Page 1

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS Configuration Commands .....................................1-1
1.1 AAA Configuration Commands.......................................................................................... 1-1
1.1.1 access-limit.............................................................................................................. 1-1
1.1.2 accounting default ................................................................................................... 1-2
1.1.3 accounting lan-access............................................................................................. 1-3
1.1.4 accounting login ...................................................................................................... 1-4
1.1.5 accounting optional ................................................................................................. 1-5
1.1.6 attribute ................................................................................................................... 1-6
1.1.7 authentication default .............................................................................................. 1-7
1.1.8 authentication lan-access........................................................................................ 1-8
1.1.9 authentication login ................................................................................................. 1-9
1.1.10 authorization command....................................................................................... 1-11
1.1.11 authorization default............................................................................................ 1-11
1.1.12 authorization lan-access ..................................................................................... 1-13
1.1.13 authorization login ............................................................................................... 1-14
1.1.14 cut connection ..................................................................................................... 1-15
1.1.15 display connection............................................................................................... 1-16
1.1.16 display domain .................................................................................................... 1-17
1.1.17 display local-user ................................................................................................ 1-19
1.1.18 domain................................................................................................................. 1-20
1.1.19 domain default..................................................................................................... 1-21
1.1.20 idle-cut................................................................................................................. 1-22
1.1.21 level ..................................................................................................................... 1-23
1.1.22 local-user............................................................................................................. 1-24
1.1.23 local-user password-display-mode...................................................................... 1-25
1.1.24 password............................................................................................................. 1-25
1.1.25 self-service-url..................................................................................................... 1-26
1.1.26 service-type......................................................................................................... 1-27
1.1.27 service-type ftp.................................................................................................... 1-28
1.1.28 state..................................................................................................................... 1-29
1.2 RADIUS Configuration Commands ................................................................................. 1-30
1.2.1 data-flow-format .................................................................................................... 1-30
1.2.2 display local-server statistics................................................................................. 1-31
1.2.3 display radius ........................................................................................................ 1-32
1.2.4 display radius statistics ......................................................................................... 1-34
1.2.5 display stop-accounting-buffer .............................................................................. 1-35
1.2.6 key......................................................................................................................... 1-37
1.2.7 local-server............................................................................................................ 1-38
i
Page 2

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches Table of Contents
1.2.8 local-server nas-ip................................................................................................. 1-39
1.2.9 nas-ip..................................................................................................................... 1-40
1.2.10 primary accounting.............................................................................................. 1-41
1.2.11 primary authentication......................................................................................... 1-42
1.2.12 radius client ......................................................................................................... 1-43
1.2.13 radius nas-ip........................................................................................................ 1-44
1.2.14 radius scheme..................................................................................................... 1-45
1.2.15 radius trap ........................................................................................................... 1-46
1.2.16 reset local-server statistics.................................................................................. 1-47
1.2.17 reset radius statistics........................................................................................... 1-47
1.2.18 reset stop-accounting-buffer ............................................................................... 1-48
1.2.19 retry ..................................................................................................................... 1-49
1.2.20 retry realtime-accounting..................................................................................... 1-50
1.2.21 retry stop-accounting........................................................................................... 1-51
1.2.22 secondary accounting ......................................................................................... 1-52
1.2.23 secondary authentication .................................................................................... 1-53
1.2.24 server-type .......................................................................................................... 1-54
1.2.25 state..................................................................................................................... 1-55
1.2.26 stop-accounting-buffer enable............................................................................. 1-56
1.2.27 timer quiet............................................................................................................ 1-57
1.2.28 timer realtime-accounting.................................................................................... 1-58
1.2.29 timer response-timeout ....................................................................................... 1-59
1.2.30 user-name-format................................................................................................ 1-60
1.3 HWTACACS Configuration Commands .......................................................................... 1-61
1.3.1 data-flow-format .................................................................................................... 1-61
1.3.2 display hwtacacs ................................................................................................... 1-62
1.3.3 display stop-accounting-buffer .............................................................................. 1-64
1.3.4 hwtacacs nas-ip..................................................................................................... 1-65
1.3.5 hwtacacs scheme.................................................................................................. 1-66
1.3.6 key......................................................................................................................... 1-67
1.3.7 nas-ip..................................................................................................................... 1-67
1.3.8 primary accounting................................................................................................ 1-68
1.3.9 primary authentication........................................................................................... 1-69
1.3.10 primary authorization........................................................................................... 1-70
1.3.11 reset hwtacacs statistics ..................................................................................... 1-71
1.3.12 reset stop-accounting-buffer ............................................................................... 1-72
1.3.13 retry stop-accounting........................................................................................... 1-73
1.3.14 secondary accounting ......................................................................................... 1-73
1.3.15 secondary authentication .................................................................................... 1-74
1.3.16 secondary authorization...................................................................................... 1-75
1.3.17 stop-accounting-buffer enable............................................................................. 1-76
1.3.18 timer quiet............................................................................................................ 1-77
ii
Page 3

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches Table of Contents
1.3.19 timer realtime-accounting.................................................................................... 1-78
1.3.20 timer response-timeout ....................................................................................... 1-79
1.3.21 user-name-format................................................................................................ 1-79
iii
Page 4

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
1.1 AAA Configuration Commands
1.1.1 access-limit
Syntax
access-limit { disable | enable max-user-number }
undo access-limit
View
ISP domain view
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
Parameter
Description
Example
disable: Specifies not to limit the number of access users that can be contained in
current ISP domain.
enable max-user-number: Specifies the maximum number of access users that can be
contained in current ISP domain. Where, max-user-number ranges from 1 to 1024.
Use the access-limit command to set the maximum number of access users that can
be contained in current ISP domain.
Use the undo access-limit command to restore the default maximum number.
By default, the number of access users that can be contained in current ISP domain is
unlimited.
Because resource contention may occur between access users, there is a need to
properly limit the number of access users in an ISP domain to provide reliable
performance to the users in the ISP domain.
# Allow ISP domain aabbc.net to contain at most 500 access users.
<Sysname>system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname]domain aabbcc.net
[Sysname-isp-aabbcc.net] access-limit enable 500
1-1
Page 5

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
1.1.2 accounting default
Syntax
accounting default { radius-scheme radius-scheme-name [ local ] |
hwtacacs-scheme hwtacacs-scheme-name [ local ] | local | none }
undo accounting default
View
ISP domain view
Parameter
radius-scheme-name: Name of RADIUS scheme, a string not exceeding 32 characters.
hwtacacs-scheme-name: Name of HWTACACS scheme, a string not exceeding 32
characters.
local: Local accounting.
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
Description
none: No accounting.
Use the accounting default command to configure an accounting scheme for all
users.
Use the undo accounting default command to restore the default accounting scheme
for all users.
By default, the local scheme is configured.
It should be noted that:
z The accounting scheme configured by the accounting default command is
applicable to all users. The priority of this configuration is lower than that of a
specific access mode.
z Local accounting is only used to support the management of local user
connections without real statistical function. The management of local connections
takes effect for local accounting rather than local authentication and authorization.
z In the login access mode, accounting is not supported for FTP services.
Related command: authentication default and authorization default.
Example
# In the default ISP domain named system, configure local as the default accounting
scheme for all users.
<Sysname>system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] domain system
[Sysname-isp-system] accounting default local
1-2
Page 6

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
# In the default ISP domain named system, configure radius as the default accounting
scheme named rd for all users and local as backup accounting. Note that the rd
scheme must be already configured. Related command: radius scheme.
<Sysname>system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] domain system
[Sysname-isp-system] accounting default radius-scheme rd local
# In the default ISP domain named system, restore the default accounting scheme for
all users.
<Sysname>system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] domain system
[Sysname-isp-system] undo accounting default
1.1.3 accounting lan-access
Syntax
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
View
Parameter
Description
accounting lan-access { radius-scheme radius-scheme-name [ local ] | local
| none }
undo accounting lan-access
ISP domain view
radius-scheme-name: Name of RADIUS scheme, a string not exceeding 32 characters.
local: Local accounting.
none: No accounting.
Use the accounting lan-access command to configure accounting for a lan-access
user. Use the undo accounting lan-access command to remove accounting for a
lan-access user.
Related command: accounting default.
Example
# In the default ISP domain named system, configure local as the accounting scheme
for the lan-access user.
<Sysname>system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
1-3
Page 7

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
[Sysname] domain system
[Sysname-isp-system]accounting lan-access local
# In the default ISP domain named system, configure radius as the accounting scheme
named rd for the lan-access user and local as backup accounting. Note that the rd
scheme must be already configured. Related command: radius scheme.
<Sysname>system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] domain system
[Sysname-isp-system] accounting lan-access radius-scheme rd local
# In the default ISP domain named system, remove the accounting scheme for the
lan-access user.
<Sysname>system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] domain system
[Sysname-isp-system] undo accounting lan-access
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
1.1.4 accounting login
Syntax
accounting login { radius-scheme radius-scheme-name [ local ] |
hwtacacs-scheme hwtacacs-scheme-name [ local ] | local | none }
undo accounting login
View
ISP domain view
Parameter
radius-scheme-name: Name of RADIUS scheme, a string not exceeding 32 characters.
hwtacacs-scheme-name: Name of HWTACACS scheme, a string not exceeding 32
characters.
local: Local accounting.
none: No accounting.
Description
Use the accounting login command to configure accounting for the login user.
Use the undo accounting login command to remove accounting for the login user.
Related command: accounting default.
1-4
Page 8

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
Example
# In the default ISP domain named system, configure local as the accounting scheme
for the login user.
<Sysname>system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] domain system
[Sysname-isp-system] accounting login local
# In the default ISP domain named system, configure radius as the accounting scheme
named rd for the login user and local as backup accounting. Note that the rd scheme
must be already configured. Related command: radius scheme.
<Sysname>system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] domain system
[Sysname-isp-system] accounting login radius-scheme rd local
# In the default ISP domain named system, remove the accounting scheme for the login
user.
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
<Sysname>system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] domain system
[Sysname-isp-system] undo accounting login
1.1.5 accounting optional
Syntax
accounting optional
undo accounting optional
View
ISP domain view
Parameter
None
Description
Use the accounting optional command to open the accounting-optional switch.
Use the undo accounting optional command to close the accounting-optional switch.
By default, the accounting-optional switch is closed.
Note that:
1-5
Page 9

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
z When the system charges an online user but it does not find any available
RADIUS accounting server or fails to communicate with any RADIUS accounting
server, the user can continue the access to network resources if the accounting
optional command has been used; otherwise, the user is disconnected from the
system. The accounting optional command is often used in the cases where
only authentication is needed and no accounting is needed.
z With the accounting optional command executed, the system does not send real
time accounting updating packets and accounting-stop packets to all users in
RADIUS scheme.
Example
# Open the accounting-optional switch for the ISP domain named aabbcc.net.
<Sysname> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] domain aabbcc.net
[Sysname-isp-aabbcc.net] accounting optional
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
1.1.6 attribute
Syntax
attribute { ip ip-address | mac mac-address | idle-cut minute | access-limit
max-user-number | vlan vlan-id | location { nas-ip ip-address port portnum | port
portnum } } *
undo attribute { ip | mac | idle-cut | access-limit | vlan | location }*
View
Local user view
Parameter
ip ip-address: Sets the IP address of the user. The attribute ip command for a local
user only applies to H3C 802.1x clients. If you configure this command on a non-H3C
client, local authentication will fail.
mac mac-address: Sets the MAC address of the user. Where, mac-address is in H-H-H
format.
idle-cut minute: Allows the local user to enable the idle-cut function. Where, minute is
the idle time before cutting down, which ranges from 1 minutes to 120 minutes.
access-limit max-user-number: Sets the maximum number of users who can access
the switch with current user name. Where, max-user-number ranges from 1 to 1024.
vlan vlan-id: Sets the VLAN attribute of the user (that is, which VLAN the user belongs
to). Where, vlan-id is an integer ranging from 1 to 4094.
location: Sets the port binding attribute of the user.
1-6
Page 10

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
nas-ip ip-address: Sets the IP address of the remote access server port to which the
user is bound to. Where, ip-address is in dotted decimal notation and is 127.0.0.1
(representing this device) by default. If the user is bound to a remote port, you must
specify the nas-ip parameter. If the user is bound to a local port, you need not specify
the nas-ip parameter.
port port-number: Sets the port bound with the user.
Description
Use the attribute command to set the attributes of a user whose service type is
lan-access.
Use the undo attribute command to cancel attribute settings of the user.
Related command: display local-user.
Example
# Set the IP address of user1 to 10.110.50.1.
<Sysname> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] local-user user1
[Sysname-luser-user1] attribute ip 10.110.50.1
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
1.1.7 authentication default
Syntax
authentication default { radius-scheme radius-scheme-name [ local ] |
hwtacacs-scheme hwtacacs-scheme-name [ local ] | local | none }
undo authentication default
View
ISP domain view
Parameter
radius-scheme-name: Name of RADIUS scheme, a string not exceeding 32 characters.
hwtacacs-scheme-name: Name of HWTACACS scheme, a string not exceeding 32
characters
local: Local authentication.
none: No authentication.
Description
Use the authentication default command to configure authentication scheme for all
users.
1-7
Page 11

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
Use the undo authentication default command to restore the default authentication
scheme for all users.
By default, the local authentication is used.
The authentication scheme configured by the authentication default command is
applicable to all users. But its priority is lower than that configured by a special access
mode.
Related command: authorization default and accounting default.
Example
# In the default ISP domain named system, configure local as the default
authentication for all users.
<Sysname>system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] domain system
[Sysname-isp-system] authentication default local
# In the default ISP domain named system, configure radius as the default
authentication scheme named rd for all users and local as backup authentication. Note
that the rd scheme must be already configured. Related command: radius scheme.
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
<Sysname>system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] domain system
[Sysname-isp-system] authentication default radius-scheme rd local
# In the default ISP domain named system, restore the default authentication scheme
for all users.
<Sysname>system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] domain system
[Sysname-isp-system] undo authentication default
1.1.8 authentication lan-access
Syntax
authentication lan-access { radius-scheme radius-scheme-name [ local ] | local |
none }
undo authentication lan-access
View
ISP domain view
1-8
Page 12

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
Parameter
radius-scheme-name: Name of RADIUS scheme, a string not exceeding 32 characters.
local: Local authentication.
none: No authentication.
Description
Use the authentication lan-access command to configure authentication scheme for
a lan-access user.
Use the undo authentication lan-access command to remove authentication scheme
for a lan-access user.
Related command: authentication default.
Example
# In the default ISP domain named system, configure local as the authentication
scheme for the lan-access user.
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
<Sysname>system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] domain system
[Sysname-isp-system] authentication lan-access local
# In the default ISP domain named system, configure radius as the default
authentication named rd for the lan-access user and local as backup authentication.
Note that rd authentication must be already configured. Related command: radius
scheme.
<Sysname>system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] domain system
[Sysname-isp-system] authentication lan-access radius-scheme rd local
# In the default ISP domain named system, remove the authentication scheme for the
lan-access user.
<Sysname>system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] domain system
[Sysname-isp-system] undo authentication lan-access
1.1.9 authentication login
Syntax
authentication login { radius-scheme radius-scheme-name [ local ] |
hwtacacs-scheme hwtacacs-scheme-name [ local ] | local | none }
1-9
Page 13

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
undo authentication login
View
ISP domain view
Parameter
radius-scheme-name: Name of RADIUS scheme, a string not exceeding 32 characters.
hwtacacs-scheme-name: Name of HWTACACS scheme, a string not exceeding 32
characters.
local: Local authentication.
none: No authentication.
Description
Use the authentication login command to configure authentication for a login user.
Use the undo authentication login command to remove authentication for a login
user.
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
Example
Related command: authentication default.
# In the default ISP domain named system, configure local as the authentication
scheme for the login user.
<Sysname>system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] domain system
[Sysname-isp-system] authentication login local
# In the default ISP domain named system, configure radius as the default
authentication named rd for the login user and local as backup authentication. Note
that the rd authentication must be already configured. Related command: radius
scheme.
<Sysname>system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] domain system
[Sysname-isp-system] authentication login radius-scheme rd local
# In the default ISP domain named system, remove the authentication scheme for the
login user.
<Sysname>system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] domain system
[Sysname-isp-system] undo authentication login
1-10
Page 14

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
1.1.10 authorization command
Syntax
authorization command hwtacacs-scheme hwtacacs-scheme-name
undo authorization command
View
ISP domain view
Parameter
hwtacacs-scheme-name: Name of a HWTACACS scheme, a string of up to 32
characters.
Description
Use the authorization command command to configure the authorization scheme for
a CLI user
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
Use the undo authorization command command to remove the authorization
scheme for a CLI user
Related command: authorization default.
Example
# In the default ISP domain named system, configure HWTACACS as the authorization
scheme named hw for the CLI user. Note that the hw authorization must be already
configured. Related command: hwtacacs scheme.
<Sysname>system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] domain system
[Sysname-isp-system] authorization command hwtacacs-scheme hw
1.1.11 authorization default
Syntax
authorization default { radius-scheme radius-scheme-name [ local ] |
hwtacacs-scheme hwtacacs-scheme-name [ local ] | local | none }
View
Parameter
undo authorization default
ISP domain view
radius-scheme-name: Name of RADIUS scheme, a string not exceeding 32 characters.
1-11
Page 15

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
hwtacacs-scheme-name: Name of HWTACACS scheme, a string not exceeding 32
characters.
local: Local authorization.
none: Direct authorization. In this case, the user passes the authentication directly, but
only owns the default rights.
Description
Use the authorization default command to configure the default authorization for all
users.
Use the undo authorization default command to restore the default authorization
scheme for all users.
By default, the local authorization is used.
It should be noted that:
z The authorization scheme configured by the authorization default command is
applicable to all users. Its priority is lower than that configured by a specified
access mode.
z As a special procedure, RADIUS authorization takes effect when the radius
schemes for authentication and authorization are similar. In case of failure to all
RADIUS authorization, the reason returned to NAS is that the Server did not
respond.
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
Example
Related command: authentication default and accounting default.
# In the default ISP domain named system, configure local as the default authorization
for all users.
<Sysname>system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] domain system
[Sysname-isp-system] authorization default local
# In the default ISP domain named system, configure radius as the default
authorization named rd for all users and local as backup authorization. Note that the rd
scheme must be already configured. Related command: radius scheme.
<Sysname>system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] domain system
[Sysname-isp-system] authorization default radius-scheme rd local
# In the default ISP domain named system, restore the default authorization scheme for
all users.
<Sysname>system-view
1-12
Page 16

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] domain system
[Sysname-isp-system] undo authorization default
1.1.12 authorization lan-access
Syntax
authorization lan-access { radius-scheme radius-scheme-name [ local ] | local |
none }
undo authorization lan-access
View
ISP domain view
Parameter
radius-scheme-name: Name of RADIUS scheme, a string not exceeding 32 characters.
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
Description
Example
local: Local authorization.
none: Direct authorization. In this case, the user passes the authentication directly, but
only owns the default rights.
Use the authorization lan-access command to configure authorization for a
lan-access user.
Use the undo authorization lan-access command to remove authorization for a
lan-access user.
Related command: authorization default.
# In the default ISP domain named system, configure local as the authorization
scheme for the lan-access user.
<Sysname>system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] domain system
[Sysname-isp-system]authorization lan-access local
# In the default ISP domain named system, configure radius as the authorization
scheme named rd for the lan-access user and local as backup authorization. Note that
the rd scheme must be already configured. Related command: radius scheme.
<Sysname>system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] domain system
1-13
Page 17

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
[Sysname-isp-system] authorization lan-access radius-scheme rd local
# In the default ISP domain named system, remove the authorization scheme for the
lan-access user.
<Sysname>system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] domain system
[Sysname-isp-system] undo authorization lan-access
1.1.13 authorization login
Syntax
authorization login { radius-scheme radius-scheme-name [ local ] |
hwtacacs-scheme hwtacacs-scheme-name [ local ] | local | none }
undo authorization login
View
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
Parameter
Description
Example
ISP domain view
radius-scheme-name: Name of RADIUS scheme, a string not exceeding 32 characters.
hwtacacs-scheme-name: Name of HWTACACS scheme, a string not exceeding 32
characters.
local: Local authorization.
none: Direct authorization. In this case, the user passes the authentication directly, but
only owns the default rights.
Use the authorization login command to configure authorization for a login user.
Use the undo authorization login command to remove authorization for a login user.
Related command: authorization default.
# In the default ISP domain named system, configure local as the authorization
scheme for the login user.
<Sysname>system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] domain system
[Sysname-isp-system] authorization login local
1-14
Page 18

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
# In the default ISP domain named system, configure radius as the authorization
scheme named rd for the login user and local as backup authorization. Note that the rd
scheme must be already configured. Related command: radius scheme.
<Sysname>system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] domain system
[Sysname-isp-system] authorization login radius-scheme rd local
# In the default ISP domain named system, remove the authorization scheme for the
login user.
<Sysname>system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] domain system
[Sysname-isp-system] undo authorization login
1.1.14 cut connection
Syntax
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
View
Parameter
cut connection { all | access-type { dot1x | mac-authentication } | domain
domain-name | interface interface-type interface-number | ip ip-address | mac
mac-address | vlan vlan-id | ucibindex ucib-index | user-name user-name }
System view
all: Cuts down all user connections.
access-type { dot1x | mac-authentication }: Cuts down user connections using the
specified access method. dot1x is used to cut down all 802.1x user connections, and
mac-authentication is used to cut down all MAC authentication user connections.
domain isp-name: Cuts down all user connections in the specified ISP domain. Where,
isp-name is the name of an ISP domain. It is a character string of up to 24 characters.
You can only specify an existing ISP domain.
interface interface-type interface-number: Cuts down all user connections under the
specified port. Where interface-type is the port type and interface-number is the port
number.
ip ip-address: Cuts down the connection of the user with the specified IP address.
mac mac-address: Cuts down the user connection with the specified MAC address.
Where, mac-address is in the H-H-H format.
vlan vlan-id: Cuts down all user connections of the specified VLAN. Where, vlan-id
ranges from 1 to 4094.
1-15
Page 19

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
ucibindex ucib-index: Cuts down the user connection with the specified connection
index. Where, ucib-index ranges from 0 to 4294967295.
user-name user-name: Cuts down the user connection of the specified user. Where,
user-name is a character string of up to 80 characters. The string cannot contain the
following characters: /:*?<>. It can contain no more than one @ character. The pure
user name (user ID, that is, the part before @) cannot contain more than 55 characters,
Description
Use the cut connection command to cut down one user connection or one type of user
connections forcibly.
This command cannot cut down the connections of Telnet, SSH and FTP users.
Related command: display connection.
Example
# Cut down all user connections in the ISP domain named aabbcc.net.
<Sysname> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] cut connection domain aabbcc.net
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
1.1.15 display connection
Syntax
display connection [ access-type { dot1x | mac-authentication } | domain
domain-name | interface interface-type interface-number | ip ip-address | mac
mac-address | vlan vlan-id | ucibindex ucib-index | user-name user-name ]
View
Any view
Parameter
access-type { dot1x | mac-authentication }: Displays the user connections in
specified access mode. Where, dot1x is used to display all 802.1x user connections,
and mac-authentication is used to display all MAC authentication user connections.
domain isp-name: Displays all user connections under the specified ISP domain.
Where, isp-name is the name of an ISP domain, a character string of up to 24
characters. You can only specify an existing ISP domain.
interface interface-type interface-number: Displays all user connections on the
specified port.
ip ip-address: Displays all user connections with the specified IP address.
1-16
Page 20

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
mac mac-address: Displays the connection of the user with the specified MAC address.
Where, mac-address is in dotted hexadecimal notation (in the form of H.H.H).
vlan vlan-id: Displays all user connections of the specified VLAN. Where, vlan-id
ranges from 1 to 4094.
ucibindex ucib-index: Displays the user connection with the specified connection
index. Where, ucib-index ranges from 0 to 4294967295.
user-name user-name: Displays the user connection with the specified user name.
Where, user-name is a character string in the format of pure-username@domain-name.
The pure-username cannot be longer than 55 characters, and the whole string cannot
be longer than 80 characters.
Description
Use the display connection command to display information about specified or all
user connections.
If you execute this command without specifying any parameter, all user connections will
be displayed.
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
This command cannot display information about the connections of the FTP users.
Related command: cut connection.
Example
# Display information about all user connections.
<Sysname> display connection
Total 0 connections matched ,0 listed.
1.1.16 display domain
Syntax
display domain [ isp-name ]
View
Any view
Parameter
isp-name: Name of an ISP domain, a character string of up to 24 characters. This must
be the name of an existing ISP domain.
Description
Use the display domain command to display the configuration information about one
specific or all ISP domains.
Related command: access-limit, domain and state.
1-17
Page 21
Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
Example
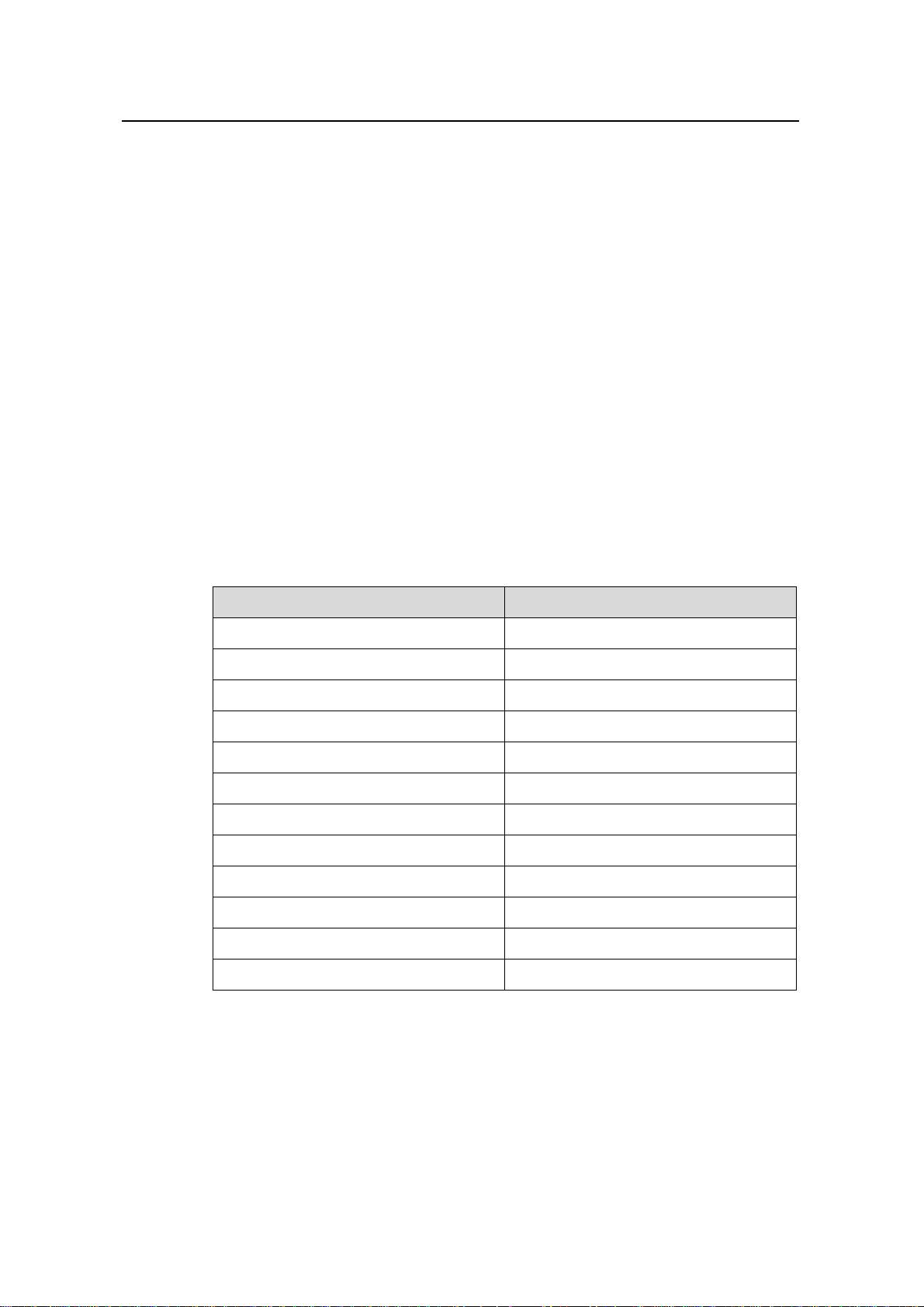
# Display the configuration information about all ISP domains.
<Sysname>display domain
0 Domain = system
State = Active
Access-limit = Disable
Accounting method = Required
Default authentication scheme : local
Default authorization scheme : local
Default accounting scheme : local
Domain User Template:
Idle-cut = Disable
Self-service = Disable
Default Domain Name: system
Total 1 domain(s).
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
Table 1-1 Description on the fields of the display domain command
Field Description
Domain Domain name
State State
Access-Limit Limit on the number of access users
Accounting method Accounting method
default Authentication scheme default Authorization scheme
default Authorization scheme default Authorization scheme
default Accounting scheme default Accounting scheme
Domain User Template Domain user template
Idle-Cut State of the idle-cut function
Self-service State of the self service
Default Domain Name Default domain name
Total 1 domain(s) There is totally one domain
1-18
Page 22

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
1.1.17 display local-user
Syntax
display local-user [ domain isp-name | idle-cut { disable | enable } | vlan vlan-id |
service-type { lan-access | telnet | ssh | terminal | ftp } | state { active | block } |
user-name user-name ]
View
Any view
Parameter
domain isp-name: Displays all local users belonging to the specified ISP domain.
Where, isp-name is the name of an ISP domain, a character string of up to 24
characters. You can only specify an existing ISP domain.
idle-cut { disable | enable }: Displays the local users who are inhibited from enabling
the idle-cut function, or the local users who are allowed to enable the idle-cut function.
Where, disable specifies the inhibited local users and enable specifies the allowed
local users.
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
Description
vlan vlan-id: Displays the local users belonging to the specified VLAN. Where, vlan-id
ranges from 1 to 4094.
service-type: Displays the local users of the specified type. You can specify one of the
following user types: lan-access (generally, this type of users are Ethernet access
users, for example, 802.1x users), telnet (for Telnet users), ssh (for SSH users),
terminal (this type of users are terminal users who log into the switch through the
Console port), and ftp for FTP users.
state { active | block }: Displays the local users in the specified state. Where active
represents the users allowed to request network services, and block represents the
users inhibited to request network services.
user-name user-name: Displays the local user who has the specified user name.
Where, user-name is a character string of up to 80 characters. The string cannot
contain the following characters: /:*?<>. It can contain no more than one @ character.
The pure user name (user ID, that is, the part before @) cannot be longer than 55
characters.
Use the display local-user command to display information about specified or all local
users.
Example
Related command: local-user.
# Display information about all local users.
1-19
Page 23
Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
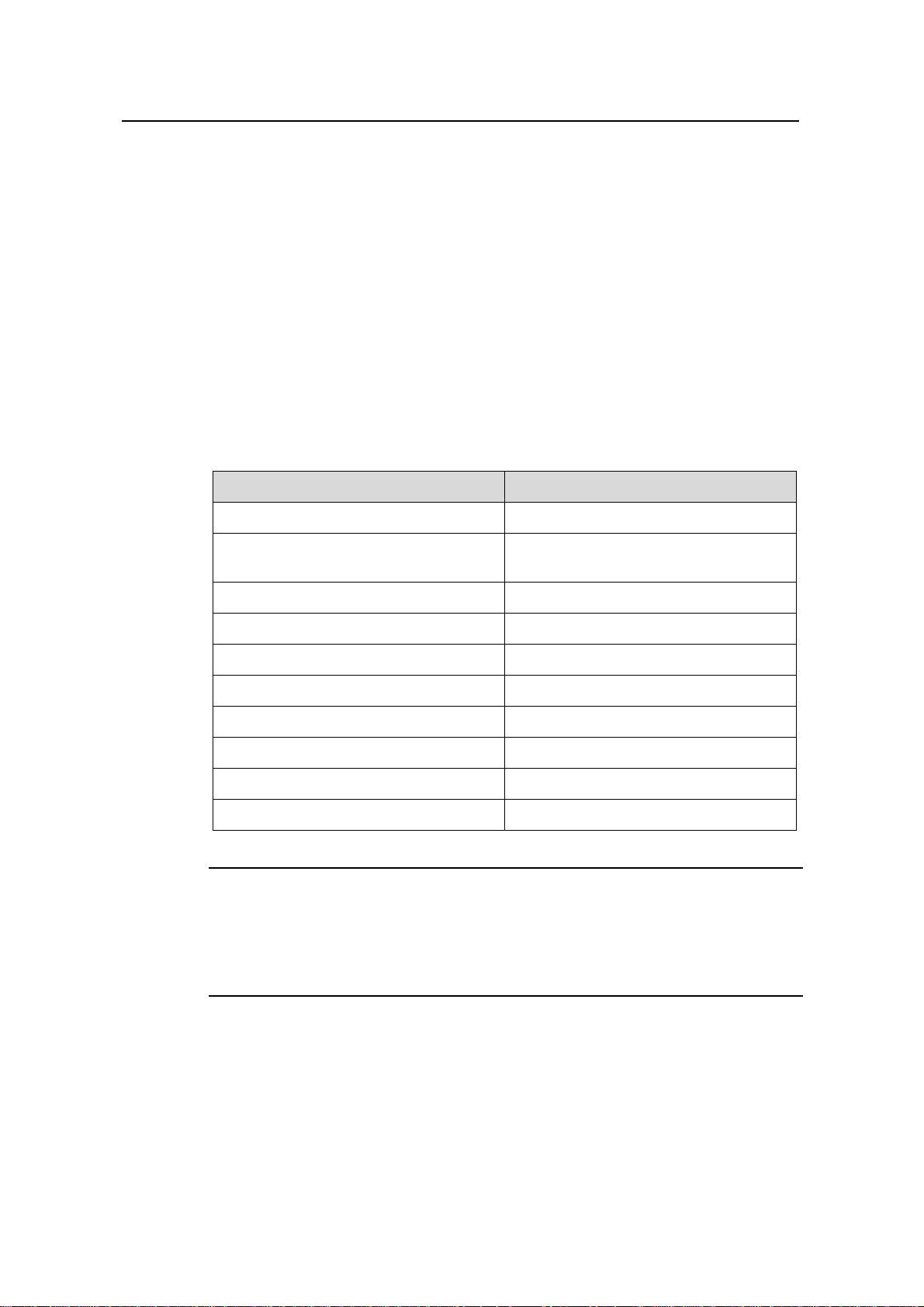
<Sysname> display local-user
The contents of local user user1:
State: Active
ServiceType: lan-access/telnet
Idle-cut: Disable
Access-limit: Disable Current AccessNum: 0
Bind location: Disable
Vlan ID: Disable
IP address: Disable
MAC address: Disable
User Privilege: 3
Total 1 local user(s) Matched,1 listed..
Table 1-2 Description on the fields of the display local-user command
Field Description
State State of the local user: Active or Block
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
ServiceType
ServiceType (ftp, lan-access, ssh,
telnet, or terminal)
Idle-Cut State of the idle-cut function
Access-Limit Limit on the number of access users
Current AccessNum Number of current access users
Bind location Whether or not bound to a port
Vlan ID VLAN of the user
IP address IP address of the user
MAC address MAC address of the user
User Privilege User Privilege
Note:
When the local RADIUS authentication server (local-server) is enabled, the value of
“Current AccessNum” may be inconsistent with the actual number of accessed users
and the displayed value here is just for reference.
1.1.18 domain
Syntax
domain isp-name
1-20
Page 24

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
undo domain isp-name
View
System view
Parameter
isp-name: Name of a ISP domain, a character string of 1 to than 24 characters
(case-insensitive). This string cannot contain the following characters: /:*?<>@.
default: Manually configures the default ISP domain, which is "system" by default.
There is one and only one default ISP domain.
disable: Disables the configured default ISP domain.
enable: Enables the configured default ISP domain.
Description
Use the domain command to create an ISP domain and enter its view, or enter the view
of an existing ISP domain, or configure the default ISP domain.
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
Use the undo domain command to delete a specified ISP domain.
After you execute the domain command, the system creates an ISP domain if the
specified ISP domain does not exist. Once an ISP domain is created, it is in the active
state.
Related command: state, display domain.
Example
# Create a new ISP domain "aabbcc.net" and enter its view.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] domain aabbcc.net
[Sysname-isp-aabbcc.net]
1.1.19 domain default
Syntax
domain default { disable | enable isp-name }
View
Parameter
System view
disable: Disables the specified ISP domain from being configured as the default.
enable: Configures the specified ISP domain as the default.
isp-name: ISP domain name.
1-21
Page 25

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
Description
Use the domain default command to configure the default ISP domain manually.
The default ISP domain is "system".
Note that:
z There is one and only one default ISP domain.
z You can manually configure only an existing domain as the default ISP domain.
z To remove the default ISP domain defined, you need to use the domain default
disable command first.
Related command: state, display domain
Example
# Create a new ISP domain with the name "aabbcc.net" and configure it as the default
ISP domain.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] domain aabbcc.net
[Sysname-isp-aabbcc.net] quit
[Sysname] domain default enable aabbcc.net
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
1.1.20 idle-cut
Syntax
idle-cut { disable | enable minute }
View
ISP domain view
Parameter
disable: Inhibits users from enabling the idle-cut function.
enable: Allows users to enable the idle-cut function.
minute: Maximum idle time, ranging from 1 minute to 120 minutes.
Description
Use the idle-cut command to set the user idle-cut function in current ISP domain.
By default, this function is disabled.
Related command: domain.
1-22
Page 26

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
Example
# Allow users in ISP domain aabbcc.net to enable the idle-cut attribute in user template
(that is, allow the user to use the idle-cut function), with the maximum idle time of 50
minutes.
<Sysname> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] domain aabbcc.net
[Sysname-isp-aabbcc.net] idle-cut enable 50
1.1.21 level
Syntax
level level
undo level
View
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
Parameter
Description
Local user view
level: Priority level of the user. It is an integer ranging from 0 to 3 and defaulting to 0.
Use the level command to set the priority level of the user.
Use the undo level command to restore the default priority level of the user.
Note that:
z If the configured authentication method is none or requires a password, the
command level that a user can access after login is determined by the level of the
user interface.
z If the configured authentication method requires a user name and a password, the
command level that a user can access after login is determined by the priority level
of the user. For SSH users, when they use RSA shared keys for authentication,
the commands they can access are determined by the levels sets on the user
interfaces.
Related command: local-user.
Example
# Set the level of user1 to 3.
<Sysname> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] local-user user1
1-23
Page 27

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
[Sysname-luser-user1] level 3
1.1.22 local-user
Syntax
local-user user-name
undo local-user { user-name | all [ service-type { lan-access | telnet | ssh | terminal
| ftp } ] }
View
System view
Parameter
user-name: Name of the local user, a character string of up to 80 characters. This string
cannot contain the following characters: /:*?<>. It can contain no more than one @
character. The pure user name (user ID, that is, the part before @) cannot be longer
than 55 characters. User names are case-sensitive. For example, the system regards
UserA and usera as two different users.
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
Description
Example
all: Specifies all local users.
service-type: Specifies the local users of the specified type. You can specify one of the
following user types: ftp, lan-access (generally, this type of users are Ethernet access
users, for example, 802.1x users), ssh, telnet, and terminal (this type of users are
terminal users who log into the switch through the Console port).
Use the local-user command to add a local user and enter local user view.
Use the undo local-user command to delete one or more specified local users.
By default, there is no local user in the system.
“a”, “al”, “all” cannot be name of the local user.
Related command: display local-user and service-type.
# Add a local user named user1.
<Sysname> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] local-user user1
[Sysname-luser-user1]
1-24
Page 28

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
1.1.23 local-user password-display-mode
Syntax
local-user password-display-mode { cipher-force | auto }
undo local-user password-display-mode
View
System view
Parameter
cipher-force: Adopts the forcible cipher mode so that the passwords of all local users
must be displayed in cipher text.
auto: Adopts the automatic mode so that the passwords of local users are displayed in
the modes set with the password command.
Description
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
Use the local-user password-display-mode command to set the password display
mode of all local users
Use the undo local-user password-display-mode command to restore the default
password display mode of all local users.
By default, the password display mode of all access users is auto.
When the cipher-force mode is adopted, all passwords will be displayed in cipher text
even through some users have specified to display their passwords in plain text by
using the password command with the simple keyword.
Related command: display local-user and password.
Example
# Specify to display all local user passwords in cipher text forcibly.
<Sysname>system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] local-user password-display-mode cipher-force
1.1.24 password
Syntax
View
password { simple | cipher } password
undo password
Local user view
1-25
Page 29

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
Parameter
simple: Specifies to display passwords in simple text.
cipher: Specifies to display passwords in cipher text.
password: Password you want to set, a character string.
z For simple mode, the password must be in plain text.
z For cipher mode, the password can be either in cipher text or in plain text, which it
is depends on your input.
A password in plain text can be a string with of up to 63 consecutive characters, for
example, aabbcc. Encrypted text password string can contain 24, 32, 44, 56, 64, 76, 88,
characters such as_(TT8F]Y\5SQ=^Q`MAF4<1!!.
Description
Use the password command to set a password for the local user.
Use the undo password command to cancel the password of the local user.
Note that, after the local-user password-display-mode cipher-force command is
executed, the password will be displayed in cipher text even though you use the
password command to set the display mode of the password to simple.
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
Related command: display local-user.
Example
# Set the password of user1 to 20030422 and specify to display the password in plain
text.
<Sysname> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] local-user user1
[Sysname-luser-user1] password simple 20030422
1.1.25 self-service-url
Syntax
self-service-url { disable | enable url-string }
undo self-service-url
View
ISP domain view
1-26
Page 30

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
Parameter
url-string: URL of the web page used to modify user password on the self-service server.
It is a character string with 1 character to 64 characters. The string must begin with
"http://”, and it cannot contain the character “?”.
Description
Use the self-service-url enable command to enable the self-service server location
function
Use the self-service-url disable command to disable the self-service server location
function
Use the undo self-service-url command to restore the default state of this function.
By default, this function is disabled.
Note that:
z This command must be used with the cooperation of a self-service-supported
RADIUS server (such as CAMS). Through self-service, users can manage and
control their accounts or card numbers by themselves. A server installed with the
self-service software is called a self-service server.
z After this command is executed on the switch, users can locate the self-service
server through the following operation: choose [change user password] on the
802.1x client, the client opens the default browser (for example, IE or Netscape)
and locates the specified URL page used to change user password on the
self-service server. Then, the user can change the password.
z A user can choose the [change user password] option on the client only after
passing the authentication. If the user fails the authentication, this option is in grey
and is unavailable.
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
Example
# Under the default ISP domain "system", set the URL of the web page used to modify
user password on the self-service server to
d1x.jsp|userName
<Sysname> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] domain system
[Sysname-isp-system] self-service-url enable
http://10.153.89.94/selfservice/modPasswd1x.jsp|userName
1.1.26 service-type
Syntax
service-type { lan-access | { telnet | ssh | terminal }* [ level level ] }
http://10.153.89.94/selfservice/modPassw
.
1-27
Page 31

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
undo service-type { lan-access | { telnet | ssh | terminal }* }
View
Local user view
Parameter
lan-access: Specifies that this is a LAN access user (who is generally an Ethernet
access user, for example, 802.1x user).
telnet: Authorizes the user to access the Telnet service.
ssh: Authorizes the user to access the SSH service.
terminal: Authorizes the user to access the terminal service (that is, allows the user to
log into the switch through the Console port).
level level: Specifies the level of the Telnet, terminal or SSH user. Where, level is an
integer ranging from 0 to 3 and defaulting to 0.
Description
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
Use the service-type command to authorize the user to access the specified type(s) of
service(s).
Use the undo service-type command to inhibit the user from accessing the specified
type(s) of service(s).
By default, the user is inhibited from accessing any type of service.
Example
# Authorize user1 to access the Telnet service.
<Sysname> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] local-user user1
[Sysname-luser-user1] service-type telnet
1.1.27 service-type ftp
Syntax
service-type ftp [ ftp-directory directory ]
undo service-type ftp [ ftp-directory ]
View
Local user view
1-28
Page 32

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
Parameter
ftp-directory directory: Specifies the directory of the FTP user, directory is a character
string of up to 64 characters.
Description
Use the service-type ftp command to configure the FTP service type and accessible
directories for users. Use the undo service-type ftp command to restore the default
settings.
By default, anonymous users cannot access the switch using FTP or are not authorized
with any FTP service; authorized FTP users can only access the root directory.
Related command: service-type.
Example
# Configure the user with FTP server type.
<Sysname>system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] local-user user1
[Sysname-luser-user1] service-type ftp
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
1.1.28 state
Syntax
state { active | block }
View
ISP domain view or local user view
Parameter
active: Activates the current ISP domain (in ISP domain view) or local user (in local
user view), to allow users in current ISP domain or current local user to access the
network.
block: Hangs up the current ISP domain (in ISP domain view) or local user (in local
user view), to inhibit users in current ISP domain or current local user from accessing
the network.
Description
Use the state command to set the status of current ISP domain (in ISP domain view) or
the status of the local user (in local user view).
By default, an ISP domain is in the active state once it is created, and a local user is in
the active state once the user is created.
1-29
Page 33

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
After an ISP domain is set to the block state, except the online users, the users under
this domain are not allowed to access the network.
After the local user is set to the block state, the user is not allowed to access the
network.
Related command: domain.
Example
# Set the ISP domain aabbcc.net to the block state, so that all its offline users cannot
access the network.
<Sysname> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] domain aabbcc.net
[Sysname-isp-aabbcc.net] state block
# Set user1 to the block state.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] local-user user1
[Sysname-luser-user1] state block
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
1.2 RADIUS Configuration Commands
1.2.1 data-flow-format
Syntax
data-flow-format { data { byte | giga-byte | kilo-byte | mega-byte } | packet
{ giga-packet | kilo-packet | mega-packet | one-packet } }*
undo data-flow-format { data | packet }
View
RADIUS scheme view
Parameter
data: Sets the unit of measure for data.
byte: Specifies to measure data in bytes.
giga-byte: Specifies to measure data in gigabytes.
kilo-byte: Specifies to measure data in kilobytes.
mega-byte: Specifies to measure data in megabytes.
packet: Sets the unit of measure for packets.
giga-packet: Specifies to measure packets in giga-packets.
kilo-packet: Specifies to measure packets in kilo-packets.
1-30
Page 34

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
mega-packet: Specifies to measure packets in mega-packets.
one-packet: Specifies to measure packets in packets.
Description
Use the data-flow-format command to set the units of data flows sent to RADIUS
servers.
Use the undo data-flow-format command to restore the default units of data flows
sent to RADIUS servers.
By default, the unit of measure for data is byte and that for packets is one-packet.
Related command: display radius.
Example
# Specify to measure data and packets in data flows sent to RADIUS server in kilobytes
and kilo-packets respectively.
<Sysname> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] radius scheme radius1
[Sysname-radius-radius1] data-flow-format data kilo-byte packet kilo-packet
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
1.2.2 display local-server statistics
Syntax
display local-server statistics
View
Any view
Parameter
None
Description
Use the display local-server statistics command to display the statistics about all
local RADIUS authentication servers.
Related command: local-server.
Example
# Display the statistics about local RADIUS authentication server.
<Sysname> display local-server statistics
The localserver packet statistics:
Receive: 30 Send: 30
Discard: 0 Receive Packet Error: 0
1-31
Page 35

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
Auth Receive: 10 Auth Send: 10
Acct Receive: 20 Acct Send: 20
Table 1-3 Description on the fields of the display local-server statistics command
Field Description
Receive Number of packets received
Send Number of packets sent
Discard Number of packets dropped
Receive Packet Error Number of error packets received
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
Auth Receive
Auth Send Number of authentication packets sent
Acct Receive Number of accounting packets received
Acct Send Number of accounting packets sent
1.2.3 display radius
Syntax
display radius [ radius-scheme-name ]
View
Any view
Parameter
radius-scheme-name: Name of a RADIUS scheme, a character string of up to 32
characters.
Number of authentication packets
received
Description
Example
Use the display radius scheme command to display the configuration information
about one specific or all RADIUS schemes
Related command: radius scheme.
# Display the configuration information about all RADIUS schemes.
<Sysname> display radius
-----------------------------------------------------------------SchemeName =system
Index=0 Type=extended
Primary Auth IP =127.0.0.1 Port=1645 State=block
1-32
Page 36

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
Primary Acct IP =127.0.0.1 Port=1646 State=block
Second Auth IP =0.0.0.0 Port=1812 State=block
Second Acct IP =0.0.0.0 Port=1813 State=block
Auth Server Encryption Key= Not configured
Acct Server Encryption Key= Not configured
Interval for timeout(second) =3
Retransmission times for timeout =3
Interval for realtime accounting(minute) =12
Retransmission times of realtime-accounting packet =5
Retransmission times of stop-accounting packet =500
Quiet-interval(min) =5
Username format =without-domain
Data flow unit =Byte
Packet unit =one
-----------------------------------------------------------------Total 1 RADIUS scheme(s).
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
Table 1-4 Description on the fields of the display radius command
Field Description
SchemeName Name of the RADIUS scheme
Index Index number of the RADIUS scheme
Type Type of the RADIUS servers
Primary Auth IP/ Port/ State
Primary Acct IP/ Port/ State
Second Auth IP/ Port/ State
Second Acct IP/ Port/ State
IP address/access port status of the
primary authentication server
IP address/access port status of the
primary accounting server
IP address/access port status of the
secondary authentication server
IP address/access port status of the
secondary accounting server
Auth Server Encryption Key Shared key of the authentication servers
Acct Server Encryption Key Shared key of the accounting servers
Interval for timeout(second) RADIUS server response timeout time
Retransmission times for timeout Retransmission times for timeout
Interval for realtime accounting(minute) Interval for realtime accounting
Retransmission times of
realtime-accounting packet
Retransmission times of
stop-accounting packet
1-33
Retransmission times of
realtime-accounting packet
Retransmission times of
stop-accounting packet
Page 37

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
Field Description
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
Quiet-interval(min)
Username format User name format
Data flow unit Unit of measure for data in data flows
Packet unit Unit of measure for packets
Total 1 RADIUS scheme(s) There is a total of one RADIUS scheme.
1.2.4 display radius statistics
Syntax
display radius statistics
View
Any view
Parameter
None
Wait time for the primary servers to
restore the active state
Description
Example
Use the display radius statistics command to display the statistics about RADIUS
packets.
Related command: radius scheme.
# Display the statistics about RADIUS packets.
<Sysname> display radius statistics
state statistic(total=1024):
DEAD=1024 AuthProc=0 AuthSucc=0
AcctStart=0 RLTSend=0 RLTWait=1
AcctStop=0 OnLine=1 Stop=0
StateErr=0
Received and Sent packets statistic:
Sent PKT total :38 Received PKT total:2
Resend Times Resend total
1 12
2 12
Total 24
1-34
Page 38

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
RADIUS received packets statistic:
Code= 2,Num=1 ,Err=0
Code= 3,Num=0 ,Err=0
Code= 5,Num=1 ,Err=0
Code=11,Num=0 ,Err=0
Running statistic:
RADIUS received messages statistic:
Normal auth request , Num=13 , Err=0 , Succ=13
EAP auth request , Num=0 , Err=0 , Succ=0
Account request , Num=1 , Err=0 , Succ=1
Account off request , Num=0 , Err=0 , Succ=0
PKT auth timeout , Num=36 , Err=12 , Succ=24
PKT acct_timeout , Num=0 , Err=0 , Succ=0
Realtime Account timer , Num=0 , Err=0 , Succ=0
PKT response , Num=2 , Err=0 , Succ=2
EAP reauth_request , Num=0 , Err=0 , Succ=0
PORTAL access , Num=0 , Err=0 , Succ=0
Update ack , Num=0 , Err=0 , Succ=0
PORTAL access ack , Num=0 , Err=0 , Succ=0
Session ctrl pkt , Num=0 , Err=0 , Succ=0
RADIUS sent messages statistic:
Auth accept , Num=0
Auth reject , Num=0
EAP auth replying , Num=0
Account success , Num=0
Account failure , Num=0
Cut req , Num=0
RecError_MSG_sum:0 SndMSG_Fail_sum :0
Timer_Err :0 Alloc_Mem_Err :0
State Mismatch :0 Other_Error :0
No-response-acct-stop packet =0
Discarded No-response-acct-stop packet for buffer overflow =0
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
1.2.5 display stop-accounting-buffer
Syntax
display stop-accounting-buffer { radius-scheme radius-scheme-name | session-id
session-id | time-range start-time stop-time | user-name user-name }
1-35
Page 39

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
View
Any view
Parameter
radius-scheme radius-scheme-name: Displays the buffered stop-accounting requests
of the specified RADIUS scheme. Where, radius-scheme-name is a character string of
up to 32 characters.
session-id session-id: Displays the buffered stop-accounting requests of the specified
session ID. Where, session-id is a character string of up to 50 characters.
time-range start-time stop-time: Displays the buffered stop-accounting requests in the
specified request time range. Where, start-time is the start time of the request time
range, and the earliest time can be 00:00:00-01/01/1970. stop-time is the end time of
the request time range, and both are in the format hh:mm:ss-mm/dd/yyyy or
hh:mm:ss-yyyy/mm/dd. This parameter is used to display the buffered stop-accounting
requests from the start time to the end time.
user-name user-name: Displays the buffered stop-accounting requests of the specified
user. Where, user-name is a character string of up to 80 characters.
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
Description
Use the display stop-accounting-buffer command to display the no-response
stop-accounting request packets buffered in the device.
Note:
z You can choose to display the buffered stop-accounting packets of a specified
RADIUS scheme, session ID, or user name. You can also specify a time range to
display those which are sent within the specified time range. The displayed packet
information helps you to diagnose and resolve problems relevant to RADIUS.
z When the switch sends out a stop-accounting packet but gets no response from the
RADIUS server, it first buffers the packet and then retransmits it until the maximum
number of retransmission attempts (set by the retry stop-accounting command) is
reached.
Related command: reset stop-accounting-buffer, stop-accounting-buffer enable
and retry stop-accounting.
Example
# Display the buffered stop-accounting requests from 0:0:0 08/31/2002 to 23:59:59
08/31/2002.
1-36
Page 40

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
<Sysname> display stop-accounting-buffer time-range 0:0:0-08/31/2002
23:59:59-08/31/2002
Total find 0 record(s)
1.2.6 key
Syntax
key { accounting | authentication } string
undo key { accounting | authentication }
View
RADIUS scheme view
Parameter
accounting: Specifies to set a shared key for the RADIUS accounting packets.
authentication: Specifies to set a shared key for the RADIUS
authentication/authorization packets.
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
Description
Example
string: Shared key, a character string of up to 16 characters.
Use the key command to set a shared key for the RADIUS authentication/authorization
packets or accounting packets.
Use the undo key command to restore the corresponding default shared key.
Note that the shared key configured on the device and that on the RADIUS server must
be the same.
Related command: primary accounting, primary authentication and radius
scheme.
# Set the shared key for the RADIUS authentication/authorization packets in RADIUS
scheme radius1 to hello.
<Sysname> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] radius scheme radius1
New Radius scheme
[Sysname-radius-radius1] key authentication hello
# Set the shared key for the RADIUS accounting packets in RADIUS scheme radius1 to
ok.
<Sysname> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
1-37
Page 41

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
[Sysname] radius scheme radius1
New Radius scheme
[Sysname-radius-radius1] key accounting ok
1.2.7 local-server
Syntax
local-server nas-ip ip-address key password
undo local-server nas-ip ip-address
View
System view
Parameter
nas-ip ip-address: Specifies the IP address of the local RADIUS server. Where,
ip-address is in dotted decimal notation.
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
Description
key password: Specifies the shared key of the authentication server and access server.
Where, password is a character string of up to 16 characters.
Use the local-server command to create a local RADIUS authentication server (that is,
set the related parameters of the server).
Use the undo local-server command to delete the specified local RADIUS
authentication server.
By default, a local RADIUS authentication server, with NAS-IP 127.0.0.1, has already
been created.
Note that:
z The switch not only supports the traditional RADIUS client service to accomplish
user AAA management through foreign authentication/authorization server and
accounting server, but also provides a simple local RADIUS server function for
authentication and authorization. This function is called local RADIUS
authentication server function.
z When you use the local RADIUS authentication server function, the UDP port
number for the authentication/authorization service must be 1645, the UDP port
number for the accounting service is 1646.
z The packet encryption key set by the local-server command with the key
password parameter must be identical with the authentication/authorization
packet encryption key set by the key authentication command in RADIUS
scheme view.
z The switch supports at most 16 IP addresses and shared keys of the network
access server (including the default local RADIUS authentication server); that is,
1-38
Page 42

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
when the switch serves as a RADIUS authentication server, it can support at most
16 network access servers simultaneously to provide authentication.
Related command: radius scheme and state.
Example
# Create a network access server granted by the RADIUS authentication server with an
IP address of 10.110.1.2 and a shared key of aabbcc.
<Sysname> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] local-server nas-ip 10.110.1.2 key aabbcc
1.2.8 local-server nas-ip
Syntax
local-server nas-ip ip-address key password
undo local-server nas-ip ip-address
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
View
Parameter
Description
System view
nas-ip ip-address: Sets the IP address, represented in dotted decimal notation, of the
network access server allowed by the local RADIUS server.
key password: Sets the shared key, a string of up to 16 characters, of the local server.
Use the local-server nas-ip command to configure the related parameters of the local
RADIUS server.
Use the undo local-server nas-ip command to remove a local RADIUS server
configured.
By default, the system has created a local RADIUS server with 127.0.0.1 as NAS-IP
address and a null string as shared key.
Note that:
z When the local RADIUS authentication server function is used, the UDP port
number used for authentication/authorization must be 1645 and that for
accounting must be 1646.
z The shared key configured with this command and that configured with the key
{ accounting | authentication } command in RADIUS scheme view for
authentication/authorization or accounting packets must be the same.
z The device supports up to 16 local RADIUS authentication servers.
1-39
Page 43

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
Related command: radius scheme, state, local-server enable
Example
# Set the IP address of the network access server allowed by the local RADIUS
authentication server to 10.110.1.2 and the shared key to aabbcc.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] local-server nas-ip 10.110.1.2 key aabbcc
1.2.9 nas-ip
Syntax
nas-ip ip-address
undo nas-ip
View
RADIUS scheme view
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
Parameter
Description
ip-address: Source IP address for RADIUS packets, an IP address of this device. This
address can neither be an all-zero address, class D address or loopback address.
Use the nas-ip command to set the source IP address used by the switch to send
RADIUS packets.
Use the undo nas-ip command to remove the source IP address setting.
By default, the IP address of the outbound interface is used as the source IP address of
the packet.
Note:
The nas-ip command in RADIUS scheme view has the same function as the radius
nas-ip command in system view; and the priority of configuration in RADIUS scheme
view is higher than in system view.
You can specify the source IP address used to send RADIUS packets to prevent the
unreachability of the packets returned from the server due to physical interface trouble.
It is recommended to use the loopback interface address as the source IP address.
Related command: radius nas-ip.
1-40
Page 44

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
Example
# Set the source IP address used by the switch to send the RADIUS packets to
10.1.1.1.
<Sysname> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] radius scheme radius1
New Radius scheme
[Sysname-radius-radius1] nas-ip 10.1.1.1
1.2.10 primary accounting
Syntax
primary accounting ip-address [ port-number ]
undo primary accounting
View
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
Parameter
Description
RADIUS scheme view
ip-address: IP address, in dotted decimal notation.
port-number: UDP port number, ranging from 1 to 65535. By default, the UDP port for
accounting service is 1813.
Use the primary accounting command to set the IP address and port number of the
primary RADIUS accounting server.
Use the undo primary accounting command to restore the default IP address and
port number of the primary RADIUS accounting server.
Note that:
z You are not allowed to assign the same IP address to both primary and secondary
accounting servers; otherwise, unsuccessful operation is prompted.
z By default, the system defines the RADIUS scheme system, with the IP address of
the primary accounting server as 127.0.0.1 and port number as 1646.
Related command: key, radius scheme and state.
Example
# Set the IP address and UDP port number of the primary accounting server of the
RADIUS scheme radius1 to 10.110.1.2 and 1813.
<Sysname> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
1-41
Page 45

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
[Sysname] radius scheme radius1
New Radius scheme
[Sysname-radius-radius1] primary accounting 10.110.1.2 1813
1.2.11 primary authentication
Syntax
primary authentication ip-address [ port-number ]
undo primary authentication
View
RADIUS scheme view
Parameter
ip-address: IP address, in dotted decimal notation.
port-number: UDP port number, ranging from 1 to 65535.
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
Description
Use the primary authentication command to set the IP address and port number of
the primary RADIUS authentication/authorization server.
Use the undo primary authentication command to restore the default IP address and
port number of the primary RADIUS authentication/authorization server.
By default, the system defines the RADIUS scheme system, with the IP address of the
primary accounting server as 127.0.0.1 and UDP port number as 1646; for a
newly-defined RADIUS scheme, the IP address of the primary accounting server is
127.0.0.1 and UDP port number is 1812.
Note that:
z After creating a new RADIUS scheme, you should configure the IP address and
UDP port number of each RADIUS server you want to use in this scheme. These
RADIUS servers fall into two types: authentication/authorization, and accounting.
And for each kind of server, you can configure two servers in a RADIUS scheme:
primary and secondary servers. A RADIUS scheme has the following attributes: IP
addresses of the primary and secondary servers, shared keys, and types of the
RADIUS servers.
z In an actual network environment, you can configure the above parameters as
required. But you should configure at least one authentication/authorization server
and one accounting server, and at the same time, you should keep the RADIUS
service port settings on the switch consistent with those on the RADIUS servers.
z You are not allowed to assign the same IP address to both primary and secondary
authentication/authorization servers; otherwise, unsuccessful operation is
prompted
1-42
Page 46

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
Related command: key, radius scheme and state.
Example
# Set the IP address and UDP port number of the primary authentication/authorization
server used by the RADIUS scheme radius1 to 10.110.1.1 and 1812.
<Sysname> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] radius scheme radius1
New Radius scheme
[Sysname-radius-radius1] primary authentication 10.110.1.1 1812
1.2.12 radius client
Syntax
radius client enable
undo radius client
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
View
Parameter
Description
System view
None
Use the radius client enable command to enable the RADIUS client port.
Use the undo radius client command to disable the RADIUS client port.
By default, a RADIUS client port is enabled.
Note that:
z After the RADIUS client port is disabled, for online users, Accounting-Request
(stop) packets can neither be sent nor be buffered. Meanwhile, the RADIUS server
cannot receive the packets of the online users going offline; in this case, an offline
user may remain connected to the server for a period of time. If the local device is
used as the RADIUS server, after the port is disabled, the number of connected
local users remains that before the port is disabled and cannot be updated
automatically.
z After the RADIUS client port is disabled, if a RADIUS + local
authentication/authorization/accounting scheme is used for a new authentication
request, local authentication/authorization/accounting scheme is used if the
request fails RADIUS authentication.
1-43
Page 47

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
z After the RADIUS client port is disabled, the sending of real-time
accounting-request packets buffered fails and these packets will be removed for
the buffer after the number of sending failures reaches the limit.
Related command: radius scheme
1.2.13 radius nas-ip
Syntax
radius nas-ip ip-address
undo radius nas-ip
View
System view
Parameter
ip-address: Source IP address, an IP address of this device. This address cannot be an
all-zero address, class D address, or loopback address.
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
Description
Use the radius nas-ip command to set the source IP address used by the switch to
send RADIUS packets.
Use the undo radius nas-ip command to restore the default setting.
By default, no source IP address is specified, and the IP address of the outbound
interface is used as the source IP address of the packet.
Note:
The nas-ip command in RADIUS scheme view has the same function as the radius
nas-ip command in system view; and the priority of configuration in RADIUS scheme
view is higher than in system view.
Note that:
z You can specify the source IP address used to send RADIUS packet to prevent
the unreachability of the packets returned from the server due to physical interface
trouble. It is recommended to use the loopback interface address as the source IP
address.
z You can specify only one source IP address by using this command. When you
use this command again, the newly specified source IP address will overwrite the
old one.
1-44
Page 48

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
Related command: nas-ip.
Example
# Set the source IP address used by the switch to send the RADIUS packets to
129.10.10.1.
<Sysname> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] radius nas-ip 129.10.10.1
1.2.14 radius scheme
Syntax
radius scheme radius-scheme-name
undo radius scheme radius-scheme-name
View
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
Parameter
Description
System view
radius-scheme-name: Name of the RADIUS scheme, a character string of up to 32
case-insensitive characters.
To avoid the case where the display radius statistics command is shown in a fuzzy
matching manner when you enter the display radius keywords, you are not
recommended to define radius-scheme-name as “statistics” or the first several
characters.
Use the radius scheme command to create a RADIUS scheme and enter its view.
Use the undo radius scheme command to delete the specified RADIUS scheme.
By default, a RADIUS scheme named "system" has already been created in the
system.
Note that:
z All the attributes of the RADIUS scheme "system" take the default values, which
you can see by using the display radius scheme command.
z The RADIUS protocol configuration is performed on a RADIUS scheme basis. For
each RADIUS scheme, you should specify at least the IP addresses and UDP port
numbers of the RADIUS authentication/authorization and accounting servers, and
the parameters required for the RADIUS client to interact with the RADIUS
servers.
z A RADIUS scheme can be referenced by multiple ISP domains simultaneously.
1-45
Page 49

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
z The undo radius scheme command cannot be used to delete the default
RADIUS scheme. In addition, you cannot delete a RADIUS scheme which is being
used by an online user.
Related command: key, retry realtime-accounting, timer realtime-accounting,
stop-accounting-buffer enable, retry stop-accounting, server-type, state,
user-name-format, retry, display radius and display radius statistics.
Example
# Create a RADIUS scheme named radius1 and enter its view.
<Sysname> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] radius scheme radius1
New Radius scheme
[Sysname-radius-radius1]
1.2.15 radius trap
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
Syntax
View
Parameter
Description
radius trap { accounting-server-down | authentication-server-down }
undo radius trap { accounting-server-down | authentication-server-down }
System view
accounting-server-down: Enables sending traps when the RADIUS accounting
server gives no response.
authentication-server-down: Enables sending traps when the RADIUS
authentication server gives no response.
Use the radius trap command to enable the RADIUS trap function.
Use the undo radius trap command to disable the RADIUS trap function.
By default, RADIUS trap is disabled.
After the RADIUS trap function is enabled, the following happens. If the RADIUS server
does not respond to the accounting or authentication request packets from an NAS, the
NAS retransmits accounting or authentication request packets to the server. When the
number of packet transmissions from the NAS to the server reaches one half of the
maximum transmission number, the system sends a trap message once; when this
number reaches the maximum, the system sends a trap message once again.
1-46
Page 50

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
If the maximum transmission number is an odd number, "one half of the maximum
transmission number" takes the value of the smallest integer that is greater than one
half of the maximum transmission number.
Example
# Enable sending traps when the RADIUS accounting server gives no response.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] radius trap accounting-server-down
# Disable sending traps when the RADIUS accounting server gives no response.
[Sysname] undo radius trap accounting-server-down
1.2.16 reset local-server statistics
Syntax
reset local-server statistics
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
View
User view
Description
Use the reset local-server statistics command to clear the statistics about the local
server.
Related command: display local-server statistics
Example
# Clear the statistics about the local server.
<Sysname> reset local-server statistics
1.2.17 reset radius statistics
Syntax
reset radius statistics
View
Parameter
User view
None
1-47
Page 51

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
Description
Use the reset radius statistics command to clear the statistics about the RADIUS
protocol.
Related command: display radius.
Example
# Clear the statistics about the RADIUS protocol.
<Sysname> reset radius statistics
1.2.18 reset stop-accounting-buffer
Syntax
reset stop-accounting-buffer { radius-scheme radius-scheme-name | session-id
session-id | time-range start-time stop-time | user-name user-name }
View
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
Parameter
Description
User view
radius-scheme radius-scheme-name: Deletes the buffered stop-accounting requests
depending on the specified RADIUS scheme. Where, radius-scheme-name is the
name of a RADIUS scheme. This name is a character string of up to 32 characters.
session-id session-id: Deletes the buffered stop-accounting requests depending on
the specified session ID. Where, session-id is a character string of up to 50 characters.
time-range start-time stop-time: Deletes the buffered stop-accounting requests
depending on the time of the stop-accounting request. Where, start-time is the start
time of the request period., the stop-time is the end time of the request period, and both
are in the format hh:mm:ss-mm/dd/yyyy or hh:mm:ss-yyyy/mm/dd.
user-name user-name: Deletes the buffered stop-accounting request packets
depending on the specified user name. Where, user-name is a character string of up to
80 characters.
Use the reset stop-accounting-buffer command to delete the buffered no-response
stop-accounting request packets.
Related command: stop-accounting-buffer enable, retry stop-accounting and
display stop-accounting-buffer.
1-48
Page 52

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
Example
# Delete the stop-accounting request packets buffered in the system for the user
user0001@aabbcc.net.
<Sysname> reset stop-accounting-buffer user-name user0001@aabbcc.net
# Delete the stop-accounting request packets buffered from 0:0:0 08/31/2002 to
23:59:59 08/31/2002 in the system.
<Sysname> reset stop-accounting-buffer time-range 00:00:00-08/31/2002
23:59:59-08/31/2002
1.2.19 retry
Syntax
retry retry-times
undo retry
View
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
Parameter
Description
RADIUS scheme view
retry-times: Maximum number of RADIUS packet transmission attempts, ranging from
1 to 20.
Use the retry command to set the maximum number of RADIUS packet transmission
attempts.
Use the undo retry command to restore maximum number of RADIUS packet
transmission attempts to the default value.
By default, the maximum number of RADIUS packet transmission attempts is 3.
Note that:
z The communication in RADIUS is unreliable because this protocol adopts UDP
packets to carry data. Therefore, it is necessary for the switch to retransmit a
RADIUS request if it gets no response from the RADIUS server after the response
timeout timer expires. If the maximum number of transmission attempts is reached
but the switch still receives no response, the switch considers that the request
fails.
z Appropriately set this maximum number of transmission attempts according to the
network situation can improve the reacting speed of the system.
z The product of the maximum RADIUS packet transmission attempts and the
response timeout timer for the RADIUS server can be no more than 75 seconds.
Related command: radius scheme and timer response-timeout.
1-49
Page 53

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
Example
# Set the maximum transmission times of RADIUS requests in the RADIUS scheme
radius1 to five.
<Sysname> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] radius scheme radius1
New Radius scheme
[Sysname-radius-radius1] retry 5
1.2.20 retry realtime-accounting
Syntax
retry realtime-accounting retry-times
undo retry realtime-accounting
View
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
Parameter
Description
RADIUS scheme view
retry-times: Maximum number of real-time accounting request attempts, ranging from 1
to 255.
Use the retry realtime-accounting command to set the maximum number of real-time
accounting request attempts.
Use the undo retry realtime-accounting command to restore the default maximum
number of real-time accounting request attempts.
By default, the system can allow five real-time accounting request attempts at most.
Note that:
z Generally, the RADIUS server uses the connection timeout timer to determine
whether a user is online or not. If the RADIUS server receives no real-time
accounting packet for a specified period of time, it will consider that the line or the
switch is in trouble and stop the accounting of the user. To make the switch
cooperate with this feature on the RADIUS server, it is necessary to cut down the
user connection on the switch as soon as possible after the RADIUS server
terminates the charging and connection of the user in the case of unforeseen
trouble. For this purpose, you can limit the number of continuous real-time
no-response accounting requests, and the switch will cut down the user
connection if it sends out the maximum number of real-time accounting requests
but does not receive any response.
1-50
Page 54

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
z A real-time account request may be sent multiple times (set by the retry command
in RADIUS scheme view) for an accounting attempt. If no response is received
even after the number of transmission attempts reaches the maximum, the
accounting attempt fails. Suppose that the response timeout time of the RADIUS
server is three seconds (set by the timer response-timeout command), that the
maximum number of transmission attempts (set by the retry command) is 3, and
that the real-time accounting interval is 12 minutes (set by the timer
realtime-accounting command), the maximum number of real-time accounting
request attempts is 5 (set by the retry realtime-accounting command). In this
case, the switch sends an accounting request every 12 minutes; if the switch does
not receive a response within 3 seconds after it sends out an accounting request, it
resends the request; if the switch continuously sends the accounting request for
three times but does not receive any response; it considers this real-time
accounting a failure. Then, the switch sends the accounting request every 12
minutes; if the number of accounting failures exceeds five, the user connection is
cut down. In general, the product of T and retry-times should be less than t.
Related command: radius scheme and timer realtime-accounting.
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
Example
# Allow the switch to continuously send at most 10 real-time accounting requests if it
gets no response for the RADIUS scheme radius1.
<Sysname> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] radius scheme radius1
New Radius scheme
[Sysname-radius-radius1] retry realtime-accounting 10
1.2.21 retry stop-accounting
Syntax
retry stop-accounting retry-times
undo retry stop-accounting
View
RADIUS scheme view
Parameter
retry-times: Maximum number of stop-accounting request failures allowed, ranging
from 10 to 65,535.
1-51
Page 55

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
Description
Use the retry stop-accounting command to set the maximum number of
stop-accounting request failures. After this number is reached, the device removes the
buffered stop-accounting request packets.
Use the undo retry stop-accounting command to restore the default maximum
number of stop-accounting request failures.
By default, up to 500 stop-accounting request failures are allowed.
Note that:
z Stop-accounting requests are critical to billing and will eventually affect the
charges of the users; they are important for both the users and the ISP. Therefore,
the switch should do its best to transmit them to the RADIUS accounting server. If
the RADIUS server does not respond to such a request, the switch should first
buffer the request on itself, and then retransmit the request to the RADIUS
accounting server until it gets a response, or the maximum number of
transmission attempts is reached (in this case, it discards the request).
z Assume the response timeout timer for the RADIUS server is set to 3 seconds
(with the timer response-timeout command), transmission attempts to 5 (with
the retry command), and the device allows up to 20 stop-accounting request
failures (with the retry stop-accounting command). This means that if the device
receives no response to the stop-accounting request it has sent within 3 seconds,
the device retransmits the request; if the device receives no response after it
sends the request five times, the device considers that the stop-accounting
request failed and buffers the request on itself. Then, the device sends another
request to repeat the above-mentioned process. If no response is received with 20
request attempts made, the device removes the buffered stop-accounting request
packets.
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
Related command: reset stop-accounting-buffer, radius scheme and display
stop-accounting-buffer.
Example
# In RADIUS scheme radius1, specify that up to 1,000 stop-accounting request failures
are allowed.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] radius scheme radius1
[Sysname-radius-radius1] retry stop-accounting 1000
1.2.22 secondary accounting
Syntax
secondary accounting ip-address [ port-number ]
1-52
Page 56

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
undo secondary accounting
View
RADIUS scheme view
Parameter
ip-address: IP address, in dotted decimal notation. By default, the IP address of the
secondary accounting server is 0.0.0.0.
port-number: UDP port number, ranging from 1 to 65535. By default, the UDP port
number of the secondary accounting service is 1813.
Description
Use the secondary accounting command to set the IP address and port number of
the secondary RADIUS accounting server.
Use the undo secondary accounting command to restore the default IP address and
port number of the secondary RADIUS accounting server.
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
You are not allowed to assign the same IP address to both primary and secondary
accounting servers; otherwise, unsuccessful operation is prompted
Related command: key, radius scheme and state.
Example
# Set the IP address and UDP port number of the secondary accounting server of the
RADIUS scheme radius1 to 10.110.1.1 and 1813.
<Sysname> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] radius scheme radius1
New Radius scheme
[Sysname-radius-radius1] secondary accounting 10.110.1.1 1813
1.2.23 secondary authentication
Syntax
secondary authentication ip-address [ port-number ]
undo secondary authentication
View
Parameter
RADIUS scheme view
ip-address: IP address, in dotted decimal notation. By default, the IP address of the
secondary authentication/authorization server is 0.0.0.0.
1-53
Page 57

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
port-number: UDP port number, ranging from 1 to 65535. By default, the UDP port
number of the secondary authentication/authorization service is 1812.
Description
Use the secondary authentication command to set the IP address and port number of
the secondary RADIUS authentication/authorization server.
Use the undo secondary authentication command to restore the default IP address
and port number of the secondary RADIUS authentication/authorization server.
Related command: key, radius scheme and state.
Example
# Set the IP address and UDP port number of the secondary
authentication/authorization server used by the RADIUS scheme radius1 to 10.110.1.2
and 1812.
<Sysname> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] radius scheme radius1
New Radius scheme
[Sysname-radius-radius1] secondary authentication 10.110.1.2 1812
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
1.2.24 server-type
Syntax
server-type { extended | standard }
undo server-type
View
RADIUS scheme view
Parameter
extended: Specifies to use extended RADIUS protocol (such as the procedure and
packet format) to interact with the Huawei RADIUS server, which is generally the
CAMS.
standard: Specifies to use standard RADIUS protocol. That is, it is required that the
RADIUS client (on the switch) and the RADIUS server interact with each other following
the procedure and packet format of the standard RADIUS protocol (RFC2138/2139 or
above).
Description
Use the server-type command to specify the RADIUS server type supported by the
switch.
1-54
Page 58

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
Use the undo server-type command to restore the default RADIUS server type
supported by the switch.
By default, the switch supports the standard type of RADIUS server. The type of
RADIUS server in the default RADIUS scheme "system" is extended.
Related command: radius scheme.
Example
# Set the RADIUS server type in RADIUS scheme radius1 to extended.
<Sysname> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] radius scheme radius1
New Radius scheme
[Sysname-radius-radius1] server-type extended
1.2.25 state
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
Syntax
View
Parameter
Description
state { primary | secondary } { accounting | authentication } { block | active }
RADIUS scheme view
primary: Specifies the server to be set is a primary RADIUS server.
secondary: Specifies the server to be set is a secondary RADIUS server.
accounting: Specifies the server to be set is a RADIUS accounting server.
authentication: Specifies the server to be set is a RADIUS
authentication/authorization server.
block: Sets the status of the specified RADIUS server to block (that is, the down state).
active: Sets the status of the specified RADIUS server to active (that is, the normal
working state).
Use the state command to set the status of a RADIUS server.
By default, all the RADIUS servers in a user-defined RADIUS scheme are in the active
state;
For the primary and secondary servers (authentication/authorization servers, or
accounting servers) in a RADIUS scheme, note that:
1-55
Page 59

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
z When the switch fails to communicate with the primary server due to some server
trouble, the switch will actively exchange packets with the secondary server.
z After the time the primary server keeps in the block state exceeds the time set with
the timer quiet command, the switch will try to communicate with the primary
server again when it has a RADIUS request. If the primary server recovers, the
switch immediately restores the communication with the primary server instead of
communicating with the secondary server, and at the same time restores the
status of the primary server on the switch to the active state while keeping the
status of the secondary server unchanged.
z When both the primary and secondary servers are in the active state, the switch
sends packets only to the primary server.
Related command: radius scheme, primary authentication, secondary
authentication, primary accounting and secondary accounting.
Example
# Set the status of the secondary authentication server in RADIUS scheme radius1 to
active.
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
<Sysname> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] radius scheme radius1
New Radius scheme
[Sysname-radius-radius1] state secondary authentication active
1.2.26 stop-accounting-buffer enable
Syntax
stop-accounting-buffer enable
undo stop-accounting-buffer enable
View
RADIUS scheme view
Parameter
None
Description
Use the stop-accounting-buffer enable command to enable the switch to buffer the
stop-accounting requests that bring no response.
Use the undo stop-accounting-buffer enable command to disable the switch from
buffering the stop-accounting requests that bring no response.
1-56
Page 60

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
By default, the switch is enabled to buffer the stop-accounting requests that bring no
response.
Stop-accounting requests are critical to billing and will eventually affect the charges;
they are important for both the users and the ISP. Therefore, the switch should do its
best to transmit them to the RADIUS server. If the RADIUS accounting server does not
respond to such a request, the switch should first buffer the request on itself, and then
retransmit the request to the RADIUS accounting server until it gets a response, or the
maximum number of transmission attempts is reached (in this case, it discards the
request).
Related command: reset stop-accounting-buffer, radius scheme and display
stop-accounting-buffer.
Example
# Enable the switch to buffer the stop-accounting requests that bring no response from
the servers in RADIUS scheme radius1.
<Sysname> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] radius scheme radius1
New Radius scheme
[Sysname-radius-radius1] stop-accounting-buffer enable
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
1.2.27 timer quiet
Syntax
timer quiet minutes
undo timer quiet
View
RADIUS scheme view
Parameter
minutes: Wait time, ranging from 1 minute to 255 minutes. By default, it is 5 minutes.
Description
Use the timer quiet command to set the wait time for the primary server to restore the
active state.
Use the undo timer quiet command to restore the default wait time.
Related command: display radius.
Example
# Set the wait time for the primary server to restore the active state to 10 minutes.
1-57
Page 61

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
<Sysname> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] radius scheme radius1
New Radius scheme
[Sysname-radius-radius1] timer quiet 10
1.2.28 timer realtime-accounting
Syntax
timer realtime-accounting minutes
undo timer realtime-accounting
View
RADIUS scheme view
Parameter
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
Description
minutes: Real-time accounting interval. It ranges from 3 minutes to 60 minutes and
must be a multiple of 3. By default, this interval is 12 minutes.
Use the timer realtime-accounting command to set the real-time accounting interval.
Use the undo timer realtime-accounting command to restore the default real-time
accounting interval.
Note that:
z To charge the users in real time, you should set the interval of real-time accounting.
After the setting, the switch sends the accounting information of online users to the
RADIUS server at regular intervals.
z The setting of the real-time accounting interval depends to some degree on the
performance of the switch and the RADIUS server. The higher the performance of
the switch and the RADIUS server is, the shorter the interval can be. You are
recommended to set the interval as long as possible when the number of users is
relatively great (ú1000).
Table 1-5 lists the numbers of users and the
corresponding recommended intervals.
Table 1-5 Numbers of users and corresponding recommended intervals
Number of users Real-time accounting interval
1 to 99 3
100 to 499 6
500 to 999 12
1-58
Page 62

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
Number of users Real-time accounting interval
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
1000
ú
Related command: retry realtime-accounting and radius scheme.
Example
# Set the real-time accounting interval of the RADIUS scheme radius1 to 51 minutes.
<Sysname> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] radius scheme radius1
New Radius scheme
[Sysname-radius-radius1] timer realtime-accounting 51
1.2.29 timer response-timeout
Syntax
timer response-timeout seconds
undo timer response-timeout
ú
15
View
Parameter
Description
RADIUS scheme view
seconds: Response timeout time of RADIUS servers, ranging from 1 second to 10
seconds.
Use the timer response-timeout command to set the response timeout time of
RADIUS servers.
Use the undo timer response-timeout command to restore the default response
timeout timer of RADIUS servers.
By default, the response timeout time of the RADIUS server is 3 seconds.
Note that:
z If the switch gets no response from the RADIUS server after sending out a
RADIUS request (authentication/authorization request or accounting request) and
waiting for a time, it should retransmit the packet to ensure that the user can obtain
the RADIUS service. This wait time is called response timeout time of RADIUS
servers; and the timer in the switch system that is used to control this time is called
the response timeout timer of RADIUS servers. You can use the timer
response-timeout command to set the timeout time of this timer.
1-59
Page 63

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
z Appropriately setting the timeout time of this timer according to the network
situation can improve the performance of the system.
z The product of the maximum RADIUS packet transmission attempts and the
response timeout timer for the RADIUS server can be no more than 75 seconds.
Related command: radius scheme and retry.
Example
# Set the response timeout time in the RADIUS scheme radius1 to five seconds.
<Sysname> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] radius scheme radius1
New Radius scheme
[Sysname-radius-radius1] timer response-timeout 5
1.2.30 user-name-format
Syntax
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
View
Parameter
Description
user-name-format { with-domain | without-domain }
RADIUS scheme view
with-domain: Specifies to include ISP domain names in the user names to be sent to
RADIUS servers.
without-domain: Specifies to exclude ISP domain names from the user names to be
sent to RADIUS servers.
Use the user-name-format command to set the format of the user names to be sent to
RADIUS server
By default, except for the default RADIUS scheme "system", the user names sent to
RADIUS servers in any RADIUS scheme carry ISP domain names.
Note that:
z Generally, an access user is named in the userid@isp-name format. Where,
isp-name behind the @ character represents the ISP domain name, by which the
device determines which ISP domain it should ascribe the user to. However, some
old RADIUS servers cannot accept the user names that carry ISP domain names.
In this case, it is necessary to remove the domain names carried in the user
names before sending the user names to the RADIUS server. For this reason, the
1-60
Page 64

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
user-name-format command is designed for you to specify whether or not ISP
domain names are carried in the user names sent to the RADIUS server.
z For a RADIUS scheme, if you have specified that no ISP domain names are
carried in the user names, you should not use this RADIUS scheme in more than
one ISP domain. Otherwise, such errors may occur: the RADIUS server regards
two different users having the same name but belonging to different ISP domains
as the same user (because the user names sent to it are the same).
Related command: radius scheme.
Example
# Specify that the user names sent to a RADIUS server in RADIUS scheme radius1
does not carry ISP domain names.
<Sysname> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] radius scheme radius1
New Radius scheme
[Sysname-radius-radius1] user-name-format without-domain
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
1.3 HWTACACS Configuration Commands
1.3.1 data-flow-format
Syntax
data-flow-format { data { byte | giga-byte | kilo-byte | mega-byte } | packet
{ giga-packet | kilo-packet | mega-packet | one-packet } }*
undo data-flow-format { data | packet }
View
HWTACACS view
Parameter
data: Sets data unit.
byte: Sets 'byte' as the unit of data flow.
giga-byte: Sets 'giga-byte' as the unit of data flow.
kilo-byte: Sets 'kilo-byte' as the unit of data flow.
mega-byte: Sets 'mega-byte' as the unit of data flow.
packet: Sets data packet unit.
giga-packet: Sets 'giga-packet' as the unit of packet flow.
kilo-packet: Sets 'kilo-packet' as the unit of packet flow.
mega-packet: Sets 'mega-packet' as the unit of packet flow.
1-61
Page 65

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
one-packet: Sets 'one-packet' as the unit of packet flow.
Description
Use the data-flow-format command to configure the unit of data flows sent to the
TACACS server.
Use the undo data-flow-format command to restore the default.
By default, the data unit is byte and the data packet unit is one-packet.
Related command: display hwtacacs.
Example
# Set the unit of data flow destined for the HWTACACS server to kilo-byte and the data
packet unit to kilo-packet.
<Sysname> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] hwtacacs scheme hwt1
[Sysname- hwtacacs-hwt1] data-flow-format data kilo-byte
[Sysname- hwtacacs-hwt1] data-flow-format packet kilo-packet
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
1.3.2 display hwtacacs
Syntax
display hwtacacs [ hwtacacs-scheme-name [ statistics ] ]
View
Any view
Parameter
hwtacacs-scheme-name: HWTACACS scheme name, a string of 1 to 32
case-insensitive characters. If no HWTACACS scheme is specified, the system
displays the configuration of all HWTACACS schemes.
statistics: Displays complete statistics about the HWTACACS server.
Description
Use the display hwtacacs command to view configuration or statistics information of
specified or all HWTACACS schemes.
Related command: hwtacacs scheme.
Example
# View configuration information of HWTACACS scheme gy.
<Sysname> display hwtacacs gy
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
1-62
Page 66

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
HWTACACS-server template name : gy
Primary-authentication-server : 0.0.0.0:0
Primary-authorization-server : 0.0.0.0:0
Primary-accounting-server : 0.0.0.0:0
Secondary-authentication-server : 0.0.0.0:0
Secondary-authorization-server : 0.0.0.0:0
Secondary-accounting-server : 0.0.0.0:0
Current-authentication-server : 0.0.0.0:0
Current-authorization-server : 0.0.0.0:0
Current-accounting-server : 0.0.0.0:0
Nas-IP address : 0.0.0.0
key authentication : key authorization : key accounting : Quiet-interval(min) : 5
Realtime-accounting-interval(min) : 12
Response-timeout-interval(sec) : 5
Acct-stop-PKT retransmit times : 100
Domain-included : Yes
Data traffic-unit : B
Packet traffic-unit : one-packet
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total 1 HWTACACS scheme(s),1 listed
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
Table 1-6 Description on the fields of the display hwtacacs command
Field Description
HWTACACS-server template name HWTACACS server scheme name
Primary-authentication-server Primary authentication server
Primary-authorization-server Primary authorization server
Primary-accounting-server Primary accounting server
Secondary-authentication-server Secondary authentication server
Secondary-authorization-server Secondary authorization server
Secondary-accounting-server Secondary accounting server
Current-authentication-server Current authentication server
Current-authorization-server Current authorization server
Current-accounting-server Current accounting server
NAS-IP-address NAS IP address
key authentication Authentication key
1-63
Page 67

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
Field Description
key authorization Authorization key
key accounting Accounting key
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
Quiet-interval
Realtime-accounting-interval Real-time accounting interval
Response-timeout-interval Response timeout time of the server
Acct-stop-PKT retransmit times
Domain-included Domain included
Data traffic-unit Unit of data traffic
Packet traffic-unit Unit of packet traffic
1.3.3 display stop-accounting-buffer
Syntax
display stop-accounting-buffer { hwtacacs-scheme hwtacacs-scheme-name |
session-id session-id | time-range start-time stop-time | user-name user-name }
View
Wait time for the primary servers to
restore the active state
Accounting-stop packet retransmission
times
Parameter
Any view
hwtacacs-scheme hwtacacs-scheme-name: Displays information on buffered
stop-accounting requests according to the HWTACACS scheme specified by
hwtacacs-scheme-name, the name of HWTACACS scheme, a character string of up to
32 characters.
session-id session-id: Displays information on buffered stop-accounting requests
according to the session ID specified by session-id, a character string of up to 50
characters.
time-range start-time stop-time: Displays information on buffered stop-accounting
requests according to the request time, where, start-time is the start time of the
stop-accounting request; stop-time is the end time of stop-accounting request. This
argument is in the format hh:mm:ss - mm/dd/yyyy or hh:mm:ss-yyyy/mm/dd and is
used to display the buffered stop-accounting requests from the start time to the end
time.
1-64
Page 68

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
user-name user -name: Displays information on buffered stop-accounting requests
according to the user name specified by user-name, a character string of up to 80
characters,
Description
Use the display stop-accounting-buffer command to view information on the
stop-accounting requests buffered in the switch.
Related command: reset stop-accounting-buffer, stop-accounting-buffer enable,
and retry stop-accounting.
Example
# Display the stop-accounting requests buffered in the HWTACACS scheme “hwt1".
<Sysname> display stop-accounting-buffer hwtacacs-scheme hwt1
1.3.4 hwtacacs nas-ip
Syntax
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
View
Parameter
Description
hwtacacs nas-ip ip-address
undo hwtacacs nas-ip
System view
ip-address: Specifies a source IP address for the switch, which cannot be an all-zero
address, class D address or loopback address.
Use the hwtacacs nas-ip command to specify the source address of the hwtacacs
packet sent from NAS.
Use the undo hwtacacs nas-ip command to restore the default setting.
By default, the source address is not specified, that is, the address of the interface
sending the packet serves as the source address.
Note that:
z By specifying the source address of the hwtacacs packet, you can avoid
destination unreachable packets as returned from the server upon interface failure.
The source address is normally recommended to be a loopback interface address.
z This command specifies only one source address; therefore, the newly configured
source address may overwrite the original one.
1-65
Page 69

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
z The nas-ip command in HWTACACS scheme view only takes effect for the
current HWTACACS scheme, while that in system view is for all HWTACACS
schemes. The former one takes priority in implementation.
Related command: nas-ip.
Example
# Configure the router to send hwtacacs packets from 129.10.10.1.
<Sysname> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] hwtacacs nas-ip 129.10.10.1
1.3.5 hwtacacs scheme
Syntax
hwtacacs scheme hwtacacs-scheme-name
undo hwtacacs scheme hwtacacs-scheme-name
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
View
Parameter
Description
Example
System view
hwtacacs-scheme-name: Specifies an HWTACACS server scheme, with a character
string of up to 32 case-insensitive characters.
Use the hwtacacs scheme command to create an HWTACACS scheme and enter its
view.
Use the undo hwtacacs scheme command to delete the HWTACACS scheme.
By default, no HWTACACS scheme exists.
# Create an HWTACACS scheme named "hwt1" and enter the relevant HWTACACS
view.
<Sysname> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] hwtacacs scheme hwt1
[Sysname-hwtacacs-hwt1]
1-66
Page 70

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
1.3.6 key
Syntax
key { accounting | authentication | authorization } string
undo key { accounting | authentication | authorization }
View
HWTACACS scheme view
Parameter
accounting: Specifies a shared key for the accounting server.
authentication: Specifies a shared key for HWTACACS authentication packets.
authorization: Specifies a shared key for HWTACACS authorization packets.
string: Shared key, a string of 1 to 16 characters.
Description
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
Use the key command to configure a shared key for HWTACACS authentication,
authorization or accounting.
Use the undo key command to delete the configuration.
By default, no key is set for any HWTACACS server.
Related command: display hwtacacs.
Example
# Use hello as the shared key for HWTACACS accounting packets.
<Sysname> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] hwtacacs scheme hwt1
[Sysname-hwtacacs-hwt1] key accounting hello
1.3.7 nas-ip
Syntax
nas-ip ip-address
undo nas-ip
View
HWTACACS scheme view
1-67
Page 71

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
Parameter
ip-address: Specified source IP address which cannot be an all-zero address, class D
address or loopback address.
Description
Use the nas-ip command to specify the source address for sending HWTACACS
packets.
Use the undo nas-ip command to restore the default setting.
Note that:
z By specifying the source address of the hwtacacs packet, you can avoid
destination unreachable packets as returned from the server upon interface failure.
The source address is normally recommended to be a loopback interface address.
z This command specifies only one source address; therefore, the newly configured
source address may overwrite the original one.
z The nas-ip command in HWTACACS scheme view only takes effect for the
current HWTACACS scheme, while that in system view is for all HWTACACS
schemes. The former one takes priority in implementation.
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
Related command: hwtacacs nas-ip.
Example
# Set the source IP address of the HWTACACS packets to 10.1.1.1.
<Sysname> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] hwtacacs scheme hwt1
[Sysname-hwtacacs-hwt1] nas-ip 10.1.1.1
1.3.8 primary accounting
Syntax
primary accounting ip-address [ port-number ]
undo primary accounting
View
HWTACACS scheme view
Parameter
ip-address: IP address of the server, a valid unicast address in dotted decimal format.
By default, the IP address of the primary accounting server is 0.0.0.0.
port-number: Port number of the server, which is in the range 1 to 65535 and defaults to
49.
1-68
Page 72

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
Description
Use the primary accounting command to configure a primary HWTACACS
accounting server.
Use the undo primary accounting command to delete the configured primary
HWTACACS accounting server.
Note that:
z You are not allowed to assign the same IP address to both primary and secondary
accounting servers; otherwise, unsuccessful operation is prompted.
z If you repeatedly use this command, the latest configuration overwrites the
previous one.
z You can remove an accounting server only when it is not being used by any active
TCP connections, and the removal impacts only packets forwarded afterwards.
Example
# Configure a primary accounting server.
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
<Sysname> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] hwtacacs scheme test1
[Sysname-hwtacacs-test1] primary accounting 10.163.155.12 49
1.3.9 primary authentication
Syntax
primary authentication ip-address [ port-number ]
undo primary authentication
View
HWTACACS scheme view
Parameter
ip-address: IP address of the server, a valid unicast address in dotted decimal format.
By default, the IP address of the primary authentication server is 0.0.0.0.
port-number: Port number of the server, which is in the range 1 to 65535 and defaults to
49.
Description
Use the primary authentication command to configure a primary HWTACACS
authentication server.
Use the undo primary authentication command to delete the configured
authentication server.
1-69
Page 73

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
Note that:
z You are not allowed to assign the same IP address to both primary and secondary
authentication servers; otherwise, unsuccessful operation is prompted.
z If you repeatedly use this command, the latest configuration overwrites the
previous one.
z You can remove an authentication server only when it is not being used by any
active TCP connections, and the removal impacts only packets forwarded
afterwards.
Related command: display hwtacacs.
Example
# Configure a primary authentication server.
<Sysname> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] hwtacacs scheme hwt1
[Sysname-hwtacacs-hwt1] primary authentication 10.163.155.13 49
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
1.3.10 primary authorization
Syntax
primary authorization ip-address [ port-number ]
undo primary authorization
View
HWTACACS scheme view
Parameter
ip-address: IP address of the server, a valid unicast address in dotted decimal format.
By default, the IP address of the primary authentication server is 0.0.0.0.
port-number: Port number of the server, which is in the range 1 to 65535 and defaults to
49.
Description
Use the primary authorization command to configure a primary HWTACACS
authorization server.
Use the undo primary authorization command to delete the configured primary
authorization server.
Note that:
z You are not allowed to assign the same IP address to both primary and secondary
authorization servers; otherwise, unsuccessful operation is prompted.
1-70
Page 74

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
z If you repeatedly use this command, the latest configuration overwrites the
previous one.
z You can remove an authorization server only when it is not being used by any
active TCP connections, and the removal impacts only packets forwarded
afterwards.
Related command: display hwtacacs.
Example
# Configure a primary authorization server.
<Sysname> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] hwtacacs scheme hwt1
[Sysname-hwtacacs-hwt1] primary authorization 10.163.155.13 49
1.3.11 reset hwtacacs statistics
Syntax
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
View
Parameter
Description
Example
reset hwtacacs statistics { accounting | authentication | authorization | all }
User view
accounting: Clears all the HWTACACS accounting statistics.
authentication: Clears all the HWTACACS authentication statistics.
authorization: Clears all the HWTACACS authorization statistics.
all: Clears all statistics.
Use the reset hwtacacs statistics command to clear HWTACACS protocol statistics.
Related command: display hwtacacs.
# Clear all HWTACACS protocol statistics.
<Sysname> reset hwtacacs statistics all
1-71
Page 75

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
1.3.12 reset stop-accounting-buffer
Syntax
reset stop-accounting-buffer { hwtacacs-scheme hwtacacs-scheme-name |
session-id session-id | time-range start-time stop-time | user-name user-name }
View
User view
Parameter
hwtacacs-scheme hwtacacs-scheme-name: Configures to delete the stop-accounting
requests from the buffer according to the specified HWTACACS scheme name. The
hwtacacs-scheme-name specifies the HWTACACS scheme name with a character
string of up to 32 characters.
session-id session-id: Displays information on buffered stop-accounting requests
according to the session ID specified by session-id, a character string of up to 50
characters.
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
Description
Example
time-range start-time stop-time: Displays information on buffered stop-accounting
requests according to the request time, where, start-time is the start time of the
stop-accounting request; stop-time is the end time of stop-accounting request. This
argument is in the format hh:mm:ss - mm/dd/yyyy or hh:mm:ss-yyyy/mm/dd and is
used to display the buffered stop-accounting requests from the start time to the end
time.
user-name user -name: Displays information on buffered stop-accounting requests
according to the user name specified by user-name, a character string of up to 80
characters,
Use the reset stop-accounting-buffer command to clear the stop-accounting
requests that have no response and are buffered on the switch.
Related command: stop-accounting-buffer enable, retry stop-accounting, display
stop-accounting-buffer.
# Delete the buffered stop-accounting requests that are according to the HWTACACS
scheme “hwt1”.
<Sysname> reset stop-accounting-buffer hwtacacs-scheme hwt1
1-72
Page 76

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
1.3.13 retry stop-accounting
Syntax
retry stop-accounting retry-times
undo retry stop-accounting
View
HWTACACS scheme view
Parameter
retry-times: Maximum number of real-time stop-accounting request attempts. It is in the
range 1 to 300 and defaults to 100.
Description
Use the retry stop-accounting command to enable stop-accounting packet
retransmission and configure the maximum number of stop-accounting request
attempts.
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
Use the undo retry stop-accounting command to restore the default setting.
By default, stop-accounting packet retransmission is enabled and has 100 attempts for
each request.
Related command: reset stop-accounting-buffer, hwtacacs scheme, and display
stop-accounting-buffer.
Example
# Enable stop-accounting packet retransmission and allow up to 50 attempts for each
request.
<Sysname> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] hwtacacs scheme hwt1
[Sysname-hwtacacs-hwt1] retry stop-accounting 50
1.3.14 secondary accounting
Syntax
secondary accounting ip-address [ port-number ]
View
undo secondary accounting
HWTACACS scheme view
1-73
Page 77

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
Parameter
ip-address: IP address of the server, a valid unicast address in dotted decimal format.
By default, the IP address of the secondary accounting server is 0.0.0.0.
port-number: Port number of the server, which is in the range of 1 to 65535 and defaults
to 49.
Description
Use the secondary accounting command to configure a secondary HWTACACS
accounting server.
Use the undo secondary accounting command to delete the configured secondary
TACACS accounting server.
Note that:
z You are not allowed to assign the same IP address to both primary and secondary
accounting servers; otherwise, unsuccessful operation is prompted.
z If you repeatedly use this command, the latest configuration overwrites the
previous one.
z You can remove an accounting server only when it is not being used by any active
TCP connections.
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
Example
# Configure a secondary accounting server.
<Sysname> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] hwtacacs scheme hwt1
[Sysname-hwtacacs-hwt1] secondary accounting 10.163.155.12 49
1.3.15 secondary authentication
Syntax
secondary authentication ip-address [ port-number ]
undo secondary authentication
View
HWTACACS scheme view
Parameter
ip-address: IP address of the server, a valid unicast address in dotted decimal format.
By default, the IP address of the secondary authentication server is 0.0.0.0.
port-number: Port number of the server, which is in the range of 1 to 65535 and defaults
to 49.
1-74
Page 78

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
Description
Use the secondary authentication command to configure a secondary HWTACACS
authentication server.
Use the undo secondary authentication command to delete the configured
secondary authentication server.
Note that:
z You are not allowed to assign the same IP address to both primary and secondary
authentication servers; otherwise, unsuccessful operation is prompted.
z If you repeatedly use this command, the latest configuration overwrites the
previous one.
z You can remove an authentication server only when it is not being used by any
active TCP connections.
Related command: display hwtacacs.
Example
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
# Configure a secondary authentication server.
<Sysname> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] hwtacacs scheme hwt1
[Sysname-hwtacacs-hwt1] secondary authentication 10.163.155.13 49
1.3.16 secondary authorization
Syntax
secondary authorization ip-address [ port-number ]
undo secondary authorization
View
HWTACACS scheme view
Parameter
ip-address: IP address of the server, a valid unicast address in dotted decimal format.
By default, the IP address of the secondary authorization server is 0.0.0.0.
Description
port-number: Port number of the server, in the range of 1 to 65535. By default, it is 49.
Use the secondary authorization command to configure a secondary HWTACACS
authorization server.
Use the .undo secondary authorization command to delete the configured
secondary authorization server.
1-75
Page 79

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
Note that:
z You are not allowed to assign the same IP address to both primary and secondary
authorization servers.
z If you repeatedly use this command, the latest configuration overwrites the
previous one.
z You can remove an authorization server only when it is not being used by any
active TCP connections.
Related command: display hwtacacs.
Example
# Configure the secondary authorization server.
<Sysname> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] hwtacacs scheme hwt1
[Sysname-hwtacacs-hwt1] secondary authorization 10.163.155.13 49
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
1.3.17 stop-accounting-buffer enable
Syntax
stop-accounting-buffer enable
undo stop-accounting-buffer enable
View
HWTACACS scheme view
Parameter
None
Description
Use the stop-accounting-buffer enable command to enable the switch to buffer the
stop-accounting requests that bring no response.
Use the undo stop-accounting-buffer enable command to disable the switch from
buffering the stop-accounting requests that bring no response.
By default, the switch is enabled to buffer the stop-accounting requests that bring no
response.
Stop-accounting requests are critical to billing and will eventually affect the charges;
they are important for both the users and the ISP. Therefore, the switch should do its
best to transmit them to the RADIUS server. If the RADIUS accounting server does not
respond to such a request, the switch should first buffer the request on itself, and then
retransmit the request to the RADIUS accounting server until it gets a response, or the
1-76
Page 80

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
maximum number of transmission attempts is reached (in this case, it discards the
request).
Related command: reset stop-accounting-buffer, hwtacacs scheme, display
stop-accounting-buffer.
Example
# Enable the switch to buffer the stop-accounting requests that bring no response from
the servers in HWTACACS scheme hwt1.
<Sysname>system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] hwtacacs scheme hwt1
[Sysname-hwtacacs-hwt1] stop-accounting-buffer enable
1.3.18 timer quiet
Syntax
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
View
Parameter
Description
Example
timer quiet minutes
undo timer quiet
HWTACACS scheme view
minutes: Length of the timer in minutes, in the range of 1 to 255. By default, the primary
server must wait five minutes before it resumes the active state.
Use the timer quiet command to set the duration that a primary server must wait
before it can resume the active state.
Use the undo timer quiet command to restore the default (five minutes).
Related command: display hwtacacs.
# Set the quiet timer for the primary server to ten minutes.
<Sysname> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] hwtacacs scheme hwt1
[Sysname-hwtacacs-hwt1] timer quiet 10
1-77
Page 81

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
1.3.19 timer realtime-accounting
Syntax
timer realtime-accounting minutes
undo timer realtime-accounting
View
HWTACACS scheme view
Parameter
minutes: Real-time accounting interval, which is a multiple of 3 in the range 3 to 60
minutes.
Description
Use the timer realtime-accounting command to configure a real-time accounting
interval.
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
Use the undo timer realtime-accounting command to restore the default setting.
By default, the real-time accounting interval is 12 minutes.
Note that:
z Real-time accounting interval is necessary for real-time accounting. After an
interval value is set, the switch transmits the accounting information of online
users to the TACACS accounting server at intervals of this value.
z The setting of real-time accounting interval depends somewhat on the
performance of the switch and the TACACS server: A shorter interval requires
higher device performance. You are therefore recommended to adopt a longer
interval when there are a large number of users (more than 1000, inclusive). The
following table recommends the real-time accounting intervals for different
numbers of users.
Table 1-7 Recommended intervals for different numbers of users
Number of users
Real-time accounting interval
(minute)
1 – 99 3
100 – 499 6
500 – 999 12
≥1000 ≥15
1-78
Page 82

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
Example
# Set the real-time accounting interval in the HWTACACS scheme “hwt1” to 51
minutes.
<Sysname> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] hwtacacs scheme hwt1
[Sysname-hwtacacs-hwt1] timer realtime-accounting 51
1.3.20 timer response-timeout
Syntax
timer response-timeout seconds
undo timer response-timeout
View
HWTACACS scheme view
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
Parameter
Description
Example
seconds: Length of the response timer in seconds. It ranges from 1 to 300 and defaults
to 5.
Use the timer response-timeout command to set the response timeout timer of the
TACACS server.
Use the undo timer response-timeout command to restore the default (five seconds).
As the HWTACACS is based on TCP, either the server response timeout and/or the
TCP timeout may cause disconnection to the TACACS server.
Related command: display hwtacacs.
# Set the response timeout time of the TACACS server to 30 seconds.
<Sysname> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] hwtacacs scheme hwt1
[Sysname-hwtacacs-hwt1] timer response-timeout 30
1.3.21 user-name-format
Syntax
user-name-format { with-domain | without-domain }
1-79
Page 83

Command Manual – AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS
H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches
View
HWTACACS scheme view
Parameter
with-domain: Specifies to send the username with a domain name to the TACACS
server.
without-domain: Specifies to send the username without any domain name to the
TACACS server.
Description
Use the user-name-format command to configure the username format sent to the
TACACS server.
By default, an HWTACACS scheme acknowledges that the username sent to it
includes an ISP domain name.
Note that:
Chapter 1 AAA & RADIUS & HWTACACS
Configuration Commands
Example
z The supplicants are generally named in userid@isp-name format. The part
following the @ sign is the ISP domain name, according to which the switch
assigns a user to the corresponding ISP domain. However, some earlier TACACS
servers reject the user name including an ISP domain name. In this case, the user
name is sent to the TACACS server after its domain name is removed.
Accordingly, the switch provides this command to decide whether the username
sent to the TACACS server carries an ISP domain name or not.
z If a HWTACACS scheme is configured to reject usernames including ISP domain
names, the TACACS scheme shall not be simultaneously used in more than one
ISP domains. Otherwise, the TACACS server will regard two users in different ISP
domains as the same user by mistake, if they have the same username,
(excluding their respective domain names.)
Related command: hwtacacs scheme.
# Specify to send the username without any domain name to the HWTACACS scheme
"hwt1".
<Sysname> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[Sysname] hwtacacs scheme hwt1
[Sysname-hwtacacs-hwt1] user-name-format without-domain
1-80
 Loading...
Loading...