Page 1

Imaging Guide
Document Reader
Page 2

Disclaimer
Hand Held Products (“Hand Held Products”) reserves the right to make changes in specifications and other information contained
in this document without prior notice, and the reader should in all cases consult Hand Held Products to determine whether any
such changes have been made. The information in this publication does not represent a commitment on the part of Hand Held
Products.
Hand Held Products shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein; nor for incidental or
consequential damages resulting from the furnishing, performance, or use of this material.
This document contains proprietary information that is protected by copyright. All rights are reserved. No part of this document
may be photocopied, reproduced, or translated into another language without the prior written consent of Hand Held Products.
©2007 Hand Held Products All rights reserved.
Web Address: www.handheld.com
Microsoft
countries.
Macintosh
Other product names or marks mentioned in this document may be trademarks or registered trademarks of other companies and
are the property of their respective owners.
®
Windows® is either a registered trademark or trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or other
®
is a trademark of Apple Computer, Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries.
FCC Class A Compliance Statement
This device complies with part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
• This device may not cause harmful interference.
• This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC
Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated
in a commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and
used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no
guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to
cause harmful interference, in which case the user will be required to correct the interference at his own expense.
Caution: Any changes or modifications made to this device that are not expressly approved by Hand Held Products, Inc. may
void the user's authority to operate the equipment.
Note: To maintain compliance with FCC Rules and Regulations, cables connected to this device must be shielded cables, in
which the cable shield wire(s) have been grounded (tied) to the connector shell.
Canadian Class A Compliance
This Class A digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003.
Conformité à la règlementation canadienne
Cet appareil numérique de la Classe A est conforme à la norme NMB-003 du Canada.
The CE mark on the product indicates that the system has been tested to and conforms with the provisions noted
within the 2004/108/EC Electromagnetic Compatibility Directive and the 2006/95/EC Low Voltage Directive.
For further information please contact:
Hand Held Products
Nijverheidsweg 9-13
5627 BT Eindhoven
The Netherlands
Hand Held Products shall not be liable for use of our product with equipment (i.e., power supplies, personal computers, etc.) that
is not CE marked and does not comply with the Low Voltage Directive.
Patents
Please refer to the product packaging for a list of patents.
Page 3

LED Safety Statement
This device has been tested in accordance with IEC60825-1 LED safety, and has been certified to be under the limits of a Class
1 LED device.
Laser Eye Safety Statement
This product is under the limits of a class 2 laser device.
This device has been tested in accordance with and complies with IEC60825-1: 1993+A1+A2 and 21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11,
except for deviations pursuant to Laser Notice No. 50, dated July 26, 2001.
LASER LIGHT, DO NOT STARE INTO BEAM, CLASS 2 LASER PRODUCT, 1.0 mW MAX OUTPUT: 650nM.
Caution: Use of controls or adjustments or performance of procedures other than those specified herein may result in hazardous
radiation exposure.
UL and cUL Statement
UL and cUL listed: UL60950-1 and CSA C22.2 No.60950-1-03.
C-Tick Statement
Conforms to AS/NZS 3548. C-Tick number: N10410.
Solids and Water Protection
The 4800dr has a rating of IP40, immunity of foreign particles and dripping water.
GS Mark
This product has been issued a GS certificate.
Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment Information
Note: Hand Held Products complies with Directive 2002/96/EC OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL of
27 January 2003 on waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE).
This product has required the extraction and use of natural resources for its production. It may contain hazardous substances
that could impact health and the environment, if not properly disposed.
In order to avoid the dissemination of those substances in our environment and to diminish the pressure on the natural resources,
we encourage you to use the appropriate take-back systems for product disposal. Those systems will reuse or recycle most of
the materials of the product you are disposing in a sound way.
The crossed out wheeled bin symbol informs you that the product should not be disposed of along with municipal waste
and invites you to use the appropriate separate take-back systems for product disposal.
If you need more information on the collection, reuse, and recycling systems, please contact your local or regional waste
administration.
You may also contact your supplier for more information on the environmental performances of this product.
Page 4
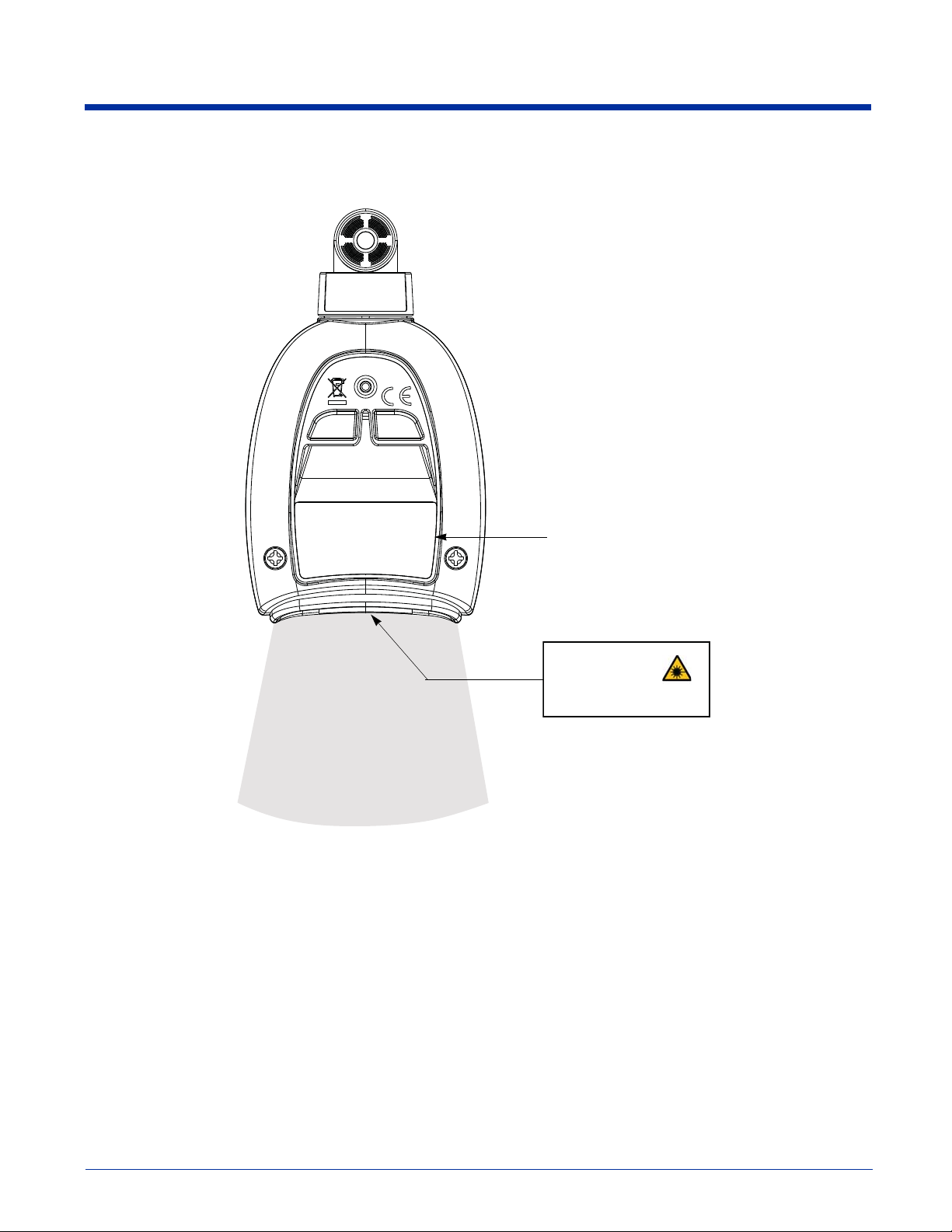
Document Reader Identification
Compliance Label
location
Laser Light Emissions
LASER LIGHT. DO NOT STARE INTO BEAM
CLASS 2 LASER PRODUCT
1.0 mW MAX OUTPUT: 650nM
IEC60825-1: 1993+A1+A2
Complies with 21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11
except for deviations pursuant to Laser
Notice No. 50, dated July 26, 2001.
Page 5

Table of Contents
Chapter 1 - Imaging Commands
Single-Use Basis ................................................................................................................................. 1-1
Command Syntax ................................................................................................................................ 1-1
Step 1 - Take a Picture Using IMGSNP ....................................................................................1-1
Image Snap - IMGSNP ....................................................................................................................... 1-1
IMGSNP Modifiers ...................................................................................................................... 1-1
P - Imaging Style ................................................................................................................... 1-1
B - Beeper ............................................................................................................................. 1-1
T - Wait for Trigger .............................................................................................................. 1-2
L - LED State ........................................................................................................................ 1-2
A - Aimer Lines .................................................................................................................... 1-2
E - Exposure .......................................................................................................................... 1-2
G - Gain ................................................................................................................................. 1-3
W - Target White Value ........................................................................................................ 1-3
D - Delta for Acceptance ...................................................................................................... 1-3
U - Update Tries .................................................................................................................... 1-3
% - Target Set Point Percentage ........................................................................................... 1-4
Step 2 - Ship a Picture Using IMGSHP or IMGACP ...............................................................1-5
Image Ship - IMGSHP ........................................................................................................................ 1-5
Image Auto Crop - IMGACP.............................................................................................................. 1-5
IMGSHP/IMGACP Modifiers...................................................................................................... 1-6
A - Infinity Filter ................................................................................................................... 1-6
C - Compensation .................................................................................................................. 1-6
D - Pixel Depth ..................................................................................................................... 1-6
E - Edge Sharpen ................................................................................................................... 1-7
F - File Format ...................................................................................................................... 1-7
H - Histogram Stretch ........................................................................................................... 1-7
I - Invert Image ..................................................................................................................... 1-8
IF- Noise Reduction .............................................................................................................. 1-8
IU - Image Adaptive Text Filter ........................................................................................... 1-9
IS - Unsharp/Brighten Filter ............................................................................................... 1-10
J - JPEG Image Quality ....................................................................................................... 1-10
K - Gamma Correction ........................................................................................................ 1-10
L, R, T, B, M - Image Cropping ......................................................................................... 1-11
P - Protocol .......................................................................................................................... 1-11
S - Pixel Ship ....................................................................................................................... 1-12
U - Document Image Filter ................................................................................................. 1-12
V - Blur Image .................................................................................................................... 1-13
W - Histogram Ship ............................................................................................................ 1-13
Intelligent Signature Capture - IMGBOX.........................................................................................1-14
IMGBOX Modifiers ................................................................................................................... 1-14
A - Output Image Width ..................................................................................................... 1-14
B - Output Image Height ..................................................................................................... 1-15
i
Page 6

D - Pixel Depth ....................................................................................................................1-15
F - File Format .....................................................................................................................1-15
H - Height of Signature Capture Area .................................................................................1-15
K - Gamma Correction ........................................................................................................1-15
R - Resolution of Signature Capture Area ...........................................................................1-16
S - Barcode Aspect Ratio ....................................................................................................1-16
W - Width of Signature Capture Area .................................................................................1-16
X - Horizontal Barcode Offset ............................................................................................1-16
Y - Vertical Barcode Offset .................................................................................................1-16
Chapter 2 - Serial Default Commands
Conventions .........................................................................................................................................2-1
Menu Command Syntax ......................................................................................................................2-1
Query Commands .........................................................................................................................2-1
Concatenation of Multiple Commands .........................................................................................2-2
Responses......................................................................................................................................2-2
Examples of Query Commands ....................................................................................................2-2
Menu Commands.................................................................................................................................2-3
Chapter 3 - Customer Support
Technical Assistance ...........................................................................................................................3-1
Online Technical Assistance.........................................................................................................3-1
For Further Information ................................................................................................................3-1
Product Service and Repair .................................................................................................................3-1
Online Product Service and Repair Assistance.............................................................................3-2
ii
Page 7

1
Imaging Commands
The document reader is like a digital camera in the way it captures, manipulates, and transfers images. The following commands
allow you to alter the way the document reader performs these functions.
Single-Use Basis
Imaging Commands with their modifiers send instructions to the document reader on a single-use basis, and take effect for a
single image capture. Once that capture is complete, the document reader reverts to its imaging default settings. If you want to
permanently change a setting, you must use the serial default commands (see Chapter 2). When the serial default command is
used, that selection becomes the new, permanent setting for the document reader.
Command Syntax
Multiple modifiers and commands can be issued within one sequence. If additional modifiers are to be applied to the same
command, just add the modifiers to that command. For example, to add 2 modifiers to the Image Snap command, such as setting
the Imaging Style to 1P and the Wait for Trigger to 1T, you would enter IMGSNP1P1T.
Note: After processing an image capture command (IMGSNP or IMGBOX), you must follow it with an IMGSHP or IMGACP
command if you want to see it on your terminal.
To add a command to a sequence, each new command is separated with a semicolon. For example, to add the Image Ship
command to the above sequence, you would enter IMGSNP1P1T;IMGSHP.
The imaging commands are:
Image Snap - IMGSNP (page 1-1)
Image Ship - IMGSHP (page 1-5)
Intelligent Signature Capture - IMGBOX (page 1-14)
The modifiers for each of these commands follow the command description.
Step 1 - Take a Picture Using IMGSNP
Image Snap - IMGSNP
An image is taken whenever the hardware button is pressed, or when the Image Snap (IMGSNP) command is processed.
The image snap command has many different modifiers that can be used to change the look of the image in memory. Modifiers
always begin with numbers and end with a letter (case insensitive). Any number of modifiers may be appended to the IMGSNP
command. For example, you can use the following command to snap an image, increase the gain, and have the beeper sound
once the snap is complete:
IMGSNP2G1B
IMGSNP Modifiers
P - Imaging Style
This sets the Image Snap style.
0P Decoding Style. This processing allows a few frames to be taken until the exposure parameters are met. The
last frame is then available for further use.
1P Photo Style
2P Manual Style. This is an advanced style that should only be used by an experienced user. It allows you the
most freedom to set up the document reader, and has no auto-exposure.
B - Beeper
Causes a beep to sound after an image is snapped.
0B No beep (default)
1B Sounds a beep when the image is captured.
(default)
. This mimics a simple digital camera, and results in a visually optimized image.
Document Reader Imaging Guide 1 - 1
Page 8

T - Wait for Trigger
Example of Aimer Lines Off (0A): Example of Aimer Lines On (1A) with LEDs off (0L):
Example of Exposure at 7874E with fluorescent lighting: Example of Exposure at 100E with fluorescent lighting:
Waits for a hardware button push before taking the image. This is only available when using Photo Style (1P).
0T Takes image immediately (default)
1T Waits for a button push, then takes the image
L - LED State
Determines if the LEDs should be on or off, and when. Ambient illumination (0L) is preferred for taking pictures of color
documents, such as ID cards, especially when the document reader is in a stand. LED illumination (1L) is preferred when
the document reader is hand held. LED State is not available when using Decoding Style (0P).
0L LEDs off (default)
1L LEDs on
A - Aimer Lines
Sets whether the aimer lines will be captured with the image or not. In order to capture the aimer lines, the LEDs must also
be off. If the LEDs are on, the aimer lines will not be captured.
0A Aimer Lines off (default)
1A Aimer Lines on
E - Exposure
Exposure is used in Manual Style only (2P), and allows you to set the exposure time. This is similar to setting a shutter
speed on a camera. The exposure time determines how long the imager takes to record an image. On a bright day,
exposure times can be very short because plenty of light is available to help record an image. At nighttime, exposure time
can increase dramatically due to the near absence of light. Units are 127 microseconds. (Default = 7874)
nE Range: 1 - 7874
1 - 2 Document Reader Imaging Guide
Page 9

G - Gain
Example of Gain at 1G: Example of Gain at 4G: Example of Gain at 8G:
Example of White
Value at 75W:
Example of White
Value at 125W:
Example of White
Value at 200W:
Gain is used in Manual Style only (2P). Like a volume control, the gain modifier boosts the signal and multiplies the pixel
value. As you increase the gain, the noise in an image is also amplified.
1G No gain (default)
2G Medium gain
4G Heavy gain
8G Maximum gain
W - Target White Value
Sets the target for the median grayscale value in the captured image. For capturing close-up images of high contrast
documents, a lower setting, such as 75, is recommended. Higher settings result in longer exposure times and brighter
images, but if the setting is too high, the image may be overexposed. Target White Value is only available when using Photo
Style (1P). (Default = 125)
nW Range: 0 - 255
D - Delta for Acceptance
This sets the allowable range for the white value setting (see W - Target White Value). Delta is only available when using
Photo Style (1P). (Default = 25)
nD Range: 0 - 255
U - Update Tries
This sets the maximum number of frames the document reader should take to reach the D - Delta for Acceptance. Update
Tries is only available when using Photo Style (1P). (Default = 6)
nU Range: 0 - 10
Document Reader Imaging Guide 1 - 3
Page 10

% - Target Set Point Percentage
Example of Target Set
Point Percentage at 97%:
Example of Target Set
Point Percentage at 40%:
Example of Target Set
Point Percentage at 50%:
Sets the target point for the light and dark values in the captured image. A setting of 75% means 75% of the pixels are at
or below the target white value, and 25% of the pixels are above the target white value. Altering this setting from the default
is not recommended under normal circumstances. To alter grayscale values, W - Target White Value should be used.
(Default = 97)
n% Range: 1 - 99
1 - 4 Document Reader Imaging Guide
Page 11

Step 2 - Ship a Picture Using IMGSHP or IMGACP
Image taken without Autocrop: Image taken with Autocrop:
Image Ship - IMGSHP
An image is taken whenever the button is pressed, or when the Image Snap (IMGSNP) command is processed. The last image
is always stored in memory. You can “ship” the image by using the IMGSHP or IMGACP command.
The image ship and image auto crop commands have many different modifiers that can be used to change the look of the image
output by the document reader. Modifiers affect the image that is transmitted, but do not affect the image in memory. Modifiers
always begin with a number and end with a letter (case insensitive). Any number of modifiers may be appended to the IMGSHP
or IMGACP command. For example, you can use the following command to snap and ship a bitmap image with gamma
correction and document image filtering:
IMGSNP;IMGSHP8F75K26U
Image Auto Crop - IMGACP
Image Auto Crop removes unwanted portions of an image, such as blank space surrounding an image. Image Auto Crop uses
artificial intelligence to search for the area of the image that contains text. It then crops the image to just that area and adjusts it
to a horizontal display. Depending on the size and position of the document, this may possibly result in an upside-down or
sideways image. The image can then be rotated to the proper orientation using your local software. Smaller documents will crop
more quickly than larger documents. The accuracy of auto crop is affected by the density of the text, amount of non-text features,
and contrast in the image.
Note: Any modifiers to IMGACP are applied to the resultant, auto cropped image.
The same modifiers are used for image ship and image auto crop. The following command was used to take and crop an image
that had the white value lowered and the edge sharpen filter on:
IMGSNP75W;IMGACP14E
Document Reader Imaging Guide 1 - 5
Page 12
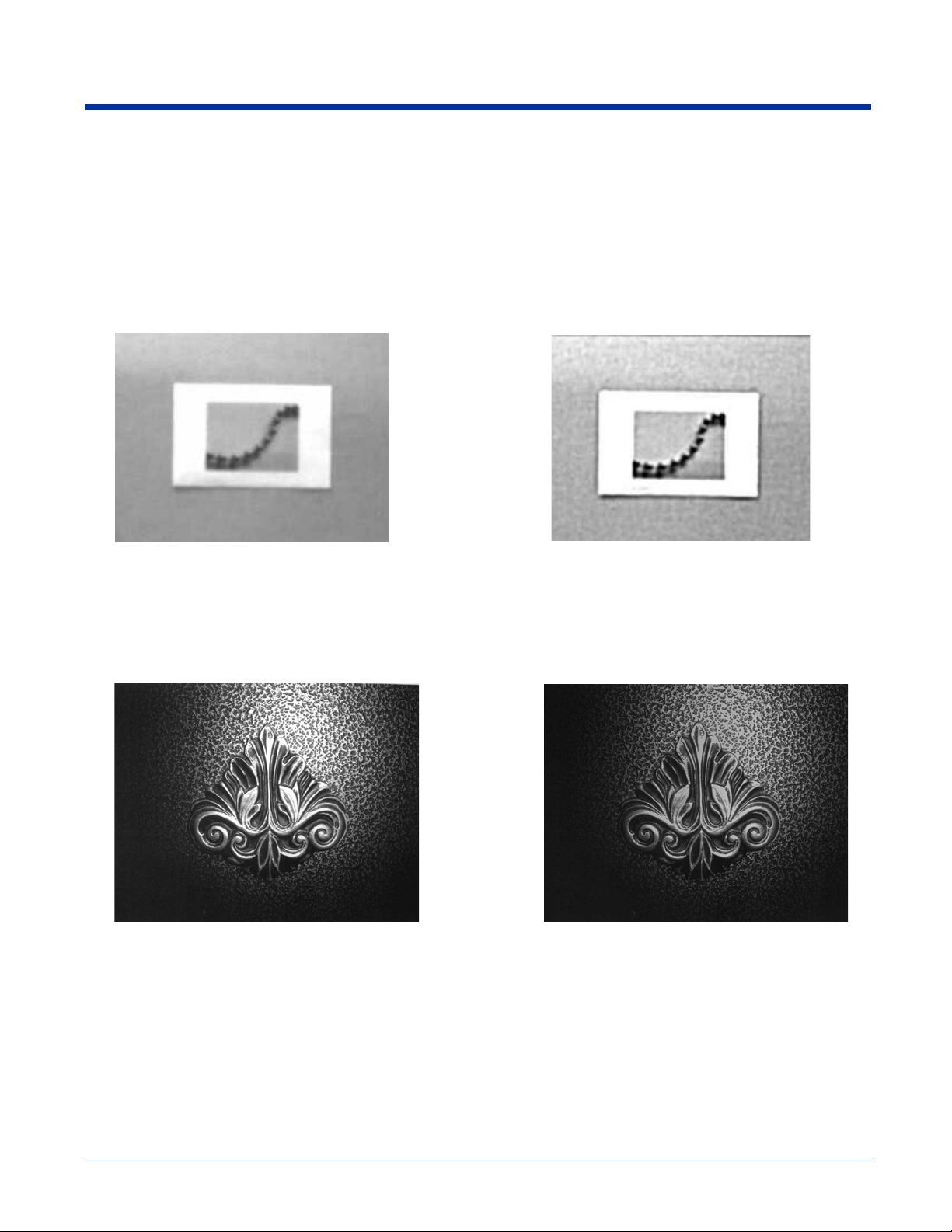
IMGSHP/IMGACP Modifiers
Example of Infinity Filter off (0A)
from approximately 12 feet (3.66m) away:
Example of Infinity Filter on (1A)
from approximately 12 feet (3.66m) away:
Example of Compensation at 0C: Example of Compensation at 1C:
A - Infinity Filter
Enhances pictures taken from very long distances (greater than 10 feet or 3m). The Infinity Filter should not be used with
Image Auto Crop - IMGACP (page 1-5).
0A Infinity filter off (default)
1A Infinity filter on
C - Compensation
Flattens the image to account for variations in illumination across the image.
0C Compensation disabled (default)
1C Compensation enabled
D - Pixel Depth
Indicates the number of bits per pixel in the transmitted image (KIM or BMP format only).
8D 8 bits per pixel, grayscale image (default)
1D 1 bit per pixel, black and white image
1 - 6 Document Reader Imaging Guide
Page 13

E - Edge Sharpen
Example of Edge Sharpen at 0E: Example of Edge Sharpen at 24E:
Example of Histogram Stretch at 0H: Example of Histogram Stretch at 1H:
An edge sharpen filter cleans up the edges of an image, making it look cleaner and sharper. While edge sharpening does
make the image look cleaner, it also removes some fine detail from the original image. The strength of the edge sharpen
filter can be entered from 1 to 24. Entering a 23E gives the sharpest edges, but also increases noise in the image.
0E Don’t sharpen image (default)
14E Apply edge sharpen for typical image
ne Apply edge sharpen using strength n (n = 1-24)
F - File Format
Indicates the desired format for the image.
0F KIM format
1F TIFF binary
2F TIFF binary group 4, compressed
3F TIFF grayscale
4F Uncompressed binary (upper left to lower right, 1 pixel/bit, 0 padded end of line)
5F Uncompressed grayscale (upper left to lower right, bitmap format)
6F JPEG image (default)
8F BMP format (lower right to upper left, uncompressed)
H - Histogram Stretch
Increases the contrast of the transmitted image. Not available with some image formats.
0H No stretch (default)
1H Histogram stretch
Document Reader Imaging Guide 1 - 7
Page 14
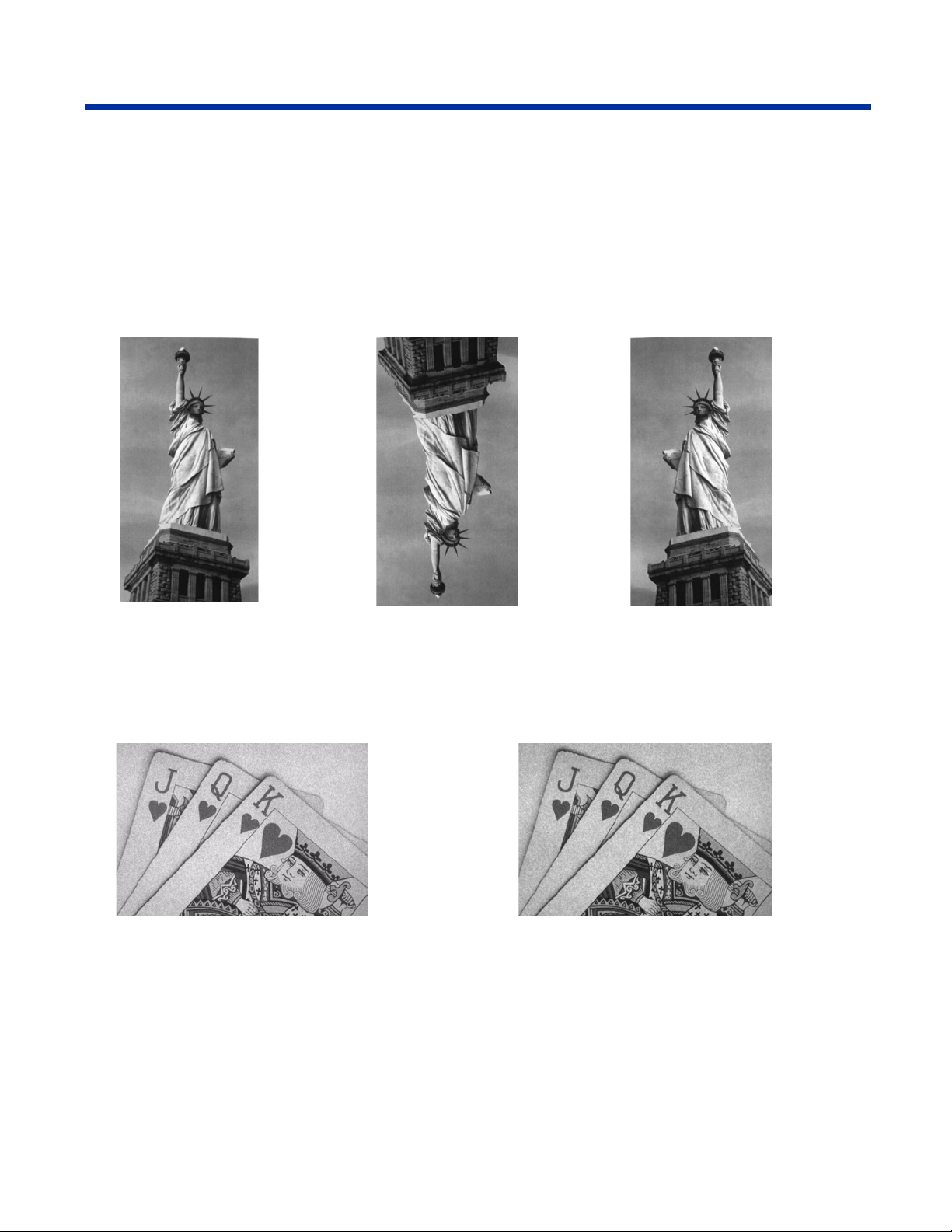
I - Invert Image
Example of image
with Invert Image set to 1ix:
Example of image not inverted: Example of image
with Invert Image set to 1iy:
Example of Noise Reduction On (1if):Example of Noise Reduction Off (0if):
Invert image is used to rotate the image around the X or Y axis.
Note: This feature should only be used with Image Ship - IMGSHP (page 1-5). Using this feature with Image Auto Crop -
IMGACP (page 1-5) may produce undesired results since Image Auto Crop attempts to rotate an image to a horizontal
display.
1ix Invert around the X axis (flips picture upside down)
1iy Invert around the Y axis (flips picture left to right)
IF- Noise Reduction
Used to reduce the salt and pepper noise in an image.
0if No salt and pepper noise reduction (default)
1if Salt and pepper noise reduction
1 - 8 Document Reader Imaging Guide
Page 15

IR - Image Rotate
Example of Image Rotate set to 0
ir
:
Example of Image Rotate set to 2
ir
:
Example of Image Rotate set to 1
ir
:
Example of Image Rotate set to 3
ir
:
Example of Adaptive Text Filter On (1iu):Example of Adaptive Text Filter Off (0iu):
Note: This feature should only be used with Image Ship - IMGSHP (page 1-5). Using this feature with Image Auto Crop -
IMGACP (page 1-5) may produce undesired results since Image Auto Crop attempts to rotate an image to a horizontal
display.
0ir Image as snapped (rightside up) (default)
1ir Rotate image 90 degrees to the right
2ir Rotate image 180 degrees (upside down)
3ir Rotate image 90 degrees to the left
IU - Image Adaptive Text Filter
The Adaptive Text Filter automatically sharpens the edges and smooths the area between the edges of text in an image.
The Adaptive Text Filter enhances images of documents such as ID cards and prescriptions, resulting in crisper text.
See U - Document Image Filter (page 1-12) for information about setting the Document Image Filter manually.
Note: The Adaptive Text Filter should not be used concurrently with the IS - Unsharp/Brighten Filter.
0iu Adaptive Text Filter off (default)
1iu Adaptive Text Filter on
Document Reader Imaging Guide 1 - 9
Page 16

IS - Unsharp/Brighten Filter
Example of Unsharp/Brighten Filter Off (0
is
): Example of Unsharp/Brighten Filter On (1
is
):
Example of Gamma Correction
set to 50K:
Example of Gamma Correction
set to 0K:
Example of Gamma Correction
set to 255K:
The Unsharp/Brighten Filter automatically sharpens the text and brightens the contrast of the image, making text more
readable. This is similar to the Image Adaptive Text Filter, however it brightens the image as well. You should test both
image processing techniques to determine which filter works best for your environment.
Note: The Unsharp/Brighten Filter should not be used concurrently with the IU - Image Adaptive Text Filter.
0is Unsharp/Brighten Filter off (default)
1is Unsharp/Brighten Filter on
J - JPEG Image Quality
Sets the desired quality when the JPEG image format is selected. Higher numbers result in higher quality, but larger files.
Smaller numbers result in greater amounts of lossy compression, faster transmission times, lower quality, but smaller files.
(Default = 50)
nJ Image is compressed as much as possible while preserving quality factor of n (n = 0 - 100)
0J worst quality (smallest file)
100J best quality (largest file)
K - Gamma Correction
Gamma measures the brightness of midtone values produced by the image. You can brighten or darken an image using
gamma correction. A higher gamma correction yields an overall brighter image. The lower the setting, the darker the image.
The optimal setting for text images is 50K.
0K Gamma correction off (default)
50K Apply gamma correction for brightening typical document image
nK Apply gamma correction factor n (n = 0-1,000)
1 - 10 Document Reader Imaging Guide
Page 17

L, R, T, B, M - Image Cropping
Example of Image
Crop set to 300L:
Example of Image
Crop set to 300R:
Example of Image Crop set to 200T:
Example of Image Crop set to 200B:
Uncropped Image:
Example of Image
Crop set to 238M:
Note: Image Cropping should not be used with Image Auto Crop - IMGACP (see page 1-5).
Ships a window of the image by specifying the left, right, top, and bottom pixel coordinates. Device columns are numbered
0 through 1279, and device rows are numbered 0 through 959.
nL The left edge of the shipped image corresponds to column n of the image in memory. Range: 000 - 1279.
(Default = 0)
nR The right edge of the shipped image corresponds to column n - 1 of the image in memory. Range: 000 - 1279.
(Default = all columns)
nT The top edge of the shipped image corresponds to row n of the image in memory. Range: 000 - 959. (Default =
0)
nB The bottom edge of the shipped image corresponds to row n - 1 of the image in memory. Range: 000 - 959.
(Default = all rows)
Alternately, specify the number of pixels to cut from the outside margin of the image; thus only the center pixels are
transmitted.
nM Margin: cut n columns from the left, n + 1 columns from the right, n rows from the top, and n + 1 rows from the
bottom of the image. Ship the remaining center pixels. Range: 0 - 478.
(Default = 0, or full image)
P - Protocol
Used for shipping an image. Protocol covers two features of the image data being sent to the host. It addresses the protocol
used to send the data (Hmodem, which is an Xmodem 1K variant that has additional header information), and the format of
the image data that is sent.
0P None (raw data)
2P None (default for USB)
3P Hmodem compressed (default for RS-232)
4P Hmodem
Document Reader Imaging Guide 1 - 11
Page 18

S - Pixel Ship
Example of Pixel Ship set to 1S:
Example of Pixel Ship set to 2S:
Example of Pixel Ship set to 4S:
Example of Pixel Ship set to 3S:
Example of Document Image
Filter set to 0U:
Example of Document Image
Filter set to 26U:
Pixel Ship sizes an image in proportion to its original size. It decimates the image by shipping only certain, regularly spaced
pixels. For example, 4S would transmit every fourth pixel from every fourth line. The smaller number of pixels shipped, the
smaller the image, however, after a certain point the image becomes unusable.
1S ship every pixel (default)
2S ship every 2nd pixel, both horizontally and vertically
3S ship every 3rd pixel, both horizontally and vertically
U - Document Image Filter
Allows you to input parameters to sharpen the edges and smooth the area between the edges of text in an image. This filter
should be used with gamma correction (see page 1-10), with the document reader in a stand, and the image captured using
the command:
IMGSNP1P0L168W90%32D
This filter typically provides better JPEG compression than the standard E - Edge Sharpen command (see page 1-13). This
filter also works well when shipping pure black and white images (1 bit per pixel). The optimal setting is 26U.
Note: If you want to use an automatic image filter, rather than changing these settings manually, refer to IU - Image Adaptive
Text Filter (page 1-9).
0U Document image filter off (default)
26U Apply document image filter for typical document image
nU Apply document image filter using grayscale threshold n. Use lower numbers when the image contrast is lower.
1U will have a similar effect to setting E - Edge Sharpen (page 1-7) to 22e. Range: 0-255.
1 - 12 Document Reader Imaging Guide
Page 19

V - Blur Image
Example of Blur Image Off (0V): Example of Blur Image On (1V):
Image used for histogram: Histogram of image at left:
Smooths transitions by averaging the pixels next to the hard edges of defined lines and shaded areas in an image.
0V Don’t blur (default)
1V Blur
W - Histogram Ship
A histogram gives a quick picture of the tonal range of an image, or key type. A low-key image has detail concentrated in
the shadows; a high-key image has detail concentrated in the highlights; and an average-key image has detail concentrated
in the midtones. This modifier ships the histogram for an image.
0W Don’t ship histogram (default)
1W Ship histogram
Document Reader Imaging Guide 1 - 13
Page 20

Intelligent Signature Capture - IMGBOX
Example of Image Width set to 200A: Example of Image Width set to 600A:
IMGBOX allows you to configure the size and location of a signature capture area relative to its proximity to a barcode. This
allows you to tailor a signature capture area to a specific form. In order to use IMGBOX, you need a set form where the signature
box location is in a known location relative to a barcode. You can input the overall size of the signature area, as well as specify
how far the signature area is from the barcode, vertically and horizontally. You can also set the resolution and file format for the
final output of the signature capture image.
Note: IMGBOX commands can only be triggered by one of the following types of barcodes: PDF417, Code 39, Code 128, Aztec,
Codabar, and Interleaved 2 of 5. Once one of these symbologies has been read, the image is retained for a possible
IMGBOX command.
The following IMGBOX example was executed and viewed using QuickView software. This software is available at
www.handheld.com. Click on Services and Support-Download Software. Select 4800dr from the Products list, then select
QuickView Software Utility.
Below is an example of a signature capture application. In this example, the aimer is centered over the signature capture area
and the trigger is pressed. A single beep is emitted, indicating that the imager has read a Code 128 barcode and the data has
been transferred to the host. An IMGBOX command may now be sent from the host to specify the coordinates of the signature
capture area below that code, and indicating that only that area containing the signature should be transferred as an image to
the host.
To see this example, align the aimer with the signature area (not with the barcode), then press the trigger.
Send the following IMGBOX command string after the button push:
IMGBOX245w37h55y.
Note: Case is not important in the command string. It is used here only for clarity.
The following image is captured:
The IMGBOX commands have many different modifiers that can be used to change the size and appearance of the signature
image output by the document reader. Modifiers affect the image that is transmitted, but do not affect the image in memory.
Modifiers always begin with a number and end with a letter (case insensitive). Any number of modifiers may be appended to the
IMGBOX command.
Note: The IMGBOX command will return a NAK unless a window size (width and height) are specified. See H - Height of
Signature Capture Area (page 1-15) and W - Width of Signature Capture Area (page 1-16).
IMGBOX Modifiers
A - Output Image Width
This option is used to size the image horizontally. If using this option, set the resolution (R) to zero.
1 - 14 Document Reader Imaging Guide
Page 21

B - Output Image Height
Example of Image Height set to 50B: Example of Image Height set to 100B:
Example: IMGBOX245w37h55y.
Example of Gamma Correction
set to 50K:
Example of Gamma Correction
set to 0K:
Example of Gamma Correction
set to 255K:
This option is used to size the image vertically. If using this option, set the resolution (R) to zero.
D - Pixel Depth
This indicates the number of bits per pixel in the transmitted image, which defines whether it will be grayscale or black and
white.
8D 8 bits per pixel, grayscale image (default)
1D 1 bit per pixel, black and white image
F - File Format
This option indicates the type of file format in which to save the image.
0F KIM format
1F TIFF binary
2F TIFF binary group 4, compressed
3F TIFF grayscale
4F Uncompressed Binary
5F Uncompressed grayscale
6F JPEG image (default)
7F Outlined image
8F BMP format
H - Height of Signature Capture Area
The height of the signature capture area must be measured in inches divided by .01. In the example, the height of the area
to be captured is 3/8 inch, resulting in a value of H = .375/0.01 = 37.5.
K - Gamma Correction
Gamma measures the brightness of midtone values produced by the image. You can brighten or darken an image using
gamma correction. A higher gamma correction yields an overall brighter image. The lower the setting, the darker the image.
The optimal setting for text images is 50K.
0K Gamma correction off (default)
50K Apply gamma correction for brightening typical document image
nK Apply gamma correction factor n (n = 1-255)
Document Reader Imaging Guide 1 - 15
Page 22

R - Resolution of Signature Capture Area
Example of Resolution set to 1000R:
Example of Resolution set to 0R:
Example of Resolution set to 2000R:
Example: IMGBOX245w37h55y.
Example of Horizontal Offset set to -75X:Example of Horizontal Offset set to 75X:
Example of Vertical Offset set to -7Y:
Example of Vertical Offset set to 65Y:
The resolution is the number of pixels that the document reader outputs per each minimum bar width. The higher the value
for R, the higher the quality of the image, but also the larger the file size. Values begin at 1000. The document reader
automatically inserts a decimal point between the first and second digit. For example, use 2500 to specify a resolution of
2.5. Set to zero when using the A and B modifiers (see A - Output Image Width and B - Output Image Height on page 1-15).
S - Barcode Aspect Ratio
All dimensions used in IMGBOX are measured as multiples of the minimum element size of the barcode. The barcode
aspect ratio allows you to set the ratio of the barcode height to the narrow element width. In the example, the narrow element
width is .010 inches and the barcode height is 0.400 inches, resulting in a value of S = 0.4/0.01 = 40.
W - Width of Signature Capture Area
The width of the signature capture area must be measured in inches divided by .01. In the example, the width of the area
to be captured is 2.4 inches, resulting in a value of W = 2.4/0.01 = 240. (A value of 245 was used in the example to
accommodate a slightly wider image area.)
X - Horizontal Barcode Offset
The horizontal barcode offset allows you to offset the horizontal center of the signature capture area. Positive values move
the horizontal center to the right and negative values to the left. Measurements are in multiples of the minimum bar width.
Y - Vertical Barcode Offset
The vertical barcode offset allows you to offset the vertical center of the signature capture area. Negative numbers indicate
that the signature capture is above the barcode, and positive numbers indicate that the area is below the barcode.
Measurements are in multiples of the minimum bar width.
1 - 16 Document Reader Imaging Guide
Page 23

2
Serial Default Commands
The following serial default commands are used to program the imaging features for your document reader. For complete
descriptions of each command, refer to the corresponding page in this manual. For non-imaging programming commands, refer
to the Barcode Manual.
The following commands can be sent via a PC COM port using terminal emulation software.
Conventions
The following conventions are used for menu and query command descriptions:
parameterA label representing the actual value you should send as part of a command.
[option] An optional part of a command.
{Data} Alternatives in a command.
bold Names of menus, menu commands, buttons, dialog boxes, and windows that appear on the screen.
Menu Command Syntax
Menu commands have the following syntax (spaces have been used for clarity only):
Prefix Tag SubTag {Data} [, SubTag {Data}] [; Tag SubTag {Data}] […] Storage
Prefix Three ASCII characters: SYN M CR (ASCII 22,77,13).
Tag A 3 character case-insensitive field that identifies the desired menu command group. For example, all RS-232 con-
figuration settings are identified with a Tag of 232.
SubTag A 3 character case-insensitive field that identifies the desired menu command within the tag group. For example,
the SubTag for the RS-232 baud rate is BAD.
Data The new value for a menu setting, identified by the Tag and SubTag.
Storage A single character that specifies the storage table to which the command is applied. An exclamation point (!) per-
forms the command’s operation on the device’s volatile menu configuration table. A period (.) performs the command’s operation on the device’s non-volatile menu configuration table. Use the non-volatile table only for semipermanent changes you want saved through a power cycle.
Query Commands
Several special characters can be used to query the device about its settings.
^ What is the default value for the setting(s).
? What is the device’s current value for the setting(s).
* What is the range of possible values for the setting(s). (The device’s response uses a dash (-) to indicate a con-
tinuous range of values. A pipe (|) separates items in a list of non-continuous values.)
Tag Field Usage
When a query is used in place of a Tag field, the query applies to the entire set of commands available for the particular storage
table indicated by the Storage field of the command. In this case, the SubTag and Data fields should not be used because they
are ignored by the device.
SubTag Field Usage
When a query is used in place of a SubTag field, the query applies only to the subset of commands available that match the Tag
field. In this case, the Data field should not be used because it is ignored by the device.
Data Field Usage
When a query is used in place of the Data field, the query applies only to the specific command identified by the Tag and SubTag
fields.
Document Reader Imaging Guide 2 - 1
Page 24

Concatenation of Multiple Commands
Multiple commands can be issued within one Prefix/Storage sequence. Only the Tag, SubTag, and Data fields must be repeated
for each command in the sequence. If additional commands are to be applied to the same Tag, then the new command sequence
is separated with a comma (,) and only the SubTag and Data fields of the additional command are issued. If the additional
command requires a different Tag field, the command is separated from previous commands by a semicolon (;).
Responses
The device responds to serial commands with one of three responses:
ACK Indicates a good command which has been processed.
ENQ Indicates an invalid Tag or SubTag command.
NAK Indicates the command was good, but the Data field entry was out of the allowable range for this Tag and SubTag
combination, e.g., an entry for a minimum message length of 100 when the field will only accept 2 characters.
When responding, the device echoes back the command sequence with the status character inserted directly before each of the
punctuation marks (the period, exclamation point, comma, or semicolon) in the command.
Examples of Query Commands
In the following examples, a bracketed notation [ ] depicts a non-displayable response.
Example #1:What is the range of possible values for Imaging Style?
Enter: snpsty*.
Response: SNPSTY0-2[ACK]
This response indicates that Imaging Style (SNPSTY) has a range of values from 0 to 2.
Example #2: What is the default value for Imaging Style?
Enter: snpsty^.
Response: SNPSTY1[ACK]
This response indicates that the default setting for Imaging Style (SNPSTY) is 1, or Photo.
Example #3: What is the device’s current setting for Imaging Style?
Enter: snpsty?.
Response: SNPSTY2[ACK]
This response indicates that the device’s Imaging Style (SNPSTY) is set to 2, or Manual.
2 - 2 Document Reader Imaging Guide
Page 25

Menu Commands
The following chart lists the settings for each of the serial default commands. The factory default setting is indicated by an
asterisk (*).
Selection
Imaging Default Commands
Image Snap (IMGSNP)
Image Ship (IMGSHP)
Setting
* Indicates default
Default all Imaging Commands IMGDFT 1-1
Imaging Style - Decoding SNPSTY0 1-1
*Imaging Style - Photo SNPSTY1 1-1
Imaging Style - Manual SNPSTY2 1-1
Beeper On SNPBEP1 1-1
*Beeper Off SNPBEP0 1-1
Aimer Lines On SNPAIM1 1-2
*Aimer Lines Off SNPAIM0 1-2
Exposure (1-7874 microseconds) SNPEXP 1-2
*Gain - None SNPGAN1 1-3
Gain - Medium SNPGAN2 1-3
Gain - Heavy SNPGAN4 1-3
Gain - Maximum SNPGAN8 1-3
Delta for Acceptance (0-255) *25 SNPDEL### 1-3
*LED State - Off SNPLED0 1-2
LED State - On SNPLED1 1-2
*Wait for Trigger Off SNPTRG0 1-2
Wait for Trigger On SNPTRG1 1-2
Update Tries (0-10) *6 SNPTRY## 1-3
Target White Value (0-255) *125 SNPWHT### 1-3
Target Set Point Percentage (1-99) *97 SNPPCT## 1-4
*Infinity Filter - Off IMGINF0 1-6
Infinity Filter - On IMGINF1 1-6
*Compensation Off IMGCOR0 1-6
Compensation On IMGCOR1 1-6
*Pixel Depth - 8 bits/pixel (grayscale) IMGBPP8 1-6
Pixel Depth - 1 bit/pixel (B&W) IMGBPP1 1-6
*Don’t Sharpen Edges IMGEDG0 1-7
Sharpen Edges (0-23) IMGEDG## 1-7
*File Format - JPEG IMGFMT6 1-7
File Format - KIM IMGFMT0 1-7
File Format - TIFF binary IMGFMT1 1-7
File Format - TIFF binary group 4, compressed IMGFMT2 1-7
File Format - TIFF grayscale IMGFMT3 1-7
File Format - Uncompressed binary IMGFMT4 1-7
File Format - Uncompressed grayscale IMGFMT5 1-7
File Format - BMP IMGFMT8 1-7
*Histogram Stretch Off IMGHIS0 1-7
Histogram Stretch On IMGHIS1 1-7
Serial Command
# Indicates a numeric entry
For full description,
see page
Document Reader Imaging Guide 2 - 3
Page 26

Selection
Image Ship (continued)
Image Auto Crop (IMGACP)
Setting
* Indicates default
Invert Image around X axis IMGNVX1 1-8
Invert Image around Y axis IMGNVY1 1-8
*Noise Reduction Off IMGFSP0 1-8
Noise Reduction On IMGFSP1 1-8
*Rotate Image Off IMGROT0 1-9
Rotate Image 90° right IMGROT1 1-9
Rotate Image 180° IMGROT2 1-9
Rotate Image 90° left IMGROT3 1-9
*Adaptive Text Filter Off IMGAUT0 1-9
Adaptive Text Filter On IMGAUT1 1-9
*Unsharp/Brighten Filter Off IMGSNZ0 1-10
Unsharp/Brighten Filter On IMGSNZ1 1-10
JPEG Image Quality (0-100) *50 IMGJQF### 1-10
*Gamma Correction Off IMGGAM0 1-10
Gamma Correction On (0-1,000) IMGGAM### 1-10
Image Crop - Left (0-1279) *0 IMGWNL### 1-11
Image Crop - Right (0-1279) *1279 IMGWNR### 1-11
Image Crop - Top (0-959) *0 IMGWNT### 1-11
Image Crop - Bottom (0-959) *959 IMGWNB### 1-11
Image Crop - Margin (0-478) *0 IMGMAR### 1-11
Protocol - None (raw) IMGXFR0 1-11
Protocol - None (default USB) IMGXFR2 1-11
Protocol - Hmodem IMGXFR3 1-11
Protocol - Hmodem Compressed IMGXFR4 1-11
*Ship Every Pixel IMGSUB1 1-12
Ship Every 2nd Pixel IMGSUB2 1-12
Ship Every 3rd Pixel IMGSUB3 1-12
*Document Image Filter Off IMGUSH0 1-12
Document Image Filter On (0-255) IMGUSH### 1-12
*Blur Image Off no serial command 1-13
Blur Image On no serial command 1-13
*Don’t Ship Histogram IMGHST0 1-13
Ship Histogram IMGHST1 1-13
*Infinity Filter - Off IMGINF0 1-6
Infinity Filter - On IMGINF1 1-6
*Compensation Off IMGCOR0 1-6
Compensation On IMGCOR1 1-6
*Pixel Depth - 8 bits/pixel (grayscale) IMGBPP8 1-6
Pixel Depth - 1 bit/pixel (B&W) IMGBPP1 1-6
*Don’t Sharpen Edges IMGEDG0 1-7
Sharpen Edges (0-23) IMGEDG## 1-7
*File Format - JPEG IMGFMT6 1-7
File Format - KIM IMGFMT0 1-7
File Format - TIFF binary IMGFMT1 1-7
File Format - TIFF binary group 4, compressed IMGFMT2 1-7
Serial Command
# Indicates a numeric entry
For full description,
see page
2 - 4 Document Reader Imaging Guide
Page 27

Selection
Image Auto Crop (continued)
Intelligent Signature Capture (IMGBOX)
Setting
* Indicates default
File Format - TIFF grayscale IMGFMT3 1-7
File Format - Uncompressed binary IMGFMT4 1-7
File Format - Uncompressed grayscale IMGFMT5 1-7
File Format - BMP IMGFMT8 1-7
*Histogram Stretch Off IMGHIS0 1-7
Histogram Stretch On IMGHIS1 1-7
Invert Image around X axis IMGNVX1 1-8
Invert Image around Y axis IMGNVY1 1-8
*Noise Reduction Off IMGFSP0 1-8
Noise Reduction On IMGFSP1 1-8
*Rotate Image Off IMGROT0 1-9
Rotate Image 90° right IMGROT1 1-9
Rotate Image 180° IMGROT2 1-9
Rotate Image 90° left IMGROT3 1-9
*Adaptive Text Filter Off IMGAUT0 1-9
Adaptive Text Filter On IMGAUT1 1-9
*Unsharp/Brighten Filter Off IMGSNZ0 1-10
Unsharp/Brighten Filter On IMGSNZ1 1-10
JPEG Image Quality (0-100) *50 IMGJQF### 1-10
*Gamma Correction Off IMGGAM0 1-10
Gamma Correction On (1-255) IMGGAM### 1-10
Protocol - None (raw) IMGXFR0 1-11
Protocol - None (default USB) IMGXFR2 1-11
Protocol - Hmodem Compressed IMGXFR3 1-11
Protocol - Hmodem IMGXFR4 1-11
Ship Every Pixel IMGSUB1 1-12
Ship Every 2nd Pixel IMGSUB2 1-12
Ship Every 3rd Pixel IMGSUB3 1-12
*Document Image Filter Off IMGUSH0 1-12
Document Image Filter On (0-255) IMGUSH### 1-12
*Blur Image Off no serial command 1-13
Blur Image On no serial command 1-13
*Don’t Ship Histogram IMGHST0 1-13
Ship Histogram IMGHST1 1-13
Output Image Width no serial command 1-14
Output Image Height no serial command 1-15
*Pixel Depth - 8 bits/pixel (grayscale) IMGBPP8 1-15
Pixel Depth - 1 bit/pixel (B&W) IMGBPP1 1-15
*File Format - JPEG IMGFMT6 1-15
File Format - KIM IMGFMT0 1-15
File Format - TIFF binary IMGFMT1 1-15
File Format - TIFF binary group 4, compressed IMGFMT2 1-15
File Format - TIFF grayscale IMGFMT3 1-15
File Format - Uncompressed binary IMGFMT4 1-15
File Format - Uncompressed grayscale IMGFMT5 1-15
Serial Command
# Indicates a numeric entry
For full description,
see page
Document Reader Imaging Guide 2 - 5
Page 28

Selection
Intelligent Signature Capture (continued)
Setting
* Indicates default
File Format - BMP IMGFMT8 1-15
Height of Signature Capture Area no serial command 1-15
*Gamma Correction Off IMGGAM0 1-15
Gamma Correction On (1-255) IMGGAM### 1-15
Resolution of Signature Capture Area (0-2500) no serial command 1-16
Barcode Aspect Ratio no serial command 1-16
Width of Signature Capture Area no serial command 1-16
Horizontal Barcode Offset no serial command 1-16
Vertical Barcode Offset no serial command 1-16
Serial Command
# Indicates a numeric entry
For full description,
see page
2 - 6 Document Reader Imaging Guide
Page 29

3
Customer Support
Technical Assistance
If you need assistance installing or troubleshooting, please call your Distributor or the nearest Hand Held Products technical
support office:
North America/Canada
Telephone: (800) 782-4263
Fax number: (315) 554-6705
E-mail: natechsupport@handheld.com
Latin America
Telephone: (803) 835-8000
Telephone: (800) 782-4263
E-mail: latechsupport@handheld.com
Brazil
Telephone: +55 (21) 3535-9100
Fax: +55 (21) 3535-9105
E-mail: brsuporte@handheld.com
Mexico
Telephone: (803) 835-8000
E-mail: latechsupport@handheld.com
Europe, Middle East, and Africa
Telephone: +31 (0) 40 7999 393
Fax: +31 (0) 40 2425 672
E-mail: eurosupport@handheld.com
Asia Pacific
Telephone - Hong Kong: +852-3188-3485 or 2511-3050
Telephone - China: +86 21 6361 3818
E-mail: aptechsupport@handheld.com
Japan
Telephone: +813 5770-6312
E-mail: aptechsupport@handheld.com
Malaysia
Telephone: +603-6201-7020
E-mail: aptechsupport@handheld.com
Online Technical Assistance
You can also access technical assistance online at www.handheld.com.
For Further Information
To download the full User’s Guide for these products, visit our website at www.handheld.com.
Product Service and Repair
Hand Held Products provides service for all its products through service centers throughout the world. To obtain warranty or
non-warranty service, return the unit to Hand Held Products (postage paid) with a copy of the dated purchase record attached.
Contact the appropriate location below to obtain a Return Material Authorization number (RMA #) before returning the product.
North America
Telephone: (800) 782-4263
Fax: (803) 835-8012
E-mail: naservice@handheld.com
Document Reader Imaging Guide 3 - 1
Page 30

Latin America
Telephone: (803) 835-8000
Telephone: (800) 782-4263
Fax: (239) 263-9689
E-mail: laservice@handheld.com
Brazil
Telephone: +55 (21) 3535-9100
Fax: +55 (21) 3535-9105
E-mail: brservice@handheld.com
Mexico
Telephone: +52 (55) 5203-2100
Fax: +52 (55) 5531-3672
E-mail: mxservice@handheld.com
Europe, Middle East, and Africa
Telephone: +31 (0) 40 2901 633
Fax: +31 (0) 40 2901 631
E-mail: euservice@handheld.com
Asia Pacific
Telephone: +852-2511-3050
Fax: +852-2511-3557
E-mail: apservice@handheld.com
Japan
Telephone: +813-5770-6312
Fax: +813-5770-6313
E-mail: apservice@handheld.com
Online Product Service and Repair Assistance
You can also access product service and repair assistance online at www.handheld.com.
3 - 2 Document Reader Imaging Guide
Page 31

Page 32

™
Hand Held Products, Inc.
700 Visions Drive
P.O. Box 208
Skaneateles Falls, NY 13153-0208
4800dr-IMG Rev A
12/07
 Loading...
Loading...