Page 1
Instruction Manual
SPECIFICATIONS
INSTRUCTIONS
REFERENCES
HI 3831T
Total Chlorine
Test Kit
www.hannainst.com
Dear Customer,
Thank you for choosing a Hanna Product.
Please read the instructions carefully before using the chemical
test kit. It will provide you with the necessary information for
correct use of the kit.
Remove the chemical test kit from the packing material and
examine it carefully to make sure that no damage has
occurred during shipping. If there is any noticeable damage,
notify your Dealer or the nearest Hanna office immediately.
Each kit is supplied with:
• 1 Color Comparator Cube;
• Reagent 1 (20 mL);
• Reagent 2 (15 mL);
• Reagent 3 (15 mL).
Range 0 to 2.5 mg/L (ppm) Chlorine
Smallest Increment 0.5 mg/L (ppm) Chlorine
Analysis Method Colorimetric
Sample Size 5 mL
Number of Tests 50 (average)
Case Dimensions 220x145x55 mm (8.7x5.7x2.1")
Shipping Weight 205 g (7.7 oz.)
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
In pools and drinking water supplies, chlorination serves to
kill or deactivate disease-producing microorganisms. It can
also improve water quality by reacting with ammonia, iron,
sulfide and some organic substances. However, an excess
concentration of chlorine in water can produce adverse conditions, such as formation of carcinogenic chloroform or other
toxins. To maximize the purpose for chlorination and minimize any adverse effects, it is essential to monitor the
chlorine levels closely.
The Hanna Chlorine Test Kit determines the Total Chlorine
concentration in water via a color cube. This makes the test
kit practical for field use. No iodine or bromine can be
present for this test to work properly.
CHEMICAL REACTION
The addition of chlorine to water produces hydrochloric and
hypochlorous acids. The hypochlorous acid acts as the disinfectant and bleaching agent. The formation of chloramines
and nitrogen trichloride will occur if ammonia is present.
These are known as bound chlorine. Total chlorine is measured by a colorimetric method.
The reaction if buffered at approx. 6.3 pH; in presence of an
excessive quantity of iodide ions, the DPD (N,N-diethyl-pphenylenediamine) is oxidized by chlorine producing a reddish
color. The color intensity of the solution determines the total
chlorine concentration.
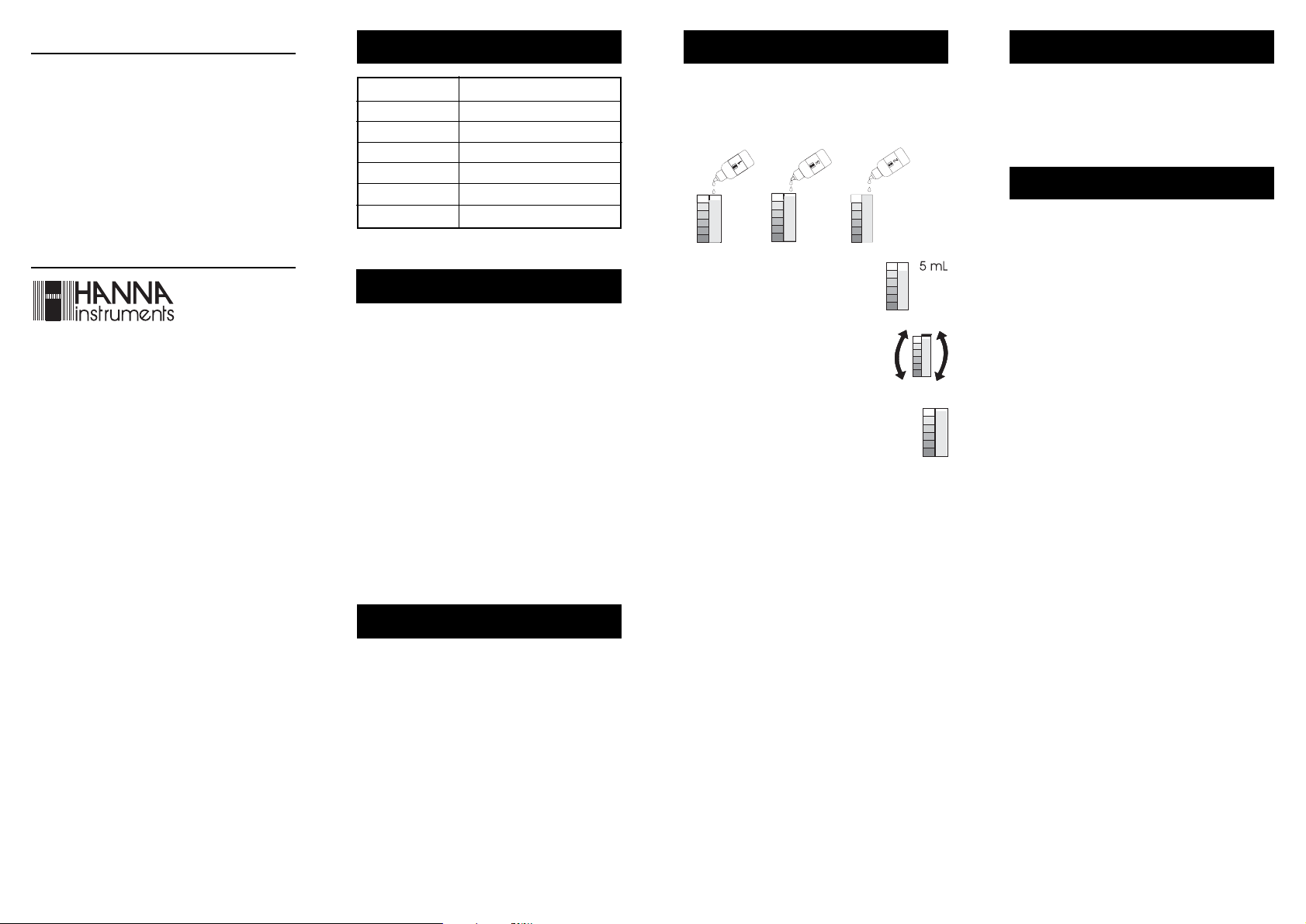
READ THE ENTIRE INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE USING THE KIT
• Add 5 drops of Reagent 1, 2 drops Reagent 3 and 3
drops of Reagent 2 to the color comparator cube.
523
• Fill the color comparator cube with water sample to the 5 mL mark.
• Replace the cap and mix by carefully swirling the cube in tight circles and inverting
it several times.
• Determine which color matches the solution in
the vessel and record the results in mg/L (ppm)
total chlorine.
BOUND CHLORINE
The concentration of bound chlorine in the sample is determined by subtracting the Free Chlorine (HI 3831F) result
from the Total Chlorine result (HI 3831T).
Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 18th Edition, 1992, pages 445-446.
HEALTH AND SAFETY
The chemicals contained in this kit may be hazardous if
improperly handled. Read Health and Safety Data Sheet
before performing this test.
Note: Any damaged or defective item must be returned in
its original packing materials.
ISTR3831TR1 10/01 PRINTED IN ITALY
Page 2

 Loading...
Loading...