Page 1
HI 4101
AMMONIA
Instruction Manual
HI 4101HI 4101
HI 4101
HI 4101HI 4101
Ammonia
Ion
Selective Electrode
1
Page 2

2
Page 3

HI 4101 Ammonia ElectrodeHI 4101 Ammonia Electrode
HI 4101 Ammonia Electrode
HI 4101 Ammonia ElectrodeHI 4101 Ammonia Electrode
I. I.
Introduction:Introduction:
I.
Introduction:
I. I.
Introduction:Introduction:
The Hanna HI 4101 Ammonia gas selective electrode is a
combination electrode designed for the measurement of
ammonia in aqueous solutions such as waste water samples,
wine, beer. Ammonium ions are also measured by conversion to ammonia gas upon ISA addition.
II.II.
SpecificationsSpecifications
II.
Specifications
II.II.
SpecificationsSpecifications
Type: NH3 gas sensing
electrode with glass pH
internal, Ag/ AgCl
reference and gas
permeable PTFE
membrane.
Species Measured: NH
+
, NH
4
3
Measurement Range: 1.0 M to 1x 10-6M
17000 to 0.02 ppm
Interfering ions: Surfactants, wetting
agents, volatile amines.
Operating Temperature: 0 to 40°C
Operating pH: >11 pH
Dimensions: 12 mm (OD) X 120
mm (insertion)
0.47”x 4.72”
Wetted materials: Delrin®, body and cap
PTFE gas membrane
Connection: BNC
3
Page 4

III.III.
Theory of OperationTheory of Operation
III.
Theory of Operation
III.III.
Theory of OperationTheory of Operation
::
:
::
The ammonia electrode is a complete potentiometric cell
that contains both a silver/silver chloride (Ag/AgCl) reference and a pH measurement element. These elements are
housed within a thermoplastic body in a chloride ion-containing electrolyte, and are isolated from the sample by a
gas permeable membrane made of polytetrafluoroethylene
(PTFE).
Dissolved gas in the sample solution diffuses into the membrane and changes the pH in the thin film of electrolyte on
the surface of the pH glass. Diffusion continues until the
partial pressures of the gas in the sample and thin film are
equal. The change in pH is proportional to the concentration of dissolved gas in the sample solution.
The Nernst expression for an ammonia sensor is expressed
in the equation below. Note that the potential is a function
of the ammonia gas, which in turn is related to the hydroxyl
ion concentration. The glass internal, Ag/AgCl reference,
and Henry’s law constant are rolled into the E’ and E
constants. The Nernst equation for the sensor becomes the
equation noted below:
o
E = E’–2.3RT/nF log [A]= Eo–0.059 log [OH-]
E = observed potential
E’ = Reference and fixed internal voltages
R = gas constant (8.314 J/K Mol)
n= Charge on ion (equivalents/mol)
A
= ion activity in sample
ion
T = absolute temperature in K
F = Faraday constant (9.648 x 104 C/equivalent)
The mV should decrease in a Nernstian manner as the
ammonia partial pressure increases in the sample.
4
Page 5
IV.IV.
Design ElementsDesign Elements
IV.
Design Elements
IV.IV.
Design ElementsDesign Elements
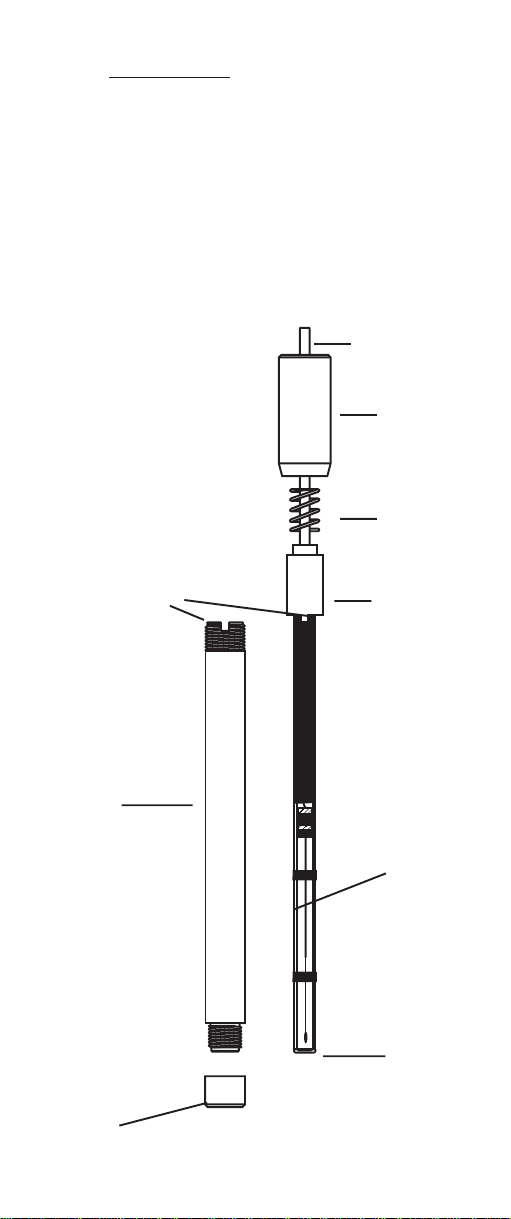
The Hanna HI 4101 ammonia gas sensor has 3 main
parts. These are the membrane/membrane cap, outer probe
body with antirotation key and the pH/reference assembly
which includes the outer electrode cap, spring, inner cap
and pH/reference electrode assembly.
pH/reference electrode assembly
cable
outer electrode
cap
spring
antirotation key inner cap
Outer probe body
reference
electrode
pH
sensitive
membrane
membrane/membrane cap
5
Page 6

V.V.
Equipment Required:Equipment Required:
V.
Equipment Required:
V.V.
Equipment Required:Equipment Required:
• Hanna HI 4222 pH/ISE/mV meter or other suitable
ion or pH/mV meter. (Note: log/linear graph paper is
useful if an ISE meter is not available).
• Hanna HI 180 magnetic stirrer or equivalent with
stirring bars. (Note: Isolate beakers from stirrer motor
heat by placing insulating material such as foam or
cork between them).
• 2 or 3 necked flask with stoppers or
• Hanna HI 76404 electrode holder or equivalent with
Beakers or other suitable measurement vessel with
plastic sealing film or wrap.
VI. VI.
Solutions Required for Calibration:Solutions Required for Calibration:
VI.
Solutions Required for Calibration:
VI. VI.
Solutions Required for Calibration:Solutions Required for Calibration:
Ionic Strength Adjuster (ISA): HI 4001-00
Hanna 0.1 M standard: HI 4001-01
Hanna 100 ppm N standard: HI 4001-02*
Hanna 1000 ppm N standard: HI 4001-03*
*Please Note: These calibration standards are ppm as
NH3-N.
See Section XVII for additional solutions used for maintenance.
Using volumetric pipettes and glassware make dilutions of
the standard to bracket the concentration of the samples.
Standards with concentrations less than 10-3M should be
prepared fresh daily. Store solution in a tightly sealed
bottle without ISA added. 2 mL of HI 4001-00 ISA should
be added to each 100 mL sample of standard and samples
just prior to measurement. ISA adjusts the pH of the sample
or standard to about pH 11 thus converting ammonium ion
to ammonia. It also provides samples and standards a
constant ionic strength background that stabilizes the solutions activity coefficient and permits concentration to be
measured directly. The ISA provides color indication to verify
it has been added to the solution and a complexing agent
to remove metal ions (i.e copper, zinc) from solution. These
6
Page 7

ions are capable of reducing the ammonia concentration.
If other volumes of sample/standard are used, add ISA at 2
parts per 100 parts standard/sample.
VIIVII
General GuidelinesGeneral Guidelines
VII.
General Guidelines
VIIVII
General GuidelinesGeneral Guidelines
• Calibration standards and sample solutions should
have the same ionic strength. ISA should be added to
both samples and standards immediately before taking measurements.
• Calibration standards and sample solutions should be
at the same temperature. Thermally insulate solution
vessel from magnetic stirrer with cork or other insulating medium.
• Calibration standards and sample solutions should
be stirred at the same rate using identical sized stir
bars.
• Surface coating or “wetting“ the PTFE membrane will
effect the response. Inspect sensor before using. Replace PTFE membrane if damage is evident.
• Rinse electrode with distilled or deionized water between samples and dab dry with lab wipe or other soft
disposable absorbent toweling.
• Check calibration every 1-2 hours.
• Position sensors at an angle of approximately 20° to
lessen bubble adherence from solution out-gassing
due to temperature change.
• Close container with plastic wrap or use
2 or 3 necked flask to prevent gas from leaving.
• Gently pulling cable will permit an exchange of fill
solution at membrane surface. Re-Calibration is required.
7
Page 8
VIII. VIII.
Inner Electrode CheckInner Electrode Check
VIII.
Inner Electrode Check
VIII. VIII.
Inner Electrode CheckInner Electrode Check
Before assembling the electrode for the
first timefirst time
first time or if
first timefirst time
reactivating it after storage, the inner electrode assembly
should be conditioned and then tested as a pH electrode.
Prepare pH test solutions HI 4000-47-4 and HI 4000-477 by mixing and dissolving each buffer packet in separate
containers with 50 mL deionized water. These pH solutions
contain chloride ions and pH buffers that are used to verify
the inner electrode (pH internal) is operational. See
Section XVII for replacement accessories and maintenance
items.
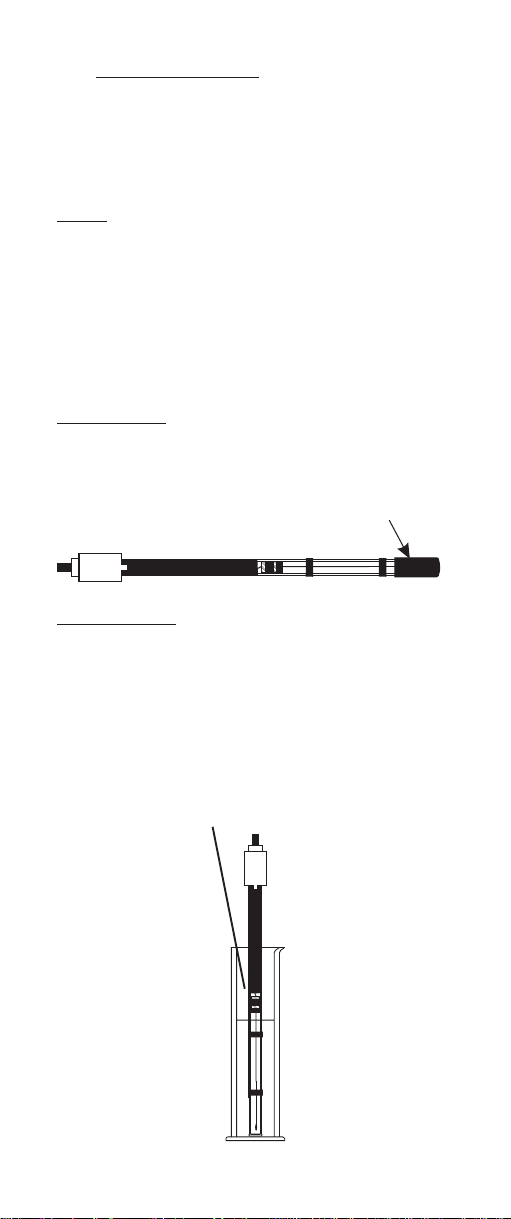
For a new sensor:
Remove the protective shipping cap from the glass inner
electrode.
Protective shipping cap
For existing sensor:
Unscrew the upper cap on the top of the electrode and
carefully withdraw the internal pH/reference assembly.
For stable readings, glass should be covered to the
bottom of the long black band.
Use test
tube or
Test buffer
can be
used as a
conditioning
solution
for the
pH internal
graduated
cylinder
(weighed
Bottom) when
testing or
conditioning
pH internal
8
Page 9

• If sensor has been stored or shipped dry, it should be
“conditioned” by soaking the pH/reference assembly 1 hour or more in one of the pH test solutions.
• Avoid touching the pH glass with your fingers.
• Attention: The pH/reference assembly is fragile!
Support the upper portion of the internal cell while
immersing the glass and reference assembly. A tall
narrow container with weighted bottom is best. The
pH test solution should cover the bottom of the large
black ban.
Test: Connect the BNC connector on the electrode cable to a
pH/mV (mV or ORP mode) meter. Carefully immerse
the sensor assembly into one of the buffers. When the
measurment stabilizes record the mV generated. Rinse
sensor tip in deionized water and dab dry between
buffers to prevent solution carry-over. Do not rub the
glass. Take a measurement in the second buffer and
record mV. Pay attention to minus sign if present.
Calculate the difference in mV between the two solutions.
Example of typical values:
HI 4000-47- 7 -90.2 mV
HI 4000-47-4 80.66 mV
Difference 170.8 mV= 80.6-(-90.2)
A calculated value equal or greater than 160 mV is acceptable for ambient temperatures between 20° and 25°C.
IX. IX.
Electrode PreparationElectrode Preparation
IX.
Electrode Preparation
IX. IX.
Electrode PreparationElectrode Preparation
1) Remove glass internal from sensor body and perform
inner electrode check. (See section VIII).
2) Install membrane on the outer probe body. Use twee-
zers provided and avoid touching working area of
membrane with your fingers as skin oil will change
the hydrophobic properties. Discard the paper backing (blue) found between white PTFE membranes.
Hold membrane at corner with tweezers and drape
over lower opening of outer probe body.
9
Page 10
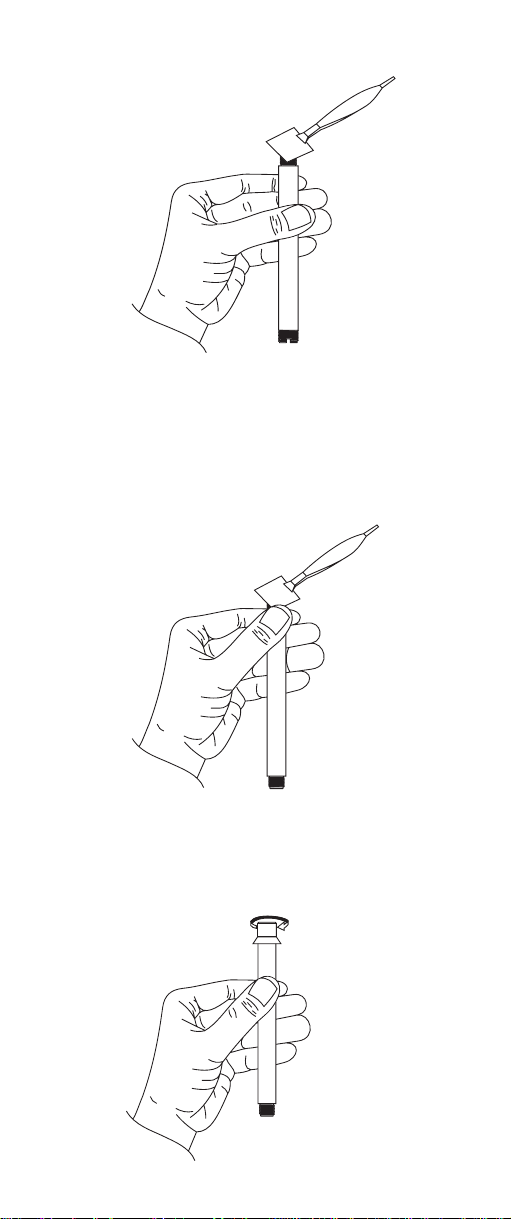
3) Hold one corner against the threads with thumb while
gently stretching membrane over opening and capturing opposite membrane corner against threads .
Smooth excess membrane material around the threads.
4) Screw outer membrane cap onto body
thus capturing the membrane between the cap and
outer body threads.
10
Page 11
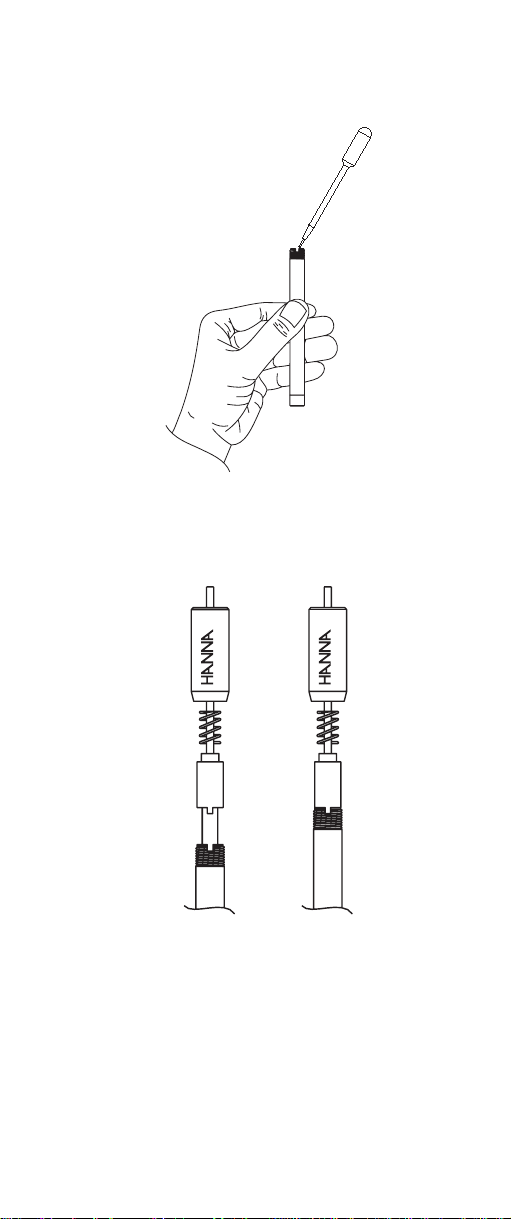
5.) Using dropper provided, add about 2 mL of ammonia internal electrolyte HI 4001-40 into outer probe
body.
6) Insert and position the inner glass/reference assembly into the outer body so that the anti-rotation key
sits in the cut out on the outer probe body.
HI 4101
IA
N
O
M
M
A
HI 4101
IA
N
O
M
M
A
7) Holding the electrode upright, slide spring and electrode cap down cable and screw cap on outer body
until fully engaged. Do not invert electrode. Do not
overtighten.
8) Install assembled electrode in gas sensor test vessel
or in electrode holder and connect cable connector to
pH/mV meter.
11
Page 12

X. X.
Quick Check of Electrode SlopeQuick Check of Electrode Slope
X.
Quick Check of Electrode Slope
X. X.
Quick Check of Electrode SlopeQuick Check of Electrode Slope
• Connect BNC (connector) to pH/mV/ISE meter.
• Place meter in mV mode.
• Place 100 mL of deionized water into a vessel with
stir bar. Add 2 mL of ISA Hanna HI 4001-00.
• Place sensor into prepared sample.
• Add 1 mL of 1000 ppm or 0.1 M Ammonia standard
to beaker. Record the mV value when stable.
• Add an additional 10 mL of standard to the solution.
Record the mV when reading has stabilized. This
value should be less than the previous noted (more
negative).
• Determine the difference between the two mV values.
An acceptable value for this slope is 54±4 mV at
ambient temperatures between 20 and 25°C.
XI.XI.
Corrective actionCorrective action
XI.
Corrective action
XI.XI.
Corrective actionCorrective action
• Verify that the upper cap has been screwed in all the
way.
• Verify electrode is connected properly to meter and the
meter is is powered.
• Verify ISA has been added in the correct ratio to the
standard.
• Examine the white membrane and check for electrolyte that might have leaked through the PTFE film.
Replace membrane if damaged.
• If sensor does not change mV verify the the glass
assembly is operational (See section VIII).
12
Page 13

XII. XII.
Sample HandlingSample Handling
XII.
Sample Handling
XII. XII.
Sample HandlingSample Handling
• Keep samples stored in tightly covered bottles to prevent ammonia loss or ammonia contamination from
other sources.
• Alkaline samples must be measured at once or acidified for storage. (HCl may be added to bring pH to 6).
• Acidic samples such as wine or juice may require
addition ISA. Samples should be approximately pH
11 for measurement.
• Measure sample and standards quickly after adding
ISA because ammonia gas will escape from the solution.
• For solutions containing organically bound nitrogen
such as oil, sludge, waste, or samples which may
contain surfactants; digest sample first using a total
Kjeldahl nitrogen (TKN) procedure. This involves
oxidation with hot sulfuric acid which converts bound
nitrogen to ammonium ions. Consult Method 4500N
from Standard Methods for the Examination of
org
Water and Wastewater.
• For samples found to penetrate or “wet” the mem-
brane, measurements may be made above the sample
in a small headspace of a sealed system such as HI
4000-71 test vessel, provided the concentration of
NH3 is greater than 10
-3
M. The headspace should be
.
saturated with water vapor and the membrane end of
the electrode suspended in the gas sample above the
sample with ISA added. Expect a longer response
time from the sensor when gas phase measurements
are made.
13
Page 14

XIII. XIII.
Direct Calibration and MeasurementDirect Calibration and Measurement
XIII.
Direct Calibration and Measurement
XIII. XIII.
Direct Calibration and MeasurementDirect Calibration and Measurement
The direct method can be used in the linear working regions of the sensor. (See figure for typical sensor response).
A direct reading ISE meter (HI 4222 or equivalent) determines concentration of the unknown by a direct reading
after calibrating the meter with the standards. The meter is
calibrated with two or more freshly made standards that
are in the measurement range of the unknowns. HI 400100 ISA is added just before measurement of the standard
or sample. Covering the vessel to prevent gas loss is advised.
A pH/mV meter in mV mode and semi-log graph paper
may also be used. Two or freshly prepared standards that
are in the measurement range of the unknowns (with ISA
added), are measured in mV mode on the meter. These
standards are plotted on semilog graph paper and their
points are connected to form a straight-line curve. When
samples are measured, their mV values are converted to
concentration by following the mV to the concentration axis
on the semi-log plot.
Method 4500-NH3 D. from Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater is a direct measurement method for water samples.
For both direct reading and mV convertion, ISA is added
prior to measurement and the vessel should be covered to
prevent gas loss.
In the lower concentration ranges the electrode calibration
becomes less linear, many more calibration points are
needed, and calibration will need to be repeated more
frequently. Known addition method may also be used in
these regions provided the actual slope of the sensor has
been determined.
Direct Measurement Procedure
1) Follow section IX to prepare sensor.
2) Follow section VI to prepare standards and solutions.
14
Page 15

• Standards should bracket the measurement range of
V
interest and differ from each other by a factor of 10 in
the linear regions.
• Standards and solutions should be at the same temperature. 2 mL of ISA is added to each 100 mL of
sample and standard. A color change should occur to
indicate the ISA has been added.
• Protect these solutions from loss of dissolved gas by
covering and using promptly.
3) Follow section VII; General Guidelines to optimize test
set-up.
4) During calibration it is best to start with lower concentration samples first. Wait for a stable reading before
reading/recording values.
5) To prevent carry over and contamination of samples,
rinse sensors with deionized water and blot dry between samples.
6) Between measurements suspend sensor tip in a small
sample of NH3 Conditioning solution;
HI 4001-45. Rinse body with deionized water and
blot dry before placing in next sample.
Typical calibration curve for HI 4101 Ammonia ISE
-300
-250
-200
-150
m
-100
-50
0
0123456
50
Typical Linearity for HI 4101 Electrode
-Log of [M
]
15
Page 16

XIVXIV
. .
Other Measurement TOther Measurement T
XIV
.
Other Measurement T
XIVXIV
. .
Other Measurement TOther Measurement T
echniquesechniques
echniques
echniquesechniques
Known addition
An unknown concentration of ammonia can be determined
by adding a known amount (volume and concentration) of
ammonia standard to a known volume of the sample. This
technique is extremely useful for ammonia as the sensor
may drift from calibrated values over time, however the
slopes remain constant. With known addition, the standard and sample are measured within minutes of one
another. The technique can use an ideal sensor slope, but
actual slopes at the temperature of measurement should
be determined and used if possible. This will improve accuracy. Known addition is Method 4500-NH3 E. from
Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater.
1) The volume of the unknown sample (V
Sample
) is measured accurately and placed into the closed sample
vessel. The sensor is secured in the vessel and then the
vessel is placed on a stirrer.
2) ISA is added at 1 part per 50 parts sample.
3) When the measurement is stable the mV value is
noted.
4) A known amount, volume (V
(C
), of NH
Standard
mV values are again noted when the measurement is
standard is then added to the sample.
3
) and concentration
Standard
stable.
5) The mV change is then calculated (∆E).
6) Using the measured and calculated values, the
sample concentration (C
) can be determined.
Sample
C
sample
C
=
(V
(V
standardVstandard
)10
T
∆E/S
(V
sample+Vstandard+VISA
sample+VISA
- (VS’)
)= V
16
S’
)= V
V
S’
V
sample
T
Page 17

7) The procedure can be repeated with a second standard
addition to verify slope and operation of the method.
Note:
This method is preprogrammed in the Hanna HI
4222pH/ISE/mV meter, which simplifies the method
greatly and permits repeated determinations easily.
Example:
Ammonia determination with known addition:
1. A 50 mL sample of unknown (V
) is placed in an
SAMPLE
clean vessel with an electrode. 1 mL of ISA is added
to the sample and the color change is noted. The
sample is covered and permitted to mix. The mV is
then recorded when the sensor has stabilized.
2. 5 mL (V
STANDARD
) of 0.1 M (C
) standard is then
STANDARD
added to the vessel and is permitted to mix. The mV
value decreases as the concentration increases. (Note:
for other concentration samples, add a known volume
and concentration of standard to produce a 30 mV
change or greater.
3. The unknown ammonia concentration in the original
sample (C
) can then be determined by using the
SAMPLE
equation provided.
17
Page 18

XV. XV.
Storage and Care of the HI 4101 sensorStorage and Care of the HI 4101 sensor
XV.
Storage and Care of the HI 4101 sensor
XV. XV.
Storage and Care of the HI 4101 sensorStorage and Care of the HI 4101 sensor
The HI 4101 sensor can be stored assembled and ready to
use in HI 4001-45 Conditioning solution overnight or
between measurements. After overnight storage, gently pull
on the cable to compress the spring mechanism thus
permitting electrolyte to exchange from the bulk to the thin
film between the membrane and glass. Calibration is
required after doing this.
For longer term storage (over a week), disassemble the
sensor completely and rinse off the internal pH/reference
assembly, the outer body and the membrane cap. Discard
the white PTFE membrane. (Note: keep black membrane
cap). Cover the glass tip with the protective shipping cap
and store parts securely in the original shipping box. When
reassembling the sensor follow section IX.
XVI. XVI.
Conversion TConversion T
XVI.
Conversion T
XVI. XVI.
Conversion TConversion T
ablesables
ables
ablesables
For NHFor NH
For NH
For NHFor NH
33
3
33
Multiply byMultiply by
Multiply by
Multiply byMultiply by
Moles/L (M) NH3 to ppm NH3 (mg/L) 1.70 X 10
ppm NH3 (mg/L) to M (Moles/L) 5.882 X 10
For N-NH3 (ppm as nitrogen)For N-NH3 (ppm as nitrogen)
For N-NH3 (ppm as nitrogen)
For N-NH3 (ppm as nitrogen)For N-NH3 (ppm as nitrogen)
Multiply byMultiply by
Multiply by
Multiply byMultiply by
Moles/L (M) NH3 to ppm N-NH3 (mg/L) 1.40 X 10
4
-5
4
18
Page 19

XVII. XVII.
XVII.
XVII. XVII.
HI 4101 AHI 4101 A
HI 4101 A
HI 4101 AHI 4101 A
ccessories and Replacement Pccessories and Replacement P
ccessories and Replacement P
ccessories and Replacement Pccessories and Replacement P
artsarts
arts
artsarts
For CalibrationFor Calibration
For Calibration
For CalibrationFor Calibration
CodeCode
Code
CodeCode
::
:
::
HI 4001-00 Ionic Strength Adjuster (500 mL)
HI 4001-01 Hanna 0.1 M standard (500 mL)
HI 4001-02* Hanna 100 ppm N standard
(500 mL)
HI 4001-03* Hanna 1000 ppm N standard
(500mL)
HI 4001-30 Nitrate test kit (Bulk pkg)
*Please Note: These calibration standards are ppm as
NH3-N.
For Maintenance:For Maintenance:
For Maintenance:
For Maintenance:For Maintenance:
HI 4001-40 Hanna Ammonia Fill solution
(4 X 30 mL)
HI 4001-45 Hanna Ammonia conditioning
solution (500 mL)
HI 4000-47 Bulk package of 10 each
HI 4000-47-4 and HI 4000-47-7
buffer packets
HI 4000-52 Replacement membrane cap
HI 4001-51 Replacement membranes kit
(20 pieces)
HI 4000-51 Replacement pH/reference electrode
assembly
HI 740155P Capillary Pipettes (20 piece)
HI 740159 Plastic tweezers (1 piece)
19
Page 20

MAN4101 10/08 R5
WARRANTY WARRANTY
WARRANTY
WARRANTY WARRANTY
Hanna Instruments Ion Selective Electrodes are warranted to
be free of defects in material and workmanship for 6 months
from date of purchase when used for their intended purpose
and maintained according to instructions. If they fail to work
when first used contact your dealer immediately. Damage due
to accidents, misuse, misapplication, tampering or lack of
prescribed maintenance is not covered.
Hanna Instruments reserves the right to modify the design,
construction or appearance of its products without advance
notice.
20
Page 21

HI 4101
AMMONIA
Instruction Manual
HI 4101HI 4101
HI 4101
HI 4101HI 4101
Ammonia
Ion
Selective Electrode
1
Page 22

2
Page 23

HI 4101 Ammonia ElectrodeHI 4101 Ammonia Electrode
HI 4101 Ammonia Electrode
HI 4101 Ammonia ElectrodeHI 4101 Ammonia Electrode
I. I.
Introduction:Introduction:
I.
Introduction:
I. I.
Introduction:Introduction:
The Hanna HI 4101 Ammonia gas selective electrode is a
combination electrode designed for the measurement of
ammonia in aqueous solutions such as waste water samples,
wine, beer. Ammonium ions are also measured by conversion to ammonia gas upon ISA addition.
II.II.
SpecificationsSpecifications
II.
Specifications
II.II.
SpecificationsSpecifications
Type: NH3 gas sensing
electrode with glass pH
internal, Ag/ AgCl
reference and gas
permeable PTFE
membrane.
Species Measured: NH
+
, NH
4
3
Measurement Range: 1.0 M to 1x 10-6M
17000 to 0.02 ppm
Interfering ions: Surfactants, wetting
agents, volatile amines.
Operating Temperature: 0 to 40°C
Operating pH: >11 pH
Dimensions: 12 mm (OD) X 120
mm (insertion)
0.47”x 4.72”
Wetted materials: Delrin®, body and cap
PTFE gas membrane
Connection: BNC
3
Page 24

III.III.
Theory of OperationTheory of Operation
III.
Theory of Operation
III.III.
Theory of OperationTheory of Operation
::
:
::
The ammonia electrode is a complete potentiometric cell
that contains both a silver/silver chloride (Ag/AgCl) reference and a pH measurement element. These elements are
housed within a thermoplastic body in a chloride ion-containing electrolyte, and are isolated from the sample by a
gas permeable membrane made of polytetrafluoroethylene
(PTFE).
Dissolved gas in the sample solution diffuses into the membrane and changes the pH in the thin film of electrolyte on
the surface of the pH glass. Diffusion continues until the
partial pressures of the gas in the sample and thin film are
equal. The change in pH is proportional to the concentration of dissolved gas in the sample solution.
The Nernst expression for an ammonia sensor is expressed
in the equation below. Note that the potential is a function
of the ammonia gas, which in turn is related to the hydroxyl
ion concentration. The glass internal, Ag/AgCl reference,
and Henry’s law constant are rolled into the E’ and E
constants. The Nernst equation for the sensor becomes the
equation noted below:
o
E = E’–2.3RT/nF log [A]= Eo–0.059 log [OH-]
E = observed potential
E’ = Reference and fixed internal voltages
R = gas constant (8.314 J/K Mol)
n= Charge on ion (equivalents/mol)
A
= ion activity in sample
ion
T = absolute temperature in K
F = Faraday constant (9.648 x 104 C/equivalent)
The mV should decrease in a Nernstian manner as the
ammonia partial pressure increases in the sample.
4
Page 25

IV.IV.
Design ElementsDesign Elements
IV.
Design Elements
IV.IV.
Design ElementsDesign Elements
The Hanna HI 4101 ammonia gas sensor has 3 main
parts. These are the membrane/membrane cap, outer probe
body with antirotation key and the pH/reference assembly
which includes the outer electrode cap, spring, inner cap
and pH/reference electrode assembly.
pH/reference electrode assembly
cable
outer electrode
cap
spring
antirotation key inner cap
Outer probe body
reference
electrode
pH
sensitive
membrane
membrane/membrane cap
5
Page 26

V.V.
Equipment Required:Equipment Required:
V.
Equipment Required:
V.V.
Equipment Required:Equipment Required:
• Hanna HI 4222 pH/ISE/mV meter or other suitable
ion or pH/mV meter. (Note: log/linear graph paper is
useful if an ISE meter is not available).
• Hanna HI 180 magnetic stirrer or equivalent with
stirring bars. (Note: Isolate beakers from stirrer motor
heat by placing insulating material such as foam or
cork between them).
• 2 or 3 necked flask with stoppers or
• Hanna HI 76404 electrode holder or equivalent with
Beakers or other suitable measurement vessel with
plastic sealing film or wrap.
VI. VI.
Solutions Required for Calibration:Solutions Required for Calibration:
VI.
Solutions Required for Calibration:
VI. VI.
Solutions Required for Calibration:Solutions Required for Calibration:
Ionic Strength Adjuster (ISA): HI 4001-00
Hanna 0.1 M standard: HI 4001-01
Hanna 100 ppm N standard: HI 4001-02*
Hanna 1000 ppm N standard: HI 4001-03*
*Please Note: These calibration standards are ppm as
NH3-N.
See Section XVII for additional solutions used for maintenance.
Using volumetric pipettes and glassware make dilutions of
the standard to bracket the concentration of the samples.
Standards with concentrations less than 10-3M should be
prepared fresh daily. Store solution in a tightly sealed
bottle without ISA added. 2 mL of HI 4001-00 ISA should
be added to each 100 mL sample of standard and samples
just prior to measurement. ISA adjusts the pH of the sample
or standard to about pH 11 thus converting ammonium ion
to ammonia. It also provides samples and standards a
constant ionic strength background that stabilizes the solutions activity coefficient and permits concentration to be
measured directly. The ISA provides color indication to verify
it has been added to the solution and a complexing agent
to remove metal ions (i.e copper, zinc) from solution. These
6
Page 27

ions are capable of reducing the ammonia concentration.
If other volumes of sample/standard are used, add ISA at 2
parts per 100 parts standard/sample.
VIIVII
General GuidelinesGeneral Guidelines
VII.
General Guidelines
VIIVII
General GuidelinesGeneral Guidelines
• Calibration standards and sample solutions should
have the same ionic strength. ISA should be added to
both samples and standards immediately before taking measurements.
• Calibration standards and sample solutions should be
at the same temperature. Thermally insulate solution
vessel from magnetic stirrer with cork or other insulating medium.
• Calibration standards and sample solutions should
be stirred at the same rate using identical sized stir
bars.
• Surface coating or “wetting“ the PTFE membrane will
effect the response. Inspect sensor before using. Replace PTFE membrane if damage is evident.
• Rinse electrode with distilled or deionized water between samples and dab dry with lab wipe or other soft
disposable absorbent toweling.
• Check calibration every 1-2 hours.
• Position sensors at an angle of approximately 20° to
lessen bubble adherence from solution out-gassing
due to temperature change.
• Close container with plastic wrap or use
2 or 3 necked flask to prevent gas from leaving.
• Gently pulling cable will permit an exchange of fill
solution at membrane surface. Re-Calibration is required.
7
Page 28

VIII. VIII.
Inner Electrode CheckInner Electrode Check
VIII.
Inner Electrode Check
VIII. VIII.
Inner Electrode CheckInner Electrode Check
Before assembling the electrode for the
first timefirst time
first time or if
first timefirst time
reactivating it after storage, the inner electrode assembly
should be conditioned and then tested as a pH electrode.
Prepare pH test solutions HI 4000-47-4 and HI 4000-477 by mixing and dissolving each buffer packet in separate
containers with 50 mL deionized water. These pH solutions
contain chloride ions and pH buffers that are used to verify
the inner electrode (pH internal) is operational. See
Section XVII for replacement accessories and maintenance
items.
For a new sensor:
Remove the protective shipping cap from the glass inner
electrode.
Protective shipping cap
For existing sensor:
Unscrew the upper cap on the top of the electrode and
carefully withdraw the internal pH/reference assembly.
For stable readings, glass should be covered to the
bottom of the long black band.
Use test
tube or
Test buffer
can be
used as a
conditioning
solution
for the
pH internal
graduated
cylinder
(weighed
Bottom) when
testing or
conditioning
pH internal
8
Page 29

• If sensor has been stored or shipped dry, it should be
“conditioned” by soaking the pH/reference assembly 1 hour or more in one of the pH test solutions.
• Avoid touching the pH glass with your fingers.
• Attention: The pH/reference assembly is fragile!
Support the upper portion of the internal cell while
immersing the glass and reference assembly. A tall
narrow container with weighted bottom is best. The
pH test solution should cover the bottom of the large
black ban.
Test: Connect the BNC connector on the electrode cable to a
pH/mV (mV or ORP mode) meter. Carefully immerse
the sensor assembly into one of the buffers. When the
measurment stabilizes record the mV generated. Rinse
sensor tip in deionized water and dab dry between
buffers to prevent solution carry-over. Do not rub the
glass. Take a measurement in the second buffer and
record mV. Pay attention to minus sign if present.
Calculate the difference in mV between the two solutions.
Example of typical values:
HI 4000-47- 7 -90.2 mV
HI 4000-47-4 80.66 mV
Difference 170.8 mV= 80.6-(-90.2)
A calculated value equal or greater than 160 mV is acceptable for ambient temperatures between 20° and 25°C.
IX. IX.
Electrode PreparationElectrode Preparation
IX.
Electrode Preparation
IX. IX.
Electrode PreparationElectrode Preparation
1) Remove glass internal from sensor body and perform
inner electrode check. (See section VIII).
2) Install membrane on the outer probe body. Use twee-
zers provided and avoid touching working area of
membrane with your fingers as skin oil will change
the hydrophobic properties. Discard the paper backing (blue) found between white PTFE membranes.
Hold membrane at corner with tweezers and drape
over lower opening of outer probe body.
9
Page 30
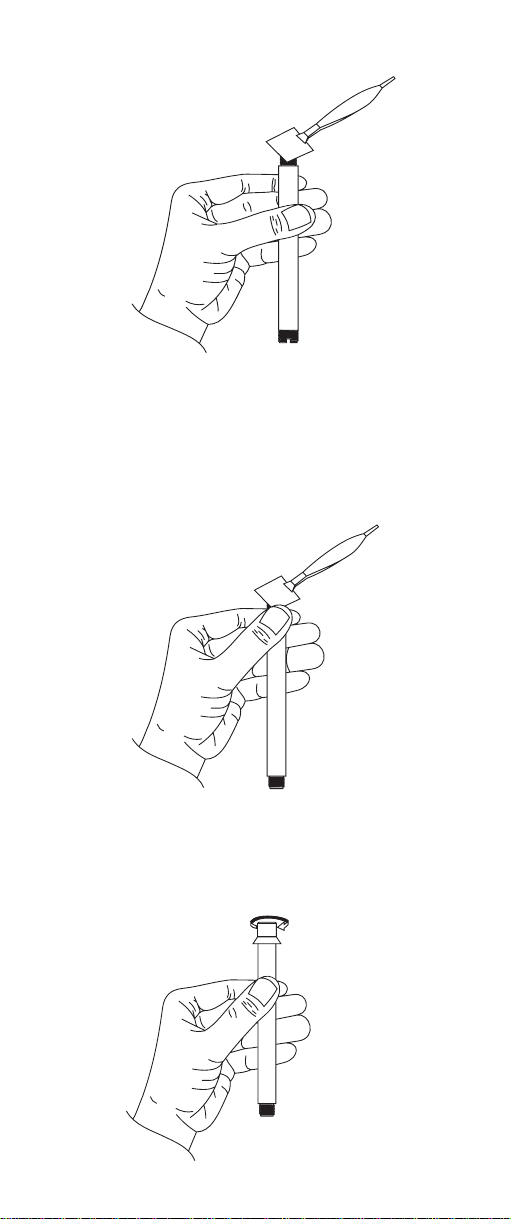
3) Hold one corner against the threads with thumb while
gently stretching membrane over opening and capturing opposite membrane corner against threads .
Smooth excess membrane material around the threads.
4) Screw outer membrane cap onto body
thus capturing the membrane between the cap and
outer body threads.
10
Page 31

5.) Using dropper provided, add about 2 mL of ammonia internal electrolyte HI 4001-40 into outer probe
body.
6) Insert and position the inner glass/reference assembly into the outer body so that the anti-rotation key
sits in the cut out on the outer probe body.
HI 4101
IA
N
O
M
M
A
HI 4101
IA
N
O
M
M
A
7) Holding the electrode upright, slide spring and electrode cap down cable and screw cap on outer body
until fully engaged. Do not invert electrode. Do not
overtighten.
8) Install assembled electrode in gas sensor test vessel
or in electrode holder and connect cable connector to
pH/mV meter.
11
Page 32

X. X.
Quick Check of Electrode SlopeQuick Check of Electrode Slope
X.
Quick Check of Electrode Slope
X. X.
Quick Check of Electrode SlopeQuick Check of Electrode Slope
• Connect BNC (connector) to pH/mV/ISE meter.
• Place meter in mV mode.
• Place 100 mL of deionized water into a vessel with
stir bar. Add 2 mL of ISA Hanna HI 4001-00.
• Place sensor into prepared sample.
• Add 1 mL of 1000 ppm or 0.1 M Ammonia standard
to beaker. Record the mV value when stable.
• Add an additional 10 mL of standard to the solution.
Record the mV when reading has stabilized. This
value should be less than the previous noted (more
negative).
• Determine the difference between the two mV values.
An acceptable value for this slope is 54±4 mV at
ambient temperatures between 20 and 25°C.
XI.XI.
Corrective actionCorrective action
XI.
Corrective action
XI.XI.
Corrective actionCorrective action
• Verify that the upper cap has been screwed in all the
way.
• Verify electrode is connected properly to meter and the
meter is is powered.
• Verify ISA has been added in the correct ratio to the
standard.
• Examine the white membrane and check for electrolyte that might have leaked through the PTFE film.
Replace membrane if damaged.
• If sensor does not change mV verify the the glass
assembly is operational (See section VIII).
12
Page 33

XII. XII.
Sample HandlingSample Handling
XII.
Sample Handling
XII. XII.
Sample HandlingSample Handling
• Keep samples stored in tightly covered bottles to prevent ammonia loss or ammonia contamination from
other sources.
• Alkaline samples must be measured at once or acidified for storage. (HCl may be added to bring pH to 6).
• Acidic samples such as wine or juice may require
addition ISA. Samples should be approximately pH
11 for measurement.
• Measure sample and standards quickly after adding
ISA because ammonia gas will escape from the solution.
• For solutions containing organically bound nitrogen
such as oil, sludge, waste, or samples which may
contain surfactants; digest sample first using a total
Kjeldahl nitrogen (TKN) procedure. This involves
oxidation with hot sulfuric acid which converts bound
nitrogen to ammonium ions. Consult Method 4500N
from Standard Methods for the Examination of
org
Water and Wastewater.
• For samples found to penetrate or “wet” the mem-
brane, measurements may be made above the sample
in a small headspace of a sealed system such as HI
4000-71 test vessel, provided the concentration of
NH3 is greater than 10
-3
M. The headspace should be
.
saturated with water vapor and the membrane end of
the electrode suspended in the gas sample above the
sample with ISA added. Expect a longer response
time from the sensor when gas phase measurements
are made.
13
Page 34

XIII. XIII.
Direct Calibration and MeasurementDirect Calibration and Measurement
XIII.
Direct Calibration and Measurement
XIII. XIII.
Direct Calibration and MeasurementDirect Calibration and Measurement
The direct method can be used in the linear working regions of the sensor. (See figure for typical sensor response).
A direct reading ISE meter (HI 4222 or equivalent) determines concentration of the unknown by a direct reading
after calibrating the meter with the standards. The meter is
calibrated with two or more freshly made standards that
are in the measurement range of the unknowns. HI 400100 ISA is added just before measurement of the standard
or sample. Covering the vessel to prevent gas loss is advised.
A pH/mV meter in mV mode and semi-log graph paper
may also be used. Two or freshly prepared standards that
are in the measurement range of the unknowns (with ISA
added), are measured in mV mode on the meter. These
standards are plotted on semilog graph paper and their
points are connected to form a straight-line curve. When
samples are measured, their mV values are converted to
concentration by following the mV to the concentration axis
on the semi-log plot.
Method 4500-NH3 D. from Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater is a direct measurement method for water samples.
For both direct reading and mV convertion, ISA is added
prior to measurement and the vessel should be covered to
prevent gas loss.
In the lower concentration ranges the electrode calibration
becomes less linear, many more calibration points are
needed, and calibration will need to be repeated more
frequently. Known addition method may also be used in
these regions provided the actual slope of the sensor has
been determined.
Direct Measurement Procedure
1) Follow section IX to prepare sensor.
2) Follow section VI to prepare standards and solutions.
14
Page 35

• Standards should bracket the measurement range of
V
interest and differ from each other by a factor of 10 in
the linear regions.
• Standards and solutions should be at the same temperature. 2 mL of ISA is added to each 100 mL of
sample and standard. A color change should occur to
indicate the ISA has been added.
• Protect these solutions from loss of dissolved gas by
covering and using promptly.
3) Follow section VII; General Guidelines to optimize test
set-up.
4) During calibration it is best to start with lower concentration samples first. Wait for a stable reading before
reading/recording values.
5) To prevent carry over and contamination of samples,
rinse sensors with deionized water and blot dry between samples.
6) Between measurements suspend sensor tip in a small
sample of NH3 Conditioning solution;
HI 4001-45. Rinse body with deionized water and
blot dry before placing in next sample.
Typical calibration curve for HI 4101 Ammonia ISE
-300
-250
-200
-150
m
-100
-50
0
0123456
50
Typical Linearity for HI 4101 Electrode
-Log of [M
]
15
Page 36

XIVXIV
. .
Other Measurement TOther Measurement T
XIV
.
Other Measurement T
XIVXIV
. .
Other Measurement TOther Measurement T
echniquesechniques
echniques
echniquesechniques
Known addition
An unknown concentration of ammonia can be determined
by adding a known amount (volume and concentration) of
ammonia standard to a known volume of the sample. This
technique is extremely useful for ammonia as the sensor
may drift from calibrated values over time, however the
slopes remain constant. With known addition, the standard and sample are measured within minutes of one
another. The technique can use an ideal sensor slope, but
actual slopes at the temperature of measurement should
be determined and used if possible. This will improve accuracy. Known addition is Method 4500-NH3 E. from
Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater.
1) The volume of the unknown sample (V
Sample
) is measured accurately and placed into the closed sample
vessel. The sensor is secured in the vessel and then the
vessel is placed on a stirrer.
2) ISA is added at 1 part per 50 parts sample.
3) When the measurement is stable the mV value is
noted.
4) A known amount, volume (V
(C
), of NH
Standard
mV values are again noted when the measurement is
standard is then added to the sample.
3
) and concentration
Standard
stable.
5) The mV change is then calculated (∆E).
6) Using the measured and calculated values, the
sample concentration (C
) can be determined.
Sample
C
sample
C
=
(V
(V
standardVstandard
)10
T
∆E/S
(V
sample+Vstandard+VISA
sample+VISA
- (VS’)
)= V
16
S’
)= V
V
S’
V
sample
T
Page 37

7) The procedure can be repeated with a second standard
addition to verify slope and operation of the method.
Note:
This method is preprogrammed in the Hanna HI
4222pH/ISE/mV meter, which simplifies the method
greatly and permits repeated determinations easily.
Example:
Ammonia determination with known addition:
1. A 50 mL sample of unknown (V
) is placed in an
SAMPLE
clean vessel with an electrode. 1 mL of ISA is added
to the sample and the color change is noted. The
sample is covered and permitted to mix. The mV is
then recorded when the sensor has stabilized.
2. 5 mL (V
STANDARD
) of 0.1 M (C
) standard is then
STANDARD
added to the vessel and is permitted to mix. The mV
value decreases as the concentration increases. (Note:
for other concentration samples, add a known volume
and concentration of standard to produce a 30 mV
change or greater.
3. The unknown ammonia concentration in the original
sample (C
) can then be determined by using the
SAMPLE
equation provided.
17
Page 38

XV. XV.
Storage and Care of the HI 4101 sensorStorage and Care of the HI 4101 sensor
XV.
Storage and Care of the HI 4101 sensor
XV. XV.
Storage and Care of the HI 4101 sensorStorage and Care of the HI 4101 sensor
The HI 4101 sensor can be stored assembled and ready to
use in HI 4001-45 Conditioning solution overnight or
between measurements. After overnight storage, gently pull
on the cable to compress the spring mechanism thus
permitting electrolyte to exchange from the bulk to the thin
film between the membrane and glass. Calibration is
required after doing this.
For longer term storage (over a week), disassemble the
sensor completely and rinse off the internal pH/reference
assembly, the outer body and the membrane cap. Discard
the white PTFE membrane. (Note: keep black membrane
cap). Cover the glass tip with the protective shipping cap
and store parts securely in the original shipping box. When
reassembling the sensor follow section IX.
XVI. XVI.
Conversion TConversion T
XVI.
Conversion T
XVI. XVI.
Conversion TConversion T
ablesables
ables
ablesables
For NHFor NH
For NH
For NHFor NH
33
3
33
Multiply byMultiply by
Multiply by
Multiply byMultiply by
Moles/L (M) NH3 to ppm NH3 (mg/L) 1.70 X 10
ppm NH3 (mg/L) to M (Moles/L) 5.882 X 10
For N-NH3 (ppm as nitrogen)For N-NH3 (ppm as nitrogen)
For N-NH3 (ppm as nitrogen)
For N-NH3 (ppm as nitrogen)For N-NH3 (ppm as nitrogen)
Multiply byMultiply by
Multiply by
Multiply byMultiply by
Moles/L (M) NH3 to ppm N-NH3 (mg/L) 1.40 X 10
4
-5
4
18
Page 39

XVII. XVII.
XVII.
XVII. XVII.
HI 4101 AHI 4101 A
HI 4101 A
HI 4101 AHI 4101 A
ccessories and Replacement Pccessories and Replacement P
ccessories and Replacement P
ccessories and Replacement Pccessories and Replacement P
artsarts
arts
artsarts
For CalibrationFor Calibration
For Calibration
For CalibrationFor Calibration
CodeCode
Code
CodeCode
::
:
::
HI 4001-00 Ionic Strength Adjuster (500 mL)
HI 4001-01 Hanna 0.1 M standard (500 mL)
HI 4001-02* Hanna 100 ppm N standard
(500 mL)
HI 4001-03* Hanna 1000 ppm N standard
(500mL)
HI 4001-30 Nitrate test kit (Bulk pkg)
*Please Note: These calibration standards are ppm as
NH3-N.
For Maintenance:For Maintenance:
For Maintenance:
For Maintenance:For Maintenance:
HI 4001-40 Hanna Ammonia Fill solution
(4 X 30 mL)
HI 4001-45 Hanna Ammonia conditioning
solution (500 mL)
HI 4000-47 Bulk package of 10 each
HI 4000-47-4 and HI 4000-47-7
buffer packets
HI 4000-52 Replacement membrane cap
HI 4001-51 Replacement membranes kit
(20 pieces)
HI 4000-51 Replacement pH/reference electrode
assembly
HI 740155P Capillary Pipettes (20 piece)
HI 740159 Plastic tweezers (1 piece)
19
Page 40

MAN4101 10/08 R5
WARRANTY WARRANTY
WARRANTY
WARRANTY WARRANTY
Hanna Instruments Ion Selective Electrodes are warranted to
be free of defects in material and workmanship for 6 months
from date of purchase when used for their intended purpose
and maintained according to instructions. If they fail to work
when first used contact your dealer immediately. Damage due
to accidents, misuse, misapplication, tampering or lack of
prescribed maintenance is not covered.
Hanna Instruments reserves the right to modify the design,
construction or appearance of its products without advance
notice.
20
 Loading...
Loading...