Hanwell IKVM-101Plus User Manual

IKVM-101Plus
User Manual
HANWELL
Single Port KVM over IP
◄ V1.0 ►
www.hanwell.com.tw
Hanwell Technology

Single Port KVM over IP
Certifications
FCC
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with Part 15 of the FCC
Rules.
Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
(1) This device may not cause harmful interference
(2) This device must accept any interference received, including interference
that may cause undesired operation.
CE
This equipment is in compliance with the requirements of the following
regulations:
EN 55022: CLASS B
RoHS
All contents of this package, including products, packing materials and
documentation comply with RoHS.
© 2008 by Hanwell Technology
Hanwell Technology Co. Ltd. reserves the right to make changes in the hardware, packaging, and any
accompanying documentation without prior written not ice.
No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical,
photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without prior writte n permission of Hanwell Technology Co. Ltd.
2 / 109

Single Port KVM over IP
Contents
1. Product Overview........................................................................8
1.1 Introduction ............................................................................. 8
1.2 Main Feature ............................................................................ 8
2. Installation and Start up .............................................................9
2.1 Package Check List.................................................................... 9
2.2 Panel Views.............................................................................. 9
2.3 System requirement.................................................................10
Hardware ...........................................................................10
Software ............................................................................10
2.4 When the server is up and running.............................................10
2.5 When the server is dead ...........................................................10
2.6 Rack Mounting.........................................................................11
2.7 Cable Connections (stand-alone)................................................12
2.8 Cable Connections (with Multi-port KVM Switch)...........................13
2.9 LED Indicators, Button..............................................................15
2.10 Initial IP Configuration Via Network ............................................15
2.11 Configuration Setup via Serial Console ......................................158
2.12 Keyboard, Mouse, and Video configuration.................................159
2.12.1 IP-KVM keyboard settings....................................................19
2.12.2 Remote Mouse Settings.......................................................19
2.12.3 Automatic mouse speed and mouse synchronization ...............19
2.12.4 Host system mouse settings ................................................20
2.12.5 Single and Double Mouse Mode ............................................21
2.12.6 Recommended Mouse Settings.............................................21
2.12.7 Video Modes......................................................................21
3. Usage ........................................................................................22
3.1 Prerequisites ...........................................................................22
3.2 Login into the IP-KVM and logout ...............................................23
4.2.1 Login into the IP-KVM...........................................................23
4.2.2 Login out from the IP-KVM....................................................26
3.3 The Remote Console.................................................................26
3.3.1 Main Window of Remote Console............................................27
3.3.2 Control Bar of Remote Console ..............................................28
3.3.3 Status Line of Remote Console ..............................................39
4. Menu Options ............................................................................40
4.1 Remote Control........................................................................40
3 / 109

Single Port KVM over IP
4.1.1 KVM Console ....................................................................... 41
4.1.2 Telnet Console.....................................................................41
4.2 Virtual Media...........................................................................43
4.2.1 Floppy Disk.........................................................................44
4.2.2 CD–ROM Image...................................................................46
4.2.3 Drive redirection ..................................................................51
4.2.3.1 Driver Redirection Utility Installation..............................53
4.2.3.2 Built-in Java Drive Redirection ......................................58
4.2.4 Options ..............................................................................59
4.2.4.1 Creating an Image......................................................60
4.2.4.1.1Floppy Images .........................................................60
4.2.4.1.2CD ROM/ISO Images ................................................61
4.3 User Management....................................................................62
4.3.1 Change Password.................................................................62
4.3.2 Users and Groups ................................................................63
4.4 KVM Settings...........................................................................65
4.4.1 User Console.......................................................................65
4.4.2 Keyboard/Mouse..................................................................69
4.4.3 Video ................................................................................. 71
4.5 Device Settings........................................................................73
4.5.1 Network .............................................................................73
4.5.2 Dynamic DNS......................................................................77
4.5.3 Security .............................................................................79
4.5.4 Certificate...........................................................................82
4.5.5 Serial Port ..........................................................................86
4.5.6 Date / Time ........................................................................88
4.5.7 Event Log...........................................................................89
4.6 Maintenance............................................................................92
4.6.1 Device Information ..............................................................92
4.6.2 Even log.............................................................................94
4.6.3 Update Firmware .................................................................94
4.6.4 Unit Reset...........................................................................96
5. Technical Specifications ............................................................97
6. Troubleshooting ........................................................................98
7. FAQs........................................................................................100
8. Addendum ...............................................................................102
A. Key Codes..................................................................................102
B. Video Modes ...............................................................................103
C. User Role Permissions..................................................................104
D. IP-KVM TCP port number..............................................................104
4 / 109

Single Port KVM over IP
E. Bandwidth Consumption...............................................................105
F. Cable Connectors.........................................................................106
G. Well-Known TCP/UDP Port Numbers...............................................107
H. Protocol Glossary ........................................................................108
5 / 109

Single Port KVM over IP
Figures
Figure 2-1 Panel Views ......................................................................... 9
Figure 2-2 Cable Connections (stand-alone) ...........................................12
Figure 2-3 Cable Connections (with a Multi-port KVM Switch)....................14
Figure 3-1 The Internet Explorer displaying the encryption key length........23
Figure 3-2 Remote Console Control Bar..................................................28
Figure 3-3 Remote Console Options Menu ..............................................29
Figure 3-4 Remote Console Exclusive Mode ............................................30
Figure 3-5 Remote Console Options Menu:Scaling ...................................30
Figure 3-6 Remote Console Options Menu:Cursor ....................................32
Figure 3-7 Video Settings Panel ............................................................33
Figure 3-8 Soft Keyboard.....................................................................34
Figure 3-9 Soft Keyboard Mapping ........................................................35
Figure 3-10 Remote Console Confirmation Dialog ....................................36
Figure 3-11 Encoding Compression........................................................37
Figure 3-12 Predefined Compression......................................................37
Figure 3-13 Lossy Compression ............................................................38
Figure 3-12 Encoding Color depth .........................................................38
Figure 3-13 Status line ........................................................................39
Figure 3-14 Status line transfer rate......................................................39
Figure 4-1 KVM Console.......................................................................41
Figure 4-2 Telnet Console.....................................................................41
Figure 4-3 Virtual Media - Floppy Disk ...................................................44
Figure 4-4 Virtual Media – CD-ROM Image .............................................47
Figure 4-5 Explorer context menu .........................................................50
Figure 4-6 Share configuration dialog ....................................................50
Figure 4-7 Options of Drive Redirection..................................................51
Figure 4-8 Drive Redirection Setup........................................................54
Figure 4-9 Drive Redirection dialog ........................................................55
Figure 4-10 Built-in Java Drive Redirection .............................................58
Figure 4-11 USB mass storage option....................................................59
Figure 4-12 RawWrite for Windows selection dialog .................................60
Figure 4-13 Nero selection dialog..........................................................61
Figure 4-14 Setting Password...............................................................62
Figure 4-15 User Console Setting..........................................................66
Figure 4-16 Keyboard and Mouse Settings..............................................69
Figure 4-17 Video Settings...................................................................71
6 / 109

Single Port KVM over IP
Figure 4-18 Network Settings ...............................................................74
Figure 4-19 Dynamic DNS....................................................................77
Figure 4-20 Dynamic DNS Scenario.......................................................77
Figure 4-21 Device Security .................................................................79
Figure 4-22 Chain Rules of IP Filtering ...................................................81
Figure 4-23 Certificate Settings.............................................................82
Figure 4-24 SSL Certificate Upload ........................................................84
Figure 4-25 CSR string ........................................................................84
Figure 4-26 Serial Port ........................................................................86
Figure 4-27 Date / Time ......................................................................88
Figure 4-28 Event Log.........................................................................89
Figure 4-29 Device Information ............................................................92
Figure 4-30 Connected Users................................................................93
Figure 4-31 Event Log List ...................................................................94
Figure 4-32 Update Firmware ...............................................................94
Figure 4-33 Unit Reset.........................................................................96
7 / 109

Single Port KVM over IP
1. Product Overview
1.1 Introduction
The KVM-over-IP (hereafter call IP-KVM for simplicity) redirects local keyboard,
mouse and video data to a remote administration console. It allows you to
control one or many computers locally at the server site or remotely via the
Internet using a standard browser. Y ou can securely gain BIOS level access
to systems for maintenance, support, or failure recovery over the Internet.
Communication is secure via SSL authentication and encryption. Use in
conjunction with a KVM switch for multiple-server access.
The IP-KVM provides convenient, remote KVM access and control via LAN or
Internet. It captures, digitizes, and compresses video signal and transmits it
with keyboard and mouse signals to and from a remote computer. IP-KVM
provides a non-intrusive solution for remote access and control. Remote access
and control software runs on its embedded processors only but not on
mission-critical servers, so that there is no interference with server operation
or impact on network performance.
1.2 Main Feature
■ Manage servers around the world.
■ Rack mountable
■ KVM (keyboard, video, and mouse) access over IP or analogous telephone
line (modem needed).
■ Full control under any OS, in BIOS mode, during boot, at Blue Screens
■ No additional software necessary on servers
■ SSL Certificate management
■ 256-bit SSL encryption of all transmitted data
■ Automatically senses video resolution for best possible screen capture
■ High-performance mouse tracking and synchronization
■ Automatic adjustment of data rate to transmission line
■ Remote mass storage control and redirection
■ Can be remote controlled over java-enabled Browsers
■ Firmware update via web interface
■ Port to connect a user console for direct analogous access to KVM switch
■ Can be used with most standard KVM
8 / 109

Single Port KVM over IP
2. Installation and Start up
2.1 Package Check List
The IP-KVM package consists of followings items:
1x the single port IP-KVM unit
1x CD-ROM (software utilities and User’s manual)
1x AC to DC Power Adapter (DC 5V / 2.6A)
1x Rack Mount Kit (Brackets and screws)
1x Null modem cable (6 feet)
1x USB A-to-B cable (6 feet)
1x 3-to-3 KVM cable (3 feet)
2.2 Panel Views
<Font View>
<Rear View>
Figure 2-1 Panel Views
9 / 109

Single Port KVM over IP
2.3 System requirement
Hardware
Item Description
Local host side One PC or Server or the console port of KVM switch
Local console side One PS/2 Keyboard, one PS/2 Mouse and one
monitor
Remote Console side One PC or Multiple PCs are linked into the network
Software
Item Description
Local host side No additional software necessary
Remote Console side (1) Java Runtime Environment : version 1.4.2 or
above
(2) Browser: Microsoft Internet Explorer version 6.0
or above or Netscape or Mozilla or Safari
2.4 When the server is up and running
The IP-KVM gives you a full control over the remote server. The Management
Console allows you to access the remote server’s graphics, keyboard and
mouse and to send special commands to the server. You can also perform
periodic maintenance of the server. Using the Console Redirection Service, you
are able to do the following:
I. Reboot the system
II. Watch the boot process.
III. Boot the system from a separate partition to load the diagnostic
environment.
IV. Run special diagnostic programs
2.5 When the server is dead
Obviously, fixing hardware defects is not possible through a remote
management device. Nevertheless IP-KVM gives the administrator valuable
information about the type of a hardware failure. Serious hardware failures can
be categorized into five different categories with different chances to happen:
I. Hard disk failure 50%
II. Power cable detached, power supply failure 28%
III. CPU, Controller, main board failure 10%
IV. CPU fan failure 8%
V. RAM failure 4%
Using IP-KVM, administrators can determine which kind of serious hardware
10 / 109

Single Port KVM over IP
failure has occurred
Type of failure Detected by
Hard disk failure Console screen, CMOS set-up
information
Power cable detached, power
supply failure
Server remains in power off state after
power on command has been given.
CPU Controller, main board
failure.
Power supply is on, but there is no
video output.
CPU fan failure By server specific management
software
RAM failure Boot-Sequence on boot console
2.6 Rack Mounting
In addition to desk top placement, the IP-KVM can be mounted on 19”/1U
rack:
1. Screw the mounting brackets into the sides of the unit.
2. Slide the unit into the rack and secure it to the rack.
11 / 109

Single Port KVM over IP
2.7 Cable Connections (stand-alone)
The figure below depicts the installation connection.
Host side
Console side
Figure 2-2 Cable Connections (stand-alone)
12 / 109

Single Port KVM over IP
Connect cables to the Host and Console devices as the figure depicts above.
Leave the Serial interface open for now. After applying power to the unit, it’d
take about 60 seconds to complete the bootup process, and then enter normal
running state.
Please perform the following steps:
1. Power down your computer and IP-KVM
2. Connect the power supply to IP-KVM
3. Connect the monitor to the IP-KVM console side.
4. Connect the keyboard to the IP-KVM console side.
5. Connect the mouse to the IP-KVM console side.
6. Connect a VGA cable (15-pin HDDB Male / Male) with the Male side to both
of the host computer/KVM and the host port of the IP-KVM.
7. Connect one purple end of 3-in-1 cable to the PS/2 mouse port on the host
computer/KVM, and the other end of 3-in-1 cable to the host PS/2 mouse
port on the IP-KVM.
8. Connect one green end of 3-in-1 cable to PS/2 keyboard port on the host
computer/KVM, and the other end of 3-in-1 cable to the host PS/2 keyboard
port on the IP-KVM.
9. (Optional) Connect the type A connector of USB A-B cable to the host
computer, while using remote mass storage control.
10. Connect Ethernet to LAN port and/or modem to serial port, depending on
how you want to access to the IP-KVM
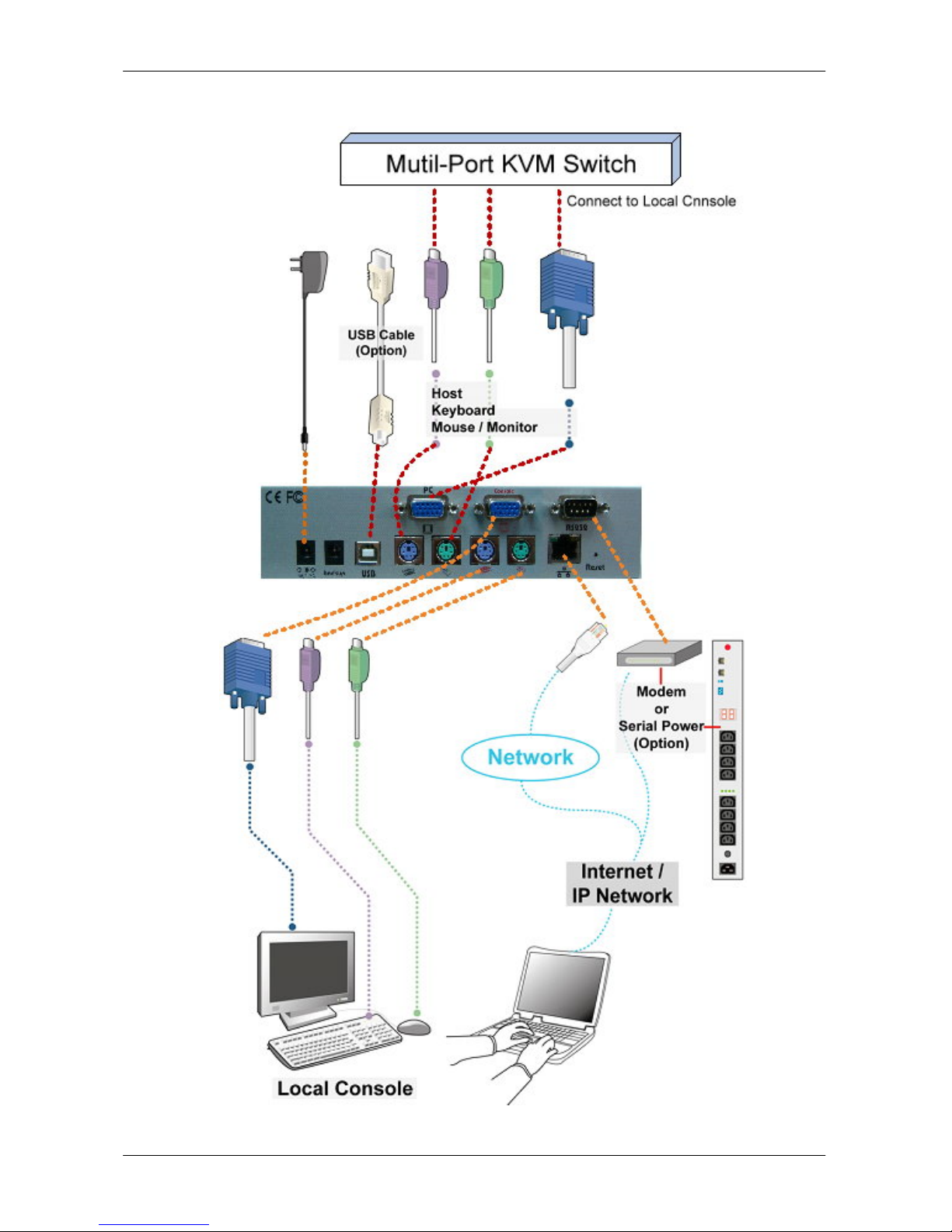
2.8 Cable Connections (with Multi-port KVM Switch)
Instead of connecting to a computer, the IP-KVM host side can be connected to
a multi-port KVM
Switch system. In installation procedures are as for stand alone computer,
except that the host signals are connected to the Local Console of the KVM
Switch. The figure below depicts the installation connection.
13 / 109
Single Port KVM over IP
Host side
Console side
Figure 2-3 Cable Connections (with a Multi-port KVM Switch)
14 / 109

Single Port KVM over IP
2.9 LED Indicators, Button
LED
Describe
Power RED – on when power applied
IOIO
Blue –RS-232 Data Link Indicate
LAN
Ethernet Link/Act/10/100Mbps:
Orange -- 10BaseT Ethernet connection
established
Green -- 100BaseT Ethernet connection
established
Blinking:
ON: when no data in activity and link
connected
Link Green -- blinking when data in activity
RESET button: on the rear panel, press the button to reboot the
IP-KVM unit Configuration
2.10 Initial IP Configuration via Network
The Factory default settings for the IP-KVM unit are as below:
DHCP: Disable
Default IP address: 192.168.0.70
Default Net Mask: 255.255.255.0
If DHCP mode is enabled (IP auto configuration = DHCP), the IP-KVM will try
to contact a DHCP server in the subnet to which it is physically connected. If a
DHCP server is found, it may provide a valid IP address, gateway address and
net mask. Before you connect the device to your local subnet, be sure to
complete the corresponding configuration of your DHCP server. It is
recommended to configure a fixed IP assignment to the MAC address of the
IP-KVM. You can find the MAC address labeled on the bottom side of the metal
housing.
There is a Network Setup Software tool (PSetup) for setting up the network
configuration (IP address, Subnet mask, DHCP, etc). It is useful when you want
to change the network settings or you can not access to the unit due to not
knowing the network settings of the unit. In this case, you can view or change
the settings via this utility.
15 / 109

Single Port KVM over IP
IP-KVM Setup Tool
If this initial configuration does not meet your local requirements, use the
setup tool to change the configurations to your needs. The setup tool PSetup
can be found on the CD ROM delivered with this package. You can follow the
procedures described below.
DHCP
If you have installed the IP-KVM on a network that enables DHCP, you can use
the PSetup to find out the IP-KVM’s IP.
(1) Plug Ethernet cable to IP-KVM. IP-KVM will get an IP via DHCP.
(2) Using PSetup to look for IP-KVM.
a. Click Refresh Devices button to detect connected devices
b. Select MAC address of the IP-KVM in “Device MAC address” box. You can
find the MAC address labeled on the bottom side of xRemote. MAC address is
detected as connection from computer and IP-KVM is valid through USB or
network.
c. If wireless connection is implemented, tick “Enable Wireless
Connection...”
d. Click Query Device to find the IP configuration on the right pane.
Notes:
BOOTP, a static configuration protocol, uses a table that
maps IP addresses to physical addresses.
DHCP, an extension to BOOTP that dynamically assigns
configuration information. DHCP is backward compatible with
16 / 109

Single Port KVM over IP
Setup fixed IP
a. Setup “IP auto configuration” as “None” ; setup IP address and
Subnet mask
b. Enter Super user login and password for Authentication (default :
super/pass)
c. Click Setup Device. If super login was authenticated, it’ll show
“Successfully configured device”. Otherwise it’ll show “Permission Denied”.
Authentication
To adjust the authentication settings, enter your login as a super user,
and change your password.
Super user login
Enter the login name of the super user. The initial value is “super”. All
characters are in lower case.
Super user password
Enter the current password for the super user. This initial value is “pass”.
All characters are in lower case.
New super user password
Enter the new password for the super user.
New password (confirm)
Re-type the new password for the super user for confirmation.
To close the window and accept the changes, press the “OK” button;
otherwise press the “Cancel” button.
17 / 109

Single Port KVM over IP
2.11 Configuration Setup via Serial Console
For using serial terminal, the IP-KVM has a serial line interface (host side).
This connector is compliant with the RS-232 serial line standard. The
serial line has to be configured with the parameters given in Table below.
Parameter Value
Bits/second 115200
Data bits 8
Parity No
Stop bits 1
Flow Control None
When configuring with a serial terminal, e.g., Hyper Terminal, reset the
IP-KVM and immediately press the “ESC” key. You will see some device
information, and a “=>” prompt. Enter “config”, press “Enter” key and
wait for a few seconds for the configuration questions to appear. As you
proceed, the following questions will appear on the screen. To accept the
default values shown in square brackets below, press “Enter” key.
IP auto configuration (none/dhcp/bootp):
IP [192.168.0.70]:
Net mask [255.255.255.0]:
Gateway (0.0.0.0 for none) [0.0.0.0]:
IP auto-configuration
With this option, you can specify whether the IP-KVM should get its
network settings from a DHCP or BOOTP server. For DHCP, enter “dhcp”,
and for BOOTP enter “bootp”. If you do not specify any of these, the IP
auto-configuration is disabled and subsequently you will be asked for
the following network settings.
IP address
The IP address the IP-KVM. This option is only available if IP
auto-configuration is disabled.
Net mask
The net mask of the connected IP subnet. This option is only available if
IP auto-configuration is disabled.
Gateway address
The IP address of the default router for the connected IP subnet. If you
do not have a default router, enter 0.0.0.0. This option is only available
if IP auto-configuration is disabled.
18 / 109

Single Port KVM over IP
2.12 Keyboard, Mouse, and Video configuration
Between the IP-KVM and the host, there are two interfaces available for
transmitting keyboard and mouse data: USB and PS/2. The correct
operation of the remote mouse depends on several settings which will be
discussed in the following subsections.
2.12.1 IP-KVM keyboard settings
The IP-KVM settings for the host's keyboard type have to be corrected in
order to make the remote keyboard work properly. Check the settings in
the IP-KVM Web front-end. See section 6.5.2 for details.
2.12.2 Remote Mouse Settings
A common seen problem with KVM devices is the synchronization between
the local and remote mouse cursors. The IP-KVM addresses this situation
with an intelligent synchronization algorithm. There are two mouse modes
available on the IP-KVM:
Auto mouse speed
The automatic mouse speed mode tries to detect the speed and
acceleration settings of the host system automatically. See the section
below for a more detailed explanation.
Fixed mouse speed
This mode just translates the mouse movements from the Remote
Console in a way that one pixel move will result in n-pixel moves on
the remote system. This parameter n is adjustable with the scaling.
Please note that this works only when mouse acceleration is turned off
on the remote system.
2.12.3 Automatic mouse speed and mouse synchronization
The automatic mouse speed mode performs the speed detection during
mouse synchronization. Whenever the local and remote mouse cursors
move synchronously or not, there are two ways for re-synchronizing local
and remote mouse cursors:
Fast Sync
The fast synchronization is used to correct a temporary, but fixed
skew. Choose the option using the Remote Console options menu or
press the mouse synchronization hotkey sequence in case you defined
one.
19 / 109

Single Port KVM over IP
Intelligent Sync
If the fast sync does not work or the mouse settings have been
changed on the host system, use the intelligent resynchronization.
This method takes more time than the fast one and can be accessed
with the appropriate item in the Remote Console option menu. The
intelligent synchronization requires a correctly adjusted picture. Use
the auto adjustment function to setup the picture, and make sure that
there are no window at the top left corner of the remote desktop that
are able to change the mouse cursor shape from the normal state. The
Sync mouse button on top of the Remote Console can behave
differently, depending on the current state of mouse synchronization.
Usually pressing this button leads to a fast sync, except in situations
where the KVM port or the video mode changed recently.
Note: At first start, if the local mouse pointer is not synchronized with
the remote mouse pointer, press the Auto Adjust Button once.
2.12.4 Host system mouse settings
The host's operating system knows various settings from the mouse driver.
Note: The following limitations do not apply in case of USB and
Mouse Type
“Windows >= 2000, MacOSX”.
While the IP-KVM works with accelerated mice and is able to synchronize
the local with the remote mouse pointer, there are the following limitations,
which may prevent this synchronization from working properly:
Special Mouse Driver
There are mouse drivers that influence the synchronization process
and lead to desynchronized mouse pointers. If this happens, make
sure you do not use a special vendor-specific mouse driver on your
host system.
Windows XP Mouse Settings
Windows XP knows a setting named “improve mouse acceleration”,
which has to be deactivated.
Active Desktop
If the Active Desktop feature of Microsoft Windows is enabled do not
use a plain background. Instead, use some kind of wallpaper. As an
alternative, you could also disable the Active Desktop completely.
20 / 109

Single Port KVM over IP
Navigate your mouse pointer into the upper left corner of the applet
screen and move it slightly forth and back. Thus the mouse will be
resynchronized. If re-synchronizing fails, disable the mouse
acceleration and repeat the procedure.
2.12.5 Single and Double Mouse Mode
The information above applies to the Double Mouse Mode, where remote
and local mouse pointers are visible and need to be synchronized. The
IP-KVM also features another mode, the Single Mouse Mode, where only
the remote mouse pointer is visible. Activate this mode in the open
Remote Console and click into the window area. The local mouse pointer
will be hidden and the remote one can be controlled directly. To leave this
mode, it is necessary to define a mouse hotkey in the Remote Console
Settings Panel. Press this key to free the captured local mouse pointer.
2.12.6 Recommended Mouse Settings
For the different operating systems we can give the following advice:
MS Windows
In general, we recommend the usage of a mouse via USB. Choose USB
without Mouse Sync. For a PS/2 mouse choose Auto Mouse Speed. For XP
disable the option “enhance pointer precision” in the Control Panel. In
general, we recommend the usage of a mouse via USB. Choose USB
without Mouse Sync. For a PS/2 mouse choose Auto Mouse Speed. For XP
disable the option enhance pointer precision in the Control Panel.
SUN Solaris
Adjust the mouse settings either via xset m 1 or use the CDE Control Panel
to set the mouse to “1:1, no acceleration”. As an alternative you may also
use the Single Mouse Mode.
MAC OS X
We recommend using the Single Mouse Mode.
2.12.7 Video Modes
The IP-KVM recognizes a limited number of common video modes. When
running X11 on the host system, please do not use any custom mode lines
with special video modes. If you do, the IP-KVM may not be able to detect
them. We recommend using any of the standard VESA video modes,
instead.
21 / 109

Single Port KVM over IP
3. Usage
3.1 Prerequisites
The IP-KVM features an embedded operating system and applications offering
a variety of standardized interfaces. This chapter will describe both these
interfaces, and the way to use them in a more detailed manner. The interfaces
are accessed using the TCP/IP protocol family, thus they can be accessed
using the LAN port of the device.
The following interfaces are supported:
HTTP/HTTPS
Full access is provided by the embedded web server. The IP-KVM
environment can be entirely managed using a standard web browser. You
can access the IP-KVM using the insecure HTTP protocol, or using the
encrypted HTTPS protocol. Whenever possible, use HTTPS.
Telnet
A standard Telnet client can be used to access an arbitrary device
connected to the IP-KVM's serial port via a terminal mode.
The primary interface of the IP-KVM is the HTTP interface. This is covered
extensively in this chapter. Other interfaces are addressed in subtopics.
In order to use the Remote Console window of your managed host system,
the browser has to come with a Java Runtime Environment version 1.4.2 or
above. If the browser has no Java support (such as on a small handheld
device), you are still able to maintain your IP-KVM using the administration
forms displayed by the browser itself.
For secure connection to the IP-KVM, we recommend the following browsers
versions:
■ Microsoft Internet Explorer version 6.0 or higher
■ Netscape Navigator 7.0 or Mozilla 1.6 or higher
In order to access the remote host system using a securely encrypted
connection, you need a browser that supports the HTTPS protocol. Strong
security is only assured by using a key length of 128 Bit. Some of the old
browsers do not have a strong 128 Bit encryption algorithm.
22 / 109

Single Port KVM over IP
Using the Internet Explorer, open the menu entry “?” and “Info” to read about
the key length that is currently activated. The dialog box contains a link that
leads you to information on how to upgrade your browser to a state of the art
encryption scheme. Figure below shows the dialog box presented by the
Internet Explorer 6.0.
Figure 3-1 The Internet Explorer displaying the encryption key
length
Newer web browsers generally support strong encryption on default.
3.2 Login into the IP-KVM and logout
3.2.1 Login into the IP-KVM
Launch your web browser. Direct it to the address of your IP-KVM, which
you configured during the installation process. The address used might be
an IP address or a domain name, in the case where you have given your
IP-KVM a symbolic name in the DNS. For instance, type the following in the
URL field of your browser when establishing an unsecured connection:
http://<IP address of IP-KVM>
When using a secure connection, type in:
https://<IP address of IP-KVM>
This will lead you to the IP-KVM login page as shown below
23 / 109

Single Port KVM over IP
The IP-KVM has a built-in super user that has all permissions to administrate
your IP-KVM:
Username
super (factory default)
Password
pass (factory default)
Warning
The user “super” is not allowed to login via the serial interface of
the IP-KVM.
Warning
Please make sure to change the super user password immediately
after you have installed and accessed your IP-KVM for the first time.
Unchanging of the password for the super user is a severe security
risk and might result in unauthorized access to the IP-KVM and to
the host system including all possible consequences!
Warning
Your web browser has to accept cookies, or else login is not possible.
Navigation
Having logged into the IP-KVM successfully, the main page of the IP-KVM
appears. This page consists of three parts; each of them contains specific
information. The buttons on the upper side allow you to navigate within the
front end. Within the right frame, task-specific information is displayed
that depends on the section you have chosen before.
24 / 109

Single Port KVM over IP
The Buttons of the front end:
Return to main page of IP-KVM access page
Open the IP-KVM remote console
Exit from the IP-KVM front end.
Warning
If there is no activity for 30 minutes, the IP-KVM will log you out,
automatically. A click on one of the links will bring you back to
the login screen.
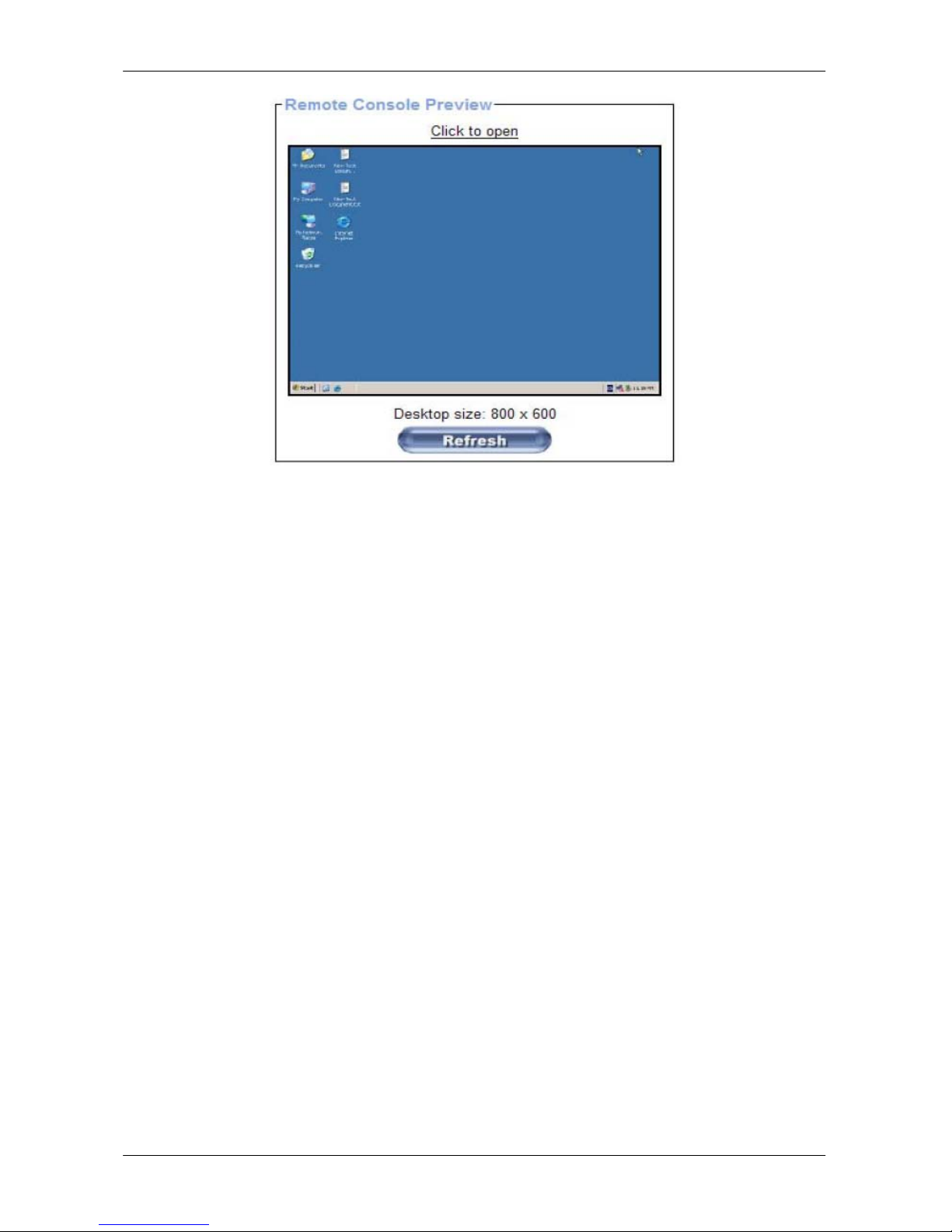
Remote Console Preview
Click on Click to open to start the remote console redirection
Click on Refresh to refresh the picture.
25 / 109
Single Port KVM over IP
3.2.2 Login out from the IP-KVM
This link logs out the current user and presents a new login screen. Please
note that an automatic logout will be performed in case there is no activity
for 30 minutes.
3.3 The Remote Console
The Remote Console is the redirected screen, keyboard and mouse of the
remote host system that IP-KVM controls.
The Remote Console window is a Java Applet that tries to establish its own
TCP connection to the IP-KVM. The protocol that is run over this connection
is neither HTTP or HTTPS, but RFB (Remote Frame Buffer Protocol). As
default, RFB tries to establish a connection to TCP port number 443. Your
local network environment has to allow this connection to be made, i.e.
your firewall and, in case you have a private internal network, your NAT
(Network Address Translation) settings have to be configured accordingly.
In case the IP-KVM is connected to your local network environment and
your connection to the Internet is available using a proxy server only
without NAT being configured, the Remote Console is very unlikely to be
able to establish the desired connection. This is because today's web
proxies are not capable of relaying the RFB protocol.
26 / 109

Single Port KVM over IP
In case of problems, please consult your network administrator in order to
provide an appropriate networking environment.
3.3.1 Main Window of Remote Console
To open the KVM console either click on the icon Console or Remote
Control > KVM Console of the menu entry on the left or Click to open
of the console picture on the right.
Starting the Remote Console opens an additional window. It displays the
screen content of your host system. The Remote Console will behave
exactly in the same way as if you were sitting locally in front of the screen
of your remote system. That means keyboard and mouse can be used in
the usual way. However, be aware of the fact that the remote system will
react to keyboard and mouse actions with a slight delay. The delay
depends on the bandwidth of the link to which you use to connect to the
IP-KVM.
With respect to the keyboard, the very exact remote representation might
lead to some confusion as your local keyboard changes its keyboard layout
according to the remote host system. If you use a German administration
system, and your host system uses a US English keyboard layout, for
instance, special keys on the German keyboard will not work as expected.
Instead, the keys will result in their US English counterpart. You can
circumvent such problems by adjusting the keyboard of your remote
system to the same mapping as your local one.
27 / 109

Single Port KVM over IP
The Remote Console window always tries to show the remote screen with
its optimal size. That means it will adapt its size to the size of the remote
screen initially and after the screen resolution of the remote screen has
been changed. However, you can always resize the Remote Console
window in your local window system as usual.
Warning
In difference to the remote host system, the Remote Console window
on your local window system is just one window among others. In
order to make keyboard and mouse work, your Remote Console
window must have the local input focus.
3.3.2 Control Bar of Remote Console
The upper part of the Remote Console window contains a control bar.
Using its elements you can see the state of the Remote Console and adjust
the local Remote Console settings. A description for each control follows.
Figure 3-2
Remote Console Control Bar
Ctrl+Alt+Delete
Special button key to send the “Control Alt Delete” key combination to
the remote system (see also section 6.4.1 for defining new button
keys).
Auto Adjust button
If the video display is of bad quality or distorted in some way, press
this button and wait a few seconds while the IP-KVM tries to detect the
video mode of VGA port to the controlled host and adjust itself for the
best possible video quality.
Sync mouse
Activates the mouse synchronization process. Choose this option in
order to synchronize the local with the remote mouse cursor. This is
especially necessary when using accelerated mouse settings on the host
28 / 109

Single Port KVM over IP
system. In general, there is no need to change mouse settings on the
host.
Single/Double mouse mode
Switches between the Single Mouse Mode (where only the remote
mouse pointer is visible) and the Double Mouse Mode (where remote
and local mouse pointers are visible and need to be synchronized).
Single mouse mode is only available if using SUN JVM 1.4.2 or higher.
Options
To open the Options menu, click on the button “Options”.
Figure 3-3 Remote Console Options Menu
A short description of the options as follows.
• Monitor Only
Toggles the Monitor only filter on or off. If the filter is switched on no
remote console interaction is possible, and monitoring is possible.
• Exclusive Access
If a user has the appropriate permission, he or she can force the
Remote Consoles of all other users to close. No one can open the
Remote Console at the same time again until this user disables the
exclusive access, or logs off.
29 / 109

Single Port KVM over IP
A change in the access mode is also visible in the status line.
Figure 3-4 Remote Console Exclusive Mode
• Scaling
Allow you to scale down the Remote Console. You can still use both
mouse and keyboard, however the scaling algorithm will not preserve
all display details.
When you designate 25%, 50%, or100% scaling, the size of Remote
Console window is calculated according to the remote host video
setting with scaling algorithm execution. When you designate “Scale
to fit”, the remote video displaying is scaled to fit the size of Remote
Console window.
Figure 3-5 Remote Console Options Menu:Scaling
• Mouse Handling
The submenu for mouse handling offers two options for synchronizing
the local and the remote mouse cursors.
30 / 109
 Loading...
Loading...