOL, and a virtual
volume as the S-VOL. A pair created to store snapshot data is referred to as a snapshot pair. A snapshot
pair displays showing the snapshot attribute.
When you create a Fast Snap pair, the status changes to "PAIR" and snapshot data is stored. You can
use Fast Snap to store a maximum of 1,024 snapshots of data (including the number of clones when you
clone a volume).
Updating the P-VOL first copies the differential data as snapshot data in pool volumes (pool-VOL), and
then updates the data. Snapshot data is a copy of differential data in Fast Snap P-VOLs. If your storage
system experiences a data storage failure, you can restore the data using the snapshot data in the pool.
Splitting a Fast Snap pair saves a snapshot and stops the copying of replaced data in the pool.
The following figure provides a basic illustration of storing snapshot data.
You can use snapshot data in open-system volumes.
More information
How Fast Snap uses V-VOLs on page 22
Splitting Fast Snap pairs to store snapshot data on page 120
Workflow for storing Fast Snap snapshot data
1. Create a Fast Snap pair. You can create a pair with the snapshot attribute (snapshot pairs). The pair is
in "PAIR" status.
2. The host updates the primary volume.
3. Split the snapshot pairs. The snapshot data of the primary volume is stored (Snapshot data A in the
figure below).
8 Overview of Fast Snap
Page 9
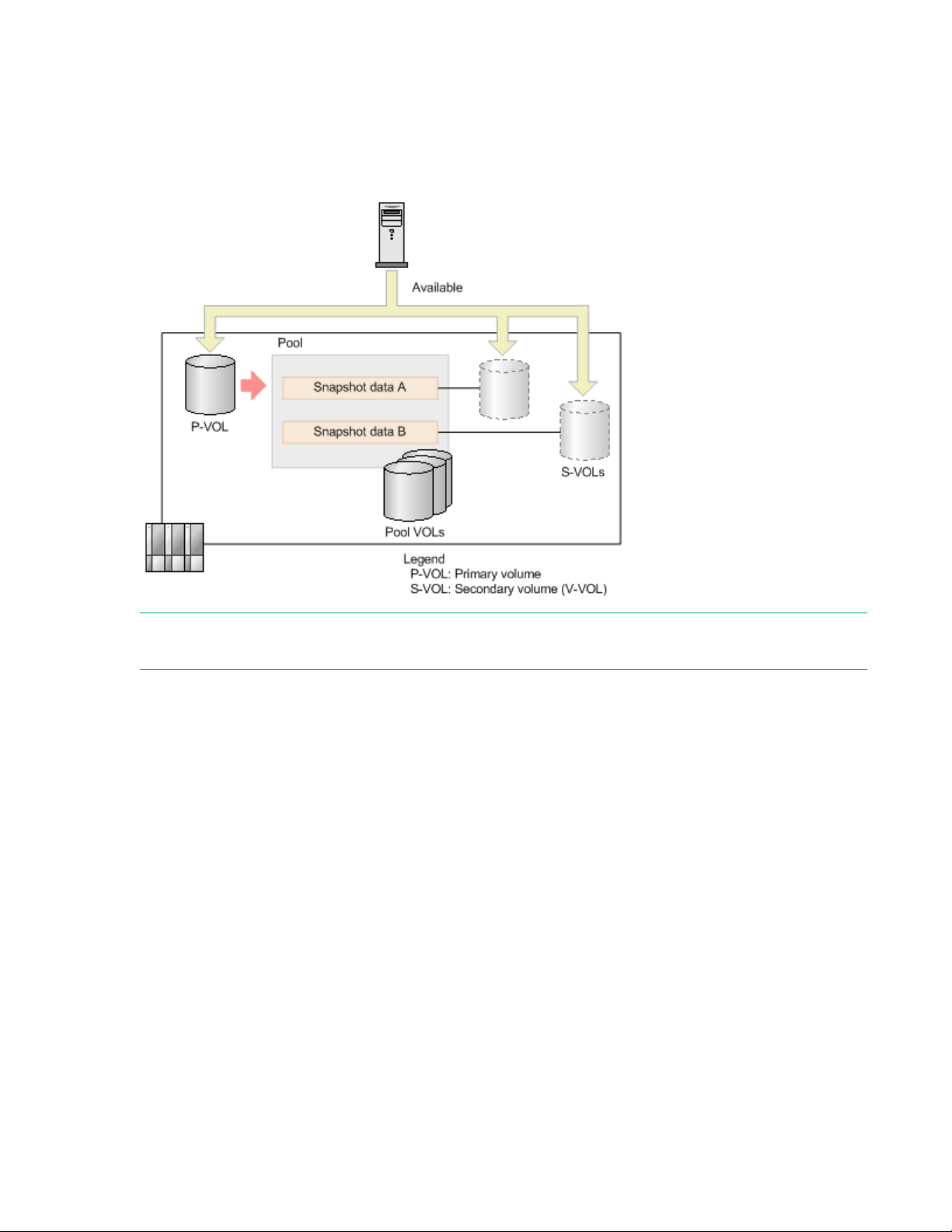
4. The host updates the primary volume again.
5. Split the snapshot pairs. The updated data in the primary volume is stored as snapshot data
(Snapshot data B in the following figure). In the event of data corruption, you can recover using this
snapshot data.
The following figure illustrates how data in the pool is replaced.
NOTE: Because Snapshot data A and Snapshot data B are handled as a Fast Snap S-VOL of a snapshot
pair, the host can reference the P-VOL, Snapshot data A, and Snapshot data B.
Components of Fast Snap
Fast Snap components:
• Fast Snap pairs (clone and snapshot pairs).
• Volume related components (P-VOL, S-VOL, and pools)
• Snapshot tree related components (root volume, node volumes, and leaf volumes)
Groups:
• Consistency groups
• Snapshot groups
Software applications for XP7 Storage systems:
• Fast Snap
• Thin Provisioning (THP)
• RAID Manager
Components of Fast Snap 9
Page 10

You can run RAID Manager commands to perform Fast Snap tasks (see Pair tasks using RAID
Manager or Remote Web Console on page 194). When using RAID Manager, run commands
directly from the host instead of using a management client.
10 Overview of Fast Snap
Page 11

Fast Snap pairs
Type Volume that can
be used as P-VOL
Pairs with the
snapshot attribute
Logical volume
(LDEV)
Volume that can
be used as S-VOL
Fast Snap V-VOL
(V-VOL of which
provisioning type is
Snapshot in RWC,
or V-VOL created
by the raidcom
add ldev -pool
snap command in
RAID Manager)
THP V-VOL Yes
Cascade
capability
No
Description
Pairs used to store
snapshot data.
The logical volume
of the P-VOL
contains THP VVOLs (V-VOL of
which provisioning
type is Thin
Provisioning in
RWC, or V-VOL
created by the
raidcom add
ldev -pool
command in RAID
Manager).
Pairs used to store
snapshot data. To
create a cascaded
pair with the
snapshot attribute,
use a THP V-VOL
as the S-VOL. To
use a THP V-VOL
as the S-VOL,
make sure to
specify a cascaded
pair (with the
cascade attribute
enabled)
regardless of
whether it is in a
cascaded
configuration.
Pairs with the clone
attribute
Logical volume
(LDEV)
THP V-VOL Yes
The logical volume
of the P-VOL
contains THP VVOLs (V-VOL of
which provisioning
type is Thin
Provisioning in
RWC, or V-VOL
created by the
raidcom add
ldev -pool
command in RAID
Manager).
Pairs to be cloned.
Fast Snap pairs 11
Page 12

Type Volume that can
Volume components
Volume type Volumes that can be used Description
Primary Logical volume (LDEV) Logical volume of a P-VOL
be used as P-VOL
Volume that can
be used as S-VOL
Cascade
capability
contains THP V-VOLs (V-VOLs of
which provisioning type is Thin
Provisioning in RWC, or V-VOL
created by raidcom add ldev
-pool in RAID Manager).
Description
The logical volume
of the P-VOL
contains THP VVOLs (V-VOL of
which provisioning
type is Thin
Provisioning in
RWC, or V-VOL
created by the
raidcom add
ldev -pool
command in RAID
Manager).
Secondary Fast Snap V-VOL (V-VOL of
which provisioning type is
Snapshot in RWC, or V-VOL
created by raidcom add ldev
-pool snap in RAID Manager)
THP V-VOL
Pool Logical volume (LDEV) Volumes that configure a pool
Use this volume to create
snapshot pairs. Cannot be used
for cascaded or cloned pairs.
This volume is required to create
a pair with the S-VOL specified.
Use this volume to create
cascaded or cloned pairs.
This volume is required to create
a pair with the S-VOL specified.
Cloned pairs must be created
with the S-VOL specified.
When a THP V-VOL is used as
an S-VOL, you must specify a
cascaded or cloned pair.
which stores snapshot data.
Differential data of a P-VOL is
stored in a pool volume as
snapshot data.
12 Volume components
Page 13

Snapshot tree components
Volume type Volumes that can be used Description
Root Logical volume (LDEV)
Node THP V-VOL
Leaf THP V-VOL
Volume (L1 pair of the P-VOL) in
the top layer of a snapshot tree.
The logical volume of the P-VOL
contains THP V-VOLs (V-VOL of
which provisioning type is Thin
Provisioning in RWC, or V-VOL
created by raidcom add ldev
-pool in RAID Manager).
Volumes located between the
root volume and leaf volumes.
S-VOL of the root volume (or
another node volume), and the PVOL of a leaf volume (or another
node volume).
Volumes in the bottom layer of a
snapshot tree.
S-VOL of the root volume or a
node volume, which is not a PVOL of any pair.
Maximum number of Fast Snap pairs
The maximum number of pairs that can be created on the XP7 storage system is 1,048,575.
Consistency and snapshot groups
A consistency group can include Fast Snap (FS), Business Copy (BC), and Business Copy MF (BC MF)
pairs. Use consistency groups to split the Fast Snap pairs that are defined in the group. Splitting the pairs
using the group assures data consistency at the time the XP7 Storage system receives the request.
A snapshot group is a group of only Fast Snap pairs. Use consistency or snapshot groups to perform Fast
Snap tasks on all of the pairs within the group. You define Fast Snap pairs to a snapshot group when you
create the pairs.
The following table shows the differences between consistency groups and snapshot groups.
Item Consistency group Snapshot group
Pair limit per group 8,192 8,192
Limit 2,048 2,048
Data consistency Guaranteed Not guaranteed
Software application from which you can define pairs FS, BC, and BC MF FS
For more information about defining Cnt Ac-S pairs in consistency groups, see the HPE XP7 Continuous
Access Synchronous User Guide.
Snapshot tree components 13
Page 14
For more information about defining Cnt Ac-J pairs in consistency groups, see the HPE XP7 Continuous
Access Journal User Guide.
For more information about defining BC pairs in consistency groups, see the HPE XP7 Business Copy
User Guide.
More information
Workflow for creating groups and storing snapshot data using RAID Manager on page 26
Adding Fast Snap pairs to snapshot or consistency groups using RAID Manager on page 119
Removing Fast Snap snapshot groups on page 130
Pair tasks using RAID Manager or Remote Web Console on page 194
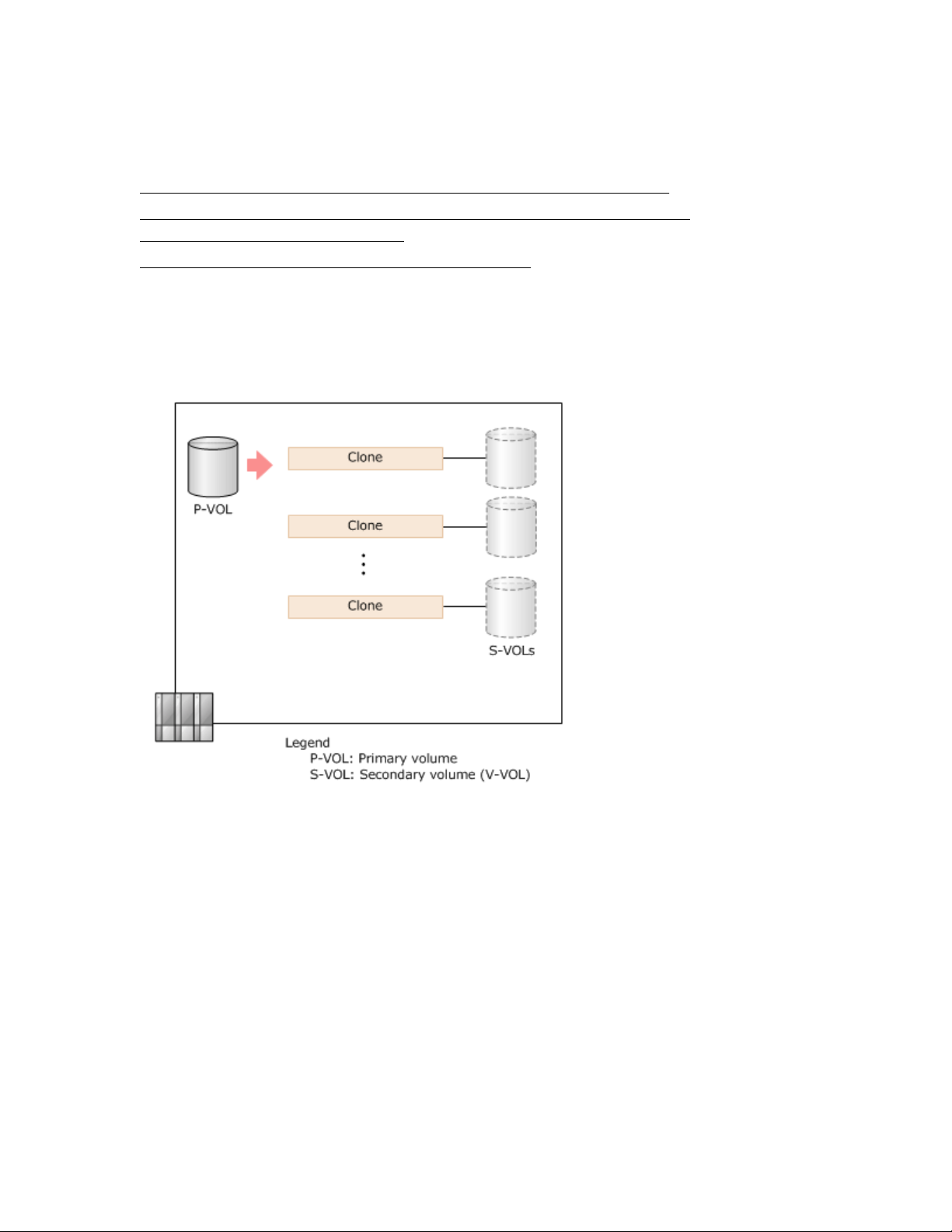
Snapshot Clones
When distributing data in a storage system, you can use clones to improve efficiency.
The following figure illustrates cloning.
When cloning pairs, use a logical volume as the P-VOL and a THP V-VOL as the S-VOL.
If you split pairs that have the clone attribute, the data of the entire P-VOL is copied to the S-VOL
asynchronously to create a clone of the primary volume. When the copy completes, pairs are deleted and
the S-VOL is unpaired (becomes a THP V-VOL). This volume can be used as a volume in the same
status as the P-VOL. This operation is referred to as cloning pairs.
A maximum of 1,024 clones (including the number of snapshots if you store them) can be created by
using Fast Snap.
Cloning pairs includes operations after the P-VOL is copied to the S-VOL, until volumes are unpaired.
Volumes created by cloning are not included.
Snapshot trees and cascaded pairs
The volume in the top layer of the snapshot tree is the root volume. Volumes in the bottom layer are leaf
volumes.
14 Snapshot Clones
Page 15
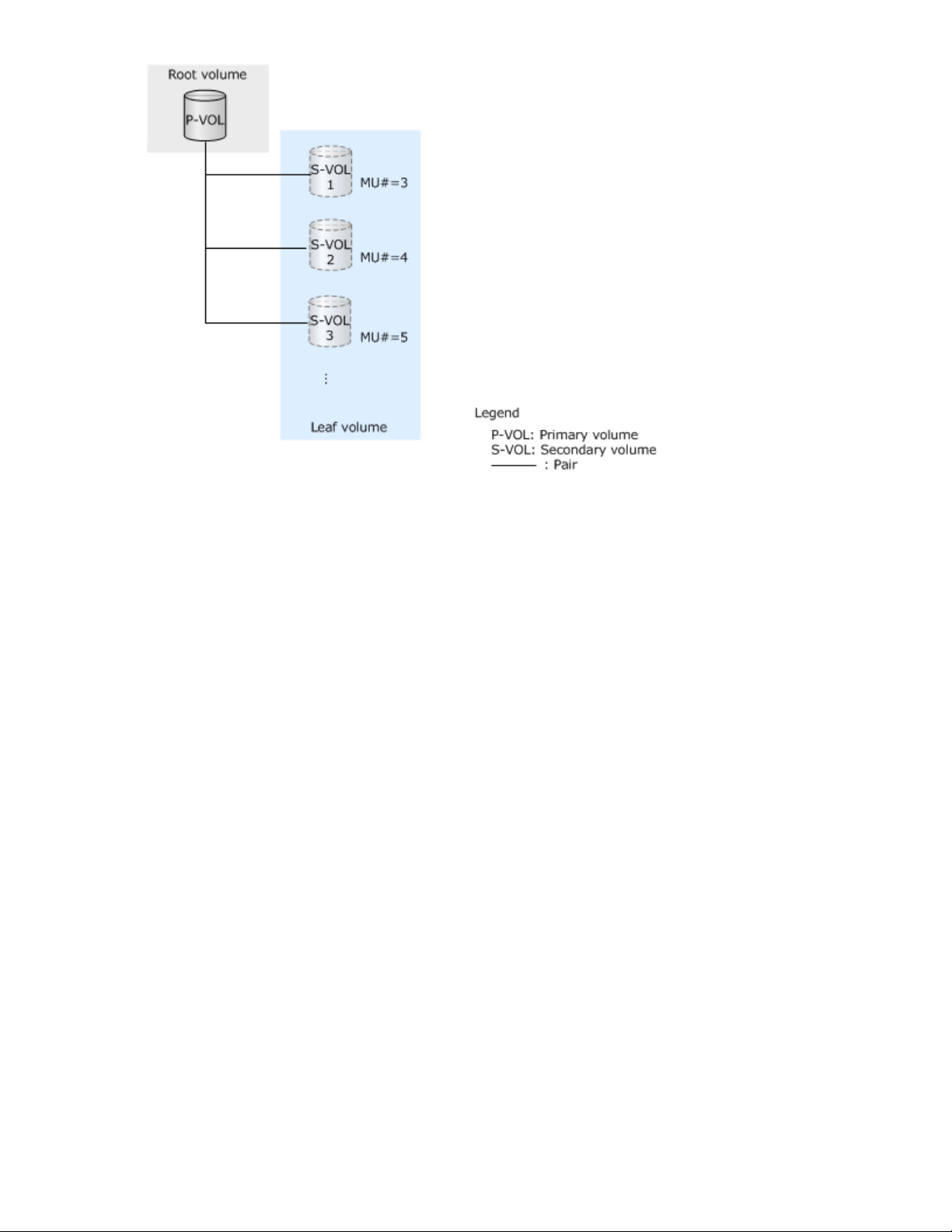
Creating cascaded pairs
Fast Snap S-VOLs can be paired with secondary layer S-VOLs. First layer (L1) S-VOLs can also be
paired with secondary layer (L2) S-VOLs. A maximum of 64 layers can be created, and a maximum of
1,024 S-VOLs can be used for a P-VOL. In this case, the snapshot tree is cascaded.
L2 to L64 pairs are called cascaded pairs. The following figure illustrates the configuration of cascaded
snapshot trees.
Creating cascaded pairs 15
Page 16
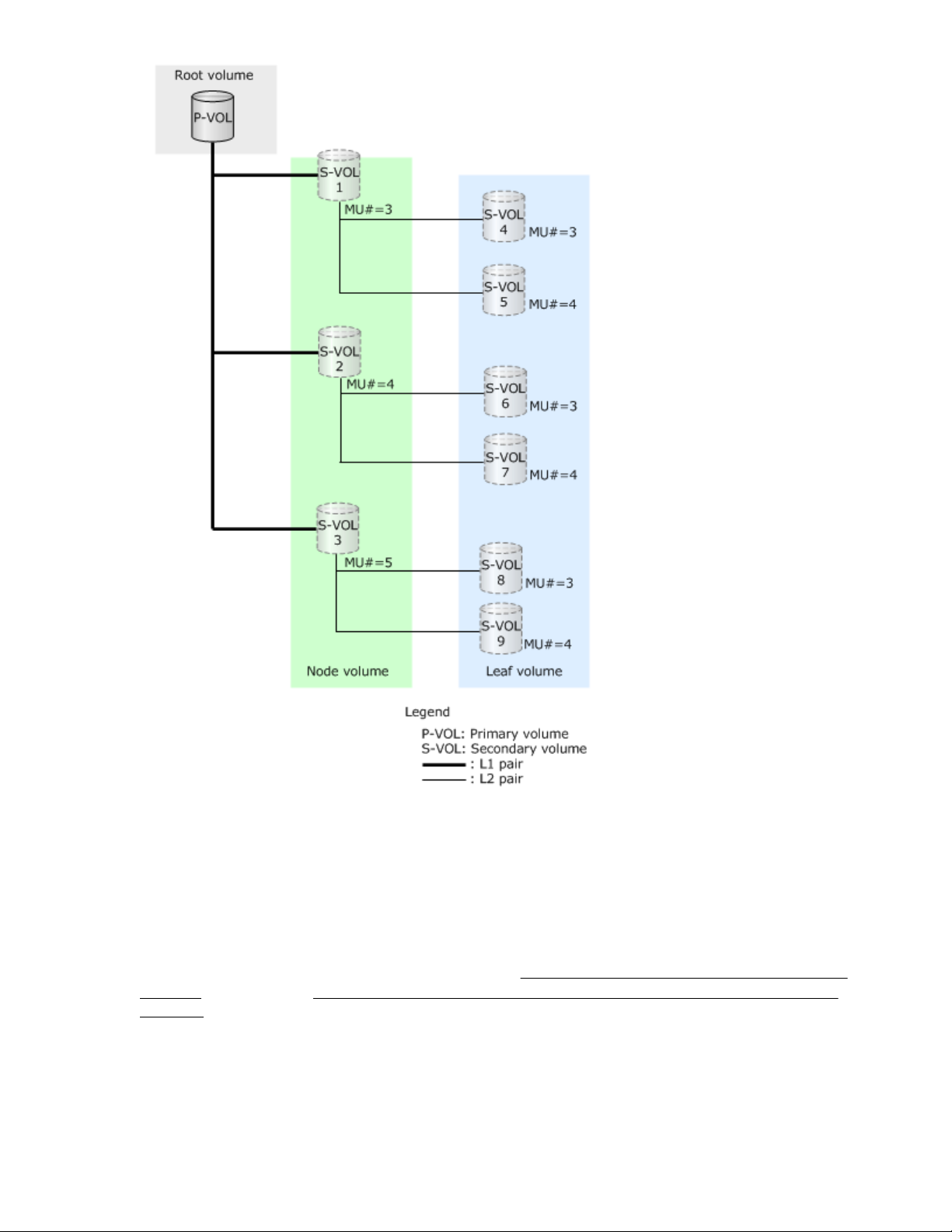
• The volume in the top layer of the snapshot tree (P-VOL of the L1 pair) is the root volume.
• Volumes between the root and leaf volumes are node volumes.
• Volumes in the bottom layer of the snapshot tree are leaf volumes.
To create a Fast Snap pair that can be used in a cascaded snapshot tree, open the Create FS Pairs
window and select Enable for Cascade in RWC or use the raidcom add snapshot -snap_mode
cascade command in RAID Manager. For details, see Creating Fast Snap pairs using Remote Web
Console on page 114 or Adding Fast Snap pairs to snapshot or consistency groups using RAID
Manager on page 119.
When the S-VOL of a Fast Snap pair you created for a P-VOL for the first time is a THP V-VOL, you can
create cascaded pairs. If a Fast Snap pair whose secondary volume is a Fast Snap V-VOL (which has the
Snapshot provisioning type) is created, remove the pair first, and then create another Fast Snap pair
whose secondary volume is a THP V-VOL.
16 Overview of Fast Snap
Page 17
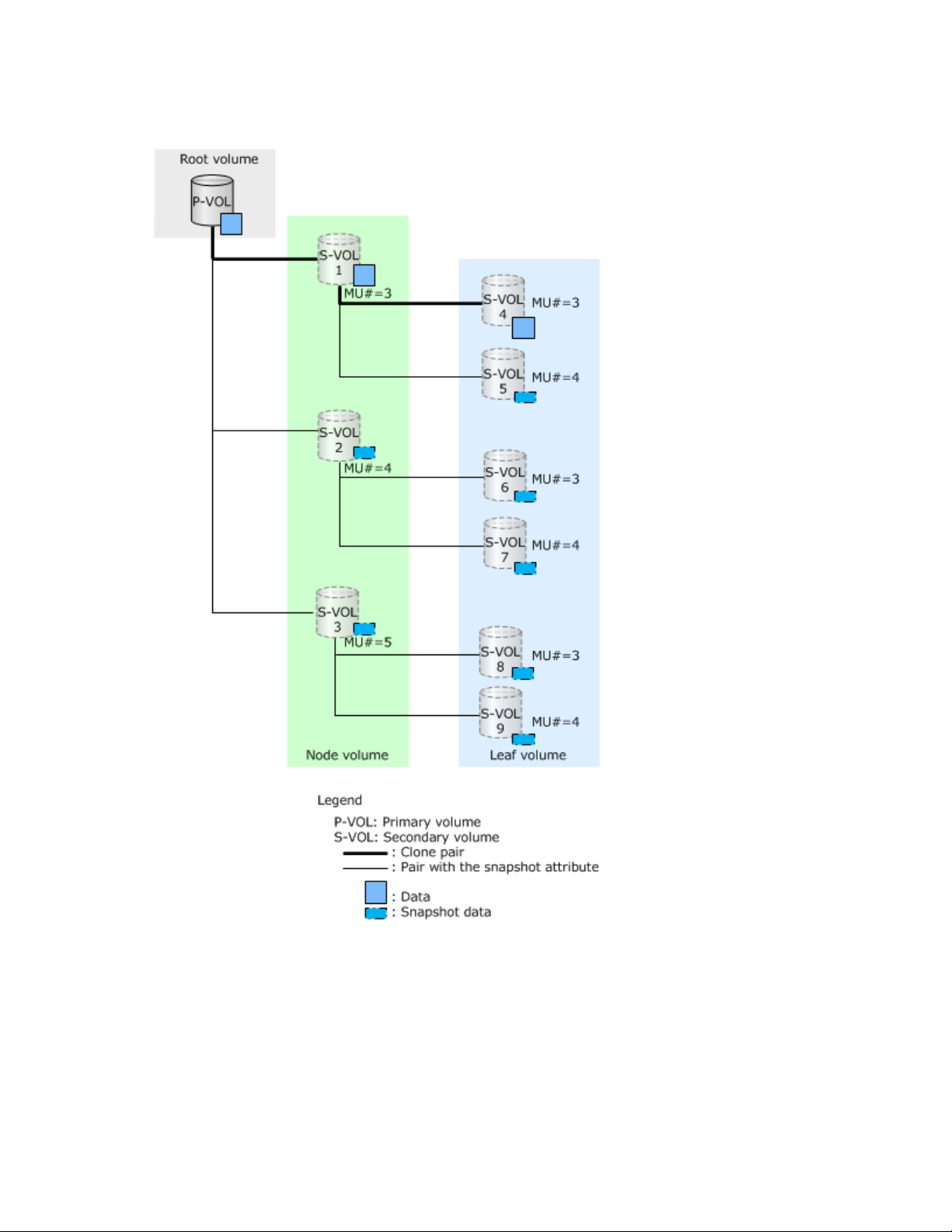
A snapshot tree can be configured by combining snapshot and cloned pairs. As shown in the following
figure, you can also cascade pairs that are being cloned, but you can only clone up to three pairs
concurrently. The following figure shows an example of when pairs that are being cloned are also
cascaded.
You can use the S-VOL of a cascaded and cloned pair as a new L1 pair of the P-VOL. In this case, the
volume is the root volume, and a node or leaf volume.
Volume differences between Fast Snap and Business Copy
The following table summarizes the volume and other differences between Fast Snap and Business
Copy.
Volume differences between Fast Snap and Business Copy 17
Page 18
Item Fast Snap Business Copy
Initial copy operation
Number of S-VOLs per P-VOL Up to 1,024 Up to 9
Capacity efficiency High. Only differential data is
Operation of copied volumes Always used with the P-VOL. Can be used separately from the
P-VOL physical failures S-VOL data cannot be
S-VOL or pool physical failures If a physical failure occurs in a
*When a pool is full (the depletion threshold is exceeded in a pool for which the capacity for Fast Snap
pairs is limited), data in all S-VOLs using the pool cannot be guaranteed.
The following figures explain the relation of data when a failure occurs in the P-VOL.
Not required.
Volumes can be copied faster.
copied from the P-VOL.
guaranteed.
pool*, data in all S-VOLs that use
the pool cannot be guaranteed.
Required.
Low. The entire P-VOL is copied.
P-VOL.
P-VOL data can be restored
using the S-VOL.
If a physical failure occurs in an
S-VOL, data in the S-VOL cannot
be guaranteed.
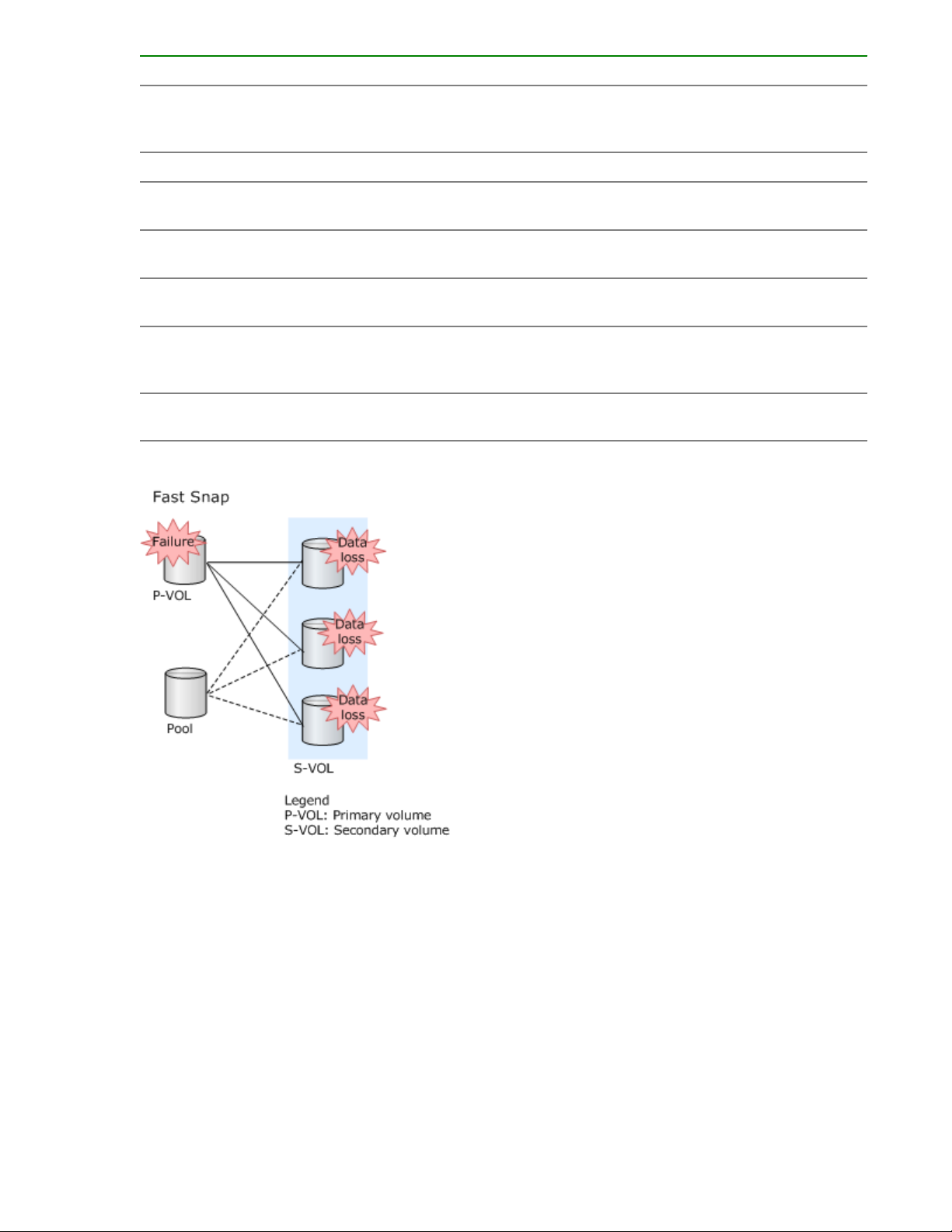
Fast Snap S-VOLs reference data in the P-VOL. Therefore, if a failure occurs in the P-VOL, data in all SVOLs under the P-VOL is lost.
18 Overview of Fast Snap
Page 19
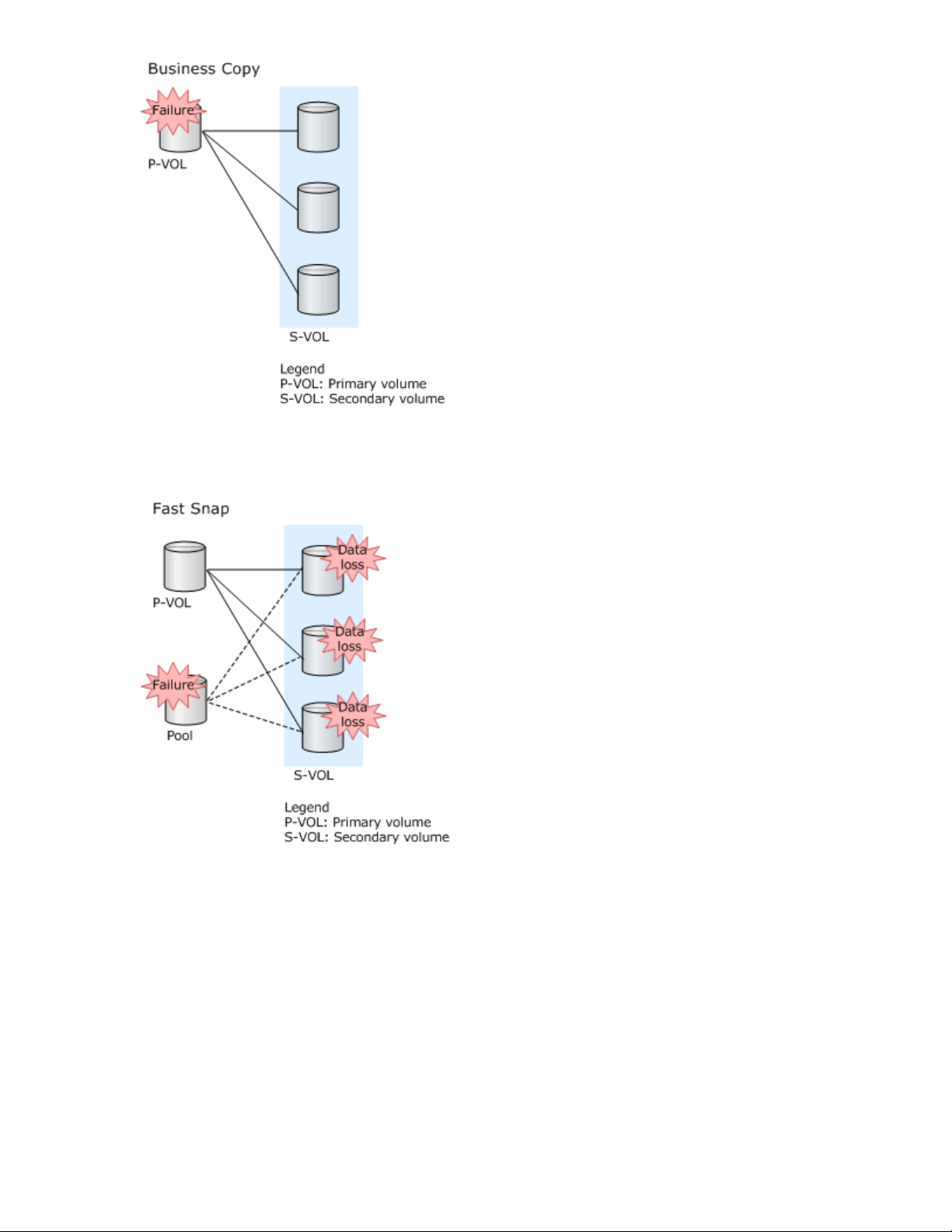
Business Copy S-VOLs retain all P-VOL data. Therefore, if a failure occurs in the P-VOL, data in the SVOLs is not lost.
The following figure explains the relation of data when a failure occurs in a pool.
Fast Snap S-VOLs reference data in the pool. If the pool cannot be used because a failure occurs in the
pool or the pool becomes full, data in all S-VOLs that use the pool is lost. In addition, if a pool failure
occurs or the pool becomes full during restoration, data in the P-VOL which is being restored cannot be
used.
The following figure explains the relation of data when a failure occurs in an S-VOL.
Overview of Fast Snap 19
Page 20

For Business Copy, each S-VOL independently retains data. Therefore, only data in the failed S-VOL is
affected. In addition, if a failure occurs in an S-VOL during restoration, data in the P-VOL which is being
restored cannot be used.
XP7 Storage software applications for Fast Snap
Fast Snap
Use the Fast Snap software on the Remote Web Console (RWC) computer that is connected to the
service processor (SVP) by means of the TCP/IP local area network (LAN).
Thin Provisioning
Use the THP software on the RWC computer. A user license is required to use THP.
Since Fast Snap uses a portion of the THP licensed capacity for its pool capacity, reserve enough THP
licensed capacity to run both THP and Fast Snap and to accommodate the Fast Snap pairs or pools that
you will create.
Fast Snap and THP pool-VOLs are also referred to as used volumes. The licensed capacity must exceed
the total capacity of used volumes.
RAID Manager
When you use RAID Manager to define multiple Fast Snap pairs in a consistency group, you can only
specify one consistency group for a group defined by the configuration definition file for RAID Manager.
NOTE: The configuration definition file for RAID Manager is a group that is not a consistency group.
If you create a new pair and define the pairs in a consistency group for a group you defined using the
configuration definition file for RAID Manager, and the pair is already defined in a consistency group, the
pair is defined in the same consistency group even if you try to create a new pair and assign it to a
different consistency group.
More information
Splitting Fast Snap pairs to store snapshot data using RAID Manager on page 121
20 XP7 Storage software applications for Fast Snap
Page 21
How Fast Snap works
How Fast Snap uses pools and pool volumes
Fast Snap stores snapshot data in THP pools (Pool Type: Thin Provisioning) or Fast Snap pools (Pool
Type: Fast Snap). Unless they are defined otherwise, both THP pools and Fast Snap pools are referred to
as "pools". A pool consists of multiple pool volumes (pool-VOLs) which are, as a group, the container for
the snapshot data.
You must create pools to use Fast Snap. You can create pools and add and delete pool-VOLs from them
using Fast Snap.
The following figure illustrates the relationship between a Fast Snap pair and a pool.
CAUTION: When creating pools, calculate the pool capacity and reserve a sufficient amount of pool
capacity. When you write data to Fast Snap pair volumes and the amount of pool usage exceeds
the pool capacity, the Fast Snap pair is suspended (“PSUE” status), snapshot data is not stored,
and you cannot create additional Fast Snap pairs.
More information
Creating Fast Snap data pools on page 89
Increasing pool capacity on page 155
Decreasing pool capacity on page 159
Deleting pools on page 170
Restoring suspended Fast Snap pairs on page 126
Usage level rebalancing among parity groups
Rebalancing is performed as if each parity group were a single pool-VOL. After rebalancing, the usage
rates of LDEVs in a parity group may not be balanced, but the usage rate in the entire pool is balanced.
How Fast Snap works 21
Page 22

The usage level among parity groups is automatically rebalanced when expanding or shrinking pool
capacity operations are in progress.
If you expand the pool capacity, Thin Provisioning moves data to the added space on a per-page basis.
When the data is moved, the usage rate among parity groups of the pool-VOLs is rebalanced.
Host I/O performance may decrease when data is moved. If you do not want to have the usage level of
parity groups automatically balanced, call HPE technical support.
You can see the rebalancing progress of the usage level among parity groups in the View Pool
Management Status window in RWC. In RAID Manager, you can use the raidcom get pool -key
command to see if the usage levels among parity groups are rebalanced. Thin Provisioning automatically
stops balancing the usage levels among parity groups if the cache memory is not redundant or the pool
usage rate reaches up to the threshold.
More information
Viewing formatted pool capacity and pool usage rates on page 154
How Fast Snap uses V-VOLs
Fast Snap uses Fast Snap V-VOLs (V-VOLs of provisioning type Snapshot in RWC, or V-VOLs created by
the raidcom add ldev -pool snap command in RAID Manager) or THP V-VOL as V-VOLs. Fast
Snap V-VOLs and THP V-VOLs are referred to as virtual volumes (V-VOLs) in this document. Use THP VVOLs to create cascaded or cloned pairs. Use Fast Snap V-VOLs to create snapshot pairs. Note that you
can use THP V-VOLs to cascade snapshot pairs.
Fast Snap uses V-VOLs to access snapshot data from hosts or clone pairs, so if you create clone pairs or
use snapshot pairs (a pair with the snapshot attribute) to access snapshot data from hosts, then V-VOLs
are required to create Fast Snap pairs or assign an S-VOL to snapshot data. If the storage system or
snapshot pair does not need to access snapshot data from hosts, V-VOLs are not necessary.
You can release the V-VOLs that are being used as Fast Snap S-VOLs from assignment of snapshot
data. Released V-VOLs can be assigned to other snapshot data. However, you cannot release allocation
of V-VOLs used as node volumes to snapshot data or allocate the V-VOL to different snapshot data. Also,
you cannot release allocation of V-VOLs which are being used for the S-VOL of a clone pair to snapshot
data, or allocate it to different snapshot data.
If you release a V-VOL being used as a Fast Snap S-VOL from assignment to snapshot data, and then
assign the V-VOL to different snapshot data, this V-VOL becomes the S-VOL of another pair. Therefore,
each time you assign a V-VOL to snapshot data, execute the command which allows the host server to
recognize the device.
You cannot release definitions of V-VOLs if the V-VOLs are being used as Fast Snap secondary volumes;
you must first release the Fast Snap pairs that are using the V-VOLs.
How Fast Snap pairs are created
Create Fast Snap pairs in the Create FS Pairs window in RWC, or by using the raidcom add
snapshot command in RAID Manager.
When creating a Fast Snap pair, you need to specify the pool to be used for the pair. If multiple Fast Snap
pairs share the same primary volume, the pairs must also share the same pool. For example, if you
specify three secondary volumes for one primary volume, you must specify the same pool for the three
Fast Snap pairs.
If you release a Fast Snap pair, the volume status becomes SMPL. Immediately after a volume becomes
SMPL, you cannot use the volume to create a Fast Snap pair. If you want to create Fast Snap pairs using
SMPL volumes, you should wait for a while before creating the pairs. The wait time required depends on
your system environment.
22 How Fast Snap uses V-VOLs
Page 23
You can check the status of volumes in the Local Replication window and the View Pair Properties
window in RWC, or by using the raidcom get snapshot command in RAID Manager.
More information
Creating Fast Snap pairs using Remote Web Console on page 114
Viewing pair properties on page 140
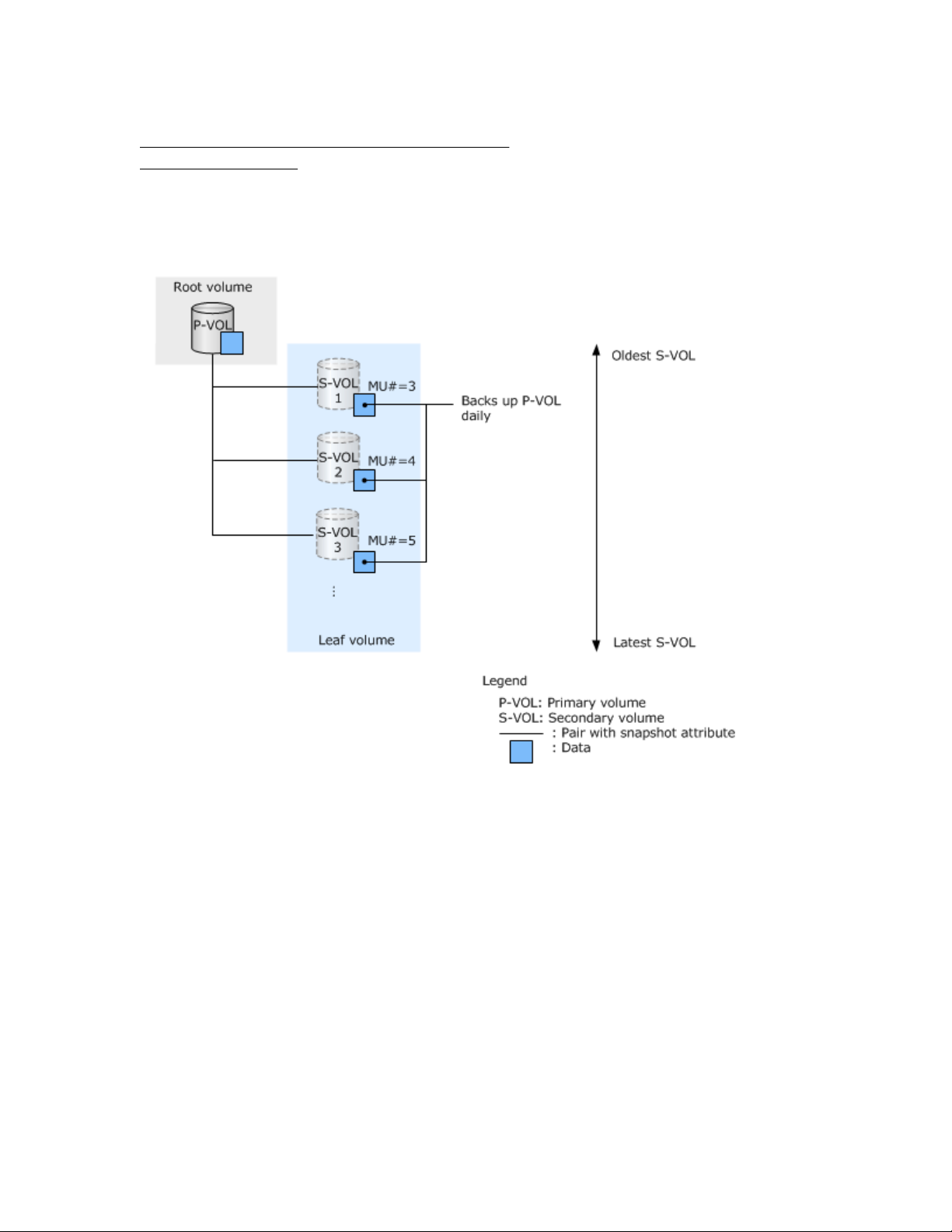
Using snapshot pairs (not cascaded)
Data in the P-VOL is backed up one time every day. The P-VOL can be restored using the S-VOL if a
logical failure occurs during data update or if there is a virus in the P-VOL.
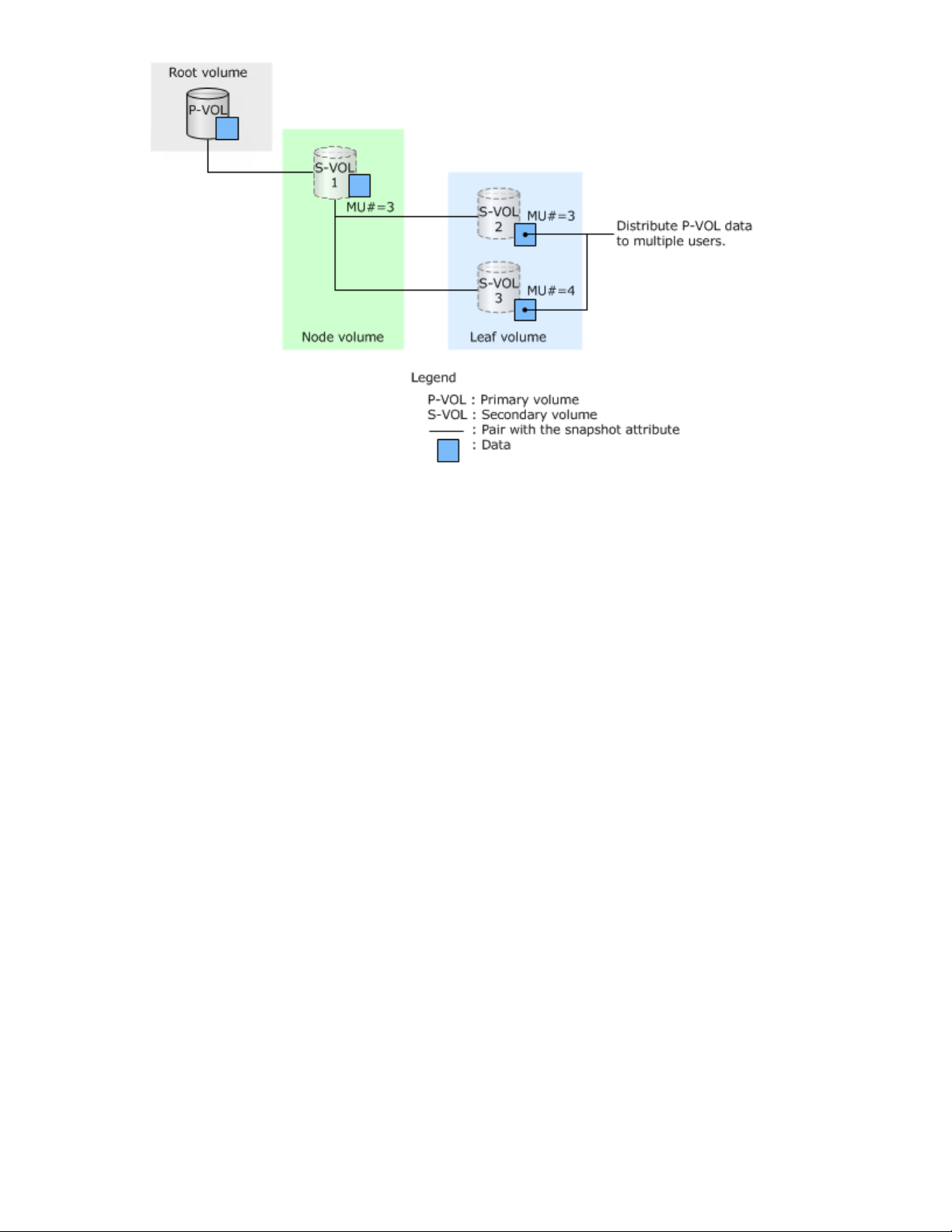
Using cascaded pairs
Distributing data in the P-VOL to multiple users
Create the same number of leaf volumes as the number of users to whom you want to distribute data.
This allows you to distribute data in the P-VOL without increasing loads to the P-VOL.
Using snapshot pairs (not cascaded) 23
Page 24
24 Overview of Fast Snap
Page 25
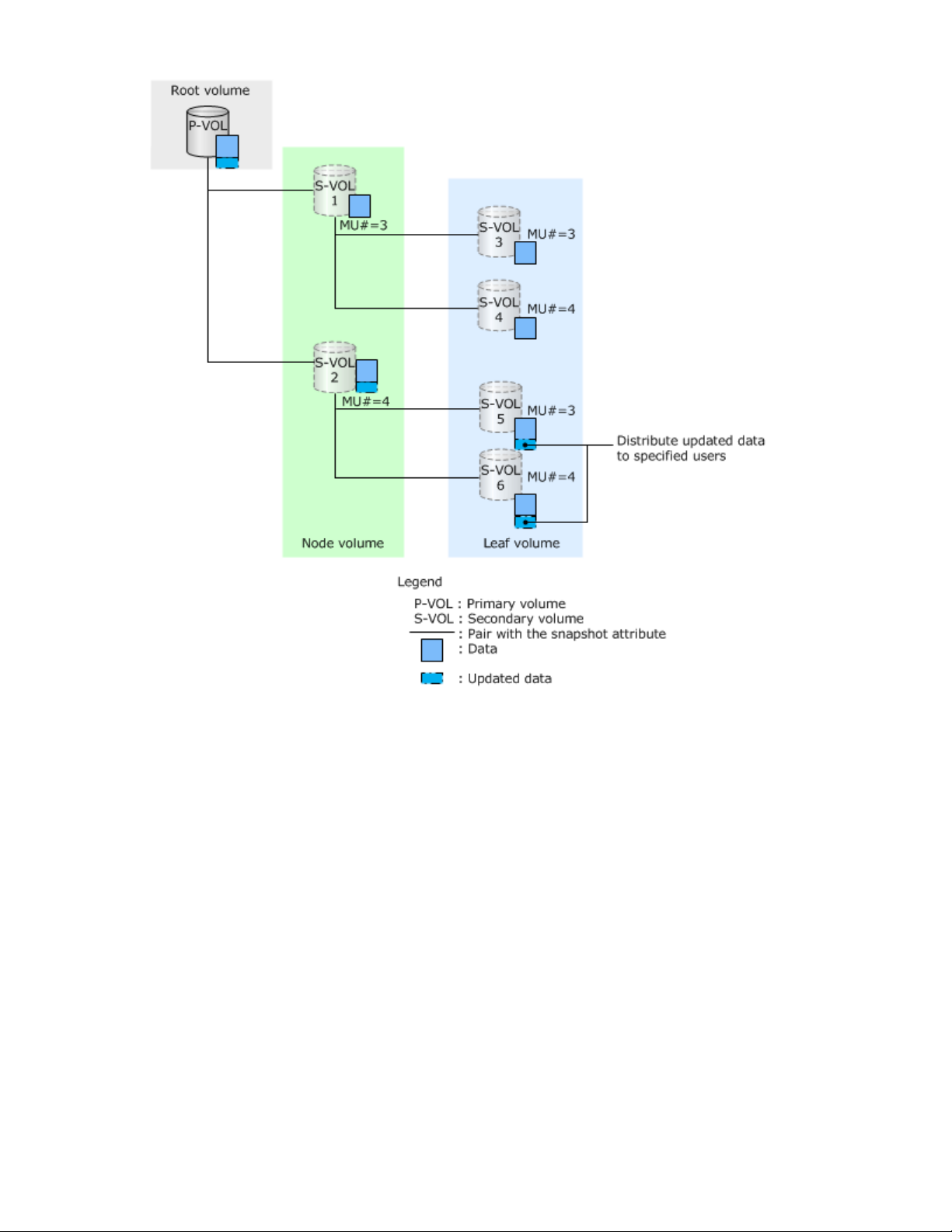
Distributing updated data in the P-VOL to specified users
When you update the P-VOL and want to give it only to the specified users (S-VOLs 5 and 6 in the
figure), do the following:
1. Create cascaded pairs, and distribute data in the P-VOL. Assign users to whom you want to distribute
the updated data, and users to whom you do not want to distribute the updated data to separate node
volumes.
2. Delete the pairs in the node volume where you assigned users you do not want to distribute the
updated data to (S-VOL 1 in the figure).
3. Update the P-VOL.
Overview of Fast Snap 25
Page 26
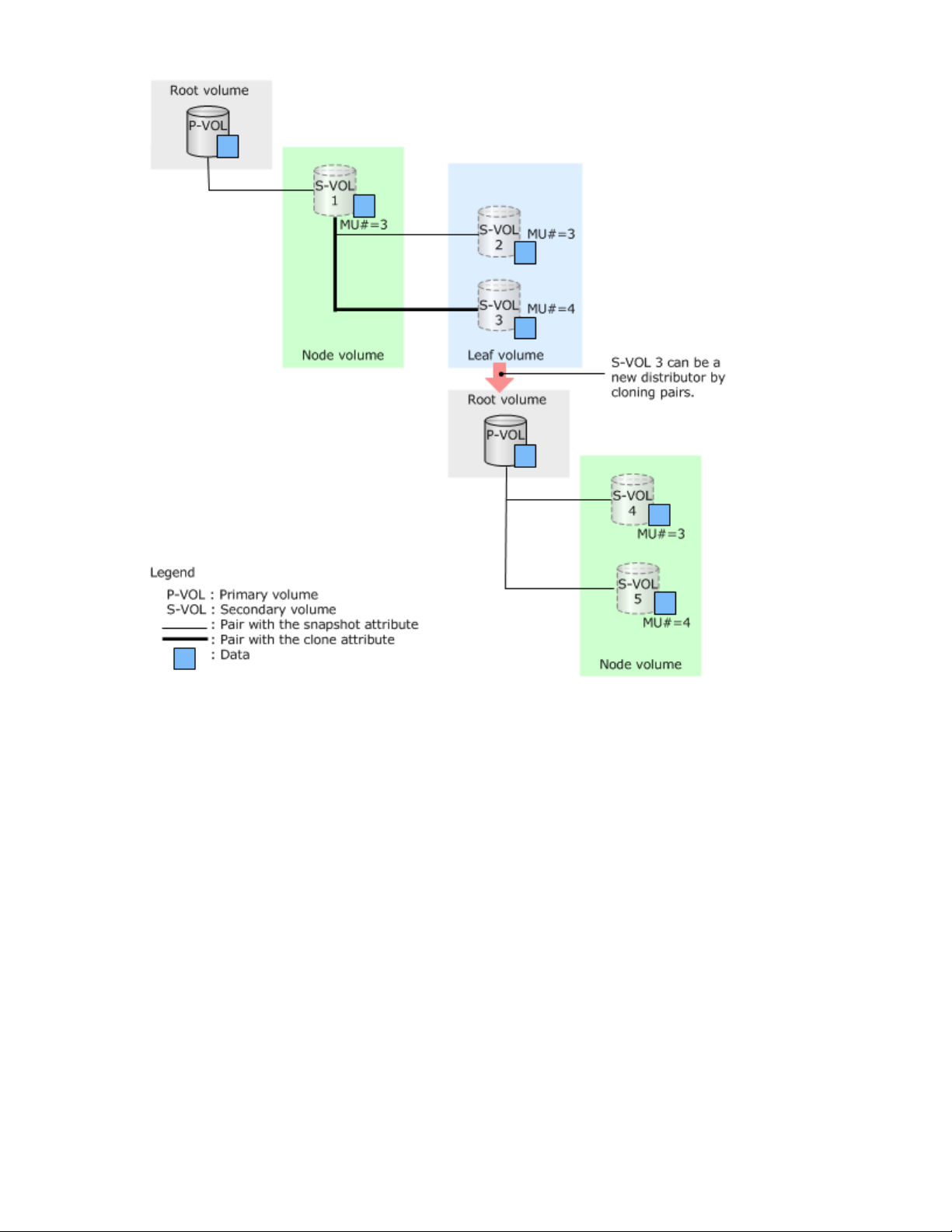
Creating a new distributor with cloned pairs
1. Create cascaded pairs and distribute data in the P-VOL. Assign the clone attribute to the volume to be
a new distributor (S-VOL 3 in the figure).
2. Clone pairs.
By cloning pairs, S-VOL 3 and S-VOL 1 become unpaired volumes (THP V-VOLs) in the same status,
and S-VOL 3 can be a new distributor. As a result, the overhead of the Fast Snap pairs can be reduced.
Workflow for creating groups and storing snapshot data using RAID Manager
With Fast Snap, Business Copy, and Business Copy MF, you can create up to 2,048 consistency groups
in an XP7 Storage system.
The following figure illustrates how snapshot data is stored for a consistency or snapshot group using
RAID Manager raidcom commands.
26 Workflow for creating groups and storing snapshot data using RAID Manager
Page 27
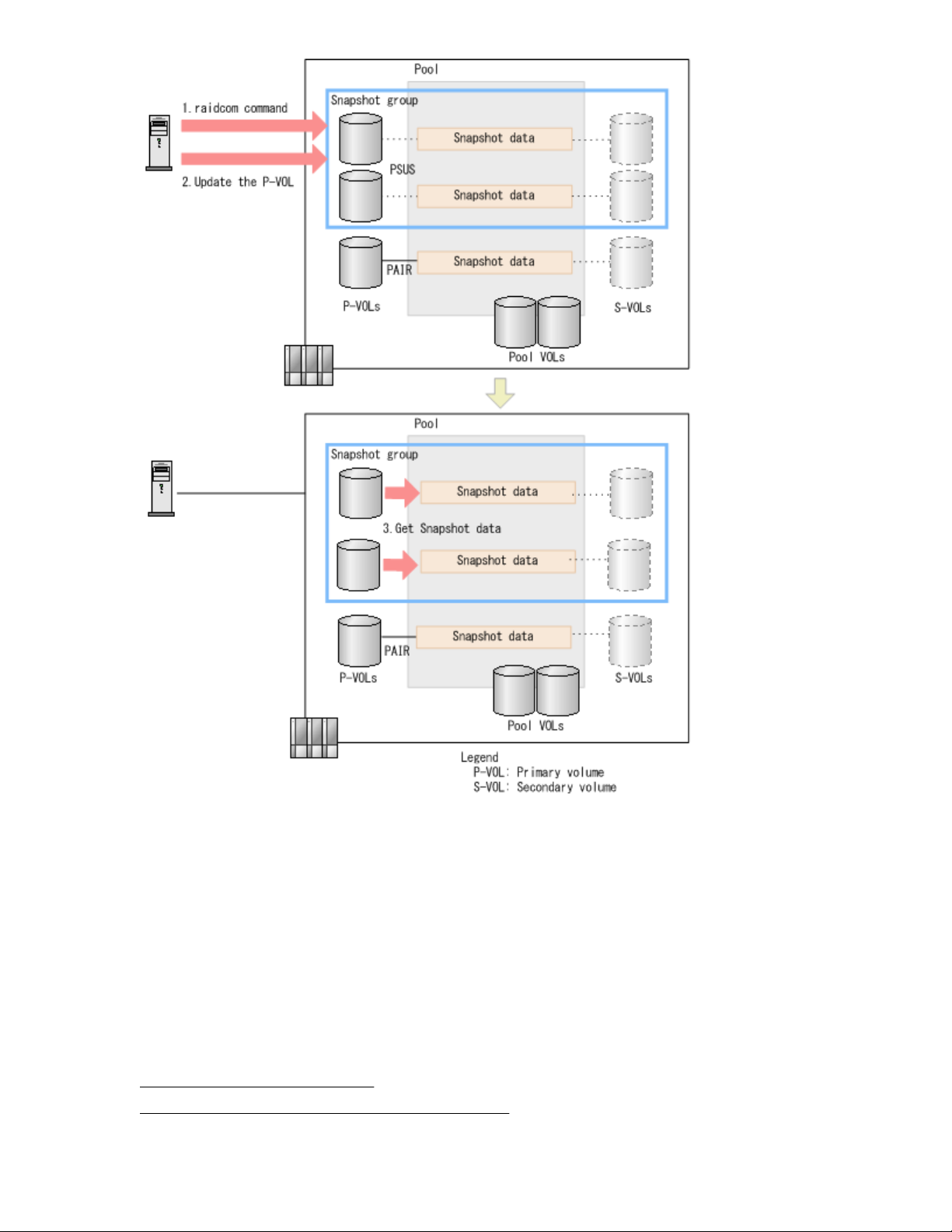
Use the following workflow to create a snapshot group and store volume snapshot data in the group:
1. Split the pair and store snapshot data for a group. To do this using RAID Manager, run the following
raidcom command:
raidcom modify snapshot -snapshot_data create
2. The host issues a write request to each P-VOL in the group.
Snapshot data for the volumes are stored.
A RAID Manager command is used to store snapshot data for a consistency group or a snapshot group.
Remote Web Console can only be used to reference consistency groups and snapshot groups.
More information
Consistency and snapshot groups on page 13
Creating Fast Snap pairs using Remote Web Console on page 114
Overview of Fast Snap 27
Page 28
Removing Fast Snap snapshot groups on page 130
Pair tasks using RAID Manager or Remote Web Console on page 194
Methods of storing snapshot data
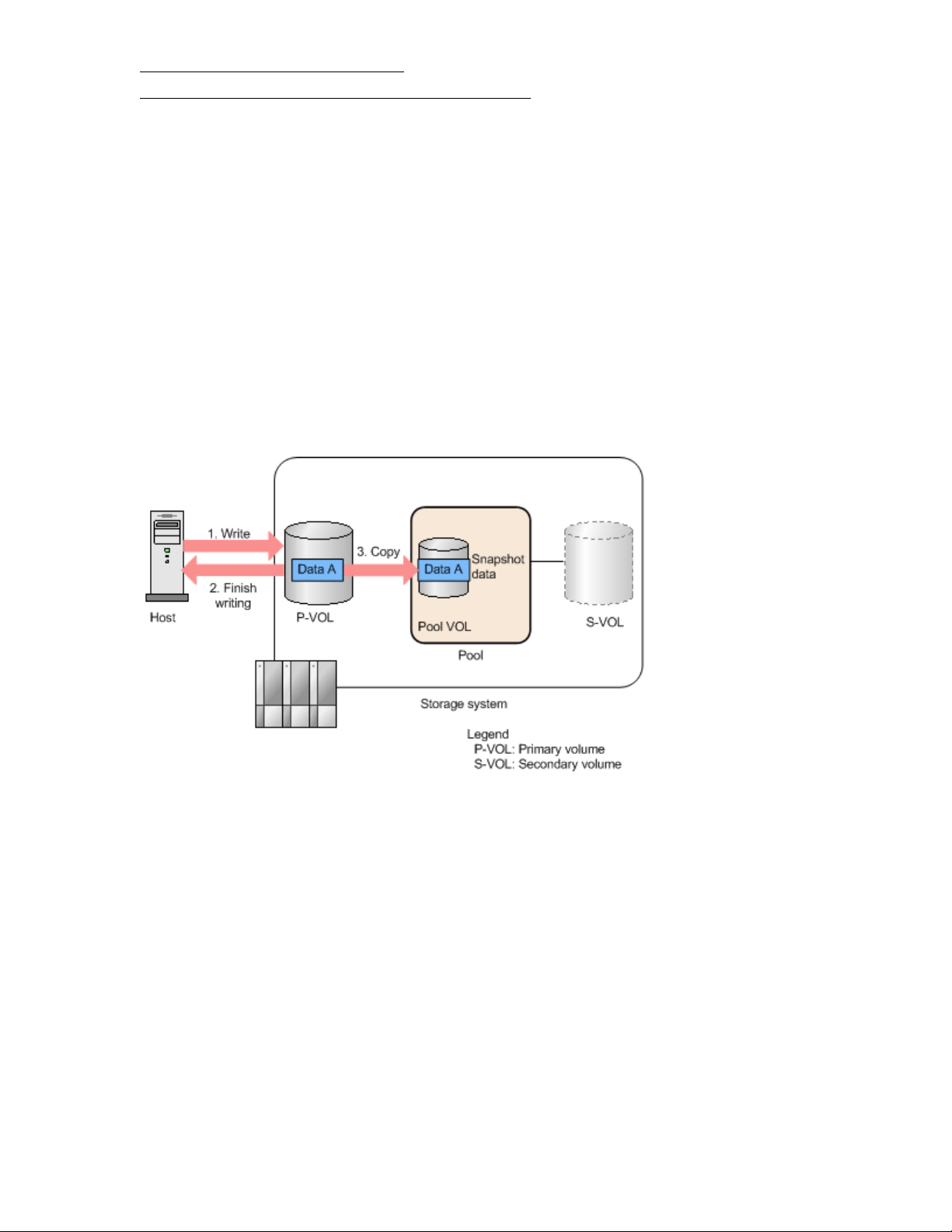
In the CAW method, writing the P-VOL snapshot data changes the status to “write completion”. In the
COW method, storing the P-VOL snapshot data changes the status to "write completion". The CAW
method wait time is shorter than that of the COW method.
Workflow for the CAW method
The following workflow describes the CAW method and how an XP7 Storage system stores snapshot
data:
1. The host writes data to a P-VOL.
2. The storage system returns the write completion status to the host.
3. The storage system stores snapshot data for the P-VOL in the background.
The following figure illustrates the CAW method.
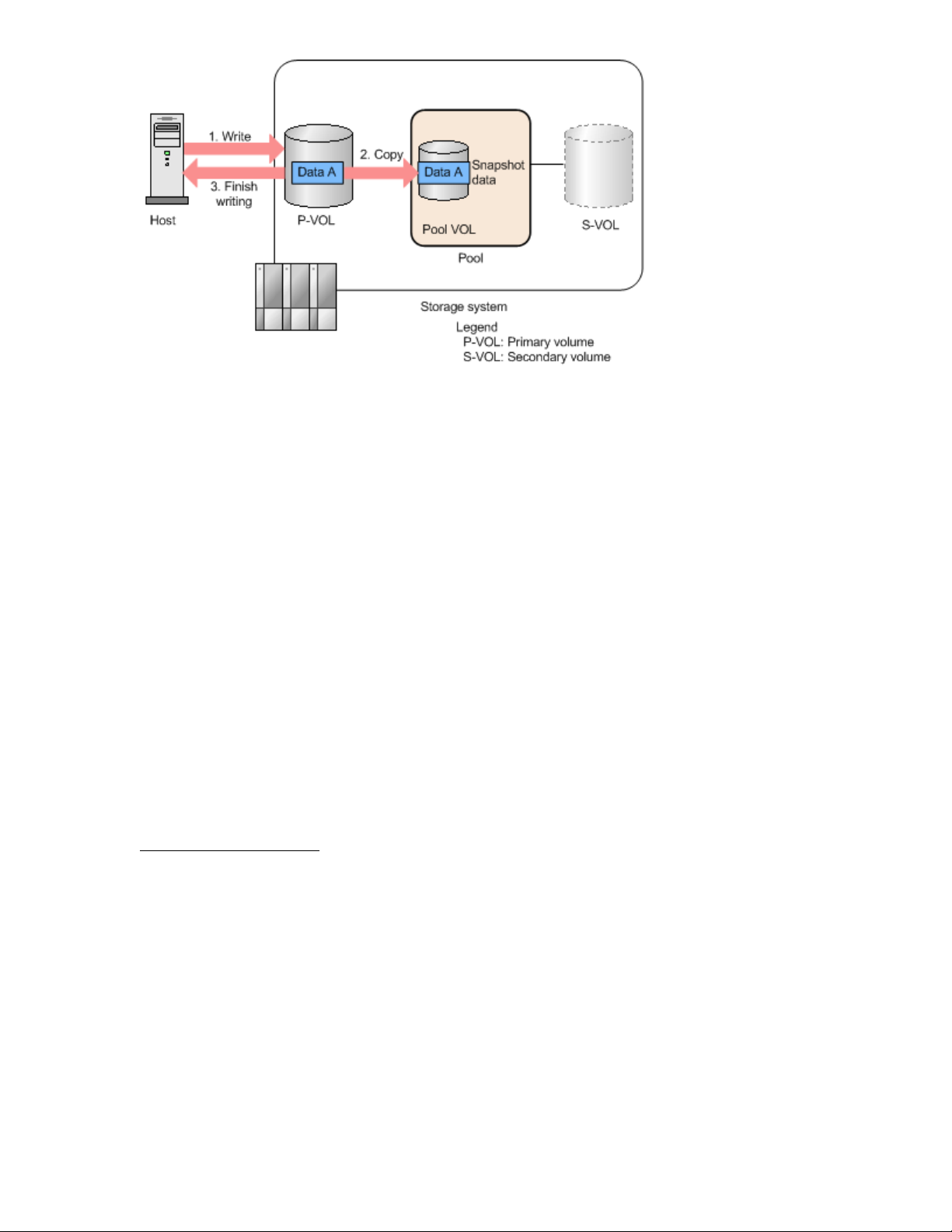
Workflow for the COW method
The following workflow describes the COW method and how an XP7 Storage system stores snapshot
data:
1. The host writes data to a P-VOL.
2. The storage system stores snapshot data for the P-VOL.
3. The storage system returns the write completion status to the host.
The following figure illustrates the COW method.
28 Methods of storing snapshot data
Page 29
Fast Snap pair restoration
Overwriting snapshot data to P-VOLs is also referred to as restoring Fast Snap pairs.
If data is written to a secondary volume, this particular data (not snapshot data) is overwritten to the
primary volume when the Fast Snap pair is restored.
If a problem occurs in P-VOL data due to a failure, restoring the pair restores the P-VOL data saved when
the snapshot data was stored. However, if the pair status is PSUE, the pair cannot be restored.
The time for restoring a Fast Snap pair depends on the following, even if the pair synchronization rate is
100%:
• The amount of pool capacity a pair is using.
• The number of pairs being operated concurrently.
The pair synchronization rate shows the rate that S-VOL data matches that of the next generation of the
S-VOL. If the S-VOL is the latest one, the synchronization rate is computed by comparing the S-VOL with
the P-VOL.
For the Fast Snap pair where the cascade attribute is enabled, the information displayed in
Synchronization Rate (%) of the View Pair Synchronization Rate window varies depending on the pair
status.
More information
Restoring Fast Snap pairs on page 124
How Fast Snap pair status changes
The following figure illustrates status changes to Fast Snap and snapshot pairs.
Fast Snap pair restoration 29
Page 30
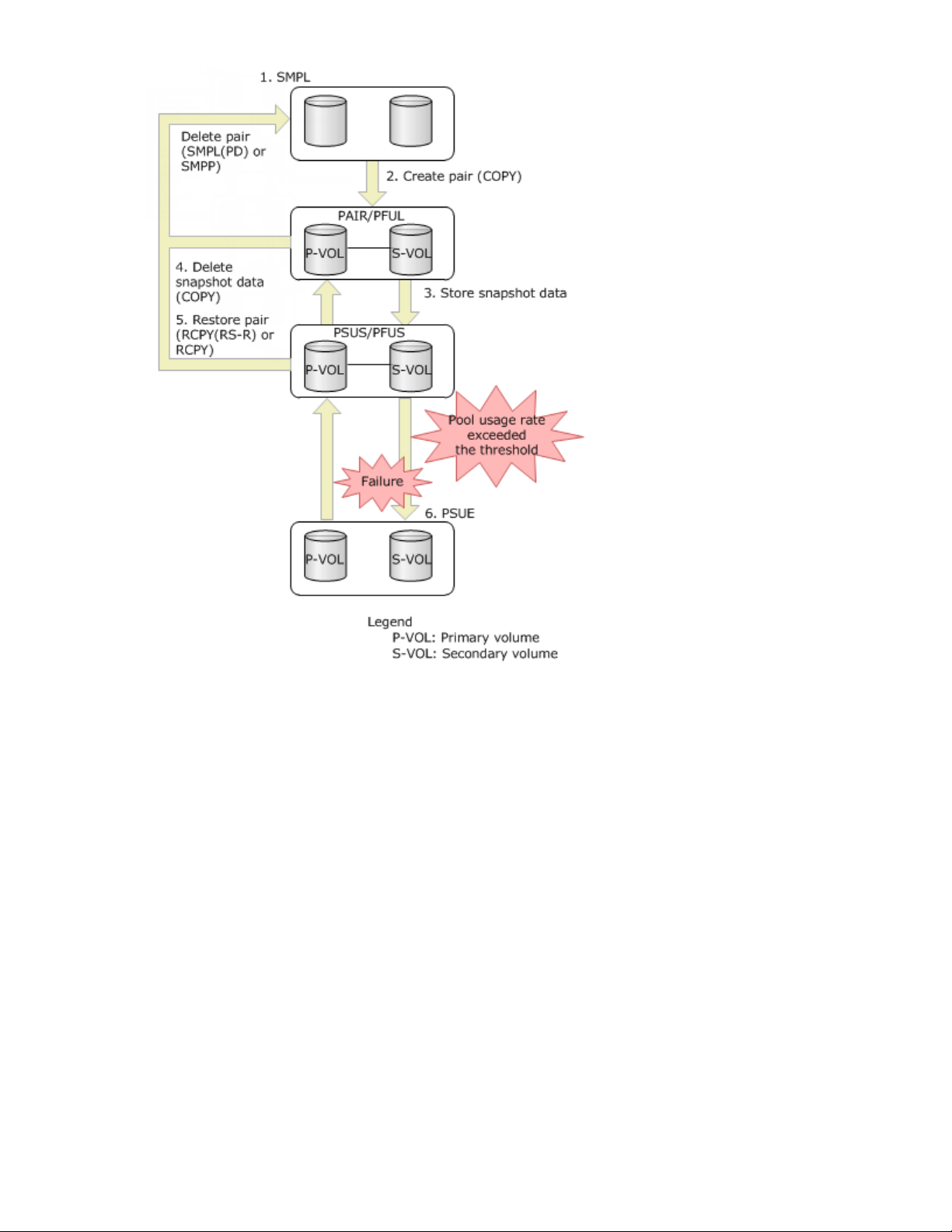
The following workflow describes the Fast Snap pair status changes:
1. You choose two volumes that are in SMPL status and are not in use as a Fast Snap pair.
2. You create a pair. If the primary volume has not previously been paired with any secondary volume,
the pair status changes to "COPY" at first, and then to "PAIR" after the pair creation finishes.
• Creation of a Fast Snap pair may be time consuming if you create a pair immediately after deleting
the last snapshot data for the primary volume.
• If the pool threshold is exceeded when the Fast Snap pair is in "PAIR" status, the pair status
changes to "PFUL."
• Fast Snap pairs cannot be created when the pool threshold (warning threshold when snapshot data
is stored in a THP pool) is exceeded.
3. Snapshot data is stored when you split a pair in "PAIR" status. After snapshot data is stored, the pair
status is "PSUS." If the pool threshold is exceeded when the Fast Snap pair is in "PSUS" status, the
pair status changes to "PFUS."
4. If you only want to delete snapshot data but do not want to release the Fast Snap pair, you delete the
snapshot data for the pair in "PSUS" or "PFUS" status.
30 Overview of Fast Snap
Page 31

5. If you restore a Fast Snap pair in "PSUS" status, snapshot data is overwritten to the primary volume.
The pair status is "COPY(RS-R) or RCPY" when the restore process is in progress. The pair status is
"PAIR" after the restore process finishes.
6. The pool can only contain data of predetermined capacity. If the total capacity of snapshot data in the
pool exceeds the pool capacity, the status of the Fast Snap pair becomes "PSUE." In addition, the pair
status changes to "PSUE" if a failure occurs during the restore process or if the pool usage rate
reaches 100 percent. Even if the restore process is not in progress, the pair status may change to
"PSUE" when a failure occurs. When snapshot data is stored in the THP pool, the timing of changing
to PSUE is determined by the setting in "Suspend FS pairs when the deletion threshold is exceeded"
in RWC, or by the setting specified by using the raidcom modify pool -suspend_tipair
<yes|no> command in RAID Manager. For details, see the HPE XP7 Provisioning for Open Systems
User Guide.
Fast Snap host access and pair status
The following table explains the host access and pair status for snapshot pairs.
FS pair status P-VOL S-VOL
Read Write Read Write
SMPL Yes Yes No No
SMPL(PD) or SMPP Yes Yes No No
COPY Yes Yes No No
PAIR/PFUL Yes Yes No No
PSUS/PFUS Yes Yes Yes Yes
COPY(RS-R) or RCPY Yes Yes No No
PSUE Yes Yes No No
Legend
Yes: Hosts can access the volume
No: Hosts cannot access the volume
CAUTION: If a host uses a software application to monitor Fast Snap pair volumes other than Fast
Snap, the S-VOL status determines if the software application ends abnormally. For example, if the
S-VOLs are in a status other than "PSUS" and "PFUS," the host can reject access.
If a host connects to at least two ports, an abnormality can occur with ports that are not connected
to S-VOLs rejecting access from hosts. To resolve these issues, close the software application that
monitors volumes.
Workflow for Fast Snap pair status changes
Fast Snap host access and pair status 31
Page 32

The following workflow describes Fast Snap pair status changes:
1. You choose two volumes that are in the SMPL status and are not in use as a Fast Snap pair.
2. You create a pair. If the P-VOL has not previously been paired with any S-VOL, the pair status
changes to COPY at first, and then to PAIR after the pair creation finishes.
3. You split a pair. When you split a pair in the PAIR status, the pair status changes to PSUS(SP) or
PSUP, and copying data is started asynchronously. When the copy operation completes, the pair
status changes to SMPL(PD) or SMPP. When the pair deletion completes, the pair status changes to
SMPL. The S-VOL becomes unpaired (a THP V-VOL) and can be used as a volume in the same
status as the P-VOL.
NOTE: If you delete a pair when the pair status is PSUS(SP) or PSUP, copying data stops at the time
when the pair deletion is accepted, and the status changes to SMPL. If this happens, data in the SVOL is not guaranteed.
4. The THP pool can only contain data of predetermined capacity. If the total capacity of data in the pool
exceeds the pool capacity, the status of the Fast Snap pair changes to PSUE. In addition, the pair
status also changes to PSUE if a failure occurs during the process or if the pool usage rate reaches
100 percent. When snapshot data is stored in the THP pool, the timing of changing to PSUE is
determined by the setting in "Suspend FS pairs when the deletion threshold is exceeded" in RWC, or
by the setting specified by using the raidcom modify pool -suspend_tipair <yes|no>
command in RAID Manager. For details, see the HPE XP7 Provisioning for Open Systems User
Guide.
5. You delete a pair. When a pair is deleted, the pair status changes to SMPL(PD) or SMPP. After that, it
changes to SMPL when pair deletion completes.
Whether the host can read or write data from and to a Fast Snap pair P-VOL or S-VOL is determined by
the pair status. The following table describes whether the host can access volumes, and their cloned pair
status.
32 Overview of Fast Snap
Page 33

Pair status Primary volume Secondary volume
Read Write Read Write
SMPL Y Y Y Y
COPY Y Y N N
PAIR Y Y N N
PSUS(SP) or
PSUP
SMPL(PD) or
SMPP
PSUE Y Y N N
Y Y Y Y
Y Y Y Y
Copy threshold option and host server I/O performance for Fast Snap
I/O performance of the host server might be lowered as the workload on the storage system increases. If
you perform Fast Snap restore operations when the workload on the storage system is high, I/O
performance of the host server is more likely to be lowered because replication processes for the primary
volumes are triggered. The copy threshold option can be used to temporarily stop the replication
processes triggered by the restore operations when the workload on the storage system is high. The copy
threshold option can contribute to minimizing the decline in I/O performance of the host server.
The copy threshold option is applicable only when the workload on the storage system is excessively
heavy. If the copy threshold option is applied, all the replication processes triggered by restore operations
are stopped.
Replication processes stopped by the copy threshold option will be restarted as the workload on the
storage system is lowered. Enabling the copy threshold option stops replication processes for Fast Snap
and the following products when the storage system is overloaded.
• Business Copy
• Business Copy MF
• Compatible FlashCopy
• Auto LUN V2
For more information about enabling the copy threshold option, call HPE technical support.
For more information about Compatible FlashCopy, see the HPE XP7 for Compatible FlashCopy
Mirroring User Guide.
More information
Fast Snap pair restoration on page 29
Sharing Fast Snap volumes with other software applications
You can create Fast Snap (FS) pairs using pair volumes for other replication software applications, such
as Business Copy and Continuous Access Synchronous. You can also create Fast Snap pairs using
volumes to which you define attributes using Data Retention or RAID Manager.
You can share Fast Snap volumes with the following software application volumes:
Copy threshold option and host server I/O performance for Fast Snap 33
Page 34

• Data Retention
• Auto LUN V2
• Business Copy (BC)
• Continuous Access Synchronous (Cnt Ac-S)
• Continuous Access Journal (Cnt Ac-J)
• High Availability (HA)
The following table shows when you can share Fast Snap pair volumes with other software application
volumes. If a volume that you share with a Fast Snap volume is shown in the table, the pair status
determines whether you can perform tasks. If the S-VOL is not assigned to snapshot data, you cannot
share Fast Snap volumes with other software applications, because the S-VOL does not exist.
NOTE: For node or leaf volumes, see the Used as an FS S-VOL column instead of the Used as an FS
P-VOL column.
Software application volume type Used as an FS P-VOL Used as an FS S-VOL
BC P-VOL Yes
3
No
BC S-VOL Yes No
Cnt Ac-S P-VOL Yes No
Cnt Ac-S S-VOL Yes No
Cnt Ac-J P-VOL Yes No
Cnt Ac-J S-VOL Yes No
Cnt Ac-J journal volume No No
HA P-VOL Yes No
HA S-VOL Yes No
HA volume with reservation attribute No No
HA volume for quorum disk No No
Auto LUN source volume No No
Auto LUN target volume No No
Read Only volume
Protect volume
1, 4, 6
S-VOL Disable volume
34 Overview of Fast Snap
1, 4, 6
4, 6
Yes Yes
Yes Yes
Yes No
Table Continued
Page 35

Software application volume type Used as an FS P-VOL Used as an FS S-VOL
Zero Read Capacity volume
Invisible volume
2, 5, 6
THP V-VOL Yes Yes
V-VOL with capacity saving enabled
Deduplication system data volume
2, 5, 6
Yes Yes
Yes Yes
Yes
Yes
No No
7
8
1. If you use RWC to share the volume with other software applications, the pair status determines
whether you can share the volume.
2. To share the volume with other software applications, you must use RAID Manager.
3. You cannot use Quick Restore.
4. Use the Data Retention to set this attribute.
5. RAID Manager is required to set this attribute. For setting the attribute, use the raidvchkset -vg
command.
6. Use the Data Retention or use the raidvchkdsp -v gfalg command to confirm whether this
attribute is set to volume.
7. Can be shared if the pair is cascaded or has the clone attribute.
8. Can be set on an S-VOL of a cascaded pair or a clone attribute pair. Note that only the clone attribute
enables capacity saving.
Sharing Fast Snap volumes that have Data Retention access attributes
Depending on access attributes of the P-VOL, S-VOL, or pool volume, you cannot perform some pair
tasks and pool tasks with Fast Snap. The Fast Snap pair tasks you can perform are different depending
on whether you assign Data Retention access attributes using RAID Manager or RWC. The tables below
explain whether you can perform Fast Snap pair tasks and pool tasks on volumes that have access
attributes assigned by Data Retention. If you release assignment of snapshot data after assigning access
attributes to a Fast Snap S-VOL, the Fast Snap tasks you can perform are the same as those that can be
performed when the Read/Write attribute is assigned to the S-VOL.
Also, you can assign access attributes to Fast Snap P-VOL and S-VOLs. The tables below also explain
Fast Snap pair tasks and pool tasks after access attributes are assigned.
Access attributes and supported Fast Snap pair tasks
The following table lists the relationship between P-VOL and S-VOL access attributes and Fast Snap pair
tasks when using RWC to assign Data Retention access attributes.
Sharing Fast Snap volumes that have Data Retention access attributes 35
Page 36

Volume access attributes specified for the FS pair FS pair task
P-VOL S-VOL Create, split,
suspend,
Resync pair
Resync
(Reverse
1
Copy)
Delete
(Normal Copy)
Read/Write Read/Write Yes
Read Only, Protect, S-VOL
No
Disable
Read Only, Protect, S-VOL
Read/Write Yes No Yes
Disable
Read Only, Protect, S-VOL
No
Disable
Reverse Copy does not copy S-VOL access attributes to P-VOLs (see Pair resynchronization
methods).
The following table lists the relationship between P-VOL and S-VOL access attributes and Fast Snap pair
tasks when using RAID Manager to assign Data Retention access attributes.
Volume access attributes specified for the FS pair FS pair task
P-VOL S-VOL Create, split,
suspend,
Resync pair
Resync
(Reverse
1
Copy)
Delete
(Normal Copy)
Read/Write, Read Only,
Protect
Read/Write, Read Only,
Protect
Yes
S-VOL Disable No
S-VOL Disable Read/Write, Read Only,
Yes No Yes
Protect
S-VOL Disable No
Reverse Copy does not copy S-VOL access attributes to P-VOLs (see Pair resynchronization
methods).
Access attributes and supported Fast Snap pool tasks
The following table lists the relationship between P-VOL and S-VOL access attributes specified by Fast
Snap and Fast Snap pool tasks when using RAID Manager or RWC to assign Data Retention access
attributes.
36 Overview of Fast Snap
Page 37

Volume access attributes specified by FS
Read/Write Yes
Read Only No
Protect No
S-VOL Disable No
NOTE: Performing a Fast Snap task does not change the volume access attributes.
Required Fast Snap pair status when using Data Retention to assign access attributes to some
volumes
The following table shows the Fast Snap pair status that is required to use Data Retention to assign
access attributes to some Fast Snap P-VOLs and S-VOLs when also using RWC to assign Data
Retention access attributes.
FS volume Access attribute to be assigned
Pair status Volume Read/Write Read Only
Pool-VOL setting
Protect
S-VOL Disable
COPY P-VOL Yes Yes
S-VOL Yes No
PAIR, PFUL P-VOL Yes Yes
S-VOL Yes Yes
PSUS, PFUS P-VOL Yes Yes
S-VOL Yes Yes
SMPL(PD) P-VOL Yes Yes
S-VOL Yes No
RCPY P-VOL Yes No
S-VOL Yes No
PSUE P-VOL Yes Yes
S-VOL Yes No
The following table shows the Fast Snap pair status that is required to use Data Retention to assign
access attributes to some Fast Snap P-VOLs and S-VOLs when also using RAID Manager to assign Data
Retention access attributes.
Overview of Fast Snap 37
Page 38

FS volume Access attribute to be assigned
Pair status Volume Read/Write
Read Only
Protect
COPY P-VOL Yes Yes
S-VOL Yes No
PAIR, PFUL P-VOL Yes Yes
S-VOL Yes Yes
PSUS, PFUS P-VOL Yes Yes
S-VOL Yes Yes
SMPL(PD) P-VOL Yes Yes
S-VOL Yes No
RCPY P-VOL Yes No
S-VOL Yes No
S-VOL Disable
PSUE P-VOL Yes Yes
S-VOL Yes No
Sharing Fast Snap volumes with Auto LUN
You cannot do the following:
• Perform Fast Snap tasks on volumes reserved for Auto LUN without regard to the migration plan
status.
• Use Fast Snap pair volumes or pool-VOLs as volumes reserved for Auto LUN V2.
For more information about the migration plan status and Auto LUN tasks, see the HPE XP7 Auto LUN
User Guide.
Sharing Fast Snap volumes with Business Copy
Available Fast Snap tasks
The following table lists the Fast Snap tasks you can perform when sharing a Fast Snap P-VOL with a
Business Copy P-VOL.
38 Sharing Fast Snap volumes with Auto LUN
Page 39

FS task BC pair status
COPY(PD
)/COPY
PAIR COPY(SP
)/COPY
PSUS(SP
)/PSUS
PSUS COPY(RS
)/COPY
COPY(RS
-R)/RCPY
PSUE
Create pair Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes No Yes
Store snapshot data Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes No Yes
Restore pair No No No No Yes No No Yes
Delete snapshot data Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Release pair Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Legend:
Yes: You can perform the task.
No: You cannot perform the task (the command is rejected).
The following table lists the Fast Snap tasks you can perform when sharing a Fast Snap P-VOL with a
Business Copy S-VOL.
FS task BC pair status
COPY(P
D)/COPY
PAIR COPY(SP
)/COPY
PSUS(SP
)/PSUS
PSUS COPY(R
S)/COPY
COPY(R
S-R)/
PSUE
RCPY
Create pair No No No No Yes No No No
Store snapshot data N/A No No No Yes No No No
Store snapshot data
N/A No No No Yes
*
No No No
for a consistency
group
Restore pair N/A No No No Yes No No No
Delete snapshot
N/A Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
data
Release pair N/A Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
* The BC pair status must be "PSUS" during the period between when you create the FS pair to store
snapshot data and when FS starts to store snapshot data for a consistency group, and when all of the
pairs in the consistency group are split ("PSUS" status). If the BC pair status changes to a status other
than "PSUS" while FS is storing snapshot data for the consistency group, the snapshot data consistency
cannot be guaranteed.
Available Business Copy tasks
The following table lists the Business Copy tasks you can perform when sharing a Fast Snap P-VOL with
a Business Copy P-VOL.
Overview of Fast Snap 39
Page 40

BC task FS pair status
COPY PAIR, PFUL PSUS, PFUS SMPL(PD) RCPY PSUE
Create pair Yes Yes Yes Yes No Yes
Create and split pair Yes Yes Yes Yes No Yes
Split pair Yes Yes Yes Yes No Yes
Normal Copy Yes Yes Yes Yes No Yes
Reverse Copy Yes Yes Yes Yes No Yes
Quick Restore No No No No No No
Suspend replication Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Delete pair Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
The following table lists the Business Copy tasks you can perform when sharing a Fast Snap P-VOL with
a Business Copy S-VOL.
BC task FS pair status
COPY PAIR, PFUL PSUS, PFUS SMPL(PD) RCPY PSUE
Create pair No No No No No No
Create and split pair No No No No No No
Split pair Yes Yes Yes Yes No Yes
Normal Copy Yes Yes Yes Yes No Yes
Reverse Copy Yes Yes Yes Yes No Yes
Quick Restore No No No No No No
Suspend replication Yes Yes Yes Yes No Yes
Delete pair Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
You can perform Business Copy pair tasks after you store snapshot data, but the consistency of the
stored snapshot data is not guaranteed.
Fast Snap S-VOLs use the data in the P-VOL. You cannot Quick Restore in Business Copy.
For more information about Business Copy tasks and pair statuses, see the HPE XP7 Business Copy
User Guide.
40 Overview of Fast Snap
Page 41

CAUTION: Fast Snap uses MU numbers 0 to 1,023, and they are assigned in the order of 3 to
1,023, followed by 0 to 2. Business Copy uses MU numbers 0 to 2. Fast Snap cannot use the MU
numbers 0 to 2 if you want to share Fast Snap volumes with Business Copy.
To share Fast Snap volumes with Business Copy if Fast Snap is using the MU numbers 0 to 2:
1. Delete the Fast Snap pair of the MU number 0 to 2.
2. Create the Business Copy pairs and Fast Snap pairs.
Sharing Fast Snap volumes with Continuous Access Synchronous and Continuous Access Journal
The following tables list the relationship between pair tasks and status.
The following table lists the Fast Snap tasks you can perform when the P-VOL is shared with a
Continuous Access Synchronous or Continuous Access Journal P-VOL.
FS task Cnt Ac-S/Cnt Ac-J status
COPY PAIR PSUS PSUE Suspending Deleting
Create pair Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Store snapshot data Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Restore pair No No Yes Yes No No
Delete snapshot data Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Delete pair Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
The following table lists the Fast Snap tasks you can perform when the P-VOL is shared with a
Continuous Access Synchronous or Continuous Access Journal S-VOL.
FS task Cnt Ac-S/Cnt Ac-J status
COPY PAIR PSUS PSUE SSWS Suspending Deleting
Create pair Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Store snapshot data No Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Restore pair* No No No No No No No
Delete snapshot data Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Delete pair Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
*When restoring an FS pair and you are using the P-VOL as a Cnt Ac-S or Cnt Ac-J S-VOL, switch tasks
to the remote storage system using the horctakeover command.
Sharing Fast Snap volumes with Continuous Access Synchronous and Continuous Access Journal 41
Page 42

The following table lists the Continuous Access Synchronous/Continuous Access Journal tasks you can
perform when the Fast Snap P-VOL is shared with a Continuous Access Synchronous or Continuous
Access Journal P-VOL.
Cnt Ac-S/Cnt Ac-J task FS status
COPY PAIR, PFUL PSUS, PFUS RCPY PSUE
Create pair Yes Yes Yes No Yes
Split pair Yes Yes Yes N/A Yes
Resynchronize pair Yes Yes Yes No Yes
Delete pair Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Switch to remote storage Yes Yes Yes No Yes
The following table lists the Continuous Access Synchronous/Continuous Access Journal tasks you can
perform when the Fast Snap P-VOL is shared with a Continuous Access Synchronous or Continuous
Access Journal S-VOL.
Cnt Ac-S/Cnt Ac-J task FS status
COPY PAIR, PFUL PSUS, PFUS RCPY PSUE
Create pair No No No No No
Split pair Yes Yes Yes N/A Yes
Resynchronize pair Yes Yes Yes N/A Yes
Delete pair Yes Yes Yes N/A Yes
Switch to remote storage Yes Yes Yes N/A Yes
*Use a Cnt Ac-S/Cnt Ac-J S-VOL as an FS P-VOL.
Volume backup with Fast Snap, Continuous Access Synchronous, and Continuous
Access Journal in a 3DC multitarget configuration workflow
The following figure shows how to back up the volumes.
42 Volume backup with Fast Snap, Continuous Access Synchronous, and Continuous Access Journal in a
3DC multitarget configuration workflow
Page 43

• Pair 1 is a Continuous Access Synchronous pair.
• Pair 2 is a Continuous Access Journal pair.
• Pair 3 is a Continuous Access Journal pair for delta resync.
• Pairs 4, 5, and 6 are Fast Snap pairs.
You must create 3DC multitarget and delta resync pairs (pairs 1, 2, and 3) before creating pairs 5 and 6,
but pair 4 can be created at any time.
Volume backup with Fast Snap and Continuous Access Journal in a 3DC multitarget
configuration workflow
The following figure shows how to back up the volumes.
• Pairs 1 and 2 are Continuous Access Journal pairs.
• Pair 3 is a Continuous Access Journal pair for delta resync.
• Pairs 4, 5, and 6 are Fast Snap pairs.
You must create pairs 1 and 2 before creating pairs 5 and 6, but pair 4 can be created at any time.
Volume backup with Fast Snap and Continuous Access Journal in a 3DC cascade
configuration workflow
The following figure shows how to back up the volumes.
Volume backup with Fast Snap and Continuous Access Journal in a 3DC multitarget configuration workflow
43
Page 44

• Pairs 1 and 2 are Continuous Access Journal pairs.
• Pair 3 is a Continuous Access Journal pair for delta resync.
• Pairs 4, 5, and 6 are Fast Snap pairs.
You must create pairs 1 and 2 before creating pairs 5 and 6, but pair 4 can be created at any time.
Sharing Fast Snap volumes with High Availability
The following tables list the relationship between Fast Snap tasks and HA pair status.
NOTE: If you share HA volumes with Fast Snap volumes, stop I/O to a volume before storing snapshot
data. Snapshot consistency cannot be guaranteed if you store snapshot data without stopping I/O to the
volume.
For more information about HA, see the HPE XP7 High Availability User Guide.
The following table lists the Fast Snap tasks you can perform when the P-VOL is shared with an HA PVOL.
HA status I/O
mode
COPY Mirror
(RL)
PAIR Mirror
(RL)
PSUS Local Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Block Yes Yes No Yes Yes
PSUE Local Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Block Yes Yes No Yes Yes
The following table lists the Fast Snap tasks you can perform when the P-VOL is shared with an HA SVOL.
HA status I/O
mode
FS task
Create
pair
Yes Yes No Yes Yes
Yes Yes No Yes Yes
FS task
Create
pair
Store
snapshot
data
Store
snapshot
data
Restore
pair
Restore
pair
Delete
snapshot
data
Delete
snapshot
data
Delete pair
Delete pair
COPY Block No No No No Yes
PAIR Mirror
(RL)
44 Sharing Fast Snap volumes with High Availability
Yes Yes No Yes Yes
Table Continued
Page 45

HA status I/O
mode
SSUS Block Yes Yes No Yes Yes
PSUE Block Yes Yes No Yes Yes
SSWS Local Yes Yes No Yes Yes
FS task
Create
pair
Store
snapshot
data
Storage system configuration with Fast Snap and HA
When you create a Fast Snap pair using a volume from an HA pair, the server recognizes the HA P-VOL
and S-VOL as a single volume. If you create Fast Snap pairs using both the P-VOL and S-VOL of an HA
pair, the server recognizes the HA P-VOL and S-VOL as a single volume being paired with multiple
volumes by Fast Snap.
Supported configurations
The following figure shows a supported storage system configuration with a Fast Snap pair using an HA
P-VOL.
Restore
pair
Delete
snapshot
data
Delete pair
Storage system configuration with Fast Snap and HA 45
Page 46

The following figure shows a supported storage system configuration with a Fast Snap pair using an HA
S-VOL.
46 Overview of Fast Snap
Page 47

The following figure shows a supported storage system configuration with Fast Snap pairs using an HA PVOL and S-VOL.
Overview of Fast Snap 47
Page 48

Unsupported configuration
You cannot create an HA pair using Fast Snap volumes that are already being used as an HA P-VOL and
S-VOL. The following figure shows this unsupported storage system configuration.
48 Overview of Fast Snap
Page 49

Consistency group configuration with Fast Snap and HA
Pairs in a Fast Snap consistency group must be in the same storage system. Therefore, if an HA P-VOL
and S-VOL are each used in Fast Snap pairs, the Fast Snap pairs cannot be registered to the same
consistency group.
Supported configuration
The following figure shows a supported consistency group configuration.
Consistency group configuration with Fast Snap and HA 49
Page 50

Unsupported configuration
The following figure shows an unsupported consistency group configuration.
50 Overview of Fast Snap
Page 51

Snapshot group configuration with Fast Snap and HA
Pairs in a Fast Snap snapshot group must be in the same storage system. Therefore, if an HA P-VOL and
S-VOL are each used in Fast Snap pairs, the Fast Snap pairs cannot be registered to the same snapshot
group.
Supported configuration
The following figure shows a supported snapshot group configuration.
Snapshot group configuration with Fast Snap and HA 51
Page 52

Unsupported configuration
The following figure shows an unsupported snapshot group configuration.
52 Overview of Fast Snap
Page 53

Sharing Fast Snap volumes with Thin Provisioning and Thin Provisioning MF in a single storage system
If you are using Fast Snap, Thin Provisioning, and Thin Provisioning MF in a single storage system, note
the following when creating Fast Snap pairs:
• Data compressed or deduplicated by the capacity saving function is copied to a volume. The capacity
saving function is not performed immediately for copied data. Before creating or resynchronizing a
Fast Snap pair, make sure that the available capacity in the copy destination volume is greater than
the used capacity in the copy origination volume. For details, see the HPE XP7 Provisioning for Open
Systems User Guide.
• If you create a Fast Snap pair using a volume with the capacity saving function enabled, the
compressed or deduplicated data is copied. Because of this, copy or I/O performance may be
degraded.
Sharing Fast Snap volumes with Thin Provisioning and Thin Provisioning MF in a single storage system 53
Page 54

• When the capacity saving function is used, management information is stored in a pool. As a result,
there may be difference between a P-VOL and an S-VOL in the number of used pages or licensed
capacity.
• The capacity saving function can be set on the P-VOL or S-VOL of a cascaded or clone pair, but only
works on the clone pair. The deduplication system data volume cannot be used as a Fast Snap P-VOL
or S-VOL.
• You can create a Fast Snap pair whose P-VOL or S-VOL is a Thin Provisioning V-VOL only if you are
not currently expanding the Thin Provisioning V-VOL capacity.
• Performing a Fast Snap paircreate operation while zero pages are being reclaimed (including
reclamation by WriteSame, Unmap command, or rebalancing) results in the zero-page operation being
interrupted.
• When the WriteSame or Unmap command is issued to the P-VOL or the S-VOL for a Fast Snap pair,
zero pages are not reclaimed by the command.
• Fast Snap pair creation might be rejected if the Unmap command operation is in progress with system
option mode 905 ON. Wait a while and then retry the operation. If the operation still fails, set system
option mode 905 to OFF and try again.
• You can use a maximum size Thin Provisioning volume as a Fast Snap P-VOL or S-VOL. For
information about the maximum size for Thin Provisioning volumes, see the HPE XP7 Provisioning for
Open Systems User Guide.
More information
Creating V-VOLs for Fast Snap S-VOLs on page 100
Creating Fast Snap pairs using Remote Web Console on page 114
Sharing Fast Snap volumes with Resource Partition
For more information about resource groups, see the HPE XP7 Provisioning for Open Systems User
Guide.
Acronyms and abbreviations for XP7 Storage system software applications used in this guide
• FC MF: Compatible FlashCopy
• FCSE: Compatible FlashCopy
• HA: High Availability
• BC: Business Copy
• BC MF: Business Copy MF
• Cnt Ac-S: Continuous Access Synchronous
• Cnt Ac-S MF: Continuous Access Synchronous MF
• FS: Fast Snap
• Cnt Ac-J: Continuous Access Journal
• Cnt Ac-J MF: Continuous Access Journal MF
54 Sharing Fast Snap volumes with Resource Partition
Page 55

Fast Snap system and planning requirements
Before you start working with Fast Snap, review the requirements associated with licensed capacity,
shared memory, volume, data pool, and for general planning and management tasks.
Fast Snap system requirements
The following are requirements for completing Fast Snap tasks:
• . The software is a prerequisite for Fast Snap. On the License Keys window, verify that the license is
installed.
• Fast Snap. On the License Keys window, verify that the Fast Snap license is installed. If it is not
installed, install it. For details, see the HPE XP7 Remote Web Console User Guide.
Fast Snap licensed capacity requirements
Fast Snap requires licensed capacity for the Fast Snap P-VOLs and pools.
Fast Snap uses a portion of the Thin Provisioning licensed capacity for its pool capacity. Make sure you
have enough Thin Provisioning licensed capacity to run both THP and Fast Snap. Use the maintenance
utility to ensure that the license key for the Thin Provisioning program product is installed.
The following table shows the Fast Snap volumes and capacity calculated as the Fast Snap usage. The
total amount of these values must not exceed the Fast Snap licensed capacity.
Intended volumes Intended capacity
Software application Volume type Normal volume or
THP V-VOL
FS P-VOL Normal volume The volume capacity
THP V-VOL The pool capacity used by the
volume
Pool-VOL Normal volume
Notes:
1. For the volume with capacity saving enabled, FS licensed capacity is the data capacity before
saving.
2. Not including the volumes of pools which are not in use by Fast Snap pairs.
• Fast Snap pool: volume
• THP pool: volume
1
capacity
capacity
2
For more information about licenses, see the HPE XP7 Remote Web Console User Guide for your
storage system.
Fast Snap system and planning requirements 55
Page 56

More information
XP7 Storage software applications for Fast Snap on page 20
Fast Snap shared memory requirements
Fast Snap requires dedicated shared memory (SM) for the Fast Snap pair management area.
The Fast Snap pair management area is an area used to store information for associating Fast Snap
pairs. It is automatically created when you install shared memory.
Additional shared memory is required when the total capacity of all pools exceeds 1.1 PB. When Thin
Provisioning, Smart Tiers, Real Time Smart Tier, Fast Snap, and dedupe and compression are used, the
capacity of a pool or V-VOL that can be created is also expanded according to the shared memory
expansion status.
The following table shows the shared memory requirements:
Shared memory function Pool/V-VOL capacity
None* Under 1.1 PB
THP/Smart/Real Time Smart Tier/FS Extension1 Under 3.4 PB
THP/Smart/Real Time Smart Tier/FS Extension2 Under 7.9 PB
THP/Smart/Real Time Smart Tier/FS Extension3 Under 12.3 PB
You can reduce or remove shared memory if the pools for Thin Provisioning, Smart Tiers, Real Time
Smart Tier, and Fast Snap have been deleted. When creating cascaded pairs or clone pairs, you must
add shared memory: 64KLDEV Extension, BC, VM Extension, TPF, iSCSI, dedupe and compression.
For more information about how to expand, reduce, or remove shared memory, contact HPE Technical
Support.
More information
Switching off the power supply on page 176
Deleting pools on page 170
Fast Snap volume requirements
Fast Snap operations require the following three types of volumes:
• P-VOLs: Contain the original data
• S-VOLs: Contain the snapshot of the original data in the associated P-VOL
• Pool-VOLs: Pool volumes that make up Fast Snap pools.
NOTE: The term "Pool VOLs" refers to Fast Snap pool volumes. For information about THP pool
volumes, see the HPE XP7 Provisioning for Open Systems User Guide.
The following table lists the requirements for Fast Snap P-VOLs.
56 Fast Snap shared memory requirements
Page 57

Item Requirement
Volume type Logical volumes (LDEVs).
You cannot specify the following volumes as FS P-VOLs:
• Pool-VOLs
• FS S-VOLs
For more information about creating pairs using other software
applications, see Sharing Thin Image volumes with other
software applications.
Emulation type OPEN-V
Volume limit 32,768
For more information about the maximum number of FS pairs,
see Thin Image planning requirements.
Path definitions Required. (Not required for cascaded pairs and pairs with the
clone attribute)
Volume capacity limit 256 TB
Maximum number of cascades 64 layers (L64). For each primary volume, 1,024 S-VOLs can be
used.
Maximum number of clones
You can create a Fast Snap pair with or without an S-VOL. The following table lists the requirements for
Fast Snap S-VOLs.
Item Requirement
Volume type Fast Snap V-VOL (V-VOLs of provisioning type Snapshot in
Emulation type OPEN-V
1,024. When storing snapshot data, this number includes the
number of snapshots.
RWC or V-VOL for the raidcom add ldev -pool snap
command in RAID Manager) or THP V-VOL.
You cannot specify the following volumes as FS S-VOLs:
• Volumes that are already used as S-VOLs.
• Volumes that other software applications are using for pairs
or migration plans.
• Deduplication system data volume.
Table Continued
Fast Snap system and planning requirements 57
Page 58

Item Requirement
Maximum number of volumes 32,768
For more information about the maximum number of FS pairs,
see Thin Image planning requirements.
Path definitions Required. (Not required for cascaded pairs and pairs with the
clone attribute)
The following table lists the requirements for Fast Snap pool-VOLs.
58 Fast Snap system and planning requirements
Page 59

Item Requirement
Volume type Logical volumes (LDEVs).
To maintain performance levels, use the following configurations:
• Place normal volumes and pool-VOLs in separate parity groups (see
Thin Image licensed capacity requirements).
• Ensure that pool-VOLs consist of LDEVs from more than one parity
group.
You cannot specify the following volumes as FS pool-VOLs:
• LDEV whose LDEV status in RWC is other than Normal, Correction
Access, or Copying. In RAID Manager, use the raidcom get ldev
command to check the volume type.
• Volumes that are already being used as FS P-VOL or S-VOLs.
• Volumes that are already contained in FS, THP, Smart, or Real Time
Smart Tier pools.
• Volumes used as migration plans or pair volumes for another product.
• Volumes for which you have used the Data Retention to set Read Only,
Protect, or S-VOL Disable attributes.
• Cache Residency volumes.
• Command device volumes.
• HA volumes with the reservation attribute.
• HA volumes for quorum disks.
• External volumes with the Data Direct Mapping attribute.
• THP V-VOLs with the Data Direct Mapping attribute.
Note: The following restrictions apply to volumes used in the same data
pool:
• Volumes must be in the same resource group.
• External pool-VOLs must have the same cache mode, either enabled or
disabled.
• When using both internal and external volumes, the external volumes
must have cache mode enabled.
Emulation type OPEN-V
RAID level
All RAID levels are supported.
Table Continued
Fast Snap system and planning requirements 59
Page 60

Item Requirement
Data drive type You can use SAS, SSD, FMD, FMD DC2, and FMD-HDE.
Regardless of the type of the volume (internal volume or external volume),
you can use pool-VOLs with different drive types in the same pool. For best
performance, use pool-VOLs with the same drive type in the same pool.
For more information about data drive type, see Pool creation and data
drive type priority on page 94.
CLPR Registering pool-VOLs to Cache Logical Partition Numbers (CLPRs) in
pools:
You can register pool-VOLs assigned to different CLPRs in a pool.
Changing CLPRs:
You can change CLPRs in the parity group belonging to the pool-VOL. In
this case, regardless of the CLPR in the pool-VOL, the CLPR ID in the
parity must be the same as that of the P-VOL that you are using.
Pool limit 1,024
Volume capacity 8 GB to 4 TB
Path definition Define only needed paths to a volume so that you can specify the volume
as a pool-VOL.
Fast Snap data pool requirements
The following table lists the requirements for Fast Snap data pools.
For information about THP pools, see the HPE XP7 Provisioning for Open Systems User Guide.
Item Requirement
Pool capacity Calculate the pool capacity (see Calculating and assigning pool
capacity on page 69).
The maximum total capacity of pools in a storage system depends
on the storage system model:
12.3 PB (if THP/Smart/Real Time Smart Tier/FS Extension1, THP/
Smart/Real Time Smart Tier/FS Extension2, or THP/Smart/Real
Time Smart Tier/FS Extension3 is added in the shared memory
capacity).
The maximum pool capacity that can be used for each Fast Snap
P-VOL is 768 TB.
Pool-VOL limit per pool 1,024
Note: You cannot assign a volume that is already assigned to a
pool as a pool-VOL to another pool.
60 Fast Snap data pool requirements
Table Continued
Page 61

Item Requirement
Pool limit per storage system 128
Pool IDs are assigned from 0 to 127.
This can include THP (including Smart and Real Time Smart Tier),
THP MF (including Smart MF and Real Time Smart Tier for
Mainframe), and FS pool types.
Increasing capacity Dynamically increase the pool-VOL capacity. To do this, increase
the capacity for at least one parity group.
Decreasing pool capacity Use the following workflow to decrease pool capacity:
1. Delete the pool-VOLs (see Decreasing pool capacity on page
159).
2. Reconfigure the pool (see Creating Fast Snap data pools on
page 89).
Deleting pools The pool is not used by an FS pair.
For more information about deleting pools, see Deleting pools on
page 170.
Data pool warning threshold Value: Warning Threshold
Range: 20 - 95%, in 1% increments.
Default: 80%
Note: If you exceed the data pool warning threshold, a warning is
issued through a service information message (SIM) and an SNMP
trap reporting excessive pool usage.
For more information:
• About editing the data pool warning threshold, see Editing the
data pool warning threshold on page 163.
• About checking alerts and checking the details of a SIM, see
the HPE XP7 Remote Web Console User Guide.
• About SNMP traps, see the HPE XP7 SNMP Agent User Guide.
Fast Snap consistency group requirements
The attributes of Fast Snap consistency groups, such as the pair limit and pair type, have usage
requirements. Review these requirements before creating consistency groups.
Fast Snap consistency group requirements 61
Page 62

Item Requirement
Consistency group ID Value: 0 to 2,047
With BC, BC MF, and FS, you can create up to 2,048 consistency
groups in a storage system.
Manual assignment of a consistency group ID to an FS pair using
the paircreate command:
Specify a consistency group ID from 0 to 255.
Automatic assignment of a consistency group ID to an FS pair using
the paircreate or raidcom add snapshot commands:
• Using the paircreate command, if a number is not specified,
an unassigned number from 0 to 255 is automatically assigned.
• Using the raidcom add snapshot command, if a number is
not specified, an unassigned number from 0 to 2,047 is
automatically assigned.
2
Consistency group ID is displayed in the following windows in RWC:
• Consistency Groups tab in Local Replication window.
• Consistency Group Properties window.
• In RAID Manager, use the raidcom get snapshot command
to view the consistency group ID.
Pair limit 8,192 pairs per consistency group.
Pair type
BC, BC MF, and Fast Snap pairs cannot be contained in a single
consistency group. For Fast Snap consistency groups, only Fast
Snap pairs can be defined in a group.
Snapshot and cloned pairs cannot be contained in a single
consistency group.
1
Notes:
1. Fast Snap assigns a number in ascending order from 0 to 255.
2. Business Copy uses numbers from 0 to 127. Because of this, Fast Snap assigns an unassigned
number from 128 to 2,047 first. If there is no unassigned number from 128 to 2,047, then Fast Snap
assigns an unassigned number from 0 to 127.
For microcode versions earlier than 80-05-0X-XX/XX, Fast Snap assigns a number from 0 to 2,047.
Therefore, if a consistency group was created in an earlier version, a number from 0 to 127 may be used
as its consistency group ID even if there is an unassigned number from 128 to 2,047.
Consistency group restrictions:
62 Fast Snap system and planning requirements
Page 63

• Fast Snap pairs that share P-VOLs or are in higher and lower layers of a snapshot tree cannot be
defined in the same consistency group. If they are defined in the same consistency group, the
raidcom add snapshot command is rejected.
• Do not place pairs that are not in consistency groups, in a group defined by the RAID Manager
configuration definition file. If these pairs are in the same group, the pairsplit command may
terminate and the snapshot data may not be the P-VOL data generated when a storage system
received the pairsplit command.
• Only one consistency group can be specified for a group defined in the RAID Manager configuration
definition file.
• When a pair for which a consistency group is specified and is already created, if you specify another
consistency group to create a pair, the pair is added to the same consistency group.
• To specify multiple consistency groups, use the RAID Manager configuration definition file to define the
same number of groups as the consistency groups you want to specify.
Fast Snap snapshot group requirements
Item Requirement
Name Character limit: 32.
You can change snapshot group names using RAID Manager
commands. For details about RAID Manager commands, see
Appendix A and the HPE XP Storage RAID Manager Installation
and Configuration User Guide.
Group and FS pair limit
Pair type Snapshot and cloned pairs cannot be contained in a single snapshot
Restrictions for Snapshot groups:
• When creating a Fast Snap cascaded pair with the CTG mode specified using RAID Manager, a
volume belonging to the snapshot group and the following volumes cannot be contained in the same
snapshot group:
◦ The P-VOL or S-VOL of a volume belonging to the snapshot group
◦ A volume that uses the same P-VOL with a different MU number as the volume belonging to the
snapshot group
• Snapshot groups per storage system: 2,048.
• FS pairs per snapshot group: 8,192.
group.
Fast Snap planning requirements
When you create Fast Snap pairs for a P-VOL for the first time, the number of pairs that you can create in
a storage system depends on several variables.
Fast Snap snapshot group requirements 63
Page 64

• The number of Fast Snap pairs that you can create based on the number of available pair tables.
• The snapshot estimated manageable capacity.
• The number of cache management devices that you must make available.
The smallest of the three calculations is the maximum number of Fast Snap pairs that you can create in
the storage system.
When you create Fast Snap pairs again, you only need to know the number of pair tables to calculate the
number of pairs that you can create. You do not need to know the snapshot estimated manageable
capacity or the number of cache management devices.
If you have multiple P-VOLs, calculate the number of Fast Snap pairs that you can create for each P-VOL
in the storage system.
Calculating the number of Fast Snap pairs based on pair tables
Pair tables contain information that is required to manage FS pairs. Each FS pair requires one pair table.
The maximum number of pair tables is the maximum number of pairs that can be used in a storage
system.
The number of FS pairs that you can create is maximum-number-of-pair-tables-per-storage-system number-of-existing-pairs.
The maximum number of pair tables is 1,048,575.
To view the number of existing FS pairs in RWC, use the Local Replication window. In RAID Manager,
use the raidcom get snapshot command. For details, see Viewing local replication summary
information on page 137.
More information
Calculating Fast Snap pairs based on the snapshot estimated manageable capacity on page 64
Calculating Fast Snap pairs based on cache management devices on page 65
Calculating the number of cache management devices on page 66
Calculating the Fast Snap pair capacity for THP pools on page 66
Calculating and assigning pool capacity on page 69
External Storage and external volumes used as pool-VOLs on page 71
Simultaneous processing of multiple Fast Snap pair tasks on page 71
Pair operations when pairs are cascaded on page 72
Pair operations when pairs are not cascaded on page 83
Pair operations when a P-VOL is shared by multiple S-VOLs on page 84
Data recovery and backup differences between Fast Snap and Business Copy on page 85
Fast Snap cache management device requirements on page 68
Calculating Fast Snap pairs based on the snapshot estimated manageable capacity
You can calculate the number of FS pairs you can create based on the snapshot estimated manageable
capacity.
To view the snapshot estimated manageable capacity in RWC, see Viewing local replication summary
information on page 137.
64 Calculating the number of Fast Snap pairs based on pair tables
Page 65

Calculate the number of FS pairs that you can create using the following formulas, where SM refers to
shared memory:
Number of FS pairs that you can create =
Snapshot estimated manageable capacity / Snapshot management capacity in a P-VOL
Snapshot estimated manageable capacity in a P-VOL [GB] =
(P-VOL capacity of FS pairs [TB] / 2.6) * 3,024 + (168 * 2 (consumed shared memory [GB]))
More information
Calculating the number of Fast Snap pairs based on pair tables on page 64
Calculating Fast Snap pairs based on cache management devices on page 65
Calculating the number of cache management devices on page 66
Calculating the Fast Snap pair capacity for THP pools on page 66
Calculating and assigning pool capacity on page 69
External Storage and external volumes used as pool-VOLs on page 71
Simultaneous processing of multiple Fast Snap pair tasks on page 71
Pair operations when pairs are cascaded on page 72
Pair operations when pairs are not cascaded on page 83
Pair operations when a P-VOL is shared by multiple S-VOLs on page 84
Data recovery and backup differences between Fast Snap and Business Copy on page 85
Viewing the list of primary volumes on page 139
Fast Snap cache management device requirements on page 68
Calculating Fast Snap pairs based on cache management devices
Cache management devices are the unit for controlling the cache in association with logical volumes
(LDEVs). They are required to perform FS tasks, such as creating FS pairs for a volume.
To view the number of cache management devices in RWC, see Viewing the number of cache
management devices on page 150.
Use the following formula to calculate the number of FS pairs that you can create based on the number of
cache management devices:
Number of FS pairs that you can create =
Number of cache management devices / ceil (the P-VOL capacity of FS pairs [TB]) / 2.6)
More information
Calculating the number of Fast Snap pairs based on pair tables on page 64
Calculating Fast Snap pairs based on the snapshot estimated manageable capacity on page 64
Calculating the number of cache management devices on page 66
Calculating the Fast Snap pair capacity for THP pools on page 66
Calculating and assigning pool capacity on page 69
External Storage and external volumes used as pool-VOLs on page 71
Simultaneous processing of multiple Fast Snap pair tasks on page 71
Pair operations when pairs are cascaded on page 72
Pair operations when pairs are not cascaded on page 83
Pair operations when a P-VOL is shared by multiple S-VOLs on page 84
Data recovery and backup differences between Fast Snap and Business Copy on page 85
Calculating the number of remaining cache management devices on page 190
Calculating Fast Snap pairs based on cache management devices 65
Page 66

Fast Snap cache management device requirements on page 68
Calculating the number of cache management devices
You can calculate the number of cache management devices you must reserve to initially create a Fast
Snap pair for a volume.
8,192 cache management devices are required to create FS pools in a system for the first time. For
details about the number of cache management devices required for creating THP pools, see the
Provisioning Guide. Fast Snap must reserve 4,096 cache management devices out of 8,192.
When you create Fast Snap pairs in volumes for the first time, confirm that at least 4,097 cache
management devices are reserved. If the number is less than 4,097, pairs might not be created.
Use the following formula:
Number of cache management devices that you must reserve =
ceil (Size of P-VOL [TB] / 2.6)
If the amount of pool usage for the P-VOL exceeds 70 percent of the total capacity of the cache
management devices reserved for the P-VOL, you must reserve another cache management device. You
can reserve a maximum of 256 cache management devices for each P-VOL.
More information
Calculating the number of Fast Snap pairs based on pair tables on page 64
Calculating Fast Snap pairs based on the snapshot estimated manageable capacity on page 64
Calculating Fast Snap pairs based on cache management devices on page 65
Calculating the Fast Snap pair capacity for THP pools on page 66
Calculating and assigning pool capacity on page 69
External Storage and external volumes used as pool-VOLs on page 71
Simultaneous processing of multiple Fast Snap pair tasks on page 71
Pair operations when pairs are cascaded on page 72
Pair operations when pairs are not cascaded on page 83
Pair operations when a P-VOL is shared by multiple S-VOLs on page 84
Data recovery and backup differences between Fast Snap and Business Copy on page 85
Fast Snap cache management device requirements on page 68
Calculating the Fast Snap pair capacity for THP pools
When creating a THP pool, you can set the maximum reserved V-VOL capacity against the pool capacity.
For details about the maximum reserved capacity, see the HPE XP7 Provisioning for Open Systems User
Guide.
When storing snapshot data in a THP pool, set the maximum reserved V-VOL capacity against the THP
pool by calculating the V-VOL capacity of a Fast Snap pair (Fast Snap pair capacity) using the following
formula.
Fast Snap pair capacity = Σ↑(P-VOL capacity (MB)
× Number of pairs × 2 ÷ 42 (MB))↑ × 42 (MB) + Σ↑(P-VOL capacity (MB) × Number of pairs
× 2 ÷ 2,921,688 (MB))↑ × 175,434 (MB)
Decimal places of the value enclosed by arrows (↑value↑) are rounded up.
As for Number of pairs in the formula, allocated pages are not released if you delete pairs. Because of
this, use the maximum number of FS pairs you want to create in the applicable snapshot tree as Number
of pairs instead of using the number of pairs currently created in the applicable snapshot tree.
66 Calculating the number of cache management devices
Page 67

If a pair or snapshot data is deleted, allocated pages are not released. As a result, if you delete pairs or
snapshot data, the FS pair capacity is not decreased. To decrease the FS pair capacity by releasing
allocated pages, you must delete all FS pairs and snapshot data created in the applicable snapshot tree.
The following example illustrates how the FS pair capacity is calculated.
When you create three FS pairs using the 500 GB (500 x 1024 MB) volume as the P-VOL, the FS pair
capacity is calculated as follows:
↑(500 × 1,024 × 3 × 2 ÷ 42)↑ × 42 + ↑(500 × 1,024 × 3 × 2 ÷ 2,921,688)↑
× 175,434 = 3,422,874 (MB)
Afterward, if you delete two pairs, the maximum number of FS pairs you can create in the applicable
snapshot tree is the same: The FS pair capacity does not change.
Fast Snap system and planning requirements 67
Page 68

Also, if you you split pairs twice, the maximum number of FS pairs you can create in the snapshot tree is
the same, and the FS pair capacity remains unchanged.
More information
Calculating the number of Fast Snap pairs based on pair tables on page 64
Calculating Fast Snap pairs based on the snapshot estimated manageable capacity on page 64
Calculating Fast Snap pairs based on cache management devices on page 65
Calculating the number of cache management devices on page 66
Calculating and assigning pool capacity on page 69
External Storage and external volumes used as pool-VOLs on page 71
Simultaneous processing of multiple Fast Snap pair tasks on page 71
Pair operations when pairs are cascaded on page 72
Pair operations when pairs are not cascaded on page 83
Pair operations when a P-VOL is shared by multiple S-VOLs on page 84
Data recovery and backup differences between Fast Snap and Business Copy on page 85
Fast Snap cache management device requirements on page 68
Fast Snap cache management device requirements
The following table shows the cache management device requirements for performing Fast Snap tasks.
For information about THP tasks, see the HPE XP7 Provisioning for Open Systems User Guide.
Task Number of cache management devices
Initially create an FS pool. 8,192*
Create a volume. 1
68 Fast Snap cache management device requirements
required
*FS assigns 4,096 of the 8,192 devices that are
available.
Table Continued
Page 69

Task Number of cache management devices
Create a P-VOL. 256
Initially create an FS pair for a volume. 4,097
The number of cache management devices that can be used in a system is 65,280.
More information
Calculating the number of Fast Snap pairs based on pair tables on page 64
Calculating Fast Snap pairs based on the snapshot estimated manageable capacity on page 64
Calculating Fast Snap pairs based on cache management devices on page 65
Calculating the number of cache management devices on page 66
Calculating the Fast Snap pair capacity for THP pools on page 66
Calculating and assigning pool capacity on page 69
External Storage and external volumes used as pool-VOLs on page 71
Simultaneous processing of multiple Fast Snap pair tasks on page 71
Pair operations when pairs are cascaded on page 72
Pair operations when pairs are not cascaded on page 83
Pair operations when a P-VOL is shared by multiple S-VOLs on page 84
Data recovery and backup differences between Fast Snap and Business Copy on page 85
required
Calculating and assigning pool capacity
Use the following formula to calculate the capacity of the snapshot data that you can store in the Fast
Snap pool:
Capacity of the snapshot data that you can store in the pool =
Total capacity of pool-VOLs in the pool - Capacity of V-VOL management areas
The capacity of V-VOL management areas is 3% of the pool capacity.
Use the following formula to calculate the capacity of the snapshot data that you can store in the THP
pool:
Capacity of the snapshot data that you can store in the pool =
Total capacity of pool-VOLs in the pool - (Capacity of pool VOLs used by THP V-VOLs +
Capacity of V-VOL management areas)
Use the following formula to calculate the pool capacity:
Capacity of the pool [MB] =
Total number of pages * 42 - 4200
Use the following formula to calculate the total number of pages:
Total number of pages =
Sigma (floor (floor (pool-VOL number of blocks / 512) / 168)) for each pool-VOL
Calculating and assigning pool capacity 69
Page 70

floor( ): Truncates the value calculated from the formula in parentheses after the decimal point.
Estimate pool-VOL capacity in multiples of 42 MB. Specifying a pool-VOL capacity in other multiples less
than 42 MB truncates the fraction.
If you install THP/Smart/FS Extension in the shared memory, the available pool capacity per P-VOL is
768 TB, and the total capacity of all pools is 12.3 PB.
More information
Calculating the number of Fast Snap pairs based on pair tables on page 64
Calculating Fast Snap pairs based on the snapshot estimated manageable capacity on page 64
Calculating Fast Snap pairs based on cache management devices on page 65
Calculating the number of cache management devices on page 66
Calculating the Fast Snap pair capacity for THP pools on page 66
External Storage and external volumes used as pool-VOLs on page 71
Simultaneous processing of multiple Fast Snap pair tasks on page 71
Pair operations when pairs are cascaded on page 72
Pair operations when pairs are not cascaded on page 83
Pair operations when a P-VOL is shared by multiple S-VOLs on page 84
Data recovery and backup differences between Fast Snap and Business Copy on page 85
Fast Snap cache management device requirements on page 68
Fast Snap shared memory requirements on page 56
Resolving insufficient pool capacity
Make sure you have sufficient pool capacity. If the pool capacity is insufficient, the storage system can
suspend Fast Snap pairs ("PSUE" status).
NOTE: When the setting, Suspend FS pairs when depletion threshold is exceeded, is set to Yes in
RWC or in RAID Manager by uisng the command, raidcom modify pool -suspend_tipair
<yes> for a THP pool, the status of FS pairs using the pool might change to PSUE if the depletion
threshold is exceeded. When it is set to No in RWC or in RAID Manager by uisng the command,
raidcom modify pool -suspend_tipair <no> for an FS pool or a THP pool, the status of FS
pairs using the pool might change to PSUE if the pool becomes full.
Procedure
1. Estimate the capacity of snapshot data to be copied to the pool.
If the capacity of snapshot data to be copied to the pool varies hour by hour, ensure that the largest
capacity is your pool capacity.
2. Assign the pool capacity based on the estimate.
Pool capacity calculations
Use the following formula:
Capacity of snapshot data to be copied =
Capacity of data written to the same area in the P-VOL during the period
from when snapshot data is stored to when the snapshot data is deleted
Although the pool capacity is decided according to the estimation, if the pool capacity exceeds the
threshold, address the issue.
70 Resolving insufficient pool capacity
Page 71

If multiple snapshot data are stored, the data may be shared in a pool. In this case, you can release Fast
Snap pairs, but the snapshot data cannot be deleted from the pool. If you release all Fast Snap pairs that
have snapshot data containing the shared data, the snapshot data are also deleted from the pool.
Creating a backup of data
During creation of a backup copy, a significant amount of data is read from the secondary volume. This
may increase the accesses to the primary volume and degrade the host I/O performance.
Procedure
1. Store the snapshot data, or clone pairs.
2. Use an S-VOL.
More information
Splitting Fast Snap pairs to store snapshot data on page 120
External Storage and external volumes used as pool-VOLs
In Ext Stor, an XP7 Storage system is referred to as a local storage system, and the other storage
systems are referred to as external storage systems. With Ext Stor installed, you can use external and
internal volumes as pool-VOLs. Volumes in local storage systems are referred to as internal volumes, and
volumes in external storage systems are referred to as external volumes.
NOTE: Using external volumes increases the likelihood of a failure, and disaster recovery is more
complex and challenging. Using multiple external volumes as pool-VOLs in a pool increases the likelihood
of the pool being blocked.
To minimize the adverse effects of failure, use only one pool per external storage system. An external
pool-VOL that is blocked due to a failure blocks the pool. You must restore blocked pools.
For more information about external storage systems and disaster recovery methods for external
volumes, see the HPE XP7 External Storage for Open and Mainframe Systems User Guide.
More information
Calculating the number of Fast Snap pairs based on pair tables on page 64
Calculating Fast Snap pairs based on the snapshot estimated manageable capacity on page 64
Calculating Fast Snap pairs based on cache management devices on page 65
Calculating the number of cache management devices on page 66
Calculating the Fast Snap pair capacity for THP pools on page 66
Calculating and assigning pool capacity on page 69
Simultaneous processing of multiple Fast Snap pair tasks on page 71
Pair operations when pairs are cascaded on page 72
Pair operations when pairs are not cascaded on page 83
Pair operations when a P-VOL is shared by multiple S-VOLs on page 84
Data recovery and backup differences between Fast Snap and Business Copy on page 85
Fast Snap cache management device requirements on page 68
Simultaneous processing of multiple Fast Snap pair tasks
For each of the following pair tasks, the number of simultaneous instances processed in the background
is equal to the total number of MP blades in the storage system:
Creating a backup of data 71
Page 72

• Creating pairs.
• Restoring pairs.
• Deleting snapshot data and deleting pairs.
When you execute additional pair task operations above these limits, the tasks are processed in the order
requested.
More information
Calculating the number of Fast Snap pairs based on pair tables on page 64
Calculating Fast Snap pairs based on the snapshot estimated manageable capacity on page 64
Calculating Fast Snap pairs based on cache management devices on page 65
Calculating the number of cache management devices on page 66
Calculating the Fast Snap pair capacity for THP pools on page 66
Calculating and assigning pool capacity on page 69
External Storage and external volumes used as pool-VOLs on page 71
Pair operations when pairs are cascaded on page 72
Pair operations when pairs are not cascaded on page 83
Pair operations when a P-VOL is shared by multiple S-VOLs on page 84
Data recovery and backup differences between Fast Snap and Business Copy on page 85
Creating Fast Snap pairs using Remote Web Console on page 114
Restoring Fast Snap pairs on page 124
Resynchronizing Fast Snap pairs on page 127
Deleting Fast Snap pairs on page 129
Fast Snap cache management device requirements on page 68
Pair operations when pairs are cascaded
The following table explains pair operations according to the pair status. The status of pair B is SMPL.
Pair type Pair A
status
With the
snapshot
attribute
COPY(PD)N N N N N N YN
PAIR Y N N N Y N YN
PSUS Y N N N Y N YN
COPY(RS)N N N N N N YN
COPY(RS
-R)
PSUE N N N N N N YN
Operation for pair B
Pair with snapshot attribute Pair with clone
Create Split Resync Restore Create Split Delete
N N N N N N YN
attribute
Snapshot
/ clone
attribute
common
Table Continued
72 Pair operations when pairs are cascaded
Page 73

Pair type Pair A
status
SMPL(PD)N N N N N N YN
Operation for pair B
Pair with snapshot attribute Pair with clone
attribute
Create Split Resync Restore Create Split Delete
Snapshot
/ clone
attribute
common
With the
clone
attribute
Y: Operation successful.
YN: Operation not performed, process terminated.
N: Process terminated abnormally.
The following table explains operations of cascaded pair B when pair B has the snapshot attribute, and its
pair status is COPY(PD).
Pair Type Pair A
COPY(PD)N N N N N N YN
PAIR Y N N N Y N YN
PSUS(SP)Y N N N Y N YN
PSUE N N N N N N YN
SMPL(PD)N N N N N N YN
Operation for pair B
status
Pair with snapshot attribute Pair with clone
attribute
Snapshot
/ clone
attribute
common
With the
snapshot
attribute
Create Split Resync Restore Create Split Delete
COPY(PD)N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
PAIR YN N YN YN N N N
PSUS YN N YN YN N N N
COPY(RS)YN N YN YN N N N
COPY(RS
-R)
PSUE YN N YN YN N N N
SMPL(PD)N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
YN N YN YN N N N
Table Continued
Fast Snap system and planning requirements 73
Page 74

Pair Type Pair A
status
Operation for pair B
Pair with snapshot attribute Pair with clone
attribute
Create Split Resync Restore Create Split Delete
Snapshot
/ clone
attribute
common
With the
clone
attribute
Y: Operation successful.
YN: Operation not performed, process terminated.
N: Process terminated abnormally.
The following table explains operations of cascaded pair A when pair B has the snapshot attribute, and its
pair status is COPY(PD).
Pair Type Pair A
COPY(PD)YN N YN YN N N N
PAIR YN N YN YN N N N
PSUS(SP)YN N YN YN N N N
PSUE YN N YN YN N N N
SMPL(PD)N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
Operation for pair A
status
Pair with snapshot attribute Pair with clone
attribute
Snapshot
/ clone
attribute
common
With the
snapshot
attribute
With the
clone
attribute
Create Split Resync Restore Create Split Delete
COPY(PD)N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
PAIR N Y YN YN N N N
PSUS N YN Y Y N N N
COPY(RS)YN N YN YN N N N
COPY(RS
-R)
PSUE YN N YN YN N N N
SMPL(PD)N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
COPY(PD)N N N N N N N
PAIR N N N N N Y N
YN N YN YN N N N
Table Continued
74 Fast Snap system and planning requirements
Page 75

Pair Type Pair A
status
PSUS(SP)N N N N N YN N
PSUE N N N N N N N
SMPL(PD)N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
Y: Operation successful.
YN: Operation not performed, process terminated.
N: Process terminated abnormally.
The following table explains operations of cascaded pair B when pair B has the clone attribute, and its
pair status is COPY(PD).
Operation for pair A
Pair with snapshot attribute Pair with clone
attribute
Create Split Resync Restore Create Split Delete
Snapshot
/ clone
attribute
common
Pair Type Pair A
status
With the
snapshot
attribute
With the
clone
attribute
COPY(PD)N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
PAIR N N N N N N Y
PSUS N N N N N N Y
COPY(RS)N N N N N N Y
COPY(RS
-R)
PSUE N N N N N N Y
SMPL(PD)N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
COPY(PD)N N N N N N Y
PAIR N N N N N N Y
Operation for pair B
Pair with snapshot attribute Pair with clone
attribute
Create Split Resync Restore Create Split Delete
N N N N N N Y
Snapshot
/ clone
attribute
common
PSUS(SP)N N N N N N Y
PSUE N N N N N N Y
Table Continued
Fast Snap system and planning requirements 75
Page 76

Pair Type Pair A
status
SMPL(PD)N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
Y: Operation successful.
N: Process terminated abnormally.
The following table explains operations of cascaded pair A when pair B has the clone attribute, and its
pair status is COPY(PD).
Operation for pair B
Pair with snapshot attribute Pair with clone
attribute
Create Split Resync Restore Create Split Delete
Snapshot
/ clone
attribute
common
Pair type Pair A
status
With the
snapshot
attribute
With the
clone
attribute
COPY(PD)N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
PAIR N Y YN YN N N N
PSUS N YN Y Y N N N
COPY(RS)YN N YN YN N N N
COPY(RS
-R)
PSUE N N N N N N N
SMPL(PD)N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
COPY(PD)N N N N N N N
PAIR N N N N N Y N
Operation for pair A
Pair with snapshot attribute Pair with clone
attribute
Create Split Resync Restore Create Split Delete
YN N YN YN N N N
Snapshot
/ clone
attribute
common
PSUS(SP)N N N N N YN N
PSUE N N N N N N N
SMPL(PD)N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
Y: Operation successful.
YN: Operation not performed, process terminated.
N: Process terminated abnormally.
76 Fast Snap system and planning requirements
Page 77

The following table explains operations of cascaded pair B when pair B has the snapshot attribute and its
pair status is PAIR.
Pair type Pair A
status
With the
snapshot
attribute
With the
clone
attribute
COPY(PD)N N YN YN N N Y
PAIR N N YN YN N N Y
PSUS N Y YN YN N N Y
COPY(RS)N N YN YN N N Y
COPY(RS
-R)
PSUE N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
SMPL(PD)N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
COPY(PD)N N YN YN N N Y
PAIR N N YN YN N N Y
Operation for pair B
Pair with snapshot attribute Pair with clone
attribute
Create Split Resync Restore Create Split Delete
N N YN YN N N Y
Snapshot
/ clone
attribute
common
PSUS(SP)N Y YN YN N N Y
PSUE N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
SMPL(PD)N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
Y: Operation successful.
YN: Operation not performed, process terminated.
N: Process terminated abnormally.
The following table explains operations of cascaded pair A when pair B has the snapshot attribute, and its
pair status is PAIR.
Fast Snap system and planning requirements 77
Page 78

Pair type Pair A
status
Operation for pair A
Pair with snapshot attribute Pair with clone
attribute
Create Split Resync Restore Create Split Delete
Snapshot
/ clone
attribute
common
With the
snapshot
attribute
With the
clone
attribute
COPY(PD)YN N YN YN N N N
PAIR N Y YN YN N N N
PSUS N YN Y Y N N N
COPY(RS)YN N YN YN N N N
COPY(RS
-R)
PSUE N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
SMPL(PD)N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
COPY(PD)N N N N N N N
PAIR N N N N N Y N
PSUS(SP)N N N N N YN N
PSUE N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
SMPL(PD)N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
YN N YN YN N N N
Y: Operation successful.
YN: Operation not performed, process terminated.
N: Process terminated abnormally.
The following table explains operations of cascaded pair B when pair B has the clone attribute and its pair
status is PAIR.
Pair type Pair A
status
With the
snapshot
attribute
COPY(PD)N N N N N N Y
PAIR N N N N N N Y
Operation for pair B
Pair with snapshot attribute Pair with clone
attribute
Create Split Resync Restore Create Split Delete
Snapshot
/ clone
attribute
common
Table Continued
78 Fast Snap system and planning requirements
Page 79

Pair type Pair A
status
PSUS N N N N N Y Y
COPY(RS)N N N N N N Y
Operation for pair B
Pair with snapshot attribute Pair with clone
attribute
Create Split Resync Restore Create Split Delete
Snapshot
/ clone
attribute
common
COPY(RS
-R)
PSUE N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
SMPL(PD)N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
With the
clone
attribute
Y: Operation successful.
YN: Operation not performed, process terminated.
N: Process terminated abnormally.
The following table explains operations of cascaded pair A when pair B has the clone attribute, and its
pair status is PAIR.
COPY(PD)N N N N N N Y
PAIR N N N N N Y Y
PSUS(SP)N N N N N Y Y
PSUE N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
SMPL(PD)N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
N N N N N N Y
Pair type Pair A
status
With the
snapshot
attribute
COPY(PD)YN N YN YN N N N
PAIR N Y YN YN N N N
PSUS N YN Y Y N N N
COPY(RS)YN N YN YN N N N
Operation for pair A
Pair with snapshot attribute Pair with clone
attribute
Create Split Resync Restore Create Split Delete
Fast Snap system and planning requirements 79
Snapshot
/ clone
attribute
common
Table Continued
Page 80

Pair type Pair A
status
Operation for pair A
Pair with snapshot attribute Pair with clone
attribute
Snapshot
/ clone
attribute
common
Create Split Resync Restore Create Split Delete
COPY(RS
YN N YN YN N N N
-R)
PSUE N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
SMPL(PD)N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
With the
COPY(PD)N N N N N N N
clone
attribute
PAIR N N N N N Y N
PSUS(SP)N N N N N YN N
PSUE N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
SMPL(PD)N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
Y: Operation successful.
YN: Operation not performed, process terminated.
N: Process terminated abnormally.
The following table explains operations of cascaded pair B when the status of pair B is not SMPL,
COPY(PD), and PAIR.
Pair
type
With the
snapshot
attribute
Pair A
status
Pair B
status
Operation for pair B
Pair with snapshot attribute Pair with clone
attribute
Create Split Resync Restore Create Split Delete
PSUS PSUS 1N YN Y Y N N Y
PSUS COPY(R
1
S)
PSUS COPY(R
S-R)
YN N YN YN N N N
YN N YN YN N N N
1
PSUS PSUE 1N N Y N N N Y
PSUS SMPL(P
1
D)
N N N N N N YN
Table Continued
Snapsh
ot /
clone
attribute
commo
n
80 Fast Snap system and planning requirements
Page 81

Pair
type
Pair A
status
Pair B
status
Operation for pair B
Pair with snapshot attribute Pair with clone
attribute
Snapsh
ot /
clone
attribute
commo
n
Create Split Resync Restore Create Split Delete
With the
clone
attribute
PSUS PSUS(S
2
P)
PSUS(SP)PSUS(S
2
P)
PSUS(SP)PSUE 2N N N N N N Y
PSUS(SP)SMPL(P
2
D)
N N N N N N Y
N N N N N N Y
N N N N N N YN
PSUS(SP)PSUS 1N YN Y Y N N N
Y: Operation successful.
YN: Operation not performed, process terminated.
N: Process terminated abnormally.
Notes
1. Pair B has snapshot attribute.
2. Pair B has clone attribute.
The following table explains operations of cascaded pair A when the status of pair B is not SMPL,
COPY(PD), and PAIR.
Pair
type
Pair A
status
Pair B
status
Operation for pair A
Pair with snapshot attribute Pair with clone
attribute
Create Split Resync Restore Create Split Delete
With the
snapshot
attribute
PSUS PSUS 1N YN N N N N N
PSUS COPY(R
1
S)
PSUS COPY(R
S-R)
N YN N N N N N
N YN N N N N N
1
PSUS PSUE 1N YN N N N N N
Table Continued
Snapsh
ot /
clone
attribute
commo
n
Fast Snap system and planning requirements 81
Page 82

Pair
type
Pair A
status
Pair B
status
Operation for pair A
Pair with snapshot attribute Pair with clone
attribute
Snapsh
ot /
clone
attribute
commo
n
Create Split Resync Restore Create Split Delete
With the
clone
attribute
PSUS SMPL(P
1
D)
PSUS PSUS(S
2
P)
PSUS(SP)PSUS(S
2
P)
PSUS(SP)PSUE 2N N N N N YN N
PSUS(SP)SMPL(P
2
D)
N YN N N N N N
N YN N N N N N
N N N N N YN N
N N N N N YN N
PSUS(SP)PSUS 1N N N N N YN N
Y: Operation successful.
YN: Operation not performed, process terminated.
N: Process terminated abnormally.
Notes
1. Pair B has snapshot attribute.
2. Pair B has clone attribute.
More information
Calculating the number of Fast Snap pairs based on pair tables on page 64
Calculating Fast Snap pairs based on the snapshot estimated manageable capacity on page 64
Calculating Fast Snap pairs based on cache management devices on page 65
Calculating the number of cache management devices on page 66
Calculating the Fast Snap pair capacity for THP pools on page 66
Calculating and assigning pool capacity on page 69
External Storage and external volumes used as pool-VOLs on page 71
Simultaneous processing of multiple Fast Snap pair tasks on page 71
Pair operations when pairs are not cascaded on page 83
Pair operations when a P-VOL is shared by multiple S-VOLs on page 84
Data recovery and backup differences between Fast Snap and Business Copy on page 85
Fast Snap cache management device requirements on page 68
82 Fast Snap system and planning requirements
Page 83

Pair operations when pairs are not cascaded
The following table explains pair operations according to the pair status.
Pair type Pair A
status
N/A SMPL Y N N N Y N YN
With the
snapshot
attribute
COPY(PD)YN N YN YN N N N
PAIR N Y YN YN N N Y
PSUS N YN Y Y N N Y
COPY(RS)YN N YN YN N N N
COPY(RS
-R)
PSUE N N Y N N N Y
SMPL(PD)N N N N N N YN
Operation for pair A
Pair with snapshot attribute Pair with clone
attribute
Create Split Resync Restore Create Split Delete
YN N YN YN N N N
Snapshot
/ clone
attribute
common
With the
clone
attribute
Y: Operation successful.
YN: Operation not performed, process terminated.
N: Process terminated abnormally.
More information
Calculating the number of Fast Snap pairs based on pair tables on page 64
Calculating Fast Snap pairs based on the snapshot estimated manageable capacity on page 64
Calculating Fast Snap pairs based on cache management devices on page 65
Calculating the number of cache management devices on page 66
Calculating the Fast Snap pair capacity for THP pools on page 66
Calculating and assigning pool capacity on page 69
External Storage and external volumes used as pool-VOLs on page 71
Simultaneous processing of multiple Fast Snap pair tasks on page 71
COPY(PD)N N N N N N Y
PAIR N N N N N Y Y
PSUS(SP)N N N N N YN Y
PSUE N N N N N N Y
SMPL(PD)N N N N N N YN
Pair operations when pairs are not cascaded 83
Page 84

Pair operations when pairs are cascaded on page 72
Pair operations when a P-VOL is shared by multiple S-VOLs on page 84
Data recovery and backup differences between Fast Snap and Business Copy on page 85
Fast Snap cache management device requirements on page 68
Pair operations when a P-VOL is shared by multiple S-VOLs
The following table explains pair operations according to the pair status.
Pair type Pair
status of
other S-
VOLs
With the
snapshot
attribute
With the
clone
attribute
COPY(PD)Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
PAIR Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
PSUS Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
COPY(RS)Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
COPY(RS
-R)
PSUE N Y Y Y N Y Y
SMPL(PD)Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
COPY(PD)Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
PAIR Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
Operation for the target S-VOL
Pair with snapshot attribute Pair with clone
attribute
Create Split Resync Restore Create Split Delete
Y N Y N Y N Y
Snapshot
/ clone
attribute
common
PSUS(SP)Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
PSUE N Y Y Y N Y Y
SMPL(PD)Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
Y: Operation successful.
N: Process terminated abnormally.
More information
Calculating the number of Fast Snap pairs based on pair tables on page 64
Calculating Fast Snap pairs based on the snapshot estimated manageable capacity on page 64
Calculating Fast Snap pairs based on cache management devices on page 65
Calculating the number of cache management devices on page 66
Calculating the Fast Snap pair capacity for THP pools on page 66
Calculating and assigning pool capacity on page 69
84 Pair operations when a P-VOL is shared by multiple S-VOLs
Page 85

External Storage and external volumes used as pool-VOLs on page 71
Simultaneous processing of multiple Fast Snap pair tasks on page 71
Pair operations when pairs are cascaded on page 72
Pair operations when pairs are not cascaded on page 83
Data recovery and backup differences between Fast Snap and Business Copy on page 85
Fast Snap cache management device requirements on page 68
Data recovery and backup differences between Fast Snap and Business Copy
Item Fast Snap (FS) Business Copy (BC)
P-VOL physical failures such as
hard disks.
P-VOL logical failures such as
data update errors or viruses.
Capacity required for backup. Less capacity is required for
Impact on P-VOL performance
when accessing backed up data.
S-VOL or pool physical failures If a physical failure occurs in a
Notes:
1. For snapshot pairs. When a cloned pair is created, all data in the P-VOL is retained and more
capacity is required for backup.
2. For snapshot pairs. When a cloned pair is created, the P-VOL and the S-VOL can be separated and
the P-VOL performance is not affected.
3. When a pool is full (the depletion threshold is exceeded in a pool for which the capacity for FS pairs
is limited), data in all S-VOLs using the pool cannot be guaranteed.
P-VOL data cannot be
guaranteed.
P-VOL data can be recovered
using the S-VOL.
backups because only differential
data of the P-VOL is retained.
P-VOL performance is affected
because data in the P-VOL is
shared.
pool3, data in all S-VOLs that use
the pool cannot be guaranteed.
2
1
P-VOL data can be recovered
using the S-VOL.
P-VOL data can be recovered
using the S-VOL.
More capacity is required for
backup because all data in the PVOL is retained.
P-VOL performance is not
affected because the P-VOL and
the S-VOL can be disconnected.
If a physical failure occurs in an
S-VOL, data in the S-VOL cannot
be guaranteed.
Recommended usage
To maintain backed up data for long periods, save it on magnetic tapes or other media. For temporary
backups use FS or BC. When backing up data to magnetic tapes use BC. To reduce the capacity
necessary for backups use FS, but note that this affects P-VOL performance.
Use BC to minimize the impact from P-VOL physical failures. If you need four or more generations of
backups, use both BC and FS as shown in the following figure.
Data recovery and backup differences between Fast Snap and Business Copy 85
Page 86

Use FS to minimize P-VOL logical failures.
More information
Calculating the number of Fast Snap pairs based on pair tables on page 64
Calculating Fast Snap pairs based on the snapshot estimated manageable capacity on page 64
Calculating Fast Snap pairs based on cache management devices on page 65
Calculating the number of cache management devices on page 66
Calculating the Fast Snap pair capacity for THP pools on page 66
Calculating and assigning pool capacity on page 69
External Storage and external volumes used as pool-VOLs on page 71
Simultaneous processing of multiple Fast Snap pair tasks on page 71
Pair operations when pairs are cascaded on page 72
Pair operations when pairs are not cascaded on page 83
Pair operations when a P-VOL is shared by multiple S-VOLs on page 84
Fast Snap cache management device requirements on page 68
Removing Fast Snap
Use this procedure to remove Fast Snap from RWC.
86 Removing Fast Snap
Page 87

Procedure
1. Delete all Fast Snap pairs.
2. Delete all FS pools and all THP pools that contain FS pairs.
3. Disable or remove the Fast Snap license. For details about disabling and removing licenses, see the
System Administrator Guide for your storage system.
More information
Deleting Fast Snap pairs on page 129
Deleting pools on page 170
Fast Snap system and planning requirements 87
Page 88

Configuring Fast Snap
Prerequisites for configuring Fast Snap
Before you perform Fast Snap configuration tasks, complete the following tasks:
• Install a sufficient amount of shared memory.
For more information about installing shared memory, contact HPE technical support.
• Create a V-VOL management area in the shared memory. This area is automatically created when you
install additional shared memory.
Workflow for configuring Fast Snap
The following image shows the configuration tasks workflow and the workflow for creating and managing
Fast Snap pairs.
Steps for configuring Fast Snap:
NOTE: The V-VOL management area must be created in shared memory. It is created automatically
when you add shared memory. For details, contact HPE technical support.
88 Configuring Fast Snap
Page 89

1. Create the Fast Snap data pools (see Creating Fast Snap data pools on page 89).
2. Create and register the V-VOLs for the pair (see Workflow for registering virtual volumes on page
95).
3. Create and manage the Fast Snap pairs (see Workflow for creating and managing Fast Snap pairs
on page 89).
Workflow for creating and managing Fast Snap pairs
1. Create the Fast Snap pairs (see Workflow for creating and managing Fast Snap pairs on page
113).
2. Split the Fast Snap pair to store the snapshot data using one of the available methods (see Storing
snapshot data or cloning pairs on page 119).
3. If a failure occurs and the pair is suspended ("PSUE" status), complete the following:
a. Recover the data by recovering the Fast Snap pair (see Restoring suspended Fast Snap pairs
on page 126).
b. Restore the pair, which writes snapshot data over the P-VOL (see
page 124).
4. Maintain the Fast Snap pair status (see How Fast Snap pair status changes on page 29).
5. Delete the Fast Snap pairs (see Deleting Fast Snap pairs on page 129).
For pairs with the snapshot attribute, create a Fast Snap pair to store snapshot data. Note, however, that
you can create up to 1,024 pairs for a P-VOL. Therefore, you must delete snapshot data or Fast Snap
pairs that are no longer necessary. When you delete a Fast Snap pair, snapshot data stored by the pair is
also deleted from the pool.
When a failure occurs, if you perform restoration, snapshot data can be overwritten in the P-VOL. If a
Fast Snap pair is already being restored, another Fast Snap pair might not be restored.
For details about operations and statuses for Fast Snap pairs, see How Fast Snap pair status changes
on page 29. For details about how to create THP pools, see the HPE XP7 Provisioning for Open Systems
User Guide.
Creating Fast Snap data pools
You can create Fast Snap data pools using RWC. For information about the creation of THP pools, see
the HPE XP7 Provisioning for Open Systems User Guide.
According to the capacity of the pool to create, you must add shared memory. For details about the
relation between shared memory to add and the pool capacity, see Fast Snap shared memory
requirements on page 56.
Restoring Fast Snap pairs on
NOTE: You can only register volumes that you have not already registered as a pool-VOL.
For more information about data pool requirements, including the maximum number of pool-VOLs, see
Fast Snap data pool requirements on page 60.
You can add external and internal volumes to data pools.
Workflow for creating and managing Fast Snap pairs 89
Page 90

NOTE: There are limitations to adding external and internal volumes to data pools. For more information
about these limitations, see the requirements for Fast Snap pool-VOLs listed in Fast Snap volume
requirements on page 56.
Prerequisites
You must have the Storage Administrator (Provisioning) role.
In RAID Manager, use the raidcom add snap_pool command.
Procedure
1. In the Explorer pane, click Storage Systems, expand the storage system tree, and then click Pools.
2. In the Pools window, select Create Pools.
3. In the Create Pools window of the Create Pools wizard, complete the following items for the pool you
want to create, and then click Add:
• Pool Type
Select Fast Snap as the pool type.
Default: Thin Provisioning
Required: Yes
• System Type
Value: Open
Default: Open
• Pool Volume Selection
Select the pool volume you want to use for the pool. Complete the following:
90 Configuring Fast Snap
Page 91

Drive Type/RPM: Select your pool-VOL’s data drive type and RPM. Select External Storage when
you use external volumes (for FS pool-vols).
RAID Level: Select your pool-VOL’s RAID level. If you selected External Storage as the Drive
Type/RPM, a hyphen (-) is displayed for this item and this item is unavailable.
Default: Mixable
Required: Yes
• Pool Name
Enter a name for the pool, using 32 alphanumeric characters or fewer. This field is case sensitive.
• Initial Pool ID
The initial pool identifier. Enter 0 and an integer number.
Integer number range: 0 - 127
Default: The smallest available number displays as the default. If no available pool ID exists, no
number appears. If an already registered pool ID is entered, the smallest available pool ID that is
larger than the one entered is used.
• Warning Threshold
The data pool capacity threshold.
Range (%): 20 - 95
Default (%): 80
The pool-VOL is added to the Selected Pools table of the Create Pools window. Up to 1,024 volumes
can be added to a pool.
NOTE: If you are adding an LDEV belonging to a parity group for which capacity expansion is
enabled, see the related section in the Provisioning Guide for your storage system.
4. Click Finish, and then confirm the settings.
Configuring Fast Snap 91
Page 92

5. Accept the default task name or enter a unique name.
You can enter up to 32 letters, numbers, and symbols, except the following:
\ / : , ; * ? " < > |
6. If you want to monitor the task after submitting it, select Go to tasks window for status.
7. Click Apply to submit the task.
What to do next
Select the pool volumes.
More information
Selecting pool volumes on page 92
Increasing pool capacity on page 155
Selecting pool volumes
Procedure
1. In the Explorer pane, click Storage Systems, expand the storage system tree, and then click Pools.
2. In the Pools window, select Create Pools.
92 Selecting pool volumes
Page 93

3. In the Create Pools window of the Create Pools wizard, in the Pool Volume Selection section, click
Select Pool VOLs.
4. In the Select Pool VOLs window, from the Available Pool Volumes table, select the pool-VOL you
want to add to the pool, and then click Add.
The pool-VOL is added to the Selected Pool Volumes table. You can add a maximum of 1,024
volumes in a pool.
NOTE: Before you add an LDEV belonging to a parity group which has the capacity expansion setting
enabled, see the information about whether capacity expansion can be enabled in the HPE XP7
Provisioning for Open Systems User Guide.
Configuring Fast Snap 93
Page 94

NOTE: Note the following when you add an external volume:
• External volumes with cache mode enabled and external volumes with cache mode disabled
cannot be contained in the same pool.
• External volumes with cache mode disabled and internal volumes cannot be contained in the same
pool.
• When setting the tier rank of an external volume to a value other than Middle, select the tier rank
from External LDEV Tier Rank, and then click Add.
NOTE:
• To specify conditions to display pool volumes, click Filter to open the menu, specify the filtering
conditions, and then click Apply.
• To select all pool-VOLs in the table, click Select All Pages. To cancel the selection, click Select All
Pages again.
• To specify the unit or the number of rows to be displayed, click Options.
5. Click OK.
The selected pool-VOL is shown in the Selected Pools table in the Create Pools window.
Pool creation and data drive type priority
Creating pools automatically sets the new pool-VOL with system area according to the priority of data
drive types.
The following table shows the priority of pool-VOLs with system area when creating pools.
Priority Data drive type
1 SAS7.2K
2 SAS10K
3 SAS15K
4 SSD or FMD
5 External volume
If more than one pool-VOL of the same data drive type exists in the storage system, the pool-VOL priority
is determined according to the storage system’s internal index information.
94 Pool creation and data drive type priority
Page 95

Workflow for registering virtual volumes
1. (Optional) Edit the SSID of the V-VOL you want to register to the pool-VOL’s paired volume (see
Editing the SSID for virtual volumes on page 95).
2. (Optional) Change the V-VOL settings (see Changing V-VOL settings on page 98).
3. Register the V-VOL (see Creating V-VOLs for Fast Snap S-VOLs on page 100).
Editing the SSID for virtual volumes
Prerequisites
You must have the Storage Administrator (Provisioning) role.
For more information about registering V-VOLs, see Creating V-VOLs for Fast Snap S-VOLs on page
100.
Procedure
1. In the Explorer pane, click Storage Systems, expand the storage system tree, and then click
Pools.
2. In the Pools window, in the Pools tab, click Create LDEVs.
Workflow for registering virtual volumes 95
Page 96

3. In the Create LDEVs window of the Create LDEVs wizard, in the Selected LDEVs table, click Edit
SSIDs.
In the Edit SSIDs window, in the SSIDs table, existing SSIDs and those to be generated are shown
in the list.
4. In the Edit SSIDs window, select the row of the SSID you want to edit, and then click Change
SSIDs.
96 Configuring Fast Snap
Page 97

5. In the Change SSIDs window, for Initial SSID, enter the new SSID and click OK.
6. In the Edit SSIDs window, click OK.
7. Click Finish, and then confirm the settings.
8. Accept the default task name or enter a unique name.
You can enter up to 32 letters, numbers, and symbols, except the following:
\ / : , ; * ? " < > |
Configuring Fast Snap 97
Page 98

9. If you want to monitor the task after submitting it, select Go to tasks window for status.
10. Click Apply to submit the task.
More information
Monitoring pool information on page 151
Replication window on page 208
Changing V-VOL settings
Prerequisites
You must have the Storage Administrator (Provisioning) role.
In RAID Manager, use the raidcom modify ldev command.
You can edit the V-VOL settings before registering a V-VOL.
Procedure
1. In the Explorer pane, click Storage Systems, expand the storage system tree, and then click Pools.
2. In the Pools window, in the Pools tab, click Create LDEVs.
98 Changing V-VOL settings
Page 99

3. In the Create LDEVs window of the Create LDEVs wizard, in the Selected LDEVs table, select an
LDEV, and then click Change LDEV Settings.
4. In the Change LDEV Settings window, complete the following items, and then click OK:
• LDEV Name
Configuring Fast Snap 99
Page 100

Enter the prefix characters and the initial number for the LDEV.
• Initial LDEV ID
Enter the LDKC, CU, and LDEV numbers, and the interval. To confirm used LDEVs, click View
LDEV IDs.
• MP Blade
Select the MP blade identifier to which you want to assign the LDEV. To specify an MP blade
identifier, select the MP blade ID. To assign an arbitrary MP blade identifier, click Auto.
5. Click Finish, and then confirm the settings.
6. Accept the default task name or enter a unique name.
You can enter up to 32 letters, numbers, and symbols, except the following:
\ / : , ; * ? " < > |
7. If you want to monitor the task after submitting it, select Go to tasks window for status.
8. Click Apply to submit the task.
Creating V-VOLs for Fast Snap S-VOLs
Prerequisites
You must have the Storage Administrator (Provisioning) role.
Change the pair status of V-VOLs you want the host server to recognize to PSUS or unpaired.
In RAID Manager, use the raidcom add ldev -pool snap command.
Depending on the types of pairs with which you are working, there are two options for creating a V-VOL
for a Fast Snap S-VOL. For pairs with the snapshot attribute (snapshot pairs) for which the cascade
attribute is enabled (cascaded pairs) or for clone pairs, create a THP V-VOL. You can use a noncascaded snapshot tree (using only root volumes and leaf volumes) even when you create snapshot pairs
that are cascaded. For information about creating a THP V-VOL, see the Provisioning Guide for your
storage system. For snapshot pairs for which the cascade attribute is disabled, create a Fast Snap VVOL.
Procedure
1. In the Explorer pane, click Storage Systems, expand the storage system tree, and then click Pools.
100 Creating V-VOLs for Fast Snap S-VOLs
 Loading...
Loading...