
User Guide

© Copyright 2018 HP Development Company,
L.P.
AMD and Catalyst are trademarks of Advanced
Micro Devices, Inc. Bluetooth is a trademark
owned by its proprietor and used by HP Inc.
under license. Intel is a trademark of Intel
corporation or its subsidiaries in the U.S.
and/or other countries. Linux® is the registered
trademark of Linus Torvalds in the U.S. and
other countries. Microsoft and Windows are
either registered trademarks or trademarks of
Microsoft Corporation in the United States
and/or other countries. NVIDIA is a trademark
or registered trademark of NVIDIA Corporation
in the U.S. and other countries. Red Hat
Enterprise Linux is a registered trademark of
Red Hat, Inc. in the United States and other
countries.
The information contained herein is subject to
change without notice. The only warranties for
HP products and services are set forth in the
express warranty statements accompanying
such products and services. Nothing herein
should be construed as constituting an
additional warranty. HP shall not be liable for
technical or editorial errors or omissions
contained herein.
Product notice
This guide describes features that are common
to most products. Some features may not be
available on your computer.
Not all features are available in all editions or
versions of Windows. Systems may require
upgraded and/or separately purchased
hardware, drivers, software or BIOS update to
take full advantage of Windows functionality.
See http://www.microsoft.com.
To access the latest user guides, go to
http://www.hp.com/support, and follow the
instructions to nd your product. Then select
User Guides.
Software terms
By installing, copying, downloading, or
otherwise using any software product
preinstalled on this computer, you agree to be
bound by the terms of the HP End User License
Agreement (EULA). If you do not accept these
license terms, your sole remedy is to return the
entire unused product (hardware and software)
within 14 days for a full refund subject to the
refund policy of your seller.
For any further information or to request a full
refund of the price of the computer, please
contact your seller.
First Edition: July 2018
Part number: L30691-001

About this guide
This guide provides information about computer features, setting up the computer, using the software, and
technical specications.
The following types of alerts may appear in this guide.
WARNING! Indicates a hazardous situation that, if not avoided, could result in death or serious injury.
CAUTION: Indicates a hazardous situation that, if not avoided, could result in minor or moderate injury.
IMPORTANT: Indicates information considered important but not hazard-related (for example, messages
related to property damage). An important alert warns the user that failure to follow a procedure exactly as
described could result in loss of data or in damage to hardware or software. Also contains essential
information to explain a concept or to complete a task.
NOTE: Contains additional information to emphasize or supplement important points of the main text.
TIP: Provides helpful hints for completing a task.
iii

iv About this guide

Table of contents
1 Locating HP resources .................................................................................................................................... 1
Product information .............................................................................................................................................. 1
Support .................................................................................................................................................................. 1
Product documentation ......................................................................................................................................... 2
Product diagnostics ............................................................................................................................................... 2
Product updates ..................................................................................................................................................... 3
2 Computer features ......................................................................................................................................... 4
Components ........................................................................................................................................................... 4
Front .................................................................................................................................................... 4
Left ....................................................................................................................................................... 4
Rear ...................................................................................................................................................... 5
Product specications ........................................................................................................................................... 6
Physical characteristics ....................................................................................................................... 6
Environmental specications .............................................................................................................. 6
3 Setting up the computer ................................................................................................................................ 7
Setting up the computer ........................................................................................................................................ 7
Ensuring proper ventilation ................................................................................................................ 7
Setup procedure .................................................................................................................................. 8
Mounting the computer .................................................................................................... 8
Connecting the computer ................................................................................................. 9
Connecting Bluetooth devices ............................................................................................................. 9
Disabling Bluetooth devices .............................................................................................................. 10
Disabling WLAN ................................................................................................................................. 11
Adding monitors .................................................................................................................................................. 12
Planning for additional monitors ...................................................................................................... 12
Entry model ..................................................................................................................... 12
Performance model ........................................................................................................ 12
Planning process ............................................................................................................. 13
Matching graphics card connector to monitor connectors ............................................................... 14
Identifying monitor connection requirements ................................................................................. 14
Connecting and conguring monitors .............................................................................................. 14
Customizing the monitor (Windows) ................................................................................................ 15
Installing optional components .......................................................................................................................... 15
Security ................................................................................................................................................................ 15
v

Product recycling ................................................................................................................................................. 15
4 Backing up, restoring, and recovering ........................................................................................................... 16
Using Windows tools ........................................................................................................................................... 16
Using the HP Cloud Recovery Download Tool to create recovery discs .............................................................. 16
Restoring and recovery ........................................................................................................................................ 16
5 Setting up Linux .......................................................................................................................................... 17
Linux-ready systems ........................................................................................................................................... 17
HP Linux driver discs ............................................................................................................................................ 17
Setting up Red Hat® Enterprise Linux® (RHEL) ................................................................................................... 17
HP driver disc ..................................................................................................................................... 18
Installing with the HP Red Hat Linux driver disc ............................................................................... 18
Setting up SUSE Linux Enterprise Desktop (SLED) .............................................................................................. 18
Installing SLED with the HP driver disc ............................................................................................. 18
Setting up Ubuntu ................................................................................................................................................ 18
Using the HP driver disc .................................................................................................................... 19
Proprietary graphics drivers ................................................................................................................................ 19
6 Updating the computer ................................................................................................................................ 20
Updating the computer after rst boot ............................................................................................................... 20
Updating the BIOS ................................................................................................................................................ 20
Determining the current BIOS version .............................................................................................. 20
Upgrading BIOS .................................................................................................................................. 20
Upgrading device drivers ..................................................................................................................................... 21
7 Maintenance, diagnostics, and minor troubleshooting .................................................................................... 22
Turning o the computer ..................................................................................................................................... 22
If you encounter issues ........................................................................................................................................ 22
For more information ........................................................................................................................ 22
Visual inspection ............................................................................................................................... 22
At startup ........................................................................................................................ 22
During operation ............................................................................................................. 23
Customer Self Repair ...................................................................................................... 23
Blink or beep codes: interpreting POST diagnostic LEDs and audible codes ................................... 24
Basic troubleshooting ....................................................................................................................... 24
HP Support ........................................................................................................................................ 24
Calling Support ............................................................................................................... 24
Locating warranty information ....................................................................................... 25
vi

8 Using HP PC Hardware Diagnostics ................................................................................................................ 26
Using HP PC Hardware Diagnostics Windows ..................................................................................................... 26
Downloading HP PC Hardware Diagnostics Windows ....................................................................... 26
Downloading the latest HP PC Hardware Diagnostics Windows version ....................... 26
Downloading HP Hardware Diagnostics Windows by product name or number
(select products only) ..................................................................................................... 27
Installing HP PC Hardware Diagnostics Windows ............................................................................. 27
Using HP PC Hardware Diagnostics UEFI ............................................................................................................. 27
Starting HP PC Hardware Diagnostics UEFI ....................................................................................... 27
Downloading HP PC Hardware Diagnostics UEFI to a USB ash drive .............................................. 28
Downloading the latest HP PC Hardware Diagnostics (UEFI) version ............................ 28
Downloading HP PC Hardware Diagnostics (UEFI) by product name or number
(select products only) ..................................................................................................... 28
Using HP Remote PC Hardware Diagnostics UEFI settings (select products only) ............................................. 28
Downloading HP Remote PC Hardware Diagnostics UEFI ................................................................. 29
Downloading the latest HP Remote PC Hardware Diagnostics UEFI version ................. 29
Downloading Remote HP PC Hardware Diagnostics UEFI by product name or
number ............................................................................................................................ 29
Customizing HP Remote PC Hardware Diagnostics UEFI settings .................................................... 29
9 Routine care ................................................................................................................................................ 30
General cleaning safety precautions ................................................................................................................... 30
Cleaning the chassis ............................................................................................................................................ 30
Cleaning the keyboard ......................................................................................................................................... 30
Cleaning the monitor ........................................................................................................................................... 31
Cleaning the mouse ............................................................................................................................................. 31
10 Accessibility .............................................................................................................................................. 32
Accessibility ......................................................................................................................................................... 32
Finding the technology tools you need ............................................................................................ 32
Our commitment ............................................................................................................................... 32
International Association of Accessibility Professionals (IAAP) ....................................................... 32
Finding the best assistive technology .............................................................................................. 33
Assessing your needs ..................................................................................................... 33
Accessibility for HP products .......................................................................................... 33
Standards and legislation .................................................................................................................................... 34
Standards .......................................................................................................................................... 34
Mandate 376 – EN 301 549 ............................................................................................ 34
Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) ................................................................ 34
Legislation and regulations .............................................................................................................. 34
United States ................................................................................................................... 35
vii

21st Century Communications and Video Accessibility Act (CVAA) ............................... 35
Canada ............................................................................................................................. 35
Europe ............................................................................................................................. 36
United Kingdom .............................................................................................................. 36
Australia .......................................................................................................................... 36
Worldwide ....................................................................................................................... 36
Useful accessibility resources and links .............................................................................................................. 37
Organizations .................................................................................................................................... 37
Educational institutions .................................................................................................................... 37
Other disability resources ................................................................................................................. 37
HP links .............................................................................................................................................. 37
Contacting support .............................................................................................................................................. 38
Index ............................................................................................................................................................. 39
viii

1 Locating HP resources
Read this chapter to learn about where to nd additional HP resources.
Product information
Topic Location
Technical specications To nd the QuickSpecs for your product, go to http://www.hp.com/go/quickspecs. Click
the link for the Hewlett Packard Enterprise QuickSpecs experience. Click Search all
QuickSpecs, type your model name in the search box, and then click Go.
Regulatory, Safety and Environmental
Notices
Accessories For complete and current information about supported accessories and components, go
System board A diagram of the system board is located on the inside of the chassis. Additional
Serial number, Agency/Environmental,
and operating system labels
Support
Topic Location
Product support For HP support, go to http://www.hp.com/support.
See the Regulatory, Safety and Environmental Notices for product regulatory information.
You can also see the Agency/Environmental label.
To access this guide:
▲ Select the Start button, select HP Help and Support, and then select HP
Documentation.
to http://www.hp.com/go/workstations and select Displays & accessories.
information is located in the computer Maintenance and Service Guide on the Web at
http://www.hp.com/support.
To access this guide:
▲ Select the Start button, Select your product, select HP Help and Support, and then
select Product Information.
The serial number, Agency/Environmental, and operating system labels might be on the
bottom of the computer, on the rear panel of the computer, or under the service door.
Here you can access the following types of support:
● Online chat with an HP technician
● Support telephone numbers
● HP service center locations
Warranty information To access this document:
▲ Select the Start button, select HP Help and Support, and then select HP
Documentation.
– or –
▲ Go to http://www.hp.com/go/orderdocuments.
Product information 1

Topic Location
Product documentation
Topic Location
IMPORTANT: You must be connected to the Internet to access the latest version of
the warranty.
You can nd your HP Limited Warranty located with the user guides on your product. The
warranty may also be provided on a CD or DVD provided in the box. In some countries or
regions, HP may provide a printed warranty in the box. For countries or regions where the
warranty is not provided in printed format, you can request a copy from
http://www.hp.com/go/orderdocuments. For products purchased in Asia Pacic, you can
write to HP at POD, PO Box 161, Kitchener Road Post Oice, Singapore 912006. Include
your product name, and your name, phone number, and postal address.
HP user documentation, white papers,
and third-party documentation
Removal and replacement videos To learn how to remove and replace computer components, go to http://www.hp.com/go/
Product notications Subscriber's Choice is an HP program that allows you to sign up to receive driver and
Technical specications The Product Bulletin contains QuickSpecs for HP computers. QuickSpecs include
Bulletins and Notices To nd advisories, bulletins, and notices:
Product diagnostics
Topic Location
User documentation is located on your hard drive. Select the Start button, select HP Help
and Support, and then select HP Documentation. For the latest online documentation, go
to http://www.hp.com/support. The documentation incudes this user guide and the
Maintenance and Service Guide.
sml.
software alerts, proactive change notications (PCNs), the HP newsletter, customer
advisories, and more. Sign up at https://h41369.www4.hp.com/alerts-signup.php.
information about the operating system, power supply, memory, processor, and many
other system components. To access the QuickSpecs, go to http://www.hp.com/go/
quickspecs/.
1. Go to http://www.hp.com/support.
2. Select your product.
3. Select Advisories or Bulletins and Notices.
Windows® diagnostics tools The HP PC Hardware Diagnostics Windows utility and HP PC Hardware Diagnostics UEFI
Audible beep and light code denitions See the computer Maintenance and Service Guide at http://www.hp.com/support.
POST error codes See the computer Maintenance and Service Guide at http://www.hp.com/support.
2 Chapter 1 Locating HP resources
utility are preinstalled on select Windows computers. See Using HP PC Hardware
Diagnostics UEFI on page 27.
For additional information, see the computer Maintenance and Service Guide at
http://www.hp.com/support.

Product updates
Topic Location
Driver and BIOS updates Go to http://www.hp.com/support and select Get software and drivers to verify that you
Operating systems For information, go to the following locations:
have the latest drivers for the computer.
For more information about updating the drivers and BIOS, see Updating the computer
on page 20.
● Windows operating systems, go to http://www.support.microsoft.com.
Linux® operating systems, go to http://www.linux.com.
●
Product updates 3
2 Computer features
For complete and current information about supported accessories and components for the computer, go to
http://partsurfer.hp.com.
●
Components
●
Product specications
Components
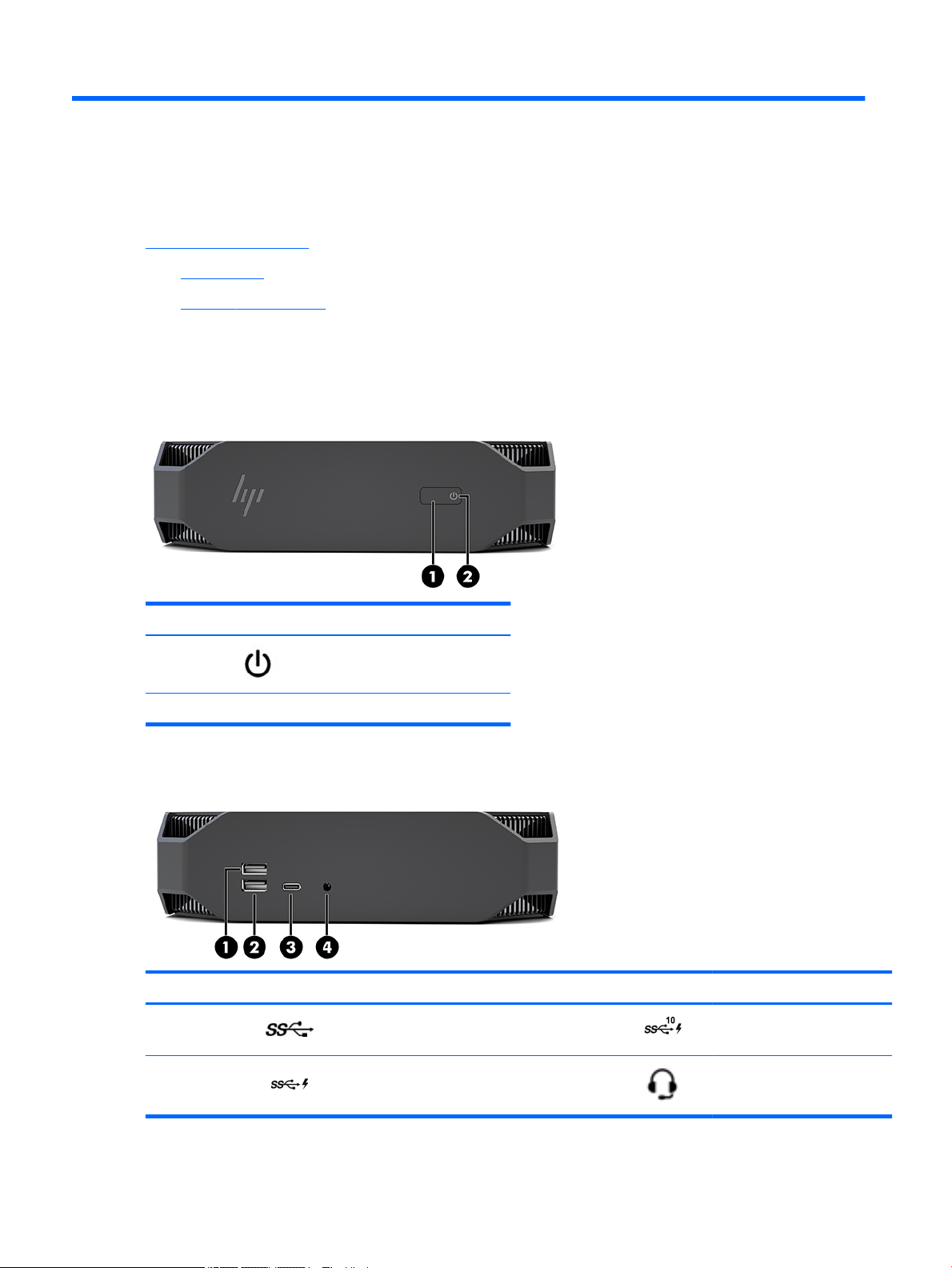
Front
Left
Item Icon Component
1 Power button
2 Power light
Item Icon Component Item Icon Component
1 USB SuperSpeed port 3
2
USB SuperSpeed port with HP
Sleep and Charge
4
USB Type-C SuperSpeed Plus
port with HP Sleep and Charge
Audio-out (headphone)/Audioin (microphone) combo jack
4 Chapter 2 Computer features

Rear
NOTE: Actual components may vary.
Item Icon Component Item Icon Component
1 security cable slot 6 power connector
2 Access panel release latch 7
3 Serial port (optional) 8 USB Type-C SuperSpeed port
4 RJ-45 (network) jack 9
Hard drive activity light
5
On: The computer is on.
Blinking: The hard drive is being
accessed.
10 USB SuperSpeed ports (2)
DisplayPort Plus connectors (3)
Driven by discrete GPU
HP Flex IO module (optional)
Supports:
● VGA port
● HDMI port
● DisplayPort™ port
● 2nd network jack
● USB-C 3.1 Gen2 Charging
Data Port
● Thunderbolt™ 3.0 port
Components 5

Product specications
Physical characteristics
Weight
Dimensions
Performance model
Entry model
Height
Width
Depth
Environmental specications
Operating
Non-operating
Temperature
Humidity
Altitude
Shock
NOTE: The ambient upper limit of 35°C is good up to 1524 m (5000 ft) elevation. Derate by 1°C for
every 305 m (1000 ft) above 1524 m (5000 ft). For example, at 3,048 m (10,000 ft), the upper
ambient air temperature limit is 30°C.
Operating
Non-operating
Operating
Non-operating
Operating
Non-operating
2.08 kg (4.58 lb)
1.87 kg (4.12 lb)
58 mm (2.3 in)
216 mm (8.5 in)
216 mm (8.5 in)
5°C to 35°C (40°F to 95°F)
-40°C to 60°C (-40°F to 140°F)
8% to 85% relative humidity, non-condensing
8% to 90% relative humidity, non-condensing
0 to 3,048 m (10,000 ft)
0 to 9,144 m (30,000 ft)
½-sine: 40g, 2-3ms (~62 cm/sec)
● ½-sine: 160 cm/s, 2-3ms (~105g)
● 20g, square: 422 cm/s
Vibration
Operating random
Non-operating random
NOTE: Values represent individual shock events and do not
indicate repetitive shock events.
0.5g (rms), 5-300 Hz, up to 0.0025 g2/Hz
2.0g (rms), 5-500 Hz, up to 0.0150 g2/Hz
NOTE: Values do not indicate continuous vibration.
6 Chapter 2 Computer features

3 Setting up the computer
●
Setting up the computer
●
Adding monitors
●
Installing optional components
●
Security
●
Product recycling
Setting up the computer
Ensuring proper ventilation
Proper ventilation for the system is important for computer operation. To be sure that there is adequate
ventilation:
● Operate the computer on a sturdy, level surface.
● Provide at least 15.24 cm (6.00 in) of clearance at the front and back of the computer. (This is the
minimum distance for all computer models.)
● Be sure that the ambient air temperature surrounding the computer falls within the specied limits (see
Environmental specications on page 6).
● For cabinet installation, ensure that cabinet ventilation is adequate and that the ambient temperature
within the cabinet does not exceed specied limits.
● Never restrict the incoming or outgoing airow of the computer by blocking any vents or air intakes.
Setting up the computer 7

Setup procedure
WARNING! To reduce the risk of electric shock or damage to your equipment:
● Plug the power cord into an AC outlet that is easily accessible at all times.
● Disconnect power from the computer by unplugging the power cord from the AC outlet (not by
unplugging the power cord from the computer).
● If your power cord has a 3-pin attachment plug, plug the cord into a grounded (earthed) 3-pin outlet. Do
not disable the power cord grounding pin, for example, by attaching a 2-pin adapter. The grounding pin
is an important safety feature.
For more safety and regulatory information, the Regulatory, Safety and Environmental Notices located with
the user guide on your computer.
Mounting the computer
The computer can be attached to a wall, swing arm, or other mounting xture.
NOTE: This apparatus is intended to be supported by UL or CSA Listed wall mount bracket.
1. Pull o the rubber feet on the bottom of the computer to expose the VESA mounting holes.
Store the feet on the underside of the computer top cover.
2. To attach the computer to a swing arm (sold separately), insert four M4 x 10mm screws through the
holes on the swing arm plate and into the mounting holes on the computer.
CAUTION: This computer supports the VESA industry standard 100 mm mounting holes. To attach a
third-party mounting solution to the computer, four M4 x 10mm screws are required. These screws
should be supplied in the third-party mounting solution kit. Longer screws must not be used because
they may damage the computer. It is important to verify that the manufacturer’s mounting solution is
compliant with the VESA standard and is rated to support the weight of the computer. For best
performance, it is important to use the power and other cables provided with the computer.
To attach the computer to other mounting xtures, follow the instructions included with the mounting
xture to ensure that the computer is safely attached.
NOTE: If the computer is to be mounted horizontally, be sure to position the computer so that all cords
and cables will hang straight down from the connectors.
8 Chapter 3 Setting up the computer

Connecting the computer
WARNING! To reduce the risk of electric shock or damage to your equipment, observe these practices:
• Plug the power cord into an AC outlet that is easily accessible.
• Disconnect power from the computer by unplugging the power cord from the AC outlet (not by unplugging
the power cord from the computer).
• Plug the cord into a grounded (earthed) three-pin outlet. Do not disable the power cord grounding pin (for
example, by attaching a two-pin adapter). The grounding pin is an important safety feature.
To set up the computer:
1. Connect the mouse and keyboard to the computer.
2. Connect the monitor to the computer.
3. Connect other peripheral components (such as a printer) according to the instructions included with the
device.
4. Connect a network cable to the computer and to a network router or LAN device.
5. Connect the power cord to the AC adapter (1).
6. Connect the power cord and monitor power cord to an AC outlet (2).
7. Connect the AC adapter to the computer (3).
Connecting Bluetooth devices
The computer is Bluetooth-enabled. To connect a Bluetooth® wireless device:
1. Make your Bluetooth device send out a radio signal so that it is discoverable by the computer (see the
device documentation for instructions).
2. Press the Start button, and then select Settings. Select Devices, and then select Add Bluetooth or other
device.
In the Windows Control Panel, go to Hardware and Sound, and then to Devices and Printers.
● Select Add a network, wireless or Bluetooth printer, and follow the on-screen instructions.
● For all other devices, select Add a device, select Bluetooth devices, and then follow the on-screen
instructions.
Setting up the computer 9

Disabling Bluetooth devices
The Bluetooth features can be disabled through the system BIOS, through the operating system, or by
removing the wireless modules from the system.
NOTE: Disabling the Bluetooth features through the system BIOS or by removing the wireless modules from
the system will also disable the WLAN functionality.
To disable the Bluetooth features using the system BIOS, do the following:
1. During system boot, press F10 to enter the BIOS setup.
2. Locate and select the Advanced menu from the available menu selections displayed near the top of the
screen.
3. Select System Options.
4. Select M.2 WLAN/BT.
5. Use the arrow keys to change Enabled to Disabled, and then press F10 to accept the change.
6. Select File from the header menus, and then select Save Changes and Exit.
To disable the Bluetooth features in Windows 10, do the following:
1. In Control Panel, change View By from Category to either Large Icon or Small Icon.
2. Go to Device Manager.
3. Expand Bluetooth.
4. Double-click Intel® Wireless Bluetooth® to open the properties window.
5. Go to the Driver tab and select Disable Device.
6. Select Yes.
7. To re-enable, select Enable Device.
To remove the wireless modules, see one of the following for information about removal and replacement of
components:
● The Maintenance and Service Guide for your computer: go to http://www.hp.com/support, follow
instructions to nd your product, and select User Guides.
● Videos for your computer at http://www.hp.com/go/sml.
10 Chapter 3 Setting up the computer

Disabling WLAN
NOTE: If the computer is congured with WLAN, WLAN will be enabled by default.
NOTE: Disabling the WLAN functionality through the system BIOS or by removing the wireless modules from
the system will also disable the Bluetooth features.
The WLAN can be disabled through the system BIOS, through the operating system, or by removing the
wireless modules from the system.
To disable the WLAN using the system BIOS, do the following:
1. During system boot, press F10 to enter the BIOS setup.
2. Locate and select the Advanced menu from the available menu selections displayed near the top of the
screen.
3. Select System Options.
4. Select M.2 WLAN/BT.
5. Select Disabled, and then press F10 to accept the change.
6. Select File from the header menus, and then select Save Changes and Exit.
To disable the WLAN in Windows 10, do the following:
1. In Control Panel, change View By from Category to either Large Icon or Small Icon.
2. Go to Device Manager.
3. Expand Network Adapters.
4. Select Intel® Wireless-AC 9560.
5. Go to Driver menu.
6. Select Disable Device.
7. Select Yes.
8. To re-enable, select Enable.
To remove the wireless modules, see one of the following for information about removal and replacement of
components:
● The Maintenance and Service Guide for your computer: go to http://www.hp.com/support, follow
instructions to nd your product, and select User Guides.
● Videos for your computer at http://www.hp.com/go/sml.
Setting up the computer 11

Adding monitors
Planning for additional monitors
Entry model
The entry model supports up to three monitors running simultaneously on the Intel integrated GPU. Each
monitor is capable of resolutions up to 4096 x 2160 @ 60 Hz.
It is also possible to drive a monitor at a resolution of 5120 x 2880 @ 60 Hz by using two of the DisplayPort
1.2 outputs together. The monitor must support this method of achieving this resolution for this to be
possible.
Performance model
The performance model is capable of operating in two distinct modes: Discrete GPU–only mode or Discrete
GPU + Intel GPU mode. The Discrete GPU–only mode oers the best performance, while the Discrete GPU +
Intel GPU mode allows the system to drive an additional two monitors.
Discrete GPU–only mode:
● The default conguration.
● Oers the best performance because every DisplayPort 1.2 port is driven directly by the discrete GPU.
● Capable of driving up to four independent monitors at a maximum resolution of 4096 x 2160 @ 60 Hz.
● It is also possible to drive a monitor at a resolution of 5120 x 2880 @60 Hz by using two of the
DisplayPort 1.2 outputs together. The monitor must support this method of achieving this resolution for
this to be possible.
Discrete GPU + Intel GPU mode:
● The discrete GPU can support a maximum of four independent monitors. To support an additional two
monitors, the system can be congured to simultaneously use both the discrete GPU and the Intel
integrated GPU.
● This mode is congured in the system BIOS.
1. Press the power button on the system, and then repeatedly press the F10 key until you’ve reached
the system BIOS GUI.
2. Navigate to the Advanced tab.
3. Select Built-In Device Options.
4. Select Enable Intel graphics on Flex IO port if an HP DP Flex IO module is installed, otherwise
choose Enable Intel graphics on DisplayPort #1.
5. Press F10 to save your changes and exit.
● This mode is capable of driving up to six independent monitors.
12 Chapter 3 Setting up the computer

● Because the system has three native DisplayPort 1.2 ports, DisplayPort Multi-Stream Transport
● If an HP DP Flex Module is installed, two monitors will be daisy-chained together from the HP DP
● Each DisplayPort 1.2 output on the system can drive a monitor at a resolution of 4096 x 2160 @ 60
● Performance is dependent upon which GPU is running the application. For the best performance of a
particular application, ensure that the application is running on the discrete GPU.
Planning process
The process for adding monitors depends on the type and number of monitors you add.
Use the following process to plan for adding more monitors:
1. Assess your monitor needs.
a. Determine how many monitors you require.
b. Determine the kind of graphics performance you want. For maximum performance, ensure that
(MST) must be used to daisy-chain multiple monitors together to achieve a six-monitor
conguration. This requires monitors that support MST or DisplayPort hubs capable of MST.
Flex Module and two monitors will be daisy-chained together from DisplayPort #3. Intel graphics
will need to be enabled on the Flex IO port. If an HP DP Flex Module is not installed, two monitors
will be daisy-chained together from each native DisplayPort port. Intel graphics will need to be
enabled on DisplayPort #1.
Hz. When two monitors are daisy-chained together from a single DisplayPort 1.2 port, each
monitor in the daisy chain is bandwidth-limited to a maximum resolution of 2560 x 1600 @ 60 Hz.
your monitor is driven by the discrete GPU.
c. Note the type of graphics connector used by each monitor. The computer has DisplayPort (DP)
interfaces, but you can use adapters for other graphics formats, including DVI-I, HDMI, or VGA.
TIP: Some adapters for older legacy hardware may cost more than others. You may want to
compare the cost of acquiring adapters with the cost of getting a newer monitor that doesn't need
adapters.
2. Install drivers and congure resolutions.
a. Be sure that you have the correct drivers for the card. See http://www.hp.com for HP-qualied
drivers.
b. Congure each monitor’s resolution, orientation, and placement through Windows Display
Settings. For details, see Windows Help or go to http://www.microsoft.com.
c. For monitor setup in Linux, you can often use the settings tool for the graphics cards (e.g., NVIDIA
nvidia-settings). In some recent Linux releases, the window manager system (e.g., Gnome 3)
preferences must also be modied.
TIP: To simplify troubleshooting of possible problems, enable the rst monitor and be sure that it
works properly before enabling the next monitor, and so on.
®
Adding monitors 13

Matching graphics card connector to monitor connectors
The following table describes monitor conguration scenarios.
Graphics card interface connector Monitor connector
VGA DVI Dual Link DVI
DISPLAYPORT
DisplayPort–to–
VGA adapter
(sold
separately)
NOTE: DisplayPort connections have the highest performance; VGA connections have the lowest.
Identifying monitor connection requirements
The system has three native DisplayPort 1.2 outputs. You can connect a monitor to each connector. Use the
proper adapters, if required.
Connecting and conguring monitors
1. Connect the monitor cable adapters (if required) to the computer, then connect the appropriate monitor
cables to the adapters or directly to the graphics card.
2. Connect the other ends of the monitor cables to the monitors.
DP–to–DVI
adapter
DP–to–DL DVI
adapter
DisplayPort
(DP)
DP cable
HDMI
DP–to–HDMI
adapter
3. Connect one end of the monitor power cord to the monitor and the other end to an AC outlet.
4. Congure the monitor. For details, see Microsoft Help or go to http://www.microsoft.com.
For monitor setup in Linux, you can often use the settings tool for the graphics cards (e.g., NVIDIA
nvidia-settings or AMDTM Catalyst Control Center). In some recent Linux releases, the window manager
system (e.g., Gnome 3) preferences must also be modied.
14 Chapter 3 Setting up the computer

Customizing the monitor (Windows)
You can manually select or change the monitor model, refresh rates, screen resolution, color settings, font
sizes, and power management settings.
● To change settings, press the Start button, and then select Settings. Select System, and then select
Display.
For more information about customizing your monitor, see the following resources:
● Online documentation provided with the graphics controller utility
● Documentation included with your monitor
Installing optional components
You can install additional components such as memory, hard drives, and wireless modules in your computer.
● To view component installation videos, go to http://www.hp.com/go/sml.
● For installation guidelines and technical information, see the Maintenance and Service Guide. Go to
www.hp.com/support and enter your product name or serial number or select Find your product, and
then follow the on-screen instructions.
Security
You can secure your computer by attaching a lock to the security cable slot. The computer includes several
security features to reduce the risk of theft and to warn of chassis intrusion. See the Maintenance and Service
Guide for information about additional hardware and software security features available for your system.
Product recycling
HP encourages customers to recycle used electronic hardware, HP original print cartridges, and rechargeable
batteries.
For information about recycling HP components or products, go to http://www.hp.com/go/recycle.
Installing optional components 15

4 Backing up, restoring, and recovering
This chapter provides information about the following processes, which are standard procedure for most
products:
● Backing up your personal information—You can use Windows tools to back up your personal
information (see Using Windows tools on page 16).
● Creating a restore point—You can use Windows tools to create a restore point (see Using Windows
tools on page 16).
● Restoring and recovery—Windows oers several options for restoring from backup, refreshing the
computer, and resetting the computer to its original state (see Using Windows tools on page 16).
Using Windows tools
IMPORTANT: Windows is the only option that allows you to back up your personal information. Schedule
regular backups to avoid information loss.
You can use Windows tools to back up personal information and create system restore points and recovery
discs, allowing you to restore from backup, refresh the computer, and reset the computer to its original state.
NOTE: If computer storage is 32 GB or less, Microsoft System Restore is disabled by default.
For more information and steps, see the Get Help app.
▲ Select the Start button, and then select the Get Help app.
NOTE: You must be connected to the Internet to access the Get Help app.
Using the HP Cloud Recovery Download Tool to create recovery discs
To create HP Recovery discs using the HP Cloud Recovery Download Tool:
1. Go to http://www.hp.com/support.
2. Select Software and Drivers, and then follow the on-screen instructions.
Restoring and recovery
Restoring and recovery can be performed using Windows tools.
IMPORTANT: This method may not be available on all products.
Windows oers several options for restoring, resetting, and refreshing the computer. For details, see Using
Windows tools on page 16.
16 Chapter 4 Backing up, restoring, and recovering

5 Setting up Linux
This chapter describes how to set up and restore the Linux operating system.
CAUTION: Do not add optional hardware or third-party devices to the computer until the operating system
is successfully installed. Adding hardware might cause errors and prevent the operating system from
installing correctly.
NOTE: After you set up the operating system, be sure that the latest BIOS, drivers, and software updates are
installed. See Updating the computer on page 20.
NOTE: To create recovery discs, you must have either a high-quality blank USB ash drive or an external
optical drive with DVD writer capability. If you use an optical drive, you must use only high-quality blank DVDR, DVD+R, DVD-R DL, or DVD+R DL discs. A compatible external optical drive may be purchased from HP.
Linux-ready systems
The Linux-ready option provides a system with a minimally functional OS preload (for example, FreeDOS). It is
intended for situations where the customer is going to install an OS when the system arrives. The option does
not include a license for any operating system.
The Linux-ready option does not include the Linux operating system, which the user must supply. Commercial
Linux distributions are available for purchase from vendors such as Red Hat and SUSE. A variety of other Linux
distributions are available for free (e.g., Ubuntu). To view supported congurations and operating systems, go
to http://www.hp.com/support/linux_hardware_matrix.
HP Linux driver discs
Driver ISO images that support proper use and behavior of some Linux OSes on HP computers may be
available on the HP website. Such images include tested drivers that augment and/or replace those found in
RHEL, SLED, Ubuntu, or other OSes. Each image is specic to a particular Linux OS release.
These images also can be downloaded using the following steps:
1. Go to http://www.hp.com/support.
2. Enter your product name or serial number or select Find your product.
3. Select the desired operating system.
4. Select the download link for the appropriate package (typically the most recent revision).
5. Download the software ISO image and burn it to a high-quality blank DVD-R, DVD+R, DVD-R DL, or DVD
+R DL disc using an external optical drive with DVD writer capability. This disc is your HP driver disc.
NOTE: A compatible external optical drive may be purchased from HP.
Setting up Red Hat® Enterprise Linux® (RHEL)
For details of RHEL support for a particular platform, see the Linux Hardware Matrix for HP Workstations at
http://www.hp.com/support/linux_hardware_matrix.
Linux-ready systems 17

For information about Red Hat certications on HP computers, go to https://access.redhat.com/ecosystem,
select Certied Hardware, and then follow the on-screen instructions.
HP driver disc
Recent versions of Red Hat Linux typically require only driver updates with minor xes to support HP
computers. These releases can usually be supported with the appropriate driver USB ash drive or optical disc
from the HP website, which can be used as a post-installation utility for the standard Red Hat Linux install.
For more information, see HP Linux driver discs on page 17.
After you complete the standard Red Hat install and restart the system, a Red Hat rst-boot utility runs. After
you specify a number of settings (such as the security level, time and date, ‘root’ password, and user
accounts), the utility lets you load an additional USB
The driver disc is used during this phase. All content added by HP is in the /HP directory on the disc. You can
use it to build your own image or to browse the HP content.
Please see the /HP directory on the disc for any last-minute README pointers for elements on the disc.
ash drive or optical disc.
Installing with the HP Red Hat Linux driver disc
1. If you do not have the appropriate HP driver disc for a supported stream, create one (see HP Linux driver
discs on page 17).
2. Install the operating system using the disc included in the Red Hat Linux box set.
3. If you have a Red Hat driver USB ash drive or optical disc for the OS version you are installing, type
linux dd when the initial install splash screen appears, and then press Enter.
4. When asked if you have a driver disc, select Yes. Place the Red Hat driver USB ash drive or optical disc in
the drive, and select the appropriate drive:hd[abcd]. Continue the normal installation.
5. After successfully installing the operating system, reboot the computer.
For RHEL 6 or RHEL 7, insert your HP driver USB ash drive or optical disc. The driver installation
software automatically starts. Follow the on-screen instructions to install the contents.
Setting up SUSE Linux Enterprise Desktop (SLED)
Various versions of SLED are certied and supported by SUSE on HP computers. For more information, go to
the SUSE certication bulletin search page at https://www.suse.com/yessearch/Search.jsp.
Installing SLED with the HP driver disc
1. If an HP driver disc did not come with your computer, create one (see HP Linux driver discs on page 17).
2. Install the operating system using the discs included in the SUSE box set.
3. After successfully installing the operating system, reboot the computer.
4. Insert your HP driver disc. The driver installation software automatically starts. Follow the on-screen
instructions to install the contents.
Setting up Ubuntu
Various versions of Ubuntu are certied and supported by Canonical on HP computers. For more information,
go to the Ubuntu Desktop certied hardware search page at http://www.ubuntu.com/certication/desktop
and search for your computer product. Ubuntu is available at no cost from http://www.ubuntu.com.
18 Chapter 5 Setting up Linux

Using the HP driver disc
Ubuntu does not require registration to obtain software package updates. Updates can be obtained from
various repositories on the Web using a variety of tools built into the OS. An Internet connection and proxy
may be all that are required.
The HP-provided Linux driver disc for Ubuntu relies on the same mechanisms in order to satisfy dependencies
during installation. So the same Internet access is needed, as well as capability to elevate from the current
user session to administrator privileges.
In some cases, HP-tested proprietary graphics drivers may be the only “payload” delivered by the driver disc.
1. Install the operating system from your own installation disc.
2. Restart the computer.
3. Insert your HP driver disc. The driver installation software automatically starts.
4. When prompted for the administrator password, type the password in the eld.
5. Follow the on-screen instructions to install the drivers appropriate to your hardware conguration.
Proprietary graphics drivers
Most HP computers can be ordered with graphics cards that have been through extensive verication by HP.
For a list of supported cards, see Linux Hardware Matrix for HP Workstations at http://www.hp.com/support/
linux_hardware_matrix.
NOTE: Not all graphics cards are supported on every computer. Limitations generally occur for cards that
consume large amounts of power in lower-power computers.
Third-party proprietary graphics drivers are supported by HP. The list of graphics vendors is available with
the SLED 11 and Ubuntu preloads and from HP support. Go to www.hp.com/support and enter your product
name or serial number or select Find your product, and then follow the on-screen instructions.
These proprietary drivers are not a standard part of the RHEL, SLED, or Ubuntu distributions because they are
not open source. Driver revisions more recent than those at the HP support website are supported directly by
the vendor.
Proprietary graphics drivers 19

6 Updating the computer
HP is constantly working to improve your total computer experience. To ensure that the computer leverages
the latest enhancements, HP recommends that you install the latest BIOS, driver, and software updates on a
regular basis.
Updating the computer after rst boot
After successfully booting the computer for the rst time, follow these guidelines to be sure that the
computer is up to date:
● Be sure that you have the latest system BIOS version loaded. See Updating the BIOS on page 20.
● Be sure that you have the latest drivers for your system. See Upgrading device drivers on page 21.
● Become familiar with your available HP resources. See HP Support on page 24.
● Consider a subscription to Driver Alerts at https://h41369.www4.hp.com/alerts-signup.php.
Updating the BIOS
For optimum performance, determine the BIOS version on the computer, and upgrade it if necessary.
Determining the current BIOS version
1. Press Esc during startup (boot).
2. Press F10 to enter Computer Setup (F10).
3. Select Main, and then select System Information. Note the Computer System BIOS version.
NOTE: For procedures for upgrading the BIOS as well as the Computer Setup (F10) BIOS Menu settings, see
the Maintenance and Service Guide at http://www.hp.com/support. Enter your product name or serial number
or select Find your product, and then follow the on-screen instructions.
Upgrading BIOS
To nd and download the latest available BIOS version, which includes the latest enhancements:
1. Go to http://www.hp.com/support and select your product.
2. Select Software and Drivers and follow the instructions to locate the latest BIOS version available for
the computer.
3. Compare the BIOS version on your computer to the BIOS versions on the website (see Determining the
current BIOS version on page 20). If the BIOS version on the website is the same as the version on your
system, no further action is required.
4. If the BIOS version on the website is a version later than the one on your system, download the
appropriate version for the computer. Follow the instructions in the release notes to complete the
installation.
20 Chapter 6 Updating the computer

Upgrading device drivers
If you install a peripheral device (such as a printer, display adapter, or network adapter), conrm that you have
the latest device drivers loaded. If you purchased your device through HP, go to the HP website to download
the latest drivers for your device. These drivers have been tested to ensure the best compatibility between
your device and your HP computer.
If you did not purchase your device from HP, HP recommends that you go to the HP website rst to see if your
device and its drivers have been tested for HP computer compatibility. If no driver is available, go to the
device manufacturer's website to download the latest drivers.
To upgrade device drivers:
1. Go to http://www.hp.com/support and select your product.
2. Follow the instructions to nd the latest drivers available for the computer.
If a required driver is not found, see the website of the manufacturer of the peripheral device.
Upgrading device drivers 21

7 Maintenance, diagnostics, and minor
troubleshooting
Turning o the computer
To properly turn o the computer, shut down the operating system software.
CAUTION: HP does not recommend holding down the power button to shut o the system. Doing so can
cause loss of user data and may damage the storage device. If the system becomes unstable and no other
alternative is available, please give the system suicient time to wake up completely after you reboot the
computer. This may take several minutes, especially on larger-capacity or solid-state devices.
▲ Click the Start icon, click the Power icon, and then select Shut down.
If you encounter issues
To diagnose and resolve issues, HP recommends a sequential troubleshooting approach:
● Visual inspection
● Blink or beep codes
● Basic troubleshooting, including HP PC Hardware Diagnostics
● HP support
● System restore and recovery
For more information, see HP Support on page 24.
These troubleshooting strategies are explained in the following sections.
For more information
You can nd more troubleshooting information in the comprehensive Maintenance and Service Guide (English
only) available at http://www.hp.com/support.
Visual inspection
If you encounter a problem with the computer, monitor, or software, the following general suggestions might
help you isolate and focus on the problem before taking further action.
At startup
● Verify that the computer is plugged into a functional AC outlet.
● Remove all optical discs and USB ash drives before starting the computer.
● Verify that the computer is on and the power light is on.
● If you have installed an operating system other than the factory-installed operating system, conrm
that it is supported on your system by going to http://www.hp.com/go/quickspecs.
22 Chapter 7 Maintenance, diagnostics, and minor troubleshooting

● Verify that the monitor is lit.
● If you have an optional external monitor:
– Verify that the monitor is plugged into a functional AC outlet.
– Verify that the monitor is on and the green monitor light is on.
– If the monitor is dim, turn up the brightness and contrast controls.
During operation
●
Beeps and blinking lights on the computer are error codes that can help you diagnose problems. For
more information about interpreting these codes, see the Diagnostic LED and audible (beep) codes
section in the Maintenance and Service Guide for your computer.
● Press and hold any key. If the system beeps, your keyboard is operating correctly.
● Check all cables for loose or incorrect connections.
● Start the computer by pressing the power button or any key on the keyboard. If the system remains in
standby, shut down the system by pressing and holding the power button for at least four seconds. Then
press the power button again to restart the system.
If the system does not shut down, unplug the power cord, wait a few seconds, and then plug it in again.
If the system does not restart, press the power button.
● Be sure that all required device drivers have been installed. For example, if you have connected a printer,
you must install a printer driver.
● If you are working on a network, use another cable to plug your computer into the network connection.
If you still cannot connect, there might be a problem with the network plug.
● If you recently added new hardware, remove the hardware to see whether the computer functions
properly.
● If you recently installed new software, uninstall the software to see whether the computer functions
properly.
● If the monitor head on an all-in-one computer is blank, open the computer and be sure that both ends of
the cable between the system board and the monitor head are connected. If you are using a graphics
card, verify that the card is properly installed.
● Upgrade the BIOS. A new release of the BIOS might have been released that supports new features or
xes your problem.
● For more detailed information, see the troubleshooting chapter in the Maintenance and Service Guide at
http://www.hp.com/support.
Customer Self Repair
Under the Customer Self Repair program, you can order a replacement part and install the part without onsite HP technical assistance. Customer Self Repair might be required for some components. For more
information, go to http://www.hp.com/go/selfrepair and select your product.
NOTE: Some components are not eligible for Customer Self Repair and must be returned to HP for service.
Call support for further instructions before attempting to remove or repair these components.
If you encounter issues 23

Blink or beep codes: interpreting POST diagnostic LEDs and audible codes
If the power LED on the computer is ashing or if you hear beeps, see the Maintenance and Service Guide
(English only) for interpretation and recommended action.
Basic troubleshooting
WARNING! When the computer is plugged into an AC power source, voltage is always applied to the system
board. To reduce the risk of personal injury from electrical shock and/or hot surfaces, be sure to disconnect
the power cord from the wall outlet and allow the internal system components to cool before you touch them.
If you are having problems with the computer, try the appropriate solutions as described in the previous
sections and summarized below to try to isolate the exact problem before calling for technical support.
● If the screen is blank, plug the monitor into a dierent video port on the computer if one is available. Or,
replace the monitor with a monitor that you know is functioning properly.
● If you are working on a network:
– Use a dierent network cable to connect your computer to the network.
– Connect a dierent computer with a dierent cable to the network.
If your problem is not resolved, the network jack on your computer or the network wall jack might be
faulty.
● If you recently added new hardware, remove the hardware.
● If you recently installed new software, uninstall the software.
● If the computer will turn on but will not boot into the operating system, run the preboot diagnostics
HP Support
Online support resources include the following:
● Web-based troubleshooting tools
● Technical knowledge databases
● Driver and patch downloads
● Online communities
● Documentation
● Software and drivers
● Product change notication services
● Advisories
● Bulletins and Notices
Go to www.hp.com/support and enter your product name or serial number or select Find your product, and
then follow the on-screen instructions.
utility, HP PC Hardware Diagnostics. See Using HP PC Hardware Diagnostics on page 26.
Calling Support
At times you might encounter an issue that requires support. Before you call support:
24 Chapter 7 Maintenance, diagnostics, and minor troubleshooting

● Have the computer readily accessible.
● Write down the computer serial number, product number, model name, and model number and have
them in front of you. This information is provided on labels. This information might be on the bottom of
the computer, on the rear panel of the computer, or under the service door.
● Note any applicable error messages.
● Note any add-on options.
● Note the operating system.
●
Note any third-party hardware or software.
● Note the details of any blinking lights on the front of the computer (tower and desktop congurations)
or on the side of the computer (all-in-one congurations).
● Note the applications you were using when you encountered the problem.
NOTE: When calling in for service or support, you might be asked for the product number (example:
PS988AV) of the computer. If the computer has a product number, it is generally located next to the 10- or 12digit serial number of the computer.
NOTE: The serial number and product number labels can be found on the rear panel of the computer.
For a support phone number, go to http://www.hp.com/support, select your region, and then, under
Customer Support, select Contact Support.
Locating warranty information
To locate warranty information, refer to the warranty that came with your product, either printed or on the
image. HP Care Pack Services oer upgraded service levels to extend and expand a standard product
warranty.
NOTE: For sales information and warranty upgrades (HP Care Packs), call your local authorized service
provider or dealer.
If you encounter issues 25

8 Using HP PC Hardware Diagnostics
Using HP PC Hardware Diagnostics Windows
HP PC Hardware Diagnostics Windows is a Windows-based utility that allows you to run diagnostic tests to
determine whether the computer hardware is functioning properly. The tool runs within the Windows
operating system in order to diagnose hardware failures.
If HP PC Hardware Diagnostics Windows is not installed on your computer, rst you must download and install
it. To download HP PC Hardware Diagnostics Windows, see Downloading HP PC Hardware Diagnostics
Windows on page 26.
After HP PC Hardware Diagnostics Windows is installed, follow these steps to access it from HP Help and
Support.
1. To access HP PC Hardware Diagnostics Windows from HP Help and Support:
a. Select the Start button, and then select HP Help and Support.
b. Right-click HP PC Hardware Diagnostics Windows, select More, and then select Run as
administrator.
2. When the tool opens, select the type of diagnostic test you want to run, and then follow the on-screen
instructions.
NOTE: If you need to stop a diagnostic test at any time, select Cancel.
3. When HP PC Hardware Diagnostics Windows detects a failure that requires hardware replacement, a 24-
digit Failure ID code is generated. For assistance in correcting the problem, contact support, and then
provide the Failure ID code.
Downloading HP PC Hardware Diagnostics Windows
● The HP PC Hardware Diagnostics Windows download instructions are provided in English only.
● You must use a Windows computer to download this tool because only .exe les are provided.
Downloading the latest HP PC Hardware Diagnostics Windows version
To download HP PC Hardware Diagnostics Windows, follow these steps:
1. Go to http://www.hp.com/go/techcenter/pcdiags. The HP PC Diagnostics home page is displayed.
2. In the HP PC Hardware Diagnostics section, select Download, and then select the installation location:
To run the tool on your computer, download it to the computer desktop.
– or –
To run the tool from a USB ash drive, download it to a USB ash drive.
3. Select Run.
26 Chapter 8 Using HP PC Hardware Diagnostics

Downloading HP Hardware Diagnostics Windows by product name or number (select products only)
NOTE: For some products, it may be necessary to download the software to a USB ash drive by using the
product name or number.
To download HP PC Hardware Diagnostics Windows by product name or number (select products only), follow
these steps:
1. Go to http://www.hp.com/support.
2. Select Get software and drivers, and then enter the product name or number.
3. In the HP PC Hardware Diagnostics section, select Download, and then select the installation location:
To run the tool on your computer, download it to the computer desktop.
– or –
To run the tool from a USB ash drive, download it to a USB ash drive.
4. Select Run.
Installing HP PC Hardware Diagnostics Windows
▲ To install HP PC Hardware Diagnostics Windows, navigate to the folder on your computer or the USB
ash drive where the .exe le was downloaded, double-click the .exe le, and then follow the on-screen
instructions.
Using HP PC Hardware Diagnostics UEFI
HP PC Hardware Diagnostics UEFI (Unied Extensible Firmware Interface) allows you to run diagnostic tests to
determine whether the computer hardware is functioning properly. The tool runs outside the operating
system so that it can isolate hardware failures from issues that are caused by the operating system or other
software components.
If your PC will not boot into Windows, you can use HP PC Hardware Diagnostics UEFI to diagnose hardware
issues.
When HP PC Hardware Diagnostics UEFI detects a failure that requires hardware replacement, a 24-digit
Failure ID code is generated. For assistance in correcting the problem, contact support, and provide the Failure
ID code.
NOTE: To start diagnostics on a convertible computer, your computer must be in notebook mode, and you
must use the attached keyboard.
NOTE: If you need to stop a diagnostic test, press esc.
Starting HP PC Hardware Diagnostics UEFI
To start HP PC Hardware Diagnostics UEFI, follow these steps:
1. Turn on or restart the computer, and quickly press esc.
2. Press f2.
The BIOS searches three places for the diagnostic tools, in the following order:
a. Connected USB ash drive
Using HP PC Hardware Diagnostics UEFI 27

NOTE: To download the HP PC Hardware Diagnostics UEFI tool to a USB ash drive, see
Downloading HP Hardware Diagnostics Windows by product name or number (select products only)
on page 27.
b. Hard drive
c. BIOS
3. When the diagnostic tool opens, select the type of diagnostic test you want to run, and then follow the
on-screen instructions.
Downloading HP PC Hardware Diagnostics UEFI to a USB ash drive
Downloading HP PC Hardware Diagnostics UEFI to a USB ash drive can be useful in the following situations:
● HP PC Hardware Diagnostics UEFI is not included in the preinstall image.
● HP PC Hardware Diagnostics UEFI is not included in the HP Tool partition.
● The hard drive is damaged.
NOTE: The HP PC Hardware Diagnostics UEFI download instructions are provided in English only, and you
must use a Windows computer to download and create the HP UEFI support environment because only .exe
les are provided.
Downloading the latest HP PC Hardware Diagnostics (UEFI) version
To download the latest HP PC Hardware Diagnostics (UEFI) version to a USB ash drive:
1. Go to http://www.hp.com/go/techcenter/pcdiags. The HP PC Diagnostics home page is displayed.
2. Select Download HP Diagnostics UEFI, and then select Run.
Downloading HP PC Hardware Diagnostics (UEFI) by product name or number (select products only)
NOTE: For some products, it may be necessary to download the software to a USB ash drive by using the
product name or number.
To download HP PC Hardware Diagnostics (UEFI) by product name or number (select products only) to a USB
ash drive:
1. Go to http://www.hp.com/support.
2. Enter the product name or number, select your computer, and then select your operating system.
3. In the Diagnostics section, follow the on-screen instructions to select and download the specic UEFI
Diagnostics version for your computer.
Using HP Remote PC Hardware Diagnostics UEFI settings (select products only)
HP Remote PC Hardware Diagnostics UEFI is a rmware (BIOS) feature that downloads HP PC Hardware
Diagnostics UEFI to your computer. It can then execute the diagnostics on your computer, and it may upload
results to a precongured server. For more information about HP Remote PC Hardware Diagnostics UEFI, go
to http://www.hp.com/go/techcenter/pcdiags, and then select Find out more under Remote Diagnostics.
28 Chapter 8 Using HP PC Hardware Diagnostics

Downloading HP Remote PC Hardware Diagnostics UEFI
NOTE: HP Remote PC Hardware Diagnostics UEFI is also available as a Softpaq that can be downloaded to a
server.
Downloading the latest HP Remote PC Hardware Diagnostics UEFI version
To download the latest HP Remote PC Hardware Diagnostics UEFI version, follow these steps:
1. Go to http://www.hp.com/go/techcenter/pcdiags. The HP PC Diagnostics home page is displayed.
2. In the Remote Diagnostics section, select Remote Diagnostics, and then select Run.
Downloading Remote HP PC Hardware Diagnostics UEFI by product name or number
NOTE: For some products, it may be necessary to download the software by using the product name or
number.
To download HP Remote PC Hardware Diagnostics UEFI by product name or number, follow these steps:
1. Go to http://www.hp.com/support.
2. Select Get software and drivers, enter the product name or number, select your computer, and then
select your operating system.
3. In the Diagnostics section, follow the on-screen instructions to select and download the Remote UEFI
version for the product.
Customizing HP Remote PC Hardware Diagnostics UEFI settings
Using the HP Remote PC Hardware Diagnostics setting in Computer Setup (BIOS), you can perform the
following customizations:
● Set a schedule for running diagnostics unattended. You can also start diagnostics immediately in
interactive mode by selecting Execute Remote HP PC Hardware Diagnostics.
● Set the location for downloading the diagnostic tools. This feature provides access to the tools from the
HP website or from a server that has been precongured for use. Your computer does not require the
traditional local storage (such as a hard drive or USB ash drive) to run remote diagnostics.
● Set a location for storing the test results. You can also set the user name and password settings used for
uploads.
● Display status information about the diagnostics run previously.
To customize HP Remote PC Hardware Diagnostics UEFI settings, follow these steps:
1. Turn on or restart the computer, and when the HP logo appears, press f10 to enter Computer Setup.
2. Select Advanced, and then select Settings.
3. Make your customization selections.
4. Select Main, and then Save Changes and Exit to save your settings.
Your changes take eect when the computer restarts.
Using HP Remote PC Hardware Diagnostics UEFI settings (select products only) 29

9 Routine care
General cleaning safety precautions
● Never use solvents or ammable solutions to clean the computer.
● Never immerse any component in water or cleaning solutions; apply any liquids to a clean cloth and then
use the cloth on the component.
● Always unplug the computer before cleaning the keyboard, mouse, or air vents.
● Always disconnect the keyboard before cleaning it.
● Wear safety glasses equipped with side shields when cleaning the keyboard.
Cleaning the chassis
● Follow the safety precautions in the Maintenance and Service Guide for your computer before cleaning
the computer.
● To remove light stains or dirt, use plain water with a clean, lint-free cloth or swab.
● For stronger stains, use a mild dishwashing liquid diluted with water. Rinse well by wiping the computer
with a cloth or swab dampened with clear water.
● For stubborn stains, use isopropyl (rubbing) alcohol. No rinsing is required because the alcohol
evaporates quickly and does not leave a residue.
● After cleaning, always wipe the computer with a clean, lint-free cloth.
● Occasionally, clean the air vents on the computer. Lint and other foreign matter can block the vents and
limit the airow.
Cleaning the keyboard
CAUTION: Use safety glasses equipped with side shields before attempting to clean debris from under the
keys.
● If the keyboard has an on/o switch, turn it o.
● Follow the safety precautions in the Maintenance and Service Guide for your computer before cleaning
the computer.
● Visible debris underneath or between the keys can be removed by vacuuming or shaking.
● Canned, pressurized air can be used to clean debris from under the keys. Use caution because too much
air pressure can dislodge lubricants applied under the wide keys.
● To remove a key, use a specially designed key remover to prevent damage to the keys. This tool is
available from many electronics supply outlets.
CAUTION: Never remove a wide key (like the space bar key) from the keyboard. If these keys are
improperly removed or installed, the keyboard might not function properly.
30 Chapter 9 Routine care

● Clean under a key with a swab moistened with isopropyl alcohol and squeezed out. Be careful not to
wipe away lubricants necessary for proper key functions. Allow the parts to air dry before reassembly.
● Use tweezers to remove any bers or dirt in conned areas.
Cleaning the monitor
● Follow the safety precautions in the Maintenance and Service Guide for your computer before cleaning
the monitor.
● To clean the monitor, wipe the monitor screen with a towelette designed for cleaning monitors or a clean
cloth moistened with water.
CAUTION: Do not use sprays or aerosols directly on the screen—the liquid might seep into the housing
and damage a component.
Never use solvents or ammable liquids on the monitor because display or housing damage may result.
Cleaning the mouse
1. Follow the safety precautions in the Maintenance and Service Guide for your computer before cleaning
the mouse.
2. If the mouse has an on/o switch, turn it o.
3. Wipe the body of the mouse with a damp cloth.
4. Clean the following components as directed:
● Laser or LED—Use a cotton swab dampened with cleaning solution to gently brush out any dust
around the laser or LED, and then wipe again with a dry swab. Do not wipe the laser or LED directly
with the swab.
● Scroll wheel—Spray canned, pressurized air into the gap between the scroll wheel and the click
buttons. Do not blow air directly on one spot for very long or condensation can form.
● Roller ball—Remove and clean the roller ball, remove any debris from the ball socket, wipe out the
socket with a dry cloth, and reassemble the mouse.
Cleaning the monitor 31

10 Accessibility
Accessibility
HP is working to weave diversity, inclusion and work/life into the fabric of our company, so it is reected in
everything we do. Here are some examples of how we are putting dierences to work to create an inclusive
environment focused on connecting people to the power of technology throughout the world.
Finding the technology tools you need
Technology can unleash your human potential. Assistive technology removes barriers and helps you create
independence at home, at work, and in the community. Assistive technology helps increase, maintain, and
improve the functional capabilities of electronic and information technology. For more information, see
Finding the best assistive technology on page 33.
Our commitment
HP is committed to providing products and services that are accessible for people with disabilities. This
commitment supports our company's diversity objectives and helps us ensure that the benets of technology
are available to all.
Our accessibility goal is to design, produce, and market products and services that can be eectively used by
everyone, including people with disabilities, either on a stand-alone basis or with appropriate assistive
devices.
To achieve our goal, this Accessibility Policy establishes seven key objectives to guide our actions as a
company. All HP managers and employees are expected to support these objectives and their implementation
in accordance with their roles and responsibilities:
● Raise the level of awareness of accessibility issues within our company, and provide our employees with
the training they need to design, produce, market, and deliver accessible products and services.
● Develop accessibility guidelines for products and services, and hold product development groups
accountable for implementing these guidelines where competitively, technically, and economically
feasible.
● Involve people with disabilities in the development of accessibility guidelines, and in the design and
testing of products and services.
● Document accessibility features and make information about our products and services publicly
available in an accessible form.
● Establish relationships with leading assistive technology and solution providers.
● Support internal and external research and development that will improve assistive technology relevant
to our products and services.
● Support and contribute to industry standards and guidelines for accessibility.
International Association of Accessibility Professionals (IAAP)
IAAP is a not-for-prot association focused on advancing the accessibility profession through networking,
education, and certication. The objective is to help accessibility professionals develop and advance their
careers and to better enable organizations to integrate accessibility into their products and infrastructure.
32 Chapter 10 Accessibility

HP is a founding member, and we joined to participate with other organizations to advance the eld of
accessibility. This commitment supports our company’s accessibility goal of designing, producing, and
marketing products and services that can be eectively used by people with disabilities.
IAAP will make our profession strong by globally connecting individuals, students, and organizations to learn
from one another. If you are interested in learning more, go to http://www.accessibilityassociation.org to join
the online community, sign up for newsletters, and learn about membership options.
Finding the best assistive technology
Everyone, including people with disabilities or age-related limitations, should be able to communicate,
express themselves, and connect with the world using technology. HP is committed to increasing accessibility
awareness within HP and with our customers and partners. Whether it’s large fonts that are easy on the eyes,
voice recognition that lets you give your hands a rest, or any other assistive technology to help with your
specic situation—a variety of assistive technologies make HP products easier to use. How do you choose?
Assessing your needs
Technology can unleash your potential. Assistive technology removes barriers and helps you create
independence at home, at work, and in the community. Assistive technology (AT) helps increase, maintain,
and improve the functional capabilities of electronic and information technology.
You may choose from many AT products. Your AT assessment should allow you to evaluate several products,
answer your questions, and facilitate your selection of the best solution for your situation. You will nd that
professionals qualied to do AT assessments come from many elds, including those licensed or certied in
physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech/language pathology, and other areas of expertise. Others,
while not certied or licensed, may also provide evaluation information. You will want to ask about the
individual's experience, expertise, and fees to determine if they are appropriate for your needs.
Accessibility for HP products
The following links provide information on accessibility features and assistive technology, if applicable,
included in various HP products. These resources will help you select the specic assistive technology
features and product(s) most appropriate for your situation.
● HP Elite x3–Accessibility Options (Windows 10 Mobile)
● HP PCs–Windows 7 Accessibility Options
● HP PCs–Windows 8 Accessibility Options
● HP PC’s–Windows 10 Accessibility Options
● HP Slate 7 Tablets–Enabling Accessibility Features on Your HP Tablet (Android 4.1/Jelly Bean)
● HP SlateBook PCs–Enabling Accessibility Features (Android 4.3, 4.2/Jelly Bean)
● HP Chromebook PCs–Enabling Accessibility Features on Your HP Chromebook or Chromebox (Chrome
OS)
● HP Shopping–peripherals for HP products
If you need additional support with the accessibility features on your HP product, see Contacting support
on page 38.
Additional links to external partners and suppliers that may provide additional assistance:
● Microsoft Accessibility information (Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Microsoft Oice)
● Google Products accessibility information (Android, Chrome, Google Apps)
Accessibility 33

● Assistive Technologies sorted by impairment type
● Assistive Technologies sorted by product type
● Assistive Technology vendors with product descriptions
● Assistive Technology Industry Association (ATIA)
Standards and legislation
Standards
Section 508 of the Federal Acquisition Regulation (FAR) standards was created by the US Access Board to
address access to information and communication technology (ICT) for people with physical, sensory, or
cognitive disabilities. The standards contain technical criteria specic to various types of technologies, as well
as performance-based requirements which focus on functional capabilities of covered products. Specic
criteria cover software applications and operating systems, web-based information and applications,
computers, telecommunications products, video and multi-media, and self-contained closed products.
Mandate 376 – EN 301 549
The EN 301 549 standard was created by the European Union within Mandate 376 as the basis for an online
toolkit for public procurement of ICT products. The standard
requirements applicable to ICT products and services, together with a description of the test procedures and
evaluation methodology for each accessibility requirement.
species the functional accessibility
Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG)
Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) from the W3C's Web Accessibility Initiative (WAI) helps web
designers and developers create sites that better meet the needs of people with disabilities or age-related
limitations. WCAG advances accessibility across the full range of web content (text, images, audio, and video)
and web applications. WCAG can be precisely tested, is easy to understand and use, and allows web
developers exibility for innovation. WCAG 2.0 has also been approved as ISO/IEC 40500:2012.
WCAG specically addresses barriers to accessing the web experienced by people with visual, auditory,
physical, cognitive, and neurological disabilities, and by older web users with accessibility needs. WCAG 2.0
provides characteristics of accessible content:
● Perceivable (for instance, by addressing text alternatives for images, captions for audio, adaptability of
presentation, and color contrast)
● Operable (by addressing keyboard access, color contrast, timing of input, seizure avoidance, and
navigability)
● Understandable (by addressing readability, predictability, and input assistance)
● Robust (for instance, by addressing compatibility with assistive technologies)
Legislation and regulations
Accessibility of IT and information has become an area of increasing legislative importance. This section
provides links to information on key legislation, regulations, and standards.
● United States
● Canada
● Europe
34 Chapter 10 Accessibility

● United Kingdom
● Australia
● Worldwide
United States
Section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act species that agencies must identify which standards apply to the
procurement of ICT, perform market research to determine the availability of accessible products and
services, and document the results of their market research. The following resources provide assistance in
meeting Section 508 requirements:
● www.section508.gov
● Buy Accessible
The U.S. Access Board is currently updating the Section 508 standards. This eort will address new
technologies and other areas where the standards need to be modied. For more information, go to Section
508 Refresh.
Section 255 of the Telecommunications Act requires telecommunications products and services to be
accessible to people with disabilities. FCC rules cover all hardware and software telephone network
equipment and telecommunications equipment used in the home or oice. Such equipment includes
telephones, wireless handsets, fax machines, answering machines, and pagers. FCC rules also cover basic and
special telecommunications services, including regular telephone calls, call waiting, speed dialing, call
forwarding, computer-provided directory assistance, call monitoring, caller identication, call tracing, and
repeat dialing, as well as voice mail and interactive voice response systems that provide callers with menus of
choices. For more information, go to Federal Communication Commission Section 255 information.
21st Century Communications and Video Accessibility Act (CVAA)
The CVAA updates federal communications law to increase the access of persons with disabilities to modern
communications, updating accessibility laws enacted in the 1980s and 1990s to include new digital,
broadband, and mobile innovations. Regulations are enforced by the FCC and documented as 47 CFR Part 14
and Part 79.
● FCC Guide on the CVAA
Other U.S. legislation and initiatives
● Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), Telecommunications Act, the Rehabilitation Act and others
Canada
The Accessibility for Ontarians with Disabilities Act was established to develop and implement accessibility
standards to make goods, services, and facilities accessible to Ontarians with disabilities and to provide for
the involvement of persons with disabilities in the development of the accessibility standards. The rst
standard of the AODA is the customer service standard; however, standards for transportation, employment,
and information and communication are also being developed. The AODA applies to the Government of
Ontario, the Legislative Assembly, every designated public sector organization, and to every other person or
organization that provides goods, services, or facilities to the public or other third parties and that has at
least one employee in Ontario; and accessibility measures must be implemented on or before January 1,
2025. For more information, go to Accessibility for Ontarians with Disability Act (AODA) .
Standards and legislation 35

Europe
EU Mandate 376 ETSI Technical Report ETSI DTR 102 612: "Human Factors (HF); European accessibility
requirements for public procurement of products and services in the ICT domain (European Commission
Mandate M 376, Phase 1)" has been released.
Background: The three European Standardization Organizations have set up two parallel project teams to
carry out the work specied in the European Commission "Mandate 376 to CEN, CENELEC and ETSI, in Support
of Accessibility Requirements for Public Procurement of Products and Services in the ICT Domain."
ETSI TC Human Factors Specialist Task Force 333 has developed ETSI DTR 102 612. Further details about the
work performed by STF333 (e.g., Terms of Reference,
the work, previous drafts, listing of comments received and means to contact the task force) can be found at
the Special Task Force 333.
The parts relating to the assessment of suitable testing and conformity schemes were carried out by a
parallel project, detailed in CEN BT/WG185/PT. For further information, go to the CEN project team website.
The two projects are closely coordinated.
● CEN project team
● European Commission mandate for e-accessibility (PDF 46KB)
● Commission takes low prole on e-accessibility
United Kingdom
The Disability Discrimination Act of 1995 (DDA) was enacted to ensure that websites are accessible to blind
and disabled users in the United Kingdom.
specication of the detailed work tasks, time plan for
● W3C UK Policies
Australia
The Australian government has announced their plan to implement Web Content Accessibility Guidelines 2.0.
All Australian government websites will require Level A compliance by 2012, and Double A by 2015. The new
standard replaces WCAG 1.0, which was introduced as a mandated requirement for agencies in 2000.
Worldwide
● JTC1 Special Working Group on Accessibility (SWG-A)
● G3ict: The Global Initiative for Inclusive ICT
● Italian accessibility legislation
● W3C Web Accessibility Initiative (WAI)
36 Chapter 10 Accessibility

Useful accessibility resources and links
The following organizations may be good resources for information about disabilities and age-related
limitations.
NOTE: This is not an exhaustive list. These organizations are provided for informational purposes only. HP
assumes no responsibility for information or contacts you may encounter on the Internet. Listing on this page
does not imply endorsement by HP.
Organizations
● American Association of People with Disabilities (AAPD)
● The Association of Assistive Technology Act Programs (ATAP)
● Hearing Loss Association of America (HLAA)
● Information Technology Technical Assistance and Training Center (ITTATC)
● Lighthouse International
● National Association of the Deaf
● National Federation of the Blind
● Rehabilitation Engineering & Assistive Technology Society of North America (RESNA)
● Telecommunications for the Deaf and Hard of Hearing, Inc. (TDI)
● W3C Web Accessibility Initiative (WAI)
Educational institutions
● California State University, Northridge, Center on Disabilities (CSUN)
● University of Wisconsin - Madison, Trace Center
● University of Minnesota computer accommodations program
Other disability resources
● ADA (Americans with Disabilities Act) Technical Assistance Program
● Business & Disability network
● EnableMart
● European Disability Forum
● Job Accommodation Network
● Microsoft Enable
● U.S. Department of Justice - A Guide to disability rights Laws
HP links
Our contact webform
HP comfort and safety guide
HP public sector sales
Useful accessibility resources and links 37

Contacting support
NOTE: Support is in English only.
● Customers who are deaf or hard of hearing that have questions about technical support or accessibility
of HP products:
– Use TRS/VRS/WebCapTel to call (877) 656-7058 Monday through Friday, 6 a.m. to 9 p.m. Mountain
Time.
● Customers with other disabilities or age-related limitations who have questions about technical support
or accessibility of HP products, choose one of the following options:
– Call (888) 259-5707 Monday through Friday, 6 a.m. to 9 p.m. Mountain Time.
– Complete the Contact form for people with disabilities or age-related limitations.
38 Chapter 10 Accessibility

Index
A
accessibility 32
accessibility needs assessment 33
assistive technology (AT)
nding 33
purpose 32
AT (assistive technology)
nding 33
purpose 32
B
backing up 16
blink or beep codes 24
Bluetooth devices
connecting 9
disabling 10
C
cable lock 15
care, routine 30
computer components 4
front 4
left side 4
rear 5
computer features 4
computer setup 7
security 15
computer, updating 20
conguring monitors 14
connecting
Bluetooth devices 9
power 9
connecting monitors 14
connection requirements, monitors
14
Customer Self Repair 23
customer support, accessibility 38
D
diagnostics 2
disabling Bluetooth devices 10
documentation 2
G
graphics cards
matching to monitor
connectors 14
H
HP Assistive Policy 32
HP driver disc
RHEL setup 18
SLED setup 18
Ubuntu setup 19
HP PC Hardware Diagnostics UEFI
downloading 28
starting 27
using 27
HP PC Hardware Diagnostics Windows
downloading 26
installing 27
using 26
HP resources 1
I
International Association of
Accessibility Professionals 32
L
links
HP Customer Self Repair 23
HP.com 13
Linux Hardware Matrix for HP
computers 17
Red Hat Certication 18
Software & driver downloads 17
SUSE certication bulletin search
page 18
Ubuntu 18
Linux
HP Linux driver discs 17
proprietary graphics drivers 19
RHEL 17
setup 17
solutions 17
Linux-ready systems
creating a disc 17
Linux versions 17
M
monitors
adding 12
conguring 14
connecting 14
customizing the monitor 15
identifying connection
requirements 14
matching graphics cards to
connectors 14
monitor setup 15
planning for additional 12
planning for entry model 12
planning for performance
model 12
planning process 13
setup 12
mounting the computer 8
O
optional components 15
P
physical characteristics 6
power, connecting 9
product
information 1
R
recovering 16
recycling 15
Red Hat Linux driver disc, RHEL
setup 18
Remote HP PC Hardware Diagnostics
UEFI settings
customizing 29
using 28
resources, accessibility 37
restoring 16
RHEL
HP driver disc 18
Linux 17
Red Hat Linux driver disc 18
setup 17
Index 39

routine care 30
cleaning chassis 30
cleaning keyboard 30
cleaning monitor 31
cleaning mouse 31
cleaning safety 30
S
Section 508 accessibility standards
34, 35
security 15
setup
Linux 17
monitors 12
RHEL 17
SLED 18
Ubuntu 18
ventilation 7
setup procedure 8
SLED
HP driver disc 18
setup 18
specications
environmental 6
product 6
standards and legislation,
accessibility 34
support 1
SUSE certication bulletin search
page 18
Ubuntu 18
urls
HP.com 13
V
ventilation 7
W
WLAN, disabling 11
T
technical support 24
troubleshooting 22
at startup 22
Customer Self Repair 23
during operation 23
turning o computer 22
U
Ubuntu
HP driver disc 19
setup 18
updates 3
updating the computer 20
URLs
HP Customer Self Repair 23
Linux Hardware Matrix for HP
computers 17
Red Hat Certication 18
Software & driver downloads 17
40 Index
 Loading...
Loading...