H3C S5130S-10P-EI, S5130S-52P-EI, S5130S-28P-EI-M, S5130S-28TP-EI, S5130S-12TP-EI Installation Manual
...Page 1

New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd.
http://www.h3c.com
Document version: 6W102-20180205
H3C S5130S-EI Switch Series
Installation Guide
Page 2
Copyright © 2017-2018, New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd. and its licensors
All rights reserved
No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written
consent of New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd.
Trademarks
H3C, , H3CS, H3CIE, H3CNE, Aoly nk, , H
3
Care, , IRF, NetPilot, Netflow, SecEngine,
SecPath, SecCenter, SecBlade, Comware, ITCMM and HUASAN are trademarks of New H3C Technologies
Co., Ltd.
All other trademarks that may be mentioned in this manual are the property of their respective owners
Notice
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. All contents in this document, including
statements, information, and recommendations, are believed to be accurate, but they are presented without
warranty of any kind, express or implied. H3C shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions
contained herein.
Environmental protection
This product has been designed to comply with the environmental protection requirements. The storage, use,
and disposal of this product must meet the applicable national laws and regulations.
Page 3

Preface
H3C S5130S-EI Switch Series Installation Guide describes the appearance, installation, power-on,
maintenance, and troubleshooting of the H3C S5130S-EI Switch Series.
This preface includes the following topics about the documentation:
• Audience.
• Conventions
• Documentation feedback
Audience
This documentation is intended for:
• Network planners.
• Field technical support and servicing engineers.
• Network administrators working with the S5130S-EI switch series.
Conventions
The following information describes the conventions used in the documentation.
Command conventions
Convention Description
Boldface Bold
Italic
[ ] Square brackets enclose syntax choices (keywords or arguments) that are optional.
{ x | y | ... }
[ x | y | ... ]
{ x | y | ... } *
[ x | y | ... ] *
&<1-n>
# A line that starts with a pound (#) sign is comments.
GUI conventions
Convention Description
Boldface
text represents commands and keywords that you enter literally as shown.
Italic text represents arguments that you replace with actual values.
Braces enclose a set of required syntax choices separated by vertical bars, from which
you select one.
Square brackets enclose a set of optional syntax choices separated by vertical bars,
from which you select one or none.
Asterisk marked braces enclose a set of required syntax choices separated by vertical
bars, from which you select a minimum of one.
Asterisk marked square brackets enclose optional syntax choices separated by vertical
bars, from which you select one choice, multiple choices, or none.
The argument or keyword and argument combination before the ampersand (&) sign
can be entered 1 to n times.
Window names, button names, field names, and menu items are in Boldface. For
example, the
New User
window opens; click OK.
File
>
Multi-level menus are separated by angle brackets. For example,
Folder
.
>
Create
>
Page 4
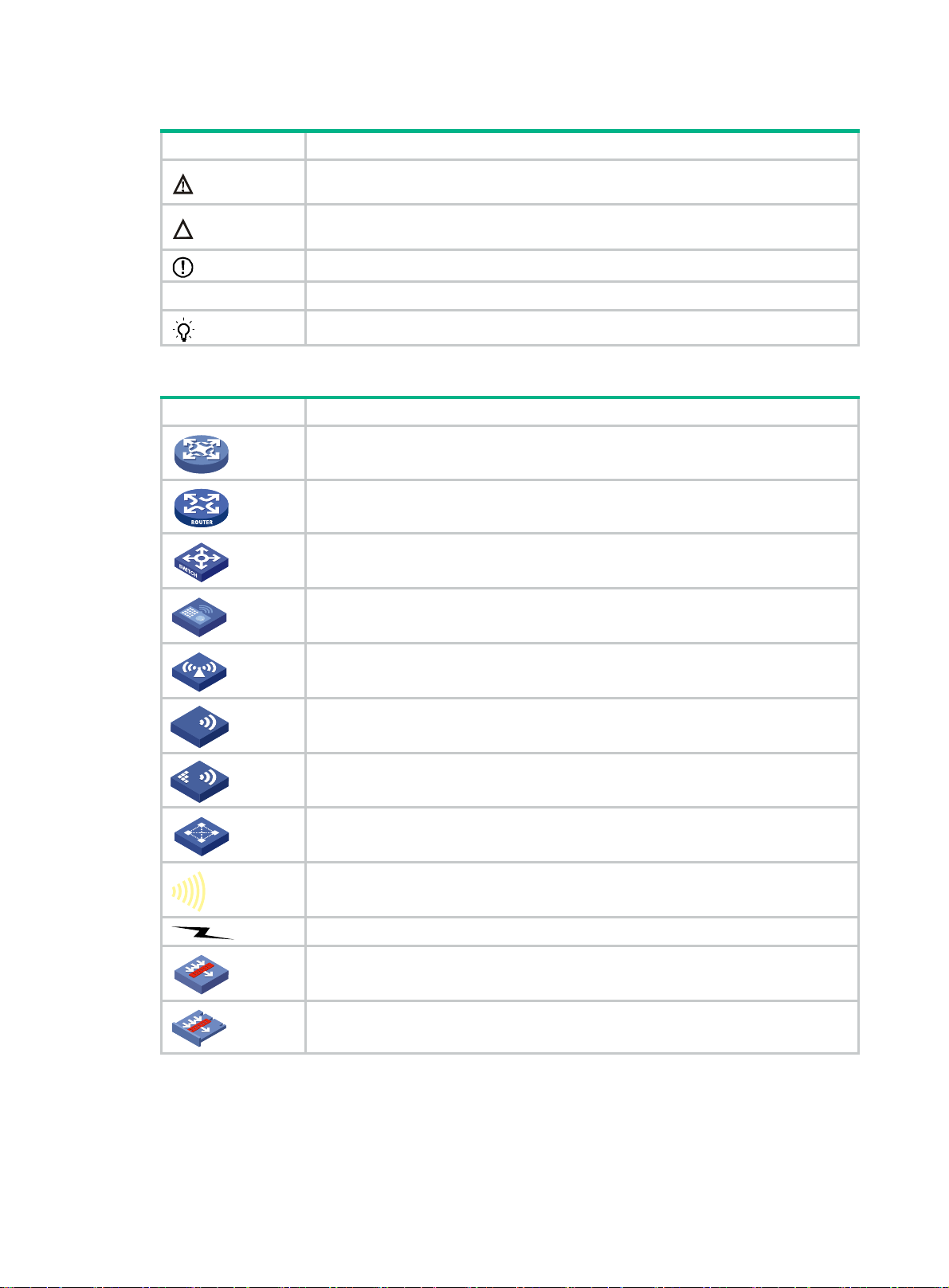
Symbols
Convention Description
WARNING!
An alert that calls attention to important information that if not understood or followed
can result in personal injury.
CAUTION:
IMPORTANT:
NOTE:
TIP:
Network topology icons
Convention Description
An alert that calls attention to important information that if not understood or followed
can result in data loss, data corruption, or damage to hardware or software.
An alert that calls attention to essential information.
An alert that contains additional or supplementary information.
An alert that provides helpful information.
Represents a generic network device, such as a router, switch, or firewall.
Represents a routing-capable device, such as a router or Layer 3 switch.
Represents a generic switch, such as a Layer 2 or Layer 3 switch, or a router that
supports Layer 2 forwarding and other Layer 2 features.
Represents an access controller, a unified wired-WLAN module, or the access
controller engine on a unified wired-WLAN switch.
Represents an access point.
T
T
T
T
Wireless terminator unit.
Wireless terminator.
Represents a mesh access point.
Represents omnidirectional signals.
Represents directional signals.
Represents a security product, such as a firewall, UTM, multiservice security
gateway, or load balancing device.
Represents a security module, such as a firewall, load balancing, NetStream, SSL
VPN, IPS, or ACG module.
Examples provided in this document
Examples in this document might use devices that differ from your device in hardware model,
configuration, or software version. It is normal that the port numbers, sample output, screenshots,
and other information in the examples differ from what you have on your device.
Page 5

Documentation feedback
You can e-mail your comments about product documentation to info@h3c.com.
We appreciate your comments.
Page 6

Contents
Preparing for installation ···································································· 1
Safety recommendations ············································································································· 1
Examining the installation site ······································································································· 2
Temperature/humidity ·········································································································· 2
Cleanliness ························································································································ 2
EMI ·································································································································· 3
Laser safety ······················································································································· 3
Installation tools ························································································································· 3
Installing the switch ·········································································· 4
Installing the switch in a 19-inch rack ····························································································· 4
Mounting brackets ··············································································································· 4
Attaching the mounting brackets to the switch ··········································································· 6
Rack-mounting the switch ····································································································· 8
Mounting the switch on a workbench ···························································································· 10
Mounting the switch on a wall ····································································································· 10
Grounding the switch ················································································································ 12
Grounding the switch with a grounding strip ············································································ 12
Grounding the switch with a grounding conductor buried in the earth ground ·································· 13
Grounding the switch by using the PE wire of the AC power cord ················································ 14
Installing and removing power modules ························································································ 14
Installing a power module ···································································································· 15
Removing a power module ·································································································· 15
Connecting the power cord ········································································································ 16
Connecting the AC power cord for a switch with fixed power modules··········································· 17
Connecting the DC power cord for a switch with fixed power modules ·········································· 17
Connecting the power cord for a PSR75-12A/PSR150-A1 power module ······································ 18
Connecting the power cord for a PSR150-D1 power module ······················································· 19
Verifying the installation ············································································································· 20
Accessing the switch for the first time ················································· 21
Setting up the configuration environment ······················································································ 21
Connecting the serial console cable ····························································································· 21
Connecting the micro USB console cable ······················································································ 22
Setting terminal parameters ······································································································· 24
Powering on the switch ············································································································· 24
Setting up an IRF fabric ··································································· 26
IRF fabric setup flowchart ·········································································································· 26
Planning IRF fabric setup ··········································································································· 27
Planning IRF fabric size and the installation site ······································································· 27
Identifying the master switch and planning IRF member IDs ······················································· 27
Planning IRF topology and connections·················································································· 27
Identifying IRF physical ports on the member switches ······························································ 28
Planning the cabling scheme ······························································································· 29
Configuring basic IRF settings ···································································································· 31
Connecting the IRF physical ports ······························································································· 31
Verifying the IRF fabric setup ······································································································ 31
Maintenance and troubleshooting ······················································ 32
Fixed power module failure ········································································································ 32
AC input failure ················································································································· 32
RPS DC input failure ·········································································································· 32
Concurrent RPS and AC inputs failure ··················································································· 33
Removable power module failure ································································································ 33
Symptom ························································································································· 34
Solution ··························································································································· 34
i
Page 7

Fan tray failure ························································································································ 34
Symptom ························································································································· 34
Solution ··························································································································· 34
Configuration terminal issues ······································································································ 34
No display on the configuration terminal ················································································· 34
Garbled display on the configuration terminal ·········································································· 35
Appendix A Chassis views and technical specifications ·························· 36
Chassis views ························································································································· 36
S5130S-10P-EI ················································································································· 36
S5130S-12TP-EI ··············································································································· 37
S5130S-20P-EI ················································································································· 37
S5130S-28P-EI/S5130S-28P-EI-M ························································································ 38
S5130S-28TP-EI ··············································································································· 39
S5130S-52P-EI/S5130S-52P-EI-M ························································································ 39
S5130S-52TP-EI ··············································································································· 40
S5130S-28S-EI/S5130S-28S-EI-M ························································································ 41
S5130S-52S-EI/S5130S-52S-EI-M ························································································ 41
S5130S-10P-HPWR-EI ······································································································· 42
S5130S-12TP-HPWR-EI ····································································································· 43
S5130S-20P-PWR-EI ········································································································· 43
S5130S-28P-PWR-EI ········································································································· 44
S5130S-28P-HPWR-EI ······································································································· 45
S5130S-52P-PWR-EI ········································································································· 46
S5130S-28S-PWR-EI ········································································································· 46
S5130S-28S-HPWR-EI ······································································································· 47
S5130S-52S-PWR-EI ········································································································· 48
S5130S-28F-EI ················································································································· 49
S5130S-52F-EI ················································································································· 50
Technical specifications ············································································································· 50
Appendix B FRUs ··········································································· 59
Appendix C Ports and LEDs ····························································· 60
Ports ····································································································································· 60
Console port ····················································································································· 60
10/100/1000BASE-T autosensing Ethernet port ······································································· 60
SFP port ·························································································································· 60
SFP+ port ························································································································ 64
Combo interface ················································································································ 65
LEDs ····································································································································· 65
System status LED ············································································································ 65
Power module status LED ··································································································· 66
RPS status LED ················································································································ 66
Mode LED (MODE) ············································································································ 66
SFP/SFP+ port LED ··········································································································· 67
10/100/1000BASE-T autosensing Ethernet port LED ································································ 67
Index ··························································································· 68
ii
Page 8

Preparing for installation
The H3C S5130S-EI Switch Series includes the following models:
• S5130S-10P-EI.
• S5130S-12TP-EI.
• S5130S-20P-EI.
• S5130S-28P-EI.
• S5130S-28P-EI-M.
• S5130S-28TP-EI.
• S5130S-52P-EI.
• S5130S-52P-EI-M.
• S5130S-52TP-EI.
• S5130S-28S-EI.
• S5130S-28S-EI-M.
• S5130S-52S-EI.
• S5130S-52S-EI-M.
• S5130S-10P-HPWR-EI.
• S5130S-12TP-HPWR-EI.
• S5130S-20P-PWR-EI.
• S5130S-28P-PWR-EI.
• S5130S-28P-HPWR-EI.
• S5130S-52P-PWR-EI.
• S5130S-28S-PWR-EI.
• S5130S-28S-HPWR-EI.
• S5130S-52S-PWR-EI.
• S5130S-28F-EI.
• S5130S-52F-EI.
NOTE:
The available chassis models and accessories vary by country and region. This document describes
only the preceding models. For the chassis models and accessories available in your country or
region, contact the local H3C marketing personnel.
Safety recommendations
To avoid equipment damage or bodily injury, read the following safety recommendations before
installation. Note that the recommendations do not cover every possible hazardous condition.
• Before cleaning the switch, remove all power cords from the switch. Do not clean the switch
with wet cloth or liquid.
• Do not place the switch near water or in a damp environment. Prevent water or moisture from
entering the switch chassis.
• Do not place the switch on an unstable case or desk.
1
Page 9

• Ensure good ventilation at the installation site and keep the air inlet and outlet vents of the
switch free of obstruction.
• Connect the yellow-green protection grounding cable before power-on.
• Make sure the power source voltage is as required.
• To avoid electrical shocks, do not open the chassis while the switch is operating or when the
switch is just powered off.
• To avoid ESD damage, wear an ESD wrist strap to hot-swap a power module.
Examining the installation site
The S5130S-EI switches must be used indoors. You can mount your switch in a rack or on a
workbench, but make sure:
• Adequate clearance is reserved at the air inlet and exhaust vents for ventilation.
• The rack or workbench has a good ventilation system.
• The rack is sturdy enough to support the switch and its accessories.
• The rack or workbench is reliably grounded.
To ensure correct operation and long service life of your switch, install it in an environment that meets
the requirements described in the following subsections.
Temperature/humidity
Maintain temperature and humidity in the equipment room as described in "Technical specifications."
• Lasting high relative humidity can cause poor insulation, electricity leakage, mechanical
property change of materials, and metal corrosion.
• Lasting low relative humidity can cause washer contraction and ESD and cause problems
including loose mounting screws and circuit failure.
• High temperature can accelerate the aging of insulation materials and significantly lower the
reliability and lifespan of the switch.
For the temperature and humidity requirements of different switch models, see "Appendix A Chassis
views a
nd technical specifications."
Cleanliness
Dust buildup on the chassis might result in electrostatic adsorption, which causes poor contact of
metal components and contact points, especially when indoor relative humidity is low. In the worst
case, electrostatic adsorption can cause communication failure.
Table 1 Dust concentration limit in the equipment room
Substance Concentration limit (particles/m³)
Dust
≤ 3 x 104 (no visible dust on the tabletop over three days)
NOTE:
Dust diameter ≥ 5 μm
The equipment room must also meet strict limits on salts, acids, and sulfides to eliminate corrosion
and premature aging of components, as shown in Tab l e 2 .
2
Page 10

Table 2 Harmful gas limits in the equipment room
EMI
Gas Maximum concentration (mg/m
SO
2
H2S 0.006
NH3 0.05
Cl2 0.01
0.2
3
)
All electromagnetic interference (EMI) sources, from outside or inside of the switch and application
system, adversely affect the switch in the following ways:
• A conduction pattern of capacitance coupling.
• Inductance coupling.
• Electromagnetic wave radiation.
• Common impedance (including the grounding system) coupling.
To prevent EMI, use the following guidelines:
• If AC power is used, use a single-phase three-wire power receptacle with protective earth (PE)
to filter interference from the power grid.
• Keep the switch far away from radio transmitting stations, radar stations, and high-frequency
devices to make sure the EMI levels do not exceed the compliant range.
• Use electromagnetic shielding when necessary. For example, use shielded interface cables.
• To prevent signal ports from getting damaged by overvoltage or overcurrent caused by lightning
strikes, only route interface cables indoors.
Laser safety
WARNING!
Disconnected optical fibers or transceiver modules might emit invisible laser light. Do not stare into
beams or view directly with optical instruments when the switch is operating.
The S5130S-EI switches are Class 1 laser devices.
Installation tools
No installation tools are provided with the switch. Prepare them yourself as required.
• Flat-blade screwdriver
• Phillips screwdriver
• ESD wrist strap
• Needle-nose pliers
• Diagonal pliers
• Crimping tool
• Marker
• Heat gun
3
Page 11

Installing the switch
CAUTION:
Keep the tamper-proof seal on a mounting screw on the chassis cover intact, and if you want to open
the chassis, contact H3C for permission. Otherwise, H3C shall not be liable for any consequence.
Figure 1 Hardware installation flow
Start
Install the switch
Ground the switch
Select and install power
modules
Yes
Hot-swap power
Connect power cords
Verify the installation
Turn on the circuit breakers
Operating correctly?
Install interface connectors
modules?
No
Yes
and cables
End
Troubleshoot the switch
No
Turn off the circuit
breakers
Installing the switch in a 19-inch rack
Mounting brackets
Table 3 describes the mounting brackets applicable to the switch.
4
Page 12

Table 3 Mounting brackets applicable to the switch
Switch model Mounting brackets Views
S5130S-28P-EI
S5130S-28P-EI-M
S5130S-28TP-EI
S5130S-52P-EI
S5130S-52P-EI-M
S5130S-52TP-EI
S5130S-28S-EI
S5130S-28S-EI-M
S5130S-52S-EI
S5130S-52S-EI-M
S5130S-28P-PWR-EI
S5130S-28P-HPWR-EI
S5130S-52P-PWR-EI
S5130S-28S-PWR-EI
S5130S-28S-HPWR-EI
S5130S-52S-PWR-EI
Mounting brackets A (provided) See A in Figure 2.
S5130S-28F-EI
S5130S-52F-EI
S5130S-20P-EI
S5130S-10P-HPWR-EI
S5130S-12TP-HPWR-EI
S5130S-20P-PWR-EI
S5130S-10P-EI
S5130S-12TP-EI
Mounting brackets B (provided) See B in Figure 2.
Mounting brackets C with product code
SOHO-SWITCH-FL-02
(optional)
Mounting brackets D with product code
SOHO-SWITCH-FL-01
(optional)
See C in Figure 2.
See D in Figure 2.
5
Page 13

Figure 2 Mounting brackets
(1) Screw hole for attaching the bracket to the switch
(2 ) Screw hole for attaching the bracket to the rack post
Attaching the mounting brackets to the switch
1. Determine the installation position for the mounting brackets.
{ The S5130S-28F-EI and S5130S-52F-EI switches provide two installation positions for the
mounting brackets: port side mounting position and power module side mounting position.
{ The other S5130S-EI switches provide only the port side mounting position for the mounting
brackets.
2. Align one mounting bracket with the screw holes at the mounting position. Use M4 screws to
attach the mounting bracket to the chassis. See Figure 3 for installi
A, Figure 4 a
bracket C, and Figure 7 for installing mo
M4 screws are provided only for switches shipped with mounting brackets.
An optional mounting bracket kit contains M4 screws.
3. Repeat step 2 to attach the other mo
nd Figure 5 for installing mounting bracket B, Figure 6 for installing mounting
unting bracket D.
unting bracket to the chassis.
ng mounting bracket
6
Page 14

Figure 3 Attaching mounting bracket A (S5130S-28P-HPWR-EI switch)
Figure 4 Attaching mounting bracket B to the port side mounting position (S5130S-52F-EI
switch)
Figure 5 Attaching mounting bracket B to the power module side mounting position
(S5130S-52F-EI switch)
Figure 6 Attaching mounting bracket C (S5130S-20P-PWR-EI switch)
7
Page 15

Figure 7 Attaching mounting bracket D (S5130S-10P-EI switch)
Rack-mounting the switch
This task requires two people. To mount the switch in the rack:
1. Wear an ESD wrist strap and make sure it makes good skin contact and is reliably grounded.
2. Verify that the mounting brackets have been securely attached to the switch chassis.
3. Install cage nuts in the mounting holes in the rack posts.
No cage nuts are provided with the switch. Prepare them yourself.
4. One person holds the switch chassis and aligns the mounting brackets with the mounting holes
in the rack posts, and the other person attaches the mounting brackets to the rack with M6
screws.
M6 screws are provided only for switches shipped with mounting brackets. For switches not
shipped with mounting brackets, prepare M6 screws yourself.
5. Verify that the switch chassis is horizontal and secure.
Figure 8 Mounting an S5130S-52F-EI switch in the rack (port side mounting position for the
mounting brackets)
8
Page 16

Figure 9 Mounting an S5130S-52F-EI switch in the rack (power module side mounting
position for the mounting brackets)
Figure 10 Mounting an S5130S-20P-PWR-EI switch in the rack
Figure 11 Mounting an S5130S-10P-EI switch in the rack
9
Page 17

Mounting the switch on a workbench
IMPORTANT:
• Ensure 10 cm (3.9 in) of clearance around the chassis for heat dissipation.
• Do not place heavy objects on the switch.
If a standard 19-inch rack is not available, you can place you switch on a workbench.
To mount the switch on a workbench:
1. Verify that the workbench is sturdy and reliably grounded.
2. Place the switch with bottom up, and clean the round holes in the chassis bottom with dry cloth.
3. Attach the rubber feet to the four round holes in the chassis bottom.
4. Place the switch with upside up on the workbench.
Mounting the switch on a wall
CAUTION:
• Before drilling holes in a wall, make sure no electrical lines exist in the wall.
• Leave a minimum clearance of 10 mm (0.39 in) around the chassis for heat dissipation.
Table 4 describes the switch models that support wall mounting and installation holes distances
required for wall-mounting the switch. Screw anchors and screws as shown in Figure 12 are
provided with these switches for wall-mounting.
Table 4 Installation hole distances for switch models that support wall mounting
Switch model Hole distance
S5130S-10P-EI
S5130S-12TP-EI
S5130S-20P-EI 176 mm (6.93 in)
S5130S-10P-HPWR-EI
S5130S-12TP-HPWR-EI
S5130S-20P-PWR-EI 116 mm (4.57 in)
170 mm (6.69 in)
102 mm (4.02 in)
Figure 12 Screw anchor and screw
To mount the switch on a wall:
1. Mark two installation holes on the wall. Make sure the two holes are on the same horizontal line.
See Table 4 f
or the distance requirement between the two holes.
10
Page 18

Figure 13 Installing the switch on a wall (1)
2. Drill two holes with a diameter of 6 mm (0.24 in) and a depth of 25 mm (0.98 in) at the marked
locations. Hammer the screw anchors into the wall and use a Phillips screwdriver to fasten the
screw into the screw anchor. Leave 1.5 mm (0.06 in) between the screw head and the wall for
hanging the switch.
Figure 14 Installing the switch on a wall (2)
3. Align the installation holes in the switch rear with the screws on the wall and hang the switch on
the screws. Make sure the port side faces down and the left and right sides are perpendicular to
the ground.
Figure 15 Installing the switch on a wall (3)
11
Page 19

Grounding the switch
WARNING!
Correctly connecting the switch grounding cable is crucial to lightning protection and EMI protection.
The power input end of the switch has a noise filter, whose central ground is directly connected to the
chassis to form the chassis ground (commonly known as PGND). You must securely connect this
chassis ground to the earth to minimize the potential for system damage, maximize the safety at the
site, and minimize EMI susceptibility of the system.
You can ground the switch in one of the following ways, depending on the grounding conditions
available at the installation site:
• Grounding the switch with a grounding strip
• Grounding the switch with a grounding conductor buried in the earth ground
• Grounding the switch by using the PE wire of the AC power cord
NOTE:
The chassis views and power module and grounding terminal positions in the following figures are
for illustration only.
Grounding the switch with a grounding strip
WARNING!
Connect the grounding cable to the grounding system in the equipment room. Do not connect it to a
fire main or lightning rod.
If a grounding strip is available at the installation site, use the grounding strip to ground the switch.
To ground the switch by using a grounding strip:
1. Attach the ring terminal end of the grounding cable to the grounding hole in the switch.
a. Remove the grounding screw from the grounding hole in the rear panel of the switch.
b. Attach the grounding screw to the ring terminal of the grounding cable.
c. Use a screwdriver to fasten the grounding screw into the grounding screw hole.
12
Page 20

Figure 16 Attaching the grounding cable to the grounding hole of the switch
(S5130S-28P-HPWR-EI switch)
(1) Grounding screw (2) Ring terminal
(3) Grounding sign (4) Grounding hole
(5) Grounding cable
2. Connect the other end of the grounding cable to the grounding strip.
a. Cut the grounding cable to a length according to the distance between the switch and the
grounding strip.
b. Peel 20 mm (0.79 in) of insulation sheath by using a wire stripper.
c. Use the needle-nose pliers to bend the bare wire.
d. Hook the grounding cable to the post on the grounding strip, and use the hex nut to secure
the cable to the post.
Figure 17 Connecting the grounding cable to a grounding strip
1 2
34
(1) Grounding post (2) Grounding strip
(3) Grounding cable (4) Hex nut
Grounding the switch with a grounding conductor buried in the earth ground
If the installation site has no grounding strips, but earth ground is available, hammer a 0.5 m (1.64 ft)
or longer angle iron or steel tube into the earth ground to serve as a grounding conductor.
The dimensions of the angle iron must be at least 50 × 50 × 5 mm (1.97 × 1.97 × 0.20 in). The steel
tube must be zinc-coated and its wall thickness must be at least 3.5 mm (0.14 in).
13
Page 21

Weld the yellow-green grounding cable to the angel iron or steel tube and treat the joint for corrosion
protection.
Figure 18 Grounding the switch by burying the grounding conductor into the earth ground
(1) Grounding screw (2) Grounding cable (3) Earth
(4) Joint (5) Grounding conductor (6) Chassis rear panel
Grounding the switch by using the PE wire of the AC power cord
If the installation site has no grounding strips or earth ground, ground an AC-powered switch through
the PE wire of the power cord. Make sure the following requirements are met:
• The power cord has a PE wire.
• The ground contact in the power outlet is securely connected to the ground in the power
distribution room or on the AC transformer side.
• The power cord is securely connected to the power outlet. If the ground contact in the power
outlet is not connected to the ground, report the problem and reconstruct the grounding system.
NOTE:
To guarantee the grounding effect, use the grounding cable provided with the switch to connect to
the grounding strip in the equipment room.
Installing and removing power modules
CAUTION:
Provide a circuit breaker for each power module and make sure the circuit breaker is off before
installation.
This section applies only to the switch models that support removable power modules.
The S5130S-28F-EI and S5130S-52F-EI switches each provide two power module slots. They come
with power module slot 1 empty and power module slot 2 installed with a filler panel. You can install
one power module, or two power modules for redundancy. For information about power modules
available for the S5130S-52F-EI switch, see "Appendix B FRUs."
14
Page 22

When two power modules are installed, you can hot-swap a power module. To avoid device damage
and bodily injury, follow the procedures in Figure 19 and Figure 20 to install
module.
Figure 19 Installation procedure
Figure 20 Removal procedure
The installation and removal procedures are the same for power modules. This guide uses the
PSR150-A1 power module as an example.
Installing a power module
1. Wear an ESD wrist strap and make sure it makes good skin contact and is reliably grounded.
2. Unpack the power module and verify that the power module model is as required.
3. Remove the filler panel (if any) from the target slot.
If you require only one power module, install it in power module slot 1 and make sure a filler
panel is installed in power module slot 2.
4. Orient the power module with the upside up. Grasp the handle of the power module with one
hand and support its bottom with the other, and slide the power module slowly along the guide
rails into the slot. See callout 1 in Figure 21.
To preve
power module gently. If you encounter a hard resistance or the power module tilts while
inserting the power module, pull out the power module, realign it with the slot, and then insert it
again.
5. Fasten the captive screws on the power module with a Phillips screwdriver to secure the power
module in the chassis. See callout 2 in Figure 21.
If the captive scre
nt damage to the power module and the connector on the switch backplane, insert the
w cannot be tightly fastened, examine the installation of the power module.
and replace a power
Figure 21 Installing a power module
Removing a power module
1. Wear an ESD wrist strap and make sure it makes good skin contact and is reliably grounded.
2. Power off the power module and remove the power cord.
15
Page 23

3. Loosen the captive screws on the power module with a Phillips screwdriver until they are
completely disengaged from the chassis.
4. Grasp the handle of the power module with one hand and pull the module part way out. Support
the module bottom with the other hand, and pull the power module slowly along the guide rails
out of the slot.
5. Place the removed power module in an antistatic bag.
Figure 22 Removing a power module
Connecting the power cord
CAUTION:
• Provide a circuit breaker for each power cord.
• Before connecting the power cord, make sure the circuit breaker on the power cord is turned off.
Table 5 Power cord connection procedures at a glance
Switch model Available power source Connection procedure reference
S5130S-28P-HPWR-EI
S5130S-52P-PWR-EI
S5130S-28S-HPWR-EI
S5130S-52S-PWR-EI
S5130S-28F-EI
S5130S-52F-EI
AC power source
H3C RPS1600-A
AC power source
240V high-voltage DC power
source
–48 VDC power source in the
equipment room
H3C RPS800-A or
RPS1600-A
Connecting the AC power cord for a
switch with fixed power modules
Connecting the DC power cord for a
witch with fixed power modules
s
Connecting the power cord for a
PSR75-12A/PSR150-A1 power module
Connecting the power cord for a
PSR75-12A/PSR150-A1 power module
Connecting the power cord for a
PSR150-D1 power module
Connecting the power cord for a
PSR150-D1 power module
Other S5130S-EI switches AC power source
Connecting the AC po
switch with fixed power modules
wer cord for a
The S5130S-28F-EI and S5130S-52F-EI switches use removable power modules. The PSR75-12A,
PSR150-A1, and PSR150-D1 power modules are available for the switch. The PSR150-A1 power
module uses AC power. The PSR75-12A power module uses AC or 240V high-voltage DC power.
The PSR150-D1 power module uses –48 VDC power or RPS power.
16
Page 24

Connecting the AC power cord for a switch with fixed power modules
1. Connect the plug of the AC power cord to the AC-input power receptacle on the switch.
See Figure 23.
2. Use a ca
See Figure 24.
3. Con
Figure 23 Connecting the AC power cord for a switch with fixed power modules (1)
ble tie to secure the power cord to the handle near the AC power receptacle.
nect the other end of the power cord to an AC power source.
Figure 24 Connecting the AC power cord for a switch with fixed power modules (2)
Connecting the DC power cord for a switch with fixed power modules
CAUTION:
• To connect the switch to a –48 VDC power source, use the DC power cord provided by H3C. To
avoid connection mistakes, identify the positive (+) and negative (-) marks on the two wires of the
DC power cord before connection.
• To connect the switch to an H3C RPS, use a power cord compatible with the RPS.
17
Page 25

To connect a DC power cord for a switch with fixed power modules:
1. Correctly orient the DC power cord plug and insert the plug into the power receptacle on the
power module.
If you orient the DC power cord plug upside down, you cannot insert the plug into the power
receptacle.
2. Use a flat-head screwdriver to fasten the screws on the power cord connector, as shown
in Figure 25.
3. Con
Figure 25 Connecting the DC power cord for a switch with fixed power modules
(S5130S-52P-PWR-EI)
nect the other end of the power cord to a –48 VDC power source or an RPS.
2
1
Connecting the power cord for a PSR75-12A/PSR150-A1 power module
1. Pull the bail latch leftward, as shown in Figure 26.
2. Connect the plug of the power cord to the power receptacle on the switch. See Figure 27.
3. Pull the bail latch rig
4. Con
nect the other end of the power cord to a power source.
For a PSR150-A1 power module, connect the power cord to an AC power source. For a
PSR75-12A power module, connect the power cord to an AC power source or a 240V
high-voltage DC power source.
htward to secure the plug to the power receptacle. See Figure 27.
18
Page 26

Figure 26 Connecting the power cord for a PSR75-12A/PSR150-A1 power module (1)
Figure 27 Connecting the power cord for a PSR75-12A/PSR150-A1 power module (2)
Connecting the power cord for a PSR150-D1 power module
CAUTION:
• Connect the other ends of the wires for a PSR150-D1 power module to a –48 VDC power source,
with the negative wire (– or L–) to the negative terminal (–) and the positive wire (+ or M/N) to the
positive terminal (+).
• To use an H3C RPS to supply power to the power module, use a compatible RPS power cord to
connect the RPS to the power module.
• The power cord color code scheme in Figure 28 is for
your country or region might use a different color scheme. When you connect the power cord,
always identify the polarity symbol on its wires.
To connect the power cord for a PSR150-D1 power module:
1. Correctly orient the plug at one end of the cable with the power receptacle on the power module,
and insert the plug into the power receptacle. See callout 1 in Figure 28.
If you cannot inse
rt the plug into the receptacle, re-orient the plug rather than use excessive
force to push it in.
2. Tighten the screws on the plug with a flat-blade screwdriver to secure the plug in the power
receptacle. See callout 2 in Figure 28.
3. Con
nect the other end of the power cord to a –48 VDC power source or an RPS.
illustration only. The cable delivered for
19
Page 27

Figure 28 Connecting the DC power cord for a PSR150-D1 power module (S5130S-52F-EI)
Verifying the installation
After you complete the installation, verify that:
• There is enough space for heat dissipation around the switch, and the rack or workbench is
stable.
• The grounding cable is securely connected.
• The correct power source is used.
• The power cords are correctly connected.
• All the interface cables are cabled indoors. If any cable is routed outdoors, verify that the socket
strip with lightning protection and lightning arresters for network ports have been correctly
connected.
20
Page 28

Accessing the switch for the first time
Setting up the configuration environment
You can access the S5130S-28TP-EI, S5130S-52TP-EI, S5130S-28S-EI, S5130S-28S-EI-M,
S5130S-52S-EI, S5130S-52S-EI-M, S5130S-28S-PWR-EI, S5130S-28S-HPWR-EI,
S5130S-52S-PWR-EI, S5130S-28F-EI, and S5130S-52F-EI switches through the serial console port
or the micro USB console port. If you connect both ports, only the micro USB console port is
available.
You can access other S5130S-EI switch models only through the serial console port.
No serial console cable or micro USB console cable is provided with the switch. Prepare yourself or
purchase it from H3C.
Figure 29 Connecting the serial console port to a PC
Connecting the serial console cable
A serial console cable is an 8-core shielded cable, with a crimped RJ-45 connector at one end for
connecting to the serial console port of the switch, and a DB-9 female connector at the other end for
connecting to the serial port on the configuration terminal.
Figure 30 Serial console cable
A side
Pin 9
A
Pin 1
Main label
8
1
B side
B
21
Page 29

Table 6 Serial console cable pinouts
RJ-45 Signal DB-9 Signal
1 RTS 8 CTS
2 DTR 6 DSR
3 TXD 2 RXD
4 SG 5 SG
5 SG 5 SG
6 RXD 3 TXD
7 DSR 4 DTR
8 CTS 7 RTS
To connect a terminal (for example, a PC) to the serial console port on the switch:
1. Plug the DB-9 female connector of the serial console cable to the serial port of the PC.
2. Connect the RJ-45 connector to the serial console port of the switch.
NOTE:
• Identify the mark on the serial console port and make sure you are connecting to the correct port.
• The serial ports on PCs do not support hot swapping. To connect a PC to an operating switch,
first connect the PC end. To disconnect a PC from an operating switch, first disconnect the switch
end.
Connecting the micro USB console cable
1. Connect the standard USB connector to the USB port of the PC or configuration terminal.
2. Connect the micro USB connector to the micro USB console port on the switch.
3. Click the following link, or copy it to the address bar on the browser to download the USB
console driver.
http://www.h3c.com.hk/Technical_Support___Do
/USB_Console/USB_Console/
4. Select a driver program according to the operating system you use:
{ XR21V1410_XR21B1411_Windows_Ver1840_x86_Installer.EXE—32-bit operating
system.
{ XR21V1410_XR21B1411_Windows_Ver1840_x64_Installer.EXE—64-bit operating
system.
5. Click Next on the installation wizard.
cuments/Software_Download/Other_Product
22
 Loading...
Loading...