Harris Semiconductor IP82C59A-5 Datasheet
SEMICONDUCTOR
4-252
August 1996
82C59A
CMOS Priority Interrupt Controller
Features
• 12.5MHz, 8MHz and 5MHz Versions Available
- 12.5MHz Operation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .82C59A-12
- 8MHz Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82C59A
- 5MHz Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .82C59A-5
• High Speed, “No Wait-State” Operation with 12.5MHz
80C286 and 8MHz 80C86/88
• Pin Compatible with NMOS 8259A
• 80C86/88/286 and 8080/85/86/88/286 Compatible
• Eight-Level Priority Controller, Expandable to
64 Levels
• Programmable Interrupt Modes
• Individual Request Mask Capability
• Fully Static Design
• Fully TTL Compatible
• Low Power Operation
- ICCSB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10µA Maximum
- ICCOP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1mA/MHz Maximum
• Single 5V Power Supply
• Operating Temperature Ranges
- C82C59A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0
o
C to +70oC
- I82C59A. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . -40
o
C to +85oC
- M82C59A. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . -55
o
C to +125oC
Description
The Harris 82C59A is a high performance CMOS Priority
Interrupt Controller manufactured using an advanced 2µm
CMOS process. The 82C59A is designed to relieve the system CPU from the task of polling in a multilevel
priority system. The high speed and industry standard
configuration of the 82C59A make it compatible with microprocessors such as 80C286, 80286, 80C86/88, 8086/88,
8080/85 and NSC800.
The 82C59A can handle up to eight vectored priority interrupting sources and is cascadable to 64 without additional
circuitry. Individual interrupting sources can be masked or
prioritized to allow custom system configuration. Two modes
of operation make the 82C59A compatible with both 8080/85
and 80C86/88/286 formats.
Static CMOS circuit design ensures low operating power.
The Harris advanced CMOS process results in performance
equal to or greater than existing equivalent products at a
fraction of the power.
Ordering Information
PACKAGE
TEMPERATURE
RANGE 5MHz 8MHz 12.5MHz PKG. NO.
Plastic DIP 0oC to +70oC CP82C59A-5 CP82C59A CP82C59A-12 E28.6
-40oC to +85oC IP82C59A-5 IP82C59A IP82C59A-12 E28.6
PLCC 0oC to +70oC CS82C59A-5 CS82C59A CS82C59A-12 N28.45
-40oC to +85oC IS82C59A-5 IS82C59A IS82C59A-12 N28.45
CERDIP 0oC to +70oC CD82C59A-5 CD82C59A CD82C59A-12 F28.6
-40oC to +85oC ID82C59A-5 ID82C59A ID82C59A-12 F28.6
-55oC to +125oC MD82C59A-5/B MD82C59A/B MD82C59A-12/B F28.6
SMD# 5962-8501601YA 5962-8501602YA - F28.6
LCC -55oC to +125oC MR82C59A-5/B MR82C59A/B MR82C59A-12/B J28.A
SMD# 5962-85016013A 5962-85016023A - J28.A
SOIC 0oC to +70oC CM82C59A-5 CM82C59A CM82C59A-12 M28.3
CAUTION: These devices are sensitive to electrostatic discharge. Users should follow proper IC Handling Procedures.
Copyright
© Harris Corporation 1996
File Number 2784.2
4-253
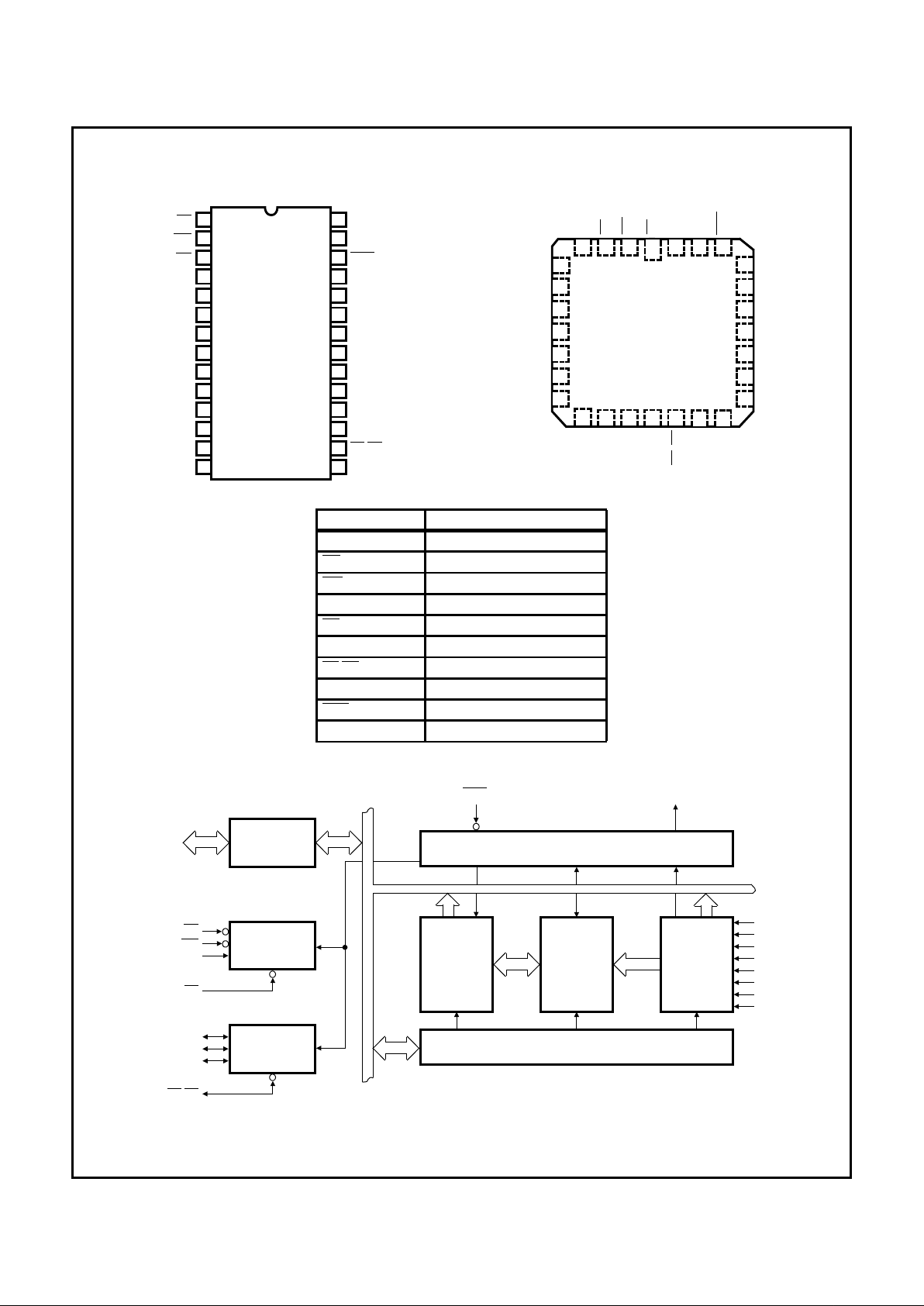
Functional Diagram
Pinouts
28 LEAD DIP
TOP VIEW
28 LEAD LCC
TOP VIEW
PIN DESCRIPTION
D7 - D0 Data Bus (Bidirectional)
RD Read Input
WR Write Input
A0 Command Select Address
CS Chip Select
CAS 2 - CAS 0 Cascade Lines
SP/EN Slave Program Input Enable
INT Interrupt Output
INTA Interrupt Acknowledge Input
IR0 - IR7 Interrupt Request Inputs
CS
WR
RD
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
CAS 0
CAS 1
GND
V
CC
INTA
IR7
IR6
IR5
IR3
IR1
IR0
INT
SP/EN
CAS 2
A0
IR4
IR2
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
23
24
25
22
21
20
19
11
3 2
1
4
14 15 16 17 18
12
13
28 27 26
10
5
6
7
8
9
D7
V
CC
A0
RD
WR
CS
INTA
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
IR7
IR6
IR5
IR4
IR3
IR2
IR1
CAS 0
IR0
CAS 1
GND
CAS 2
SP/ EN
INT
PRIORITY
RESOLVER
IR0
IR1
IR2
IR3
IR4
IR5
IR6
IR7
INTERRUPT
REQUEST
REG
(IRR)
INTERRUPT MASK REG
(IMR)
CONTROL LOGIC
INTERNAL BUS
INT
DATA
BUS
BUFFER
CASCADE
BUFFER
COMPARATOR
CAS 0
CAS 1
CAS 2
READ/
WRITE
LOGIC
SP/EN
WR
RD
INTA
IN -
SERVICE
REG
(ISR)
CS
D
7-D0
A
0
FIGURE 1.
82C59A
4-254
Functional Description
Interrupts in Microcomputer Systems
Microcomputer system design requires that I/O devices such
as keyboards, displays, sensors and other components
receive servicing in an efficient manner so that large
amounts of the total system tasks can be assumed by the
microcomputer with little or no effect on throughput.
The most common method of servicing such devices is the
Polled approach. This is where the processor must test each
device in sequence and in effect “ask” each one if it needs
servicing. It is easy to see that a large portion of the main
program is looping through this continuous polling cycle and
that such a method would have a serious, detrimental effect
on system throughput, thus, limiting the tasks that could be
assumed by the microcomputer and reducing the cost effectiveness of using such devices.
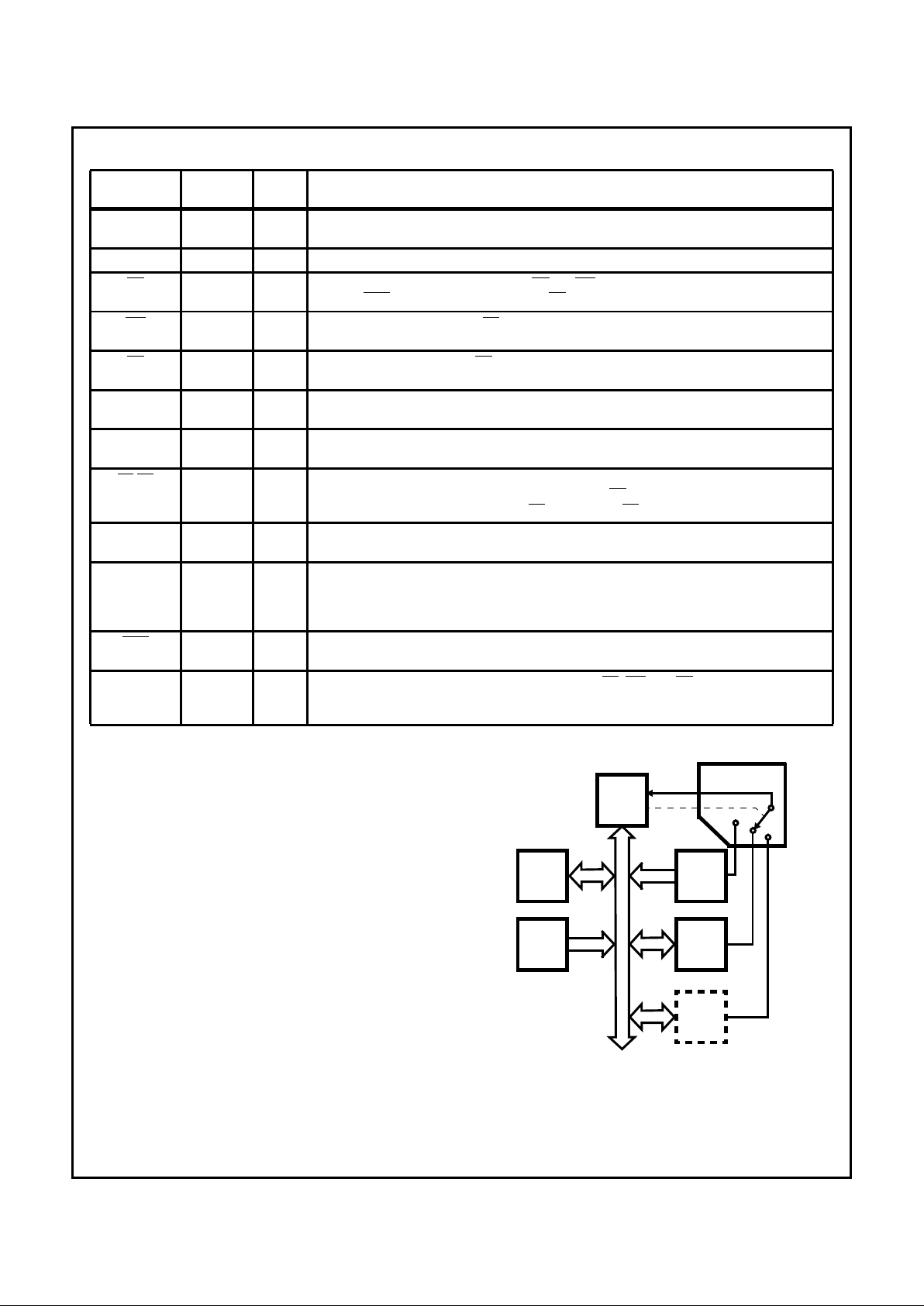
Pin Description
SYMBOL
PIN
NUMBER TYPE DESCRIPTION
V
CC
28 I VCC: The +5V power supply pin. A 0.1µF capacitor between pins 28 and 14 is recommended for
decoupling.
GND 14 I GROUND
CS 1 I CHIP SELECT: A low on this pin enablesRD and WR communications between the CPU and the
82C59A. INT A functions are independent ofCS.
WR 2 I WRITE: A low on this pin when CS is low enables the 82C59A to accept command words from
the CPU.
RD 3 I READ: A low on this pin when CS is low enables the 82C59A to release status onto the data bus
for the CPU.
D7 - D0 4 - 11 I/O BIDIRECTIONAL DATA BUS: Control, status, and interrupt-vector information is transferred via
this bus.
CAS0 - CAS2 12, 13, 15 I/O CASCADE LINES: The CAS lines form a private 82C59A bus to control a multiple 82C59A struc-
ture. These pins are outputs for a master 82C59A and inputs for a slave 82C59A.
SP/EN 16 I/O SLAVE PROGRAM/ENABLE BUFFER: This is a dual function pin. When in the Buffered Mode it
can be used as an output to control buffer transceivers (EN). When not in the Buffered Mode it is
used as an input to designate a master (SP = 1) or slave (SP = 0).
INT 17 O INTERRUPT: This pin goes high whenever a valid interrupt request is asserted. It is used to inter-
rupt the CPU, thus, it is connected to the CPU's interrupt pin.
IR0 - IR7 18 - 25 I INTERRUPT REQUESTS: Asynchronous inputs. An interrupt request is executed by raising an
IR input (low to high), and holding it high until it is acknowledged (Edge Triggered Mode), or just
by a high level on an IR input (Level Triggered Mode). Internal pull-up resistors are implemented
on IR0 - 7.
INTA 26 I INTERRUPT ACKNOWLEDGE: This pin is used to enable 82C59A interrupt-vector data onto the
data bus by a sequence of interrupt acknowledge pulses issued by the CPU.
A0 27 I ADDRESS LINE: This pin acts in conjunction with the CS, WR, and RD pins. It is used by the
82C59A to decipher various Command Words the CPU writes and status the CPU wishes to read.
It is typically connected to the CPU A0 address line (A1 for 80C86/88/286).
ROM
I/O (N)
I/O (2)
I/O (1)RAM
CPU
CPU - DRIVEN
MULTIPLEXER
FIGURE 2. POLLED METHOD
82C59A
4-255
A more desirable method would be one that would allow the
microprocessor to be executing its main program and only
stop to service peripheral devices when it is told to do so by
the device itself. In effect, the method would provide an
external asynchronous input that would inform the processor
that it should complete whatever instruction that is currently
being executed and fetch a new routine that will service the
requesting device. Once this servicing is complete, however,
the processor would resume exactly where it left off.
This is the Interrupt-driven method. It is easy to see that system throughput would drastically increase, and thus, more
tasks could be assumed by the microcomputer to further
enhance its cost effectiveness.
The Programmable Interrupt Controller (PlC) functions as an
overall manager in an Interrupt-Driven system. It accepts
requests from the peripheral equipment, determines which
of the incoming requests is of the highest importance (priority), ascertains whether the incoming request has a higher
priority value than the level currently being serviced, and
issues an interrupt to the CPU based on this determination.
Each peripheral device or structure usually has a special
program or “routine” that is associated with its specific functional or operational requirements; this is referred to as a
“service routine”. The PlC, after issuing an interrupt to the
CPU, must somehow input information into the CPU that can
“point” the Program Counter to the service routine associated with the requesting device. This “pointer” is an address
in a vectoring table and will often be referred to, in this document, as vectoring data.
82C59A Functional Description
The 82C59A is a device specifically designed for use in real
time, interrupt driven microcomputer systems. It manages
eight levels of requests and has built-in features for expandability to other 82C59As (up to 64 levels). It is programmed
by system software as an I/O peripheral. A selection of priority modes is available to the programmer so that the manner
in which the requests are processed by the 82C59A can be
configured to match system requirements. The priority
modes can be changed or reconfigured dynamically at any
time during main program operation. This means that the
complete interrupt structure can be defined as required,
based on the total system environment.
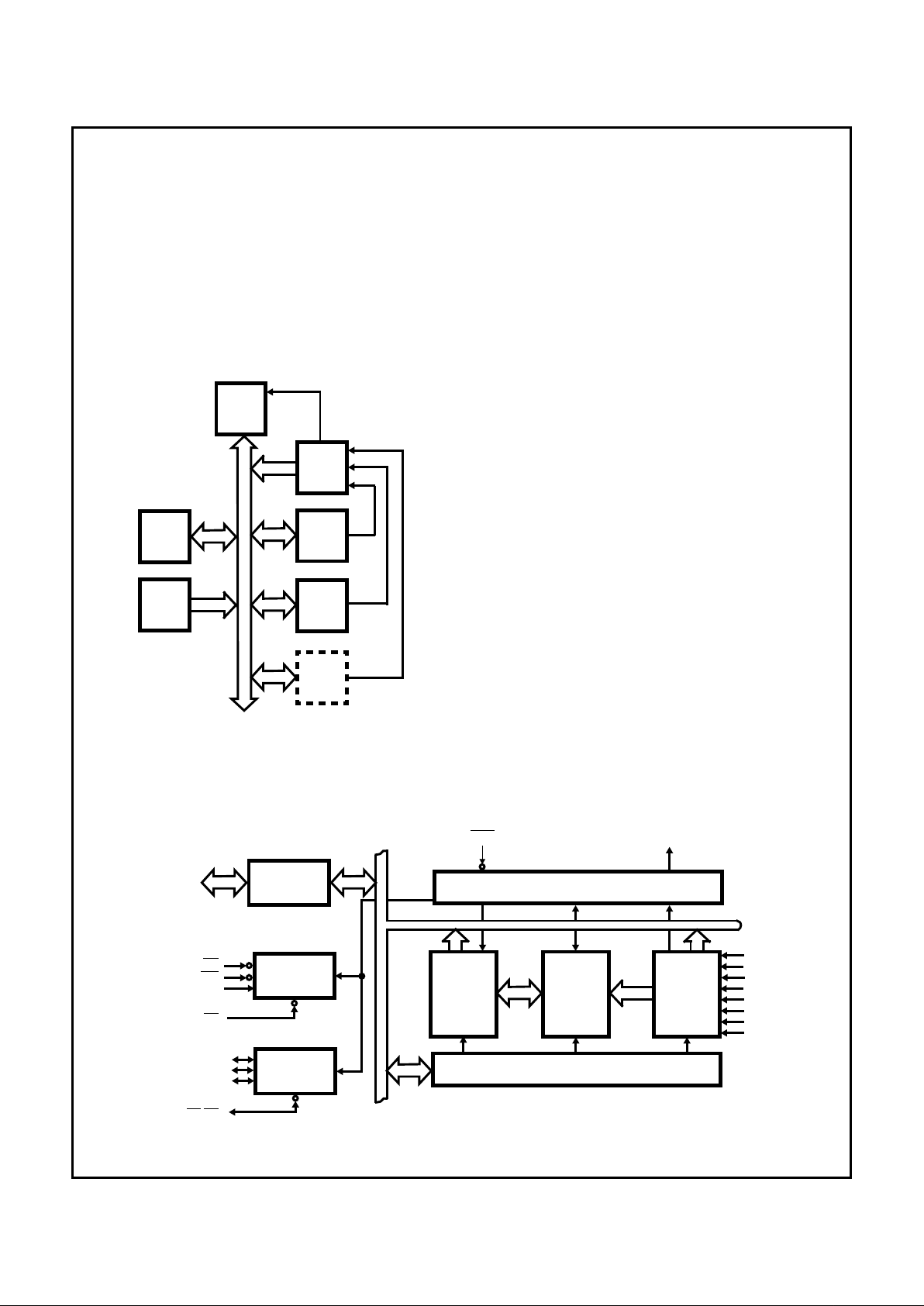
Interrupt Request Register (IRR) and In-Service Register
(ISR)
The interrupts at the IR input lines are handled by two registers
in cascade, the Interrupt Request Register (lRR) and the InService Register (lSR). The IRR is used to indicate all the interrupt levels which are requesting service, and the ISR is used to
store all the interrupt levels which are currently being serviced.
ROM
I/O (2)
RAM
CPU
INT
I/O (1)
I/O (N)
PIC
FIGURE 3. INTERRUPT METHOD
IR0
IR1
IR2
CASCADE
BUFFER
COMPARATOR
READ/
WRITE
LOGIC
DAT A
BUS
BUFFER
IN
SERVICE
REG
(ISR)
PRIORITY
RESOLVER
INTERRUPT MASK REG
(IMR)
INTERRUPT
REQUEST
REG
(IRR)
CONTROL LOGIC
INT
INTA
IR3
IR4
IR5
IR6
IR7
CAS 0
CAS 1
CAS 2
RD
WR
A
0
SP/EN
CS
D
7
- D
0
INTERNAL BUS
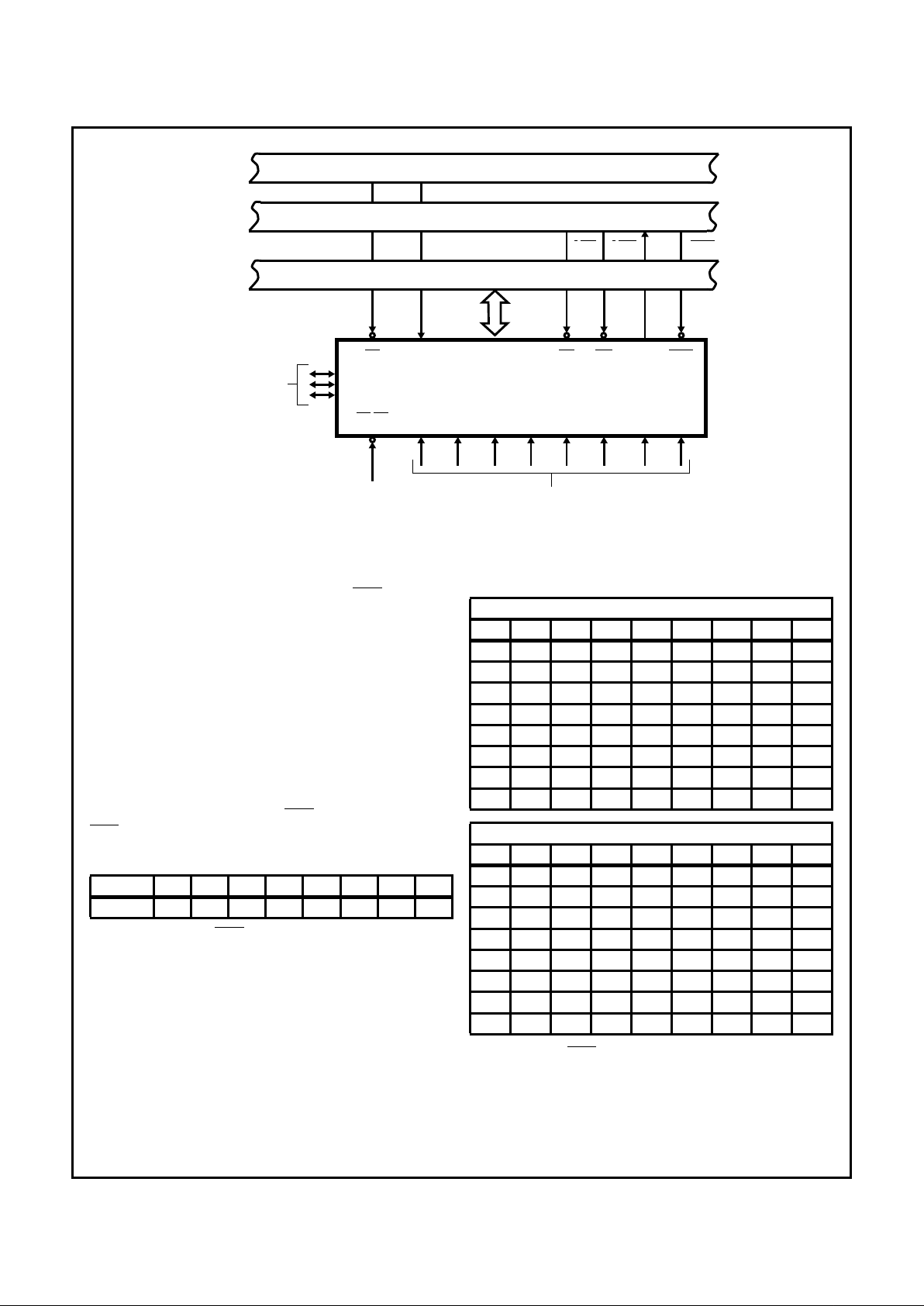
FIGURE 4. 82C59A FUNCTIONAL DIAGRAM
82C59A
4-256
Priority Resolver
This logic block determines the priorities of the bits set in the
lRR. The highest priority is selected and strobed into the corresponding bit of the lSR during the INTA sequence.
Interrupt Mask Register (IMR)
The lMR stores the bits which disable the interrupt lines to
be masked. The IMR operates on the output of the IRR.
Masking of a higher priority input will not affect the interrupt
request lines of lower priority.
Interrupt (INT)
This output goes directly to the CPU interrupt input. The
VOH level on this line is designed to be fully compatible with
the 8080, 8085, 8086/88, 80C86/88, 80286, and 80C286
input levels.
Interrupt Acknowledge (
INTA)
INTA pulses will cause the 82C59A to release vectoring
information onto the data bus. The format of this data
depends on the system mode (µPM) of the 82C59A.
Data Bus Buffer
This 3-state, bidirectional 8-bit buffer is used to interface the
82C59A to the System Data Bus. Control words and status
information are transferred through the Data Bus Buffer.
Read/Write Control Logic
The function of this block is to accept output commands from
the CPU. It contains the Initialization Command Word (lCW)
registers and Operation Command Word (OCW) registers
which store the various control formats for device operation.
This function block also allows the status of the 82C59A to
be transferred onto the Data Bus.
Chip Select (
CS)
A LOW on this input enables the 82C59A. No reading or
writing of the device will occur unless the device is selected.
Write (
WR)
A LOW on this input enables the CPU to write control words
(lCWs and OCWs) to the 82C59A.
Read (
RD)
A LOW on this input enables the 82C59A to send the status
of the Interrupt Request Register (lRR), In-Service Register
(lSR), the Interrupt Mask Register (lMR), or the interrupt
level (in the poll mode) onto the Data Bus.
A0
This input signal is used in conjunction with
WR and RD signals to write commands into the various command registers,
as well as to read the various status registers of the chip.
This line can be tied directly to one of the system address
lines.
The Cascade Buffer/Comparator
This function block stores and compares the IDs of all
82C59As used in the system. The associated three I/O pins
(CAS0 - 2) are outputs when the 82C59A is used as a master and are inputs when the 82C59A is used as a slave. As a
master, the 82C59A sends the ID of the interrupting slave
device onto the CAS0 - 2 lines. The slave, thus selected will
send its preprogrammed subroutine address onto the Data
Bus during the next one or two consecutive
INTA pulses.
(See section “Cascading the 82C59A”.)
Interrupt Sequence
The powerful features of the 82C59A in a microcomputer
system are its programmability and the interrupt routine
addressing capability. The latter allows direct or indirect
jumping to the specified interrupt routine requested without
any polling of the interrupting devices. The normal sequence
of events during an interrupt depends on the type of CPU
being used.
These events occur in an 8080/8085 system:
1. One or more of the INTERRUPT REQUEST lines
(IR0 - IR7) are raised high, setting the corresponding IRR
bit(s).
2. The 82C59A evaluates those requests in the priority
resolver and sends an interrupt (INT) to the CPU, if
appropriate.
3. The CPU acknowledges the lNT and responds with an
INTA pulse.
4. Upon receiving an
lNTA from the CPU group, the highest
priority lSR bit is set, and the corresponding lRR bit is
reset. The 82C59A will also release a CALL instruction
code (11001101) onto the 8-bit data bus through D0 - D7.
5. This CALL instruction will initiate two additional
INTA
pulses to be sent to 82C59A from the CPU group.
6. These two
INTA pulses allow the 82C59A to release its
preprogrammed subroutine address onto the data bus.
The lower 8-bit address is released at the first
INTA pulse
and the higher 8-bit address is released at the second
INTA pulse.
7. This completes the 3-byte CALL instruction released by
the 82C59A. In the AEOI mode, the lSR bit is reset at the
end of the third
INTA pulse. Otherwise, the lSR bit
remains set until an appropriate EOI command is issued
at the end of the interrupt sequence.
The events occurring in an 80C86/88/286 system are the
same until step 4.
4. The 82C59A does not drive the data bus during the first
INTA pulse.
5. The 80C86/88/286 CPU will initiate a second
INTA pulse.
During this
INTA pulse, the appropriate ISR bit is set and
the corresponding bit in the IRR is reset. The 82C59A
outputs the 8-bit pointer onto the data bus to be read by
the CPU.
82C59A
4-257
6. This completes the interrupt cycle. In the AEOI mode, the
ISR bit is reset at the end of the second
INTA pulse. Otherwise, the ISR bit remains set until an appropriate EOI
command is issued at the end of the interrupt subroutine.
If no interrupt request is present at step 4 of either sequence
(i.e., the request was too short in duration), the 82C59A will
issue an interrupt level 7. If a slave is programmed on IR bit
7, the CAS lines remain inactive and vector addresses are
output from the master 82CS9A.
Interrupt Sequence Outputs
8080, 8085 Interrupt Response Mode
This sequence is timed by three
INTA pulses. During the first
lNTA pulse, the CALL opcode is enabled onto the data bus.
First Interrupt Vector Byte Data: Hex CD
During the second
INTA pulse, the lower address of the
appropriate service routine is enabled onto the data bus.
When interval = 4 bits, A5 - A7 are programmed, while
A0 - A4 are automatically inserted by the 82C59A. When
interval = 8, only A6 and A7 are programmed, while A0 - A5
are automatically inserted.
During the third
INTA pulse, the higher address of the appropriate service routine, which was programmed as byte 2 of the
initialization sequence (A8 - A15), is enabled onto the bus.
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Call Code 11001101
ADDRESS BUS (16)
CONTROL BUS
DATA BUS (8)
I/OR I/OW INT INTA
CASCADE
LINES
CAS 0
CAS 1
CAS 2
SP/EN
CS RD WR INTAINTD7 - D
0
A
0
SLAVE PROGRAM/
ENABLE BUFFER
INTERRUPT
REQUESTS
82C59A
IRQ IRQ IRQ IRQ IRQ IRQ IRQ IRQ
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
FIGURE 5. 82C59A STANDARD SYSTEM BUS INTERFACE
CONTENT OF SECOND INTERRUPT VECTOR BYTE
IR Interval = 4
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
7A7A6A511100
6A7A6A511000
5A7A6A510100
4A7A6A510000
3A7A6A501100
2A7A6A501000
1A7A6A500100
0A7A6A500000
IR Interval = 8
D7 D6 DS D4 D3 D2 Dl DO
7A7A6111000
6A7A6110000
5A7A6101000
4A7A6100000
3A7A6011000
2A7A6010000
1A7A6001000
0A7A6000000
82C59A
 Loading...
Loading...