Page 1
Instruction Manual
HI 3875
Free Chlorine
Medium Range
Test Kit with
Checker Disc
SPECIFICATIONS
Range 0 to 3.5 mg/L (ppm) as Free Chlorine
Smallest Increment 0.1 mg/L
Analysis Method Colorimetric
Sample Size 5 mL
Number of Tests 100
Case Dimensions 235x175x115 mm (9.2x6.9x4.5")
Shipping Weight 984 g (34.7 oz.)
INSTRUCTIONS
READ THE ENTIRE INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE USING THE KIT
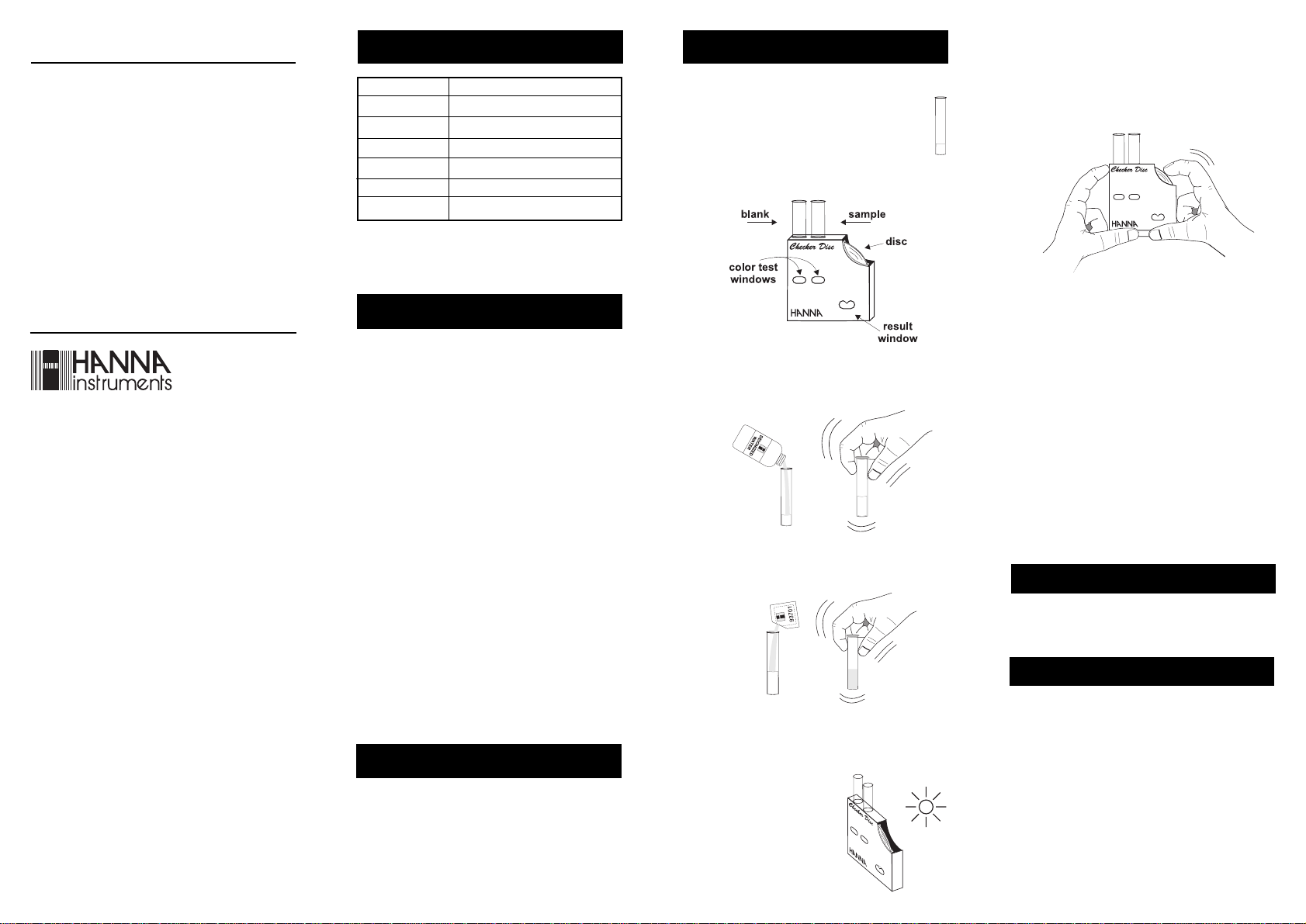
• Use the pipette to fill each glass vial with
5 mL of sample (up to the mark).
5 mL
• Insert one of the vials into the left hand opening of the
checker disc. This is the blank.
• Keep the checker disc at a distance of 30-40 cm (1216") from the eyes to match the color. Rotate the disc
while looking at the color test windows and stop when
you find the color match. Read the value in the result
window directly in mg/L (or ppm) of Chlorine.
www.hannainst.com
Dear Customer,
Thank you for choosing a Hanna Product.
Please read the instruction sheet carefully before using the
test kit. It will provide you with the necessary information
for correct use of the kit. If you need additional information,
do not hesitate to e-mail us at tech@hannainst.com.
Remove the chemical test kit from the packing material and
examine it carefully to make sure that no damage has
occurred during shipping. If there is any noticeable damage, notify your Dealer or the nearest Hanna office
immediately.
Each kit is supplied with:
HI 93701-0 Free Chlorine Reagent, packets (100 pcs);
•
• Deionized Water, 1 bottle (500 mL);
• 1 checker disc (containing the disc);
• 2 glass vials with caps;
• 1 plastic pipette (3 mL).
Note: Any damaged or defective item must be returned in
its original packing materials.
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Chlorine is the most commonly used water disinfectant in
applications that vary from treatment of drinking water
and wastewater, pool and spa sanitization, to food processing and sterilization. Chlorine present in water binds with
bacteria, leaving only a part of the original quantity (free
chlorine) to continue its disinfecting action. If the free
chlorine level is improper with respect to pH, water will have
an unpleasant taste and odor and the disinfecting potential of the chlorine will be diminished.
Free chlorine reacts with ammonium ions and organic
compounds to form chlorine compounds resulting in diminished disinfecting capabilities compared with free chlorine.
Chlorine compounds together with chloramines form combined chlorine. Combined chlorine and free chlorine together
result in total chlorine.
While free chlorine has a much higher disinfectant potential,
combined chlorine has a much higher stability and has a
lesser volatility.
Note: mg/L is equivalent to ppm (parts per million).
CHEMICAL REACTION
The reaction between chlorine and the DPD reagent causes
a pink tint in the sample which is proportional to the
chlorine concentration.
ISTR3875 02/00 PRINTED IN ITALY
• Add to the other vial deionized water up to the 10 mL
mark. Replace the cap and shake to mix.
• Remove the cap and add 1 packet of HI 93701-0
reagent. Replace the cap and mix. This is the reacted
sample.
• Remove the cap and insert the reacted sample into the
right hand opening of the checker disc.
• Hold the checker disc so that a
light source illuminates the
samples from the back of the
windows.
For best results: Perform the reading three times and take
the average value (divide by 3 the sum of the three
numbers). Intensely colored samples will make the color
matching difficult and they should be adequately treated
before performing the test. Suspended matter in large
amounts should be removed by prior filtration.
Caution: Ultraviolet radiation may cause fading of colors.
When not in use, keep the disc protected from light,
in a cool and dry place.
Interferences: bromine, iodine, fluorine, ozone, oxidized
manganese and chromium.
REFERENCES
Adaptation of the EPA recommended DPD method 330.5.
HEALTH AND SAFETY
The chemicals contained in this kit may be hazardous if
improperly handled. Read the relevant Health and Safety
Data Sheet before performing this test.
 Loading...
Loading...