HEI GL6965 Datasheet
Telephone Speech Network with Dialer Interface
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
11
16
19
V
TO1
TO0
MFI
TPO
TPI 1
TPI 2
MUTE
GND
RO 1
RO 2
BT 1
RPO
RPI 1
RPI 2
REF
PADC
UP
Description
The GL6965 is a bipolar integrated circuit for
use in electronic telephones.
The GL6965 has low operating voltage, it provides an excellent branch performance.
It has line voltage increasing circuit by the
exter-nal terminal. Transmitting and receiving
gains automatically vary according to the line
current.
Features
• Externally adjustable transmitting,
receiving and Sidetone gains.
• Switching between transmitting output
and DTMF output is possible.
• Direct interface with light and compact
ceramic transmitter-receiver is possible.
• Receiver follow impedance type can
also be used.
GL6965
GL6965
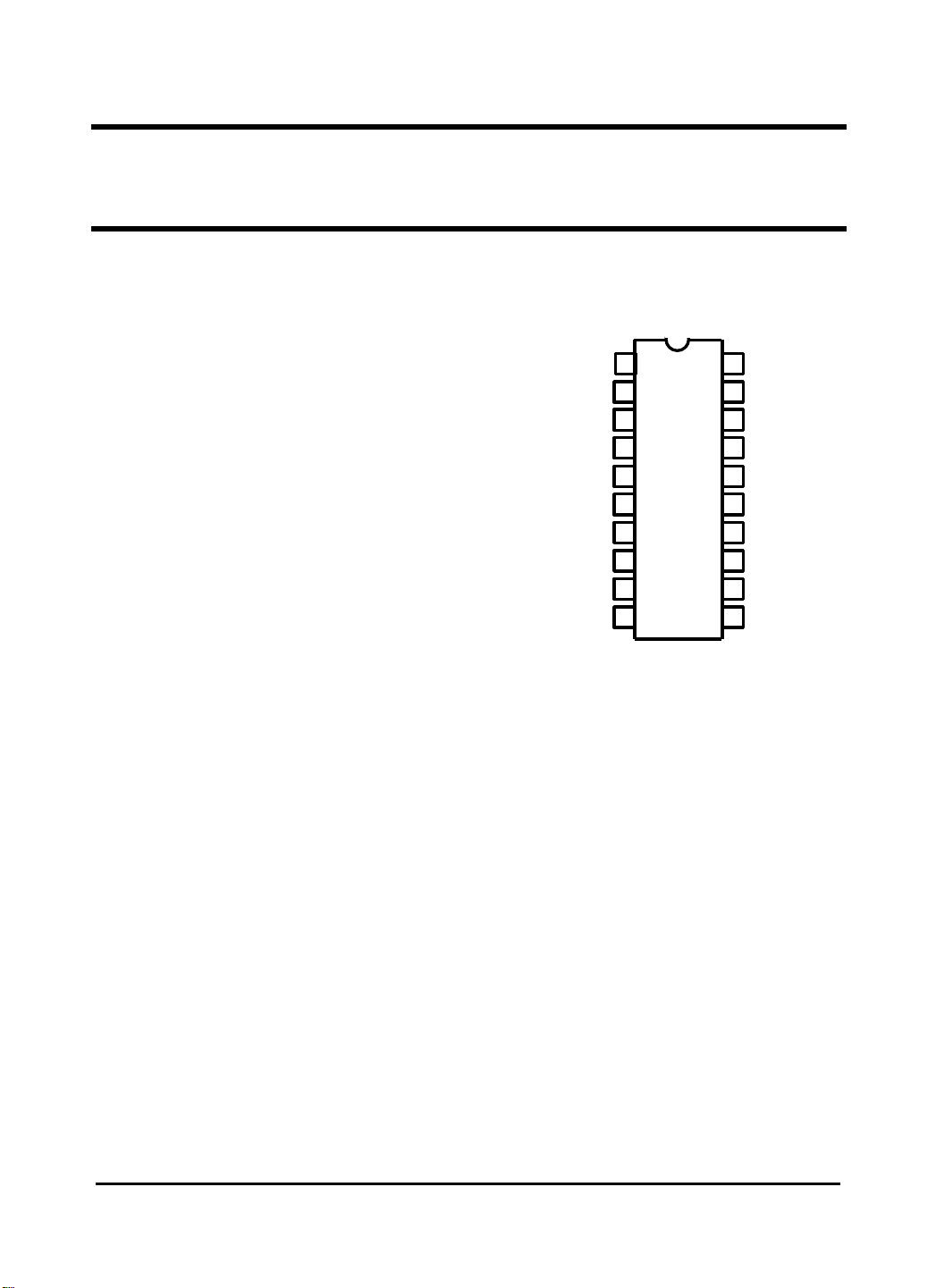
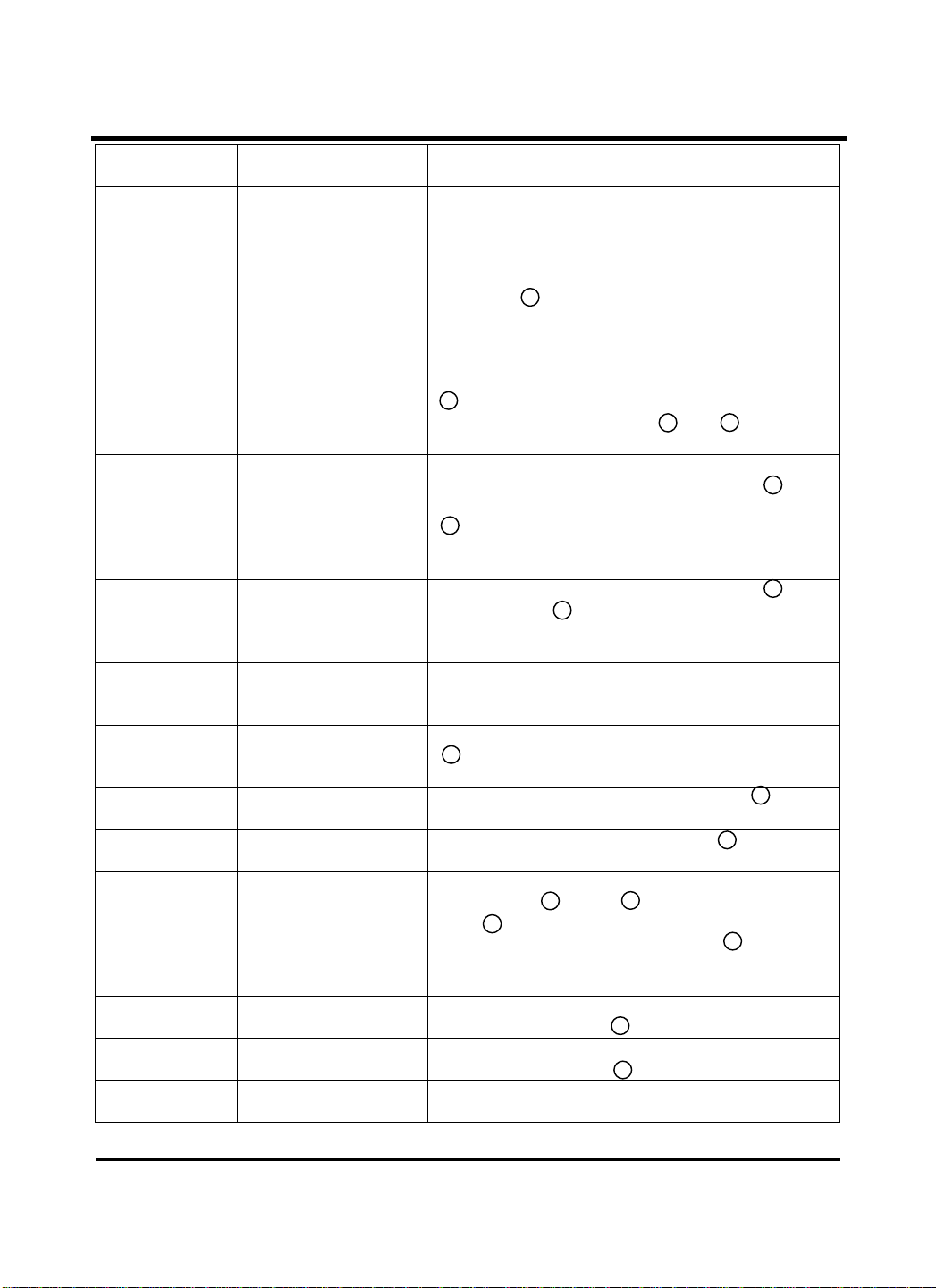
Pin Configurations
AC BIAS
10
• Gain is automatically controlled according to the line current (Auto-PAD
function).
• The line voltage can be increased by
the external terminal (Up function).
• PKG is 20 pin DIP.
V
20
CC
18
17
15
14
13
12
1
C
25Ta°=
70
~30
−
150
~55
−
C
°
C
°
C
25Ta°=
1
9
10
2
3
17
16
15
14
13
12
20
11
4
5
6 7 8
18
19
+ +
+
GL6965
Absolute Maximum Ratings (
Parameter Symbol Value Unit
Line Voltage
Line Current
Power Dissipation
Operating Temperature
Storage Temperature
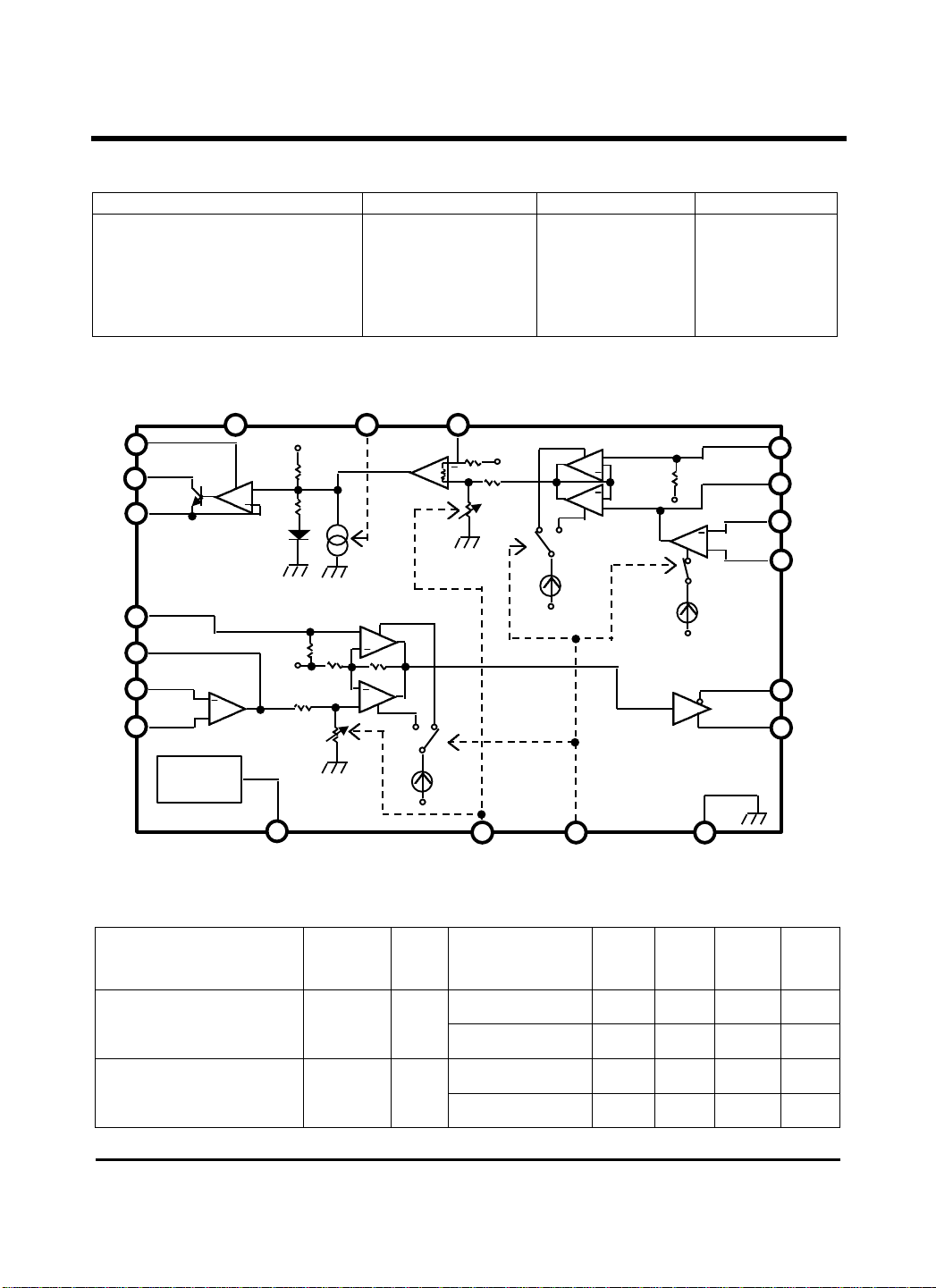
Block Diagram
+
+
RECEIVING
INPUT
AMP
VCC
VCC
10K
9.3K
Vref
REF
5.5K
SW/BUFFERRECEIVING
17.7K
RECEIVING
CONTROLLER
RPI1
RPI2
VL
TOl
TOO
BTI
RPO
LINE DRIVER
INTERNAL
REFERENCE
CIRCUIT
GAIN
Iup
+
AC Bias
+
17.7K
UP
VCC
)
V
L
I
L
P
D
T
opr
T
stg
AMP
4K
TRANSMIT
GAIN
CONTROLLER
AC Bias
Vref
PADC
15
150
1300
TRANSMIT SW/BUFFER
+
VCC
MUTE
27.4K
Vref
VCC
RECEIVING
DRIVE AMP
mA
mW
TRANSMIT
INPUT
AMP
GND
V
MFI
TPO
TPI1
TPI2
RO2
RO1
Electrical Characteristics (
Parameter Symbol
)
Test
Cir-
Test Condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
cuit
IL=20mA 2.9 3.2 3.6 V
Line Voltage
Internal Power Supply
Voltage
V 1
L
V 1
CC
IL=120mA 9 11 14 V
IL=20mA 1.75 1.90 2.20 V
IL=120mA 5.8 6.1 6.6 V
2
KHz1f
−
=
KHz1f
−
=
KHz1f
−
=
KHz1f
−
=
Test
Cir-
Test Conditon Min,. Typ. Max. Unit
cuit
Parameter
Line Voltage Rise up
Sym
-bol
V∆ 2 IL=20mA 1.1 1.5
L
Amount
Transmit Gain
Receiving Gain
MF Gain
Beep Gain
Transmit Dynamic Range
Receiving Dynamic Range
G 4
T
G 5
R
G 6
MF
G 8
BP
D 4
RT
D 5
RR
IL=20mA 43 46 48 dB
IL=120mA
IL=20mA 40 43.5 46 dB
IL=120mA
IL=20mA 24 26.8 28 dB
IL=120mA
IL=20mA 21 24 27 dB
IL=120mA
IL=20mA
IL=120mA
IL=20mA 3.0 — —
IL=120mA
=
dBV55V
in
=
dBV55V
in
=
dBV30V
in
=
dBV30V
in
Distortion
Ratio 4%
Distortion
Ratio 10%
MFI Input Resistance ZI(MF) — 21 30
BTI Input Resistance ZI(BP) — 7 10
AC BIAS Input
Resistance
MUTE Terminal High
Level
ZI(AB) —
)MU(V
IH
—
21 30
IL=20mA-120mA
Input Voltage
MUTE Terminal Low
Level
)MU(V
IL
—
IL=20mA-120mA 0 — 0.2 V
Input Voltage
GL6965
2.1
40 43.2 45 dB
34.5 38 40.5 dB
21.5 24 25.5 dB
21.5 24.5 27.5 dB
2.0 — —
4.0 — —
6.0 — —
V -
CC
0.5
—
V
— Ωk
— Ωk
— Ωk
CC
V
V
V
V
V
p.p
p.p
p.p
p.p
V
Reference data
Test
Cir-
Test Condition Typ Unit
cuit
IL=20mA 0.66 V Internal Reference Voltage
3
IL=120mA 2.8 V
RO
R
11
IL=20mA 14.5 dB Total Receiving Gain
IL=120mA
(Balancing Network
circuit included.)
9 IL=20mA VIL=0.2V -50 µA
10 IL=20mA at GND connection -35 µA
9.0 dB
Parameter Symbol
V
REF
RO1, RO2 Output Impedance
Z — IL=30mA f=1KHz 200
G
(Total)
MUTE Terminal Input Current )MU(I
UP Terminal Input Current )MP(I
IL
IL
AC Impedance |Z|TEL — IL=50mA f=1KHZ 580
Phase θ — IL=50mA f=1KHZ 3 DEG
3
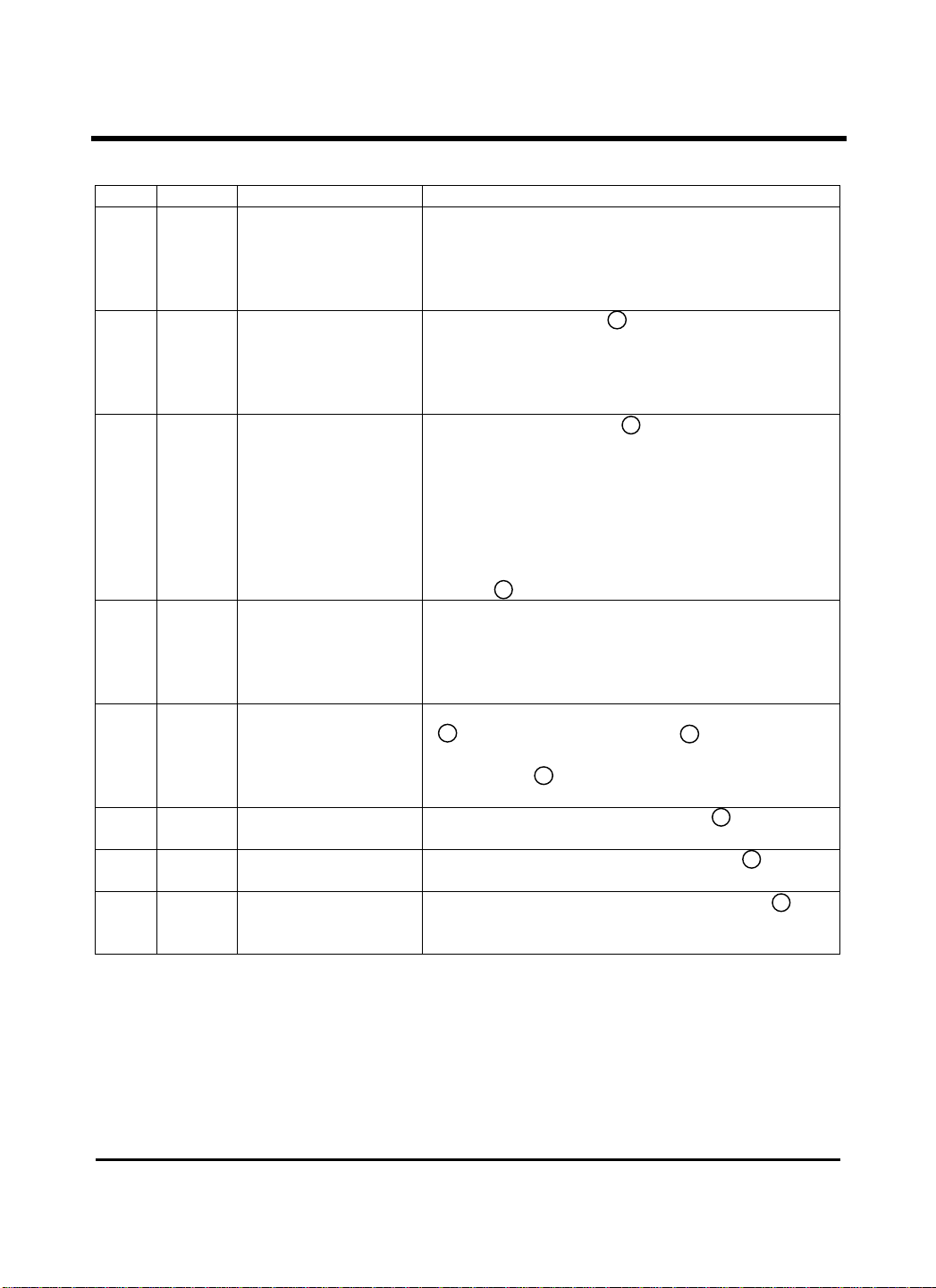
Pin Descriptions
1
1
1
913
7
6
Pin No. Symbol Function Explanation
1 VL Line Current flow-in and
2 TOI Current flow-in terminal
3 TOO Current output terminal
4 AC
5 MFI Input terminal of DTMF
6 TPO Output terminal of
7 TPI1 Inversion input terminal
8 TPI2 Non-inversion input
Bias
Line Voltage terminal
of transmit output
of transmit output
AC signal reference
Voltage terminal
or external input signal
transmit input Amp.
of transmit input Amp.
terminal of transmit input
Amp.
Connected to positive output of diode bridge circuit. DC
potential of this terminal determines line voltage and if AC
signal is not input, the highest DC potential appears.
Transmit output signal and output signal of opposite transfer
side are intermingled and output at this terminal in actual use.
Connected to VL terminal ( pin) through 43 Ω . Since
almost all the line currents flow in from this terminal, set
allowable power of resistance 43 Ω to be connected to VL
terminal from this terminal considering the maximum line
cur-rent expected to be used.
Connected to GND terminal ( pin) through 15 Ω . Since
almost all the line currents flow out from this terminal, set
allowable power of resistance 15 Ω to be connected to GND
terminal from this terminal considering the maximum line
cur-rent expected to be used.
Transmit signal is sent from this terminal. Signal of this terminal varies current which is input from line through connected resistance 15 Ω , and makes it be output at VL
terminal ( pin)
When AC signal is input to this terminal through capacitor
(for blocking DC), signal is sent to line, Input from this terminal is output to line without any relation to gain control
(PAD) or MUTE since this input does not pass through gain
control circuit or MUTE function
Signal which is input to this terminal is output at VL terminal
( pin) only when MUTE terminal ( pin) is in “L” state.
Since this terminal is biased to almost the same potential as
REF terminal ( pin), avoid direct impressing external
DC potential by using capacitor at inputting external terminal.
Makes negative feedback to TPI1 terminal ( pin)
Receives negative feedback from TPO terminal ( pin)
Applies DC bias to this terminal from REF terminal ( pin)
through resistance
GL6965
10
13
4
11119 18 10
15 19 18 19 18 93
Pin No. Symbol Function Explanation
9 MUTE
MUTE terminal Switching terminal of transmit signal with MFI input signal
in transmitting system.
Switching terminal of receiving signal with BTI input signal
in receiving system.
“L” State— Signal which is input from MFI is output to
VL terminal ( pin)
Signal which is input from BTI is output to
terminals RO1 and RO2.
“H” or “ OPEN” state
Transmitting input signal is output to VL terminal
( pin). Receiving input signal is
output to terminals RO1 and RO2 ( pin, pin)
This terminal is pulled up by constant-current circuit
10 GND Ground terminal Connected to negative output of diode bridge circuit.
11 UP DC impedance control
terminal
When this terminal is connected to GND terminal ( pin)
directly or through resistance. DC potential of VL terminal
( pin) can be in-creased up to max. 1.5V (TYP.) in the
same line current.
This function has no relation to the state of MUTE terminal.
12 PADC
Pad control terminal When this terminal is connected to GND terminal ( pin)
or
V terminal ( pin) through resistance, operation cur-
CC
20
rent of gain control (Auto-PAD) performed by line current
can be controlled.
13 REF Internal reference voltage
Output terminal
Voltage of this terminal is used as a reference voltage of in-
ternal amplifiers.
Never used this terminal for an external power supply.
14 RPI2 Non-inversion input
terminal
Apply DC bias to this terminal from REF terminal
13
( pin) through resistance.
of receiving Input Amp.
15 RPI1 Inversion Input terminal
Receives negative feedback from RPO terminal ( pin).
of receiving input Amp.
16 RPO Output terminal of
Makes negative feedback to RPI1 terminal ( pin).
Receiving input Amp.
17 BTI Dial confirmation sound
(Beep Tone, DTMF),
monitor
sound input terminal
Signal which is input to this terminal is output to terminals
RO1 and RO2 ( pin and pin) only when MUTE ter-
minal ( pin) is in “L” state. Since this terminal is biased
to about the same potentialas REF terminal ( pin), avoid
direct impressing external DC voltage through capacitor at
in-putting external signal
18 RO2 Receiving output terminal
19 RO1 Receiving output terminal
20
Inversion output
Non-inversion output
V Internal power supply
CC
Output terminal to receiver. Signal of which phase is
negative to RO1 terminal ( pin), is output.
Output terminal to receiver, Signal of which phase is
negative to RO2 terminal ( pin), is output
Power supply of internal amplifiers
voltage terminal
GL6965
10
16
5
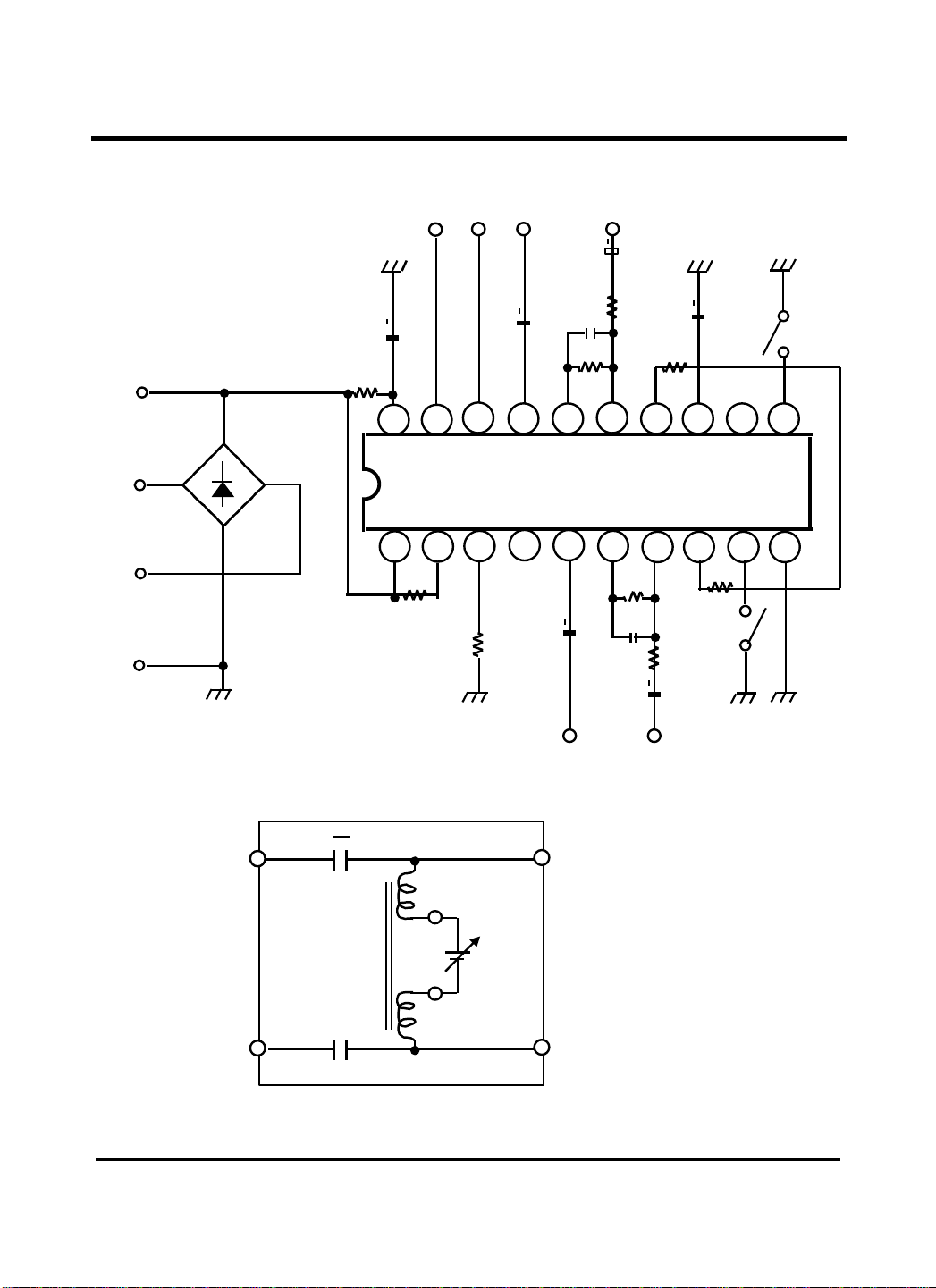
Test Circuit
20
18
15 14 13 12 11
1
3
7 8 9 10
2.2K
+ + + + +
+
–
~
C8
C6
R4
R6
1µF 100
µF µ
2.2KΩ 22KΩ 15Ω 1µ
~
+
–
GL6965
R1 R2 Beep
R2
260
µF
+
19
V
L
L1
L2
2
R1
43
GND
Telephone line Simulation Equivalent circuit
T1
Trunk
2T
2µF
Fì2
Power
C5
330pF
17 16
4 5
DTMF
Line 1
Line 2
R9
22K
R
6
C2
330pF
22K
R5
F
T(+)
R8
2.2K
F
µF
R7
6
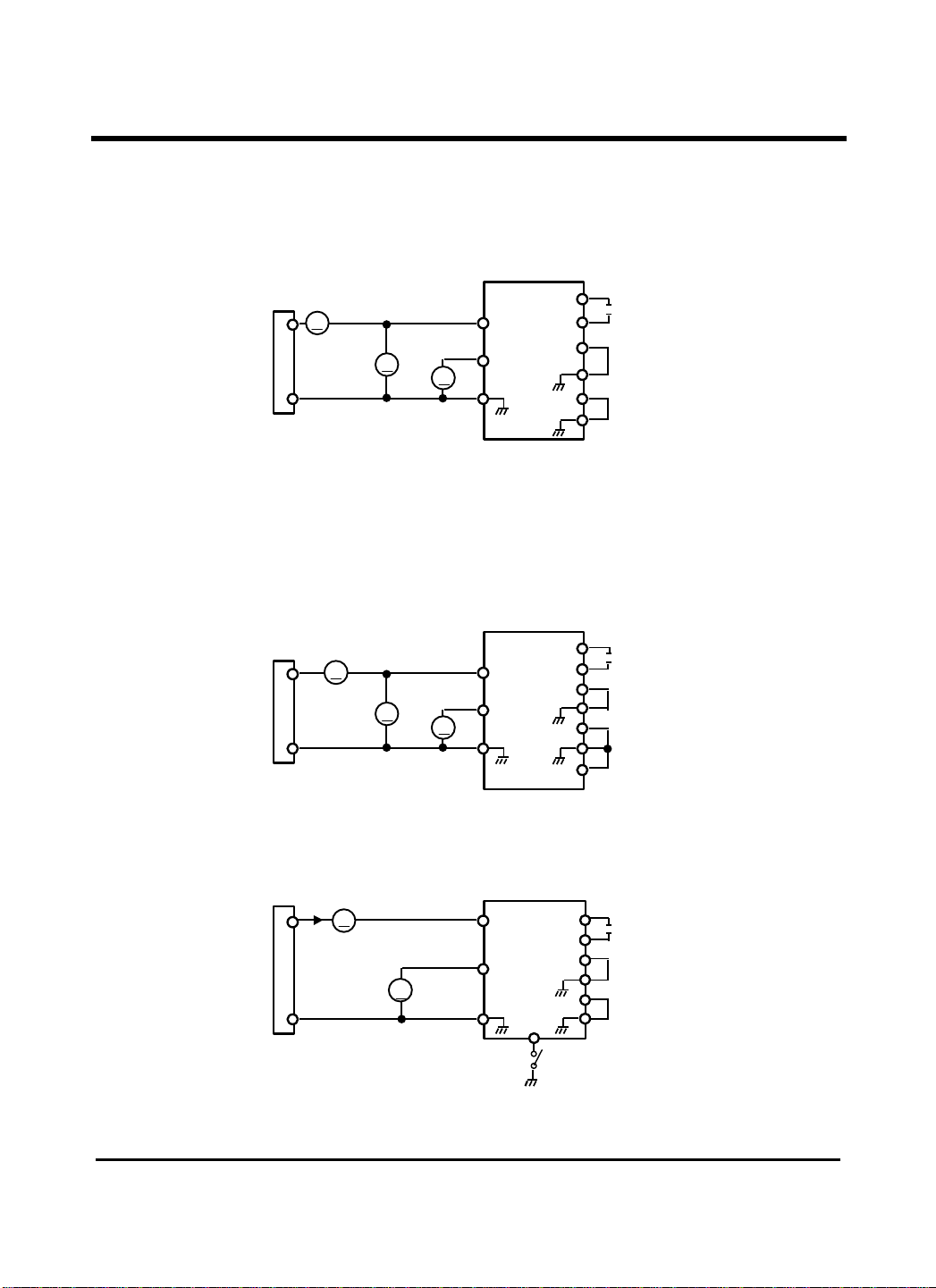
Test Circuit (continued)
V
LLV
CC
V
CC
R
R
LLV
CC
V
CC
R
R
LLVVV R
R
I
UP
1. LV , CCV
2. LV , CCV (UP)
3.
REF
GL6965
A
V
V
A
V
V
A
V
V
V
GND
T(+)
V
V
GND
T(+)
T(+)
SW
55nF
R
55nF
R
55nF
R
7
 Loading...
Loading...