Hafei HFJ6371, HFJ6371B, HFJ6371C, HFJ6371E, HFJ1012 Service manual
...
1 GENERAL
1.1 Performance Data
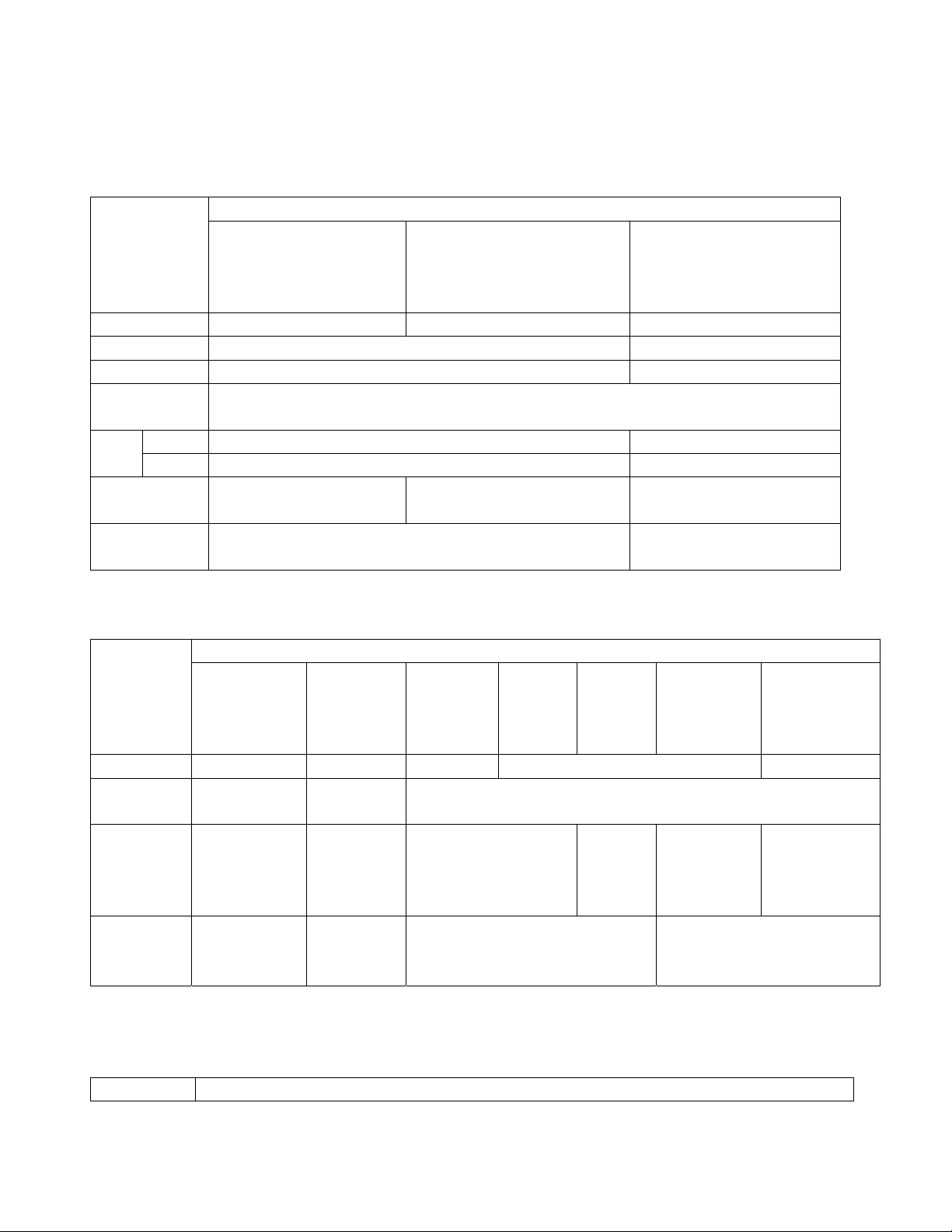
1.Main dimension (Table 1-1)
T able 1-1
Data
HFJ6371、HFJ6371B、
Item
HFJ6371C、HFJ6371E、
HFJ1012、HFJ1012B、
HFJ1012C 、HFJ1012E
Length(mm) 3721 3745 3562
Width(mm) 1480 1480
Height(mm) 1918 1918
Wheel
base(mm)
(mm)
Front
Rear 1220 (1200) 1220
Front
942 966 783
1235 (1215)
overhang(mm)
Rear
overhang(mm)
2.Mass data (Table 1-2)
Item
HFJ6350C
HFJ6351C、
HFJ6351CA
Cu r b w e i g ht 940kg 970kg 980kg 960kg 940kg
Max. total
1460kg 1460kg 1530kg
weight
The rated
load
660kg/800kg
6~8
670kg/790kg
6~8
(passenger
numbers)
Empty
480kg/460kg 495kg/475kg --- --axle-load
(front/rear)
3.Performance data(Table 1-3)
Table 1-3
Item Data
HFJ6376、HFJ6376E
HFJ1016 、HFJ1016E
HFJ6350C、HFJ6351C、
HFJ6351CA
1960
1235 Tread
819 819
Data
HFJ6371、
HFJ6371E
HFJ6376、
HFJ6376E
5~8
(5~7)
HFJ6371B
、HFJ6371E
HFJ6376、
HFJ6376E
HFJ6371C
5~8
HFJ1012
HFJ1016
HFJ1016E、
、
HFJ1012E
2+440kg
or 5+245kg
Table 1-2
HFJ1012E、
HFJ1012B
HFJ1016
HFJ1012C
2+460kg
or 5+265kg
HFJ6371、HFJ6376
HFJ1012、HFJ1016、
HFJ6371B、HFJ6376
HFJ1012B、HFJ1016
HFJ6371C
HFJ1012C
HFJ6350C HFJ6351CA
HFJ6351C
Engine mode DA465Q-1A DA465Q DA462-1A DA462-1A DA465Q
Max. speed
Max. slope of
≥105km/h ≥100km/h ≥95km/h ≥100km/h ≥110km/h
≥20%
climb
Fuel
≤5.8L(40km/h) ≤5.5L(40km/h)
consumption
of 100km at
constant
speed
T ank capacity 36L
Min. turning
9.0m
diameter
Min. ground
≥150mm ≥165mm ≥150mm
clearance
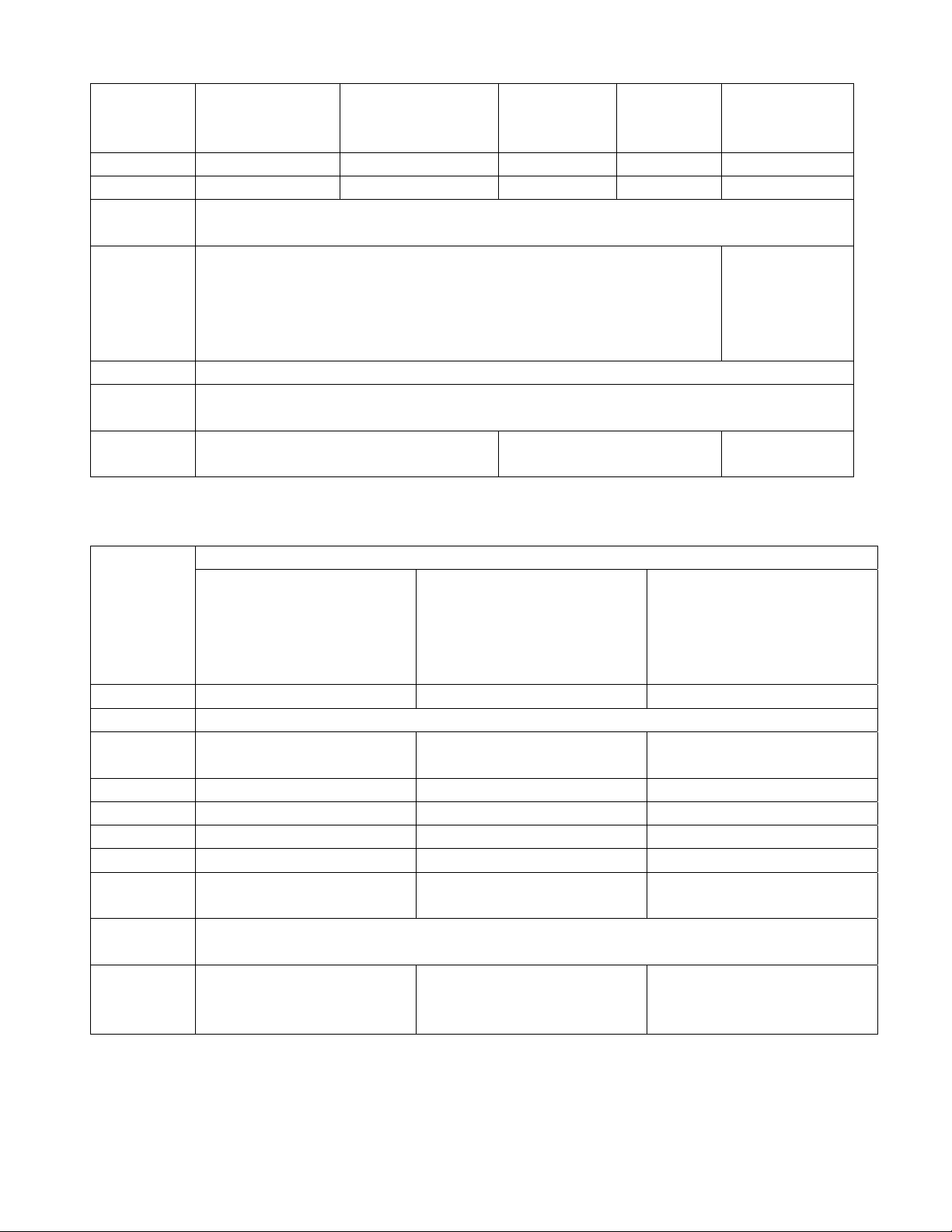
4. Engine data( T able 1-4)
Table 1-4
Data
HFJ6371C
HFJ1012C、HFJ6350C
Item
HFJ6371、HFJ6376
HFJ1012、HFJ1016
、HFJ6371E、HFJ6376E
HFJ1012E、HFJ1016E、
HFJ6351C
HFJ6371B、HFJ6376
HFJ1012B、HFJ1016、HFJ6371E、
HFJ6376E
HFJ1012E、HFJ1016E、
HFJ6351CA
Mode DA465Q-1A DA465Q DA462-1A
Type
Cylinder
Four cylinder, four stroke, tandem, water cool, overhead camshaft,electronic fuel injection (EFI)
65.5mm 65.5mm 62mm
diameter
Stroke 78mm 72mm 72mm
Displacement 1051ml 970ml 870ml
Rated power 38.5kW/5200r/min 35.5kW/5000r/min 27kW/5200r/min
Rated torque
Compression
83N.m/3000~3500r/min 74N.m/3000~3500r/min 60N.m/3000~3500r/min
9.0:1
8.8:1 8.7:1
ratio
Ignition
6°~7°
advance angle
Min. fuel
275g/(kW·h) 275g/(kW·h) 300g/(kW·h)
consumption
rate
5.Transmission system (Table 1-5)
Table 1-5
Item 4MT 5MT
Clutch type
Gear box type
Main gear reduction ratio
Gear ratio 1
Reverse gear
2
3
4
5
st
gear
nd
rd
th
gear
th
gear
Single disc, dry and with diaphragm spring
Synchromesh type
5.125
3.505
gear
2.043
gear
1.383
1.000
3.536
Single disc, dry and with diaphragm
spring
Synchromesh type
5.125/4.444
3.652
1.948
1.424
1.000
0.795
3.466
5.125/4.444
3.505
2.043
1.383
1.000
0.806
3.536
6. Wheel and suspension (Table 1-6)
Table 1-6
Item
HFJ6350C、HFJ6351C、HFJ6371series HFJ6376 系列
Tire type 165/70 R 13 155R12C 165/70 R 13
Air pressure empty load(front/rear)
Full load(front/rear)
210kPa/250kPa 200kPa/220kPa
250kPa/250kPa
300kPa/350 kPa 220kPa/250 kPa
180kPa/220 kPa
Front suspension type MC, pherson type independent suspension
Rear suspension type Parallel leaf spring type rigid axle suspension
7.Steering system(Table 1-7)
Item
Steering gear type
Kingpin inclination
Caster
Camber
Toe-in
HFJ6350C、HFJ6351C、HFJ6376series、HFJ6371series
Rack and pinion type
12°±30'
6°±30'
0°±30'
0~5mm
8.Brakes(Table 1-8)
Item HFJ6350C
HFJ6351Cseries 、 HFJ6376series 、
HFJ6371series
Brake type
Front wheel brake
Rear wheel brake
Parking brake
Dual hydraulic lines braking
Balanced double leading shoes and
drum type brake
Unbalanced leading/trailing shoes and
drum type brake
Mechanical cable type(acting on rear
wheels)
Dual hydraulic lines braking(with
vacuum power)
Full sliding caliper disc brake/ Balanced
double leading shoes and drum type
brake
Unbalanced leading/trailing shoes and
drum type brake
Mechanical cable type(acting on rear
wheels)
Table 1-7
Table1-8

第 1 页 共 5页
2 INSPECTION DATA AND MAINTENANCE PERIOD
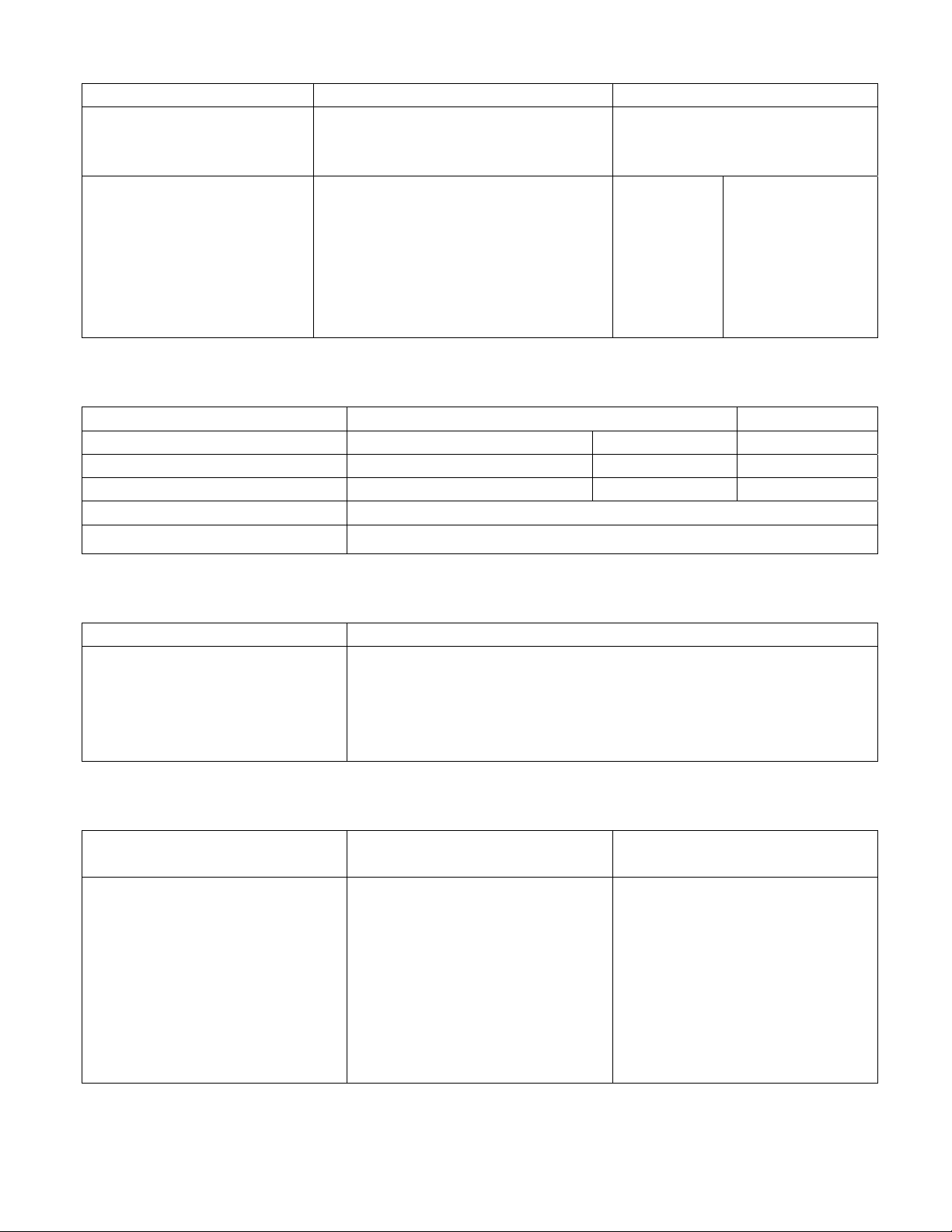
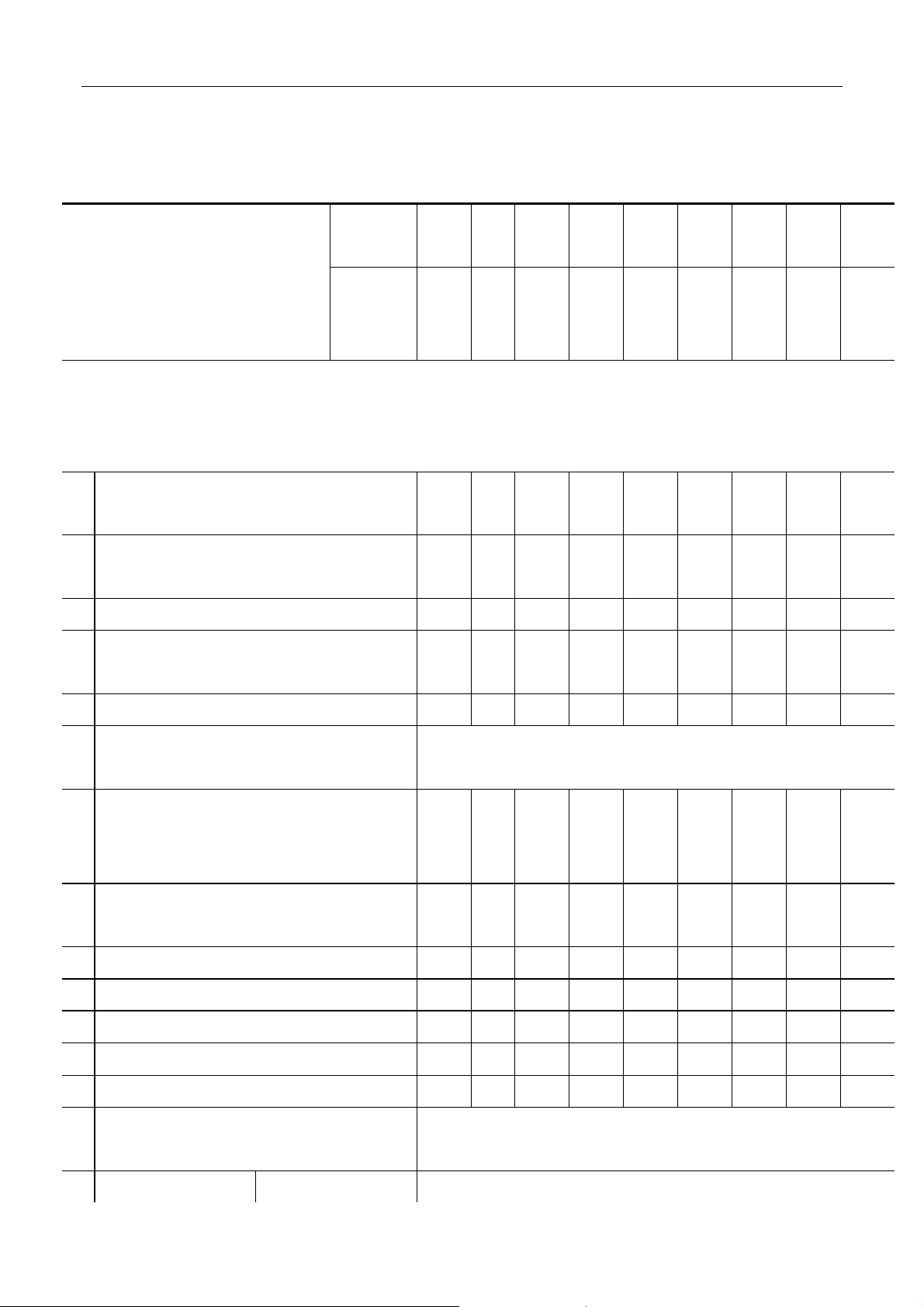
2.1 TORQUE
The tightening performance of connecting bolt and nut is performed by screw thread. Each
fastener should be tightened to the torque specified in each section with moment wrench during
maintenance.
Table 2-1
System
Tighten position
Specified torque(N·m)
N·m kgf·m
Engine Cylinder head setscrew
Spark plug
Intake and exhaust manifold nut
Driven synchronous gear screw
Valve adjust nut
Initiative synchronous gear
screw
Connecting rod bearing cap nut
Crankshaft main bearing cap bolt
Flywheel screw
Oil plate screw
Oil drain plug
Rocker arm cap screw
Synchronous chain cover setscrew
Setscrew of oil pump
Oil pressure sensor
Oil filter stand
Setscrew of oil filter nib
Rear engine bracket-Body
fastening bolt
Oil pump safety valve spring seat
Left and right engine hangers
fastening bolt
Bracket mounting bolt
Tension pulley bracket bolt and
nut
Ignition shock sensor screw
sensor
O
2
Coolant temperature sensor
55~60
19.6~29.4
17.7~22.6
49.0~58.8
14.7~19.6
49.0~58.8
27.5~31.4
42.2~47.1
39.2~44.1
3.92~4.90
19.6~24.6
3.92~4.90
2.94~3.92
7.85~9.81
11.8~14.7
9.81~14.7
19.6~24.5
10.8~13.7
14.7~19.6
17.7~22.6
24.5~29.4
14.7~22.6
15~25
40~60
Max.20
5.5~6.0
2.0~3.0
1.8~2.3
5~6
1.5~2
5~6
2.8~3.2
4.3~4.8
4.0~4.5
0.4~0.5
2.0~2.5
0.4~0.5
0.3~0.4
0.8~1.0
1.2~1.5
1.0~1.5
2.0~2.5
1.1~1.4
1.5~2.0
1.8~2.3
2.5~3.0
1.5~2.3
1.5~2.6
4~6
Max.2
1
第 2 页 共 5页
Transmission
Cluth Cluth pressure plate bolt 17.7~27.5 1.8~2.8
Transmission case screw
Drain plug and oil filler
Extention case bolt
Rear bracket mounting bolt
Gear shift shaft case screw(M8)
Gear shift shaft case screw(M6)
Gear shift crossing shaft lock
screw
Connecting bolt of transmission
and cylinder
2.2 INSPECTION DATAS
14.7~19.6
29.4~49.0
14.7~19.6
14.7~19.6
8.83~11.8
5.88~9.81
14.7~19.6
19.6~24.5
1.5~2.0
3.0~5.0
1.5~2.0
1.5~2.0
0.9~1.2
0.6~1.0
1.5~2.0
2.0~2.5
The content of engine refers to 《HFJ6351B service manual》。
2
第 3 页 共 5页
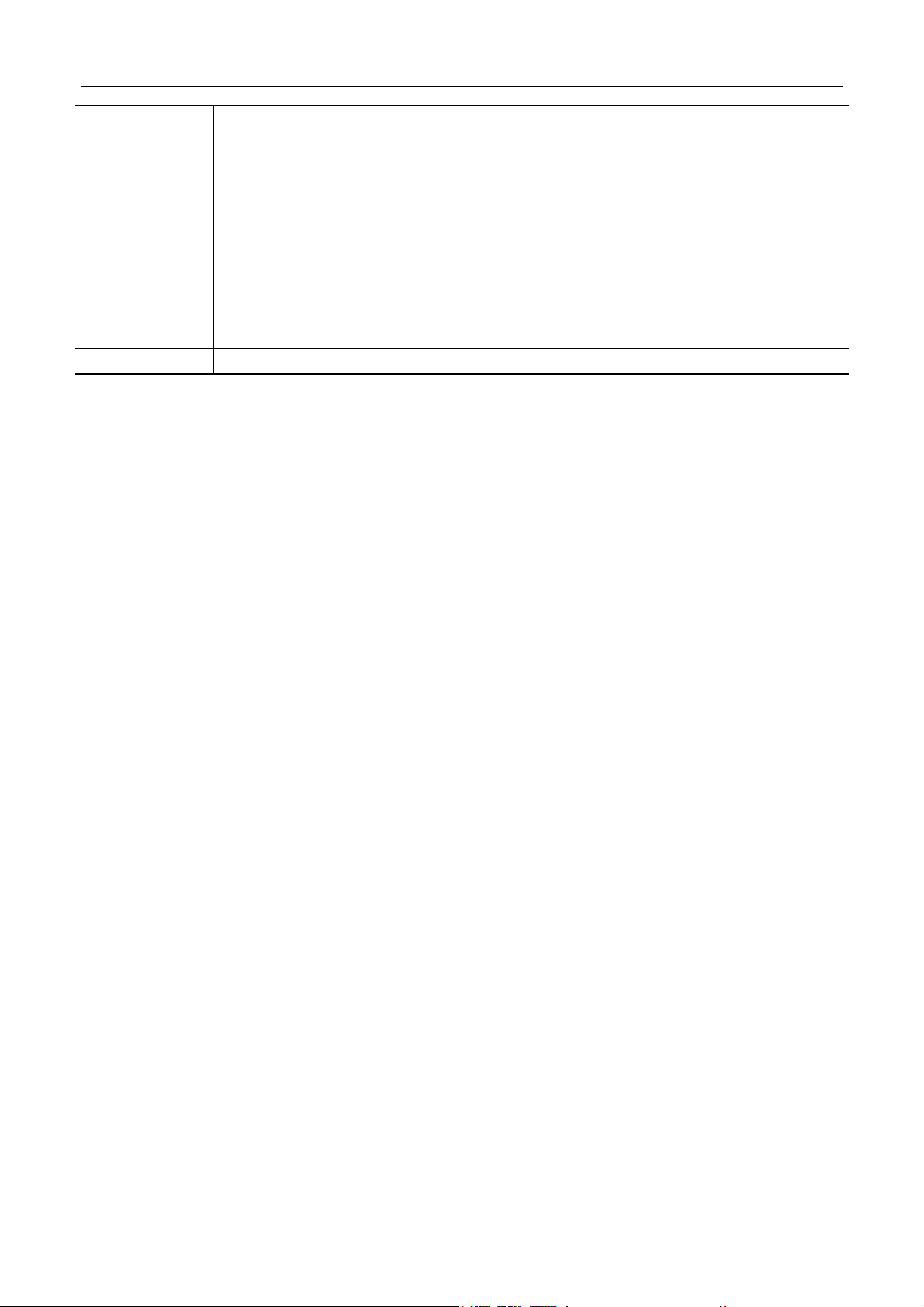
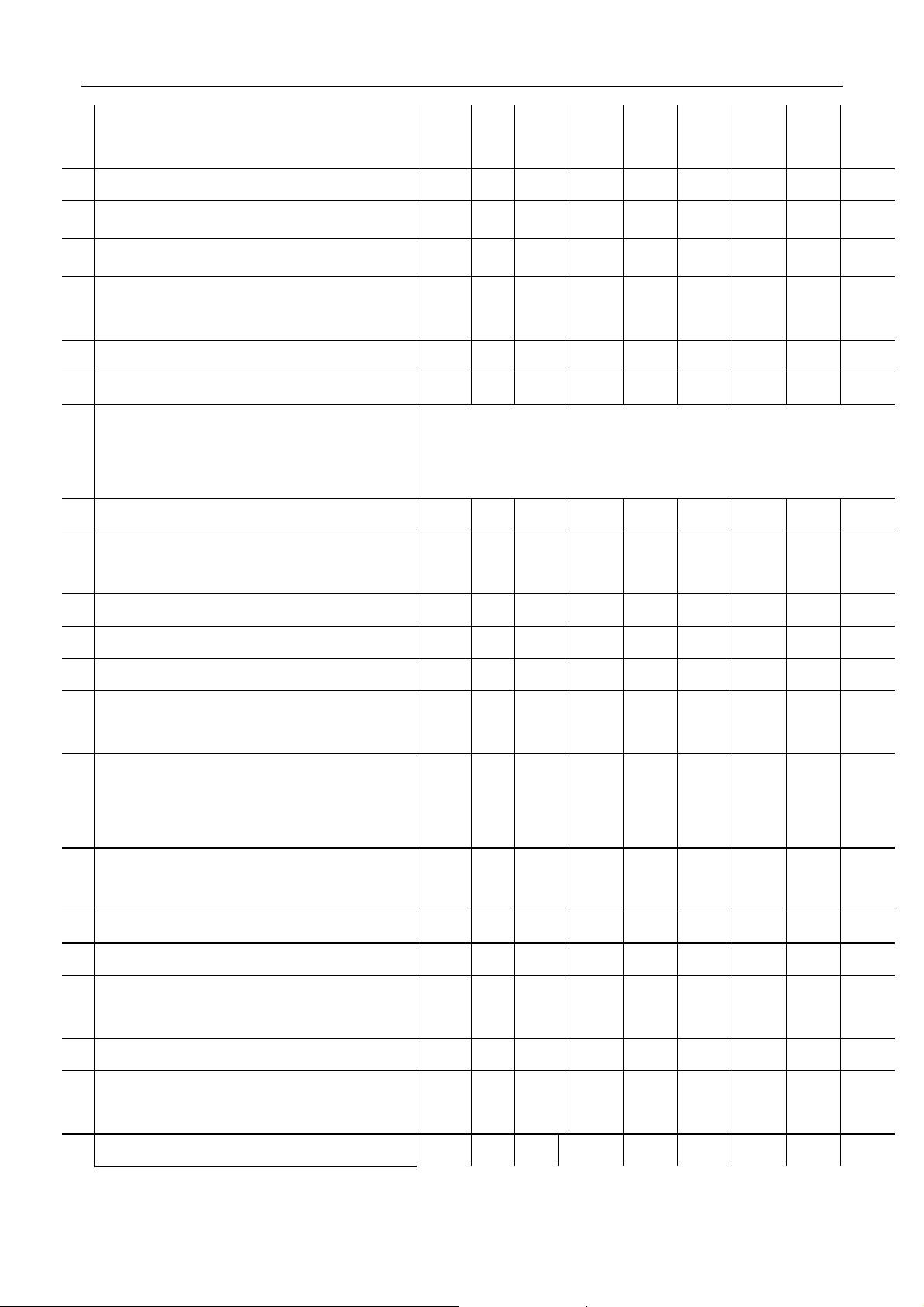
2.3 MAINTENANCE SCHEDULE
Interval:
km×
2.5 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80
This interval should be
1000
judged by odometer reading
or months, whichever comes
months 2 6 12 18 24 30 36 42 48
first.
ENGINE
Water pump(fan) drive belt(tension,
1
damage)
synchronizing toothed belt
2
(wear and damage)
3 IN and EH valve clearance A — A — A — A — A
Engine bolts (All cylinder head and
4
manifold fixings)
A — I — R — I — R
I — I — I — I — I
T — T — T — T — T
5 Engine oil filter R R R R R R R R R
Replace every 5000km. More frequent replacement if
6 Engine oil
under dusty driving conditions
Fuel hoses and connections ( hoses
7
aging , connections crack, damage or
loosening)
Cooling system hoses and connections
8
(leakage, damage)
I I I I I I I I I
—— I — — I — — I
9 High tension cords(aging and damage) —— I — — I — — I
Crankcase hose and nib
10
Spark plugs
11
Ignition timing
12
- -I - - I - - I
— R R R R R R R R
A A A A A A A A
I
13 Ignition shock sensor tightening torque A A A A A A A A A
Clean every 1000km on asphalt road and clean every
14 Air filter
2500km on dusty road
z Dust road Check referring to hard driving
3
第 4 页 共 5页
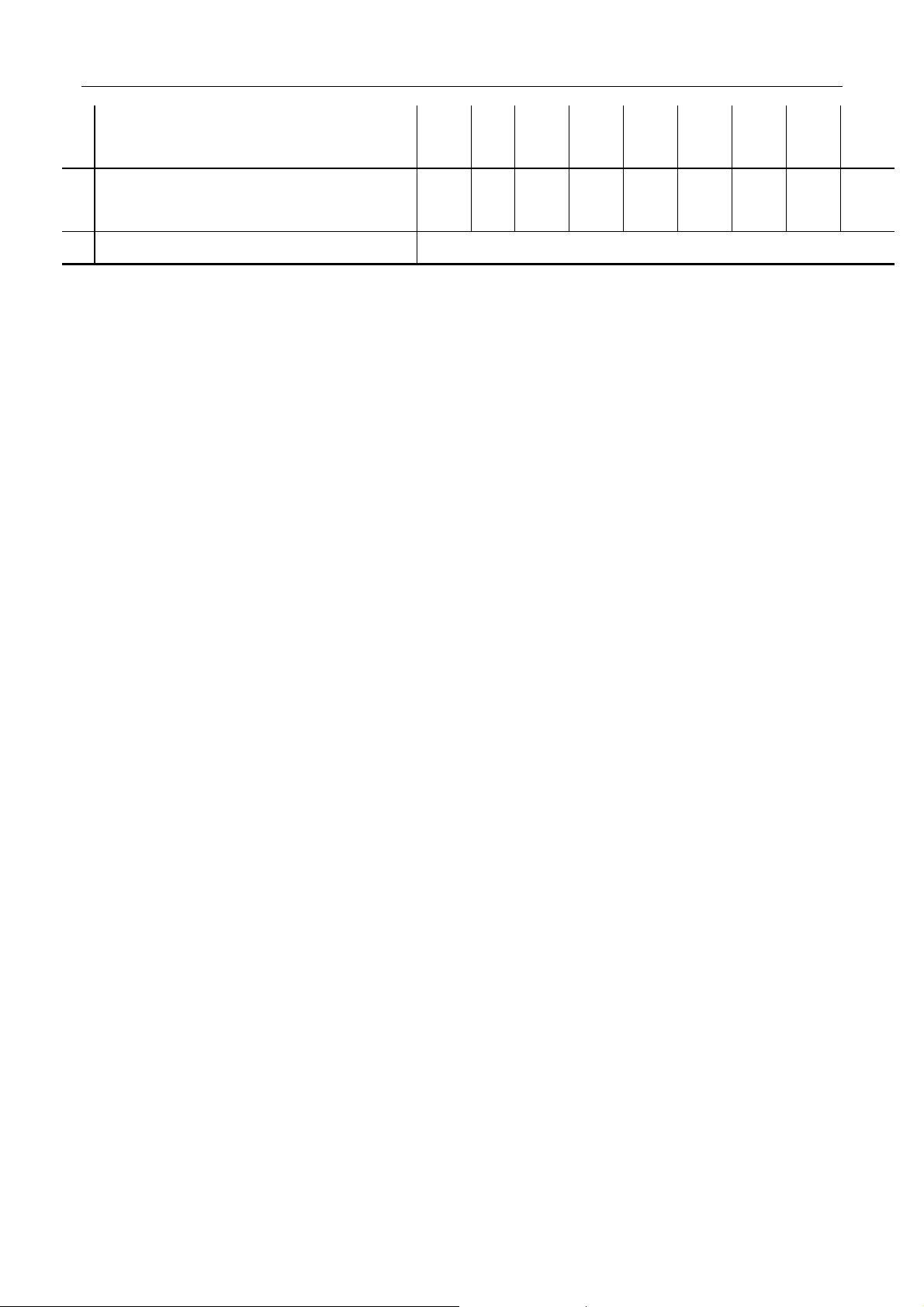
Acceleration cable and throttle valve
15
spindle
—
I.
I.L I.L I.L I.L I.L I.L I.L
L
16 Fuel filter ——— — R — — — R
17 PCV valve — — I — I — I — I
18 Clutch gap
Gear oil of transmission(check leakage
19
at normal level)
R I I I R I I I R
20 Damage and fastness of harness I I I I I I I I I
21 Coolant ——— — R — — — R
Replace every 50000km. More frequent check if under
22 Charcoal canister
dusty driving condition. Replace in time if clogging
or liquid fuel found.
23 Catalytic converter - - - - - - - - I
Wiring hardness connections and
— — I — I — I - I
24
headlights
25 Clutch pedal play I I I I I I I I I
26 Brake fluid(lever、leakage) I I I I R I I I I
27 Brake pedal play I I I I I I I I I
Parking brake lever and cable
28
I I I I I I I I I
(stroke and damage)
Brake discs and pads (wear, damage)
29
Brake drums and shoes (wear,
- I I I I I I I I
damage)
Brake hoses and pipes (leakage,
30
- I I I I I I I I
damage, clamp)
31 Tires (abnormal wear and pressure) - I I I I I I I I
32 Wheel, wheel nut(damage、torque) I I I I I I I I I
Shock absorber(oil leakage 、
33
I I I I I I I I I
damage)
34 Propeller shaft (damage) - - I - I - I - I
Transmission and Differential oil
35
R I I I R I I I R
(leakage, lever)
36 Main bolt and nut (tightness) T - T - T - T - T
4
第 5 页 共 5页
Steering (tightness, damage,
37
I I I I I I I I I
rattle, breakage)
Middle arm bush assy(lubrication
38
and tightness)
39 Test drive Test drive on completion of each service
Notice :
“A”-Inspection and connect ;“R”-Replace or repair;“T” -Tighten to the specified
torque;“L” -Lubricate “I” -Inspection and correct or replace if necessary;
5
第 1 页 共 3页
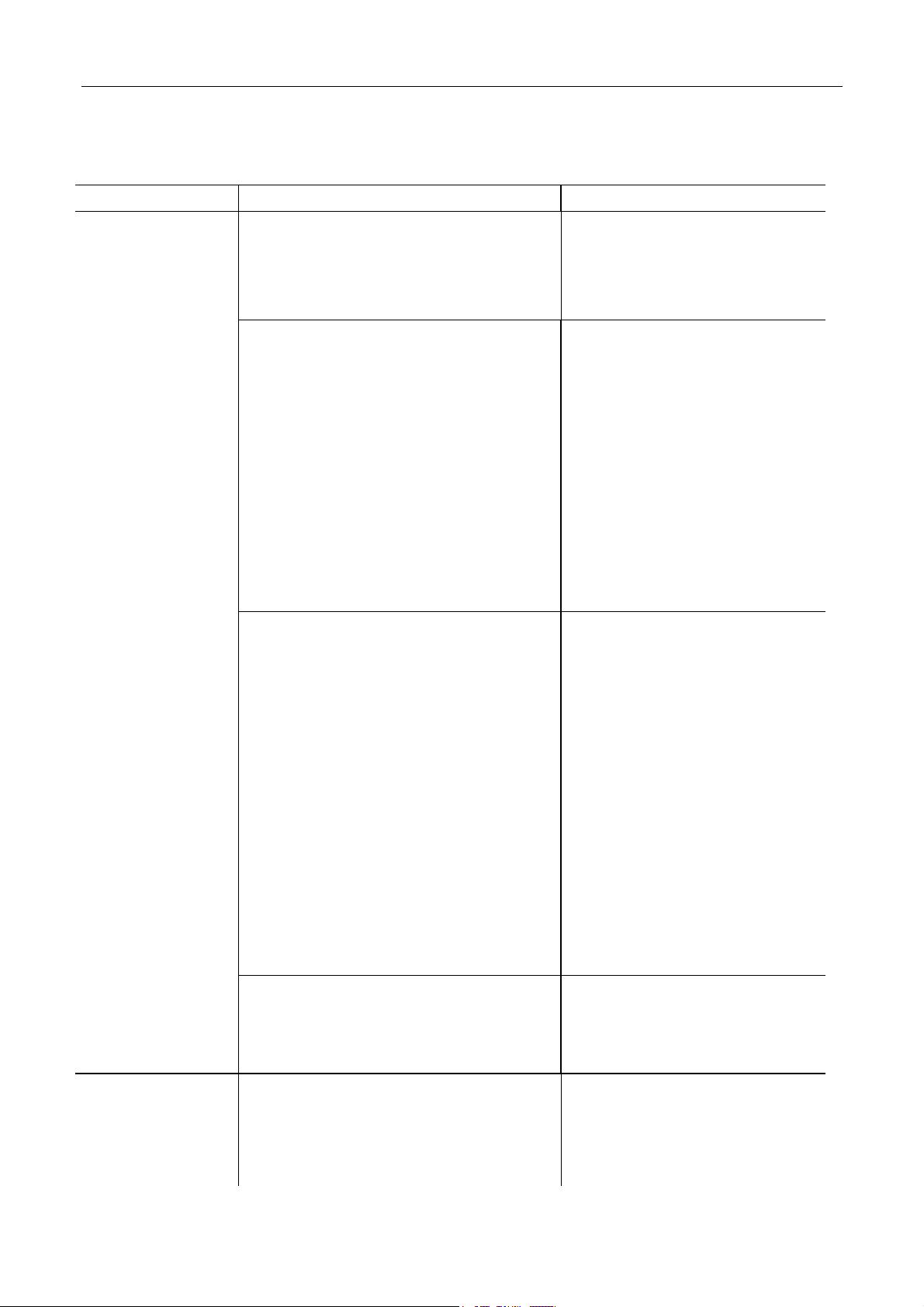
3 TROUBLE SHOOTING
3.1 ENGINE
TABLE 3-1
Condition Possible cause Correction
Hard starting
High idling
a、Starter will not run
1. Loose battery terminal connection
2 Brack-circuited in cord connection
3 Defective of starter
b、No sparking
1 Improper ignition timing
2 Poor grounded
3 Cracked rotor or cap in distributer
Defective ignition coil
4
5 Improper clearance or burnted in
spark
6 Brack-circuited or short-circuited
in cord connection
7 Connector loose or damaged
8 Damage of main breaker contact
9 Defective ECU
c、Malfunction of the fuel system
1. Electronic fuel pump feed fuel
pressure
Lack
2. Fuel injectors damaged or clogged
3 Fuel hose fold and fuel filter clogged
4 Vacuum hose or fuel pressure adjuster
broken off or damaged
5 Connector loose or damaged
6 Damage of main breaker contact or oil
pump breaker contact
7 short-circuited or open-circuited
8 Defective ECU
d、Inadequate compression
1 Damaged cylinder gasket
2 Improper valve clearance
3 Wornpistons,rings or cylinder
1. ECU doesn’t self-study after break
2. Throttle can’t restore completely
3. Intake system leakage
4. Idle adjuster (stepper motor) damaged
Clean and retighten
Check or repair
Repair or replace
Adjust
Repair
Replace
Replace
Adjust or replace
Check or repair
Adjust or replace
Replace
Repair or replace
Repair or replace
Replace or Clean
Replace
Installation or replace
Replace or adjust
Replace
Check and repair
Replace
replace
Adjust、repair or replace
repair or replace
Flameout, then self-study
check and adjust
check and repair
replace
1
第 2 页 共 3页
Not enough power
Enging noise
Overheating
Excessive engine
oil consumption
Hard shifting
1Accelerator control and throttle cable
improperly adjusted
2 Cylinder compression pressure reduce
3Improper ignition timin
4Fuel pressure adjuster damaged and make
fuel feeding reduce
5Insufficient intake
6Clogged exhaust
7Defective spark plug or improper spark
clearance
8 Firing a gun when engine racing
9 Fuel injectors clogged or damaged
10 Clogged fuel filter
11 Damaged throttle position sensor
12 Defective fuel pump or insufficient
pressure
1 Worn bearing, crank and arm.
2 Worn crankshaft,connecting-rod bearing and
piston
3 Worn piston ring
4 Improper valve clearance
5 Valve clearance too large
1 Improper ignition timing
2 Inexactitude clearance of spark plug
or accumulated carbon.
3 Loose of air intake manifold or jam
of exhaust manifold.
4 .Loose of water wheel belt
5 Lack of coolant or jam of hose.
6 Inexactitude clearance or damage of
water pump
7 Lack of oil
8 Damage of oil pump or jam of
lubricating way.
9 Damage of cyclinder gasket
10 Slipping cluth
11 Jam of radiator
1 Defective valve guide bushes oil seals
2 Sticky piston ring
3 Worn piston ring groove and ring
4 Improper location of piston ring gap
5 Badly worn valves or valve guide bushes
6 Exhaust of oil through breeze hole by
high pressure which caused by overheat.
1 Wron synchronizer hub
2 Wron synchronizer gear
3 Broken locating balls
4 Distorted or unevenly worn shift fork shaft
Adjust
1 check valve、 spark plug、
cylinder gasket leakage;
2 Valve rubbing
Adjust
Adjust or replace
Check inlet system
Check exhaust system or clear
away carbon deposit
Adjust or replace
Check high voltage wire
Clean or replace
Replace
Replace
Repair or replace
Replace
Replace or repair
Replace
Adjust
Adjust
Adjust
Clean or adjust
Retighten or clean
Adjust
Refill or clean
Repair or replace
Refill
Clean or replace
Replace
Repair or replace
Clean or replace
Replace
Replace
Adjust
Replace
Replace
Check relative position
Replace
Replace
Replace
Repair or replace
2
第 3 页 共 3页
Noisy clutch
Bright of trouble
pilot lamp in panel
Poor emission
1. Worn or broken release bearing
2. Input shaft front bearing worn down
3 Excessive rattle of clutch disc hug
4 Cracked clutch disc
5 Pressure plate and diaphragm spring
rattling
6 Clutch facings soaked with oil
7 Weakened torsion spring
1 Trouble of EFI system
2 Trouble of wire
1 Damage of TWC and O
sensor, which
2
caused by use of lead fuel.
2 Damage of TWC and O
sensor, which
2
caused by misfire of ignition system.
3 Leakage of exhaust system, ECU can’t
get the right signal of O
sensor,
2
causing air/fuel ratio rich
Replace
Replace
Repair
Replace
Repair or replace
Clean or replace
Replace
Diagnose with Hi-Scan
Check ( if connect firmly 、
break-circuit or short-circuit)
Replace
Replace
Repair
3
4 ENGINE
4.1 General
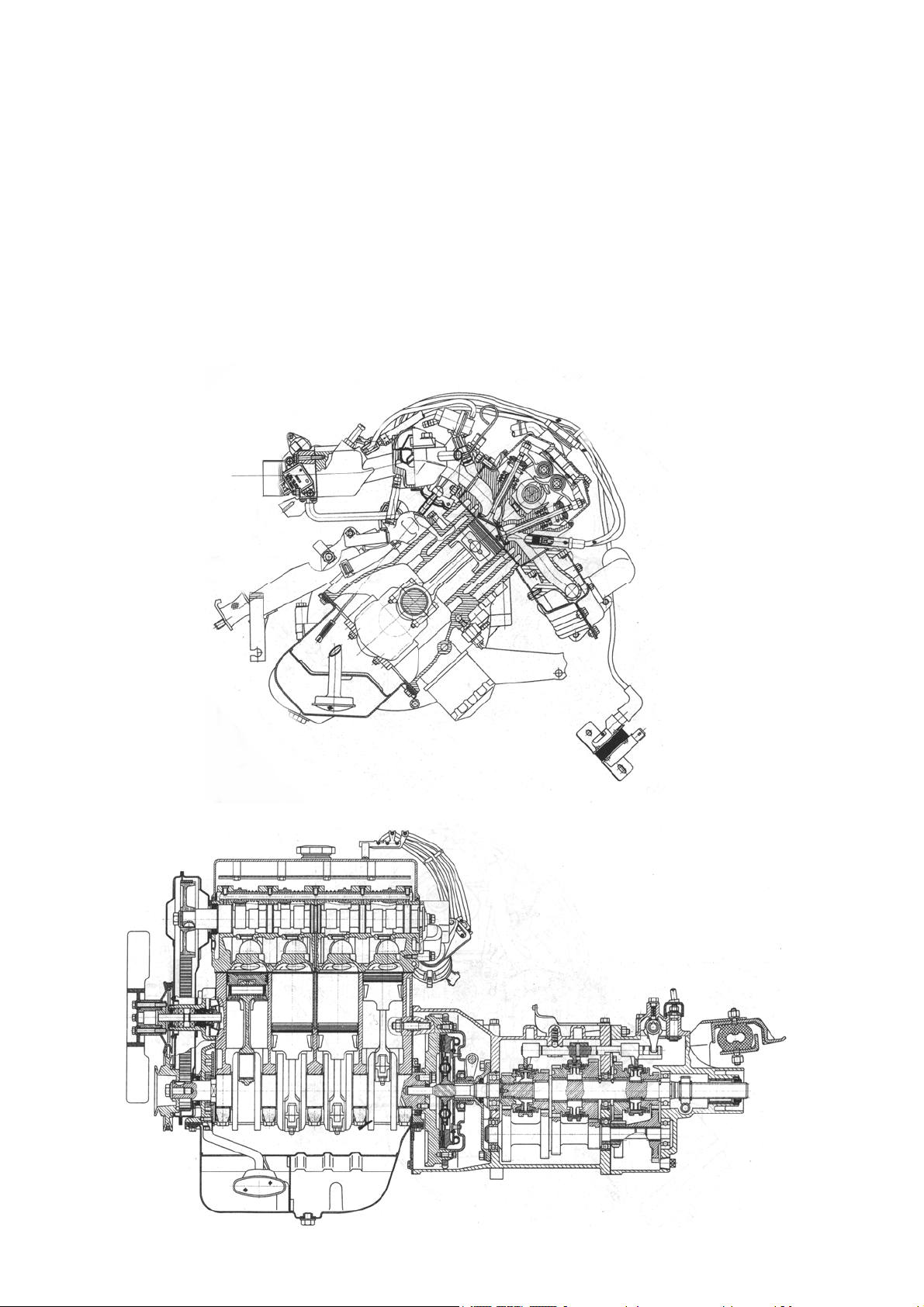
The engine is in-line 4-cylinders, water-cooled, 4-stroke cycle MPI gasoline unit
with valve mechanism arranged for “V”-type valve configuration and overhead camshaft,
which is installed in cylinder head and driven by crankshaft with timing chain. With
compare to general model, no valve lifter is available in the model, so that valves is driven
in more directive method and open or close more promptly (See Fig.4-1).

Fig.4-1
The engine adopts BOSCH M1.5.4 EMS or DELPHI EFI system. Comparing with
carburetor engine, a great improvement has made in power, economic and low
temperature starting performances.
The engine that has functions of sequential ignition, sequential injection, knock
closed-loop control, idle closed-loop control, canister control, A/C control etc, with
distributor, is a closed-loop control engine manage system. Sensors available for the
system include TPS(throttle position sensor), MAT/MAP(manifold air temperature &
pressure sensor), knock sensor, coolant temperature sensor, oxygen sensor, rotation speed
sensor ( in distributor,also called Hall sensor). The actuators include fuel pump (inside
fuel tank), injectors, ignition coils, idle adjustor(also as stepper motor), purge valve.
·ENGINE CHARACTERISTICS
· Valves in the head is arrayed in V type with inlet pipe and exhaust pipe in
configuration of orthogonal flowing pattern, so that efficiency of charge and exhaust is
high.
·Combustion chamber shape is multi-sphere, with low burning consumption and high
power performance.
·The camshaft and the rocker arm shaft are installed in the head for more solid
construction, which reduce noise from inlet system and quantity of parts in induction
system. These make engine more compact.
·The timing chain driving camshaft has characteristics of light weight and small
operating noise.
·The engine block uses material of high quality iron-casting and has a construction of
gantry for high rigidity.
· The crankshaft are constructed of one-piece forged alloy steel , which supports with
five bearings and have an advantage of low vibration.
· The exhaust manifold and pipe adopt double pipe type, for no interference with each
other. One pipe is connected to 1st and 4th cylinders, the other to 2nd and 3rd cylinders.
·Electronic fuel injection system has a central unite of ECU(electronic control unit),
which control accurately quantity of injecting fuel, ignition advance, so that engine works
well under varies operation conditions.
·Use three-way catalytic converter to reduce CO, HC and NOx, emissions in exhaust, in
order to make the vehicle become GREEN MOTOR.
·Crankcase emission controls
Leakage pipeline is located in the block. The leakage flows to the head
through crankcase, and fuel is separated from the air with separation plate
in the head before it is taken out.

4.2 PRINCIPLE AND CONSTRUCTION OF EMS
1. Parts
As general electronic control system, there are three portions that
construct electronic control fuel injection system: sensors, control unit,
actuators.
(1)Sensors
Sensor is a device that responds to a physical stimulus (heat, light, sound,
pressure, motion, flow, and so on), and produces a corresponding electrical
signal, which can be used by ECU. General sensors in EFI include load sensor
which responds to air volume every cycle directly or indirectly, rotation
speed sensor which responds to engine speed, crankshaft position sensor which
responds 1st cylinder TDC; TPS, coolant temperature sensor, air charge
temperature, barometric pressure sensor, oxygen sensor which responds to
oxygen volume in exhaust and is used by closed control, manifold inlet
pressure sensor.
(2)Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
The device is applied to receive and handle signals from sensors, instruct
actuators to control engine.
(3)Actuators
Actuators are applied to do instructions of ECU and control fuel quantity.
Main parts include power fuel pump and magnetic injectors.
·Variables
Control variables are applied to decide instructions for actuators by
ECM, such as gasoline load, engine speed, coolant temperature, air
temperature, air pressure etc. features. In general, one sensor informs
one piece of information.
Tow more important variables in varies variables of engine (known as
main control variables) are engine speed and engine load.
For engine, the load can be informed with air volume each cycle. When
knowing engine speed, it is easy to know air volume every cycle according
air volume every time unit. So generally use air charge as load.
ECU decides basic injecting quality and basic ignition BTDC by main control
variables value and modify those values by other sub information such as
coolant temperature, air temperature, so that accept last values about
injecting quantity and ignition advance.
·INFORMATION FLOW OF EMS
Information flow of EMS is shown in Fig.4-2.

Opened-loop control
Load sensor
Rotation speed sensor
Other sensors
ECU
Closed-loop control for λ
Closed-loop control for knock
Closed-loop control for idle speed
Fuel-metering actuator
Ignition timing actuator
Other actuators
Engine
Oxygen sensors
Knock sensors
Rotation speed sensor
Fig.4-2
ECU receives various information about engine responded by sensors to
calculate and product instructions to actuators to make engine operate in
perfect condition, which the power fuel pump and the injectors carry out
fuel-metering injection, and the ignition coil and the distributor carry out
ignition control.
Results of control is unknown by the way of the foregoing statement.
Sometimes it is necessary to keep a feature in a range, for example, to make
air/fuel close to theory air/fuel ratio 14.7 for satisfying emissions
requirements or keep idle speed near 850r/minn or prevent knock on high-load
condition. Closed-loop control is a way that forms close circuit in EMS. On
the other hand, opened-loop control system is a control system that doesn’t
form close circuit. The portion of short-line is closed-loop control, the
portion of solid-line is opened-loop control (Fig 4-2).
It is necessary to indicate that it is impossible for electronic control
system to change engine operating condition. Only external conditions, like
man or engine operating environment, can change engine operating condition
by changing engine main control variables. For example, engine operating
condition is changed because throttle open degree is changed, which air volume
charged is changed, or a vehicle is driven on upright from flat ground, engine
speed will reduces though other conditions aren’t changed.
2. Principle
Electronic fuel injection system is a system that the central part is
engine electronic control unit.
Sensors installed on positions of engine respond to various operating

features and inform ECU.
According these information, engine–ECU controls injecting quantity,
ignition advance accurately, based on preparing control program to make
engine operate perfectly in various conditions.
When ignition switch ON, ECU or ECM is powered. As soon as the first crank
rotation signal is checked, the fuel pump is powered and fuel press out with
the pump. The fuel flows to fuel distribution pipe on engine through fuel
filter and then the injectors installed on inlet manifold near intake ports,
which inject fuel into cylinders. The fuel pressure, which is controlled with
the pressure regulator on end of fuel rail, is 300kPa for both systems. Because
pressure difference is constant with pressure regulator and section area of
injector is constant too, so ECU can control injecting quantity every cycle
by means of controlling the injector on-time. When injector opens, fogging
fuel is injected into manifold which mixes with air and is inducted cylinder
on inlet stroke to fire.
Driver can control throttle open degree with acceleration pedal to control
air volume. ECU receives information such as air temperature, coolant
temperature, air pressure, engine speed etc. and calculate out air volume
and basic injecting period.
In a real run, after the basic injecting period is calculated, a modified
value is prepared by information of feedback signal of oxygen sensor on
exhaust system, instant load, battery voltage etc. ECU corrects the injecting
quantity to actual injecting quality. ECU decides accurate injecting phase
by preprogramming data, engine speed or crank position signals.
BOSCH M1.5.4 EMS adopts a pattern of sequential ignition with distributor.
DELPHI adopts a pattern of directive ignition without distributor. Drive
circuit in ECU open or close ignition coil primary circuit, and supply
ignition signals to 1-4 cylinders and 2-3 cylinders.
Both systems have self-diagnosis function. The service light in meter is
lighted when troubles occurs.
Vehicle will operate in hirple pattern while parts in the system have
trouble. There is a connector for tester.
BOSCH M1.5.4 is shown in Fig.4-3 a).
DELFHI system is shown in Fig 4-3 b).

Knock sensor
Fig.4-3a)
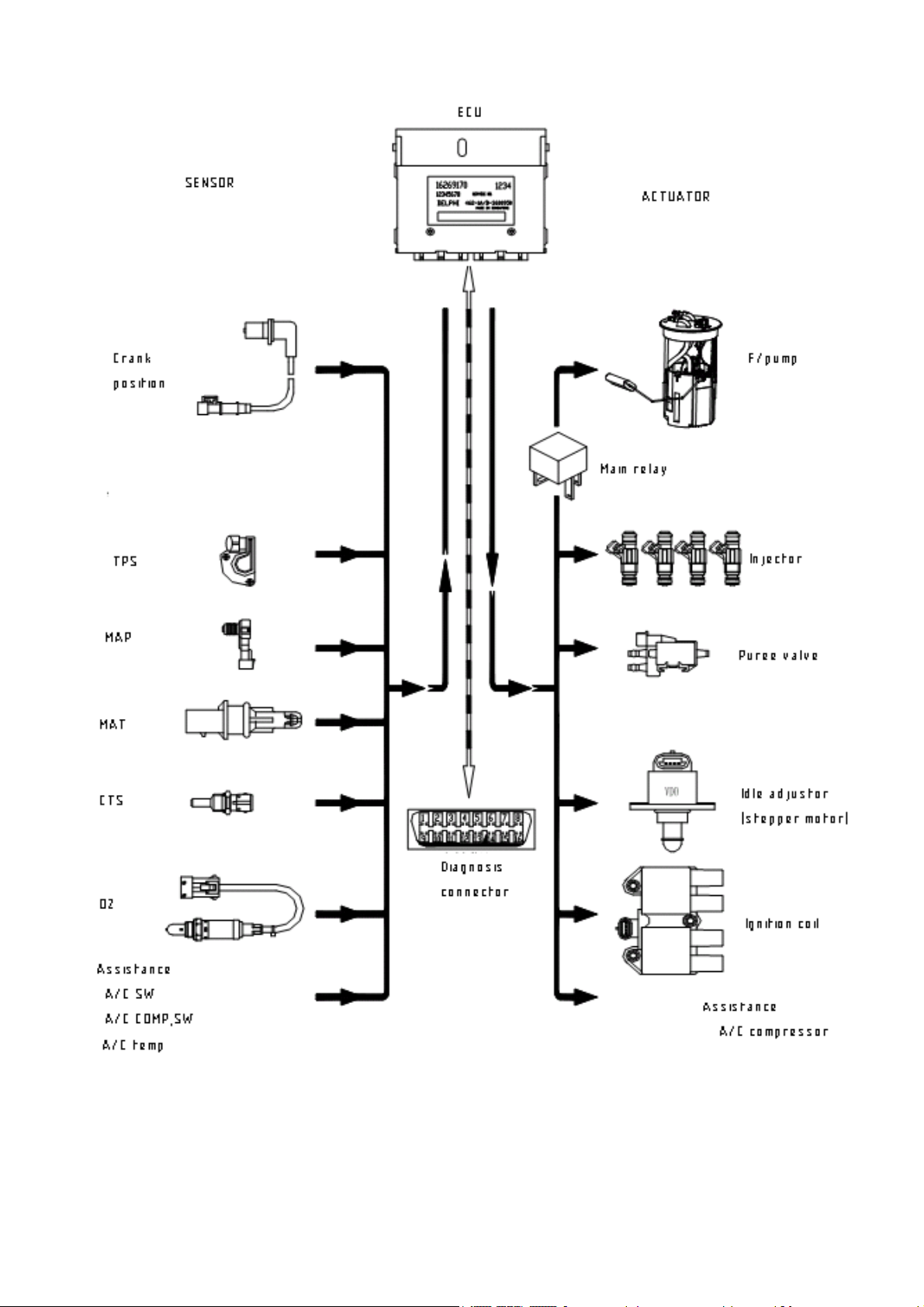
Fig 4-3b)
·SENSORS
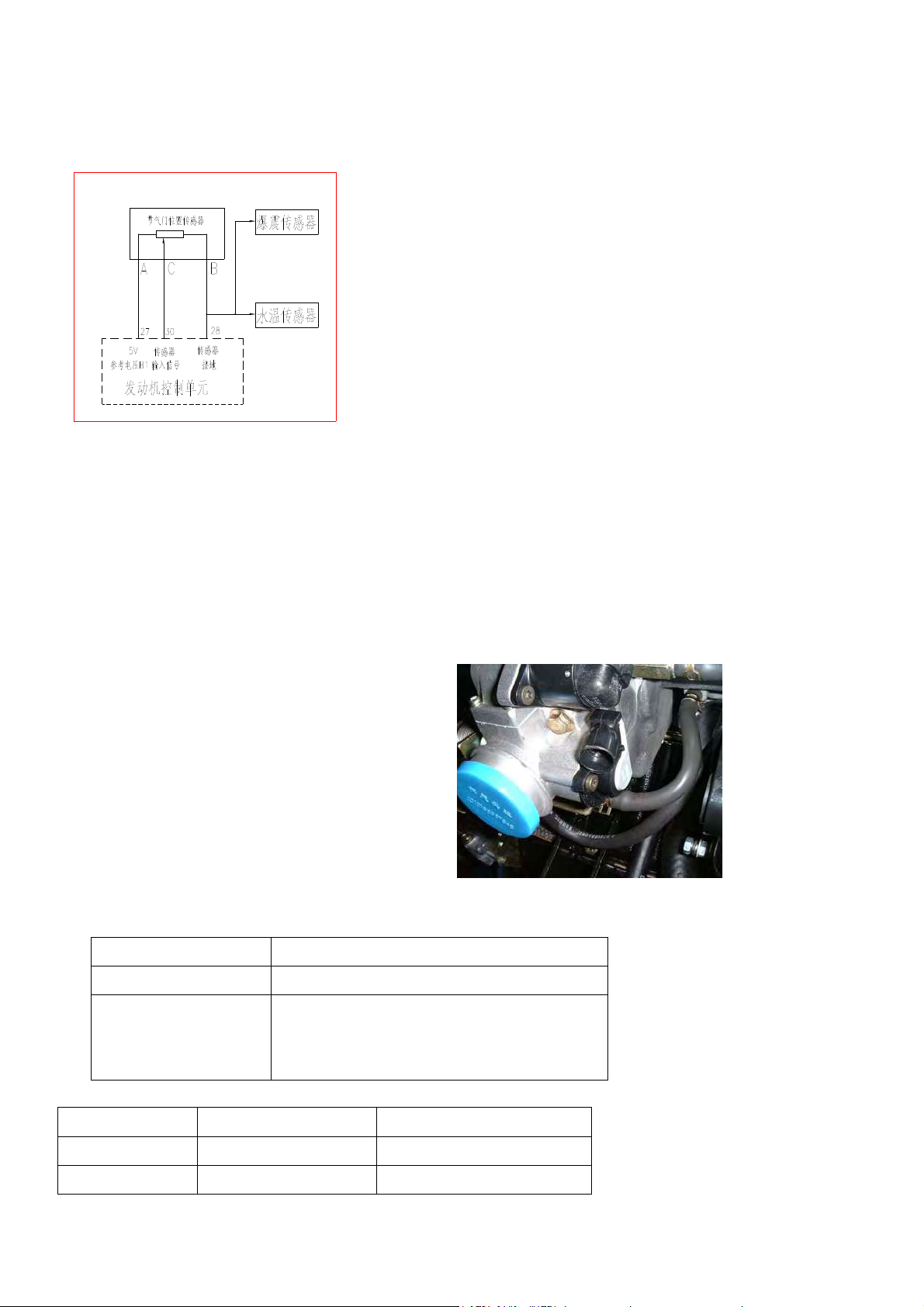
1) Throttle position sensor
A sensor which is installed on throttle assembly coaxially (throttle assembly install
on the front end of intake pipe),provide load, load range and acceleration information.
Throttle position sensor monitors open degree of the throttle. The sensor is resistance type, which
is powered with 5V by ECU and products voltage signal to ECU. The circuit diagram sees Fig. 4-4a).
a)(DELPHI)
节气门位置传感器-Throttle position sensor(TPS)
爆震传感器- Knock sensor
水温传感器-Coolant temperature sensor
参考电压-Ref. Voltage
传感器输入信号-Sensor input signal
传感器接地-Sensor earth
发动机控制单元-Engine-ECU
b)(BOSCH) c)(DELPHI)
FIG.4-4
Item BOSCH(Fig.4-4b)
Resistance(1-3) 1.95~2.10KΩ
Resistance(2-3)
1.10~2.80KΩ
Full close -full
open
Item BOSCH(Fig.4-4a) DELPHI(Fig.4-4c)
Full close 0.1V~0.9V 0~0.25V
Full open 3.0V~4.8V 0~5V
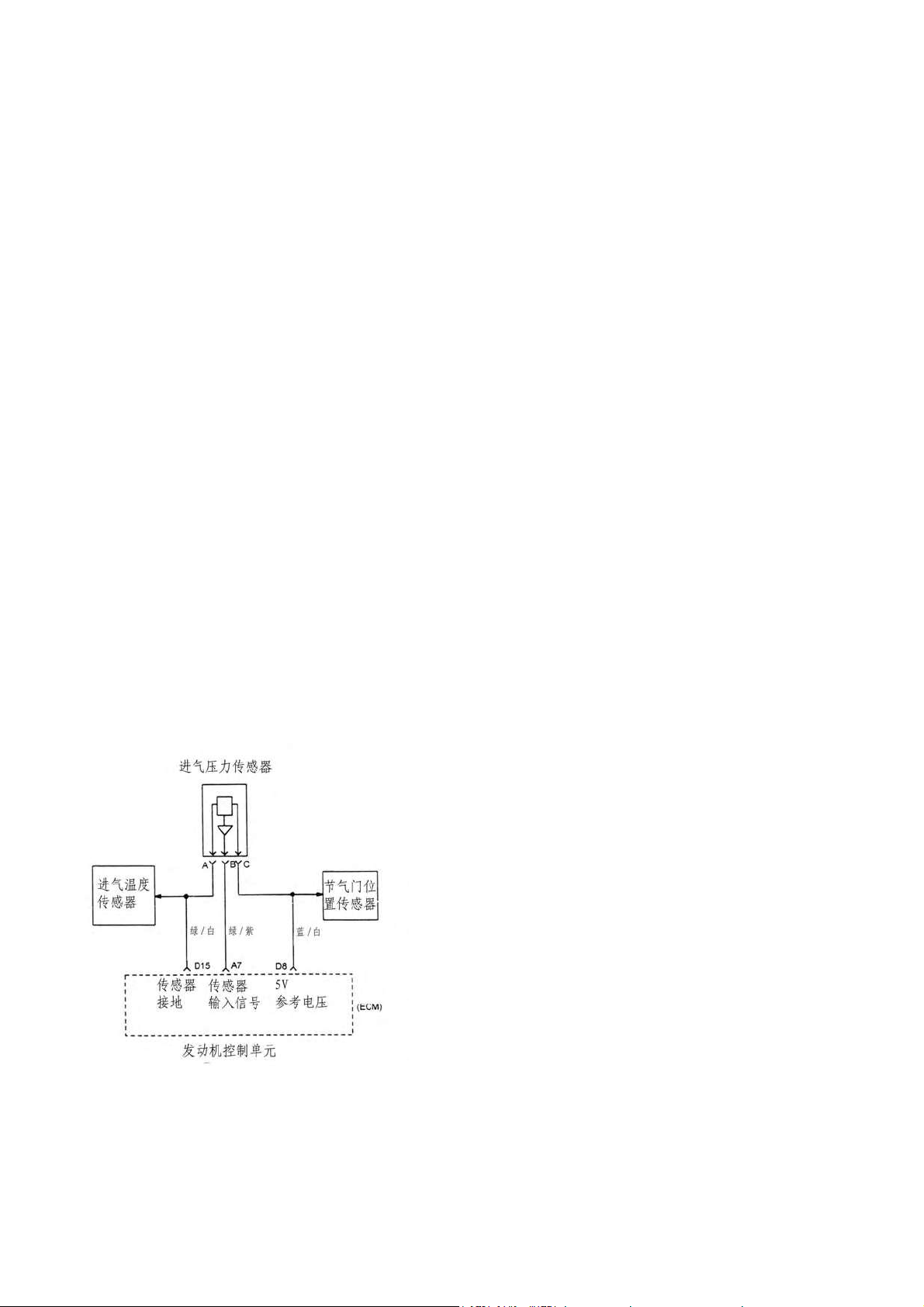
2) Intake temperature/pressure sensor(Fig4-5a),Fig.4-5b))
A sensor is installed on the intake manifold stable pressure chamber to
offer engine load and temperature information, which is used to decided
injecting quantity and ignition timing.
For BOSCH M1.5.4 , the voltage of 5V, which is supplied by ECU powers the sensor.
Voltage between terminal 4 and ground is in a range of 3.8 – 4.2V. Voltage responded to
pressure is 0.8 - 1.3V while idling,1.521 - 1.683V for 40kpa and 4.859~5.043V for
102kpa。Using ohmmeter to measure resistance between terminals 1,2, the value should be
2.2~2.7KΩ for 20℃ and 1.1~1.4KΩ for 30℃. If faulty, replace the sensor, see
fig.4-5) .
Fig.4-5a)
·Intake pressure sensor for DELPHI system
Be installed on the intake manifold stable pressure chamber to provide engine load information.
ECU provide 5V voltage to the sensor, the sensor responds to manifold pressure of different lode and
rotate speed which is changed to voltage single and transmitted to ECU,FIG. 4-5b),FIG.4-5c)。
Operation voltage:0.122~0.382V/15kPa
1.521~1.683V/40kPa
4.438~4.600V/94kPa
4.859~5.043V/102kPa
FIG.4-5b)
进气压力传感器: Intake pressure sensor
进气温度传感器: Intake temperature sensor
节气门位置传感器: Throttle position sensor(TPS)
传感器接地: Sensor earth
传感器输入信号: Sensor input signal
参考电压: Ref. Voltage
发动机控制单元: Engine-ECU
篮/白-LW
绿/白-GW
绿/紫-GV
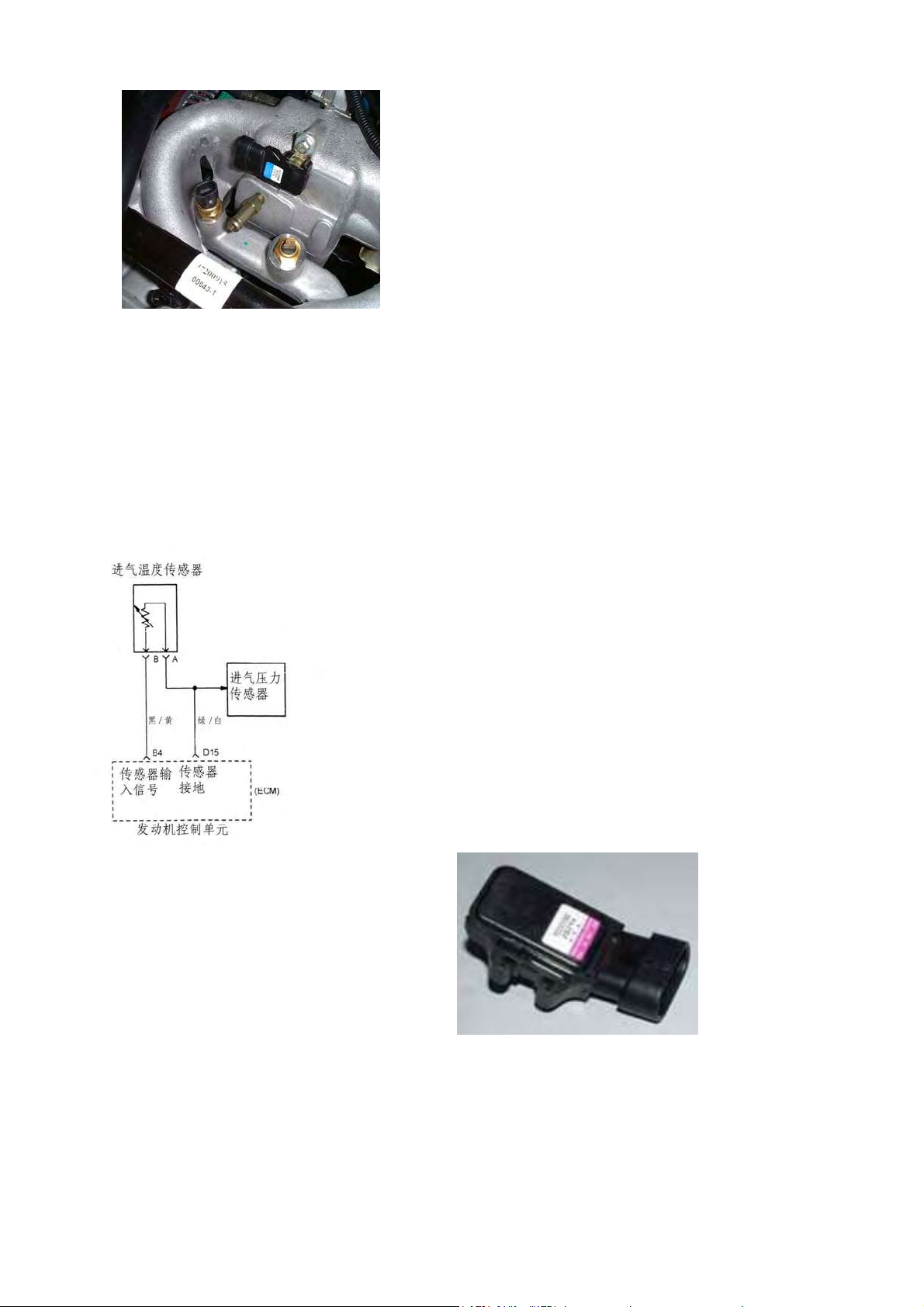
FIG.4-5c)
·Intake temperature sensor for DELPHI system
Installing in air fillter and provice air temperature information which is used to confirm amount
of injection and ignition timing. The end voltage is direct ratio change with resistance . Its resistance
decreases with temperature increasing.
Intake temperature sensor responds to temperature and product voltage signal which is transmitted
to ECU or ECM to control injecting quantity and ignition timing.FIG.4-5d),FIG.4-5e),MT20 see 4-5f)。
Resistance value:
178±2.3Ω/100℃ 333.8±2Ω/80℃ 3511±2.6Ω/20℃
进气压力传感器: Intake pressure sensor
进气温度传感器: Intake temperature sensor
传感器接地: Sensor earth
传感器输入信号: Sensor input signal
发动机控制单元: Engine-ECU
绿/白-GW
黑/黄-BY
FIG.4-5d)
FIG.4-5e) FIG.4-5f)
 Loading...
Loading...