Page 1

Page 2

Limited Warranty
Hawking Technology guarantees that every HWDN2 Hi-Gain
TM
Wireless-N Network USB Dish Adapter is free
from physical defects in material and workmanship under normal use for one (1) year from the date of
purchase. If the product proves defective during this one-year warranty period, call Hawking Customer
Service in order to obtain a Return Authorization number. Warranty is for repair or replacement only.
Hawking Technology does not issue any refunds. BE SURE TO HAVE YOUR PROOF OF PURCHASE.
RETURN REQUESTS CAN NOT BE PROCESSED WITHOUT PROOF OF PURCHASE. When returning a
product, mark the Return Authorization number clearly on the outside of the package and include your original
proof of purchase. For Warranty (RMA) Terms and Conditions, please go to
http://www.hawkingtech.com/support/customerservice.php#rma
. Standard shipping & handling charges may
apply.
IN NO EVENT SHALL HAWKING TECHNOLOGY’S LIABILTY EXCEED THE PRICE PAID
FOR THE PRODUCT FROM DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL
DAMAGES RESULTING FROM THE USE OF THE PRODUCT, IT IS ACCOMPANYING SOFTWARE OR
ITS DOCUMENTATION. Hawking Technology makes no warranty or representation, expressed, implied or
statutory, with respect to its products or the contents or use of this documentation and all accompanying
software, and specifically disclaims its quality, performance, merchantability, or fitness for any particular
purpose. Hawking Technology reserves the right to revise or updates its products, software, or
documentation without obligation to notify any individual or entity. Please direct all inquiries to:
techsupport@hawkingtech.com
Trademarks & Copyright
© Copyright 2009 Hawking Technologies, Inc. All rights reserved. All other brands and product names ar e
trademarks of their respective companies. No part of this publication may be reproduced in any form or by
any means or used to make any derivative (such as translation, transformation or adaptation) without the
express written consent of the manufacturer as stipulated by the United States Copyri ght Act of 1976.
Warning Statement:
Federal Communication
Commission Interference Statement
Federal Communications
Commission (FCC) Requirements, Part 15
1. Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
2. Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
3. Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected.
4. Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help. This device complies with Part 15 of the
FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
(1) This device may not cause harmful interference.
(2) This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired
operation.
FCC Caution:
FCC RF Exposure Statement:
This Transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other antenna or transmitter.
This equipment complies with FCC RF radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled environment.
This equipment should be installed and operated with a minimum distance of 20 centimeters between the
radiator and your body. Unauthorized antenna, modification, or attachments could damage the transmitter
and may violate FCC regulations.
R&TTE Compliance Statement
This equipment complies with all the requirements of DIRECTIVE 1999/5/EC OF THE EUROPEAN
PARLIAMENT AND THE COUNCIL of March 9, 1999 on radio equipment and telecommunication terminal
Equipment and the mutual recognition of their conformity (R&TTE)
2
Page 3
The R&TTE Directive repeals and replaces in the directive 98/13/EEC (Telecommunications Terminal
Equipment and Satellite Earth Station Equipment) As of April 8, 2000.
Safety
This equipment is designed with the utmost care for the safety of those who install and use it. However,
special attention must be paid to the dangers of electric shock and static electricity when working with
electrical equipment. All guidelines of this and of the computer manufacture must therefore be allowed at all
times to ensure the safe use of the equipment.
EU Countries Intended for Use
The ETSI version of this device is intended for home and office use in Austria, Belgium, Denmark, Finland,
France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Portugal, Spain, Sweden, and the
United Kingdom.
The ETSI version of this device is also authorized for use in EFTA member states: Iceland, Liechtenstein,
Norway, and Switzerland.
EU Countries not intended for use
None.
Regulatory information/Disclaimers:
Any changes or modifications made to this device that are not expressly approved by the manufacturer may
void the user's authority to operate the equipment.
3
Page 4
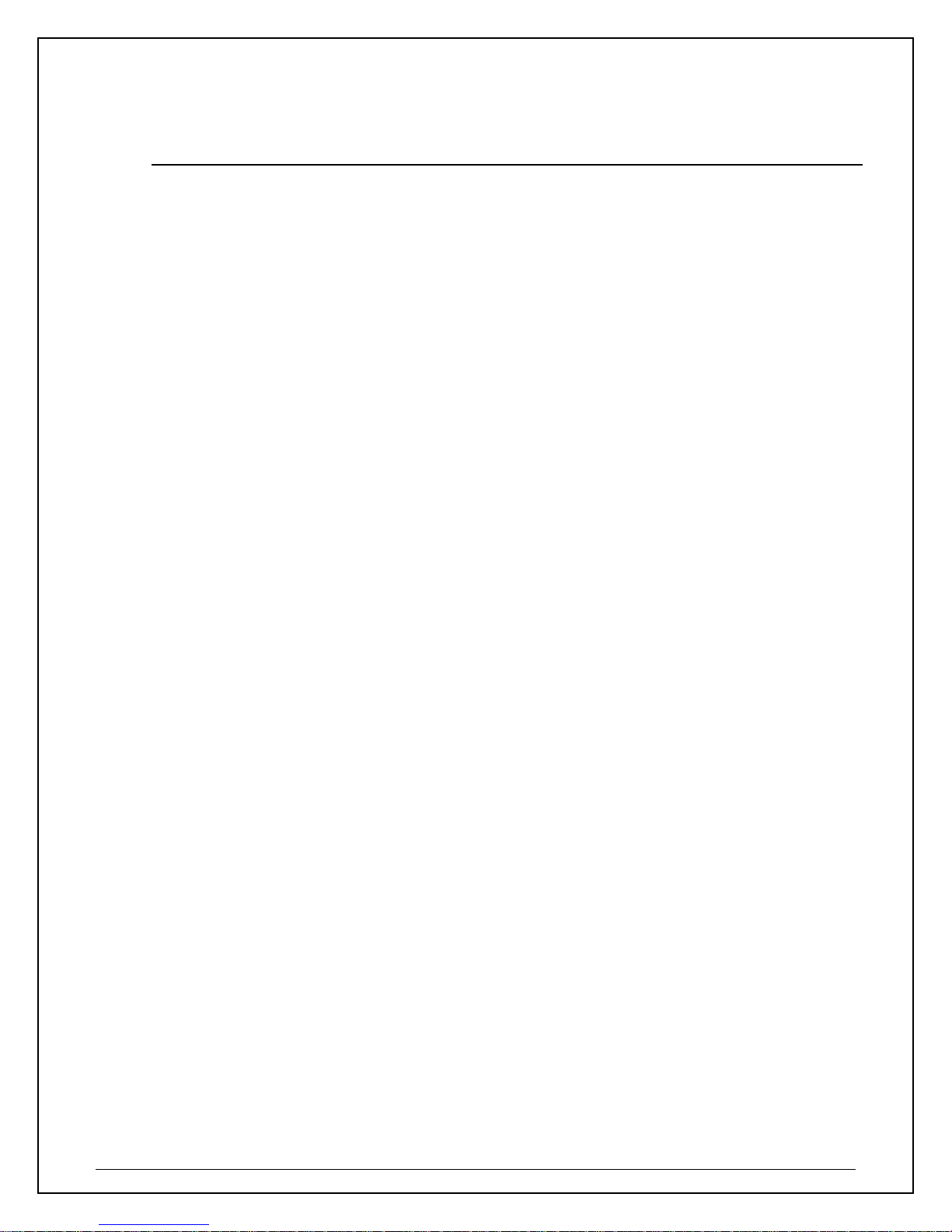
TABLE OF CONTENTS
I. OVERVIEW ......................................................................................................................................................... 5
1. FEATURES ......................................................................................................................................................... 5
2. PACKAGE CONTENTS ....................................................................................................................................... 6
3. SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS ................................................................................................................................. 6
II. FOR WINDOWS USERS .................................................................................................................................... 7
1. INSTALLATION FOR WINDOWS 7/ VISTA .......................................................................................................... 7
1.1
Connecting to a Wireless Network (Windows 7) ........................................................................... 9
1.2 Connecting to a Wireless Network (Windows Vista) ................................................................... 11
1.3 Using Windows Configuration (Windows V ist a / 7) ................................................................... 12
2. INSTALLATION (WINDOWS 2000/XP) ............................................................................................................ 14
2.1 Verify installation (Windows 2000/XP) ....................................................................................... 17
2.2 Network Configuration (Windows 2000/XP) .............................................................................. 18
2.3 Connect - Using HWDN2 Wireless Utility .................................................................................. 19
3. H
AWKING WIRELESS UTILITY ...................................................................................................................... 21
3.1 Utility Overview .......................................................................................................................... 21
3.2 Available Network T ab ................................................................................................................ 22
3.3 General Tab .................................................................................................................................. 23
3.4 Profile T ab ................................................................................................................................... 24
3.5 Statistics ....................................................................................................................................... 30
3.6 Wi-Fi Protect Setup (WPS) .......................................................................................................... 31
3.7 NETWORK SECURITY (WEP, WPA…) ................................................................................... 33
4. U
NINSTALLING HAWKING UTILITY/DRIVER ................................................................................................. 36
III. FOR MAC USERS ............................................................................................................................................. 37
1. I
NSTALLATION FOR MAC OSX 10.4 OR LATER ............................................................................................. 37
ONNECTING TO YOUR WIRELESS NETWORK (MAC 10.5 OR LATER) ........................................................ 40
2. C
3. C
ONNECTING TO YOUR WIRELESS NETWORK (MAC 10.4~10.4.9) ............................................................. 42
AWKING HWDN2 WIRELESS UTILITY ....................................................................................................... 45
4. H
4.1 Available Network ....................................................................................................................... 46
4.2 Profiles ......................................................................................................................................... 47
4.3 Link Status Page .......................................................................................................................... 51
4.4 Information .................................................................................................................................. 52
5. U
NINSTALLING HAWKING UTILITY (MAC) ................................................................................................... 52
IV.
APPENDIX A – SPECIFICA TIONS ................................................................................................................ 54
V. INDEX ................................................................................................................................................................ 55
VI. PRODUCT SUPPORT INFORMATION ........................................................................................................ 58
Note: Manual contents are subject to change without prior notice. Please check the hawking website for the latest information.
4
Page 5

I. OVERVIEW
Thank you for purchasing the Hawking HWDN2 Hi-GainTM Wireless N USB Dish Adapter. Now you can
enjoy the latest Wireless-N technology with excellent speeds, of up to 150Mbps*. Designed with Hi-Gain
Dish Technology, the Wireless N USB Adapter extends your wireless network coverage by up to 3 times
the speed and 5 times the range more than a standard Wireless-G Network. It allows you to connect a
notebook or desktop to any wireless network** using the USB port. Now, you can stream HD video, play
games online, download music, images and data whil e maintaining your freedom of mobility.
The HWDN2 is also packed with security applications. For more security-sensitive applications, the
HWDN2 supports Hardware-based IEEE 802.11i encryption/decryption engine, including 64-bit/128-bit
WEP, TKIP, and AES. Also, it supports Wi-Fi alliance WPA and WPA2 encryption.
1. Features
Work with 802.11b/g/n wireless network devices.
High-speed transfer data rate - up to 150 Mbps.
High throughput supports multi-media data bandwidth requirement.
Support 64/128-bit WEP Data Encryption, WPA, WPA2.
Automatic fallback increases data security and reliability.
Supports the most popular operating system: Windows 2000/XP/Vista/7
Supports USB 2.0 interface.
* Theoretical wireless signal rate based on IEEE standard of 802.11a, b, g chipset used. Actual
throughput may vary. Network conditions and environmental factors lower actual throughput rate.
**Preferably Wireless-N network for maximum through pts.
** *All specifications are subject to change without notice.
5
Page 6
gy
p
2. Package Contents
Before you begin the installation, please check the items of your package. The package should include
the following items.
• One HWDN2 Hi-Gain Wireless N USB Dish Adapter
• One USB cable (1.0 meter ~ 39 inches)
• One CD-ROM with User’s Manual & Drivers for Windows and Mac
• Quick Installation Guide
Dual Antenna –
Dish T echnolo
USB port
LED Description
LINK Blinks when active connection is available else remains switched OFF
PWR
WPS (Wi-Fi Protection Setu
Blinks rapidly when data communication in progress else remains
switched OFF
LED
indicator
3. System Requirements
To begin using the HWDN2 Dish Adapter, your PC/Notebook must meet the following minimum
requirements:
• Operating System – Microsoft Windows 2000/XP/Vista or Mac OS 10.4 or later
• An Available USB Port on your Laptop or Desktop
• 256MB system memory or larger
• 750MHz CPU or higher configuration
6
Page 7
II. FOR WINDOWS USERS
1. Installation for Windows 7/ Vista
Important!
(1) If you have installed the Wireless PC Adapter driver & utility before, please uninstall the old version first.
(2) Be sure to save all your work, your system may automatically restart after installation.
a. Insert the included CD an auto load page will appear instantly on you screen.
b. Select Driver & Utility Setup
c. Choose a setup language
7
Page 8

d. Please wait a while the Wizard prepares for setup. Select “Next” to continue.
e. Please wait during the setup status screen, then Select “Install” to begin Installation.
f. Please wait until the Install Wizard completes. Note: A Windows Security screen might show up at
this point. Select “Install this driver software anyway” to Continue.
g. Select “Finish.”
8
Page 9
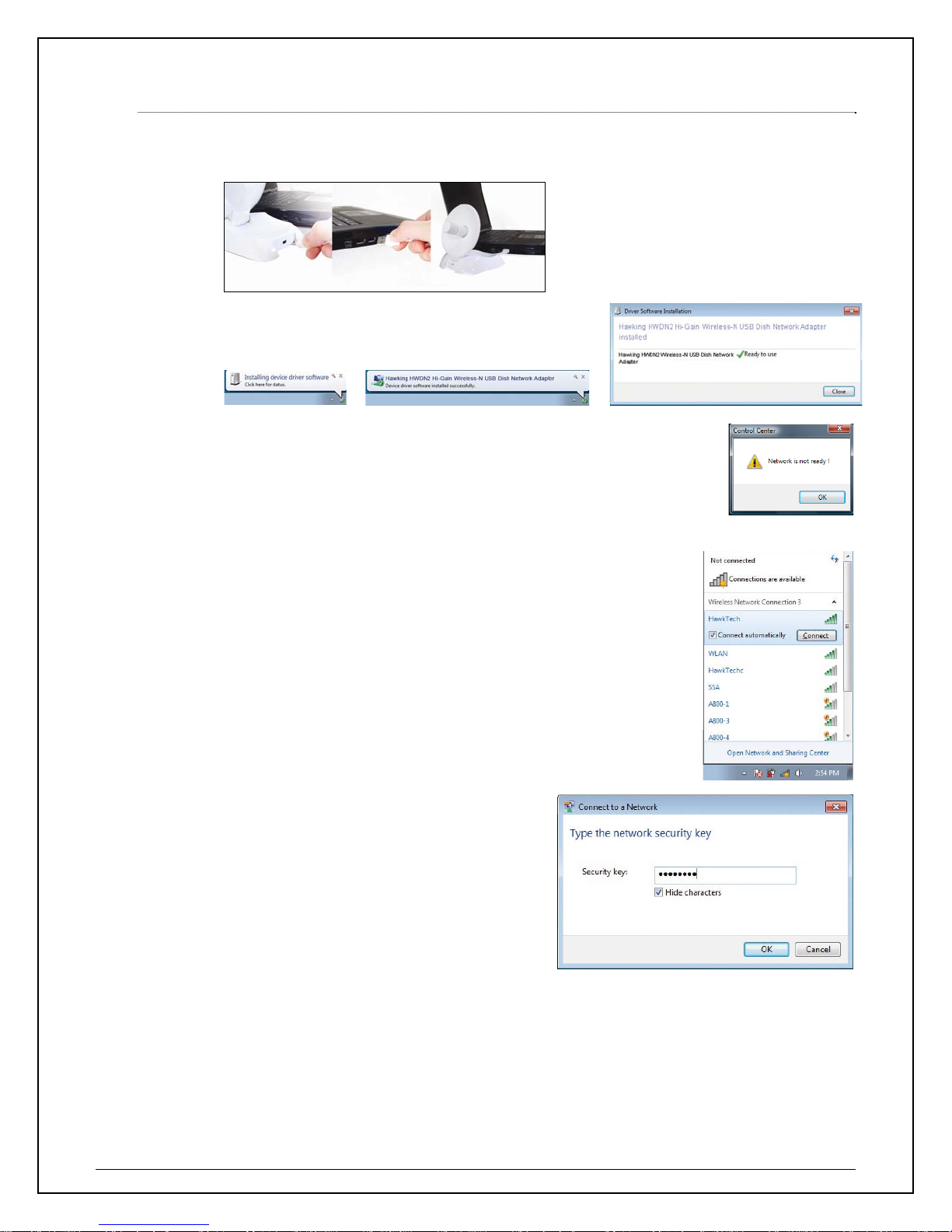
1.1 Connecting to a Wireless Network (Windows 7)
a. At this point, your system may prompt you to restart your computer. Plug in the HWDN2 to
an available USB after computer restarts.
b. Please wait until your system completes with the
driver installation.
c. When Installation is complete, Control Center will indicate that your
network is ready. Select “OK.”
d. The Adapter will automatically search and locate an open network.
Select a desired network.
You can locate search for the available network by clicking on the
wireless icon on your system tray (bottom-right corner).
e. If your selected network is
encrypted/password protected, please enter
the network security key and click “OK”. If you
don’t have the network security key, please
contact your network administrator.
9
Page 10
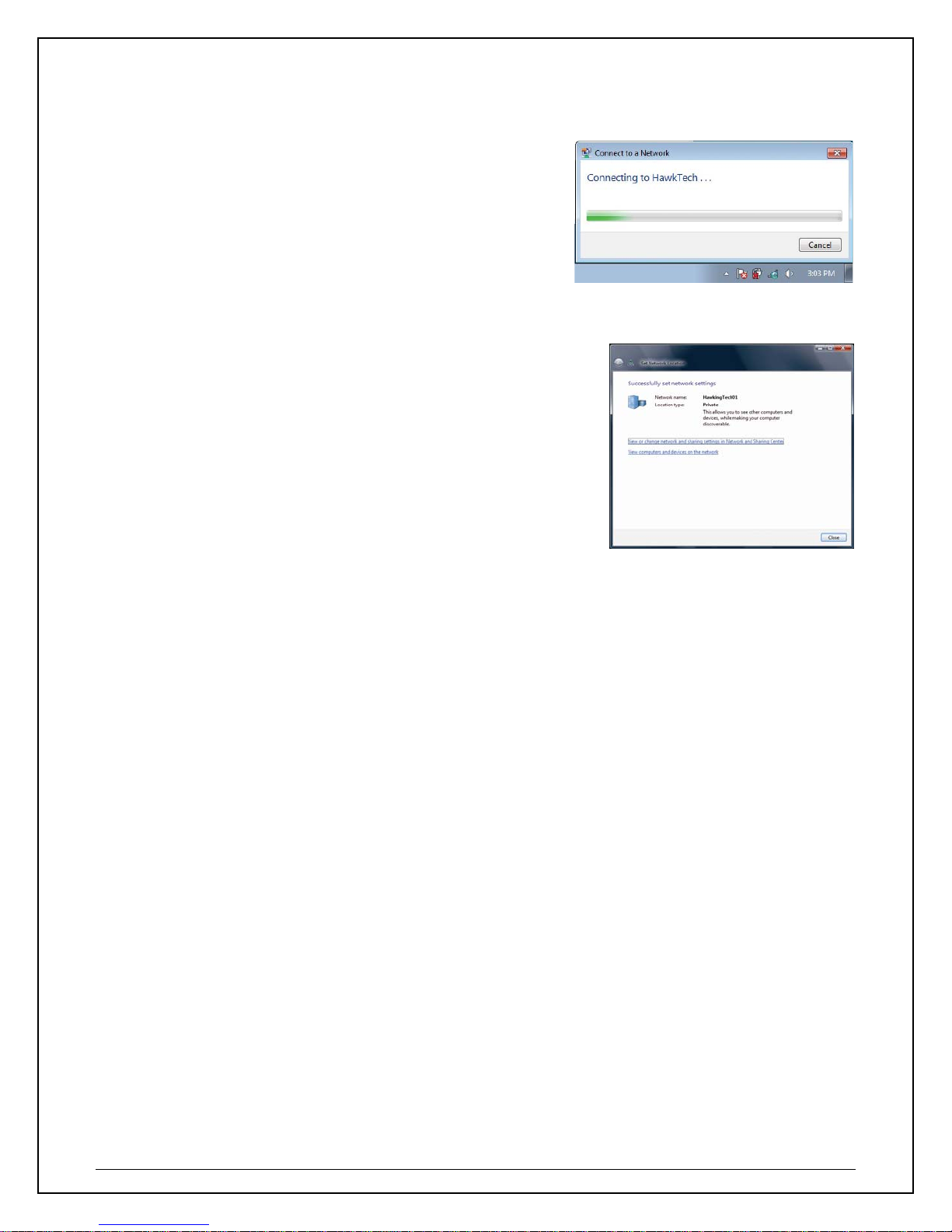
f. Congratulations! you are now successfully
connected!
10
Page 11
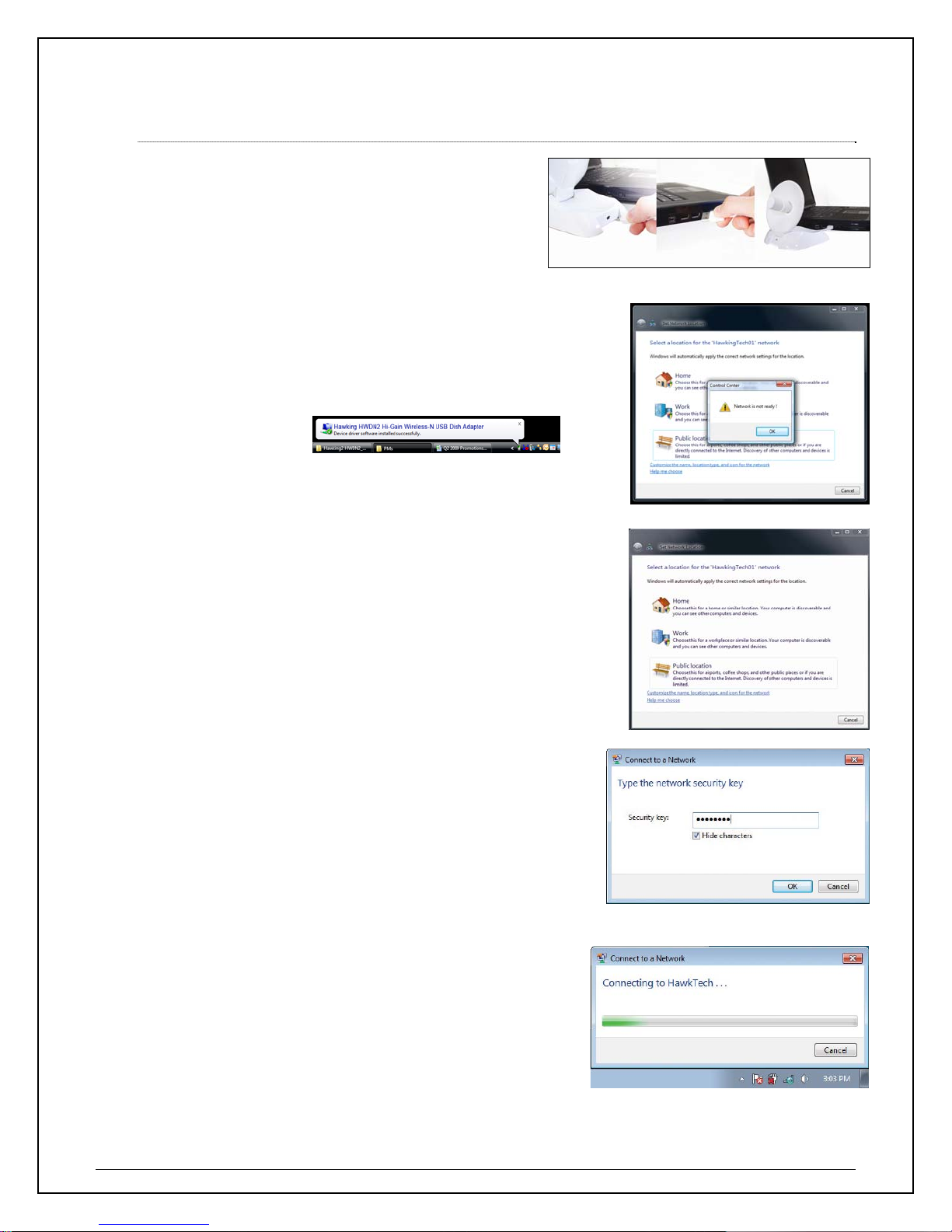
1.2 Connecting to a Wireless Network (Windows Vista)
a. At this point, your system may prompt you to
restart your computer. Plug in the HWDN2 to
an available USB after computer restarts.
b. Your system will automatically search for the installed
driver for your HWDN2 adapter and will prompt you when
it is ready.
g. Select a location for your network.
h. If your selected network is encrypted/password
protected, please enter the network security key and
click “OK”. If you don’t have the network security key,
please contact your network administrator.
i. Congratulations! you are now successfully
connected!
11
Page 12
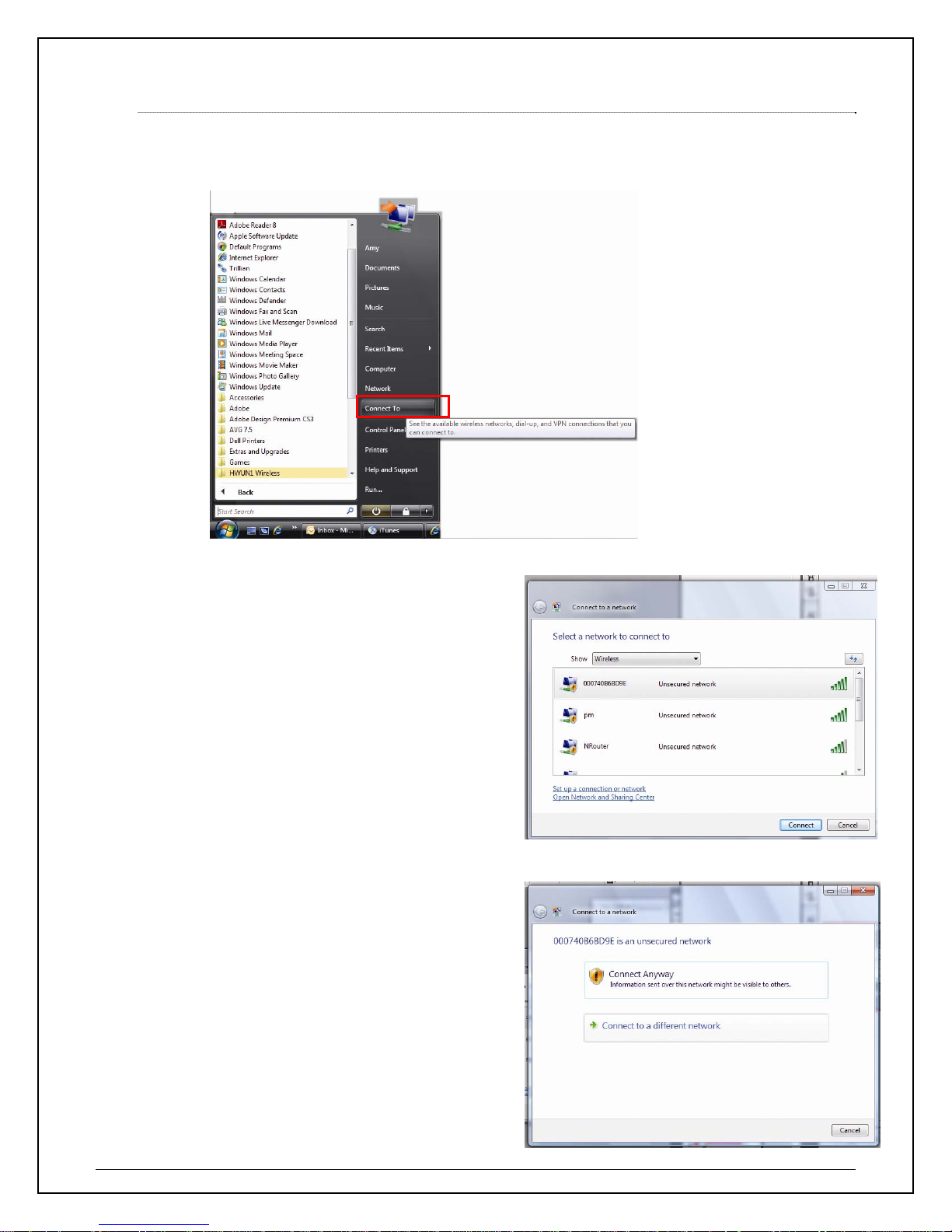
1.3 Using Windows Configuration (Windows / 7)
It is recommended that you use the Windows Configuration for the Wireless-N Adapter.
a. To open up the Windows Configuration, go to Start ÆConnect To
b. Select the Ne twork you wish to connect to.
If you are connecting to an unsecure
network, go to step c. If you are
connecting to a secured network, go to
step d.
c. If you are connecting to an open network
(unsecured network), a warning may
appear indicating that the network is an
unsecured network. Select Connect
Anyway and skip step
12
Page 13
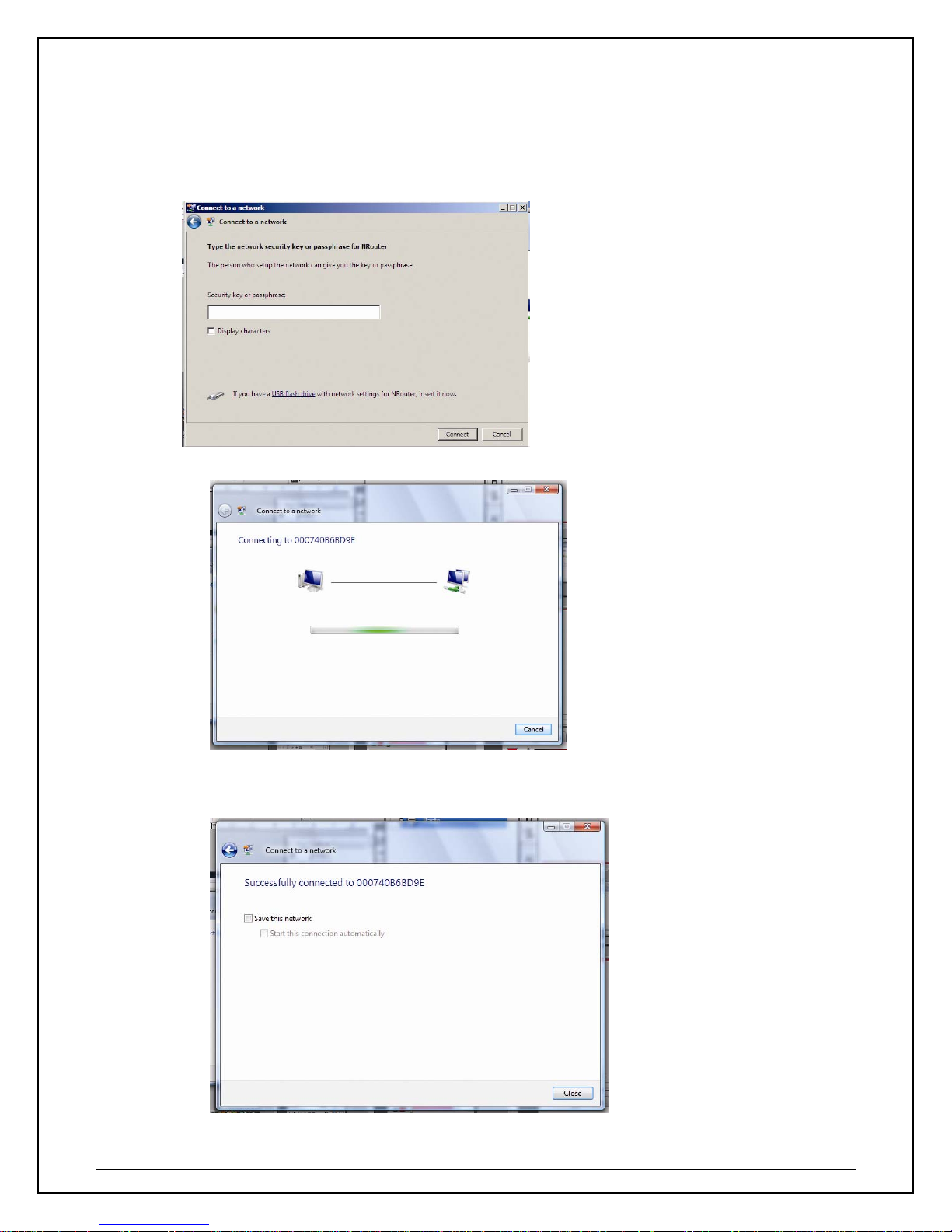
d. If your sele cted network is a secured (encryption) network, then a window will prompt you to
enter security key or passphrase. If you are connecting to a network that is security enabled,
but do not have the security key or passphrase, please obtain the passphrase from your
Network Administrator.
e. Please wait while your HWDN2 is connecting.
f. The HWDN2 Wireless Dish Adapter is now connected; you may save this network as your
preferred network.
13
Page 14
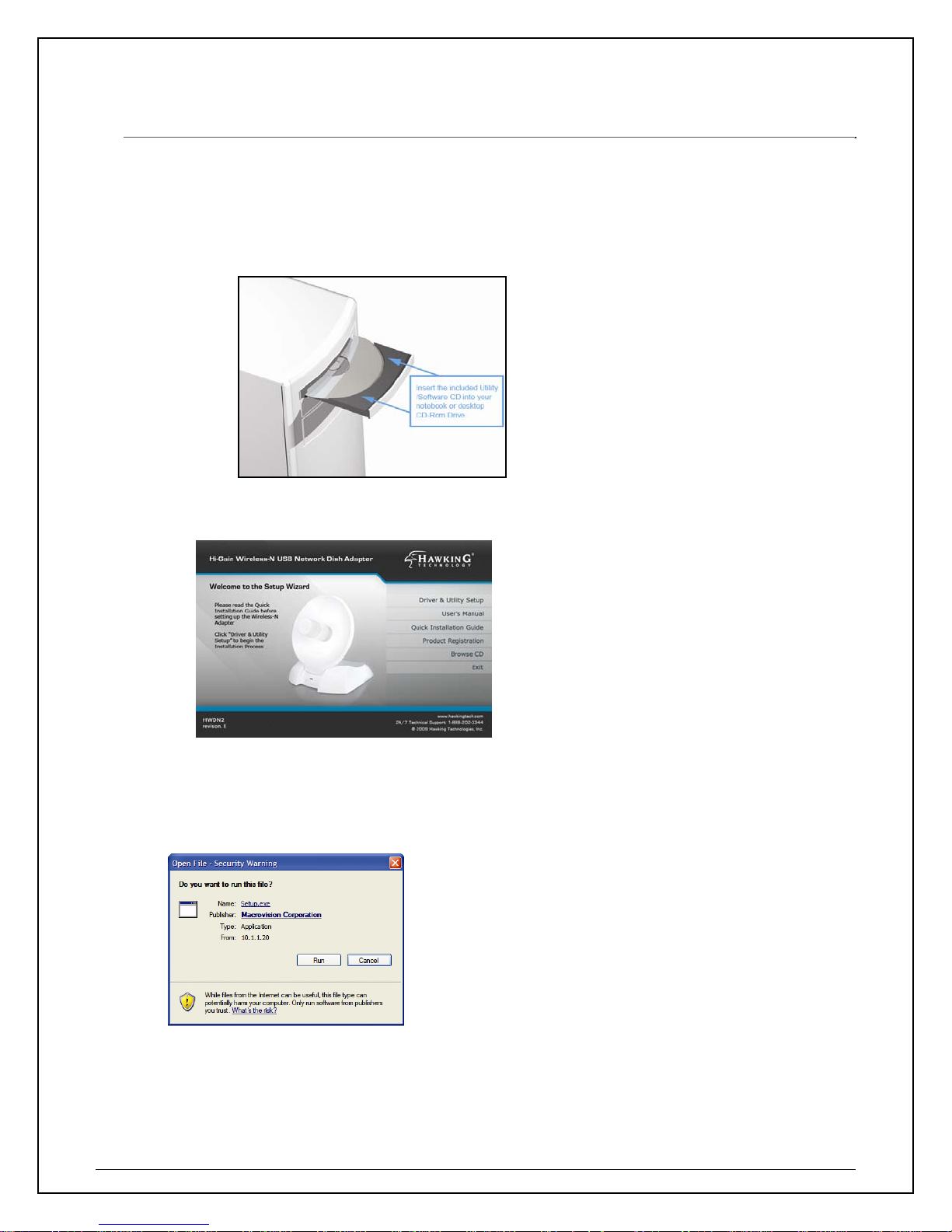
2. Installation (Windows 2000/XP)
Important! Please Install the HWDN2 Driver & Utility before connecting the HWDN2 into the USB
port on your computer. The HWDN2 Driver & Utility is located on the CD.
The following installation was operated under Windows XP. Procedures are similar for Windows 2000.
1. Insert the support CD into your CD Drive.
2. The CD drive should auto-load the following.
3. Open the file and you can briefly see the following. Select Run.
4. Select Setup Language and click “Next” and “Next again in the following screen.
14
Page 15
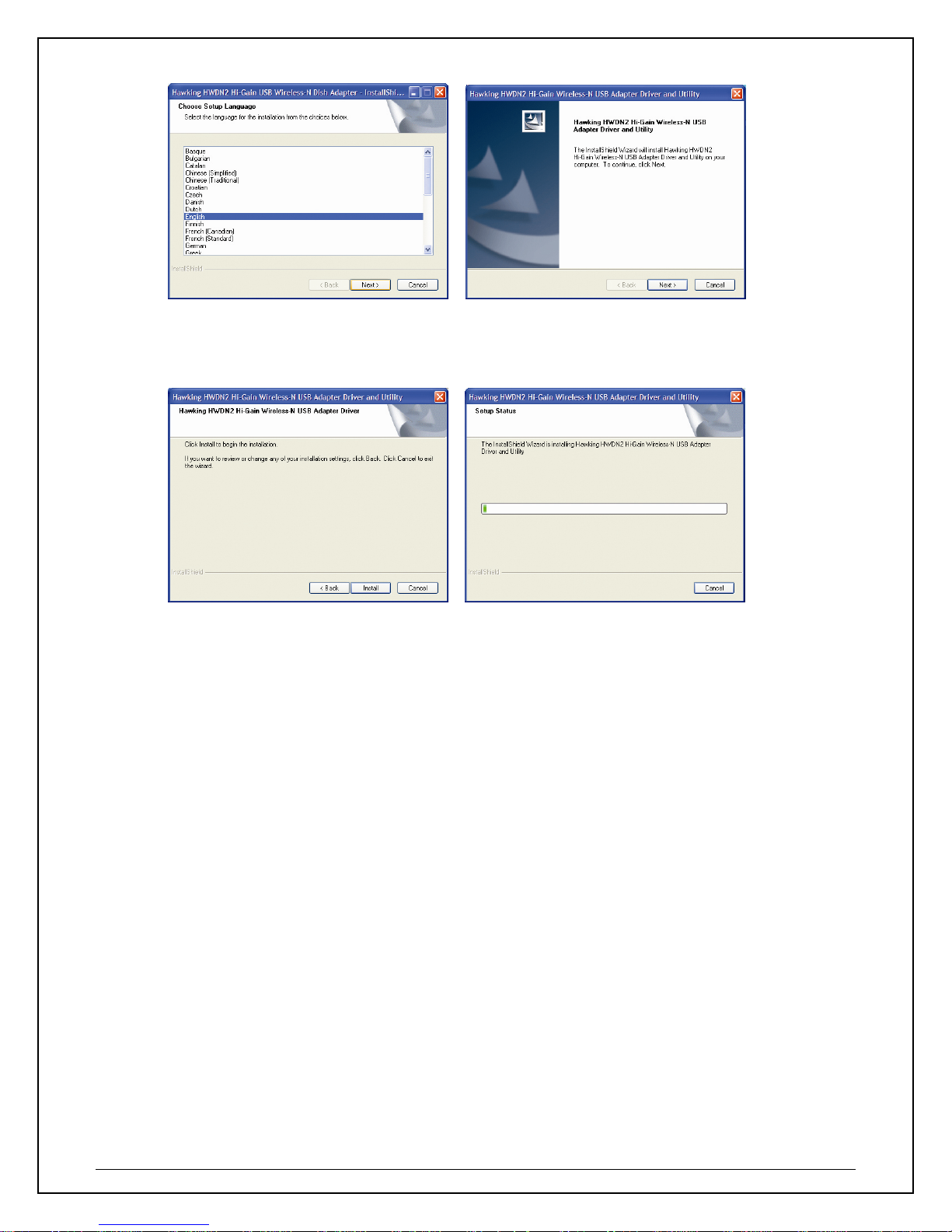
5. No w you’ll see the following message, please click ‘Install’ to begin the installation. Wait while
your system begins to install.
15
Page 16
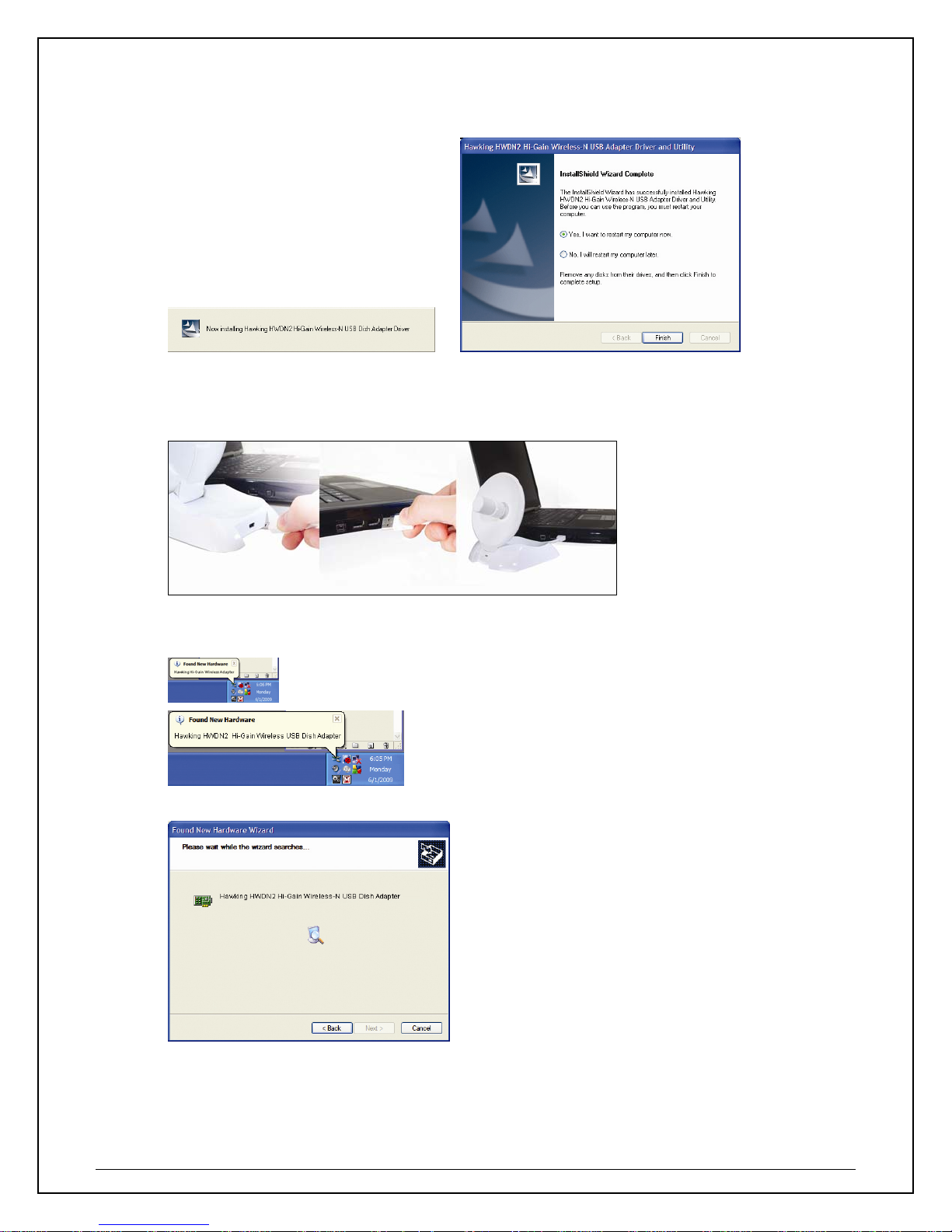
6. Select “Ye s” to restart your computer, then click “Finish” to complete the driver and utility
installation.
7. At this point, your system may prompt you to restart your computer. Plug in the HWDN2 to an
available USB after computer restarts.
8. Your system will recognize the new hardware, HWDN2 adapter. Please wait while it searches for
the installed driver and utility.
16
Page 17
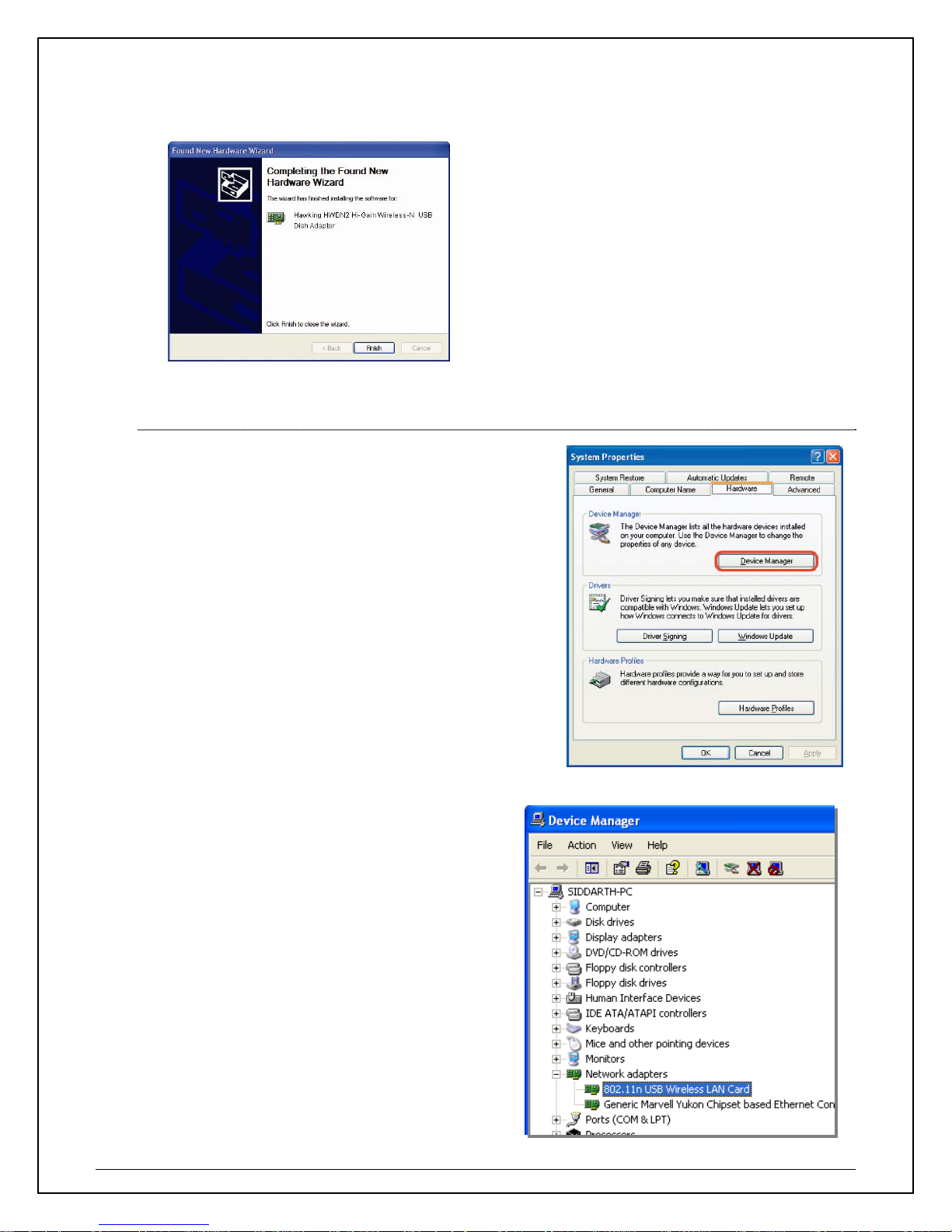
9. Finally select “Finish” to complete your hardware installation.
2.1 Verify installation (Windows 2000/XP)
1. Open Control Panel ÆDouble-click on System.
2. Select Hardware tabÆClick on Device Manager.
Select and double-click on 802.11N USB wireless
LAN card.
17
Page 18

Verify the device status of the 802.11N USB Wireless LAN Card
This device is working properlyÆClick OK
2.2 Network Configuration (Windows 2000/XP)
• Go to Start Menu ÆControl Panel Æ Network.
• Right-click on Wireless Network.
• Select ÆLocal Area Connection icon Æ select
Properties.
• Select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) ÆClick Properties.
Select the [General] tab.
a. If your Wireless Router supports [DHCP]
function, please select both [Obtain an IP
address automatically] and [Obtain DNS
server address automatically].
b. If the router does not support [DHCP]
function, you have to configure the IP and
DNS settings.
18
Page 19

2.3 Connect - Using HWDN2 Wireless Utility
NOTE:
• The HWDN2 Adapter must be connected to your computer at this point.
• Your home/office environment should have a wireless LAN Access Point (AP) that is
available for your use.
• You should readily have the (security keys) to connect to those Wireless LAN Access
Points (AP)
• Configuration utility will first automatically link with the Wireless AP if there is no security
key required. If the connection is successful, a message will appear on taskbar.
• The HWDN2 Wireless Utility works best with Windows XP and 2000. For Windows 7 and
Windows Vista, it is recommended to use the Windows Configuration.
1. Open Up the Hawking Wireless Utility. There are several ways to open up the Hawking
Wireless Configuration Utility.
From your desktop, double click on the desktop shortcut.
From your system tray
(Note: the icon may be green if the HWDN2 Adapter is already connected to a wireless
network).
- Connected to a Wireless Network or AP:
- Not Connected to a Wireless Network or AP:
- The HWDN2 is disabled
- The HWDN2 is not detected.
For more options, right click the wireless icon from the system tray.
- Open Config Utility: Select “Open Config Utility” to open the
configuration utility.
- About: Select “About” to show the utility information.
- Hide: Select “Hide” to hide the utility in the system tray.
- Quit : Select “Quit” to quit the utility in the system tray.
2. From the Available network tab, double click on the SSID or Access the SSID and click on
Connect.
, double click on the wireless bar icon .
19
Page 20

To see a list of available wireless networks,
select Available Network tabÆ Select
Refresh. All detected service set identifiers
(SSID) will be listed under SSID column.
Encryption/Security/Authentication:
If the selected SSID is an open network or
has no encryption, “none” will be listed under
the Encryption column.)
If the selected SSID has encryption (WEP,
TKIP, WPA), please enter the password in the
network key field and confirm network key
fields. If you don’t have the password, please
contact your network administrator.
When you are successfully connected, a green
signal meter will appear in the status bar
.
When the HWDN2 fails to connect, a red bar signal
meter appear in the status
bar.
Note: If you mouse over the red bar, it will indicate that
the Adapter is disconnected.
.
20
Page 21

3. Hawking Wireless Utility
3.1 Utility Overview
NOTE: The HWDN2 Wireless Utility works best with Windows XP and 2000. For Windows 7 and
Windows Vista, it is recommended to use the default Windows Zero Configuration Wireless Utility.
There are several parts to the utility screen. Please refer to the following table for the description.
B
C
A
D
21
Page 22

PARAMETER DESCRIPTION
Refresh - Refresh the list of adapters on your computer: “B“ block
Mode - There are two modes: Station and Access Point. If “Station" is selected,
the adapter works as a standard wireless adapter. If “Access Point" is selected,
A
the adapter will works as a wireless AP.
View – Allows for viewing of specific items with your adapter such as the
current status.
About - To check the version of the software utility, select this item.
B
C
D
E
This is a list for you to configure several adapters in your PC from the utility.
Show Tray Icon – To show the icon in the system tray, select the item.
Disable Adapter – This function is for you to disable or enable the adapter.
Windows Zero Config – To configure the adapter from Windows XP Zero
Configuration, check the item. (Recommended for Vist a and Windows 7)
Radio Off – This function is for you to turn off or turn on the radio in the
adapter. If the radio is turned off, the adapter will not work.
Status bar that displays the current status of the utility. To close it, please
disable the “Status Bar" in the “View" item.
Utility and Configuration tabs for the HWDN2 Adapters: General, Profiles,
Available Network, Status, Statistics, and Wi-Fi Protected Setup. The
following section will go over each tab in details
3.2 Available Network Tab
When you open the Configuration Utility, the utility will do an initial scan of all the networks within your
vicinity and automatically connect to the wireless network with the highest signal strength. From the
“Available Network” tab, all the networks nearby will be listed. Here you can change the network that
you are connected to.
22
Page 23

Parameter Description
Available Network(s) This list shows all information of the available wireless networks
within the range of your adapter . The information includes SSID,
Channel, Encryption, Network Authentication, Signal and etc. If
you want to connect to any network on the list, double-click the
selected network.
Refresh Click “Refresh” to update the available networks list. It is
Add to Profile A profile stores the setting of a network, so that you can connect
recommended that refresh the list while you have changed the
connection network.
to the network quickly. To add the selected network to a profile,
click this button.
3.3 General Tab
To check the connection status of the adapter, select “General”. This screen shows the information of
Link Speed, Network Type, Encryption Method, SSID, Signal Strength, Link Quality and Network
Address of the adapter.
Parameter Description
Status Shows the connection status of the adapter.
Speed Shows the cu rrent speed
Infrastructure – This operation mode requires the presence of an
802.11 Access Point. All communication is done via the Access Point or
Router.
IBSS – Select this mode if you want to connect to other wireless stations
in the Wireless LAN network without through an Access Point or Router.
IBSS – Select this mode if you want to connect to other wireless stations
in the Wireless LAN network without through an Access Point or Router.
23
Page 24

Encryption It displays the encryption setting of the current connection including
SSID The SSID (up to 32 printable ASCII characters) is the unique name
Signal Strength Indicates the wireless signal strength
Link Quality Indicates the wireless link quality
Network Address It shows the MAC, IP address and other information of the adapter.
3.4 Profile Tab
The “Profiles List” lets you manage the networks you connect to frequently. You are able to
add/Remove/Edit/Duplicate/Set Default to manage a profile.
None, WEP, TKIP or AES.
identified in a WLAN. The ID prevents the unintentional merging of two
co-located WLANs.
Parameter Description
Available
Profile(s)
Add/ Remove/
Edit Button
Duplicate If you like to build up the new profile with the same settings as
Set Default To designate a profile as the default network for the connection
This list shows the preferred networks for the wireless
connection. You can add, remove, edit, duplicate the preferred
networks or set one of the networks as the default connection.
Click these buttons to add/ delete/ edit the selected profiles.
the current profile, then you can select this feature.
from the available profiles list, click the button.
24
Page 25

Configure a Network Profile
Parameter Description
Profile Name
Define a recognizable profile name for you to identify the
different networks you are saving
The SSID (up to 32 printable ASCII characters) is the unique
name for the wireless network you are saving. The ID prevents
the unintentional merging of two co-located wireless networks.
Network Name
(SSID)
You may specify a SSID for the adapter and then only the
device with the same SSID can interconnect to the adapter.
25
Page 26

There are two kinds of network type described as follows.
This is a
computer-tocomputer (ad
hoc) network;
wireless
access points
are not used.
Channel
Infrastructure – This operation mode requires the presence of
an 802.11 Access Point. All communication is done via the
Access Point or Router.
Ad Hoc – Connect directly to another wireless adapter in the
Wireless LAN network without going through a router or access
point.
If this item is selected, the adapter will work in Ad Hoc mode.
This setting is only available for Ad Hoc mode. Select the
number of the radio channel used for the ad hoc connection.
The channel setting should be the same with the computer your
are connecting with.
This setting has to be consistent with the wireless networks that
the adapter intends to connect to.
Open System – No authentication is needed among the wireless
network.
Network
Authentication
Shared Key – Only wireless stations using a shared key (WEP
Key identified) are allowed to connect with each other.
WPA-PSK – Designed for home and small business users who
do not have access to network authentication servers. In this
mode, known as Pre-Shared Key, the user manually enters the
starting password in their access point or gateway, as well as in
each wireless station in the network. WPA-PSK takes over
automatically from that point, keeping unauthorized users that
don’t have the matching password from joining the network,
while encrypting the data traveling between authorized devices.
WPA2-PSK – WPA2-PSK is also for home and small business.
The difference between WPA-PSK and WPA2-PSK is that
WPA2-PSK provides data encryption via the AES. In contrast,
WPA-PSK uses Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) which is
not fully certified. AES is recommended.
26
Page 27

WPA 802.1X – WPA provides a scheme of mutual
authentication using either IEEE 802.1x/Extensible
Authentication Protocol (EAP) authentication or pre-shared key
(PSK) technology. It provides a high level of assurance to
enterprises, small businesses and home users that data will
remain protected and that only authorized users may access
their networks. For enterprises that have already deployed IEEE
802.1x authentication, WPA offers the advantage of leveraging
existing authentication databases and infrastructure.
WPA2 802.1X – Like WPA, WPA2 supports IEEE 802.1 x/EAP
authentications or PSK technology. It also includes a new
advanced encryption mechanism using the Advanced
Encryption Standard (AES). AES is required to the corporate
user or government users. The difference between WPA and
WPA2 is that
WPA2 provides data encryption via the AES. In contrast, WPA
uses Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP).
Data
Encryption
WEP 802.1X – It’s a special mode for using IEEE 802.1x/EAP
technology for authentication and WEP keys for data encryption.
Disabled – Disable the WEP Data Encryption.
WEP – Enable the WEP Data Encryption. When the item is
selected, you have to continue setting the WEP Encryption
keys.
TKIP – TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol) changes the
temporal key every 10,000 packets (a packet is a kind of
message transmitted over a network.) This insures much
greater security than the standard WEP security. (Note: This
mode is not certified. Performance may vary under this setting.)
AES – AES has been developed to ensure the highest degree
27
Page 28

of security and authenticity for digital information and it is the
most advanced solution defined by IEEE 802.11i for the security
in the wireless network.
Note: All devices in the network should use the same encryption
method to ensure the communication.
ASCII
PASSPHRASE
Key Length
WEP Key can be ASCII format. Alphanumeric values or signs
are allowed to be the WEP key. It is more recognizable for user.
It is a text string with a maximum of 32 alphanumeric
characters, for example: “Test“. The WEP Key is based upon
the Passphrase determined by you. This passphrase may not
work with other vendors’ products due to possible incompatibility
with other vendors’ passphrase generators. You must use the
same passphrase or WEP key settings for all wireless
computers within the network.
When you select the “WEP and “PASSPHRASE" and this
function will display in the current status of the utility.
The keys are used to encrypt data transmitted in the wireless
network. Fill the text box by following the rules below.
64-bit – Input 10-digit Hex values as the encryption keys. For
example: “0123456aef“.
128-bit – Input 26-digit Hex values as the encryption keys. For
example: “01234567890123456789abcdef“.
Key Index
(advanced)
Network Key
Confirm
Network Key
EAP Type
Select one of the four keys to be the data encryption key.
Please enter network security key here to make sure the
password is correct.
Please enter network security key here again.
GTC – GTC is an authentication protocol which allows the
exchange of clear text authentication credentials across the
network.
TLS – TLS is the most secure of the EAP protocols but not easy
28
Page 29

to use. It requires that digital certificates be exchanged in the
authentication phase. The server presents a certificate to the
client. After validating the server’s certificate, the client presents
a client certificate to the server for validation.
LEAP – LEAP is a pre-EAP, Cisco-proprietary protocol, with
many of the features of EAP protocols. Cisco controls the ability
of other vendors to implement this protocol, so it should be
selected for use only when limited vendor choice for client,
access-point, and server products is not a concern. When you
have set up LEAP authentication, you have to enter the user
name and password of your computer.
PEAP & TTLS – PEAP and TTLS are similar and easier than
TLS in that they specify a stand-alone authentication protocol be
used within an encrypted tunnel. TTLS supports any protocol
within its tunnel, including CHAP, MSCHAP, MSCHAPv2 and
PAP. PEAP specifies that an EAP-compliant authentication
protocol must be used; this adaptor supports MD5, TLS, GTC
(Generic Token Card) and MSCHAPv2. The client certificate is
optional required for the authentication.
Tunnel Includes MD5, GTC, TLS, MSCHAP-v2.
Username The certificate username in the RADIUS server.
Identity User’s identity in the RADIUS server.
Password User’s password in the RADIUS server.
Certificate Select the certificate for RADIUS server authentication
Status
This screen provides information regarding Hawking Technologies, the driver version, settings of the
wireless network the adapter is connected to, the link time and link status.
29
Page 30

3.5 Statistics
You can get real time information
about packet transmissions and
receiving statuses during wireless
communications. If you want to
recount the statistics value, please
click “Reset“.
30
Page 31

3.6 Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS)
Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS) is the latest
wireless network technology which make s
wireless network setup very simple. If you
have a WPS-enabled wireless access point,
and you want to establish a secure
connection to it, you don’t have to configure
the wireless access point and setup data
encryption by yourself. All you have to do is to
go to the WPS setup page of this wireless
card, click the WPS button, and then press a
WPS button or enter a set of 8-digit code on
the wireless access point you wish to
establish a secure connection.
3.6.1 Pin Input Config (PIN)
1. The PIN co de of your wireless network card is an eight-digit number located at the upperright position of configuration utility. Remember it, and input the number to your wireless
access point as the WPS PIN code (Please refer to the user manual of your wireless
access point for instructions about how to do this)
2. Click ‘Pin Inp ut Config (PIN)’ button now, and
the following message will appear on your
computer, click ‘Yes’ to select a specific
wireless access point or click ‘No’ to start PIN
method of WPS .
3. If you click ‘Yes’, and the following
message will appear on your computer,
please select the SSID of wireless
access point that you wish to connect
and click ‘Select’.
31
Page 32

4. Please wait while the install procedure is running and wait for few seconds to two minutes.
If a wireless access point with correct PIN code is found, you’ll be connected to that
access point.
3.6.2 Push Button Config (PBC)
a. Start PBC pairing p ro cedure at access point side (please refer to the instruction given by your
access point’s manufacturer), then click ‘PBC’ button in wireless configuration utility to start to
establish wireless connection by WPS. Please be patient (This may require several second s
to one minute to complete).
32
Page 33

2. Whe n the connection between this wireless network card and access point is
successfully established by WPS, and the information about access point you connected
to will be displayed.
3.7 NETWORK SECURITY (WEP, WPA…)
If your AP/Router has a networking security key, you must enter the same security key and setting. If
you do not have the Network Encryption key, please request it from the Network Administrator or the
person who set up your wireless network.
After you obtained the network security information, open up Hawking Wireless Utility. Continue
below to set up your Network Security Code.
3.7.1 WEP Setup
If the SSID or Access
Point you wish to connect
has WEP authentication,
select the SSID and click
on Connect.
33
Page 34

Make sure the 1. Network
Authentication and 2. Data encryption
matches your selected Network.
Finally, enter the 3. Network Key.
WEP Setup Instructions:
Windows V ista/ 7
Windows XP/2000
(All settings should correspond with settings of the wireless AP that you are connecting to.)
a. Network Authentication field: indicates the authentication type of the AP/Router. Please
confirm the setting of the AP/Router.
• Open: WEP open system is based on request and grant. It is essentially no
authentication.
• Shared: WEP shared key is based on request, challenge, challenge response,
grant/deny.
b. Data Encryption field: Select WEP
34
Page 35

c. Enter in AP encryption keys (64/128bits) in the box Key1~Key4. Please accept the auto
selected setting of [Hex]/ [ASCII].
d. Select the current AP encryption keys from Key1~Key4.
e. Press [OK] to finish setting.
3.7.2 WPA Setup
WPA encryption type can be divided into WPA-PSK, WPA2-PSK, WPA (also known as
WPA-EAP), and WPA2 (also known as WPA2-EAP). All settings should correspond
with the wireless AP that you wish to connect to.
Setting the Authentication and Security Page:
a. Network Authentication: Select WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK (note: your AP must
support this function).
1
b. Data Encryption: Select TKIP
the Value on your AP)
c. Enter the WAP Preshared Key and click OK.
or AES in the drop down menu.(Must Correspond to
WPA and WPA2
1. If you wish to connect to an AP with WPA or WPA2 authentication, select the AP or
SSID and select Connect. (For example the N Router is being selected, the security
settings must correspond to Wireless Access Point)
2. Setting the Authentication and Security Page:
a. Network Authentication: select WPA or WPA2-PSK (AP must support the
function).
1
b. Data Encryption: select TKIP
or AES (Same as AP)
c. If the AP/router has 802.1x setting function, click it for advanced settings. Please
consult your network administrator for details or check the user manual of the
Wireless Access Point. (See the Screen shot on the next page)
Click OK to finish setting.
1
TKIP Encryption: This mode is not certified. Performance may vary under this setting.
35
Page 36

4. Uninstalling Hawking Utility/Driver
Select Uninstall option from the start menu.
Select "Yes" to remove all its features.
Removing the utility is in progress.
HWDN2 Driver and Utility has finished uninstalling. Select Finish.
36
Page 37

III. FOR MAC USERS
1. Installation for Mac OSX 10.4 or later
IMPORTANT:
• Please do not install the wireless adapter into your Mac desktop or notebook before installing the
software program from the CD.
• The following installation was operated under Apple OSX 10.5 Leopard. (Installation Proced ures
are similar in other OS. However, the installation images and screens may not look the same as
the ones in this manual)
• If you have previously installed other Wireless Adapter Drivers & Utilities, please uninstall the
older version first.
1. Powe r on your Computer and insert the
Setup CD into your CD-ROM Drive. A folder
should automatically open. If there is no
folder opening up automatically, click on the
CD icon on your desktop to manually open
the folder.
a. Double click the icon in the folder
that is titled “CLICK HERE TO
ST ART”
2. Please select a Mac OS Setup according to the system you are operating:
Note: If you are uncertain about which
version of the Mac OS X your are using,
click on the Apple icon lo cated on the left
corner of the menu bar and select
“About This Mac.” The version number
should appear in a pop up window.
Tiger: Mac 10.4 ~10.4.9
Leopard: Mac 10.5 ~10.5.x
37
Page 38

3. Welcome to the Hawking HWDN2 Hi-Gain
Adapter Driver Installer. Select “Continue”.
4. Rea d the Important information in the following
screen, then “Continue”.
5. Software License Agreement: select “Continue”.
6. Click Agree to continue.
38
Page 39

7. Select a de stination and “Continue”.
8. The drive r wil l take 2.5MB of space on your
computer. Click “Install” to continue.
9. If your compu t er is password protected, please
enter your password to continue.
10. Again, make sure you save all your work, then
select “Continue Installation”.
39
Page 40

11. Please wait while your wizard is installing the
HWDN2 Driver.
12. Finally, select “Restart”.
2. Connecting To Your Wireless Network (Mac 10.5 or later)
1. Whe n your computer has successfully restarted. Insert the HWDN2 Hi-Gain Wireless-N USB
Dish Adapter into an available USB port on your desktop or notebook computer.
• Insert the USB dish adapter firmly into the USB port to ensure a proper connection is made.
• When the adapter is inserted carefully lift the antenna unit upright.
NOTE: If your computer or laptop already has
a built-in Airport Card, please turn it off by
going to the Wireless Icon on the top right
corner or your screen and select “TURN OFF
AIRPORT.”
40
Page 41

If this is your first time using the Wireless-N USB Dish Adapter on your computer, you will need to
enable the HWDN2 in your Network Preference.
2. After plugging in the Adapter, the Hawking HWDN2 Wireless Utility will automatically pop up. You
will be asked to enable your WLAN card. When a NOTICE comes up, select “OK”. Then, select
“Network Preferences.”
Please note the “Ethernet Adapter
(en15)”network interface. You will need to enable
this in the Network Preferences. Note: the screen
above shows “Ethernet Adapter (en15)” network
interface, however it may be vary slightly on your
computer.
3. Enabling the USB Adapter in your Network
Preferences by selecting “Ethernet Adapter (....)”,
then click “Apply.”
SIDE NOTE: Configure IP Manually vs. Automatic (DHCP)
• If you plan on using a “Static” (Manually entered) IP address for your computer you may do so here by
double clicking the “USB Wireless Adapter” selection and selecting TCP/IP.
• If you are using an automatically assigned IP address (MOST NETWORKS) you do not have to worry
about this. Simply close the window to proceed.
HOW TO CHANGE YOUR IP ADDRESS TO STATIC MODE
(Change from DHCP to Manual Configuration)
- If your wireless network uses a static IP address or requires manual configuration you may do so by
highlighting the USB wireless adapter (Shown above).
- Select “Configure” to enter the configuration menu for the wireless adapter.
- Select the Tab that is named TCP/IP
- Select the menu button for “Configure IPv4” and choose the appropriate selection
- You can manually configure your IP Address, DNS Servers and other information here.
- Please contact a network administrator if you are uncertain of the settings that are required to connect to
your network.
- When you have finished select APPLY NOW to continue.
41
Page 42

4. From Hawking HWDN2 Wireless Utility,
select “Available Network” tab. Then select
your desired Wireless Network (SSID).
5. If your sele cted network has encryption,
please enter the network key and confirm it.
If the selected network has encryption,
please enter the password and confirm it.
6. Con gratulations! the asterisk sign (*) next to the
selected network indicates that your are connected.
3. Connecting To Your Wireless Network (Mac 10.4~10.4.9)
1. Whe n your computer has successfully restarted. Insert the HWDN2 Hi-Gain Wireless-N USB
Dish Adapter into an available USB port on your desktop or notebook computer.
• Insert the USB dish adapter firmly into the USB port to ensure a proper connection is made.
• When the adapter is inserted carefully lift the antenna unit upright.
42
Page 43

NOTE: If your computer or laptop already has a built-in Airport
Card, please turn it off by going to the Wireless Icon on the top
right corner or your screen and select “TURN OFF AIRPORT.” If
this is your first time using the Wireless-N USB Dish Adapter on
your computer, you will need to enable the HWDN2 in your
Network Preference.
2. After plugging in the Adapter, the Hawking HWDN2 Wireless
Utility will automatically pop up. You will be asked to enable
your WLAN card. When a NOTICE comes up, select “OK”.
3. System Preferences and Network Settings:
a) Click the APPLE icon on the top left corner of your desktop
and open the SYSTEM PREFERENCES menu.
b) If this is your first time using the Wireless-
150N USB Dish Adapter on your computer,
you will need to enable the device before
using the Wireless Utility. In the System
Preferences page, locate the NETWORK icon
and double click it to access the control panel.
4. The new USB wireless adapter will automatically be
detected. Click “OK” to continue.
43
Page 44

5. Click “APPLY NOW” to confirm the selection.
- If you are using an automatically assigned IP
address (MOST NETWORKS) you do not
have to worry about this. Simply close the
window to proceed.
- If you plan on using a “Static” (Manually
entered) IP address for your computer you
may do so here by double clicking the “USB
Wireless Adapter” selection and selecting
TCP/IP.
SIDE NOTE: Configure IP Manually vs. Automatic (DHCP)
• If you plan on using a “Static” (Manually entered) IP address for your computer you may do so here by
double clicking the “USB Wireless Adapter” selection and selecting TCP/IP.
• If you are using an automatically assigned IP address (MOST NETWORKS) you do not have to worry
about this. Simply close the window to proceed.
HOW TO CHANGE YOUR IP ADDRESS TO STATIC MODE
(Change from DHCP to Manual Configuration)
- If your wireless network uses a static IP address or requires manual configuration you may do so by
highlighting the USB wireless adapter (Shown above).
- Select “Configure” to enter the configuration menu for the wireless adapter.
- Select the Tab that is named TCP/IP
- Select the menu button for “Configure IPv4” and choose the appropriate selection
- You can manually configure your IP Address, DNS Servers and other information here.
- Please contact a network administrator if you are uncertain of the settings that are required to connect to
your network.
- When you have finished select APPLY NOW to continue.
7. From Hawking HWDN2 Wireless Utility, select
“Available Network” tab. Then select your
desired Wireless Network (SSID).
44
Page 45

8. If your selected network has encryption, please
enter the network key and confirm it. If the
selected network has encryption, please enter
the password and confirm it.
9. Congratulations! the asterisk sign (*) next to the
selected network indicates that your are
connected.
4. Hawking HWDN2 Wireless Utility
The Hawking HWDN2 Wireless Utility is an application that helps you configure the HWDN2A and monitor the
link status and statistics of your wireless connection.
Each time you insert the HWDN2 the Hawking Wireless Utility should automatically
load. In the case that it doesn’t you may manually load the Utility by using “FINDER”
to view your “APPLICATIONS” folder and selecting the Hawking Wireless Utility Icon
displayed on the left.
45
Page 46

4.1 Available Network
When you open the Wireless Utility, the system will scan all wireless channels to find all access
points/stations within the accessible range of your adapter and automatically connect to the wireless
device with the highest signal strength. When using the “Available Network” option, all nearby
networks will be listed. You can change your connection to another network or you may add one of
the networks to your own profile list.
Parameter Description
Available Network This list shows all available wireless networks within range of
Refresh Button
your card. It also displays the information of the networks
including the SSID, BSSID, Channel, Encryption, Authentication
and Network Type. If you want to connect to any networks on the
list, double-click the item on the list, and the adapter will
automatically connect to the selected network. An asterisk sign (*)
in the Associated col umn shows that you are connected to the
corresponding network (SSID)
Click “Refresh” button to view all the wireless networks nearby.
.
46
Page 47

Connect Button
Add to Profile Button
4.2 Profiles
The “Profiles List” is for you to manage the networks you connect to frequently. You are able to
Add/Delete/Edit/Activate a profile.
Click “Connect” to connect to the selected network.
Add the selected network to Profiles list.
Parameter Description
Profiles List The profiles list display all the profiles and the relative information
including Profile Name, SSID, Channel, etc.
Add/ Edit/Remove/Duplicate
Button
Apply
Click these buttons to Add/ Edit/Remove/Duplicate the selected
profiles.
Click “Apply” to connect to the selected profile.
4.2.1 Configure the Profile
47
Page 48

Parameter Description
Profile Name
Define a recognizable profile name for you to identify the different
networks
The SSID (up to 32 printable ASCII characters) is the unique name
identified in a WLAN. The ID prevents the unintentional merging of two
Network Name (SSID)
co-located WLANs.
You may specify a SSID for the adapter and then only the device with
the same SSID can interconnect to the adapter.
There are two kinds of network type described as follows.
This is a computer-tocomputer (ad hoc)
network; wireless
access points are not
used.
Infrastructure – This operation mode requires the pre sen ce of an
802.11 Access Point. All communication is done via the Access Point or
Router.
Ad Hoc – Connect to another wireless adapter in the Wireless LAN
network without through an Access Point or Router.
If this item is selected, the adapter will work in Ad Hoc mode.
This setting is only available for Ad Hoc mode. Select the number of the
Channel
radio channel used for the networking. The ch annel setting should be
the same with the network you are connecting to.
This setting has to be consistent with the wireless networks that the
adapter intends to connect.
Open System – No authentication is needed among the wireless
network.
Network Authentication
Shared Key – Only wireless stations using a shared key (WEP Key
identified) are allowed to connecting each other.
WPA-PSK – It is a special mode designed for home and small business
users who do not have access to network authentication servers. In this
48
Page 49

Data Encryption
mode, known as Pre-Shared Key, the user manually enters the starting
password in their access point or gateway, as well as in each wireless
station in the network. WPA-PSK takes over automatically from that
point, keeping unauthorized users that don’t have the matching
password from joining the network, while encrypting the data traveling
between authorized devices.
WPA2-PSK – WPA2-PSK is also for home and small business. The
difference between WPA-PSK and WPA2-PSK is that WPA2-PSK
provides data encryption via the AES. In contrast, WPA-PSK uses
Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP).
WPA 802.1X – WPA provides a scheme of mutual authentication using
either IEEE 802.1x/Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP)
authentication or pre-shared key (PSK) technology. It provides a high
level of assurance to enterprises, small businesses and home users that
data will remain protected and that only authorized users may access
their networks. For enterprises that have already deployed IEEE 802.1x
authentication, WPA offers the advantage of leveraging existing
authentication databases and infrastructure.
WPA2 802.1X – Like WPA, WPA2 supports IEEE 802.1 x/EAP
authentications or PSK technology. It also includes a new advanced
encryption mechanism using the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES).
AES is required to the corporate user or government users. The
difference between WPA and WPA2 is that
WPA2 provides data encryption via the AES. In contrast, WPA uses
Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP).
WEP 802.1X – It’s a special mode for using IEEE 802.1x/EAP
technology for authentication and WEP keys for data encryption.
Disabled – Disable the WEP Data Encryption.
WEP – Enable the WEP Data Encryption. When the item is selected,
you have to continue setting the WEP Encryption keys.
TKIP – TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol) changes the temporal key
every 10,000 packets (a packet is a kind of message transmitted over a
network.) This insures much greater security than the standard WEP
security. (Note: This mode is not certified. Performance may vary under
this setting.)
AES – AES has been developed to ensure the highest degree of
security and authenticity for digital information and it is the most
advanced solution defined by IEEE 802.11i for the security in the
49
Page 50

wireless network.
Note: All devices in the network should use the same encryption method
to ensure the communication.
ASCII
PASSPHRASE
Key Length
Key Index (advanced) Select one of the four keys to be the data encryption key.
Network Key
Confirm Network Key Please enter network security key here again.
EAP T ype
WEP Key can be ASCII format. Alphanumeric values or signs are
allowed to be the WEP key. It is more recognizable for user.
It is a text string with a maximum of 32 alphanumeric characters, for
example: “Test“. The WEP Key is based upon the Passphrase
determined by you. This passphrase may not work with other vendors’
products due to possible incompatibility with other vendors’ passphrase
generators. You must use the same passphrase or WEP key settings for
all wireless computers within the network.
When you select the “WEP and “PASSPHRASE" and this function will
display in the current status of the utility.
The keys are used to encrypt data transmitted in the wireless network.
Fill the text box by following the rules below.
64-bit – Input 10-digit Hex values as the encryption keys. For example:
“0123456aef“.
128-bit – Input 26-digit Hex values as the encryption keys. For example:
“01234567890123456789abcdef“.
Please enter network security key here to make sure the p assword is
correct.
GTC – GTC is an authentication protocol which allows the exchange of
clear text authentication credentials across the network.
TLS – TLS is the most secure of the EAP protocols but not easy to use.
It requires that digital certificates be exchanged in the authentication
phase. The server presents a certificate to the client. After validating the
server’s certificate, the client presents a client certificate to the server for
validation.
LEAP – LEAP is a pre-EAP, Cisco-proprietary protocol, with many of the
features of EAP protocols. Cisco controls the ability of other vendors to
implement this protocol, so it should be selected for use only when
limited vendor choice for client, access-point, and server products is not
a concern. When you have set up LEAP authentication, you have to
enter the user name and password of your computer.
PEAP & TTLS – PEAP and TTLS are si milar and easier than TLS in that
they specify a stand-alone authentication protocol be used within an
encrypted tunnel. TTLS supports any protocol within i ts tunnel, including
CHAP, MSCHAP, MSCHAPv2 and PAP. PEAP specifies that an EAPcompliant authentication protocol must be used; this adaptor supports
MD5, TLS, GTC (Generic Token Card) and MSCHAPv2. The client
certificate is optional required for the authentication.
50
Page 51

4.3 Link Status Page
The Link Status page gives you information regarding your current wireless channel, transmit rate (speed)
and link/signal quality. You will use this utility to figure out which antenna position results in the best
performance and connection.
Obtaining the Strongest Connection
First you must determine where the location of your Wireless Access Point is within your network.
Position the directional antenna towards the location of the Access Point.
While viewing your Link Status utility, rotate the antenna clockwise and counter-clockwise slowly to
figure out which position gives you the highest Link Quality and Signal Strength. Once you have
determined which position gives you the best signal, leave the antenna in that orientation
51
Page 52

4.4 Information
By choosing this option, you can the information about the Driver and Utility.
5. Uninstalling Hawking Utility (Mac)
1. Insert the Original Setup CD. Select “Sofware_MAC” folder.
52
Page 53

2. Select your Mac OS (10.4 or
10.5) and the
“Uninstall.command
3. Click on “Password” and enter the
password for your computer, then
“enter”. If your computer is not
password protected, then press
enter.
53
Page 54

IV. APPENDIX A – SPECIFICATIONS
• Standard: IEEE 802.11b/g/n
• Interface: USB 2.0 Type A
• Frequency Band: 2.4000 ~ 2.4835GHz (Industrial Scientific Medical Band)
• Data Rate:
11b: 1/2/5.5/11Mbps
11g: 6/9/12/24/36/48/54Mbps
11n (20MHz): MCS0-7 (up to 72Mbps)
11n (40MHz): MCS0-7 (up to 150Mbps)
• Security: 64/128-bit WEP Data Encryption, WPA, WPA2
• Antenna: Hi-Gain Dual Antenna – Dish Technology
• Drivers: Windows 2000/XP/Vista or Mac 10.4 or later
• LEDs: Link/Activity
• Transmit Power: 11n: 14±1.5dBm, 11g: 14±1.5dBm, 11b: 17±1.5dBm
• Dimension: 4.17(L) in x 4.9(W) in x 5.14(H) in
• Weight: 137 gram / 4.8 oz
• Temperature: Operating 32~104˚F (0 ~40˚C), Storage -13~149˚F (-25~65˚C)
• Humidity: Max. 95% (Non-Condensing)
• Certification: FCC
54
Page 55

V. INDEX
This chapter provides solutions to problems usually encountered during the installation and operation of the
adapter.
1. What is the IEEE 802.11n standard?
802.11n is an IEEE 802.11 wireless network standard that increases transmission speeds from a
traditional 11Mbps (802.11b) to over 100Mbps. Currently, the HWDN2 supports up to 150Mbps. 802.11n
can handle legacy 11a, 11b and 11g transmission in a mixed mode or only 11n nodes for maximum
performance. It supports the 2.4GHz and 5GHz frequency bands.
The key to the 802.11n standard is the use of multiple antennas, known as MIMO (Multiple input/multiple
output). MIMO technology enables two data streams, transmitter and receiver, to be se nt simultaneously
over longer distances and to improve the overall system performan ce.
2. What does IEEE 802.11 feature support?
The product supports the following IEEE 802.11 functions:
z CSMA/CA plus Acknowledge Protocol
z Multi-Channel Roaming
z Automatic Rate Selection
z RTS/CTS Feature
z Fragmentation
z Power Mana gement
3. What is Ad-hoc?
An Ad-hoc integrated wireless LAN is a group of computers, each has a Wireless LAN adapter,
Connected as an independent wireless LAN. Ad hoc wireless LAN is applicable at a departmental scale
for a branch or SOHO operation.
4. What is Infrastructure?
An integrated wireless and wireless and wired LAN is called an Infrastructure configuration. Infrastructure
is applicable to enterprise scale for wireless access to central database, or wireless appli cation for mobile
workers.
5. What is BSS ID?
A specific Ad hoc LAN is called a Basic Service Set (BSS). Computers in a BSS must be configured with
the same BSS ID.
6. What is WEP?
WEP is Wired Equivalent Privacy, a data privacy mechanism based on a 40 bit shared key algorithm, as
described in the IEEE 802 .11 standard.
55
Page 56

7. What is TKIP?
TKIP is a quick-fix method to quickly overcome the inherent weaknesses in WEP security, especially the
reuse of encryption keys. TKIP is involved in the IEEE 802.11i WLAN security standard, and the
specification might be officially released by early 2003.
8. What is AES?
AES (Advanced Encryption Standard), a chip-based security, has been developed to ensure the highest
degree of security and authenticity for digital information, wherever and however communicated or stored,
while making more efficient use of hardware and/or sof t ware than previous encryption standards. It is
also included in IEEE 802.11i standard. Compare with AES, TKIP is a temporary protocol for replacing
WEP security until manufacturers implement AES at the hardware level.
9. Can Wireless products support printer sharing?
Wireless products perform the same function as LAN products. Therefore, Wireless products can work
with Netware, Windows 2000, or other LAN operating systems to support printer or file sharing.
10. Would the information be intercepted while transmitting on air?
WLAN features two-fold protection in security. On the hardware side, as with Direct Sequence Spread
Spectrum technology, it has the inherent security feature of scrambling. On the software side, WLAN
series offer the encryption function (WEP) to enhance security and Access Control. Users can set it up
depending upon their needs.
11. What is DSSS?What is FHSS?And what are their differences?
Frequency-hopping spread-spectrum (FHSS) uses a narrowband carrier that changes frequency in a
pattern that is known to both transmitter and receiver. Properly synchronized, the net effect is to maintain
a single logical channel. To an unintended receiver, FHSS appears to be short-duration impulse noise.
Direct-sequence spread-spectrum (DSSS) generates a redundant bit pattern for each bit to be
transmitted. This bit pattern is called a chip (or chipping code). The longer the chip is, the greater the
probability that the original data can be recovered. Even if one or more bits in the chip are dam aged
during transmission, statistical techniques embedded in the radio can recover the original data withoutthe need for retransmission. To an unintended receiver, DSSS appears as low power wideband noise and
is rejected (ignored) by most narrowband receivers.
12. What is Spread Spectrum?
Spread Spectrum technology is a wideband radio frequency technique developed by the military for use in
reliable, secure, mission-critical communication systems. It is designed to trade off bandwidth efficiency for
reliability, integrity, and security. In other words, more bandwidth is consum ed than in the case of
narrowband transmission, but the trade off produces a signal that is, in effect, louder and thus easier to
detect, provided that the receiver knows the parameters of the spread-spectrum signal being broadcast. If a
receiver is not tuned to the right frequency, a spread –spectrum signal looks like backgrou nd noise. There
are two main alternatives, Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) and Frequency Hopping S pread
Spectrum (FHSS).
56
Page 57

13. What is Hi-Gain and dBi?
Hi-Gain is Hawking Technologies’ high performance wireless distance extending product line. It
encompasses a group of products and technologies used to help solve distance issues accomp anied with
Wi-Fi products. A unit of measurement on antenna strength and power is dBi. The higher the dBi or gain
level of an antenna the more powerful it is.
14. What is the difference between directional and omni-directional antennas?
Directional and omni-directional antennas determine the wireless output pattern of antenna s. In standard
installations it is normally the wireless access point that uses the omni-dire ction al antenna (360 degree
wireless output) whiles the clients (desktop or laptops) that use the directional antennas (concentrated
narrow wireless signal) to create a stronger link directly to the access point.
15. How do I get an Optimal Wireless Connection with the HWDN2?
If pointing the antenna directly at the access point is not providing a sufficient signal connectio n then you
can try bouncing the signals off walls. Wireless signals can reflect off walls or through windows to get to
their desired location so try different positions to find the best antenna orientation for your network.
57
Page 58

VI. PRODUCT SUPPORT INFORMATION
Thank you for choosing Hawking Technologies. Please do not hesitate to contact us if you have
any questions regarding the installation of your product. We’re here to help you 24 hours a day, 7
days a week!
PHONE SUPPORT
888.202.3344
•
Toll-Free 24/7 Technical Support Line (US & Canada Only)
WEBSITE SUPPORT
http://www.hawkingtech.com/support
•
You’ll find: (a) Firmware/Driver updates with the latest features and news on your product
(b) Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) with answers to common asked questions about
your product.]
EMAIL SUPPORT
techsupport@hawkingtech.com
•
DOCUMENT SUPPORT
Product User’s Manual
•
(Normally located on the product CD)
You’ll find detail install instruction on your product and default user name and password.
RMA (RETURN MERCHANDISE AUTHORIZATION)
http://www.hawkingtech.com/support/customerservice.php
•
CUSTOMER SERVICE
Email: customerservice@hawkingtech.com
•
Tel: 949.206.6900 ext:1000
•
We want to hear from you! We hope you will have a wonderful experience using
our hawking product. If there is any concern, please email us at
customerservice@hawkingtech.com.
58
 Loading...
Loading...