Page 1

CYANIDE
HI 4009
HI 4109
CYANIDE
COMBINATION
Instruction Manual
HI 4009HI 4009
HI 4009
HI 4009HI 4009
HI 4109HI 4109
HI 4109
HI 4109HI 4109
Cyanide Ion
Selective Electrode
Half-cell
Combination
1
Page 2

HI 4009 Cyanide Half-cellHI 4009 Cyanide Half-cell
HI 4009 Cyanide Half-cell
HI 4009 Cyanide Half-cellHI 4009 Cyanide Half-cell
HI 4109 Cyanide Combination ElectrodeHI 4109 Cyanide Combination Electrode
HI 4109 Cyanide Combination Electrode
HI 4109 Cyanide Combination ElectrodeHI 4109 Cyanide Combination Electrode
I. I.
Introduction:Introduction:
I.
Introduction:
I. I.
Introduction:Introduction:
The Hanna HI 4009 and HI 4109 are ion selective electrodes designed for the measurement of Cyanide ions in
aqueous solutions. The HI 4009 is a solid state half-cell
sensor that requires a separate reference. The HI 4109 is a
combination ion selective electrode.
IIII
SpecificationsSpecifications
II.
Specifications
IIII
SpecificationsSpecifications
Type: Solid State electrode with
a Silver halide pellet.
- -
-
Ion(s) measured: Cyanide (CN
- -
)
Measurement range: 10
-2
M to 1X 10
-6
M
260 to 0.26 ppm
Interfering ions: Silver, Sulfide and
Mercury must be absent.
Ratio of interfering ion to
--
-
--
CN
must be less than the
ratio indicated below:
--
-
1.0 for I
500 for Br
500 for Cl
--
Iodide
--
-
--
Bromide
--
-
--
Chloride
Operating Temperature: 0-80°C
Operating pH: 11 to 14 pH
(recommended)
Dimensions: 12 mm (OD) X 120 mm
nominal insertion
(0.47” X 4.72”)
Connection: BNC
WARNING:
HCN GAS IS TOXIC IF BREATHED, OR ABSORBED THROUGH
SKIN. USE OF A HOOD AND PROTECTIVE CLOTHING IS
STRONGLY ADVISED. USE ISA TO ADJUST pH ABOVE 11.
2
Page 3

III. III.
Theory of OperationTheory of Operation
III.
Theory of Operation
III. III.
Theory of OperationTheory of Operation
::
:
::
The HI 4009 or HI 4109 Cyanide electrodes are potentiometric devices used for the rapid determination of free Cyanide ions in effluent, for electroplating bath analysis and
as a detector for titration of cyanide with silver nitrate.
The electrode functions as a sensor or ionic conductor. The
HI 4009 requires a separate reference electrode to complete
its electrolytic circuit. The HI 4109 incorporates a reference
electrode. The silver halide pellet is practically insoluble in
the test solutions being measured and produces a potential
change due to changes in the sample’s ion activity. When
the ionic strength of the sample is fixed by the addition of
ISA, the voltage is proportional to the concentration of Cyanide ions in solution and the electrode follows the Nernst
equation.
E= E
+ 2.3 RT/nF log A
a
ion
E= observed potential
Ea= Reference and fixed internal voltages
R= gas constant (8.314 volt coulomb/K Mole)
n= Charge on ion (1-)
A i=ion activity in sample
T= absolute temperature in K
F= Faraday constant (9.648 x 104 coulomb/mole)
3
Page 4
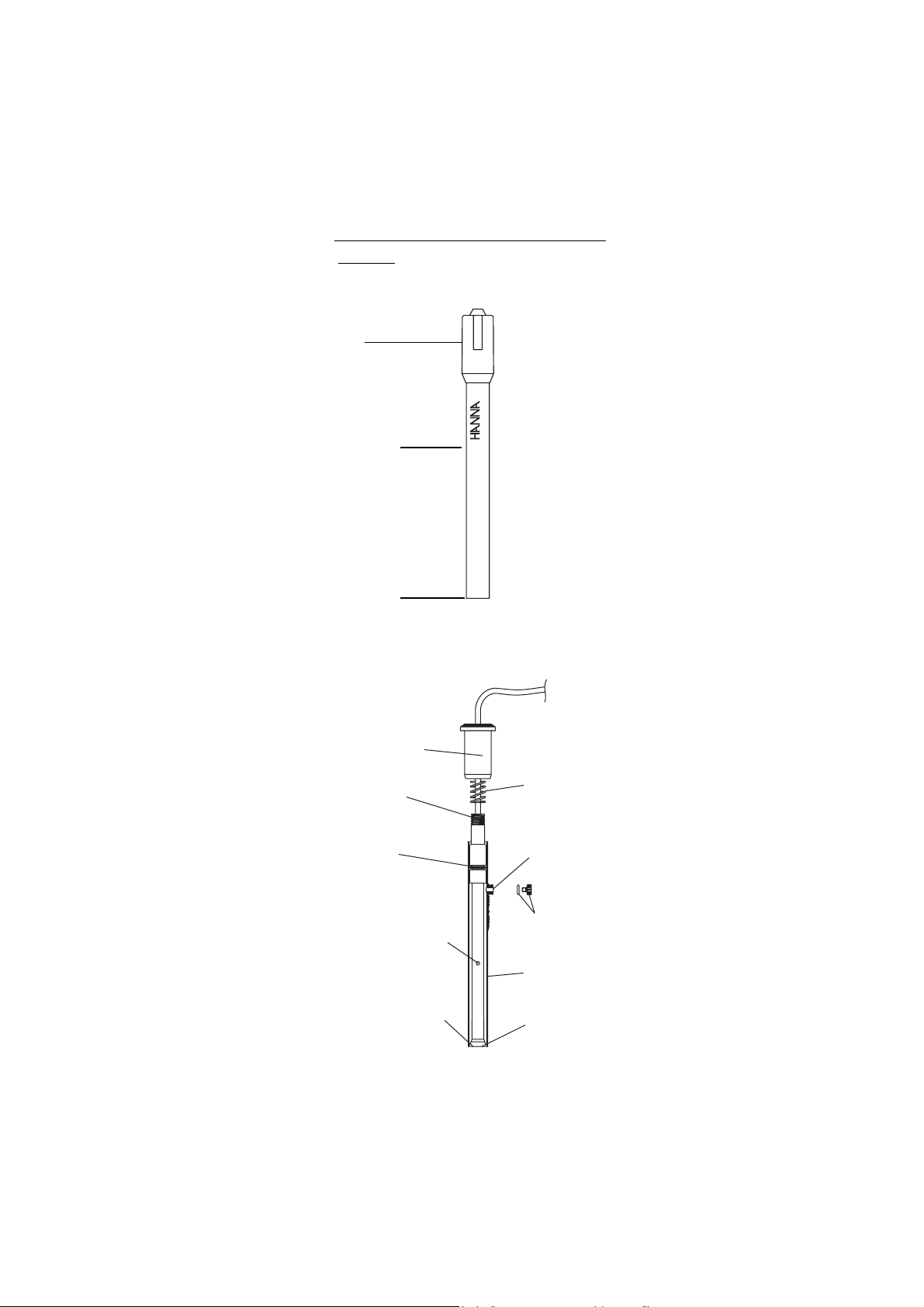
IV. IV.
Design elements of the HI 4009 and HI 4109Design elements of the HI 4009 and HI 4109
IV.
Design elements of the HI 4009 and HI 4109
IV. IV.
Design elements of the HI 4009 and HI 4109Design elements of the HI 4009 and HI 4109
electrodeselectrodes
electrodes
electrodeselectrodes
Cap
HI 4009
Sensor Body
Sensing
Membrane
Upper Cap
Upper
Threads
O-Ring
CYANIDE
Spring
Fill Hole
Ceramic Junction
on Inner Stem
Liquid junction
O-Ring and
Plug
Outer Sleeve
Sensing
Membrane
4
Page 5

V. V.
Equipment required:Equipment required:
V.
Equipment required:
V. V.
Equipment required:Equipment required:
• Hanna HI 5315 Double Junction Reference Electrode
with HI 7072 Fill Solution for HI 4009.
• Hanna HI 4222 pH/ISE/mV meter or other suitable
ion or pH/mV meter. (Note: log/linear graph paper is
useful if an ISE (ion) meter is not available).
• Hanna HI 180 Magnetic Stirrer or equivalent with TFE
coated stirring bars (HI 731320). Note: isolate beakers from stirrer motor heat by placing insulating
material such as foam or cork between them.
• Hanna HI 76404 Electrode Holder or equivalent.
• Plastic beakers (HI 740036P) or other suitable mea-
surement vessel.
VI. VI.
Solutions RequiredSolutions Required
VI.
Solutions Required
VI. VI.
Solutions RequiredSolutions Required
for Cyanide Measurementsfor Cyanide Measurements
for Cyanide Measurements
for Cyanide Measurementsfor Cyanide Measurements
ISA, 500 mL HI 4001-00
User supplied standards:
Note: These solutions should only be used for making more
dilute standards. The sensing surface will be damaged if
submersed in this high a concentration.
Molar Stock solution:
0.01M stock solution (1 Liter): To a one liter volumetric
flask add approximately 300 mL deionized water and 10mL of HI 4001-00 ionic strength (pH) adjuster. On an
analytical balance weigh 0.490g of dry NaCN salt and
transfer to the volumetric flask. Swirl contents until dissolved. Add deionized water to bring the flask to its 1 liter
calibrated mark. Mix thoroughly and store in tightly capped
plastic bottle.
ppm stock solution:
1000 ppm stock solution (1 Liter): To a one liter volumetric
flask add approximately 300 mL deionized water and
10 mL of HI 4001-00 ionic strength (pH) adjuster. On an
analytical balance weigh 1.88g of dry NaCN salt and transfer
to the 1-liter volumetric flask. Swirl contents until dissolved. Add deionized water to bring the flask to its 1 liter
calibrated marking. Mix thoroughly and store in tightly
5
Page 6

capped plastic bottle. Using volumetric pipettes and glassware make dilutions to bracket the concentration of the
samples. Store standards in plastic bottles. Standards with
concentrations < 10-3M should be prepared daily. One mL
of Hanna ISA and pH adjuster (HI 4001-00) should be
added to each 100 mL of sample or standard.
VIIVII
General GuidelinesGeneral Guidelines
VII.
General Guidelines
VIIVII
General GuidelinesGeneral Guidelines
• Use of a hood and protective clothings is strongly
advised. Use ISA to adjust pH above 11.
• Calibration standards and sample solutions should
have the same ionic strength. ISA should be added to
both samples and standards in the same ratio. 1 part
ISA to 100 parts standard is the normal dosing.
• Concentrated samples (>.005 M) should be diluted
before measurement. Multiply the final result by the
corresponding dilution factor.
• For high ionic strength samples, use standard addi-
tion or titration methods.
• Calibration standards and sample solutions should
be at same temperature and at elevated pH.
• The magnetic stirrer may generate heat. Thermally
insulate beaker containing standard or sample from
magnetic stirrer by placing cork or other insulative
sheet between beaker and stirrer plate.
• Calibration standards and sample solutions should
be stirred at the same rate using identical sized TFE
coated stir bars.
• Rinse electrode pair with distilled or deionized water
between samples and gently dab dry with soft disposable absorbent toweling. Do not rub electrodes.
• Presoaking cyanide sensor in a dilute standard will
optimize response. Use concentrations approximately
-3
10
M or less with ISA added.
• A scratched, pitted, or tarnished pellet surface can
cause drift, a loss of low level response, or poor repeatability. Optimum response can be restored by removing the damaged surface with the microabrasive strip
6
Page 7

HI 4000-70.
• Avoid large changes in temperature (thermal shock)
as it may damage the sensor.
• Gas bubbles may form from solution out-gassing due
to temperature change. Gently tap body of sensor to
dislodge them from sensing membrane.
HI 4009
• Remove protective cover from sensor tip.
• Prepare HI 5315 reference electrode by filling electro-
lyte reservoir with HI 7072 fill solution.
• Place sensor and reference electrodes into electrode
holder and connect cable connectors to meter.
HI 4109
• Remove the protective plastic wrap that covers the
ceramic junction before assembling sensor for the first
time.
• HI 7072 reference fill solution should be added daily
to electrolyte reservoir before electrode use.
• During measurement always operate electrode with
the fill hole open.
• During normal use, fill solution will slowly drain out
of the tapered cone junction at the lower portion of the
electrode. Excessive loss (>4 cm drop within 24 hours)
is not normal. If this occurs verify cap is tightened and
the interface between the internal cone and outer
body is free of debris.
• Add fill solution daily to maintain a good head pres-
sure. For optimum response, this level should be maintained and not be allowed to drop more than 2-3 cm
(1-inch) below fill hole. It must cover the ceramic
found on the inner stem.
• If an erratic measurement occurs, check to see if for-
eign matter is seen trapped near the internal cone.
Drain and refill with fresh fill solution.
7
Page 8

VIII. VIII.
Electrode PreparationElectrode Preparation
VIII.
Electrode Preparation
VIII. VIII.
Electrode PreparationElectrode Preparation
HI 4009
1. Remove protective cover from sensor tip.
2. Prepare reference electrode by filling outer electrolyte
reservoir with HI 7072.
3. Place sensor and reference electrodes into electrode
holder and connect cable connectors to meter.
HI 4109
1. Unwrap plastic film seal found over ceramic junction
on inner stem and discard. This is only used for shipping and long term storage.
2. Rinse inner stem with deionized water making certain
to wet the o-ring found on the inner stem.
Remove
Water
Deionized
3. Reassemble electrode by gently pushing the inner
assembly into the outer body, sliding spring down
cable, and screwing cap into place.
4. Remove fill hole cover and o-ring on fill hole spout.
5. Using the dropper pipette provided, add a few drops
HI 7072 fill solution to the electrode, wetting the oring and rinsing out the fill solution chamber.
8
Parafilm
Page 9

6. Holding the body of the electrode gently press upper
cap with your thumb. This permits the fill solution to
drain out of the body. Release cap and verify electrode returns to its original position. (You may need to
gently assist for this to occur).
COMBINATION
CYANIDE
HI 4109
7. Tighten the electrode cap onto the body and fill electrode body until fill solution volume is just below fill
hole.
8. Position electrode in a Hanna HI 76404 electrode
holder (or equivalent) and connect plug to meter.
9
Page 10

IX. IX.
Quick Check of Electrode SlopeQuick Check of Electrode Slope
IX.
Quick Check of Electrode Slope
IX. IX.
Quick Check of Electrode SlopeQuick Check of Electrode Slope
Use of a hood and protective clothing is strongly advised.
• Connect sensors to pH/mV/ISE meter
• Place meter in mV mode.
• Place 100 mL of deionized water into a beaker with
stir bar and 1 mL of HI 4001-00 ISA.
• Place electrodes into prepared sample.
• Add 1 mL of the stock standard (either M or ppm) to
the beaker. Record the mV value when stable.
• Add an additional 10 mL of stock standard to the
solution. Record the mV when reading has stabilized.
This value should be less than the previous noted
(more negative).
• Determine the difference between the two mV values.
An acceptable value for this slope is -56 ± 4 mV.
X. X.
Corrective actionCorrective action
X.
Corrective action
X. X.
Corrective actionCorrective action
• Verify protective cap has been removed (HI 4009).
• Verify plastic film has been removed from inner stem
(HI 4109).
• Verify electrodes are connected properly to meter and
meter is powered.
• Verify dilute standards are freshly made and stored.
Remake solutions if appropriate.
• If the sensor slope just misses the suggested slope
window, soaking the sensor in a dilute standard may
solve the problem. (<10
-3
M standard).
• A scratched sensing surface can be polished with HI
4000-70 polishing strip. Cut off approximately 1
inch of the micro-abrasive strip. Wet the frosted side
with deionized water and place against damaged
membrane of the electrode. Place your gloved thumb
against the shiny backing and slowly rotate back and
forth while applying gentle pressure. Continue polishing until you are satisfied with the surface. If dark
deposits appear on polishing strip move the paper
slightly and continue polishing.
10
Page 11

• If the membrane is damaged, the response becomes
extremely sluggish, or the slope of the electrode has
decreased significantly, and procedures above have
not helped, the sensor should be replaced.
XI. XI.
Direct Calibration and MeasurementDirect Calibration and Measurement
XI.
Direct Calibration and Measurement
XI. XI.
Direct Calibration and MeasurementDirect Calibration and Measurement
This method is a simple procedure for measuring many
samples. Use of a hood and protective clothing is strongly
advised when handling cyanide samples and standards.
A direct reading ISE meter (HI 4222 or equivalent) determines concentration of the unknown by a direct reading
after calibrating the meter with the standards. The meter is
calibrated with two or more freshly made standards that
are in the linear measurement range of the unknowns.
One mL of ISA (HI 4001-00) is added to each 100 mL
volume of standard or sample. More calibration standards
are required in non-linear regions. Unknowns are read
directly.
Samples with higher concentration should be diluted to
be within the working range of the electrodes. The final
result must be multiplied by the corresponding dilution
factor to determine the actual concentration.
A pH/mV meter in mV mode with semi-log graph paper
may also be used. Two or more freshly prepared standards
that are in the measurement range of the unknowns are
measured in mV mode on the meter.
These values are plotted on the semi-log paper and the
points are connected to form a straight-line curve. When
samples are measured, their mV values are converted to
concentration by following the mV to the concentration axis
on the semi-log plot.
11
Page 12

Procedure
1) Follow sections VIII and IX to prepare sensors for
measurement.
2) Follow section VI to prepare standards / solution.
Standards should bracket and fall within the range of
interest.
One mL HI 4001-00 ISA is added to 100 mL of both
samples and standards Add stir bar and mix before
taking measurements.
3) Follow section VII; General Guidelines to optimize test
set-up.
4) During calibration it is best to start with lower concentration samples first. Wait for a stable measurement
before recording values. Slightly longer equilibrations are required at lower concentrations .
5) To prevent carry over and contamination of samples,
rinse sensors with deionized and dab dry between
samples.
Typical HI 4009 and H I 4109 Linearity
0
-50
-100
-150
mV
-200
-250
-300
1234567
- Log [M]
12
Page 13

XII. XII.
Other Measurement TOther Measurement T
XII.
Other Measurement T
XII. XII.
Other Measurement TOther Measurement T
echniquesechniques
echniques
echniquesechniques
Known Addition (for CN-)
An unknown concentration can be determined by adding a
known amount (volume and concentration) of measured
ion to a known volume of the sample. This technique is
called Known Addition. The method can use an ideal
sensor slope, but actual determined slopes at the temperature of measurement should be used if known. The volume
and concentration of the added standard must cause a mV
change of at least 30 mV. This method is preprogrammed
in the Hanna HI 4222 pH/ISE/mV meter, which simplifies
the method greatly. The method is recommended for
samples with higher ionic strengths.
Example: Cyanide ion determination in samples with concentrations less than 5 X 10 -4 M using known addition.
1. A 50 mL sample of unknown (Vsample) is placed in
a clean plastic beaker with a cyanide sensor. 500 uL
(0.5 mL) of HI 4001-00 ISA (V
) is added to the 50
ISA
mL sample and allowed to mix. The stable mV value
(mV 1) is recorded.
2. 10 mL (Vstd) of 10-2M (Cstd) stock standard is added
to the beaker and the mV value decreases. The unknown cyanide concentration in the original sample
(Csample) can then be determined by the following
equation.
C
=
sample
(V
(V
sampl e+Vstandard+VISA
(V
sample+VISA
C
standardVstandard
∆E/S
)10
T
)= V
- (VS’)
)= V
S’
V
S’
V
sample
T
3. The procedure can be repeated with a second stan-
dard addition to verify slope and operation of the
method.
13
Page 14

Titration
A cyanide electrode may be used as an indicator to follow
the progress and detect the endpoint of a complexation
-
titration of CN
with silver nitrate standard. Time must be
allowed for the alkali salt to redissolve and mV to settle.
The end point is reached when the formation of insoluble
silver cyanoargentate precipitates occurs. The electrode can
be used in colored samples, or high or variable ionic strength
samples to increase accuracy of the determination. During
the titration the sensor follows the decrease in cyanide
concentration while small additions of silver nitate titrant
are added. The silver reacts with the cyanide ions forming
a precipitate.
Ag+ + 2CN- <—> [Ag(CN)2]
[Ag(CN)2]- <—> Ag+ 2AgCN
-
(soluble)
(insoluble)
At the stoichiometric end point, a large change in mV
occurs. This technique may be useful in obtaining the actual
value of cyanide standards. Measurements may be
automated by use of the Hanna Titrator HI 901 or titrated
manually.
XIII.XIII.
pH pH
XIII.
pH
XIII.XIII.
pH pH
The HI 4109 and HI 4009 electrodes may be used in
solutions with pH values between 11 and 13. Samples
that fall beyond this range should be adjusted.
XIV. SXIV. S
torage and Care of the HI 4009 andtorage and Care of the HI 4009 and
XIV. S
torage and Care of the HI 4009 and
XIV. SXIV. S
torage and Care of the HI 4009 andtorage and Care of the HI 4009 and
HI 4109 sensors HI 4109 sensors
HI 4109 sensors
HI 4109 sensors HI 4109 sensors
The HI 4009 sensor can be stored in very dilute standards
(<10-3M) for short periods of time and should be stored
dry with the protective cap on when not in use.
The model HI 4109 combination electrode can be left in
dilute standards (<10-3 M) for short time periods.
For long term storage, the electrode should be drained and
washed of salts with distilled or deionized water. Unscrew
the upper cap and move outer sleeve up cable. Wrap the
ceramic junction on the inner stem with Parafilm® or other
sealing wrap. Place the protective cap provided over the
14
Page 15

sensor membrane. Store dry disassembled electrode in
storage box provided with electrode.
XVXV
. .
Conversion TConversion T
XV
.
Conversion T
XVXV
. .
Conversion TConversion T
For CNFor CN
For CN
For CNFor CN
--
-
--
ablesables
ables
ablesables
Multiply byMultiply by
Multiply by
Multiply byMultiply by
Moles/L (M) to ppm (mg/L) 2.602 x 10
ppm (mg/L) to M (moles/L) 3.843 x 10
XVI.XVI.
Disposal of CyanidesDisposal of Cyanides
XVI.
Disposal of Cyanides
XVI.XVI.
Disposal of CyanidesDisposal of Cyanides
4
-5
Sodium Cyanide is a deadly poison and extreme care must
be taken during use and in disposal after use.
Test solutions and standards may be neutralized before
discharging. Consult your waste manager for exact
procedures. The overview of the process is below.
Caution: Neutralization reactions should be carried out in a
hood.
1) Cyanide is oxidized to cyanate at an elevated pH. pH
and ORP measurements can aid the progress of this
reaction.
CN- +OH- + HOCl- -> CNO
-
2) Cyanate is then oxidized to N2 and CO2 which bubble
off as harmless gases. pH and ORP measurements
can aid this step also.
2CNO- +2OH- +HOCl-->Cl- +2CO2 +N2 +2H2O
15
Page 16

MAN4109 02/07R1
WARRANTY WARRANTY
WARRANTY
WARRANTY WARRANTY
Hanna Instruments Ion Selective Electrodes are warranted
to be free of defects in material and workmanship for 6
months from date of purchase when used for their intended
purpose and maintained according to instructions. If they
fail to work when first used contact your dealer immediately.
Damage due to accidents, misuse, misapplication, tampering
or lack of prescribed maintenance is not covered.
Hanna Instruments reserves the right to modify the design,
construction or appearance of its products without advance
notice.
16
 Loading...
Loading...