Page 1

PODOLSKI
version 1.2.2
USER GUIDE!
u-he • Heckmann Audio GmbH • Berlin
Page 2

Wednesday, 22. January 2020
Table of Contents
Introduction 3
About Podolski 3 ......................................................
Installation 3 .............................................................
GUI Elements 4 ........................................................
Control Bar 5 ............................................................
Synthesis 6
Global Settings 6 ......................................................
Oscillator 7 ...............................................................
Envelope 10 .............................................................
Amplifier 11 ...............................................................
LFO global / LFO voice 12 .......................................
Filter 13 ....................................................................
Delay 14 ...................................................................
Chorus / Flanger 15 .................................................
Arpeggiator 16
Switches in the global panel 16 ................................
Arpeggiator Control Sequence 17 ............................
Preset Browser 19
Directory Panel 20 ....................................................
Presets panel 22 ......................................................
Preset Tagging 23 ....................................................
Search Functions 24 ................................................
Configuration 26
About MIDI CC 26 ....................................................
Preferences 29 .........................................................
NKS 31
Page 3

INTRODUCTION
Introduction
About Podolski
Podolski is a freeware virtual analogue synthesizer featuring a flexible, Zebra2-style
arpeggiator / step sequencer, plus delay and chorus effects.
Main Features
•
Oscillator – the Warp and Invert functions can be used to create many different waveforms, including (of course) the classic sawtooth, triangle and pulse / PWM
•
Envelope – only one envelope here, but Gate can be used for the amplifier instead
•
2 LFOs – one global (i.e. for all voices) and one per voice
•
Filter – classic owpass, Bandpass or Highpass with extra parameters Drive, Click (an
impulse at Note On) and AutoFM (bipolar frequency modulation from the oscillator)
•
Arpeggiator – combined arpeggiator, step sequencer and modulator, like in Zebra2
•
2 effects – stereo delay and chorus / flanger with feedback
•
resizable GUI – with 3 alternative skins. Version 1.2.1 introduces 10% GUI scaling
Installation
Go to the Podolski page, grab the installer for Mac or PC, double-click on the downloaded
file and follow further instructions. To update, simply install over the existing version.
File locations
The precise locations depend on your installation paths:
Win
Presets (local) C:\Users\*YOU*\Documents\u-he\Podolski.data\Presets\Podolski\!
Presets (user) C:\Users\*YOU*\Documents\u-he\Podolski.data\UserPresets\Podolski\!
Preferences C:\Users\*YOU*\Documents\u-he\Podolski.data\Support\ (*.txt files)
Mac
Presets (local) Macintosh HD/Library/Audio/Presets/u-he/u-he/Podolski/!
Presets (user) *YOU*/Library/Audio/Presets/u-he/Podolski/!
Preferences *YOU*/Library/Application Support/u-he/com.u-he.podolski... (*.* files)!
Resources Macintosh HD/Library/Application Support/u-he/Podolski/
To uninstall, delete the plugin(s) and the associated files / directories."
intro oscillator envelope amplifier LFO filter effects arpeggiator presets configuration 3
Page 4

INTRODUCTION
Team 2020
Urs Heckmann (boss, concepts)
William Rodewald (student life-support code)
Sebastian Greger (GUI design, 3D stuff)
Rob Clifton-Harvey (IT admin, backend development)
Viktor Weimer (support, presets, the voice)
Jan Storm (framework, more code)
Thomas Binek (QA, bug-hunting, presets)
Howard Scarr (user guides, presets, necessary grump)
Sascha Eversmeier (code, bad puns)
Frank Hoffmann (more framework, new browser)
Alexandre Bique (all things Linux)
Henna Gramentz (office supervision)
Jayney Klimek (office management)
Alf Klimek (tagging & repairs, studio)
Melina Garbisch (studio attendant)
Oddvar Manlig (everything else!)
GUI Elements
Knobs
Podolski’s knobs work like vertical faders (click and drag). You can also hover over any
control and roll your mouse wheel if there is one. Values appear in the data display,
which reverts to showing the name of the current preset after a few seconds.
For fine control, hold down a SHIFT key on your computer keyboard before moving a
knob. Values can be reset to the default by double-clicking on any knob. Alternatively,
try alt+click (Mac) or ctrl+click (Win).
Switches
For the sake of simplicity, the pop-up menus dotted around Podolski’s GUI are called
“switches” throughout this manual. Select from a menu via mouse-click, or scroll
through the options using a mouse wheel.
Appearance
The window can be resized from (70% to 200%) by right-clicking anywhere in the background. There is a choice of 2 skins: Cozy and Blue Steel.
The skin selection and GUI size can be made more permanent – see Configuration."
intro oscillator envelope amplifier LFO filter effects arpeggiator presets configuration 4
Page 5

INTRODUCTION
Control Bar
The bar at the top is used for switching the view as well as calling a few utility functions:
SYNTHESIS | ARPEGGIATOR | PRESETS
The 3 large buttons select the panel view. Each has its own chapter in this user guide.
PODOLSKI
Either side of the central label you will see information about the plujgin format as well
as the revision number.
MIDI
An indicator for any MIDI activity e.g. playing a note.
UNDO / REDO
Click on the curved arrows to UNDO or REDO an action. You can even undo a change of
preset so that you don’t lose edits made to the previous one. If an UNDO or REDO step is
available, the arrow will be highlighted (white).
SAVE
Stores the loaded preset in either the User folder or the currently open folder, depending
on the status of the Save Presets To preference.
Right-clicking on the [SAVE] button lets you select the preset format you will be using.
Standard is .h2p, which has the great advantage of being cross-platform compatible.
The .h2p extended format is similar but also allows per-line comments (the preset files are
therefore a bit larger). If you loaded the VST2 version you will also see the option .nks in
the list. See the NKS chapter.
Selecting Tag this patch opens a window where you can specify one or more Categories,
Features and Characters for the currently loaded preset. See Preset Tagging.
U-HE Badge
Click on the badge to open a popup menu containing links to this guide, to our web- site,
to our support forum at KVR as well as our address in various social networks.
Configuration cogwheel
Clicking on the cogwheel symbol top-right opens the configuration pages where you can
set up remote control (via MIDI CC) as well as various global preferences. For details,
read the Configuration chapter."
intro oscillator envelope amplifier LFO filter effects arpeggiator presets configuration 5
Page 6
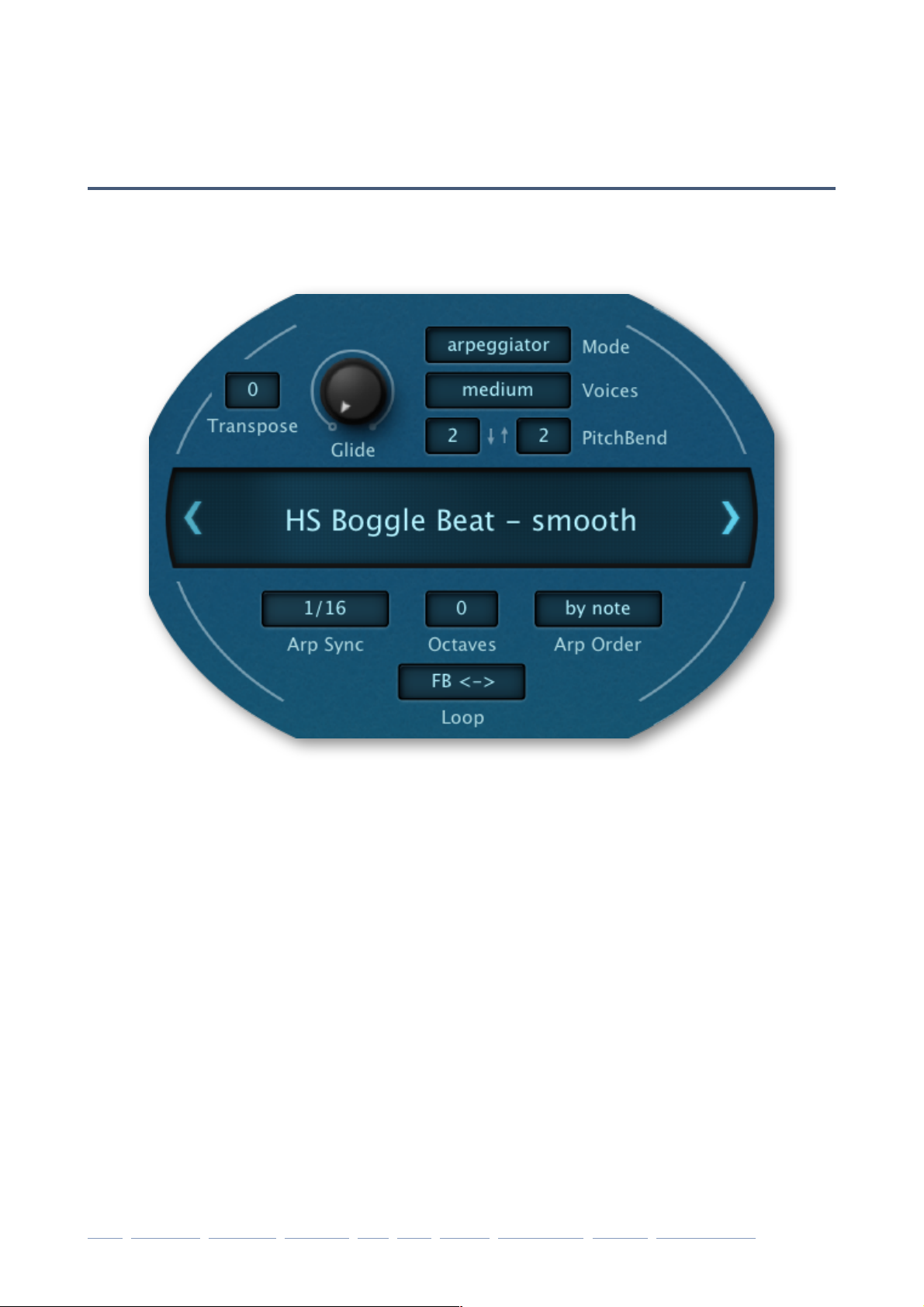
SYNTHESIS
Synthesis
Global Settings
The main views, SYNTHESIS, ARPEGGIATOR and PRESETS are selected using the row
of buttons at the top left of Podolski’s window. The Synthesis and Arpeggiator views both
have a few panels in common, including the global settings:
Data Display
The bar in the middle normally shows the name of the selected preset. While you are
editing the preset, however, it shows the value of the parameter being adjusted. After a
few seconds of inactivity it reverts to displaying the preset name again.
Clicking on the data display lets you select a preset from the current folder. You can use
the arrows to the left and right of the display to step through presets – even stepping
“across the boundary” into neighbouring folders.
Initialize function: Whenever you want to start programming a sound from scratch,
simply right-click on the data display and select init.
Voice settings
There are six voice-related controls immediately above the data display...
Transpose
Adjusts the overall pitch in semitones within a +/- 2 octave range.
Glide
Controls portamento (glide) rate. Turn this up to slew between consecutive notes."
intro oscillator envelope amplifier LFO filter effects arpeggiator presets configuration 6
Page 7

SYNTHESIS
Mode
Selects one of 4 basic voice modes:
poly polyphonic i.e. you can play chords and overlapping notes
mono monophonic: each new note triggers the envelope
legato monophonic: the envelope is not retriggered until after a space has been
left between consecutive notes – great for expressive solos
arpeggiator polyphonic: arpeggios are defined in the Arpeggiator panel
Voice s
Specifies the maximum number of notes available at the same time, usually to save
CPU but also quite useful for characterful “voice-stealing” effects:
few 4 voice polyphony (arpeggiator: 6)
medium 8 voice polyphony (arpeggiator: 12)
many 16 voice polyphony
PitchBend
These two small switches define the pitch bend ranges (down and up), from 0 to 24
semitones. Set down and up to different values (e.g. 12 and 3), then try the pitch bender
on your MIDI keyboard.
Arpeggiator settings
Below the Data Display are four arpeggiator controls. For a description of these switches as well as all the other arpeggiator parameters, read the Arpeggiator chapter.
Oscillator
Podolski’s oscillator is basically a sawtooth wave with adjustable symmetry (via Warp).
Podolski’s oscillator also includes an inverted wave that can be mixed in via the Inv/PWM
knob. As the two signals can be phase-shifted apart, variable width pulse waves and other
waveforms are available…
intro oscillator envelope amplifier LFO filter effects arpeggiator presets configuration 7
Page 8
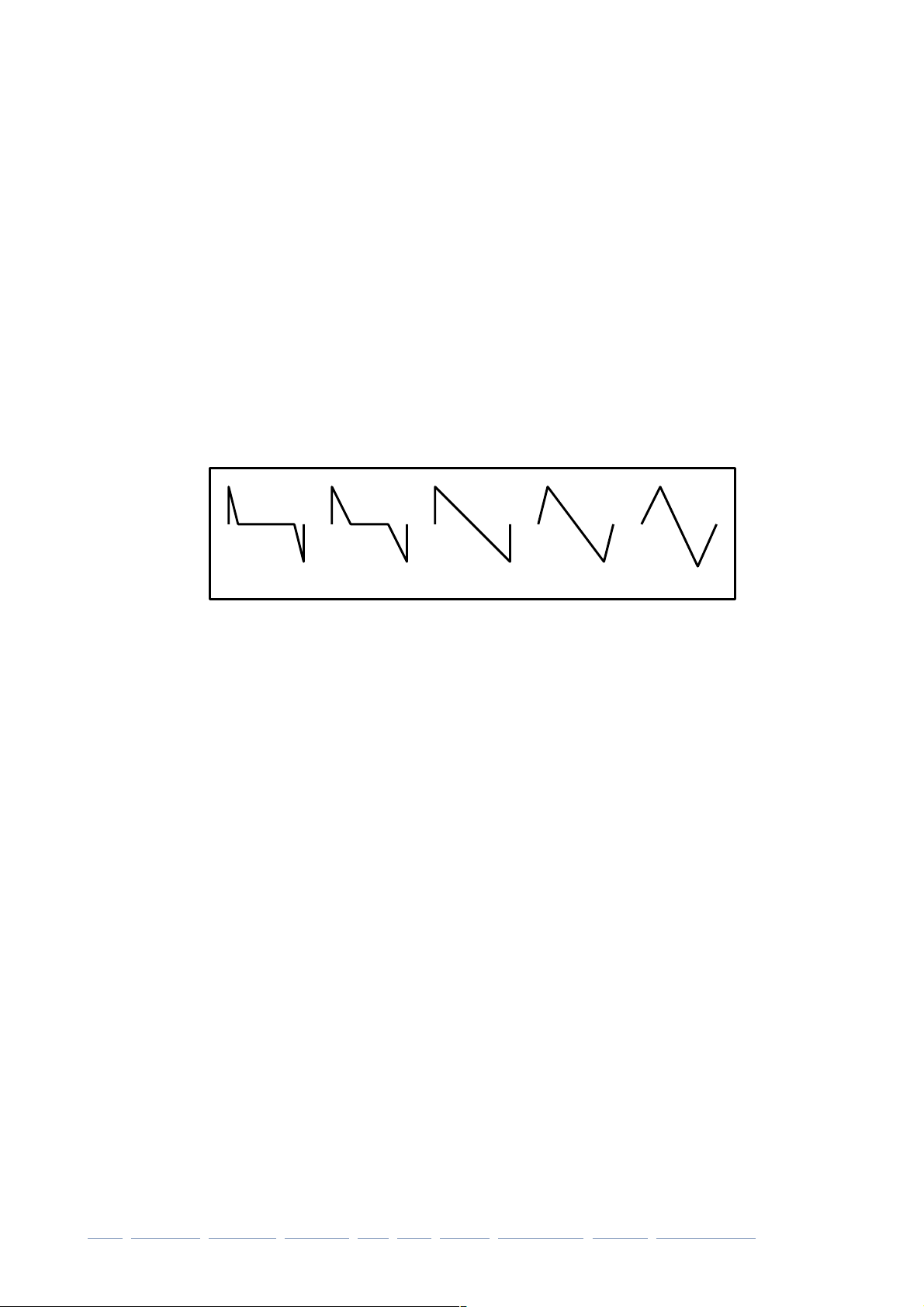
SYNTHESIS
Tune / TuneMod / Vibrato
Tune
The Tune knob adjusts the oscillators basic pitch by +/- 24 semitones.
TuneMod
The TuneMod knob sets the amount of Tune modulation from a source selected in the
neighbouring switch. Experiment with different modulation sources and amounts.
Vibrato
Sets the amount of Tune modulation from a fixed source, namely LFO voice (LFO1).
WaveWarp / WarpMod
WaveWarp
Controls the basic oscillator shape.
The minimum setting gives you a bright spike, the centre position (50%) is a classic
sawtooth which morphs into a triangle as you turn WaveWarp up to maximum.
WarpMod
The knob sets the amount of WaveWarp modulation from a source selected in the associated switch. Experiment with different modulation sources and amounts.
Phase / PhaseMod / Inv-PWM
Phase
The Phase knob shifts (in opposite directions) the phases of the two oscillator signals.
PhaseMod
The PhaseMod knob sets the amount of Phase modulation from a source selected in
the neighbouring switch. Experiment with different modulation sources and amounts!
Inv/PWM
Controls the relative mix between the ‘normal’ and ‘inverted’ waves. Facilitates PWM..."
intro oscillator envelope amplifier LFO filter effects arpeggiator presets configuration 8
0% 25% 50% 75% 100%
Page 9
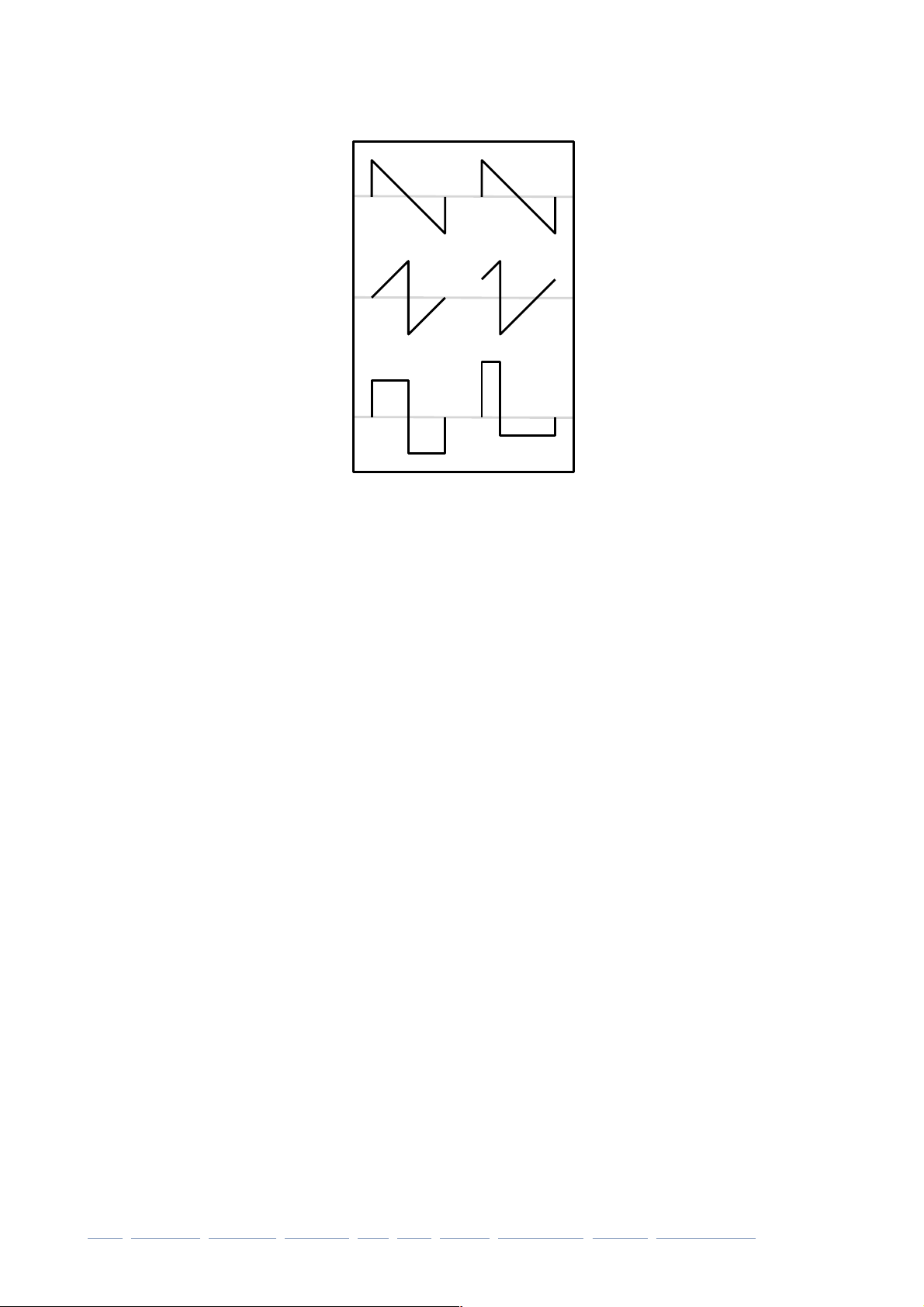
SYNTHESIS
How to do PWM
Although the oscillator is sawtooth-based, it is also capable of generating variable-width
pulse waves. To achieve this, Podolski’s oscillator includes an inverted version of the
waveform and lets you shift the relative phases apart.
The centre-left waveform in this image is the same as the one above it, but inverted vertically and precisely 180° (i.e. half the total wavelength) out of phase. Adding these two
results in a square wave.
The phase of the centre-right waveform is much closer to the top wave. It is only shifted
by about 90°, resulting in a much narrower pulse.
This means that cyclic PWM (pulse width modulation) can be achieved by e.g. using an
LFO to modulate the phase difference…
1. Load init via right-click on the data display
2. Set oscillator Inv/PWM to the centre i.e. 0.00 (WaveWarp and Phase are at 50.00)
3. Select LFO1 as PhaseMod source and turn the amount up to about 20
4. Change the LFO VOICE Sync to 1s
5. Push the modulation wheel…
Of course you could try a different modulator for the Phase e.g. the envelope…
intro oscillator envelope amplifier LFO filter effects arpeggiator presets configuration 9
+ +
= =
Page 10

SYNTHESIS
Envelope
Synthesizer envelopes are used to shape the volume and/or tone of each note...
Mode
Podolski lets you select one of four envelope modes – adsr exp, adsr ln, hdsr exp and
hdsr ln. Those abbreviations have the following meanings:
adsr classic envelope type with Attack, Decay, Sustain and Release stages, plus ............
an extra Fall-Rise stage that modifies the sustain (see below)
hdsr similar to adsr, but the Attack stage is replaced by a Hold stage: The level ............
starts at maximum and remains there for the time set by the Attack knob
exp short for ‘exponential’: the attack, decay and release stages are all curves .............
like in the image below
ln short for ‘linear’: the attack, decay and release are all straight lines .................
Stages (Attack, Decay...)
Attack
This knob controls either the time it takes for the envelope to rise from zero to maximum
level (in adsr mode) or the length of the Hold stage at maximum level (in hdsr mode)
Decay
The time it takes to fall from maximum down to the sustain level
Sustain
The level after Decay. Normally remains at this position until the note is released..."
intro oscillator envelope amplifier LFO filter effects arpeggiator presets configuration 10
note on note off
Attack Decay Sustain Release
Rise
Fall
Sustain
Level
Page 11

SYNTHESIS
Fall-Rise
...but what happens during the sustain stage can be modified by using Fall-Rise:
Negative values: time to ‘fall’ from the current sustain level down to zero!
Positive values: time to ‘rise’ up from the current sustain level to maximum
Note: Fall-Rise settings close to the centre (0.00) are slow, larger values are faster
Release
After a note is released, the time it takes to fall from the current sustain level to zero.
Velocity
How much MIDI velocity (how ‘hard’ a note is played) affects the level of the envelope.
Note: Remember that Podolski’s envelope can modulate various parameters, not just
the amplifier. For instance, if you want the envelope to control e.g. filter frequency without affecting the volume in any way, you could try switching the VCA switch in the amplifier section to Gate instead of Envelope1...
Amplifier
This panel contains the main volume control plus a few extras...
Pan
The stereo position. Can also be useful for balancing the stereo image of presets that
have a lop-sided delay effect.
VCA
Envelope1 uses the envelope to control volume!
Gate notes start immediately, are held and have just enough release time to
avoid clicks. Using Gate here frees up the envelope for other tasks.
Output
The main volume control. Note that some presets – those with very high filter resonance
– have relatively low Output values to prevent unwanted distortion.
Modulation
Output level modulation e.g. for tremolo effects (LFO), or to balance levels across the
keyboard (KeyFollow). The neighbouring knob controls the amount.
intro oscillator envelope amplifier LFO filter effects arpeggiator presets configuration 11
Page 12

SYNTHESIS
LFO global / LFO voice
Podolski has two LFOs (low frequency oscillators) which can be either synchronized to the
host tempo (from 1/64 to 8 bars) or set to absolute times (0.1s, 1s or 10s).
The main difference between the LFOs is that there is only one global LFO, while each
note gets its own voice LFO. The parameters on this page are common to both LFOs:
Sync
Sets the LFO speed. Except for three absolute times (see the note below), LFO rates in
Podolski are synchronized to the song tempo. The range is from a 64th to 8 bars, including several triplet (“3 in the space of 2”) and dotted (“half as much again”) values.
Note: At the top of the list are three absolute times measured in seconds (0.1s, 1s, 10s).
LFO speeds in Podolski can’t be modulated, however – consider them a bonus!
Waveform
sine pure sine wave!
triangle pure triangle wave!
saw up rising saw (‘ramp’)!
saw down falling saw !
sqr hi-lo square wave, restarted at the higher level!
sqr lo-hi square wave, restarted at the lower level!
rand hold random steps!
rand glide random curves
Restart
Determines when and how the LFOs are retriggered. The options differ:
Global LFO
The global LFO can be restarted in sync with the host application. The values are off,
each bar, 2 bars ... 32 bars.
Voice LFO
sync never restarts – LFOs for all notes are always in phase!
gate restarts per note at the specified Phase (see below)!
single similar to sync, but restarts at the next note after all notes are released!
random restarts at a random phase per note (the value of Phase is ignored)"
intro oscillator envelope amplifier LFO filter effects arpeggiator presets configuration 12
Page 13

SYNTHESIS
Phase
Sets the phase (i.e. the position within its cycle) at which the LFO will be restarted according to the Restart setting. Ignored by the voice LFO if Restart is set to random.
Delay
Voice LFO only. The level of the LFO is faded in whenever a note is played – this knob
controls how slowly this happens.
Tip: you can use the Delay feature to turn the voice LFO into a simple ramp envelope by
setting it to a slow square wave in Gate mode – see the preset HS Mix Area Musik.
DepthMod
Unlike the global LFO, the level of the voice LFO can be modulated. A typical use of this
feature is to control vibrato amount from a modulation wheel.
Filter
Podolski’s filter offers you the classic choice of Lowpass, Bandpass or Highpass...
Cutoff
The edge-frequency. In Podolski, integer steps are precise semitones apart.
Resonance
Resonance is an internal feedback loop that emphasizes the cutoff frequency. Tip: High
resonance can lead to a very hot output signal, so you might need to turn that a long
way down to compensate. Even as little as 5.00.
intro oscillator envelope amplifier LFO filter effects arpeggiator presets configuration 13
Page 14

SYNTHESIS
Type
The basic filter mode: Lowpass, Bandpass or Highpass.
Modulation 1 / Modulation 2
The filter has a pair of cutoff modulation switches / knobs. In the above image, cutoff is
modulated by a random amount as well as the voice LFO. The most commonly used
modulation source here is probably Envelope1.
KeyFollow
The key-follow parameter controls the amount of cutoff modulation from the played MIDI
note – the higher the note, the higher the cutoff. At 100%, it follows semitones exactly.
Note that the ‘pivot note’ (where key-follow always outputs zero) in Podolski is E3.
Drive
The filter has its own Drive parameter which can be used to distort the filtered signal.
The effect can be subtle, but is particularly strong when Rez is turned up.
Click
Click feeds a short impulse into the filter, which can be used to e.g. add punch or cause
immediate resonance, whatever the signal from the oscillator.
AutoFM
Podolski’s filter can be frequency-modulated from it own input signal i.e. the oscillator,
either negatively or positively. This feature is rare in digital synthesizers, although it can
deliver very lively timbres which, depending on the polarity and amount of FM, range
from silky-smooth to dirty-grungy. Especially effective with very low notes and/or PWM!
Delay
Podolski has a simple stereo delay unit featuring two host-synchronized delay times and
two types of feedback:
Sync Left / Right
The two Sync switches specify the repeat rate of each delay channel, measured in musical note lengths. The range is from one 64th to whole-bar triplets. Tip: You will usually
find that the non-triplet times are more suitable for rhythmic effects, and a mixture of
triplet and dotted times are often best for washy effects.
intro oscillator envelope amplifier LFO filter effects arpeggiator presets configuration 14
Page 15

SYNTHESIS
Feedback
Controls how much of the signal is fed back into the same delay channel.
Cross
Similar to Feedback, but this one controls how much of the signal from the right channel
is fed into the left and vice versa. Experiment with Feedback and Cross together.
Mix
Balance control between 100% dry and 100% wet (delay only).
Chorus / Flanger
Although often frowned upon by analogue synth purists, chorus is a popular effect in polyphonic synthesizers. Podolski’s chorus is a fairly basic delay-based unit, but includes resonant feedback in two flavours (negative and positive)...
Center
The Center knob controls the nominal delay times (from about 2 to 10 milliseconds).
Tip: Use lower values for typical chorus/ensemble effects, and higher values for more
complex flanging effects.
Speed
The chorus effect requires an internal LFO to modulate the delay times. The Speed
knob regulates its rate. Note that lower values are faster than high values i.e. the knob
works in the opposite direction from what you might expect!
Depth
Modulation intensity. Set fairly high values for deep effects, or turn all the way down for
static colouration effects.
Feedback
Sends some of the output signal back into the input. When fed back, the short delays
create resonant frequencies that can sound very dramatic. Set to the centre for regular
chorus, or set negative / positive values for different-sounding resonance.
Mix
Balance control between 100% dry and 100% wet (delays only). Values above the centre (50%) increase the stereo width, but may reduce the tonal colouration."
intro oscillator envelope amplifier LFO filter effects arpeggiator presets configuration 15
Page 16

ARPEGGIATOR
Arpeggiator
Clicking on the Arpeggiator button in the upper bar gives us the following view:
The right half of the window is now filled with arpeggiator parameters. The envelope panel
stays where it was, while the global section and the filter (simplified) are shifted to the left.
The remaining filter parameters and the oscillator are only visible in the SYNTHESIS view.
Switches in the global panel
First of all, you will need to select arpeggiator Mode. The parameters Arp Sync, Octaves,
Arp Order and Loop are also here in the global panel:
Mode
Remember: This is where you turn the arpeggiator on or off!
Arp Sync
Sets the arpeggio rate relative to the song tempo received from your host program.
intro oscillator envelope amplifier LFO filter effects arpeggiator presets configuration 16
Page 17

ARPEGGIATOR
Octaves
0, 1 or 2 times: How often the octave is shifted up after all notes in the buffer have been
played back.
Arp Order
Incoming notes are ordered within a note buffer in one of two ways. Note: The buffer is
then played back in the direction set by the Loop parameter.
by note notes are reordered according to MIDI note number!
as played retains the original order in which notes were played is retained
Loop
Determines the direction in which the note buffer is played back. See Arp Order.
f --> forwards !
b <-- backwards!
fb <-> forwards / backwards!
bf >-< backwards / forwards
Note: The Loop setting does not affect the direction in which the sequence runs.
Arpeggiator Control Sequence
Half of the Arpeggiator view is taken up by 16 columns of note parameters:
It may look daunting at first, but like e.g. an audio mixer, once you have understood a single channel strip you are most of the way towards understanding the “whole shebang”.
intro oscillator envelope amplifier LFO filter effects arpeggiator presets configuration 17
Page 18

ARPEGGIATOR
Glide on Legato
When the Slide switch is on, any Glide set in the global panel will only be applied to
connected notes (see Gate below).
Step
The switch to the left sets the number of steps used. Tip: For longer sequences, you
don’t always need more than a few steps. 3 steps are enough to create a 15-note sequence (or 24 in fb or bf Loop mode) if you set Octaves to 2 and play a 5-note chord.
The symbols to the right determine which note (in the buffer) is played. Tip: for typical
monophonic arpeggios, set all steps to last:
next: play the next note
same: repeat the same note
first: play the first note (see Arp Order on the previous page)
last: play the most recent note (see Arp Order on the previous page)
Length
Step lengths are defined as multiples of the Arp Sync value:
single, 2 times, 3 times, 4 times
Gate
As arpeggiators automatically play / release notes, the gate times need to be defined:
0, 1 ,2, 3, 4 from very short to almost the length of ArpSync!
5 (legato) connected to the next step – see also Glide on Legato above
The step following a 5 (legato) will not be triggered unless it uses more than one Voice.
Voices
Sets the maximum number of notes that can be played simultaneously, from 0 (mute the
step) to a 6 note chord.
Transp
Pitches may already be jumping around, but in addition to this movement the individual
steps can be transposed +/- 12 semitones. Unpredictability is to be expected!
ARP MOD
At the bottom of the Arpeggiator panel is a row of bipolar sliders which can be used to
modulate anything in sync with the arpeggiator. For instance, let the arpeggiator control
cutoff by selecting ArpModulator in one of the filter’s ‘Cutoff Mod’ switches."
intro oscillator envelope amplifier LFO filter effects arpeggiator presets configuration 18
Page 19

PRESETS
Preset Browser
To open the preset browser, click on the PRESETS button in the upper bar.
Folders appear on the left, presets appear in the centre and information about the currently active preset appear on the right. If you can’t see any presets at all, click on Local. If
you can’t see the PRESET INFO panel on the right, click on the button in the top right and
select Show Preset Info.
The Local root directory contains a representative selection of presets copied from the
subfolders. After selecting a preset here you can step through the others using your com-
puter’s cursor keys.
If you want the preset browser to open automatically every time you load a new instance of
Podolski, right-click on the [PRESETS] button while the browser is active and select set as
default view. To revert to showing the synth panels by default, do the same while the preset browser is closed.
Default preset
Whenever Podolski is started it checks whether Local contains a preset called default. If
this file exists, it is loaded instead of the ‘vanilla’ preset. Note that default will not appear in
the browser.
Check that the ‘Local’ root directory is currently open then [SAVE] your preset under the
name default. If a fresh instance of Podolski doesn’t automatically load your new preset it
probably landed in ‘User’ instead of ‘Local’. If so, go into the Preferences and change the
Save Presets To option to selected folder instead of user folder, then repeat the above.
intro oscillator envelope amplifier LFO filter effects arpeggiator presets configuration 19
Page 20

PRESETS
Directory Panel
Local
Podolski’s factory presets are sorted into folders 1 through 7. We recommend that you
do not add or remove presets here, but save all your creations and other soundsets in
the ‘User’ folder (see below).
MIDI Programs
‘Local’ also contains a special folder called ‘MIDI Programs’ which is normally empty.
When the first instance of Podolski starts, up to 128 presets from that folder are loaded
into memory, to be selected via MIDI Program Change messages.
All presets (up to 128) present in this folder will be loaded into memory when the first
instance of Podolski starts and can be switched via ‘Program Change’ messages.
As MIDI Programs are accessed in alphabetical order it makes sense to prefix each
name with an index ‘000 rest-of-name’ to ‘127 rest-of-name’.
IMPORTANT: Unlike regular presets, MIDI Programs can’t be added, removed or renamed on the fly. Changes will only take effect after the host software is restarted!
The MIDI Programs folder can contain up to 127 sub-folders of 128 presets, switched
via MIDI ‘Bank Select’ messages (CC#0) preceding the Program Change message. The
MIDI Programs folder itself is bank 0, sub-folders are addressed in alphabetical order
starting with bank 1."
intro oscillator envelope amplifier LFO filter effects arpeggiator presets configuration 20
Page 21

PRESETS
When Podolski receives a program change message, it will display the bank and program numbers to the left of the preset name e.g. “0:0” for the first preset in the first
bank. In certain hosts, however, the first bank / preset is designated “1” instead of the
more correct “0”.
To avoid another possible source of confusion, make sure that there are no junked presets in the MIDI Programs folder. All files there are addressed, even if hidden!
User
The best address for your own creations as well as soundsets from other sources. You
can either select User immediately before saving the preset, or set a global preference
(Save Preset To) which ensures that it will always be saved to this folder.
Tip: It’s worth finding out where the User folder actually resides on your computer.
Right-click on User and select reveal in Finder (Mac) or open in Explorer (Win).
Smart Folders
The other folders don’t contain files, but display the results of querying a database of
presets. The content is dynamic i.e. it will change whenever the data changes.
Search History
Click on this folder to display the results of past searches (maximum 10). Whenever you
need to make the results of a search more permanent, right-click and select save
Search... The entry will be moved to the Saved Searches folder – see below. To remove
all searches from the list, right-click on the Search History folder and select clear.
Saved Searches
This folder contains searches that have been saved via right click from Search History.
To remove individual saved searches, right-click on the search and select delete.
Tip: Entries dragged from Saved Searches and dropped onto real folders within Local or
User will create a folder containing copies of all found presets!
Favourites
8 smart folders, one for each Favourite colour. See Presets context menu on the next
page. Presets dropped onto one of the Favourites folders will be marked as such.
Junk
A smart folder pointing to all junked presets. See Presets context menu on the next
page. Pre- sets dropped onto this folder will be junked, and will therefore disappear
from the rest of the browser unless made visible (see show junk in the Presets context
menu).
Tags
Smart folders for each Category/Subcategory, Features and Character tag. Presets
dropped onto these folders will adopt the tag. Presets dropped onto the Untagged folder
will have all Category/Subcategory, Features and Character tags removed.
Author
Smart folders for each Author. Tip: Instead of signing each of your creations, you could
sign just one of them, then select them all and drag them onto Author/(You)/. As the
process cannot be undone, please use this feature with caution!
intro oscillator envelope amplifier LFO filter effects arpeggiator presets configuration 21
Page 22

PRESETS
Directory context menu
Right-clicking on any folder within Local or User will open this menu:
refresh: Update the contents of the browser. This is necessary after you have moved, added, removed or renamed any
folders or presets using Explorer / Finder.
create new: Insert an empty subdirectory.
rename: Edit the folder name.
reveal in Finder / open in Explorer: Opens a system win-
dow for the clicked folder. After adding, removing or renaming
preset files or folders outside of Podolski’s own browser, it is
best to refresh the directory.
move to Trash / Recycle Bin: Moves the selected folder to the system trash.
on open expand to: These options determine how deeply the browser will open subdi-
rectories whenever the GUI is (re)opened or the refresh function is called. The first none
option collapses all folders, while the final all levels option reveals all nested folders.
Presets panel
Right-click to open a menu of functions that can be applied to individual presets.
mark as favourite: Choose one of eight ‘favourite’ marks. The
selected entry in the menu will be replaced with unmark as
favourite.
mark as junk: Instead of deleting any unloved presets, you can
mark them as ‘junk’ so that they disappear from the browser...
show junk: Activate this option to display junked files (see
above) in- stead, but mark them with a STOP symbol.
select all, deselect: See Multiple Selection below.
rename: You can change the names of presets using this func-
tion. Note that only the most recently selected preset can be
renamed i.e. you can’t rename multiple files at once.
copy to User folder / duplicate: This entry depends on the
status of the Save Presets To preference as well as on the lo-
cation of the source preset(s) i.e. whether they are in the Local
or the User folder. Selected presets are copied with a number
appended to the name, which increments so that presets can
not be overwritten by mistake.
reveal in Finder / open in Explorer: Opens a system window for the selected preset.
After adding, removing or renaming preset files outside of Podolski’s own browser, remember to refresh the directory.
convert to native / h2p / h2p extended / nks: Converts selected preset(s) into the
format previously specified via right-click on the [SAVE] button.
move to Trash / Recycle Bin: Moves selected presets to the system trash.
intro oscillator envelope amplifier LFO filter effects arpeggiator presets configuration 22
refresh
create new…
rename…
reveal in Finder *
move to Trash
on open expand to
show folder icons
mark as favourite
select all
deselect
show junk
rename…
copy to User folder
reveal in Finder *
convert to h2p
move to Trash
mark as junk
mark as favourite
mark as favourite
mark as favourite
mark as favourite
mark as favourite
mark as favourite
mark as favourite
Page 23

PRESETS
RESTORE
You can audition as many presets as you like in the browser without losing track of the
one that was loaded immediately before you opened the browser: Clicking on
[RESTORE] navigates to that preset and loads it again.
Multiple selection, drag & drop
A block of adjacent presets can be selected via shift+click, and individual presets can be
added to the selection via cmd-click (Mac) / alt+click (Win). Presets can be moved to a
different folder via drag & drop. Use SHIFT etc. on your computer keyboard to highlight
the files you want to move, click and drag them from the files area and drop them onto a
target folder. To deselect, either click on an unselected preset or choose deselect from
the context menu.
Note: unmark as favourite (see mark as favourite above) will not appear in the presets
context menu for multiple files unless you right-click on an existing favourite.
Preset Tagging
Tags are elements of metadata, information added to presets so that they can be found
more easily.
IMPORTANT: The tags are updated automatically – clicking on the [SAVE] button isn’t
required. The main advantage is that presets don’t have to be saved every time you edit
a tag. However, this means you should only edit tags after saving your preset!
For instance, if you decide to edit tags while creating a second version of an existing
preset, please remember that you are actually changing the tags in the original preset!
The Tagging Window
Right-click on the [SAVE] button and select Tag this patch:
Category describes a preset by analogy to instrument types or typical usage, and each
one has an appropriate set of subcategories. Features are technical classifications, and
Character tags are pairs of opposites from which you can choose only one.
intro oscillator envelope amplifier LFO filter effects arpeggiator presets configuration 23
Pads
Leads
Keys
FX
Drums
Seq+Arp
Other
Bass Acoustic
FX Bass
Plucks
Vocal
Sub
E-Bass
Dry
Soft Attack
Chord
Mono
BPM
Slow Release
Percussive
Glide
Phat
Soft
Constant
Bright
Clean
Aggressive
Moving
Dirty
Thin
Dark
Poly
Modulated
Synth
CHARACTERFEATURESCATEGORY
Page 24

PRESETS
Tagging via PRESET INFO
In the PRESET INFO panel, right-click on the Category, Features or Character and
select or unselect tags from the menu. Note that this method only works for individual
presets. If you right-click on an existing tag, the first option becomes remove tag. The
function create Search from Tags finds all presets with exactly the same set of tags.
Tagging via smart folder
You can tag presets by dropping (“drag & drop”) any number of presets onto one of the
Tag s smart folders. To remove all tags, drag them onto the Tags / Untagged folder.
Search Functions
Search by Tags
Click on the TAGS tab to open this view. The buttons here let you set up search criteria
according to existing tags with just a few mouse clicks:
Below the Search field are four sets of buttons (CATEGORIES, FEATURES, CHARACTER and FAVOURITES). The first three correspond to the tags in the tagging window
(see the previous page), while the bottom row lets you find any presets you have
tagged as Favourites. Clicking on the [^] icon to the right of each heading hides the options for that set of tags.
Categories and Subcategories
Each Category has its own set of subcategories. Not selecting any subcategory here
means “show me presets tagged with any subcategory”. Click on [Leads]...
You can select multiple categories without specifying any subcategory if you hold cmd
(Mac) or alt (Windows) while clicking on the category. Try that with the [Keys] button.
Selecting the subcategory with the same name as the category means “show me presets tagged without a subcategory”. You will not find any in the factory presets.
intro oscillator envelope amplifier LFO filter effects arpeggiator presets configuration 24
Search
CATEGORIES
FEATURES
CHARACTER
Bass
Bright Dark
Mono Poly Chord
Glide
Constant Moving Soft Aggressive Phat ThinClean Dirty
FAVOURITES
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Soft Attack
Pads Leads Keys FX Drums Seq+Arp Other
Slow Release
PercussiveModulatedBPM
TAGS
Page 25

PRESETS
Completed category+subcategory tags appear below the subcategories as buttons with
‘off’ switches [X] so you can add other main categories by simply clicking on them.
Features, Character and Favourites
Unlike multiple Category tags, which expand the search, selecting these types restrict
the search. Let’s find all thin sounding presets with a slow release:
Click on the TAGS tab. If any Categories are highlighted, deselect them. Then select
FEATURES = [Slow Release] and CHARACTER = [Thin].
Summary / Recap
In the DIRECTORY panel, specify a search path via double-click. In the TAGS panel,
select category tags. Add others if required to extend the search, but remember to hold
down cmd (Mac) or alt (Windows) if you want to retain category tags that don’t specify
a subcategory. Select Features, Character and/or Favourites tags to refine the search.
Exit any search path by clicking on the [X] to the right. You’ll soon get the hang of it!
Search by Text
The Search field lets you find presets according to a string of characters i.e. text. Here’s
an easy example: If you remember that the preset you’re looking for has the word
“clock” in its name or description, enter “clock” into the Search field and hit Return.
The search normally looks into the preset name, author, DESCRIPTION and USAGE
(see the PRESET INFO panel). Searches are not case-sensitive, and quotes are not
required unless you need to include spaces.
To restrict the search to a particular path, for instance Local/02 Pads, double click on a
folder. This path will appear beneath the Search field instead of the preset folders, and
you will only see smart folders (unless the specified path contains sub-folders).
See the image below. The [^] button to the left moves the Search path up one level, in
this case to /Local. The [X] button to the right sets the search path to the default Local
plus User (i.e. all ACE presets), and the preset folders become visible again.
Try a text search: Enter three or four letters then hit Return. For instance, star will find
all files containing the text string star (e.g. mustard or starters). Entering “star
wars" (with the quotes) would find e.g. Battlestar Warship, if such existed in the presets."
intro oscillator envelope amplifier LFO filter effects arpeggiator presets configuration 25
Search History
Saved Searches
Favourites
Junk (0)
Tags
Author
/Local/02 Pads
Search
DIRECTORY
s
Page 26

CONFIGURATION
Configuration
Clicking on the cogwheel icon at the top right opens the global configuration pages where
you can adjust the window size and brightness, or connect parameters to MIDI continuous
controllers (CC) etc..
The 4 buttons are MIDI Learn [L], MIDI Table [≣], Preferences [tools] and Close [X]:
Tip: Right-click within the button area to set the currently selected page as default!
About MIDI CC
Before connecting knobs and sliders on your master keyboard to Podolski parameters
(see the next page), it’s best to know what a MIDI CC is…
CC stands for MIDI continuous controller (more recently ‘control change’), a multi-purpose message format used for editing and performing presets. CC isn’t the only kind of
MIDI performance data — there are specific messages for note on/off with velocity, pitch
bend and two different types of aftertouch.
Although the MIDI Manufacturers Association (MMA) was kind enough to leave most of the
128 CC numbers undefined, a few of them have specific meanings that Podolski also rec-
ognizes. Please note that you don’t need a real breath controller or expression pedal to
make use of these!
CC 01 = modulation wheel
CC 02 = breath controller
CC 11 = expression pedal
CC 64 = hold pedal
Later MMA recommendations even included a bunch of esoteric CC definitions such as
‘Celeste Detune Depth‘, probably at the request of a home organ manufacturer or two. We
can safely ignore all such nonsense!
Although CC is mostly general purpose, please avoid controllers 120 to 127. These are
reserved for channel mode messages such as Local Control On/Off."
intro oscillator envelope amplifier LFO filter effects arpeggiator presets configuration 26
Page 27

CONFIGURATION
MIDI Learn
The MIDI Learn page is where you can connect MIDI CC to Podolski parameters. The CC
data can be generated by e.g. knobs or sliders on your hardware controller, or by a track in
your host sequencer. Click on the configuration button and select the ‘L’ MIDI icon:
MIDI-learnable elements are outlined. Elements that have already been assigned a MIDI
CC appear solid colour (like the three filter knobs in this image), and the outline of the active element awaiting MIDI CC is highlighted in white – like the Cutoff Mod2 knob here.
Try it: Click on the Cutoff knob and send some MIDI CC data e.g. move a knob / fader on
your MIDI controller — the connection is made instantly. Make a few more assignments in
the same way, then go to the MIDI Table page and see what you have done…"
intro oscillator envelope amplifier LFO filter effects arpeggiator presets configuration 27
Page 28

CONFIGURATION
MIDI Table
Click on the configuration button and select the righthand (≣) MIDI button…
Parameter
The first field displays/selects one of Podolski’s parameters, which are sorted into submenus according to module (mainly). Click on the ‘ADD’ button at the bottom left and
experiment with this field, then delete the assignment again by clicking on the small [X]
to the right of the line you just created.
Channel / Controller
The next two fields are for MIDI channel and CC number. Podolski is channel-sensitive,
so you can map up to 16 channels for a total of about 2000 control assignments.
Mode
Specifies the range and/or resolution of values.
Normal: full range, continuous
Integer: full range, whole numbers only
Fine: 0.01 steps between the two integers closest to the current value
Type
Specifies the type of hardware (by far the most common is Continuous 7-bit).
Encoder 127: unipolar encoder
Encoder 64: bipolar encoder
Continuous 7-bit: 7-bit MIDI CC (normal resolution, common)
Continuous 14-bit: 14-bit MIDI CC (high resolution, rare)
Remove
To remove individual assignments, click on the [x] to the right of each line. To remove all
assignments, click on the DELETE ALL button at the bottom of the window.
Per Instance Control
These two selectors override the Control A/B Default settings (see 2 pages down) for
the current instance of Podolski. Note: They are a bit sensitive in this version, so hovering over the fields and rolling your mouse wheel is probably easier than click and drag."
intro oscillator envelope amplifier LFO filter effects arpeggiator presets configuration 28
Page 29

CONFIGURATION
Preferences
Click on the ‘tools’ icon to open this overlay…
Mouse Wheel Raster
If your mouse wheel is rastered (you can feel it clicking slightly as you roll the wheel),
set this option to ‘on’ so that each little click increments the value in sensible steps.
Default Size
The GUI size for each new instance. You can temporarily change GUI size without
opening Preferences by right-clicking in the background.
Default Skin
Sets one of the available skins as global default.
Gamma
Determines how bright Podolski appears.
Text Antialiasing
Switches the smoothing of labels and values on or off. Normally left on, only in certain
cases will switching it off improve readability."
intro oscillator envelope amplifier LFO filter effects arpeggiator presets configuration 29
Page 30

CONFIGURATION
Auto Versioning
If switched on, an index is appended to the preset name and automatically incremented
each time you save it. For instance, saving ‘Space’ three times in a row would give you
three files: ‘Space’, ‘Space 2’ and ‘Space 3’.
Save Presets To
The user folder option prevents Podolski from saving presets into the Local folder. In-
stead, they will land in the User folder (or a subfolder if selected).
Scan On Startup
Whether the preset library should be scanned and the database recreated when the first
instance of Podolski is started, e.g. when you reopen a project.
Base Latency
If you are certain that your audio system – hardware as well as software – uses buffers
that are a multiple of 16 samples in size (please refer to the respective documentation),
you can safely disable Podolski’s base latency. Otherwise leave it set to the default ‘16
samples’ to prevent crackles.
Note that a new Base Latency setting will only take effect when the host allows e.g. on
playback or after switching the sample rate. Reloading Podolski will always work.
Control A/B Default
Apart from the modulation wheel, the list of sources in the previous version included two
extra fixed MIDI controls: Breath (CC#02) and Xpress (CC#11). While retaining backwards compatibility, we have replaced those with the user-definable Control A and Control B sources. These settings can be overriden per instance – see MIDI Table above.
MIDI Control Slew
Adjusts the smoothing of Pitch Bend, Mod Wheel, Breath and Expression. Note that
Pressure has a fixed slew rate and is therefore not affected by this parameter.
With MIDI Control Slew switched off, Podolski is much more responsive to modulation
wheel data (for instance), but can sound too grainy. The default setting (‘Fast’) is a pretty good compromise between speed and smoothness."
MORE ABOUT BUFFERS
Podolski processes audio in chunks of n x 16 samples. This so-called ‘block
processing’ method significantly reduces the CPU load and memory usage of
all our plug-ins.
If the number of samples to be processed is say 41, Podolski processes the first
32 and keeps the remaining 9 in a small buffer (16 samples is enough). Those 9
samples are then processed at the start of the next call… and so on.
The extra buffer is only necessary if either the host or audio driver processes
‘unusual’ buffer sizes. In the many host applications that process buffers of e.g.
64, 128, 256 or 512 samples (all multiples of 16), try switching it off so that
Podolski can process latency-free.
intro oscillator envelope amplifier LFO filter effects arpeggiator presets configuration 30
Page 31

NKS
NKS
Podolski now supports Native Instruments NKS format so that it can be integrated into the
Komplete Kontrol software or Maschine environments. Podolski’s factory presets are optionally also installed as tagged .nks files.
Saving in NKS format
While the native, h2p and h2p extended options cause Podolski to save presets into the
currently selected preset directory, .nks files go directly into the preset location used for
Komplete Kontrol or Maschine, so they do not appear in Podolski’s preset browser. To
make them visible in Komplete Kontrol, open its preferences and rescan the preset locations.
Batch conversion
First, right-click the [save] button and set the target format to nks. Via command-click
(Mac) or alt- click (Win), select all presets in the current folder you want to convert, then
right-click any of the selected presets and choose convert to nks. Note: The original files
are not affected.
What to do if Podolski doesn't show up in Komplete Kontrol / Maschine.
First of all, make sure your NKS software is up to date: Komplete Kontrol V1.5+ or Maschine V2.4 are the minimum requirements for u-he. In Windows, Komplete Kontrol must
know the plug-in folder containing Podolski: Open Komplete Kontrol preferences, go to
Locations and add your plug-in directory if necessary, hit Rescan and check whether
Podolski appears. Maybe the NKS preset folder is empty? If so, please reinstall Podolski
with the correct VST path and the NKS option checked. The preset folder locations are:
Mac: Macintosh HD/Library/Application Support/u-he/Podolski/NKS/Podolski/!
Win: C:\Users\*YOU*\Documents\u-he\Podolski.data\NKS\Podolski\
Perhaps the XML-File is missing from this location (abbreviated to fit on one line):
MacHD/Library/AppSupport/Native Instruments/Service Center/u-he-Podolski.xml or!
C:\Program Files\Common Files\Native Inst\Service Center\u-he-Podolski.xml
A re-install with the NKS-option checked should also remedy this issue.
What to do if Komplete Kontrol / Maschine is unable to load Podolski
Either Podolski wasn't installed as VST2, or it wasn’t installed with the correct path. The
default VST path is fixed in MacOSX, but in Windows it can be freely assigned:
Mac: Macintosh HD/Library/Audio/Plug-Ins/VST/u-he/!
Win: <User VST Folder> / (path for the VST plug-in set during installation)
If Podolski’s VST plug-in cannot be found in one of these locations, run the installer again
making sure that you set the correct path and have activated ‘VST’ as installation option.
intro oscillator envelope amplifier LFO filter effects arpeggiator presets configuration 31
 Loading...
Loading...