Page 1

INSTALLATION
AND
OPERATING MANUAL
FOR
BDA-8XX-0.5/0.5W-XX-AX
MINI-BI-Directional Amplifier
Page 2

TABLE OF CONTENTS
PARAGRAPH PAGE NO
Mini-BDA OVERVIEW 3
Mini-BDA BLOCK DIAGRAM DESCRIPTION 3
Mini-BDA OPTIONS 3
Mini-BDA BLOCK DIAGRAM DRAWING (Figure 1) 4
ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS 5
FREQUENCY RANGES (Table 1) 6
SYSTEM SPECIFICATIONS (Table 2) 6
MECHANICAL CONNECTIONS 7
ENVIRONMENTAL CONDITIONS 7
Mini-BDA CONNECTIONS 7
MECHANICAL OUTLINE DRAWING (Figure 3 & 3a) 8
RF EXPOSURE WARNING 9
Mini-BDA INSTALLATION 10
Mini-BDA OPERATION 11
MECHANICAL OUTLINE- ADJUSTMENT (Figure 4) 12
DIAGNOSTICS GUIDE 13
Page 2
Page 3
Mini-BDA OVERVIEW:
The Mini-BDA assembly extends the coverage area of radio communications in
buildings and RF shielded environments. The Mini-BDA has dual RF paths to extend
coverage in two distinct frequency bands.
The unit features low noise figure and wide dynamic range. It is based on a duplexed
path configuration with sharp out of band attenuation allowing improved isolation
between the receiving and transmitting paths.
Mini-BDA BLOCK DIAGRAM DESCRIPTION
:
Refer to Figure 1 for the following discussion.
The Mini-BDA Downlink path receives RF signals from the base station and amplifies
and transmits them to the subscriber. The Mini-BDA Uplink path receives RF signals
from the subscriber and amplifies and transmits them to the base station. The Uplink
and Downlink occupy two distinct frequency bands. For example, the SMR frequency
bands are as follows: 806-821 MHz for the Uplink and 851-866 MHz for the Downlink.
Two diplexers isolate the paths and route each signal to the proper amplifying
channel.
An Automatic Level Control (ALC) allows for output power limiting. A variable step
attenuator gives 0 – 30 dB of attenuation in 2 dB steps. The use of these controls is
covered in the “OPERATION” section, later in this document.
Mini-BDA Options:
An optional 9 pin D-sub connector is available for external alarm monitoring (See
Figures 3 & 3a).
Page 3
Page 4
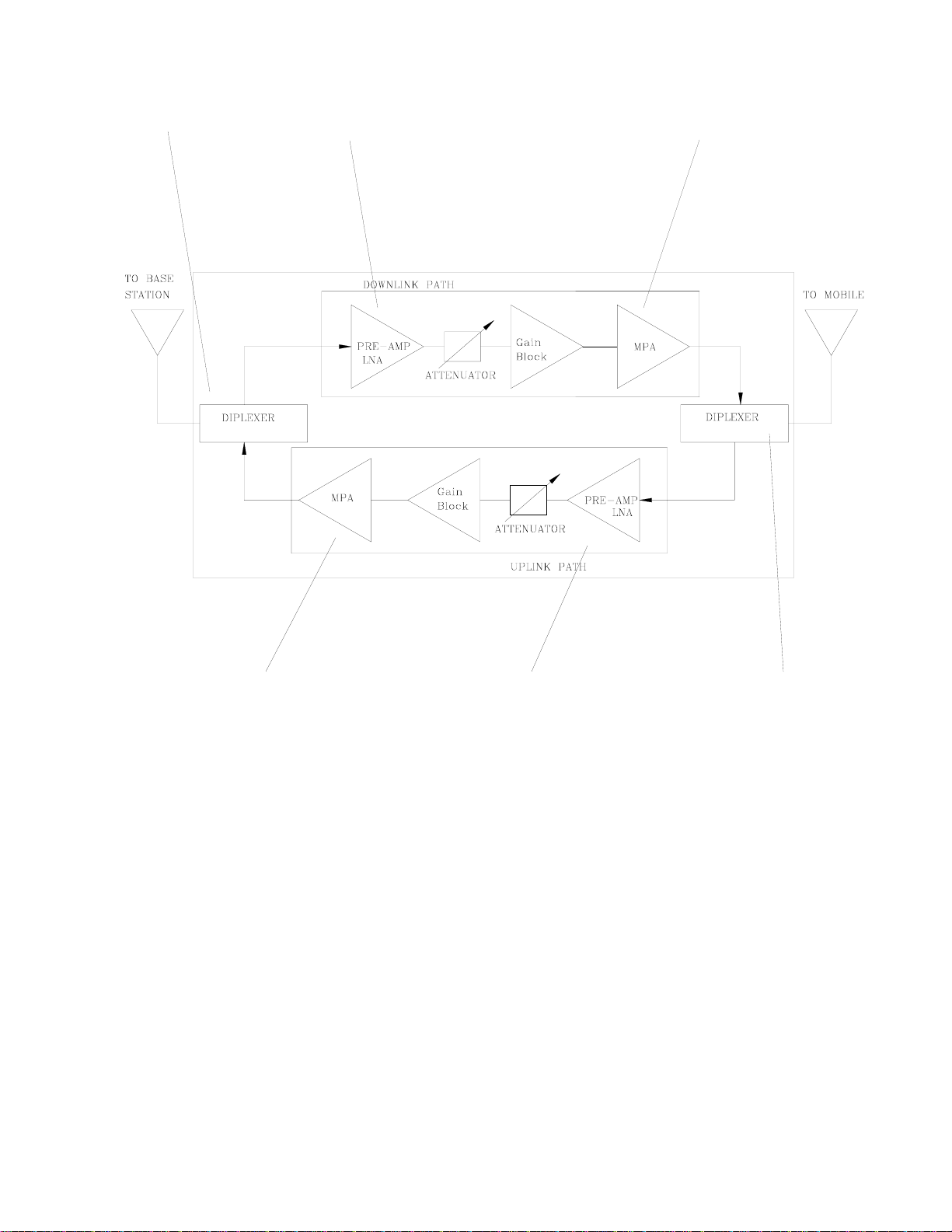
Figure 1
1. 2. 3.
4. 5. 6.
Mini-BDA BLOCK DIAGRAM
1. Uplink Diplexer - has low pass ban d insertion loss and high selectivity.
2. Downlink Pre-amp - is a low noise amplifier that drives the Downlink MPA and offers
38dB Gain.
3. Downlink MPA – is a medium power amplifier with an ALC circuit which offers 40dB
Gain.
4. Uplink MPA – is a medium power amplifier with an ALC circuit which offers 40dB
Gain.
5. Uplink Pre-amp - is a low noise amplifier that drives the Uplink MPA and offers 38dB
Gain.
6. Downlink Diplexer - has low pass band insertion loss and high selectivity.
Page 4
Page 5

ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS:
Frequency Range : See Table 1
Pass band Gain @ min attenuation : See Table 2
Variable Step Attenuator Range : 0-30 dB
(2-dB steps)
Pass band Ripple : ±1.5 dB typical
Noise Figure @+25
20 dB Bandwidth
Uplink : 32 MHz
Downlink : 32 MHz
3rd Order Intercept point : See Table 2
Output Power @ 1dB Compression : See Table 2
Isolation between Up/Down Link : 80 dB min., 90 typical.
Input/ Output Impedance : 50 Ohms
VSWR (Input/Output) : 1.5: 1 max
Power Supply (Local) : 15VDC/1.67 Amp
°C at max gain : 3.0 dB max.
Page 5
Page 6

Table 1
Frequency
Band
SMR 851-866 MHz 806-821 MHz
CELL A 869-880 MHz 824-835 MHz
CELL B 880-894 MHz 835-849 MHz
CELL AB 869-894 MHz 824-849 MHz
GSM F 935-960 MHz 890-915 MHz
GSM H 947-960 MHz 902-915 MHz
GSM L 935-947 MHz 890-902 MHZ
NPS PAC 866-869 MHz 821-824 MHz
2PG 929-942 MHz 898-904 MHz
2PGN 929-942 MHz 900-903 MHz
PS8 851-869 MHz 806-824 MHz
PS9 935-941 MHz 896-902 MHz
Frequency Ranges
Downlink
Uplink
Frequency Ranges
Table 2
System
3rd Order
Pass band
Gain
Uplink Downlink Uplink Downlink Uplink Downlink Uplink Downlink
(dB) Min.
Intercept
Point
(dBm)
Typ.
Output Power
@ 1dB
Compression
(dBm) Typ.
ALC Factory
Set Point
(dBm)
.5/.5 Watt
70 dB Gain
The Manufacturer's rated output power of this equipment is for single carrier operation. For situations when
multiple carrier signals are present, the rating would have to be reduced by 3.5 dB, especially where the output
signal is re-radiated and can cause interference to adjacent band users. This power reduction is to be by means
of input power or gain reduction and not by an attenuator at the output of the device.
70 70 40 40 27 27 18 18
Page 6
Page 7

MECHANICAL SPECIFICATIONS
:
Size : 8.75 x 6.20 x 3.0 inch
: (222.3 x 157.5 x 76.2 mm)
RF Connectors : N-type Female
Weight : 2.0 Lbs. (4.4 kg.) approx.
ENVIRONMENTAL CONDITIONS:
The unit is designed for indoor applications:
Operating temperature: - 20°C to + 50°C
Storage temperature: - 50°C to + 90°C
Mini-BDA CONNECTIONS
The Mini-BDA is powered by a +15 VDC/1.67 Amp Wall Plug-In AC adapter with a
2.5 mm output connector. The Wall Plug-In power adapter is highly reliable and
compact, designed for use in telecommunications. The power adapter is CE and UL
approved. The metal enclosure of the Mini-BDA is connected to ground.
A 9-pin D-Sub connector provides failure alarm output contacts.
The RF connections are made via two type “N” female connectors. The RF connector
labeled “BASE” must be connected to the antenna pointing towards the base station.
The RF connection labeled “MOBILE” must be connected to the antenna facing the
area to be covered by the Mini-BDA.
The RF connections must be made through cables with characteristic impedance of
50 ohms.
The isolation between the base station antenna and the mobile antenna should
be at least 12 dB higher than the Mini-BDA gain
can cause gain ripple across the band. Isolation equal to or less than the MiniBDA gain will give rise to oscillations which will saturate the amplifiers and
possibly cause damage to the Mini-BDA.
Page 7
. Isolation less than this value
Page 8

Mini-BDA Mechanical Outline
(Heat Sink included with 2 Watt Models)
Figure 3
24
26
2
2
2
0
8
2
3
8
0...30 dB
0
1
0
6
1
Gain Adjustment
2
4
1
4
2
DOWNLINK
1
6
0
1
8
24
2
2
6
2
2
0
8
2
3
8
0...30 dB
Gain Adjustment
UPLINK
IN BUILDING REPEATER
1
6
1
4
1
2
1
0
1
2PGN
0
0
2
4
6
8
Downlink Alarm Uplink Alarm
Figure 3a
Conditions for Optional Alarm
Non
The alarm monitors current of both uplink
and downlink amplifiers. An alarm condition
will occur if either uplink or downlink amplifiers
are under its current tolerance or if there is no
DC power present.
Page 8
(Relay Shown in
-Alarm Condition)
N.O.
COM.
N.C.
Page 9

RF EXPOSURE WARNING
In order to satisfy the FCC RF exposure requirements, the Mini-BDA/antenna
installation must comply with the following:
The outdoor antenna (Yagi type or similar directional antenna) must be installed so
as to provide a minimum separation distance of 0.3 meters (30 cm) between the
antenna and persons within the area. (This assumes a typical antenna with gain of
[10.1 dBi, VSWR ≤ 1.5:1, Zo= 50 ohms, and a cable attenuation of between 1-10 dB).
The indoor antenna (omni directional) must be installed so as to provide a minimum
separation distance of 0.2 meters (20 cm) between the antenna and persons within
the area. (This assumes a typical wide-beam type antenna with gain of 0-2 dBi,
VSWR ≤ 2:1, Zo= 50 ohms, and a cable attenuation of between 1-10 dB).
Page 9
Page 10

Mini-BDA INSTALLATION
DO NOT APPLY A.C. POWER TO THE Mini-BDA UNTIL CABLES
ARE CONNECTED TO BOTH PORTS OF THE Mini-BDA AND
ANTENNAS.
1. Mount the Mini-BDA on the wall with the RF connectors pointing DOWN. Using
appropriate screws and anchors, attach the Mini-BDA to the wall at the four mounting
holes on the side flanges.
2. Ensure that the isolation between the donor antenna and the service antenna is at
least 12 dB greater than the Mini-BDA gain. (Use the higher of the Uplink and
Downlink gains reported on the Mini-BDA test data sheet).
3. Connect the cable from the donor antenna to the Mini-BDA connector labeled
“BASE” and the cable from the service antennas to the Mini-BDA connector labeled
“MOBILE”.(Note: If used as a line amplifier, connect the external bias-tee between
the service antenna cable and the Mini-BDA connector labeled “MOBILE”, with the
RF+DC side of the bias-tee connected towards the service antenna cable.)
4. Connect the 2.5mm connector of the Wall Plug-In power adapter to the Mini-BDA
and then to the AC power source. Turn the Power switch to the “ON” position and
verify that the “System GO” lamp is illuminated.
Installation of the Mini-BDA is now complete. To adjust the gain controls to suit the
specific signal environment, refer to the next section of the manual.
Note
: For repeat installations of existing equipment, make sure the attenuation
is positioned to its maximum setting (30 dB). After the attenuation is verified,
follow the above steps starting with step 1.
Page 10
THE
Page 11

Mini-BDA OPERATION
Refer to figure 3 and 4 for adjustment access location and label.
Variable Step Attenuator
Mini-BDA gain can be reduced by up to 30 dB in 2 dB steps using the variable step
attenuator. Gain adjustment is made with rotary switches accessible from the top of
the Mini-BDA enclosure (See Figure 4). Arrows on the shafts of these switches point
to the value of attenuation selected. The Mini-BDA gain can be determined by
subtracting the attenuation value from the gain reported on the Mini-BDA Test Data
Sheet for that side of the unit. The attenuators are labeled for Uplink and Downlink.
ALC (Automatic Level Control)
To minimize intermodulation products, each amplifier in the Mini-BDA contains an
ALC feedback loop. The ALC circuit senses the output power and limits it to the
factory preset level (See Table 2). A red indicator lamp is located on the front panel
of the Mini-BDA and illuminates when the output power exceeds the ALC set point
(See below).
Downlink ALC Uplink ALC
To establish proper operating gain on the Uplink and Downlink sides, start with the
Uplink. Verify that the ALC switch is in the “ON” position. Observe the red indicator
lamp on the Uplink amplifier. Units are shipping with maximum attenuation. Decrease
attenuation one step at a time until the lamp is lit. Then, using the Uplink step
attenuator, increase the attenuation until the lamp goes off. Repeat the process for
the Downlink. The level indicator is accurate to +/- 0.4 dB of the ALC set point.
Operation of BDA-8XX-0.5/0.5W-XX-AX at maximum gain with greater than -40
dBm average power incident on either BASE or MOBILE ports can cause
damage to the Mini-BDA.
Page 11
Page 12

Figure 4
2
6
2
2
0
2
8
1
6
1
4
1
2
1
2
8
3
0
0
2
4
6
0
1
8
0
1
0
6
4
2
0
3
8
2
12
1
4
16
1
8
20
2
2
6
2
4
2
Adjustment Access and Label
Page 12
Page 13

DIAGNOSTICS GUIDE
The Mini-BDA provides long term, care-free operation and requires no periodic
maintenance. There are no user-serviceable components inside the Mini-BDA.
This section covers possible problems that may be related to the installation or
operating environment.
a. Gain Reduction
Possible causes: Bad RF cables and RF connections to antennas, Damaged
antennas.
b. Excessive Intermodulation or Spurious
Possible causes:
Amplifier oscillation caused by insufficient isolation. The isolation between two
antennas is given by the equation:
Isolation = 92.5 + 20 Log (F x D) – Gt – Gr
Where:
F = frequency (GHz)
D = separation (Km)
Gt = transmit antenna gain (in the direction of the receive antenna).
Gr = receive antenna gain (in the direction of the transmit antenna).
For the SMR frequencies, the antenna isolation at 100 m separation is about 71 dB
for omni-directional antennas (0 dB gain). To increase isolation, the antennas should
have higher directivity and must be pointed away from each other.
c. Occasional Drop-out of some Channels
Possible causes: One channel with very strong power dominates the RF
output of the amplifier.
38 Leuning Street
South Hackensack, NJ 07606
Tel. 201-343-3140 Fax 201-343-6390
sales@gwaverf.com
www.gwaverf.com
Page 13
 Loading...
Loading...