HEI GDC21D003 Datasheet

GDC21D003
(VSB Receiver)
Version 1.0
Mar, 99
HDS-GDC21D003-9908 / 10

GDC21D003
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice.
The information contained herein is presented only as a guide for the applications of our products. No
responsibility is assumed by Hyundai for any infringements of patents or other rights of the third parties
which may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or
patent rights of Hyundai or others.
These Hyundai products are intended for usage in general electronic equipment (office equipment,
communication equipment, measuring equipment, domestic electrification, etc.).
Please make sure that you consult with us before you use these Hyundai products in equipment which
require high quality and / or reliability, and in equipment which could have major impact to the welfare of
human life (atomic energy control, airplane, spaceship, traffic signal, combustion control, all types of
safety devices, etc.). Hyundai cannot accept liability to any damage which may occur in case these
Hyundai products were used in the mentioned equipment without prior consultation with Hyundai.
Copyright 1999 Hyundai Micro Electronics Co.,Ltd.
All Rights Reserved
3

GDC21D003
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. General Description.................................................................................................................8
2. Features....................................................................................................................................8
3. Internal Block Diagram..........................................................................................................11
4. Pin Description.......................................................................................................................11
4.1 Pin Configuration ..............................................................................................................11
4.2 Pin Description..................................................................................................................14
4.3 Pin Assignment.................................................................................................................16
5. I2C Bus I/F & Registers..........................................................................................................17
5.1 I2C Bus I/F Description......................................................................................................17
5.1.1 Write Operation...........................................................................................................17
5.1.2 Read Operation...........................................................................................................17
5.2 I2C Bus Register Configuration.........................................................................................18
5.3 I2C Bus Register Description ............................................................................................20
6. Functional Description..........................................................................................................29
6.1 ADC ..................................................................................................................................29
6.1.1 Electrical Characteristics.............................................................................................30
6.1.2 Timing Diagram...........................................................................................................32
6.1.3 Application Circuits......................................................................................................33
6.2 Clock Divider.....................................................................................................................35
6.3 Synchronizer.....................................................................................................................36
6.3.1 Input Control................................................................................................................36
6.3.2 DC Reduction..............................................................................................................39
6.3.3 Auto Gain Control(AGC) .............................................................................................39
6.3.4 Polarity Correction.......................................................................................................40
6.3.5 Data Segment Sync Recovery....................................................................................41
6.3.6 Polarity Decision..........................................................................................................42
6.3.7 Timing Recovery .........................................................................................................43
6.3.8 Field Sync Recovery...................................................................................................46
6.3.9 VSB Mode Detect........................................................................................................47
6.3.10 NTSC Rejection.........................................................................................................48
6.4 Equalizer...........................................................................................................................50
6.4.1 Block Diagram.............................................................................................................50
6.4.2 Training/Data Mode Equalization................................................................................51
6.4.3 Error Estimation...........................................................................................................52
6.4.4 Adaptive Filter .............................................................................................................53
6.4.5 Equalizer Clock Scheme.............................................................................................53
6.4.6 I2C Bus I/F...................................................................................................................54
6.4.7 Coefficient Reading/Writing.........................................................................................56
4

GDC21D003
6.5 Phase Tracker ..................................................................................................................56
6.5.1 Error Detection............................................................................................................57
6.5.2 Gain & Offset Loop......................................................................................................58
6.5.3 Phase Loop.................................................................................................................58
6.5.4 I2C Bus I/F ..................................................................................................................59
6.6 Channel Decoder..............................................................................................................60
6.6.1 12 Symbol Intrasegment Deinterleaver.......................................................................61
6.6.2 Segment Sync Suspension.........................................................................................61
6.6.3 Viterbi Decoder............................................................................................................62
6.6.4 Symbol-to-Byte Converter...........................................................................................64
6.6.5 Convolutional Deinterleaver........................................................................................65
6.6.6 Reed-Solomon Decoder..............................................................................................65
6.6.7 Data Derandomizer.....................................................................................................66
6.6.8 I/F to Transport Demultiplexer.....................................................................................67
6.7 PLL....................................................................................................................................74
7. Electrical Characteristics......................................................................................................75
8. Package Dimensions.............................................................................................................77
9. Application Notes ..................................................................................................................78
Figures
Figure 3.1 Functional Block Diagram ..............................................................................10
Figure 5.1.1 I2C Write Operation Example ..........................................................................17
Figure 5.1.2 I2C Read Operation Example ..........................................................................18
Figure 6.1.1 The Block Diagram of ADC .............................................................................29
Figure 6.1.2 Timing Diagram of ADC ..................................................................................32
Figure 6.1.3 ADC Application Circuit ...................................................................................33
Figure 6.1.4 Equivalent Circuits ..........................................................................................34
Figure 6.3.1 The Block Diagram of Input Selection ............................................................36
Figure 6.3.2 Digital Input Setting Up & Chip I/F Circuit(1) ..................................................37
Figure 6.3.3 Digital Input Setting Up & Chip I/F Circuit(2) ..................................................38
Figure 6.3.4 The Block Diagram of DC Reduction ..............................................................39
Figure 6.3.5 The Block Diagram of AGC ............................................................................40
Figure 6.3.6 AGC Signal I/F for DTV System .....................................................................40
Figure 6.3.7 The Block Diagram of Polarity Correction .......................................................41
Figure 6.3.8 The Block Diagram of Data Segment Sync Recovery ....................................41
Figure 6.3.9 Polarity signal I/F Circuit .................................................................................42
Figure 6.3.10 Timing Recovery Block ....................................................................................43
Figure 6.3.11 Timing Recovery I/F Circuit(1) .........................................................................44
Figure 6.3.12 Timing Recovery I/F Circuit(2) .........................................................................45
Figure 6.3.13 Field Sync Structure ........................................................................................46
Figure 6.3.14 The Block Diagram of Field Sync Recovery ....................................................46
Figure 6.3.15 Comb Filter Block ............................................................................................48
5

GDC21D003
Figure 6.3.16 The Block Diagram of NTSC Rejection............................................................49
Figure 6.4.1 Channel Equalizer ...........................................................................................50
Figure 6.4.2 VSB Slicer .......................................................................................................51
Figure 6.4.3 Training/Data Equalization ..............................................................................51
Figure 6.4.4 VSB Slice Level ..............................................................................................52
Figure 6.4.5 Coefficient Update Filter .................................................................................53
Figure 6.4.6 I2C Bus I/F .......................................................................................................54
Figure 6.5.1 Phase Tracker .................................................................................................57
Figure 6.5.2 Error Detection ................................................................................................57
Figure 6.5.3 Coefficients of Hilbert Transform Filter ...........................................................58
Figure 6.5.4 Complex Multiplier ..........................................................................................58
Figure 6.6.1 Block Diagram of Channel Decoder ...............................................................60
Figure 6.6.2 12-Symbol Intrasegment Deinterleaver ..........................................................61
Figure 6.6.3 Segment Sync Suspension .............................................................................62
Figure 6.6.4 Viterbi Decoding with and without NTSC Rejection Filter ...............................63
Figure 6.6.5 Internal Block Diagram of Viterbi Decoder ......................................................63
Figure 6.6.6 Convolutional Deinterleaver ............................................................................65
Figure 6.6.7 Derandomizer Polynomial ...............................................................................66
Figure 6.6.8 I/F to Transport Demultiplexer when Register64[7:0] is set to
Default Value ....................................................................................................68
Figure 6.6.9 I/F to Transport Demultiplexer when Register64[3] (Derand_on)
is set to ‘ 0’ ........................................................................................................69
Figure 6.6.10 I/F to Transport Demultiplexer when Register64[2](Errorflg_ins)
is set to ‘ 0’ ........................................................................................................69
Figure 6.6.11 I/F to Transport Demultiplexer when Register64[1](Vsbdvalid_pol)
is set to ‘ 0’ ........................................................................................................70
Figure 6.6.12 I/F to Transport Demultiplexer when Register64[0](Vsbclk_sup)
is set to ‘ 0’ ........................................................................................................70
Figure 6.6.13 I/F to Transport Demultiplexer(MMDS 8VSB Mode) .......................................71
Figure 6.6.14 I/F to Transport Demultiplexer at Serial Output Mode .....................................71
Figure 6.6.15 Connection with VSB Receiver and Transport Demultiplexer
Chip(GDC21D301A) ........................................................................................72
Figure 6.6.16 Connection with VSB Receiver and Transport Demultiplexer
Chip(L64007) ...................................................................................................72
Figure 6.6.17 Connection with VSB Receiver and Transport Demultiplexer
Chip(AVIA-MAX) ..............................................................................................73
Figure 6.7.1 Clock Scheme .................................................................................................74
Figure 7.1 Clock Reset Stabilization Timing .....................................................................76
Figure 7.2 Input and Output Timing ..................................................................................76
Figure 8.1 Physical Dimensions ........................................................................................77
Figure 9.1 VSB Receiver Application Circuit .....................................................................78
6

GDC21D003
Tables
Table 6.2.1 Register Setting Up for Clock Divider .............................................................35
Table 6.3.1 Input Signal Path Setting Up ..........................................................................36
Table 6.3.2 DATAPOLP & DATAPOLN Output ................................................................42
Table 6.3.3 VSB Mode Data for Each VSB Mode .............................................................47
Table 6.3.4 VSB Mode Signal Control ..............................................................................47
Table 6.3.5 Comb Filter Control through I2C Bus ..............................................................49
Table 6.4.1 Contents of I2C Bus Register33 for Equalizer ................................................55
Table 6.4.2 Contents of I2C Bus Register33 for Filter Control ..........................................55
Table 6.5.1 Contents of I2C Bus Register33 for Phase Tracker ........................................59
Table 6.5.2 Contents of I2C Bus Register33 for Gain Control ...........................................59
Table 6.6.1 Bypassed Sub-blocks by the Values of I2C Bus Register64 ..........................60
Table 6.6.2 Symbol-to-Byte Conversion ...........................................................................64
Table 6.6.3 I2C Register64 Flags controlling Transport Demultiplexer I/F ........................67
7

GDC21D003
VSB Receiver
GDC21D003
1. General Description
The VSB Receiver(GDC21D003) is an ATSC
compliant single chip communications device that
synchronizes, equalizes, and corrects errors of
ATSC 8/16 VSB and MMDS (Multichannel
Multipoint Distribution System) 2/4/8/16 VSB
modulated signal.
The on-chip 10-bit 10.76Msps Analog-to-Digital
Converter has an input sample-and-hold amplifier.
By implementing a multistage pipelined
architecture with output correction logic, the ADC
offers accurate performance and guarantees no
missing codes over the full operating temperature.
Clock divider divides output clock of external
VCXO and generates symbol clock (CLKFS) and
ADCCLK. The CLKFS has 10.76MHz frequency
as symbol frequency used in DTV transmitter,
ADCCLK is used for external A/D converter. At
this time, if you use digital signal as input of chip,
CLKFS or ADCCLK are used for external A/D
converter clock.
Synchronizer removes DC entered from transmitter
and DC generated by analog circuit used in
receiver. Also it checks gain of input signal and
sends it to demodulator, detects polarity, and
corrects it. It recovers Data Segment Sync period
and Field Sync period entered from transmitter. It
detects VSB mode of current input signal and
removes NTSC co-channel interference in channel.
Equalizer corrects linear distortion created during
transmission. It uses Least-Mean-Square algorithm
and has decision feedback equalizer structure. It
uses adaptive filter having coefficient update
structure consisted of multiplier, adder, and
memory structure in every tap.
Phase Tracker compensates phase distortion due to
phase noise and it consists of gain correction loop
for gain error, offset correction loop for offset error,
and phase correction loop for phase error.
Channel Decoder consists of Viterbi Decoder,
Convolutional Deinterleaver, Reed-Solomon
Decoder, Data Derandomizer, and etc. It decodes
ATSC 8/16 VSB signal and MMDS 2/4/8/16 VSB
signal. Also it has internal segment error counter
that send out the number of segment errors per
second and offers tri-state parallel/serial Transport
Demultiplexer interface.
2. Features
General features
• ATSC compliant 8/16 VSB receiver
• MMDS 2/4/8/16 VSB receiver
• SNR threshold 14.9 dB on AWGN channel
• Tri-state parallel/serial MPEG-2 transport
interface
• Supports I2C bus interface
• Boundary Scan Test circuit complies with
IEEE Std. 1149.1
ID-Code = 0D0031C1
• Operating voltage : 3.3V
• 0.35µm CMOS technology
• 128 pin HQFP package
ADC
• Resolution : 10bits (≤ ±1⁄2 LSB DNL error)
• Sampling rate : 10.76 Msps
• Differential input range : 2Vpp(1.7 ± 0.5V
differential)
Clock Divider
• Generates symbol clock(10.76MHz)
• Uses one of two VCXOs, fs(10.76MHz) and
2fs(21.52MHz) as input
Synchronizer
• Input control
• DC reduction and polarity correction
- Correction of polarity ambiguity caused
by FPLL
• Non-coherent and coherent automatic gain
control (AGC)
• Data Segment Sync and Field Sync recovery
• Timing recovery
• Polarity decision
- Polarity decision after Data Segment
Sync is locked
• VSB mode detection
• Comb control
- Comb filter for the rejection of NTSC
co-channel interface
8

Equalizer
• Decision feedback equalizer
• Supports training sequence and blind
equalization
• Concurrent coefficients update in symbol
time
• Available 3 different step-size
• Capability of reading equalizer coefficients
• Ghost cancellation in the range from -2.86µs
to 20.76µs
Phase Tracker
• Intelligent loop control according to noise
environment
• Phase tracking from -60° to 60° with
resolution of 0.004 degree
• Phase, offset, and gain correction at a time
Channel Decoder
• Concatenated Viterbi/Reed-Solomon Decoder
with Deinterleaver and Derandomizer
• Internal segment error counter
• Tri-state parallel/serial MPEG-2 Transport
Demultiplexer interface
GDC21D003
9
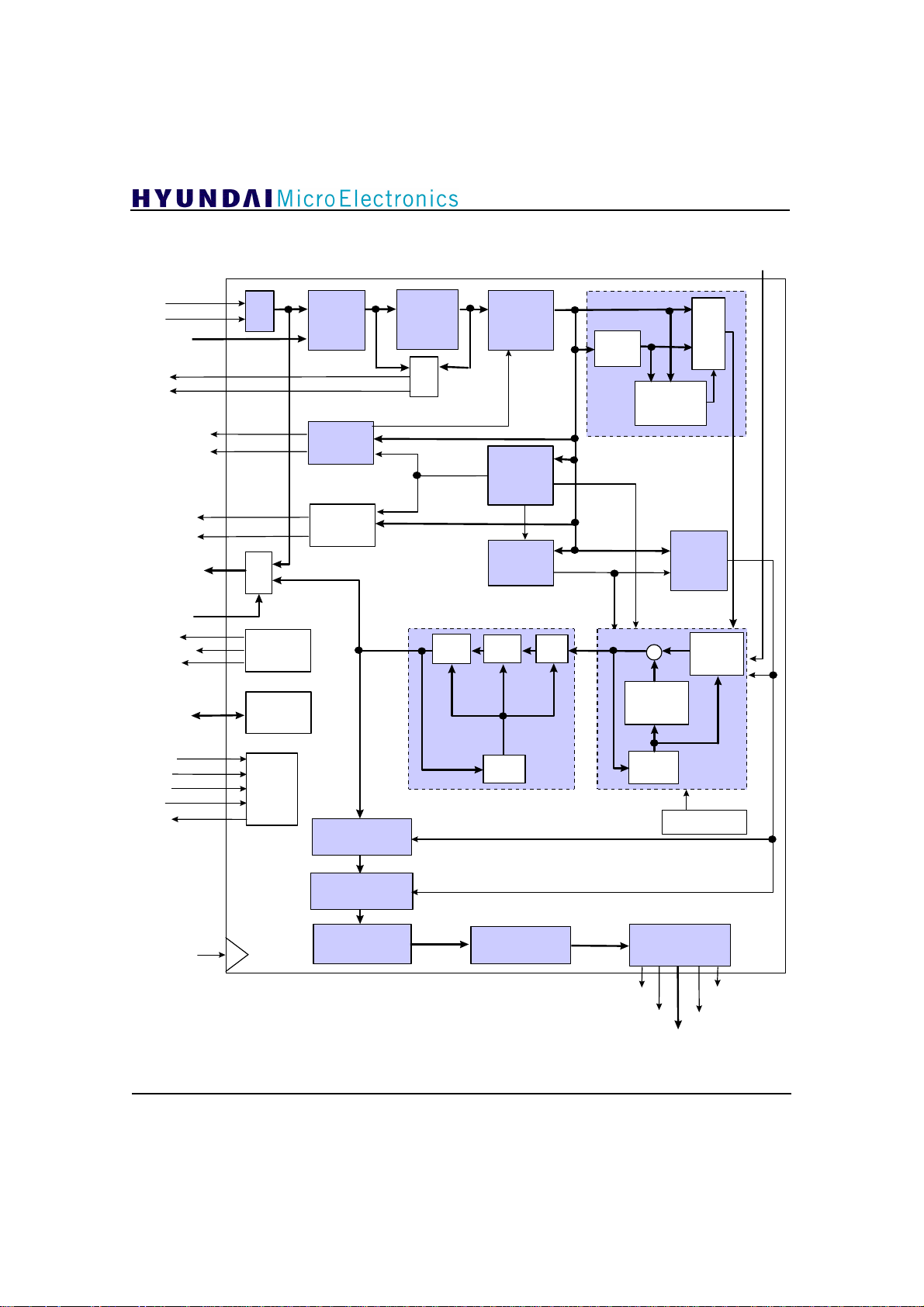
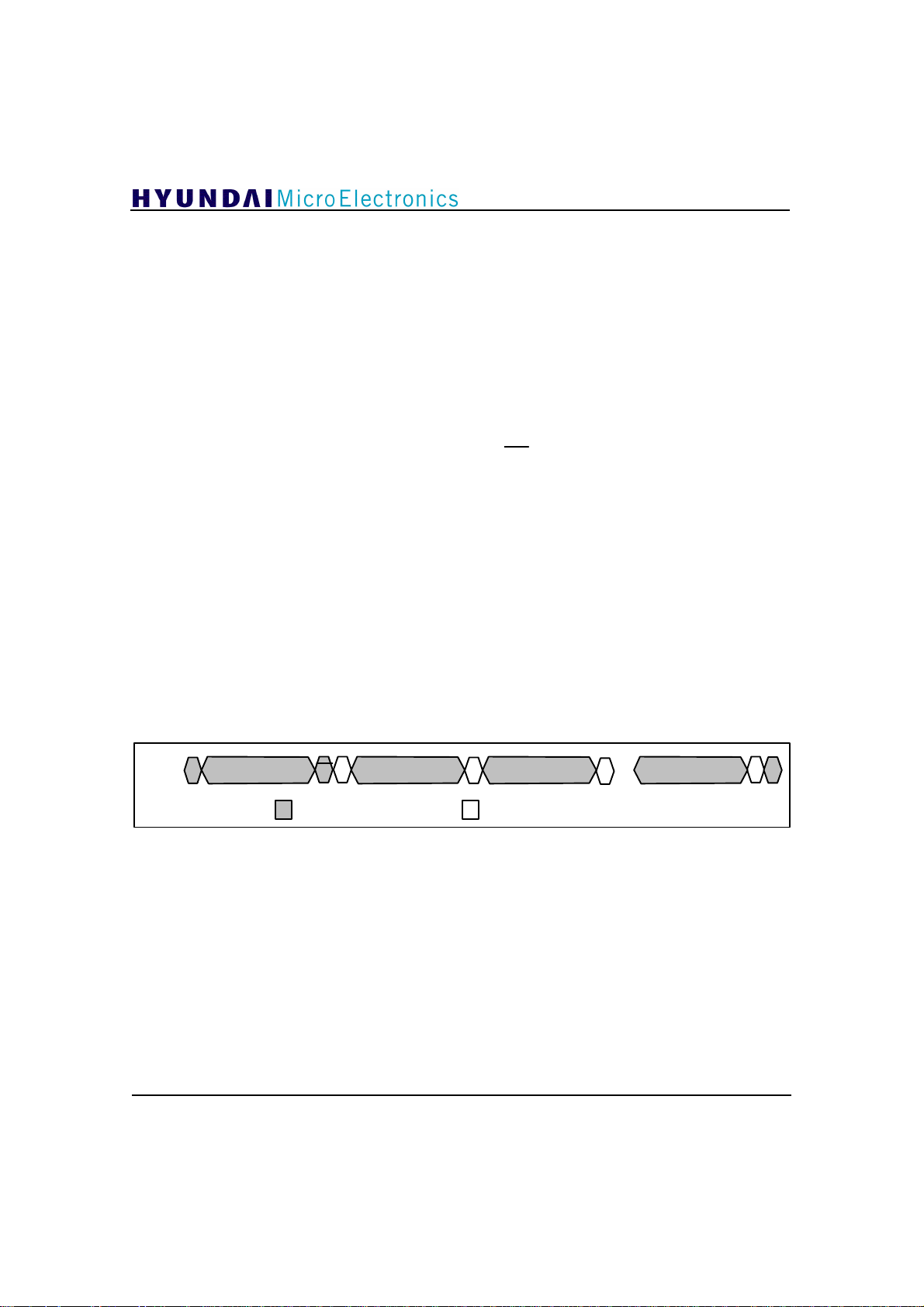
3. Internal Block Diagram
GDC21D003
NADTONDATA
INN
INP
DIN[9:0]
GUP
GDN
DATAPOLP
DATAPOLN
NCHGUP
NCHGDN
DOUT[9:0]
TM[2:0]
VCXO
ADCCLK
CLKFS
I2C BUS
ADC
Mux
Clock
Divider
I2C
Interface
Input
SelectionDCReduction
AGC
Polarity
Decision
Timing
Recovery
Phase
Loop
Polarity
Correction
Data
Segment
Sync
Recovery
Field
Sync
Recovery
Offset
Loop
Gain
Loop
Comb
Filter
Comparator
NTSC Rejection
Σ
192 Tap
Feedback
Filter
Mux
MSE
&
VSB
Mode
Detect
64 Tap
Forward
Filter
TRST
TMS
TCK
TDI
TDO
SYMCLK
10
JTAG
Error
Detect
Phase Tracker
Deinterleaver/
Viterbi Decoder
Convolutional
Deinterleaver
Reed-Solomon
Decoder
Data
Derandomizer
Figure 3.1 Functional Block Diagram
Error
Control
Equalizer
Transport
Demultiplexer I/F
VSBCLK
VSBDVALID
VSBDATA[7:0]
4x Clock
4X PLL
VSBSOP
NVSBERRFLG

4. Pin Description
4.1 Pin Configuration
GDC21D003
∗
128 PIN HQFP, 28X28 mm BODY, 1.60/0.33 mm FORM, 3.37mm THICK, 0.8 mm PITCH
11
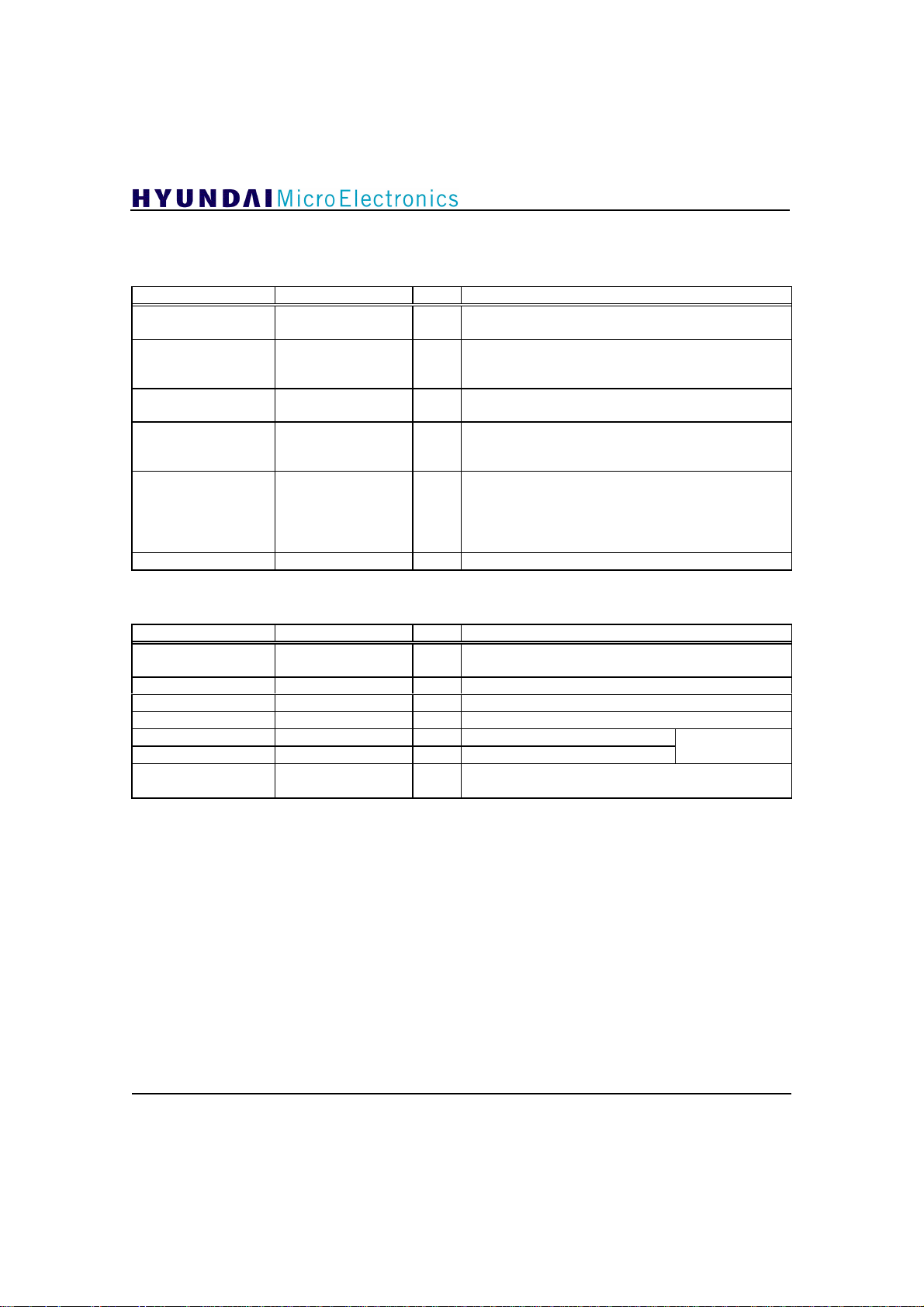
4.2 Pin Description
Clock/Reset ; 6 Pins
PIN NAME TYPE DESCRIPTION
38
12
14
18
37
41
A/D Converters ; 7 Pins
PIN NAME TYPE DESCRIPTION
2
121
123
124
125
126
128
NRESET I
VCXO I
ADCCLK O Clock for Off-chip ADC(21.52MHz or 10.76MHz);
CLKFS O
CLK4FS I/O Test clock/4x symbol clock;
SYMCLK I System clock input(10.76MHz)
REF I
COM I Common voltage(1.5V)
REFN I Reference voltage(bottom: 1.2V)
REFP I Reference voltage(top: 2.2V)
INN I Analog data input(negative)
INP I Analog data input(positive)
BIAS I
GDC21D003
System reset(active low); This signal should be
activated on channel change or power on.
Clock input generated in VCXO; This pin can be
connected to one of two VCXOs whose output
frequencies are fs(10.76MHz) and 2fs(21.52MHz).
This clock is generated by dividing VCXO input signal.
System clock; This clock is generated from dividing
VCXO input signal. Its frequency is the same of symbol
rate(10.76MHz).
When PLLEN(pin35) input is set to ‘1’, this pin is used
as 4x symbol clock output.
When PLLEN(pin35) input is set to ‘0’, this pin is used
as test clock(43.04MHz) input.
Bias register for internal ADC; This pin should be
connected to AVDD(3.3V) via 12k ohm register.
1.65 ± 0.5V
differential
Bias input(2V typical) for On-chip ADC; This pin
should be connected to AVSS via 0.1µF capacitor.
12
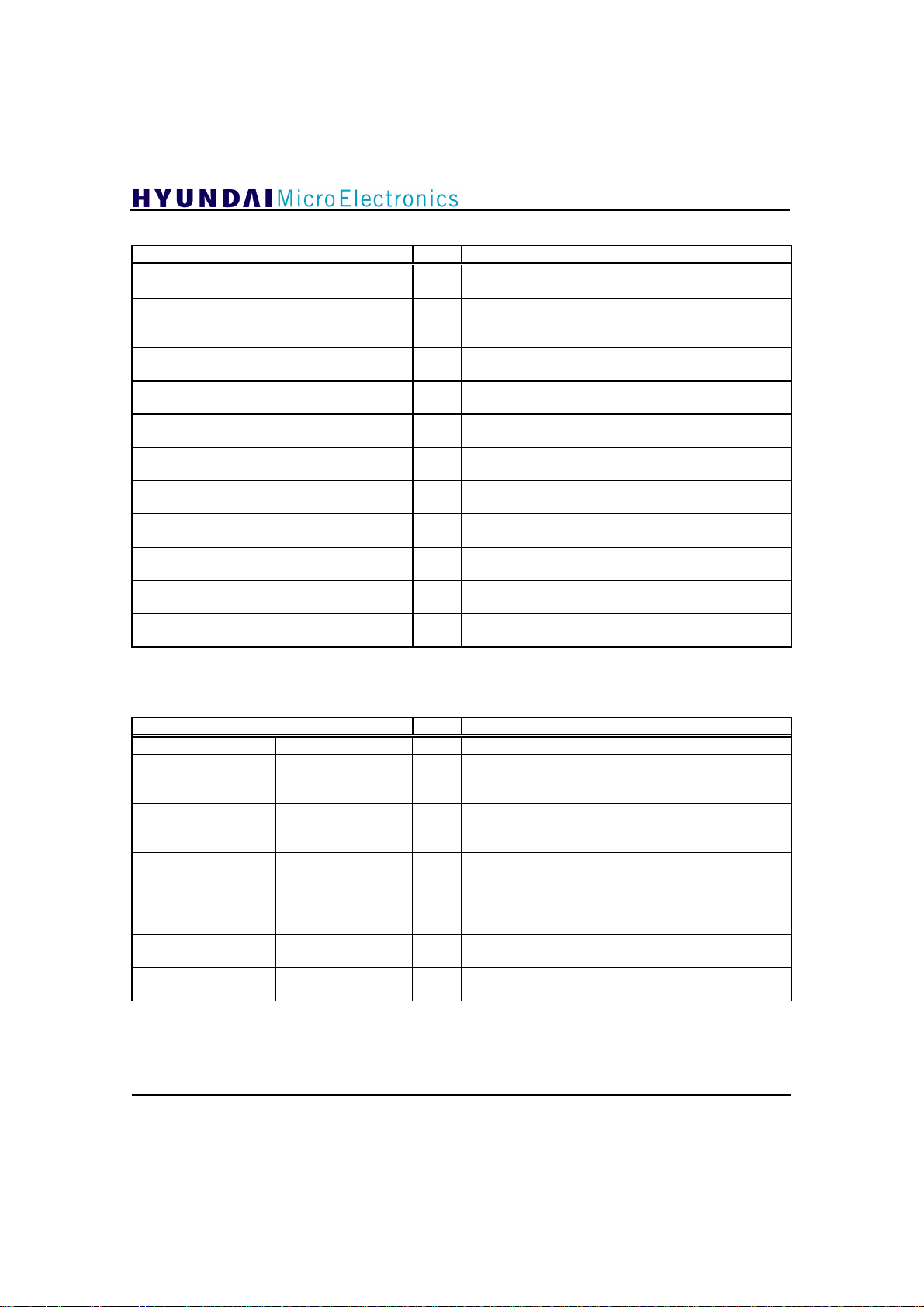
GDC21D003
Sync Recovery ; 20 Pins
PIN NAME TYPE DESCRIPTION
20, 22-24, 26-28,
30-32
44
43
46
52
53
55
56
57
66
90
(NOTE) * These five I/O pins are used as input pin only for chip test.
DIN[9:0]
Bit9 : MSB
DATAPOLP I/O
DATAPOLN I/O*Inverted polarity signal of input data(active high);
SEGSYNCLOCK I/O*Stability Indication of Data Segment Sync
GUP I/O
GDN I/O
NFSYNC O
NCHGUP O Charging signal for charge pump in the timing
NCHGDN O Discharging signal for charge pump in the timing
FOE O
NSEGSYNC O
Equalizer ; 6 Pins
PIN NAME TYPE DESCRIPTION
35
108
110
114
116
117
(NOTE) When I2C is enabled, operation is performed either using these pins or via I2C register, but
when disabled, only these pins are used. If you want to control Equalizer fast, use these external
input pins. Otherwise use I2C bus registers.
PLLEN I
NCOUPDTWIN O
EQSTAT O
NADTONDATA I Data mode coefficient update(active low);
NINITEQ I
NFREEZEEQ I
Digital data input; This data input comes from
I
external ADC.
*
Polarity signal of input data(active high); If this
output value is ‘1’, it means the plus polarity.
This signal should be applied to demodulator IC.
This signal should be applied to demodulator IC.
recovery(active high)
*
Input data gain increasing signal(active high); This
signal should be applied to demodulator IC.
*
Input data gain decreasing signal(active high); This
signal should be applied to demodulator IC.
Field Sync(active low); If this output value is ‘0’, it
means Field Sync interval.
recovery block(active low)
recovery block(active low)
Field status indicator(active high); If this output value
is ‘1’, it means inverted field.
Data Segment Sync(active low); If this output value is
‘0’, it means Data Segment Sync interval.
PLL enable(active high); This pin should be set to ‘1’.
Coefficient update window(active low); If this output
value is ‘0’, the Equalizer adapts its coefficients.
Otherwise, it doesn't adapt its coefficients.
Equalizer status; If this output value is ‘1’, the
Equalizer is in normal status.
Otherwise, the Equalizer has diverged.
If this input is set to ‘0’, the Equalizer adapts its
coefficients during training sequence and data interval.
Otherwise, the Equalizer adapts its coefficients during
only training sequence interval.
Equalizer initialization(active low); If this input is set
to ‘0’, the Equalizer is initialized.
Equalizer freeze(active low); If this input is set to ‘0’,
the Equalizer coefficient does not be adapted.
13
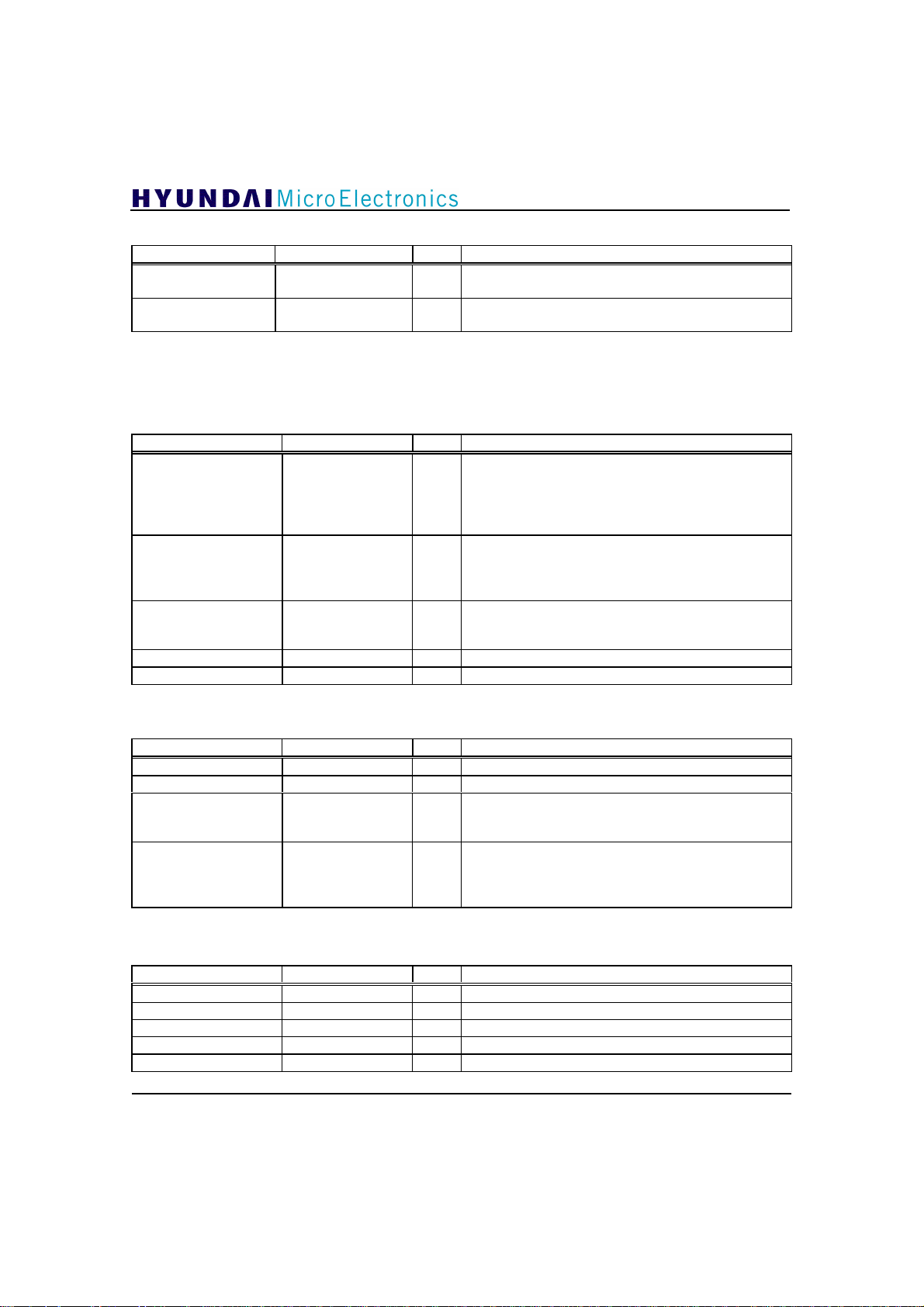
GDC21D003
Phase Tracker ; 2 Pins
PIN NAME TYPE DESCRIPTION
111
112
(NOTE) When I2C is enabled, operation is performed either using these pins or via I2C register, but
when disabled, only these pins are used. If you want to control Equalizer fast, use these
external input pins. Otherwise use I2C bus registers.
NINITPH I
NFREEZEPH I
Channel Decoder ; 12 Pins
PIN NAME TYPE DESCRIPTION
68,69,71,72,74,75,77,
80
83
84
85
89
VSBDATA[7:0]
Bit7 : MSB
NVSBERRFLG O
VSBDVALID O Valid data indication flag;
VSBSOP O Start byte indicator of a packet
VSBCLK O Data clock of packet data
Phase tracker initialization(active low); If this input
is set to ‘0’, the Phase Tracker is initialized.
Phase tracker freeze(active low) ; If this input is set to
‘0’, the Phase Tracker stops phase tracking..
O Data output to transport multiplexer;
VSBDATA[7] : Used as start bit indicator of a byte in
serial output mode.
VSBDATA[0] : Used as serial data output in serial
output mode.
Packet error indication flag(active low); This output
indicates whether the packet has error or not.
0 : with error
1 : without error
1: valid when register64[1](Vsbdvalid_pol = ‘1’)
0 :valid when register64[1](Vsbdvalid_pol = ‘0’)
I2C Bus Interface ; 4 Pins
PIN NAME TYPE DESCRIPTION
9
10
39
119
SCL I I2C bus serial clock input
SDA I/O I2C bus serial data input/output
NI2CEN I
I2CSEL I I2C bus device address selection;
Boundary Scan Signal ; 5 Pins
PIN NAME TYPE DESCRIPTION
3
4
5
6
7
TRST I Boundary scan test reset
TMS I Boundary scan test mode selection
TCK I Boundary scan test clock
TDI I Boundary scan test data input
TDO O Boundary scan test data output
14
2
I
C bus enable(active low); If this input is set to ‘0’,
the chip is controlled by I2C bus.
Otherwise, stand alone mode.
2
0 : I
C device address is set to b"1011001".
2
1 : I
C device address is set to b"0001110".
(default value)
Miscellaneous ; 18 Pins
PIN NAME TYPE DESCRIPTION
58,59,63
91, 93, 95-97, 100,
102-104, 106
16,48,50,61,87
TM[2:0]
Bit2 : MSB
DOUT[9:0]
Bit9 : MSB
NC No connection
Supply Voltages ; 48 Pins
PIN NAME TYPE DESCRIPTION
8, 13, 17, 25, 42, 45,
49,60,64,65,73,78,
79,86,94,101,105,
109,118
11,15,19,21,29,40,
VDD Digital positive supply voltage(3.3V)
VSS Digital negative supply voltage(ground)
47,51,54,62,67,70,
76,81,82,88,92,98
99,107,113,115
1,36,122
33,34,120,127
AVDD Analog positive supply voltage(3.3V)
AVSS Analog negative supply voltage(ground)
GDC21D003
I Tmode;
“111” : normal mode with ADC output
“011” : normal mode with Phase Tracker output
others : reserved for chip test
Data output; Either ADC or Phase Tracker block
O
output is selected by tmode as dout[9:0] output.
15

GDC21D003
4.3 Pin Assignment
PIN NAME TYPE PIN NAME TYPE PIN NAME TYPE
1 AVDD 44 DATAPOLP I/O 87 NC
2 REF I 45 VDD 88 VSS
3 TRST I 46 SEGSYNCLOCK I/O 89 VSBCLK O
4 TMS I 47 VSS 90 NSEGSYNC O
5 TCK I 48 NC 91 DOUT[0] O
6 TDI I 49 VDD 92 VSS
7 TDO O 50 NC 93 DOUT[1] O
8 VDD 51 VSS 94 VDD
9 SCL I 52 GUP I/O 95 DOUT[2] O
10 SDA I/O 53 GDN I/O 96 DOUT[3] O
11 VSS 54 VSS 97 DOUT[4] O
12 VCXO I 55 NFSYNC O 98 VSS
13 VDD 56 NCHGUP O 99 VSS
14 ADCCLK O 57 NCHGDN O 100 DOUT[5] O
15 VSS 58 TM[2] I 101 VDD
16 NC 59 TM[1] I 102 DOUT[6] O
17 VDD 60 VDD 103 DOUT[7] O
18 CLKFS O 61 NC 104 DOUT[8] O
19 VSS 62 VSS 105 VDD
20 DIN[9] I 63 TM[0] I 106 DOUT[9] O
21 VSS 64 VDD 107 VSS
22 DIN[8] I 65 VDD 108 NCOUPDTWIN O
23 DIN[7] I 66 FOE O 109 VDD
24 DIN[6] I 67 VSS 110 EQSTAT O
25 VDD 68 VSBDATA[0] O 111 NINITPH I
26 DIN[5] I 69 VSBDATA[1] O 112 NFREEZEPH I
27 DIN[4] I 70 VSS 113 VSS
28 DIN[3] I 71 VSBDATA[2] O 114 NADTONDATA I
29 VSS 72 VSBDATA[3] O 115 VSS
30 DIN[2] I 73 VDD 116 NINITEQ I
31 DIN[1] I 74 VSBDATA[4] O 117 NFREEZEEQ I
32 DIN[0] I 75 VSBDATA[5] O 118 VDD
33 AVSS 76 VSS 119 I2CSEL I
34 AVSS 77 VSBDATA[6] O 120 AVSS
35 PLLEN I 78 VDD 121 COM I
36 AVDD 79 VDD 122 AVDD
37 CLK4FS I/O 80 VSBDATA[7] O 123 REFN I
38 NRESET I 81 VSS 124 REFP I
39 NI2CEN I 82 VSS 125 INN I
40 VSS 83 NVSBERRFLG O 126 INP I
41 SYMCLK I 84 VSBDVALID O 127 AVSS
42 VDD 85 VSBSOP O 128 BIAS I
43 DATAPOLN I/O 86 VDD
16
GDC21D003
5. I2C Bus I/F & Registers
5.1 I2C Bus I/F Description
When NI
may be controlled over I2C bus interface which
consists of two signals, serial data(SDA) and serial
clock(SCL) that can control a large number of
devices on a common bus. The Device Address of
this chip is “1011001”b or “0001110”b which can
be selected by I2CSEL pin. The data on the I2C bus
can be transferred at a rate up to 100 kbits/s in the
standard mode, or up to 400 kbits/s in the fast
mode. In the GDC21D003, SDA is bi-directional
but SCL is only used as input, since the IC can only
act as a slave device. In normal operations, data
transfers are clocked by the SCL signal with one
SCL pulse per data bit, and SDA is required to be
stable during the high period of the SCL signal.
Transitions of SDA while SCL is high are
performed by the interface signals of start(S),
stop(P), and repeated start(Sr) conditions. The start
condition is defined as a high-to-low transition of
SDA while SCL is high, and the stop condition is
the low-to-high transition of SDA while SCL is
high. Data transmissions are always proceeded by a
start condition and ended with a stop condition, and
may contain repeated starts within the transmission
to alter the direction of the data flow or to change
register base addresses. All data transmission
2
CEN pin is set to Low, the GDC21D003
operations occur in 8-bit blocks with each block
acknowledged through the designated receiver by
the generation of an acknowledge signal(A). This
signal is generated on the ninth pulse of SCL for
each transferred block.
5.1.1 Write Operation
In order to perform a write operation, the interface
is accessed in following manner. The master first
generates a start condition by pulling SDA down to
low while SCL is high. The master next sends a 7bit Device Address and a one bit R/W signal, and
each slave compares this address with its own
address and acknowledges the master if the device
address sent by the master coincides with that of its
own. If not so, the slave ignores the rest of current
data being transmitted. If the master is writing to
the GDC21D003, the chip interprets the next data
byte as a register base address. This is used as the
location to store the next received data byte. This
base address increases as each data byte is received
allowing a contiguous register block to be
programmed in a single transmission. Noncontiguous blocks may be programmed in multiple
transmissions or by using a repeated start condition,
which allows a new Device Address and register
base address to be specified without the master
giving up control of the bus. The transmission is
terminated with the receipt of a stop condition.
A BASE ADDRESS A DATA #1
ISSUED BY MASTER
SDA
DEV. ADDRESS W
S
Figure 5.1.1 I
5.1.2 Read Operation
Read operation is performed in a manner similar
to write operation. The master first generates a
start condition and then sends the Device Address
and R/W signal. The master will acknowledge
each byte as receiving if it desires another byte to
be sent. At the end of the transmission, the master
will not acknowledge the slave and will then be
ISSUED BY GDC21D003
2
C Write Operation Example
free to generate a stop condition to terminate the
transmission. The base address register contents
are used to determine the location to be read, and
once again this address will be increased with each
successive read. Because the base address register
can only be programmed through a write operation,
a general read will require two accesses or a single
access with a embedded repeated start to change
the direction of transmission.
…
A
DATA #N A
P
17
GDC21D003
A
A
A
P S DEV. ADDRESSDEV. ADDRESS
DEV. ADDRESS
DATA #2
ISSUED BY GDC21D003
ASDA SrW
R
…
A
R DATA #1
DATA #N
A
SDA
DEV. ADDRESS
S
S
A BASE ADDRESS
DATA #1
A BASE ADDRESS
W
ISSUED BY MASTER
C Read Operation Example
Figure 5.1.2 I
2
5.2 I2C Bus Register Configuration
Add
ress
0
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Dinmode Dinsel ADCCLKSEL ADCCLKPH DCbypass DChold AGChold AGCoffsetW 11110000
1
2
VSBmod[2:0] “ 10010 ” 10110010
3
4
5
“ 00 “ PolarityW Polarity “ 10 “ nSyncLockrst VSBmodW 00001000
VCXOSEL[1:0] nCombW nComb Combouthalf NoCombgain[1:0] “ 0 “ 00011010
6
7
8
X nSyncLock nSegLock Combstat nVSBmodstart DATAPOLN nPolLock nFldLock
9
10
11
X nFrmLock nVSBLock “ 0101 “ XXXX0101
X VSBmodA[2:0]
12
13
14
15
nSyncLockPH U U nCombPH nSyncLockEQ nDSsycnEQ nFsyncEQ nCombEQ
32
nFreezePHI2 InitPHI2 PHASmodeIN[1:0] nFreezeEQI2 InitEQI2 STEPsizeIN[1:0] 10001011
33
EQmodeIN TRAINmodeIN[1:0]
34
nIIR16ONIN nIIRONIN nAdtOnDataI2 BLIDmodeIN[1:0] nRingENIN nCoefRead nMakeRingIN 10100101
35
36
PredicIN[1:0] LoopgainIN[2:0] nOPERmodeIN nDNgainIN nDNgainThIN 11000011
37
DATA BYTE
AGCoffset[7:0] 01100000
“ 11001000 “ 11001000
DCvalue[7:0]
X
X
X
X
X nCombLock
X
CombOutHalfI
N
TapAddress[7:0] 00000000
nDSadptIN nEQoutIN FLTtestIN[1:0] 00010000
A
A P
Initial
Value
P
18
GDC21D003
Add
ress
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
64
65
66
67
128
DATA BYTE
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
WrCoef[11:8] RdCoef[11:8] 0000XXXX
WrCoef[7::0] 00000000
RdCoef[7:0]
UpdtRngIN[9:8] MeanErrINE[18:16] MeanErrOUTE[18:16] 00XXXXXX
UpdtRngIN[7:0] 10010000
MeanErrINE[15:8]
MeanErrINE[7:0]
MeanErrOUTE[15:8]
MeanErrOUTE[7:0]
MenErrOUTP[18:16] UPlimitIN[9:8] UDlimitIN[9:8] DCinformRD[8] XXX0111X
MenErrOUTP [15:8]
MenErrOUTP [7:0]
UPlimitIN[7:0] 00000000
UDlimitIN[7:0] 00000000
DCinformRD[7:0]
U GAINcnt[2:0] “ 1101 “ XXXX1101
Pase Viterbi_on Deint_on RSdec_on Derand_on Errorflag_ins Vsbdvalid_pol Vsbclk_sup 11111111
Err_count[7:0]
U U U Data_out_en X XXX1XXXX
Err_count[15:8]
“ 0 “ X 0XXXXXXX
Initial
Value
Where U: unused register bit, X: don’t care
19
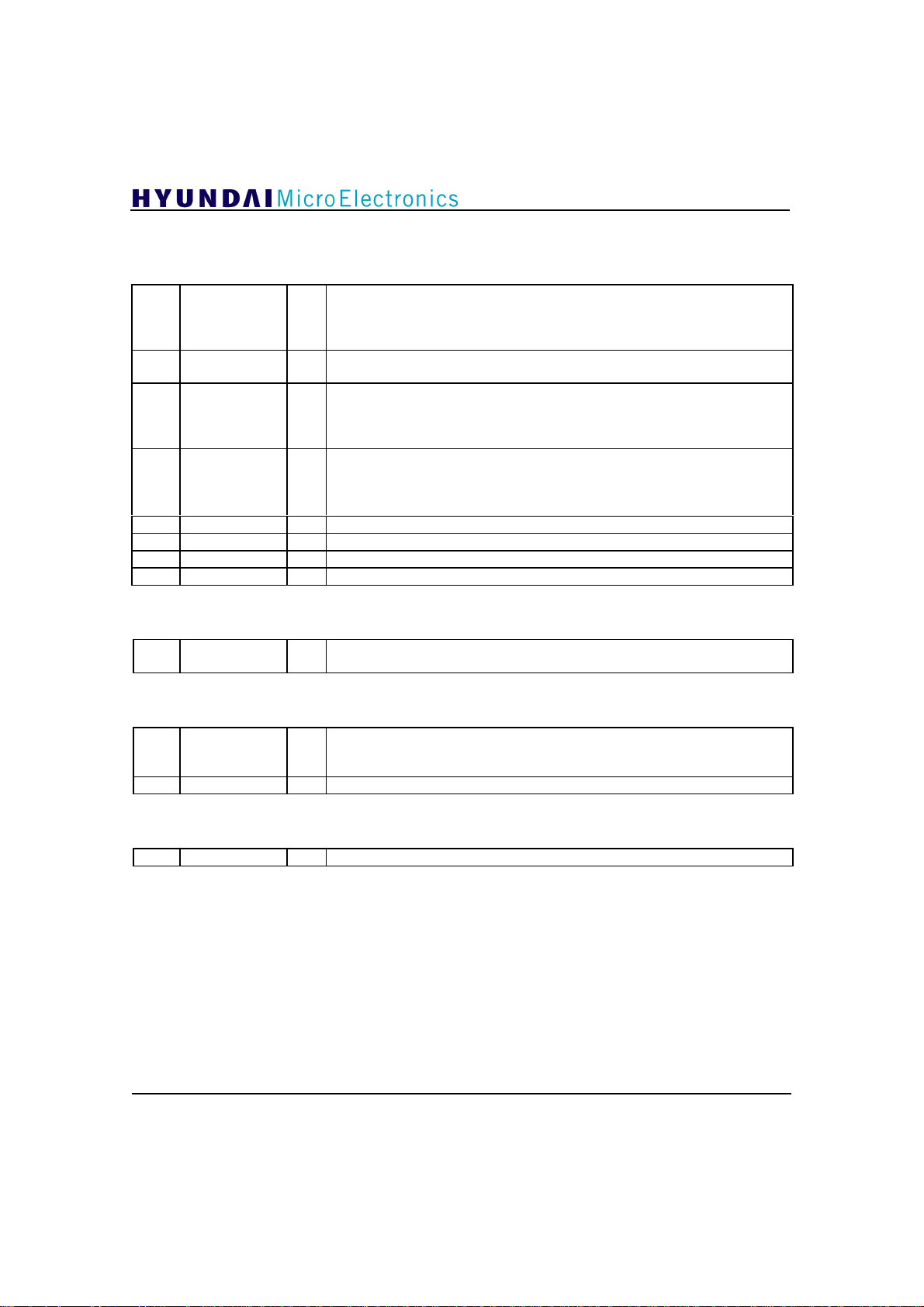
5.3 I2C Bus Register Description
Address 0:
Most significant bit (MSB) inversion control signal of data input (DIN[9:0]).
7 Dinmode W
6 Dinsel W
5 ADCCLKSEL W
4 ADCCLKPH W
3 DCbypass W DC remove block bypass (active high). Initial value is ‘ 0’.
2 DChold W DC remove block hold (active high). Initial value is ‘0’ .
1 AGChold W AGC block hold (active high). Initial value is ‘0’.
0 AGCoffsetW W AGC offset write enable (active high). Initial value is ‘0’.
Address 1:
AGCoffset
[7:0]
[7:0]
If data input form is unsigned, the MSB of digital data input should be inverted
because all of functions in this chip use their complement data. If this bit is set
to ‘1’, it indicates the inversion of MSB. Initial value is ‘ 1’ . (refer to table 6.3.1)
Digital data input path selection signal. If this bit is set to ‘1’, it indicates output
of the internal ADC. Initial value is ‘1’. (refer to table 6.3.1)
ADC Clock Select. When the frequency of VCXO is 2fs(21.52MHz), the output
frequency of ADCCLK can be one of the two following frequencies,
fs(10.76MHz) and 2fs. If this bit is set to ‘1’, the frequency of ADCCLK is
always fs. Initial value is ‘1’. (refer to table 6.2.1)
ADC Clock Phase Select. This signal can choose one of the ADCCLK output
phases. If this bit is set to ‘0’, the ADCCLK output phase is rotated 180° off with
respect to CLKFS phase, and otherwise 0°. Default value is ‘1’. (refer to table
6.2.1)
AGC offset value. If AGCoffsetW is set to ‘1’, this signal is used for the
W
reference of AGC block. Default value is “01100000”.
GDC21D003
Address 2:
[7:5]
VSBmod[2:0] W
[4:0] W Initial value is “10010”. It would be better set to “10110”.
VSB mode signal. If VSBmodW is set to ‘1’, this signal is used for VSB mode
signal. Otherwise the VSBmod[2:0] signal is generated internally. Initial value
is “101”.
Address 3:
[7:0] W Always set to “11001000”.
20
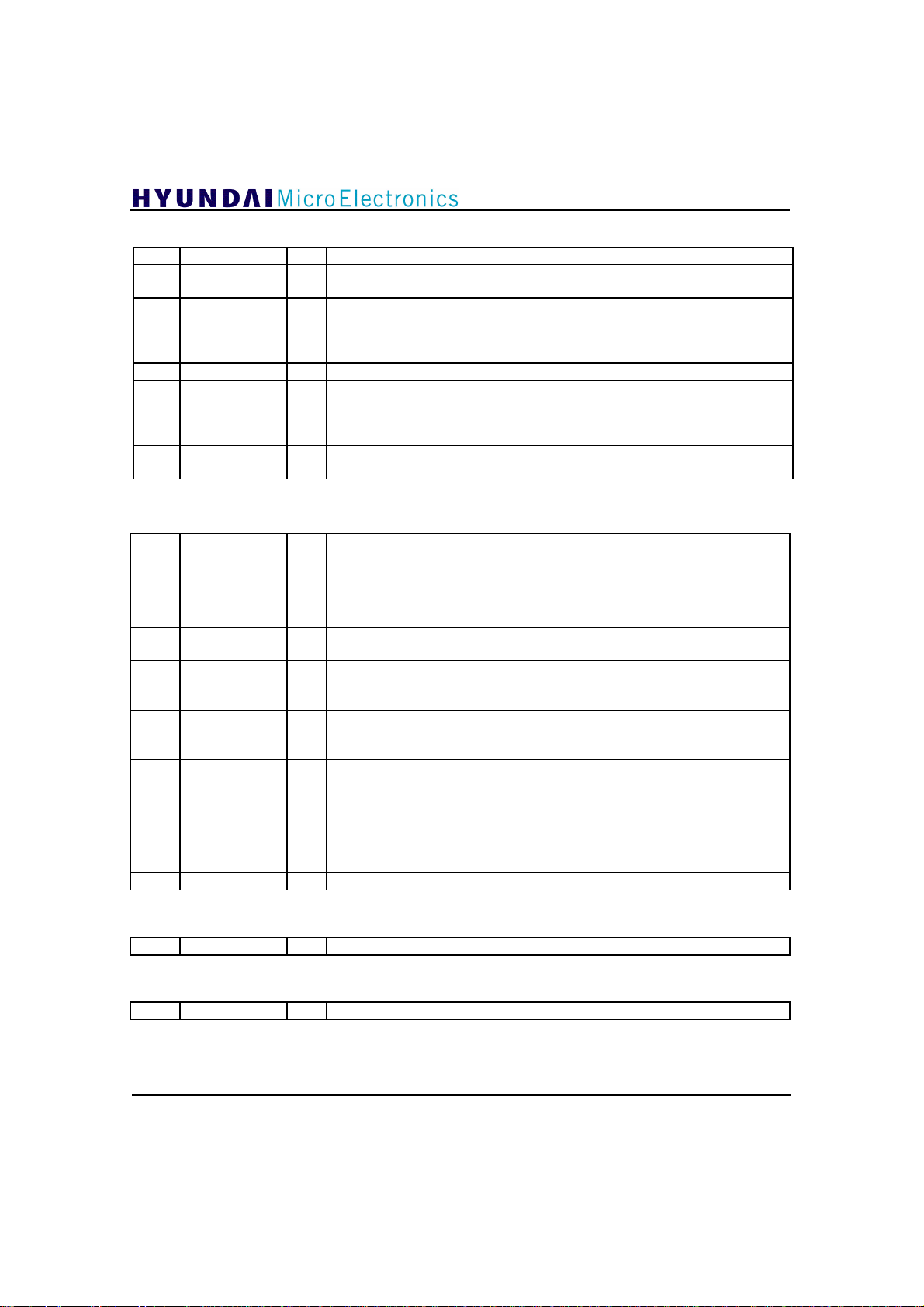
Address 4:
[7:6] W Initial value is “00”. It would be better set to “01”.
5 PolarityW W
4 Polarity W
[3:2] W Always set to “10”.
1 nSyncLockrst W
0 VSBmodW W
Polarity signal write enable. If this bit is set to ‘1’, it means write enable.
Initial value is ‘0’.
Polarity signal for polarity control and DATAPOLP/DATAPOLN. If
PolarityW is ‘1’, this signal is used for polarity control and the generation of
DATAPOLP/DATAPOLN signal output. Otherwise the polarity control block
uses internally calculated signal. Initial value is ‘0’. (refer to table 6.3.2)
nSyncLock reset control signal. If this bit is set to ‘0’, nSyncLock signal isn't
initialized by the change of VSB mode. Otherwise, nSyncLock signal is
initialized and changed to ‘0’ for the next Field sync duration. Initial value is
‘0’.
VSB mode write enable. If this bit is set to ‘1’, it means write enable.
Initial value is ‘0’.
Address 5:
VCXO Selection. These pins should be set as follows according to the output
[7:6]
5 nCombW W
4 nComb W
3 Combouthalf W
[2:1]
0 W Always set to ‘0’.
VCXOSEL
[1:0]
NoCombgain
[1:0]
frequency of VCXO.
VCXOSEL[1:0] The output frequency of VCXO
W
00 fs(10.76Mhz)
01 2fs(21.52Mhz)
Initial value is “00”.
nComb signal write enable. If this bit is set to ‘1’, it means write enable.
Initial value is ‘0’.
Comb filter ON/OFF signal. If nCombW are ‘1’, this signal is used for Comb
filter ON/OFF signal. Otherwise the Comb filter ON/OFF signal is generated
internally. Initial value is ‘1’.
Comb filter output gain selection signal. If this bit is set to ‘0’, the gain of the
Comb filter output is 1. Otherwise its gain is 1/2. When Comb filter is activated
this signal is valid. Initial value is ‘1’.
NoComb path gain selection signal. The gain is as follows;
NoCombgain[1:0] the gain of normal path
“00” 1(0dB)
W
“01” 1.125(1.023dB)
“10” 1.1875(1.493dB)
“11” 1.25(1.938dB)
Initial value is “01”.
GDC21D003
Address 6:
[7:0] DCvalue[7:0] R Calculated DC value of input data.
Address 7:
[7:0] R don’ t care
21
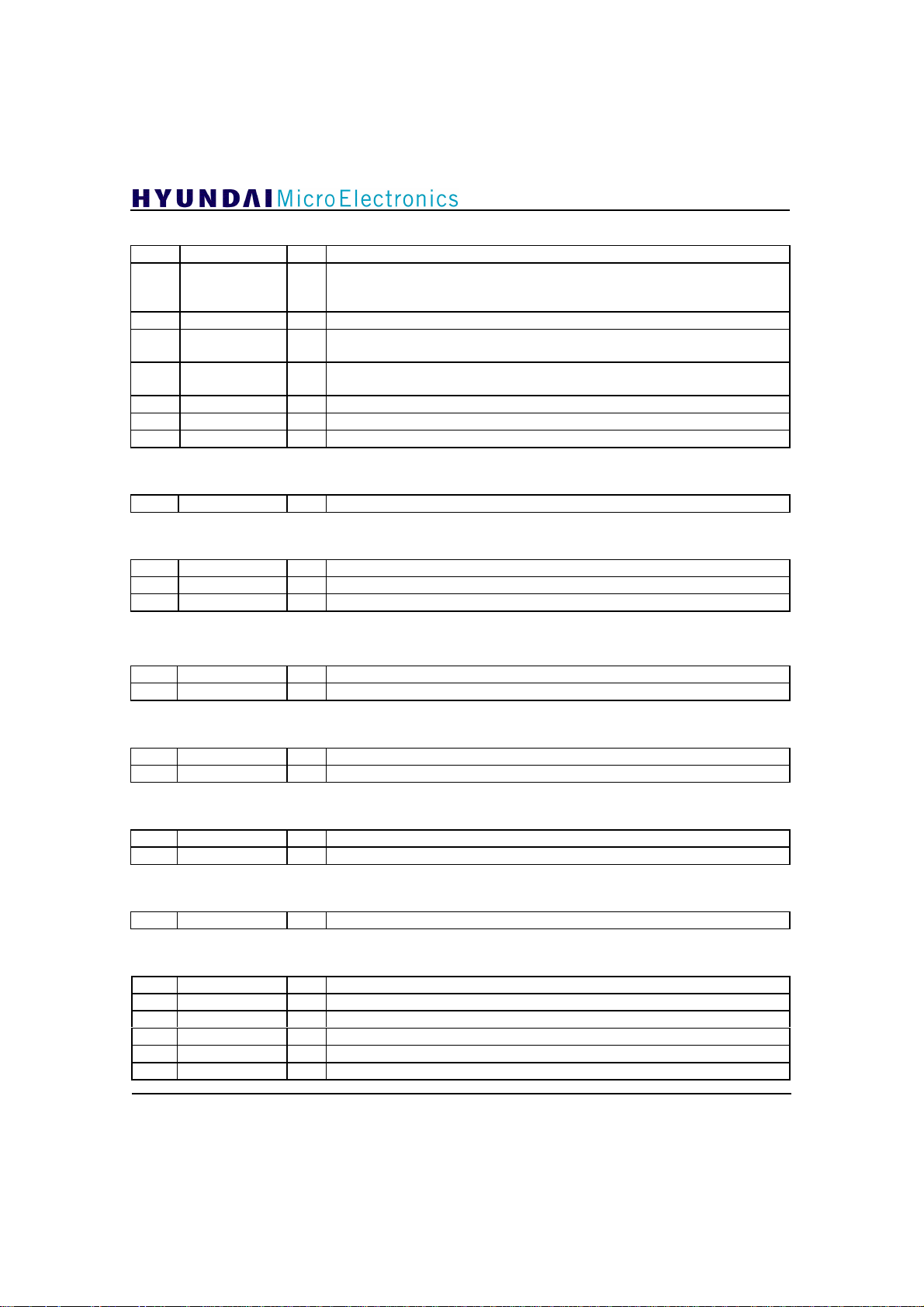
GDC21D003
Address 8:
7 R don’t care
Stability Indication of Data Sync Recovery block (active low). If the value of
6 nSyncLock R
5 nSegLock R Stability Indication of Data Segment Sync Recovery (active low).
4 Combstat R
3 nVSBmodstart R
2 DATAPOLN R Inverted polarity signal of input data.
1 nPolLock R Stability Indication of Polarity Decision (active low).
0 nFldLock R Stability Indication of Field Sync Recovery (active low).
Address 9:
[7:0] R don’ t care
Address 10:
[7:6] R don’ t care
5 nFrmLock R Stability Indication of inverted/non-inverted Field decision (active low).
4 nVSBLock R Stability Indication of current VSB mode detection (active low).
this bit is ‘0’, Data Segment Sync Recovery and Field Sync Recovery blocks
are stable.
Comb filter ON/OFF status. If the value of this bit is ‘0’, it indicates the Comb
filter is ON.
Start indication of VSB mode detector which in the Equalizer. If the value of
this bit is ‘1’, it means detector is reset.
Address 11:
[7:3] R don’ t care
[2:0]
VSBmodA[2:0]
R Internally decided VSB mode.
Address 12, 13:
[7:0] R don’ t care
[7:0] R don’ t care
Address 14:
[7:1] R don’ t care
0 nCombLock R Stability Indication of Comb filter ON/OFF decision (active low).
Address 15:
[7:0] R don’ t care
Address 32 :
7 nSyncLockPH R the state of the nSyncLock at the output of Phase Tracker
4 nCombPH R indicates whether comb filter is on or not at the output of Phase Tracker
3 nSyncLockEQ R the state of the nSyncLock at the output of Equalizer
2 nDSsyncEQ R the state of Data Segment Sync at the output of Equalizer
1 nFsyncEQ R the state of Field Sync at the output of Equalizer
0 nCombEQ R indicates whether Comb filter is on or not at the output of Equalizer
22

Address 33 :
7 nFreezePHI2
6 InitPHI2
PHASmodeIN
[5:4]
[1:0]
3 nFreezeEQI2
2 InitEQI2
STEPsizeIN
[1:0]
[1:0]
GDC21D003
‘0’ : Freezes the Phase Tracker in the device, which means phase tracking does
not occur.
‘1’ : normal operation
W/R
If you want to control Phase Tracker fast, use external input pins.
Initial value is ‘1’.
‘1’ : Initialize the Phase Tracker in the device.
‘0’ : normal operation
W/R
If you want to control Phase Tracker fast, use external input pins.
Initial value is ‘0’.
There are three loops in the Phase, which are gain, offset, and phase loop
Tracker.
00 : all loops on
01 : offset loop off
W/R
10 : offset and gain loops off
11 : all loops off
Initial value is “00”.
‘0’ : Freezes the Equalizer in the device, which means coefficient update does
not occur.
W/R
‘1’ : normal operation
If you want to control Equalizer fast, use external input pins.
Initial value is ‘1’.
‘1’ : Initializes the Equalizer in the device.
‘0’ : normal operation
W/R
If you want to control Equalizer fast, use external input pins.
Initial value is ‘0’.
There are three available step-sizes in the Equalizer.
10,11 : smallest step-size
W/R
01 : middle step-size
00 : largest step-size
Initial value is “11”.
23
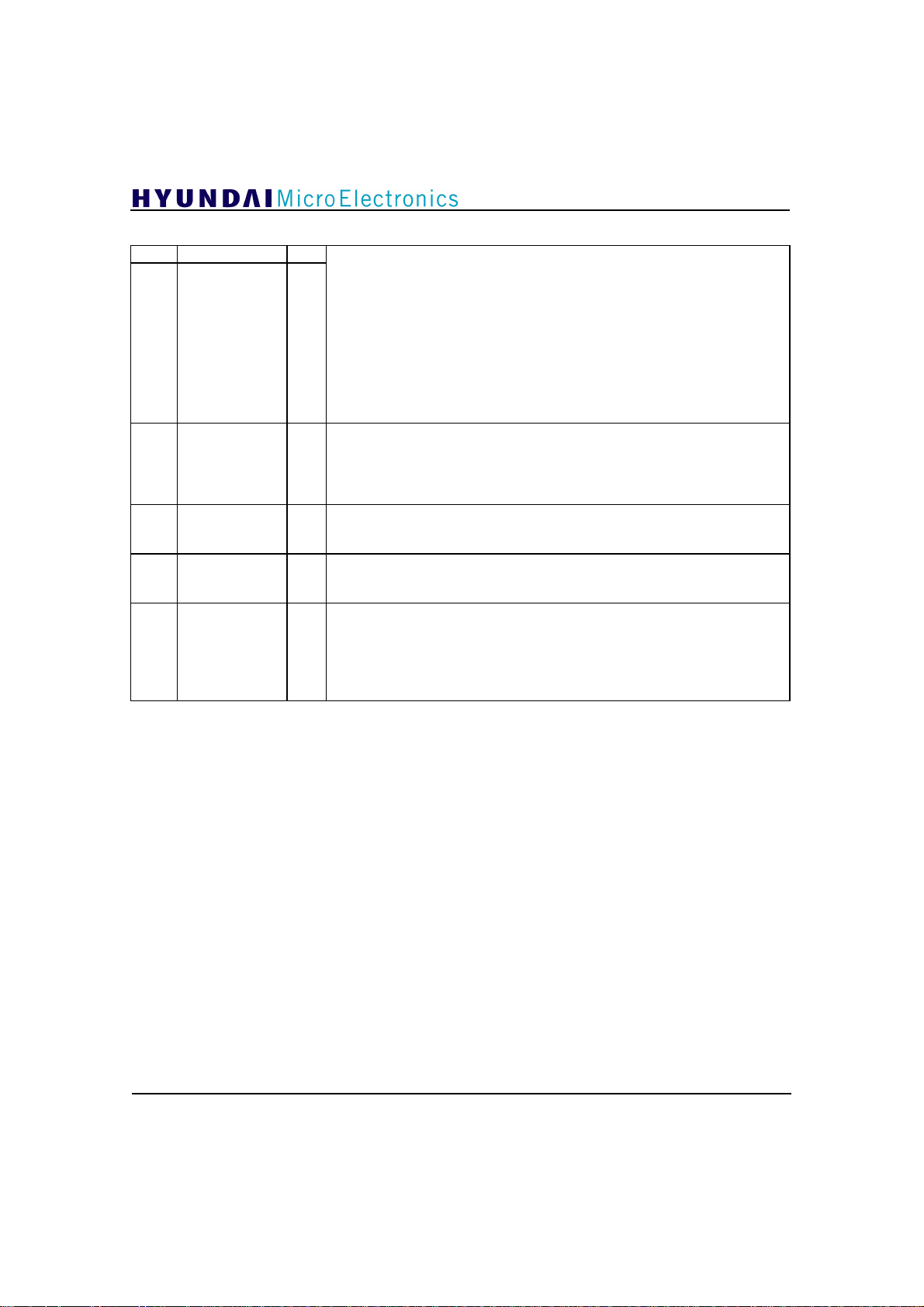
Address 34 :
7 EQmodeTIN
[6:5]
4 CombOutHalfIN
3 nDSadptIN
2 nEQoutIN
[1:0] FLTtestIN[1:0]
TRAINmodeIN
[1: 0]
GDC21D003
Updating range of the training sequence. The range value can be changed with
W/R
combination of these three bits. Initial value is “000”.
EQmodeTIN is ‘0’
00 : 574 symbols of field sync are used for equalization.
01 : 637 symbols of field sync are used for equalization.
10 : 700 symbols of field sync are used for equalization.
W/R
11 : 820 symbols of field sync are used for equalization.
EQmodeTIN is ‘1’
00 : 574 symbols of field sync are used for equalization.
01 : 637 symbols of field sync are used for equalization.
10,11 : 700 symbols of field sync are used for equalization.
Comb filter output gain selection signal.
‘0’ : the gain of the Comb filter output is 0
‘1’ : the gain of the Comb filter output is 1/2
W/R
When Comb filter is activated this signal is valid.
Initial value is ‘1’.
‘0’ : uses data segment during equalization.
‘1’ : not uses data segment during equalization.
W/R
Default value is ‘0’.
‘0’ : noise removed output from Equalizer
W/R
‘1’ : bypassed output
Initial value is ‘0’.
The location of center tap can be changed using these two bits. Initial value is
“00”.
00 : Center tap is 32nd tap
W/R
01 : Center tap is 44th tap
10 : Center tap is 52nd tap
11 : Center tap is 60th tap
24

Address 35 :
7 nIIR16ONIN
6 nIIRONIN
5 nAdtOnDataI2
[4:3]
2 nRingENIN
1 nCoefRead
0 nMakeRingIN
BLNDmodeIN
[1:0]
Address 36:
[7:6] PredicIN[1: 0]
[5:3]
2 nOPERmodeIN
1 nDNgainIN
0 nDNgainThIN
LOOPgainIN
[2 : 0]
GDC21D003
‘0’ : feedback filter is on in 16 VSB mode
W/R
‘1’ : feedback filter is off
Initial value is ‘1’.
‘0’ : feedback filter is on in 2, 4 and 8 VSB mode
‘1’ : feedback filter is on only in 8 VSB mode
W/R
Initial value is ‘0’.
‘0’ : coefficient adaptation during training sequence and data interval
‘1’ : coefficient adaptation during training sequence interval only
W/R
Initial value is ‘1’. If you want to control Equalizer fast, use external input pins.
“00” : does not use blind equalization
“01” : uses blind equalization with 4-level data
W/R
“10”, “11” : uses blind equalization with 2-level data
Initial value is “00”.
‘1’ : can not change nMakeRingIN
‘0’ : can change nMakeRingIN
W/R
Initial value is ‘1’.
‘0’ : read coefficient
W/R
‘1’ : write coefficient
Initial value is ‘1’.
‘0’ : can read and write the coefficients
‘1’ : normal operation
W/R
Initial value is ‘1’.
Determines whether to use slice predictor in Phase Tracker. Initial value is “11”.
“00” : Slice Prediction is OFF.
W/R
“01” : not use.
“10” : not use.
“11” : Slice Prediction is ON.
Determines use of automatic gain routine and type of loop gain to be used in
Phase Tracker. Initial value is “000”.
“000” : Automatic gain change.
“001” : phase tracker is OFF.
W/R
“010” : smaller gain.
“011” : normal gain.
“1xx” : not use.
Sets the operation mode
‘0’ : -60° ~ 60°
W/R
‘1’ : -45° ~ 45°
Initial value is ‘0’.
Choose the value of loop gain. Initial value is ‘1’.
W/R
Choose the threshold value of loop gain when gain loop is used in automatic
W/R
mode. Initial value is ‘1’.
Address 37:
TapAddress
[7:0]
[7: 0]
Filter tap address in Equalizer. Initial value is “00000000”.
address 0 to address 63 : feed forward filter
W/R
address 64 to address 255 : feed back filter
25
 Loading...
Loading...