
Tag Reader
Installation Manual and User Guide
Document Number: 07-00002-000
Signpost – Installation Manual and User Guide
N
Introduction
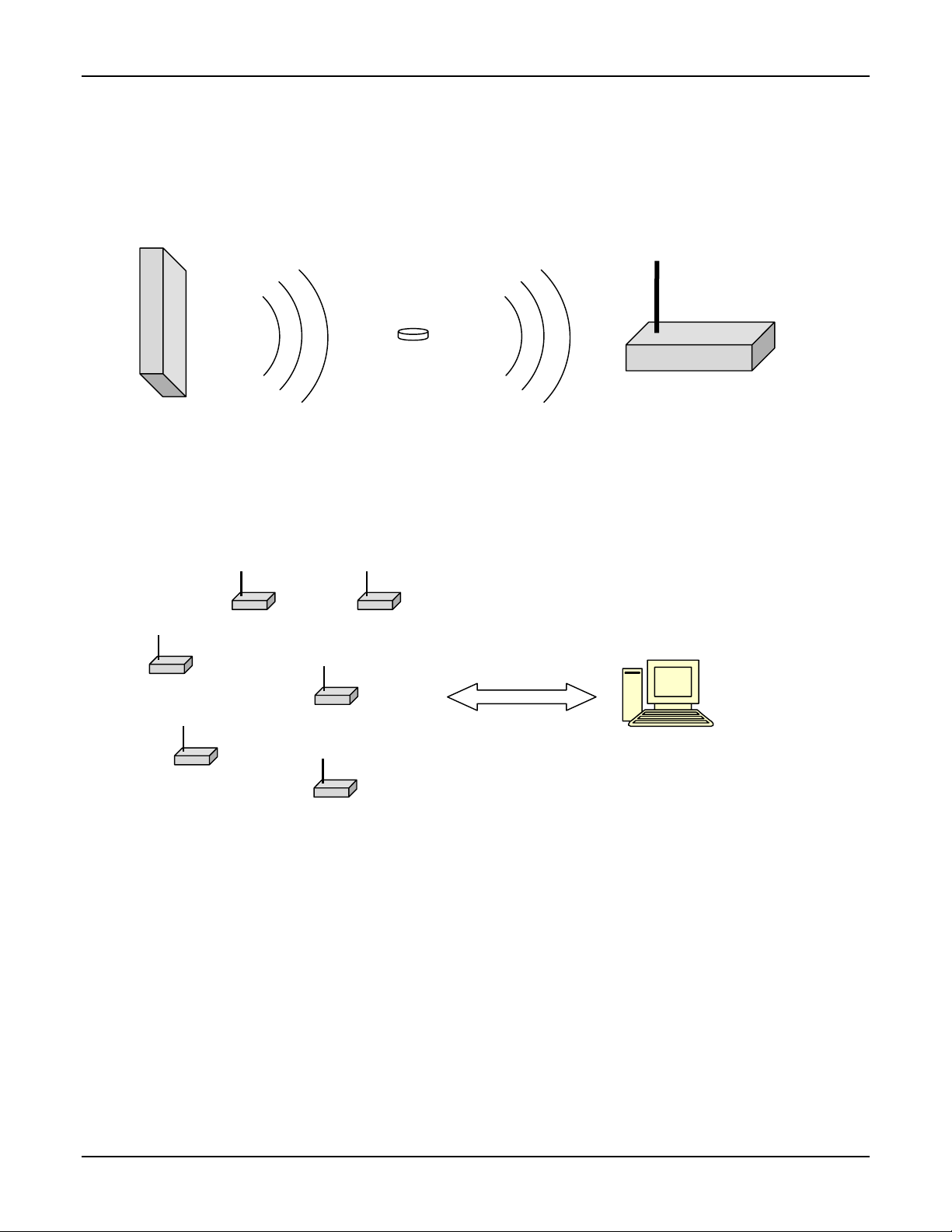
Tag Reader is a device that is designed to operate in conjunction with a Tag and a Signpost. Basic Tag
Reader functionality is shown in diagram below:
Signpost
The Signpost generates modulated RF signal at 125 kHz frequency, which is detected by the Tag. Upon
detection of Signpost signal, the Tag transmits its own signal on 434 MHz frequency to one or more Tag
Readers. Tag Readers process information and based on internal database, they activate outputs while
simultaneously passing information to the Server computer which is running application software.
125 kHz
434 MHz
Tag Tag Reader
Ethernet
etwork
There are two types of tag Readers: Tag Reader Door Controller and Tag Reader Receiver.
Tag Reader Receiver is used when only to collect all the messages from the Tags and pass them toi the
Server. Tag Reader Door Controller has the same functionality, but additionally, it is used for perimeter
protection by controlling the door it is assigned to.
Installation
Position
The main function of a Tag Reader is to receive RF communication from Tags. It is important to select
carefully mounting location of the Tag Reader which will not interfere with a cap ability of the device to
receive RF messages from the Tags. This is accomplished by avoiding mounting in the proximity of metal
objects, cables, electrical devices, etc.
Guard RFID Solutions Inc. Page 2 of 7

Signpost – Installation Manual and User Guide
Due to a nature of RF communication, it is hard to predict communication range between a Tag and a Tag
Reader. This is heavily dependent on surrounding ambient, architecture, even people and equipment
movement. However, in order to install the system, the assumption of certain communication range has to
be made. To achieve complete RF coverage of a typical office style area (including typical healthcare
facility), good starting point is to position Tag Readers in a grid pattern with 25-foot centers. During
system testing this assumption may need some adjusting (accomplished by moving Tag Readers in either
direction), but in majority of cases, it is proven to be a good general rule of thumb.
Locations in which Tag Reader is shielded by metal tiles or walls should be avoided, or density of Tag
Readers should be increased.
Wiring
Tag Reader requires 3 types of wiring to be fully functional:
- Power Supply:
o 12VDC power supply which is capable of delivering 0.3A of continuous current. AWG-
18 or heavier wire should be used (depending on wire length).
- Networking:
o Ethernet CAT-5 cable with RJ-45 should be used for communication between a Tag
Reader and the Server.
- Peripheral:
o This is applicable To Tag Reader DC only. It includes wiring for Door Switch Input,
Bypass Input and Relay Output. Door Switch and Bypass Inputs can use AWG-20 or
heavier wire, but Relay Output should use AWG-18 or heavier wire.
All Tag Reader’s wiring connections are accessible without opening the enclosure.
Configuration
Tag Reader configuration is accomplished via 3-position DIP switch located inside the enclosure.
The functionality of these switches is as follows:
- Switch 1: Communication to Host disabled.
o “0” Æ Communication enabled
o “1” Æ Communication disabled
- Switch 2: Mode of alarm operation
o “0” Æ Continuous Alarm (Tag Reader will continue alarming after the Tag has left
Signpost field until the alarm is acknowledged by Bypass)
o “1” ÆNon-Continuous Alarm (Tag Reader will stop alarming when the tag leaves the
Signpost field)
- Switch 3: Alarm Buzzer enabled
o “0” Æ Alarm Buzzer disabled
o “1” Æ Alarm Buzzer enabled
Guard RFID Solutions Inc. Page 3 of 7

Signpost – Installation Manual and User Guide
Switch configuration change can be done while the unit is powered up.
Tag Reader Receiver should always have Switch 3 in position ”0” (Alarm Buzzer disabled).
User Guide
Functionality
The functionality of Tag Reader Receiver is just tom receive messages from Tags and pass them to the
Server.
The functionality of Tag Reader Door Controller is more complex as it includes interaction between Tag,
Signpost and peripheral door controlling hardware.
Tag Reader Database
The Tag Reader has a local database that enables it to function without any interaction with the Host
Server. This database has default set of rules for different Tag types which are used if no rule is stored for a
particular Tag. Tag Rules for individual Tags are downloaded from the Host Server whenever the tag is
assigned to a person or asset.
Tag Rules specify what action should be taken by the Tag Reader upon detection of a particular Tag and in
what time period (e.g. activate alarm if the tag is detected between 2:00PM and 2:30PM)
Tag Reader database is volatile and it has to be downloaded every time after reset.
Alarm and Pre-Alarm
When the Tag is detected in a Signpost field and Tag Rules database specifies that it should generate alarm
condition, the door state defines is it Alarm or Pre-Alarm condition.
If the door is closed
Tag moves out of the Signpost field, Pre-Alarm is stopped and the tag Reader reverts back to Idle mode of
operation (note that Switch 2 has no impact on Pre-Alarm).
While in Pre-Alarm, the Tag Reader can be bypassed by activating Bypass Input (shorting it) or by sending
a command from the Host Server.
If the door is open
beeping long beeps. Switch 2 defines what happens when the tag moves out of the Signpost field; the tag
Reader either reverts back to Idle mode (Switch 2 = “1”), or the Tag Reader remains in Alarm Mode until
Bypass is started (Switch 2 = “1”).
, the Tag Reader will lock the door and signal Pre-Alarm (short “chirping”). When the
, the Tag Reader will not activate the maglock, but it will signal Alarm condition by
Bypass
Bypass can be started by either shorting Bypass Input and Com terminals or by receiving the command
from the Host Server. In either case, the Bypass is indicated by 3 short “chirps” every 1 second.
While in Bypass, the Tag Reader will not enter Alarm or Pre-Alarm state, but rather it will remain in
Bypass state. If the Tag Reader is already in Alarm or Pre-Alarm state, it while exit this states and go into
Bypass state.
Anti-piggybacking feature
will generate the Alarm or Pre-Alarm.
Guard RFID Solutions Inc. Page 4 of 7
: All new Tags entering the field 10 seconds after the Bypass has been started

Signpost – Installation Manual and User Guide
The Bypass state will last until either all the Tags leave the field or until the door is opened and closed. If
the Bypass is terminated by opening and closing the door, the Tag Reader will ignore Tags that were
already in the field for 5 seconds (this is Post-Bypass state), after which time it will revert to Idle state and
be able to detect all the Tags again. Note that while in Post-Bypass state the Tag Reader will en ter Alarm
or Pre-Alarm state for all the new Tags entering the field.
Audio-Visual Indication
There are 4 LEDs and the buzzer which provide information about Tag Reader state:
- NET LED
Server. The LED goes solid when Tag Reader establishes communication with the Host.
- RF LED
- HCI LED
- PMI LED is not used.
Tag Reader buzzer is used for indication purposes and annunciation of Alarm, Pre-Alarm and Bypass
states.
is red and is blinking while there is no communication established with the Host
is red and flashes briefly whenever a massage from a Tag is received.
is yellow and flashes briefly whenever a message has been sent to the Host Server.
System Verification
Guard RFID systems are designed to assist staff in providing a high degree of safety for people and assets
and therefore should only be used as a component of a comprehensive security program of policies,
procedures, and processes. As with every security system, Guard RFID highly recommends regular system
operational checks to verify functional integrity.
Guard RFID Solutions Inc. Page 5 of 7

Signpost – Installation Manual and User Guide
SPECIFICATIONS
Physical Specifications
Operating Temperature……………………… 32 degree F to 131 degree F
Humidity ……………………………………. 0% - 90% non-condensing
Size (WxHxD) ……………………………… 3.3” x 1.5” x 5.3”
Weight ………………………………………. 0.3 lb. (180g)
Electrical Specifications:
Power Requirement …………………………. 0.3 A @ 12VDC +/- 5%
RF Frequency ……………………………….. 125KHz
Guard RFID Solutions Inc. Page 6 of 7

Signpost – Installation Manual and User Guide
FCC Regulations
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
(1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and
(2) This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired
operation.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for Class B Digital Device, pursuant to
Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates and can radiate radio frequency energy
and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular
installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can
be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the
interference by one or more of the following measures.
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna
• Increase the separation between the equipment and Receiver
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the Receiver is connected
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help
Modifications
Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by Guard RFID for compliance could void
the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
Guard RFID Solutions Inc. Page 7 of 7
 Loading...
Loading...