Page 1

Instruction Manual
HI 993310
Portable
Water Conductivity
& Soil Activity Meter
www.hannainst.com
1
Page 2

Dear Customer,
Thank you for choosing a Hanna product.
Please read this instruction manual carefully before using the meter.
This manual will provide you with the necessary information for correct
use of the instrument, as well as a more precise idea of its versatility.
If you need additional technical information, do not hesitate to e-mail
us at tech@hannainst.com.
This instrument is in compliance with the directives.
WARRANTY
All Hanna Instruments meters are warranted for two years against
defects in workmanship and materials when used for their intended
purpose and maintained according to instructions. The electrodes and
the probes are warranted for a period of six months. This warranty
is limited to repair or replacement free of charge.
Damages due to accidents, misuse, tampering or lack of prescribed
maintenance are not covered.
If service is required, contact the dealer from whom you purchased the
instrument. If under warranty, report the model number, date of
purchase, serial number and the nature of the failure. If the repair is not
covered by the warranty, you will be notified of the charges incurred. If
the instrument is to be returned to Hanna Instruments, first obtain a
Returned Goods Authorization number from the Customer Service department and then send it with shipping costs prepaid. When shipping any
instrument, make sure it is properly packaged for complete protection.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION ...................................................... 3
GENERAL DESCRIPTION .............................................................. 3
SOIL ACTIVITY ........................................................................... 4
WATER CONDUCTIVITY ................................................................ 8
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION ...................................................... 12
SPECIFICATIONS....................................................................... 13
CALIBRATION ........................................................................... 14
OPERATIONAL GUIDE ............................................................... 15
PROBE MAINTENANCE .............................................................. 16
BATTERY REPLACEMENT ............................................................ 17
ACCESSORIES ........................................................................... 18
2
Page 3

PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION
Remove the instrument from the packing material and examine it
carefully to make sure that no damage has occurred during shipping.
If there is any noticeable damage, notify your Dealer or the nearest
Hanna office immediately.
The meter is supplied with:
• HI 76304 plastic body, conductivity probe with built-in temperature sensor and 1 m (3.3’) cable
• HI 76305 probe for direct soil measurements with stainless steel
conic tip, built-in temperature sensor and 1 m (3.3’) cable
• one 9V battery & Instruction manual
Note: Save all packing materials until you are sure that the
instrument functions correctly. Any damaged or defective item
must be returned in its original packing materials together
with the supplied accessories.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The soil activity, the conductivity of nutritive solutions, irrigation water
and saturated soil-paste are important parameters for growers and
horticulturists.
With HI 993310 it is possible to directly measure, in a quick and simple
way, the soil activity in the ground as well as the conductivity of irrigation
water, nutritive solutions and saturated soil-paste.
The meter is supplied with two probes: HI 76305 with stainless steel conic
tip for direct soil measurements, and HI 76304 for fertilizer enriched
solutions.
The meter allows readings in two different scales and is provided with two
LED’s for indicating which parameter is being tested.
HI 993310 is also equipped with an alarm LED that automatically lights
up if the soil is too dry, or nutritive substances are lacking.
Calibration for conductivity measurements can be performed with a simple
knob located on the front of the meter, and, since the conductivity and
the soil activity are correlated parameters, the soil activity measurements
are calibrated through the conductivity calibration.
Conductivity measurements are influenced by temperature, while the soil
activity depends on the soil texture and its hydric property; both the
supplied probes incorporate a temperature sensor which allows the meter
to automatically compensate for the temperature variations.
HI 993310 comes in a rugged splashproof case suitable to outdoor
measurements.
3
Page 4

SOIL ACTIVITY
SOIL ACTIVITY
Plants absorb nutritive elements dissolved in irrigation water. The ion
concentration of the soil solution depends on the type of soil. Soil can
be rich or poor in nutrients depending on its chemical composition
and its property in retaining water and chemical elements. For
example, clay soil retains more water than sandy soil since it holds
more cations and has a greater microporosity, so that there is a
different availability of ions for the roots.
If the soil is dry, fewer ions are at plant’s disposal. This is the reason
why conductivity readings have to be considered referring to water
presence and soil type.
The HI 76305 soil probe makes it easier to control the soil conditions
and to manage the crops.
SOIL PROBE
The HI 76305 soil probe provides a rapid response and an easy way
to test the soil activity in a variety of applications, as fertilization and
irrigation.
How to use the soil probe:
- Insert the probe in the soil where the roots are more dense or
numerous.
- The recommended depth is 10-15 cm (4-6") for lawn and young
plants, 20-30 cm (8-12") for vegetables and small plants.
- For plants with deep roots (e.g. trees, maize, sunflower, etc.), take
measurements at different depths, e.g. 30 and 50 cm (12 and 20").
- Take measurements in more spots to have a representative average.
- The soil has to be wet. If the soil is dry, add demineralized water.
- The probe tip must be in complete contact with the soil. If the
substrate is too soft, press it with your fingers to achieve a proper
contact.
- Wait until the value on the display is stabilized.
FERTILIZATION
By measuring the salt contents in soil and substrates, before and
after the fertilization, it is possible to have information about the soil
fertility and to design an appropriate fertilization plan. Consequently,
the plants will receive the right quantity of nutrients resulting in a
regular and rapid growth, greater resistance to disease and a more
appealing state manifesting their well being.
The younger plants, especially those that have just germinated, are
4
Page 5

particularly sensitive to soil activity. They require a lower quantity of
fertilizer because they utilize the reserve of nutrients in the seed. This
is true even for resistant species such as sugar beet and alfalfa.
Later on, plants can grow faster with proper fertilization, particularly
in conjunction with optimum lighting and temperature.
If slow releasing fertilizers are employed, their effectiveness can be
regularly controlled by testing the soil activity.
HIGH SOIL ACTIVITY
Soluble salts are indispensable for plant nutrition. However, when
dosed in excess, they can cause various anomalies as toxicity,
alteration of the nutrient absorption equilibrium, difficulty in absorbing water, changing of the pH value and damaging of the soil
structure. For accurate pH measurements, use the Hanna HI 99121
pH meter, specially dedicated to soil application.
Some types of soils are naturally rich in salts. Apart from these, an
excessive use of fertilizers must be avoided and particular attention
must be paid to the use of water with high salt concentration.
If high values are detected, use the appropriate techniques to reduce
the presence of salts (washing away irrigation, reduction of fertilizer
dosages, addition of gypsum if the activity is caused by sodium, etc.).
IRRIGATION
Low measured values can be due to dry soil. In this case, add
demineralized water to the soil, and then repeat the tests. Even soils
rich in nutrients can give low values if they are not wet enough.
Irrigation schedules can then be made based on the measured value.
In case of waterlogged soil, very high values indicate stressed plants.
Find in the following pages a table with some indicative values for soil
activity required by some common plants.
5
Page 6
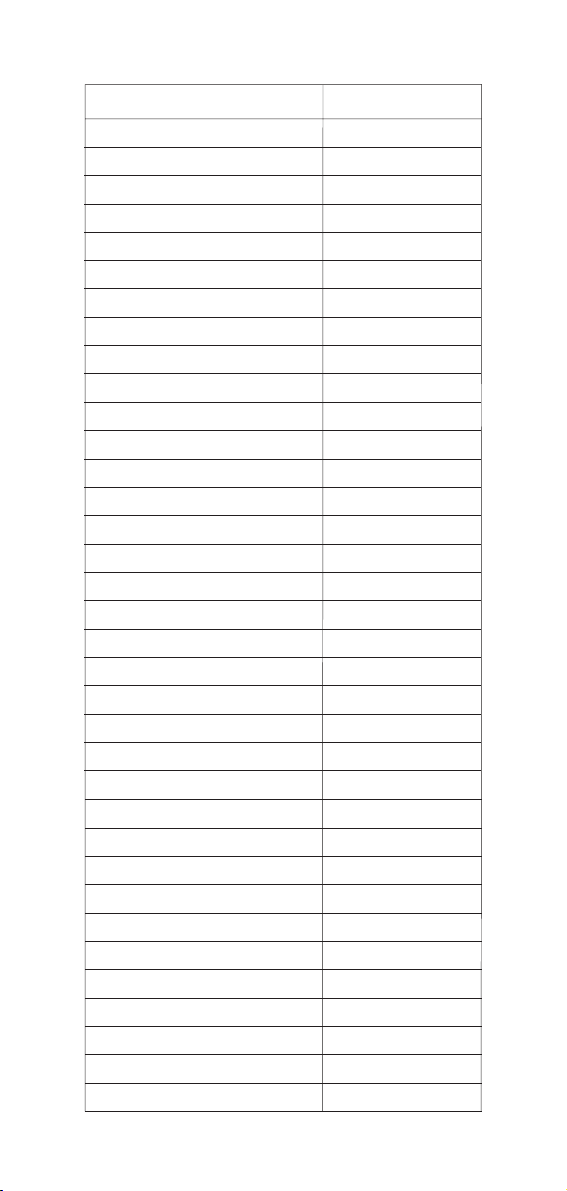
ORNAMENTAL PLANTS & FLOWERS
Amaranthus
Anthurium
Azalea
Begonia
Chrysanthemum
Croton
Cyclamen
Dahlia
Dieffenbachia
Dracaena
Euphorbia
Ficus
Gerbera
Kalanchoe
Lilium
Orchid
Pelargonium
Peperomia
Philodendron
Rose
Saintpaulia
Violet
LAWN IDEAL VALUES
Lawn 0.1-0.4
ORCHARD IDEAL VALUES
Apricot
Orange
Cherry
Lemon
Apple
Walnut
Pear
Peach
Plum
Grapevine
IDEAL VALUES
0.4-0.6
0.2-0.4
0.3-0.5
0.3-0.6
0.4-0.7
0.2-0.4
0.4-0.6
0.4-0.5
0.4-0.6
0.2-0.4
0.4-0.6
0.4-0.7
0.4-0.6
0.2-0.5
0.3-0.6
0.2-0.4
0.2-0.4
0.3-0.5
0.4-0.6
0.2-0.5
0.3-0.5
0.2-0.4
0.2-0.4
0.1-0.3
0.2-0.4
0.1-0.3
0.2-0.3
0.2-0.4
0.2-0.4
0.2-0.4
0.2-0.4
0.2-0.4
6
Page 7

VEGETABLES
& HERBACEOUS CULTIVATIONS
Asparagus
Sugar beet
Carrot
Cauliflower
Cucumber
Onion
Watermelon
Cotton
Lettuce
Maize
Egg plant
Melon
Bean
Strawberry
Wheat
Oat
Potato
Pepper
Pea
Tomato
Soybean
Spinach
Tobacco 0.2-0.4
IDEAL VALUES
0.2-0.4
0.3-0.5
0.2-0.4
0.3-0.5
0.3-0.5
0.2-0.5
0.2-0.4
0.2-0.4
0.3-0.5
0.3-0.5
0.2-0.4
0.2-0.4
0.2-0.4
0.2-0.4
0.2-0.4
0.2-0.4
0.2-0.5
0.2-0.4
0.2-0.3
0.2-0.6
0.2-0.3
0.2-0.4
7
Page 8

WATER CONDUCTIVITY
NUTRITIVE SOLUTIONS
The nutritive solutions constitute one of the most important factors in
determining the plant’s growth and yield. Hence, putting the right
solution at the plant’s disposal is indispensable to get the best result.
Conductivity (EC) of nutritive solutions must be checked regularly to ensure
that it agrees with plant’s requirements. The plants also have seasonal
preferences, typically requiring lower concentrations in the summer.
PLANT PREFERRED EC VALUES
Asparagus
Watermelon
Carrot
Cabbage
Cucumber
Chrysanthemum
Onion
Bean
Strawberry
Lettuce
Egg plant
Melon
Potato
Pepper
Pea
Tomato
Celery
Marrow
1.50-2.00 mS/cm
1.50-2.50 mS/cm
1.50-2.00 mS/cm
2.00-3.00 mS/cm
2.00-3.00 mS/cm
1.50-2.50 mS/cm
1.50-2.00 mS/cm
2.00-2.50 mS/cm
2.00-2.50 mS/cm
1.00-1.50 mS/cm
2.50-3.00 mS/cm
1.50-2.50 mS/cm
2.00-3.00 mS/cm
2.00-3.00 mS/cm
1.00-1.50 mS/cm
2.50-5.00 mS/cm
2.00-2.50 mS/cm
2.00-2.50 mS/cm
8
Page 9

IRRIGATION WATER
The irrigation water must be checked regularly, especially in the hydroponics industry. Conductivity is the most important parameter to check
since plants can be seriously damaged by too high EC value.
Water used for irrigation has been classified in four classes, depending on
its conductivity:
Class I
Class II
Class III
Class IV
Class I: This type of water can be used without any quantity limitation.
Class II: Only a limited quantity should be used depending on the
irrigation techniques and the crop.
Class III: May be used occasionally, but only for tolerant plants and/or
well-drained soils.
Class IV: To be used only if there is no other alternative and as little as
possible.
SATURATED SOIL-PASTE CONDUCTIVITY
The conductivity value of the saturated soil-paste can be used for
classifying the salinity level of the soil and also provides indications
about the soil productivity, depending on plants (see also the table
on next page for reference).
Response of cultivations depends also from different saturated soilpaste conductivity values.
Find below a schematic classification made by the U.S. Salinity Lab.
Riverside - CA.
• EC = 0 mS/cm : the salinity effect is negligible.
• EC = 2 mS/cm : the crop of the more sensible cultivations can be
reduced.
• EC = 4 mS/cm : the crop of many cultivations is reduced.
• EC = 8 mS/cm : only tolerant plants produce a satisfactory crop.
• EC = 16 mS/cm : only a few very tolerant plants produce a
satisfactory crop.
EC < 0.75 mS/cm
EC = 0.75 to 2.50 mS/cm
EC = 2.50 to 4.00 mS/cm
EC > 4.00 mS/cm
9
Page 10

Tolerance of some common plants to the soil conductivity (Ayers &
Westcot, 1976).
• EC0 = maximum of tolerated soil conductivity (salinity).
• EC75 = with this soil conductivity value the 75% of the maximum
yield is produced.
• EC
= minimum soil conductivity value, then the yield starts
100
decreasing.
ORCHARD
Grapevine
Orange & Lemon
Apple & Pear
Walnut
Plum
Peach
Apricot
EC0 (mS/cm)
12
8
8
8
7
6.5
6
VEGETABLES &
HERBACEOUS CULTIVATIONS
Melon
Spinach
Cauliflower
Tomato
Watermelon
Potato
Lettuce
Pepper
Carrot
Onion
Strawberry
Oat
Cotton
Sugar beet
Soybean
Maize
Bean
16
15
13.5
12.5
10
10
9
8.5
8
7.5
4
28
27
24
10
10
6.5
EC75 (mS/cm)
4.1
3.3
3.3
3.3
2.9
2.9
2.6
5.7
5.3
5.5
5.0
4.4
3.8
3.2
3.3
2.8
2.8
1.8
13
13
11
6.2
3.8
2.3
EC
(mS/cm)
100
1.5
1.7
1.7
1.7
1.5
1.7
1.6
2.2
2.0
2.8
2.5
2.5
1.7
1.3
1.5
1.0
1.2
1.0
7.7
5.0
1.7
1.0
8
7
10
Page 11

How to prepare the saturated soil-paste samples for analysis
A) Soil extraction:
1) Extract the soil as indicated below:
- Take one sample for every 1000 m2 (0.25 acre) of homogeneous plot of land.
- For smaller plots, at least 2 samples are recommended (the
more samples are taken, the more representative the end-result
will be).
2) Avoid extracting samples from soil showing obvious anomalies.
Treat this type of soil separately.
3) Take the same quantity of soil for each sample. For example,
use bags with the same dimensions (1 bag per sample).
4) Depth of extraction:
- General: dig and discard 5 cm (2") of the topsoil.
- Herbaceous crops: from 20 to 40 cm (8" to 16").
- Orchards: from 20 to 60 cm (8" to 24'’).
B) Soil sample preparation:
1) Spread the soil samples on the page of a newspaper and let
them dry in a shady place, or in an oven at 40°C (104°F).
2) Crumble the dried soil and mix all the samples together to
obtain an homogeneous mixture. Discard stones and vegetable
residues.
3) From this mixture, take the soil sample for the analysis.
C) Saturated soil-paste preparation:
1) Strain the soil with a 2-mm sieve.
2) Mix for about 30 seconds one part of soil and two parts of distilled
water.
3) Wait for 1 hour.
4) Filter the solution and measure the conductivity.
11
Page 12

FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
1) Liquid Crystal Display (LCD)
2) ON/OFF key
3) Water Conductivity selection key
4) Calibration knob
5) Soil Activity selection key
6) LED indicators
7) Alarm LED
12
Page 13
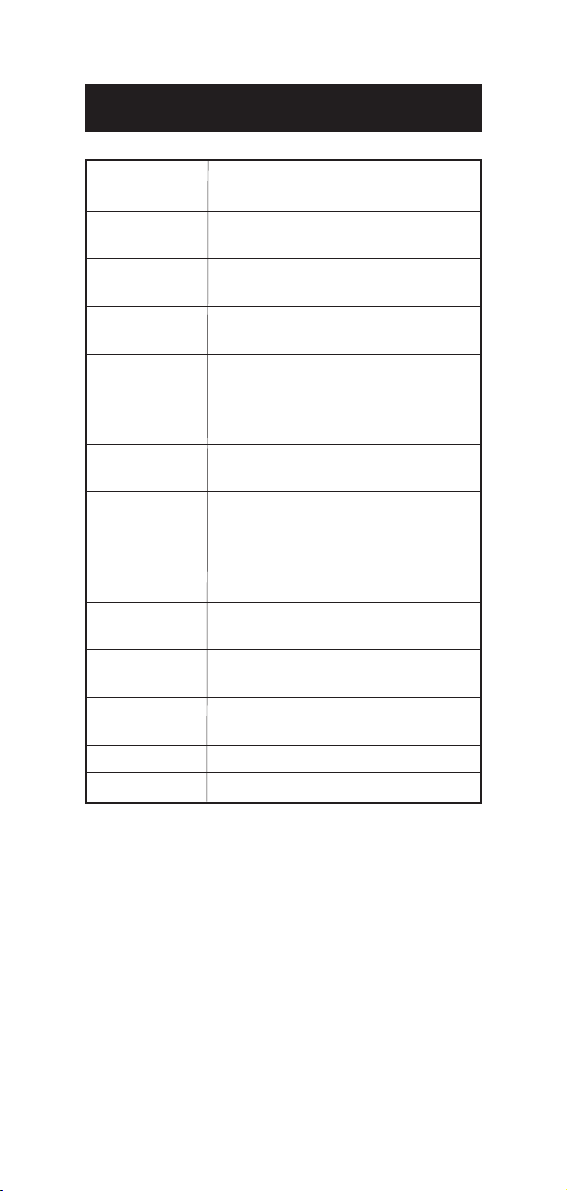
SPECIFICATIONS
Range Act. 0.00 to 1.00
EC 0.00 to 19.99 mS/cm
Resolution Act. 0.01
EC 0.01 mS/cm
Accuracy ±2% F.S. (from 0 to 15.00 mS/cm)
(@20°C/68°F) excluding probe error
Typical EMC ±2 % F.S.
Deviation
Calibration Conductivity: Manual, single-point
through knob
Soil Activity: calibrated through
the conductivity range calibration
Temperature Automatic, from 0 °C to 50 °C
Compensation with ß=2%/°C
Probes (included) HI 76305
stainless steel conic tip, ATC probe
for direct soil meas. with 1 m (3.3’) cable
HI 76304 plastic body, ATC,
conductivity probe with 1 m (3.3’) cable
Alarm Active when soil activity value is
lower than 0.20 and higher than 1.00
Environment 0 to 50°C (32 to 122°F);
max 95% RH non-condensing
Battery Type 1 x 9V (IEC 6LR61) alkaline
Life approx. 100 hours of continuous use
Dimensions 185 x 82 x 52 mm (7.3 x 3.2 x 2.0")
Weight 275 g (9.7 oz.)
13
Page 14

CALIBRATION
The soil activity range is calibrated by performing the calibration of
the conductivity range.
Should the soil activity measurements be not calibrated, contact the
nearest Hanna service center for re-calibration.
CALIBRATION PROCEDURE
• Pour sufficient quantity of a conductivity
calibration solution (e.g. HI 7030) into
a beaker. If possible, use plastic beaker
to minimize any EMC interference.
• Immerse the conductivity probe in the
solution (approximately 5 cm/2").
• Press the ON/OFF button to turn the meter on, and then press
the "W" button to enter the Water Conductivity mode.
• Wait a couple of minutes for thermal equilibrium to be reached.
• Turn the calibration knob until the display shows the conductivity
value of the calibration solutions at 25°C (e.g. 12.88 mS/cm).
• All subsequent measurements will be compensated to 25°C (77°F).
The calibration is now complete and the meter is ready for use.
Notes:
• It is recommended to calibrate the meter at least once a month,
and every time the probe or the battery is changed.
• For more accurate measurements, use a calibration solution close to
the range to be measured. See the "Accessories" section for a
selection of conductivity calibration solutions.
14
Page 15

OPERATIONAL GUIDE
• Each meter is supplied complete with a 9V battery. Slide off the
battery compartment cover on the back of the meter and install
the battery while paying attention to its polarity.
• Connect the proper probe to the meter: use HI 76305 for
measuring soil activity or HI 76304 for conductivity.
• Securely connect the probe to the meter
by aligning the pins with the socket and
pushing the plug in. Always detach the
probe by holding it by the connector
(and not by the cable).
• Make sure the meter has been calibrated before taking any
measurements.
• Immerse the conductivity probe into the
sample to be measured (approximately
5 cm/2"). If possible, use plastic beakers
or containers to minimize EMC interferences.
• For soil activity measurements, directly insert the stainless steel
probe in the soil to a depth of 15 cm (6").
• Turn the instrument on by pressing the
ON/OFF key.
• Press "W" if using conductivity probe for,
or "S" if using soil probe.
Note: Change the probe for taking different type of measurement.
• For Water Conductivity range, wait a couple of minutes for
reaching thermal equilibrium before taking any measurements.
If the sample's temperature is lower than 20°C or higher than
30°C, allow more time for the thermal equilibrium to be achieved.
• The meter provides for a LED alarm when measuring soil activity.
If the LED lights up, the soil is too dry for a proper measurement
or it lacks nutritive substances.
Wet the soil with a moderate quantity of demineralized water
and carry out the measurement again. If the alarm LED lights
up, the soil lacks nutritive elements.
15
Page 16

Note: Before taking any soil measurement, it is recommended to rub
the tip of the HI 76305 soil probe with fine sandpaper.
• After measurements have been completed, switch the meter off, or
it will automatically turn itself off after approximately 2 minutes of
non-use.
• Clean and dry the probes after use (see the below section).
PROBE MAINTENANCE
HI 76305
Clean the tip with fine sandpaper prior to each measurement. After
use, dry the probe with a cloth.
HI 76304
Rinse with tap water after a series of measurements. If a more
thorough cleaning is required, clean the probe with a dry cloth.
After probe cleaning, recalibrate the meter.
Recommendations for Users
Before using this product, make sure that it is entirely suitable for the environment in which
they are used.
Operation of this instrument in residential area could cause unacceptable interference to
radio and TV equipment, requiring the operator to take all necessary steps to correct
interferences.
The metal band at the end of the probe is sensitive to electrostatic discharges. Avoid
touching this metal band at all times.
During calibration of the instrument, ESD wrist straps should be worn to avoid possible
damage to the probe by electrostatic discharge.
Any variation introduced by the user to the supplied equipment may degrade the
instruments' EMC performance.
To avoid electrical shock, do not use these instruments when voltages at the measurement
surface exceed 24VAC or 60VDC.
Use plastic beakers to minimize any EMC interferences.
To avoid damage or burns, do not perform any measurement in microwave ovens.
16
Page 17

BATTERY REPLACEMENT
The instrument is powered by a 9 V battery and is provided with the
Battery Error Prevention System (BEPS), which turns the unit off when
a low battery signal is detected.
When the remaining battery level is less
than 10%, the “V” tag lights up on the
display to indicate a low battery condition.
It is recommended to replace the battery as soon as the low battery
condition is detected.
Remove the cover on the meter's back by applying pressure in the
indicated direction. Unplug the rundown battery and replace it with
a new one.
Battery replacement must only take place in a non-hazardous area
using a 9V alkaline battery.
17
Page 18

ACCESSORIES
CONDUCTIVITY CALIBRATION SOLUTIONS
HI 7030L 12.88 mS/cm calibration solution, 500 mL bottle
HI 7030M 12.88 mS/cm calibration solution, 230 mL bottle
HI 7031L 1.41 mS/cm calibration solution, 500 mL bottle
HI 7031M 1.41 mS/cm calibration solution, 230 mL bottle
HI 7039L 5.00 mS/cm calibration solution, 500 mL bottle
HI 7039M 5.00 mS/cm calibration solution, 230 mL bottle
PROBES
HI 76305 Direct soil probe with stainless steel conic tip, built-in
temperature sensor and 1m (3.3’) cable
HI 76304 Conductivity probe for liquids with built-in temperature
sensor and 1m (3.3’) cable
OTHER ACCESSORIES
HI 710002 Soft carrying case (for meter only)
HI 710009 Blue rubber boot
HI 710010 Orange rubber boot
HI 721313 Rugged carrying case
All rights are reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part is
prohibited without the written consent of the copyright owner.
Hanna Instruments reserves the right to modify the design, construction and appearance of its products without advance notice.
18
Page 19

OTHER PRODUCTS FROM HANNA
• CALIBRATION AND MAINTENANCE SOLUTIONS
• CHEMICAL TEST KITS
• CHLORINE METERS
• DISSOLVED OXYGEN METERS
• HYGROMETERS
• ION SPECIFIC METERS
• MAGNETIC STIRRERS
• Na/NaCl METERS
• pH/ORP METERS
• PROBES and ELECTRODES
• PUMPS
• REAGENTS
• SOFTWARE
• THERMOMETERS
• TITRATORS
• TRANSMITTERS
• TURBIDITY METERS
• Wide Range of Accessories
Most Hanna meters are available in the following formats:
• BENCH-TOP METERS
• POCKET-SIZED METERS
• PORTABLE METERS
• PRINTING/LOGGING METERS
• PROCESS CONTROLLERS (Panel and Wall-mounted)
• METERS FOR FOOD INDUSTRY
For additional information, contact your dealer or the nearest Hanna
Customer Service Center, or e-mail us at tech@hannainst.com.
19
Page 20

SALES AND TECHNICAL SERVICE CONTACTS
Australia:
Tel. (03) 9769.0666 • Fax (03) 9769.0699
China:
Tel. (10) 88570068 • Fax (10) 88570060
Egypt:
Tel. & Fax (02) 2758.683
Germany:
Tel. (07851) 9129-0 • Fax (07851) 9129-99
Greece:
Tel. (210) 823.5192 • Fax (210) 884.0210
Indonesia:
Tel. (21) 4584.2941 • Fax (21) 4584.2942
Japan:
Tel. (03) 3258.9565 • Fax (03) 3258.9567
Korea:
Tel. (02) 2278.5147 • Fax (02) 2264.1729
Malaysia:
Tel. (603) 5638.9940 • Fax (603) 5638.9829
Singapore:
Tel. 6296.7118 • Fax 6291.6906
South Africa:
Tel. (011) 615.6076 • Fax (011) 615.8582
Taiwan:
Tel. 886.2.2739.3014 • Fax 886.2.2739.2983
Thailand:
Tel. (662) 619.0708.11 • Fax (662) 619.0061
United Kingdom:
Tel. (01525) 850.855 • Fax (01525) 853.668
USA:
Tel. (401) 765.7500 • Fax (401) 765.7575
For e-mail contacts and complete list of Sales and
Technical offices, please see www.hannainst.com
20
MAN993310R2
03/05
 Loading...
Loading...