Page 1

(V1.0.1)
DSO8000E SERIES
HANDHELD OSCILLOSCOPE
8072E/8102E/8152E/8202E
USER’S MANUAL
Page 2

Contents
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual i
Contents
Contents ........................................................................................................................................... i
Copyright Declaration ................................................................................................................... iv
Chapter 1 Safety Tips ................................................................................................................. 1
General Safety Summary .................................................................................................. 1 1.1
Safety Terms and Symbols ................................................................................................ 1 1.2
Terms on Product ............................................................................................................... 2 1.3
Symbols on Product ........................................................................................................... 2 1.4
Product Scrapping ............................................................................................................. 2 1.5
Chapter 2 Overview .................................................................................................................... 3
Brief Introduction to DSO8000E Series ............................................................................. 3 2.1
Help System ....................................................................................................................... 3 2.2
Ports and Extentions .......................................................................................................... 4 2.3
Chapter 3 Getting Started Guide .............................................................................................. 5
Installation .......................................................................................................................... 5 3.1
Functional Check ............................................................................................................... 5 3.2
3.2.1 Power on the oscilloscope .......................................................................................... 5
3.2.2 Connect the oscilloscope ........................................................................................... 5
3.2.3 Observe the waveform ............................................................................................... 6
Probe Examination............................................................................................................. 6 3.3
3.3.1 Safety .......................................................................................................................... 6
3.3.2 Use of Probe Check Wizard ....................................................................................... 7
Manual Probe Compensation ............................................................................................ 7 3.4
Probe Attenuation Setting .................................................................................................. 8 3.5
Self Calibration ................................................................................................................... 8 3.6
Communication with PC .................................................................................................... 9 3.7
3.7.1 Install software ............................................................................................................ 9
3.7.2 Install driver .............................................................................................................. 12
Chapter 4 Main Feature Description ...................................................................................... 16
Oscilloscope Setup .......................................................................................................... 16 4.1
Trigger .............................................................................................................................. 16 4.2
Data Acquisition ............................................................................................................... 17 4.3
Waveform Scaling and Positioning .................................................................................. 18
4.4
Waveform Measurement.................................................................................................. 19 4.5
Chapter 5 Basic Operation ...................................................................................................... 20
DisplayArea ...................................................................................................................... 21 5.1
5.1.1 XY Format ................................................................................................................. 23
Horizontal Controls .......................................................................................................... 24 5.2
5.2.1 Scan Mode Display (Roll Mode) ............................................................................... 26
Page 3

Contents
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual ii
Vertical Controls ............................................................................................................... 26 5.3
5.3.1 Math FFT .................................................................................................................. 28
Trigger Controls ............................................................................................................... 33 5.4
Menu and Option Buttons ................................................................................................ 39 5.5
5.5.1 SAVE/RECALL ......................................................................................................... 39
5.5.2 MEASURE ................................................................................................................ 40
5.5.3 UTILITY .................................................................................................................... 42
5.5.4 DISPLAY ................................................................................................................... 43
5.5.5 ACQUIRE ................................................................................................................. 44
5.5.6 CURSOR .................................................................................................................. 46
Fast Action Buttons .......................................................................................................... 47 5.6
5.6.1 AUTOSET ................................................................................................................. 47
Signal Connectors............................................................................................................ 48 5.7
Chapter 6 Application Examples ............................................................................................ 50
Example 1: Taking Simple Measurements ...................................................................... 50 6.1
Example 2: Taking Cursor Measurements....................................................................... 52 6.2
Example 3: Analyzing Input Signals to Eliminate Random Noise ................................... 55 6.3
Example 4: Capturing Single-shot Signal ........................................................................ 56 6.4
Example 5: Using X-Y Mode ............................................................................................ 57 6.5
Example 6: Triggering on Pulse Width ............................................................................ 58 6.6
Example 7: Triggering on Video Signal ........................................................................... 59 6.7
Example 8: Using Slope Trigger to Capture Particular Slope Signal .............................. 61 6.8
Example 9: Using Overtime Trigger to Measure Long Pulse Signal ............................... 62 6.9
Example 10: Using Math Functions to Analyze Waveforms ............................................ 63 6.10
Example 11: Measuring Data Propagation Delay ............................................................ 64
6.11
6.12 Example 12: Back light control ........................................................................................ 65
6.13 Example 13: Auto shut down ........................................................................................... 66
Chapter 7 Multimeter ................................................................................................................ 67
Chapter 8 Recorder .................................................................................................................. 76
Multimeter Trend .............................................................................................................. 77 8.1
Oscilloscope Trend .......................................................................................................... 79 8.2
Waveform Recorder ......................................................................................................... 80 8.3
Chapter 9 Waveform Generator .............................................................................................. 83
Waveform Generator ....................................................................................................... 83 9.1
Generate Arbitrary waveform ........................................................................................... 86
9.2
9.2.1 Edit Arb waveform by DDS_ARB ............................................................................. 86
9.2.2 Edit Arb waveform by slave computer ...................................................................... 89
Chapter 10 Troubleshooting .................................................................................................. 92
Problem Settlement ......................................................................................................... 92 10.1
Chapter 11 Specifications ...................................................................................................... 93
Page 4

Contents
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual iii
Technical Specifications ................................................................................................... 93 11.1
11.2 Accessories ...................................................................................................................... 99
Open Source Information ............................................................................................... 100 11.3
License: GPLV2 See Appendix B ....................................................................................... 100
Chapter 12 General Care and Cleaning .............................................................................. 101
General Care ................................................................................................................. 101 12.1
Cleaning ......................................................................................................................... 101 12.2
Battery Replacement ..................................................................................................... 101 12.3
Chapter 13 Services and Support ....................................................................................... 102
Appendix A Harmful and Poisonous Substances or Elements .......................................... 103
Appendix B .................................................................................................................................. 104
GNU GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE ............................................................................................ 104
Version 2, June 1991 .................................................................................................................. 104
Page 5

Copyright Declaration
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual iv
Copyright Declaration
All rights reserved; no part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by
any means, electronic or mechanical, without prior written permission from Qingdao Hantek
Electronic Co., Ltd (hereinafter referred to as ‘Hantek’).
Hantek reserves all rights to modify this document without prior notice. Please contact Hantek for
the latest version of this document before placing an order.
Hantek has made every effort to ensure the accuracy of this document but does not guarantee the
absence of errors. Moreover, Hantek assumes no responsibility in obtaining permission and
authorization of any third party patent, copyright or product involved in relation to the use of this
document.
Page 6

Safety Tips
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 1
Chapter 1 Safety Tips
General Safety Summary 1.1
Read the following safety precautions to avoid injury and prevent damage to this product or any
products connected to it. To evade potential hazards, use this product only as specified.
Only qualified personnel should perform maintenance.
Avoid fire or personal injury.
Connect and disconnect properly. Connect a probe with the oscilloscope before it is connected
to measured circuits; disconnect the probe from the oscilloscope after it is disconnected from
measured circuits.
Connect the probe in a right way. The probe ground lead is at ground potential. Do not connect
the ground lead to an elevated voltage.
Check all terminal ratings. To avoid fire or shock hazard, check all ratings and markings on the
product. Refer to the product manual for detailed information about ratings before making
connections to the product.
Do not operate without covers. Do not operate this product with covers or panels removed.
Avoid exposed circuitry. Do not touch exposed connections and components when power is
present.
Do not operate with suspected failures. If you suspect there is damage to this product, have it
inspected by qualified service personnel.
Assure good ventilation.
Do not operate in wet/damp environments.
Do not operate in an explosive atmosphere.
Keep product surfaces clean and dry.
Safety Terms and Symbols 1.2
The following terms may appear in this manual:
WARNING. Warning statements point out conditions or practices that could result in injury
or loss of life.
CAUTION. Caution statements identify conditions or practices that could result in damage
to this product or other property.
Page 7

Safety Tips
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 2
Terms on Product
1.3
The following terms may appear on the product:
DANGER indicates an injury hazard immediately accessible as you read the marking.
WARNING indicates an injury hazard not immediately accessible as you read the marking.
CAUTION indicates a possible hazard to this product or other property.
Symbols on Product 1.4
The following symbols may appear on the product:
Product Scrapping 1.5
Device Recycling
We need extract and utilize natural resources to produce this device. If you do not reclaim the
device in a proper way, some substances it contains may become harmful or poisonous to
environments or human bodies. To avoid them being released outside and to minimize the waste
of natural resources, we suggest you reasonably call back this device to ensure proper recovery
and recycling of most materials within it.
Protective
Ground
(Earth)
Terminal
Measurement
Ground
Terminal
CAUTION
Refer to Manual
Measurement
Input Terminal
Mains
Disconnected
OFF (Power)
Mains
Connected
ON (Power)
High Voltage
Page 8

Overview
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 3
Chapter 2 Overview
Brief Introduction to DSO8000E Series 2.1
Model
Channel
Bandwidth
Sample Rate
LCD
DSO8072E
2
70MHz
1GS/s
5.6 TFT
DSO8102E
2
100MHz
1GS/s
5.6 TFT
DSO8152E
2
150MHz
1GS/s
5.6 TFT
DSO8202E
2
200MHz
1GS/s
5.6 TFT
Table 2-1 Model List of DSO8000E Series
DSO8000E Series oscilloscopes cover the bandwidths from 70MHz to 200MHz, and provide
the real-time and equivalent sample rates respectively up to 1GSa/s and 25GSa/s. In addition,
they have maximum 2M memory depth for better observation of the waveform details, and 5.6 inch
color TFT LCD as well as WINDOWS-style interfaces and menus for easy operation.
What’s more, the plenty menu information and the easy-to-operate buttons allow you to gain
information as much as possible in measurement; the multifunctional and powerful shortcut keys
help you save a lot of time in operation; the Autoset function lets you detect sine and square
waves automatically; the Probe Check Wizard guides you to adjust the probe compensation and
set the Probe option attenuation factor. By using these the methods the oscilloscope provides
(context-sensitive, hyperlinks, and an index), you may master all operations on the device in quite
a short time so as to greatly improve your efficiency in production and development.
Help System 2.2
This oscilloscope has a Help system with topics covering all of its features. You can use the Help
system to display several kinds of information:
General information about understanding and using the oscilloscope, such as Using the Menu
System.
Information about specific menus and controls, such as the Vertical Position Control.
Advice to problems you may come across while using an oscilloscope, such as Reducing
Noise.
Keep pressing a Function Menu button(including “SAVE/RECALL”, “MEAS”, “UTILITY”,
“CURSOR”, “CH1”, “CH2”, “MATH”, “HORI” and “TRIG”) for 3s to turn on the help file for the
function.
Page 9
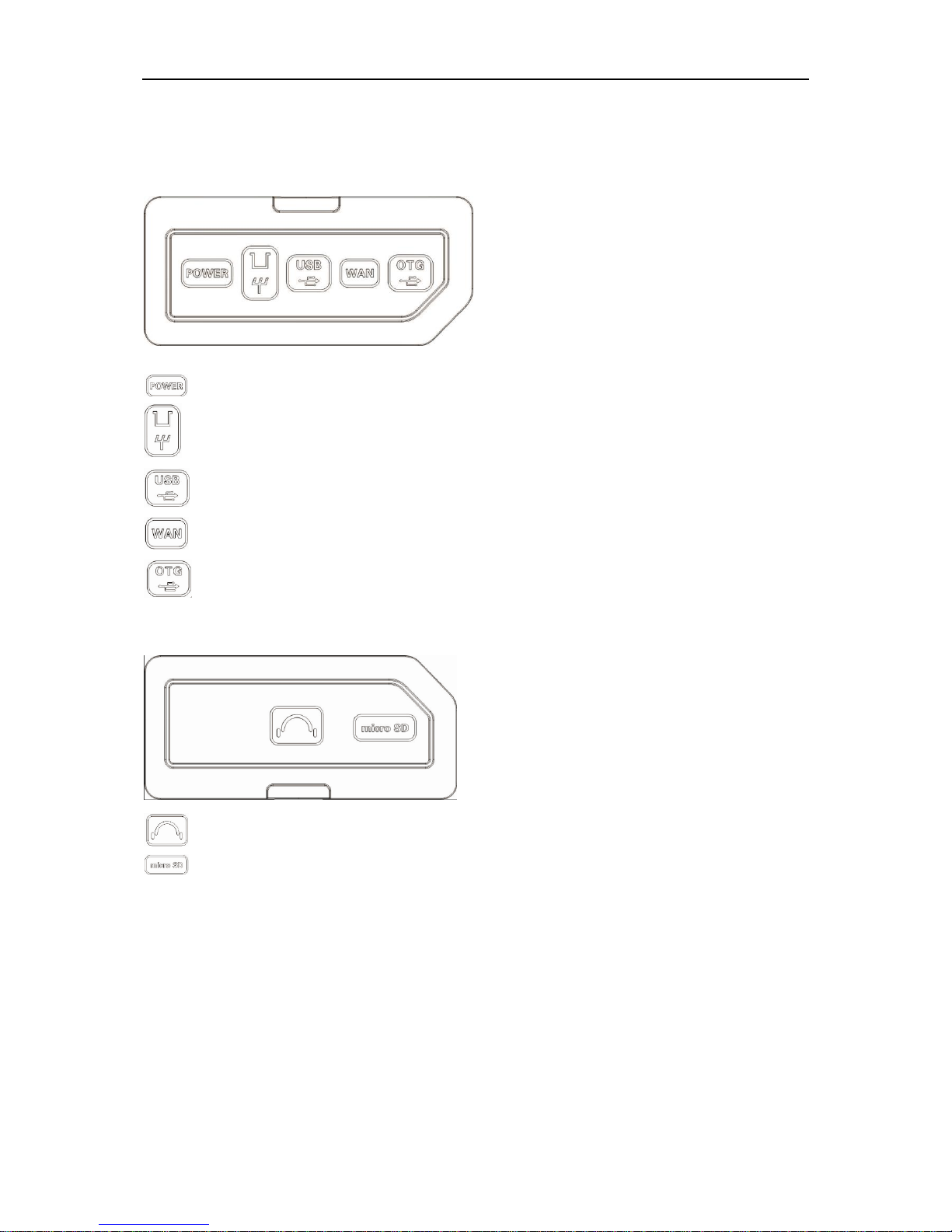
Overview
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 4
Ports and Extentions
2.3
On the right side of the unit,
On the left side of the unit,
Attention: SD card memory should be less than or equal to 4GB.
Power Input DC 12V, 3000mA
Probe calibration signal output 1 KHz, 2Vpp
Type USB-A port for USB flash disk
LAN/Wifi connection port (optional)
Mini USB OTG port
Headphone, not available for this product.
Socket for Micro SD card (optional).
Page 10

Getting Started Guide
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 5
Chapter 3 Getting Started Guide
Installation 3.1
To keep proper ventilation of the oscilloscope in operation, leave a space of more than 5cm away
from the top and the two sides of the product.
Functional Check 3.2
Follow the steps below to perform a quick functional check to your oscilloscope.
3.2.1 Power on the oscilloscope
Press the ON/OFF button. The default Probe option attenuation setting is 10X.
The default probe parameter
Note 1: Between pressing the power key and the first screen appears on the screen, there is a
1~2 seconds delay without any screen.
Note 2: Right after power on, there are beep sounds at regular interval in the first few minutes. It
indicates that the multimeter is initializing and has no influence on use.
3.2.2 Connect the oscilloscope
Set the switch on the probe to 1X and connect the probe to Channel 1 on the oscilloscope. First,
align the slot in the probe connector with the protuberance on the CH1 BNC and push to connect;
then, turn to right to lock the probe in place; after that, connect the probe tip and reference lead to
the PROBE COMP connectors. The Probe COMP: ~2V@1KHz.
CH1
CH2
Page 11

Getting Started Guide
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 6
3.2.3 Observe the waveform
Press the AUTO button and you should see within a few seconds a square wave of about 2V
peak-to-peak at 1KHz in the display. Press the CH1 MENU button and remove Channel 1. Push
the CH2 MENU button and repeat Step 2 and Step 3 to observe Channel 2.
Probe Examination 3.3
3.3.1 Safety
When using the probe, keep your fingers behind the guard on the probe body to avoid electric
shock. Do not touch metallic portions of the probe head while it is connected to a voltage source.
Connect the probe to the oscilloscope and connect the ground terminal to ground before you start
any measurements.
PROBE COMP
Page 12
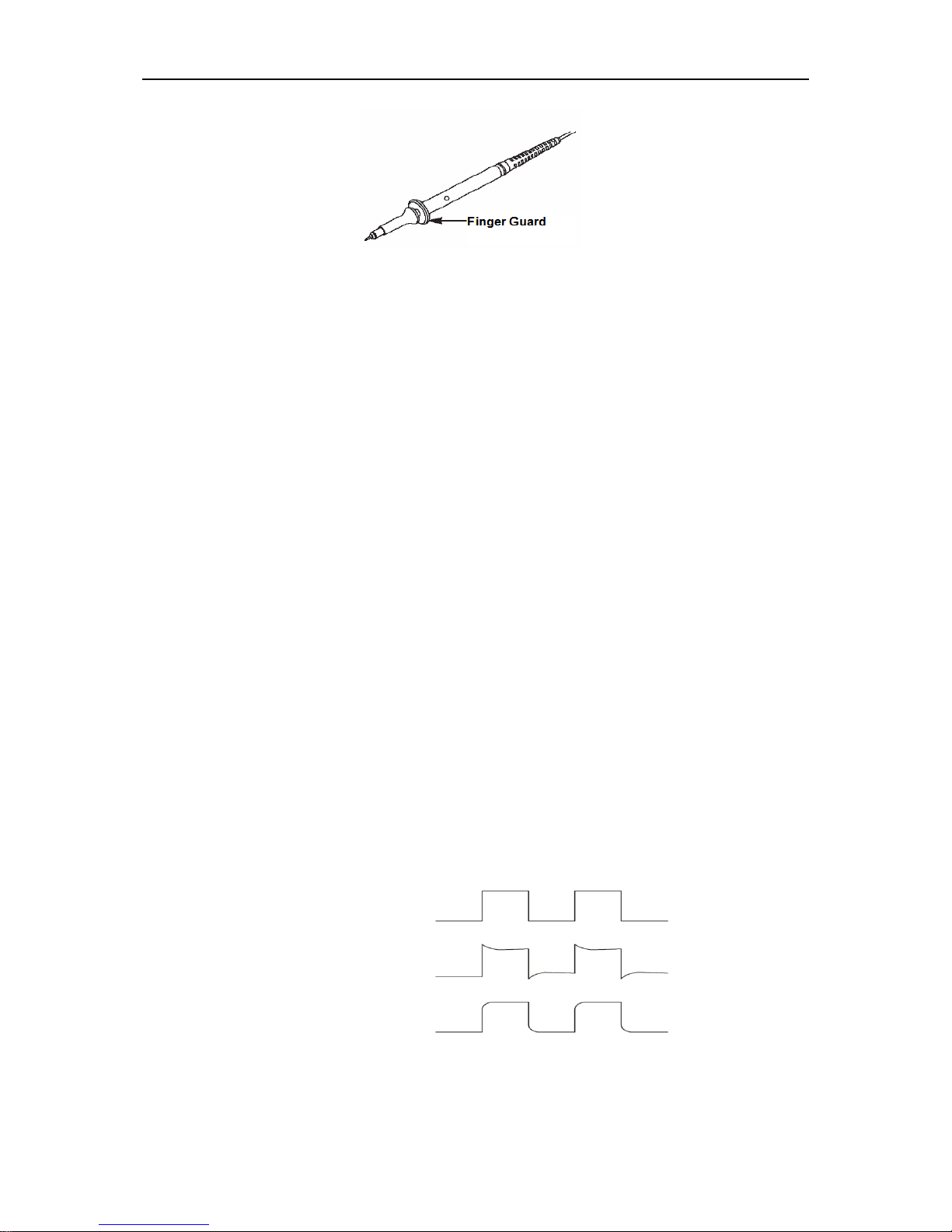
Getting Started Guide
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 7
3.3.2 Use of Probe Check Wizard
Every time you connect a probe to an input channel, you should use the probe check wizard to
verify that this probe is operating correctly. There are two ways to do this:
1) Use the vertical menu (for example, push the CH1 MENU button) to set the Probe option
attenuation factor.
2) Press UTILITY key and turn to 3/5 page and then press the Probe CK key to use the Probe
Check Wizard and configure the probe option attenuation factor properly following menu
prompts.
Manual Probe Compensation 3.4
Upon the first connection of a probe and an input channel, you should manually perform this
adjustment to match the probe to the input channel. Uncompensated or miscompensated probes
may lead to errors or faults in measurement. To adjust the probe compensation, follow the steps
below.
1. Set the Probe option attenuation in the channel menu to 10X. Set the switch on the probe to
10X and connect the probe to Channel 1 on the oscilloscope. If you use the probe hook-tip,
ensure it is firmly inserted onto the probe. Attach the probe tip to the PROBE COMP
~2V@1KHz connector and the reference lead to the PROBE COMP Ground connector.
Display the channel and then press the AUTO button.
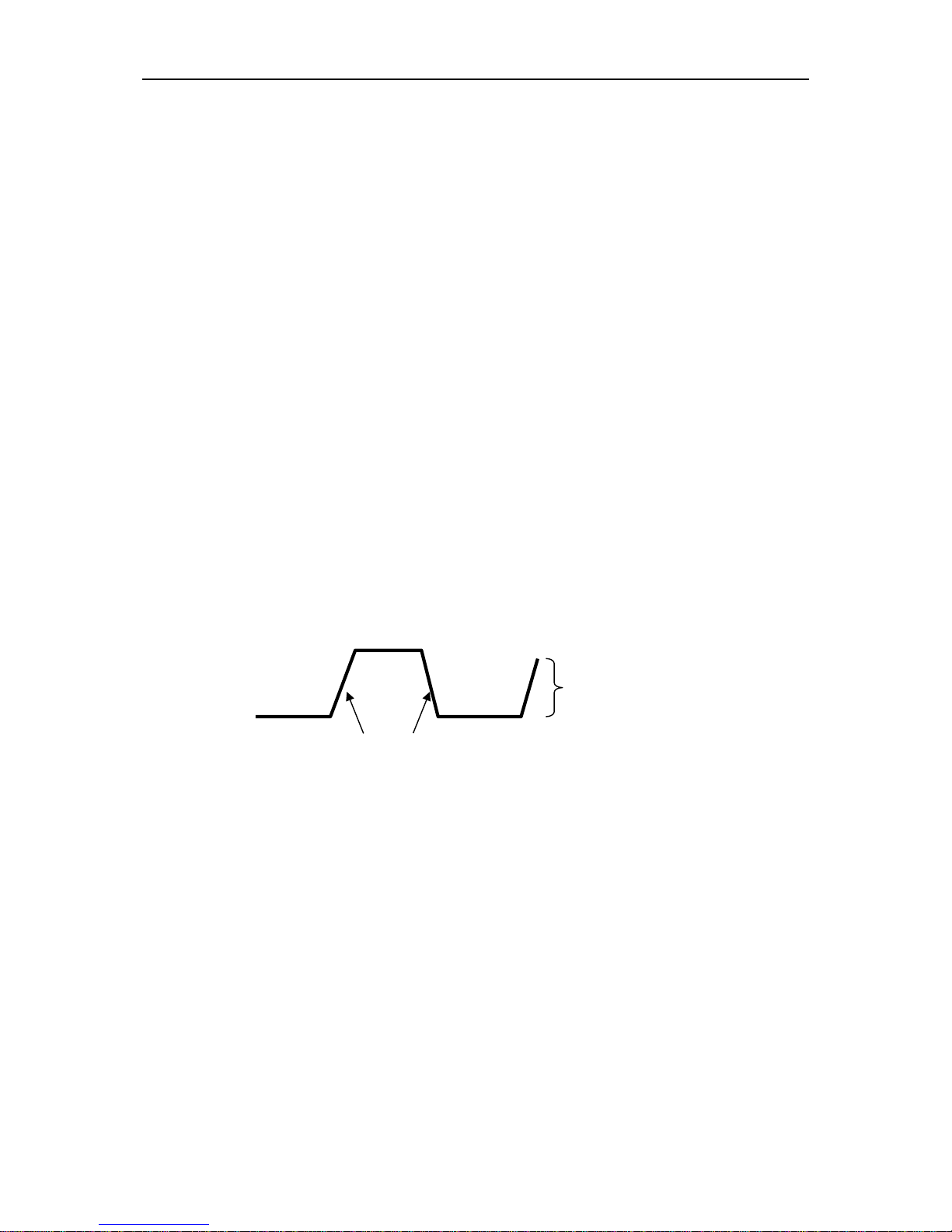
2. Check the shape of the displayed waveform.
3. If necessary, use a nonmetallic screwdriver to adjust the variable capacity of your probe until
the shape of the waveform turns to be the same as the above figure. Repeat this step as
Compensated correctly
Overcompensated
Undercompensated
Page 13
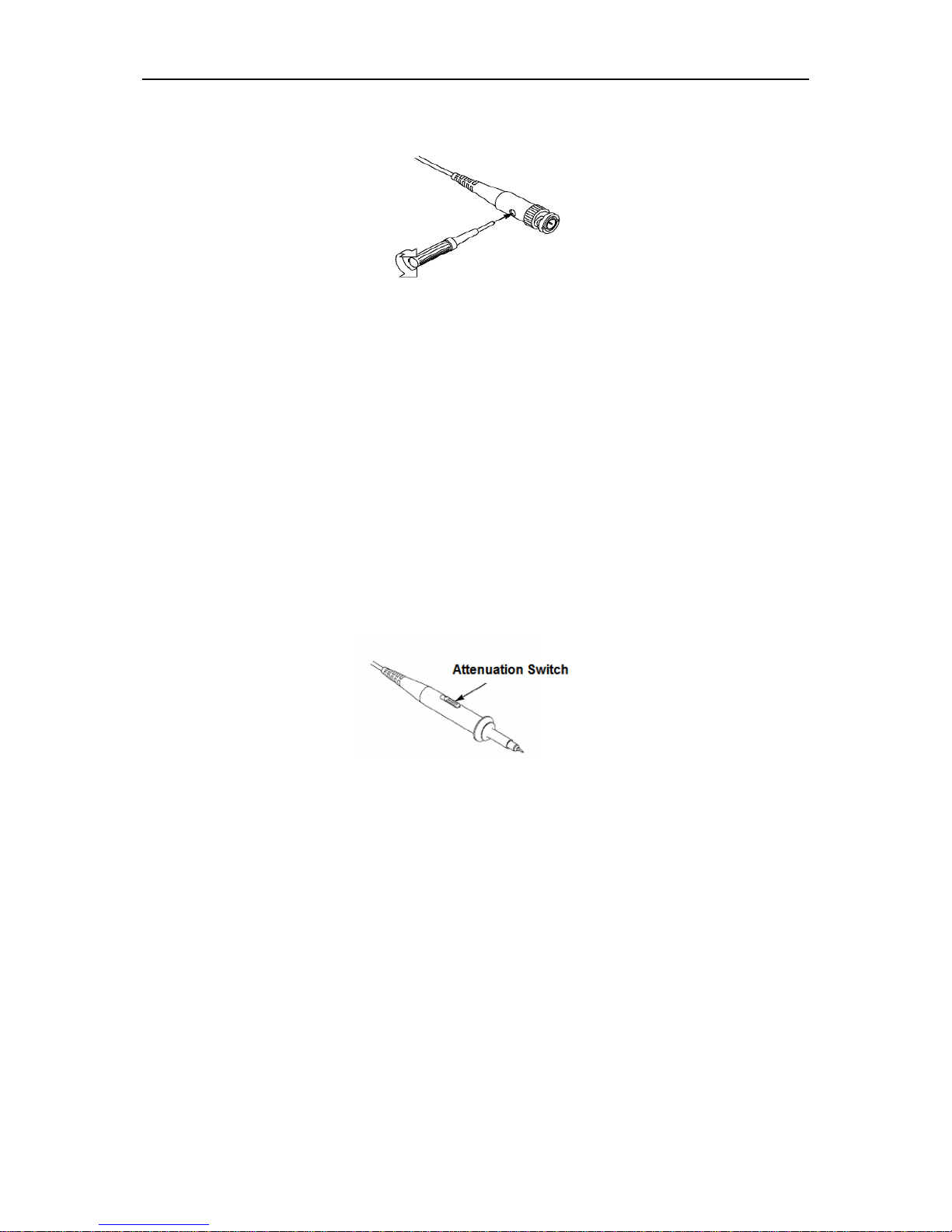
Getting Started Guide
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 8
necessary. See the figure below for the way of adjustment.
Probe Attenuation Setting 3.5
Probes are of various attenuation factors which affect the vertical scale of the signal. The Probe
Check function is used to verify if the Probe attenuation option matches the attenuation of the
probe.
As an alternative method to Probe Check, you can push a vertical menu button (such as the CH 1
MENU button) and select the Probe option that matches the attenuation factor of your probe.
Make sure that the Attenuation switch on the probe matches the Probe option in the oscilloscope.
Switch settings are 1X and 10X.
When the Attenuation switch is set to 1X, the probe limits the bandwidth of the oscilloscope to
6MHz. To use the full bandwidth of the oscilloscope, be sure to set the switch to 10X.
Self Calibration 3.6
The self calibration routine helps optimize the oscilloscope signal path for maximum measurement
accuracy. You can run the routine at any time but should always run it if the ambient temperature
changes by 5℃ or more. For a more accurate calibration, please power on the oscilloscope and
wait for 20 minutes until it has adequately warmed up.
To compensate the signal path, disconnect any probes or cables from the front-panel input
connectors. Then, push the UTILITY button, select the Self Cal option and follow the directions on
the screen.
Page 14
Getting Started Guide
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 9
Communication with PC
3.7
3.7.1 Install software
Caution: You must install the software before using the oscilloscope with Windows PC.
1. While in Windows, insert the installation CD into the CD-ROM drive.
2. The installation should start up automatically. Otherwise in Windows Explorer, switch to the
CD-ROM driver and run Setup.exe.
3. The software Installation is started. Click 'Next' to continue.
Page 15

Getting Started Guide
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 10
4. Choose a destination directory. Click ‘Next’ to continue.
5. Check the setup information. Click Next to start copying of files.
6. This Status dialog is displayed during copying of files.
Page 16

Getting Started Guide
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 11
7. Updating your system configuration.
8. The installation is complete.
Page 17

Getting Started Guide
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 12
3.7.2 Install driver
Caution: You must install the driver before connect the device with Windows PC via USB cable.
1. Connect the A-Type Plug of USB cable to your PC’s USB port.
2. Connect the B-Type Plug of USB cable to DSO’s USB port.
3. New hardware is found.
4. New hardware search wizard starts.
Page 18
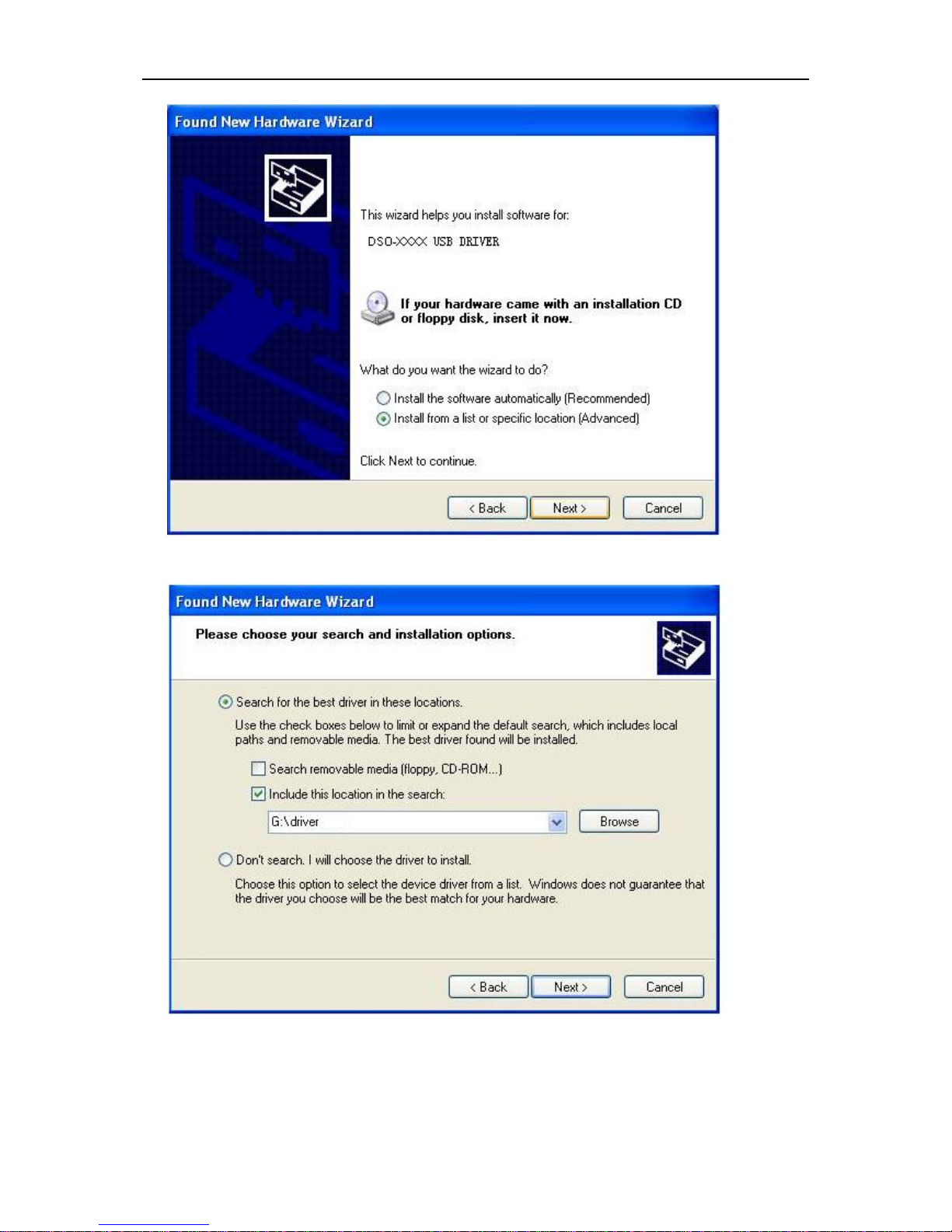
Getting Started Guide
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 13
5. New hardware search wizard starts to search the drive.
6. New hardware wizard installs software
Page 19
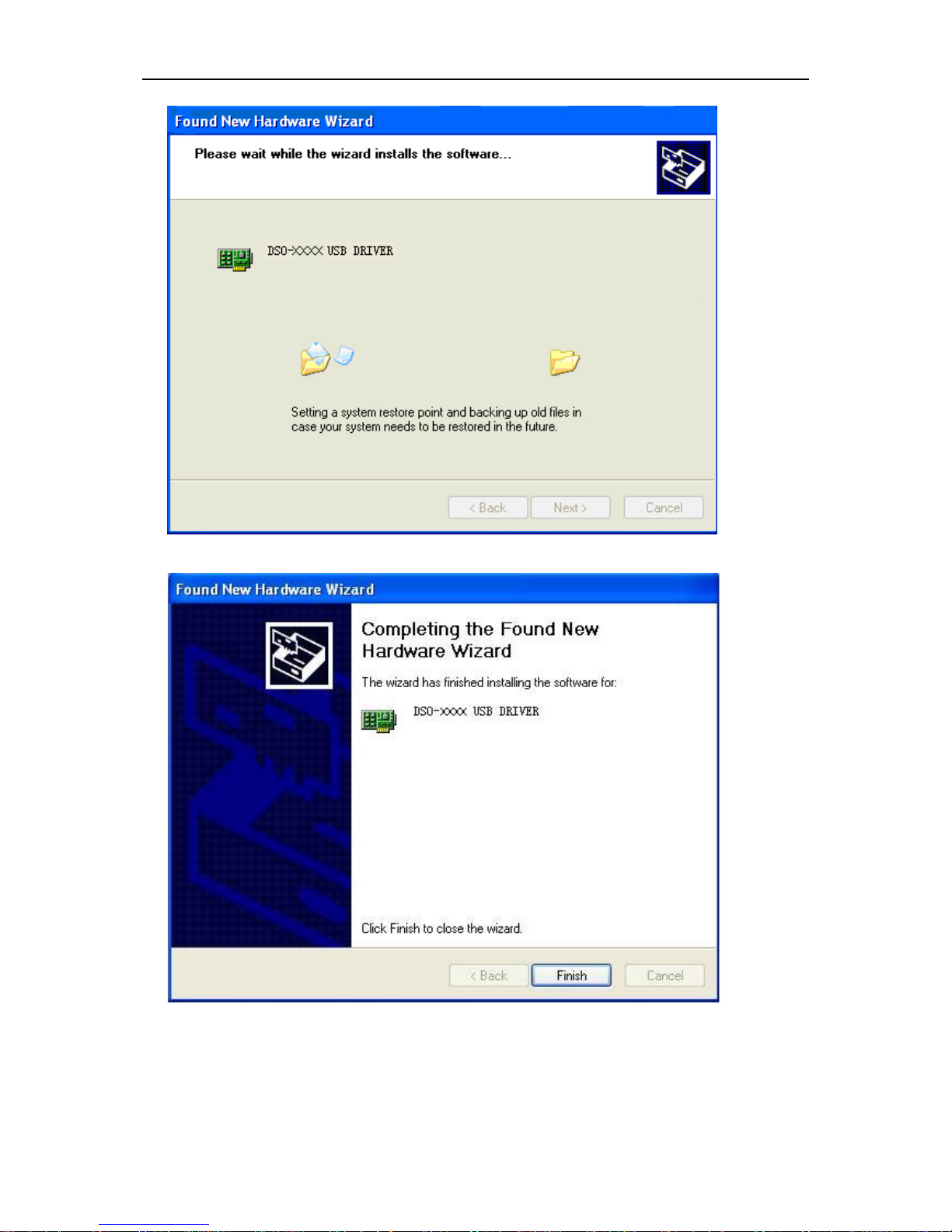
Getting Started Guide
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 14
7. Finish new hardware search wizard.
12. Your new hardware is installed and ready to use.
Page 20
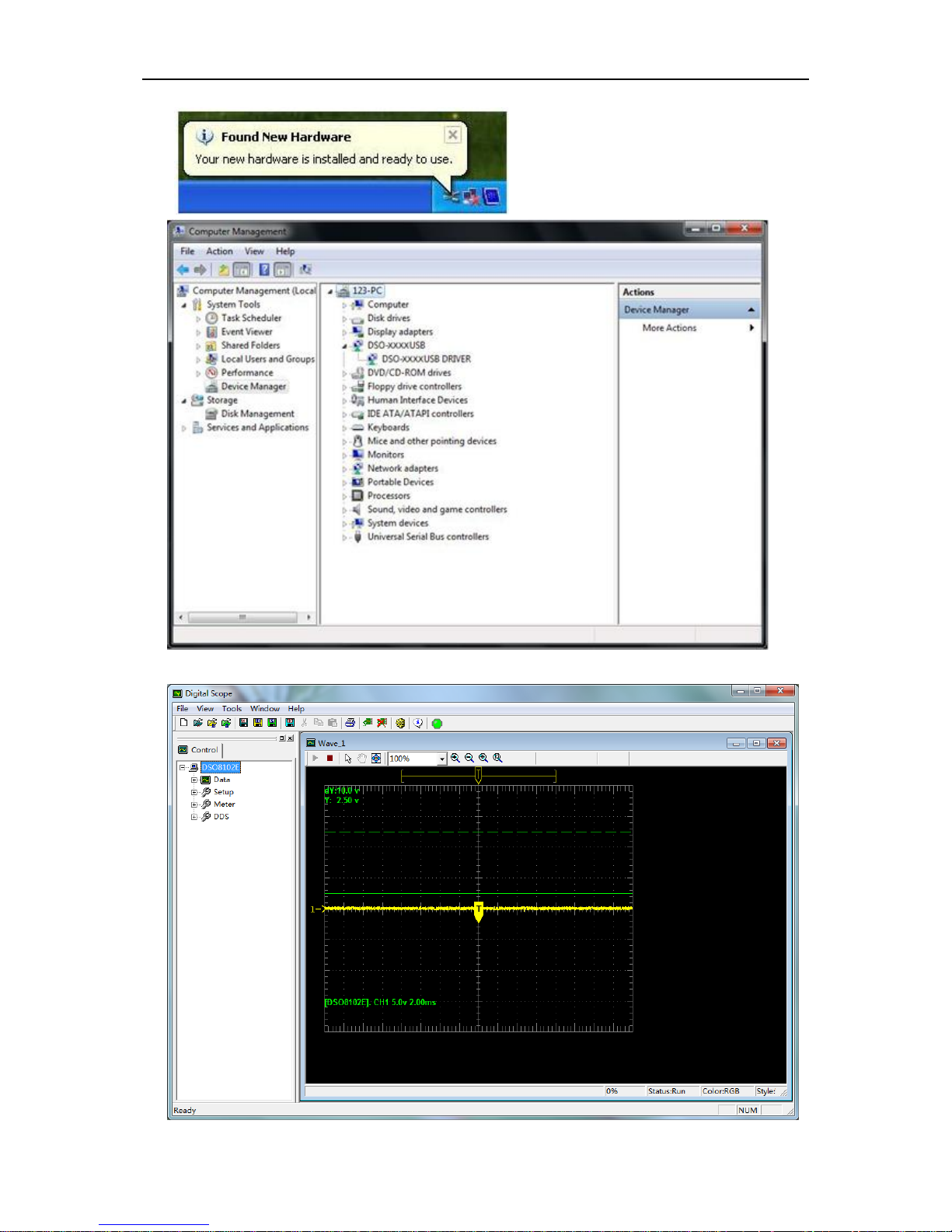
Getting Started Guide
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 15
13. Now you can open the software to use.
Page 21

Main Feature Description
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 16
Chapter 4 Main Feature Description
This chapter provides some general information that you need to learn before using an
oscilloscope. It contains:
1. Oscilloscope setup
2. Trigger
3. Data acquisition
4. Waveform scaling and positioning
5. Waveform measurement
Oscilloscope Setup 4.1
While operating the oscilloscope, you may often use thr feature: Autoset.
Autoset: This function can be used to adjust the horizontal and vertical scales of the oscilloscope
automatically and set the trigger coupling, type, position, slope, level and mode, etc., to acquire a
stable waveform display.
Trigger 4.2
The trigger determines when the oscilloscope begins to acquire data and display a waveform.
Once a trigger is properly set up, the oscilloscope can convert unstable displays or blank screens
to meaningful waveforms. Here introduce some basic concepts about trigger.
Trigger Source: The trigger can be generated with multiple sources. The most common one is the
input channel (alternative between CH1 and CH2). Whether the input signal is displayed or not, it
can trigger normal operations.
Trigger Type: The oscilloscope has six types of triggers: Edge, Video, Pulse Width, Slope,
Overtime and Alter.
Edge Trigger uses the analog or digital test circuits for triggering. It happens when the
input trigger source crosses a specified level in a specified direction.
Video Trigger performs a field or line trigger through standard video signals.
Pulse Width Trigger can trigger normal or abnormal pulses that meet trigger conditions.
Slope Trigger uses the rise and fall times on the edge of signal for triggering.
Overtime Trigger happens after the edge of signal reaches the set time.
Alter Trigger, as a feature of analog oscilloscopes, gives stable displays of signals at
Page 22
Main Feature Description
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 17
two different frequencies. Mainly it uses a specific frequency to switch between two
analog channels CH1 and CH2 so that the channels will generate alter trigger signals
through the trigger circuitry.
Trigger Mode: You can select the Auto or Normal mode to define how the oscilloscope acquires
data when it does not detect a trigger condition. Auto Mode performs the acquisition freely in
absence of valid trigger. It allows the generation of untriggered waveforms with the time base set
to 80ms/div or slower. Normal Mode updates the displayed waveforms only when the
oscilloscope detects a valid trigger condition. Before this update, the oscilloscope still displays the
old waveforms. This mode shall be used when you want to only view the effectively triggered
waveforms. In this mode, the oscilloscope displays waveforms only after the first trigger. To
perform a single sequence acquisition, push the SINGLE SEQ button.
Trigger Coupling: Trigger Coupling determines which part of the signal will be delivered to the
trigger circuit. This can help to obtain a stable display of the waveform. To use trigger coupling,
push the TRIG MENU button, select an Edge or Pulse trigger, and then select a Coupling option.
Trigger Position: The horizontal position control establishes the time between the trigger position
and the screen center.
Slope and Level: The Slope and Level controls help to define the trigger. The Slope option
determines whether the trigger point is on the rising or falling edge of a signal. To perform the
trigger slope control, press the TRIG MENU button, select an Edge trigger, and use the Slope
button to select rising or falling. The LEVEL button controls the trigger point is on which position of
the edge.
Data Acquisition 4.3
When you acquire an analog signal, the oscilloscope will convert it into a digital one. There are
two kinds of acquisition: Real-time acquisition and Equivalent acquisition. The real-time acquisition
has three modes: Normal, Peak Detect, and Average. The acquisition rate is affected by the
setting of time base.
Normal: In this acquisition mode, the oscilloscope samples the signal in evenly spaced intervals to
establish the waveform. This mode accurately represents signals in most time. However, it does
not acquire rapid variations in the analog signal that may occur between two samples, which can
result in aliasing and may cause narrow pulses to be missed. In such cases, you should use the
Peak Detect mode to acquire data.
Peak Detect: In this acquisition mode, the oscilloscope gets the maximum and minimum values of
Trigger slope can be rising or falling
Rising Edge
Falling Edge
Trigger level can be
adjusted vertically
Page 23

Main Feature Description
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 18
the input signal over each sample interval and uses these values to display the waveform. In this
way, the oscilloscope can acquire and display those narrow pulses that may have otherwise been
missed in Normal mode. However, noise will appear to be higher in this mode.
Average: In this acquisition mode, the oscilloscope acquires several waveforms, averages them,
and displays the resulting waveform. You can use this mode to reduce random noise.
Equivalent Acquisition: This kind of acquisition can be utilized for periodic signals. In case the
acquisition rate is too low when using the real-time acquisition, the oscilloscope will use a fixed
rate to acquire data with a stationary tiny delay after each acquisition of a frame of data. After
repeating this acquisition for N times, the oscilloscope will arrange the acquired N frames of data
by time to make up a new frame of data. Then the waveform can be recovered. The number of
times N is related to the equivalent acquisition rate.
Time Base: The oscilloscope digitizes waveforms by acquiring the value of an input signal at
discrete points. The time base helps to control how often the values are digitized. Use the
TIME/DIV button to adjust the time base to a horizontal scale that suits your purpose.
Waveform Scaling and Positioning 4.4
The display of waveforms on the screen can be changed by adjusting their scale and position.
Once the scale changes, the waveform display will increase or decrease in size. Once the position
changes, the waveform will move up, down, right, or left.
The channel reference indicator (located on the left of the graticule) identifies each waveform on
the screen. It points to the ground level of the waveform record.
Vertical Scale and Position: The vertical position of a waveform can be changed by moving it up
and down on the screen. To compare data, you may align a waveform over another. When you
push the VOLTS button to change the vertical scale of a waveform, the waveform display will
contract or expand vertically to the ground level.
Horizontal Scale and Position: Pretrigger Information
You can adjust the HORIZONTAL POSITION control to view waveform data before the trigger,
after the trigger, or some of each. When you change the horizontal position of a waveform, you are
actually changing the time between the trigger position and the screen center.
For example, if you want to find out the cause of a glitch in your test circuit, you should trigger on
the glitch and make the pretrigger period long enough to capture data before the glitch. Then you
can analyze the pretrigger data and perhaps find the cause. You are allowed to change the
horizontal scale of all the waveforms by clicking the TIME/DIV button. For example, you may want
to see just one cycle of a waveform to measure the overshoot on its rising edge. The oscilloscope
shows the horizontal scale as time per division in the scale readout. Since all active waveforms
use the same time base, the oscilloscope only displays one value for all the active channels.
Page 24
Main Feature Description
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 19
Waveform Measurement
4.5
The oscilloscope displays graphs of voltage versus time and can help to measure the displayed
waveform. There are several ways to take measurements, using the graticule, the cursors or
performing an automatic measurement.
Graticule: This method allows you to make a quick, visual estimate and take a simple
measurement through the graticule divisions and the scale factor.
For example, you can take simple measurements by counting the major and minor graticule
divisions involved and multiplying by the scale factor. If you counted 6 major vertical graticule
divisions between the minimum and maximum values of a waveform and knew you had a scale
factor of 50mV/division, you could easily calculate your peak-to-peak voltage as follows:
6 divisions x 50mV/division = 300mV.
Cursor: This method allows you to take measurements by moving the cursors. Cursors always
appear in pairs and the displayed readouts are just their measured values. There are two kinds of
cursors: Amplitude Cursor and Time Cursor. The amplitude cursor appears as a horizontal broken
line, measuring the vertical parameters. The time cursor appears as a vertical broken line,
measuring the horizontal parameters.
When using cursors, please make sure to set the Source to the waveform that you want to
measure on the screen. To use cursors, push the CURSOR button.
Automatic Measurement: The oscilloscope performs all the calculations automatically in this
mode. As this measurement uses the waveform record points, it is more precise than the graticule
and cursor measurements. Automatic measurements show the measurement results by readouts
which are periodically updated with the new data acquired by the oscilloscope.
Cursor
Cursor
Page 25

Basic Operation
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 20
Chapter 5 Basic Operation
The front panel of the oscilloscope is divided into several functional areas. In this chapter we will
give a quick overview of all control buttons on the front panel as well as the displayed information
on the screen and relative testing operations. The figure below illustrates the front panel of the
DSO8000E series digital oscilloscope.
Front Panel of DSO8000E Series
Description
1. LCD Display
2. F1~F5: Sets or switch options for the menu
3. Power light.
4. MEAS: Shows Measurement menu
Page 26
Basic Operation
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 21
5. AUTORANGE:
6. MENU OFF: Turn on/off the menu
7. MENU: Turn on/off the menu
8. AUTO: Be used for auto setting under the oscilloscope operation mode
9. RUN/STOP: key for running or stopping the operation
10. Direction Keys
11. TRIG: Shows Trigger menu
12. LEVEL: Adjust the trigger level
13. TIME/DIV: Decrease or Increase the time base
14. POSITION: Adjust the horizontal trigger position
15. HORI: Shows Horizontal menu
16. VERTICAL: Adjust the signal vertical position
17. VOLTS: Decrease or Increase the voltage/div
18. Power key.
19. REF: Shows the REF menu
20. MATH: Shows the Math or REF menu
21. CH2: Shows the CH2 menu
22. CH1: Shows the CH1 menu
23. UTILITY: Shows Utility menu
24. SAVE RECALL: Shows SAVE or RECALL menu
25. RECORDER:
26. SCOPE/DMM: Switch DMM, Scope function or Waveform Generator function interface.
27. CURSOR: Shows Cursor menu
DisplayArea 5.1
1. Hantek logo
2. Display Format:
: YT
: Vectors
: Gray indicates auto persistence; Green means persistence display is enabled. When
the icon is set to green, the time for persistence display will be shown behind it.
: XY
: Dots
Page 27
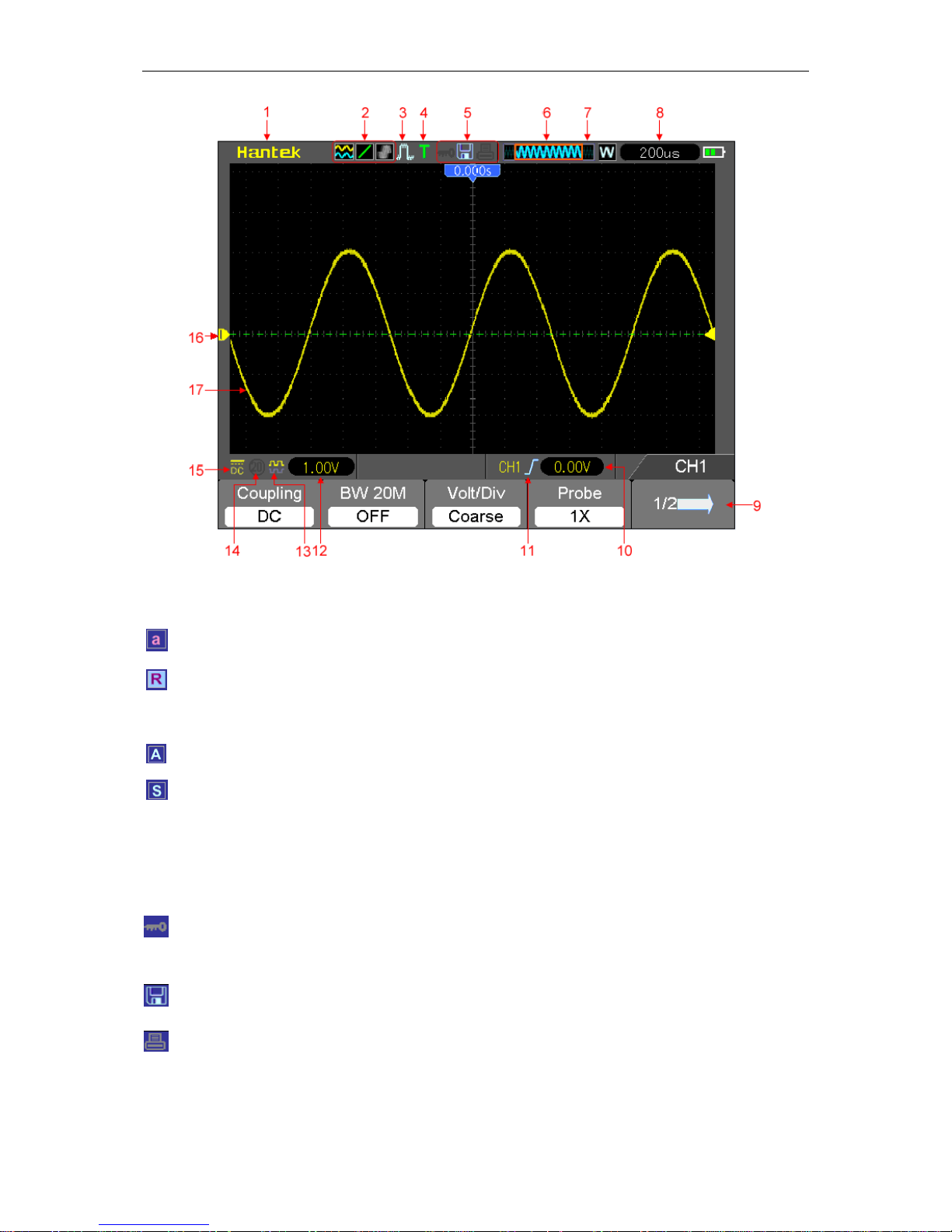
Basic Operation
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 22
3. Acquisition Mode: Normal, Peak Detect or Average
4. Trigger Status:
The oscilloscope is acquiring pretriggered data.
All pretriggered data have been acquired and the oscilloscope is ready to accept a trigger.
T The oscilloscope has detected a trigger and is acquiring the posttrigger information.
The oscilloscope works in auto mode and is acquiring waveforms in the absence of triggers.
The oscilloscope is acquiring and displaying waveform data continuously in scan mode.
● The oscilloscope has stopped acquiring waveform data.
S The oscilloscope has finished a single sequence acquisition.
5. Tool Icon:
: If this icon lights up, it means the keyboard of the oscilloscope is locked by the host computer
via USB control.
: If this icon lights up, it means the USB disk has been connected.
: This icon lights up only when the USB slave interface is connected with the computer.
6. Main Time Base Window
7. Display of window’s position in data memory and data length.
Page 28

Basic Operation
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 23
8. Window Time Base
9. Operating Menu shows different information for different function keys.
10. Trig Level.
11. Trigger Type:
: Edge trigger on the rising edge.
: Edge trigger on the falling edge.
: Video trigger with line synchronization.
: Video trigger with field synchronization.
: Pulse Width trigger, positive polarity.
: Pulse Width trigger, negative polarity.
12. Level Range.
13. Icon indicates whether the waveform is inverted or not.
14. 20M Bandwidth Limit. If this icon lights up, it means the bandwidth limit is enabled, otherwise
disabled.
15. Icon indicates channel coupling.
16. Channel Marker
17. Window displays waveform.
5.1.1 XY Format
The XY format is used to analyze phase differences, such as those represented by Lissajous
patterns. The format plots the voltage on CH1 against the voltage on CH2, where CH1 is the
horizontal axis and CH2 is the vertical axis. The oscilloscope uses the untriggered Normal
acquisition mode and displays data as dots. The sampling rate is fixed at 1 MS/s.
The oscilloscope can acquire waveforms in YT format at any sampling rate. You may view the
same waveform in XY format. To perform this operation, stop the acquisition and change the
display format to XY.
The table below shows how to operate some controls in XY format.
Controls
Usable or not in XY format
CH1 VOLTS and VERTICAL POSITION controls
Set the horizontal scale and position
CH2 VOLTS and VERTICAL POSITION controls
Continuously set the vertical scale and
position
Reference or Math
Unusable
Cursors
Unusable
Autoset (display format reset to YT)
Unusable
Time base controls
Unusable
Trigger controls
Unusable
Page 29

Basic Operation
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 24
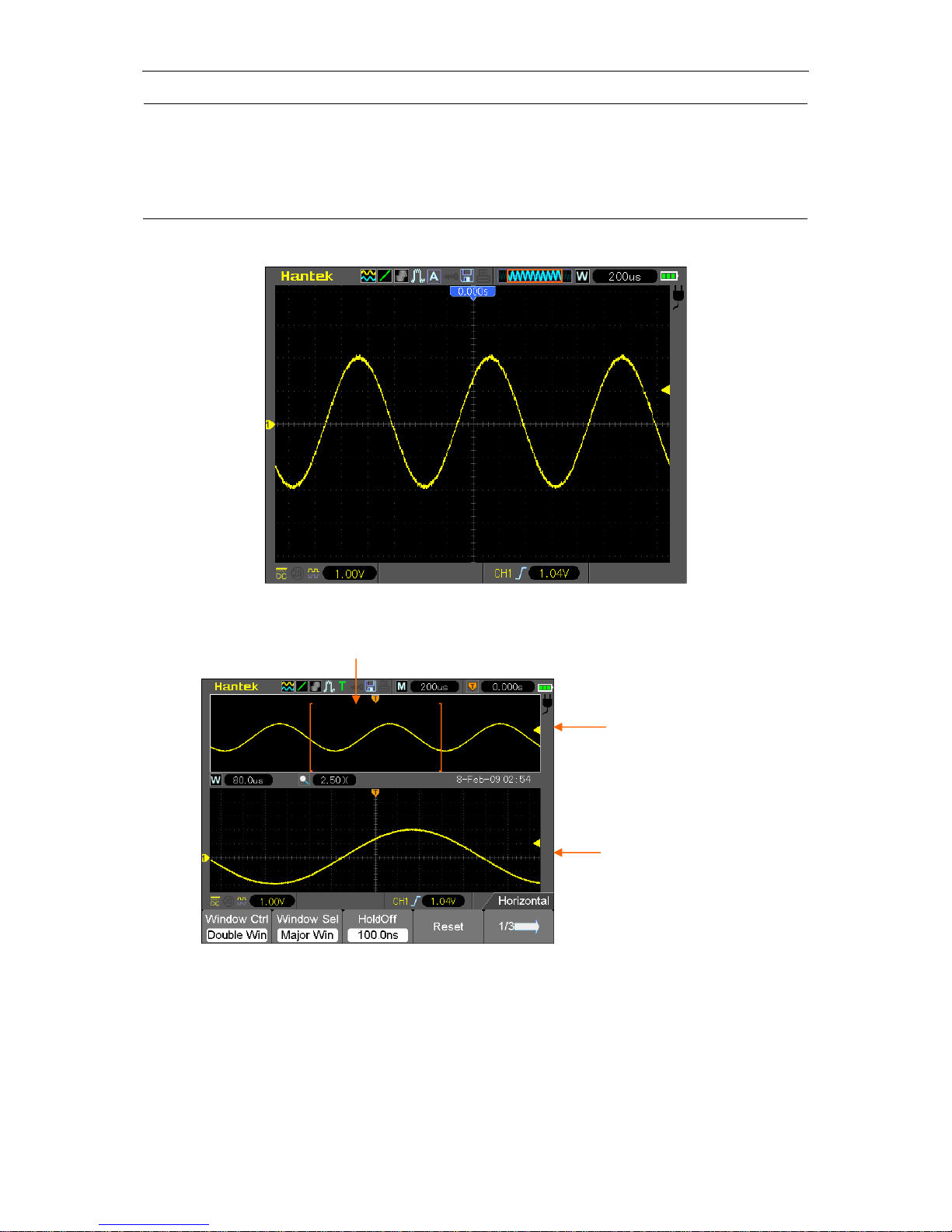
Horizontal Controls
5.2
Use the horizontal controls to change the horizontal scale and position of waveforms. The
horizontal position readout shows the time represented by the center of the screen, using the
trigger time as zero. When you change the horizontal scale, the waveform will expand or contract
to the screen center. The readout near the upper right of the screen shows the current horizontal
position in second. M represents ‘Main Time Base’, and W indicates ‘Window Time Base’. The
oscilloscope also has an arrow icon at the top of the graticule to indicate the horizontal position.
1. HORIZONTAL POSITION BAR: Used to control the trigger position against the screen center.
2. Each option in HORI MENU is described as follows.
Options
Settings
Comments
Window Ctrl
Double Win
Single Win
Set the Current window mode to single or double window.
Window Sel
Major Win
Minor Win
Selects the major or minor window in dual-window mode.
The window is highlighted once selected. Press this option
button in single-window mode to enter the daul-window
mode.
HoldOff
Select this menu and click the up and down Arrow keys to
adjust the trigger holdoff time within the range of
100ns-10s.
Reset
Recover the horizontal trigger postion to the middle screen.
Pre Mark
This function is usable only in dual-window mode. It sets
marks at some waveform record locations that users are
interested in, and searches for these marks by right and left
arrows. Then it positions the window to this mark for further
observation.
Next Mark
This function is usable only in dual-window mode. It sets
marks at some waveform record locations that users are
interested in, and searches for these marks by right and left
arrows. Then it positions the window to this mark for further
observation.
Set/Clear
Set or Clear the current Mark.
Page 30
Basic Operation
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 25
Play/Stop
This function is usable in dual-window mode. Push this
menu button and auto move it from left to right at a
specified speed. In the expanded window will display
corresponding waveforms until it stops once reaching the
rightmost side of the major scan window.
Single-window Mode
Dual-window Mode (Full Screen)
3.TIME/DIV: Used to change the horizontal time scale so as to magnify or compress the waveform
horizontally. If the waveform acquisition is stopped (by using the RUN/STOP button), the TIME
/DIV control will expand or compress the waveform. In dual-window mode, push button F1 to
select major or minor window. When the major window is selected, the F1 button provides the
same functions as it provides in single-mode window. When the minor window is selected, press
TIME/DIV button to scale the waveform whose magnification is up to 1000.
Major Window
Minor Window
(Expanded Window)
Location of expanded window data in memory
Page 31

Basic Operation
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 26
5.2.1 Scan Mode Display (Roll Mode)
With the TIME/DIV control set to 80ms/div or slower and the trigger mode set to Auto, the
oscilloscope works in the scan acquisition mode. In this mode, the waveform display is updated
from left to right without any trigger or horizontal position control.
Vertical Controls 5.3
Vertical controls can be used to display and remove waveforms, adjust vertical scale and position,
set input parameters and perform math calculations. Each channel has a separate vertical menu
to set. See below for menu description.
1. VERTICAL POSITION Bar: Move the channel waveform up and down on the screen. In
dual-window mode, move the waveforms in both windows at the same time in a same direction.
Two channels correspond to two bars.
2. Menu (CH1, CH2): Display vertical menu options; turn on or off the display of channel
waveforms.
Options
Settings
Comments
Coupling
DC
AC
GND
DC passes both DC and AC components of the input
signal.
AC blocks the DC component of the input signal and
attenuates signals below 10Hz.
Ground disconnects the input signal.
20MHz Bandwidth
Limit
Unlimited
Limited
Limits the bandwidth to reduce display noise; filters the
signal to eliminate noise and other unnecessary HF
components.
Volt/Div
Coarse
Fine
Selects the resolution of the VOLTS bar.
Coarse defines a 1-2-5 sequence. Fine changes the
resolution to small steps between the Coarse settings.
Probe
1X
10X
100X
1000X
Selects a value according to the probe attenuation
factor so as to ensure correct vertical readouts. Reduce
bandwidth to 6MHz when using a 1X probe.
Invert
Off
On
Inverts the waveform relative to the reference level.
Reset
Set the channel vertical postion to the middle of the
vertical screen,
Page 32

Basic Operation
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 27
Ground Coupling
Use to display a zero-volt waveform. Internally, the channel input is connected with a zero-volt
reference level.
Fine Resolution
In the fine resolution setting, the vertical scale readout displays the actual VOLTS setting. The
vertical scale changes only after you adjust the VOLTS control and set to coarse.
Remove Waveform Display
To remove a waveform from the screen, first push the menu button to display the vertical menu,
then push again to remove the waveform. A channel waveform which is unnecessary to be
displayed can be used as a trigger source or for math operations.
3. VOLTS
Control the oscilloscope to magnify or attenuate the source signal of the channel waveform. The
vertical size of the display on the screen will change (increase or decrease) to the ground level.
Also you may use the key F3 to switch between coarse and fine.
4. MATH MENU: Display the waveform math operations. See the table below for details.
The MATH menu contains source options for all math operations.
Operations
Source Options
Comments
+
CH1+CH2
Add Channel 1 to Channel 2.
-
CH1-CH2
Subtract the Channel 2 waveform from the
Channel 1 waveform.
CH2-CH1
Subtract the Channel 1 waveform from the
Channel 2 waveform.
X
CH1XCH2
Multiply CH1 with CH2.
/
CH1/CH2
CH1 Dvided by CH2
CH2/CH1
CH2 Dvided by CH1
Position
Set the Math channel’s position.
Scale
Set the Vertical Scale.
FFT
Window
Five types of window available for selection:
Hanning, Flattop, Rectangular, Bartletta and
Blackman
Source
CH1
CH2
FFT zoom
Use the FFT Zoom button to adjust the window
size. Scale: x1, x2, x5, x10.
Vertical Base
dBrms
Vrms
Note: All selected menus are highlighted in orange.
Page 33

Basic Operation
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 28
5.3.1 Math FFT
This chapter elaborates how to use the Math FFT (Fast Fourier Transform). You can use the Math
FFT mode to convert a time-domain (YT) signal into its frequency components (spectrum), and to
observe the following types of signals:
Analyze harmonics in power cords;
Measure harmonic content and distortion in systems;
Characterize noise in DC power supplies;
Test impulse response of filters and systems;
Analyze vibration.
To use the Math FFT mode, perform the following tasks:
Set the source (time-domain) waveform;
Display the FFT spectrum;
Choose a type of FFT window;
Adjust the sample rate to display the fundamental frequency and harmonics without aliasing;
Use zoom controls to magnify the spectrum;
Use cursors to measure the spectrum.
5.3.1.1 Setting Time-domain Waveform
It is necessary to set the time-domain (YT) waveform before using the FFT mode. Follow the steps
below.
1. Push the AUTO button to display a YT waveform.
2. Click the Vertical Position key to vertically move the YT waveform to the center (zero division)
so as to ensure the FFT will display a true DC value.
3. Click the Horizontal Position key to position the part of the YT waveform to be analyzed in the
center eight divisions of the screen. The oscilloscope uses the 2048 center points of the
time-domain waveform to calculate the FFT spectrum.
4. Click the VOLTS Key to ensure the entire waveform remains on the screen. If the entire
waveform is invisible, the oscilloscope may display wrong FFT results by adding
high-frequency components.
5. Click the TIME/DIV key to provide the resolution you need in the FFT spectrum.
6. If possible, set the oscilloscope to display multiple signal cycles.
If you click the TIME/DIV key to select a faster setting (fewer cycles), the FFT spectrum will display
a larger frequency range and reduce the possibility of FFT aliasing.
To set the FFT display, follow the steps below.
1. Push the M/R button;
Page 34

Basic Operation
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 29
2. Set the Operation option to FFT;
3. Select the Math FFT Source channel.
In many situations, the oscilloscope can also generate a useful FFT spectrum despite the YT
waveform not being triggered. This is especially true if the signal is periodic or random (such as
noise).
Note: You should trigger and position transient or burst waveforms as close as possible to
the screen center.
Nyquist Frequency
The highest frequency that any real-time digital oscilloscope can measure without errors is half of
the sample rate, which is called the Nyquist frequency. Frequency information beyond the Nyquist
frequency is undersampled which brings about the FFT aliasing. The math function can convert
the center 2048 points of the time-domain waveform to an FFT spectrum. The resulting FFT
spectrum contains 1024 points from DC (0Hz) to the Nyquist frequency. Usually, the screen
compresses the FFT spectrum horizontally to 250 points, but you can use the FFT Zoom function
to expand the FFT spectrum so that you can clearly view the frequency components at each of the
1024 data points in the FFT spectrum.
Note: The oscilloscope’s vertical response is a little bit larger than its bandwidth (70MHz,
100MHz, 150MHz or 200MHz, depending on the model; or 20MHz when the Bandwidth Limit
option is set to Limited). Therefore, the FFT spectrum can display valid frequency
information above the oscilloscope bandwidth. However, the amplitude information near or
above the bandwidth will not be accurate.
5.3.1.2 Displaying FFT Spectrum
Push the MATH MENU button to display the Math menu. Use the options to select the Source
channel, the Window algorithm and the FFT Zoom factor. Only one FFT spectrum can be
displayed at a time.
Math FFT
Options
Settings
Comments
Source
CH1, CH2
Choose a channel to be the FFT source.
Window
Hanning, Flattop,
Rectangular, Bartlett,
Blackman
Select a type of the FFT window. For more
information, refer to Section 5.3.1.3.
FFT Zoom
X1, X2, X5, X10
Change the horizontal magnification of the FFT
display. For detailed information, refer to Section
5.3.1.6.
Vertical Base
dBrms,
Vrms
Set dBrms to be the vertical base;
Set Vrms to be the vertical base
Page 35

Basic Operation
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 30
1. Frequency at the center graticule line
2. Vertical scale in dB per division (0dB=1V
RMS
)
3. Horizontal scale in frequency per division
4. Sample rate in number of samples per second
5. FFT window type
5.3.1.3 Selecting FFT Window
Using windows can eliminate the spectral leakage in the FFT spectrum. The FFT algorithm
assumes that the YT waveform repeats all the time. When the number of cycles is integral (1, 2,
3 ...), the YT waveform starts and ends at the same amplitude and there are no discontinuities in
the signal shape.
If the number of cycles is nonintegral, the YT waveform starts and ends at different amplitudes and
transitions between the start and end points will cause discontinuities in the signal that introduces
high-frequency transients.
1
Fundamental frequency component
Frequency component
5
2 3 4
Page 36

Basic Operation
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 31
Applying a window to the YT waveform changes the waveform so that the start and stop values
are close to each other, which reduces the discontinuities.
The Math FFT function has three FFT Window options. There is a trade-off between frequency
resolution and amplitude accuracy for each type of window. You shall determine which one to
choose according to the object you want to measure and the source signal characteristics.
Window
Measurement
Characteristics
Hanning
Periodic Waveform
Better frequency, poorer amplitude accuracy than
Flattop
Flattop
Periodic Waveform
Better amplitude, poorer frequency accuracy than
Hanning
Rectangular
Pulse or Transient Waveform
Special-purpose window applicable to
discontinuous waveforms. This is actually the
same as no windows.
Page 37

Basic Operation
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 32
Bartlett
Blackman
Best magnitude, worst
frequency resolution.
Single frequency waveforms, to
Find higher order harmonics.
5.3.1.4 FFT Aliasing
Problems occur when the time-domain waveform acquired by the oscilloscope contains frequency
components higher than the Nyquist frequency. The frequency components above the Nyquist
frequency will be undersampled and displayed as lower frequency components that ‘fold back’
from the Nyquist frequency. These erroneous components are called aliases.
5.3.1.5 Eliminating Aliases
To eliminate aliases, use the following methods.
Click the TIME/DIV key to set a faster sample rate. Because the Nyquist frequency increases
as you increase the sample rate, the aliased frequency components will be displayed correct.
If too many frequency components appear on the screen, you may use the FFT Zoom option
to magnify the FFT spectrum.
If there is no need to observe the frequency components above 20MHz, set the Bandwidth
Limit option to Limited.
Filter the signal input from outside and limit the bandwidth of the source waveform to lower
than the Nyquist frequency.
Identify and ignore the aliased frequencies.
Use zoom controls and cursors to magnify and measure the FFT spectrum.
5.3.1.6 Magnifying and Positioning FFT Spectrum
You may scale the FFT spectrum and use cursors to measure it through the FFT Zoom option
which enables the horizontal magnification. To vertically magnify the spectrum, use the vertical
controls.
Horizontal Zoom and Position
You can use the FFT Zoom option to magnify the FFT spectrum horizontally without changing the
sample rate. The available zoom factors are X1(default), X2, X5 and X10. When the zoom factor is
set to X1 and the waveform is located at the center graticule, the left graticule line is at 0Hz and
the right is at the Nyquist frequency.
You magnifies the FFT spectrum to the center graticule line when you change the zoom factor.
That is, the axis for horizontal magnification is the center graticule line. Click the Horizontal
Position Key to move the FFT spectrum to the right.
Page 38

Basic Operation
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 33
Vertical Zoom and Position
When the FFT spectrum is being displayed, the channel vertical keys become the zoom and
position controls corresponding to their respective channels. The VOLTS key provides the
following zoom factors: X1(default), X2, X5 and X10. The FFT spectrum is magnified vertically to
the marker M (math waveform reference point on the left edge of the screen). Click the Vertical
Position key to move up the spectrum.
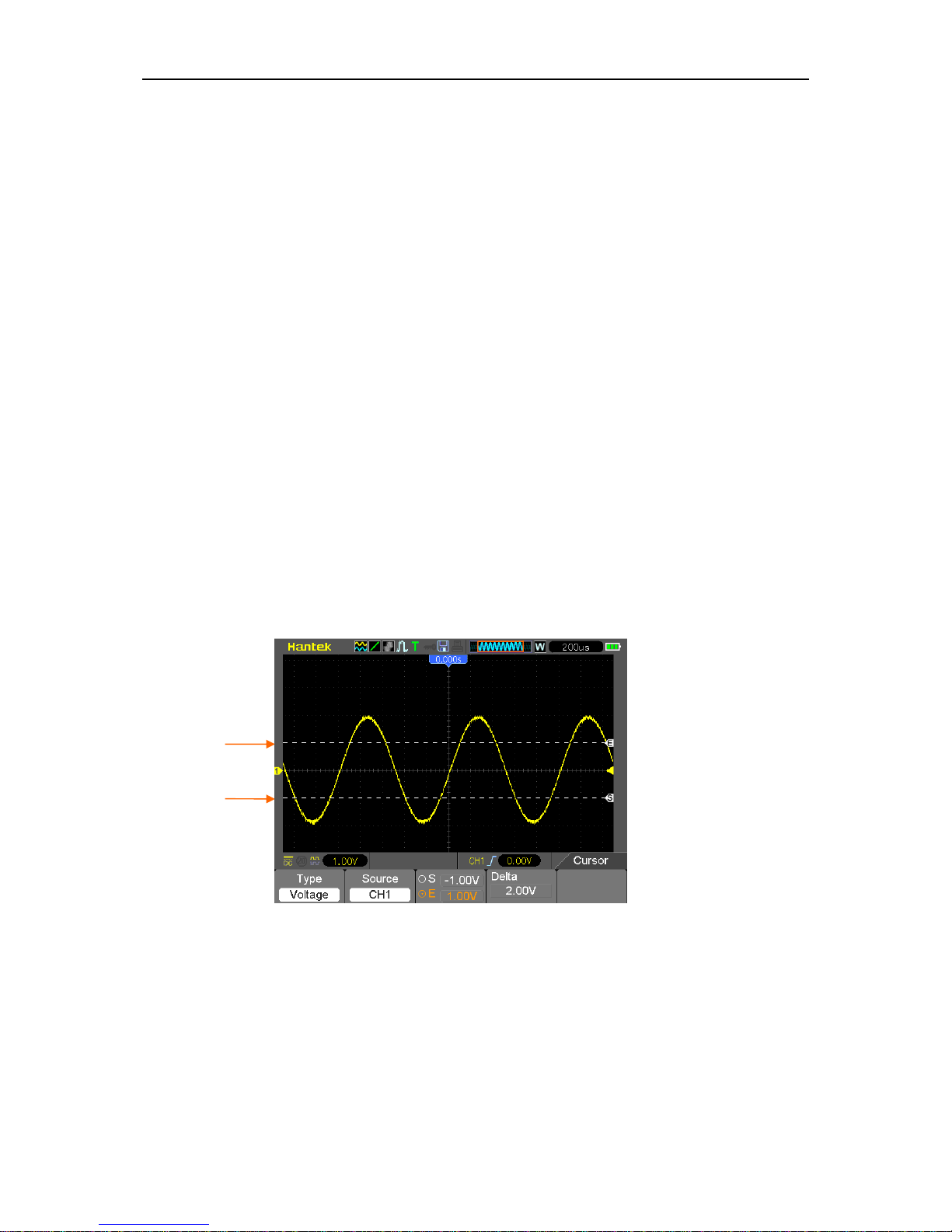
5.3.1.7 Using Cursors to Measure FFT Spectrum
You may use cursors to take two measurements on the FFT spectrum: amplitude (in dB) and
frequency (in Hz). Amplitude is referenced to 0db that equals 1VRMS here. You may use cursors
to measure at any zoom factor.
Push the CURSOR button, choose the Source option and then select Math. Press the Type option
button to select between Amplitude and Frequency. Click the SELECT CURSOR option to choose
a cursor. Then move Cursor S and Cursor E. Use the horizontal cursor to measure the amplitude
and the vertical cursor to measure the frequency. Now the display at the DELTA menu is just the
measured value, and the values at Cursor S and Cursor E.
Delta is the absolute value of Cursor S minus Cursor E.
Trigger Controls 5.4
The trigger can be defined through the Trigger Menu. There are six types of trigger: Edge, Video,
Pulse Width, Alter, Slope and Overtime. Refer to the following tables to find a different set of
options for each type of trigger.
TRIG MENU
Push this button to display trigger menus. The edge trigger is in common use. See the table below
for details.
Frequency Cursors
Amplitude Cursors
Page 39

Basic Operation
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 34
TRIG Level
It sets the amplitude level the signal must cross to cause an acquisition when using the Edge or
Pulse Width trigger.
Options
Settings
Comments
Trigger Type
Edge
By default the oscilloscope uses the edge trigger which
triggers the oscilloscope on the rising or falling edge of the
input signal when it crosses the trigger level (threshold).
Source
CH1
CH2
EXT/5
Select the input source as the trigger signal.
CH1, CH2: No matter the waveform is displayed or not, a
certain channel will be triggered.
EXT/5: Same as EXT option, but attenuates the signal by
a factor of 5 and allows a trigger level range of +6V to -6V.
Mode
Auto
Normal
Single
Select a trigger mode.
By default, the oscilloscope uses the Auto mode. In this
mode, the oscilloscope is forced to trigger when it does
not detect a trigger within a certain amount of time based
on the TIME/DIV setting. The oscilloscope goes into the
scan mode at 80ms/div or slower time base settings.
In the Normal mode, the oscilloscope updates the display
only when it detects a valid trigger condition. New
waveforms are not displayed until they replace old ones.
Use this mode to just view valid triggered waveforms.
Only after the first trigger does the display appear.
Coupling
AC
DC
Noise Reject
HF Reject
LF Reject
Select the components of the trigger signal applied to the
trigger circuitry.
AC: Blocks DC components and attenuates signals below
10Hz.
DC: Passes all components of the signal.
Noise Reject: Attenuates the noise conponents.
HF Reject: Attenuates the high-frequency components
above 80kHz.
LF Reject: Blocks DC components and attenuates the
low-frequency components below 8kHz.
50%
Set the vertical trigger postion to the channel zero level
postion.
NOTE: Trigger coupling only affects the signal passed through the trigger system. It does
not affect the bandwidth or coupling of the signal displayed on the screen.
Video Trigger
TRIG MENU
TRIG Level
Page 40

Basic Operation
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 35
Options
Settings
Comments
Video
With Video highlighted, an NTSC, PAL or SECAM
standard video signal will be triggered. The trigger
coupling is preset to AC.
Source
CH1
CH2
EXT/5
Select the input source as the trigger signal. Ext/5 use
the signal applied to the EXT TRIG connector as the
source.
Polarity
Normal
Inverted
Normal: Triggers on the negative edge of the sync
pulse.
Inverted: Triggers on the positive edge of the sync
pulse.
Sync
All Lines
Line Number
Odd Field
Even Field
All Fields
Choose a proper video sync. When selecting Line
Number for the Sync option, you may use the User
Select it to specify a line number.
Standard
NTSC
PAL/SECAM
Choose a video standard for sync and line number
count.
Note: When you choose Normal Polarity, the trigger always occurs on negative-going sync
pulses. If the video signal contains positive-going sync pulses, use the Inverted Polarity
option.
Pulse Width Trigger
You can use it to trigger on aberrant pulses.
Options
Settings
Comments
Pulse
With Pulse highlighted, the trigger occurs on pulses that
meet the trigger condition (defined by the Source, When
and Set Pulse Width options).
Source
CH1
CH2
EXT/5
Select the input source as the trigger signal.
EXT/5: Does not display the trigger signal and allows a
trigger level range of +6V to -6V.
Polarity
Positive, Negative
Mode
Auto
Normal
Single
Select the type of trigger. The Normal mode is best for
most pulse width trigger applications.
Coupling
AC
DC
Noise Reject
HF Reject
LF Reject
Select the components of the trigger signal applied to the
trigger circuit.
When
=
≠
<
>
Select the trigger condition.
Pulse Width
20ns to 10.0sec
With Set Pulse Width highlighted, set the pulse width.
50%
Trigger When: The pulse width of the source must be ≥5ns so that the oscilloscope can detect the
pulse.
Page 41

Basic Operation
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 36
=, ≠: Within a ±5% tolerance, triggers the oscilloscope when the signal pulse width is equal to
or not equal to the specified pulse width.
<, >: Trigger the oscilloscope when the source signal pulse width is less than or greater than
the specified pulse width.
Slope Trigger: Judges trigger according to the time for rising or falling, more flexible and accurate
than the Edge trigger.
Options
Settings
Comments
Slope
Source
CH1
CH2
EXT/5
Select the input source as the trigger signal.
Slope
Rising
Falling
Select the slope type of signal.
Mode
Auto
Normal
Select the type of trigger. The Normal mode is best for
most pulse width trigger applications.
Coupling
AC
DC
Noise Reject
HF Reject
LF Reject
Selects the components of the trigger signal applied to
the trigger circuitry.
Vertical
V1
V2
Adjust the vertical window by setting two trigger levels.
Select this option and press F3 to choose V1 or V2.
When
=
≠
<
>
Select the trigger condition.
Time
20ns to 10.0sec
With this option highlighted, set the time span.
Triggers when pulse is
equal to width setting ±5%
= Trigger Point
Threshold level
Triggers when pulse is
greater than width setting
Triggers when pulse is not
equal to width setting ±5%
Tolerance
Tolerance
Threshold level
Triggers when pulse is
less than width setting
Page 42

Basic Operation
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 37
Alter Trigger: As a feature of analog oscilloscopes, it gives stable displays of signals at two
different frequencies. Mainly it uses a specific frequency to switch between two analog channels
CH1 and CH2 so that the channels will generate Alter trigger signals through the trigger circuitry.
Options
Settings
Comments
Alter
Mode
Auto
Normal
Select the type of trigger.
Channel
CH1
CH2
Push an option such as CH1, select the channel trigger
type and set the menu interface.
Below list options in submenus. Alter Trigger allows CH1 and CH2 to select different trigger
modes and to display waveforms on a same screen. That is both channels can choose the
following four trigger modes.
Type
Edge
Slope
Rising
Falling
Coupling
AC
DC
Noise Reject
HF Reject
LF Reject
Select the components of the trigger signal applied to the
trigger circuitry.
Type
Video
Polarity
Normal
Inverted
Standard
NTSC
PAL/SECAM
Sync
All Lines
Line Number
Odd Field
Even Field
All Fields
Choose a proper video sync. When selecting Line Number
for the Sync option, you may use the User Select it to
specify a line number.
Type
Pulse
Polarity
Positive
Negative
When
=
≠
<
>
Select the trigger condition.
Set PW
Pulse Width
Set the pulse width.
Coupling
AC
DC
Noise Reject
HF Reject
LF Reject
Selects the components of the trigger signal applied to the
trigger circuitry.
Type
O.T.
Page 43

Basic Operation
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 38
Polarity
positive
Negative
Overtime
20ns to 10.0sec
Set the time span.
Coupling
AC
DC
Noise Reject
HF Reject
LF Reject
Selects the components of the trigger signal applied to the
trigger circuitry.
Overtime Trigger: In Pulse Width trigger, you may sometimes be puzzled with the long time for
trigger, as you do not need a complete pulse width to trigger the oscilloscope, but want the trigger
occurs just upon the overtime point. This is called Overtime Trigger.
Options
Settings
Comments
Type
O.T.
Source
CH1
CH2
Select the trigger source.
Polarity
Positive
Negative
Select to trigger on positive or negative pulses.
Mode
Auto
Normal
Overtime
Coupling
AC
DC
Noise Reject
HF Reject
LF Reject
Selects the components of the trigger signal applied to the
trigger circuitry.
50%
Holdoff: To use Trigger Holdoff, push the HORI button and set the Holdoff Time option. The
Trigger Holdoff function can be used to generate a stable display of complex waveforms (such as
pulse trains). Holdoff is the time between when the oscilloscope detects one trigger and when it is
ready to detect another. During the holdoff time, the oscilloscope will not trigger. For a pulse train,
the holdoff time can be adjusted to let the oscilloscope trigger only on the first pulse in the train.
Trigger Level
Indicates
Trigger Points
Holdoff
Holdoff
Acquisition Interval
Acquisition Interval
Page 44

Basic Operation
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 39
Menu and Option Buttons
5.5
As shown below, these four buttons at the front panel are used mainly to recall relative setup
menus.
SAVE/RECALL: Displays the Save/Recall menu for setups and waveforms.
MEASURE: Displays the Measure menu.
UTIILITY: Displays the Utility menu.
CURSOR: Displays the Cursor menu.
5.5.1 SAVE/RECALL
Press the SAVE/RECALL button to save or recall oscilloscope setups or waveforms.
Options
Settings
Comments
Wave
Enter the Save Wave menu.
Setup
Enter the S/R Setup menu.
CSV
Enter the CSV menu.
Default
Recall default setup.
Save Wave
Save the screen picture.
Options
Settings
Comments
Wave
Source
CH1, CH2
Select a waveform display to store.
Media
USB
Flash
SD
Select media.
Location
0-1000
Save
Save the source waveform to the selected reference location.
Recall
Display the reference waveform on the screen.
Delete
Delete waveform.
Options
Settings
Comments
Setup
Source
Local
USB disk
SD
Store the current setups to the USB disk or the memory of the
oscilloscope.
Location
0 to 9
Specify the memory location in which to store the current
waveform settings or from which to recall the waveform settings.
Save
Complete the saving operation.
Recall
Recall the oscilloscope settings stored in the location selected in
the Setup field. Push the Default Setup button to initialize the
Page 45

Basic Operation
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 40
oscilloscope to a known setup.
Options
Settings
Comments
CSV
Source
CH1
CH2
Select a waveform channel to store.
File List
Open
Close
Open or Close File List.
Save
Save the source waveform to the selected location.
Recall
Display the reference waveform on the screen
Media
USB disk
SD
Delete waveform.
5.5.2 MEASURE
Push the MEAS button to perform auto measurements. There are 32 types of measurements and
up to 4 types can be displayed on the screen. User can turn directions keys to select
measurement item, or push “Modify -> Type” to select the measurement type.
Press “Modify” button to select the measure source (CH1 or CH2) and measure type. Then press
“OK”button to change successfully.
Click the MEAS key then the following menu appears.
Options
Settings
Comments
Source
CH1
CH2
Select the measure source.
Measurement Type
1
Frequency
Calculate the waveform frequency by measuring the first cycle.
2
Period
Calculate the time of the first cycle.
3
Mean
Calculate the arithmetic mean voltage over the entire
waveform.
4
Pk-Pk
Calculate the absolute difference between the greatest and the
smallest peaks of the entire waveform.
5
CRMS
Calculate the Root Mean Square voltage over the entire
waveform.
6
PRMS
Calculate the actual RMS measurement of the first complete
cycle in the waveform.
7
Min
The most negative peak voltage measured over the entire
waveform.
8
Max
The most positive peak voltage measured over the entire
waveform.
9
Rising
Measure the time between 10% and 90% of the first rising
edge of the waveform.
Page 46

Basic Operation
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 41
10
Falling
Measure the time between 90% and 10% of the first falling
edge of the waveform.
11
+ Width
Measure the time between the first rising edge and the next
falling edge at the waveform 50% level.
12
- Width
Measure the time between the first falling edge and the next
rising edge at the waveform 50% level.
13
+ Duty
Measure the first cycle waveform. Positive Duty Cycle is the
ratio between positive pulse width and period.
14
- Duty
Measure the first cycle waveform. Negative Duty Cycle is the
ratio between positive pulse width and period.
15
Base
Measure the highest voltage over the entire waveform.
16
Top
Measure the lowest voltage over the entire waveform.
17
Middle
Measure the voltage of the 50% level from base to top.
18
Amplitude
Voltage between Vtop and Vbase of a waveform.
19
Overshoot
Defined as (Base - Min)/Amp x 100 %, Measured over the
entire waveform.
20
Preshoot
Defined as (Max - Top)/Amp x 100 %, Measured over the entire
waveform.
21
PMean
Calculate the arithmetic mean voltage over the first cycle in the
waveform.
22
FOVShoot
Defined as (Vmin-Vlow)/Vamp after the waveform falling.
23
RPREShoot
Defined as (Vmin-Vlow)/Vamp before the waveform falling.
24
BWidth
The duration of a burst measured over the entire waveform.
25
Delay 1-2 ↑
The time between the first rising edge of source 1 and the first
rising edge of source 2.
26
Delay 1-2 ↓
The time between the first falling edge of source 1 and the first
falling edge of source 2.
27
LFF
The time between the first falling edge of source 1 and the last
falling edge of source 2.
28
LFR
The time between the first falling edge of source 1 and the last
rising edge of source 2.
29
LRF
The time between the first rising edge of source 1 and the last
falling edge of source 2.
30
LRR
The time between the first rising edge of source 1 and the last
rising edge of source 2.
31
FFR
The time between the first falling edge of source 1 and the first
rising edge of source 2.
32
FRF
The time between the first rising edge of source 1 and the first
falling edge of source 2.
Off
Do not take any measurement.
Page 47

Basic Operation
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 42
Taking Measurements: For a single waveform (or a waveform divided among multiple
waveforms), up to 4 automatic measurements can be displayed at a time. The waveform channel
must stay in an ‘ON’ (displayed) state to facilitate the measurement. The automatic measurement
can not be performed on reference or math waveforms, or in XY or Scan mode.
5.5.3 UTILITY
Push the UTILITY key to display the Utility Menu as follows.
Options
Comments
System Info
Display the software and hardware versions, serial number and some other
information about the oscilloscope.
Update
Insert a USB disk with upgrade program and the disk icon at the top left corner is
highlighted. Press the Update Program button and the Software Upgrade dialog
pops up.
Self Cal
Press this option and the Self Calibration dialog pops up. Press F6 to perform
the self calibration.
System
Turn on/off sound, Change Language and interface, and Time Set
Shutdown
Set Action and Time
Probe Ck
Refer to 3.3.2
Pass/Fail
Pass/ Fail test
Record
Record and play back.
Filter
Set Filter function.
Display
Refer to 5.5.6
Acquire
Refer to 5.5.3
DMM
Tun on/off DMM fuction.
Frequency
Turn on/off frequency counter
More..
Sys Status, System Features, Flash and Waveform Color.
The readouts in big font size on
the menu are just results of the
corresponding measurements.
Page 48

Basic Operation
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 43
Self Cal: The self calibration routine can optimize the precision of the oscilloscope to fit the
ambient temperature. To maximize the precision, you should perform the self calibration once the
ambient temperature changes by 5℃ or more. Follow the instructions on the screen.
Shutdown
Press “UTILITY” key to enter the Utility menu and turn to the page 2/5 and then push the
Shutdown key to set the shutdowm parameter.
Power Off:
1. Press F1 button to select PowerOff.
2. Press F2 to select Time.
3. Press F3 button to confirm.
4. Press F4 button to cancel, and the device will shutdown later.
Restart:
1. Press F1 button to select Restart.
2. Press F3 button to confirm, the device will restart.
Tip: Press any menu button on the front panel to remove the status display and enter a
corresponding menu.
5.5.4 DISPLAY
The waveform display is affected by settings of the oscilloscope. A waveform can be measured
once it is captured. The different styles to display a waveform on the screen give significant
information about it.
There are two modes to display waveforms Single-window and Dual-window. Refer to Horizontal
Controls for more information.
The DISPLAY menu.
Options
Settings
Comments
Type
Vectors
Dots
Vectors fill up the space between adjacent sample
points in the display; Dots only display the sample
points.
Persistency
OFF
0.2S-8S selectable
Infinite
Sets the time length to display each displayed
sample point.
DSO Mode
YT
XY
YT format shows the vertical voltage in relation to
time (horizontal scale); XY format displays a dot
between CH1 and CH2 each time when a sample is
acquired, where the voltage or current of CH1
determines the X coordinate of the dot (horizontal)
and the voltage or current of CH2 determines the Y
coordinate (vertical). For detailed information, refer
to descriptions on XY format in the following text.
Page 49

Basic Operation
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 44
Contrast
0-15 16 ranks adjustable.
Grid
Dotted line
Real line
OFF
Off only displays the horizontal and vertical
coordinates at the center graticule on the screen.
Grid Intensity
0-15 16 ranks adjustable.
Refresh Rate
Auto
50 Frames
40 Frames
30 Frames
Wave Bright
0-15 16 ranks adjustable.
BL Keep
5s,10,30s,60s,Unlimited
Press keys (except the power button) to wake up
Menu Keep
5s,10,30s,60s,Unlimited
5.5.5 ACQUIRE
Press “UTILITY” key to enter the Utility menu and turn to the page 4/5 and then Push the
ACQUIRE key to set the acquisition parameter.
Options
Settings
Comments
Type
Real Time
Equ-Time
Acquire waveforms by real-time digital technique.
Rebuild waveforms by equivalent sample technique.
Mode
(Real Time)
Normal
Peak Detect
Average
Acquire and accurately display most waveforms.
Detect glitches and eliminate the possibility of
aliasing.
Reduce random or uncorrelated noise in signal
display. The number of averages is selectable.
Averages
(Real Time)
4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128
Select the number of averages.
LongMem
(Real Time)
4K, 40K, 512K, 1M, 2M
Select the memory depth for different board models.
Normal: For the oscilloscope model with the bandwidth of 100MHz, the maximum sample rate is
1GS/s. For time base with insufficient sample rate, you may use the Sine Interpolation Algorithm to
interpolate points between sampled points to produce a complete waveform record (4K by
default).
Page 50

Basic Operation
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 45
Peak Detect: Use this mode to detect glitches within 10ns and to limit the possibility of aliasing.
This mode is valid at the TIME/DIV setting of 4µs/div or slower. Once you set the TIME/DIV setting
to 4µs/div or faster, the acquisition mode will change to Normal because the sample rate is fast
enough that Peak Detect is unnecessary. The oscilloscope does not display a message to tell you
that the mode has been changed to Normal.
Average: Use this mode to reduce random or uncorrelated noise in the signal to be displayed.
Acquire data in Normal mode and then average a great number of waveforms. Choose the
number of acquisitions (4, 16, 64 or 128) to average for the waveform.
Stop the Acquisition: When you are running the acquisition, the waveform display is live. Stop
the acquisition (press the RUN/STOP button) to freeze the display. In either mode, the waveform
display can be scaled or positioned by vertical and horizontal controls.
Equivalent Acquisition: Just repeat the Normal acquisition. Use this mode to take a specific
observation on repeatedly displayed periodic signals. You can get a resolution of 40ps, i.e.
25GSa/s sample rate, which is much higher than that obtained in real-time acquisition.
The acquisition principle is as follows.
As shown above, acquire input signals (cycle repeatable) for more than once at a slow sample rate,
arrange the sample points by the time they appear, then recover waveforms.
Sample Points
Normal Acquisition Intervals
8 3 7 2 4 5 6 1 9
10
Normal Mode Acquires a Single Sample Point in Each Interval
Input repeated signals
First Acquisition
Second Acquisition
Third Acquisition
Fourth Acquisition
Page 51

Basic Operation
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 46
5.5.6 CURSOR
The Cursor Menu
Options
Settings
Comments
Type
Off
Voltage
Time
Select a measurement cursor and display it.
Voltage measures amplitude while Time measures time and
frequency.
Source
CH1
CH2
MATH
REFA
REFB
Select a waveform to take the cursor measurement.
Use the readouts to show the measurement.
Select
Cursor
S
E
S indicates Cursor 1. E indicates Cursor 2.
A selected cursor is highlighted, which can be moved freely. Both
cursors can be selected and moved at the same time. The box
behind the cursor displays the location of the cursor.
Delta
Display the
difference
(delta)
between the
cursors.
Display the measurement in the box under this option.
Moving Cursors: Press the key F3 to select a cursor and move it with the Arrow key. Cursors can
be moved only when the Cursor Menu is displayed.
Time Cursor
Voltage Cursor
Page 52

Basic Operation
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 47
Fast Action Buttons
5.6
AUTORANGE: Automatically set the oscilloscope controls to generate a usable display of the
input signals in real time.
AUTOSET: Automatically set the oscilloscope controls to generate a usable display of the input
signals. Refer to the following table for relative content.
RUN/STOP: Continuously acquire waveforms or stop the acquisition.
5.6.1 AUTOSET
Autoset is one of the advantages digital oscilloscopes have. When you push the AUTO button, the
oscilloscope will identify the type of waveform (sine or square wave) and adjust controls according
to input signals so that it can accurately display the waveform of the input signal.
Functions
Settings
Acquire Mode
Adjusted to Normal or Peak Detect
Cursor
Off
Display Format
Set to YT
Display Type
Set to Vectors for an FFT spectrum; otherwise, unchanged
Horizontal Position
Adjusted
TIME/DIV
Adjusted
Trigger Coupling
Adjusted to DC, Noise Reject or HF Reject
Trigger Holdoff
Minimum
Trigger Level
Set to 50%
Trigger Mode
Auto
Trigger Source
Adjusted
Trigger Slope
Adjusted
Trigger Type
Edge
Trigger Video Sync
Adjusted
Trigger Video Standard
Adjusted
Vertical Bandwidth
Full
Vertical Coupling
DC (if GND was chosen before); AC for the video signal; otherwise,
unchanged
VOLTS
Adjusted
The Autoset function examines all channels for signals and displays corresponding waveforms.
Autoset determines the trigger source according to the following conditions.
If multiply channels get signals, the oscilloscope will use the channel with the lowest
Page 53

Basic Operation
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 48
frequency signal as the trigger source.
If no signals are found, the oscilloscope will use the lowest-numbered channel displayed
in Autoset as the trigger source.
If no signals are found and no channels are displayed, the oscilloscope will display and
use Channel 1 as the trigger source.
Sine Wave:
When you use the Autoset function and the oscilloscope determines that the signal is similar to a
sine wave, the oscilloscope displays the following options.
Sine Wave Options
Details
Multi-cycle Sine
Display multiple cycles that have appropriate vertical and
horizontal scales.
Single-cycle Sine
Set the horizontal scale to display about one cycle of the
waveform.
Cancel
Let the oscilloscope recall the previous setup.
Square Wave or Pulse:
When you use the Autoset function and the oscilloscope determines that the signal is similar to a
square wave or pulse, the oscilloscope displays the following options.
Square Wave Options
Details
Multi-cycle
Display multiple cycles that have appropriate vertical and
horizontal scales.
Single-cycle
Set the horizontal scale to display about one cycle of the
waveform. The oscilloscope displays Min, Mean and Positive
Width automatic measurements.
Rising
Display the rising edge.
Falling
Display the falling edge.
Cancel
Let the oscilloscope recall the previous setup.
Signal Connectors 5.7
See the figure below to find the four signals connectors and a pair of metal electrodes at the
bottom of the oscilloscope panel.
CH1
OUTPUT
EXT TRIG/SYNC
CH2
Page 54

Basic Operation
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 49
1. CH1, CH2: Input connectors for waveform display, through which to connect and input the
signal to be measured.
2. OUTPUT: Waveform output BNC connector.
3. EXT TRIG/SYNC:
1) Input connector for an external trigger source, though with to connect and input the
external trigger signal.
2) Sync output connector for waveform signal.
4. Probe COMP: Voltage probe compensation output and ground, used to electrically match the
probe to the oscilloscope input circuit. The probe compensation ground and BNC shields
connect to earth ground and are considered to be ground terminals. To avoid damages, do not
connect a voltage source to any of these ground terminals.
PROBE COMP
Page 55

Application Examples
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 50
Chapter 6 Application Examples
This chapter unfolds a further description on main features of the oscilloscope by giving eleven
simplified application examples for reference to help solve your own test problems.
1. Taking simple measurements
Using AUTO
Using the Measure menu to take auto measurements
2. Taking cursor measurements
Measuring ring frequency and ring amplitude
Measuring pulse width
Measuring rise time
3. Analyzing input signals to eliminate random noise
Observing a noisy signal
Eliminating random noise
4. Capturing a single-shot signal
5. Using X-Y mode
6. Triggering on a pulse width
7. Triggering on a video signal
Observing triggers on video fields and video lines
8. Using Slope Trigger to capture a particular slope signal
9. Using Overtime Trigger to measure a long pulse signal
10. Using math functions to analyze waveforms
11. Measuring data propagation delay
12. Back light control
13. Auto shut down
Example 1: Taking Simple Measurements 6.1
When you want to observe an unknown signal in a certain circuit without having its amplitude and
frequency parameters, you may use this function to take a fast measurement on the frequency,
period and peak-to-peak amplitude of the signal.
Follow the steps below.
1. Set the switch on the oscilloscope probe to 10X;
2. Push the CH1 MENU button and set the Probe option attenuation to 10X;
3. Connect the CH1 probe to the test point of the circuit;
4. Press the AUTO button.
Page 56

Application Examples
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 51
The oscilloscope will automatically set the waveform to a best display. If you want to further
optimize the waveform display, you may manually adjust the vertical and horizontal controls until
the waveform meets your particular requirement.
Taking Auto Measurements
The oscilloscope can display most signals by automatic measurements. To measure such
parameters as the signal frequency, period, peak-to-peak amplitude, rise time and positive width,
follow the steps below.
1. Push the MEAS button to see the Measure menu.
2. Select the first ‘unspecified’ option (marked by red arrow), and then enter the submenu.
3. Select CH1 for the Source option. Then repeatedly select measure items in the Type menu.
Push the back menu to go back to the measure interface. The corresponding box under the
measure item shows the measurements.
4. Repeat Step 2 and Step 3. Then select other measure items. Totally 4 measure items can be
displayed.
Note: All readouts change with the measured signals.
The figure below shows three measure items as an example. The boxes under them display the
measurements in large fonts.
Page 57

Application Examples
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 52
Example 2: Taking Cursor Measurements 6.2
You can use the cursor to quickly measure the time and amplitude of a waveform.
Measuring Ring Time (convertible to Frequency) and Amplitude on Rising Edge of Pulse
To measure the ring time on the rising edge of the pulse, follow the steps below.
1. Push the CURSOR button to view the Cursor menu.
2. Push F1 the Type option button and select Time.
3. Push F2 the Source option button and select CH1.
4. Select a cursor. If S is selected, move Cursor S on the screen; if E is selected, move Cursor E;
if both are selected, move them at the same time.
5. Put Cursor S on the first peak of the ring.
6. Put Cursor E on the second peak of the ring.
7. At Delta displays the measured time and at Cursor S an Cursor E display the positions of
these two cursors.
8. Push the Type option button and select Voltage.
9. Put Cursor S on the highest peak of the ring.
10. Put Cursor E on the lowest point of the ring. The amplitude of the ring will be displayed at
Delta.
See figures below for better understanding.
Page 58

Application Examples
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 53
Measuring Pulse Width
To analyze a pulse signal and to know its width, follow the steps below.
1. Push the CURSOR button to view the Cursor menu.
2. Push F1 the Type option button and select Time.
3. Push F2 the Source option button and select CH1.
4. Select a cursor. If S is selected, move Cursor S on the screen; if E is selected, move Cursor E;
if both are selected, move them at the same time.
5. Place Cursor S on the rising edge of the pulse and Cursor E on the falling edge.
6. Thus at Delta displays the measured time and at Cursor S and Cursor E displays the time
relative to the trigger.
See the figure below for better understanding.
Page 59

Application Examples
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 54
Measuring Rise Time of Pulse
You may need to measure the rise time of the pulse in many application environments, usually, to
measure the rise time between the 10% and 90% levels of the pulse waveform. To do so, follow
the steps below.
1. Click the TIME/DIV key to display the rising edge of the waveform.
2. Click the VOLTS and Vertical Position keys to adjust the waveform amplitude to about 5
divisions.
3. Push the CH1 MENU button.
4. Push the VOLTS option button and select Fine. Click the Vertical Position key to accurately
separate the waveform into 5 divisions.
5. Click the Vertical Positon key to center the waveform. Position the waveform baseline to 2.5
divisions below the center graticule.
6. Press the CURSOR button.
7. Push the Type option button and select Time. Push the Source option button to select CH1.
8. Select Cursor S and place it at the 10% level of the waveform.
9. Select Cursor E and place it at the 90% level of the waveform.
10. The Delta readout in the Cursor Menu is the rise time of the pulse.
See the figure below for better understanding.
Page 60

Application Examples
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 55
Example 3: Analyzing Input Signals to Eliminate 6.3
Random Noise
In certain circumstances, to display a noisy signal on the oscilloscope and to get its details, you
may follow the steps below to analyze this signal.
Observing Noisy Signal
1. Enter the Acquire menu.
2. Push the Type option button and select Real Time.
3. Push the Peak Detect option button.
4. If necessary, enter the DISPLAY menu and set the Contrast option to view the noise more
clearly.
See the figure below for better understanding.
5 divisions
Page 61

Application Examples
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 56
Eliminating Random Noise
1. Enter the Acquire menu.
2. Push the Type option button and select Real Time.
3. Push the Average option button.
4. Push the Averages option button and adjust the number of running averages to watch the
change in the waveform display.
Note: Averaging reduces random noise and let you view the signal details more easily.
See the figure below for better understanding
Example 4: Capturing Single-shot Signal 6.4
You may refer to the following example to easily capture some aperiodic signals like pulses and
glitches.
Page 62

Application Examples
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 57
To set for a single-shot acquisition, follow the steps below.
1. First, set up the oscilloscope probe and the attenuation factor of CH1.
2. Click the vertical VOLTS and horizontal TIME/DIV keys to a proper position for a better
examination of the signal.
3. Enter the Acquire menu.
4. Push the Mode button to select Peak Detect.
5. Push the TRIG MENU button and select Rising for the Slope option. Then adjust the trigger
level properly.
6. Select Single mode to start the acquisition.
Using this feature can help you to capture occasional events more easily. This is an advantage of
the HandHeld oscilloscope.
Example 5: Using X-Y Mode 6.5
Viewing Phase Differences between Two Channel Signals
For example, you need to measure the change in a phase across a circuit network.
Connect the oscilloscope with circuitry and view the input and output of the circuit in XY mode.
Follow the steps below.
1. First, prepare two oscilloscope probes and set the switches to 10X on both probes.
2. Push the CH1 MENU button and set the Probe option attenuation to 10X; push the CH2
MENU button and set the Probe option attenuation to 10X.
3. Connect the CH1 probe to the input of the network, and connect the CH2 probe to the output.
4. Push the AUTO button.
Page 63

Application Examples
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 58
5. Click the VOLTS keys to display approximately the same amplitude signals on each channel.
6. Enter the Display menu.
7. Push the DSO Mode button and select XY.
8. Now the oscilloscope displays a Lissajous pattern to characterize the input and output of the
circuit.
9. Click the VOLTS and Vertical Position keys to properly scale the waveform display.
10. Use the Lissajous's oscillographic method to observe and calculate the phase differences
following the formula below.
As sinθ=A/B or C/D, in which θ is the phase difference angle between channels and A, B, C, D
represent what shown in the figure below, you can get the value of the phase difference angle by
the formula: θ=±arcsin(A/B) or ±arcsin(C/D).
If the principal axes of the ellipse are in the first and third quadrants, the phase difference angle
should be in the first and fourth quadrants, i.e. within (0~π/2) or (3π/2~2π). If the principal axes of
the ellipse are in the second and fourth quadrants, the phase difference angle should be in the
second and third quadrants, i.e. within (π/2~π) or (π-3π/2). See the figure below for better
understanding.
Example 6: Triggering on Pulse Width 6.6
Triggering on a Specific Pulse Width
While testing the pulse width of a signal in a circuit, you may need to verify the pulse width is
consistent with the theoretic value. Or even if the edge triggering shows that your signal has the
same pulse width with the specific signal, you still doubt about the result. Then you can follow the
steps below.
1. Set the Probe option attenuation to 10X.
A
B
C
D
Signal Horizontal
Centering
Page 64

Application Examples
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 59
2. Push the AUTO button to trigger a stable waveform display.
3. Push the Single Cycle option button in the Autoset menu and read out the signal pulse width.
4. Push the TRIG MENU button.
5. Select Pulse for the Type option; Select CH1 for the Source option; Click the TRIGGER
LEVEL key to set the trigger level at the bottom of the signal.
6. Select the When option button and select ‘=’.
7. Push the Set Pulse Width option button. Set the pulse width to the value read out in Step 3.
8. Click the TRIGGER LEVEL key to set the pulse width to the value read out in Step 3.
9. Push the More option button and select Normal for the Mode option. Once triggering on
normal pulses, the oscilloscope can give a stable waveform display.
10. When option is set to >, < or ≠ and there appear any aberrant pulses that meet the specified
condition, the oscilloscope will trigger. For example, the signal contains such aberrant pulses
as shown below, you may select ‘≠’ or ‘<’ to trigger on the pulse.
As shown in the above figure, you can get a stable waveform display if inputting a square wave at
the frequency of 1KHz, with pulse width set to 500μs.
Example 7: Triggering on Video Signal 6.7
Assume that you are monitoring the video signals of a television to see if they are input normally,
and the video signal is of an NTSC system. You can get a stable display by using the video trigger.
Triggering on Video Fields
To trigger on the video fields, follow the steps below.
1. Push the TRIG MENU button to see the Trigger menu.
2. Push F1 to select Video for the Type option.
Page 65

Application Examples
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 60
3. Push the Source option button to select CH1; push the Polarity option button to select Normal;
push the Standard option button to select NTSC.
4. Push the Sync option button to select Odd Field, Even Field or All Fields.
5. Push the Trigger Level button to adjust the trigger level and stabilize video signals.
6. Push the horizontal TIME/DIV and the Vertical Position keys to display on the screen a
complete video signal triggering on a video field.
The figure below shows a stable signal triggering on a video field.
Triggering on Video Lines
To trigger on the video lines, follow the steps below.
1. Push the TRIG MENU button to see the Trigger menu.
2. Select Video for the Type option.
3. Push the Source option button to select CH1; push the Polarity option button to select Normal;
push the Standard option button to select NTSC; push the Sync option button to select Line
Number.
4. Click the Trigger Level key to adjust the trigger level and stabilize video signals.
5. Adjust the line number (NTSC: 0-525 lines).
6. Click the horizontal TIME/DIV and the vertical VOLTS keys to display on the screen a
complete video signal triggering on a video line. See the figure below.
Page 66

Application Examples
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 61
Example 8: Using Slope Trigger to Capture Particular 6.8
Slope Signal
In many occasions, we are not only concerned about the edge of the signal, but also want to know
the rise and fall times of the signal. To better observe this kind of signals, we bring in the slope
trigger. Follow the steps below.
1. Push the TRIG MENU button to see the Trigger menu.
2. Select Slope for the Type option.
3. Push the Source option button to select CH1; push the Slope option button to select Rising;
push the Mode option button to select Auto; push the Coupling option button to select DC.
4. Click the ‘Next Page’ button and select Vertical. Adjust V1 and V2 to proper locations. Select
the When option button and set it to ‘=’.
5. Select ‘Time’ and adjust the time until you get a stable display of waveforms. See the figure
below.
Page 67

Application Examples
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 62
Example 9: Using Overtime Trigger to Measure Long 6.9
Pulse Signal
It is not easy to observe some part of a long pulse signal by using the edge or pulse width trigger.
In such case, you can use the overtime trigger by following steps.
1. Push the TRIG MENU button to see the Trigger menu.
2. Select O.T. for the Type option; push the Polarity option button to select Normal; push the
Mode option button to select Auto; push the Coupling option button to select DC.
3. Click the Trigger Level key to adjust the trigger level and stabilize video signals.
4. Adjust the line number (NTSC: 0-525 lines).
5. Clck the horizontal TIME/DIV and the vertical VOLTS keys to display on the screen a
complete video signal triggering on a video line. See the figure below.
Page 68

Application Examples
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 63
Note: The difference between the overtime and the delay triggers is that the overtime
trigger can identify the pulse you need according to your set time and trigger on any point
of the pulse. In the other word, the overtime trigger occurs based on pulse identification. It
is similar to the > mode of the pulse width trigger, but not the same.
Example 10: Using Math Functions to Analyze 6.10
Waveforms
Using math functions to analyze input waveforms is another advantage of the digital oscilloscope.
For example, you want to get the instantaneous difference between two channel waveforms. By
using the math function of the oscilloscope, you can get a better representation of the waveform
on the screen. To observe this signal, follow the steps below.
1. Set the Probe option attenuation to 10X.
2. Open CH1 and CH2 at the same time, both with the attenuation of 10X.
3. Push the AUTO button to trigger a stable waveform.
4. Push the M/R MENU button to see the Math menu.
5. Push the Operation option button and select ‘CH1+CH2’.
6. Click the horizontal TIME/DIV and the vertical VOLTS keys to properly scale the waveform for
easy check.
In addition, the oscilloscope also supports the - and FFT functions. For a detailed analysis on FFT,
refer to Chapter 5.3.1 Math FFT.
Note: You should compensate both probes before performing the math operation;
otherwise, differences in probe compensation will appear as errors in the differential
signal.
As illustrated in the above figure, input a 1KHz sine wave from CH1 and a 1KHz square wave
Page 69

Application Examples
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 64
from CH2.
Follow the above steps to set up the Math menu, and observe the subtracted waveform as shown
in the figure below.
Those in pink are added waveforms.
Example 11: Measuring Data Propagation Delay 6.11
When you doubt that there appear instabilities in a serial data propagation control circuit, you can
set the oscilloscope to measure the propagation delay between the enable signal and the transfer
data.
To set the propagation delay measurement, follow the steps below.
1. Connect two oscilloscope probes respectively to the CS (chip-select) pin and the DATA pin on
the chip.
2. Set the Probe option attenuation to 10X for both probes.
3. Open CH1 and CH2 at the same time, both with the attenuation of 10X.
4. Push the AUTO button to trigger a stable waveform display.
5. Adjust the horizontal and vertical controls to optimize the waveform display.
6. Push the CURSOR button to view the Cursor menu.
7. Push the Type option button and select Time.
8. Select Cursor S and place it on the active edge of the enable signal.
9. Select Cursor E and place it on the data output transition (See the figure below).
Page 70

Application Examples
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 65
10. Read the data propagation delay in the Delta readout.
6.12 Example 12: Back light control
1. Press the UTILITY button, entering the UTILITY menu.
2. Press F5 to page down.
3. After reaching the page four, then press F3 to enter the Display menu.
4. Press F5 button to page 3 of display menu, press F3.
5. Set backlight time using the direction button.
CH2
CS
DATA
CH1
CS
DATA
Page 71

Application Examples
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 66
6.13 Example 13: Auto shut down
1. Press the UTILITY button, entering the UTILITY menu.
2. Press F5 to page down.
3. After reaching the page two, then press F3 to enter the Shutdown menu.
4. Press F1 button to select PowerOff, press F2 to select Time then set the time using the
direction button.
5. Press F3 button to confirm.
6. Press F4 buttom to cancel.
Page 72

Multimeter
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 67
Chapter 7 Multimeter
About this chapter
This chapter provides an introduction to the multimeter functions of DSO8000E Series. The
introduction gives guides to show how to use the menus and perform basic measurements.
Connecting the Meter
Use the 4-mm safety banana jack inputs for the Meter functions: 10A , mA, COM,V/Ω/C.
Multimeter Operation Window
Figure 7-1 Multimeter operation window
Description
1) Measurement mode indictors:
DC: Direct electric measurement
AC: Alternating electric measurement
2)The symbol of Mutimeter current mode.
3) Manual/Auto range indictors, among which the MANUAL refers to measuring range in manual
operation mode and Auto means the measuring range in automatic operation mode.
4) The reading value of measurement.
5) The bar graph indictor.
6) DC or AC Measurement mode control.
7) Absolute /relative magnitude measuring control: The sign “||” expresses the absolute magnitude
measuring control and “ ” represents the relative magnitude measuring control.
8) Manually or automatically measuring range control.
Page 73

Multimeter
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 68
9) Measure type, including VOLT, A, OHM, DIODE, CON, CAP.
Operating the Multimeter
If you are in the oscilloscope window, press SCOPE/DMM key, the oscilloscope will switch to the
multimeter mode window.Then the screen will display the measure mode window that was in use
the last time before you quit multimeter measure. When you switch to the multimeter measurement
the first time, the default measure mode is DC voltage mode.
Measuring Resistance Values
To measure a resistance, do the following:
1) Press the F1 key to select OHM then resistance measurement window appears on the screen.
2) Insert the black lead into the COM banana jack input and the red lead into the V/O/C banana jack
input.
3) Connect the red and black test leads to the resistor. The resistance value is shown on the screen
in Ohm.
Then, the screen will look like the following figure 7-2.
Figure 7-2 Resistance Measurement
Making a Diode Measurement
To make a measurement on the diode, do the following:
1) Press the F1 key to select DIODE and a diode symbol appears at the top of the screen. .
2) Insert the black lead into the COM banana jack input and the red lead into the V/O/C banana jack
input.
3) Connect the red and black leads to the diode and the voltage value of the diode is displayed on
the screen in volt.
Then, the screen will look like the following figure 7-3.
Page 74

Multimeter
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 69
Figure 7-3 Diode Measurement
Making an On-off Measurement
To perform an On-off test, do the following:
1) Press the F1 key to select CON and then On-off indictor appears on the top of the screen.
2) Insert the black lead into the COM banana jack input and the red lead into the V/O/C banana jack
input.
3) Connect the red and black leads to the tested points. If the resistance value of the tested points
is less than 30 Ω, you will hear beep sound from the test tool.
Then, the screen will look like the following figure 7-4.
Figure 7-4 On-off Measurement
Page 75

Multimeter
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 70
Making a Capacitance Measurement
To measure a capacitance, do the following:
1) Press the F1 key to select CAP and a capacitor symbol appears on the top of the screen.
2) Insert the black lead into the COM banana jack input and the red lead into the V/O/C banana jack
input.
3) Connect the red and black leads to the capacitor and the capacitance value is displayed on the
screen in µF or nF.
Then, the screen will look like the following figure 7-5.
Note: Before testing on low capacitance, please press【||/△】to make zero for a better accuracy.
Figure 7-5 Capacitance Measurement
Making a DC Voltage Measurement
To measure a DC voltage, do the following:
1. Press the F1 key to select VOLT and DC appears at the top of the screen.
2. Insert the black lead into the COM banana jack input and the red lead into the V/O/C banana jack
input.
3.Connect the red and black leads to the measured points and the voltage value of measured
points is displayed on the screen.
Then ,the screen will look like the following figure 7-6.
Page 76

Multimeter
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 71
Figure 7-6 DC voltage Measurement
Making an AC Voltage Measurement
To measure the AC voltage, do the following:
1) Press the F1 key to select VOLT and DC appears on the screen.
2) Press the F2 key and AC appears on the screen.
3) Insert the black lead into the COM banana jack input and the red lead into the V/O/C banana jack
input.
4) Connect the red and black leads to the measured points and the AC voltage value of measured
points will be displayed on the screen.
Then, the screen will look like the following figure 7-7.
Figure 7-7 AC voltage Measurement
Making a DC Current Measurement
Page 77

Multimeter
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 72
To measure a DC current which is less than 600 mA , do the following:
1) Press the F1 key to select A and then DC appears on the screen. The unit on the main reading
screen is mA. Press F3 to switch the measurement between mA and 10A. 600mA is acquiescently.
2) Insert the black lead into the COM banana jack input and the red lead into the mA banana jack
input.
3) Connect the red and black leads to the measured points and the DC current value of measured
points will be displayed on the screen.
Then, the screen will look like the following figure 7-8.
Figure 7-8 DC current Measurement for 600 Measurement
To measure a DC current which is larger than 600 mA, do the following:
1) Press the F1 key to select A and then DC appears on the screen. The unit on the main reading
screen is mA.
2) Press F3 key to switch to 10A measurement, the unit on the main reading screen is A.
3) Insert the black lead into the COM banana jack input and the red lead into the 10A banana jack
input.
4) Connect the red and black leads to the measured points and the DC current value of the
measured points will be displayed on the screen.
5) Press F2 to return to 600 mA measurement.
Then, the screen will look like the following figure 7-9.
Page 78

Multimeter
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 73
Figure 7-9 DC Current Measurement for 10A
Making an AC Current Measurement
To measure an AC current which is less than 600 mA, do the following:
1) Press the F1 key to select A and then DC appears on the screen. The unit on the main reading
screen is mA,and mA will display on the bottom of the screen, press F2 to switch the measurement
between mA and 10A. 600mA is acquiescently.
2) Press the F2 key once and AC will display on the bottom of the screen.
3) Insert the black lead into the COM banana jack input and the red lead into the mA banana jack
input.
4) Connect the red and black leads to the measured points and the AC current value of measured
points will be displayed on the screen.
Then, the screen will look like the following figure 7-10.
Figure 7-10 AC Current Measurement for 600 mA
Page 79

Multimeter
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 74
To measure an AC current which is larger than 600 mA, do the following:
1) Press the F1 key to select A and then DC appears on the screen. The unit on the main reading
screen is mA.
2) Press F3 key to switch to10A measurement, the unit on the main reading screen is A.
3) Press the F1 key once and AC will display on the bottom of the screen.
4) Insert the black lead into the COM banana jack input and the red lead into the 10A banana jack
input.
5) Connect the red and black leads to the measured points and the AC current value of the
measured points will be displayed on the screen.
6) Press F3 to return to 600 mA measurement.
Then, the screen will look like the following figure 7-11.
Figure 7-11 AC Current Measurement for 10A
Taking a Relative Measurement
A currently measured result relative to the defined reference value is displayed in a relative
measurement.
The following example shows how to take a relative measurement. At first, it is required to
acquire a reference value.
1) Press the OHM.
2) Insert the black lead into the COM banana jack input and the red lead into the V/O/C banana jack
input.
3) Connect the red and black test leads to the resistor. The resistance value is shown on the screen
in Ohm.
4) When the reading leveling off, press F2 key and then ||/△is displayed on the top of the screen.
The saved reference value is displayed beside.
Then, the screen will look like the following figure 7-12.
Page 80

Multimeter
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 75
Figure 7-12 Relative Measurement
Selecting Automatic/Manual Range Adjustment
The default range mode of the instrument is automatic range. Suppose you are using the
DC voltage mode, to switch to the manual range, perform the following steps:
1) Press F3 key to enter the manual range mode and then Manual is displayed on the top of the
screen.
2) Under the manual range mode, the measuring range is increased by a stage when pressing F4
key each time, and when reaching the highest stage, it jumps to the
lowest stage by pressing F4 key once again.
3) Press F3 key to switch back to the automatic range mode and then Auto is displayed on the top
of the screen.
Attention: capacitance measurement without manual range mode.
Then,the screen will look like the following figure 7-13.
Figure 7-13 The Manual Range Mode
Page 81

Recorder
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 76
Chapter 8 Recorder
About this Chapter
This chapter provides a step-by-step introduction to the recorder functions of DSO8000E series
Handheld Digital Oscilloscope. The introduction gives basic examples to show how to use the
menus and perform basic operations.
The recorder mainly includes the following functions:
Trend Plot: Trend plot is to save the measurements in the memory and then plot a graph of Scope
or Meter measurements as a function of time. The maximal recording length of trend plot is 1.2M
data points.
Waveform Recorder: Record real time waveform without gap or space. That is to say every time
the device can save all captured waveform data and then replay them. The maximal recording
length of waveform recorder is 8M data points.
Page 82

Recorder
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 77
Multimeter Trend
8.1
1. Current recorded time
2. The percentage of the current data in the whole memory
3. The parameter value of the recorded data at the moment
4. The real time
5. The sample time of the cursor point.
6. The parameter measurement value of the cursor point
7. Vertical scale
8. Vertical scale
Multimeter Trend Function Menu
Function
Setting
Instruction
Restart
Quilt the current data and start to record afresh.
Sa Rate
10Sa…0.05Sa
Set sampling rate
Page 83

Recorder
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 78
Display mode
normal
Display the recorded data up to the minute.
All view
Display all dots.
Record Status
Run
Record data automatically
Stop
Stop record data
1/2 Enter the second page of the menu
Manual
Off
Record data automatically
On
Record data manually. A Record presses a record.
Save
Save the trend to the U disk or SD.
Exit Exit the trend.
Multimeter trend application example
Start trend function
Operation steps:
1. Input a measured signal correctly. See chapter 7 Multimeter.
2. Press 【F4】or【F5】to enter Trend at the multimeter main menu.
Also user can press "RECORDER" button to enter the "Trend" and press 【F1】 to choose
DMMTrend.
The device will record the measurement value of the input port continuously and plot
measurements over time.
3. Press【F4】to stop or run recording data.
4. At the second page of the menu you can choose manual or auto mode to record the data.
After select Manual as “On”, record data manually. A Record presses a record.
Display the record data
5. Press 【F3】 to choose data display mode.
Normal mode: the screen displays the data up to the minute. The recorded data before saved in
the memorizer.
All view mode: the screen display all recorded data in the memorizer.
6. Data analysis: move cursor, analyzing data over time. Please press direction key to move
cursor.
Save the trend
7. At the second page of the menu, press 【F4】to save the trend.
File List: Open or close the file list.
Save: Save the trend to the U disk.
Recall: Recall the trend from the U disk.
Return: Return to the previous page.
Media: Choose a place to save.
8. Press 【Exit】to exit trend.
Page 84

Recorder
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 79
Oscilloscope Trend
8.2
Scope Trend Function Menu
Option
Setting
Instruction
Restart
Quilt the current data and start to record afresh.
Source
Select the source
CH1, CH2
Param
Choose the
parameter to be
measured.
Mean, Pk-Pk, Frequency, Period, Minimum, Maximum
Status
Run
Continue recording data
Stop
Stop or continue recording data
1/2 Enter the second page of the menu.
Display
Normal
Display the data up to the minute
View All
Display all date in a compressing proportion
Manual
Off
Record data automatically
On
Record data manually. A Record presses a record.
Save/Recall
Save the trend to the U disk or SD.
Exit Exit the trend.
First choose a source and a measurement. You can choose the recorder functions from the
waveform recorder main menu. To open the main menu, do the following:
Press 【Recorder】 to open the recorder main menu.
Scope Trend Application Example
Operation steps:
Open trend function
1. Input a signal to CH1 or CH2.
2. Press【Recorder】 to enter the recorder main menu.
3. Press【F2】to choose ScopeTrend.
4. Choose measured parameter and start recording the trend plot.
5. Press【F4】to pause or continue recording data.
Display recorded data
6. Press 【F5】to enter the second page of trend plot menu.
7. Press 【F1】to choose data display mode.
Normal: the screen displays the data up to the minute.
View All: the screen displays all data in the memory.
8. Data analysis: move cursor, analyzing data over time.
Save the trend
Page 85

Recorder
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 80
9. At the second page of the menu, press 【F4】to save the trend.
File List: Open or close the file list.
Save: Save the trend to the U disk.
Recall: Recall the trend from the U disk.
Return: Return to the previous page.
Media: Choose a place to save.
10. Press 【Exit】 to exit trend.
Oscilloscope Recorder 8.3
Press 【Recorder】to enter recorder main menu under scan time base, then press 【F3】 to
choose ScopeRec.
Waveform Recorder Function Menu
Option
Instruction
Record
Record waveform without gap.
Replay
Replay the recorded waveform.
Return
Exit waveform recorder function
Waveform Recorder Saving Mode Function Menu
Option
Instruction
Start
Begin to record waveform
Pause
Stop to record waveform
Restart
Mode
Continuous:
Single:
1/2
Enter the second page of the menu.
Save
Save the record to the U disk or SD.
Media
Choose a place to save record.
Return
Exit the submenu and return to the waveform recorder main
2/2
Return to the first page of the menu
Page 86

Recorder
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 81
Waveform Recorder Replaying Mode Function Menu
Option
Instruction
Start
Pause playing waveform automatically, you can change the time base to
observe the waveform in the memory.
Pause
Continue playing waveform automatically, you can change the time base
to observe the waveform in the memory.
Restart
Replay the waveform
Mode
Continuous:
Single:
1/3
Enter the second page of the menu.
Recall
Recall the waveform stored in the memory
File List
Open or close file list
Unit
Frame: When replaying the screen waveform updates the whole screen
according to the time of sampling every frame data
Point: When replaying, the screen waveform updates every dot from left
to right.
2/3
Enter the third page of the menu.
Prev
Back the waveform and then play.
Next
Speed the playing of the waveform.
Return
Exit the replaying menu.
3/3
Return to the first page of the menu
Waveform recorder application example
Startup the waveform recorder function:
1. Press【Recorder】 to open the main menu.
2. Press【F3】to choose scopeRec.
3. Press【F1】to set the waveform recorder. Such as set “Continuous” and “Single”.
4. Press【F1】to start recording data.
The waveform will not move right and the recorded data saved to memory. The recorded time will
be different according to the time base. You can pause or stop at any time.
Waveform replay
Page 87

Recorder
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 82
5. Press 【F2】to replay waveform.
You can replay the recorded waveform for several times and you can Prev or Next at any time.
6. Press 【F5】to exit the waveform recorder.
Page 88

Waveform Generator
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 83
Chapter 9 Waveform Generator
DSO8000E Series oscilloscope is equipped with waveform generator function, with one channel of
arbitrary waveform output, 8 Bits output, synchronized signal out puts. User can edit the waveform
by the mouse or choose the regular waveforms such as Sine, Ramp, Square, Trapezia, DC,
Exponent, AM/FM.
Waveform Generator 9.1
Waveform Parameter Setup
Select a wave type, and you can set the “Parameters” by the near key.
Generate the Sine waveform
To output a Sine Wave, please do the following steps:
1. Press F1 button to select "Sine".
2. Set the Wave Parameter:
Frequency: Set the output wave frequency.
Amplitude: Set the output wave amplitude.
Offset: Set the output wave vertical level offset.
Generate the Ramp waveform
To output a Ramp Wave, please do the following steps:
1. Press F1 button to select "Ramp".
2. Set the Wave Parameter:
Frequency: Set the output wave frequency.
Amplitude: Set the output wave amplitude.
Offset: Set the output wave vertical level offset.
Duty: The duty of the output wave.
Generate the Square waveform
To output a Square Wave, please do the following Step:
1. Press F1 button to select "Square".
2. Set the Wave Parameter:
Frequency: Set the output wave frequency.
Amplitude: Set the output wave amplitude.
Offset: Set the output wave vertical level offset.
Page 89

Waveform Generator
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 84
Duty: The duty of the output wave.
Generate the Trapezia waveform
To output a Trapezia wave, please do the following steps:
1. Press F2 button to select "Trap".
2. Set the Wave Parameter:
Frequency: Set the output wave frequency.
Amplitude: Set the output wave amplitude.
Offset: Set the output wave vertical level offset.
Duty: The duty of the output wave.
Rise Duty: Set the output wave rise duty.
High Duty: Set the output wave high duty.
Fall Duty: Set the output wave fall duty.
Generate the Exponent waveform
To output an Exponent Waveform, please do the following steps:
1. Press F1 button to select the wave "Exp".
2. Set the Wave Parameters:
Frequency: Set the output wave frequency.
Amplitude: Set the output wave amplitude.
Offset: Set the output wave vertical level offset.
Phase: Set the output wave phase.
Time: Set the ouput wave Tao param.
Exp Type: Set the output wave slope.
Generate the AM/FM waveform
To output an AM/FM Wave, please do the following Steps:
1. Press F1 button to select "AM/FM Wave".
2. Set the Wave Parameter:
Frequency: Set the output wave frequency.
Amplitude: Set the output wave amplitude.
Offset: Set the output wave vertical level offset.
Depth: Set the output wave Depth.
Type: Change the output wave "AM" into "FM"
Max Freq: Set the output wave Max Frequency.
FM: Change the output wave "AM" into "FM".
Page 90

Waveform Generator
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 85
Output waveform: Set output type to continuous, single or OFF.
Continuous: Continuous output waveform.
Ext Trig:
When an edge of the external trigger signal is triggered, even if the external trigger signal is
disconnected, the waveform can be output continuously. If the external trigger signal is
disconnected, only when the settings are changed, the settings in the front will be cleared.
Sync:
Burst: Press the button, the signal will output continuous; Press the button again, the signal will
stop output. Sync output is synchronized signal of output.
Single: Press once, output waveform once.
Ext Trig:
When an edge of the external trigger signal is triggered, the signal output once. If the external
trigger signal is continuous, the waveform can output continuously. If the external trigger signal
is disconnected, the waveform will stop output.
Sync:
Burst: Press the button once, a cycle waveform output once; if you do not press, no signal
output. Sync output is synchronized signal of output.
OFF: Not output wavefrom.
Notes:
External trigger signal port: For the model of waveform generator function, it can be used as an
external trigger of the oscilloscope and waveform generator.
Synchronized output port: Only for the model with waveform generator function.
Page 91

Waveform Generator
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 86
Generate Arbitrary waveform
9.2
User can edit arbitrary waveform directly under DDS interface for the device, or use DDS_ARB
software to generate a waveform file and load it again.
9.2.1 Edit Arb waveform by DDS_ARB
User can use DDS-ARB software to edit arbitrary waveform.
1. Install software
Please double click “Setup.exe” in Tools folder and install DDS-ARB software according to
installation wizard.
After DDS-ARB software installed successfully, you can see DDS-ARB icon on desktop.
2. Install driver
Power on and connect DSO8000E to PC via USB cable. Right click “Computer
Management->Device Manager” to install the driver.
3. The menu:
1) File: Save or open the .csv file.
2) Edit: Edit points and zoom in/out the display waveform.
3) Wave parameter: Set the parameter of waveform.
4) Display:Change the color of Background, XY Line, Curve, Cursor.
Page 92

Waveform Generator
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 87
5) Utility:
Click “Utility->Language” to change language to English or Chinese.
4. Edit arbitrary waveform by software
1) Double-click the icon to open the software.
2) Click “Wave Parameter->Parameter” to set waveform frequency.
3) Click “Wave Parameter->Arb” and drag left mouse to edit points.
Page 93

Waveform Generator
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 88
Also user can click “Edit->Points Edit” to set pointindex and voltage.
4) Click “Wave Parameter->Download” to download the edited waveform to DSO8000E,
then you can view the waveform by oscilloscope as follows:
5) Also, user can click “File->Save CSV”, and save CSV file to U disk or other paths.
The time interval between two points
The quantity of the points per cycle
Page 94

Waveform Generator
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 89
The relation: Frequency =
1
Size∗Deltatime
.
Insert U disk to the USB port of the device, select wave as "Arb". Then press "Recall"
menu to recall saved file. View the waveform by oscilloscope as follows:
9.2.2 Edit Arb waveform by slave computer
1. Press F1 button to select "Arb".
2. Set the Wave Parameter
All points move: The setting quantity of the X axis points.
Where move: Where to start setting.
Y points move: The setting quantity of the Y axis points.
Frequency: Set the output wave frequency.
Amplitude: Set the output wave amplitude.
Offset: Set the output wave vertical level offset.
3. Output waveform: Set output type to continuous, single or OFF.
Continuous: Continuous output waveform.
Ext Trig:
External trigger signal port: For the model of waveform generator function, it can be used as an
external trigger of the oscilloscope and waveform generator.
Page 95

Waveform Generator
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 90
When an edge of the external trigger signal is triggered, even if the external trigger signal is
disconnected, the waveform can be output continuously. If the external trigger signal is
disconnected, only when the settings are changed, the settings in the front will be cleared.
Sync:
Synchronized output port: Only for the model with waveform generator function.
Burst: Press the button, the signal will output continuous; Press the button again, the signal will
stop output. Sync output is synchronized signal of output.
Single: Press once, output waveform once.
Ext Trig:
When an edge of the external trigger signal is triggered, the signal output once. If the external
trigger signal is continuous, the waveform can output continuously. If the external trigger signal
is disconnected, the waveform will stop output.
Sync:
Burst: Press the button once, a cycle waveform output once; if you do not press, no signal
output. Sync output is synchronized signal of output.
OFF: Not output wavefrom.
4. Save, recall or delete .csv file
Save: Save the edited waveform as .csv file in U disk.
Recall: Load .csv file in U disk.
Delete: Delete .csv file in U disk.
Page 96

Waveform Generator
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 91
Attention: For the editing of arbitrary waveform, DDS-ARB is much more convenient than slave
computer. So it is recommended to use DDS-ARB to edit arbitrary waveform.
Page 97

Troubleshooting
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 92
Chapter 10 Troubleshooting
Problem Settlement 10.1
1. If the oscilloscope does not start up at power on, follow these steps:
1) Check the power cord to verify it has been connected properly;
2) Check the power on/off button to ensure it has been pushed;
3) Then restart the oscilloscope.
Contact your local distributor or directly keep touch with our Support department if the oscilloscope
still can not be turned on normally.
2. If there is no display of waveforms on the screen when the oscilloscope is turned on,
follow these steps:
1) Check the probe to assure its proper connection to the input BNC;
2) Check the channel switch (such as CH1, CH2 menu buttons) to make sure it has been turned
on;
3) Check the input signal to verify it has been connected to the probe correctly;
4) Affirm that all measured circuits have signals to output;
5) Turn up the magnitude for DC signals with large magnitude;
6) In addition, you may press the Auto Measure button to perform an automatic detection of
signals at first.
Contact our Technical Support department in time if there is still no display of waveforms.
3. If the waveform of the input signal is distorted seriously, follow these steps:
1) Check the probe to assure its proper connection to the channel BNC;
2) Check the probe to assure its good connection to the measured object;
3) Check the probe to verify it has been well calibrated. Otherwise, refer to the content about
calibration described in this manual.
4. If the waveform is rolling continuously on the screen but can not be triggered, follow
these steps:
1) Check the trigger source to make sure it consistent with the input channel;
2) Check the trigger level to assure its correct adjustment.
3) Check the trigger mode to confirm it is a right choice for the input signal. The default trigger
mode is edge trigger. However, it is not suitable for all kinds of input signals.
Page 98

Specifications
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 93
Chapter 11 Specifications
Technical Specifications 11.1
All specifications herein mentioned apply to the DSO8000E series oscilloscopes. Before checking
an oscilloscope to see if it complies with these specifications, make sure it meets the following
conditions:
The oscilloscope must have been operating continuously for twenty minutes under the
specified operating temperature.
The Do Self Cal operation must be performed through the Utility menu if the operating
temperature changes by more than 5℃.
The oscilloscope must be within the factory calibration interval.
All specifications are guaranteed unless noted ‘typical’.
Oscilloscope Specifications
Horizontal
Sample Rate Range
1GS/s
Waveform Interpolation
(sin x)/x
Record Length
Maximum 2M samples per single-channel; maximum 1M
samples per dual-channel (4K, 40K, 512K, 1M optional)
TIME/DIV Range
DSO8072E
DSO8102E
DSO8152E
DSO8202E
4ns/div to 2Ks/div, in a 2, 4, 8
sequence
2ns/div to 2Ks/div, in a 2, 4,
8 sequence
Sample Rate and
Delay Time Accuracy
±50ppm over any ≥1ms time interval
Delta Time Measurement
Accuracy
(Full Bandwidth)
Single-shot, Normal mode
± (1 sample interval +100ppm × reading + 0.6ns)
>16 averages
± (1 sample interval + 100ppm × reading + 0.4ns)
Sample interval = s/div ÷ 200
Position Range
DSO8072E DSO8102E
4ns/div to 8ns/div
(-8div × s/div) to 20ms
20ns/div to 80μs/div
(-8div × s/div) to 40ms
200μs/div to 2Ks/div
(-8div × s/div) to 2Ks
DSO8152E DSO8202E
2ns/div to 10ns/div
(-4div × s/div) to 20ms
Page 99

Specifications
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 94
Vertical
A/D Converter
8-bit resolution,
each channel sampled simultaneously
VOLTS Range
2mV/div to 100V/div at input BNC
Position Range
±400V(100V/div-20V/div)
±50V(10V/div-5V/div)
±40V(2V/div-500mV/div)
±2V(200mV/div-50mV/div)
±400mV(20mV/div-2mV/div)
Selectable Analog Bandwidth Limit,
typical
20MHz
Low Frequency Response (-3db)
≤10Hz at BNC
Rise Time at BNC, typical
DSO8072E
DSO8102E
DSO8152E
DSO8202E
<5.0ns
<3.5ns
≤2.3ns
<1.8ns
DC Gain Accuracy
±3% for Normal or Average acquisition mode, 100V/div
to 10mV/div
±4% for Normal or Average acquisition mode, 5mV/div
to 2mV/div
DC Measurement Accuracy,
Average Acquisition Mode
Measurement Type: Average of ≥16 waveforms with
vertical position at zero
Accuracy: ± (3% × reading + 0.1div + 1mV) when
10mV/div or greater is selected
Measurement Type: Average of ≥16 waveforms with
vertical position not at zero
Accuracy: ± [3% × (reading + vertical position) + 1% of
vertical position + 0.2div]
Add 2mV for settings from 2mV/div to 200mV/div; add
50mV for settings from 200mV/div to 5V/div
Volts Measurement Repeatability,
Average Acquisition Mode
Delta volts between any two averages of ≥16
waveforms acquired under same setup and ambient
conditions
Note: Bandwidth reduced to 6MHz when using a 1X probe.
Trigger
Trigger Sensitivity
(Edge Trigger Type)
Coupling
Sensitivity
DC
Source
DSO8072E
DSO8102E
DSO8152E
DSO8202E
CH1
CH2
1div from DC to
10MHz;
1.5div from 10MHz to
Full
1.5div from 10MHz
to 100MHz;
2div from 100MHz
to Full
Page 100

Specifications
DSO8000E Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 95
EXT/5
1V from DC to Full
1V from DC to
100MHz;
1.75V from
100MHz to Full
AC
Attenuates signals below 10Hz
HF Reject
Attenuates signals above 80kHz
LF Reject
Same as the DC-coupled limits for frequencies above
150kHz; attenuates signals below 150kHz
Trigger Level Range
Source
Range
CH1, CH2
±8 divisions from center of screen
EXT/5
±6V
Trigger Level
Accuracy, typical
(Accuracy is for
signals having rise
and fall times ≥20ns)
Source
Accuracy
CH1, CH2
0.2div × volts/div within ±4 divisions from center of screen
EXT/5
± (6% of setting + 200mV)
Set Level to 50%,
typical
Operates with input signals ≥50Hz
Note: Bandwidth reduced to 6MHz when using a 1X probe.
Video Trigger Type
Source
Range
CH1, CH2
Peak-to-peak amplitude of 2 divisions
EXT/5
2V
Signal Formats and
Field Rates, Video
Trigger Type
Supports NTSC, PAL and SECAM broadcast systems for any field or
any line
Holdoff Range
100ns to 10s
Pulse Width Trigger
Pulse Width Trigger
Mode
Trigger when < (Less than), > (Greater than), = (Equal), or ≠ (Not Equal);
Positive pulse or Negative pulse
Pulse Width Trigger
Point
Equal: The oscilloscope triggers when the trailing edge of the pulse
crosses the trigger level.
Not Equal: If the pulse is narrower than the specified width, the trigger
point is the trailing edge. Otherwise, the oscilloscope triggers when a
pulse continues longer than the time specified as the Pulse Width.
Less than: The trigger point is the trailing edge.
Greater than (also called overtime trigger): The oscilloscope triggers
when a pulse continues longer than the time specified as the Pulse
Width.
Pulse Width Range
Selectable from 20ns to 10s
 Loading...
Loading...