Page 1

Page 2

Table of Contents
INTRODUCTION..................................................................................................... 3
Wireless Router Features............................................................................... 3
Package Contents ..........................................................................................5
Physical Details.............................................................................................. 7
INSTALLATION ..................................................................................................... 9
Requirements................................................................................................. 9
Procedure ...................................................................................................... 9
SETUP ................................................................................................................11
Overview......................................................................................................11
Configuration Program ................................................................................12
Setup Wizard...............................................................................................14
Configuration via Web ................................................................................. 19
PC CONFIGURATION...........................................................................................35
Overview......................................................................................................35
Windows Clients..........................................................................................35
Macintosh Clients.........................................................................................48
Linux Clients................................................................................................48
Other Unix Systems......................................................................................48
Wireless Station Configuration ....................................................................49
APPENDIX A TROUBLESHOOTING..........................................................50
Overview......................................................................................................50
General Problems........................................................................................50
Internet Access.............................................................................................50
Wireless Access ...........................................................................................51
APPENDIX B ABOUT WIRELESS LANS .................................................... 53
Modes .......................................................................................................... 53
BSS/ESS ......................................................................................................53
Channels......................................................................................................53
WEP .............................................................................................................54
Wireless LAN Configuration.........................................................................54
APPENDIX C SPECIFICATIONS ...........................................................................55
Multi-Function Wireless Router.................................................................... 55
Wireless Interface ........................................................................................55
Regulatory Approvals...................................................................................56
Page 3
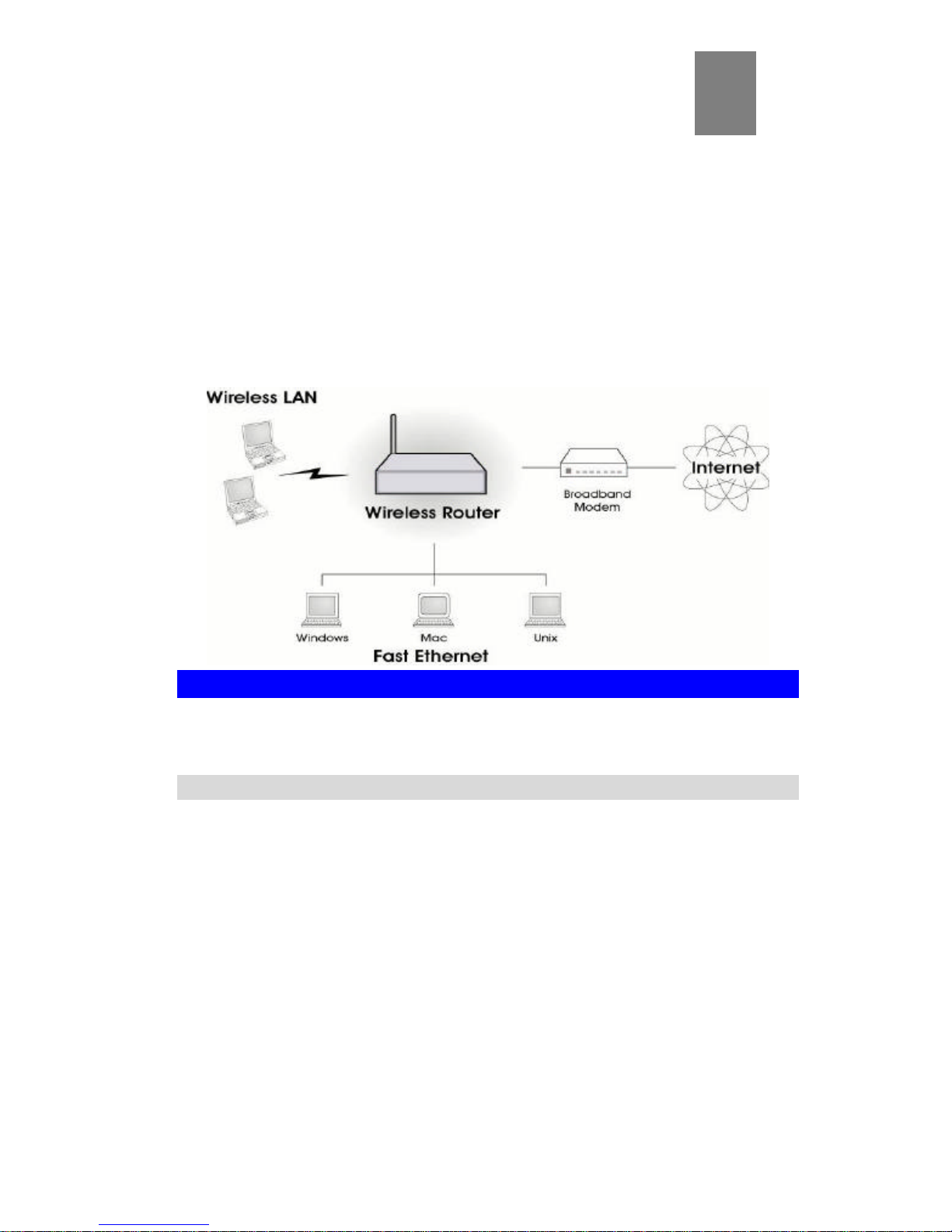
Introduction
Introduction
This Chapter provides an overview of the Hawking Technologies’ Hi-Speed
Wireless-G Router's features and capabilities.
Congratulations on the purchase of your new Hi-Speed, 54Mbps, Hawking Technologies
Wireless-G Router. The Wireless-G Router is a multi-function device providing the
following services:
• Shared Broadband Internet Access for all LAN users.
• 4-Port Switching Hub for 10BaseT or 100BaseT connections.
• Wireless Access Point for 802.11b and 802.11g Wireless Stations.
Wireless Router Features
The Wireless-G Router incorporates many advanced features, carefully designed to
provide sophisticated functions while being easy to use.
Internet Access Features
• Shared Internet Access. All users on the LAN or WLAN can access the
Internet through the Wireless Router, using only a single external IP Address. The
local (invalid) IP Addresses are hidden from external sources. This process is called
NAT (Network Address Translation).
• DSL & Cable Modem Support. The Wireless Router has a 10/100BaseT
Ethernet port for connecting a DSL or Cable Modem. All popular DSL and Cable
Modems are supported. SingTel RAS and Big Pond (Australia) login support is also
included.
• PPPoE, and PPTP. The Internet (WAN port) connection supports PPPoE (PPP
over Ethernet), PPTP (Peer-to-Peer Tunneling Protocol), as well as "Direct Connection" type services. Unnumbered IP with PPPoE is also supported.
• Fixed or Dynamic IP Address, the Wireless-G Router supports both Dynamic
IP Address (IP Address is allocated on connection) and Fixed IP Address.
1
Page 4

Advanced Internet Functions
• Communication Applications. Support for Internet communication applica-
tions, such as interactive Games, Telephony, and Conferencing applications, which
are often difficult to use when behind a Firewall, is included.
• Special Internet Applications. Applications which use non-standard connec-
tions or port numbers are normally blocked by the Firewall. The ability to define and
open ports for whatever your application may be is supported.
• Virtual Servers. This feature allows Internet users to access Internet servers on
your LAN. The required setup is quick and easy.
• DDNS Support. DDNS (Dynamic DNS) allows Internet users to connect to
Virtual Servers on your LAN using a domain name, even if your IP address is not
fixed.
• Multi-DMZ. For each WAN (Internet) IP address allocated to you, only one (1)
PC on your local LAN can be configured to allow unrestricted 2-way communication
with Servers or individual users on the Internet. This provides the ability to run programs which are incompatible with Firewalls.
• URL Filter. Use the URL Filter to block access to undesirable Web sites by LAN
users.
• I nternet Access Log. See which Internet connections have been made.
• Access Control. Using the Access Control feature, you can assign LAN users
to different groups, and determine which Internet services are available to each
group.
• VPN Pass through Support. PCs with VPN (Virtual Private Networking)
software using PPTP, L2TP and IPSec are transparently supported - no configuration is required.
Wireless Features
• Standards Compliant. The Wireless Router complies with the IEEE802.11g
(DSSS) specifications for Wireless LANs.
• Supports both 802.11b and 802.11g Wireless Stations. The 802.11g
standard provides for backward compatibility with the 802.11b standard, so both
802.11b and 802.11g Wireless stations can be used simultaneously.
• Speeds to 54Mbps. All speeds up to the 802.11g maximum of 54Mbps are
supported.
• WEP support. Support for WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) is included. Key
sizes of 64 Bit and 128 Bit are supported.
• Wireless MAC Access Control. The Wireless Access Control feature can
check the the MAC address (hardware address) of Wireless stations to ensure that
only trusted Wireless Stations can access your LAN.
• Simple Configuration. If the default settings are unsuitable, they can be
changed quickly and easily.
LAN Features
• 4-Port Switching Hub. The Wireless Router incorporates a 4-port 10/100BaseT
switching hub, making it easy to create or extend your LAN.
Page 5
Introduction
• DHCP Server Support. Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol provides a dy-
namic IP address to PCs and other devices upon request. The Wireless Router can
act as a DHCP Server for devices on your local LAN and WLAN.
• Multi Segment LAN Support. LANs containing one or more segments are
supported, using the Wireless Router's RIP (Routing Information Protocol) support
and built-in static routing table.
Configuration & Management
• Easy Setup. Use your WEB browser from anywhere on the LAN or WLAN for
configuration.
• Configuration File Upload/Download. Save (download) the configuration
data from the Wireless Router to your PC, and restore (upload) a previously-saved
configuration file to the Wireless-G Router.
• Remote Management. The Wireless-G Router can be managed from any PC
on your LAN. And, if the Internet connection exists, it can also (optionally) be configured via the Internet.
• Network Diagnostics. You can use the Wireless-G Router to perform a Ping or
DNS lookup.
• UPnP Support. UPnP (Universal Plug and Play) allows automatic discovery and
configuration of the Wireless Router. UPnP is by supported by Windows ME, XP, or
later.
Security Features
• Password - protected Configuration. Optional password protection is
provided to prevent unauthorized users from modifying the configuration data and
settings.
• Wireless LAN Security. WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) is supported, as well
as Wireless access control to prevent unknown wireless stations from accessing
your LAN.
• NAT Protection. An intrinsic side effect of NAT (Network Address Translation)
technology is that by allowing all LAN users to share a single IP address, the loc ation and even the existence of each PC is hidden. From the external viewpoint, there
is no network, only a single device - the Wireless Router.
• Protection against DoS attacks. DoS (Denial of Service) attacks can flood
your Internet connection with invalid packets and connection requests, using so
much bandwidth and so many resources that Internet access becomes unavailable.
The Wireless Router incorporates protection against DoS attacks.
Package Contents
The following items should be included:
• Hi-Speed Wireless-G Router Unit
• Power Adapter
• Quick Installation Guide
• One Ethernet Cable
• CD-ROM containing User’s Manual and Setup Wizard.
Page 6

If any of the above items are damaged or missing, please contact your dealer immediately.
Page 7
Introduction
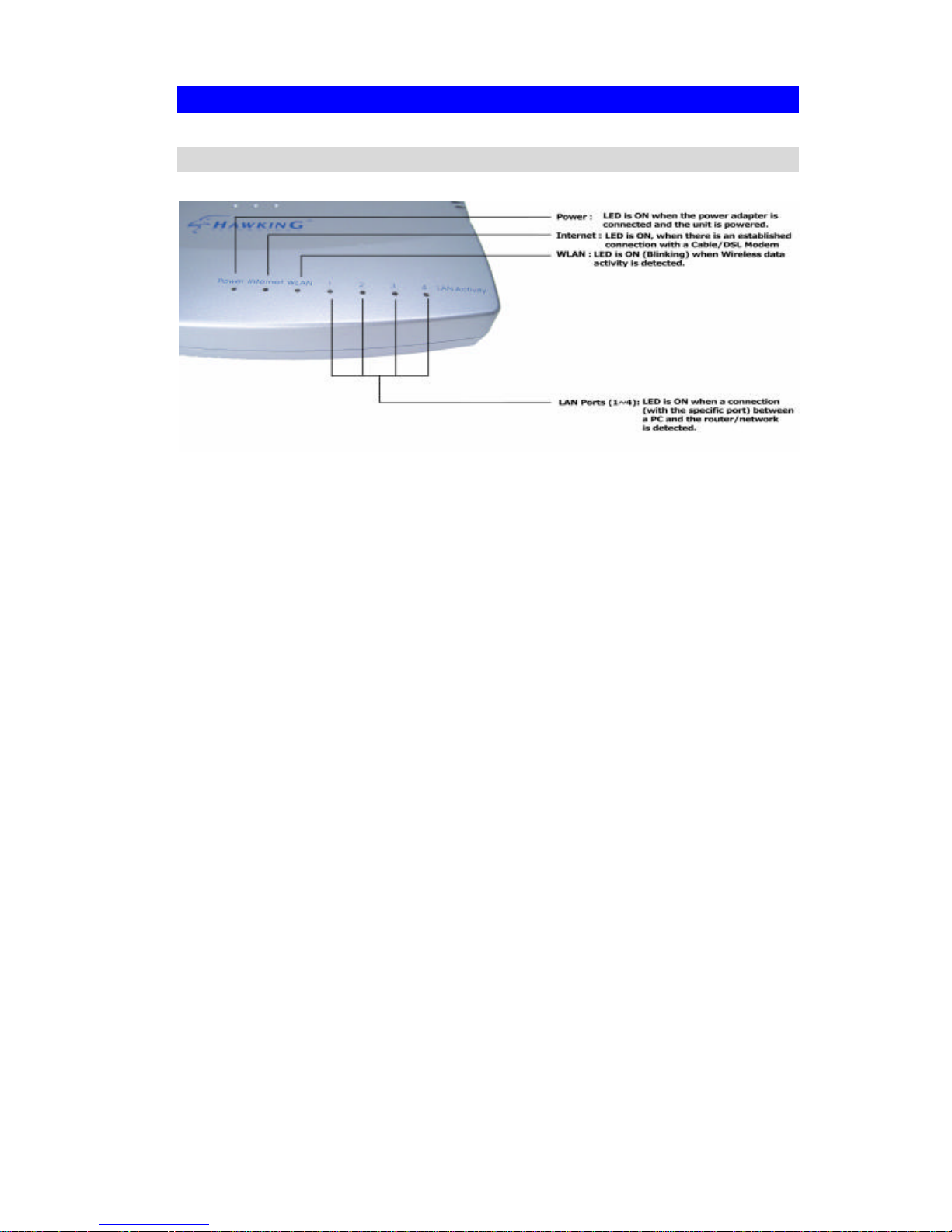
Physical Details
Front-mounted LEDs
Power LED On - Power on.
Off - No power.
Internet LED On - Connection to the Broadband Modem attached to the WAN
(Internet) port is established.
Off - No connection to the Broadband Modem.
Flashing - Data is being transmitted or received via the WAN port.
WLAN LED On - Wireless connection available; Wireless Access Point is ready
for use.
Off - No Wireless connection available.
Flashing - Data is being transmitted or received via the Wireless
access point. Data includes "network traffic" as well as user data.
LAN LEDs For each port, there are 2 LEDs
• Link/Act
• On - Corresponding LAN (hub) port is active.
• Off - No active connection on the corresponding LAN (hub)
port.
• Flashing - Data is being transmitted or received via the cor-
responding LAN (hub) port.
• 100
• On - Corresponding LAN (hub) port is using 100BaseT.
• Off - Corresponding LAN (hub) port connection is using
10BaseT, or no active connection.
Page 8

Rear Panel
Figure 1: Rear Panel
Power port Connect the supplied power adapter here.
10/100BaseT
LAN port
Use standard LAN cables (RJ45 connectors) to connect your
PCs to these ports.
If required, any port can be connected to another hub. Any LAN
port will automatically function as an "Uplink" port when necessary.
Internet port
(10/100BaseT)
Connect the DSL or Cable Modem here. If your modem came
with a cable, use the supplied cable. Otherwise, use a standard
LAN cable.
Reset Button This button has two (2) functions:
• Reboot. When pressed within 3~5 seconds, the power
LED lights amber then released, the Wireless Router will reboot (restart).
• Clear All Data . This button can also be used to clear ALL
data and restore ALL settings to the factory default values.
To Clear All Data and restore the factory default values:
1. After Power On.
2. Hold the Reset Button down.
3. Keep holding the Reset Button more than 5 seconds, until
the Amber LED has flashed.
4. Release the Reset Button. The Wireless Router is now
using the factory default va lues.
Page 9

Installation
This Chapter covers the physical installation of the Wireless Router.
Requirements
• Network cables. Use standard 10/100BaseT network (UTP) cables with RJ45 con-
nectors.
• TCP/IP protocol must be installed on all PCs.
• For Internet Acces s, an Internet Access account with an ISP, and either of a DSL or
Cable modem (for WAN port usage)
• To use the Wireless Access Point, all Wireless devices must be compliant with the
IEEE802.11b or IEEE802.11g specifications.
Procedure
1. Choose an Installation Site
Select a suitable place on the network to install the Wireless Router.
Ensure the Wireless Router and the DSL/Cable modem are powered OFF.
2
Page 10

For best Wireless reception and performance, the Wireless
Router should be positioned in a central location with minimum obstructions between the Wireless Router and the PCs.
Also, if using multiple Access Points, adjacent Access Points
should use different Channels to avoid interference.
2. Connect LAN Cables
Use standard LAN cables to connect PCs to the Switching Hub ports on the Wireless Router. Both 10BaseT and 100BaseT connections can be used simultaneously.
If required, connect any port to a normal port on another Hub, using a standard LAN
cable. Any LAN port on the Wireless Router will automatically function as an "Uplink" port when required.
3. Connect WAN Cable
Connect the DSL or Cable modem to the WAN port on the Wireless Router. Use the
cable supplied with your DSL/Cable modem. If no cable was supplied, use a standard cable.
4. Power Up
• Power on the Cable or DSL modem.
• Connect the supplied power adapter to the Wireless Router and power up.
Use only the power adapter provided. Using a different one may cause hardware
damage
5. Check the LEDs
• The Power LED should be ON.
• The Power LED should flash, then turn Off. If it stays on, there is a hardware error.
• For each LAN (PC) connection, the LAN Link/Act LED should be ON (provided the
PC is also ON.)
• The Internet LED should be ON.
• The WLAN LED should be ON
For more information, refer to Front-mounted LEDs in Chapter 1.
Page 11
Setup
This Chapter provides Setup details of the Wireless Router.
Overview
This chapter describes the setup procedure for:
• Internet Access
• LAN configuration
• Wireless setup
• Assigning a Password to protect the configuration data.
PCs on your local LAN may also require configuration. For details, see Chapter 4 - PC
Configuration.
Other configuration may also be required, depending on which features and functions of
the Wireless Router you wish to use. Use the table below to locate detailed instructions
for the required functions.
To Do this: Refer to:
Configure PCs on your LAN. Chapter 4:
PC Configuration
Check Wireless Router operation and Status. Chapter 5:
Operation and Status
Use any of the following Advanced features:
• Access Control
• Dynamic DNS
• Advanced Internet (Special Applications, DMZ,
URL Filter)
• Virtual Servers (Port Forwarding)
• WAN Port Setup
Chapter 6:
Advanced Features
Use any of the following Administration Configuration
settings or features:
• Config File download/upload
• Logs
• Network Diagnostics (Ping, DNS Lookup)
• Options (Backup DNS, TFTP, UPnP, Firewall)
• PC Dat abase
• Remote Management
• Security settings
• Firmware Upgrade
Chapter 7
Advanced Administration
3
Page 12

Configuration Program -
The Wireless Router contains an HTTP server. This enables you to connect to it, and
configure it, using your Web Browser. Your Browser must support JavaScript.
The configuration program has been tested on the following browsers:
• Netscape V4.08 or later
• Internet Explorer V4 or later
Mac Installation
• Mac OSX users may also follow these instructions for setup. (IE browser recom-
mended)
Preparation
Before attempting to configure the Wireless Router, please ensure that:
• Your PC can establish a physical connection to the Wireless Router. The PC and
the Wireless Router must be directly connected (using the Hub ports on the Wireless Router) or on the same LAN segment.
• The Wireless Router must be installed and powered ON.
• If the Wireless Router's default IP Address (192.168.1.254) is already used by
another device, the other device must be turned OFF until the Wireless Router is allocated a new IP Address during configuration.
Using UPnP
If your Windows system supports UPnP, an icon for the Wireless Router will appear in
the system tray, notifying you that a new network device has been found, and offering to
create a new desktop shortcut to the newly-discovered device.
• Unless you intend to change the IP Address of the Wireless Router, you can accept
the desktop shortcut.
• Whether you accept the desktop shortcut or not, you can always find UPnP devices
in My Network Places (previously called Network Neighborhood).
• Double - click the icon for the Wireless Router (either on the Desktop, or in My
Network Places ) to start the configuration. Refer to the following section Setup Wizard for details of the initial configuration process.
Using your Web Browser
To establish a connection from your PC to the Wireless Router:
1. After installing the Wireless Router in your LAN, start your PC. If your PC is already
running, restart it.
2. Start your WEB browser.
3. In the Address box, enter "HTTP://" and the IP Address of the Wireless Router, as
in this example, which uses the Wireless Router's default IP Address:
HTTP://192.168.1.254
Because the default password is blank, you will not be prompted for a password. However, you should assign a password. See the Password Setup section later in this
chapter for details.
Page 13

Advanced Administration
If you can't connect
If the Wireless Router does not respond, check the following:
• The Wireless Router is properly installed, LAN connection is OK, and it is
powered ON. You can test the connection by using the "Ping" command:
• Open the MS-DOS window or command prompt window.
• Enter the command:
ping 192.168. 1.254
If no response is received, either the connection is not working, or
your PC's IP address is not compatible with the Wireless Router's IP
Address. (See next item.)
• If your PC is using a fixed IP Address, its IP Address must be within the
range 192.168. 1.1 to 192.168.1.253 to be compatible with the Wireless
Router's default IP Address of 192.168. 1.254. Also, the Network Mask
must be set to 255.255.255.0. See Chapter 4 - PC Configuration for details on checking your PC's TCP/IP settings.
• Ensure that your PC and the Wireless Router are on the same network
segment. (If you don't have a router, this must be the case.)
• Ensure you are using the wired LAN interface. The Wireless interface can
only be used if its configuration matches your PC's wireless settings.
Page 14

Setup Wizard
The Setup Wizard provides brief and basic configuration of this device, you may enter
each screen to change the default settings. For more detailed settings, you may refer
to the “Configuration via Web” section.
1. View the listed configuration items and click Next to continue.
2. Configure Time Zone and NTP server by enabling NTP client update. Click Next to
continue.
3. Configure the parameters for area network (If you want to change the default parameter) by entering New IP Address and Subnet Mask.
Page 15
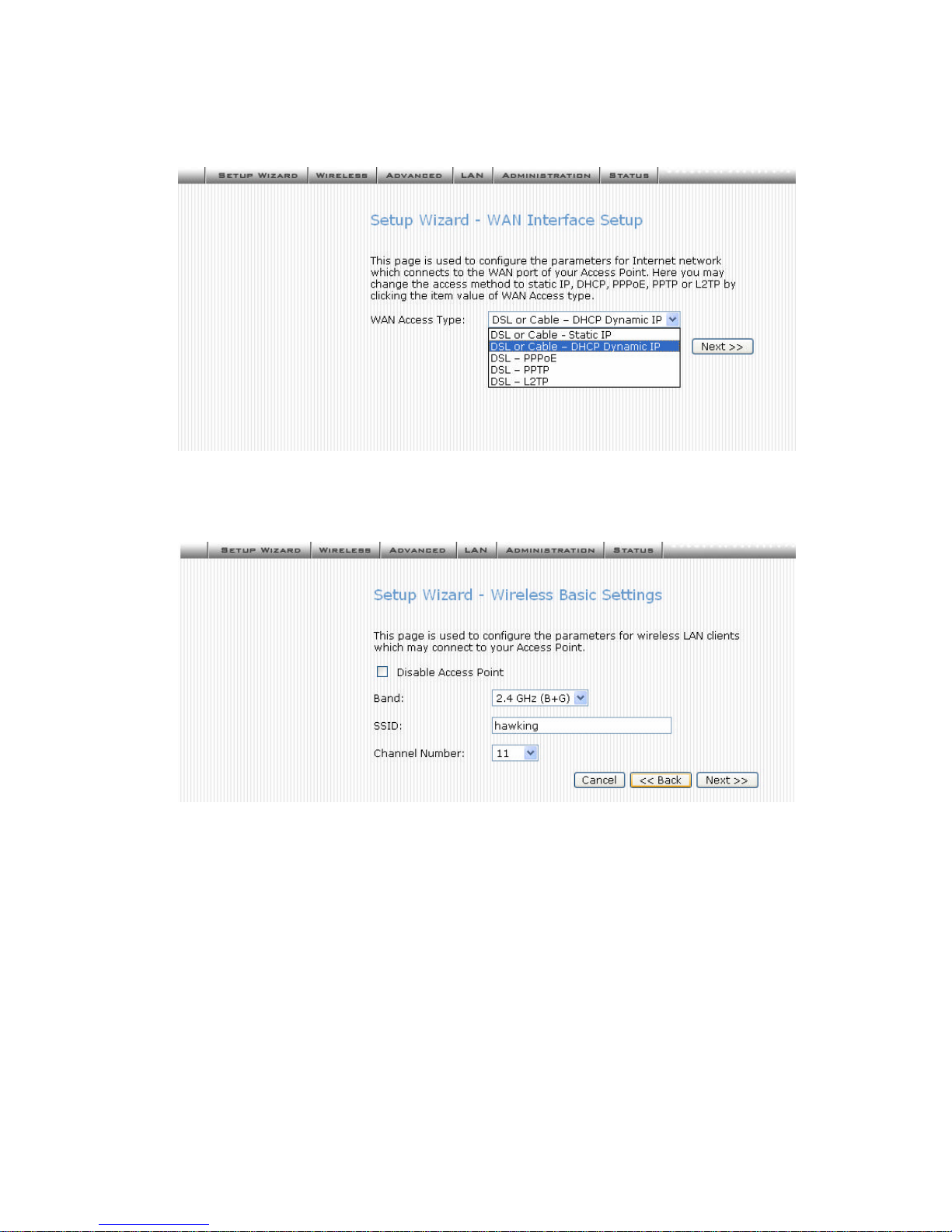
Advanced Administration
4. Change the access method (Static IP, DHCP, PPPoE, PPTP) by selecting for the
pull-down menu. Enter the appropriate/required information for your selection. (If you
do not know what to input in these fields please call your ISP for more information.
Click Next to continue.
5. Configure the parameters for wireless LAN clients. Check the Disable Access Point
to disable the settings of this screen and disable your wireless connection. Click
Next to continue.
Page 16
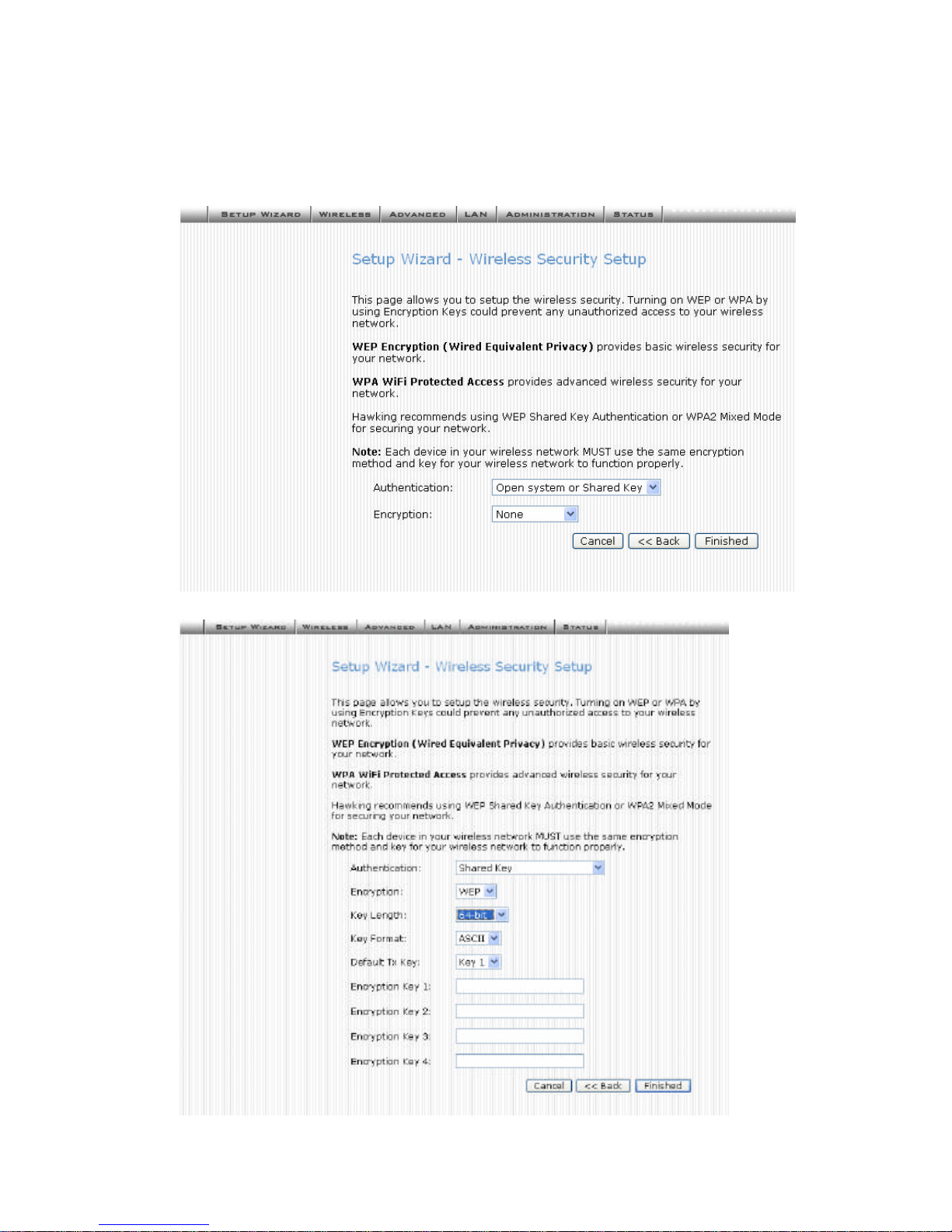
6. To manage your wireless network security by selecting the encryption type (None,
WEP, WPA and WPA2) from the pull-down menu. Enter the required information for
your specific security setting selection. Note that all wireless devices within your
network must have the same settings in order for the network to function properly.
(WPA2 is an advanced security setting and may not yet be available with some networking devices)
WEP Wired Equivalent Privacy
Page 17

Advanced Administration
WEP is a basic wireless security setting. It is not full proof and may be hacked into by experienced hackers. For WEP there are two types of security keys 64-bit and 128-bit. The higher the
number the more secure. You will have to input the corresponding key (10 digit hex key) for 64Bit and (28-digit hex key) for 128-Bit.
WPA WiFi Protected Access
WPA is a more advnaced standard of security. WPA2 is a newer version of WPA. WPA gives
you a choice of two encryption methods: TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol) and AES
(Advanced Encryption System ). You simply enter in a passphrase which will be converted to a
valid encryption key that will be used throughout your system. Hawking recommends that
WPA be used within your network for tighter security.
Note that implementing encryption may have a slight negative effect on your network’s performance.
Common Connection Types
Cable Modems
Type Details ISP Data required
Dynamic
IP Address
Your IP Address is allocated
automatically, when you
connect to you ISP.
Usually, none.
However, some ISP's may
require you to use a particular
Hostname, Domain name, or
MAC (physical) address.
Static (Fixed)
IP Address
Your ISP allocates a permanent IP Address to you.
IP Address allocated to you.
Some ISP's may also require
you to us e a particular Hostname, Domain name, or MAC
Page 18

(physical) address.
DSL Modems
Type Details ISP Data required
Dynamic
IP Address
Your IP Address is allocated
automatically, when you
connect to you ISP.
None.
Static (Fixed)
IP Address
Your ISP allocates a permanent IP Address to you.
IP Address allocated to you.
PPPoE You connect to the ISP only
when required. The IP
address is usually allocated
automatically.
User name and password.
PPTP Mainly used in Europe.
You connect to the ISP only
when required. The IP
address is usually allocated
automatically, but may be
Static (Fixed).
• PPTP Server IP Address.
• User name and pas sword.
• IP Address allocated to
you, if Static (Fixed).
Other Modems (e.g. Broadband Wireless)
Type Details ISP Data required
Dynamic
IP Address
Your IP Address is allocated
automatically, when you
connect to you ISP.
None.
Static (Fixed)
IP Address
Your ISP allocates a permanent IP Address to you.
IP Address allocated to you.
Page 19

Advanced Administration
Configuration via Web
LAN Interface Setup
IP Address Default: 192.168.1.254 (this is the local address of this
Router)
Subnet Mask Default: 255.255.255.0
DHCP
Disable: Select to disable this Router to distribute IP
Addresses (Disabled)
Server: Select to enable this Router to distribute IP
Addresses (DHCP Server). And the following field will be
activated for you to enter the starting IP Address
DHCP Client Range The starting address of this local IP network address
pool. The pool is a piece of continuous IP address
segment. Keep the default value 192.168.1.1 should
work for most cases.
• Maximum: 253. Default value 253 should
work for most cases.
Note: If “Continuous IP address poll starts” is set at
192.168.1.1 and the “Number of IP address in pool” is 253,
the device will distribute IP addresses from 192.168.1.1 to
192.168.1.253 to all the computers in the network that
request IP addresses from DHCP server (Router)
Show Client Click to show Active DHCP Client table.
Save
After completing the settings on this page, click Save to
save the settings.
Page 20

Reset
Click Reset to restore to default values.
Password Setup
New Password Maximum input is 36 alphanumeric characters (case
sensitive)
Confirmed Password Key in the password again to confirm.
Save
After completing the settings on this page, click Save to
save the settings.
Reset
Click Reset to clear settings.
Status
Internet Shows the internet connection status
LAN Shows the Local area network information
System Briefly shows the device name and firmware information
Connection Details Click to show more details of the internet connection
Page 21

Advanced Administration
System Data Click to show the detailed information of the system
Refresh Screen Click to refresh all the data
Wireless Basic Settings
Disable Access Point Check to disable the Access Point function.
(Disables Wireless Access in your Network)
The wireless (WLAN) LED on front panel will remain OFF if
the Wireless interface is disabled.
Band
You can choose one mode of the following you need.
¤ 2.4GHz (B): 802.11b supported rate only.
¤ 2.4GHz (G): 802.11g supported rate only.
¤ 2.4GHz (B+G): 802.11b supported rate and 802.11g sup-
ported rate.
The default is 2.4GHz (B+G) mode.
Channel Number Select which channel be located (from 1 to 11).
Associated Clients Click to show all the listed active clients.
Save
After completing the settings on this page, click Save to save
the settings.
Reset
Click Reset to restore to default values.
Page 22

Wireless Advanced Settings
Authentication
Type
Open System: If your access point/wireless router is using
"Open " authentication, then the wireless adapter will need to
be set to the same authentication type.
Shared Key: Shared Key is when both the sender and the
recipient share a secret key.
Auto: Select Auto Switch for the adapter to automatically
select the appropriate
Preamble Type
A preamble is a signal used in wireless environment to synchronize the transmitting timing including Synchronization and Start
frame delimiter. (Note: If you want to change the Preamble type into
Long or Short, please check the setting of AP.)
Broadcast SSID
Enable: This wireless AP will broadcast its SSID to stations.
Disable: This wireless AP will not broadcast its SSID to stations. If
stations want to connect to this wireless AP, this AP’s SSID should
be known in advance to make a connection.
Save
After completing the settings on this page, click Save to save
the settings.
Reset
Click Reset to restore to default values.
Page 23

Advanced Administration
Wireless Security Setup
Encryption
WEP : WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) is a data
security mechanism based on a 64 Bit/128 Bit shared key
algorithm.
WPA (TKIP): ( WiFi Protected Access) is more secure
than WEP, and should be used if possible.
Set WEP key
KEY1 ~ KEY 4: You can specify up to 4 different keys, but only
one can be used at a time.
A key of 10 hexadecimal characters (0-9, A-F) is required if a
64-bit Key Size is selected.
A key of 26 hexadecimal characters (0-9, A -F) is required if a
128-bit Key Size is selected.
WPA-PSK (Pre-Shared
key)
WPA Pre -Shared Key: In the Passphrase field, enter
the key that you are sharing with the network for the
WLAN connection.
WPA2-PSK TKIP and
AES
WPA2 Pre -Shared Key: WPA2 is a more advanced
security setting than WPA. It has the most advanced
security technology to keep your data encrypted. Setup is
the same as WPA. Simply enter a passphrase for use
throughout your network.
WPA/WPA2 Radius WPA and WPA2 Radius: If you wish to use an authenti-
cation server you will need to input the correct information
regarding your Radius server.
Save
After completing the settings on this page, click Save to
save the settings.
Page 24

Reset
Click Reset to restore to default values.
Wireless Trusted Stations
Wireless Access Control
Mode
Select the Access Control Mode from the pull-down
menu.
Disable: Select to disable Wireless Access Control
Mode.
Allow Listed: Only the stations shown in the table
can associate with the AP.
MAC Address The Mac address of the station associated with the
AP.
Description You may key in a description for the MAC Address
Current Access Control List Shows the current access control list.
Delete Selected Select the MAC Address(es) you want to delete and
then click the Delete Selected button to delete the
selected items.
Delete All Click to delete all the MAC Address (es) listed.
Save After completing the settings on this page, click
Save to save the settings.
Reset
Click Reset to restore to default values.
Page 25
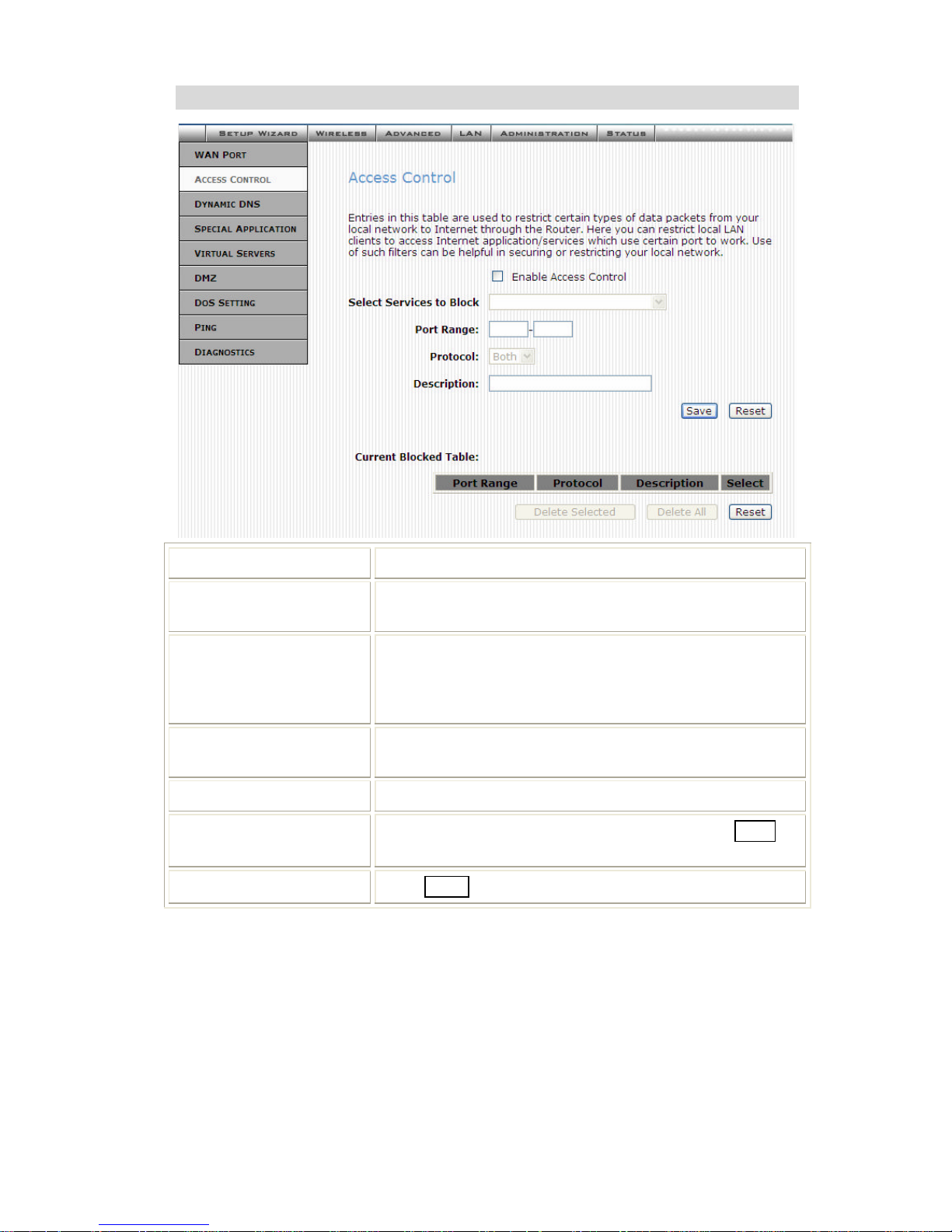
Advanced Administration
Access Control
Enable Access Control Select to enable Access Control function.
Select Services to
Block
This lists all defined Services. Select the Services you
wish to block.
Port Range For TCP and UDP Services, enter the beginning of the
range of port numbers used by the service. If the service
uses a single port number, enter it in both the start and
finish fields.
Protocol Select the protocol (TCP, UDP or Both) used to the remote
system or service.
Description You may key in a description for port range.
Save
After completing the settings on this page, click Save to
save the settings.
Reset
Click Reset to restore to default values.
Page 26

Dynamic DNS
Enable DDNS Select to enable DDNS function.
This free service is very useful when combined with the Virtual
Server feature. It allows Internet users to connect to your Virtual
Servers using a URL, rather than an IP Address. This also
solves the problem of having a dynamic IP address. With a
dynamic IP address, your IP address may change whenever
you connect, which makes it difficult to connect to you.
Service Provider
• Select the desired DDNS Service Provider from the list.
• Details of your DDNS account (Name, password, Domain
name) must then be entered and saved on this screen.
• This device will then automatically ensure that your current
IP Address is recorded by the DDNS Service Provider.
• From the Internet, users will now be able to connect to your
Virtual Servers (or DMZ PC) using your Domain name.
Domain Name
• Apply for a Domain Name, and ensure it is allocated to
you.
User Name/Email
Enter your Username for the DDNS Service.
Password/key
Enter your current password for the DDNS Service.
Save
After completing the settings on this page, click Save to save
the settings.
Reset
Click Reset to restore to default values.
? Normally, this message should be "Update successful"
? If the message is "No host" or some other error message, you need to connect to the
DDNS Service provider and correct the problem.
Page 27

Advanced Administration
DMZ
Enable DMZ If the DMZ Host Function is enabled, it means that you set up
DMZ host at a particular computer to be exposed to the
Internet so that some applications/software, especially Internet / online game can have two-way connections.
DMZ Host IP Address
Input the IP address of a particular host in your LAN that will
receive all the packets originally going to the WAN port/Public
IP address above.
Note: You need to give your LAN PC clients a fixed/static IP
address for DMZ to work properly.
Save
After completing the settings on this page, click Save to save
the settings.
Reset
Click Reset to restore to default values.
Virtual Server
Page 28

Enable Virtual Servers
Check to enable virtual server function.
Servers You can set up a local server with specific port number
that stands for the service (e.g. web (80), FTP (21),
Telnet (23)). When this device receives an incoming
access request for this specific port, it will be forwarded
to the corresponding internal server. You can add virtual
servers by either port numbers or by names.
Maximum 24 Server entries are allowed and each port
number can only be assigned to one IP address.
Local IP Address Enter the Local Server’s IP address.
Protocol Select the protocol (TCP, UDP or Both) used to the remote
system or service.
Port Range For TCP and UDP Services, enter the beginning of the range
of port numbers used by the service. If the service uses a
single port number, enter it in both the start and finish fields.
Description You may key in a description for the local IP address.
Save
After completing the settings on this page, click Save to save
the settings.
Reset
Click Reset to restore to default values.
Page 29

Advanced Administration
WAN Port Configuration
WAN Access Type Select the WAN access type (Static IP, DHCP, PPPoE and
PPTP) from the pull-down menu.
DNS 1-3
This is the ISP’s DNS server IP address that
they gave you; or you can specify your own
preferred DNS server IP address
The secondary and third DNS servers are optional. You can
enter another DNS
server’s IP address as a backup. The secondary and third
DNS servers will be used should the above DNS fail.
Clone MAC Address
Your ISP may require a particular MAC address in order for you
to connect to the Internet. This MAC address is the PC’s MAC
address that your ISP had originally connected your Internet
connection to. Type in this Clone MAC address in this section
to replace the WAN MAC address with the MAC address of
that PC.
Enable Web Server
Access via WAN
Remote administration. To enable web server by which allows
user to configure system via remote site.
Save
After completing the settings on this page, click Save to save
the settings.
Page 30

Reset
Click Reset to restore to default values.
Config File
This feature allows you to download the current settings from the Wireless Router, and
save them to a file on your PC.
You can restore a previously-downloaded configuration file to the Wireless Router, by
uploading it to the Wireless Router.
This screen also allows you to set the Wireless Router back to its factory default configuration. Any existing settings will be deleted.
An example Config File screen is shown below.
Backup Config Use this to download a copy of the current configuration,
and store the file on your PC. Click Download to start
the download.
Restore Config
This allows you to restore a previously-saved configuration file back to the Wireless Router.
Click Browse to select the configuration file, then click
Restore to upload the configuration file.
WARNING !
Uploading a configuration file will destroy (overwrite) ALL
of the existing settings.
Default Config
Clicking the Restore Defaults button will reset the
Wireless Router to its factory default settings.
WARNING !
This will delete ALL of the existing settings.
Page 31

Advanced Administration
System Log
The Logs record various types of activity on the Wireless Router. This data is useful for
troubleshooting, but enabling all logs will generate a large amount of data and adversely
affect performance.
Enable Log Click to enable log function.
Enable Remote
Log
Click to enable the remote log function. The log record will be
saved into a remote server.
Save
After completing the settings on this page, click Save to save
the settings.
Refresh Click to refresh the logs.
Clear Click Clear to delete the logs.
Page 32

IP Filtering
Enable IP Filtering Check to enable the IP filtering function.
Local IP Address Enter the client IP address.
Protocol Select the protocol (TCP, UDP or Both) used to the remote
system or service.
Description You may key in a description for the local IP address
Current Filter
Table
Shows the current filter information.
Save
After completing the settings on this page, click Save to save
the settings.
Reset
Click Reset to restore to default values.
Page 33

Advanced Administration
MAC Filtering
Enable MAC Filte ring
Check to enable MAC filtering function.
MAC Address Enter the client MAC address.
Description You may key in a description for the MAC address.
Current Filter
Table
Shows the current filter information.
Save
After completing the settings on this page, click Save to save
the settings.
Reset
Click Reset to restore to default values.
Statistics
Refresh Click to refresh the statistics table.
Page 34

Time Zone Setting
Current Time Enter the current time of this wireless router.
Enable NTP client
update
Check to enable NTP (Network Time Protocol Server) client
update function.
Time Zone Select Select the time zone from the pull-down menu.
NTP server
You may choose to select NTP server from the pull-down menu
or enter an IP address of a specific server.
Save
After completing the settings on this page, click Save to
save the settings.
Reset
Click Reset to restore to default values.
Refresh Click to refresh the current time.
Upgrade Firmware
Browse Click the Browse button, find and open the firmware file
(the browser will display to correct file path).
Start Upgrade Click the Start Upgrade button to perform
Page 35

Advanced Administration
Reset
Click Reset to restore to default values.
Navigation & Data Input
• Use the menu bar on the left of the screen, and the "Back" button on your Browser,
for navigation.
• Changing to another screen without clicking "Save" does NOT save any changes
you may have made. You must "Save" before changing screens or your data will be
ignored.
PC Configuration 4
This Chapter details the PC Configuration required on the local ("Internal") LA N.
Overview
For each PC, the following may need to be configured:
• TCP/IP network settings
• Internet Access configuration
• Wireless configuration
Windows Clients
This section describes how to configure Windows clients for Internet access via the
Wireless Rout er.
The first step is to check the PC's TCP/IP settings.
The Wireless Router uses the TCP/IP network protocol for all functions, so it is essential
that the TCP/IP protocol be installed and configured on each PC.
TCP/IP Settings - Overview
If using the default Wireless Router settings, and the default Windows
TCP/IP settings, no changes need to be made.
• By default, the Wireless Router will act as a DHCP Server, automatically providing a
suitable IP Address (and related information) to each PC when the PC boots.
• For all non-Server versions of Windows, the default TCP/IP setting is to act as a
DHCP client.
Page 36

If using a Fixed (specified) IP address, the following changes are required:
• The Gateway must be set to the IP address of the Wireless Router
• The DNS should be set to the address provided by your ISP.
Page 37

Advanced Administration
Checking TCP/IP Settings - Windows 98/ME:
1. Select Control Panel - Network. You should see a screen like the following:
2. Select the TCP/IP protocol for your network card.
3. Click on the Properties button. You should then see a screen like the following.
Ensure your TCP/IP settings are correct, as follows:
Using DHCP
To use DHCP, select the radio button Obtain an IP Address automatically. This is the
default Windows setting. Using this is recommended. By default, the Wireless Router
will act as a DHCP Server.
Restart your PC to ensure it obtains an IP Address from the Wireless Router.
Using "Specify an IP Address"
If your PC is already configured, check with your network administrator before making
the following changes:
• On the Gateway tab, enter the Wireless Router's IP address in the New Gateway
field and click Add, as shown below. Your LAN administrator can advise you of the
IP Address they assigned to the Wireless Router.
Page 38

• On the DNS Configuration tab, ensure Enable DNS is selected. If the DNS Server
Search Order list is empty, enter the DNS address provided by your ISP in the fields
beside the Add button, then click Add.
Page 39

Advanced Administration
Checking TCP/IP Settings - Windows NT4.0
1. Select Control Panel - Net work, and, on the Protocols tab, select the TCP/IP protocol, as shown below.
2. Click the Properties button to see a screen like the one below.
Page 40
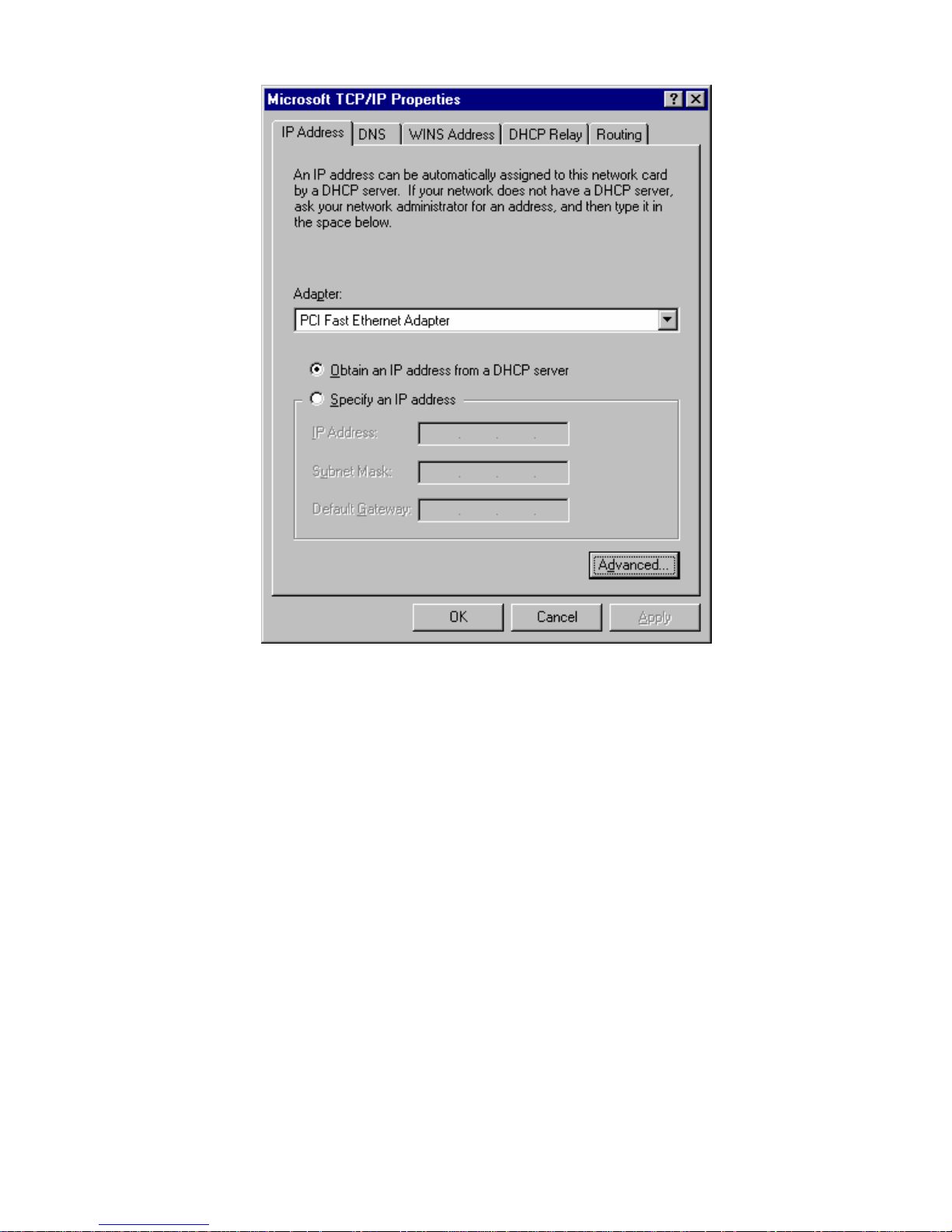
3. Select the network card for your LAN.
4. Select the appropriate radio button - Obtain an IP address from a DHCP Server or
Specify an IP Address, as explained below.
Obtain an IP address from a DHCP Server
This is the default Windows setting. Using this is recommended. By default, the
Wireless Router will act as a DHCP Server.
Restart your PC to ensure it obtains an IP Address from the Wireless Router.
Specify an IP Address
If your PC is already configured, check with your network administrator before making
the following changes.
1. The Default Gateway must be set to the IP address of the Wireless Router. To set
this:
• Click the Advanced button on the screen above.
• On the following screen, click the Add button in the Gateways panel, and enter
the Wireless Router's IP address.
• If necessary, use the Up button to make the Wireless Router the first entry in
the Gateways list.
Page 41

Advanced Administration
2. The DNS should be set to the address provided by your ISP, as follows:
• Click the DNS tab.
• On the DNS screen, shown below, click the Add button (under DNS Service
Search Order), and enter the DNS provided by your ISP.
Page 42

Page 43

Advanced Administration
Checking TCP/IP Settings - Windows 2000:
1. Select Control Panel - Network and Dial-up Connection.
2. Right - click the Local Area Connection icon and select Properties. You should see
a screen like the following:
3. Select the TCP/IP protocol for your network card.
4. Click on the Properties button. You should then see a screen like the following.
Page 44
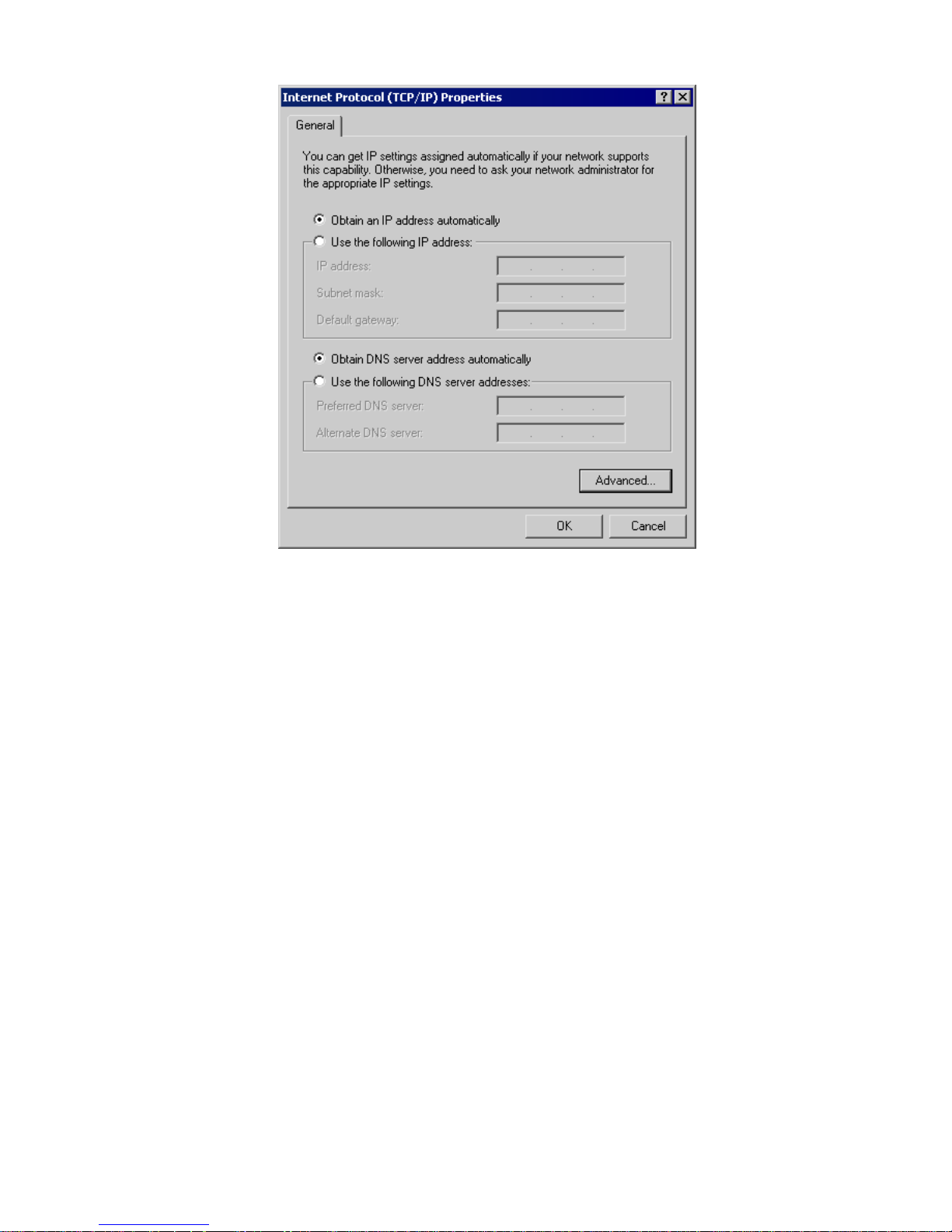
5. Ensure your TCP/IP settings are correct, as described below.
Using DHCP
To use DHCP, select the radio button Obtain an IP Address automatically. This is the
default Windows setting. Using this is recommended. By default, the Wireless Router
will act as a DHCP Server.
Restart your PC to ensure it obtains an IP Address from the Wireless Router.
Using a fixed IP Address ("Use the following IP Address")
If your PC is already configured, check with your network administrator before making
the following changes.
• Enter the Wireless Router's IP address in the Default gateway field and click OK.
(Your LAN administrator can advise you of the IP Address they assigned to the
Wireless Router.)
• If the DNS Server fields are empty, select Use the following DNS server addresses,
and enter the DNS address or addresses provided by your ISP, then click OK.
Page 45

Advanced Administration
Checking TCP/IP Settings - Windows XP
1. Select Control Panel - Network Connection.
2. Right click the Local Area Connection and choose Properties. You should see a
screen like the following:
3. Select the TCP/IP protocol for your network card.
4. Click on the Properties button. You should then see a screen like the following.
Page 46

5. Ensure your TCP/IP settings are correct.
Using DHCP
To use DHCP, select the radio button Obtain an IP Address automatically. This is the
default Windows setting. Using this is recommended. By default, the Wireless Router
will act as a DHCP Server.
Restart your PC to ensure it obtains an IP Address from the Wireless Router.
Using a fixed IP Address ("Use the following IP Address")
If your PC is already configured, check with your network administrator before making
the following changes.
• In the Default gateway field, enter the Wireless Router's IP address and click OK.
Your LAN administrator can advise you of the IP Address they assigned to the Wireless Router.
• If the DNS Server fields are empty, select Use the following DNS server addresses,
and enter the DNS address or addresses provided by your ISP, then click OK.
Page 47

Advanced Administration
Internet Access
To configure your PCs to use the Wireless Router for Internet access:
• Ensure that the DSL modem, Cable modem, or other permanent connection is
functional.
• Use the following procedure to configure your Browser to access the Internet via the
LAN, rather than by a Dial-up connection.
For Windows 9x/ME/2000
1. Select Start Menu - Settings - Control Panel - Internet Options.
2. Select the Connection tab, and click the Setup button.
3. Select "I want to set up my Internet connection manually, or I want to connect
through a local area network (LAN)" and click Next.
4. Select "I connect through a local area network (LAN)" and click Next.
5. Ensure all of the boxes on the following Local area network Internet Configuration
screen are unchecked.
6. Check the "No" option when prompted "Do you want to set up an Internet mail
account now?".
7. Click Finish to close the Internet Connection Wizard.
Setup is now completed.
For Windows XP
1. Select Start Menu - Control Panel - Network and Internet Connections.
2. Select Set up or change your Internet Connection.
3. Select the Connection tab, and click the Setup button.
4. Cancel the pop-up "Location Information" screen.
5. Click Next on the "New Connection Wizard" screen.
6. Select "Connect to the Internet" and click Next.
7. Select "Set up my connection manually" and click Next.
8. Check "Connect using a broadband connection that is always on" and click Next.
9. Click Finish to close the New Connection Wizard.
Setup is now completed.
Accessing AOL
To access AOL (America On Line) through the Wireless Router, the AOL for Windows
software must be configured to use TCP/IP network access, rather than a dial-up connection. The configuration process is as follows:
• Start the AOL for Windows communication software. Ensure that it is Version 2.5,
3.0 or later. This procedure will not work with earlier versions.
• Click the Setup button.
• Select Create Location, and change the location name from "New Locality" to
"Wireless Router".
• Click Edit Location. Select TCP/IP for the Network field. (Leave the Phone Number
blank.)
• Click Save, then OK.
Configuration is now complete.
• Before clicking "Sign On", always ensure that you are using the "Wireless Router"
location.
Page 48

Macintosh Clients
From your Macintosh, you can access the Internet via the Wireless Router. The proc edure is as follows.
1. Open the TCP/IP Control Panel.
2. Select Ethernet from the Connect via pop-up menu.
3. Select Using DHCP Server from the Configure pop-up menu. The DHCP Client ID
field can be left blank.
4. Close the TCP/IP panel, saving your settings.
Note:
If using manually assigned IP addresses instead of DHCP, the required changes are:
• Set the Router Address field to the Wireless Router's IP Address.
• Ensure your DNS settings are correct.
Linux Clients
To access the Internet via the Wireless Router, it is only necessary to set the Wireless
Router as the "Gateway".
Ensure you are logged in as "root" before attempting any changes.
Fixed IP Address
By default, most Unix installations use a fixed IP Address. If you wish to continue using
a fixed IP Address, make the following changes to your configuration.
• Set your "Default Gateway" to the IP Address of the Wireless Router.
• Ensure your DNS (Name server) settings are correct.
To act as a DHCP Client (recommended)
The procedure below may vary according to your version of Linux and X -windows shell.
1. Start your X Windows client.
2. Select Control Panel - Network
3. Select the "Interface" entry for your Network card. Normally, this will be called
"eth0".
4. Click the Edit button, set the "protocol" to "DHCP", and save this data.
5. To apply your changes
• Use the "Deactivate" and "Activate" buttons, if available.
• OR, restart your system.
Other Unix Systems
To access the Internet via the Wireless Router:
• Ensure the "Gateway" field for your network card is set to the IP Address of the
Wireless Router.
• Ensure your DNS (Name Server) settings are correct.
Page 49

Advanced Administration
Wireless Station Configuration
This section applies to all Wireless stations wishing to use the Wireless Router's Access Point, regardless of the operating system which is used on the client .
To use the Wireless Access Point in the Wireless Router, each Wireless Station must
have compatible settings, as follows:
Mode The mode must be set to Infrastructure.
SSID (ESSID) This must match the value used on the Wireless Router. The default
value is Untitled
Note! The SSID is case sensitive.
WEP By default, WEP on the Wireless Router is dis abled.
• If WEP remains disabled on the Wireless Router, all stations
must have WEP disabled.
• If WEP is enabled on the Wireless Router, each station must
use the same settings as the Wireless Router.
Note:
By default, the Wireless Router will allow both 802.11b and 802.11g connections.
Page 50

Appendix A
Troubleshooting
This Appendix covers the most likely problems and their solutions.
Overview
This chapter covers some common problems that may be encountered while using the
Wireless Router and some possible solutions to them. If you follow the suggested steps
and the Wireless Router still does not function properly, contact your dealer for further
advice.
General Problems
Problem 1: Can't connect to the Wireless Router to configure it.
Solution 1: Check the following:
• The Wireless Router is properly installed, LAN connections are
OK, and it is powered ON.
• Ensure that your PC and the Wireless Router are on the same
network segment. (If you don't have a router, this must be the
case.)
• If your PC is set to "Obtain an IP Address automatically" (DHCP
client), restart it.
• If your PC uses a Fixed (Static) IP address, ensure that it is using
an IP Address within the range 192.168.1.1 to 192.168.1.253 and
thus compatible with the Wireless Router's default IP Address of
192.168.1.254.
Also, the Network Mask should be set to 255.255.255.0 to match
the Wireless Router.
In Windows, you can check these settings by using Control Panel-
Network to check the Properties for the TCP/IP protocol.
Internet Access
Problem 1: When I enter a URL or IP address I get a time out error.
Solution 1: A number of things could be causing this. Try the following trouble-
shooting steps.
• Check if other PCs work. If they do, ensure that your PCs IP
settings are correct. If using a Fixed (Static) IP Address, check the
Network Mask, Default gateway and DNS as well as the IP Address.
• If the PCs are configured correctly, but still not working, check the
Wireless Router. Ensure that it is connected and ON. Connect to it
and check its settings. (If you can't connect to it, check the LAN
and power connections.)
• If the Wireless Router is configured correctly, check your Internet
Page 51

Appendix A - Troubleshooting
connection (DSL/Cable modem etc) to see that it is working correctly.
Problem 2: Some applications do not run properly when using the Wireless
Router.
Solution 2: The Wireless Router processes the data passing through it, so it is not
transparent.
Use the Special Applications feature to allow the use of Internet applications which do not function correctly.
If this does solve the problem you can use the DMZ function. This
should work with almost every application, but:
• It is a security risk, since the firewall is disabled.
• Only one (1) PC can use this feature.
Wireless Access
Problem 1: My PC can't locate the Wireless Access Point.
Solution 1: Check the following.
• Your PC is set to Infrastructure Mode. (Access Points are always
in Infrastructure Mode)
• The SSID on your PC and the Wireless Access Point are the
same.
Remember that the SSID is case-sensitive. So, for example
"Workgroup" does NOT match "workgroup".
• Both your PC and the Wireless Router must have the same setting
for WEP. The default setting for the Wireless Router is disabled,
so your wireless station should also have WEP disabled.
• If WEP is enabled on the Wireless Router, your PC must have
WEP enabled, and the key must match.
• If the Wireless Router's Wireless screen is set to Allow LAN
access to selected Wireless Stations only, then each of your Wire-
less stations must have been selected, or access will be blocked.
• To see if radio interference is causing a problem, see if connection
is possible when close to the Wireless Router.
Remember that the connection range can be as little as 100 feet in
poor environments.
Problem 2: Wireless connection speed is very slow.
Solution 2: The wireless system will connect at the highest possible speed, de-
pending on the distance and the environment. To obtain the highest
possible connection speed, you can experiment with the following:
• Wireless Router location.
Try adjusting the location and orientation of the Wireless Router.
• Wireless Channel
If interference is the problem, changing to another channel may
show a marked improvement.
• Radio Interference
Other devices may be causing interference. You can experiment
by switching other devices Off, and see if this helps. Any "noisy"
devices should be shielded or relocated.
Page 52

• RF Shielding
Your environment may tend to block transmission between the
wireless stations. This will mean high access speed is only possible when close to the Wireless Router.
Page 53

Appendix B
About Wireless LANs
This Appendix provides some background information about using Wireless LANs (WLANs).
Modes
Wireless LANs can work in either of two (2) modes:
• Ad-hoc
• Infrastructure
Ad-hoc Mode
Ad-hoc mode does not require an Access Point or a wired (Ethernet) LAN. Wireless
Stations (e.g. notebook PCs with wireless cards) communicate directly with each
other.
Infrastructure Mode
In Infras tructure Mode, one or more Access Points are used to connect Wireless
Stations (e.g. Notebook PCs with wireless cards) to a wired (Ethernet) LAN. The
Wireless Stations can then access all LAN resources.
Access Points can only function in "Infrastructure" mode, and
can communicate only with Wireless Stations which are set
to "Infrastructure" mode.
BSS
BSS
A group of Wireless Stations and a single Access Point, all using the same ID (SSID),
form a Basic Service Set (BSS).
Using the same SSID is essential. Devices with different SSIDs are unable to communicate with each other.
Channels
The Wireless Channel sets the radio frequency used for communication.
• Access Points use a fixed Channel. You can select the Channel used. This allows
you to choose a Channel which provides the least interference and best performance. In the USA and Canada, 11 channel are available. If using multiple Access
Points, it is better if adjacent Access Points use different Channels to reduce interference.
B
Page 54

• In "Infrastructure" mode, Wireless Stations normally scan all Channels, looking for
an Access Point. If more than one Access Point can be used, the one with the
strongest signal is used. (This can only happen within an ESS.)
WEP
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) is a standard for encry pting data before it is transmitted.
This is desirable because it is impossible to prevent snoopers from receiving any data
which is transmitted by your Wireless Stations. But if the data is encrypted, then it is
meaningless unless the receiver can decrypt it.
If WEP is used, the Wireless Stations and the Access Point must have the same
settings for each of the following:
WEP Off, 64 Bit, 128 Bit
Key For 64 Bit encryption, the Key value must match.
For 128 Bit encryption, the Key value must match
WEP Authentication Open System or Shared Key.
Wireless LAN Configuration
To allow Wireless Stations to use the Access Point, the Wireless Stations and the
Access Point must use the same settings, as follows:
Mode On client Wireless Stations, the mode must be set to "Infrastruc-
ture".
(The Access Point is always in "Infrastructure" mode.)
SSID (ESSID) Wireless Stations should use the same SSID (ESSID) as the
Access Point they wish to connect to. Alternatively, the SSID can
be set to "any" or null (blank) to allow connection to any Access
Point.
WEP The Wireless Stations and the Access Point must use the same
settings for WEP (Off, 64 Bit, 128 Bit).
WEP Key: If WEP is enabled, the Key must be the same on the
Wireless Stations and the Access Point.
WEP Authentication: If WEP is enabled, all Wireless Stations
must use the same setting as the Access Point (either "Open
System" or "Shared Key").
Page 55

Appendix C
Specifications
Wireless-G Router
Model HWR54G Rev. R
Dimensions 141mm(W) * 100mm(D) * 27mm(H)
Operating Tempera-
ture
-10° C to 55° C
Storage Temperature -20° C to 70° C
Network Prot ocol: TCP/IP
Network Interface: 5 Ethernet:
4 * 10/100BaseT (RJ45) LAN connection
1 * 10/100BaseT (RJ45) for WAN
LEDs 12
Power Adapter 12 V DC / 0.8A External
Wireless Interface
Standards IEEE802.11g WLAN, JEIDA 4.2, roaming support
Frequency 2.4 to 2.4835GHz (Industrial Scientific Medical Band )
Channels Maximum 14 Channels, depending on regulatory authorities
Modulation DSSS BPSK/QPSK/CCK , OFDM/CCK
Data Rate Up to 54 Mbps
Coverage Area Indoors : 15m @54Mbps, 120m @6Mbps or lower
Outdoors : 40m @54Mbps, 300m @6Mbps or lower
Security 64Bit, 128Bit WEP, WPA, WPA2, WPA-Radius, WPA2-Radius
TKIP, AES
Output Power 13dBm (typical)
Receiver Sensitivity -80dBm Min.
C
Page 56

Regulatory Approvals
CE Standards
This product complies with the 99/5/EEC directives, including the following safety and
EMC standards:
• EN300328-2
• EN301489-1/-17
• EN60950
CE Marking Warning
This is a Class B product. In a domestic environment this product may cause radio
interference in which case the user may be required to take adequate measures.
 Loading...
Loading...