Hartke HA5000 Owners Manual
Hartke Systems
BASS AMPLIFIER
5000/7000

Introduction 3
Features 4
Guided Tour 5
Front Panel 5
Rear Panel 7
Setting Up and Using the Model 5000/7000 9
About Equalization 11
About Compression 13
Appendix A: Impedance vs. Expected Power 14
Appendix B: Block Diagram 15
Appendix C:
Changing the Model 5000/7000 Voltage 16
Specifications 17

Introduction
3
Congratulations on purchasing the Hartke Systems Model 5000 /7000 Bass
Amplifier! Although these units are designed for easy operation, we suggest you
first take some time to go through these pages so you can fully understand how
we’ve implemented a number of unique features.
Both the Model 5000 and Model 7000 are optimized for use with electric bass
instruments, and the front panel controls in both are virtually identical; the two
differ only in their power ratings (the Model 5000 provides two channels of 250
watts of power [into 4 ohms], while the Model 7000 provides two channels of
350 watts of power [into 4 ohms]). You’ll find either to be an excellent bass
amplifier for live performance use in medium and large-size venues, and both
offer a number of advanced features which makes them ideal for use in recording environments as well.
In these pages, you’ll find a detailed description of the many features of the
Model 5000/7000 Bass Amplifiers, as well as a guided tour through their front
and rear panels, step-by-step instructions for setting up and using each product,
detailed discussions about equalization and compression, and full specifications.
You’ll also find a warranty card enclosed—please don’t forget to fill it out and
mail it so that you can receive online technical support and so we can send you
updated information about these and other Hartke and Samson products in the
future.
SPECIAL NOTE: Should your unit ever require servicing, a
Return
Authorization
number (RA) is necessary. Without this number, the unit will not
be accepted. Please call Samson Technologies at (516) 932-1062 for a Return
Authorization number prior to shipping your unit. Please retain the original packing material and, if possible, return the unit in its original carton and packing
materials.

4
Features
The Hartke Systems Model 5000/7000 Bass Amplifiers offer all the newest
concepts in bass amplification. Here are some of their main features:
• Two independent amplifiers within each chassis, with power to spare—in the
case of the Model 5000, 250 watts per channel (into 4 ohms), and, in the
case of the Model 7000, a full 350 watts (into 4 ohms).
• Our unique Transient Attack® circuitry which ensures that every nuance of
your bass performance is reproduced faithfully.
• Two Pre-Amp input knobs, allowing custom blending of tube and solid state
sounds.
• Ten bands of high-quality graphic equalization, allowing you to create a
broad range of tonal colors for your bass instrument. A dedicated in/out
button allows you to preset an equalization curve.
• LEDs that show you the settings of the graphic equalizer in low-light environments as well as a two-color LED that continuously shows the status of the
compression circuitry in response to your playing.
• Two fully adjustable contour knobs (high pass and low pass), which provide
further control over shaping your bass sound.
• A built-in compressor which not only adds real “punch” to your bass sound,
but also allows you to smooth out volume differences between notes.
• Two independent inputs that accommodate both passive and active bass
guitars.
• Protection relay circuitry that protects connected speakers from dangerous
overloading and also prevents “thumps” when powering on or off.
• Two pairs of dedicated speaker outputs (one for high frequency speakers
and the other for low frequency speakers), along with front-panel Crossover
Frequency and Balance controls.
• A Bi-Amp switch that enables you to activate or bypass the electronic
crossover circuitry.
• Effects loop send and return jacks that allow you to connect to professional
outboard effects processors.
• An electronically balanced direct output that provides a means of routing
signal to professional mixing consoles in both live performance and recording environments. A ground loop switch helps prevent hum or buzz from
entering the signal, and a pre/post switch allows the direct signal to be
derived either before or after the amp EQ section.
• Rugged construction that make both the Model 5000 and Model 7000
eminently road-worthy.
5
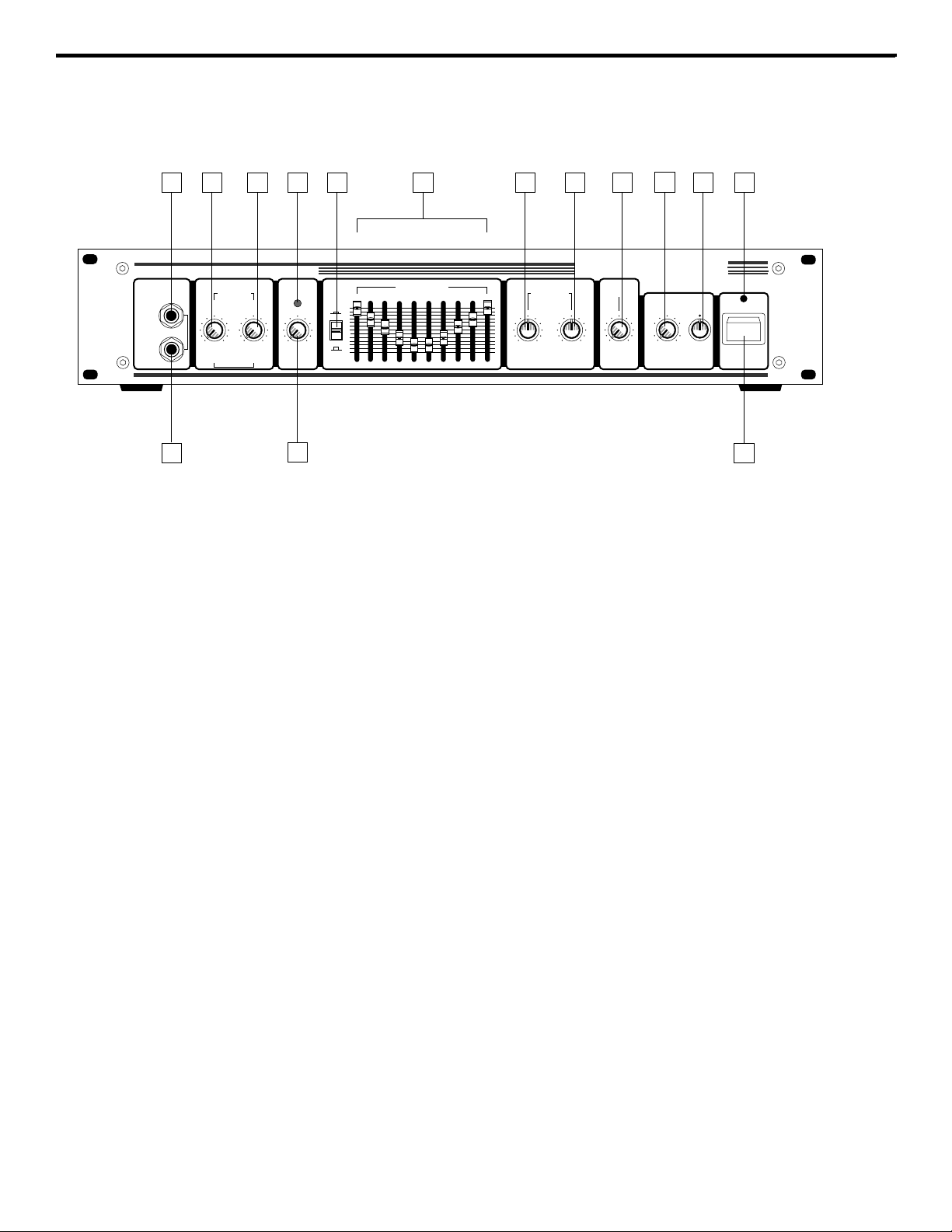
Guided Tour - Front Panel
1. Passive Input jack - If your bass guitar has passive circuitry, connect it to the Model
5000/7000 here. This standard 1/4” unbalanced jack provides a high impedance (100 k Ohms)
input sensitivity of 20 millivolts.
2. Active Input jack - If your bass guitar has active circuitry,* connect it to the Model 5000/7000
here. This standard 1/4” unbalanced jack provides a high impedance (100 k Ohms) input sensitivity of 60 millivolts.
3. Pre-Amp A (Tube) control - This determines the amount of preamplification being provided
by special circuitry which simulates the sound of a classic tube amplifier (this circuitry actually
includes a real tube!). Note that when both Pre-Amp knobs are used at equal settings, the
amplifier will be twice as loud as when only one is used. Avoid setting both Pre-Amp knobs
on maximum (“10”), since the result will almost always be undesirable distortion.
4. Pre-Amp B (Solid State) control - This determines the amount of preamplification being
provided by special circuitry which simulates the sound of a solid state amplifier. Note that when
both Pre-Amp knobs are used at equal settings, the amplifier will be twice as loud as when only
one is used. Avoid setting both Pre-Amp knobs on maximum (“10”), since the result will almost
always be undesirable distortion.
5. Compression LED - Provides a visual indicator of the status of the compression circuitry.
When lit steadily green (for example, when the Compression knob [see #6 below] is set to “Off”),
no compression is being applied. When unlit, compression is being applied to the incoming signal at a ratio of approximately 2:1. When flashing red, the compression ratio is approaching
infinity (limiting is being applied to peak signals). When lit steadily red, the entire signal is being
limited. This LED “follows” the incoming signal, changing continuously as different amounts of
compression and/or limiting are being applied. For more information, see the “About
Compression” section on page 11 of this manual.
6. Compression control - This determines the amount of compression (peak signal reduction)
by simultaneously adjusting both threshold and compression ratio (which ranges from 2:1 to
infinity [limiting]). At the fully counterclockwise “Off” position, the circuitry is bypassed and no
compression is applied (the knob clicks when set to the “Off” position). As the knob is raised
clockwise (at settings from “1” to “∞”) increasing amounts of compression are applied. For more
information, see the “About Compression” section on page 11 of this manual.
* Bass guitars that have active circuitry normally require a battery for the circuitry to be functional.
3 4
1
MODEL 7000 350 WATTS + 350 WATTS
INPUT PRE AMP CONTOUR MASTER
PASSIVE
ACTIVE
AB
5
6
4
4
3
3
7
2
2
8
1
1
9
0
0
10
TUBE SOLID STATE
5
6
7
3
8
2
1
9
0
10
COMPRESSION
2
7
5
8
9
10
Hartke Systems
GRAPHIC EQUALIZER
5
4
+15
6
IN
7
0
8
9
OUT
∞
-15
6
8KHz
5KHz3KHz2KHz1KHz500Hz250Hz125Hz64Hz30Hz
+15
+12
+9
3
+6
+3
5
+2
0
10
-2
15
-3
-6
-18
-9
-12
-15
LOW PASS HIGH PASS
8KHz
5KHz3KHz2KHz1KHz500Hz250Hz125Hz64Hz30Hz
0
0
3
3
3
5
5
5
10
10
15
15
15
-18
+18
+18
12
CROSSOVER
500Hz
80Hz
FREQUENCY
1KHz
13
LOW
BALANCE
14
o
HIGH
POWER
11
Transient Attack
5
6
4
3
7
250Hz
2
1
0
VOLUME
8
9
10
10
15

6
Guided Tour - Front Panel
7. Graphic Equalizer In/Out switch - When pressed in (the “In” position), the Model 5000/
7000’s graphic equalizer circuitry (as described in #8 below) is operational. When pressed out
(the “Out” position), it is bypassed. The provision of this switch allows you to set up a custom
equalization curve (an equalization “preset”) with the graphic EQ sliders, which can then be
activated with the press of a single button.
8. Graphic Equalizer - These sliders allow you to “draw” the tonal response of the system by
adding 15 dB of boost or attenuation to ten different narrow-band frequency areas (30 Hz, 64 Hz,
125 Hz, 250 Hz, 500 Hz, 1 kHz, 2 kHz, 3 kHz, 5 kHz, and 8 kHz), affecting the main output signal
of the Model 5000/7000. When a slider is at its center detented (“0”) position, the selected frequency area is unaffected (it is said to be
flat). When a slider is moved up (above the “0” posi-
tion, towards the “+15” position), the selected frequency area is boosted, and when it is moved
down (below the “0” position, towards the “-15” position), the selected frequency area is attenuated. For more information, see the “About Equalization” section on pages 9 - 10 of this manual.
9. Contour Low Pass control - This acts as a broad-band low frequency equalizer, providing
18 dB of boost or attenuation at 100 Hz. You should generally adjust this control (and the
Contour High Pass control, described in #10 below) prior to “fine-tuning” the system with the
graphic equalizer (as described in #8 above). For more information, see the “About Equalization”
section on pages 9 - 10 of this manual.
10. Contour High Pass control - This acts as a broad-band high frequency equalizer, providing
18 dB of boost or attenuation at 10 kHz. You should generally adjust this control (and the
Contour Low Pass control, described in #9 above) prior to “fine-tuning” the system with the
graphic equalizer (as described in #8 above). For more information, see the “About Equalization”
section on pages 9 - 10 of this manual.
11. Master Volume control - This is the overall volume control. For best signal-to-noise ratio,
keep the output of your bass at or near maximum and adjust the amp’s Master Volume to the
desired level.
12. Crossover Frequency control - The Model 5000/7000 actually contains two discrete amplifiers. When the rear-panel Bi-Amp switch (see page 6) is in the “On” position, the Crossover
Frequency control is active. When the rear-panel Bi-Amp switch is in the “Mono” position, the
Crossover Frequency control has no function. When active, this control determines the “cutoff”
points for the High/Low Frequency speaker output pairs (see page 5) as follows: only frequencies
below the cutoff value are output from the Low Frequency speaker jacks, while only frequencies above the cutoff value are output from the High Frequency speaker jacks. For example, if
you set the Cutoff Frequency to 500 Hz (the 12 o’clock position), frequencies from 20 Hz (the
lowest possible frequency you can hear) to 500 Hz are output from the Low Frequency speaker
jacks, while frequencies of 500 Hz and higher are output from the High Frequency speaker jacks.
The maximum setting of the Crossover Frequency control (fully clockwise) is 2.5 kHz. This maximum setting is particularly useful when connecting the High speaker jacks to small diameter
speakers such as tweeter arrays.
13. Balance control - Located in the Crossover section of the front panel, this control determines the relative signal levels output to the Low and High speaker jacks. When set at the
center detented “0” position, equal signal levels are routed to both pairs of speaker outputs.
14. Power LED - Lights whenever the Model 5000/7000 is powered on.
15. Power switch - Use this to power the Model 5000/7000 on or off.
 Loading...
Loading...